英语语法之情态动词的用法分享(一)
- 格式:pdf
- 大小:452.74 KB
- 文档页数:9

英语情态动词用法拓展(初)知识定位纵观近几年全国各地中考英语试题中的动词类,总会考到情态动词。
情态动词是一种本身有一定的词义,表示说话人的情绪、态度或与语气的动词,但不能单独作谓语,只能和其他动词原形构成谓语。
无人称和数的变化,情态动词后面跟的动词需用原形,否定式构成是在情态动词后面加“not”。
个别情态动词有现在式和过去式两种形式,过去式用来表达更加客气,委婉的语气, 时态性不强,可用于过去,现在或将来。
情态动词属非及物动词,故没有被动语态。
知识梳理情态动词特点:情态动词无人称和数的变化,情态动词后面跟的动词须用原形,否定式构成是在情态动词后面加"not"。
个别情态动词有现在式和过去式两种形式,过去式用来表达更加客气,委婉的语气,时态性不强,可用于过去,现在或将来。
情态动词属非及物动词,故没有被动语态。
He could be here soon.他很快就来。
We can't carry the heavy box.我们搬不动那箱子。
I'm sorry I can't help you.对不起,我帮不上你。
基本助动词与情态助动词最主要的区别之一是:基本助动词本身没有词义,而情态助动词则有自己的词义,能表示说话人对有关动作或状态的看法,或表示主观设想:What have you been doing since? (构成完成进行体,本身无词义)I am afraid I must be going. (一定要)You may have read some account of the matter. (或许已经)除此之外,情态助动词还有如下词法和句法特征:1)除ought 和used 以外,其他情态动词后面只能接不带to 的不定式。
如果我们把ought to和used to 看做是固定词组的话,那么,所有情态动词无一例外地只能接不带to 的不定式:We used to grow beautiful roses.我们过去常常种这种漂亮的玫瑰花I asked if he would come and repair my television set.我问他是否来修我的电视机2)情态助动词在限定动词词组总是位居第一:They need not have been punished so severely.3)情态助动词用于第三人称单数现在时的时候,没有词形变化,即其词尾无-s 形式:She dare not say what she thinks.4)情态动词没有非限定形式,即没有不定式和分词形式,也没有相应的动名词:Still,she needn't have run away.5)情态助动词的“时”的形式并不是时间区别的主要标志。

情态动词的用法总结情态动词是一种非常重要的英语语法结构,它们可以表达不同的句子语意,有助于我们更准确地表达自己的情感。
其用法乍一看有些复杂,但其实它也只是英语中一种普通的语法结构,只要理解它的用法规则,就可以轻松地学会使用它了。
本文将对情态动词的用法进行总结,帮助读者更好地理解情态动词的用法。
情态动词是一类不及物动词,它们不能单独使用,而是需要和句子的谓语动词一起使用。
它们在句子中起着勾画语气的作用。
其用法可以分为以下几种:一、表示能力。
情态动词canbe able to以用来表示能力,意为“能够”,强调说话者的能力。
例如:I can speak English.会说英语。
二、表示推测。
情态动词may, might, must等用来表示推测,意为“可能”,强调的是说话者的推测。
例如:He may be late. 他可能会迟到。
三、表示请求或允许。
情态动词can, could, may和might可以用来表示请求或允许,意为“请求允许”,强调的是说话者的请求。
例如:Can I borrow your pen?可以借你的钢笔吗?四、表示义务或建议。
情态动词should, ought to和have to 可以用来表示义务或建议,意为“应该”,强调的是说话者的情感。
例如:You should finish your homework. 你应该完成家庭作业。
五、表示抑制或否定。
情态动词 cannot, cannot, won可以用来表示抑制或否定,意为“不能”或“不会”,强调的是说话者的态度。
例如:He won do it. 他不会去做。
六、表示猜测。
情态动词 shouldought to可以用来表示猜测,意为“可能”,强调的是说话者的推测。
例如:She should be here soon.应该很快就到了。
情态动词是一种非常重要的英语语法结构,它们拥有多种用法,可以丰富我们句子的语言表达,有助于说话者更准确地表达自己的意思和情感。

【英语语法】情态动词can的用法(附练习及答案)一、can是情态动词情态动词,本身有一定的词义,但不能独立作谓语,不以人称和数量的变化而变化,后接动词原形,也就是说情态动词和动词原形一起构成谓语。
我们常见的情态动词有:can (could),may (might),must,will (would)等。
接下来,我们就来学习一下情态动词"can"的用法。
二、情态动词can具体用法1)表示"能、会",指脑力或体力方面的"能力"。
I can speak English. 我会讲英语。
Jim can swim but I can't. 吉姆会游泳,但我不会。
2)表示"可能",常用于否定句或疑问句中,指某种可能性。
Han Mei can't be in the classroom. 韩梅不可能在教室里。
Can he come here today, please? 请问他今天能到这里来吗?3)表示"可以",常用于口语中,指许可或请求做某事。
Can I have a cup of tea, please? 请问我可以喝一杯茶吗?You can go out. 你可以出去了。
补充:①can在口语中可以代替may,表示许可或可以。
②can't在口语中代替mustn't时,表示禁止或不准。
You can't play football in the street. 不准在马路上踢足球。
③情态动词can的过去式could,用于现在时,可使语气更委婉、更客气。
Could you help me with my English? 你能帮助我学习英语吗?三、情态动词can的基本句型1)肯定句型为:主语+can+动词原形+其它。
They can play basketball. 他们能打篮球。

情态动词英语语法知识点情态动词,本身有一定的词义,表示语气的单词。
但是不能独立作谓语,只能和动词原形一起构成谓语。
这次小编给大家整理了情态动词英语语法知识点,供大家阅读参考。
1 情态动词的语法特征1) 情态动词不能表示正在发生或已经发生的事情,只表示期待或估计某事的发生。
2) 情态动词除 ought 和 have 外,后面只能接不带 to 的不定式。
3) 情态动词没有人称,数的变化,即情态动词第三人称单数不加-s。
4) 情态动词没有非谓语形式,即没有不定式,分词,等形式。
1 情态动词的语法特征1) 情态动词不能表示正在发生或已经发生的事情,只表示期待或估计某事的发生。
2) 情态动词除 ought 和 have 外,后面只能接不带 to 的不定式。
3) 情态动词没有人称,数的变化,即情态动词第三人称单数不加-s。
4) 情态动词没有非谓语形式,即没有不定式,分词,等形式。
2 比较 can 和 be able to1)can could 表示能力;可能 (过去时用 could),只用于现在式和过去式(could)。
be able to 可以用于各种时态。
They will be able to tell you the news soon. 他很快就能告诉你消息了。
