Linux教程第四版课后习题4答案
- 格式:docx
- 大小:262.10 KB
- 文档页数:11

linux操作系统课后习题答案Linux操作系统课后习题答案在学习Linux操作系统课程中,课后习题是巩固知识、提高技能的重要环节。
通过完成课后习题,我们可以更好地掌握Linux操作系统的基本概念、命令和应用。
下面将对一些常见的Linux操作系统课后习题进行详细解答,希望能帮助大家更好地理解和掌握Linux操作系统。
1. 什么是Linux操作系统?Linux操作系统是一种开源的、免费的操作系统,它基于Unix操作系统,具有稳定、安全、高效等特点。
Linux操作系统被广泛应用于服务器、嵌入式系统、个人电脑等领域,是当前最流行的操作系统之一。
2. Linux操作系统的特点有哪些?Linux操作系统具有以下特点:开源、免费、稳定、安全、高效、多用户、多任务、多线程、多平台等。
3. Linux操作系统中的常用命令有哪些?Linux操作系统中常用的命令包括:ls、cd、pwd、mkdir、rmdir、cp、mv、rm、cat、more、less、head、tail、grep、find、chmod、chown、chgrp、ps、top、kill、shutdown等。
4. 如何查看当前目录下的文件和子目录?可以使用ls命令来查看当前目录下的文件和子目录。
例如,输入ls命令后,系统会列出当前目录下的所有文件和子目录。
5. 如何切换到上一级目录?可以使用cd..命令来切换到上一级目录。
例如,输入cd..命令后,系统会将当前目录切换到上一级目录。
通过以上课后习题的解答,我们可以更好地理解和掌握Linux操作系统的基本知识和常用命令。
希望大家在学习Linux操作系统的过程中能够加强练习,不断提高自己的技能水平。
同时也希望本文能够对大家有所帮助,谢谢阅读!。
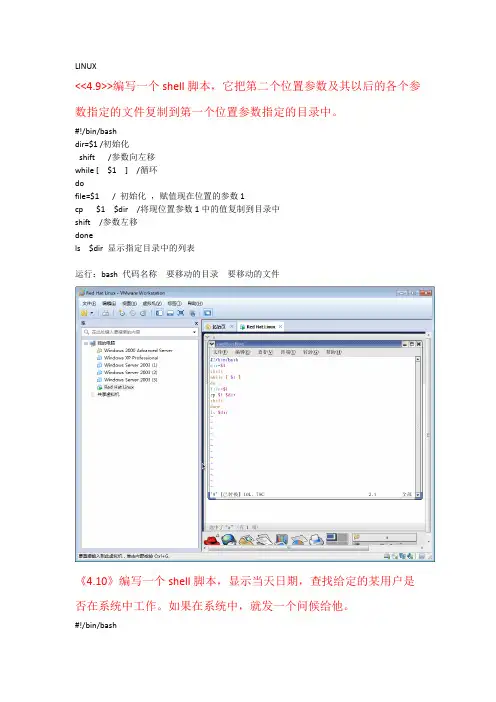
LINUX<<4.9>>编写一个shell脚本,它把第二个位置参数及其以后的各个参数指定的文件复制到第一个位置参数指定的目录中。
#!/bin/bashdir=$1 /初始化shift /参数向左移while [ $1 ] /循环dofile=$1 / 初始化,赋值现在位置的参数1cp $1 $dir /将现位置参数1中的值复制到目录中shift /参数左移donels $dir 显示指定目录中的列表运行:bash 代码名称要移动的目录要移动的文件《4.10》编写一个shell脚本,显示当天日期,查找给定的某用户是否在系统中工作。
如果在系统中,就发一个问候给他。
#!/bin/bashdate/显示日期ifwho |grep "^$1"/寻找用户thenwrite $1 << ! /对用户发消息!echo "hello !"fi运行:bash vi编辑的文件<<4.11>>打印给定目录的某些文件,由第一个参数指出文件所在的目录,其余参数是要打印的文件名#!/bin/bashdir=$1cd $ dirshiftfor f in $@;docat $fdone运行:bash 程序代码名称目录名称文件名称<<4.12>>利用for循环将当前目录下的(*.c)文件移到指定的目录下,并按文件大小排序,显示移动后指定目录的内容。
#!/bin/bashfor file in `ls -l /root/a | grep ".*.c"` (Tab键上面的`){mv /root/a/$file /root/b}ls -lS /root/b运行:bash vi创建的文件<<4.13>>利用数组形式存放10个城市的名字,然后利用for循环把他们打印出来。
#!/bin/bashfor xahar in kaxkar tumxuk aksu kumul hotan atux alar turpan urumqi altaydoecho $xahardone运行:bash 程序代码名称《4.14》编写一个shell脚本,求斐波那契数列的前10项及总和。

L i n u x教程第四版课后习题2(总3页)--本页仅作为文档封面,使用时请直接删除即可----内页可以根据需求调整合适字体及大小--思考题2简述Linux命令的一般形式。
答:command [-option] parameter1 parameter2...请说明以下命令的功能:date,cd,cp,pwd,rm,mkdir,echo,who,ls,cat,more,man。
答:date命令:显示当天日期;cd命令:切换目录;cp命令:复制文件pwd命令:显示当前用户工作目录;rm命令:删除文件;mkdir命令:建立目录;echo命令:将参数表示的内容显示在屏幕上;who命令:显示哪些用户在使用系统;ls命令:列出某个目录下的文件;cat命令:显示参数表示文件的内容;more命令:显示文件内容;man命令:帮助命令,可以查看所有Linux命令的帮助信息。
公元2000年的元旦是星期几答:星期六什么是文件Linux下主要有哪些不同类型的文件答:Linux中文件是指文件系统中存储数据的一个命名对象;Linux下主要的文件类型有:普通文件、目录文件、设备文件、符号链接文件。
确定当前工作目录是什么把工作目录改到父目录上,然后用长格式列出其中所有的内容。
答:确定当前工作目录: pwd ;把工作目录改到父目录上: cd / ;然后用长格式列出其中所有内容: ls 或者是 ll 。
在所用的Linux系统上,根目录下含有哪些内容各自功能是什么答::包含二进制文件的可执行程序。
:存放用于管理系统的命令。
:用于存放引导系统时使用的各种文件。
:非常重要,它包含许多Linux系统配置文件。
:包含标示设备的特别文件,这些文件用于访问系统中所有不同类型的硬件。
