东南大学通信原理试卷及参考答案
- 格式:doc
- 大小:367.00 KB
- 文档页数:10

通信原理2011-1-11√√电子工程类 081、082、083 、084、085[ A卷 ]一、填空(共20分,1分/空):(1).数字通信系统的__ _用频带利用率描述; _ _用系统的输出误码率描述。
(2).白噪声的特点是:功率谱密度为 _ ,任意两不同时刻的值 _ __ _ 。
(3).调制信道是指从系统调制器的_ 端到解调器的端。
(4).信号在恒参信道中传输时主要有__ ___失真和__ ___失真。
(5).为了更好地适应信道的传输特性,大多数信号需要通过__ ___后传输。
(6).幅度调制是用__ ___去控制__ ___的__ ___参量。
(7).一个均值为零的窄带平稳高斯过程,其包络的一维分布是_ __,其相位的一维分布是_ _ 。
(8).双极性基带信号,当满足__ ___条件时,其功率谱中无离散谱分量。
(9).2DPSK、2ASK、2PSK和2FSK中,占用带宽最宽的是__ ___,对信道特性变化敏感的是__ ___,当采用相干解调时,抗信道加性高斯白噪声最好的是__ ___ ,最差的是__ ___,它们的误码率都取决于解调器的_ _ 。
二、简答题(共36分):1、按照消息传递的方向与时间的关系,通信方式分为几类?各举一例。
(6分)2、请写出“各态历经性”的含义并说明其意义?(6分)3、包络检波有时会出现门限效应,什么是门限效应?产生的根本原因是什么?(6分)4、请写出改善实际数字基带传输系统性能的两项措施及两项措施各自所针对改善的对象?(6分)5、请写出2DPSK信号的产生和解调方法?(6分)6、什么是非均匀量化?与均匀量化相比,非均匀量化的主要优缺点?(6分)三、作图题(共14分)1、已知信息代码为 1 0 1 0 0 0 0 0 1 1 0 0 0 0 1 1,求相应的AMI码及HDB3码,并分别画出它们的波形图。
(8分)2、根据图三-2所示的调制信号波形,试画出DSB及AM信号的波形图,并说明它们分别通过包络检波器后的波形差别。

通信原理高校试题及答案一、选择题(每题2分,共20分)1. 以下哪个选项不是模拟信号的特点?A. 连续的B. 离散的C. 随时间连续变化D. 可以是周期性的答案:B2. 在数字通信中,以下哪个选项不是数字信号的特点?A. 离散的B. 数值有限C. 随时间连续变化D. 可以进行编码答案:C3. 以下哪个选项不是调制的作用?A. 频带压缩B. 信号放大C. 信号传输D. 抗干扰能力增强答案:B4. 在通信系统中,以下哪个选项不是信道的作用?A. 传输信号B. 放大信号C. 转换信号D. 接收信号答案:B5. 以下哪个选项不是信噪比(SNR)的影响因素?A. 发射功率B. 接收机灵敏度C. 信号的频带宽度D. 传输介质的损耗答案:C6. 在通信系统中,以下哪个选项不是信道编码的目的?A. 错误检测B. 错误纠正C. 信号放大D. 提高传输的可靠性答案:C7. 以下哪个选项不是数字信号处理的优点?A. 抗干扰能力强B. 易于实现加密C. 信号传输稳定D. 信号传输距离远答案:D8. 在通信系统中,以下哪个选项不是多路复用技术?A. 频分复用B. 时分复用C. 码分复用D. 信号放大答案:D9. 以下哪个选项不是信号调制的类型?A. 调幅B. 调频C. 调相D. 调时答案:D10. 在通信系统中,以下哪个选项不是信号解调的目的?A. 还原信号B. 放大信号C. 提取信息D. 降低噪声答案:B二、填空题(每题2分,共20分)1. 在数字通信中,信号的传输速率通常用______来表示。
答案:比特率2. 调制解调器(Modem)的作用是将数字信号转换为______信号,以便在模拟信道上传输。
答案:模拟3. 在通信系统中,信噪比(SNR)是信号功率与______功率的比值。
答案:噪声4. 信号的带宽是指信号所占据的频率范围,通常用______来表示。
答案:赫兹(Hz)5. 在通信系统中,多路复用技术可以将多个信号合并到一个______上进行传输。

通信原理考试试题及答案一、选择题1. 在通信系统中,基带信号的频谱是:A. 具有无限带宽B. 具有有限带宽C. 具有单一频率D. 没有频谱答案:A2. 模拟调制的主要目的是:A. 放大信号B. 滤波信号C. 将基带信号转换为适合传输的频带信号D. 编码信号答案:C3. 以下哪种调制方式属于频率调制:A. AMB. FMC. PMD. DSB-SC答案:B4. 在数字通信中,误码率(BER)是衡量系统性能的重要指标,它表示:A. 信号的平均功率B. 信号的平均频率C. 传输错误比特数与总传输比特数的比值D. 系统的带宽答案:C5. 以下关于信道编码的描述,错误的是:A. 信道编码可以提高信号的抗干扰能力B. 信道编码可以减少传输错误C. 信道编码可以增加传输速率D. 信道编码可以提高信号的传输距离答案:C二、填空题1. 通信系统中,信号的调制过程是指将_________信号转换成适合在信道中传输的_________信号的过程。
答案:基带,带通2. 在数字通信中,常用的调制方式有_________调制、_________调制和_________调制。
答案:幅度键控(ASK)、频率键控(FSK)、相位键控(PSK)3. 信噪比(SNR)是衡量通信系统性能的一个重要指标,它表示信号功率与_________的比值。
答案:噪声功率4. 通信系统中的带宽限制是指信道能够传输信号的_________范围。
答案:频率5. 在通信系统中,多普勒效应会导致接收端接收到的信号频率与发射端发射的信号频率之间存在_________。
答案:频移三、简答题1. 请简述数字调制技术与模拟调制技术的主要区别。
答案:数字调制技术是将数字基带信号转换为适合在信道中传输的数字带通信号,它通常涉及数字信号的幅度、频率或相位的变化。
模拟调制技术则是将模拟基带信号转换为模拟带通信号,主要涉及信号的幅度、频率或相位的变化。
数字调制技术具有更好的抗干扰性,可以更有效地利用信道资源,而模拟调制技术则在某些特定应用中更为简单和经济。

通信原理考试试题及答案一、单项选择题(每题2分,共20分)1. 在数字通信系统中,以下哪项不是衡量信道容量的指标?A. 信噪比B. 带宽C. 传输速率D. 调制方式答案:D2. 以下哪种调制方式不是线性调制?A. ASKB. FSKC. PSKD. QAM答案:A3. 在通信系统中,信道编码的主要目的是什么?A. 提高信号的传输速率B. 提高信号的带宽利用率C. 增强信号的抗干扰能力D. 降低信号的功率消耗答案:C4. 以下哪种多址技术适用于卫星通信?A. FDMAB. TDMAC. CDMAD. SDMA答案:C5. 在无线通信中,以下哪种技术用于减少多径效应的影响?A. 均衡器B. 分集接收C. 信道编码D. 功率控制答案:B二、填空题(每题2分,共20分)1. 在数字通信中,信道容量C可以通过香农公式计算,公式为:C =W log2(1 + S/N),其中W是信道带宽,S是信号功率,N是噪声功率,log2是以2为底的对数。
2. 信号的带宽决定了信号的传输速率,根据奈奎斯特定理,理想情况下,信道的最大传输速率为2W log2(M),其中W是带宽,M是调制方式的阶数。
3. 在无线通信中,多径效应会导致信号的衰落和时延扩展,可以通过使用_________技术来减少其影响。
答案:分集接收4. 为了提高信号的安全性,可以采用_________技术对信号进行加密。
答案:密钥加密5. 在数字通信中,信噪比(SNR)是衡量信号质量的重要指标,它定义为信号功率与噪声功率的比值,通常用分贝(dB)表示。
三、简答题(每题10分,共40分)1. 简述数字通信与模拟通信的主要区别。
数字通信使用数字信号传输信息,具有抗干扰能力强、易于加密、便于存储和处理等优点。
模拟通信使用模拟信号传输信息,信号容易受到干扰,且不易加密和存储。
2. 什么是信道编码?它在通信系统中有什么作用?信道编码是将原始数据通过特定的编码规则转换成冗余的编码数据,以提高数据传输的可靠性。
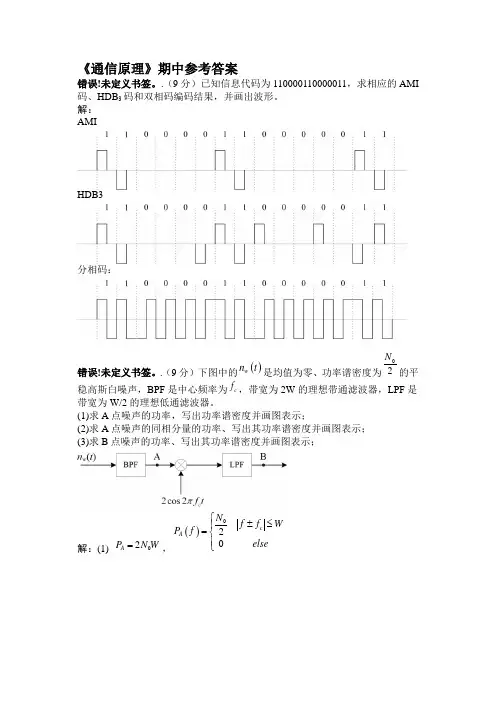
《通信原理》期中参考答案错误!未定义书签。
.(9分)已知信息代码为110000110000011,求相应的AMI 码、HDB 3码和双相码编码结果,并画出波形。
解: AMIHDB3分相码:错误!未定义书签。
.(9分)下图中的()w n t 是均值为零、功率谱密度为02N 的平稳高斯白噪声,BPF 是中心频率为c f ,带宽为2W 的理想带通滤波器,LPF 是带宽为W/2的理想低通滤波器。
(1)求A 点噪声的功率,写出功率谱密度并画图表示;(2)求A 点噪声的同相分量的功率、写出其功率谱密度并画图表示; (3)求B 点噪声的功率、写出其功率谱密度并画图表示;解:(1) 02A P N W =,()020c A N f f W P f else⎧±≤⎪=⎨⎪⎩(2) ()()()cos sin 2A c c s c n t n t f t n t f t ππ=2-。
()c n t 的功率是02N W ,从频谱搬移关系可知其带宽是W ,形状是矩形,因此矩形的高度必然是0N ,即()0c n N f W P f else⎧≤=⎨⎩(3)B 点的输出是()c n t 经过LPF 的输出,因此()020B WNf P f else⎧≤⎪=⎨⎪⎩B 点功率为0B P N B =错误!未定义书签。
