语言学期末考试
- 格式:doc
- 大小:55.00 KB
- 文档页数:3

《语言学概论》期末试卷1。
(单选题) 下列关于“语言"的说法,不正确的一项是(D )(本题2.0分)A、语言系统是由多个子系统组合而成的B、语言是一个符号系统C、语言符号具有任意性和线条性特征D、语言符号的音义关系可以任意改变2。
( 单选题)下列元音音素都是后元音的一组是(B)(本题2.0分)A、[u, ε]B、[α, Λ]C、[α,y]D、[o,a]3。
(单选题) 下列辅音音素都是塞音的一组是( B)(本题2。
0分)A、[k, 1]B、[p,k]C、[p, n]D、[t,v]4。
( 单选题)从语音的社会功能角度划分出来的最小语音单位是( A)(本题2.0分)A、音位C、音节D、音渡5。
( 单选题) 汉语普通话中的“我"和助词“的”单念时发音分别为[uo]和[te],而在实际语流中,“我的”发音是[uo de],这是语流音变中的( A)(本题2.0分)A、顺同化现象B、逆同化现象C、弱化现象D、异化现象6。
(单选题) 语音的本质属性是(C )(本题2。
0分)A、物理属性B、生理属性C、社会属性D、心理属性7. (单选题) 英语“students”中的“—s”是(C)(本题2.0分)A、虚词语素B、词根语素C、构形语素D、构词语素8。
(单选题)从词的构造方式看,下列各项中属于复合词的是( D)(本题2。
0分)B、念头C、苦头D、山头9. (单选题)划分词类的最本质的标准是(A )(本题2。
0分)A、分布标准B、意义标准C、形态标准D、逻辑标准10。
(单选题) 下面词组中,结构类型与其他各组不同的一组是( D)(本题2。
0分)A、年轻漂亮/朴素大方B、我们大家/首都北京C、铁路民航/工人农民D、贯彻执行/讨论研究11. (单选题) 目前已知的最古老的拼音文字是(C)(本题2.0分)A、古埃及文字B、古希腊文字C、腓尼基文字D、中国的甲骨文12. (单选题) 判断两种话是不同语言还是同一种语言的不同方言应该主要参考(C)(本题2.0分)A、相互理解程度B、语言结构的差异程度C、共同的历史文化传统和民族认同感D、地域临近程度13。
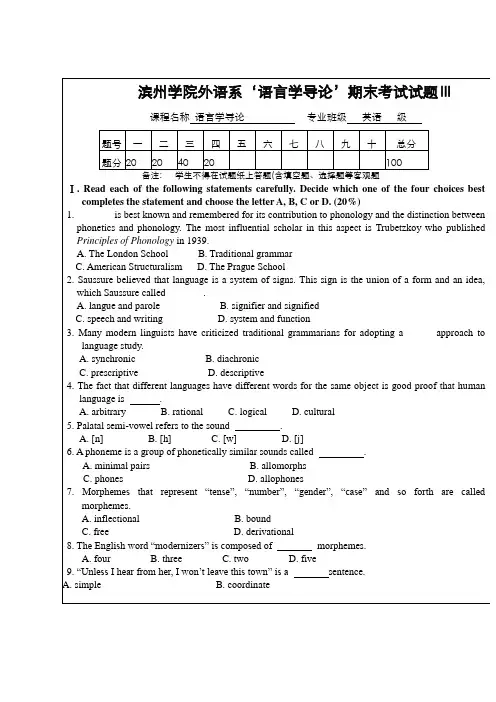
武汉理工大学教务处试题标准答案及评分标准用纸课程名称语言学导论(B卷)Ⅰ. Read each of the following statements carefully. Decide which one of the four choices best completes the statement and choose the letter A, B, C or D. (120=20)1. A2. D3.A4. C5. B6. C7. D8. D9. D 10. B11.A 12. A 13. C 14. D 15. C 16. B 17.C 18. C 19. B 20.DⅡ. Decide whether the following statements are true or false. Write T for true and F for false. (120=20) 1. T 2. F 3. T 4. F 5. T 6. T 7. F 8. T 9. F 10. T11. F 12. T 13. F 14. F 15. T 16. T 17. F 18. F 19. T 20. TⅢ. Explain the following linguistic terms and notions in English. (210=20)1. Trace—(By Chomsky) A phonetically null element to occupy the position from which a syntactic element has beenmoved. That is, after the movement of an element, there will be a trace left in the original position.2. Displacement--It means that human lges enable their users to symbolize (refer to) objects, events and concepts whichare not present (in time and space) at the moment of communication.3. Stem—Any morpheme or combination of morphemes to which an inflection affix can be added. A stem can be equivalentto a root or may contain a root and a derivational affix.4. Dissimilation-- It refers to the influence exercised by one sound segment on the production of another, so that the twosounds in a sequence become less alike or different.5. Diacritics--A set of symbols added to the letter symbols to make minute (slight) difference between variations of the samesound than the letters alone make possible.6. Theme--It refers to “that which is known or at least obvious in the given situation and from which the speaker proceeds”7. Relational opposites--Converse antonymy is typically seen in reciprocal social roles, kinship relations, temporal andspatial relations, there are always 2 entities involved, one presupposes the other.8. Sapir-Whorf Hypotheses--Our lge helps mould our way of thinking, and therefore, different lges may probably expressour unique way of understanding the world. On the one hand, lge may determine our thinkingpatterns; on the other hand, similarity between lges is relative, the greater their structuraldifferentiation is, the more diverse their conceptualization of the world will be.9. Predicate logic--It studies the internal structure of simple propositions. (Or, it deals with expressions containing predicates,arguments and quantifiers).10. Conversational implicature--It is a type of implied meaning, which can be deduced on the basis of the conventionalmeaning of words together with the context, under the guidance of the CP and its maxims.It is comparable to illocutionary force in that they are both concerned with the contextualmeaning.IV. Give brief answers to the following questions. (12+8=20)1. What are the main concerns of general linguistics?General linguistics includes at least five parameters, namely, phonology, morphology,syntax, semantics and pragmatics. The following are the main branches of linguistics. (2)Phonetics studies the speech sounds, including the production of the speech.Phonology studies the rules governing the structure,distribution, and sequencing of speech sounds and the shape of syllables.(2 points)Morphology is concerned with the internal organization of words.It studies the minimal units of meaning ---morphemes and word-formation. (2)Syntax is about principles of forming and understanding correct English sentences. The form or structure of a sentence is governed by the rules of syntax. (2)Semantics studies how meaning is encoded in a language.(2)Pragmatics is the study of meaning in context. (2)2. Explain the speech act theory with examples.Speech act theory was put forward by J Austin in 1950s. His first shot at the theory is the claim that there are two types of sentences: performative and constatives. (2) The uttering of these sentences is the doing of an action. They are called performatives. (1) E.g. a. I name this ship the queen Elizabeth. b. I promise to finish the work in time. c. I bet you sixpence it will rain tomorrow. (2) While a sentence like this "I pour some liquid into the tube." is called constative. It is a description of what the speaker is doing at the time of speaking.(3)。

语言学概论期末考试及答案(一)一、单项选择题(本大题共26小题,每小题1分,共26分)在每小题列出的四个备选项中只有一个是符合题目要求的,请将其代码填写在题后的括号内。
错选、多选或未选均无分。
1.关于“说话”这种口头交际行为,下列说法正确的一项是()A.只涉及心理问题,不涉及物理和生理问题B.只涉及物理问题,不涉及生理和心理问题C.只涉及生理问题,不涉及物理和心理问题D.既涉及心理问题,又涉及生理和物理问题2.判断两种话是不同语言还是同一种语言的不同方言应该主要参考()A.相互理解程度B.语言结构的差异程度C.共同的历史文化传统和民族认同感D.是否属于同一个国家3.关于语音四要素,下列说法不正确...的一项是()A.在任何语言中,音高变化都是语调的主要构成要素B.能起区别语言意义作用的是绝对的音高、音强和音长C.音长是由发音体振动的持续时间决定的D.音强是由发音体振动的振幅大小决定的4.下列关于区别特征的表述中,不正确...的一项是()A.音位是通过区别特征相互区别的B.区别特征完全取决于语音的自然属性C.音位的辨义功能由区别特征负担D.区别特征通常都表现为二项对立5.关于“复辅音”,下列说法不正确...的一项是()A.复辅音是一个音节内两个或几个辅音的组合B.复辅音内的几个辅音彼此之间有过渡音联结C.复辅音内的几个辅音的音质变化是突变式的D.复辅音并不是所有语言中都存在的语音现象6.下列各项中,都是低元音的一组是()A.[y,æ]B.[a,Λ]C.[u,ε]D.[Aα,]7.下列各组辅音中,发音部位相同的一组是()A.[k,η]B.[m, n]C.[n, η]D.[k,p]8.北京话“面”单念时读作[miæn],但“面包”却读作[miæmpαu],这种语流音变现象是()A.弱化B.增音C.同化D.异化9.关于现代汉语“洗”和“浴”两个语素,下列说法不正确...的一项是()A.“洗”是成词语素,“浴”是不成词语素B.“洗”是自由语素,“浴”是黏着语素C.“洗”是不定位语素,“浴”是定位语素D.“洗”和“浴”都是实义语素10.下列各组中,三个复合词构词类型不一致...的一组是()A.席卷耳鸣地震B.打倒切断推翻C.发光散热出气D.天地欢乐爱好11.下列各组词,吸收外来成分的手段存在不一致...情况的一组是()A.丹麦挪威法兰西B.沙拉咖啡麦当劳C.卡车啤酒立邦漆D.香波克隆好莱坞12.语法规则的“抽象性”是指()A.对语言的结构和成分进行类的概括B.相同规则可在一个结构里重复使用C.语法规则之间可以相互推导和解释D.语法规则的发展变化过程十分缓慢13.语法现象可以分成“核心语法现象”和“外围语法现象”,其中“核心语法现象”主要是指()A.词语搭配问题B.意义表达问题C.语音实现问题D.句法结构问题14.主要功能是用来“造句”的同一级语法单位是指()A.语素和语素组B.语素组和词C.词和词组D.词组和句子15.汉语中的词类(词的语法分类)可以首先分出的两个大类是()A.基本词和非基本词B.实词和虚词C.典型词和兼类词D.体词和谓词16.下列关于“直接组成成分分析法”(层次分析法)的表述,不正确...的一项是()A.从最大的词组开始逐层切分,一直切分到词为止B.从最小的词开始逐层组合,一直组合到词组为止C.分析时要依据两条原则:“成结构”和“有意义”D.分析时采用的方法是“先分主干”和“后添枝叶”17.“汽车”和“卡车”是()A.上下位词B.同义词C.等义词D.近义词18.下列各项中,语义结构属于复合述谓结构的一项是()A.这样做不值得B.他跑过去开门C.我们单位需要增加编制D.他们正在研究如何筹集资金19.下列各项中,甲和乙是预设关系的一项是()A.(甲)他买了一支钢笔//(乙)他买了一支笔B.(甲)老王在小李的左边//(乙)小李在老王的右边C.(甲)他早就不在学校工作了//(乙)他以前在学校工作过D.(甲)什么水果他都吃过//(乙)他吃过苹果20.文字最基本的单位是()A.笔画B.字符C.偏旁D.部首21.根据字符跟什么样的语言单位相联系的标准来分类,已知自源文字都属于()A.词语文字B.语素文字C.音节文字D.音位文字22.在语言谱系分类的层级体系中,最大的类别是()A.语族B.语支C.语系D.语群23.在儿童学会说话的过程中,“双词阶段”标志着儿童产生的语言能力是()A.语音能力B.语汇能力C.语法能力D.语义能力24.“萨丕尔(E.Sapir)-沃尔夫(B. L. Whorf)假说”之所以被称作“语言相关论”,主要是因为他们认为()A.思维决定语言B.语言决定思维C.语言和思维互不相干D.语言和思维相互作用25.关于“中介语”现象,下列说法正确的一项是()A.“中介语”越到外语学习后期发展越快B.较高级的“中介语”也不能用于交际C.人们的中介语发展遵循大致相同的规律D.儿童学习母语过程中存在中介语现象26.从语言信息处理技术本身来看,下列各项中,属于未来一段时间研究的主攻方向的是()A.文字编码B.语音识别C.文本检索D.机器翻译二、多项选择题(本大题共5小题,每小题2分,共10分)在每小题列出的五个备选项中有二个至五个是符合题目要求的,请将其代码填写在题后的括号内。

XX 大学成人教育学院2023-2023学年度第二学期期末考试《语言学概论》复习试卷2一单选题(共12题,总分值12分,下列选项中有且仅有一个选项符合题目要求,请在答题卡上正确填涂。
)1 .下列属于汉语借词的是(C )。
(1分)B.卡车电话哈巴狗 D.啤酒沙发小提琴2 .“涕”在古汉语中指“眼泪”,在现代汉语中指“鼻涕”,这种演变是词义的(C )。
(1分)A.扩大B.缩小C.转移D .比喻 3.根据语言的谱系分类,与汉语属于同一语系的是(A )。
(1分) A.苗语 B.日语 C.英语D.阿拉伯语 4. “铁路”、“火箭炮”、“机关枪” 属于(D )。
(1分)A.借词B.音译词C.音译加意译D.意译词 5.下列语言中,属于印欧语系的是(C ) O (1分)A.维吾尔语B.苗语C.法语D.越南语 6.下列单位被称为语义角色的是(A )。
(1分) A.施事 B.主语 C.宾语D.谓语 7.关于共同语的形成,下列说法不正确的一项是(D )。
(1分) A.并不意味着方言分歧已经消失B.并不意味着方言分歧将会扩大C.并不意味着方言最终将被取代D.并不意味着语言已经实现统一 8 .一个多民族国家里各民族间共同使用的语言叫(A )。
(1分)A.民族共同语B.民族交际语C.国际交际语D.人造语9 .关于社会方言的形成,下列说法不正确的一项是(A )。
(1分)A.社会方言大多是在语言的相互接触中形成的B.社会方言是随着社会的社群分化而产生的C. 一种语言的内部有可能形成社会方言D. 一种方言的内部有可能形成社会方言10.语言混合的形式有(B )。
。
分)A.雷达足球芭蕾舞C.纳粹吉他比萨饼A.双语B.洋泾浜C,共同语 D.借词I1语言谱系分类的层级体系从下到上依次是(D)o(1分)A.语系语族语支语群B.语系语族语群语支C.语支语群语族语系D.语群语支语族语系12.下列词中具有[+物品][+有筒][+接触地面]义素的是(B)。

语言学概论期末考试试卷一、填空题(每空1分,共15分)1、语言符号的形式是表达一定内容的声音,语言符号的内容是语义。
2、音素可以分为元音和辅音两大类。
3、传统语法学把语法分成两种规则,即词法和句法;现代语法学把语法分成两个层面,即核心语法和外围语法。
4、世界上保存下来比较完整的三种最古老的文字,即距今五千多年前出现的古埃及文字和苏美尔文字以及距今三千四百年左右的中国的甲骨文。
5、研究语言的心理机制和相关表现的学科叫做心理语言学。
6、语言在思维认知活动中的作用主要表现为三个方面,一是语言可以帮助完成人的认知过程,二是语言可以储存人的认知成果,三是语言可以改造人的认知能力。
二、单项选择题(每小题1分,共10分)1、音高主要决定于( B )A.发音体振动的振幅 B.发音体振动的频率C.发音体振动的时间 D.发音体振动的声波形式2、最小的有意义的能独立使用的语言单位是( B )A.语素 B.词 C.词组 D.句子3、“的”字词组相当于( A )A.名词的词组 B.动词的词组 C.形容词的词组 D.介词词组4、人们在反映现实现象的同时,还可能表现出对该现象的主观态度,从而在词的理性意义上增添了一层附加色彩,这种色彩是(A )A.感情色彩 B.语体色彩 C.形象色彩 D.音响色彩5、有的述谓结构的变元本身是一个述谓结构,这种充当其他谓词变元的述谓结构就是( C )A.简单述谓结构B.复合述谓结构C.从属述谓结构D.降级述谓结构6、阿拉伯文字是( A )A.辅音文字 B.音节文字 C.表意文字 D.意音文字7、语言是一种( B )A.心理现象 B.社会现象 C.物理现象 D.生理现象8、语素分类中最大的类是( C )A.语族 B.语支 C.语系 D.语群9、下列词语中属于借词的是( A )A.摩登 B.妯娌 C.把戏 D.马虎10、语言是思维的工具指的是( B )A.一切思维必须由语言完成B.主要指抽象思维和其他思维高级阶段离不开语言C.主要指感性思维和发散思维离不开语言D.先有语言后有思维三、名词解释(每小题4分,共16分)1、音位2、组合规则3、语法手段4、抽象思维四、简答题(每小题7分,共21分)1、人类语言的起源必须具备哪三方面的条件?1、答:首先,人类的思维能力要发展到一定的水平,应该能够对客观世界的事物进行分类和概括,并具有一定的记忆和想象、判断和推理的能力,只有具备了这样的心理条件才有可能产生语言。

东北师范大学22春“汉语言文学”《语言学概论》期末考试高频考点版(带答案)一.综合考核(共50题)1.根据词的来源特点可把词分为古语词、方言词、外来词。
()A.正确B.错误参考答案:A2.普通话chun(春)音节的构成方式是()。
A.领音B.起音+领音C.起音+收音D.起音+领音+收音参考答案:D3.下列文字类型表示书写符号和语言音义间的关系的是()。
A.词语文字B.音节文字C.语素文字D.表意文字E.表音文字参考答案:DE4.衔接(名词解释)参考答案:衔接是形式方面的问题,是篇章的有形网络,体现于篇章的表层结构上,主要有五种:照应、替代、省略、连接和词汇手段。
5.音质(名词解释)参考答案:音质指声音的个性或特色,也叫音色,是声音的四个要素中最重要的一个,它决定于发音体振动的形式。
6.莫里斯1938年首先使用了“语用学”这一术语。
()A.正确B.错误参考答案:A7.多式综合语的特点是()。
A.词根和后缀都有相当大的独立性,构形后缀就像是粘附在词根上似的B.词在句中的语法关系主要是靠词序和虚词来表现的C.把句子成分作为附加成分包括在同一个词里D.词根或词干与构形词缀或词尾结合得很紧密参考答案:C8.用某些已有的字的复合图形来表示属于行为动作的词语,传统文字学称这类字为()。
A.形声字B.象形字C.指示字D.会意字参考答案:D9.谈谈组合关系和聚合关系的理论。
参考答案:在索绪尔的《普通语言学教程》里,组合关系和聚合关系被分别称作“句段关系”和“联想关系”。
其实这就是语言符号和语言符号之间的横向关系和纵向关系,语言符号间的纵横交错使语言系统运行起来。
1)组合关系:组合关系是指在同一层级上组合起来的各个符号之间所形成的横向关系。
比如:“鸡吃小米”,“鸡”和“吃小米”组合构成了主谓关系,而“吃”和“小米”的组合构成了述宾关系。
主谓和述宾这样的关系是组合关系在语法层面的表现。
此外这种关系在语音和语义层面也各有体现。

《英语语言学》期末考试试卷附答案一、单项选择题(在每小题的四个备选答案中,选出一个正确答案,并将正确答案的序号填在题干的括号内。