2)只用 be able toa. 位于助动词后。
b. 情态动词后。
c. 表示过去某时刻动作时。
d. 用于句首表示条件。
e. 表示成功地做了某事时,只能用 was/were able to,不能用 could。
He was able to flee Europe before the war broke out. = He managed to flee Europe before the war broke out.注意:could 不表示时态1)提出委婉的请求, (注意在回答中不可用 could)。
--- Could I have the television on?--- Yes, you can. / No, you can't.2)在否定,疑问句中表示推测或怀疑。

高中英语语法总结:情态动词和虚拟语气考向1 情态动词一、 can, could与be able to1. 表示能力(体力、知识、技能)。
☞Can you lift this heavy box?(体力)☞Mary can speak three languages.(知识)☞Can you skate?(技能)此时可用be able to代替。
can只有一般现在时和一般过去式;而be able to则有更多的时态。
☞I’ll not be able to come this afternoon.当表示"经过努力才得以做成功某事"时应用be able to,不能用can。
如:☞He was able to go to the party yesterday evening in spite of the heavy rain.2. 表示请求和允许。
☞—Can I go now?—Yes, you can. / No, you can’t. 此时可与may互换。
在疑问句中还可用could, might代替,不是过去式,只是语气更委婉,不能用于肯定句和答语中。
☞—Could I come to see you tomorrow?—Yes, you can. (No, I’m afraid not.)3. 表示客观可能性(客观原因形成的能力)。
☞They’ve changed the timetable, so we can go by bus instead. This hall can hold 500 people at least.4. 表示推测(惊讶、怀疑、不相信的态度),用于疑问句、否定句和感叹句中。
☞Can this be true?☞This can’t be done by him. How can this be true?二、 may, might1. 表示请求和允许。
might比 may语气更委婉,而不是过去式。

情态动词在从句中的用法在英语语法中,情态动词是一类非常重要的词,它们能够表达说话人的态度、情感、推测、可能性等。
而当情态动词出现在从句中时,其用法会变得更加复杂和多样。
本文将详细探讨情态动词在从句中的各种用法。
首先,我们来了解一下常见的情态动词有哪些。
常见的情态动词包括 can、could、may、might、must、shall、should、will、would 等。
这些情态动词在不同的语境中具有不同的含义和用法。
在宾语从句中,情态动词的用法常常与主句的时态和语气相关。
例如,当主句是一般现在时,宾语从句中的情态动词可以根据具体情况使用不同的形式。
如果表示客观事实或普遍真理,宾语从句中可以使用 can、may 等。
比如,“The teacher says that water can boil at 100 degrees Celsius”(老师说水在 100 摄氏度时会沸腾。
)当主句是过去时态时,宾语从句中的情态动词也要相应地变为过去式。
比如,“He said that he could swim when he was five”(他说他五岁时就会游泳。
)但要注意,如果宾语从句表达的是客观真理或不变的规律,即使主句是过去时,从句中的情态动词仍然用一般现在时。
在状语从句中,情态动词也有其独特的用法。
在条件状语从句中,如果表示真实的条件,通常使用 can、may 等;如果表示虚拟的条件,则要使用 could、might、would 等。
例如,“If you can come tomorrow,we will have a party”(如果你明天能来,我们将举办一个派对。
)“If I were you, I mig ht do it differently”(如果我是你,我可能会做得不同。
)在目的状语从句中,常用的情态动词有 can、could、may、might 等,以表达为了实现某个目的而采取的行动或具备的可能性。
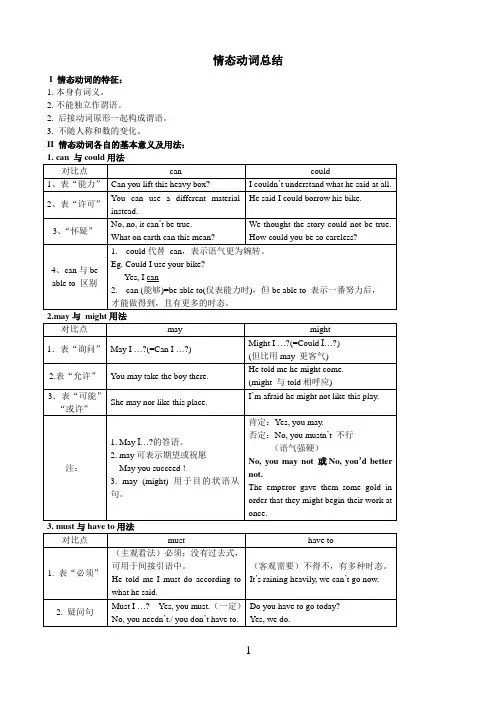
情态动词总结I 情态动词的特征:1.本身有词义。
2.不能独立作谓语。
2. 后接动词原形一起构成谓语。
3. 不随人称和数的变化。
II 情态动词各自的基本意义及用法:1.大多数情态动词(除表‘能力、许可、意志’外),都可以表示推测,其程度有差异。
按可能性程度的高低排列为:must﹥will ﹥would ﹥ought to ﹥should完全肯定完全可能很可能﹥can ﹥could﹥may ﹥might可能有可能2. 区分情态动词的否定含义:may not或许不、可能不might not可能不can’t 不可能mustn’t不许、禁止shouldn’t不应该needn’t 不必1.情态动词表推测的反意疑问句,简单来说,就是以情态动词后的时态为淮,如句子里有明确的时间状语,则以其为准。
2.以must 为例:E.g. 1. You must be hungry now, aren’t you?2. He must be watching TV , isn’t he ?3 Tom must have lived her for a long time, hasn’t he ?4. She must have arrived yesterday, didn’t she?注:如选择题中(以She must have arrived yesterday, didn’t she?为例)既有didn’t she又有hasn’t she则以didn’t she?为最佳答案。
IV 情态动词专项练习与解析一( ) 1. You _____ return the book now. You can keep it till next week if you like.A. can’tB. mustn’tC. needn’tD. may not( ) 2. Where is my pen? I _____ it.A. might loseB. would have lostC. should have lostD. must have lost( ) 3. I wish I _____ you yesterday.A. seenB. did seeC. had seenD. were to see( ) 4. I didn’t hear the phone. I _____ asleep.A. must beB. must have beenC. should beD. should have been( ) 5. If my lawyer _____ here last Saturday, he _____ me from going.A. had been; would have preventedB. had been; would preventC. were; would preventD. were; would have prevented( ) 6. He _____ you more help, even though he was very busy.A. might have givenB. might haveC. may have givenD. may give( ) 7. If it _____ for the snow, we _____ the mountain yesterday.A. were not; could have climbedB. were not; could climbC. had not been; could have climbedD. had not been; could climb( ) 8. Without electricity human life _____ quite difficult today.A. isB. will beC. would have beenD. would be( ) 9. A computer _____ think for itself, it must be told what to do.A. can’tB. couldn’tC. may notD. might not( ) 10. Jenny _____ have kept her word. I wonder why she changed her mind.A. mustB. shouldC. needD. would( )11. We _____ last night, but we went to the concert instead.A. must have studiedB. might studyC. should have studiedD. would study( ) 12. — Could I borrow your dictionary?— Yes, of course you _____.A. mightB. willC. canD. should( ) 13. Tom ought not to _____ me your secret, but he meant no harm.A. have toldB. tellC. be tellingD. having told ( ) 14. — If he _____, he _____ that food.— Luckily he was sent to the hospital immediately.A. was warned; would not takeB. had been warned; would not have takenC. would be warned; had not takenD. would have been warned; had not taken ( ) 15. Peter _____ come with us tonig ht, but he isn’t very sure yet.A. mustB. mayC. canD. will( ) 16. I told Sally how to get here, but perhaps I _____ for her.A. had to write it outB. must have written it outC. should have written it outD. ought to write it out( ) 17. I didn’t see your sister at the meeting. If she _____, she would have met my brother.A. has comeB. did comeC. cameD. had come ( ) 18. — Shall I tell John about it?—No, you _____. I’ve told him already.A. needn’tB. wouldn’tC. mustn’tD. shouldn’t ( ) 19. When a pencil is partly in a glass of water, it looks as if it _____.A. breaksB. has brokenC. were brokenD. had been broken( ) 20. It’s nearly seven o’clock. Jack _____ be here at any moment.A. mustB. needC. shouldD. can( ) 21.— There were already five people in the car but they managed to take me as well.— It _____ a comfortable journey.A. can’t beB. shouldn’t beC. mustn’t have beenD. couldn’t have been ( ) 22. Johnny, you _____ play with the knife, you _____ hurt yourself.A. won’t; can’tB. mustn’t; mayC. shouldn’t; mustD. can’t; shouldn’t ( ) 23. The fire spread through the hotel very quickly but everyone _____ get out.A. had toB. wouldC. couldD. was able to ( ) 24. — When can I come for the photos? I need them tomorrow afternoon.— They _____ be ready by 12:00.A. canB. shouldC. mightD. need( ) 25. — I stayed at a hotel while in New York.— Oh, did you? You _____ with Barbara.A. could have stayedB. could stayC. would stayD. must have stayed ( ) 26. — Will you stay for lunch?— Sorry, _____. My brother is coming to see me.A. I mustn’tB. I can’tC. I needn’tD. I won’t( ) 27. — Are you coming to Jeff’s party?—I’m not sure. I _____ go to the concert instead.A. mustB. wouldC. shouldD. might( ) 28. — Write to me when you get home.— _____.A. I mustB. I shouldC. I willD. I can( ) 29. I was really anxious about you, you _____ home without a word.A. mustn’t leaveB. shouldn’t have leftC. couldn’t have leftD. needn’t leave( ) 30. — Is John coming by train?