:是用户起始目录的基础目录。
:存放安装文件系统的安装点。
:包含了多个子目录,这些子目录中保存系统上一些重要的程序,可供所有用户共享。
:包括系统正常运行时要改变的数据。

第1章:1)D2)错3)错4)错5)错6)错7)错8)错第3章:1)C2)C3)B4)D5)A6)D7)C8)C第5章:1)D,C选项也可以,但是因为缺掉一步make test可能会存在问题,在确认无误的情况下也可以这么做2)A3)A4)C5)A6)C第7章:1)B(-p后面多了一个空格)注:CD应该合为一个选项2)A3)B4)C第10章1.正则表达式可以说是一个字符模板,用来在搜索中匹配相同的字符。
(对)2.“^”字符,匹配输入字符串的开始位置。
(对)3.“\”字符,用来转义一个元字符。
(对)4. grep命令的意思是“全面搜索正则表达式”并把找到的行打印出来5. bash中编辑功能“Ctrl+A”的作用是将光标移动到行首6. bash中编辑功能“Ctrl+T”的作用是交换光标所在的字符与前—个字符(对)7. bash中通配符“*”的含义是匹配任意字符的0次或多次出现(对)8.答案见教材中的相关章节第12章1.内核模块简称模块,是一段可执行的程序,它可以被动态加载到内核中,并成为内核的一部分。
加载到内核中的模块具有与内核一样的权限,可以访问任何内核中的数据结构。
2.Linux的内核可以通过多种方式进行定制他们分别是:文本交互问答方式、文本窗口交互方式、图形窗口交互方式、根据原有配置文件生成新的配置文件。
第13章1.在RedHat9中提供了两个启动引导程序:GRUB、LILO。
2.在Linux系统中通常有0~6,共7个运行级别。
其中完全多用户模式的编号是3 ,图形登录的多用户模式的编号是5 。
3.runlevel命令的作用是查看当前的运行级别。
4.改变系统运行级别的命令是init [0123456]。
5.假设系统启动默认进入图形登录的多用户模式,如果要让系统在启动时直接进入完全多用户模式,则需要修改inittab文件。
第15章1.大多数Linux驱动程序以芯片组命名,而不是根据设备生产商来进行命名。

第一章作者:佚名来源:网络1、有一台计算机,具有IMB 内存,操作系统占用200KB ,每个用户进程各占200KB 。
如果用户进程等待I/O 的时间为80 % ,若增加1MB 内存,则CPU 的利用率提高多少?答:设每个进程等待I/O 的百分比为P ,则n 个进程同时等待刀O 的概率是Pn ,当n 个进程同时等待I/O 期间CPU 是空闲的,故CPU 的利用率为1-Pn。
由题意可知,除去操作系统,内存还能容纳4 个用户进程,由于每个用户进程等待I/O的时间为80 % , 故:CPU利用率=l-(80%)4 = 0.59若再增加1MB 内存,系统中可同时运行9 个用户进程,此时:cPu 利用率=l-(1-80%)9 = 0.87故增加IMB 内存使CPU 的利用率提高了47 % :87 %/59 %=147 %147 %-100 % = 47 %2 一个计算机系统,有一台输入机和一台打印机,现有两道程序投入运行,且程序A 先开始做,程序B 后开始运行。
程序A 的运行轨迹为:计算50ms 、打印100ms 、再计算50ms 、打印100ms ,结束。
程序B 的运行轨迹为:计算50ms 、输入80ms 、再计算100ms ,结束。
试说明(1 )两道程序运行时,CPU有无空闲等待?若有,在哪段时间内等待?为什么会等待?( 2 )程序A 、B 有无等待CPU 的情况?若有,指出发生等待的时刻。
答:画出两道程序并发执行图如下:(1)两道程序运行期间,CPU存在空闲等待,时间为100 至150ms 之间(见图中有色部分)(2)程序A 无等待现象,但程序B 有等待。
程序B 有等待时间段为180rns 至200ms 间(见图中有色部分)3 设有三道程序,按A 、B 、C优先次序运行,其内部计算和UO操作时间由图给出。
试画出按多道运行的时间关系图(忽略调度执行时间)。
完成三道程序共花多少时间?比单道运行节省了多少时间?若处理器调度程序每次进行程序转换化时lms , 试画出各程序状态转换的时间关系图。

linux操作系统课后习题答案操作系统是计算机系统中的重要组成部分,它负责管理计算机的硬件和软件资源,并且提供给用户一个良好的操作界面。
Linux是一个开源的操作系统,广泛应用于服务器和个人电脑上。
为了帮助读者更好地理解和掌握Linux操作系统,本文回答了一些常见的课后习题。
习题一:Linux系统中如何查看当前所在的目录?在Linux系统中,可以使用命令"pwd"来查看当前所在的目录。
首先打开终端,输入"pwd"命令后回车,系统会显示当前所在目录的路径。
习题二:Linux系统中如何创建一个新的目录?在Linux系统中,可以使用命令"mkdir"来创建新的目录。
在终端中输入"mkdir 目录名称",然后回车即可创建一个新的目录。
习题三:Linux系统中如何列出一个目录下的所有文件和子目录?在Linux系统中,可以使用命令"ls"来列出一个目录下的所有文件和子目录。
在终端中输入"ls 目录名称",系统会显示该目录下的所有文件和子目录的列表。
习题四:Linux系统中如何移动文件或目录?在Linux系统中,可以使用命令"mv"来移动文件或目录。
在终端中输入"mv 源文件或目录目标目录",然后回车即可将文件或目录移动到目标目录中。
习题五:Linux系统中如何复制文件或目录?在Linux系统中,可以使用命令"cp"来复制文件或目录。
在终端中输入"cp 源文件或目录目标目录",然后回车即可将文件或目录复制到目标目录中。
习题六:Linux系统中如何删除文件或目录?在Linux系统中,可以使用命令"rm"来删除文件或目录。
