商英国贸课本课后选择 部分
- 格式:docx
- 大小:26.12 KB
- 文档页数:5
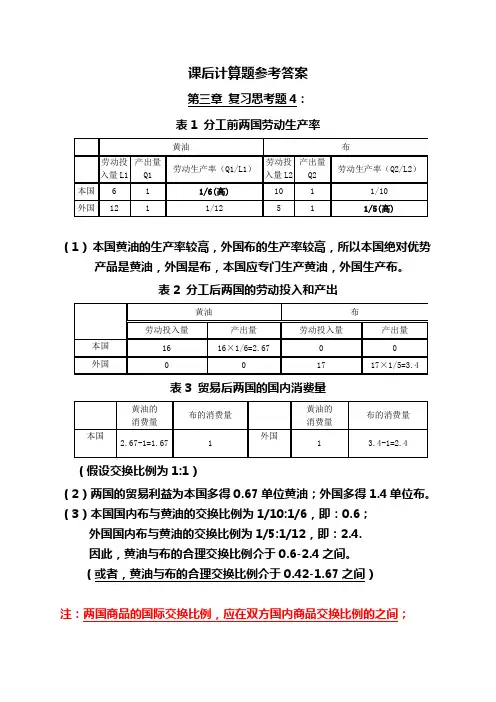
课后计算题参考答案第三章复习思考题4:表1 分工前两国劳动生产率(1)本国黄油的生产率较高,外国布的生产率较高,所以本国绝对优势产品是黄油,外国是布,本国应专门生产黄油,外国生产布。
表2 分工后两国的劳动投入和产出表3 贸易后两国的国内消费量(假设交换比例为1:1)(2)两国的贸易利益为本国多得0.67单位黄油;外国多得1.4单位布。
(3)本国国内布与黄油的交换比例为1/10:1/6,即:0.6;外国国内布与黄油的交换比例为1/5:1/12,即:2.4.因此,黄油与布的合理交换比例介于0.6-2.4之间。
(或者,黄油与布的合理交换比例介于0.42-1.67之间)注:两国商品的国际交换比例,应在双方国内商品交换比例的之间;两种商品的国内交换比例=两种商品的劳动生产率之比。
第三章复习思考题5:表1 分工前两国劳动生产率(1)生产可能性方程为:L=a Lx x+a LY Y,其中L代表总劳动力,a Lx代表X商品的生产成本,x代表X商品的产量,a LY代表Y商品的生产成本,Y代表Y商品的产量。
因此,把已知条件代入上述等式,得出本国的生产可能性方程为:2=10X+4Y,即:Y=0.5-2.5X;同理,得出外国的生产可能性方程为:1.2=3X+2Y,即:Y=0.6-1.5X。
(另一种简洁算法为:画出几何图形,生产可能性曲线与横轴的交点为投入所有劳动生产X的产量,与纵轴的交点为投入所有劳动生产Y的产量,则生产可能性方程为Y=纵轴Y的产量-斜率乘以X)(2)无贸易时的生产组合意味着求生产可能性曲线与社会无差异曲线的交点,即:生产可能性方程与效用函数的交点,在这一交点上,生产可能性方程与效用函数的斜率相等,由(1)可知本国生产可能性方程的斜率为2.5,外国生产可能性方程的斜率为1.5,而两国的效用函数均为U=XY2,效用函数的斜率为效用函数分别对X和Y求导后的比率,即:U X’/U Y’= Y2/2XY,则本国:Y2/2XY=2.5,即:Y=5X,外国:Y2/2XY=1.5,即:Y=3X,把Y=5X与本国的生产可能性方程Y=0.5-2.5X联立,解出X=1/15,Y=1/3,所以本国无贸易时的国内生产组合为(1/15,1/3);把Y=3X与外国的生产可能性方程Y=0.6-1.5X联立,解出X=2/15,Y=2/5,所以外国无贸易时的国内生产组合为(2/15,2/5)。

世纪商务英语----外贸函电<第二版><教师用书>English Letter Writing in Foreign Trade主编吴思乐胡秋华XX理工大学出版社前言《世纪商务英语—外贸函电》是新世纪高职高专教材编委会组编的商务英语类课程规划教材之一。
本书主要针对高职高专商务英语和其他涉外经贸专业的学生..也可以作为其他层次涉外经贸专业的外经贸英语教材。
同时..对正在从事或即将从事涉外经贸活动和贸易洽谈工作的广大外贸工作者来说..本书还可作为自学参考资料。
为方便教学和自学者学习..我们编写了与之配套的练习答案..并提供了常用表达部分的译文。
希望本书能对我们的读者有所帮助。
编者ContentsModule UnitModule 1 Fundamentals of Modern Business Letter Writing 现代商务函电写作基础Unit 1 Basic knowledge of Business letter Writing 商务信函写作Module 2 Preparations for Negotiation 业务磋商的准备Unit 2 Establishing Business Relations 建立业务关系Unit 3. Making Credit Investigation 资信调查Module 3 Procedures of Business Negotiation 业务磋商的主要环节Unit 4 Inquiry 询盘Unit 5 Offer 发盘Unit 6 Counter-offer 还盘Module 4 Conclusion of Business 交易的达成Unit 7 Acceptance and Confirmation 接受与确认Unit 8 Order and Contract 订单与合同Module 5 Negotiation of Main Trade Terms 主要交易条款的磋商Unit 9 Payment and L/C 支付与信用证Unit 10 Packing 包装…Unit 11 Shipment 运输Unit 12 Insurance 保险Module 6 Disputes and Settlement 争议及争议的解决Unit 13 Complaints, Claims and Settlement 申诉、抱怨与索赔、理赔Unit 1. Fundamentals of Modern English Business Letter Writing第一章现代商务英语函电写作的基本知识Part Five Practical Training1. Arrange the Following in Proper Form as They Should Be Set Out in a Letter1> Sender's name: Guangzhou International Trading Corp.2> Sender's address: 198 Yueken Road, Tianhe District, Guangzhou, China3> Sender's T elephone: 852300004> Sender's cable address: 5527GZ5> Sender's telex address: 3328 gz CN6> Date: September 15, 20077> Receiver's name: Standard Oil Company8> Receiver's address: 38 Fifth Avenue, London, U. K.9> Subject: Refrigerators10> The message:We thank you for your letter of September 3, 2007, enquiring for the captioned goods.The enclosed booklet contains details of all our refrigerators and will enable youto make a suitable selection.We look forward to receiving your specific inquiry with keen interest. Basically, there are four acceptable formats for business letters. Students can choose one of the layouts as his or her style. The following is just a sample. Guangzhou International Trading Corp.Address: 198 Yueken Road,Tianhe District, Guangzhou, 510507,P. R. ChinaTel: 85230000, Cable: 5527GZ, Telex: 3328 gz CNSeptember 15, 2010Standard Oil Company38 Fifth Avenue,London, EC4, U. K.Dear Madam or Sir:Subject..RefrigeratorsThank you for your letter of September 3, 2007, enquiring for the captioned goods. The enclosed booklet contains details