Solving Linearized Equations of the $N$-body Problem Using the Lie-integration Method
- 格式:pdf
- 大小:293.51 KB
- 文档页数:13

《人工智能》测试题答案测试题——人工智能原理一、填空题1.人工智能作为一门学科,它研究的对象是______,而研究的近期目标是____________ _______;远期目标是___________________。
2.人工智能应用的主要领域有_________,_________,_________,_________,_______和__________。
3.知识表示的方法主要有_________,_________,_________,_________和________。
4.产生式系统由三个部分所组成,即___________,___________和___________。
5.用归结反演方法进行定理证明时,可采取的归结策略有___________、___________、_________、_________、_________和_________。
6.宽度优先搜索对应的数据结构是___________________;深度优先搜索是________________。
7.不确定知识处理的基本方法有__________、__________、__________和__________。
8.AI研究的主要途径有三大学派,它们是________学派、________学派和________学派。
9.专家系统的瓶颈是________________________;它来自于两个阶段,第一阶段是,第二阶段是。
10.确定因子法中函数MB是描述________________________、而函数MD是描述________________________。
11.人工智能研究的主要领域有_________、_________、_________、_________、_______和__________。
12.一阶谓词逻辑可以使用的连接词有______、_______、_______和_______。

解偏微分方程组是现代数学和物理学中一个重要且具有挑战性的问题。
为了解决偏微分方程组,人们需要借助各种数值计算方法和计算工具。
solve_ivp就是其中之一。
1. 什么是偏微分方程组?偏微分方程组是描述自然界中各种现象的数学模型之一。
它广泛应用于物理学、工程学、生物学等领域。
偏微分方程组通常包括多个未知函数和其各自的导数,例如偏导数、二阶偏导数等。
求解偏微分方程组是理解和预测自然现象的重要方法之一。
2. solve_ivp是什么?solve_ivp是Python语言中一个用于求解初值问题的函数。
在解偏微分方程组时,人们通常将其转化为初值问题,然后使用solve_ivp来求解。
solve_ivp使用了诸如Runge-Kutta方法、Adams-Bashforth方法等数值计算方法,可以在计算机上高效求解各种复杂的初值问题。
3. solve_ivp的使用方法使用solve_ivp求解偏微分方程组可以分为以下几个步骤:(1)确定偏微分方程组的初值问题形式,即确定未知函数及其初值;(2)将偏微分方程组转化为初值问题;(3)使用solve_ivp函数,输入转化后的初值问题,并设定求解的时间区间和其他必要参数;(4)获得数值结果,并进行后续的分析和应用。
4. solve_ivp的优势和局限solve_ivp作为一个强大的数值计算工具,具有以下优势:(1)可以高效处理各种复杂的初值问题;(2)使用了多种高精度的数值计算方法,保证了求解的准确性和稳定性;(3)与Python科学计算库(如numpy、scipy)高度兼容,可以方便地与其他计算工具和数据进行集成。
然而,solve_ivp也存在一些局限:(1)对于一些特殊的偏微分方程组,可能需要进行额外的数值优化和调整;(2)对于高维的偏微分方程组,求解的时间和内存消耗会较大;(3)在处理非线性、非定常的偏微分方程组时,需要谨慎选择数值方法和参数。
solve_ivp作为求解偏微分方程组的重要工具之一,为人们在理论研究和工程应用中提供了便捷、高效的数值求解方法。

1.ABAQUS的UMAT一点看法:如果本构模型复杂,应力应变关系是非线性的隐式表达,就需要进行迭代,更新应力。
这就是UMAT 的最重要的任务。
那么这样一来,在给定应变增量的情况下更新应力,就必须求解应变对应力的导数,运用迭代,如N-R迭代。
这样一来,在UMAT中就需要求解两次导数。
(DDSDDE为一次)所以比较麻烦的。
对于时间相关的本构模型来说更是麻烦。
2.使用abaqus求解螺栓和螺母接触螺纹的强度所碰到的问题1.Solver problem. Zero pivot when processing D.O.F. 1 of 49 nodes. The nodes have been identified in node set warnnodesolvprobzeropiv_1_1_1_1_1.(是什么原因造成的?)2。
The system matrix has 6276 negative eigenvalues..(是什么原因造成的?)3。