每小题3分,共60分)1.The pair of words “lend”and “borrow”are ___.()A.gradable oppositesB.relational oppositesC.co-hyponymsD.synonyms2.The discovery of Indo-European language family began with the work of the British scholar .( )A.Jacob GrimmB.Rasmus RaskC.Franz BoppD.Sir William Jones3.A linguist regards the changes in language and language use as __.( )A.unusualB.something to be fearedC.abnormalD.natural4.__produce fast and fluent speech with good intonation and pronunciation but the content of their speech ranges from mildly inappropriate to complete nonsense,often as unintelligible.( )A.Broca's aphasicB.The linguistic deprivationC.The damage on the angular gyrusD.Wernicke's aphasic5.Some Southern learners of English in China tend to say “night” as “light”.This shows:.( )A.They cannot pronounce/n/B.Interlangue interference because there is notthe sound /n/in their mother tongueC.The teachers do not have a good teaching methodD.They do not like to pronounce nasal sounds6.A word with several meanings is called __word.( )A.a polysemousB.a synonymousC.an abnormalD.a multiple7.The function of the sentence “A nice day, isn't it?”is __.()rmativeB.phaticC.directiveD.performative8.The most recognizable differences between American English and British English are in __ and vocabulary.( )ageB.grammarC.pronunciationD.structure9.__deals with the way in which a language varies through geographical space.( )A.Linguistic geographyB.LexicologyC.LexicographyD.Sociolinguistics10.The semantic components of the word “gentleman” can be expressed as __.()A.+animate,+male,+human,-adultB.+animate,+male,+human,+adultC.+animate,-male,+human,-adultD.+animate,-male,+human,+adult11.The famous quotation from Shakespeare's play “Romeo and Juliet” ‘A rose by any other name would smell as sweet’ well illustrates _______.()A.the conventional nature of languageB.the creative nature of languageC.the universality of languageD.the big difference between human language and animal communication12.Of the following sound combinations, only _______ is permissible according to the sequential rules in English.( )A.kiblB.bkilC.ilkbD.ilbk13.The sentence that has a NP and a VP can be shown in a _______ formula "S→NP VP".()A.hierarchicalB.linearC.tree diagramD.vertical14.It is the _______ on Case assignment that states that a Case assignor and a Case recipient should stay adjacent to each other.( )A.Case ConditionB.parameterC.Adjacent ConditionD.Adjacent Parameter15.Predication analysis is a way to analyze _______ meaning.A.phonemeB.wordC.phraseD.sentence16.According to Searle,those illocutionary acts whose point is to commit the speaker to some future course of action are called _______.( )misivesB.directivesC.expressivesD.declaratives17.The term _______ linguistics may be defined as a way of referring to the approach which studies language change over various periods of time and at various historical stages.A.synchronicB.diachronicparativeD.historical comparative18.The way in which people address each other depends on their age, sex, social group, and personal relationship. The English system of address forms frequently used includes first name, last name, title+last name, _______,and kin term.A.title+first nameB.title+titleC.title aloneD.first name+last name+titlenguage and thought may be viewed as two independent circles overlapping in some parts. When language and thought are identical or closely parallel to each other, we may regard thought as "subvocal speech," and speech as "_______".( )A.vocal thoughtB.subvocal thoughtC.covert thoughtD.overt thought20.Whcih of the following best states the behaviorist view of child languageacquisition?_______.( )nguage acquisition is a process of habit formationnguage acquisition is the species-specific property of human beingsC.Children are born with an innate ability to acquire languageD.Humans are equipped with the neural prerequisites for language and language use二、判断说明题(判断下列各小题,正确的在题后括号内写“T”,错的写“F”,并说明理由。

语言学导论期末考试试题(滨州学院外语系)Ⅰ. Read each of the following statements carefully. Decide which one of the four choices best completes the statement and choose the letter A,B,C or D. (20%)1. _______ is best known and remembered for its contribution to phonology and the distinction between phonetics and phonology. The most influential scholar in this aspect is Trubetzkoy who published Principles of Phonology in 1939.A. The London SchoolB. Traditional grammarC. American StructuralismD. The Prague School2. Saussure believed that language is a system of signs. This sign is the union of a form and an idea,which Saussure called _______.A. langue and paroleB. signifier and signifiedC. speech and writingD. system and function3. Many modern linguists have criticized traditional grammarians for adopting a _____ approach to language study.A. synchronicB. diachronicC. prescriptiveD. descriptive4. The fact that different languages have different words for the same object is good proof that human language is_______.A. arbitraryB. rationalC. logicalD. cultural5. Palatal semi-vowel refers to the sound_______.A. [n]B. [h]C. [w]D. [j]6. A phoneme is a group of phonetically similar sounds called_______.A. minimal pairsB. allomorphsC. phonesD. allophones7. Morphemes that represent “tense”,“number”,“gender”,“case” and so forth are called_______morphemes.A. inflectionalB. boundC. freeD. derivational8. The English word “modernizers” is composed of_______morphemes.A. fourB. threeC. twoD. five9. “Unless I hear from her,I won’t leave this town” is a_______sentence.A. simpleB. coordinateC. complexD. compound10. In the phrase structure rule “S NP VP”,the arrow can be read as_______.A. is equal toB. consists ofC. hasD. generates11. In the following pairs of words,_______are a pair of complementary antonyms.A. old and youngB. male and femaleC. hot and coldD. buy and sell12. The stimulus-response theory was proposed by_______.A. FirthB. HallidayC. BloomfieldD. Chomsky13._______found that natural language had its own logic and thus concluded the famous Cooperative Principle.A. John AustinB. John FirthC. Paul GriceD. William Jones14. As far as the sentence “My bag is heavy” is concerned,linguists of pragmatics are more interested in its ______ meaning.A. literalB. logicalC. contextualD. grammatical15._______is defined as any regionally or socially definable human group identified by shared linguistic system.A. A speech communityB. A raceC. A societyD. A nation16. A speaker’s knowledge of the total set of rules,conventions,etc.,governing the skilled use of language in a society is termed ______.A. competenceB. performanceC. communicative competenceD. communicative strategy17. The phonemes /k/,/a:/ and /p/ are in ______ relations in the words /ka:p/ (carp)and /pa:k/ (park).A. synchronicB. syntagmaticC. diachronicD. paradigmatic18. The Prague School claims that a sentence may be analyzed from the functional side in terms of ______as well as from the grammatical side.A. theme and rhemeB. argument and predicateC. subject and predicateD. performative and constative19. In the proposition “Professor Green is a linguist”,the predicate linguist is a ______.A. no-place predicateB. one-place predicateC. two-place predicateD. three-place predicate20. The following conversation exchange clearly violates ______.A: Let’s get the kids something.B: Okey,but I veto I-C-E-C-R-E-A-M-S.A. maxim of QuantityB. maxim of QualityC. maxim of RelationD. maxim of MannerⅡ. Decide whether the following statements are true or false. Write T for true and F for false. (20%)1. By arbitrariness Saussure means that the forms of linguistic signs bear some natural relationship to their meaning.()2. Human language is,unlike animal communication systems,stimulus free.()3. Language marks our identity,physically in terms of age,sex,and voiceprints;geographically in terms of accents,dialects.()4. The sentencing of criminals is an example of emotive function of language.()5. Synchronic linguistic is the study of a language through the course of its history.()6. Pre-school children know virtually all the rules of language except for some subtleties. This means they have the underlying knowledge about the system of rules.()7. The sound〔z〕is a voiced alveolar stop.()8. The free variants of a phoneme shown in the different pronunciation of the same word,such as “tap” may be caused by habit,or individual preference,rather than by any distribution rule.()9. Voicing is a distinctive feature for English consonants.()10. A syllable that has no coda is called a closed syllable.()11. In English,inflectional affixes are mostly prefixes.()12. In the word “illegal”,“il” is an allomorph of the negativ e morpheme.()13. The word “girl” used to mean “young person of either sex”. Today it means “young woman”. This is an example of broadening of meaning.()14. The value of a linguistic sign is determined by the signs with which it can combine to form a syntagmatic relation,and the signs with which it can form a paradigmatic relation.()15. The phrase “five children” is an endocentric construction. ()16. Componential analysis can not help explain the sense relations of words.()17. The sentence I pour some liquid into the tube is a performative one.()18. The sentence like War is war is an example in which the Quality maxim is violated.()19. The weak version of the Sapir-Whorf hypothesis says that language is the shaper of our thinking patterns.()20. Malinowsky believed that the context of situation is indispensable for the understanding of the words.()Ⅲ. Explain the following linguistic terms or notions in English. (40%)1. Trace2. Displacement3. Stem4. Dissimilation5. Diacritics6. Theme7. Relational opposites8. Sapir-Whorf Hypotheses9. Predicate logic10. Conversational implicatureⅣ. Give brief answers to the following questions. (12+8=20)1. What are the main concerns of general linguistics?2. Explain the speech act theory with examples.试题标准答案及评分标准用纸课程名称语言学导论(B卷)Ⅰ. Read each of the following statements carefully. Decide which one of the four choices best completes the statement and choose the letter A,B,C or D. (120=20)1. A2. D3.A4. C5. B6. C7. D8. D9. D10. B11.A12. A13. C14. D15. C16. B17.C18. C19. B20.DⅡ. Decide whether the following statements are true or false. Write T for true and F for false. (120=20)1. T2. F3. T4. F5. T6. T7. F8. T9. F10. T11. F12. T13. F14. F15. T16. T17. F18. F19. T20. TⅢ. Explain the following linguistic terms and notions in English. (210=20)1. Trace—(By Chomsky)A phonetically null element to occupy the position from whicha syntactic element has been moved. That is,after the movement of an element,there will be a trace left in the original position.2. Displacement--It means that human lges enable their users to symbolize (refer to)objects,events and concepts which are not present (in time and space)at the moment of communication.3. Stem—Any morpheme or combination of morphemes to which an inflection affix can be added. A stem can be equivalent to a root or may contain a root and a derivational affix.4. Dissimilation-- It refers to the influence exercised by one sound segment on the production of another,so that the two sounds in a sequence become less alike or different.5. Diacritics--A set of symbols added to the letter symbols to make minute (slight)difference between variations of the same sound than the letters alone make possible.6. Theme--It refers to “that which is known or at least obvious in the given situation and from which the speaker proceeds”7. Relational opposites--Converse antonymy is typically seen in reciprocal social roles,kinship relations,temporal and spatial relations,there are always 2 entities involved,one presupposes the other.8. Sapir-Whorf Hypotheses--Our lge helps mould our way of thinking,and therefore,different lges may probably express our unique way of understanding the world. On the one hand,lge may determine our thinking patterns;on the other hand,similarity between lges is relative,the greater their structural differentiation is,the more diverse their conceptualization of the world will be.9. Predicate logic--It studies the internal structure of simple propositions. (Or,it deals with expressions containing predicates,arguments and quantifiers).10. Conversational implicature--It is a type of implied meaning,which can be deduced on the basis of the conventional meaning of words together with the context,under theguidance of the CP and its maxims. It is comparable to illocutionary force in that they are both concerned with the contextual meaning.IV. Give brief answers to the following questions. (12+8=20)1. What are the main concerns of general linguistics?General linguistics includes at least five parameters,namely,phonology,morphology,syntax,semantics and pragmatics. The following are the main branches of linguistics. (2)Phonetics studies the speech sounds,including the production of the speech.Phonology studies the rules governing the structure,distribution,and sequencing of speech sounds and the shape of syllables.(2 points)Morphology is concerned with the internal organization of words.It studies the minimal units of meaning ---morphemes and word-formation. (2)Syntax is about principles of forming and understanding correct English sentences. The form or structure of a sentence is governed by the rules of syntax. (2)Semantics studies how meaning is encoded in a language.(2)Pragmatics is the study of meaning in context. (2)2. Explain the speech act theory with examples.Speech act theory was put forward by J Austin in 1950s. His first shot at the theory is the claim that there are two types of sentences: performative and constatives. (2)The uttering of these sentences is the doing of an action.They are called performatives. (1) E.g. a. I name this ship the queen Elizabeth. b. I promise to finish the work in time. c. I bet you sixpence it will rain tomorrow. (2)While a sentence like this "I pour some liquid into the tube." is called constative. It is a description of what the speaker is doing at the time of speaking.(3)。