of all our refrigerators and will enable you to make a suitable selection.We look forward to receiving your specific inquiry with keen interest.Yours Sincerely,Li MingLi MingEncl. as stated2. Address an Envelope for the Above LetterSince we use the Full-block Style for the letter composing, we should also use the Full-block Style for the envelope.Guangzhou International Trading Corp.198 Yueken RoadTianhe District, Guangzhou,Guangdogn, ChinaStandard Oil Company38 Fifth AvenueLondon EC 4U. K.UrgentStampUnit 2 Establishing Business Relations第二章建立业务关系Part Three Other Commonly Used Expressions and SentencesTypical Sentences:1. Telling the addressee how his name is known in pleasant words. <用令人愉快的语言..说明你是怎样知道对方的>1..We are very pleased to obtain your name from the Industrial Chambers. ..很高兴从行业协会处得知贵公司的名称..2..On the recommendation of Merrs. Harvey & Co., we have learned with pleasure the name of your firm. <由于哈维公司的推荐..我们高兴地得知贵公司的名称。


1—4章试题一、单项选择题1、对外贸易量是指:以不变价格计量的对外贸易额解析:在实际工作中,往往要用以固定年份为基期计算的进口或出口商品价格指数去调整当年的进口额或出口额,得到相当于按不变价格计算的进口额或出口额。
通过这种方法计算出来的对外货物贸易额已经剔除了价格变动的影响,单纯反映对外货物贸易的数量规模,被称为对外贸易量。
故答案选D。
参见教材P42。
2、下列国际服务贸易形式属于商业存在的是:分支机构A、艺人演出(自然人流动)B、国际旅游(境外消费)C、国际长途电话服务(跨界供应)D、保险公司通过设立分支机构向当地的消费者提供服务解析:商业存在是一参加方在其他任何参加方境内通过提供服务的实体的介入而提供服务,如银行或保险公司通过设立分支机构向当地的消费者提供服务。
参见教材P44。
3、一种在规定的时间和场所,按照一定的规章和程序,通过公开叫价竞购,把事先经买主验看过的货物逐批或逐件卖给出价最高者的过程,这属于(B、拍卖)。
A、交易所交易B、拍卖C、博览会D、非固定的国际商品市场解析:拍卖是一种在规定的时间和场所,按照一定的规章和程序,通过公开叫价竞购,把事先经买主验看过的货物逐批或逐件卖给出价最高者的过程。
参见教材P64。
4、采用国际商品协定价格中,当商品的价格降到最低价格一下时应当(A、减少出口)。
解析:国际商品协定通常采用最低价格和最高价格等办法来稳定商品价格。
当有关商品价格降到最低价格以下时,就减少出口或用缓冲基金收购商品;当价格超过最高价格时,则扩大出口或抛售缓冲存货。
参见教材P67。
5、重商主义理论产生于(D、15-17)世纪资本主义生产方式准备时期,是资产阶级国际贸易理论的早期阶段。
D、15-17解析:重商主义理论产生于15-17世纪的资本主义生产方式准备时期,是资产阶级国际贸易理论的早期阶段。
参见教材P71。
6、以自由贸易精神签订的第一个贸易条约是(C、“科伯登”条约)。
解析:“科伯登”条约是以自由贸易精神签订的一系列贸易条约中的第一个,列有最惠国待遇条款。

第五章国际货物买卖合同的标的商品的品质【Case Study 1】我国出口苹果酒一批,名称为“APPLE WINE”, 我出口方在所有单据上均用“APPLE WINE”,不料,货到国外后遭受海关扣留罚款,因为该批货的内外包装均写的是“CIDER”字样。
商品的品质【Case Study 2】青岛某公司向日本出口一批苹果。
合同及来证上均写的是三级品,但发货时才发现三级苹果库存告罄,于是该公司改以二级品交货,并在发票上加注:“二级苹果仍按三级计价”。
货抵买方后,遭买方拒绝。
请问:在上述情况下,买方有无拒付的权利,为什么?【Case Study3】北京某公司向伊拉克出口北京冻鸭一批,合同规定:所有鸭子必须按伊斯兰教方法屠宰。
但该公司并不清楚伊斯兰教的宰法,在加工时改用科学的“钳杀法”。
货到国外后遭对方拒收,并通知该公司,或当地销毁,或立即退货。
问造成损失的原因是什么?【Case Study 4】A公司从国外进口一批青霉素油剂,合同规定该商品品质“以英国药局1953年标准为准”,但货到目的港后,发现商品有异样,于是请商检部门进行检验。
经反复查明,在英国药局1953年版本内没有青霉素油剂的规格标准,结果商检人员无法检验,从而使A公司对外索赔失去了根据。
商品的数量【Case Study 5】大连某进出口公司向日本出口一批大米,在洽谈时,谈妥出口2000公吨,每公吨收280美元FOB大连。
但在签订合同时,在合同上只笼统地写了2000吨,我方当事人认为合同上的吨就是指公吨而言,而发货时日商却要求按长吨供货。
问:外商的要求是否合理?我方应接受的教训是什么?【Case Study 6】合同中数量条款规定“10,000MT 5% more or less at the seller’s option”,卖方正待交货时,该货国际市场价格大幅度下跌,问:(1)如果你是卖方,拟实际交货多少数量?(2)如果你是买方,在磋商合同条款时,有何注意事项?【Case Study 7】中国某公司从国外进口小麦,合同规定:数量200万公吨,每公吨100美元。

《国际贸易实务与案例》2013年修订版参考答案第一章绪论复习题一、判断题1.×;2.√;3.×;4.√;5.√二、单项选择题1.B ;2.D三、简答题略第二章品质数量包装案例讨论一、品质案例[案例1]有一份FOB合同,出售100公吨农产品,总值50 000美元。
在交货时,所含水分超过合同规定指标10%。
讨论:买方可否撤销合同?答:不可撤销合同,只能要求损害赔偿。
因为,卖方所交农产品是含水份超标,应可食用,不构成根本性违约。
[案例2]有一份合同,出售大米10000公吨。
合同规定:“自9月份开始,每月装船1000公吨,分10批交货”。
卖方从9月份开始交货,但在交至第3批大米时,大米品质有霉变,不适合人类食用,因而买方以此为理由,主张全部合同无效,同时要求损害赔偿。
讨论:买方可否主张这种权利?如所交货物为成套的机器设备,如何处理?答:买方不可以主张全部合同无效,可主张包括第3批及以后各批无效。
因为,以后分批交货合同,每批次可作为相对独立的合同对待,1、2批次大米合格,买方须接受这两批货物。
而第3批不合格是买方有理由推断其以后各批将出现质量问题。
[案例3]有一份CIF合同,出售机床200台,货到目的港后,买方发现有部分零部件生锈。
他认为这批货是存仓太久的仓底货,因此向卖方提出25%的折价处理。
当卖方提出用全新货物换回已交付的货物时,买方已将该批货物运往非洲销售。
讨论:买方能否坚持25%的折价处理?为什么?答:买方不能坚持25%的折价处理。
因为按照《国际货物销售合同公约》,在交货不合格情况下,卖方可采取措施补救,买方需保全货物,不得做出行为使其已构成实际接受了货物。
由于在货物不合格下买方将货物转卖他人,已构成事实上接受了货物,因此丧失了索赔权。
二、数量案例[案例4]有一份CIF合同,出售100公吨绿豆,合同单价为每公吨1000美元,共100 000美元。
