推荐下载-曼昆经济学原理第二章 精品
- 格式:ppt
- 大小:1.50 MB
- 文档页数:29


曼昆经济学原理(双语)带你读《经济学原理》,每日更新,欢迎来主页查看。
翻译部分经本人校对修改,本文仅供学习交流使用,版权归相关权利人所有!第二章像经济学家一样思考2.102-2c Why Economists’ Advice Is Not Always Followed2-2c 为何经济学家的意见并非总能被采纳Any economist who advises presidents or other elected leaders knows that his recommendations are not always heeded. Frustrating as this can be, it is easy to understand. The process by which economic policy is actually made differs in many ways from the idealized policy process assumed in economics textbooks.任何为总统或其他民选领导人提供建议的经济学家都知道,他的建议并不总是得到重视。
虽然这可能令人沮丧,但很容易理解。
实际制定经济政策的过程与经济学教科书中所设想的理想化政策过程在许多方面有所不同。
Throughout this text, whenever we discuss economic policy, we often focus on one question: What is the best policy for the government to pursue? We act as if policy were set by a benevolent king. Once theking figures out the right policy, he has no trouble putting his ideas into action.纵观全文,每当我们讨论经济政策时,我们往往会集中在一个问题上:政府寻求的最佳政策是什么?我们的做法就好像政策是由仁慈的国王制定的。


曼昆《经济学原理(微观经济学分册)》第6版课后习题详解第一篇导言第1章经济学十大原理一、概念题1.稀缺性稀缺性是指在给定的时间内,相对于人的需求而言,经济资源的供给总是不足的,也就是资源的有限性与人类的欲望无限性之间的矛盾。
2.经济学经济学是研究如何将稀缺的资源有效地配置给相互竞争的用途,以使人类的欲望得到最大限度满足的科学。
其中微观经济学是以单个经济主体为研究对象,研究单个经济主体面对既定资源约束时如何进行选择的科学;宏观经济学则以整个国民经济为研究对象,主要着眼于经济总量的研究。
3.效率效率是指人们在实践活动中的产出与投入比值或者是效益与成本比值,比值大效率高,比值小效率低。
它与产出或收益大小成正比,与投入或成本成反比。
4.平等平等是指人与人的利益关系及利益关系的原则、制度、做法、行为等都合乎社会发展的需要,即经济成果在社会成员中公平分配的特性。
它是一个历史范畴,按其所产生的社会历史条件和社会性质的不同而不同,不存在永恒的公平;它也是一个客观范畴,尽管在不同的社会形态中内涵不同对其的理解不同,但都是社会存在的反映,具有客观性。
5.机会成本机会成本是指将一种资源用于某种用途,而未用于其他用途所放弃的最大预期收益。
其存在的前提条件是:①资源是稀缺的;②资源具有多种用途;③资源的投向不受限制。
6.理性人理性人是指系统而有目的地尽最大努力去实现其目标的人,是经济研究中所假设的、在一定条件下具有典型理性行为的经济活动主体.7.边际变动边际变动是指对行动计划的微小增量调整。
8.激励激励是指引起一个人做出某种行为的某种东西。
9.市场经济市场经济是指由家庭和企业在市场上的相互交易决定资源配置的经济,而资源配置实际上就是决定社会生产什么、生产多少、如何生产以及为谁生产的过程。
10.产权产权是指个人拥有并控制稀缺资源的能力,也可以理解为人们对其所交易东西的所有权,即人们在交易活动中使自己或他人在经济利益上受益或受损的权力。


第二章像经济学家一样思考复习题1.经济学如何像一门科学?答:经济学家努力以科学家的客观态度来探讨经济问题。
用科学的方法提出理论、收集资料,并分析这些资料以努力证明或否定他们提出的理论来研究社会。
经济学家研究经济的过程和方法与自然科学的科学家研究自然是一样的。
所以说经济学也是一门科学。
2.为什么经济学家要做出假设?答:假设可以使解释这个世界更为容易。
对不同的问题作出不同的假设,略去对问题的答案没有实质影响的因素,突出实质性的内容,使我们可以集中进行思考。
3.经济模型应该准确地描述现实吗?答:经济模型不需要准确地描述现实。
所有的模型都是建立在假设的基础上的,它们忽略掉了大量不会对研究结果有实质性影响的细节,向我们说明什么是真正重要的。
模型是为了增进我们对现实的理解而简化了现实。
4.说出你的家庭参与要素市场的一种方式,以及参与产品市场的一种方式。
答:略。
5.举出一种没有包括在简单的循环流量图中的经济关系。
答:略。
6.画出并解释一个生产牛奶与点心的经济的生产可能性边界。
如果一场瘟疫使该经济中的一半奶牛死亡,这条生产可能性边界会发生怎样的变动?答:假设在正常情况下,将可能得到的所有资源用于生产点心,可以生产300 千克,如果全用于生产牛奶,可以生产1 000 升。
L1 表示正常情况下该经济的生产可能性边界。
如果一场疾病造成该经济一半的奶牛死亡,生产可能性边界会向内移,即L2 线。
因为在生产率不变的情况下,可用于生产点心和牛奶的经济资源减少了。
5图2—1 生产可能性边界7.用生产可能性边界描述“效率”的思想。
答:如果经济可以利用它所得到的全部稀缺资源,就可以说这种结果是有效率的。

曼昆《经济学原理(微观经济学分册)》(第6版)第2章像经济学家一样思考课后习题详解跨考网独家整理最全经济学考研真题,经济学考研课后习题解析资料库,您可以在这里查阅历年经济学考研真题,经济学考研课后习题,经济学考研参考书等内容,更有跨考考研历年辅导的经济学学哥学姐的经济学考研经验,从前辈中获得的经验对初学者来说是宝贵的财富,这或许能帮你少走弯路,躲开一些陷阱。
以下内容为跨考网独家整理,如您还需更多考研资料,可选择经济学一对一在线咨询进行咨询。
一、概念题1.循环流量图(circular flow diagram)答:循环流量图是指表明物品和劳务、生产要素以及货币支付在家庭和企业之间如何流动的经济图形,如图2-1所示。
在这个模型中,经济由两类决策者——家庭和企业——所组成。
企业用劳动、土地和资本(建筑物和机器等)这些投入来生产物品和劳务,这些投入被称为生产要素。
家庭则拥有生产要素并消费企业生产的所有物品与劳务。
图2-1 循环流量图图2-1中,经济决策由家庭和企业做出。
家庭和企业在物品与劳务市场(在这个市场上,家庭是买者而企业是卖者)以及生产要素市场(在这个市场上,企业是买者而家庭是卖者)上相互交易。
外面一圈的箭头表示货币的流向,里面一圈的箭头表示相应的物品与劳务的流向。
循环流量图的形式是简化的,是整体经济的一个简化模型,因为它不包括国际贸易和政府。
2.生产可能性边界(production possibilities frontier)(深圳大学2007研;北京工业大学2008研)答:生产可能性边界也称为社会生产可能性边界或生产可能性曲线,指一个经济在可获得的生产要素与生产技术既定时所能生产的产品的产量的各种组合。
由于整个社会的经济资源是有限的,当这些经济资源都被充分利用时,增加一定量的一种产品的生产,就必须放弃一定量的另一种产品的生产。
整个社会生产的选择过程形成了一系列的产品间的不同产量组合,所有这些不同产量的组合就构成了社会生产的可能性边界。


E conomics Principles ofN. Gregory MankiwThinking Likean EconomistSeventh EditionCHAPTER 2 W o j c i e c h (G e r s o n ((183111901)(W o j c i e c h (G e r s o n ((183111901)(In this chapter,look for the answers to these questions • What are economists’ two roles? How do they differ? • What are models? How do economists use them? • What are the elements of the Circular-Flow Diagram? What concepts does the diagram illustrate?• How is the Production Possibilities Frontier relatedto opportunity cost? What other concepts does it illustrate?• What is the difference between microeconomics andmacroeconomics? Between positive and normative?The Economist as Scientist! Economists play two roles:1. Scientists: try to explain the world2. Policy advisors: try to improve it! In the first, economists employ thescientific method,the dispassionate development and testing of theories about how the world works.3Assumptions & Models! Assumptions simplify the complex world,make it easier to understand.! Example: To study international trade,assume two countries and two goods.Unrealistic, but simple to learn andgives useful insights about the real world.! Model: a highly simplified representation ofa more complicated reality.Economists use models to study economic issues.4Our First Model:The Circular-Flow Diagram! The Circular-Flow Diagram: a visual model of the economy, shows how dollars flow through markets among households and firms! Two types of “actors”:! households! firms! Two markets:! the market for goods and services! the market for “factors of production”9Factors of Production! Factors of production: the resources the economy uses to produce goods & services, including! labor! land! capital (buildings and machines used inproduction)10Households:! Own the factors of production,sell/rent them to firms for income! Buy and consume