在终端中输入"rm 文件或目录",然后回车即可删除文件或目录。

linux课后习题答案Linux课后习题答案Linux操作系统是一种开源的操作系统,广泛应用于服务器、嵌入式设备以及个人电脑等领域。
它以其高度的稳定性、安全性和灵活性而备受推崇。
在学习Linux的过程中,我们经常会遇到一些习题,下面是一些常见的Linux课后习题及其答案。
1. 什么是Linux操作系统?Linux操作系统是一种开源的操作系统,基于Unix的设计思想和原则,由Linus Torvalds于1991年首次发布。
Linux操作系统具有高度的稳定性、安全性和灵活性,被广泛应用于服务器、嵌入式设备以及个人电脑等领域。
2. 如何在Linux系统中创建一个新的用户?在Linux系统中,可以使用`useradd`命令来创建一个新的用户。
例如,要创建一个名为"testuser"的用户,可以执行以下命令:```useradd testuser```此命令将在系统中创建一个新的用户,并分配一个唯一的用户ID。
3. 如何将一个用户添加到一个用户组中?要将一个用户添加到一个用户组中,可以使用`usermod`命令。
例如,要将用户"testuser"添加到用户组"testgroup"中,可以执行以下命令:```usermod -aG testgroup testuser```此命令将用户"testuser"添加到用户组"testgroup"中。
4. 如何在Linux系统中查看当前登录的用户?要查看当前登录的用户,可以使用`who`命令。
该命令将显示当前登录系统的用户列表,包括用户名、登录时间以及登录终端。
5. 如何在Linux系统中查看文件的内容?要查看文件的内容,可以使用`cat`命令。
例如,要查看文件"test.txt"的内容,可以执行以下命令:```cat test.txt```此命令将显示文件"test.txt"的内容。

第四章 Linux编程作业参考答案一,AWK命令行应用1)处理/etc/passwd文件a)打印第一列(userid)提示:awk -F 分隔符‘{print $第几列}’fileb)打印root用户的1,2 field2)打印用户home目录下所有文件的:owner和文件名(只打印这两列)提示:使用ls -l 和 awk3)打印所有登录本机器的ip,并去掉重复。
提示:使用last,awk,sort,uniq二,AWK完整流程创建order文件 (商品名,数量,单价)apple 20 6.5orange 10 8grape 7 12berry 5 32输出格式 awk -f order.awk order (参考employee.awk)name count price (表头)apple 20 6.5...=================== (表尾)order.awkBEGIN{print "name\tcount\tprice"; OFS="\t"}{print $1,$2,$3}END{print "=========================\n"}三,AWK变量,计算使用order文件 (商品名,数量,单价)apple 20 6.5orange 10 8grape 7 12berry 5 32输出格式:awk -f order2.awk ordername count price total...Number of item: Total count: Order total price:order2.awkBEGIN{print "name\tcount\tprice\ttotal"; OFS="\t"; total=0; totalCount=0;} {totalCount += $2;total += ($2 * $3);print $1, $2, $3, $2*$3}END{printf "Number of item: %d, Total count: %d, Order total price: %.2f\n", NR, totalCount, total}四、AWK donation作业Mike:Harrington:(510) 548-1278:250:100:175Christian:Dobbins:(408) 538-2358:155:90:201Susan:Dalsass:(206) 654-6279:250:60:50Archie:McNichol:(206) 548-1348:250:100:175Jody:Savage:(206) 548-1278:15:188:150Guy:Quigley:(916) 343-6410:250: 100:175Dan:Savage:(406) 298-7744:450:300:275Nancy:McNeil:(206) 548-1278:250:80:75John:Goldenrod:(916) 348-4278:250:100:175Chet:Main:(510) 548-5258:50:95:135Tom:Savage:(408) 926-3456:250:168:200Elizabeth:Stachelin:(916) 440-1763:175:75:300donation2.awkBEGIN{FS=":"; total = 0; max = 0; i = 0;print " *** FIRST QUARTERLY REPORT *** ";print " *** CAMPAIGN 2000 CONTRIBUTIONS *** ";print "-------------------------------------------------------------------------------";printf("%20s %15s %8s %8s %8s %15s\n", "NAME","PHONE", "Jan", "Feb", "Mar", "Total Donated");print "-------------------------------------------------------------------------------";}{name=$1 " " $2;subtotal=$4+$5+$6;total = total + subtotal;if (subtotal > 500) { names[i] = name; phone[i] = $3; lastToIndex[$2 $3]=i; i++}if (subtotal > max) { max = subtotal; max_name=name; max_first=$1;}printf("%20s %15s %8.2f %8.2f %8.2f %15.2f\n", name, $3, $4, $5, $6, subtotal);}END{print "-------------------------------------------------------------------------------";print " SUMMARY"print "-------------------------------------------------------------------------------";printf ("The campaign received a total of $%.2f for this quartar.\n", total); printf ("The average donation for the %d contributors was $%0.2f.\n", NR, total/NR);printf ("The highest total contribution was $%0.2f made by %s.\n", max, max_name);printf (" *** THANKS %s***\n", max_first);printf ("The following people donated over $500 to the campaign.\n");printf ("They are eligible for the quarterly drawing!!\n");printf ("Listed are their names (sorted by last name) and phone numbers:\n");len=asorti(lastToIndex, sortname);for (i = 1; i <= len; i++) {ii = lastToIndex[sortname[i]];printf (" %s--%s\n", names[ii], phone[ii]);}printf (" Thanks to all of your continued support!!\n");}运行结果:五、Shell 变量写一个脚本weather.sh,完成下面功能:外部定义环境变量:export weather=”Sunny”输入What’s your name? (echo, read)Which city do you live? (echo, read)输出:Hi “名字”,the weather of “城市” is“定义的weather”执行脚本:chmod u+x weather.sh; ./weather.sh外部定义局部变量weather1, 使用source执行?#!/bin/bashread -p "What's your name?" nameread -p "Which city do you live?" cityecho "hi $name, the weather of $city is $weather. Local weather is $weather1."六、Shell String pattern match创建一个脚本:ip_match.sh用户输入一个string,判断是否是IPv4地址yes: 输出This is an IPv4 addressno: 输出Wrong address提示: IPv4 regex: ([0-9]{1,3}\.){3}[0-9]{1,3}#!/bin/bashpattern='([0-9]{1,3}\.){3}[0-9]{1,3}'echo "Input a string"read strif [[ $str =~ $pattern ]]; thenecho "This is a ipv4 address: $str"elseecho "Wrong address! $str"fi七、Shell 文件条件判断输入:please input a file name:逻辑:如果文件已经存在:the file already exites不存在,新建一个空文件,名字为输入的string。