— He should, but he _____ not. He likes driving his car.A. mustB. canC. needD. may专项练习(二)1. I didn’t see her in the meeting room this morning. She _____ at the meeting.A. mustn’t have spokenB. shouldn’t have spokenC. needn’t have spokenD. couldn’t have spoken2. One ought _____ for what one hasn’t done.A. not to be punishedB. to not be punishedC. to not punishedD. not be punished3. If you really want yourself to be in good health, you must ___ always ___ so much.A. not; be smokingB. not; have smokedC. not; to smokeD. be not; smoking4. With so much work on hand, you _____ to see the game last night.A. mustn’t goB. shouldn’t goC. couldn’t have goneD. shouldn’t have gone5. Most of the students felt rather disappointed at the English party. They say that it ______ better organized.A. had beenB. had to beC. must have beenD. could have been6. I’m surprised that he _____ in the exam.A. should failB. would have failedC. may have failedD. should have failed7. The little girl _____ there alone.A. not dare goB. dares not goC. dare not goD. dare not to go8. “Must we do it now?” “No, you _____.”A. won’tB. needn’tC. can’tD. don’t9. He said he would rather not _____ it right now.A. doingB. to doC. doD. to be doing10. You _____ to the meeting this afternoon if you have something important to do.A. needn’t to comeB. don’t need comeC. don’t need comingD. needn’t come11. Put on more clothes. You _____ be feeling cold with only a shirt on.A. canB. couldC. wouldD. must12. I _____ play football than baseball.A. would ratherB. had betterC. like betterD. prefer13. I thought you _____ like something to read, so I have brought you some books.A. mayB. mightC. couldD. must14. There was plenty of times. She _____.A. mustn’t have hurriedB. couldn’t have hurriedC. must not hurryD. needn’t have hurried15. The plant is dead. I _____ it more water.A. will giveB. would have givenC. must giveD. should have given16. You _____ return the book now. You can keep it till next week if you like.A. can’tB. mustn’tC. needn’tD. may not17. It’s still early, you _____.A. mustn’t hurryB. wouldn’t hurryC. may not hurryD. don’t have to hurry18. Please open the window, _____?A. can’t youB. aren’t youC. do youD. will you19. We _____ for her because she never came.A. mustn’t have waitedB. shouldn’t have waitedC. mustn’t waitD. needn’t wait20. — May I stop here? — No, you _____.A. mustn’tB. might notC. needn’tD. won’t21. It’s a fine day. Let’s go fishing, _____.A. won’t weB. will weC. don’t weD. shall we22. I didn’t see her in the meeting room this morning. She _____ at the meeting.A. mustn’t have spokenB. shouldn’t have spokenC. needn’t have spokenD. couldn’t have spoken23. — Please don’t make a noise. — _____. I’ll be as quiet as a mouse.A. Yes, I won’tB. No, I won’tC. No, I willD. Yes, I will24. The young man has made so much noise that he _____ not have been allowed to attend the concert.A. couldB. mustC. wouldD. should25. — Where is John? — He _____ in the library.A. should beB. must beC. can beD. must have been26. Since the road is wet this morning, _____ last night.A. it must rainB. it must be rainingC. it must have rainedD. it must have been rain27. — Will your brother stay home tonight?