.(10分)已知()()()cos 2c e t s t f t πθ=+,其中s (t )是一个功率谱密度为()S P f 的平稳随机过程,θ是与()s t 相互独立的随机变量,θ在[]0,2π内均匀分布,证明()t e 的功率谱密度为:()()()14E s c s c P f P f f P f f =++-⎡⎤⎣⎦证:()e t 的自相关函数为 ()()()()()()()()()()()()()(),cos 2cos 22cos 2cos 22cos cos 422cos 22E c c c c c c s c c c s c R t t E e t e t E s t f t s t f t f E s t s t E f t f t f R E f f t f R f ττπθτππτθτπθππτθτπτππτθτπτ+=+⎡⎤⎣⎦=++++⎡⎤⎣⎦=++++⎡⎤⎡⎤⎣⎦⎣⎦=2+++2⎡⎤⎣⎦=作傅氏变换得()()()()2221224c c j f j f s j f E S c S c R e e P f e d P f f P f f πτπτπτττ-∞--∞⎡⎤+=⨯=-++⎡⎤⎢⎥⎣⎦⎣⎦⎰错误!未定义书签。

通信原理试题及答案一、单项选择题(每题2分,共20分)1. 以下哪个是数字通信系统的特点?A. 抗干扰能力差B. 传输速率低C. 抗干扰能力强C. 传输距离远答案:C2. 香农定理描述的是:A. 信号的调制方式B. 信号的编码方式C. 信道的容量极限D. 信号的解调方式答案:C3. 在通信系统中,信噪比(SNR)通常用来衡量:A. 信号的频率B. 信号的幅度C. 信号的质量D. 信号的相位答案:C4. 以下哪个调制方式属于线性调制?A. ASKC. PSKD. QAM答案:B5. 在数字基带传输中,曼彻斯特编码的主要优点是:A. 抗干扰能力强B. 传输速率高C. 易于同步D. 频带利用率高答案:C6. 以下哪个是多路复用技术?A. TDMB. FDMC. CDMAD. 所有选项都是答案:D7. 以下哪个是无线通信中常用的天线类型?A. 偶极子天线B. 螺旋天线C. 抛物面天线D. 所有选项都是答案:D8. 在无线通信中,以下哪个因素会影响信号的传播?B. 天气C. 建筑物D. 所有选项都是答案:D9. 以下哪个是信道编码的类型?A. 线性编码B. 非线性编码C. 卷积编码D. 所有选项都是答案:D10. 在通信系统中,以下哪个是误码率的缩写?A. BERB. SNRC. QAMD. FDM答案:A二、多项选择题(每题3分,共15分)11. 数字调制技术包括以下哪些类型?A. PSKB. QAMC. FSKD. ASK答案:ABCD12. 以下哪些因素会影响通信系统的性能?A. 信道的带宽B. 信号的功率C. 噪声的强度D. 调制方式答案:ABCD13. 在通信系统中,以下哪些是信号的调制方式?A. 调频B. 调幅C. 调相D. 调色答案:ABC14. 以下哪些是数字信号处理中的基本操作?A. 傅里叶变换B. 卷积C. 滤波D. 采样答案:ABCD15. 以下哪些是通信系统中的同步技术?A. 位同步B. 帧同步C. 载波同步D. 时钟同步答案:ABC三、简答题(每题5分,共20分)16. 简述数字通信与模拟通信的主要区别。

通信原理试题及答案一、选择题1. 下列哪个不属于通信系统的要素?A. 发送端B. 接收端C. 传输介质D. 数据库答案:D2. 信号调制的主要目的是什么?A. 增强信号的能量B. 减小信号的失真C. 使信号适应传输介质D. 增大信号的频率答案:C3. 载波的作用是什么?A. 提高信号的幅度B. 携带原始信号C. 减小信号的失真D. 抵消噪声干扰答案:B4. 数字通信系统中,编码的作用是什么?A. 改变信号的幅度B. 提高信号的频率C. 使信号适应传输介质D. 减小信号的失真答案:C5. 奈氏准则用来判断什么?A. 信号是否失真B. 信号是否被干扰C. 信号是否适应传输介质D. 信号是否被传输介质损耗答案:A二、填空题1. 通信系统中,________是将信息转换为信号的设备。
答案:发送端2. 调制是将________信号转换为________信号的过程。
答案:基带,载波3. 常用的数字编码方式有________编码和________编码。
答案:二进制,十进制4. ________是指传输过程中信号受到的干扰。
答案:噪声5. 奈氏准则是判断信号是否________的依据。
答案:失真三、简答题1. 请简述模拟信号与数字信号的区别。
答:模拟信号是连续变化的信号,可以取无数个值。
而数字信号是离散的信号,只能取有限个值。
模拟信号可以表示连续的变化,例如声音的波形;数字信号则是利用二进制编码,用0和1表示。
模拟信号在传输过程中容易受到干扰和失真,而数字信号可以通过纠错码等方法进行校验和修复。
2. 请简述调制的作用及常见的调制方式。
答:调制的作用是将模拟信号转换为适合传输的信号,具体包括改变信号的频率、幅度、相位等特性。
常见的调制方式主要有调幅(AM)、调频(FM)和调相(PM)。
调幅是通过改变载波的幅度来传输信息;调频是通过改变载波频率的高低来传输信息;调相是通过改变载波的相位来传输信息。
3. 请简述数字通信系统中的编码过程及常用的编码方式。

二、问答题(23 分)1、什么是差分脉冲编码调制?什么是增量调制?(10 分)答:差分脉冲编码调制:就是利用抽样值之间的相关性,利用前面若干个时刻的抽样值来预测当前时刻的抽样值,对预测值与实际值的差值进行编码,称为差分脉冲编码调制。
----------------------- (5 分)增量调制:当抽样频率远大于奈奎斯特频率时,抽样值之间的关联程度增强,可以仅用一位编码表示抽样时刻波形的变化趋势,这种编码称为增量调制。
----------------------- (5 分)2、DSB 调制系统和 SSB 调制系统的抗噪性能是否相同?为什么?(13 分)答:相同。
----- (3 分)因为单边带信号所需带宽仅仅是双边带的一半。
因而,在噪声功率谱密度相同的情况下,双边带解调器的输入噪声功率是单边带的二倍,从而也使双边带解调器输出噪声功率比单边带的大一倍。
因此,尽管双边带解调器的制度增益比单边带的大,但它的实际解调性能不会优于单边带的解调性能。
不难看出,如果解调器的输入噪声功率谱密度相同,输入的信号功率也相同,则双边带和单边带在解调器输出端的信噪比是相等的。
这就是说,从抗噪声的观点看,单边带的解调性能和双边带是相同的。
-----(10 分)三、计算题(50 分)1、已知输入信号抽样脉冲值为I S=-990 个量化单位,采用逐次比较型编码器,按 A 律13 折线编码编成 8 位码,试求此时编码器输出码组,并计算量化误差(段内码用自然二进制码)(15 分)(1)首先确定极性码C1:由于输入抽样值I s=-990∆为负极性,所以C1= 0 。
(2)然后确定段落码C2C3C4:C2:选择权值电流I w= 128∆,则I s= 990∆>I w,所以C2= 1,也就是I s处于八个段落的后四段:5 至8 段落;C3:选择权值电流I w= 512∆,则I s= 990∆>I w,所以C3= 1 ,也就是I s处于第7 至8 段落;C4:选择权值电流I w= 1024∆,则I s= 990∆<I w,所以C4= 0 ,也就是I s处于第7 段落,其段落起点电平为512∆。

通信原理试卷一及答案一、填空题(每空1分,共20 分)1、随机过程X (t )的自相关函数ττ-+=e R X 1)(,则其均值为 ,方差为 ,平均功率为 。
2、多径传播对传输信号的影响有:(1)使载波信号变成了包络和相位受到调制的窄带信号(即衰落信号);(2) ;(3) 。
3、调制信号)(t m 是幅度为m A 的单音信号,,则已调波DSB 发送信号功率为 。
4、对于正在运行的FM 系统,若调制信号幅度m A 增大,则频偏f ∆ 、 所需传输的带宽 。
5、若将f (t )先 而后使它对载波进行FM 即得PM 。
6、在模拟调制系统AM 、DSB 、SSB 、VSB 和FM 中,调制效率最低的是 。
抗干扰能力最强的是 。
7、数字信号的码元时间长度为1ms ,如果采用八电平传输,信息速率是 。
8、16ASK 信号的带宽是2ASK 信号带宽的 倍。
9、在模数转换中,实际的抽样有两种基本形式,即 和 。
10、在能够消除码间干扰的二元数字基带传输系统中,若传输带宽为3KHz ,滚降残留谱宽度为1KHz ,则对应的奈氏带宽为 KHz ,传输速率b R = bit/s. 11、一码长n=7的汉明码,监督位r= ,编码效率= 。
12、对输入信号S(t)采用匹配滤波器进行最佳接收,该匹配滤波器的单位冲击响应h(t) 为 。
二、名词解释(5小题,每小题3分,共15分)1、GMSK2、误码率3、门限效应4、数字基带信号5、匹配滤波器三、简答题(3小题,每小题4分,共12分)1、简述线性调制和非线性调制的概念。
2、简述消除码间干扰的方法。
3、简单比较ASK 、FSK 、PSK (DPSK )系统相干解调时的性能。
四、均值为0,自相关函数为的高斯噪声,通过传输特性为(A 、B 为常数)的线性网络,试求:(1)输入噪声的一维概率密度函数;(4分) (2)输出噪声的一维概率密度函数;(4分) (3)输出噪声功率;(2分)五、某调制方框图如图1(b )所示。

通信原理试题及答案一、选择题1. 在数字通信中,误码率通常用来衡量:- A. 信号的强度- B. 信号的稳定性- C. 传输的可靠性- D. 信道的带宽2. 以下哪个不是模拟信号的特点:- A. 连续性- B. 可量化性- C. 可模拟性- D. 可存储性3. 在通信系统中,调制的主要目的是:- A. 提高信号的频率- B. 降低信号的频率- C. 提高信号的抗干扰能力- D. 增加信号的传输距离二、填空题1. 在通信系统中,_________ 是指在接收端正确接收到发送端发送的信息的概率。
2. 信道编码的目的是提高传输的_________,通过添加冗余信息来实现。
3. 移动通信中的多径效应会导致_________,影响信号的接收质量。
