整理2:时态
- 格式:doc
- 大小:118.00 KB
- 文档页数:25

11 条件式现在时 I构成:直陈式简单将来时的词尾换成直陈式未完成过去时的词尾构成。
Parler finir Venir avoir être aller je parleraistu parleraisil parleraitnous parlerionsvous parleriezils parleraient je finiraistu finiraisil finiraitnous finirionsvous finiriezils finiraient je viendraistu viendraisil viendraitnous viendrionsvous viendriezils viendraient j’auraistu auraisil auraitnous aurionsvous auriezils auraient je seraistu seraisil seraitnous serionsvous seriezils seraient j’iraistu iraisil iraitnous irionsvous iriezils iraient II⽤法: 1.⽤在表⽰结果的主句中,从句⽤si引导,其谓语⽤直陈式未完成过去时;相当于英语中表⽰现在或将来情况的虚拟条件句。
1)表⽰与现在事实相反 Si j’étais vous, j’irais chez le dentiste tout de suite. 2)表⽰将来可能实现的动作:Est-ce que cela t’ennuierait beaucoup si nous allions au cinéma un autre jour ? 如果动作实现的可能性极⼤,则主句⽤直陈式简单将来时,从句⽤直陈式现在时;相当于英语的真实条件句: S’il fait beau demain, nous irons au parc prendre des photos. 条件从句也可由其他表⽰条件的词组代替: A votre place, j’apprendrais le fran?ais comme seconde langue étrangère. Avec des si, on mettrait Paris dans une bouteille. 2.⽤在表⽰愿望、请求、建议、推测的独⽴句中,能表达委婉语⽓;相当于英语中情态动词⽤法 J’aimerais faire le tour du monde. (I’d like to travel round the world.) Pourrais-je écouter cette cassette avant de l’acheter ? (Could I listen to this cassette before buying it? ) Vous feriez mieux de suivre le conseil du médecin. (You’d better follow the doctor’s advice.) 3.⽤作直陈式过去将来时,表⽰过去某⼀动作之后将要发⽣的事情,相当于英语的⼀般过去将来时。
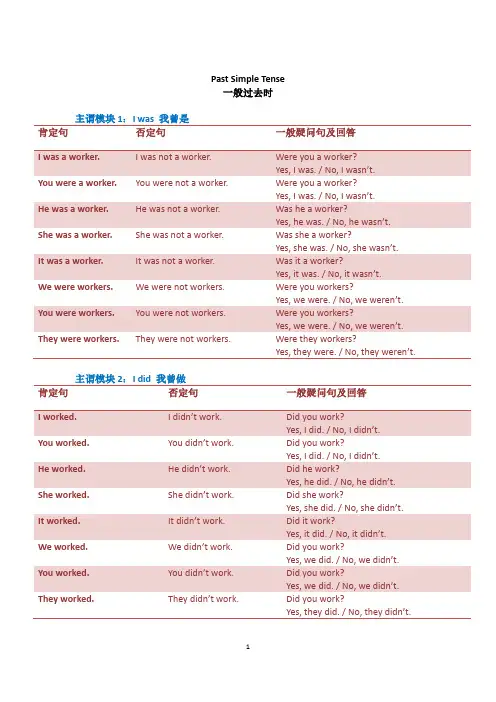
Past Simple Tense一般过去时主谓模块1:I was 我曾是肯定句否定句一般疑问句及回答Yes, I was. / No, I wasn’t.He was a worker. He was not a worker. Was he a worker?Yes, he was. / No, he was n’t. She was a worker. She was not a worker. Was she a worker?Yes, she was. / No, she was n’t.It was a worker. It was not a worker. Was it a worker?Yes, it was. / No, it was n’t.We were workers. We were not workers. Were you workers?Yes, we were. / No, we were n’t. You were workers. You were not workers. Were you workers?Yes, we were. / No, we were n’t. They were workers. They were not workers. Were they workers?Yes, they were. / No, they were n’t.主谓模块2:I did 我曾做肯定句否定句一般疑问句及回答Yes, I did. / No, I did n’t.He worked. He did n’t work.Did he work?Yes, he did. / No, he did n’t. She worked. She did n’t work. Did she work?Yes, she did. / No, she did n’t. It worked. It did n’t work. Did it work?Yes, it did. / No, it did n’t.We worked. We did n’t work. Did you work?Yes, we did. / No, we did n’t. You worked. You did n’t work.Did you work?Yes, we did. / No, we did n’t. They worked. They did n’t work.Did you work?Yes, they did. / No, they did n’t.标准句子结构●主谓模块1+X+时间模块I was a worker then. 那时我还是一个员工。