![[资料]-英语语言学期末考试试卷及答案---副本](https://uimg.taocdn.com/9f18f9428e9951e79b8927a5.webp)
[资料]-英语语言学期末考试试卷及答案---副本5. The morpheme –ed in the word “worked”is a(n) __________ morpheme.A. derivationalB.inflectionalC. freeD.word-forming6. WH-movement is __________ in Englishwhich changes a sentence from affirmative to interrogative.A. obligatoryB.optionalC. selectionalD.arbitrary7. Naming theory, one of the oldest notions concerning meaning, was proposed by _________.A. GriceB.PlatoC. SaussureD.Ogden and Richards8. “John married a blond heiress.”__________ “John married a blond.”A. is synonymous withB. isinconsistent withC. entailsD.presupposes9. In semantic analysis of a sentence, the basicunit is called _______, which is the abstraction of the meaning of a sentence. A. utterance B.referenceC. predicationD.morpheme10. In Austin’s speech act theory, ___________is the act of expressing the speaker’s intention; it is the act performed in saying something.A. a perlocutionary actB. alocutionary actC. a constative actD. anillocutionary act第二部分非选择题II. Directions: Fill in the blank in each of thefollowing statements with one word, the first letter of which is already given as a clue. Note that you are to fill in One word only, and you are not allowed to change the letter given. (1%×10=10%)11. P___________ relates the study of language to psychology. It aims to answer such questions as how the human mind works when people use language.12. A d_________ study of language is a historical study; it studies the historical development of language over a period of time.13. Language is a system, which consists of two sets of structures, or two levels. At the lower level, there is a structure of meaningless sounds, which can be combined into a large number of meaningful units at the higher level. This design feature is called d___________. 14. The articulatory apparatus of a human being is contained in three important areas: the pharyngeal cavity, the o_________ cavity and the nasal cavity.15. The localization of cognitive and perceptual functions in a particular hemisphere of the brain is called l_____________.16. S_____________ features such as stress, tone and intonation can influence the interpretation of meaning.17. Phrase structure rules can generate an infinite number of sentences, and sentences with infinite length, due to their r_________ properties.18. H__________ refers to the phenomenon that words having different meanings are identical in sound or spelling, or in both.19. Some important missions of historical linguists are to identify and classify families of related languages in a genealogical family tree, and to reconstruct the p____________, the original form of a language family that has ceased to exist.20. In Sociolinguistics, speakers are treated as members of social groups. The social group isolated for any given study is called thespeech c___________.III. Directions: Judge whether each of the following statements is true or false. Put a T for true or F for false in the brackets in front of each statement. (2%×10=20%)( ) 21. Linguists believe that whatever occurs in the language people use should be described and analyzed in their investigation.( ) 22. Language is arbitrary in the sense that there is no intrinsic connection betweenwords and what these words actually referto.( ) 23. The conclusions we reach about the phonology of one language can begeneralized into the study of anotherlanguage.( ) 24. The meaning-distinctive function of the tone is especially important in Englishbecause English, unlike Chinese, is atypical tone language.( ) 25. The syntactic rules of any language are finite in number, and yet there is no limit tothe number of sentences native speakers ofthat language are able to produce andcomprehend.( ) 26. When we think of a concept, we actually try to see the image of something in ourmind’s eye every time we come across alinguistic symbol.( ) 27. All utterances can be restored to complete sentences. For example, “Goodmorning!” can be restored to “I wish you agood morning.”( ) 28. Two people who are born and brought up in the same town and speak the sameregional dialect may speak differentlybecause of a number of social factors. ( ) 29. Black English is linguistically inferior to standard English because Black English isnot as systematic as standard English. ( ) 30. Any child who is capable of acquiring some particular human language is capableof acquiring any human languagespontaneously and effortlessly.IV. Directions: Explain the following terms. (3%×10=30%)31. parole:32. broad transcription:33. allophones:34. phrase structure rules:35. context36. Historical Linguistics:37. standard language:38. linguistic taboo:39. acculturation:40. care-taker speech:V. Answer the following questions. (10%×2=20%)41. Enumerate three causes that lead to thesystematic occurrence of errors in second language acquisition and give your examples.42. English has undergone tremendous changes since its Anglo-Saxon days. Identify the major periods in its historical development and name major historical events that led to the transition from one period to the next.参考答案第一部分选择题I. Directions: Read each of the following statements carefully. Decide which one of the four choices best completes the statement and put the letter A, B, C or D in the brackets. (2%×10=20%)1. A2. D3. C4. C5.B6. A7. B8.C 9. C 10. D第二部分非选择题II. Directions: Fill in the blank in each of the following statements with one word, the first letter of which is already given as a clue. Note that you are to fill in One word only, and you are not allowed to change the letter given.(1%×10=10%)11. Psycholinguistics12. diachronic13. duality14. oral15. lateralization16. Suprasegmental17. recursive18. Homonymy19. protolanguage20. communityIII. Directions: Judge whether each of the following statements is true or false. Put a T for true or F for false in the brackets in front of each statement. (2%X10=20%)( T ) 21. Linguists believe that whatever occurs in the language people use should be described and analyzed in their investigation.( T ) 22. Language is arbitrary in the sense that there is no intrinsic connection betweenwords and what these words actually referto.( F ) 23. The conclusions we reach about the phonology of one language can begeneralized into the study of anotherlanguage.( F ) 24. The meaning-distinctive function of the tone is especially important in Englishbecause English, unlike Chinese, is atypical tone language.( T ) 25. The syntactic rules of any language are finite in number, and yet there is no limit tothe number of sentences native speakers ofthat language are able to produce andcomprehend.( F ) 26. When we think of a concept, we actually try to see the image of something in ourmind’s eye every time we come across alinguistic symbol.( F ) 27. All utterances can be restored to complete sentences. For example, “Goodmorning!” can be restored to “I wish you agood morning.”( T ) 28. Two people who are born and brought up in the same town and speak the sameregional dialect may speak differentlybecause of a number of social factors.( F ) 29. Black English is linguistically inferior to standard English because Black English isnot as systematic as standard English.( T ) 30. Any child who is capable of acquiring some particular human language is capableof acquiring any human languagespontaneously and effortlessly.IV. Directions: Explain the following terms. (3%X10=30%)31. parole: It refers to the realization of languein actual use. It is concrete and varies with context.32. Broad transcription is the transcription withletter symbols only. It is the transcription normally used in dictionaries and teaching textbooks.33. Allophones are the different phones thatrepresent a phoneme in different phonetic environments.34. Phrase structure rules are the rewrite ruleswhich allow for the possible combination of words to form phrases and sentences.35. Context is generally considered asconstituted by the knowledge shared by the speaker and the hearer.36. Historical linguistics studies languagechange ( or historical development of language).37. Standard language is a superposed, sociallyprestigious dialect of language. It is the language employed by the government and the judiciary system, used by the mass media and taught in educational institutions.38. Linguistic taboo refers to a word orexpression that is prohibited by the “polite”society from general use.39. Acculturation is a process of adapting to theculture and value system of the secondlanguage community.40. It is simple and modified speech used byparents, baby-sitter, etc. when they talk to young children who are acquiring their native language.V. Answer the following questions. (10%X2=20%)41. Enumerate three causes that lead to thesystematic occurrence of errors in second language acquisition and give your examples.1) Mother tongue interference2) interlingual interference3) Overgeneralization42. English has undergone tremendous changes since its Anglo-Saxon days. Identify the major periods in its historical development and name major historical events that led to the transition from one period to the next.Major periods: Old English (449-1100)Middle English (1100-1500)Modern English (1500-present)Historical events: The old English period began with the invasion of the British Isles by English-speaking Anglo-Saxons from Europe, and ended with the arrival of Norman French invaders historically known as the Norman Conquest. The Middle English period is distinguished from the Old English period by the Norman Conquest. The European renaissance movement marked the beginning of the Modern English period.。