1304 nodes may have incorrect normal definitions. The nodes have been identified in node set warnnodeincorrectnormal.(这个法向量错误在模型中显示为螺母内部的接触面,但我反了一下法向量还是同样错误)4。
Program is asked to invert a singular matrix.(是什么原因造成的?)2.模型就是一个螺母和螺栓之间夹一个平板的简单模型边界条件施加如下:固定螺栓的下端,在螺栓、平板、螺母之间分别建立surface to surface接触(带摩擦),然后在螺母上施加力矩,这样来求解螺栓预紧时螺纹接触部分的应力,但总是出现上述问题,请高手分析指点,谢谢!答:检查一下两个接触面之间是不是有初始的穿透;负特征值可能是因为你的初始步长太大了,接触的问题;保证模型中的每个零件在开始时有稳定的约束,可以考虑加一些软弹簧约束住;还可以用ajust使两个接触面在一开始就起上作用。

CG算法的预处理技术:、为什么要对A进行预处理:其收敛速度依赖于对称正定阵A的特征值分布特征值如何影响收敛性:特征值分布在较小的范围内,从而加速CG的收敛性特征值和特征向量的定义是什么?(见笔记本以及收藏的网页)求解特征值和特征向量的方法:Davidson方法:Davidson 方法是用矩阵( D - θI)- 1( A - θI) 产生子空间,这里D 是A 的对角元所组成的对角矩阵。
θ是由Rayleigh-Ritz 过程所得到的A的近似特征值。
什么是子空间法:Krylov子空间叠代法是用来求解形如Ax=b 的方程,A是一个n*n 的矩阵,当n充分大时,直接计算变得非常困难,而Krylov方法则巧妙地将其变为Kxi+1=Kxi+b-Axi 的迭代形式来求解。
这里的K(来源于作者俄国人Nikolai Krylov姓氏的首字母)是一个构造出来的接近于A的矩阵,而迭代形式的算法的妙处在于,它将复杂问题化简为阶段性的易于计算的子步骤。
如何取正定矩阵Mk为:Span是什么?:设x_(1,)...,x_m∈V ,称它们的线性组合∑_(i=1)^m?〖k_i x_i \|k_i∈K,i=1,2...m〗为向量x_(1,)...,x_m的生成子空间,也称为由x_(1,)...,x_m张成的子空间。
记为L(x_(1,)...,x_m),也可以记为Span(x_(1,)...,x_m)什么是Jacobi迭代法:什么是G_S迭代法:请见PPT《迭代法求解线性方程组》什么是SOR迭代法:什么是收敛速度:什么是可约矩阵与不可约矩阵?:不可约矩阵(irreducible matrix)和可约矩阵(reducible matrix)两个相对的概念。
定义1:对于n 阶方阵A 而言,如果存在一个排列阵P 使得P'AP 为一个分块上三角阵,我们就称矩阵A 是可约的;否则称矩阵A 是不可约的。
定义2:对于n 阶方阵A=(aij) 而言,如果指标集{1,2,...,n} 能够被划分成两个不相交的非空指标集J 和K,使得对任意的j∈J 和任意的k∈K 都有ajk=0, 则称矩阵 A 是可约的;否则称矩阵A 是不可约的。
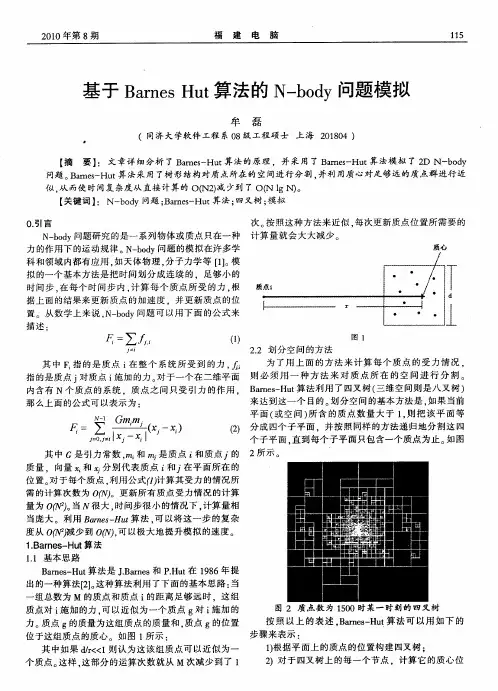

第 62 卷第 5 期2023 年9 月Vol.62 No.5Sept.2023中山大学学报(自然科学版)(中英文)ACTA SCIENTIARUM NATURALIUM UNIVERSITATIS SUNYATSENI基于Tikhonov正则化改进的IHB法求解Mathieu-Duffing系统多重解*王德亮1,2,刘济科1,刘广1,21. 中山大学航空航天学院,广东深圳 5181072. 深圳市智能微小卫星星座技术与应用重点实验室,广东深圳 518107摘要:增量谐波平衡法(IHB法)是研究强非线性振动系统的一种半数值半解析方法,然而已有研究表明,在求解含多重解的系统时该方法的收敛性强烈地依赖于初值的选择。
Tikhonov正则化常被用于优化问题中来解决可能出现的病态问题。
文章通过在原始的IHB法中引入Tikhonov正则化,提出一种改进的IHB法(TIHB法)来求解具有多重解的Mathieu-Duffing系统。
结果表明,改进的TIHB法可以快速、高效地获得系统的多个稳定或不稳定解,且算法的收敛性能要远远优于原始的IHB法。
关键词:非线性振动;IHB法;Tikhonov正则化;多重解中图分类号:V21 文献标志码:A 文章编号:2097 - 0137(2023)05 - 0078 - 07Multiple solutions of the Mathieu-Duffing system obtainedby the improved IHB method based on Tikhonov regularizationWANG Deliang1,2, LIU Jike1, LIU Guang1,21. School of Aeronautics and Astronautics,Sun Yat-sen University, Shenzhen 518107, China2. Shenzhen Key Laboratory of Intelligent Microsatellite Constellation, Shenzhen 518107, ChinaAbstract:The incremental harmonic balance method (IHB