专升本辅导2 时态一、完成时态特点:1、谓语动词一般为延续性动词2、动作发生的时间是过去,但这一动作持续到现在,而且还可能继续持续下去;3、时间状语为一段时间,说明某个动作持续了多久。
1)I’ve worked in this company since 1980.2) I have lived here for 3 years.3) We have up until now failed to take any action to decide on a common language that would further communication between nations.(until now, up to now, up till now, so far)4) Throughout history man has had to accept the fact that all living things must die, for the very nature of life includes death.( in the last few years, over the past few years, during the last three months, for the last few centuries, through centuries)4、过去发生但与现在仍有联系的动作或状态---言外之意1)He has broken his leg.2) He broke his leg.3) A: What has happened to Jane? She is crying.B: She broke the dinning-room window. She has to face the music when her father gets home.4) You should have put the milk into icebox; I expect it ____ undrinkable by now.A. becameB. had becomeC. has becomeD. becomes5、到目前的一个时间段内重复发生的动作。

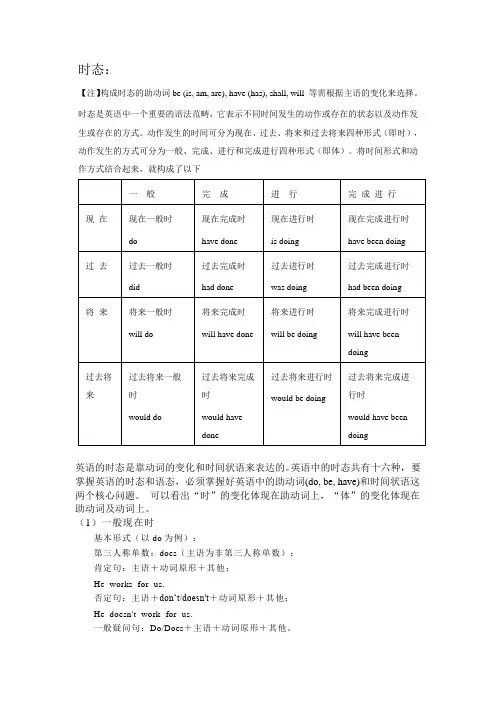
时态:【注】构成时态的助动词be (is, am, are), have (has), shall, will 等需根据主语的变化来选择。
时态是英语中一个重要的语法范畴,它表示不同时间发生的动作或存在的状态以及动作发生或存在的方式。
动作发生的时间可分为现在、过去、将来和过去将来四种形式(即时),动作发生的方式可分为一般、完成、进行和完成进行四种形式(即体)。
将时间形式和动作方式结合起来,就构成了以下英语的时态是靠动词的变化和时间状语来表达的。
英语中的时态共有十六种,要掌握英语的时态和语态,必须掌握好英语中的助动词(do, be, have)和时间状语这两个核心问题。
可以看出“时”的变化体现在助动词上,“体”的变化体现在助动词及动词上。
(1)一般现在时基本形式(以do为例):第三人称单数:does(主语为非第三人称单数);肯定句:主语+动词原形+其他;He works for us.否定句:主语+don‘t/doesn't+动词原形+其他;He doesn't work for us.一般疑问句:Do/Does+主语+动词原形+其他。
肯定回答:Yes,(+主语+do/does).否定回答:No,(+主语+don't/doesn't.)特殊疑问句:疑问词+一般疑问句语Does he work for us?Yes, he does.No, he doesn'tWhat does he do for us?He works for us.(2)一般过去时be动词+行为动词的过去式否定句式:在行为动词前加didn‘t,同时还原行为动词,或was/were+not;was或were放于句首;用助动词do的过去式did提问,同时还原行为动词例如:Did he work for us? He didn't work for us. He worked for u s.(3)一般将来时am/are/is+going to+do 或will/shall+doam/is/are/about to + doam/is/are to + do;一般将来时的表达方法be going to +动词原形be +不定式,be to+动词原形,be about to +动词原形be able to +不定式be about to+动词原形will + 动词原形;例如:He is going to work for us.He will work for us;He is coming.这是特殊的用一般现在时表达将来时态的例子!!(4)过去将来时be(was,were)going to+动词原形be(was,were)about to+动词原形be(was,were)to+动词原形肯定句:主语+be(was,were)going to+动词原形~.否定句:主语+be(was,were)not going to+动词原形~.疑问句:Be(Was,Were)+主语+going to+动词原形~?肯定句:主语+would(should)+动词原形~.否定句:主语+would(should)not+动词原形~.疑问句:Would(Should)+主语+动词原形~?He would work for us.(5)现在进行时主语+be+v.ing〔现在分词〕形式(其中v表示动词)表示现在正在进行的动作或最近在做的事。

