Interest Points in Static Images
- 格式:pdf
- 大小:460.59 KB
- 文档页数:26

向表妹介绍班级郊游时拍的照片英文作文Title: A Kodak Moment: Showcasing Our Class Picnic Through the LensAs I sat down with my young cousin, eager to share a piece of my world with her, I opened my laptop and embarked on a journey through memory lane. The soft click-clack of the keyboard broke the silence as I navigated to the folder marked ‘Class Picnic’,a digital treasure trove of our recent class outing. Her curious eyes, wide and shining with anticipation, mirrored my own excitement as I began to narrate the tale captured in those images."This is us at the break of dawn," I pointed at the photograph showing our group, bundled up against the morning chill, faces alight with the promise of adventure. "We gathered at the school before sunrise, brimming with the sort of energy that only an outing can infuse in us."As I scrolled through the pictures, each image unfolded stories of laughter and camaraderie. There was the shot of us posing by the bus, our mode of transport to the land of greenery and sunshine - our destination, a scenic spot away from the bustle of the city. I explained how we sang songs and shared tales, turning the mundane ride into a joyous journey.Upon arriving, we were greeted by a tapestry of vibrant hues and natural beauty. I showed my cousin the panoramic view we snapped, standing atop a hill that seemed to kiss the sky. "This is where we laid our picnic blanket, on a patch of grass softer than any carpet," I described, pointing out the colanders brimming with fruits and snacks, a testament to our strategic planning and communal effort.The photos took us on a zig-zag path through the day; there were action-packed shots of us playing games, competitive spirits high and voices raised in cheer or playful protest. I recounted instances where we helped each other, fostering a bond that went beyond mere classmates, transforming us into a family away from home.I could see her smile broaden as I showed her the picture of our nature walk, where we encountered creatures small and serene - butterflies dancing their ballet and squirrels playing their game of hide-and-seek. "We were one with nature, observing, learning, and appreciating its beauty," I said, my voice hushed with reverence for the moment.As the sun dipped low in the sky, signaling the end of our sojourn, we gathered for a group photograph, arms around each other, capturing the essence of unity and friendship."And this is us, the moment we promised to cherish this day forever," I told her, pointing to the golden hour glow that bathed us in its warm embrace.As the slideshow ended, her silence spoke volumes. She was enraptured by the visual narrative, her imagination ignited by the stories that leapt off the screen. This shared experience became a special connect between us, a reminder that even in the mundane lies the extraordinary, given the right company and spirit.Our conversation flowed like the gentle stream in the photographs, as she peppered me with questions about the games we played, the jokes we shared, and the secrets we whispered. I realized then that these photographs were more than just pixels arranged on a screen; they were a gateway to a world of feelings and memories, a tangible way to bridge distances and foster understanding.In that moment, I knew that the pictures from our class picnic had transcended their static form - they had become a storybook, a kaleidoscope of emotions and experiences that would remain etched in our hearts forever. And as we sat there, surrounded by the silent eloquence of those images, we were both reminded of the power of togetherness and the simplejoys that life, and a camera, can impart.。

英文动画知识点总结Animation has been an important art form for centuries, from ancient cave drawings to the modern digital animations seen in movies and video games. It is the process of creating the illusion of motion and change by rapidly displaying a sequence of static images.In this article, we will discuss the key knowledge points of animation, including its history, different techniques, and the impact of animation on popular culture. We will also explore the future of animation and its role in the digital age.History of AnimationThe history of animation can be traced back to ancient times, where people used various methods to create the illusion of motion. For example, the ancient Greeks used a device called a zoetrope, which featured a series of images on a rotating drum. When spun, it created the illusion of motion.In the late 19th century, the invention of the zoetrope and the flipbook paved the way for the development of animation as we know it today. In the early 20th century, pioneering animators such as Winsor McCay and Walt Disney made significant contributions to the art form, leading to the creation of beloved characters like Mickey Mouse and countless animated films.Techniques of AnimationThere are several different techniques used in animation, each with its own unique style and method. The most common techniques include:1. Traditional Animation: Also known as cel animation, traditional animation involves creating individual frames by hand and then filming them to create the illusion of movement. This technique was widely used in classic Disney films such as "Snow White and the Seven Dwarfs" and "The Lion King."2. Stop-Motion Animation: Stop-motion animation involves manipulating physical objects, such as clay or puppets, and taking a series of photographs to create the illusion of movement. Popular examples of stop-motion animation include "Wallace and Gromit" and "The Nightmare Before Christmas."3. Computer Animation: With advancements in technology, computer animation has become the dominant technique in the industry. This includes 2D animation, which uses digital drawing tools to create characters and scenes, and 3D animation, which uses computer-generated imagery to create lifelike characters and environments.Impacts of Animation on Popular CultureAnimation has had a significant impact on popular culture, shaping the way we consume media and influencing the way we perceive the world around us. From iconic characters likeMickey Mouse to groundbreaking films like "Toy Story," animation has become an integral part of our collective consciousness.Additionally, animation has played a crucial role in education and entertainment, providing a platform for storytelling and creativity. Animated films and television shows have entertained and inspired audiences of all ages, while educational animations have been used as a tool to teach complex concepts in an engaging and accessible way.Future of AnimationAs technology continues to advance, the future of animation holds endless possibilities. Virtual reality and augmented reality are opening up new avenues for immersive storytelling, while artificial intelligence is changing the way animators create and manipulate characters and scenes.Furthermore, the increasing accessibility of animation tools and platforms has allowed a wider range of creators to enter the industry, leading to a more diverse and inclusive landscape of animated content.ConclusionIn conclusion, animation is a versatile and dynamic art form with a rich history and a bright future. Its impact on popular culture is undeniable, and its potential for innovation and creativity is limitless. Whether it's through traditional techniques or cutting-edge technology, animation will continue to captivate and inspire audiences for generations to come.。

I.J. Image, Graphics and Signal Processing, 2012, 2, 30-36Published Online March 2012 in MECS (/)DOI: 10.5815/ijigsp.2012.02.05Human Identification by Gait Using CornerPointsMridul Ghosh11Department of Computer Science and Engineering, Seacom Engineering College, Kolkata, Indiamridulxyz@Debotosh Bhattacharjee22Department of Computer Science and Engineering, Jadavpur University, Kolkata, Indiadebotosh@Abstract—Recently human gait has become a promising and very important biometric for identification. Current research on gait recognition is usually based on an average gait image or a silhouette sequence, or a motion structure model. In this paper, the information about gait is obtained from the disparity on time and space of the different parts of the silhouette. This paper proposes a gait recognition method using edge detection, identification of corner points from edges, and selection of control points out of those corner points. Here, the images of moving human figures are subtracted from background by simple background modeling technique to obtain binary silhouettes. A gait signature of a person is taken as silhouette images of a complete gait cycle. A complete gait cycle is then divided into different frames in such a way that the information of the person’s gait style can be represented fully. One given unknown gait cycle is compared with stored gait cycles in terms of a cyclic distances between control points of an image of input gait cycle with that of corresponding image of the stored gait cycle. Experimental results show that our method is encouraging in terms of recognition accuracy. Index Terms—Gait recognition, silhouettes, Edge Detection, corner detection, control pointsI.I NTRODUCTIONGait [1] is a behavioral biometric that measures the way people walk. The demand for automatic human identification system [2][3][4]is