事后卖方只交货5公吨。
讨论:在这种情况下,买方可否主张撤销合同?为什么?如本例卖方交货90公吨。

单项选择题1.在出口合同的品质条款中( C )。
①为了明确责任,应使用两种以上的方法表示品质②为了准确,应使用两种方法表示品质③为了防止被动,一般不宜同时使用两种或两种以上的方法表示品质2.卖方与买方凭规格达成交易,并将参考样品留给买方,货到目的港经检验,各项指标均与合同规定相符,但有一项不符合参考样品,买方( B )。
①有权提出索赔,品质应符合参考样品②无权提出索赔,卖方不受参考样品的约束③有权提出索赔,品质不但要符合合同规定,还应符合参考样品3.按F.A.Q.进行买卖的商品是指( B )。
①机器设备②农产品③矿产品4.在国际贸易中,表示品质的方法有若干种( C )。
①只能单独使用某一种②不能单独使用③可视情况灵活结合使用5.凭样买卖时,样品( C )①只能由卖方提出②只能由买方提出③既可由卖方提出,也可由买方提出6.凡凭样买卖,如合同中无其它规定,则卖方所交的货物( C )。
①可以与样品大致相同②允许有合理公差③必须与样品一致7.凡货、样无法做到完全一致的商品,一般都不适宜采用(D)。
①凭规格买卖②凭等级买卖③凭标准买卖④凭样品买卖8.品质公差是指( C )。
①卖方允许买方的品质差价②买方允许卖方在交货的品质上有一个幅度③是商品本身的误差数量、包装一、选择题1.“以毛作净”实际上就是(B)。
A、按净重作为计价的基础B、按毛重作为计价的基础C、按理论重量作为计价的基础D、按法定重量作为计价的基础2.我国目前使用最多的计量方法(B)。
A、按数量计算B、按重量计算C、按长度计算D、按体积计算3.国际贸易中,大宗农副产品、矿产品以及一部分工业制成品习惯的计量方法(C。
A、按面积计算B、按长度计算C、按重量计算D、按容积计算4.在国际贸易中,木材、天然气和化学气体习惯的计量单位(C)。
A、按重量计算B、按面积计算C、按体积计算D、按容积计算5.在国际贸易中,酒类、汽油等液体商品习惯的计量单位是(D)。

国际贸易实务双语教程课后题答案解析KeyChapter1I. Answer my questions1. International trade is business whose activities involve the crossing of national borders. It includes not only international trade and foreign manufacturing but also encompasses the growing services industry in areas such as transportation, tourism, banking, advertising, construction, retailing, wholesaling, and mass communications. It includes all business transactions that involve two or more countries. Such business relationship may be private or governmental.2. Sales expansion, resource acquisition and diversification of sales and supplies.3. To gain profit.4. To seej out foreign markets and procurement.5. There are four major forms which are the following:Merchandise exports and Imports, Service Exports and Imports, Investment and Multinational Enterprise.6. It is the account which is a summary statement of the flow of all international economic and financial transactions between one nation (eg.the United States ) and the rest of the world over some period of time, usually one year.7. Merchandise Exporting and Importing.8. Yes. There are great differences between them.1) direct investment takes place when control follows the investment. It usually means high commitment of capital, personnel, and technology abroad. It aims at gaining of foreign resources and foreign markets. Direct investment may often get higher foreign sales than exporting. And sometimes it involves two or more parties. 2) While portfolio investments are not under control. And they are used primarilyfor financial purposes. Treasures of companies, for example, routinely more funds from one country to another to get a higher yield on short term investments.9. MNE is the abbreviation of the multinational enterprise. Its synonymsare NNC(the multinational corporation) and TNC (transnational corporation).10. Examples are travel, transport, fee, royalties, dividends and interest.11. The choice of forms is influenced by the objective being pursued and the environments in which the company must operate.12. It is limited by the number of people interested in a firm’s products andservices and by customers’ capacity to make purchase.13. This is because at an early stage of international involvement these operationsusually take the least commitme nt and least risk of a firm’s resources.14. Royalties means the payment for use of assets from abroad, such as fortrademarks patens, copyrights, or other expertise under contract known as licencingagreements.Royalties are also paid franchising.15. It is a way of doing business in which one party (the franchiser) the