三、简答题1. 请简述数字调制技术中,AM、FM和PM的区别。
2. 描述一下在通信系统中,信道噪声对信号传输的影响。
四、计算题1. 假设一个通信系统传输的信道带宽为3kHz,信噪比为30dB,计算该系统的信道容量。
参考答案一、选择题1. C2. B3. C二、填空题1. 误码率2. 可靠性3. 频率选择性衰落三、简答题1. 数字调制技术中,AM(幅度调制)是将数字信号转换为模拟信号的幅度变化,FM(频率调制)是将数字信号转换为模拟信号的频率变化,而PM(相位调制)则是将数字信号转换为模拟信号的相位变化。
AM对噪声较为敏感,而FM和PM的抗噪声能力较强,尤其是FM。
2. 信道噪声会干扰信号的传输,导致接收端收到的信号与发送端的原始信号产生偏差。
这种偏差可能会使得接收端无法正确解码数字信号,从而增加误码率,影响通信的可靠性。
四、计算题信道容量的计算公式为:C = B * log2(1 + SNR),其中B是信道带宽,SNR是信噪比。
将30dB转换为线性比例,即SNR = 10^(30/10)。
代入公式得:\[ C = 3000 \times \log_2(1 + 10^{30/10}) \]计算结果为:C ≈ 3000 * log2(1073741824) ≈ 29.23 kbps。

通信原理考试试题及答案一、选择题1. 通信原理是指:A. 两个人进行对话的方式B. 信息传递的过程和方法C. 无线电的发明和应用D. 电信运营商的管理规范答案:B2. 以下哪项不是通信原理的重要组成部分:A. 编码和调制B. 解码和解调C. 发射和接收D. 储存和处理答案:D3. 通信原理中,信号的调制过程是指:A. 将数字信号转化为模拟信号B. 将模拟信号转化为数字信号C. 信号的放大和衰减D. 信号的传输和接收答案:A4. 通信原理中,解调过程是指:A. 将数字信号转化为模拟信号B. 将模拟信号转化为数字信号C. 信号的放大和衰减D. 信号的传输和接收答案:B5. 以下哪项属于数字调制方式:A. 调频调制B. 调幅调制C. 相位调制D. 脉冲调制答案:D二、判断题1. 通信原理是通信工程的基础学科。
B. 错答案:A2. 调制是指将数字信号转化为模拟信号的过程。
A. 对B. 错答案:A3. 解调是指将模拟信号转化为数字信号的过程。
A. 对B. 错答案:B4. 调频调制是数字调制的一种方式。
A. 对B. 错答案:B5. 脉冲调制是数字调制的一种方式。
A. 对答案:A三、简答题1. 什么是信道容量?答案:信道容量是指在单位时间内,信道所能传输的最大信息量。
它是由信道的带宽和信噪比决定的。
2. 什么是多路复用?答案:多路复用是一种技术,通过将多个信号在时间、频率或码元上进行分解,使它们能够同时在同一个信道上进行传输,提高信道利用率。
3. 什么是码元?答案:码元是数字信号的最小单位,通常表示为高电平和低电平或者1和0。
4. 什么是调制解调器?答案:调制解调器是一种设备,用于将数字信号转化为模拟信号或将模拟信号转化为数字信号,实现信号的调制和解调功能。
四、计算题1. 一条信道的带宽为10 kHz,信噪比为20 dB,求该信道的最大传输速率。
答案:信道容量C = B log2(1 + S/N),其中B为带宽,S/N为信噪比。
山东科技大学2007—2008学年第一学期《通信原理》考试试卷(A 卷)班级 ________________ 姓名 ________________ 学号 ______________一、填空题(每空1分,共16分)1、 单边带信号产牛的方式有 _________ 和 __________ o2、 设调制信号的最高频率为你,则单边带调制信号的带宽为 __________ ,双边 带调制信号的带宽为 ________ ,残留边带调制信号的带宽为 ___________ 。
3、 线性PCM 编码的过程为 ________ , ________ , __________ 。
4、 举出1个频分复用的实例 ________________ o5、 通信系统的性能指标主要有 ___________ 和 ____________ ,在模拟通信系统 中前者用有效传输带宽衡量,后者用接收端输出的 _____________ 衡量。
6、 2ASK 的功率谱由 __________ 和 __________ 两部分组成,其带宽为基带信 号带宽的 倍。
‘7、相帝乘疵信号来说,数字信号的特点是在 ________ 上是离散的。
8、要求码组能检测5个错码同时纠正3个错码,则其最小码距是 _________ o 二、选择题(每题2分,共14分)1 •根据抽样定理,如果要对频带限制在珀以下的连续时间信号进行抽样,则 抽样频率fs 必须满足:(a) fsN2fm (b) fs23fm (c) fsW2fm (d) fsW3fm 2. 数字通信中,在对语音信号进行量化吋通常采用: (a)均匀量化 (b)非均匀量化 (c)两者均可 (d)两者均不可3•根据奈奎斯特第一准则,传输速率为& 448 Mbit/s 的数字信号,在理想情 况下要求最小传输信道的带宽为:4. 224MHz (c)2. 816 MHz (d) 16. 896MHz 复用方式为: (b)码分复用 (d)以上三者皆可第1页/共3页6•由4级移位寄存器产生的ni 序列,其周期为:(a) 13 (b) 14 (c) 15 (d) 167. 以下差错控制方式中,哪一种不属于检错重发:(a) 8. 448 MHz (b)4. PCM 数字电话采用的(a)时分复用(c)频分复用 5. 设在125毫秒内传输了 1024个二进制码元,若在5秒内有3个码元发生了 误码,则误码率为:(a) 0. 29%(b) 60 % (c) 0.0073% (d)0. 037%(a )停发等候重发 (b )返回重发 (c )选择重发(d )前向纠错三、数字通信系统模型框图如下,试填写空缺部分(10分)四、已知线性调制信号表示式如下:(每题5分,共10分) 1、cosQzcos w (.t2^ (1 + 0.5sinQr )cos w c t式中,叭=4Q 。
东南大学考试卷( A 卷)课程名称通信原理考试学期04-05-3 得分适用专业考试形式闭卷考试时间长度150分钟Section A(30%): True or False (Give your reason if False,2% for each question)1. A typical mobile radio channel is a free propagation, linear, and time invariant channel.( )2.The power spectral density of a stationary process is always nonnegative. ( )3.In a communication system, noise is unwanted and over which we have incompletecontrol. ( ) 4.If a random process is stationary, it is ergodic; if a Gaussian random process is stationary,then it is also strictly stationary. ( ) 5.Double Sideband-Suppressed Carrier (DSB-SC), Single Sideband (SSB), and FrequencyModulation (FM) are all linear modulation schemes. ( ) 6.Figure of merit (defined as (SNR)O/(SNR)C) of AM of DSB-SC is 1/3, and figure of meritof Amplitude Modulation (AM) is less than or equal to 1/3. ( )7. -law is a nonlinear compression law and A-law is a linear compression law. ( )8.The matched filter at the receiver maximizes the peak pulse signal-to-noise ratio, thus isoptimal in a baseband data transmission system with Inter-Symbol Interference (ISI).