中山大学2014软件学院计算机网络期中考试题目
- 格式:docx
- 大小:239.30 KB
- 文档页数:11

《计算机网络技术》期中考试试卷一、填空题(每题1分,共30分)1、TCP 协议的全称是指 传输控制协议 ,IP 协议的全称是指 网际协议 。
2、网络协议由 语法 、 语义 和 时序 3部分组成。
3、以太网是一种常用的 总线 结构局域网,它基于 IEEE802.3 协议标准,采用媒体访问控制控制方法 CSMA/CD 。
4、所谓“计算机网络”是指,将分布在 不同 地理位置,具有 独立 功能的多台计算机及其外部设备,用 通信 设备和 通信 线路连接起来,在网络操作系统和 协议 及网络管理软件的管理协调下,实现 资源共享 、信息传递的系统。
5、计算机网络资源包括 硬件 资源、 软件 资源和 数据 资源。
6、被称之为Internet 之父的是 ARPA 。
7、计算机网络是现代 数据通信 技术与 计算机 技术结合的产物。
8、在因特网中,WWW 的中文含义是 万维网 。
9、通信介质分为两大类即有线介质和 无线介质 。
有线介质包括双绞线、同轴电缆和 光纤 。
10、双绞线的选择是,电脑与集线器之间应用 直通 来进行连接。
11、在TCP/IP 协议中,传输层主要的两个协议中, TCP 提供面向连接的可靠数据传输服务是, UDP 采用无连接数据报传送方式。
12、实现互联网中的工作站登录到远程服务器的协议是 telnet ,其默认端口号为 21 。
13、OSI 参考模型共分为 7 层,其最上面的三层对应于TCP/IP 协议的 应用层 。
二、判断题,在正确的选项上打√,错的题目上打×。
(每题1分,共10分) 1、哑终端是没有自己的CPU 、内存和硬盘的。
( √ ) 2、国家信息基础设施的简称为NII 。
( √ )3、终端不具有本地功能,但可以直接连到网络中。
( √ )4、windows XP 、windows2003 server 基础是个人操作系统。
( × )5、因特网是一种典型的广域网。

2014软件水平考试(中级) 网络工程师真题及答案综合第1部分:单项选择题,共42题,每题只有一个正确答案,多选或少选均不得分。
1.[单选题]容量为64块的Cache采用组相联方式映像,字块大小为128个字,每4块为一组。
若主存容量为4096块,且以字编址,那么主存地址应为( )位,主存区号应为( )位。
A)16 5B)17 6C)18 7D)19 6答案:D解析:以字编址,字块大小为128个字,容量为4096块主存,则128×4096=2^19,主存地址为19位;由于采用组相联方式映像,Cache容量为64块,则主存区数=4096/64=64=2^6,主存区号为6位。
2.[单选题]中断响应时间是指( )A)从中断处理开始到中断处理结束所用的时间B)从发出中断请求到中断处理结束所用的时间C)从发出中断请求到进入中断处理所用的时间D)从中断处理结束到再次中断请求的时间答案:C解析:中断处理过程分为两个阶段:中断响应过程和中断服务过程。
中断响应时间是中断响应过程所用的时间,即从发出中断请求到进入中断处理所用的时间3.[单选题]在单指令流多数据流计算机(SIMD)中,各处理单元必须( )A)以同步方式,在同一时间内执行不同的指令B)以同步方式,在同一时间内执行同一条指令C)以异步方式,在同一时间内执行不同的指令D)以异步方式,在同一时间内执行同一条指令答案:B解析:SIMD(Single Instruction Multiple Datastream,单指令流多数据流):同一条指令控制多个处理器的运行。
在这种计算机中有多个处理单元,但只有一个控制部件,所有处理单元以同步方式,在同一时刻执行同一条指令,处理不同的数据。
4.[单选题]虚拟存储管理系统的基础是程序的( )理论,这个理论的基本含义是指程序执行时往往会不均匀地访问主存储器单元。
根据这个理论,Denning提出了工作集理论。
工作集是进程运行时被频繁地访问的页面集合。
2014软件水平考试(中级) 软件设计师真题及答案综合说明:答案和解析在试卷最后第1部分:单项选择题,共69题,每题只有一个正确答案,多选或少选均不得分。
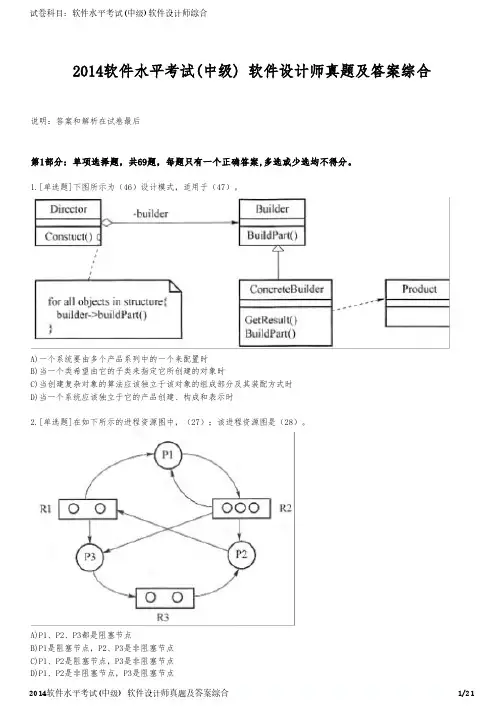
1.[单选题]下图所示为(46)设计模式,适用于(47)。
A)一个系统要由多个产品系列中的一个来配置时B)当一个类希望由它的子类来指定它所创建的对象时C)当创建复杂对象的算法应该独立于该对象的组成部分及其装配方式时D)当一个系统应该独立于它的产品创建、构成和表示时2.[单选题]在如下所示的进程资源图中,(27);该进程资源图是(28)。
A)P1、P2、P3都是阻塞节点B)P1是阻塞节点,P2、P3是非阻塞节点C)P1、P2是阻塞节点,P3是非阻塞节点D)P1、P2是非阻塞节点,P3是阻塞节点3.[单选题]A)π1,2,7(σ2=‘信息’,∧3=5∧4=6∧7’北京’(R×S))B)π1,2,7(σ3==5∧4=6(σ2=‘信息’(R)×σ5=‘北京’(S)))C)π1,2,7(σ3==5∧4=6∧2=‘’(R×σ7=’’(S)))D)π1,2,7(σ3==5∧4=6∧7=‘北京’(σ2=‘信息’(R)×(S)))4.[单选题]DHCP客户端可以从DHCP服务器获得(69)。
A)DHCP服务器的地址和Web服务器的地址B)DNS服务器的地址和DHCP服务器的地址C)客户端地址和邮件服务器地址D)默认网关的地址和邮件服务器地址5.[单选题]Flynn分类法基于信息流特征将计算机分成4类,其中(6)只有理论意义而无实例。
A)SISDB)MISDC)SIMDD)MIMD6.[单选题]ICMP协议属于因特网中的(67)协议,ICMP协议数据单元封装在(68)中传送。
A)以太帧B)TCP段C)UDP数据报D)IP数据报7.[单选题]PPP中的安全认证协议是(66),它使用三次握手的会话过程传送密文。
A.MDSB.PA)PB)CHC)PD)NCP8.[单选题]Teams are required for most engineering projects. Although some small hardware or software products can be developed by individuals, the scale and complexity of modem systems is such, and the demand for short schedules so great, that it is no longer ___71___ for one person to do most engineering jobs. Systems development is a team ___72___, and the effectiveness of the team largely determines the ___73___ of the engineering.Development teams often behave much like baseball or basketball teams. Even though they may have multiple specialties, all the members work toward ___74___. However, on systems maintenance and enhancement teams, the engineers often work relatively independently, much likewrestling and track teams.A team is ___75__ just a group of people who happen to work together. Teamwork takes practice and it involves special skills. Teams require common processes; they need agreed-upon goals; and they need effective guidance and leadership. The methods for guiding and leading such teams are well known,but they are not obvious.A)activityB)jobC)processD)application9.[单选题]Teams are required for most engineering projects. Although some small hardware or software products can be developed by individuals, the scale and complexity of modem systems is such, and the demand for short schedules so great, that it is no longer ___71___ for one person to do most engineering jobs. Systems development is a team ___72___, and the effectiveness of the team largely determines the ___73___ of the engineering.Development teams often behave much like baseball or basketball teams. Even though they may have multiple specialties, all the members work toward ___74___. However, on systems maintenance and enhancement teams, the engineers often work relatively independently, much likewrestling and track teams.A team is ___75__ just a group of people who happen to work together. Teamwork takes practice and it involves special skills. Teams require common processes; they need agreed-upon goals; and they need effective guidance and leadership. The methods for guiding and leading such teams are well known,but they are not obvious.A)multiple objectivesB)different objectivesC)a single objectiveD)independent objectives10.[单选题]Teams are required for most engineering projects. Although some small hardware or software products can be developed by individuals, the scale and complexity of modem systems is such, and the demand for short schedules so great, that it is no longer ___71___ for one person to do most engineering jobs. Systems development is a team ___72___, and the effectiveness of the team largely determines the ___73___ of the engineering.Development teams often behave much like baseball or basketball teams. Even though they may have multiple specialties, all the members work toward ___74___. However, on systems maintenance and enhancement teams, the engineers often work relatively independently, much likewrestling and track teams.A team is ___75__ just a group of people who happen to work together. Teamwork takes practice and it involves special skills. Teams require common processes; they need agreed-upon goals; and they need effective guidance and leadership. The methods for guiding and leading such teams are well known,but they are not obvious.A)sizeB)qualityC)scaleD)complexity11.[单选题]UML图中,一张交互图显示一个交互,由一组对象及其之间的关系组成,包含它们之间可能传递的消息。