robustly escalating in many important applications, particularly at a distance. It has gained an immense interest for its uses in many security-sensitive environments such as banks, military, parks and airports. Biometrics is a powerful tool for reliable human identification. It makes use of human physiology or behavioral characteristics such as face, iris and fingerprints for recognition. However, these biometrics methodologies are either informative or limited to many environments. For example, most face recognition techniques are able to recognize only frontal or side faces or with some specified angle of turn or inclination, but if the face is not shown or only the back side of head is shown then it is of no use, other biometrics such as fingerprint and iris are no longer applicable when the person suddenly appear in the surveillance. Therefore, new biometric recognition methods are strongly required in many surveillance applications, particularly recognition at a distance. Compared with the first generation biometrics, such as face, fingerprints and iris, which are widely applied in some commercial and static applications, currently, gait is the only biometric at a distance, can be used when other biometrics are either obscured or at too low a resolution to be perceived till now, though it is also affected by some factors such as drunkenness, obesity, pregnancy and injuries involving joints. So to recognize an individual’s walking characteristics, gait recognition includes visual cue extraction as well as classification. However, major issue here is the extraction and representation of the gait features in an efficient manner. Another motivation is that video footage of suspects can be made readily available, as surveillance cameras are relatively low cost and can be installed in most buildings, banks, railway stations, shopping malls, cinema hall, airport, different important locations of road, sacred places or different locations requiring a security presence. Once video footage is available then only task would be to monitor the movement of the suspect. The increase in processor speed, along with the decrease in price of high speed memory and data storage devices, there has been increased availability and applicability of computer vision and video processing techniques. Section II describes overview of the system, implementation of the present method has been described in section III, experiments conducted for this work along with results are described in section IV, and section V concludes this work.II. OVERVIEWOur investigation aims to establish an automatic gait recognition method based upon silhouette analysis measured during walking. Gait includes both the body appearance and the dynamics of human walking motion. Intuitively, recognizing people by gait depends greatly on how the silhouette shape of an individual changes over time in an image sequence. So, we may consider gait motion to be composed of a sequence of static bodyposes and expect that some distinguishable features with respect to those static body poses can be extracted and used for recognition by considering spatial variations of those observations .For any recognition system, the feature extraction is the most important thing. Person’s gait sequences need to be considered in such a way that the sequence can completely identify the person’s walking style, which is discussed in subsection III A . As we are considering the silhouette images, the information relating to silhouettes are to be extracted. The edges of silhouette image have been extracted after applying edge detection technique and we are to find some points on the edge which would be used to represent a gait movement. After proper edge detection, corner detection technique will definitely work well because corner can be defined as a point for which there are two dominant and different edge directions in a local neighborhood of the point . The corner strength is defined as the smallest sum of squared differences between the patch and its neighbors i.e. horizontal, vertical and on the two diagonals, discussed in subsection III B . From these corner points we need to select some points in such a way that the gait signature of the person’s silhouette is properly extracted and discussed in subsection III C . Distance between these points need to be calculated as these distance values are the features of the silhouettes. After extracting the features of silhouettes, they are stored in the database corresponding to their selected points in the form of matrices. After obtaining feature of the gait sequence of the testing person, it’s being compared with the feature sequence available in the database, which is discussed in subsection III D . If the trained database contains the similar sequence then the video gets authenticated.III. PRESENT METHODFigure 1. The block diagram for the training phaseEuclidean Distances between the Control Points in cyclic order are calculated and stored as features from that sequence. All these distance values from a sequence of images are kept in the database as training set for a person. Like any trainable recognition system, this gait recognition system is also consisted of two phases namely training and testing. Taking a gait silhouette sequence of a person, edges of individual image in that sequence is detected after applying Sobel Edge detector [5][6][7]. From those edges, the closed contour of the individual is extracted. From the closed contour, the corner points are identified. There may be several corner points in an image, but we need to pick up a set of fixed points such that the set represents the uniqueness of an individual by which any individual can be discriminated from others. These points are called control points. A block diagram representing the training phase is shown in figure 1.A. Gait SequenceThe database can be created by taking the video sequence of a person, then dividing this video sequence into different frames in such a way that the sequence can completely identify the persons gait style. Moreover, these images are the silhouette [8][9][10] images of persons to be included in the database. The silhouette of a person in the image can be obtained by background subtraction method [14]. Recognizing people by gait depends greatly on how the silhouette shape of an individual changes over time in an image sequence. To conduct experiments, we have used CASIA gait database, where the main assumption made is that theAfter detecting the edge of the silhouette, we find out the corner points on the edge. A corner can be defined as the intersection of two edges. A corner can also be defined as a point, for which there are two dominant and different edge directions in a local neighborhood of the point. In practice, most so-called corner detection methods detect intersecting points in general, rather than corners in particular. As a consequence, if only corners are to be detected it is necessary to do a local analysis of detected intersecting points to determine which of these real corners are. Examples of edge detection that can be used, with some post-processing, to detect corners are the Kirsch-Operator and the Frei-Chen masking set [14]. There are different types of method for corner detection e.g. Minimum Eigenvalue Method, Moravec corner detection algorithm [14], The Harris and Stephens corner detection method [14][16][17] etc. Minimum Eigenvalue Method is more computationally expensive than the Harris corner detection algorithm. Harris and Stephens improved upon Moravec's corner detector by considering the differential of the corner score with respect to direction directly, instead of using shifted patches. In order to exploit this improvised result, in this work, we have used the Harris and Stephens corner detection method to detect corner of the edge of the silhouette [15][16][17].camera is static, and the only moving object in video sequences is the walker. The gait sequence can be obtained by taking the silhouettes in such a way that the object’s posture in the first image will repeat in another image and the total number of images from the first to that repeated postured image make a sequence. Hence, to find a sequence, we accumulate all the images after recording the pose of the object in the initial image until the same pose is repeated in some image. For this database, the 26th image’s gait pose is same as first image and we have taken twenty six images of a person as a gait cycle. Such a sequence is shown in figure 2. It may be noted that, in the second sequence the images may not be in same pose as in the first sequence, i.e. first image’s posture of the first sequence may not be same as that of first image of second sequence but it will be same with some another image later in that sequence. We have tested with the gait cycle of 50 persons.Let an image be given by I. Consider taking an image patch over the area (u, v ) and shifting it by (x, y ). The weighted sum of squared differences (SSD) between these two patches, denoted as S, is given by:S(x,y) = ∑ ∑ w(u,v ) (I(u+x,v+y ) – I(u,v))2 (1)u vI (u+x,v+y) can be approximated by a Taylor expansion. Taking I x and I y be the partial derivative of I, such thatI (u+x, v+ y)≈ I (u,v) + I x (u,v)x +I y (u,v)y (2)The approximation can be written as,Figure 2. Complete gait cycle or sequence of a personS(x,y) = ∑ ∑ w(u,v)(I x (u,v)x +I y (u,v) y)2 (3)B. Corner DetectionuvThe equation (3) can be written in matrix form:Before we detect corner, we have detected edge of the image to find approximate contour of gait images. Edge detection [5][6][7][11][12][13] is a fundamental tool in image processing and computer vision, particularly in the areas of feature detection and feature extraction, which aims at identifying points in a digital image at which the image brightness changes sharply or, more formally, has discontinuities. Image Edge detection significantly reduces the amount of data and filters out useless information, while preserving the important structural properties in an image. Here, we have used Sobel operator [6] as a filter to detect edge of an image.S(x,y)≈(x y) A (4)where A is the structure tensor [17], given asA= (5)h T is matrix is a Harris matrix, and angle brackets denote averaging i.e. summation over (u, v).C. Selection of control pointsIn this work, we have first extracted the contour of animage. We find the corners on this contour of each subject. Taking these corner points, we select a subset of those with a fixed number, called as set of control points. Then we find out the distances between them in a cyclic order and stored as a feature vector for that image. Similarly, for all the twenty six images of a gait sequence, feature vectors are extracted and stored in sequence to represent the feature vector set for the entire sequence.Figure 3. C ontrol points 1, 2, 3, 4, 5 and 6.Control point selection is very important and imperative in our paper of human identification by gait. From the corner points, we have chosen some points that will rightly characterize the person’s gait characteristics.In the figure 2, we can see the control points marked as 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, and 6 on toe, ankle, thigh, hip, knee, and waist respectively. Reason for selecting these points isthat, respective positions of those points remain approximately constant for the same type of posture in different sequences but changes when the subject moves in a different posture and also, distinctly represents walking style of different individuals.D. TestingIn case of testing, we follow the same technique for an unknown person’s gait sequence and find out the distance values accordingly to compute the feature vector. Then this vector is compared with all such vectors stored in the database against a derived threshold value. If there is a match with any person’s training sequence data then that person is identified, but if there is no match then we can infer that the data of that person is not available in our training set. The detail of the testing procedure is shown in figure 4.The threshold value(T) is chosen in such a way that for the same person, after matching the training set with the testing set, it will rightly recognize the person, and for a different person, it will also recognize that both the person are not same. To declare a match between probe gait image and gallery gait images at least four control points, out of six, should match. This threshold value (T) has been identified experimentally.Figure 4. The Block Diagram describing testingIV. EXPERIMENTAL RESULTFor experimentation, we have used CASIA gait database: dataset C. We conducted our experiment with gait sequence of 50 persons to examine the effectiveness of our technique. Here, we have given sample details of two individuals. Table I shows the data of 26 images of a person (say person-A). The first column denotes the image numbers and rest of columns are distances between the control points in cyclic order. For the same person, person-A, distances are also computed for another sequence and shown in Table II. After testing, we see the two different sequences of person-A matches. Since we have considered 26 images in a sequence, both in the training and testing database there should be a match with 26 images.We computed the Euclidean distances between the coordinates of control points, as shown in figure 3, in a cyclic fashion i.e., calculated as between 1 & 2, 2 & 3, 3 & 4, 4& 5, 5 & 6, and 6 & 1. These distance values to be kept in the database as the training data for individual persons. There distances are used to compute thethreshold value, which would be used during testing. The ROC curve is drawn for this, which is shown in figure 5 and it has been found that the threshold value as 8.5 gives good result in terms of recognition. Table III shows the set of distances of another person (person-B) and that does not match with person-A. Table III. Table contains the data of person-B of a sequenceImage No. Distance between Control Points1-2 2-3 3-4 4-5 5-6 6-1 138.6005210.0498841.4367 24.20744 38.8973 24.698182 36.13862 5.09902 15.55635 25.23886 73.6817573.375753 16.2788216.0312244.28318 34.1321 71.0633520.09975459.0762211.0453644.72136 69.64194 28.8617420.615535 42.0475949 25.31798 35 54.12947101.20286 17.46425 4.12310652.23983 51.07837 8.54400497.493597 27.89265 4.12310629.12044 35.80503 40.6078827.802888 27.2029410.0498815.6205 110.0227 13.4536288.769369 55.7853 11.0453651.24451 40.81666 10.1980430.5286810256.08276336.23534 33.94113 14.7648276.9220411 26.1725 6.32455556.64804 28.79236 59.5399 109.201612 18.027768.94427229.20616 28.4605 21.4009332.1403213 68.65858 4 38.01316 38.91015 67.7421624.0831914 35.13662 5.09712 15.54635 25.23226 73.1817573.3347515 96.13012 6.08276320.24846 27.20294 76.1051975.4320916 16.1245230.0832246.27094 29.83287 78.3134719.2353817 59.0338968.007358.246211 22.82542 67.1863150.9215118 48.1663812 37.48333 38.07887 51.6236425.4951 1934.7131113.0384 76.53104 21.0238 10.6301594.1488220 31.016128 62.8172 42.94182 89.27486115.447 21 19.23538 6 56.29387 40.31129 74.6726227.2029422 31.38471 6.08276361.03278 27.313 32.7566887.2353123 52.20153 6.08276376.24303 33.42155 18.7882979.7558824 17.720059.055385102.9612 60.16644 41.5932792.8493425 21.633317.61577370.34202 39.96248 50.3587190.249652631.196916.08276345.24144 21.09502 10.6301526.2168Table I . Table contains the data of person-A of a sequenceImageNo. Distance between Control points1-2 2-3 3-4 4-5 5-6 6-1114.14214 10.04988 22.8254256.04463 34.4818844.011362 36.87818 7.28011 35.4400923.85372 38.3275461.351453 81.02469 7 38.3275427.65863 87.2811536.359324 28.44293 1.414214 68.1835833.30165 78.3134740.311295 35.0571 13 31.25725.4951 60.8276343.462636 10.19804 4 36.1247858.18075 22.8254240.311297 11.40175 1.414214 38.2099523.85372 58.3095219.313218 15.81139 1.414214 80.2246850.77401 27.2946923.853729 17.72005 1.414214 21.8403388.29496 112.285418.6815410 54.45181 1 27.5136358.5235 11.3137191.7823511 10.44031 7.28011 46.3249454.78138 84.4807725.0599312 21.9545 6.082763 34.928573.08215 1791.0933613 16.12452 8 86.4927771.30919 58.1377779.8498614 82.9759 6.324555 36.7151223.76973 55.901798.0306115 76.29548 6.708204 16.2788275.18643 83.2946623.0217316 101.7104 6.708204 32.8937754.40588 26.2488161.0327817 78.31347 5 37.3630849.0408 113.1106105.323318 26.07681 12 45.2769398.65597 38.4707722.0227219 31.257 10.04988 48.2597121.09502 60.2992524.4131120 21.37756 1.414214 94.1912986.68333 11.3137115.033321 72.1734 16.03122 80.3056718.24829 101.493828.3019422 79.40403 8 43.1740725.45584 65.3758491.4439723 14.31782 7 87.6926525.23886 14.8660785.6154224 11.18034 2.236068 13.4536298.48858 10.1980486.5852225 54.57105 8.062258 14.3178299.24717 84.8528123.0867926 16.87818 7.28011 35.44009 23.85372 38.32754 51.35145Table IV. Different recognition parameters (for threshold, T= 8.5)Table II. Table contains the data of person A of another sequencePersonCorrect Recognition rateCorrect RejectionFalseAcceptance Rate (FAR)False rejection Rate (FRR)Equal Error Rate (EER)50 84% 83% 16% 16% 0.16Image No. Control Points1-2 2-3 3-4 4-5 5-6 6-1 27 71.19691 6.082763 91.24144 21.09502 10.63015 76.2168 28 62.39391 6.082763 74.43118 56.85948 29.54657 52.55473 29 64.03124 13 26.68333 42.48529 104.1201 44.72136 30 54.07176 19.06524 15.41639 23.12714 52.80127 15.5125 31 11.31371 50.24938 106.3015 115.2085 19.10497 23.4094 32 14.56022 5.09902 52.23983 37.57659 21.84033 15.29706 33 52.46904 5.09902 73.68175 31.241 32.98485 83.9345 34 8.485281 1.414214 24.69818 69.57011 21.09502 108.8531 35 17.49286 2.236068 45.22168 49.64877 15.81139 94.59387 36 16.15549 7.211103 36.67424 30.52868 13.45362 66.24198 37 53.45091 6.324555 57.24509 25.96151 8 59.20304 38 16.27882 8.544004 13.0384 101 7.615773 100.4241 39 64.13267 11.40175 106.7942 64.62198 54.12947 102.3572 40 49.64877 4 103.9471 82.46211 29.83287 58.59181 41 80.025 17 30.41381 23.02173 37.10795 20.24846 42 55.08176 29.01724 19.41649 70.00714 62.80127 25.6125 43 73.06162 8.062258 50.08992 65.80274 25.70992 2044 17.46425 4.123106 27.65863 38.27532 46.87217 22.2036 45 51.97115 1.414214 36.68787 65.14599 11 99.0404 46 8.062258 8 32.57299 52.80152 63.15061 26.24881 47 13.89244 5.09902 34.9285 39.05125 39.84972 36.12478 48 17.08801 5 76.92204 30.88689 49.47727 112.8938 49 54.23099 6.082763 23 59.09315 8.485281 72.67049 50 41.14608 8.062258 74.72617 39.44617 47.67599 90.82401 51 63.06346 2 38.07887 52.92447 21.54066 31.257 5266.27882 6.082763 80.51828 24.29447 12.95281 80.00625ROCFRRF A RFigure 5. ROC CurveV. CONCLUSIONWith strong experiential evaluation, this paper focuses on the idea of using silhouette-based gait analysis. With the increasing demands of visual surveillance systems, human identification at a distance has recently gained more interest in the field of image processing and pattern recognition. Gait is a potential behavioral feature and many allied studies have demonstrated that it has a rich potential as a biometric for recognition. Gait is sensitive to various covariate conditions, which are circumstantial and physical conditions that can affect either gait itself or the extracted gait features. Example of these conditions includes carrying condition (backpack, briefcase, handbag, etc.), view angle, speed and shoe-wear type and etc. In this work, we have used only six control points. There is a scope of extension in number of control points. Also, for classification for feature vectors support vector machine (SVM) can be employed in future.ACKNOWLEDGEMENTThe authors would like to thank Mr.Hongyu Liang for providing the database of the silhouettes named “CASIA Human Gait Database” collected by Institute of Automation, Chinese Academy Of sciences. Their thanks also go to those who have contributed to the establishment of the CASIA database [18].REFERENCES[1] R. Zhang, C.Vogler, and D. Metaxas, “Human gait recognition” IEEE Workshop on Articulated and Nonrigid Motion, 2004[2] Jiwen Lu, ErhuZhang, “Gait recognition for human identification based on ICA and fuzzy SVM through multiple views fusion”, Pattern Recognition Letters 28 (2007) 2401–2411.