method) is a semi-numerical and semi-ana‐lytical method for strongly nonlinear dynamic systems. However, previous studies have shown that the convergence performance of the original IHB method in solving systems with multiple solutions strong‐ly depends on the selection of initial values. The Tikhonov regularization is often used in optimization problems to solve potential ill-posed problems. In this paper, by incorporating the Tikhonov regulariza‐tion into the original IHB method, an improved IHB method (TIHB method) is proposed to obtain the multiple solutions of the Mathieu-Duffing system. The results show that the improved TIHB method can obtain the stable and unstable solutions of the Mathieu-Duffing system quickly and efficiently, and the convergence performance of the TIHB method is much better than the original IHB method.Key words:nonlinear vibration; IHB method; Tikhonov regularization; multiple solution现实中的各种振动系统都含有非线性因素(陈予恕,1992;陈树辉,2007;Amabili,2008)。

broyden 法Broyden方法:数值计算中的非线性方程求解方法引言在数值计算中,非线性方程的求解一直是一个重要的问题。
非线性方程在各个科学领域中广泛存在,例如在物理学、经济学、工程学和生物学等领域中。
为了解决这一问题,数学家们提出了许多方法。
其中之一就是Broyden方法,它是一种迭代算法,能够有效地求解非线性方程组。
Broyden方法的原理Broyden方法是通过求解雅可比矩阵的逆来进行迭代的。
具体来说,假设我们要求解一个非线性方程组F(x)=0,其中F(x)是一个向量函数,x是未知变量的向量。
Broyden方法的关键思想是利用已知的解向量和函数值来逼近雅可比矩阵的逆。
具体地说,我们假设已知一个初始矩阵B0作为雅可比矩阵的逆的近似。
然后,我们可以根据以下公式来计算下一个近似矩阵Bk+1:Bk+1 = Bk + (s - Bk y) (s^T Bk) / (s^T Bk y)其中,s是解向量的增量,即s = xk+1 - xk,y是函数值的增量,即y = F(xk+1) - F(xk)。
通过迭代计算,我们可以逐渐改进对雅可比矩阵逆的近似,从而得到逼近方程组解的序列{xk}。
Broyden方法的优势和应用相对于其他非线性方程求解方法,Broyden方法具有一些明显的优势。
首先,Broyden方法无需求解雅可比矩阵的矩阵方程,避免了对方程求解求导等复杂的计算。
其次,Broyden方法在迭代过程中能够快速收敛到解,尤其是对于初始矩阵的选择较好的情况下。
Broyden方法在众多领域中有着广泛的应用。
在物理学中,Broyden方法常用于求解多体问题中的非线性方程组,如经典力学和量子力学中的方程组。
在经济学中,Broyden方法可以用于计算经济模型中的均衡解。
在工程学中,Broyden方法可以用于求解复杂的工程系统中的非线性方程组。
在生物学中,Broyden方法可以用于建模和求解生物过程中的非线性方程组。


Lyapunov-Schmidt方法是一种用于非线性方程组的求解的数值方法。
它是由俄罗斯数学家Aleksandr Lyapunov和德国数学家Ernst Schmidt分别在19世纪和20世纪提出的。
这种方法在处理非线性问题时非常有效,并且在应用数学和工程领域得到了广泛的应用。
Lyapunov-Schmidt方法的核心思想是将原始的非线性方程组转化成一系列线性方程组,从而简化求解过程。
这种方法的优势在于可以通过有限步骤来逼近非线性方程组的解,从而大大提高了求解效率。
下面我们将详细介绍Lyapunov-Schmidt方法的原理和应用。
1. Lyapunov-Schmidt方法的原理Lyapunov-Schmidt方法的原理是通过引入一组正交归一的特征函数,将原始的非线性方程组转化为一系列正交归一的线性方程组。
这样一来,原始的非线性方程组就被分解成了一系列互相独立的线性方程组,从而使得求解过程变得更加简单和高效。
2. Lyapunov-Schmidt方法的应用Lyapunov-Schmidt方法在科学和工程领域有着广泛的应用。