( ) 9.Correlative-level coding (also known as partial-response signaling) schemes are used toavoid ISI. ( ) 10.Time-Division Multiplexing (TDM) is used in Asymmetric Digital Subscriber Lines(ADSL) to separate voice signals and data transmission. ( ) 11.If coefficients of an equalizer is adjusted using the Least-Mean-Square (LMS) algorithmadaptively, then the matched filter in front of the equalizer is not necessary. ( ) 12.In an M-ary Phase-Shift Keying (M-PSK) system, if the average probability of symbolerror is P e, then the average Bit Error Rate (BER) of the system is P e/log2M. ( ) 13.With the same Signal-to-Noise Ratio (SNR), 16-ary Quadrature Amplitude Modulation(16-QAM) has better performance than 16-ary Phase-Shift Keying (16-PSK). The reason is that 16-QAM has constant envelop. ( ) 14.With the same SNR, Minimum Shift Keying (MSK) has better performance than Sunde’sFrequency-Shift Keying (FSK). They are both Continuous-Phase Frequency-Shift Keying (CPFSK). ( ) 15.If the largest frequency component of an band-limited signal X(t) is at 100 Hz, then thecorresponding Nyquist rate is 200 Hz. ( )共10 页第1 页Section B(30%): Fill in the Blanks (3% for each question)1.The power spectral density of a stationary process X(t) is S X(f), then the autocorrelationfunction of X(t) is R X(t) = .2. A random process Y(t) is defined as Y(t) = X(t) cos(2πf c t + Θ), where X(t) is a stationaryprocess, f c is a constant frequency, and the phase Θis randomly distributed over the interval [0, 2π]. Suppose the power spectral density of X(t) is S X(f), the power spectral density of Y(t) is S Y(f) = .3.In a Frequency Modulation (FM) system, the modulating signal is m(t) = 2 cos (6πt) V, thefrequency sensitivity is k f = 0.3 Hz/V. Using Carson’s rule, bandwidth of the FM signal is approximately Hz.4.An analog signal is first encoded into a binary Pulse-Code Modulation (PCM) wave.Sampling rate of the PCM system is 8 kHz, number of representation levels is 64. The binary PCM wave is transmitted over a baseband channel using a 4-ary Pulse-Amplitude Modulation (PAM) (that is, a PAM with 4 amplitude levels). The minimum bandwidth requirement for transmitting the PAM wave is kHz.5.Basic operations performed in the transmitter of a PCM systeminclude , , and .6.Bandwidth efficiency of 4-ary Quadrature Amplitude Modulation (QAM) is ;bandwidth efficiency of 8-ary Phase-Shift Keying (8PSK) is .7.In a Delta Modulation (DM) system, sampling rate is f s = 8 kHz and step size is ∆ = 0.1 V.If the input to the DM system is a 1 kHz sinusoidal signal, then to avoid slope overload, the maximum amplitude of this input signal is V.8.12 different message signals, each with a bandwidth of 20 kHz, are to be multiplexed andtransmitted. If the multiplexing and modulation methods are Frequency-Division Multiplexing (FDM) and Single-Sideband Modulation (SSB), respectively, then the minimum bandwidth required is kHz; if the multiplexing and modulation methods are Time-Division Multiplexing (TDM) and PAM, then the minimum bandwidth required is kHz;9.The binary data sequence {b k} = 1010110 is applied to a duobinary (class I partialresponse) system with precoding, as shown in Fig. P1-9 (see next page), where d k = b k⊕d k-1, ⊕denotes modulo-two addition, and a k= 2×d k–1. The initial value of d k is 1.The output of the duobinary encoder is {c k} = . If at the receiving end, the first received digit is 1.25 due to noise, then the receiver output is ˆ{}k b = .共10 页第2 页共 10 页 第 3 页Fig. P1-910. A communication system has the signal-space diagram shown in Fig. P1-10, wheremessage points have equal probability of transmitting. Assume communication channel in this system is Additive White Gaussian Noise (AWGN) channel, and E/N 0 is 12, where N 0 is single-sideband power spectral density of the AWGN. Using union band, theaverage probability of symbol error is overbounded as P e ≤ . (Express using complementary error function erfc(⋅).)1()t φ2()t φ120°120°Message point 1Message point 2Message point 3EFig. P1-10共 10 页 第 4 页Section C(40%): Calculations (8% for each question)1. In a coherent Binary Phase-Shift Keying (BPSK) system, symbols 1 and 0 are representedby signals s 1(t) and s 2(t), respectively.The signals are defined by12())0())c b c s t f t t T s t f t πππ⎧=⎪⎪≤≤⎨⎪=+⎪⎩where E b is the transmitted signal energy per bit, and T b is one bit duration.a) Determine the basis function(s) of coherent BPSK signal constellation; b) Plot the signal-space diagram of coherent BPSK system; c) Determine the error probability of BPSK;d) If there is a phase error ϕ between the phase references of the transmitter andreceiver, determine the error probability of BPSK in