[3] James B. Hayfron-Acquah, Mark S. Nixon, John N. Carter “Automatic gait recognition by symmetry analysis” Pattern Recognition Letters xxx (2003) xxx–xxx.[4] Wang, L., Tan, T., Ning, Z., Hu, W., 2003. “Silhouette analysis-based gait recognition for human identification”. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Machine Intell. 25 (9), 1505–1518.[5] Elif AYBAR,”Sobel Edge Dtection Method for Matlab” Anadolu University, Porsuk Vocational School, 26410 Eskisehir [6] SOBEL, I., An Isotropic 3×3 Gradient Operator,Machine Vision for Three – Dimensional Scenes,Freeman, H., Academic Pres, NY, 376-379, 1990.[7] SOBEL, I., Camera Models and Perception, Ph.D.thesis, Stanford University, Stanford, CA, 1970.[8] Liang Wang, Tieniu Tan, Senior Member, IEEE,Huazhong Ning, and Weiming Hu “Silhouette Analysis-Based Gait Recognition for Human Identification” IEEETransactions On Pattern Analysis And Machine Intelligence, Vol 25. No 12, December 2003[9] Brian DeCann and ArunRoss, ”Gait Curves forHuman Recoognition, Backpack Detection andSilhouette Correction in a nighttime Environmant”,USA Proc. of SPIE Conference on BiometricTechnology for Human Identification VII, (Orlando,USA), April 2010[10] L. Wang, H. Ning, W. Hu, and T. Tan, “Gaitrecognition based on procrustes shape analysis,”Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference onImage Processing, pp. 433–436, 2002.[11] E. Argyle. “Techniques for edge detection,” Proc.IEEE, vol. 59, pp. 285-286, 1971[12] Raman Maini & Dr. Himanshu Aggarwal. ”Studyand Comparison of Various Image Edge Detection Techniques” International Journal of Image Processing(IJIP), Volume (3): Issue (1).[13] R. C. Gonzalez and R. E. Woods. “Digital Image Processing”. 3rd ed. Prentice Hall, 2002.[14] C. Harris and M. Stephens (1988). "A combinedcorner and edge detector". Proceedings of the 4th AlveyVision Conference. pp. 147–151.[15] G. Veres, L. Gordon, J. Carter, and M. Nixon,“What Image Information is Important in Silhouette–based Gait Recognition?” CVPR, vol. 2, pp. 776–782,2004.[16] C. Harris and M. Stephens (1988). "A combinedcorner and edge detector". Proceedings of the 4th AlveyVision Conference. pp. 147–151.[17] J. Matthews. “An introduction to edge detection:The sobel edge detector,” Availableat / content/2002/im01.asp,2002.[18] CASIA gait database Mr. Mridul Ghosh born in October 29th,1982 and received his B.Sc ( Hons.)degree in Physics from CalcuttaUniversity, Calcutta, India; B.Tech andM.Tech degree in computer science &Engineering from University college ofscience & Technology, CalcuttaUniversity in the year of 2003, 2006 & 2008 respectively. He is currently working towards his Ph.D. (Eng.) award from Jadavpur University, Kolkata, India. His current research interest include pattern Recognition, Image processing, Fuzzy Logic.Debotosh Bhattacharjee received theMCSE and Ph. D.(Eng.) degrees fromJadavpur University, India, in 1997 and2004 respectively. He was associated withdifferent institutes in various capacitiesuntil March 2007. After that he joined hisAlma Mater, Jadavpur University. Hisresearch interests pertain to theapplications of computational intelligence techniques like Fuzzy logic, Artificial Neural Network, Genetic Algorithm, Rough Set Theory, Cellular Automata etc.in Face Recognition, OCR, and Information Security. He is a life member of Indian Society for Technical Education (ISTE, New Delhi), Indian Unit for Pattern Recognition and Artificial Intelligence (IUPRAI), and senior member of IEEE (USA).。

英语作文动画片的历史The History of AnimationAnimation, the art of creating the illusion of movement using a sequence of static images, has a rich and fascinating history that spans several centuries. From its humble beginnings as a simple form of entertainment to its current status as a global cultural phenomenon, the evolution of animation has been remarkable.The earliest known examples of animation date back to the pre-historic era, when cave paintings depicted animals in motion through a series of sequential poses. However, it was the invention of the cinema that truly gave rise to the modern concept of animation.In the late 19th century, pioneers such as Emile Cohl and J. Stuart Blackton began experimenting with the technique of stop-motion animation, using cut-out paper figures and drawings. These early animators created short, comedic films that were shown in cinemas and amusement parks, captivating audiences with their whimsical humor and innovative use of visuals.The emergence of Walt Disney Studios in the early 20th century marked a significant turning point in the history of animation. Disney's team of animators, led by pioneers like Ub Iwerks and John Hubley, revolutionized the art form by introducing techniques like cel animation and creating some of the most iconic and beloved characters in animation history, such as Mickey Mouse and Oswald the Lucky Rabbit.With the advent of television in the mid-20th century, animation found a new medium for widespread distribution and popularity. Series like "The Flintstones" and "The Jetsons" became household names, appealing to audiences of all ages with their quirky humor and innovative storytelling.In the 21st century, animation has continued to evolve and expand its reach, incorporating cutting-edge technology and innovative techniques. Computer-generated imagery (CGI) has revolutionized the animation industry, allowing for more realistic and detailed visuals than ever before. Films like "Toy Story" and "Frozen" have pushed the boundaries of animation, combining stunning visuals with heartfelt stories that resonate with audiences around the world.Moreover, the rise of streaming services and the internet has made animation more accessible to a wider audience. Independent animators and creators now have the opportunity to share their work with a global audience, fostering a diverse and vibrant animation community.In conclusion, the history of animation is a rich tapestry of creativity, innovation, and entertainment. From its humble beginnings to its current status as a global cultural phenomenon, animation has continuously evolved and adapted to the changing times. It remains a powerful medium that has the ability to captivate our imaginations and connect us through shared stories and experiences.。

英语作文应该怎么配图画When it comes to pairing illustrations with an English composition, several considerations come into play. Here are some guidelines to ensure effective integration:1. Relevance to the Topic: The chosen images should directly relate to the content of your composition. For instance, if your essay discusses environmental issues, including images of polluted landscapes or renewable energy sources would be appropriate.2. Enhancement of Understanding: The illustrations should complement the text and aid in the reader's comprehension. If you're describing a complex process or concept, such as the water cycle or the workings of a machine, incorporating diagrams or labeled illustrations can elucidate your points.3. Visual Appeal: Opt for visually appealing imagesthat capture attention and engage the reader. High-qualityphotographs, colorful graphics, or artistic representations can make your composition more visually appealing.4. Consistency: Maintain consistency in style and tone between the text and the illustrations. They should work together harmoniously to convey your message effectively.5. Placement and Integration: Strategically place the images throughout your composition to break up the text and create visual interest. Ensure they're integrated seamlessly with the written content, rather than appearing as mere decorations.6. Cultural Sensitivity: If your composition discusses cultural or social topics, be mindful of cultural sensitivities when selecting images. Avoid stereotypes or images that could be perceived as offensive.7. Copyright Considerations: Use images that are either in the public domain, licensed under Creative Commons, or obtained with proper permissions to avoid copyright infringement issues.8. Size and Resolution: Ensure that the images are of sufficient size and resolution to be clearly visible and maintain quality when printed or viewed digitally.In summary, the key to effectively pairingillustrations with your English composition lies in selecting relevant, visually appealing images that enhance understanding and complement your written content. By following these guidelines, you can create a cohesive and engaging composition that effectively communicates your message.。