goods & services FirmsHouseholds Firms:! Buy/hire factors of production,use them to produce goodsand services! Sell goods & services11Markets for Factors of Production HouseholdsFirms Markets for Goods & ServicesOur Second Model:The Production Possibilities Frontier ! The Production Possibilities Frontier (PPF): a graph that shows the combinations oftwo goods the economy can possibly produce given the available resources and the available technology! Example:! Two goods: computers and wheat! One resource: labor (measured in hours)! Economy has 50,000 labor hours per monthavailable for production.13A C T I V E L E A R N I N G1Points off the PPFA.On the graph, find the point that represents(100 computers, 3000 tons of wheat), label it F.Would it be possible for the economy to produce this combination of the two goods?Why or why not?B.Next, find the point that represents(300 computers, 3500 tons of wheat), label it G.Would it be possible for the economy to producethis combination of the two goods?The PPF: What We Know So Far Points on the PPF (like A – E)! possible! efficient: all resources are fully utilizedPoints under the PPF (like F)! possible! not efficient: some resources underutilized(e.g., workers unemployed, factories idle) Points above the PPF (like G)! not possible19The PPF and Opportunity Cost! Recall: The opportunity cost of an itemis what must be given up to obtain that item.! Moving along a PPF involves shifting resources (e.g., labor) from the production of one good to the other.! Society faces a tradeoff: Getting more of one good requires sacrificing some of the other.! The slope of the PPF tells you the opportunity cost of one good in terms of the other.20Economic growth shifts the PPF outward.The Shape of the PPF! The PPF could be a straight line or bow-shaped. ! Depends on what happens to opportunity costas economy shifts resources from one industryto the other.! If opp. cost remains constant,PPF is a straight line.(In the previous example, opp. cost of acomputer was always 10 tons of wheat.)! If opp. cost of a good rises as more of the goodis produced, PPF is bow-shaped….25At A, opp. cost of mtn bikes is low.B At B , opp. cost of mtn bikes is high.Why the PPF Might Be Bow-Shaped! So, PPF is bow-shaped when different workers have different skills, different opportunity costs of producing one good in terms of the other.! The PPF would also be bow-shaped when there is some other resource, or mix of resources with varying opportunity costs(E.g., different types of land suited fordifferent uses).29The PPF: A Summary! The PPF shows all combinations of two goods that an economy can possibly produce,given its resources and technology.! The PPF illustrates the concepts oftradeoff and opportunity cost,efficiency and inefficiency,unemployment, and economic growth.! A bow-shaped PPF illustrates the concept of increasing opportunity cost.31Microeconomics and Macroeconomics! Microeconomics is the study of how households and firms make decisions and how they interact in markets.! Macroeconomics is the study of economy-wide phenomena, including inflation, unemployment, and economic growth.! These two branches of economics are closely intertwined, yet distinct—they address different questions.32Summary• As scientists, economists try to explain the world using models with appropriate assumptions. • Two simple models are the Circular-Flow Diagram and the Production Possibilities Frontier.• Microeconomics studies the behavior of consumers and firms, and their interactions in markets. Macroeconomics studies the economy as a whole.• As policy advisers, economists offer advice onhow to improve the world.Graphing: a brief review! Graphs purposes:! Visually express ideas that might be less clear ifdescribed with equations or words! Powerful way of finding and interpreting patterns ! Graphs of a single variable! Pie chart! Bar graph! Time-series graph42Types of Graphs (a)Figure A-1The pie chart in panel (a) shows how the U.S. national income in 2011 was derivedfrom various sources.Figure A-1 Types of Graphs (b)The bar graph in panel (b) compares the 2011 average income in four countries.Types of Graphs (c)Figure A-1The time-series graph in panel (c) shows the productivity of labor in U.S.businesses from 1950 to 2010.Graphing: a brief review! Graphs of two variables: the coordinate system ! Display two variables on a single graph! Scatterplot! Ordered pairs of points! x-coordinate– Horizontal location! y-coordinate– Vertical location46Using the Coordinate SystemGrade point average is measured on the vertical axis and study time on thehorizontal axis. Albert E., Alfred E., and their classmates are represented by variouspoints. We can see from the graph that students who study more tend to get higher grades.Graphing: a brief review! Curves in the coordinate system! Data! Number of novels purchased! Price of novels! Income! Demand curve! Effect of a good s price! On the quantity of the good consumers want tobuy! For a given income48Table A-1Novels Purchased by EmmaThis table shows the number of novels Emma buys at various incomes and prices. For any given level of income, the data on price and quantity demanded can be graphed to produce Emmas demand curve for novels, as shown in Figures A-3 and A-4.Graphing: a brief review! Negatively related variables! The two variables move in opposite direction! Downward sloping curve! Positively related variables! The two variables move in the same direction! Upward sloping curve! Movement along a curve! Shifts in a curve50! Slope! Fairly flat upward-sloping line! Slope is a small positive number! Steep upward-sloping line! Slope is a large positive number! Downward sloping line! Slope is a negative number! Horizontal line! Slope is zero! Vertical line: infinite slope54。