this condition again.2. Spectrum of a message signal m(t) is shown in Fig. P3-2. This message signal is DoubleSideband-Suppressed Carrier (DSB-SC) modulated with a carrier wave A c cos(2πf c t). a) If f c = 2 kHz, plot the spectrum of the modulated signal s(t); b) What is the baseband bandwidth W of the message signal m(t)?c) What is the transmission bandwidth B T of the DSB-SC modulated signal?d) What is the lowest value of f c that keeps the DSB-SC modulation from sidebandoverlap?f1 kHz -1 kHzFig. P3-2共 10 页 第 5 页3. Consider a Quadriphase-Shift Keying (QPSK) system. The transmitted signal set isdefined as:cos[2(21)/4],0()0, otherwise c i f t i t Ts t ππ+-≤≤⎧=⎨⎩where i = 1, 2, 3, 4. Every two input bits select one of the signals in transmitted signalset to transmit. The rule of mapping is 10 → s 1(t), 00 → s 2(t), 01 → s 3(t), 11 → s 4(t). a) Determine the basis function(s) of QPSK signal constellation; b) Express s i (t) using the basis function(s);c) If the input binary sequence is 01101000, and suppose fc = 2/T, plot the QPSKwaveform;d) Is the QPSK waveform continuous phase?4. Consider the signal s(t) shown in Fig. P3-4,a) Assuming h(t) is the matched filter of s (t), plot the impulse response of h (t); b) When s (t) is applied to h (t), plot the matched filter output in the time domain.tT0A-A2T/3T/3s(t)Fig. P3-45. Suppose X(t) = Acos(2πft – Θ), where A is a constant, and f and Θ are independent. Θ isuniformly distributed over the interval [0, 2π]. Determine the power spectrum density of X(t) in terms of the probability density function of the frequency f.共 10 页 第 6 页通信原理期终考试参考答案和评分标准考试学期:04-05-3Section A: (30分)1. ⨯ The mobile radio channel is typically time variant.2. √3. √4. ⨯ Stationary is not necessary ergodic.5. ⨯ FM is not a linear modulation scheme6. ⨯ Figure of merit of DSB-SC is 1, not 1/3.7. ⨯ A-law is also a nonlinear compression law.8. ⨯ The matched filter is optimal with AWGN channel.9. ⨯ Correlative-level coding is to use ISI to achieve 2W signaling rate in abandwidth of W Hz. 10. ⨯ FDM is used in ADSL. 11. √12. ⨯ The BER is usually not P e /log 2M. 13. ⨯ 16-QAM is not constant envelop. 14. √ 15. √Section B: (30分) 1.()exp(2)X S f j f df πτ∞-∞⎰共 10 页 第 7 页2.1[()()]4X c X c S f f S f f -++ 3. 7.2 4. 125. Sampling, Quantizing, and Encoding6. 1, 1.57. 1.278. 240, 2409. 0 -2 0 2 0 0 2, 0010110 10. erfc(3)Section C:(40分)1.(a) The basis function is:1()),0c b t f t t T φπ=≤≤. (2分) (b) The signal-space diagram is: (2分)φ1(t)(c) The error probability is 1erfc 2e P =. (2分) (d) With phase error ϕ, the error probability becomes 1erfc 2e P ϕ⎫=⎪⎪⎭. (2分)2. (a) The spectrum is: (2分)共 10 页 第 8 页2 kHz -2 kHz0S(f)f(b) W = 1 kHz; (2分) (c) B T = 2 kHz; (2分)(d) To avoid sideband overlap, the lowest frequency is 1 kHz. (2分)3. (a) The basis functions are: (2分)122()cos(2),02()sin(2),0c c t f t t T Tt f t t T T φπφπ⎧=≤≤⎪⎪⎨⎪=≤≤⎪⎩(b)12()cos (21)()sin (21)(),1,2,3,42424i T T s t i t i t i ππφφ⎡⎤⎡⎤=---=⎢⎥⎢⎥⎣⎦⎣⎦ (2分)(c) The QPSK waveform is: (2分)(d) The QPSK waveform is not continuous phase. (2分)4. (a) h(t) is shown below, where k is a positive constant. (4分)共 10 页 第 9 页tT0kA-kAT/32T/3h(t)(b) The filter output is shown below. (4分)tT 0-kA 2T/3T/32T/3Response of h(t) to s(t)-kA 2T4T/35T/32T5. The autocorrelation function of X(t) is: (2分)22()[()()][cos(22)cos(2)][cos(42)cos(2)]2X R E X t X t A E Ft F Ft A E Ft F F ττππτπππτπτ=+=+-Θ-Θ=+-Θ+ Since Θ is uniformly distributed over the interval [0, 2π], we get: (2分)共 10 页 第 10 页22()[cos(2)]2()cos(2)2X F A R E F A f f f df τπτπτ∞-∞==⎰ Since X(t) is a real-valued random process, S X (f) is an even function of frequency, we also have: (2分)()()exp(2)()cos(2)X X X R S f j f dfS f j f dfτπτπτ∞-∞∞-∞==⎰⎰where S x (f) is the power spectrum density of X(t). Therefore, we get: (2分)2()()2X F A S f f f =。
通信原理期末考试试题及答案一、选择题(每题2分,共20分)1. 以下哪个是数字通信系统的基本特点?A. 抗干扰能力差B. 频带利用率高C. 传输距离短D. 需要调制解调器2. 在模拟信号调制中,以下哪种方式不是线性调制?A. AMB. FMC. PMD. QAM3. 信道编码的主要目的是:A. 提高传输速率B. 提高信号的功率C. 增加信号的带宽D. 增强信号的抗干扰能力4. 在数字通信中,以下哪个不是误码率的衡量指标?A. BERB. SERC. PERD. SNR5. 以下哪个是时分多址(TDMA)的特点?A. 频谱利用率高B. 需要复杂的同步机制C. 易于实现D. 抗干扰能力差6. 以下哪个是多普勒效应的应用?A. 雷达测速B. 卫星定位C. 无线信号传输D. 移动通信7. 以下哪个是自适应均衡器的主要功能?A. 放大信号B. 滤除噪声C. 补偿信道时延D. 调制解调8. 在无线通信中,以下哪个因素不会导致信号衰减?A. 距离B. 障碍物C. 频率D. 天气条件9. 以下哪个是光纤通信的优点?A. 抗电磁干扰能力差B. 传输距离远C. 传输速率低D. 容易受到水下环境影响10. 以下哪个是数字信号处理的主要应用?A. 音频信号放大B. 视频信号编码C. 数据信号传输D. 模拟信号调制二、简答题(每题10分,共20分)1. 简述数字通信与模拟通信的主要区别。