Chapter 11.Arbitrariness of language makes it potentially creative, and conventionality of language makes learning a language laborious. For learners of a foreign language, it is the conventionality of a language that is more worth noticing that its arbitrariness.2.In Saussure’s view, the relationship between signifier (sound image) and signified (concept) is arbitrary.3.Human language is arbitrary. This refers to the fact that there is no logical or intrinsic connection betweena particular sound and the meaning it is associated with.4.The features that define our human languages can be called design features5.Human languages enable their users to symbolize objects, events and concepts, which are not present (in time and space) at the moment of communication.This quality is labeled as displacement.6.By duality is meant the property of having two levels of structures, such that units of the level are composed of elements of the level and each of the two levels has its own principles of organization.7.Halliday proposes a theory of metafunctions of language, that is, language has ideational, interpersonal and interpersonal functions.8. Our language can be used to talk about itself. This is the metalingual function of language.9.Interpersonal function is realized by mood and modality.10.When language is used for establishing an atmosphere or maintaining social contact rather than exchanging information or ideas, its function is phatic function.11.Some sentences do not describe things. They cannot be said to be true or false. The utterance of these sentences is or is a part of the doing of an action. They are called performatives12.Linguistics is usually defined as the scientific study of language.13.The branch of linguistics which studies the sound patterns of a language is called phonetics.14. The branch of grammar which studies the internal structures of words is called morphology.15.Phonetics mainly studies the characteristics of speech sounds and provides methods for their description, classification and transcription.16.Semantics and pragmatics investigate different aspects of linguistic meaning.17.In linguistics, syntax refers to the study of the rules governing the way words are combined to form sentences in a language, or simply, the study of the formation of sentence.18.Pragmatics can be defines as the study of language in use.19.If a linguistics, synchronic study describes and analyzes the language people actually use, it is said to be descriptive; if it aims to lay down rules for “correct” behavior, it is said to be prescriptive20.In modern linguistics, synchronic study seems to enjoy priority over diachronic study. The reason is that successful studies of various states of a language would be the foundation of a historical study.ngue refers to the abstract linguistics system shared be all the members of a speech community; and parole refers to the realization of language in actual use.22.Chomsky defines competence as the ideal user’s knowledge of the rules of his language, and performance, the actual use of this knowledge in linguistic communication.23.”A rose by any other name would smell as sweet”.This famous quotation from Shakespeare illustrates that language has the design feature of arbitrariness.24.An English speaker and a Chinese speaker are both able to use language, but they are not mutually intelligible, which shows that language is culturally transmitted25.Human capacity for language has a genetic basis, but the details of language have to be taught and learned.Chapter 21.The different members of a phoneme, sounds which are phonetically different but do not make one worddifferent from another in meaning, are allophones.2. The three cavities in the articulatory apparatus are the pharynx, mouth, and nose. six places of articulation according to Fromkin and Rodman throat,palate,palate top,teeth,lips,nose,4. Name five of English front vowels: i:, i, e, æ, a.5.The sound [p] can be described with “ voiceless, bilabial, stop”6.In the production of a velar sound, the back of the tongue is raised so that it touches the soft palate to form a kind of obstruction.7. By the position of the highest part of the tongue, vowels are classified as front vowels, central vowels and back vowels.8.Pitch,as a principal suprasegmental features, can be defined as the relative intensity of soundness with which a syllable is uttered.9.In English, the sound [b] has the same phonetic features as the sound [p] except the feature of voicing.10. Assimilation refers to the change of a sound as a result of the influence of an adjacent sound.11. The oral stops in English are b, p, d, t, g and k.12.When pitch, stress and length variation are tied to the sentence rather than to the word, they are collectively known as intonation.1.The sound [p] can be described with " voiceless, bilabial, stop".2.The sound [b] can be described with " voiced, bilabial, stop"3.Consonant articulations are relatively easy to feel, and as a result are most conveniently described in terms of place and manner of articulation.4.Consonants are produced by constricting or obstructing the vocal tract at some place to divert, impede, or completely shut off the flow of air in the oral cavity.5.The present system of the cardinal vowels derives mainly from one developed in the 1920s by the British phonetician, Daniel Jones (1881-1967), and his colleagues at University of London.6.Consonant articulations are relatively easy to feel, and as a result are most conveniently described in terms of place and manner of articulation.7.The sound /k/ can be described with “voiceless,velar,stop”.8.Narrow transcription should transcribe all the possible speech sounds, including the minute shades.9.Assimilation refers to the change of a sound as a result of the influence of an adjacent sounds.10.Stress refers to the degree of force used in producing a syllable.11.The syllable structure in Chinese is CVC or CV or V.12.The different members of a phoneme, sounds which are phonetically different but do not make one word different from another in meaning, are allophone of airstream.13.In English, the two words cut and gut differ only in their initial sounds and the two sounds are two different phonemes and the 2 words are a minimal pair.14.Consonants differ from vowels in that the latter are produced without obstruction of airstream.15.In English there are a number of diphthong,.which are produced by moving from one vowel position to another through intervening positions.16.According to the maximal onset principle, when there is a choice as to where to place a consonant, it is put into the onset rather than the coda17.In phonological analysis the words fail-veil are distinguishable simply because of the two phonemes /f/ -/v/.This is an example for illustrating minimal pairs.Chapter 31.Polymorphemic words other than compounds have two parts: the roots and the affixes2. On, before and together are grammatical words ---- they are words which do not take inflectional endings.3. Give the regular allomorphs of plural in English: /n/, /i:/, /s/, /z/, /iz/.4. Give the regular allomorphs of past tense in English: /iə/, /t/, /d/.5. Nouns, verbs and adjectives are context words other than function words.6. In the addition of new words, smog is a(an) blending.7.Waltz is borrowed from German.8. As a result of assimilation, the negative morpheme in imperfect and impossible is “im-”rather than “in-”.9. The linguistic term used for the common factor of a set of verbs, such as writing, wrote, written, write and writes is lexeme.10. A bound morpheme is one that cannot constitute a word by itself.1.As the lexical words carry the main content of a language while the grammatical ones serve to link its different parts together, the lexical words are also known as content words and grammatical ones affixes.2.In traditional grammar, pronoun is the only word class which can function as a substitute for another item.3.In terms of the meaning expressed by words, they can be classified into Grammatical words and lexical words.4.The morpheme is the minimal distinctive unit in grammar, a unit which cannot be divided without destroying or drastically altering the meaning, whether lexical or grammatical.5.There are 2 fields of morphology: the study of inflectional morphology and the study of derivational morphology.6.A bound morpheme is one that cannot stand by itself7.Morphology is a branch of linguistics that studies that studies the interrelationship between phonology and morphology.8.Blending is a relatively complex form of compounding in which a new word is formed by joining the initial part of one word and the final part of another word. For example, the English word smog is made from smoke and fog.9.Back-formation”refers to an abnormal type of word-formation where a shorter word is derived by detecting an imagined affix from a longer form already in the language.10.Word is a unit of expression that has universal intuitive recognition by native speakers, whether it is expressed in spoken or written form. It is the minimum free form.11.Affix is the collective term for the type of formative that call be used only when added to another morpheme. Affixes are limited in number in a language, and are generally classified into three subtypes, namely, prefix, suffix, and infix.12.Take is the lexeme of taking, taken and took.13.Bound morphemes are classified into 2 types: affix and bound root,.14.A word formed by derivation is called a derivative, and a word formed by compounding is called a compound.Chapter 41.IC is the short form of immediate constituent used in the study of syntax.2.Coordination and subordination belong to endocentric construction.4.A coordinate sentence contains two clauses joined by a linking word, such as "and", "but", "or".5.A clause that takes a subject and a finite verb, and at the same time stands structurally alone is known as a finite clause.6.IC analysis emphasizes the hierarchical structure of a sentence, seeing it as consisting of word groups7.Syntactic movement is dictated by rules traditionally called transformational rules, whose operation may change the syntactic representation of a sentence.8.Syntactic relations include positional relation, relation of substitutability,relation of co-occurrence. three of SVO languages:English, Chinese, French2.IC is the short from of immediate constituent used in the study of syntax.3.The category of case is prominent in the grammar of Latin, with six distinctions of nominative vocative, accusative, genitive, dative and ablative.4.The generative approach to linguistics refers to the theory originated with the American linguist Norm Chomsky, who published his book Syntactic Structures in 1957.5.When the affirmative sentence “Jack sold his linguistics textbooks to Jill after the final examination” is transformed into “When did Jack sell his linguistics textbooks to Jill?”,three transformational rules are applied. They are Do -insertion, Subject-aux Inversion and Wh-movement.6.The sentence “It was John who wore his best suit to the dance last night.” is called a cleft sentence by traditional grammarians.7.Exocentric construction usually includes basic sentence, prepositional phrase, predicate (verb+object) construction, and connective(be complement)construction.8.According to Chomsky, grammar is a mechanism that should be able to generate all and only the grammatical sentences of a language.Chapter 51.Human language is arbitrary. This refers to the fact that there is no logical or intrinsic connection betweena particular sound and the meaning it is associated with.2.Predication analysis is to break down predications into their constituents:argument and predicate3.The sense relation between “A lent a book to B” and “B borrowed a book from A” is synonymy4.Antonyms like ”husband” vs. ”wife” are converse antonyms.5. Terms like ”desk” and ”stool” are hyponyms of the term “furniture”.6.According to D. Leech, conceptual meaning refers to logic, cognitive, or denotative content.7.We use the term presupposition to refer to the relation between the following two sentences:A. Jack‟s bike needs repairing.B. Jack has a bike.8.The idea that the meaning of a sentence depends on the meanings of the constituent words and the way they are combined the principle of compositionality.9. Inspired by the medieval grammarians, Ogden and Richard (1923) present the classic“semantic triangle” in their book The Meaning of Meaning.Chapter 61.Psycholinguistics is the study of language in relation to the mind.2.According to Chomsky, competence is the ideal user’s knowledge of the rules of his language.3.The most important part of the brain is the outside surface of the brain,called the cerebral cortex4.The brain is divided into two roughly symmetrical halves, called hemispheres, one on the right and one on the left.5.Brain arterialization is genetically programmed, but takes time to develop,6.In general, the two-word stage begins roughly in the second half of the child’s second year.7.The relationship between the name and the meaning of a word is quite arbitrary.8.When language and thought are identical or closely parallel to each other, we may regard thought assub-vocal speech as overt thought.9.Because language differs in many ways, Whorf believed that speakers of different languages perceive and experience the world differently, relative to their linguistic background. This notion is called linguistic relativity.10.Psycholinguists consider that the first language is acquired in the short period from about age two to puberty, which