use of atrademark that is an essential asset for the franchisers’ business.II Match each one on the left with its correct meaning on the right 1. J 2.A 3.E 4.B 5.C 6.D 7.I 8.G 9.F 10.H III Translate the following terms and phrases into Chinese1 购买⼒ 11 经济复苏;恢复2 潜在销售量 12 经济衰退3 加价,涨价 13 间接投资4 国内市场 14 有形货物5 制成品 15 有形进出⼝6 边际利润 16 收⼊及⽀出;岁⼊及岁出7 市场占有率 17 超额能⼒8 贸易歧视 18 贸易中间⼈(商);经纪⼈9 时机选择 19 全部包建的⼯程承包⽅式10 经销周期 20 许可证协定IV Translate the following into English1. Trade is often the ‘engine’ of growt h. However oversimplified this metaphormay be, it does serve to underline the importance of foreign trade in the process ofgrowth. A healthy expansion of exports may not always be sufficient condition forrapid and sustained growth, but a strong positive association between the two isclearly undeniable. Trade expansion contributes to economic growth inmany ways.Among them are the benefits of specialization; the favorable effects of internationalcompetition on domestic economic efficiency; the increased capacity to pay for theimports required in development and more generally the stimulus to investment.2. International trade is the exchange of goods and services produced in onecountry for goods and services produced in another country. In addition to visibletrade, which involves the import and export of goods and merchandise, there is alsoinvisible trade, which involves the exchange of services between nations. Nationssuch as Greece and Norway have large maritime fleets and provide transportationservice. This is a kind of invisible trade. Invisible trade can be as important to somenations as the export of raw materials or commodities is to others. In both cases, thenations earn the money to buy necessities.3. There exist different ways of conducting international business. Exclusive salemeans the seller gives the overseas client the exclusive right of selling a particularproduct in a designated area within a specified period of time. In this kind of businesstransaction, the product is bought by the exclusive seller and therefore he should sellthe product by himself, assuming sole responsibilities for his profit and loss.Exclusive sale is different from agency where only commission is involved. Anddifference exists between general contract and exclusive sales because the exclusiveseller enjoys exclusive right in a particular area.4. There is no country in the world that can produce all the products it needs.Thus countries join in international division of labor for effective production andreproduction. Sometimes a country can buy goods and services from abroad on abarter basis. Barter means doing business by exchanging goods of one sortfor goodsof another sort without using money. Barter trade itself is not enough to meat acountry’s imp ort needs. But as a form of international trade, it is still attractive indeveloping countries where foreign exchange is in short supply and inflow of foreignfunds is far from sufficient to meet their obligations in external trade.Chapter2I. Answer the following questions(Omited)II. Filling the blanks with the suitable words in the text:1.meeting/satisfying;2.agent, foreign/overseas;/doc/72314187.htmlmission;4.own;5.setting;6.patent;7.profits;8.outlets;9.joint, venture; 10.subsidiaryIII.Translate the followings into English1). Economic activity began with the cavemen, who was economically self-sufficient. He did his own hunting, found his ownshelter, and provided for hisown needs. As primitive populations grew and