2. 解释什么是信道容量,并给出影响信道容量的主要因素。
三、计算题(每题15分,共30分)1. 假设有一个数字通信系统,其信道带宽为3000Hz,信噪比为30dB。
请计算该系统的信道容量(以比特每秒计)。
2. 给定一个信号的自相关函数R(t)=J0(2πft),其中J0是零阶第一类贝塞尔函数,f是频率。
如果该信号通过一个具有脉冲响应h(t)=δ(t)-δ(t-T)的线性时不变系统,请计算输出信号的自相关函数。
四、论述题(每题15分,共15分)1. 论述现代移动通信系统中多址接入技术的种类及其优缺点。
通信原理期末考试试题及答案通信原理期末考试试题及答案一、填空题(总分24,共12小题,每空1分)分)1、数字通信系统的有效性用传输频带利用率衡量,可靠性用差错率 衡量。
衡量。
3、广义平均随机过程的数学期望、方差与时间无关,自相关函数只与时间间隔有关。
4、一个均值为零方差为2ns 的窄带平稳高斯过程,其包络的一维分布服从瑞利分布,相位的一维分布服从均匀分布。
分布。
6、信道容量是指:信道传输信息的速率的最大值 ,香农公式可表示为:)1(log 2NS B C +=。
8、对最高频率为f H 的调制信号m (t )分别进行AM 、DSB 、SSB 调制,相应已调信号的带宽分别为2f H 、2f H 、f H 。
二、简答题(总分18,共4小题)小题)1、随参信道传输媒质的特点?(3分)分)答:对信号的衰耗随时间变化、答:对信号的衰耗随时间变化、 传输的时延随时间变化、传输的时延随时间变化、 多径传播多径传播2、简述脉冲编码调制的主要过程。
(6分)抽样是把时间连续、幅值连续的信号变换为时间离散,幅值连续的脉冲信号;量化是把时间离散、幅值连续的脉冲信号变换为幅值离散、时间离散的多电平脉冲信号;编码是把幅值、时间均离散的多电平脉冲信号用一组数字序列表示。
4、简述低通抽样定理。
(3分)分)一个频带限制在(0,f H )内的时间连续信号m(t),如果以H 21f £T 的时间间隔对它进行等间隔抽样,则m(t)将被所得到的抽样值完全确定三、画图题(总分20分,共3小题)小题)2、设信息序列为100000000001100001,试编为AMI 码和HDB3码(第一个非零码编为+1),并画出相应波形。
(6分)1 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 1 1 0 0 0 0 1AMI HDB3AMIHDB3+1 0 0 0+V-B 0 0-V 0 0+1-1+B 0 0+V-1+1 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0-1+1 0 0 0 0-1+1 0 0 0+1-1 0 0-1 0 0+1-1+1 0 0+1-1四、(总分12分)现有一个由8个等概符号组成的信源消息符号集,各符号间相互独立,每个符号的宽度为0.1ms 。
通信原理试题及答案一、选择题(每题2分,共20分)1. 以下哪个不是模拟信号的特点?A. 连续性B. 可量化C. 可存储D. 可再生2. 数字通信系统相比模拟通信系统的优点不包括:A. 抗干扰能力强B. 易于加密C. 传输距离远D. 频带宽度大3. 以下调制方式中,属于线性调制的是:A. ASKB. FSKC. PSKD. QAM4. 在数字通信中,以下哪种编码方式具有错误检测和纠正功能?A. 曼彻斯特编码B. 非归零编码C. 汉明编码D. 归零编码5. 以下哪个是信号带宽的单位?A. HzB. dBC. WD. mV二、简答题(每题10分,共30分)6. 简述数字通信系统的基本组成。
7. 解释什么是信噪比,并说明它在通信系统中的重要性。
8. 描述什么是信道编码,以及它在通信中的作用。
三、计算题(每题25分,共50分)9. 给定一个信号x(t) = cos(2πft),其中f = 1kHz,计算该信号的带宽。
10. 假设一个通信系统使用QPSK调制方式,传输速率为1200波特,计算该系统的比特率。
答案一、选择题1. 答案:B(模拟信号是连续的,不可量化)2. 答案:D(数字通信系统的频带宽度通常比模拟通信系统的窄)3. 答案:A(ASK是频率键控,属于线性调制)4. 答案:C(汉明编码具有错误检测和纠正功能)5. 答案:A(Hz是频率的单位,也是信号带宽的单位)二、简答题6. 数字通信系统的基本组成包括:信源、信源编码器、调制器、信道、解调器、信道解码器和信宿。
7. 信噪比(SNR)是信号功率与噪声功率的比值,通常用dB表示。
高信噪比意味着信号质量高,通信系统能够更有效地传输信息,减少误码率。
8. 信道编码是将原始数据加上冗余信息,形成编码数据,以提高数据传输的可靠性。
在接收端,通过解码过程检测和纠正可能发生的错误。
三、计算题9. 对于信号x(t) = cos(2πft),其带宽B可以通过奈奎斯特准则计算,B = 2f = 2 * 1kHz = 2kHz。
通信原理考试题及答案1. 单选题:a) 通信系统中的调制是指:A. 将基带信号变成带通信号B. 将模拟信号转换成数字信号C. 将数字信号转换成模拟信号D. 将带通信号变成基带信号正确答案:A. 将基带信号变成带通信号b) 下列哪个是基带信号在频谱上的表现形式?A. 窄带信号B. 宽带信号C. 低频信号D. 高频信号正确答案:A. 窄带信号2. 多选题:a) 下列哪些技术属于调幅技术?A. AMB. FMC. PMD. PCM正确答案:A. AM和C. PMb) 调制的作用是:A. 增强信号的传输距离B. 减少信号的功率损耗C. 防止信号受干扰D. 使信号易于传输和处理正确答案:D. 使信号易于传输和处理3. 填空题:a) 传输介质的信号传播速度等于____________除以信号在介质中传播所需的____________。
正确答案:传播距离,时间b) 码元速率是指每秒传输的码元个数,单位为____________。
正确答案:波特(Baud)4. 简答题:请简要解释频谱扩展技术在通信中的应用。
正确答案:频谱扩展技术广泛应用于通信中的多址技术和调制技术。
在多址技术中,频谱扩展技术通过扩展码将用户数据进行编码,使得多个用户的信号能够在同一频带内传输,并在接收端进行解码以分离各个用户的信号。
在调制技术中,频谱扩展技术可以将基带信号编码后扩展到宽带信号,提高抗干扰性能和可靠性。
总结:通过以上考试题目和答案的介绍,我们可以了解到通信原理方面的基本知识和考核内容。
了解调制技术、频谱扩展技术等在通信中的应用,对于理解通信系统的原理和工作机制具有重要意义。
东南大学考试卷( A 卷)课程名称通信原理考试学期04-05-3 得分适用专业考试形式闭卷考试时间长度150分钟Section A(30%): True or False (Give your reason if False,2% for each question)1. A typical mobile radio channel is a free propagation, linear, and time invariant channel.( )2.The power spectral density of a stationary process is always nonnegative. ( )3.In a communication system, noise is unwanted and over which we have incompletecontrol. ( ) 4.If a random process is stationary, it is ergodic; if a Gaussian random process is stationary,then it is also strictly stationary. ( ) 5.Double Sideband-Suppressed Carrier (DSB-SC), Single Sideband (SSB), and FrequencyModulation (FM) are all linear modulation schemes. ( ) 6.Figure of merit (defined as (SNR)O/(SNR)C) of AM of DSB-SC is 1/3, and figure of meritof Amplitude Modulation (AM) is less than or equal to 1/3. ( )7. -law is a nonlinear compression law and A-law is a linear compression law. ( )8.The matched filter at the receiver maximizes the peak pulse signal-to-noise ratio, thus isoptimal in a baseband data transmission system with Inter-Symbol Interference (ISI).