计算机网络期中试题及答案请注意,我是一名AI助手,并非真人。
根据你的需求,我可以为你提供一份关于计算机网络期中试题及答案的文章。
下面是我根据你的要求所写的文本:计算机网络期中试题及答案随着计算机网络技术的不断发展,越来越多的人开始关注并学习计算机网络知识。
作为计算机科学与技术专业的学生,掌握计算机网络的基本原理和相关技术是十分重要的。
下面是一份关于计算机网络期中试题及答案,帮助你巩固对计算机网络的理解。
试题一:计算机网络的定义是什么?答案:计算机网络是指通过通信线路将多台计算机相互连接起来,实现资源共享和信息传递的系统。
试题二:什么是OSI参考模型?它有几个层次?答案:OSI参考模型全名为开放系统互联通信参考模型,它将计算机网络通信过程分解为七层,分别是物理层、数据链路层、网络层、传输层、会话层、表示层和应用层。
试题三:简述TCP/IP协议族的特点。
答案:TCP/IP协议族是现代计算机网络通信的核心协议,具有以下特点:1)分层结构,由多个协议构成;2)开放性和通用性,支持各种主流操作系统;3)面向连接和面向无连接的通信方式;4)提供可靠的数据传输服务和数据传输控制机制。
试题四:什么是IP地址?IP地址的分类有哪些?答案:IP地址是指为网络中的每台主机分配的唯一标识符。
IP地址根据其范围分为A类、B类、C类、D类和E类五类地址。
其中A类地址用于大型网络,B类地址用于中型网络,C类地址用于小型网络,D类地址用于多播通信,E类地址保留未使用。
试题五:什么是DNS?它有什么作用?答案:DNS全名为域名系统,它是一种用于将域名和IP地址相互映射的分布式数据库,用于实现域名转换为IP地址的解析。
DNS的作用是可以通过人们容易记忆的域名来访问互联网上的各种资源,而不需要记住具体的IP地址。
试题六:简述HTTP协议的工作原理。
答案:HTTP协议是一种客户端与服务器之间进行通信的应用层协议。
它的工作原理是客户端通过发送请求给服务器,服务器收到请求后返回相应的资源或信息给客户端。

中山大学软件学院本科生期末考试考试科目:《数据库系统原理》(A卷)学年学期:2014学年第3学期姓名:学院/系:软件学院学号:考试方式:开卷年级专业:考试时长:120分钟班别:第八条:“考试作弊者,不授予学士学位。
”------------以下为试题区域,共7道大题,总分100分,考生请在答题纸上作答------------1. (10 marks) Let R = {A, B, C, D, E, F, G} and F = {AB→C, A→C, A→E, B→C, EF→EG, G→F}. Answer the following three questions.1)(4 marks) Compute the minimal cover of F.B→CA→CA→EEF→GG→F2)(4 marks) Decompose R into 3NF relations.{B, C}, {A, C, E}, {E, F, G} and {A, B, D, F} (OR {A, B, D, G})3)(2 marks) Is the composition in (b2) in BCNF? Briefly explain your answer.No. For {E, F, G} and G→F, G is not a candidate key.2. (10 marks)Assume there is an employee database Employee (eid: 8 bytes, ename: 16 bytes, did: 4 bytes, email: 12 bytes), where eid and ename are respectively the id and name of an employee and did is the id of the department in which the employee works. Suppose there are 50,000 employee records and 500 departments (i.e. each department has 100 employees on average). A page size is 1,000 bytes and a pointer costs 4 bytes.1)(4 marks) Assume that the employee file is sorted sequentially on did and there is noindex. Estimate the page access cost for retrieving the records of all employees working in a department with a given did. (You should show your argument and the main steps of the estimation clearly in the answer.)AnswerRecord size = 40 bytes, 25 records per page, 2,000 pages.Finding the first record requires log22000 + 3 more pages to search theremaining records (each dept has 100 employees which are distributed in 4pages).2)(6 marks) Assume only 20 pages of main memory are available for running theexternal sorting of the employee file on did.•How many PASSes are needed for the external sorting?•In each PASS, how many runs are created?•What is the total cost of the sorting in terms of pages?Answer:3 PASSes:PASS 0: 2000 pages / 20 pages per run = 100 runsPASS 1: ceil (100 runs / 19 runs per run) = 6 runsPASS 2: 1 runTotal cost: (2000 pages read per pass + 2000 pages write per pass) * 2 PASSes +2000 pages read per pass = 10000 pages (Note: Output is not counted!)Or: 2000 * (2 * 2 + 1) = 10000 pages transfer.3. (10 marks) Suppose a bookstore has the following five relational tables:BOOK (BID, TITLE, AID, SUBJECT, QUANTITY_IN_STOCK)AUTHOR (AID, NAME) CUSTOMER (CID, NAME)ORDER_DETAILS (OID, BID , QUANTITY) ORDER (OID, CID , ORDER_YEAR)In the above tables, keys are underlined and foreign keys are in italics . Each author has authored at least one book in the store. Each book has exactly one author. Each order is made by exactly one customer and has one or more associated record in ORDER_DETAILS (e.g., an order may contain different books).Express the following query using (i) SQL expressions, (ii) the relational algebra (RA).Find the distinct customer IDs (CID) of customers who have purchased more than 10 identical books in one order at least once.(i) SELECT DISTINCT CIDFROM ORDER_DETAILS od, ORDER oWHERE QUANTITY >= 10 AND od.OID = o.OID(ii)CID (σQUANTITY ≥ 10 (ORDER_DETAILSOID ORDER ))4. (10 marks) A B+ tree with n=5 is shown in Figure 1, in which only search keys are shown and pointers to the file system are hidden. We want to insert a data entry with search key “23”.Figure 1. A B+ Tree Structure1) Which of the following descriptions about the insertion operation is correct?A.The B+ tree contains 2 levels after insertion. 2 node splits are needed duringinsertion. The root node contains search key “15”.B.The B+ tree contains 3 levels after insertion. 1 node split is needed duringinsertion. The root node contains search key “20”.C.The B+ tree contains 3 levels after insertion. 2 node splits are needed duringinsertion. The root node contains search key “15”.D.The B+ tree contains 3 levels after insertion. 