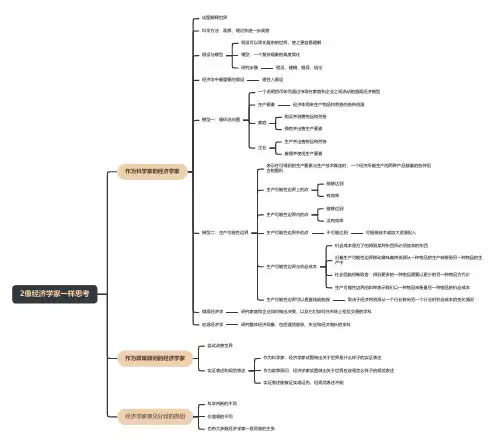
2像经济学家一样思考作为科学家的经济学家试图解释世界科学方法:观察、理论和进一步观察假设与模型假设可以简化复杂的世界,使之更容易理解模型:一个复杂现象的高度简化研究步骤假设、建模、推导、结论经济学中最重要的假设理性人假设模型一:循环流向图一个说明货币如何通过市场在家庭和企业之间流动的直观经济模型生产要素经济体用来生产物品和劳务的各种资源家庭购买并消费物品和劳务拥有并出售生产要素企业生产并出售物品和劳务雇佣并使用生产要素模型二:生产可能性边界表示在可得到的生产要素与生产技术既定时,一个经济所能生产的两种产品数量的各种组合的图形生产可能性边界上的点能够达到有效率生产可能性边界内的点能够达到没有效率生产可能性边界外的点不可能达到可提高技术或加大资源投入生产可能性边界与机会成本机会成本是为了的得到某种东西所必须放弃的东西沿着生产可能性边界移动意味着将资源从一种物品的生产转移到另一种物品的生产中社会面临权衡取舍:得到更多的一种物品需要以更少的另一种物品为代价生产可能性边界的斜率表示我们以一种物品来衡量另一种物品的机会成本生产可能性边界可以是直线或曲线取决于经济将资源从一个行业转向另一个行业时机会成本的变化情况微观经济学研究家庭和企业如何做出决策,以及它们如何在市场上相互交易的学科宏观经济学研究整体经济现象,包括通货膨胀、失业和经济增长的学科作为政策顾问的经济学家尝试改善世界实证表述和规范表述作为科学家,经济学家试图做出关于世界是什么样子的实证表述作为政策顾问,经济学家试图做出关于世界应该是怎么样子的规范表述实证表述能被证实或证伪,但规范表述不能经济学家意见分歧的原因科学判断的不同价值观的不同也有大多数经济学家一致同意的主张。
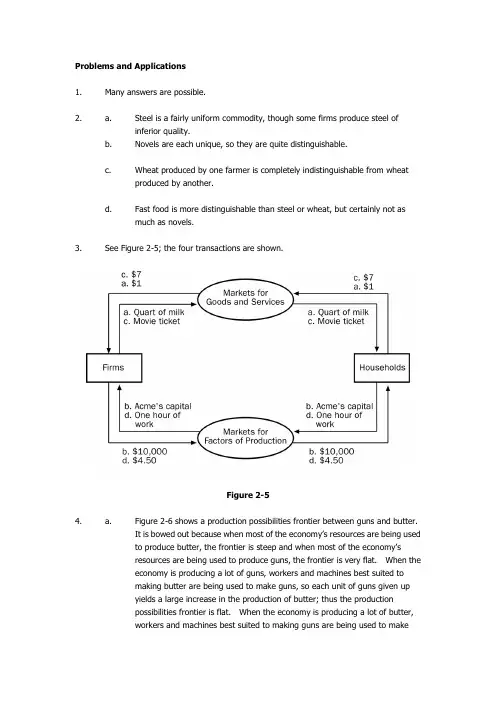
Problems and Applications1. Many answers are possible.2. a. Steel is a fairly uniform commodity, though some firms produce steel ofinferior quality.b. Novels are each unique, so they are quite distinguishable.c. Wheat produced by one farmer is completely indistinguishable from wheatproduced by another.d. Fast food is more distinguishable than steel or wheat, but certainly not asmuch as novels.3. See Figure 2-5; the four transactions are shown.Figure 2-54. a. Figure 2-6 shows a production possibilities frontier between guns and butter.It is bowed out because when most of the economy‟s resources are being usedto produce butter, the frontier is steep and when most of the economy‟sresources are being used to produce guns, the frontier is very flat. When theeconomy is producing a lot of guns, workers and machines best suited tomaking butter are being used to make guns, so each unit of guns given upyields a large increase in the production of butter; thus the productionpossibilities frontier is flat. When the economy is producing a lot of butter,workers and machines best suited to making guns are being used to makebutter, so each unit of guns given up yields a small increase in the productionof butter; thus the production possibilities frontier is steep.b. Point A is impossible for the economy to achieve; it is outside the productionpossibilities frontier. Point B is feasible but inefficient because it‟s inside theproduction possibilities frontier.Figure 2-6c. The Hawks might choose a point like H, with many guns and not much butter.The Doves might choose a point like D, with a lot of butter and few guns.d. If both Hawks and Doves reduced their desired quantity of guns by the sameamount, the Hawks would get a bigger peace dividend because the productionpossibilities frontier is much steeper at point H than at point D. As a result,the reduction of a given number of guns, starting at point H, leads to a muchlarger increase in the quantity of butter produced than when starting at pointD.5. See Figure 2-7. The shape and position of the frontier depend on how costly it is tomaintain a clean environment the productivity of the environmental industry. Gains in environmental productivity, such as the development of a no-emission auto engine, lead to shifts of the production-possibilities frontier, like the shift from PPF1 to PPF2shown in the figure.Figure 2-76. a. A family‟s decision about how much income to save is microeconomics.b. The effect of government regulations on auto emissions is microeconomics.c. The impact of higher saving on economic growth is macroeconomics.d. A firm‟s decision about how many workers to hire is microeconomics.e. The relationship between the inflation rate and changes in the quantity ofmoney is macroeconomics.7. a. The statement that society faces a short-run tradeoff between inflation andunemployment is a positive statement. It deals with how the economy is, nothow it should be. Since economists have examined data and found thatthere‟s a short-run negative relationship between inflation and unemployment,the statement is a fact, thus it‟s a positive statement.b. The statement that a reduction in the rate of growth of money will reduce therate of inflation is a positive statement. Economists have found that moneygrowth and inflation are very closely related. The statement thus tells howthe world is, and so it is a positive statement.c. The statement that the Federal Reserve should reduce the rate of growth ofmoney is a normative statement. It states an opinion about something thatshould be done, not how the world is.d. The statement that society ought to require welfare recipients to look for jobsis a normative statement. It doesn‟t state a fact about how the world is.Instead, it is a statement of how the world should be and is thus a normativestatement.e. The statement that lower tax rates encourage more work and more saving is apositive statement. Economists have studied the relationship between taxrates and work, as well as the relationship between tax rates and saving.They‟ve found a negative relationship in both cases. So the statementreflects how the world is, and is thus a positive statement.8. Two of the statements in Table 2-2 are clearly normative. They are: “5. If thefederal budget is to be balanced, it should be done over the business cycle rather than yearly” and “9. The government should restructure the welfare system along the lines of a …negative income tax.