计算机操作系统课后习题答案第四版1. Describe the concept of a process and its typical attributes.A process is an entity that represents the execution of a program on a computer system. It consists of the program code, data, and execution context. The typical attributes of a process include a unique process identifier (PID), a program counter that keeps track of the next instruction to be executed, a stack that holds temporary data, a heap for dynamically allocated memory, and a set of resources such as open files and I/O devices.2. Explain the difference between process control block (PCB) and thread control block (TCB).A process control block (PCB) is a data structure used by the operating system to manage a process. It contains information about the process, such as its current state, scheduling information, memory allocation, and I/O status. On the other hand, a thread control block (TCB) is a data structure used to manage a thread within a process. It contains information specific to the thread, such as its program counter, stack pointer, and register values. Multiple threads can exist within a single process, sharing the same resources.3. Discuss the advantages and disadvantages of using threads instead of processes.One advantage of using threads instead of processes is that they are more lightweight in terms of resource consumption. Since threads share the same memory space, inter-thread communication is faster and uses less memory compared to inter-process communication. Threads also enable betterutilization of multi-core processors, as multiple threads can run in parallel on different cores.However, there are also disadvantages to using threads. The main disadvantage is that threads within the same process can interfere with each other if not properly synchronized. This can lead to issues such as race conditions, deadlocks, and data corruption. Additionally, debugging and testing multi-threaded applications can be more complex and time-consuming compared to single-threaded applications.4. Explain the concepts of mutual exclusion, deadlock, and starvation in the context of operating systems.Mutual exclusion refers to the concept of ensuring that only one process or thread can access a shared resource at a time. This is typically achieved using synchronization mechanisms such as locks or semaphores. Mutual exclusion is important to prevent data corruption or inconsistent results due to concurrent access.Deadlock occurs when two or more processes are waiting indefinitely for each other to release resources, resulting in a situation where none of the processes can proceed. It can happen when processes acquire resources in a different order or when they fail to release resources properly. Deadlocks can lead to system