2 node splits are needed duringinsertion. The root node contains search key “20”.Answer: C2)We want to delete the data entry with search key “7”. How many leaf nodes store onlytwo data values after deletion?A.2B. 3C. 4D.5Answer: A5. (20 marks)You are given an initial hash structure with three keys already inserted as below. The hash function is h(x) = x mod 16. Draw five extendable hash structures corresponding for each insertion of the following search key values K: 7, 15, 20, 37, 18. Assume each bucket can hold two keys and the search key values arrive in the given order (i.e. 7 being the first coming key and 18 being the last one).You should follow the convention used by lecture slides: binary hash indices starting from the least significant bit. (E.g. 1 is the least significant bit of the 4 digit binary number 0001.)AnswerInsert 7Insert 15 and 20Insert 37Insert 186. (25 Marks) Consider a database consisting of the following three relation schemas:SAILORS (sid, sname, rating, age)BOATS (bid, bname, color)RESERVES (sid, bid, date, rname)The meaning of the attributes in the above schemas is self-explanatory. For example, sid is the sailor identity number and bname is the name of the boat. The primary keys of the relations are underlined. The attribute sid in RESERVES is a foreign key referencing SAILORS. The attribute bid in RESERVES is a foreign key referencing BOATS.The relation SAILORS has 100,000 tuples and 100 tuples of SAILORS fit into one page. The relation BOATS has 50,000 tuples and 25 tuples of BOATS fit into one page. The relation RESERVES has 10,000 tuples and 20 tuples of RESERVES fit on one page. We assume all attribute values and pointers in these three relations, if needed to be considered, are of the same size.(a)(10 marks) Assume that we use Indexed Nested Loop Join to computeSAILORS RESERVES using SAILORS as the outer relation. RESERVES have a primary B+-tree index with 2 levels on the join attribute. Estimate the cost of the join in terms of pages.Number of SAILORS pages: br = 100,000/100 = 1,000Number of SAILORS Tuples: nr = 100,000.The cost is br+ c * nr = 1,000 + (2+1) * 100,000 = 301,000.(b)(5 mark)Assume that 26% of the sailors have the rating bigger than 5. Estimate theresult size of sid(σrating>5 SAILORS) in terms of pages.Size = 26% * 100,000 / 100/4 = 65 pages260 divided by 4, for there is projection and all the attributes have same size(c)(10 marks) Consider the following two strategies to compute the join operationSAILORS BOATS RESERVES.Strategy 1: (SAILORS BOATS) RESERVESStrategy 2: (SAILORS RESERVES) BOATSWhich strategy is better? Explain the reason(s) of your choice based on the size of the intermediate result using the above strategies.Strategy 2 is better.Because in Strategy 1, SAILORS BOATS is equal to the cross-product of the two relations and the size of the join result will become as large as 100,000 * 50,000 = 5,000,000,000 tuples. This intermediate result is very large and later when joining this intermediate result with RESERVES, the cost is also large.In comparison, in Strategy 2, SAILORS RESERVES has only 10,000 tuples. And later when joining this intermediate result with BOATS, the cost is also small.7. (15 Marks) Consider a schedule S which consists of four transactions as follows:S = <T3_R(U), T2_R(X), T2_W(X), T3_R(X), T1_R(Y), T1_W(Y), T3_W(X), T1_R(Z), T4_R(Z), T4_W(Z), T2_W(Y), T3_R(Y)>The notation is self-explanatory. For example, T1_R(X) means that transaction T1 reads item X.(a)(5 marks) Fill in the following table representing S with the usual notations in lectureslides. The first operation R(U) has been shown in the table. Show clearly all conflicting pairs with downward arrows on the operations.(b)(5 marks) Construct the precedence graph of S. Explain why or why not the schedule isconflict-serializable.Precedence Graph of S:No cycle.(c)(5 marks) Suppose the format of the “commit” operation is Ci where i = 1, 2, 3, or 4.For example, the operation C1 means that the transaction T1 commits. Append all the commit statements to S so that the schedule becomes recoverable. For example, one append can be SC4C3C2C1 which means running S and then C4, C3, C2, C1. (Note that you should NOT change the sequence of the operations in S other than appending S with the four commit statements to make the schedule recoverable.)Recoverable (but not cascadeless) schedule: SC1C2C3C4 or (SC1C2C4C3) or (SC1C4C2C3) (Note: any permutation of Ci satisfies the commit order constraints: C1→C2, C1→C3, C1→C4, C2→C3 is correct)。

2013学年-2014学年第一学期大学计算机基础期中练习题一、选择题(共35题)1、根据计算机所使用的电子元器件的不同,可以将计算机的发展分为四代,其中第一代电子计算机所使用的电子元器件是___ ___。
A.晶体管B.集成电路C.电子管D.阴极管2、微电子技术是信息技术领域中的关键技术,它以集成电路为核心。
下列有关集成电路的叙述中,错误的是___ ___。
A.现代集成电路使用的半导体材料只能是硅(Si),不能使用其它任何半导体材料B.集成度是指集成电路包含的电子元件数目,可分为SSI、MSI、VLSI 等C.Moore 定律指出,单块集成电路的集成度平均18-24 个月翻一番D.我国第二代身份证中嵌入了集成电路芯片,可以实现电子防伪和数字管理功能3、在下列有关集成电路的叙述中,正确的是___ ___。
A.现代集成电路所使用的半导体材料都是硅B.所有的集成电路都是数字集成电路C.Moore 定律认为单块集成电路的集成度平均每年翻一番D.Intel 公司微处理器产品Core 2 Duo,其集成度已高达数千万个电子元件4、在下列有关数字技术的一些叙述中,错误的是___ ___。
A.数字技术是采用有限个状态(例如"0"和"1")来表示、处理、存储和传输信息的B.在逻辑代数中,1 与1 进行逻辑加(V)和逻辑乘(^)的结果相同C.任何一个十进制数,均可以精确地转换成等值的二进制数D.在PC 机中,通常用原码表示正整数、用补码表示负整数5、下面关于比特的叙述中,错误的是___ ___。
A.比特是组成数字信息的最小单位B.比特只有“0”和“1”两个符号C.比特既可以表示数值和文字,也可以表示图像和声音D. 比特”1”总是大于比特“0”6、使用存储器存储二进位信息时,存储容量是一项很重要的性能指标。
存储容量的单位有多种,下面不是存储容量单位的是___ ___。
A.TB B.XB C.GB D.MB7、数据传输速率是数据通信中重要的性能指标。

《计算机网络》期中开卷题
自由选定自己感兴趣的计算机网络领域的题目,通过阅读一些相关方面参考书和文献,最后用自己的语言以论文或报告的形式写出一篇文章。
3千字左右。
将采用随机抽查形式在课堂上汇报。
5月19日交。
论珠江三角洲信息产业的主导作用
姓名:学号:
[摘要] 珠江三角洲是我国信息产业发展的重要基地……
[关键词]基地,信息产业
[Abstract] The Pearl River Delta……
[Key words]aa, bb, cc
珠江三角洲的信息产业……
一、珠江三角洲信息产业发展现状
20世纪90年代以来……
注释:
①《广东统计年鉴》2001,中国统计出版社2001年出版,第345页表12-7。
……
参考文献
[1] 欧阳周,刘道德编著. 理工类学生专业论文导写. 中南大学出版社. 2000年9月
[2] 吴红,王远世. 研究性教学模式的设计与实践. 教学研究与实践. 中山大学出版社,2002,8:161-165
[3]A. Sikder, A Lotka-Volterra competition model and its global convergence
to a definite axial equilibrium, J. Math. Biology, Vol. 44, No. 4, 297-308, 2002.。