is called the critical period of the first language acquisition.11. The strong version of the Sapir-Whorf hypothesis has two aspects: linguistic determinism and linguistic reality.12. The cohort model is a supposed doctrine dealing with the spoken word recognition, whose process features that the first few phonemes of a spoken word activate a set or cohort of word candidates that are consistent with the input.13.Metaphor involves the comparison of two concepts in that one is construed in terms of the other. It’s often described in terms of a target domain and a source domain.14.Children frequently say tooths and mouses, instead of teeth and mice. These are examples of overgeneralization16.Psycholinguistics is concerned primarily with investigating the psychological reality of linguistic structures.17.According to critical period hypothesis, in child development there is a period during which language can be acquired more easily than at any other time. The period lasts until puberty (around 12or 13 years), and is due to biological development.Chapter 71.Idiolect refers to varieties of a language used by individual speakers, with peculiarities of pronunciation, grammar and vocabulary. In fact, no two speakers speak exactly the same dialect. Each speaker has certain characteristic features of his own in his way of speaking.2.We witnessed a change in language teaching in the middle of the 1970s when Hymes’ theory of communicative competence was introduced into the field as an antagonism to the traditional philosophy in language teaching.3.The social group isolated for study is any given study is called the speech community.4.Speech variety refers to any distinguishable from of speech used by speaker or group of speakers.5.From the sociolinguistic perspective,a speech variety is no more than a dialectual variety of a language.nguage standardization is also called language planning.7.Social variation gives rise to sociolects which are subdivisible into smaller speech categories that reflect their socioeconomic, educational, occupational background,etc.8.Stylistic variation in a person’s speech or writing usually ranges on a continuum from casual or colloquial to formal or polite according to the type of communicative situation.9.A reginal dialect may gain status and become standardized as the national or official language of a country.10.Variety is a neutral term, and it can be used instead of regional or official dialect, or pidgin.11.Sociolinguistics is a multidisciplinary research field focusing on the relationship between language and society.12.The differences between men and women’s language can be traced to many biological, psychological and social reasons.13.The goal of sociolinguistics is to explore the nature of language variation and language use among a variety of speech communities and in different social situation.14.Every speaker of a language is, in a stricter sense, a speaker of a distinct idiolect.15.A pidgin usually reflects the influence of the higher, or dominant, language in its lexicon and that of the lower language in their phonology and occasionally syntax.16.Social variation gives rise to sociolects which are subdivisible into smaller speech categories that reflect their socioeconomic, educational, occupational background.第1章语言1.Arbitrariness使得它有可能创造和语言的规约,使学习吃力的语言。

语言学概论期末考试试卷及答案XXXn One: Fill in the blanks (15 points in total。
1 point for each blank)nguage system has gender and sex.2.Phoneme is the smallest unit of sound that has a n in a specific language or dialect。
divided from a ic perspective.3.XXX can lead to the XXX.4.XXX psycholinguistics are semantics and syntax。
which can also be XXX linguistics.5.XXX.6.XXX。
and can also include XXX。
XXX。
etc.n Two: Multiple Choice ns (10 points in total。
1 point for each n)1.Speech is (B) a system of XXX.2.XXX (B) general linguistics.3.Vowel [o] is (C) a high back XXX.4.The phenomenon of "辛苦" [in k u] in Mandarin being read as [i k u] is (A) n.5."Swimming" is a (D) phrase.6.Among the following grammatical devices。
syntax is (C) n.7.XXX (B) XXX.8.The basic ns for the emergence。
existence and development of language are (C) the need for social n activities.9.XXXXXX (B) XXX.10.XXX of "狗" in Chinese and "dog" in English shows that(A) word meaning reflects the XXX.n Three: ns (16 points in total。
英语语言学期末考试试卷及答案英语语言学期末考试试卷第一部分选择题I.Directions: Read each of the following statements carefully. Decide which one of the four choices best completes the statement and put the letter A, B, C or D in the brackets. (2%X10=20%)1. Saussure’s distinction and Chomsky’s are very similar, but theydiffer in that ____________.A. Saussure took a sociological view of language while Chomskytook a psychological point of viewB. Saussure took a psychological view of language whileChomsky took a sociological point of viewC. Saussure took a pragmatic view of language while Chomskytook a semantic point of viewD. Saussure took a structural view of language while Chomskytook a pragmatic point of view2. Language is a system of ____________ vocal symbols used for human communication.A. unnaturalB. artificialC. superficialD. arbitrary3. We are born with the ability to acquire language, _______________.A. and the details of any language system are genetically transmittedB. therefore, we needn’t learn the details of our mother tongueC. but the details of language have to be learnt.D. and the details are acquired by instinct4. A(n)________ is a phonological unit of distinctive value. It is acollection of distinctive phonetic features.A. phoneB. allophoneC. phonemeD. sound5. The morpheme –ed in the word “worked”is a(n) __________ morpheme.A. derivationalB. inflectionalC. freeD. word-forming6. WH-movement is __________ in English which changes asentence from affirmative to interrogative.A. obligatoryB. optionalC. selectionalD. arbitrary7. Naming theory, one of the oldest notions concerning meaning, was proposed by _________.A. GriceB. PlatoC. SaussureD. Ogden andRichards8. “John married a blond heiress.”__________ “John marrieda blond.”A. is synonymous withB. is inconsistent withC. entailsD. presupposes9. In semantic analysis of a sentence, the basic unit is called_______, which is the abstraction of the meaning of a sentence.A. utteranceB. referenceC. predicationD. morpheme10. In Austin’s speech act theory, ___________ is the act ofexpressing the speaker’s intention; it is the act performed in saying something.A. a perlocutionary actB. a locutionary actC. a constative actD. an illocutionary act第二部分非选择题II. Directions: Fill in the blank in each of the following statements with one word, the first letter of which is already given as a clue. Note that you are to fill in One word only, and you are not allowed to change the letter given. (1%×10=10%) 11. P___________ relates the study of language to psychology. It aims to answer such questions as how the human mind works when people use language.12. A d_________ study of language is a historical study; itstudies the historical development of language over a period of time.13. Language is a system, which consists of two sets of structures, ortwo levels. At the lower level, there is a structure of meaningless sounds, which can be combined into a large number of meaningful units at the higher level. This design feature is called d___________.14. The articulatory apparatus of a human being is contained in threeimportant areas: the pharyngeal cavity, the o_________ cavity and the nasal cavity.15. The localization of cognitive and perceptual functions in aparticular hemisphere of the brain is called l_____________. 16. S_____________ features such as stress, tone and intonation can influence the interpretation of meaning.17. Phrase structure rules can generate an infinite number ofsentences, and sentences with infinite length, due to their r_________ properties.18. H__________ refers to the phenomenon that words havingdifferent meanings are identical in sound or spelling, or in both.19. Some important missions of historical linguists are to identifyand classify families of related languages in a genealogical family tree, and to reconstruct the p____________, the original form of alanguage family that has ceased to exist.20. In Sociolinguistics, speakers are treated as members ofsocialgroups. The social group isolated for any given study is called the speech c___________.III. Directions: Judge whether each of the following statements is true or false. Put a T for true or F for false in the brackets in front of each statement. (2%×10=20%)( ) 21. Linguists believe that whatever occurs in the language people use should be described and analyzed in their investigation.( ) 22. Language is arbitrary in the sense that there is no intrinsic connection between words and what these words actuallyrefer to.( ) 23. The conclusions we reach about the phonology of one language can be generalized into the study of another language.( ) 24. The meaning-distinctive function of the tone is especially important in English because English, unlike Chinese, is atypical tone language.( ) 25. The syntactic rules of any language are finite in number, and yet there is no limit to the number of sentences native。
《英语语⾔学概论》期末考试docI.Decide whether the following statements are True (T) or False (F). (10 points, 1 point each)1.Articulatory Phonetics studies the physical properties of speech sounds.2.Adjectives belong to open class words.3.John Austin made the distinction between a constative and a performative.4.What essentially distinguishes semantics and pragmatics is whether in the study ofmeaning the context of use is considered.5.English is a typical intonation language.6.Phones in complementary distribution should be assigned to the same phoneme.7.Pragmatics treats the meaning of language as something intrinsic and inherent.8.There are words of more or less the same meaning used in different regionaldialects.9.Transformations are the rules which can change the meaning of sentence.10.Sense and reference are two different notions of semantics, and they are related toeach other.II. Fill in the following blanks. (10 points, 1 point each)1.The word “and” is a c____________ conjunction.2.Linguistic c__________ is a native speaker’s linguistic knowledge of his language.3.The relationship between the sound and the meaning of a word is a________.4. A m________ is the smallest linguistic unit that carries meaning.5. A sentence is formed by phonological rules, m______ rules, syntactic rules andsemantic rules.6.The most recognizable difference between American English and British English arein p________ and vocabulary.7.Speech v________refers to any distinguishable form of speech used by a speaker ora group of speakers.8.P ____ refers to the realization of langue in actual use.9.Linguistics is generally defined as the s ____ study of language.10.As a type of linguistic system in L2 learning, i_______ is a product of L2 training,mother tongue interference, overgeneralization of the target language rules, and learning and communicative strategies of the learner..III. Mark the choice that can best complete the statement. (20 points, 1 point each)1. Which of the following branch of linguistics takes the inner structure of word as its main object of study?A. Phonetics.B. Semantics.C. Morphology.D. Sociolinguistics.2. ________refers to a marginal language of few lexical items and straightforward grammatical rules, used as a medium of communication.A. DialectB. IdiolectC. PidginD. Register3. Which of the following is a voiceless bilabial stop?A.