( ) 9.Correlative-level coding (also known as partial-response signaling) schemes are used toavoid ISI. ( ) 10.Time-Division Multiplexing (TDM) is used in Asymmetric Digital Subscriber Lines(ADSL) to separate voice signals and data transmission. ( ) 11.If coefficients of an equalizer is adjusted using the Least-Mean-Square (LMS) algorithmadaptively, then the matched filter in front of the equalizer is not necessary. ( ) 12.In an M-ary Phase-Shift Keying (M-PSK) system, if the average probability of symbolerror is P e, then the average Bit Error Rate (BER) of the system is P e/log2M. ( ) 13.With the same Signal-to-Noise Ratio (SNR), 16-ary Quadrature Amplitude Modulation(16-QAM) has better performance than 16-ary Phase-Shift Keying (16-PSK). The reason is that 16-QAM has constant envelop. ( ) 14.With the same SNR, Minimum Shift Keying (MSK) has better performance than Sunde’sFrequency-Shift Keying (FSK). They are both Continuous-Phase Frequency-Shift Keying (CPFSK). ( ) 15.If the largest frequency component of an band-limited signal X(t) is at 100 Hz, then thecorresponding Nyquist rate is 200 Hz. ( )共10 页第1 页Section B(30%): Fill in the Blanks (3% for each question)1.The power spectral density of a stationary process X(t) is S X(f), then the autocorrelationfunction of X(t) is R X(t) = .2. A random process Y(t) is defined as Y(t) = X(t) cos(2πf c t + Θ), where X(t) is a stationaryprocess, f c is a constant frequency, and the phase Θis randomly distributed over the interval [0, 2π]. Suppose the power spectral density of X(t) is S X(f), the power spectral density of Y(t) is S Y(f) = .3.In a Frequency Modulation (FM) system, the modulating signal is m(t) = 2 cos (6πt) V, thefrequency sensitivity is k f = 0.3 Hz/V. Using Carson’s rule, bandwidth of the FM signal is approximately Hz.4.An analog signal is first encoded into a binary Pulse-Code Modulation (PCM) wave.Sampling rate of the PCM system is 8 kHz, number of representation levels is 64. The binary PCM wave is transmitted over a baseband channel using a 4-ary Pulse-Amplitude Modulation (PAM) (that is, a PAM with 4 amplitude levels). The minimum bandwidth requirement for transmitting the PAM wave is kHz.5.Basic operations performed in the transmitter of a PCM systeminclude , , and .6.Bandwidth efficiency of 4-ary Quadrature Amplitude Modulation (QAM) is ;bandwidth efficiency of 8-ary Phase-Shift Keying (8PSK) is .7.In a Delta Modulation (DM) system, sampling rate is f s = 8 kHz and step size is ∆ = 0.1 V.If the input to the DM system is a 1 kHz sinusoidal signal, then to avoid slope overload, the maximum amplitude of this input signal is V.8.12 different message signals, each with a bandwidth of 20 kHz, are to be multiplexed andtransmitted. If the multiplexing and modulation methods are Frequency-Division Multiplexing (FDM) and Single-Sideband Modulation (SSB), respectively, then the minimum bandwidth required is kHz; if the multiplexing and modulation methods are Time-Division Multiplexing (TDM) and PAM, then the minimum bandwidth required is kHz;9.The binary data sequence {b k} = 1010110 is applied to a duobinary (class I partialresponse) system with precoding, as shown in Fig. P1-9 (see next page), where d k = b k⊕d k-1, ⊕denotes modulo-two addition, and a k= 2×d k–1. The initial value of d k is 1.The output of the duobinary encoder is {c k} = . If at the receiving end, the first received digit is 1.25 due to noise, then the receiver output is ˆ{}k b = .共10 页第2 页共 10 页 第 3 页Fig. P1-910. A communication system has the signal-space diagram shown in Fig. P1-10, wheremessage points have equal probability of transmitting. Assume communication channel in this system is Additive White Gaussian Noise (AWGN) channel, and E/N 0 is 12, where N 0 is single-sideband power spectral density of the AWGN. Using union band, theaverage probability of symbol error is overbounded as P e ≤ . (Express using complementary error function erfc(⋅).)1()t φ2()t φ120°120°Message point 1Message point 2Message point 3EFig. P1-10共 10 页 第 4 页Section C(40%): Calculations (8% for each question)1. In a coherent Binary Phase-Shift Keying (BPSK) system, symbols 1 and 0 are representedby signals s 1(t) and s 2(t), respectively.The signals are defined by12())0())c b c s t f t t T s t f t πππ⎧=⎪⎪≤≤⎨⎪=+⎪⎩where