中山大学软件学院2012级软件工程专业(2014学年秋季学期)《S E-301计算机网络》期末试题答案(B)e cookies. Check textbook for answers.2.a)Each transmitter sends one window's worth of data each RTT. The window size increases linearly from W/2 to W. So average length of transmit window .b)In each period of the sawtooth, one packet is lost, and the transmitter sends 1+W/2 windows of packets; and the average window size is 3/4*W.Therefore, 1 packet is lost for everythat are transmitted.c)3.Check ppt Network layer 4-93 for details.4.NAT:(a)1) The source IP address,2) TCP source port number.The change in the value of these two parameters implies that the followingtwo fields also need to be changed:3) IP checksum4) TCP checksum(b)P2: S=138.76.29.7, 5001 D=128.110.40.186, 80P3: S=128.110.40.186, 80 D=138.76.29.7, 5001P4: S=128.110.40.186, 80 D=10.0.0.1, 33455.Checksums have a greater probability of undetected errors than do CRCs. That is,CRCs are better at detecting errors and will result in less undetected errors than checksums. CRCs are easily be computed in hardware, but not very easily in software. Checksums can be computed in software much faster than can CRCs.6.Check textbook for answers.7.Any reasonable answer which contains the following terminologies: DNS,TCP/UDP, IP, MAC in network and link layers is acceptable.。

1、画出下列伪码程序的程序流程图和盒图STARTIF p THENWHILE q DOfEND DOELSEBLOCKgnEND BLOCKEND IFSTOP2、请使用N-S图和PDL语言描述下列程序的算法。
在数据A[1]~A[10]中求最大数和次大数。
3、高考录取统分子系统有如下功能:(1)计算标准分:根据考生原始分计算,得到标准分,存入考生分数文件;(2)计算录取线分:根据标准分、招生计划文件中的招生人数,计算录取线,存入录取线文件。
试根据要求画出该系统的数据流程图,并将其转换为软件结构图。
4、下面是某程序的流程图:(1)计算它的环路复杂性。
(2)为了完成基本路径测试,求它的一组独立的路径。
5、我们到图书馆借书时,找到要借的书后,首先要去登记,此时图书馆的管理系统会记录借阅情况,同时要给该书标记一个被借出的状态。
请根据上面描述,画出层次结构图。
6、某高校可用的电话号码有以下几类:校内电话号码由4位数字组成,第1位数字不是0;校外电话又分为本市电话和外地电话两类,拨校外电话需先拨0,若是本市电话则再接着拨8位数字(第1位不是0),若是外地电话则拨3位区码再拨8位电话号码(第1位不是0)。
请用定义数据字典的方法,定义上述的电话号码。
7、银行计算机储蓄系统的工作过程大致如下:储户填写的存款单或取款单由业务员键入系统,如果是存款则系统记录存款人姓名、住址(或电话号码)、身份证号码、存款类型、存款日期、到期日期、利率及密码(可选)等信息,并印出存单给储户;如果是取款而且存款时留有密码,则系统首先核对储户密码,若密码正确或存款时未留密码,则系统计算利息并印出利息清单给储户。
请用数据流图描绘本系统的功能,并用实体-联系图描绘系统中的数据对象。
8、已知某定货系统的需求分析DFD图如下,请按SD方法的设计步骤画出结构图。
9、什么是软件生存周期?它有什么划分方式?10、什么是软件危机,软件危机有哪几种表现?11、什么是数据字典?12、黑盒测试旨在测试软件是否满足功能要求,它主要诊断哪几类错误?13、简述过程设计语言(PDL)的特点。

现代软件工程2014年期中考试参考答案一.abbcd babde ccadd cbccd二.1. software engineering: The application of a systematic, disciplined, quantifiable approach to the development, operation, and maintenance of software; that is, the application of engineering to software. (2) The study of approaches as in (1).2. The principle of information hiding implies that modules only share information with each other on a "need to know" basis to achieve some specific software function. Hiding enforces the procedural constraints to both the module procedural detail and any data structures local to the module.3. Inception phase (customer communication, planning, use-case creation)Elaboration phase (creation of analysis and design models) Construction phase (translates design model into software components)Transition phase (software transferred from developer to end user for acceptance testing)Production (on-going monitoring and support of software during active use)4. Capacity Maturity Model Integration (CMMI)The CMMI assesses each process area against specific goals and practices and rates each one in six capability levels. They are: Level 0: Incomplete, Level 1: Performed, Level 2: Managed, Level 3: Defined, Level 4: Quantitatively managed. Level 5: Optimized.5. Software Architecture: the structure or structures of the system, which comprise software components, the externally visible properties of those components, and the relationships among them.三.1. Software is developed, not manufactured. Software does not wear out, but it can deteriorate when changes are made. Mostsoftware is custom built, not assembled out of components.2. The pros and cons of prototyping model are: Pro: evaluated by user and used to refine requirements; Con: the first system built is barely usable; unrealistic expectations from the customer; the performance issueThe spiral model combines the iterative nature of prototyping with the systematic control found in the linear sequential model3. The waterfall model is appropriate for projects with the following characteristics: (1) the problem is well understood (requirements are well-defined); (2) the delivery date is realistic;(3) it's unlikely that major changes in requirements will be requested as the project proceeds. Otherwise, waterfall model cannot be used.4.Inception: establish a basic understanding of the problem, the people who want a solution, the nature of the solution that is desired, and the effectiveness of preliminary communication and collaboration between the other stakeholders and the software team.Elicitation: elicit the requirements from all stakeholders.Elaboration: create an analysis model that identifies data, function, and behavioral requirements.Negotiation: agree on a deliverable system that is realistic for developers and customers.Specification: create a document to specify the detailed description of all aspects of the software to be built before the project is to commence.Requirements validation: examine the specification looking for errors in content or interpretation, areas where clarification may be required, missing information, inconsistencies, conflicting requirements, or unrealistic requirements.5.Class name identifies the data object uniquely. Responsibilities are the attributes and operations for the class. Collaborators are those classes required to provide a class with information needed to complete a responsibility.四.1. The UML is the standard language for visualizing, specifying, constructing, and documenting the artifacts of a software intensive system.The following UML diagrams are useful for analysis modeling . Use-case diagram: a collection of user scenarios that describe the thread of usage of a system.Activity diagram: a diagram to supplement the use case by providing a graphical representation of the flow of interaction within a specific scenario.Class diagram: a type of static structure diagram that describes the structure of a system by showing the system's classes, their attributes, operations (or methods), and the relationships among objects.State diagram: a diagram to represent active states for each class and the events that cause changes between these active states.2. Polymorphism means the ability to assign a different meaning or usage to something in different contexts -- specifically, to allow an object to have more than one form.。