— I’m not quite sure. He _____ to the cinema tonight.A. must goB. can goC. may goD. may be going28. She’s already two hours late. What ______ to her?A. can have happenedB. may have happenedC. should have happenedD. must happen29. You must be a writer, _____?A. mustn’t youB. are youC. must youD. aren’t you30. I got up early that morning, but I _____ so because I had no work to do.A. mustn’t have doneB. didn’t need to doC. needn’t have doneD. can’t have done31. He _____ have come here yesterday, but he didn’t.A. couldB. shouldC. ought toD. all the above32. I missed the last bus, so I _____ go home on foot.A. mustB. have toC. mayD. had to33. He ought to win the first prize, _____ he?A. oughtn’tB. shouldn’tC. mustn’tD. both A and B34. Everyone _____ do his best for the modernizations of our country.A. canB. mayC. shouldD. might35. Let’s clean our classroom, _____?A. will youB. don’t weC. shall weD. do you36. Let us play basketball, ______?A. will youB. don’t weC. shall weD. do you37. He asked me for this book many times. Please tell him that he _____ have it tomorrow.A. mustB. mayC. shallD. both B and C38. “Your phone number again? I _____ quite catch it.” “It’s 9568442.”A. didn’tB. couldn’tC. don’tD. can’t39. Mother _____ us stories when we were children.A. was used to tellB. is used to tellingC. used to tellD. used to telling40. She would rather _____ more money on books _____ on clothes.A. cos t … notB. to spare … don’tC. pay … thanD. spend … than专项练习(三)1. — Has Li Lin started? He said he would join in the party.— He ______. He is a man of keeping his word.A. could have leftB. must have leftC. can’t comeD. won’t be c oming2. — May I park my car here?— No, you ______. No car is allowed to park here.A. may notB. needn’tC. mustn’tD. daren’t3. — Excuse me, could you tell me where the Yajia Supermarket is?—It’s two blocks straight ahead. You ______ miss it.A. mustn’tB. can’tC. needn’tD. shouldn’t4. — I saw Mr. Sun at Tongyu Station this morning.—You ______. He’s still on holiday in Hawaii.A. couldn’t haveB. mustn’t haveC. shouldn’tD. needn’t5. — How about paying a visit to Dr. Wang, our former Chinese teacher?— Good idea. I will e-mail him today so that he ______ know ______ to expect us.A. shall; whyB. could; whenC. would; whatD. will; how6. Everything has two sides. Beautiful songs, sometimes, ______ be just noise to others.A. mustB. mayC. shouldD. could7. Someone ______ my umbrella. I found it wet yesterday.A. must be usingB. must have usedC. must useD. must have been using8. — How dangerous it was!— Yes, but for the passer-by’s quick action, th e girl ______.A. was drownedB. could have been drownedC. had drownedD. should be drowned9. You ______ scold such a pupil who always keeps silent so seriously that you ______ hurt him.A. should; canB. may; willC. mustn’t; mayD. can’t; must10. — Why does Alice know so much about Angkor Wat?— She ______ have been there, or ...A. mustB. oughtn’t toC. mayD. can’t11. —You may laugh, but I’ve been thinking of becoming a vegetarian.— Oh, you ______ be crazy. You will be hungry all the time.A. mustB. mayC. willD. need12. —What’s the matter with you?—Oh, I’m not feeling well in the stomach. I ______ so much fried fish just now.A. shouldn’t eatB. mustn’t have eatenC. shouldn’t have eatenD. mus tn’t eat13. — ______ he have been chosen as captain of the football team?— Yes, he ______.A. Can; must haveB. Must; must haveC. Can; mustD. Must; must14. Mr. Zhang ______ in Shanghai tomorrow morning.A. can have arrivedB. will have arrivedC. may have arrivedD. must have arrived15. Miss Wang started at 8 o’clock, and she ______ be there now.A. shouldB. canC. can’tD. need16. — It must be Mr. Li who did it. — No, it ______ be Mr. Li.A. mustn’tB. wouldn’tC. can’tD. may17. You ______ finish reading the book as soon as possible.A. mayB. canC. needD. should18. — Need you go to work now? — Yes, I ______.A. mustB. needC. canD. dare19. Your trousers are dirty. ______ them for you?A. Shall I washB. Will I washC. Am I going to washD. Am I washing情态动词专项练习与解析一【练习解析】1.C 从原题中You can keep it till next week if you like这一信息句可知,“你不必现在还”。