英语四个时态的结构英语中有四个基本时态:一般现在时、一般过去时、一般将来时和现在进行时。
它们有不同的结构和用法,下面将详细介绍每个时态的结构。
一、一般现在时:1.肯定句结构:主语+动词原形/第三人称单数形式+其他例如:I play football every weekend.2. 否定句结构:主语 + do/does + not + 动词原形 + 其他例如:They do not like tomatoes.3. 疑问句结构:Do/Does + 主语 + 动词原形 + 其他?例如:Do you like ice cream?4. 特殊疑问句结构:特殊疑问词 + do/does + 主语 + 动词原形 + 其他?二、一般过去时:1.肯定句结构:主语+动词过去式+其他例如:She watched a movie last night.2. 否定句结构:主语 + did not + 动词原形 + 其他例如:He did not eat dinner yesterday.3. 疑问句结构:Did + 主语 + 动词原形 + 其他?例如:Did you go to the party?4. 特殊疑问句结构:特殊疑问词 + did + 主语 + 动词原形 + 其他?例如:When did you arrive?三、一般将来时:1. 肯定句结构:主语 + will + 动词原形 + 其他例如:I will visit my grandma next week.2. 否定句结构:主语 + will not + 动词原形 + 其他3. 疑问句结构:Will + 主语 + 动词原形 + 其他?例如:Will you go to the concert?4. 特殊疑问句结构:特殊疑问词 + will + 主语 + 动词原形 + 其他?例如:Where will you travel next summer?四、现在进行时:1. 肯定句结构:主语 + am/is/are + 动词-ing + 其他例如:She is watching TV now.2. 否定句结构:主语 + am/is/are + not + 动词-ing + 其他例如:They are not studying for the exam.3. 疑问句结构:Am/Is/Are + 主语 + 动词-ing + 其他?例如:Are you playing basketball?4. 特殊疑问句结构:特殊疑问词 + am/is/are + 主语 + 动词-ing + 其他?例如:What are you doing tonight?以上就是英语四个基本时态的结构和用法。

时态复习(二)一、考点、热点回顾1、考点:过去进行时,过去将来时2、热点:2种时态具体用法3、2种时态详解一、过去进行时(一)定义:过去进行时,是表示过去某个具体时刻正在进行的事情或动作。
(二)结构:was/were +doing (现在分词)(三)用法1、过去进行时表示过去某段时间内持续进行的动作或者事情。
常用的时间状语this morning,the whole morning,all day yesterday,from nine to ten last evening,when,while 例如:We were watching TV from seven to nine last night.昨天晚上七点到九点的时候我们在看电视。
What was he researching all day last Sunday?上周日他一整天都在研究什么?My brother fell while he was riding his bicycle and hurt himself.我哥哥骑自行车的时候从车上摔下来,受伤了。
It was raining when they left the station.他们离开车站的时候天正在下雨。
When I got to the top of the mountain,the sun was shining.当我到达山顶的时候,阳光灿烂。
2. 过去进行时可以表示在过去某个时间点发生的事情。
时间点可以用介词短语、副词或从句来表示。
如:What was she doing at nine o'clock yesterday?昨天晚上九点她在做什么?(介词短语表示时间点)When I saw him he was decorating his room.当我看见他的时候他正在装饰房间。
(when从句表示时间点)3.在复合句中,如果主要动作和背景动作都是延续的或同时发生的,那么主从句的动词都可用过去进行时。