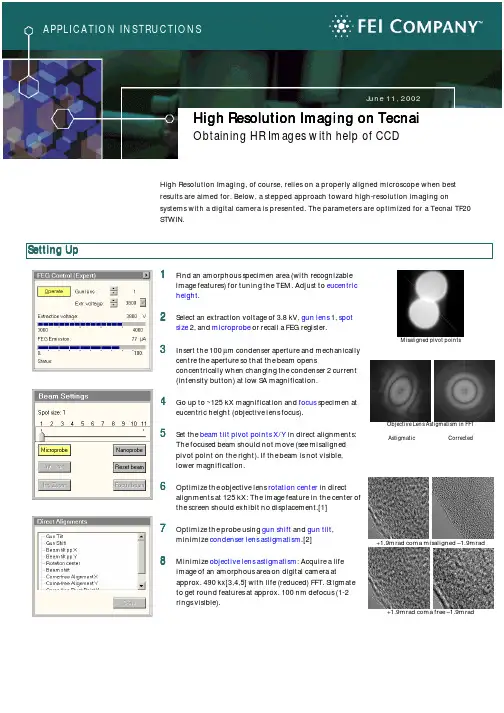
High Resolution Imaging on Tecnai High Resolution Imaging on TecnaiObtaining HR Images with help of CCDHigh Resolution Imaging, of course, relies on a properly aligned microscope when best results are aimed for. Below, a stepped approach toward high-resolution imaging onsystems with a digital camera is presented. The parameters are optimized for a Tecnai TF20 STWIN. Setting UpSetting Up1 Find an amorphous specimen area (with recognizableimage features) for tuning the TEM. Adjust to eucentricheight .2 Select an extraction voltage of 3.8 kV, gun lens 1, spotsize 2, and microprobe or recall a FEG register.3Insert the 100 µm condenser aperture and mechanically centre the aperture so that the beam opens concentrically when changing the condenser 2 current (intensity button) at low SA magnification.4 Go up to ~125 kX magnification and focus specimen ateucentric height (objective lens focus).5 Set the beam tilt pivot points X/Y in direct alignments:The focused beam should not move (see misalignedpivot point on the right). If the beam is not visible,lower magnification.6 Optimize the objective lens rotation center in directalignments at 125 kX: The image feature in the center ofthe screen should exhibit no displacement.[1]7 Optimize the probe using gun shift and gun tilt , minimize condenser lens astigmatism .[2]8 Minimize objective lens astigmatism : Acquire a lifeimage of an amorphous area on digital camera atapprox. 490 kx[3,4,5] with life (reduced) FFT. Stigmateto get round features at approx. 100 nm defocus (1-2 rings visible). Misaligned pivot points Objective Lens Astigmatism in FFT Astigmatic Corrected+1.9mrad coma misaligned –1.9mrad+1.9mrad coma free –1.9mradObtaining HR Images with help of CCD9 Optimize coma free alignment: focus image at 350 kX orhigher, select coma free alignment X/Y in directalignments and make contrast as similar as possible forboth beam orientations.[6] If adjustments were strong,repeat procedure starting at step 8 [7].Acquiring a HR Acquiring a HR--TEM image TEM image1010 Find a thin region of interest, orient on zone axis usingα and β-tilt in diffraction mode (see diffraction patternon the right). Adjust eucentric height .1111 Focus roughly, e.g. minimize contrast in a thinamorphous area or minimize Fresnel fringes at aninterface; reset defocus as a reference.1212 Increase magnification (typically to above ~800 kX for silicon) in search mode (512x512 pixels, binning 2, 0.2 sec exp. time)[4] and spread beam[5] to get about 200-500 counts (with YAG). Focus image precisely. 1313 Minimize mechanical vibrations (air conditioner, conversations).1414 In preview mode focus precisely.1515 Acquire full image with acquisition time of about 0.5-5sec.[5,8]SAED Si (110)HR TEM image of Si (110) Troubleshooting and Hints Troubleshooting and Hints[1] If there is no suitable object to minimize the image displacement during the alignment of the rotation center, focus the beam (intensity knob) and optimize rotation center to get symmetric opening and closing of the beam. This results in a rough alignment of the upper pole piece. High precision is achieved during coma free alignment.[2] See Application Instruction on FEG Gun Alignment.[3] See Application Instruction on CCD Imaging.[4] The magnification at the GIF is roughly 20 times higher than at the photo plate. Use the unfiltered EFTEM series to compensate for this extra magnification.Obtaining HR Images with help of CCD[5] Spread the beam (Intensity knob) to obtain (mostly) parallel illumination to have uniform incident beam angle and high coherence. Therefore, do not acquire HREM images in nanoprobe mode.[6] The angle for the beam-tilt can be adjusted in direct alignment in diffraction mode. The coma-free tilt pivot points need to be aligned to avoid the beam to disappear during coma-free alignment.[7] The astigmatisms can be measured using a Zemlin tableau: Go to an amorphous area close to the region of interest, set magnification to about 290 kX and defocus to have 3-4 rings visible in the reduced FFT. Acquire a series of dark-field HREM images with tilt-angles of 0 and ±4 mrad for all x and y combintations or use the automatic procedures offered e.g. with the Digital Micrograph HREM package.Zemlin tableau for a Tecnai F20 ST (without 3-fold stigmator)wellmisalignedstigmated[8] The final image should have at least up to 500 counts to obtain a good signal to noise level. The optimum signal to noise is obtained around 8000 counts, but keep in mind [5].。

附录3外文原文Experience in application of multimediain teaching of geographyThe new curriculum stressed the need to change the way teachers teach. The rapid development of multimedia technology and widely used, provides a new powerful technical support and material preparations for teachers to achieve a change in the way of teaching. Multimedia technology used in geography teaching, a change in the traditional "blackboard + chalk" a mouth, a book single teaching methods, the geography classroom becomes "live", vivid and efficient. Some experience in teaching.First,Create situations, to stimulate interestSuhomlinski pointed out that "all the intellectual work, we must rely on interest. Multimedia teaching the use of text, sound, images, animation, and network transmission means of computer technology in the classroom can be achieved combining static and dynamic sound and picture synchronization, greatly improving the students' interest, and to cultivate the students a variety of capacities, and strive to achieve the best effectiveness of teaching. Appropriate use of multimedia animation, combined with interesting graphics and wonderful sound teaching, teaching content more attractive, more focus on the students' attention. In teaching students to create a Quest situation to attract them into the imagination, abstract things concrete, to achieve the purpose of mastery of knowledge. I import the world's climate unit. Use PowerPoint to make a set of slides, 13 of the world's major climate typical landscape unfolding, accompanied by beautiful background music, the last title in the world's climate and several Questions. Students' attention all the focus to the sensual and elegant on the screen, sparking them to learn and explore the interest of "the world's climate, and actively learning.Second, focused, Overcoming DifficultiesGeography lesson many major and difficult, sometimes aloneteachers on the students understand very laborious. And the use of multimedia tools, animation, the procedure shows a partially enlarged, can not express, difficult to understand abstract and complex process of change, subtle structure into visual image rich, dynamic, innovative, interesting, beautiful music, appeal strong observation, viewing screen, can make it difficult to understand the focus of the difficulty becomes image, specific, vivid, clear and easy to understand, so that teaching a multiplier effect. "Earth's rotation and revolution impact on the climate is more abstract, both in this chapter the difficulty of teaching is the key. The seventh graders lack of spatial imagination, it is difficult to understand. I'm teaching this knowledge with Flash for a period of the Earth around the sun to the "analog animation: the vast sky, sweet music to the background, the Earth at an angle leaned to revolve around the sun, the sun in the center position steady stream of light radiation and parallel beam irradiation surface of the Earth. When the Earth's rotation to a specific location on the screen "Equinox", "summer solstice", "autumnal equinox", "Winter Solstice" and their corresponding high brightness will blink. Students through the animation very intuitive understanding of the sun's direct light point move, changing seasons, changes in the length of the day and night and polar day and polar night abstract knowledge of geography.Third, the dynamic map, vividThe map geography second language, geography teaching is inseparable from the map. But the usual map is flat, but the content is not strong, complex, targeted theme is not prominent, some space is needed to imagine geographical knowledge (such as "contour the hypsometric map"), due to the seventh graders space concept not yet established, to be completely "read" it is difficult to understand. If you use multimedia to produce two-dimensional, three-dimensional animated maps, and the use of color change, brightness, blinking, to improve map clarity, transparency, discrimination, and these problems will go away. I amteaching "the world's average temperature distribution law" knowledge points, making the electronic map. Talked about from low latitudes toward the poles temperature decreased this law, the corresponding region in the map according to the laws bright flashes, the students can understand. World average precipitation distribution and the