情态动词英语语法知识精讲情态动词(modal verb)本身有词义,表示说话人的语气或情态,但词义不完全,不能单独用作谓语动词,一般只能和动词原形一起构成谓语动词。
小编在这里整理了相关资料,希望能帮助到您。
情态动词概述特征1)情态动词(modal verb)本身有词义,表示说话人的语气或情态,但词义不完全,不能单独用作谓语动词,一般只能和动词原形一起构成谓语动词。
2)情态动词所表示的情态有:命令、允诺、请求、拒绝、愿望、愿意、义务、必要、可能、能力、敢于、需要等。
3)情态动词(ought除外)和助动词shall,will,should,would 一样,后面的动词不定式一般皆不带。
形式变化1)没有人称和数的变化,第三人称单数的现在时也无变化。
如:I can We canYou can You canHeThey canShe canIt2)有些情态动词有过去式,有少数过去式和它的原形相同。
a)有过去式的情态动词有:may -- wouldcan ―― couldmay―― nightshall -- shouldhave to -- had tob)过去式不变的情态动词有:must - must (或had to)ought to - ought toneed---needdare - dare(亦可用dared)3)大多数情态动词后面可用动词的进行式、完成式和被动形式,如:can(may,must)be doing,can(may,must) have done,can(may,must)be done等。
否定式情态动词和助动词一样,后面可直接跟否定词not。
现将情态动词的否定式及其否定式的简略式(简略式用于口语中)列举如下:shall not--shan't [FB:nt]will not---won't [wEunt]can not-can't [kB:nt]must not-mustn't [5mQsnt]should not-- shouldn'twould not-- wouldn'tcould not-- couldn'tdare not- daren't [dZEnt]need not-- needn't在疑问句中的用法情态动词在疑问句中的用法和助动词相同。

英语语法:情态动词详解情态动词有四类:①只做情态动词:must,can(could),may(might),ought to②可做情态动词又可做实义动词:need,dare③可做情态动词又可做助动词:shall(should),will(would)④具有情态动词特征:have(had,has) to,used to ,had better,would rather第一章、情态动词 can、may、must 的用法1. can 的用法(1) can 表示主语的能力=be able to。
如:The hall can seat 1,000 people. 这个大厅能坐1 000人。
Can you play the piano? 你会弹钢琴吗?They will be able to tell you the news soon. 他很快就能告诉你消息了。
He was able to flee Europe before the war broke out. = He managed to flee Europe before the war broke out.他在战争爆发之前逃离欧洲。
(2) can 表示说话人的猜测(即可能性),多用于否定句和疑问句。
如:Can it be true? 这能是真的吗?The moon can't always be at the full. 月不可能总是圆的。
What can she mean? 她可能是什么意思呢?(3) can 表示请求许可。
如:Can you help me? (表示请求) This sort of thing can't go on. 这样的事不能再继续下去了。
You can't smoke here. 你不可在这里吸烟。
(4)“can + 完成式”表示说话人对过去情况的猜测(只用于否定和疑问结构中)。
如:He can't have missed the way.I explained the route carefully and drew him a map. 他不会迷路。

你知道can的用法吗?快来一起学习吧,下面小编就和大家分享,来欣赏一下吧。
情态动词can有哪些用法?英语学习中,常常遇到can一词。
但是,can一词是不是只有“能够”这种用法?今天小编为大家梳理一下can一词的所有用法。
一、用作情态动词1.表示能力或者能够发生:能,会I can swim very fast. 我能游得很快。
2.表示知道如何做:懂得,会She can speak English. 她会说英语。
3.与动词feel, hear, see, smell, taste连用We can see beautiful flowers there. 我们可以看见那里漂亮的花。
4.表示允许:可以If you need, you can use my car. 如果你需要的话,你可以用我的车。
5.表示请求允许:可以Can I use your bike? 我可以用一下你的自行车吗?6.表示请求帮助:能Can you help me with this problem? 你能帮我解决一下这个问题吗?7.用于否定句,表示某事肯定不真实That can’t be Lucy. She is in the mall. 那不可能是露,她正在商场呢。
8.表示疑惑或惊讶:究竟能,难道会,到底是What can they be doing? 他们究竟在干什么?9.表示常有的行为和情形:有时会The little boy can be careless sometimes. 这个小男孩有时太粗心。
10.表示提出建议:可以If you like, we can see a film there. 如果你愿意,我们可以在那里看电影。
11.表示对方必须做(生气时):必须You can shut up or get out. 你给我闭嘴,要不然就滚出去!二、用作名词1.金属罐: a can of beans 豆罐头2.一听:a can of Coke 一听可口可乐3.装运液体)金属容器、塑料容器:an oil can 油罐4.牢房,厕所: the can(只有单数形式)三、用作动词1.把(食品)装罐保存2.让…卷铺盖走人,炒…的鱿鱼在日常学习中,很少遇到can用作名词和动词用法,但我们要熟知其意义及其用法,做到熟练掌握,灵活运用!情态动词can的用法,绝对没你想象得那么简单!在英语学习中,情态动词是一个很重要的语法点,其中情态动词can的用法比较常见。