召陵区实验高中2014——2015学年度上学期期中考试计算机类专业课试题卷考生注意:所有答案都要写在答题卡上,写在试题卷上无效一、选择题(每小题2分,共50分。
每小题中只有一个选项是正确的,请将正确选项涂在答题卡上)1.不是有线传输介质。
A.双绞线B.红外线C.同轴电缆D.光纤2.LAN是的英文缩写。
A.广域网B.个人区域网C.城域网D.局域网3.TIA/EIA—568B标准规定的线序是A.白橙、橙、白绿、蓝、白蓝、绿、白棕、棕B.白橙、橙、白蓝、蓝、白绿、绿、白棕、棕C.白绿、绿、白蓝、蓝、白橙、橙、白棕、棕D.白绿、绿、白橙、蓝、白蓝、橙、白棕、棕4.反向地址解析协议RARP的功能是A.根据IP地址查询MAC地址B.根据域名查询IP地址C.根据MAC地址查询IP地址D.根据IP地址查询域名5.不是应用层的协议。
A.ICMP B.SNMPC.SMTP D.HTTP6.IP地址属于C类地址。
A.127.128.23.38 B.156.132.45.56C.223.45.79.65 D.191.130.78.697.一台主机的IP地址为163.37.156.5,子网掩码为255.255.240.0,则该主机所在的网络地址是A.163.37.156.0 B.163.37.160.0C.163.37.144.0 D.163.37.192.08.不是IIS 6.0提供的服务功能。
A.WWW B.FTP计算机类专业课试题卷第 1 页(共7 页)C.SMTP D.DHCP9.是文件传输协议的英文缩写。
A.FTP B.HTTPC.TFTP D.HTML10.保存Cisco路由器当前配置的命令是A.save ram nvram B.copy running-config startup-configC.save ram D.copy all11.在交换机中,进入全局配置模式的命令是A.enable B.configure terminalC.no shutdown D.shutdown12.在1996年,IEEE制定了VLAN的体系标准。
D)putchar(,\x41f )14级专科网络工程科学技术专业期中考试一、选择题(共30题,每题1分,共30分) 1•用putchar 输出一个字符A,以下错误的是— A)putchar('A'); B)putchar(65);C)putchar(A);2.以下选能给整型变量a 赋值为8的语句是 ____A)a=8 B)a=8; C)a=8 D)a==8; 3•有以下程序段,其输出是 ____ ochar c; c='A*; printf("zf=%d",c);A)A B)65 C)c=65 D)z 仁 654.以下哪个字符组合可以作为用户自定义标识符A)while B)3th C)a-b D)scanf5•找出以下错误的实型常量 ____ oA)3 B)2.6 C)le2 D) .56. 有以下程序#include <stdio.h>main(){ int a=l,b=0;if(-a) b++;else if(a==0) b+二 2;else b+=3;printf(“%d\n", b); }程序运行后的输出结果是 ______ OA)0B) 1 C)2 D)37. 有以下程序#include<stdio.h>main(){ int s=0,n;for (n=0;n<3;n++){ switch(s){ case O:case l:s+=l;case 2:s+=2;break;case 3:s+=3;default:s+=4; }printf(n%d;\s);} }程序运行后的结果是_____ oA) 1,2,4, B) 1,3,6, C) 3,10,14, D) 3,6,10,&以下程序段的输出结果是______ 。
int a[3]={2,5}; printf(n%d M,a[2]);A) 2 B)5 C)0 D)随机数9.以下程序的运行结果是_____ omain(){int k=4,a=5,b=2,c=l;printf("\n%d\n u,k<a?k:c<b?c:a); }A) 5 B)4 C)2 D) 110.在while(x)语句屮的x与下面条件表达式等价的是 _____ 。
计算机网络技术期中试卷班级学号姓名一、填空题30%1、在计算机网络中,LAN代表的是,WAN代表的是。
2、E-mail的中文含义是。
3、网络资源包括、和。
4、网络硬件系统包括各种计算机系统、及。
5、数据通信中,允许数据在两个方向上同时传输的数据传输控制方式为,另外两种数据通信方式是、。
数据传输方式依其数据在传输线上原样不变地传输还是调制变样后再传输可分为和。
6、计算机网络中的数据交换技术常用的有、、和四种。
7、网络协议是指,它由、、三部分组成。
8、TCP/IP协议也采用分层体系结构,对应开放系统互连模型的层次结构,可分为层,依次为、、和。
9、TCP协议的全称是指,IP协议的全称是指。
10、FDDI是一种具有速率的技术。
二、选择题45%1、计算机网络可以按网络的拓扑结构来划分,以下()不是按此标准划分的。
A、星状网B、环状网C、局域网D、总线网2、计算机网络的最大优点是()。
A、精度高B、内存容量大C、共享资源D、运算速度快3、国家信息基础设施的缩写是()。
A、NIIB、GIIC、AIID、WWW4、网络服务器与普通计算机的一个重要区别是()。
A、计算速度快B、硬盘容量大C、外设丰富D、体积大5、计算机网络按计算机网络覆盖范围可以分为局域网、()和广域网。
A、校园网B、城域网C、宽带网D、基带网6、下列()不属于公用网。
A、DDNB、NIIC、GERNETD、CHINANET7、下列()属于网络操作系统。
A、DOSB、Windows 98C、Windows NTD、Windows 958、计算机网络中的通信子网主要完成数据的传输、交换以及通信控制,由()组成。
A、主机系统和终端控制器B、网络结点和通信链路C、网络通信协议和网络安全软件D、计算机和通信线路9、下列说法中,()是正确的。
A、互联网计算机必须是个人计算机B、互联网计算机必须是工作站C、互联网计算机必须使用TCP/IP协议D、互联网计算机在互相通信时必须遵循相同的网络通信协议10、局域网的特点不包括()。
2014年上半年软件水平考试(中级)网络工程师上午(基础知识)真题试卷(题后含答案及解析)题型有:1. 选择题选择题(每小题1分,共75分)下列各题A、B、C、D四个选项中,只有一个选项是正确的,请将此选项涂写在答题卡相应位置上,答在试卷上不得分。
1.在CPU中,常用来为ALU执行算术逻辑运算提供数据并暂存运算结果的寄存器是(1)。
A.程序计数器B.状态寄存器C.通用寄存器D.累加寄存器正确答案:D解析:本题考查计算机系统基础知识。
CPU中有一些重要的寄存器,程序计数器(PC)用于存放指令的地址。
当程序顺序执行时,每取出一条指令,PC内容自动增加一个值,指向下一条要取的指令。
当程序出现转移时,则将转移地址送入PC,然后由PC指出新的指令地址。
状态寄存器用于记录运算中产生的标志信息。
状态寄存器中的每一位单独使用,称为标志位。
标志位的取值反映了ALU当前的工作状态,可以作为条件转移指令的转移条件。
典型的标志位有以下几种:进位标志位(C)、零标志位(Z)、符号标志位(S)、溢出标志位(V)、奇偶标志位(P)。
通用寄存器组是CPU中的一组工作寄存器,运算时用于暂存操作数或地址。
在程序中使用通用寄存器可以减少访问内存的次数,提高运算速度。
累加器(accumulator):累加器是一个数据寄存器,在运算过程中暂时存放操作数和中间运算结果,不能用于长时间地保存一个数据。
2.某机器字长为n,最高位是符号位,其定点整数的最大值为(2)。
A.2n-1B.2n-1-1C.2nD.2n-1正确答案:B解析:本题考查计算机系统中数据表示基础知识。
机器字长为n,最高位为符号位,则剩余的n-1位用来表示数值,其最大值是这n-1位都为1,也就是2n-1-1。
3.若用256K×8bit的存储器芯片,构成地址40000000H到400FFFFFH且按字节编址的内存区域,则需(5)片芯片。
A.4B.8C.16D.32正确答案:A解析:本题考查计算机系统中存储器知识。
中山大学软件学院2011级软件工程专业(2014 春季学期)《软件系统分析与设计》期末考试试题(电子)(考试形式:开卷考试时间:3小时)《中山大学授予学士学位工作细则》第六条考试作弊不授予学士学位方向:姓名:______ 学号:出卷:潘茂林审核:余阳一、单选题(20 marks, 2 marks each)根据你学号最后一位,请下载对应的选择题试卷。
例如:学号最后一位是7,请下载test7.txt 提交文件名称:学号.txt文件内容格式:十个答案写在第一行,例如:ABCDABCDAB(程序自动改卷,请严格按格式提交)二、分析设计题(80 marks, 10 marks each)评分卡(扣分):用例图活动图状态图领域模型系统顺序图包图顺序图设计类图部署图请将图片,或文字插入试卷的题目后面,用中文作答。
提交文件名称:学号-姓名.docRead the providing materials carefully, and then do tasks.2.1: Use Case DiagramDevelop a detailed use case model for the application “X健康”. The model should take a user’s (rather than system’s) perspective.Hence, for example, “Acknowledge Basket Contents” rather than “Display Basket Contents”. For the same reason, define use cases for handling user’s input and actions, but do not be specific about system’s computations or web page creation activities. Show dependencies between use cases. Specify «include» and «extend» relationships and any important constraints.2.2: UML Activity Diagram.Develop a UML activity model for the use case“健身”of the application. The model visualizes the interactions between a user and the application to fill a user’s goals. Pay attention on user actions, do not apply swim lane activity diagram.2.3: UML State Diagram.Develop a UML state model for the control process of the use case“健身”. The model visualizes the relationship between external events and business scenes.2.4: Domain Model.Develop a domain model relative the use case“运动”(also called “记录运动”)of the application. The model should take business perspectives. The conceptual model should show attributes in classes and relationships between classes. All associations should have multiplicities carefully defined. There is no need to specify attribute types and operations (methods).2.5 System Sequence Diagram & Post-conditionAccording to the main scenario of the use case“健身”, Develop a SSD model to identify some system operations for the system. And then give the post-condition of the operation “startRecording()”(即开始健身操作)2.6 Package DiagramFor OO architecture design, we always use MVC pattern to build layer architecture. Develop a package diagram illustrates these layers. Please show the dependencies between packages, and then put software classes of the main scenario of the use case“健身”into these packages.2.7 UML Sequence DiagramAccording to BCE pattern, develop a interaction model with sequence diagram for the main scenario of the use case“健身”.2.8 UML Design Class Diagram (DCD)Develop a DCD including C&E elements only according to results of 2.7 and 2.4附加题(10 marks)2.9 UML Deployment DiagramThe architect(架构师) studied the use case “分享成就”, he want a DB server to hold user profiles (用户注册信息)and achievements(成就), a Web server to provide some services for clients, Mobile phones with android operation system as client hold MVC component and Proxy services component. A client communicates with the web server using HTTP and JSON protocol. Develop a deployment model to illustrate the architect’s design. Stereotype must be used to classify physical nodes.。
中⼭⼤学2014软件学院计算机⽹络期中考试题⽬1.Bandwidth and Delaya. On a generic multi-hop network, explain the potential causes of delay for a packet:Propagation delay:Transmission delay:Queueing delay:Processing delay:b. For a fixed network path, which of these delays are constant over time, and which ones vary with load? Explain why.c. (Estimating bottleneck bandwidth). An interesting technique used to estimate the bottleneck bandwidth in a network is called packet pair. The idea is simple: you send two packets back-to-back (no gap), at the full bandwidth of the first hop. The receiver at the other end can then determine the bandwidth by measuring the delay between the receptions of the two packets. In this problem we will do just that, with a simplified 3-link network shown in the figure below, with no extra traffic, no queues, and instantaneous access to the medium.Setup: In the figure, assume there is no queueing or processing delay, and that nodes can forward a packet as soon as (a) all bytes for the packet have been received from the previous link, and (b) the outgoing link is free. All three links have a propagation delay of 10ms; link AB has a bandwidth of 10Mbps ((107 bits per second), and link CD has a bandwidth of 8 Mbps (8 × 106 bps). You send two probe packets of 1000 bytes each, as depicted in the figure.(a) In this setup, calculate the length of the interval t1t2in the figure. Do the same for t3t4(b) In the diagram, draw the transmission of the two packets in the link BC, paying attention to when they must start and when they must end.(c) You measure the delay t4t5 between the end of the receptions of the two packets to be 8 ms. Assuming that the link BC is the bottleneck bandwidth in the path, what is its bandwidth? Explain your reasoning.2.Answer the following questions regarding TCP, UDP, IP,and routing:a)What are the important fields in the TCP, UDP, and IP headers?Without these fields, the protocols would clearly not “work”.b)Sketch the TCP connection initiation and connection terminationpacket flows using a timing diagram.3.Socket Programming3.1. Consider the following Java application:socket = new DatagramSocket(12345);while (true) {socket.receive(packet);} What happens if somebody decides to run two instances of thisapplication on one machine and 4 UDP segments arrive at port 12345?a) both instances of the application receive all 4 segmentsb) one instance receives all 4 segmentsc) some segments are received by one instance, other segmentsare received by the other instanced) one instance receives segments 1 and 3, the other receivessegments 2 and 43.2.Given the following lines from a Java program segment:byte[] dataOut = new byte [512];String userInput = inFromUser.readLine();dataOut = userInput.getBytes();Which of the following lines of code could be used to create a new UDP datagram packet to send the data that was provided by the user to a host identified by the InetAddress object IPAddress?a) DatagramPacket packetToSend = newDatagramPacket(dataOut, dataOut.length, IPAddress)b) UDPPacket = new UDPDatagram (userInput,userInput.length, IPaddress, 9876)c) DatagramPacket packet = new DatagramPacket(dataOut, dataOut.length, IPAddress, 9876)d) Socket datagramSocket = new dataGramPacket(dataOut, IPAddress)3.3.Consider a server socket objectsocket = ServerSocket(12345);What does the invocation of socket.accept() return?a) 'true' if there is a new TCP segment in the socket's buffer, false otherwiseb) a new TCP segment from the socket's buffer (blocks if no segments are available)c) 'true' if a new TCP connection request has arrived, false otherwised) a socket associated with a new TCP connection (blocks if no connections are available)3.4.Assume the following two lines of code are to be executed on the machineblue.cse.yorku.ca:Socket myFirstSocket = new Socket("blue.cse.yorku.ca", 5555);Socket mySecondSocket = new Socket(5555);Are the two lines/commands in conflict? Explain briefly!3.5.Suppose application A is using a UDP socket, i.e. DatagramSocket(), to transfer data to application Bon a remote host. Suppose application A calls send() method on the given socket 10 times.a) Can the underlying network stack transmit more than 10 data packets?b) Can the underlying network stack transmit fewer than 10 data packets? Explain briefly!4.The Transmission Control Protocol uses a method called congestioncontrol to regulate the traffic entering the network. The behavior of TCP congestion control can be represented as a graph in which the x-axis indicates the time, and the y-axis indicates congestion window size.Please use the graph shown below to the answer the followingquestions. Note that the graph does not explicitly show timeouts, but you should be able to figure out when timeouts happened based on theevents shown.