1、上次课后巩固作业复习;2、互动探究I. 时态复习【知识梳理1】现在进行时1. 表示正在发生的动作或者目前一段时刻内正在进行的动作(但说话时那个动作不一定在进行)Come on! We are choosing presents for John’s 20th birthday.What lesson are you studying this week?Mr. Brown is a teacher of maths, but he is now teaching computer lessons.2. 用look!… listen!…等开头,强调某人正在做某事.Look, it’s snowing heavily outside and everywhere is in white.Listen! Someone is playing the drum next door.3. 表示不断重复的动作,常带always, constantly, forever, all the time等频度副词,而且带有感情色彩。
Alice is always helping others and doing volunteer work in the community.He is changing his mind all the time so that it’s hard for others to understand him.2.表示在过去先后发生的两个动作中,先发生的动作通常用过去完成时。
I didn’t see the film because I had seen it before.He told me that he had made a serious mistake.When I got to the cinema, the film had been on for ten minutes.3. 过去完成时的时刻状语有:by +过去时刻点(eg. by 2021, by the time he was born) 等。

英语时态专项复习与练习郑州十一中北校李本华初中阶段所学的英语时态复习:1)一般现在时2)现在进行时1.现在时态:3)现在完成时4)现在完成进行时5)一般将来时英语的时态:1)一般过去时2)过去进行时2.过去时态:3)过去完成时4)过去将来时一. 一般现在时:1.概念:表示现在经常发生的动作或习惯性的动作以及现在所存在的状态和爱好。
例如:He often gets up at 6:00 in the morning. 他经常在早上6点钟起床。
(习惯性动作)We usually do our homework in the evening. 我们通常晚上做作业。
(经常发生的动作) Mr. Green usually goes to bed at 10:00 at night. 格林先生通常在晚上10点睡觉。
(习惯性动作)Lucy looks very happy today. 今天Lucy显得很高兴。
(状态)Jack is angry now. Jack正在发怒。
(状态)We like walking after meals. 我们饭后喜欢散步。
(爱好)My brother likes playing basketball. 我弟弟喜欢打篮球。
(爱好)He enjoys playing the violin. 他喜欢拉小提琴。
(爱好)2.一般现在时谓语动词的构成:▲be动词:be动词的一般现在时有三种形式:am , is , are .主语是第一人称单数是用am , 主语是第三人称单数时用is , 其余各人称均用are.例如:1) I am a student. 2) He is a teacher.3) She is a doctor. 4) It is a desk.5) Jack is my friend. 6) My mother is a nurse.7) You are a policeman. 8) You are all my friends.9) We are all students. 10) They are on the playground.11) Jack and Tom are both Americans.依上例句可以归纳出be动词一般现在时的三种形式am , is , are的用法口诀:I用am , you用are ; is跟着他(he)、她(she)、它(it)。

小学英语四大时态语法知识点小学英语主要是如下的四大时态:一般现在时、现在进行时、一般过去时、一般将来时。
01一般现在时一、标志词always(总是)usually(通常)often(经常)sometimes(有时)never(从不)every(每一)二、基本用法1.表示事物或人物的特征、状态。
2.表示经常性、习惯性的动作。
3.表示客观现实。
三、构成1.be动词:主语+be动词(am isare)+其它.2.行为动词:主语+行为动词+其它。
四、句型肯定句:A. be 动词:be+主语+其它。
B. 行为动词:主语+动词(注意人称变化)+其它。
否定句:A.be动词:主语+be+not+其它。
B.行为动词:主语+助动词(do/does)+not+d动词原形+其它一般疑问句:A.be动词:be+主语+其它。
B.行为动词:助动词(Do/Does)+主语+动词原形+其他.特殊疑问词:疑问词+一般疑问句02现在进行时一、标志词now(现在), look(看),listen(听)二、基本用法表示现阶段正在进行的动作三、基本结构1.肯定句:主语+be动词+动词现在分词(ing)+其它。