world's major climate type of teaching I use this electronic map, and achieved good results.Fourth, electronic blackboard, intuitive and time-savingThe multimedia blackboard supplements are a lot of teachers are often used as a method. The contents of the electronic blackboard can be accompanied by teachers on the timely, as a supplement to the knowledge-speaking general and sublimation, co-ordination with the teachers explain, greatly improving the effectiveness of teaching. At the same time, compared with the traditional blackboard, electronic blackboard can save writing time, interrupted to explain ideas to avoid writing writing on the blackboard, can improve efficiency. I produced a courseware in teaching with knowledge: in marked with five equator and the Tropic of Capricorn and Tropic of Cancer, the north and south poles and pole side of the diagram of the earth is to introduce the text description of the characteristics of boreal, temperate and tropical, side each with a typical landscape pictures, click on the picture will play the video of these landscapes and short voice. In the teaching of "the world's 13 major climate types, I also used a similar electronic blackboard, saving time and vivid, with good results.The new curriculum stressed the need to " change the way teachers ". The rapid development of multimedia technology and wide application, for teachers to achieve the teaching way transformation provides a new powerful technical support and material preparation. The application of multimedia technology in geography classroom teaching, changing the traditional " chalk blackboard + " " a mouth, a book " single teaching way, make the geography classroom become " alive", vivid and efficient. Thefollowing is my personal experience in teaching.One, the creation of context, to stimulate interestSue Home Linsky pointed out that " all intellectual work depends on interest ". Multimedia teaching the use of text, sound, image, animation, network transmission, computer science and technology, in the classroom can realize the combination of static and dynamic, synchronized sound, greatly enhance students' interest in learning, thus cultivating student's various ability, and strive to achieve the best teaching effect. We appropriately using multimedia animation, with interesting graphic and excellent sound teaching, make the teaching more attractive, more focused the attention of students. In the teaching process for students to create a quest situation, draw them into the space of imagination, the abstraction of specific things, to achieve the purpose of knowledge. I'm in " world climate " unit. Using PowerPoint produced a group of slides, will be the world's 13 major climatic types of the typical landscape of the one one show, and with beautiful background music, was last seen heading " world climate " and several questions. Students' attention to sound and picture, arouse their learning and discussing " the world's climate " interest, active learning.Two, outstanding key, breakthrough difficultyGeography class in many key, difficulty, sometimes by the teachers, students to understand very laborious. The use of multimedia means, through animation simulation, process of demonstration, zoom, can put some difficult to express, difficult to understand the abstract content, complex change process, fine structure is transformed into a visual image, dynamic rich, novel and interesting, beautiful music, and strong infection can be observed, can watch the picture, can make it difficult to understand emphasis, difficulties becomes figure, specific, vivid, easy to understand, and make the teaching more effective. " The earth's rotation, the revolution 's impact on climate " more abstract, since this chapter teaching difficulty and key. Seven grades students' lack of spaceimagination, it is difficult to understand. I was teaching the knowledge point, with Flash produced a " revolution of the earth around the sun " Animation: in the vast sky, melodious music as the background, the earth into a certain angle and revolves around the sun, the sun in the center position everfount ground radiation light beam, and parallel to the surface of the earth. As the earth rotates to a specific position on the screen, " equinox ", " summer solstice ", " equinox", " winter solstice " and their corresponding date will be in high brightness flicker. The students through the animation is very intuitive understanding of sun direct light spot moving, changing seasons, the length of day and night, night and day change abstract knowledge of geography.The three map, dynamic, vividThe map is the discipline of geography " second language ", is inseparable from the map in geography teaching. But the normal map is planar, and complicated content, pointed is not strong, the topic is not outstanding, some need the space imagination of geographical knowledge ( such as " the contour of hypsometric map" ), since the seven grade students the concept of space has not yet been established, to be completely " read " it is difficult to understand. If the use of multimedia to produce 2D, 3D animation maps, and the use of color change, luminance flicker, to improve map clarity, transparency, differentiation degree, these problems can be smoothly done or easily solved. I am teaching " the world's average temperature distribution rule of " knowledge point, making electronic map. Like that " from low latitude to the poles of the temperature decreases ." this rule, a map corresponding region according to the law of light flashes, the student can understand. In the " world average precipitation distribution " and " main world climate type " teaching I have used the electronic map, and achieved very good results.In four, electronic blackboard, intuitive and timeMultimedia as a blackboard supplementation is many teachers oftenuse a method. Electronic blackboard content can be accompanied by teachers on the show, as for talking about complementary knowledge, summary and sublimation, and the teachers cooperate each other, greatly improve the teaching effect. At the same time, with the traditional blackboard writing in electronic writing on blackboard writing, can save time, avoid writing interrupt on train of thought, can improve the efficiency of. I am teaching "five band " knowledge point, making a class: in five, marked with equator, south of the Tropic of cancer, the polar and pole of earth schematic side is boreal, temperate, and tropical introduced the characteristics of the text, one side is the typical landscape picture, click on the picture will be playing these landscape video and brief introduction to phonetics. In the teaching of " the world 13 main types of climate ", I also used a similar electronic blackboard, saving time and vivid image, the effect is very good.附录4外文译文地理教学中多媒体应用的几点体会新课标强调要“改变教师的教学方式”。

Raman Spectroscopy with the WITec Alpha 3000 MicroscopeAppropriate Samples and Sample PrepYou can attempt to analyze anything that will fit beneath the objective. Data quality will be determined by the number and intensity of Raman active vibrational modes in the materials making up the sample. If your sample is very thin (microns or less), you may observe Raman signals from your substrate convoluted with those of your analyte. It may therefore be necessary to select a substrate with a Raman spectrum that does not interfere with that of your analyte. Penetration depth in 3D images is limited by the optical properties of your sample. If your sample does not transmit the 633nm laser light well, you can expect a dramatic fall-off in signal intensity as you attempt to penetrate the surface further. Getting Started1.Turn on the power strip to the left of the cabinet.2.Open the cabinet using the foot pedal3.Rotate the 10x objective into place.4.Place your sample on the stage.5.Log into the PC.ername: labuserb.Password: Sample123!6.On the desktop, double click to start WITec Control 1.607.On the menu bar click Configurations→Raman→Raman8.In the Control window, expand the settings for Spectrograph 1 and change the LaserWavelength to 633nm, Grating to 300g/mm, and Spectral Center to 2700nm. Expand thesettings for Spec Camera 1 and type -60C in for temperature (this may be necessary even if -60C is already shown as the setting). In the Message window verify that the DV401: Cooling message shows a setpoint of -60C and the temperature is decreasing.9.To see an image of the sample on the monitor, you need to adjust the metal rod, mirror cube,and filter holder from the right side of the microscope (see pic below).a.The metal rod has two positions: in and out. To view the sample on the monitor it must bepushed in.b.The mirror cube has three positions labeled I, II, and III. While inserting the cube from theright side of the microscope, the first position you land on is I followed by II then III. To view the sample on the monitor, the cube must be in position I, which puts a dichroic mirror inplace to illuminate the sample with white light.c.The filter holder has two positions, 1 and 2. When inserting the filter holder from the rightside of the microscope, you will first land on position 1 which does not contain a filter. This is the position you want to be in while viewing your sample on the monitor. If you push the filter holder in further it will move to position two, which contains the laser