‟” Bot h are suggestions of changes that should be made,rather than statements of fact, so they are clearly normative statements.The other statements in the table are positive. All the statements concern how theworld is, not how the world should be. Note tha t in all cases, even though they‟restatements of fact, fewer than 100 percent of economists agree with them. You could say that positive statements are statements of fact about how the world is, but noteveryone agrees about what the facts are.9. As th e president, you‟d be interested in both the positive and normative views ofeconomists, but you‟d probably be most interested in their positive views. Economists are on your staff to provide their expertise about how the economy works. Theyknow many fa cts about the economy and the interaction of different sectors. So you‟d be most likely to call on them about questions of fact positive analysis. Since you‟re the president, you‟re the one who has the make the normative statements as to what should be done, with an eye to the political consequences. The normative statements made by economists represent their views, not necessarily either your‟s or theelectorate‟s.10. There are many possible answers.11. As of this writing, the chairman of the Federal Reserve is Alan Greenspan, the chair ofthe Council of Economic Advisers is Martin N. Baily, and the secretary of the treasury is Larry Summers.12. There are many possible answers.13. As time goes on, you might expect economists to disagree less about public policybecause they‟ll have opportunities to observe different policies that are put into place. As new policies are tried, their results will become known, and they can be evaluated better. It‟s likely that the disagreement about them will be reduced after they‟ve been tried in practice. For example, many economists thought that wage and price controls would be a good idea for keeping inflation under control, while others thought it was a bad idea. But when the controls were tried in the early 1970s, the results were disastrous. The controls interfered with the invisible hand of the marketplace and shortages developed in many products. As a result, most economists are now convinced that wage and price controls are a bad idea for controlling inflation.But it‟s unlikely that the differences between economists will ever be completely eliminated. Economists differ on too many aspects of how the world works. Plus, even as some policies get tried out and are either accepted or rejected, creative economists keep coming up with new ideas.。
曼昆经济学原理(双语)带你读《经济学原理》,每日更新,欢迎来主页查看。
翻译部分经本人校对修改,本文仅供学习交流使用,版权归相关权利人所有!第二章像经济学家一样思考2.112-3 Why Economists Disagree为什么经济学家意见分歧“If all economists were laid end to end, they would not reach a conclusion.” This quip from George Bernard Shaw is revealing. Economists as a group are often criticized for giving conflicting advice to policymakers. President Ronald Reagan once joked that if the game Trivial Pursuit were designed for economists, it would have 100 questions and 3,000 answers. Why do economists so often appear to give conflicting advice to policymakers? There are two basic reasons:“如果把所有经济学家聚在一起,他们也得不出一个结论。
”肖伯纳(George Bernard Shaw)的嘲讽溢于言表。
人们经常批评经济学家作为一个群体向决策者提出了相互矛盾的建议。
罗纳德•里根(Ronald Reagan)总统曾经开玩笑地说,如果小追击(Trivial Pursuit)游戏是由经济学家设计的,那么,100个问题会有3000个答案。
为什么经济学家往往给决策者提出了看来相互矛盾的建议呢?这里有两个基本原因:①Economists may disagree about the validity of alternative positive theories of how the world works.经济学家可能不同意关于世界如何运转的其他实证理论的有效性。
2 像经济学家一样思考每个研究领域都有自己的语言和思考方式:数学家谈论公理、积分和向量空间;心理学家谈论自我、本我和认知的不一致性;律师谈论案发现场、侵权行为和约定的禁止翻供。
经济学家也没有什么不同。
供给、需求、弹性、比较优势、消费者剩余和无谓损失等此类术语都是经济学家语言的一部分。
在以后各章节中,你将遇到许多新术语,还会碰上经济家以特定方式使用的一些熟悉的词汇。
乍一年,这种新语言似乎有一种不必要的神秘。
但是,正如你将了解到的,它的价值在于能够为你提供一种关于你所生活的世界的新的、有用的思维方式。
本书惟一一个最重要的目的就是帮助你学会经济学家的思维方式。
当然,正如你不可能在一夜之间成为一个数学家、心理学家或律师一样,学会像经济学家一样思考也需要一些时间。
但本书通过把理论、案例研究和新闻中的经济学事例结合起来,将给你提供充分发展和实践这种技能的机会。
在深入了解经济学的本质和细节之前,综述一下经济学家如何研究这个世界是有帮助的。
因此,本章将讨论这个领域的方法论。
经济学家处理所遇到的问题有何独特之处?像经济学家一样思考是什么意思?2.1作为科学家的经济学家经济学家努力以科学的客观性来探讨他们的主题。
他们研究经济的方法与物理学家研究物质和生物学家研究生命的方法一样:先提出理论、收集数据、分析数据,以努力证明或否定他们的理论。
对初学者来说,声称经济学是门科学似乎有点不可思议。
经济学家毕竟不用试管或望远镜进行研究工作。
但是,科学的本质是科学方法——冷静地建立并检验有关世界如何运行的各种理论。
这种研究方法适用于研究一国经济,就像适用于研究地心引力或生物进化一样。
正如阿尔伯特●爱因斯坦(Albert Einstein)曾经提出的:“所有科学不过是日常思考的提炼而已”。
虽然爱因斯坦的评论对诸如经济学的社会科学和诸如物理学的自然科学同样适用,但许多人并不习惯用科学家的眼光去观察社会。
接下来我们将讨论经济学家运用科学的逻辑来考察经济如何运行的一些方法。