2.否定句:主语+be动词+not+动词现在分词(ing)+其它。
3.一般疑问句:be动词+主语+现在分词(ing)+其它。
4.特殊疑问句:疑问词+一般疑问句。
03一般将来时一、标志词tomorrow(明天),soon(不久),will(将要=be going to)二、基本用法表示在在将来某个时间要发生的动作或存在的状态。
三、基本结构1.肯定句:主语+ be going to + 动词原形。
主语+will+动词原形。
2.否定句:主语+ be going to +动词原形。
主语+won’t + 动词原形3.一般疑问句:Be + 主语+ going to+动词原形Will + 主语+ 动词原形4.特殊疑问句:疑问词+一般疑问句04一般过去时一、标志词yesterday(昨天),ago(以前),before(在...之前)二、用法1.表示过去某个时间发生的动作或存在的状态,常和表示过去的时间状语连用。
八种时态句子怎样变否定句和一般疑问句时态是英语中考的一项至关重要的考点,广大初中学生在实际运用时,往往对时态总是倍感棘手,下面我们就对这几种时态句子的否定句和一般疑问句的变形进行一些归纳整理。
一、一般现在时:概念:表示经常、反复发生的动作或行为及现在的某种状况。
基本结构:即谓语动词形式:①be动词原形;②行为动词(原形或“三单”形式)如:1,Iamastudent.2,Theygetupearly.3,Hehelpsus.助动词:does和do方法:1,首先观察句子中的谓语动词是be动词呢还是行为动词(表示具体动作行为的词如:play)2,变一般问句:Be动词的话就把be放到句首,若是行为动词就把do放到句首。
注意当主语为第三人称单数时,用dose放句首,谓语动词要变回原形。
当然别忘句末加问号。
如上面的句子变一般问句分别为:Are youastudent?Do theygetupearly?Does he help us?3,变否定句时,如句中有be动词就在be后加not,若是行为动词就在行为动词前加don't,如主语为第三人称单数,则加doesn't,同时动词变原形。
Iamnotastudent.Theydon'tgetupearly.Hedoesn'thelpus.二、一般过去时:概念:过去某个时间里发生的动作或状态;过去习惯性、经常性的动作、行为。
基本结构:①be动词(was或were);②行为动词(动词过去式)如:1,Hewasastudenttwoyearsago.2,Theycamebacklastnight.助动词:did1,变一般问句时,①把was或were放于句首,谓语动词是行为动词时,就把did放到句首,动词变回原形。
句末加问号。
上例可变为:Was heastudenttwoyearsago?Did they come backlastnight?2,变否定句时,①was/were+not;②在行为动词前加didn't,同时还原行为动词。
英语十六时态表格总结(很全面)(word版可编辑修改)编辑整理:尊敬的读者朋友们:这里是精品文档编辑中心,本文档内容是由我和我的同事精心编辑整理后发布的,发布之前我们对文中内容进行仔细校对,但是难免会有疏漏的地方,但是任然希望(英语十六时态表格总结(很全面)(word版可编辑修改))的内容能够给您的工作和学习带来便利。
同时也真诚的希望收到您的建议和反馈,这将是我们进步的源泉,前进的动力。
本文可编辑可修改,如果觉得对您有帮助请收藏以便随时查阅,最后祝您生活愉快业绩进步,以下为英语十六时态表格总结(很全面)(word版可编辑修改)的全部内容。
英语时态表-—一般现在时、一般过去时英语时态表——一般将来时、过去将来时英语时态表-—现在进行时、过去进行时英语时态表—- 现在完成时、过去完成时英语时态表—- 英语时态举例!英语时态表——详细讲解—一般现在时通常以动词原形表示。
主语为第三人称单数时,用现单三形式。
动词be和have(表示“拥有”)各人称的单数形式为:第一人称单数第二人称单数第三人称单数Have Have Have HasBe Am Are is一般现在时的否定式、疑问式和简单回答形式如下:动词be 与 have(表示“拥有”):否定式直接把not放在动词之后,疑问式直接把动词放在主语之前,见下表:否定式疑问式Be Have Be HaveI am not (I’m not)… I have not (haven’t)… Am i…?Have i…?You are not (aren't)… You have not (haven’t)… Are you…? Have y ou…?He is not (isn't)… He has not (hasn’t)… Is he …?Has he …?动词be 的否定疑问式和简单回答:否定疑问式肯定回答否定回答Am I not (aren’t i)…? Yes, you are。
七个时态:一般现在时、现在进行时、将来时:be goingto(= will )、一般过去时、过去进行时、过去完成时、现在完成进行时。
(1)一般现在时1.一般现在时表示经常或习惯性的动作,也可表示现在的状态或主语具备的性格和能力。
2.一般现在时中,没有be动词和情态动词,主语为第三人称单数的肯定句,动词要按规则加上s,主语是非第三人称单数的肯定句,动词用原形。