line filter. If this filter is in place the image on the monitor will be very dark and have a blue/purple color.Setting up for Raman Acquisitione the remote control to raise the microscope objectivea.Repeatedly press one of the arrows on the remote control until RC: Microscope Z showsbelow the menu barb.Rotate the knob on the remote control all the way counterclockwise, then rotate itclockwise to the desired speed. Speed setting can be viewed in the Graphic Control window.c.Press and hold +Z button on the remote control to raise the microscope objective2.In the Control window, expand the settings for Illumination. Enter a value for Illumination (0 to100) and turn the illumination on. You should see a white spot on the surface of your sample. If you do not see a spot even at high settings, the mirror cube probably needs to be moved toposition Ie the remote control with a speed around 100 to lower the microscope objective. You willneed to reduce the illumination intensity as you lower the objective. As you come down the first thing you will see is the worm. Next you will see the clouds. Then your sample surface will come into focus. Use a lower speed and adjust the illumination to get a good focus on your sample.e the micrometers on the sample stage to find the area of the sample that you want to image.5.Rotate the 50X objective into position.e a slower speed to focus on your sample. You will need to increase the illumination.7.From the right side of the microscope, push the filter holder in to position 2. You should see theimage on the monitor darken indicating that that laser line filter is in the optical path. Also, push the mirror cube in to position 2 and pull the metal rod out.Warning: Make sure the laser line filter is in the optical path before you turn on thelaser. If the filter is not in place, the laser light may damage the spectral camera!8.Turn the laser on using the key on the controller. Turn the micrometer on the laser headcounterclockwise until you see the laser beam emerge from the microscope objective.9.In the Control window, expand the settings for the Oscilloscope and click Start Oscilloscope. Youshould observe a Raman spectrum of your sample in the Hardware Spectrum window.a.Scroll the mouse wheel in the Hardware Spectrum window to fit your peaks in the window.b.In the Control window under Spectrograph 1, you can adjust the settings to determine thewavelength range shown in the Raman spectrum. The Grating setting determines the width of the range while the Spectral Center determines the center wavelength. Below are settings for each grating that allow you to take a spectrum with the Rayleigh peak (shift = zero) onthe left edge of the spectrum.e the remote control to fine tune the height of the microscope objective to maximize thestrength of the Raman signal. You should need to go a few microns up as shown in the Status window.11.In the Control window under Oscilloscope, increase the Integration Time to check for additionalRaman peaks. Use the minimum integration time that provides acceptable S/N for your Raman peaks of interest.12.In the Control window under Oscilloscope click Stop.Acquiring Single Raman Spectra1.In the Control window expand the settings under Single Spectrum. Enter your desiredIntegration Time, Accumulations, Sample Name and Number then click Acc. Single Spectrum.Your spectrum will be shown in a new window.Acquiring Raman Images1.In the Control window, expand the settings under Image Scan. Under Scan Details, for a 2Dimage in a single XY plane, set Scan Mode to Single. For a 3D image, set the Scan Mode to Stack.2.Enter the desired Points per Line and Lines per Image (these control the XY spatial resolution)and Layers per Scan (these are depth or Z-axis layers for Stack scans).3.Under Geometry, enter your desired Height, Width, and Depth (stack scans only).4.Enter your desired integration time under Int. Time (Trace). Make note of the time per line: thetotal time is the trace plus the retrace. The total acquisition time for the image will be the time per line multiplied by the number of lines and the number of layers.5.Under Data Labeling, enter a Sample Name and Number.6.Click Start Scan to begin image acquisition. You can monitor the progress of your acquisition inthe Message window.Repositioning the SampleIf you want to view the sample on the monitor so that you can reposition it for another acquisition, follow these steps:1.Turn the micrometer on the laser head all the way clockwise. You should see the laser spotunder the objective disappear.2.Turn off the laser.3.Push the metal rod on the right side of the microscope in.4.From the right side of the microscope, pull the cube out to position I.5.From the right side of the microscope, pull the filter holder out to position 1.e the remote control to refocus on the sample. You should now see the sample in the video.7.window so you can reposition it using the micrometers below the sample stage.8.To acquire Raman data, start from Step 7 under Setting up for Raman Acquisition above.Data Analysis Overview:The Project Manager window shows all of the data files associated with a project. This includes raw data acquired with the microscope as well as processed data. Single spectrum data is shown as graph files represented by . Image data is shown as image graph files represented by . Images generated from acquired image graph files are represented by . You can double click any file in the Project Manager window to open it.For images and image graph files, you can use the arrow keys to move around and display Raman spectra from different points in the image. For 3D data you can use PgUp and PgDn keys to move through the vertical layers. You can click in any image to bring up the Raman spectrum from that location. You can zoom in on any image using the mouse wheel. You can hold the mouse wheel down to move around in the image.You can adjust the vertical scale of Raman spectra by positioning the pointer below the baseline and scrolling the mouse wheel. You can move the baseline up or down by positioning the pointer above the baseline and scrolling the mouse wheel.Exporting Data1.To export a picture of a Raman spectrum, right click the spectrum and select Export→Bitmapto File2.To export the raw data (XY pairs) of a Raman spectrum as an ASCII file, right click the spectrumand select Export→ASCII to File3.To export any open image as a picture, right click the image and select Export →Bitmap to File.4.To export raw image data, right click the image graph file in the Project Manager window andselect Export.Generation and Analysis of Raman Images1.Create images for each of the desired peaks in the Raman spectruma.In the Filter Manager window for your data file, click Add Sum Filter . If you don’t see thefilter manager window, right click on the spectrum and select Graphs→View→FilterManageri.In the Filter Manager window you can enter the expected left and right boundaries ofa Raman peak in wavenumbers in the Start and Stop fields.ii.Alternatively, you can select a region in the displayed spectrum: Check the Listen box in the Filter Manager window. In the Graph Tools window click Mark Region . Thenclick and drag over the peak location in the spectrum.b.Repeat the above step to add sum filters for each peak or spectral region where you want togenerate an image.c.To generate the images, click Calculate in the Filter Manager window. You can open theimages from the Project Manager window. You can click in any image to see the Ramanspectrum at that location.2.To perform cosmic ray removal, drag and drop an image graph file in the Project Managerwindow to CRR in the Drop Actions window. Adjust parameters if necessary then clickExtract. A new image graph file (CRR) will be generated in the Project Manager window.3.Background subtractiona.Drag an image graph file from the Project Manager window to Graph BackgroundSubtraction in the Drop Actions window.b.Make sure Mark Region is selected in the Graph Tools window.c.In the blue section of the new window, hold down the shift key while clicking and draggingover each peak to deselect the peaks. You may need click around in your images to bring updifferent spectra to make sure all of the peaks are deselected.d.In the Graph Background Subtraction window, change the order until the blue line on thespectrum closely follows the baseline.e.Click Extract when you are satisfied. The baseline in the new image graph file (Sub BG)should be flat.4.Obtaining pure spectraImages usually contain multiple features with unique Raman spectra. In this step you willgenerate Raman spectra corresponding to specific features or materials in the image.a.In the Image Tools window, select one of the selection tools (pen, circle, or rectangle). Use the selection tool in one of the images to select the region corresponding to a single material or feature.b.In the Image Tools window, click Make image from draw field . A new image file willappear in the Project Manager window.c.Repeat b and c for all other features of interest in the original image. You can use Clear drawfield in the Image Tools window to clear the selection.d.In the Project Manager window, ctrl+click to select all of the new images along with thedesired image graph file and drag them to Average Spectrum in the Drop Actionswindow. The pure spectra will appear as new graphs in the Project Manager window. When You Are Finished1.On the menu bar click File Save Project As to save your data.2.Turn the micrometer on the laser head all the way clockwise. You should see the laser spotunder the objective disappear.3.Turn off the laser.4.Remove your sample from the stage.5.Close the WITec Control software. There is a waiting period that must pass before the softwarecloses.Warning: Do not skip the wait period or you risk damaging the spectral camera!6.After the waiting period has passed and the software is fully closed, turn off the power strip tothe left of the cabinet.7.Close the cabinet using the foot pedal.。