经济学原理曼昆Chapter02第一篇:经济学原理曼昆Chapter 02Chapter 2 Thinking Like an EconomistMULTIPLE CHOICEFigure 2-1A12B1.Refer to Figure 2-1.Which shape refers to the markets for goods and services?a.oval Ab.oval Bc.rectangle 1d.rectangle 2a2.Refer to Figure 2-1.What is flowing from rectangle 1 to oval A?b a.revenue b.goods and services sold c.factors of productionbor, land, and capital3.Refer to Figure 2-1.Which of the following is an activity undertaken by the actors in rectangle 2? c a.produce and sell goods and services b.hire and use factors of production c.own and sell factors of production d.exchange goods and services between firms and householdsFigure 2-210987654321carsABCGDF204060E***80corn135Consider the production possibilities curve for a country that can produce cars, corn(in bushels), or a combination of the two.4.Refer to Figure 2-2.If this economy devotes all of its available resources to producing corn, then it will produced a.0 bushels of corn and 10 cars.b.135 bushels of corn and3 cars c.160 bushels of corn and 10 cars.d.160 bushels of corn and 0 cars.5.Refer to Figure 2-2.Which combination of points show production possibilities only achievable with improvementsin technology or increases in resources?d a.A, D, and E b.B and G c.C and F d.None of the above is correct.6.Refer to Figure 2-2.If this society moves from point D to point E,d a.it gives up 25 bushels of corn to get 3 cars.b.it gives up 135 bushels of corn to get 3 cars.c.it gives up 3 cars to get 135 bushels of corn.d.it gives up 3 cars to get 25 bushels of corn.7.Refer to Figure 2-2.If this society is producing at point C,d a.there is unemployment.b.production is efficient.c.growth can only be achieved through an advancement in technology.d.the opportunity cost of producing one more car is approximately 10 bushels of corn.8.Which of the following is a positive, as opposed to a normative, statement? b a.The US Department of Justice should allow a merger between AT&T and T-Mobile because it would have little effect on consumers.b.Antitrust laws should be used to prevent further concentration in the wireless telephone service market.c.The US Department of Justice sued AT&T to block its merger with T-Mobile.2d.The wireless telephone service market is too highly concentrated.9.Which of the following famous people did not major in economics in college?ba.Donald Trumpb.Natalie Portmanc.John Elwayd.Mick Jagger10.Which of the following statements is correct about environmental economists?d a.They view economics as a framework for natural resource allocation.b.They work at government agencies as well as universities and advocacy groups.c.They use economic arguments and systems to persuade companies to clean up pollution and conserve natural resources.d.All of the above arecorrect.11.In the ordered pair(20, 100), 20 is the a a.x-coordinate.b.y-coordinate.c.scatterplot.d.slope.12.Between the two ordered pairs(20, 100)and(30, 80), the slope isb a.1/2.b.-1/2.c.2.d.-2.Figure 2-4snowstorms***30405060708090snowblowers sold13.Refer to Figure 2-4.According to the graph, snowstorms aa.and snowblowers sold are positively correlated.b.and snowblowers sold are negatively correlatedc.and snowblowers sold are uncorrelated.d.are caused by more snowblowers being sold.314.Refer to Figure 2-4.Your friend John created the graph above to illustrate that snowstorms are caused by more snowblowers being sold.You inform him that his interpretation is incorrect due to a a.omitted variable bias.b.reverse causality.c.slope mismatch.d.shifting versus moving along a curve.15.Refer to Figure 2-4.Which of the following could be an omitted variable in the graph?d a.the price of snowblowers b.a change in consumers’ incomes c.a change in the seasons d.All of the above are correct.PROBLEMFigure 2-1A12B 1.2.3.4.Refer to Figure 2-1.What is the name of the model depicted in the figure?The Circular FlowRefer to Figure 2-1.What do the ovals represent in the figure?A: Markets for goods and service B: Markets for factors of productionRefer to Figure 2-1.What do the rectangles represent in the figure?1:Firms 2:HouseholdsRefer to Figure 2-1.What do the outer arrows represent in the figure?45.6.7.8.9.A to 1:revenue 1 toB :wages,rent, and profit B to 2 income 2 to A :spendingRefer to Figure 2-1.What do the inner arrows represent in the figure?A to 2:goods and services bought 2 to B:Labor,land,and capitalB to1:Factors of productionto A: goods and services soldRefer to Figure 2-1.What does the arrow going from oval A to rectangle 2 represent in the figure?A to 2:goods and services boughRefer to Figure 2-1.What does the arrow going from oval B to rectangle 2 represent in the figure?B to 2 incomeRefer to Figure 2-1.What are two elements not included in this figure that could be included in a more complex model?The three main factors of production, or categories of inputs, used by firms to produce goods and services areFigure 2-210987654321carsABCGDF204060E***80corn13510.11.12.13.Consider the production possibilities curve for a country that can produce cars, corn(in bushels), or a combination of the two.Refer to Figure 2-2.The bowed outward shape of the production possibilities curve indicates that opportunity cost of corn in terms of cars isRefer to Figure 2-2.Which point(s)on the graph is(are)efficient production possibilities?Refer to Figure 2-2.Which point(s)on the graph show unemployment of resources?Refer to Figure 2-2.Which