developed, the principle of division oflabor evolved. One person was more able to perform some activity than another, andtherefore each person concentrated on what he did best. While one hunted, anotherfished. The hunter then traded his surplus to the fisherman, and each benefited fromthe variety of diet.In today’s complex economic world, neither individuals nor nations are self-sufficient nations are self-sufficient. Nations have utilized different economicresources; people have developed different skills. This is the foundation ofinternational trade and economic activities.Foreign trade, the exchange of goods between nations, takes place for many reasons. The first, as mentioned above, is that no nation has all of the commoditiesthan it needs. Raw materials are scattered around the world. Large deposits of copperare mined in Peru and Zaire, diamonds are mined in South Africa, and petroleum isrecovered in Middle East. Countries that do not have these resources within their ownboundaries must buy from countries that export them.Foreign trade also occurs because a country often does not have enough of aparticular item to meet its needs. Although the United States is a major producer ofsugar, it consumes more than it can produce internally and thus must import sugar.Third, one nation can sell some items at a lower cost than other countries. Japanhas been able to export large quantities of radios and television sets because it canproduce them more efficiently than other countries. It is cheaper for the United Statesto buy these from Japan than to produce them domestically.Finally, foreign trade takes place because of innovation or style. Even though theUnited States produces more automobiles than any other country, it still imports largequantities of autos from Germany, Japan and Sweden, primarily because there is amarket for them in the United States.2). The different kinds of trade nations engaged in are varied and complex, amixture of visible and invisible trade. Most nations are more dependent on exportsthan on any other activity. The earnings from exports pay for the imports that theyneed and want. A nation’s balance of payment is a record of these complex transactions. By reflecting all of these transactions in monetary terms , a nation is ableto combine the income it receives, for example, from exports, tourists expenditures,and immigrant remittances. This combined incomes is then spent on such items asmanufactured goods from other countries, travel for its citizens to other countries, andthe hiring of construction engineers.Chapter3I. Translate the followings from Chinese into English:1 terms of payment2 written form of contract3 execution of the contract4 sales contract5 purchase confirmation6 terms of transaction7 trading partners 8 the setting up of a contract9 trade agreement 10 consignment contract11 the contract proper 12 extension of the contract13 the contracting parties 14 special clause15 general terms and conditionsII. Answer the following questions in English:1 A contract is an agreement which sets forth bind obligations of the relevant parties. And any part that fails to fulfill his contractual obligations may be sued and forced to make compensation.2 There are two parties of business contract negotiations: oral and written. The former refers to direct discussions abroad; written negotiations often begin with enquiries made by the buyers.3 A written contract is generally prepared and signed as the proof of the