情态动词英语语法讲解情态动词英语语法讲解本文题目:高考英语语法复习讲解:情态动词英语语法讲解根据以往英语取得高分同学的经验和海文英语辅导名师的建议,他们都一致认为英语语法和词汇是学好、考好英语的重要基础,其实完形填空是对语法、词汇的综合考查,但更关键的是学好此部分有助于对英语句子结构的分析和理解,有助于学生掌握灵活多变的句式,这样不仅有助于学生做好阅读理解,而且有助于学生做好英译汉,写好作文。
因此,我们在此编写了有关重点语法的知识点,并将陆续登出,同时将刊登一些试题。
希望同学们认真掌握,切不可因不靠它们而忽视了对英语基础知识的掌握。
(一)情态动词一.情态动词的现在完成式的用法情态动词现在完成式主要有两个功能:表示已经发生的情况和表示虚拟语气。
在这两个方面must/mustn’t,;can/cann’t;need/needn’t;may/mayn’t;might/ mightn’t;should/shouldn’t;ougtht等情态动词+完成式表示的意思是有一定区别的1.表示已经发生的情况。
1)musthave+过去分词,表示对已发生情况的肯定推测,译为“(昨天)一定……”。
如:MypainapparentthemomentIwalkedintotheroom,forthefirstman Imetaskedsympathetically:”Areyoufeelingallright?”[A]mustbe[B]hadbeen[C]musthavebeen[D]hadtobe(答案为C)2)can’t/couldn’thave+过去分词,表示对已发生情况的否定推测,译为“(昨天)一定没……”。
如:Marymyletter;otherwiseshewouldhaverepliedbeforenow.[A]couldn’thavereceived[B]oughttohavereceive d[C]hasreceived[D]shouldn’thavereceived(答案为A)3)may/mighthave+过去分词,表示对已发生的事情做不肯定、可能性很小的推测,或事实上根本没发生,译为“也许……”。
一、情态动词的概念情态动词又称为情态助动词(modal auxiliary)。
它具有词汇意义,但意义不够完整,因此一般不能直接作谓语。
情态动词表示说话人说话时的语气和态度。
二、情态动词的特征情态动词具有以下五个特征:1. 情态动词后面一般接动词原形(即不带to的不定式);2. 情态动词没有人称和数的词形变化;3. 情态动词与实义动词构成谓语时总是放在实义动词之前;4. 情态动词无非谓语形式,即没有不定式、动名词和分词形式;5. 情态动词只有现在式和过去式两种形式,但可以表示现在时间、过去时间和将来时间。
三、情态动词的用法现代英语语法还将have to, used to, had better, would rather, be going to, be about to等也都列为情态动词。
一个人说话在不同的场合其语气是不一样的,因此所使用的情态动词也是不同的。
初学者要掌握情态动词,需要多观察、多思考、多分析、多运用。
对于情态动词的基本含义和基本用法,中国学生一般都能掌握,难的就是意义相近的情态动词之间的混淆(如can, may, must等表示推测以及need和dare既可用作情态动词又可用作实义动词的用法)。
下面将对情态动词的相近用法或容易混淆的用法进行分类比较和讲解。
(一)can和be able to的区别can是普通的用词,表示一般的能力,如凭借体力、脑力或技能去做某事。
be able to比较正式,指具体的能力,尤其意味着通过努力才能做成某事,这时相当于manage to do sth. 或succeed in doing sth.。
试比较:I can speak a little French. 我能说一点法语。
After several months of hard study, I was able to speak a little French.经过几个月的努力学习,我能够说一点法语。
高一情态动词用法情态动词是英语语法中的重要组成部分,对于高一的同学来说,掌握好情态动词的用法是非常关键的。
情态动词具有一定的词义,但不能单独作谓语,需要和动词原形一起构成谓语。
它们能够表达说话人的态度、情感和推测等。
常见的情态动词有can、could、may、might、must、shall、should、will、would 等。
首先,我们来看看 can 和 could。
can 表示“能够;会”,指具备某种能力或有机会做某事。
例如:“I can speak English”(我会说英语。
)它还可以表示“许可;允许”,常用于口语中。
比如:“You can go now”(你现在可以走了。
)could 是 can 的过去式,但在很多情况下,could 并不单纯表示过去的能力,而是语气更加委婉。
比如:“Could you help me?”(你能帮我一下吗?)接下来是 may 和 might。
may 表示“可能;也许”,用于肯定句中。
例如:“It may rain tomorrow”(明天可能会下雨。
)同时,may 还可以表示“许可;允许”,不过比 can 更加正式。
比如:“May I come in?”(我可以进来吗?)might 是 may 的过去式,语气比 may 更加不确定和委婉。
例如:“He might be at home”(他也许在家。
)然后是 must。
must 表示“必须;一定”,强调主观上的必要性。
例如:“You must finish your homework before watching TV”(你必须在看电视之前完成作业。
)但要注意,must 的否定形式 mustn't 表示“禁止;不许”。
再来说说 shall 和 should。
shall 用于第一人称,表示征求对方的意见或向对方提出建议。
比如:“Shall we go shopping this afternoon?”(我们今天下午去购物好吗?)should 表示“应该;应当”,常用来给出建议或表达义务。
http://bailiedu.com 英语语法之情态动词的用法分享(一) 我们知道常见的情态动词有can, could; may, might; must; should; need; dare; ought to 等。那大家都熟悉这些单词的用法吗?英语语法之情态动词的用法分享可以帮助大家更多的了解情态动词,更好的进行雅思备考。 情态动词有一定的意义,表示人的看法和态度,不表示动作或状态,因而不能单独做谓语,必须和实意动词或系动词的原形一起构成谓语,没有人称和数的变化。把情态动词放在句首、句尾用问号便构成疑问句;在其后加上not或never等否定词就构成否定句。
一、can/could 的用法 1. 表示具备某种“能力”,但不一定做事情。仅仅表示有能力而已。Can表示现在;could表示过去。如: The nine-year boy can swim across the river. 那个九岁的男孩能游过那条河。
Can you swim across the river? 你能游过那条河吗? I could do such things then, but I can’t now. 我那时候能做这样的事情,但现在不能了。
We couldn’t get the truck to start. 我们发动不了那辆卡车。 2. 表示“请求”(疑问句中)、“允许”。Could 比 Can 委婉;两者都指现在。回答一律用 can 或 cannot, 也可以用mustn’t. 如: Can /could I smoke here? 我可以在这里抽烟吗?