(a) Slow Start:give two reasons why slow start is used, and explain why it does a better job than congestion avoidance for that function.(b) Slow Start:identify the intervals of time when TCP slow start is operating. For each interval, identify which of the above reasons apply and do not apply and explain why.(c) Congestion Avoidance: identify the intervals of time when TCP congestion avoidance is operating. Why should congestion avoidance be used instead of slow start during these intervals? Please clearly identify one specific reason.(d) Fast Retransmission: identify the intervals of time when TCP fast retransmission is used. Please explain what fast retransmission does and how it is triggered.(e) Fast Recovery: identify the intervals of time when TCP fast recovery is operating. What does fast recovery do and explain why is it beneficial.(f) Lack of fast recovery: identify the interval(s) of time when fast recovery could have happened, but did not. Identify one specific example of a circumstance that may prevent fast recovery from happening.5.NAT and IPv65.1Assume an IP packet carrying an HTTP request is going from alocal (i.e. home) area network onto the wider Internet through a NAT router. Name all header fields that the NAT router needs to change in the given packet? Explain your answer. (Hint: encapsulation as wellas the syntax/semantics of all involved protocols must be taken intoconsideration.)5.2The diagram below shows a packet traveling through a NAT router.Packet 1 is sent from the internal host (S) to the NAT router, packet 2 is sent from the NAT router to the external web server (D), packet 3is received from the web server by the NAT router, and packet 4 issent by the NAT router to the original host. Fill in the missing source and destination IP addresses and port numbers in packets 2-4.5.3 The diagram below shows an IPv6 packet tunnelled over IPv4. Fill in themissing source and destination addresses at places/packets marked 1, 2, and 3.6.Consider a datagram network using 32-bit host addresses. Suppose arouter has four links, numbered 0 through 3, and packets are to be forwarded to the link interfaces as follows: Destination Address Range Link Interface11100000 00000000 00000000 00000000Through(0) 11100000 00111111 11111111 1111111111100000 01000000 00000000 00000000Through(1)111100000 01000000 11111111 1111111111100000 01000001 00000000 00000000Through (2)11100001 01111111 11111111 11111111Otherwise(3)a) Provide a forwarding table that has five entries, uses longest prefixmatching, and forwards packets to the correct link interfaces.b) Describe how your forwarding table determines the appropriate linkinterface for datagrams with destination addresses(following):11001000 10010001 01010001 0101010111100001 01000000 11000011 00111100 11100001 10000000 00010001 01110111。
1.Bandwidth and Delaya. On a generic multi-hop network, explain the potential causes of delay for a packet:• Propagation delay:• Transmission delay:• Queueing delay:• Processing delay:b. For a fixed network path, which of these delays are constant over time, and which ones vary with load? Explain why.c. (Estimating bottleneck bandwidth). An interesting technique used to estimate the bottleneck bandwidth in a network is called packet pair. The idea is simple: you send two packets back-to-back (no gap), at the full bandwidth of the first hop. The receiver at the other end can then determine the bandwidth by measuring the delay between the receptions of the two packets. In this problem we will do just that, with a simplified 3-link network shown in the figure below, with no extra traffic, no queues, and instantaneous access to the medium.Setup: In the figure, assume there is no queueing or processing delay, and that nodes can forward a packet as soon as (a) all bytes for the packet have been received from the previous link, and (b) the outgoing link is free. All three links have a propagation delay of 10ms; link AB has a bandwidth of 10Mbps ((107 bits per second), and link CD has a bandwidth of 8 Mbps (8 × 106 bps). You send two probe packets of 1000 bytes each, as depicted in the figure.(a) In this setup, calculate the length of the interval t1t2in the figure. Do the same for t3t4(b) In the diagram, draw the transmission of the two packets in the link BC, paying attention to when they must start and when they must end.