3.在一般现在时中,句中有be动词或情态动词时,否定句在be动词和情态动词后加not,一般疑问句将be动词或情态动词放在句4.在一般现在时中,句中没有be动词或情态动词时,主语为第三人称单数的否定句在动词前加does+not (doesn’t),一般疑问句在句首加does,句子中原有动词用原形;主语为非第三人称单数,否定句用do+not (don’t),一般疑问句在句首加do,句子中动词用原形。
5.动词+s的变化规则1)一般情况下,直接加-s,如:cook-cooks, milk-milks2)以s. x. sh. ch. o结尾,加-es,如:guess-guesses,wash-washes,watch-watches, go-goes3)以“辅音字母+y”结尾,变y为i, 再加-es,如:study-studies6. 句中be动词和动词一般情况下只能有一种而且也必须有一种。
如:The childrenare very happy on Christmas Day .7.一般现在时中的be动词:一般用原形:am is aream用于第一人称单数(I);is用于第三人称单数(he she it和其他人名或称谓,如:Ben his sister等);are用于第二人称单数(you)和所有复数(包括第一人称复数we、第二人称复数you;第三人称复数they和其他复数,如his parents等)。
8.一般过去时中的动词:有两种情况:第一种情况:主语是第三人称单数(he she it 和其他,如Helen 、her cousin 等),动词后一般加s或es。
高一英语语法(2-1):动词的时态之一般现在时、现在进行时和现在完成时一、动词有4个时、4个态,一共有16个时态1. 以work为例2. 在下列数轴上标注出时态的位置1)work / works2)am / is / are working3)have / has worked二、一般现在时(work / works)、现在进行时(am / is / are working)和现在完成时(have / has worked)1.一般现在时1)表示经常发生或习惯性的动作或状态,通常与usually,often,always,sometimes,every day,once a week等时间状语连用,有时也可不加这类状语。
如:2)表示客观事实或普遍真理。
如:The earth __________ (move) around the sun. 3)按时刻表、日程表、节目单、课程表等规定将要发生的动作,也用一般现在时表示将来。
如:The plane __________ (arrive) at 8:00 and __________ (leave) at 8:30.4)在连词when,as soon as,before,until,if等引导的表示未来行为的时间或条件状语从句中,常用一般现在时代替将来时,这是英语的习惯表达法。
但he __________ (come) here, he __________ (go) to visit you.2.现在进行时1)表示此时此刻正在进行的动作。
如:They __________ (have) an English class2)表示现阶段正在进行的动作,虽然此时此刻这一动作不一定在进行。
如:The3)在时间、条件状语从句中,有时可用现在进行时代替一般将来时。
如:When you __________ (pass) my way, please drop in. (详见二-6“即将”)4)现在进行时与always,all the time,forever,constantly等副词连用,表示感叹、惊讶、赞许、厌恶等情感。
高一英语语法(2-3):动词的时态之一般将来时、过去将来时、将来完成时一、一般将来时(will work):一般将来时的5种表达方式。
1.“shall / will + V原”是将来时的最普通的表达方式,表示从现在来看以后要发生的动作或存在的状态,指事物的固有属性或必然趋势。
如:We __________ (go) to ask Miss Chen for help. (shall和will表达一般将来时有何区别?)2.“am / is / are going to + V原”多用于口语中,表示“打算或计划要做某事”。
此外,还可以表示说话人根据已有的事实或迹象,对未来进行推断。
如:They __________ (meet) outside the school gate.(打算或计划要做某事)(根据已有的迹象,对未来进行推断)3.“am / is / are about to + V原”表示“即将……”,它不与表示时间的副词或时间状语连用。
如:The English evening __________ (start).4.“am / is / are to + V原”表示“按计划、安排即将发生的动作”,还可以表示“吩咐、命令、禁止”等,与表示时间的副词或时间状语连用。
如:到10(命令)5.“am / is / are due to +V原”表示“按计划或时间表将要发生某事”。
如:The talk __________ (last) for five days. 会谈(按计划)将持续5天。
The race __________ (start) in ten minutes. (按时间表)还有10分钟比赛就该开始了。
现在进行时有时与某些表示瞬间动作的动词连用,可表示按计划、安排将要发生的动作。
常见动词有go, come, start, leave, stay, return, arrive, begin, take, meet等。