比如在物理学中,通过Lyapunov-Schmidt方法可以求解复杂的非线性波动方程,从而对物质的运动和变形进行研究。
在工程领域,Lyapunov-Schmidt方法可以用于求解具有非线性特性的结构力学问题,如弹性体的变形和弹性波的传播等。
3. 使用案例我们以一个简单的非线性方程组为例来说明Lyapunov-Schmidt方法的求解过程。
假设我们有一个非线性方程组:f(x, y) = 0g(x, y) = 0我们希望求解这个方程组的解。
我们可以通过Lyapunov-Schmidt方法将原始的非线性方程组转化为一系列正交归一的线性方程组:Φ1(x, y) = 0λ1(Φ1x + Φ1y) = 0Φ2(x, y) = 0λ2(Φ2x + Φ2y) = 0...我们可以通过求解这一系列线性方程组来逼近原始的非线性方程组的解。


newmarkbeta法-回复什么是newmarkbeta法?Newmarkbeta法,也被称为Wilson-Newmark法,是一种数值积分方法,用于求解结构动力学问题。
它是基于普通微分方程的数值求解方法之一,适用于求解线性和非线性、自由和强迫响应的结构动力学问题。
该方法基于Newmark积分方法,考虑了质量矩阵和刚度矩阵对结构响应的影响,通过引入一个积分参数beta,使得在不同的参数设定下可以得到不同阶数的数值积分方法。
注意事项:在使用Newmarkbeta法时,需要明确一些注意事项:1. 时间步长的选择:时间步长需要根据所研究的问题和模型的特性来进行选择。
通常情况下,较小的时间步长可以提高精度,但也增加了计算量。
如果时间步长选择过大,可能会导致数值解的不稳定性。
2. 弛豫因子的选择:在Newmarkbeta法中,引入了一个松弛因子gamma来平衡速度和加速度的权重。
gamma为0.5时,等效于中点积分法。
gamma为0时,等效于显式向前差分法。
根据所研究问题的稳定性和精度要求,可以选择不同的gamma值。
3. 初始条件的设定:在数值解求解之前,需要设定初始条件,即结构的初始位移和速度。
这些初始条件将影响数值解的准确性和稳定性。
通常情况下,可以根据结构的静态平衡状态设定初始条件。
数值解求解步骤:下面将一步一步介绍使用Newmarkbeta法求解结构动力学问题的步骤:步骤1:建立结构模型首先,需要根据所研究的结构问题建立相应的有限元模型。
这包括定义结构的几何形状、材料性质和边界条件等。
步骤2:离散化将结构模型离散化,将结构划分成一系列有限元单元。
对于每个有限元单元,可以根据其几何形状和材料性质计算出相应的刚度矩阵和质量矩阵。
步骤3:时间积分将时间划分成一系列离散时间步长。
通过使用Newmarkbeta法中的数值积分公式,可以迭代计算每个时间步长内的结构响应。
步骤4:计算每个时间步长内的位移和速度根据Newmarkbeta法的数值积分公式,可以计算出每个时间步长内的位移和速度。
一、介绍dpm solverdpm solver是一种用于求解常微分方程的数值方法,它可以帮助研究人员和工程师快速准确地求解各种不同类型的常微分方程。
该方法基于离散粒子模型(Discrete Particle Model),通过对微分方程进行离散化处理,将其转化为一系列代表系统状态的离散数据点,从而实现对微分方程的数值求解。
二、dpm solver的原理1. 离散粒子模型离散粒子模型是dpm solver的核心原理,它将连续的微分方程转化为离散的数据点,通过对这些数据点进行数值计算,来模拟系统的演化过程。
在离散粒子模型中,系统的状态由一系列离散的粒子表示,每个粒子代表系统在某一时刻的状态,通过对粒子之间相互作用的模拟,可以得到系统的演化轨迹,从而求解微分方程。
2. 数值计算使用dpm solver求解微分方程时,需要进行数值计算来模拟系统的演化过程。
数值计算的核心是根据微分方程的离散化表示,通过迭代计算得到系统在每个离散时间点的状态,从而得到系统的演化轨迹。
在数值计算过程中,需要考虑数值稳定性、精度和计算效率等因素,以保证求解结果的准确性和可靠性。
三、dpm solver的应用1. 工程领域dpm solver在工程领域具有广泛的应用,可以用于求解各种与工程问题相关的微分方程。
例如在力学领域,可以用dpm solver来模拟刚体、弹性体、流体等系统的运动和变形过程;在热传导领域,可以用dpm solver来求解热传导方程,模拟材料的温度分布和热传输过程;在控制领域,可以用dpm solver来求解动力学方程,设计系统的控制策略等。
2. 科学研究除了工程领域,dpm solver还在科学研究中得到了广泛的应用。
例如在物理学领域,可以用dpm solver来模拟各种物理系统的演化过程,研究其性质和行为规律;在生物学领域,可以用dpm solver来模拟生物体内部各种生理过程,研究细胞、组织和器官的功能。
第四章 抛物型微分方程有限差分法1设已知初边值问题22, 01, 0<(,0)sin , 01(0,)(1,)0, 0 u ux t t x u x x x u t u t t T π⎧∂∂=<<⎪∂∂⎪⎪=≤≤⎨⎪==≤≤⎪⎪⎩T ≤, 试用最简显格式求上述问题的数值解。