E b is the transmitted signal energy per bit, and T b is one bit duration.a) Determine the basis function(s) of coherent BPSK signal constellation; b) Plot the signal-space diagram of coherent BPSK system; c) Determine the error probability of BPSK;d) If there is a phase error ϕ between the phase references of the transmitter andreceiver, determine the error probability of BPSK in this condition again.2. Spectrum of a message signal m(t) is shown in Fig. P3-2. This message signal is DoubleSideband-Suppressed Carrier (DSB-SC) modulated with a carrier wave A c cos(2πf c t). a) If f c = 2 kHz, plot the spectrum of the modulated signal s(t); b) What is the baseband bandwidth W of the message signal m(t)?c) What is the transmission bandwidth B T of the DSB-SC modulated signal?d) What is the lowest value of f c that keeps the DSB-SC modulation from sidebandoverlap?f1 kHz -1 kHzFig. P3-2共 10 页 第 5 页3. Consider a Quadriphase-Shift Keying (QPSK) system. The transmitted signal set isdefined as:cos[2(21)/4],0()0, otherwise c i f t i t Ts t ππ+-≤≤⎧=⎨⎩where i = 1, 2, 3, 4. Every two input bits select one of the signals in transmitted signalset to transmit. The rule of mapping is 10 → s 1(t), 00 → s 2(t), 01 → s 3(t), 11 → s 4(t). a) Determine the basis function(s) of QPSK signal constellation; b) Express s i (t) using the basis function(s);c) If the input binary sequence is 01101000, and suppose fc = 2/T, plot the QPSKwaveform;d) Is the QPSK waveform continuous phase?4. Consider the signal s(t) shown in Fig. P3-4,a) Assuming h(t) is the matched filter of s (t), plot the impulse response of h (t); b) When s (t) is applied to h (t), plot the matched filter output in the time domain.tT0A-A2T/3T/3s(t)Fig. P3-45. Suppose X(t) = Acos(2πft – Θ), where A is a constant, and f and Θ are independent. Θ isuniformly distributed over the interval [0, 2π]. Determine the power spectrum density of X(t) in terms of the probability density function of the frequency f.共 10 页 第 6 页通信原理期终考试参考答案和评分标准考试学期:04-05-3Section A: (30分)1. ⨯ The mobile radio channel is typically time variant.2. √3. √4. ⨯ Stationary is not necessary ergodic.5. ⨯ FM is not a linear modulation scheme6. ⨯ Figure of merit of DSB-SC is 1, not 1/3.7. ⨯ A-law is also a nonlinear compression law.8. ⨯ The matched filter is optimal with AWGN channel.9. ⨯ Correlative-level coding is to use ISI to achieve 2W signaling rate in abandwidth of W Hz. 10. ⨯ FDM is used in ADSL. 11. √12. ⨯ The BER is usually not P e /log 2M. 13. ⨯ 16-QAM is not constant envelop. 14. √ 15. √Section B: (30分) 1.()exp(2)X S f j f df πτ∞-∞⎰共 10 页 第 7 页2.1[()()]4X c X c S f f S f f -++ 3. 7.2 4. 125. Sampling, Quantizing, and Encoding6. 1, 1.57. 1.278. 240, 2409. 0 -2 0 2 0 0 2, 0010110 10. erfc(3)Section C:(40分)1.(a) The basis function is:1()),0c b t f t t T φπ=≤≤. (2分) (b) The signal-space diagram is: (2分)φ1(t)(c) The error probability is 1erfc 2e P =. (2分) (d) With phase error ϕ, the error probability becomes 1erfc 2e P ϕ⎫=⎪⎪⎭. (2分)2. (a) The spectrum is: (2分)共 10 页 第 8 页2 kHz -2 kHz0S(f)f(b) W = 1 kHz; (2分) (c) B T = 2 kHz; (2分)(d) To avoid sideband overlap, the lowest frequency is 1 kHz. (2分)3. (a) The basis functions are: (2分)122()cos(2),02()sin(2),0c c t f t t T Tt f t t T T φπφπ⎧=≤≤⎪⎪⎨⎪=≤≤⎪⎩(b)12()cos (21)()sin (21)(),1,2,3,42424i T T s t i t i t i ππφφ⎡⎤⎡⎤=---=⎢⎥⎢⎥⎣⎦⎣⎦ (2分)(c) The QPSK waveform is: (2分)(d) The QPSK waveform is not continuous phase. (2分)4. (a) h(t) is shown below, where k is a positive constant. (4分)共 10 页 第 9 页tT0kA-kAT/32T/3h(t)(b) The filter output is shown below. (4分)tT 0-kA 2T/3T/32T/3Response of h(t) to s(t)-kA 2T4T/35T/32T5. The autocorrelation function of X(t) is: (2分)22()[()()][cos(22)cos(2)][cos(42)cos(2)]2X R E X t X t A E Ft F Ft A E Ft F F ττππτπππτπτ=+=+-Θ-Θ=+-Θ+ Since Θ is uniformly distributed over the interval [0, 2π], we get: (2分)共 10 页 第 10 页22()[cos(2)]2()cos(2)2X F A R E F A f f f df τπτπτ∞-∞==⎰ Since X(t) is a real-valued random process, S X (f) is an even function of frequency, we also have: (2分)()()exp(2)()cos(2)X X X R S f j f dfS f j f dfτπτπτ∞-∞∞-∞==⎰⎰where S x (f) is the power spectrum density of X(t). Therefore, we get: (2分)2()()2X F A S f f f =。