Yes, you can.是的,你可以。 http://bailiedu.com No, you cannot smoke here. 你不能在这里抽烟。
You can go now. 你现在可以走了。 Could you lend me $55? 你能借给我55美圆吗? Yes, of course. 当然可以。 No, I cannot/I’m sorry I cannot.不,不行/对不起,恐怕不行。 Could you tell me where John is? 你能告诉我约翰在哪儿吗? 3. :表示“可能性”。 但是并不牵涉到是否真会发生:都可以表示现在和将来,只是could的语气更加不肯定。如 That can/could be very awkward.那可就太尴尬了。
Can/Could it be true? 那会/可能是真的。 That can’t/couldn’t be true. 那不可能是真的。 Will you answer the phone? It could be your mother. 你去接电话好吗?可能是你妈妈。 What can/could they be doing? 他们可能会在干吗呢? Could/Can they be chatting in his office? 他们可能在他办公室里聊天吗? No, they can’t/couldn’t be doing that now.不, 现在他们不可能在做那事。 二、may/might 的用法 1. 表示允许或请求允许;might语气更礼貌: May I turn on the TV? 我可以把电视打开吗? http://bailiedu.com You may go home now. 你现在可以回家了。
She asked if she might have my bike.她问是否可以借用我的自行车。 He told me I might go and see him any time. 他和我说我可在任何时候去见他。 can/could和may/might 都可以表示允许和请求允许。can最直截了当;could 礼貌客气;may 既尊重又婉转礼貌;might 带者太多的虚礼,所以很少使用。如:
直截了当 Can I ask you for help? 礼貌客气 Could I 尊重婉转 May I (虚礼)尊重婉转 Might I 对所有这些问句的肯定回答:Yes, of course. Yes, you can/may. 对所有这些问句的否定回答:No, you can’t/may not /mustn’t /I’m afraid not. 2. 表示可能性,是“也许”之意。这时may和might无时间上的差别,只是might在语气上更不肯定一些。如: You may/might have some fever. 你也许发烧了。
He said that the news might be true. 他说这消息可能是真的。 They may/might be having a bath. 他们也许正在洗澡。 We may be buying a new house. 我们也许要买个新房子。 表示可能性时,may/might不用于疑问句,可用can/could或别的说法。如: http://bailiedu.com Is it likely to rain, do you think? 会下雨吗,你认为?(不说May it rain?)
Can/could they be having a bath? 他们可能正在洗澡吗? 三、 must的用法 1. 表示义务、命令或劝告,是“必须”之意。对自己、对别人均可: We must take this seriously.我们必须严肃对待这事。
You must tell me the truth. 你必须和我说实话。 Patients must use medicine according to the doctor’s orders. 病人用药必须遵医嘱。 在回答由must引起的问题时,如果是否定回答,多用needn’t 或 don’t have to,表示“不必、没必要”;而mustn’t表示“绝对不行、不可以”的意思,有时用来回答can或may开头的问句,表示口气很强的不允许:
Must the ladies wear dresses? No, they don’t have to/they needn’t. 女士们必须着连衣裙吗?不,不必。
Can/May I come in? No, you can’t/mustn’t. 可以进来吗?不行/绝对不行。 must 仅用于表示现在和未来。其他时态用have to。但在间接引语中可用must表示过去: I had to leave early because I wasn’t feeling well. 我不得不早点离开,因为我觉得不舒服。
You’ll have to take care of the child. 你将不得不照顾这个孩子。 She has had to work over ten hours a day. 她一直不得不每天工作十几个小时。 They decided they must stop smoking. 他们决定他们必须戒烟。 http://bailiedu.com He asked me if he must leave at once and I told him he didn’t have to. 他问我是否他必须马上离开,我告诉他不必。
2. 表示推测,是“肯定、一定”之意。此时,must只用于肯定句。在否定句或疑问句中,用can/could: 我们先对表示“推测”的表达法作一个总结: (1) 表示对现在和将来状况的推测:must 一定,may 可能,might 也许,can’t 不可能。从“一定”到“不可能”,可能性逐渐降低。 (2) 对已经过去的情况的推测:must, may, might, can’t/couldn’t 这些词后面分别加上have + 过去分词,表示“一定…”,“可能…”,“也许…”,“不可能…”。从“一定”到“不可能”,可能性逐渐降低。 There must be a mistake. 准是弄错了。
Can/Could there be a mistake?可能会有错吗? There can’t/couldn’t be a mistake.不可能会有错吗? He must be over sixty now. 他肯定六十多岁了。 He can’t/couldn’t be sixty now.他现在不会是六十岁。 Can/Could he be over sixty now? 他现在会有六十多岁吗? They must be watching the news now. 他们这会儿肯定在看新闻。 They can’t/couldn’t be watching the news now. 他们这会儿不可能在看新闻。 Can/Could they be watching the news now? 他们这会儿可能在看新闻吗? http://bailiedu.com 四、 need的用法 作为情态动词,need一般只用于否定句和疑问句中。 You needn’t try to explain. 你不需要解释。
She needn’t come tomorrow. 她明天不必来。 Need we stay here this evening? 今晚我们需要在这儿住下来吗? Need 作为实意动词比作为情态动词常用的多。实意动词need 可用在所有句型中。 She needs to come tomorrow.明天她需要来。 You don’t need any help from others.你不需要别人的任何帮助。 He doesn’t need to borrow money.他不需要借钱。 Do they need this? 他们需要这个吗? Plants need sun light in order to grow.植物需要阳光才能生长。 You don’t need to work so hard.你不需要这么样地努力工作。 Your shoes need cleaning/to be cleaned.你的鞋子需要清洁。 The job doesn’t need much attention or time.这份工作很省心省事。 What he needs is a good beating. He needs a good beating.需要好好揍他一顿。 五、 dare的用法 情态动词dare通常用于疑问句,否定句和条件状语从句中,表示“敢”的意思,如: Dare he swim across the river? 他敢游过这条河吗?