取h=0.1,r=0.1.0 1/10 2/10 … 1 T 2τ τt解: 1.矩形网格剖分区域. 取空间步长1, 时间2510h =0.00τ=以及0.01τ=的矩形网格剖分区域, 用节点)表示坐标点(,j k (,)(,)j k x t jh k τ=, 0,1,...1/; 0,1,...,/j h k T τ==, 如图所示.显然, 我们需要求解这(1/1)(/1)h T τ+×+个点对应的函数值. 事实上由已知初边界条件蓝标附近的点可直接得到, 所以只要确定微分方程的解在其它点上的取值即可. 沿用记号[]k(,)j j k u x t =。
u 2. 建立差分格式, 对于11,...1; 0,1,...,1Tj k hτ=−=−, 用向前差商代替关于时间的一阶偏导数, 用二阶中心差商代替关于空间的二阶偏导数, 则可定义最简显格式:1122k k k k k1jj j j u u u u u h ++−+=. 变形j τ−−有:1112(12) (k k k kj j j j u ru r u ru r h τ+−+=+−+=(4.1)用向后差商代替关于时间的一阶偏导数, 用二阶中心差商代替关于空间的二阶偏导数, 则可定义最简显格式最简隐格式:111122k k k k k j jj j j u u u u u h τ++++−−+=11+−1kj +,变形有:1111(12) k k k j j j ru r u ru u ++−−−++−= (4.2)(4.1)*0.5+(4.2)*0.5得CN 格式为:111112222k k k k k k k k j jj j j j j j u u u u u u u u h τ+++−+−−++−+=111++−1kj +x x变形有:111111(22)(22) k k k k k j j j j j ru r u ru ru r u ru ++−−+−−++−=+−+ (4.3)3 初边界点差分格式处理.对于初始条件u x (,0)sin , 01=π≤≤h 离散为(4.4)0sin 0,1,...1/j u jh j π==对于边界条件离散为(0,)(1,)0, 0 u t u t t T ==≤≤00 0,1,.../k k N u u k T τ===(4.5)总结: 联立方程(4.1)(4.4)(4.5)得到已知问题的最简显格式差分方程组:11100(12)1 1,...1; 0,1,...,1sin 0,1,...1/0 0,1,.../k k k k j j j j jk k N u ru r u ru T j k h u jh j h u u k T τπτ+−+⎧=+−+⎪⎪=−=−⎪⎨⎪==⎪⎪===⎩ 联立方程(4.2)( 4.4)( 4.5)得到已知问题的最简隐格式差分方程组:1111100(12) 1 1,...1; 0,1,...,1sin 0,1,...1/0 0,1,.../k k k k j j j j jk k N ru r u ru u T j k h u jh j h u u k T τπτ++−−+⎧−++−=⎪⎪=−=−⎪⎨⎪==⎪⎪===⎩ 联立方程(4.3)( 4.4)( 4.5)得到已知问题的CN 格式差分方程组:11111100(22)(22) 1 1,...1; 0,1,...,1sin 0,1,...1/0 0,1,.../k k k k k j j j j j jk k N ru r u ru ru r u ru T j k h u jh j h u u k T τπτ++−−+−⎧−++−=+−+⎪⎪=−=−⎪⎨⎪==⎪⎪===⎩1k j + 4 求解并显示结果利用软件计算(Matlab)如上最简显格式差分方程组.h=1/10;tau=0.0025;T=0.5; r=tau/h^2;M=1/h+1;N=T/tau+1; u=zeros(M,N);for m=1:Mu(m,1)=sin((m-1)*h*pi); endu(1,1:N)=0;u(M,1:N)=0;for n=1:N-1for m=2:M-1u(m,n+1)=r*(u(m+1,n)+u(m-1,n))+(1-2*r)*u(m,n); end end u=u’ 这样我们就计算出不同时刻不同位置k t j x 对应的函数值(,)j k u x t 取tau=0.0025, 即r=0.25绘图, 取tau=0.01, r=1再绘图,如图()图4.2 习题1数值解图示(左r=0.25, 右r=1)2.试构造初边值问题 ()()()()(), 0.51, 0,,0, 0.51,0.5,0, 1,0.51,, 0u u x x x T t x x u x x x u ⎪∂u t t u t t T x ϕ⎧∂∂∂⎛⎞=<<<≤⎜⎟⎪∂∂∂⎝⎠⎪⎪=≤≤⎨⎪==−≤≤⎪∂⎩的显格式,并给出其按最大范数稳定的充分条件。
关于序列二次规划(SQP)算法求解非线性规划问题研究兰州大学硕士学位论文关于序列二次规划(SQP)算法求解非线性规划问题的研究姓名:石国春申请学位级别:硕士专业:数学、运筹学与控制论指导教师:王海明20090602兰州大学2009届硕士学位论文摘要非线性约束优化问题是最一般形式的非线性规划NLP问题,近年来,人们通过对它的研究,提出了解决此类问题的许多方法,如罚函数法,可行方向法,Quadratic及序列二次规划SequentialProgramming简写为SOP方法。
本文主要研究用序列二次规划SOP算法求解不等式约束的非线性规划问题。
SOP算法求解非线性约束优化问题主要通过求解一系列二次规划子问题来实现。
本文基于对大规模约束优化问题的讨论,研究了积极约束集上的SOP 算法。