agreement and as the basis for its execution. A sales or purchase confirmation is less detailed than a contract, covering only the essential terms of the transaction. It is usually used for smaller deals or between familiar trade partners.4 The setting up of a contract is similar to that of a trade agreement or any other type of formal agreements. It generally contains: 1) the title. The type of the contract is indicated in the title; 2) the contract proper. It is the main part of a contract; 3) the signature of the contracting parties indicating their status as the seller or the buyer; 4) the stipulations on the back of the contract and are equally binding upon the contracting parties.5 It generally contains the time of shipment, the mode of payment described in addition to an exact description of the goods including the quantity, quality, specifications, packing methods, insurance, commodity inspection, claims, arbitration and force majeure, etc.III. Translate the following into Chinese:合同是在双⽅达成协议的基础上制定的,⽽协议⼜是双⽅进⾏商务谈判的结果。

U n i t4B u s i n e s s e t h i c sExtensive ReadingCorporate Philanthropy Responds to DisastersExercisesI.Speed Reading ComprehensionRead the text for FIVE minutes, and find the best answer to each of the following questions.1. According to the 2nd paragraph, why some companies faced internalcriticism?A. These companies have donated too much money to the communities,regardless of theirown capacity.B. These companies ignored the needs of their own employees who wereaffected by thedisasters.C. The philanthropic programs of these companies were too cheap.D. Corporate had to go back to boards for additional donation resources.2. Why is it that some companies are suggested donating cash instead ofproducts when disasters take place?A. Products are often hard to transport and warehouse.B. Using cash in the locality helps rebuild the economy.C. Product may not fit the needs of the beset community.D. All of above.3. Which of the following statement is NOT true with Pitney Bowes Inc.?A. It has operated a fund that helps employees out of personal tragedies.B. Its Employee Involvement Fund can reflect employees’ interest and support.C. It has started splitting some of its corporate giving betweenimmediate and long-term assistance in the consideration of thecomplicated nature of identifying appropriate disaster aid.D. Medical and funeral expenses will not be the focus of its fund.4. According to the text, which of the following company’s foundation is NOT long-term-focused?A. Baxter InternationalB. MitsubishiC. General Electric Co.D. Pitney Bowes Inc.5. The software module of MicroEdge Inc. helps the company’s communityfoundation the best in terms of _______.A. free-of-charge serviceB. online serviceC. accountingD. disaster reliefII.VocabularyFill in the blanks with appropriate words from the text. The initial letter of each word has been supplied for you.1. It’s wise to use just as much caution when making your charitable givingdecisions as you do when making other decisions affecting your life.2. With soil that has had its biological components destroyed, the first steptoward restoration is to stop adding any more chemical fertilizers.3. The global obesity pandemic combined with society's anti-fat bias is moredamaging to women than to men, an expert has warned at an international conference.4. Turkey’s two major cities are grappling with water shortages afterrecord-low snow and rain falls in the winter and searing