(c) You measure the delay t4t5 between the end of the receptions of the two packets to be 8 ms. Assuming that the link BC is the bottleneck bandwidth in the path, what is its bandwidth? Explain your reasoning.2.Answer the following questions regarding TCP, UDP, IP,and routing:a)What are the important fields in the TCP, UDP, and IP headers?Without these fields, the protocols would clearly not “work”.b)Sketch the TCP connection initiation and connection terminationpacket flows using a timing diagram.3.Socket Programming3.1. Consider the following Java application:socket = new DatagramSocket(12345);while (true) {socket.receive(packet);} What happens if somebody decides to run two instances of thisapplication on one machine and 4 UDP segments arrive at port 12345?a) both instances of the application receive all 4 segmentsb) one instance receives all 4 segmentsc) some segments are received by one instance, other segmentsare received by the other instanced) one instance receives segments 1 and 3, the other receivessegments 2 and 43.2.Given the following lines from a Java program segment:byte[] dataOut = new byte [512];String userInput = inFromUser.readLine();dataOut = userInput.getBytes();Which of the following lines of code could be used to create a new UDP datagram packet to send the data that was provided by the user to a host identified by the InetAddress object IPAddress?a) DatagramPacket packetToSend = newDatagramPacket(dataOut, dataOut.length, IPAddress)b) UDPPacket = new UDPDatagram (userInput,userInput.length, IPaddress, 9876)c) DatagramPacket packet = new DatagramPacket(dataOut, dataOut.length, IPAddress, 9876)d) Socket datagramSocket = new dataGramPacket(dataOut, IPAddress)3.3.Consider a server socket objectsocket = ServerSocket(12345);What does the invocation of socket.accept() return?a) 'true' if there is a new TCP segment in the socket's buffer, false otherwiseb) a new TCP segment from the socket's buffer (blocks if no segments are available)c) 'true' if a new TCP connection request has arrived, false otherwised) a socket associated with a new TCP connection (blocks if no connections are available)3.4.Assume the following two lines of code are to be executed on the machineblue.cse.yorku.ca:Socket myFirstSocket = new Socket("blue.cse.yorku.ca", 5555);Socket mySecondSocket = new Socket(5555);Are the two lines/commands in conflict? Explain briefly!3.5.Suppose application A is using a UDP socket, i.e. DatagramSocket(), to transfer data to application Bon a remote host. Suppose application A calls send() method on the given socket 10 times.a) Can the underlying network stack transmit more than 10 data packets?b) Can the underlying network stack transmit fewer than 10 data packets? Explain briefly!4.The Transmission Control Protocol uses a method called congestioncontrol to regulate the traffic entering the network. The behavior of TCP congestion control can be represented as a graph in which the x-axis indicates the time, and the y-axis indicates congestion window size.Please use the graph shown below to the answer the followingquestions. Note that the graph does not explicitly show timeouts, but you should be able to figure out when timeouts happened based on theevents shown.(a) Slow Start:give two reasons why slow start is used, and explain why it does a better job than congestion avoidance for that function.(b) Slow Start:identify the intervals of time when TCP slow start is operating. For each interval, identify which of the above reasons apply and do not apply and explain why.(c) Congestion Avoidance: identify the intervals of time when TCP congestion avoidance is operating. Why should congestion avoidance be used instead of slow start during these intervals? Please clearly identify one specific reason.(d) Fast Retransmission: identify the intervals of time when TCP fast retransmission is used. Please explain what fast retransmission does and how it is triggered.(e) Fast Recovery: identify the intervals of time when TCP fast recovery is operating. What does fast recovery do and explain why is it beneficial.(f) Lack of fast recovery: identify the interval(s) of time when fast recovery could have happened, but did not. Identify one specific example of a circumstance that may prevent fast recovery from happening.5.NAT and IPv65.1Assume an IP packet carrying an HTTP request is going from alocal (i.e. home) area network onto the wider Internet through a NAT router. Name all header fields that the NAT router needs to change in the given packet? Explain your answer. (Hint: encapsulation as wellas the syntax/semantics of all involved protocols must be taken intoconsideration.)5.2The diagram below shows a packet traveling through a NAT router.Packet 1 is sent from the internal host (S) to the NAT router, packet 2 is sent from the NAT router to the external web server (D), packet 3is received from the web server by the NAT router, and packet 4 issent by the NAT router to the original host. Fill in the missing source and destination IP addresses and port numbers in packets 2-4.5.3 The diagram below shows an IPv6 packet tunnelled over IPv4. Fill in themissing source and destination addresses at places/packets marked 1, 2, and 3.6.Consider a datagram network using 32-bit host addresses. Suppose arouter has four links, numbered 0 through 3, and packets are to be forwarded to the link interfaces as follows:Destination Address Range Link Interface11100000 00000000 00000000 00000000Through(0) 11100000 00111111 11111111 1111111111100000 01000000 00000000 00000000Through(1)111100000 01000000 11111111 1111111111100000 01000001 00000000 00000000Through (2)11100001 01111111 11111111 11111111Otherwise(3)a) Provide a forwarding table that has five entries, uses longest prefixmatching, and forwards packets to the correct link interfaces.b) Describe how your forwarding table determines the appropriate linkinterface for datagrams with destination addresses(following):11001000 10010001 01010001 0101010111100001 01000000 11000011 0011110011100001 10000000 00010001 01110111。