八种时态结构及用法
时态是表示动作进行中的时间先后顺序的语法范畴,对于学习语言的人来说,正确理解和运用时态是至关重要的。
本文将介绍八种常用的时态结构及其用法。
一、现在完成时
现在完成时表示动作从过去开始一直延续到现在,并且有可能持续下去。
它的构成是“主语+动词的现在完成时”。
二、过去进行时
过去进行时表示过去某个时间点正在进行的动作,它的构成是“主语+动词的过去进行时”。
三、将来进行时
将来进行时表示将来某个时间点正在进行的动作,它的构成是“主语+动词的将来进行时”。
四、现在进行时
现在进行时表示从过去某个时间点开始持续进行的动作,它的构成是“主语+动词的现在进行时”。
五、过去完成时
过去完成时表示过去的过去,某一动作从过去开始持续延续到现在,或从过去开始持续到现在并将延续下去。
它的构成是“主语+动词的过去完成时”。
六、将来完成时
将来完成时表示将来某一时刻之前发生的动作,或从将来某一时刻开始持续延续到现在的动作,或从将来某一时刻开始持续到现在并将延续下去。
它的构成是“主语+动词的将来完成时”。
七、现在完成进行时
现在完成进行时表示从过去某个时间点开始持续进行的动作,并且从现在开始继续延续。
它的构成是“主语+动词的现在完成进行时”。
八、将来完成进行时
将来完成进行时表示将来某一时刻之前发生的动作,或从将来某一时刻开始持续延续到现在的动作,或从将来某一时刻开始持续到现在并将延续下去。
它的构成是“主语+动词的将来完成进行时”。
综上所述,八种时态结构各有用途,我们需要根据具体语境和句子结构来正确使用它们,以使表达准确、清晰。
时态 小丸子646229018 1. Participe Passé 过去分词(1,2摘自网络)
现在分词与过去分词二者最主要的区别是 过去分词是一种被动态,被作用的,如;un enfant fatigu2.一个累了的孩子(被累着了) 现在分词是主动的,对别人起作用的 un enfant fatiguant tout le monde一个把大家都累着的孩子(孩子自己不累)
又如; un pied frapp2 par la pierre 脚被石头打着了 un pied frappant le rythme 脚拍击着节奏。 现在分词过去式,表示在主动词之前发生的动作。 Son pied,ayant frapp2 trop longtemps le rythme,commence a avoir un peu mal. 现在分词过去式, 他的脚打了太长时间的拍子,开始有点疼。
我们知道,法语中凡是复合的时态( avoir或être + 过去分词 )中都要用到谓语动词的过去分词,仅此一项就足以说明过去分词在法语中使用的频率是很高的。规则动词的过去分词形式较容易掌握:
1.第一组规则动词和不规则动词 aller去掉词尾er,加é 即成,例如: aller --- allé travailler---travaillé corriger -- corrigé 2.第二组规则动词去掉词尾 ir,加 i 即成,例如: remplir ---- rempli finir ----- fini choisir ----- choisi 然而,第三组不规则动词的过去分词的变化则五花八门,不太容易掌握但又必须要掌握,因为不规则动词大多都是常用的动词。为此,笔者编造了下面的不规则动词的过去分词的记忆口诀,尽管它登不得大雅之堂,但实践证明还是十分奏效的。
下面是口诀中涉及的不规则动词及其过去分词,请读者根据所给出的动词的顺序去理解、靠挂后面的口诀:
avoir eu,être été,ouvrir ouvert,connaître connu,accueillir accueilli,pouvoir pu
有鱼是夏天,开门屋后绿,高女还认识,欢迎正和阿哥意。 boire bu,lire lu,voir vu,devoir dû,savoir su,prendre pris,apprendre appris,comprendre compris
既能喝,又读报,一看应知首家愚。抓学习,重理解,后面还是有捕吏。
sentir senti,croire cru,pleuvoir plu,vouloir voulu 感觉是上帝,猜到要下雨,两人头上加个玉。 attendre attendu,venir venu,répondre répondu,écrire écrit,suivre suivi
想无虑,来我女,等待回答委实愚,写信表白:“爱克丽”,跟来就是要随你。
faire fait,dire dit,écrire écrit,mettre mis,recevoir reçu,falloir fallu
做要快,说为敌,安置要秘密,接受要合序,无人应该违法律。
2. Participe Présent 现在分词 现在分词(le participe présent)构成:去掉直陈式第一人称复数的词尾-ons,另加-ant faire : nous faisons ; faisant
特殊情况:avoir-ayant ; etre-etant ; savoir-sachant 用法: 1)用作定语,紧接在被修饰词之后,相当于qui引导的从句 L'étranger cherche à trouver quelqun connaissant(=qui conaisse) à la fois francasi et l'anglais.