point(s)on the graph is(are)unattainable given current resources and technology?514.15.16.17.18.19.20.21.Who would be more likely to study the effects of government spending on the unemployment rate, a macroeconomist or a microeconomist?Who would be more likely to study the effects of foreign competition on the accounting industry, a macroeconomist or a microeconomist?Who would be more likely to study the effects of rent control on housing in New York City, a macroeconomist or a microeconomist?Who would be more likely to study the inflation rate in the United States, a macroeconomist or a microeconomist?Is the following a positive or normative statement? The federal minimum wage is lower than many state minimum wages.Is the following a positive or normative statement? The Federal Reserve should set an inflation target and employ policies to meet the target.Is the following a positive or normative statement? The United States government should mandate that every citizen purchases health insurance.Is the following a positive or normative statement? The unemployment rate in Nevada is higher than the unemployment rate in New York.10987654321PriceABC***0Quantity22.Refer to Figure 2-3.What are the coordinates of point C?23.Refer to Figure 2-3.How are price and quantity related in this graph?624.Refer to Figure 2-3.What is the slope of the line?25.Refer to Figure 2-3.Is a move from point A to point B considered a shift of the curve or a movement along the curve? 第二篇:经济学原理曼昆课后答案 chapter 2Problems and Applications1.2.a.b.c.d.3.See Figure 2-5;the four transactions are shown.Fast food is more distinguishable than steel or wheat, but certainly not as much as novels.Wheat produced by one farmer is completely indistinguishable from wheat produced by another.Steel is a fairly uniform commodity, though some firms produce steel of inferior quality.Novels are each unique, so they are quite distinguishable.Many answers are possible.Figure 2-54.a.Figure 2-6 shows a production possibilities frontier between guns and butter.It is bowed out because when most of the economy‟s resources are being used to produce butter, the frontier is steep and when most of the economy‟s resources are being used to produce guns, the frontier is very flat.When the economy is producing a lot of guns, workers and machines best suited to making butter are being used to make guns, so each unit of guns given up yields a large increase in the production of butter;thus the production possibilities frontier is flat.When the economy is producing a lot of butter, workers and machines best suited to making guns are being used to make butter, so each unit of guns given up yields a small increase in the production of butter;thus the production possibilities frontier is steep.b.Point A is impossible for the economy to achieve;it is outside the production possibilities frontier.Point B is feasible but inefficient because it‟s inside the production possibilities frontier.Figure 2-6d.If both Hawks and Doves reduced their desired quantity of guns by the same amount, the Hawks would get a bigger peace dividend because the production possibilities frontier is much steeper at point H than at point D.As a result, the reduction of a given number of guns, starting at point H, leads to a much largerincrease in the quantity of butter produced than when starting at point D.5.See Figure 2-7.The shape and position of the frontier depend on how costly it is to maintain a clean environment the productivity of the environmental industry.Gains in environmental productivity, such as the development of a no-emission auto engine, lead to shifts of the production-possibilities frontier, like the shift from PPF1 to PPF2 c.The Hawks might choose a point like H, with many guns and not much butter.The Doves might choose a point like D, with a lot of butter and few guns.shown in the figure.6.a.b.c.d.e.7.a.b.c.Figure 2-7A family‟s decision about how much income to save is microeconomics.The effect of government regulations on auto emissions is microeconomics.The impact of higher saving on economic growth is macroeconomics.A firm‟s decision about how many workers to hire is microeconomics.The relationship between the inflation rate and changes in the quantity of money is macroeconomics.The statement that society faces a short-run tradeoff between inflation and unemployment is a positive statement.It deals with how the economy is, not how it should be.Since economists have examined data and found that there‟s a short-run negative relationship between inflation and unemployment, the statement is a fact, thus it‟s a positive statement.The statement that a reduction in the rate of growth of money will reduce the rate of inflation is a positive statement.Economists have found that money growth and inflation are very closely related.The statement thus tells how the world is, and so it is a positive statement.The statement that the Federal Reserve should reduce the rate of growth of money is a normative statement.It states an opinion about something that should be done, not how the world is.d.The statement thatsociety ought to require welfare recipients to look for jobs is a normative statement.It doesn‟t state a fact about how the world is.Instead, it is a statement of how the world should be and is thus a normative statement.e.The statement that lower tax rates encourage more work and more saving is a positive statement.Economists have studied the relationship between tax rates and work, as well as the relationship between tax rates and saving.They‟ve found a negative relationship in both cases.So the statement reflects how the world is, and is thus a positive statement.8.Two of the statements in Table 2-2 are clearly normative.They are: “5.If the federal budget is to be balanced, it should be done over the business cycle rather than yearly” and “9.The government should restructure the welfare system along the lines of a …negative income tax.