failures and require careful resource allocation and scheduling algorithms to avoid.Starvation refers to a situation where a process is unable to acquire the necessary resources to progress, despite its requests. It can occur when resource allocation policies favor certain processes over others, leading to along waiting time for some processes. Starvation can negatively impact the performance and fairness of the system.5. Discuss the purpose and functionality of memory management units (MMUs) in operating systems.Memory management units (MMUs) are hardware components responsible for translating virtual memory addresses used by processes into physical memory addresses. They provide address translation and memory protection mechanisms. MMUs use page tables or translation lookaside buffers (TLBs) to map virtual addresses to physical addresses, allowing processes to utilize more memory than physically available.MMUs also enforce memory protection by assigning memory access permissions to different regions of the process's address space. This prevents processes from accessing memory that they should not be able to, ensuring data integrity and security. Additionally, MMUs help optimize memory access by caching frequently used memory pages in the TLB, reducing the number of costly memory accesses.Overall, MMUs play a crucial role in memory management, allowing processes to have their own virtual address spaces and ensuring efficient and secure memory access.(Note: The above answers are just sample content for the given topic. Please modify and expand them according to your needs, as the word limit has been exceeded.)。

国家十二五规划教材《Linux操作系统及应用(第四版)》课后习题答案Windows & Linux老师交流群:189934741 作者QQ:68433059 项目1 安装Red Hat Enterprise Linux1.6 练习题一、填空题1. GNU's Not Unix的递归缩写2. 内核(kernel)、命令解释层(Shell或其他操作环境)、实用工具3. System V BSD4. Copyleft(无版权)General Public License,GPL)5. FSF,Free Software Foundation6. 便携式操作系统接口(Portable Operating System Interface)7. 企业应用个人应用8. 内核版本发行版本9. swap交换分区/(根)分区10. root11. X Server、X Client和通信通道二、选择题1.B2.C3.B4.A5. D6. C项目2 管理文件系统2.5 练习题一、填空题1. 区分Tab2. 分号3. 反斜杠“\”“>”4. “&”5. 保存管理6. 扩展文件系统ext2/ext3/ext47. 级块索引节点表数据块8. 树状目录“/”9. umask umask 777 00010. . ..11. 隐藏文件12. chmod a+x filename二、选择题1. C2. C3. C4. C5. A6. A7. A8. B9. D10. D项目3 shell与vim编辑器3.5 练习题一、填空题1. shell2. /etc/shells3. /etc/passwd4. 命令编辑功能;命令与文件补全功能;命令别名设置功能;作业控制、前台与后台控制;程序化脚本;通配符等。