emoji的未来英语作文The Future of Emoji。
In today's digital age, emojis have become an integral part of our communication. From text messages to social media posts, emojis are used to express emotions, convey messages, and add a touch of fun to our conversations. As technology continues to advance, the future of emojis is a topic of great interest and speculation.One of the most exciting possibilities for the futureof emojis is their potential to become more interactive and dynamic. With the development of augmented reality andvirtual reality technologies, emojis could evolve fromstatic images to animated, 3D characters that can be placed in real-world environments. Imagine being able to send a dancing emoji that appears to be right in front of you, ora laughing emoji that reacts to your movements and gestures. This would add a whole new dimension to our digital communication and make it even more engaging and immersive.Another trend that we can expect to see in the future is the expansion of emoji diversity. While emojis have become more inclusive in recent years with the addition of various skin tones and gender options, there is still room for improvement. In the future, we may see a wider range of emojis representing different cultures, traditions, and lifestyles from around the world. This would not only make emojis more representative of the global population, but also promote greater understanding and appreciation of diversity.Furthermore, as artificial intelligence continues to advance, we may see emojis that are able to adapt and personalize themselves based on our individual preferences and emotions. For example, a smart emoji could analyze the tone and context of a conversation and suggest the most appropriate emoji to use, or even create custom emojis based on our facial expressions and body language. This would make our communication more intuitive and tailored to our unique personalities.In addition to their role in communication, emojiscould also have practical applications in various fields. For instance, in the field of healthcare, emojis could be used to monitor and track patients' emotional well-being, providing valuable insights for doctors and caregivers. In education, emojis could be used as a visual aid to help students learn and understand complex concepts more easily. In the workplace, emojis could be used to enhance collaboration and teamwork, fostering a more positive and supportive work environment.Of course, with these exciting possibilities also come challenges and considerations. As emojis become more advanced and interactive, there will be a need for stricter regulations and guidelines to ensure that they are used responsibly and ethically. There will also be a need for ongoing research and development to address issues such as accessibility, inclusivity, and privacy.In conclusion, the future of emojis is full ofpotential and possibilities. As technology continues to evolve, we can expect to see emojis become more interactive,diverse, and personalized, with applications that extend beyond communication to various aspects of our lives. While there are challenges to overcome, the future of emojis is undoubtedly bright, and we can look forward to a more expressive, inclusive, and engaging digital communication experience. Let's embrace the future of emojis with open arms and a smiling face! 。
F r on t Ro y a lRIDGEFIELD TRACE◆ N orth Branch A 1.5 mile trail link connects the Prairie Trail to the Hebron Trail. The oak savanna, sedge meadow, wetland complex and winding banks of Nippersink Creek provide a home to numerous birds, butterflies, fish and wildflowers.◆ G lacial Park Home to theLost Valley Visitor Center, this 3,400 acre site lies within the boundaries of the Hackmatack National Wildlife Refuge and includes prairie, savanna, marshes, kames and Nippersink Creek.◆ P etersen Park Owned andmanaged by the City of McHenry, offering many recreational amenities.◆ W hispering Oaks ParkOwned and managed by the City of McHenry, this park features Fort McHenryplayground and playing fields.◆ S terne’s Woods Ownedand managed by Crystal Lake Park District, the area contains Wingate Prairie Illinois Nature Preserve. It is the most wooded and winding section of the trail.◆ R idgefield Trace The District’snewest regional trail can be accessed from Hillside Road and then South on Walkup Rd. for a 1 mile ride to Oak St. in Crystal Lake. Future phases will connect this trail to McHenry County College and then west to Route 47 in Woodstock.◆ D iverse City Prairie Located between Virginia Road Trail is marked in .5 mile increments.0 .5 1 2 mi.Prairie Trail: 26 Miles Hebron Trail: 5.5 MilesNorth Branchtrail link: 1.5 MilesRidge eld Trace: 3.5 MilesTrail is marked in .5 mile increments.0 .5 1 Prairie Trail: 26 MilesHebron Trail: 5.5 MilesNorth Branch trail link: 1.5 MilesRidge eld Trace: 3.5 MilesTrail is marked in .5 mile increments..512 mi.Points of InterestThe McHenry County Prairie Trail stretches 26 miles from Algonquin to the Wisconsin State Line. The trail follows the former Chicago and Northwesternrail line that ran from Kane County into Wisconsin. By building the Prairie Trail along portions of the corridor that were abandoned by the railroad and complementing the existing active rail with adjacent trails, the District has recycled an old mode of transportation into one for the future. The Prairie Trail’s main access points are located north of Algonquin, along Main Street in Crystal Lake, at Petersen Park in McHenry, and in Glacial Park north of Ringwood. There are also several scenic and recreational stopping points alongthe Trail, including the Fox River and Larsen Prairie. The Prairie Trail is open daily, sunrise to sunset. The Hebron Trail follows the old K.D. Railroad line, connecting to the Prairie Trail at North Branch Conservation Area near Richmond and continuing 5.5 miles to Church Street in Hebron.Algonquin to Ringwood (19 miles)This paved section provides recreational opportunities for pedestrians, bicyclists, roller bladers and cross-country skiers. Please note that while most of the trail is relatively flat, the section between Lorraine Avenue and Hillside Road in Crystal Lake (through Sterne’s Woods) is quite hilly.Ringwood to Wisconsin line (7 miles)This original rail ballast/gravel trail offers a travel route for hikers, horseback riders,bicyclists (road bicycles are not recommended) and snowmobilers (with more than 4" of snow).Prairie Trail to Hebron Trail (7 miles)Prior to reaching the Wisconsin border, the Prairie Trail connects to the North Branch trail, westbound 1.5 miles, and links to the 5.5 mile Hebron Trail.815.338.6223 • McHenry County Conservation DistrictTrail Uses• P ark in District lots or appropriate street locations along the trail.• Leash all pets and remove any animal waste.• S tay to the right side of the trail. Bicycles yield to pedestrians.• R emain on the trail unless signs indicate that there is another trail or rest area for your use. Show respect for adjacent property owners and natural areas by staying on trail surfaces. • H elp keep your trails clean. Deposit all litter and waste in designated receptacles.• C arry necessary equipment and supplies for your personal safety and comfort.• E nsure your equipment is in working order.• P ractice Trail Etiquette. Look out for fellow trailusers and report any problems or suspicious activity to a Prairie Trail Safety Watch volunteer or District police officer through the McHenry County Sheriff's Department at (815) 338-2144. During weekdays, call the District’s Main Office at (815) 338-6223 between 8 a.m. and 4:30 p.m.Site Rules◆ B etween the Kane County line andU.S. Highway 14 in Crystal Lake, the Prairie Trail is built on an abandoned rail corridor. From U.S. Highway 14 north to Ringwood, the trail is built adjacent to an active rail line, making it one of the country’s longest trails along an active rail corridor.◆ T he Prairie Trail connects eight McHenryCounty communities, including Algonquin, Lake in the Hills, Crystal Lake, Prairie Grove, McHenry, McCullom Lake, Ringwood and Richmond.◆ F rom the Prairie Trail, users have access toover 100 miles of trail network including the Hebron Trail, Ridgefield Trace, the Fox River Trail, the Great Western Trail, and the Illinois Prairie Path. ◆ T he Hebron Trail is built on the formerKenosha Division Railroad that carriedpassengers, mail and freight from Kenosha, WI to Rockford, IL. The K.D. line ran from 1860 until its final voyage in 1939.Trail FactsOverview Prairie Trailincluding the Hebron Trail03/2013 (R -9/13) 5000 (H P )18410 U.S. Highway 14, Woodstock, IL 60098Site open sunrise to sunset.Done with the map? Recycle it by placing it back in the brochure holder for the next visitor.。