[w].B. [m].C. [b].D. [p].4. The phenomenon that words having different meanings have the same form is called ________.A. hyponymyB. synonymyC. polysemyD. homonymy5. Which of the following words is NOT formed by blending?A. Smog.B. Botel.C. Brunch.D. Edit.6. What phonetic feature distinguishes the [p] in please and the [p] in speak?A.V oicingB. AspirationC. RoundnessD. Nasality7. The word boyguard is a ______.A. compound wordB. complex wordC. derivational wordD. free morpheme8. All words contain a _________.A. rootB. bound morphemeC. prefixD. suffix9. Of the following sound combinations, only ______ is permissible.A. kiblB. hkilC. ilkbD. ilbk10. Where is the primary stress of the word phonology?A. pho.B. no.C. lo.D. gy.11. Conventionally a ________ is put in slashes.A. allophoneB. phoneC. phonemeD. morpheme12. The plural affix in the word tables is a(n) _______.A. inflectional suffixB. derivational suffixC. free morphemeD. root13. Language is tool of communication. The symbol “highway closed”serves___.A. an expressive functionB. an informative functionC. a performative functionD. a persuasive function14. Which of the following groups of words is a minimal pair?A. but/pubB. wet/whichC. cool/curlD. fail/find15. Whorf believed that speakers of different languages perceive and experienced the world differently, that is relative to their linguistic background, hence the notion of ______________.A. linguistic determinationB. linguistic relativismC. linguistic nativismD. linguistic behaviorism16. What are the dual structures of language?A. Sounds and letters.B. Sounds and meaning.C. Letters and meaning.D. Sounds and symbols.17. The meaning carried by the inflectional morpheme is _______.A. lexicalB. morphemicC. grammaticalD. semantic18. According to Krashen ______ refers to the gradual and subconscious development of ability in the first language by using it naturally in daily communication.A. learningB. competenceC. performanceD. acquisition19. Which of the following is one of the core branches of linguistics?A. Phonology.B. Psycho-linguistics.C. Sociolinguistics.D. Anthropology.20. The relationship between “flower” and “tulip” is _________.A. homonymyB. hyponymyC. polysemyD. synonymyIV. Translate the following linguistic terms: (10 points, 1 point each)A. From English to ChineseB. From Chinese to English1. acoustic phonetics 6. 应⽤语⾔学2. closed class words 7. 格语法3. componential analysis 8. 积极迁移4. distinctive features 9. 历史语⾔学5. Critical Period Hypothesis 10. 声调语⾔V. Draw a tree diagram for the following sentence by applying TG Grammar. (10 points)The man saw a horse.VI. Answer the following questions briefly. (20 points)1. Define phoneme. (4 points)2. Explain complementary distribution with an example.(5 points)3. What are the four criteria for classifying English vowels. (4 points)4. Analyze the following conversation by applying the Cooperative Principles.(7points)A: Teheran is in Turkey, isn’t it, teacher?B: And London is in France, I suppose.VII. Do the following analysis. (20 points)1. Write the one proper description from the list under B for the underlined part of each word in A. (5 points, 1 point each)A B(1) terroriz ed a. free root(2) un civil ized b. bound root(3) terror ize c. inflectional suffix(4) luke warm d. derivational suffix(5) im possible e. inflectional prefixf. derivational prefix2. Consider the following sentences in Swahili, and anwer the questions:(15 points) mtu amelala The man has slept. mtu analala The man is sleeping.mtu atalala The man will sleep.watu wamelala The men have slept.watu wanalala The men are sleeping.watu watalala The men will sleep.visu vinaanguka The knives are falling.kikapu kimeanguka The basket has fallen.watoto watafika The children will arrive.1)toto in Swahili means ______ in English.2)The meaning of the morpheme wa- in Swahili is _______.3)______ in Swahili means “sleep” in English.4)Translate mtoto anaanguka into English.5)Translate vikapu vimefika into English.台州学院_____学年第___学期___级____专业《英语语⾔学概论》期末试卷A卷(闭卷)参考答案及评分说明I.Decide whether the following statements are True (T) or False (F). (10 points, 1 point each)II. Fill in the following blanks. (10 points, 1 point each)1. coordinate2. competence3. arbitrary4. morpheme5. morphological6. pronunciation7. variety8. performance9. scientific 10. interlanguage III. Mark the choice that can best complete the statement. (20 points, 1 point each)IV. Translate the following linguistic terms: (10 points, 1 point each)1. 声学语⾳学 6. applied linguistics2. 封闭词类7. case grammar3. 成分分析8. positive transfer4. 区别性特征9. historical linguistics5. 临界期假说10. tone languageV. Draw a tree diagram for the sentence by applying TG Grammar. (10 points)SNP Infl VPDet N pst V NPDet Nthe man saw a horseVI. Answer the following questions. (20 points)1. A contrastive phonological segment whose phonetic realizations are predictable by rules. (4 points)(or: A phoneme is a phonological unit; it is a unit that is of distinctive value.)2. The situation in which phones never occur in the same phonetic environment.(4 points)e.g. [p] and [p h] never occur in the same position. (1 point)3. the position of the tongue in the mouth(1 point), the openness of the mouth(1 point), the shape of the lips(1 point), and the length of the vowels. (1 point)4. According to the Cooperative Principle, the participants of the conversation should obey the four maxims of the principle: the maxim of quantity, the maxim of quality, the maxim of relation, the maxim of manner. (2 points) In this conversation, B’s reply deliberately violated the maxim of quality, (2 points) because B wanted A to infer the information that Teheran is not in Turkey. The main purpose of B is to let A know that it is absurd to make such a mistake.(3 points)VII. Do the following analysis. (20 points)1. (1) c (2) a (3) d (4) b (5) f (1 point each)2. 1) child (2 points)2) human, plural (3 points)3)lala (2 points)4)The child is falling.(4 points)5)The baskets have arrived.(4 points)。
名词解释petence and Performance:•The distinction is discussed by the American linguist N. Chomsky in the late 1950’s.•Competence----the ideal user’s knowledge of the rules of his language.•Performance----the actual realization of this knowledge in linguistic communication.(American linguist N. Chomsky in the late 1950’s proposed the distinction between competence and performance. Chomsky defines competence as the ideal user’s knowledge of the rules of his language. This internalized set of rules enables the language user to produce and understand an infinitely large number of sentences and recognize sentences that are ungrammatical and ambiguous. According to Chomsky, performance is the actual realization of this knowledge in linguistic communicatio n. Although the speaker’s knowledge of his mother tongue is perfect, his performances may have mistakes because of social and psychological factors such as stress, embarrassment, etc.. Chomsky believes that what linguists should study is the competence, which is systematic, not the performance, which is too haphazard. )2.Sociolinguistics:is the sub-field of linguistics that studies the relation between language and society, between the uses of language and the social structures in which the users of language live.( It is a field of study that assumes that human society is made up of many related patterns and behaviors, some of which are linguistic.)nguage Acquisition:refers to the child’s acquisition of his mother tongue, i.e. how the child comes to understand and speak the language of his community. (Language acquisition is concerned with language development in humans. In general, language acquisition refers to children’s development of their first language, that is, the native language of the community in which a child has been brought up.)4.the Sapir-Whorf hypothesis:The Sapir-Whorf hypothesis is a theory put forward by the American anthropological linguists Sapir and Whorf (and also a belief held by some scholars). It states that the way people view the world is determined wholly or partly by the structure of their native language. (2) The Sapir-Whorf hypothesis consists of two parts, i.e. linguistic determinism and relativism. Whorf proposed first that all higher levels of thinking are dependent on language. Or put it more bluntly, language determines thought, i.e. the notion of linguistic determinism. Because languages differ in many ways, Whorf also believed that speakers of different languages perceive and experience theworld differently, i.e. relative to their linguistic background, hence the notion of linguistic relativism.5.Phrase structure rule:The grammatical mechanism that regulates the arrangement of elements that make up a phrase is called a phrase structure rule, such as:NP→(Det) + N +(PP)……e.g. those people, the fish on the plate, pretty girls.VP→(Qual) + V + (NP)……e.g. always play games, finish assignments.AP→(Deg) + A + (PP)……very handsome, very pessimistic, familiar with,very close toPP →(Deg) + P + (NP)……on the shelf, in the boat, quite near the station.The boy liked the dog.(The combinational pattern in a linear formula may be called a phrase structural rule, or rewrite rule[重写规则]. )6.Arbitrariness:The form of linguistic signs bear no natural relationship to their meaning. The link between them is a matter of convention.( It means that there is no logical connection between meanings and sounds. For instance, there is no necessary relationship between the word dog and the animal it refers to. The fact that different sounds are used to refer to the same object in different languages and that the same sound may be used to refer to different objects is another good example. Although language is arbitrary by nature, it is not entirely arbitrary. Some words, such as the words created in the imitation of sounds by sounds are motivated in a certain degree. The arbitrary nature of language makes it possible for language to have an unlimited source of expressions. )7.narrow transcription:transcription with letter-symbols together with the diacritics. This is the transcription required and used by the phoneticians in their study of speech sounds.(The narrow transcription is the transcription with diacritics to show detailed articulatory features of sounds.)8.Second Language Acquisition:Second Language Acquisition (SLA) refers to the systematic study of how one person acquires a second language subsequent to his native language.( SLA is viewed as a process of creative construction, in which a learner constructs a series of internal representations that comprises the learner's interim knowledge of the target language, known as interlingua. This is the language that a learner constructs at a given stage of SLA. Specifically, interlanguage consists of a series of interlocking and approximate linguistic systems in-between and yet distinct from the learner's native and target languages. It represents the learner’s transitional competence moving along a learning continuum stretching from one’s LI competence to t he target language competence. As a type of linguistic system in its own right, interlanguage is a product of L2 training, mother tongue interference, overgeneralization of the target language rules, and communicative strategies of the learner. If learners were provided sufficient and the right kind of language exposure and opportunities to interact with language input, their interlanguage would develop gradually in the direction of the target language competence. )9.sense and reference:Sense and reference are both concerned with the study of word meaning. They are two related but different aspects of meaning.➢Sense—is concerned with the inherent meaning of the linguistic form. It is the collection of all the features of the linguistic form; it is abstract and de-contextualized. It is the aspect of meaning dictionary compilers are interested in.➢Reference—what a linguistic form refers to in the real, physical world; it deals with the relationship between the linguistic element and the non-linguistic world of experience.10.Interlanguage:Learns put their first language back to the whole picture and studied its role from a cognitive perspective. In this sense, native language functions as a kind of “input from inside,”therefore transfer is not transfer, but a kind of mental process.