‟” Both are suggestions of changes that should be made, rather than statements of fact, so they are clearly normative statements.The other statements in the table are positive.All the statements concern how the world is, not how the world should be.Note that in all cases, even though they‟re statements of fact, fewer than 100 percent of economists agree with them.You could say that positive statements are statements of fact about how the world is, but not everyone agrees about what the facts are.9.As the president, you ‟d be interested in both the positive and normative views of economists, but you‟d probably be most interested in their positive views.Economists are on your staff to provide their expertise about how the economy works.They know many facts about the economy and the interaction of different sectors.So you‟d be most likely to call on them about questions of fact positive analysis.Since you‟re the president, you‟re the one who has the make the normative statements as to what shouldbe done, with an eye to the political consequences.The normative statements made by economists represent their views, not necessarily either your‟s or the electorate‟s.10.11.As of this writing, the chairman of the Federal Reserve is Alan Greenspan, the chair of the Council of Economic Advisers is Martin N.Baily, and the secretary of the treasury is Larry Summers.12.13.As time goes on, you might expect economists to disagree less about public policy There are many possible answers.There are many possible answers.because they‟ll have opportunities to observe different policies that are put into place.As new policies are tried, their results will become known, and they can be evaluated better.It‟s likely that the disagreement about them will be reduced after they‟ve been tried in practice.For example, many economists thought that wage and price controls would be a good idea for keeping inflation under control, while others thought it was a bad idea.But when the controls were tried in the early 1970s, the results were disastrous.The controls interfered with the invisible hand of the marketplace and shortages developed in many products.As a result, most economists are now convinced that wage and price controls are a bad idea for controlling inflation.But it‟s unlikely that the differences between economists will ever be completely eliminated.Economists differ on too many aspects of how the world works.Plus, even as some policies get tried out and are either accepted or rejected, creative economists keep coming up with new ideas.第三篇:经济学原理曼昆课后答案 chapter 6Problems and Applications1.If the price ceiling of $40 per ticket is below the equilibrium price, then quantity demanded exceeds quantity supplied, so there’s a shortage of tickets.The policy decreases the number ofpeople who attend classical music concerts, since supply is lower because of the lower price.2.a.b.c.3.a.The imposition of a binding price floor in the cheese market is shown in Figure 6-3.In the absence of the price floor, the price would be P1 and the quantity would be Q1.With the floor set at Pf, which is greater than P1, the quantity demanded is Q2, while quantity supplied is Q3, so there is a surplus of cheese in the amount Q3$2.The quantity of beer sold declines to Q2.5.Reducing the payroll tax paid by firms and using part of the extra revenue to reduce the payroll tax paid by workers would not make workers better off because the division of the burden of a tax depends on supply and demand, not who must pay the tax.S ince the tax wedge would be larger, it’s likely that both firms and workers, who share the burden of any tax, would be worse off.6.If the government imposes a $500 tax on luxury cars, the price paid by consumers will rise less than $500, in general.The burden of any tax is shared by both producers and consumers−the price paid by consumers rises and the price received by producers falls, with the difference between the two equal to the amount of the tax.The only exceptions would be if the supply curve were perfectly elastic or the demand curve were perfectly inelastic, in which case consumers would bear the full burden of the tax and the price paid by consumers would rise by exactly $500.7.a.It doesn’t matter whether the tax is imposed on producers or consumers−the effect will be the same.With no tax, as shown in Figure 6-6, the demand curve is D1 and the supply curve is S1.If the tax is imposed on producers, the supply curve