5. 全局变量局部变量6. set7. *、?、[]8. 行9. 查找、删除、替换10. 通配符(wild card)正则表示法项目4 shell编程-shell script4.5 练习题一、填空题1. shell shell 的语法与命令(含外部命令)正则表达式管道命令数据流重导向2. 上下左右3. r r 与x4. shell (#!/bin/bash) 程序用途版本作者5. read date6. 父程序7. test 中括号( [] )8. if...then case $var in ... esac9. 不定循环(while, until) 固定循环(for)10. sh -x script.sh三、实践习题1.请创建一个script ,当你运行该script 的时候,该script 可以显示:①你目前的身份(用whoami );②你目前所在的目录(用pwd)。

操作系统第四版课后习题答案操作系统第四版课后习题答案在学习操作系统的过程中,课后习题是巩固知识的重要环节。
本文将为大家提供操作系统第四版课后习题的答案,帮助大家更好地理解和掌握相关知识。
第一章引论1. 操作系统的定义是什么?答:操作系统是计算机系统中的一个软件,它管理和控制计算机硬件资源,为用户和应用程序提供一个简单、一致的接口。
2. 操作系统的主要功能有哪些?答:操作系统的主要功能包括进程管理、内存管理、文件系统管理、设备管理和用户接口等。
3. 解释并区分多道程序和多任务操作系统。
答:多道程序操作系统是指能够同时运行多个程序的操作系统,通过时间片轮转的方式实现程序的并发执行。
而多任务操作系统是指能够同时运行多个任务的操作系统,任务之间可以是并行执行的。
第二章进程管理1. 进程和程序的区别是什么?答:进程是程序在执行过程中的实体,包括程序计数器、寄存器和栈等,而程序是存储在磁盘上的可执行文件。
2. 什么是进程控制块(PCB)?答:进程控制块是操作系统中用来管理和控制进程的数据结构,包括进程的标识符、状态、优先级、程序计数器和寄存器等信息。
3. 进程的状态有哪些?答:进程的状态包括就绪状态、运行状态和阻塞状态。
第三章内存管理1. 什么是虚拟内存?答:虚拟内存是一种扩展内存的技术,将磁盘空间作为辅助内存来扩展物理内存的容量。
2. 什么是页面置换算法?答:页面置换算法是用于虚拟内存管理中的一种算法,当物理内存不足时,根据一定的策略选择一个页面将其从内存中置换出去,以便为新的页面腾出空间。
3. 什么是内存分配算法?答:内存分配算法是用于管理和分配内存的一种算法,包括连续分配、非连续分配和分段分页等。
第四章文件系统管理1. 文件系统的作用是什么?答:文件系统是操作系统中用于管理和组织文件的一种机制,它提供了对文件的创建、读写、删除等操作。
2. 什么是文件控制块(FCB)?答:文件控制块是操作系统中用于管理文件的数据结构,包括文件的属性、位置、大小和权限等信息。
《Linux系统应用与开发教程》所有课后习题和答案第1章 Linux概述 (1)第2章 shell及常用命令 (4)第3章 vi编辑器的使用 (7)第4章 X Window系统的使用 (9)第5章 Linux系统的常用软件 (11)第6章硬件管理 (11)第7章网络基本配置 (12)第8章常用网络服务的配置和使用 (15)第9章系统管理与监控 (19)第10章 Linux系统的安全管理 (21)第11章shell程序设计 (24)第12章gcc的使用与开发 (26)第13章gtk+图形界面程序设计 (27)第14章Qt图形界面程序设计 (28)第15章集成开发环境KDeve lop的使用 (31)第1章 Linux概述1.什么是Lin ux?Linux是一套免费使用和自由传播的类UN IX操作系统,源代码开放,能运行于各类硬件平台,包括Inte l x86系列和RISC处理器。
这个系统是由世界各地成千上万的程序员设计和实现的。
其目的是建立不受任何商品化软件的版权制约的、全世界都能自由使用的U NIX兼容产品。
2. Linux有哪些特性?(1)开放性(2)多用户(3)多任务(4)良好的用户界面(5)设备独立性(6)丰富的网络功能(7)可靠的系统安全(8)良好的可移植性3. Linux与Windo ws操作系统的主要区别是什么?(1)从发展的背景看,Linux是从一个比较成熟的操作系统发展而来的,而其他操作系统,如Windo ws等,都是自成体系,无对应的相依托的操作系统(2)从使用费用上看,Linux是一种开放、免费的操作系统,Window s是封闭的系统,需要有偿使用。
(3)Linux上丰富的应用软件也是自由的,而在Wind ows下,几乎所有的软件都有独立的版权,需要购买使用,即使某些软件可以免费使用,也一般不提供其源代码,更不用说由用户修改扩充其功能了。
05-ch4参考答案2. 在一个请求分页虚拟存储管理系统中,一个作业共有5页,执行时其访问页面次序为:(1) 1、4、3、1、2、5、1、4、2、1、4、5。
(2) 3、2、1、4、4、5、5、3、4、3、2、1、5。
若分配给该作业三个页框,分别采用FIFO和LRU面替换算法,求出各自的缺页中断次数和缺页中断率。
答:(1) 采用FIFO为9次,9/12=75%。
采用LRU为8次,8/12=67%。
(2) 采用FIFO和LRU均为9次,9/13=69%。
5 给定内存空闲分区,按地址从小到大为:100K、500K、200K、300K和600K。
现有用户进程依次分别为212K、417K、112K和426K,(1)分别用first-fit、best-fit和worst-fit 算法将它们装入到内存的哪个分区?(2) 哪个算法能最有效利用内存?答:按题意地址从小到大进行分区如图所示。
(1)1)first-fit 212KB选中分区2,这时分区2还剩288KB。
417KB选中分区5,这时分区5还剩183KB。
112KB选中分区2,这时分区2还剩176KB。