( SLA is viewed as a process of creative construction, in which a learner constructs a series of internal representations that comprisesthe learner’s interim knowledge of the target language, known as interlanguage.)nguage Acquisition Device:The Language Acquisition Device (LAD) is a hypothetical brain mechanism that Noam Chomsky postulated to explain human acquisition of the syntactic structure of language. This mechanism endows children with the capacity to derive the syntactic structure and rules of their native language rapidly and accurately from the impoverished input provided by adult language users. The device is comprised of a finite set of dimensions along whichlanguages vary, which are set at different levels for different languages on the basis of language exposure. The LAD reflects Chomsky's underlying assumption that many aspects of language are universal (common to all languages and cultures) and constrained by innate core knowledge about language called Universal Grammar. This theoretical account of syntax acquisition contrasts sharply with the views of B. F. Skinner, Jean Piaget, and other cognitive and social-learning theorists who emphasize the role of experience and general knowledge and abilities in language acquisition.??????(LAD, that is Language Acquisition Device, is posited by Chomsky in the 1960s as a device effectively present in the minds of children by which a grammar of their nativelanguage is constructed.)12.Cooperative Principle: According to Grice, in making conversation, there is a general principle which all participants are expected to observe. It goes as follows: Make your conversational contribution such as required at the stage at which it occurs by the accepted purpose or direction of the talk exchange in which you are engaged.使你所说的话,在其所发生的阶段,符合你所参与的交谈的公认目标或方向。
一、请从发音部位和发音方法描述普通话中每个声母的发音情况。
1.按发音部位分类(发音部位:发音时发音器官构成阻碍的部位)①双唇音:b p m(3个)②唇齿音:f(1个)③舌尖前音:z c s(3个)④舌尖中音:d t n l(4个)⑤舌尖后音:zh ch sh r(4个)⑥舌面音:j q x(3个)⑦舌根音:ɡk h(3个)2.按发音方法分类(发音方法:发音时喉头,口腔和鼻腔节制气流的方式和状况),包括三个方面:(1)阻碍方式①塞音:b p d tɡk(6个)②塞擦音:z c zh ch j q(6个)③擦音:f h s sh r x(6个)④鼻音:m n(2个)⑤边音:l(1个)二、描述普通话中10个单元音韵母的发音情况(1)i[i]舌面、前、高、不圆唇元音(2)ü[y]舌面、前、高、圆唇元音(3)ê[ε]舌面、前、半低、不圆唇元音(4)ɑ[A]舌面、央、低、不圆唇元音(5)u[u]舌面、后、高、圆唇元音(6)e[γ]舌面、后、半高、不圆唇元音(7)o[о]舌面、后、半高、圆唇元音(8)-i(前)舌尖、前、高、不圆唇元音(9)-i(后)舌尖、后、高、不圆唇元音(10)er[]卷舌不圆唇元音三、网络流行词“锦鲤”是一般词汇还是基本词汇?为什么?是一般词汇。
因为基本词汇具有稳固性、普遍性和能产性三个特性,它们是一个民族的人民日常使用的,不容易引起变化,比较稳固,并且有较强的构词能力,是产生新词的基础。
而一般词汇指的则是基本词汇以外的词汇,它们对社会发展的变化最为敏感,并且不稳固,容易发生变化,构词能力不强甚至没有构词能力。
一般词汇所包含的词数量大,成分杂,变化快,包含外来词、行业用语等词汇。
由于网络新词具有不稳固的性质,并且无法再造词,因而网络新词属于一般词汇。
四、语言具有模糊性,会不会影响交际?为什么?不会影响交际。
词义模糊的原因主要有三点:第一,词具有概括性,在概括所指对象时,对象本身是一个渐进发展的过程,词义在过程中进行切分,必然造成模糊性。
《当代语言学》期末考试试题Please give your answers to the following questions in a separated answer sheet provided by the examiner.1. Do you think the following words are permissible in English? Why? 5%a) tpray b) btry c) tgharg2. What is the difference between open-class words and closed-class words? 5%3. What role can English inflection play in the expression of meaning? 5%4. Draw the tree diagrams for the following sentences: 10%(1) She found a book on Madison Street.(2) Jack advised Henry to see the dentist.(3) Jack promised Henry to see the doctor.5. What is the difference between sentence meaning and utterance meaning? 5%6. What is the use of metaphor in verbal communication? 5%7. In each case below decide which maxim of the cooperative principle has been flouted and what implicature might be drawn. 15%1) A: Where does Miss Rosebery live?B: Somewhere in the suburbs of the city.2) A: I'm out of petrol.B: There is a garage round the corner.3) A: How do you think of Cathy's singing?B: Well, she has produced a series of sounds that correspond closely with the score of "Home sweet home".4) Teacher: (towards the end of a lecture) What time is it now?Student: It's 10:44 and 35.6 seconds.5) A: Do you want some coffee?B: Coffee would make me awake.8. The New information in each of the following utterances is bold-typed. Please use a different sentence structure for each so that the New information can be highlighted. 10%1) He owed the tailor twenty dollars.2) The impossible has often proved possible.3) We have oral practice every other day.4) We didn't leave the flat until we could smell the smoke in the corridor.5) The football match was cancelled because of the rain.9. What is a regional dialect? And what is the relationship between a regional dialect and a standard dialect? 5%10. Do you agree to the claim that all languages in the world derived from one common ancestor? 5%11. Please explain the primacy of human language over animal communication. 10%12. The following are some questions taken from some test papers. Decide which type of test they belong to: (a) the discrete point test, (b) integrative test, and (c) the communicative test. 10%Directions: There are 30 incomplete sentences in this part. For each sentence there are four choices marked A, B, C, and D. Choose the ONE answer that best completes the sentence. Then mark the corresponding letter on the Answer Sheet with a single line through the center.1). By the time he arrives in Beijing, we _________ here for two days.A. have been stayingB. have stayedC. shall stayD. will have stayed2) Directions: In this section, you will, you will hear a passage three times. When the passage is read for the first time, you should listen carefully for the general idea. When the passage is read for the second time, you are required to fill in the blanks numbered from S1 to S7 with the exact words you have just heard. For blanks numbered S8 to S10 you are required to fill in the missing information. You can either use the exact words you have just heard or write down the main points in your own words. Finally, when the passage is read for the third time, you should check what you have written.If you are a college student, most of your concerns about your health and happiness in life are probably (S1) __________ on the present. Basically, you want to feel good physically, mentally, and (S2) __________ now. You probably don't spend much time worrying about the (S3) __________, such as whether you will develop heart disease, or (S4) __________, how you will take care of yourself in your (S5) __________ years, or how you are going to live.13. What do you think are the strong points and drawbacks of each of the following types of test:(a) the achievement test, (b) the proficiency test, (c) the aptitude test, (d) the diagnosis test, (e) the subjective test, and (f) the objective test. 10%参考答案1. These words are not permissible in English. All languages have constraints on the permitted sequences of phonemes. *tpray, *btry, *tgharg do not sound like an English word because it does not conform to the restrictions on the sequencing of phonemes. When three consonants occur, the first must be [s].2. Open-class words refer to those classes of words to which we can add new words. In English, nouns, notional verbs, adjectives and adverbs belong to this category. Such words normally convey certain semantic contents and thus are also called "content words". Closed-class words refer to those classes to which new words can hardly be added. In English, closed-class words include pronouns, determiners, conjunctions, relatives, prepositions, auxiliary verbs, modal verbs and the linking verb "to be". Their roles in the linguistic system are partly or wholly grammatical and thus are also called "grammatical words".3. Inflection refers to the process of adding an affix to a word or changing it in some other way according to the grammatical rules of the language. English inflections are used to express certain grammatical meanings: the plural morpheme {s} to change the noun into the plural-number form, the generative-case morpheme {'s} to indicate the relation of possession, the feminine-gender morpheme {ess} to change the masculine noun into its corresponding feminine-gender form, the third-person singular {s} to change the verb into the third-person singular form, the -ing participle {ing} to change the verb into the -ing participle, the past-form morpheme {ed} to change the verb into the past-tense form, the past-participle morpheme {ed} to change the verb into the -ing participle, the comparative {er} to change an adjective into the comparative-degree form, andthe superlative {est} to change an adjective into the superlative-degree form.4. 1) (a)(b)2)3)5. Sentence meaning refers to the conventional content or literal meaning of a sentence. It is the context-independent meaning. Utterance meaning refers to the meaning of an utterance in the context. In other words, it is the meaning dependent on the context. In some cases, the sentence meaning coincides with the utterance meaning. But in many situations, the utterance meaning differs from the sentence meaning.6. Metaphor is common in verbal communication. In the traditional approach, metaphor is generally interpreted as a rhetorical device to add novelty to verbal communication. But according to the cognitive and functional linguistic approach, metaphor is a basic cognitive facility with which human beings organize the world in the system of language. Much of the history of every language, according to Halliday (1994: 348), is a history of demetaphorizing: of expressions which began as metaphors gradually losing their metaphorical character. Metaphorical modes of expression are characteristic of adult discourse. On the other hand, metaphor is also an important stylistic feature. For example, literary works (such as novels and poetry) normally abound in lexical metaphor while scientific and technical registers are characterized with nominalizing metaphors.7. 1) In this dialogue, B has flouted the maxim of Manner. Here B uses an obscure expression and fails to give a brief and direct answer to A's question. The implicature of B's utterance is probably "I don't know the exact place. What I can tell you is that Miss Rosebery lives somewhere in the suburbs of the city."2) In this dialogue, B has flouted the maxim of Relevance. B's answer is not relevant to A's statement. The implicature of B's utterance is probably "There is a garage round the corner, so you can have your car refilled there."3) In this dialogue, B has flouted the maxim of Quantity. B's reply is more informative than is required for the current purposes of the exchange. The conversational implicature of B's utterance is that "I don't think too much of Cathy's singing."4) In this dialogue, the student is more informative than is required for the current purposes of the exchange and has thus flouted the maxim of Quantity. The implicature of the student's utterance is probably "It's high time you finished the lecture."8. 1) He owed the tailor twenty dollars.→It was the tailor whom he owed twenty dollars.2) The impossible has often proved possible.→It is the impossible that has often proved possible.Or: What has often proved possible is the impossible.3) We have oral practice every other day.→It is every other day that we have oral practice.4) We didn't leave the flat until we could smell the smoke in the corridor.→It was not until we could smell the smoke in the corridor that we left the flat.5) The football match was cancelled because of the rain.