shifts up by the amount of the tax(50 cents)to S2.Then the equilibrium quantity is Q2, the price paid by consumers is P2, and the price received(after taxes are paid)by producers is P250 cents.Figure 6-6Figure 6-7b.The more elastic is the demand curve, the more effective this tax will be in reducing the quantity of gasoline consumed.Greater elasticity of demand means that quantity falls more in response to the rise in the price of gasoline.Figure 6-7 illustrates this result.Demand curve D1 represents an elastic demand curve, while demand curve D2 is more inelastic.To get the same tax wedge between demand and supply requires a greater reduction in quantity with demand curve D1 than for demand curve D2.c.d.The consumers of gasoline are hurt by the tax because they get less gasoline at a higher price.Workers in the oil industry are hurt by the tax as well.With a lower quantity of gasoline being produced, some workers may lose their jobs.With a lower price received by producers, wages of workers might decline.8.a.Figure 6-8 shows the effects of the minimum wage.In the absence of the minimum wage, the market wage would be w1 and Q1 workers would be employed.With the minimum wage(wm)imposed above w1, the market wage is wm, the number of employed workers is Q2, and the number of workers who are unemployed is Q3-Q2.Total wage payments to workers are shown as the area of rectangle ABCD, which equals wm times Q2.b.An increase in the minimum wage would decrease employment.The size of the effect on employment depends only on the elasticity of demand.The elasticity of supply doesn’t matter, because there’s a surplus of labor.c.The increase in the minimum wage would increase unemployment.The size of the rise in unemployment depends on both the elasticities of supply and demand.The elasticity of demand determines the quantity of labor demanded, the elasticity of supply determines the quantity of labor supplied, andthe difference between the quantity supplied and demanded of labor is the amount of unemployment.d.If the demand for unskilled labor were inelastic, the rise in the minimum wage would increase total wage payments to unskilled labor.With inelastic demand, the percentage decline in employment would be less than the percentage increase in the wage, so total wage payments increase.However, if the demand for unskilled labor were elastic, total wage payments would decline, since then the percentage decline in employment would exceed the percentage increase in the wage.9.a.Figure 6-8Figure 6-9Figure 6-9 shows the effect of a tax on gun buyers.The tax reduces the demand for guns from D1 to D2.The result is a rise in the price buyers pay for guns from P1 to P2, and a decline in the quantity of guns from Q1 to Q2.Figure 6-10b.Figure 6-10 shows the effect of a tax on gun sellers.The tax reduces the supply of guns from S1 to S2.The result is a rise in the price buyers pay for guns from P1 to P2, and a decline in the quantity of guns from Q1 to Q2.c.Figure 6-11 shows the effect of a binding price floor on guns.The increase in price from P1 to Pf leads to a decline in the quantity of guns from Q1 to Q2.There is excess supply in the market for guns, since the quantity supplied(Q3)exceeds the quantity demanded(Q2)at the price Pf.Figure 6-11d.10.a.Figure 6-12Figure 6-12 shows the effect of a tax on ammunition.The tax on ammunition reduces the demand for guns from D1 to D2, because ammunition and guns are complements.The result is a decline in the price of guns from P1 to P2, and a decline in the quantity of guns from Q1 to Q2.Programs aimed at making thepublic aware of the dangers of smoking reduce the demand for cigarettes, shown in Figure 6-13 as a shift from demand curve D1 to D2.The price support program increases the price of tobacco, which is the main ingredient in cigarettes.As a result, the supply of cigarettes shifts to the left, from S1 to S2.The effect of both programs is to reduce the quantity of cigarette consumption from Q1 to Q2.Figure 6-13b.c.11.a.b.The combined effect of the two programs on the price of cigarettes is ambiguous.The education campaign reduces demand for cigarettes, which tends to reduce the price.The tobacco price supports raise the cost of production of cigarettes, which tends to increase the price.The taxation of cigarettes further reduces cigarette consumption, since it increases the price to consumers.As shown in the figure, the quantity falls to Q3.The effect of a 50 cent per cone subsidy is to shift the demand curve up by 50 cents at each quantity, since at each quantity a consumer’s willingness to pay is 50 cents higher.The effects of such a subsidy are shown in Figure 6-14.Before the subsidy, the price is P1.After the subsidy, the price received by sellers is PS and the effective price paid by consumers is PD, which equals PS minus 50 cents.Before the subsidy, the quantity of cones sold is Q1;after the subsidy the quantity increases to Q2.Figure 6-14Because of the subsidy, consumers are better off, since they consume more at a lower price.Producers are also better off, since they sell more at a higher price.The government loses, since it has to pay for the subsidy.第四篇:曼昆经济学原理(推荐)《经济学原理》的主要内容包括:1.人们是如何决策的。