2)表原因、时间 Voyant(=Comme elle voit) que tout le monde est dejà assis,elle va vite à sa place. Ayant(=Comme il a) mal à la tete,il décide de rester au lit.
法语中现在分词与副动词的用法: 副动词用来修饰动词,现在分词用来修饰名词或代词;现在分词多用语笔语,口语中很少使用,而副动
词可以用于口语。 副动词(le gé rondif)构成:在现在分词前加en就构成副动词 faire : en faisant 用法: 1)时间状语,表示动作的同时性 N'oubliez pas de fermer la port en sortant.出去时别忘了关门。
Ne lis pas en mangeant. 不要以便吃饭以一边看书 2)方式、方法状语 Elle arriva en courant. 她跑来了
3)条件状语 En se levant plus tot le matin, il n'arrivera pas en retard.如果早上起的早点,他就不会迟到了。 3. Indicatif Présent 直陈式 现在时 变位方法: 第一组动词(通常为-er): Aimer : j'aime ; Tu aimes ; Il /elle aime ; Nous aimons ; Vous aimez ; Ils /elles aiment
注意一些第一组动词由于发音需要,在变位时会有所变化: 以-eler, -eter结尾的第一组动词,如appeler, jeter ,在单数所有人称,以及复数第三人称的变位中,词尾字母变为"ll","tt"。
Appeler : j'appelle ; Tu appelles ; Il /elle appelle ; Nous appelons ; Vous appelez ; Ils /elles appellent
Jeter : Je jette ; Tu jettes ; Il /elle jette ; Nous jetons ; Vous jetez ; Ils /elles jettent
以-cer, -ger结尾的第一组动词,如commencer, manger, 在复数第一人称时词尾应改为 -çons, -geons 。
Commencer : Je commence ; Tu commences ; Il /elle commence ; Nous commençons ; Vous commencez ; Ils /elles commencent Manger : Je mange ; Tu manges ; Il /elle mange ; Nous mangeons ; Vous mangez ; Ils /elles mangent
以-ayer,-oyer,-uyer结尾的第一组动词,如essayer, envoyer, ennuyer, 在单数所有人称,以及复数第三人称的变位中,词尾字母
由y变为i。
Essayer : j'essaie ; Tu essaies ; Il /elle essaie ; Nous essayons ; Vous essayez ; Ils /elles essaient
第二组动词 (通常为 -ir): Finir : Je finis ; Tu finis ; Il /elle finit ; Nous finissons ; Vous finissez ; Ils /elles finissent
例外:sortir, courir, ouvrir, servir, partir, dormir 等。 Sortir : Je sors ; Tu sors ; Il /elle sort ; Nous sortons ; Vous sortez ; Ils /elles sortent
Courir : Je cours ; Tu cours ; Il /elle court ; Nous courons ; Vous courez ; Ils /elles courent
Ouvrir : j'ouvre ; Tu ouvres ; Il /elle ouvre ; Nous ouvrons ; Vous ouvrez ; Ils /elles ouvrent Servir : Je sers ; Tu sers ; Il /elle sert ; Nous servons ; Vous servez ; Ils /elles servent
Partir : Je pars ; Tu pars ; Il /elle part ; Nous partons ; Vous partez ; Ils /elles partent
Dormir : Je dors ; Tu dors ; Il /elle dort ; Nous dormons ; Vous dormez ; Ils /elles dorment
第三组动词:不规则变化。 Être : Je suis ; Tu es ; Il /elle est ; Nous sommes ; Vous êtes ; Ils /elles sont
Avoir : j'ai ; Tu as ; Il /elle a ; Nous avons ; Vous avez ; Ils /elles ont
Aller : Je vais ; Tu vas ; Il /elle va ; Nous allons ; Vous allez ; Ils /elles vont
Faire : Je fais ; Tu fais ; Il /elle fait ; Nous faisons ; Vous faites ; Ils /elles font (contrefaire /défaire /forfaire /malfaire /méfaire/parfaire/redéfaire/refaire/satisfaire)
Voir : Je vois ; Tu vois ; Il /elle voit ; Nous voyons ; Vous voyez ; Ils /elles voient (entrevoir/prévoir/ravoir/revoir)