我们在约束优化问题的s一积极约束集上构造一个二次规划子问题,通过对该二次规划子问题求解,获得一个搜索方向。
利用一般的价值罚函数进行线搜索,得到改进的迭代点。
本文证明了这个算法在一定的条件下是全局收敛的。
关键字:非线性规划,序列二次规划,积极约束集Hl兰州人学2009届硕二t学位论文AbstractNonlinearconstrainedarethemostinoptimizationproblemsgenericsubjectsmathematicalnewmethodsareachievedtosolveprogramming.Recently,Manyasdirectionit,suchfunction,feasiblemethod,sequentialquadraticpenaltyprogramming??forconstrainedInthisthemethodspaper,westudysolvinginequalityabyprogrammingalgorithm.optimizationproblemssequentialquadraticmethodaofSQPgeneratesquadraticprogrammingQPsequencemotivationforthisworkisfromtheofsubproblems.OuroriginatedapplicationsinanactivesetSQPandSQPsolvinglarge-scaleproblems.wepresentstudyforconstrainedestablishontheQPalgorithminequalityoptimization.wesubproblemsactivesetofthesearchdirectionisachievedQPoriginalproblem.AbysolvingandExactfunctionsaslinesearchfunctionsubproblems.wepresentgeneralpenaltyunderobtainabetteriterate.theofourisestablishedglobalconvergencealgorithmsuitableconditions.Keywords:nonlinearprogramming,sequentialquadraticprogrammingalgorithm,activesetlv兰州大学2009届硕士学位论文原创性声明本人郑重声明:本人所呈交的学位论文,是在导师的指导下独立进行研究所取得的成果。
ANSYS软件错误锦集1 在Ansys中出现“Shape testing revealed that 450 of the 1500 new or modified elements violate shape warning limits.”,是什么原因造成的呢?单元网格质量不够好,尽量用规则化网格,或者再较为细密一点。
2 在Ansys中,用Area Fillet对两空间曲面进行倒角时出现以下错误:Area 6 offset could not fully converge to offset distance 10. Maximum error between the two surfaces is 1% of offset distance.请问这是什么错误?怎么解决?其中一个是圆柱接管表面,一个是碟形封头表面。
ansys的布尔操作能力比较弱。
如果一定要在ansys里面做的话,那么你试试看先对线进行倒角,然后由倒角后的线形成倒角的面。
建议最好用UG、PRO/E这类软件生成实体模型然后导入到ansys。
3 在Ansys中,出现错误“There are 21 small equation solver pivot terms。
”,是否是在建立接触contact时出现的错误?不是建立接触对的错误,一般是单元形状质量太差(例如有接近零度的锐角或者接近180度的钝角)造成small equation solver pivot terms4 在Ansys中,出现警告“SOLID45 wedges are recommended only in regions of relatively low stress gradients.”,是什么意思?"这只是一个警告,它告诉你:推荐SOLID45单元只用在应力梯度较低的区域。
它只是告诉你注意这个问题,如果应力梯度较高,则可能计算结果不可信。
"5 ansys向adams导的过程中,出现如下问题“There is not enough memory for the Sparse Matrix Solver to proceed.Please shut down other applications that may be running or increase the virtual memory on your system and return ANSYS.Memory currently allocated for the Sparse Matrix Solver=50MB.Memory currently required for the Sparse Matrix Solver to continue=25MB”,是什么原因造成的?不清楚你ansys导入adams过程中怎么还需要使用Sparse Matrix Solver(稀疏矩阵求解器)。