summertemperatures.5. The importers who do not intend clearing the imported goods for "homeconsumption" straightaway may choose to warehouse the goods.6. The Foundation is a public charity that works with individuals, families,businesses and foundations, serving their philanthropic needs as well as initiating giving programs.7. As the little copyist proceeded with her work, she sent every now and thena responsive glance toward her admirer.8. Beset by rumors, and four months from a primary election, the Mayoryesterday for the first time gave his account of a 2007 incident in which he argued with a police officer.9. Like so many others around the world, we are following the devastationcaused by the earthquake and tsunami that has hit many parts ofSoutheastern Asia.10. Some coincidences are small, and seemingly inconsequential, but othershave the potential to change lives.A Question of EthicsExercisesI.Reading Comprehension1. Which of the following statements is NOT TRUE with Waterschoot's case?A. It raised the ethical concerns regarding information technology andthe managementobligation.B. Waterschoot immediately reported to her boss and the unit's legalcounsel about theproblem because there was some crucial information for Lockheed Martin in the template.C. Waterschoot found the competitor’s confidential information before5 p.m.D. Waterschoot removed the document from the server with the purpose ofprotecting a competitor of Lockheed Martin’s.2. According to the text, as e-business and IT are developing, companiesneed to put the following into consideration EXCEPT _______.A. equipping the employees with essential IT ethicsB. establishing a set of ethical guidelines in a companyC. the impacts brought by IT on the employees concernedD. how to deal with the potential problem brought by e-business partnerships3. According to the Information Week Research survey, we can infer that_______.A. If your personal data is collected by a health-care company, they aremore likely to be sold to third parties than by any other industries.B. Most companies will inform their customers know when specific typesof data of theirown are being collected.C. When evaluating the ethical and moral implications of businessdecisions, a larger number of people will rely on their personalexperience only.D. Not many people know some ethical impacts may be brought by theirbusiness decisions.4. Paragraph 7 suggests that ________.A. Canon Information Systems Inc is monitoring its employees’ online activities;B. Canon Information Systems Inc’s human resources department tries tomake sure thattheir employees are using the Internet in an ethical and legal way;C. James Underwood, manager of IS, reports to the human resourcesdepartment;D. Canon Information Systems Inc’s human resources department may beviolating theprivacy of the employees.5. Companies nowadays concern not only about the employees’ awareness ofbusiness ethics, but also about ________.A. how the employees interact with the information technology in a digital context;B. the safety when the employees are handling the digital devices;C. the protection of the privacy of its customers;D. all of above.。