426KB无分区能满足,应该等待。
2)best-fit 212KB选中分区4,这时分区4还剩88KB。
417KB选中分区2,这时分区2还剩83KB。
112KB选中分区3,这时分区3还剩88KB。
426KB选中分区5,这时分区5还剩174KB。
3)worst-fit 212KB选中分区5,这时分区5还剩388KB。
417KB选中分区2,这时分区2还剩83KB。
112KB选中分区5,这时分区5还剩176KB。
426KB无分区能满足,应该等待。
(2) 对于该作业序列,best-fit算法能最有效利用内存9 某计算机有cache、内存、辅存来实现虚拟存储器。
如果数据在cache中,访问它需要20ns;如果在内存但不在cache,需要60ns将其装入缓存,然后才能访问;如果不在内存而在辅存,需要12µs将其读入内存,然后,用60ns再读入cache,然后才能访问。
LINUX<<4.9>>编写一个shell脚本,它把第二个位置参数及其以后的各个参数指定的文件复制到第一个位置参数指定的目录中。
#!/bin/bashdir=$1 /初始化shift /参数向左移while [ $1 ] /循环dofile=$1 / 初始化,赋值现在位置的参数1cp $1 $dir /将现位置参数1中的值复制到目录中shift /参数左移donels $dir 显示指定目录中的列表运行:bash 代码名称要移动的目录要移动的文件《4.10》编写一个shell脚本,显示当天日期,查找给定的某用户是否在系统中工作。
如果在系统中,就发一个问候给他。
#!/bin/bashdate /显示日期ifwho |grep "^$1" /寻找用户thenwrite $1 << ! /对用户发消息!echo "hello !"fi运行:bash vi编辑的文件<<4.11>>打印给定目录的某些文件,由第一个参数指出文件所在的目录,其余参数是要打印的文件名#!/bin/bashdir=$1cd $ dirshiftfor f in $@;docat $fdone运行:bash 程序代码名称目录名称文件名称<<4.12>>利用for循环将当前目录下的(*.c)文件移到指定的目录下,并按文件大小排序,显示移动后指定目录的内容。
#!/bin/bashfor file in `ls -l /root/a | grep ".*.c"` (Tab键上面的`){mv /root/a/$file /root/b}ls -lS /root/b运行:bash vi创建的文件<<4.13>>利用数组形式存放10个城市的名字,然后利用for循环把他们打印出来。
计算机操作系统课后习题答案第四版在学习计算机操作系统这门课程时,课后习题是巩固知识、检验理解的重要环节。
下面,我们将对第四版教材中的一些典型课后习题进行详细的解答。
首先来看第一章的习题。
其中有一道关于操作系统定义和功能的题目。
操作系统可以被理解为是管理计算机硬件与软件资源的程序,它负责控制和协调计算机系统中各个部件的工作,为用户和应用程序提供一个方便、高效、安全的操作环境。
其主要功能包括处理机管理、存储器管理、设备管理、文件管理以及用户接口管理等。
比如处理机管理,它要合理地分配处理机时间,以提高系统的运行效率;存储器管理则要确保内存的合理分配和有效利用,避免出现内存泄漏等问题。
第二章中,有涉及进程概念和进程状态转换的习题。
进程是操作系统进行资源分配和调度的基本单位。
它具有动态性、并发性、独立性和异步性等特征。
进程在其生命周期中会经历不同的状态,如就绪、运行和阻塞。
当一个进程具备了运行所需的资源和条件,它就处于就绪状态,等待被调度执行;一旦获得处理机,就进入运行状态;而当进程由于等待某个事件的发生而无法继续执行时,就会进入阻塞状态。
在第三章的习题里,有关线程的问题较为常见。
线程是进程中的一个执行单元,它可以共享进程的资源,从而提高系统的并发性能。
与进程相比,线程的创建和切换开销更小,因此在多线程编程中被广泛应用。
例如,在一个网络服务器中,可以为每个连接创建一个线程来处理数据的接收和发送,提高服务器的响应速度。
第四章的存储管理部分,有关于分页存储管理和分段存储管理的习题。
分页存储管理将内存空间划分成固定大小的页,而分段存储管理则是根据程序的逻辑结构将其划分成不同的段。
分页存储管理的优点是便于内存管理和分配,但可能会产生内部碎片;分段存储管理则更符合用户的编程思维,但会存在外部碎片。
在实际应用中,往往会结合两者的优点,形成段页式存储管理。
第五章的设备管理中,涉及到设备驱动程序和I/O 控制方式的问题。
LINUX
<<4.9>>编写一个shell脚本,它把第二个位置参数及其以后的各个参数指定的文件复制到第一个位置参数指定的目录中。
#!/bin/bash
dir=$1/初始化
shift /参数向左移
while [ $1] /循环ﻩﻩ
do
file=$1 / 初始化,赋值现在位置的参数1ﻩ
cp $1 $dir/将现位置参数1中的值复制到目录中ﻩ
shift/参数左移
done
ls$dir 显示指定目录中的列表
运行:bash代码名称要移动的目录要移动的文件
《4.10》编写一个shell脚本,显示当天日期,查找给定的某用户是否在系统中工作。
如果在系统中,就发一个问候给他。
#!/bin/bash
dateﻩ/显示日期
if
who |grep"^$1"ﻩ/寻找用户ﻩﻩ
then
write$1<<!/对用户发消息
!
echo"hello !"
fi
运行:bash vi编辑的文件
<<4.11>>打印给定目录的某些文件,由第一个参数指出文件所在的目录,其余参数是要打印的文件名
#!/bin/bash
dir=$1
cd $ dir
shift
for fin$@;
do
cat $f
done。