lyapunov方程
拉普拉斯-马尔可夫方程首先把系统动态行为描述为一个非线性方程,然后把它转换成一个线性的状态方程。
如果把非线性方程分解为多个线性方程,那么拉普拉斯-马尔可夫方程就可以被写成一个线性状态方程:X(t+1)=AX(t)+B其中,X(t)是一个n维向量,表示系统状态在t时刻的变化,A是n×n维矩阵,表示系统的动态行为,B是n维向量,表示系统的外部输入。
拉普拉斯-马尔可夫方程也可以用来解决一个更复杂的问题,称为“Lyapunov方程”。
Lyapunov方程是一种非线性系统理论中的一种工具,它通过求解一个特殊的矩阵方程来描述系统的稳定性,也就是描述系统动态行为是否稳定。
Lyapunov 方程是一个不等式,它要求系统的状态变量满足一定的关系,这些关系可以通过拉普拉斯-马尔可夫方程求解。
arXiv:0707.3454v1 [astro-ph] 23 Jul 2007Mon.Not.R.Astron.Soc.000,1–13(2007)Printed1February2008(MNLATEXstylefilev2.2)SolvingLinearizedEquationsoftheN-bodyProblemUsingtheLie-integrationMethod
Andr´asP´al1⋆and´AronS¨uli11DepartmentofAstronomy,Lor´andE¨otv¨osUniversity,P´azm´anyP´eters´et´any1/A,BudapestH-1117,Hungary
Accepted2007July18.Received2007July13;inoriginalform2007May25ABSTRACTSeveralintegrationschemesexitstosolvetheequationsofmotionoftheN-bodyproblem.TheLie-integrationmethodisbasedontheideatosolveordinarydifferen-tialequationswithLie-series.Inthe1980sthismethodwasappliedfortheN-bodyproblembygivingtherecurrenceformulaforthecalculationoftheLie-terms.TheaimofthisworksistopresenttherecurrenceformulaeforthelinearizedequationsofmotionofN-bodysystems.Weprovealemmawhichgreatlysimplifiesthederiva-tionoftherecurrenceformulaeforthelinearizedequationsiftherecurrenceformulaefortheequationsofmotionsareknown.TheLie-integratoriscomparedwithotherwell-knownmethods.TheoptimalstepsizeandorderoftheLie-integratorarecalcu-lated.Itisshownthatafine-tunedLie-integratorcanbe30%-40%fasterthanotherintegrationmethods.
Keywords:celestialmechanics–methods:numerical–methods:N-bodysimula-tions
1INTRODUCTIONTheclassicalproblemsofcelestialmechanicsaredescribedbyasystemofordinarydifferentialequations(ODEs).TheinvestigationofthemotionsintheSolarSystem,exoplan-etarysystems,satellitesaroundtheEarthorotherceles-tialobjectsarebasedonthesolutionsofsuchODEs.How-ever,severalmodernanalysis,includingmanychaosdetec-tionmethodsrequiretosolvethelinearizedequationsoftheproblem.TheintegrationmethodbasedontheLie-series(Gr¨obner&Knapp1967)iswidelyusedincelestialmechan-icstosolveODEs(seeHanslmeier&Dvorak(1984),here-afterH&Dandarticlesreferringtoit).ThebasisofthismethodistogeneratethecoefficientsoftheTaylorexpan-sionofthesolutionbyusingrecurrencerelations.Theprin-cipalapplication,i.e.theintegrationoftheN-bodyproblemisdescribedindetailsinH&D.