→It was because of the rain that the football match was cancelled.9. Regional dialect is the kind of dialect that is spoken and used by the people in a geographical region. Every local group of people spoke the language a little differently from other groups. For instance, these differences may be found in pronunciation, spelling, and the use of words and grammatical structures. With the passage of time, a regional dialect may become the standard dialect of a nation. This is largely due to a number of socio-economic and political reasons.10. Currently, we cannot say that all languages in the world derived from one common ancestor. It might be true that some languages have diverged from one common ancestor, for example, French, Spanish, Italian and other Romance languages were clearly descended from Latin, but no evidence show that all languages in the world have the same origin. As research shows, there are at least 29 language families in the world. However, this problem will be solved when we have enough evidence to show that human beings have one common ancestor.11. Human language is primary over animal communication in the following aspects:1) Human has the ability to refer to things far remote in time and space. In contrast, it may be impossible for an animal to convey such ability.2) Human has the ability to produce and understand an indefinite number of novel utterances, but no animal can communicate creatively with another animal.3) Learning is much more important as a factor in human language than in animal communication.4) Human language structure and language use are vastly more complex than any animal communication system.5) Animal communication systems are closed-ended, whereas human languages are open-ended.12. The questions in 1) belong to the discrete point test, because the test consists of many questions on a number of linguistic points, but each question tests only one linguistic point. Besides, the questions here are objective so that the test can be scored objectively and the results are easy to be analyzed statistically. The questions in 2) belong to the integrative test, because they are a combination of cloze test and dictation. The testees are required to fill in the blanks in a passage with either a single word, a sentence or a larger unit while they are listening to the same material.13. (a) The achievement test is aimed at assessing the testee's mastery of the knowledge and skills set by the syllabus as the teaching goals the contents of a particular course. It is usually given at the end of a period of study. The achievement test focuses on the result rather than the process. Thus, it is of little use in diagnosing how the testee is getting along with the study of the target language. (b) The proficiency test is aimed at discovering what the testee has already known about the target language. It can be used to predict whether he has the ability to accomplish a certain task in the future. The proficiency test does not care what kind of language training the testee has ever received. It focuses more on the result than the process. (c) The aptitude test is designed to measure the testee's aptitude or natural ability to learn the target language. It is based on the assumption that the learner's mastery of his native language isclosely related to his potential to learn a foreign language. The drawback of the aptitude test is its failure to assess the effect of the learner's attitude, learning strategies, learning environment and other related factors. (d) The diagnosis test aims at discovering how the testee is getting along with his study of the target language. A well-designed diagnosis test can help the teacher to find out what is wrong with the student's previous study and how it can be remedied in the future study. It cares more about the process than the result. Its drawback is that it only covers a limited range of linguistic knowledge or skills and thus cannot reflect the whole process of language acquisition. (e) The subjective test is a test the result of which may be influenced by the marker's linguistic knowledge, understanding of the scoring standard, the mental state at the time of scoring and other personal factors. Its strong point is its effective assessment of the testee's comprehensive mastery of the target language. (f) The objective test is a test the result of which is free of the influence of the marker's linguistic knowledge, understanding of the scoring standard, the mental state at the time of scoring and other personal factors. The result remains consistent when the paper is scored by different markers or even by a machine. However, the knowledge and/or skill to be examined by a question is rather restricted, and the multiple-choice leaves room for the testee to get the correct answer simply by guessing and thus undermines its reliability.。
语⾔学期末题及参考答案I1、结构主义语⾔学阶段(20世纪初—20世纪50年代—⾄今)索绪尔的语⾔学理论直接导致了结构主义语⾔学的建⽴。
结构主义语⾔学可以分成五个流派:(王德春P54)1、布拉格学派2、哥本哈根学派3、美国描写语⾔学派4、伦敦学派5、莫斯科学派2、语⾔和⾔语:1、定义:(1)a、⾔语就是讲话或写作,是⼀种⾏为动作。
b、语⾔也是所讲的话或所写的⽂章,是⾏为动作的结果。
(2)“语⾔”不是⾔语活动本⾝,⽽是隐藏在⾔语活动或⾔语结果中的⼀个规则系统。
直观地说就是语⾳、词汇、语义、语法系统或者叫⾳义结合的词汇系统和语法系统。
2、区别:(1)⾔语是个⼈的⾏为,每个⼈可以⽤不同的嗓⾳进⾏说话,每个⼈都有不同的⾔语风格,每个⼈都有⾃⼰的“⾔语”。
(2)每个⼈必须按照语⾔系统的规定去说话,必须遵循这个系统的规则,但每个⼈不能创造⾃⼰的“语⾔”,语⾔是社会的,⾔语是个⼈的。
3、联系:“语⾔”和“⾔语”具有紧密的联系⽽且互为前提的:要⾔语为⼈所理解,并产⽣它的⼀切效果,必须有语⾔;但是要语⾔能够建⽴,也必须有⾔语。
从历史上看,⾔语的事实总是在前的。
语⾔和⾔语是互相依存的,语⾔既是⾔语的⼯具,⼜是⾔语的产物。
(1)⾔语是第⼀性的,语⾔是第⼆性的。
那⾥有⾔语,哪⾥就有语⾔;哪⾥没有⾔语,哪⾥就没有语⾔。
语⾔是存在于⾔语之中的。
(2)语⾔来源于⾔语,⼜反作⽤于⾔语。
语⾔虽然是第⼆性的,但它绝不是消极的。
相反,它对第⼀性的⾔语起着积极的、巨⼤的作⽤,即强制性的规范作⽤,使得任何⼀个说话的⼈或写作的⼈都必须遵照⼀定的规则进⾏,否则就不能被⼈们理解,得不到社会的承认。
3、语⾔是⼀个符号系统:1、符号:(1)符号是⼀种信号、记号、或标记。
被约定⽤来指代某种事物的标志。
(2)符号由两个部分构成,分别是能指和所指,它们合在⼀起组成⼀个符号。
(3)符号的本质特征:任意性/规定性(可变性/不变性)a、符号的能指和所指之间具有任意性和规定性的⽭盾统⼀性。
1. The study of language development over a period of time is generally termed as_____linguistics. DA. appliedB. diachronicC. comparativeD. synchronic2. The sentence that has a NP and a VP can be shown in a __C__ formula "S→NP VP".A. hierarchicalB. linearC. tree diagramD. vertical3. Which of the following sounds is a voiceless bilabial stop? AA. [p]B.[m]C.[b]D.[t]4. The words “make” and “bus” are called _____D____because they can occur unattached.A. derivational morphemes B .inflectional morphemesC. bound morphemesD. free morphemes5. The pair of words “lend” and “borrow” are____B______.A. gradable antonymyB. relational (converse) antonymyC. synonymsD. co-hyponyms6. The semantic components of the word “man” can be expressed as ____C___.A.+animate,+human,+male,-adult;B.+animate,+human,-male,-adult;C.+animate,+human,+male,+adultD.—animate,+human,-male,-adult7. What kind of function does the sentence “How do you do?” have? BA. DirectiveB. PhaticC. InformativeD. Evocative8. Nouns, verbs and adjectives can be classified as_______A____.A. lexical wordsB. grammatical wordsC. function wordsD. form words9. Which of the following best states the behaviorist view of child language acquisition?______A_.A. Language acquisition is a process of habit formationB. Language acquisition is the species-specific property of human beingsC. Children are born with an innate ability to acquire languageD. Humans are equipped with the neural prerequisites for language and language use10. The branch of linguistics that studies meaning of language in context is called__C?A. morphologyB. sociolinguisticsC. pragmaticsD. psycholinguistics11、Chomsky defines "competence" as the ideal user's knowledge of the rules of his language.12、The four sounds /p/,/b/,/m/ and /w/have one feature in common, i.e, they are all bilanial .13、Morphology is a branch of grammar which studies the internal structure of words and the rules by which words are formed.14、A sentence is a structurally independent unit that usually comprises a number of words to form a complete statement, question or command.15、In most b communities, two languages have the same in speech situations known as domains.16、The illocutionary point of r is to commit the speaker to something's being the case, to the truth of what has been said.17、.In the history of any language the speech____ form always came into being before the writing system.18--19、Syntactic categories refer to s ( ) and c ( ) only.20、As a type of linguistic system in L 2 learning, interlanguage is a product of L2 training, mother tongue interference, overgeneralization of the target language rules, and learning and communicative strategies of the learner.( F )21、In modern linguistic studies, the written form of language is given more emphasis than the spoken form for a number of reasons.( F )22、Voicing is a phonological feature that distinguishes meaning in both Chinese and English.( T)23、The compound word "bookstore" is the place where books are sold. This indicates that the meaning of a compound is the sum total of the meanings of its components.( T)24、The territory in which the Indo-European languages are mainly spoken today also includes languages that are not Indo-European.( F)25、All normal children have equal ability to acquire their first language.IV. 1. Give the phonetic symbol for each of the following sound descriptions: Symbols here in order:26. [t∫]27 [б]28. [d]29.[I]30. [э:]1) voiceless, palatal, affricate 2) voiced, dental, fricative3) voiced, alveolar, stop 4) open, close, short5) back, semi-open, long2. Give the phonetic features of each of the following sounds31 [m]32[r]33[e]34[w]35[h]31 [m]voiced, bilabial, nasal; 32[r]voiced, alveolar, liquid;33[e]front, high, semi-close; 34[w]voiced, bilabial, glide;35[h]voiceless,fricatives,glottal;V. The following sentences all contain conjoined categories. Draw a treediagram for each of the sentences:1.Mary is fond of literature but tired of statistics.2.The detective went out and the mysterious man came in..Answer the following questions as comprehensively as possible:1.What criteria are used to classify the English vowels?The criteria used to classify English vowels are:The height of the tongue raising: high, mid, and lowThe position of the highest part of the tongue: front, central, and backThe degree of lip rounding: rounded, un-roundedThe degree of tenseness/the length of sound: tense (long) or lax (short)The change of sound quality: pure (monophthong), gliding (diphthong)2 What are the four maxims of CP (Cooperative Principle)?The Cooperative PrincipleThe maxims are:Quantity: Make your contribution as informative as is required (for the current purposes of the exchange). Do not make your contribution more informative than is required.Quality –Try to make your contribution one that is true.Do not say what you believe to be false.Do not say that for which you lack adequate evidence.Relation – Be relevant.Manner – Be perspicuous. Avoid obscurity of expression. Avoid ambiguity. Be brief (avoid unnecessary prolixity). Be orderly.Explain what pragmatics studies for and how it differs from traditional semantics.A general definition: pragmatics is the study of language in use.Pragmatics studies the factors that govern our choice of language in social interaction and the effects of our choice on others. Pragmatics takes care of the aspect of meaning that is not accounted for by semantics. Semantics traditionally deals with meaning as a dyadic relation, while pragmatics deals with meaning as a triadic relation. Thus meaning in pragmatics is defined relativeto a speaker or the user of the language; whereas meaning in semantics is defined purely as a property of expressions in a given language, in abstraction from particular situations, speakers or hearers.’ Therefore, what essentially distinguishes semantics and pragmatics is whether in the study of meaning the context of use is considered. If it is not considered, the study is restricted to the area of traditional semantics; if it is considered, the study is being carried out in the area of pragmatics.To analyze the language acquisition theories you’ve learned in classes, which one do you think is more reasonable and convincing? Explain why?II. Read each of the following statements carefully. Decide which one of the four choices best completes the statement and put the letter A, B, C or D in the brackets. (2%×10=20%) (Omit)11. 12 .13 14. 15. 16. 17. 18. 19. 20.。