1.1Lie-integrationHerewesummarizethekeypointsofthismethodofnumer-icalintegration,usingalmostidenticalnotationsasusedbyHanslmeier&Dvorak(1984).Letuswritethedifferentialequationtobesolvedas
˙xi=fi(x),(1)
⋆E-mail:apal@szofi.elte.hu(AP);a.suli@astro.elte.hu(´AS)
wherex≡(x1,...,xN)isanR→RNandf≡(f1,...,fN)isanRN→RNcontinuousfunctionandNisthedimensionofthevectorxandthevectorspacewherefmapsfromandmapsto.Letusintroducethedifferentialoperator
Di:=∂
∂xi
,(3)
whichisknownastheLie-derivationorLie-operator.L0isalineardifferentialoperatorandonecanapplyLeibniz’srule,
L0(ab)=aL0(b)+bL0(a),(4)whereaandbareRN→RNdifferentiablefunctions.Itcaneasilybeproventhatthesolutionofequation(1)atagiveninstancet+∆tisformally
x(t+∆t)=exp(∆t·L0)x(t),(5)where
exp(∆t·L0)=∞Xk=0∆tkk! NX
i=1fiDi!k.(6)
ThemethodofLie-integrationisfiniteapproximationofthesumintheright-handsideofequation(6),uptotheorderofM,namely2A.P´aland´A.S¨ulix(t+∆t)≈ MXk=0∆tkk!“Lk0x(t)”.(7)Theproofofequation(5)andotherrelatedpropertiesoftheLie-derivationcanbefoundinGr¨obner&Knapp(1967)orHanslmeier&Dvorak(1984).InspiteofthefactthattheLie-derivativescanana-lyticallybecalculateduptoarbitraryorder,theformulaeyieldedbytheseexpansionsarehighlycomplicatedevenifallkindsofnewvariablesareintroduced(seee.g.equations(19d)or(19e)inH&Datpage204).Adefinitelymoreeffi-cientwaytoevaluatetheLie-derivativesistofindasetofrecurrencerelations.Theserelationsallowustoexpressthe(n+1)thLie-derivative,e.g.Ln+1xasthefunctionofthederivativeswithlowerorder,namelyLjxwhere0jn.Theinitializationofsucharecurrencerelationisevident,becauseL0x≡x.Wenotethatinseveralapplications,well-chosenauxiliaryvariableshavetobeintroducedtogainacompactsetofrecurrencerelationswhichcanefficientlybeevaluated.
1.2TheimportanceoflinearizedequationsWiderangeofproblemsrelatedtocelestialmechanicsre-quiretosolvesimultaneouslythelinearizedformoftheorig-inalequationstoo.Thenumerousexperimentsconductedinthelastdecadesshowthatchaoticbehaviouristypicalandalreadyoccursinsimplebutnonlinearsystems.Thisfind-ingthrowscompletelynewlightuponthesesystemsandthestudyofchaoticbehaviourbecameofhighconcern.Amajorpartofthefrontlineresearchfocusesonthestructureofthephasespace,thereforetheproblemtoseparateorderedandchaoticmotioninsystems,whichpossesonlyafewdegreesoffreedomandaredescribedbyODEs,hasbecomeafun-damentaltaskinawideareaofmodernresearch.Thephasespaceofthesenonlinearsystemscannotbedescribedbytheknownmathematicaltools.Tomapthephasespaceandstudythechaoticbehaviourofagivensystemfastandreli-ablenumericaltoolsareneeded.Thesetoolsareextremelyusefulinthosecaseswhentheinspecteddynamicalsystemhasmorethantwodegreesoffreedomandaccordinglyitsphasespacecannotbeexploredinadirectwayortheclas-sicalmethodofsurfaceofsection(SoS)cannotbeappliedwhichiswidelyusedinthecaseofconservativesystemswithtwodegreesandfreedom.ThebasicideaofthemethodofSoSwasinventedbyPoincar´e(1899)anditsapplicationwasrenewedbyH´enon&Heiles(1964).ThemathematicalfoundationofthetheoryofLya-punovCharacteristicExponents(LCEs)isapproximatelyofthesameageastheSoSandaroseprogressivelyinthelit-erature.TheuseofsuchexponentsdatesbacktoLyapunov(1907),butwasfirstappliedbyOseledec(1968)tocharac-terizetrajectories.H´enon&Heiles(1964)foundthatinanintegrableregionofthephasespaceofadynamicalsystemnearbyorbitsdivergelinearlywhereasinachaoticregiontheydivergeexponentially.TheLCEsexpressthesefactsinapreciseformandmanypapersweredevotedtotheappli-cationofLCEsinseveralnonlinearproblems.Unfortunatelybothmethodshaveaseriousdrawback.TocomputetheLCEstheequationshavetointegrateforin-finity,whichisnumericallyimpossible.ThemethodofSoSbecomeshardtohandleandgreatlydeceivingforsystems