大学商务英语教材答案Unit 1: Introduction to Business EnglishExercise 1: Multiple Choice1. B2. A3. C4. B5. A6. C7. B8. C9. A10. BExercise 2: True or False1. True2. True3. False4. False5. FalseExercise 3: Fill in the Blanks1. global2. multinational3. economy4. communication5. negotiationsExercise 4: Sentence Completion1. facilitate2. enhance3. crucial4. proficient5. interactUnit 2: Business Communication Exercise 1: Matching1. G2. C3. B4. E5. I6. A7. H8. D9. FExercise 2: Sentence Transformation1. Could you please provide me with the necessary information?2. I would appreciate it if you could send me the report by Friday.3. I was wondering if you would be available for a meeting next week.4. I am writing to inquire about the possibility of a collaboration.5. Can you let me know if there are any available vacancies in your company?Exercise 3: Business Letter Writing[Your Name][Your Position][Your Company][Date][Recipient's Name][Recipient's Position][Recipient's Company][Address]Dear [Recipient's Name],I am writing to express my interest in [specific product/service] offered by your company, as advertised in [source]. Having thoroughly researched the market, I believe that your product/service aligns perfectly with our company's requirements.At [Your Company], we strive to provide our clients with top-quality solutions to enhance their business operations. After reviewing your product/service, we are confident that it can bring significant benefits to our organization. We are particularly impressed with [specific feature/benefit] and believe it would greatly streamline our processes.I would like to request additional information regarding yourproduct/service, such as pricing options, implementation process, and customer support. Additionally, if possible, I would appreciate the opportunity to arrange a demonstration or trial to assess its suitability for our needs.Please find enclosed a copy of our company profile for your reference. Should you require any further details or have any questions, please do not hesitate to contact me directly at [your contact information]. I look forward to your prompt response.Thank you for considering our inquiry. We eagerly anticipate the possibility of collaborating with your esteemed company and achieving mutual success.Yours sincerely,[Your Name]Exercise 4: Role PlayStudent A:You are a sales manager from Company A. Introduce your company's latest product, highlighting its unique features and advantages. Try to convince Student B to consider purchasing the product for their company.Student B:You are a procurement manager from Company B. Listen attentively to Student A's sales pitch and ask relevant questions to gather more information about the product. Express your concerns and negotiate terms if interested.Unit 3: Business EtiquetteExercise 1: Multiple Choice1. C2. A3. B4. A5. C6. B7. A8. C9. B10. AExercise 2: True or False1. False2. True3. False4. True5. FalseExercise 3: Fill in the Blanks1. punctuality2. protocol3. initiative4. etiquette5. appropriateExercise 4: Role PlayStudent A:You are a company executive visiting a foreign country for a business meeting. Familiarize yourself with the local customs and etiquette. Discussthe importance of building relationships before conducting business and emphasize the need for respectful behavior.Student B:You are a local representative from the foreign country. Welcome Student A to your country and share insights on the cultural customs and etiquette. Highlight the significance of hierarchy, gift-giving, and dining etiquette. Encourage open-mindedness and a willingness to adapt.注意:以上答案仅供参考,不同教材可能存在差异,请以实际教材为准。

国际贸易实务双语教程课后题答案KeyChapter1I. Answer my questions1. International trade is business whose activities involve the crossing of national borders. It includes not only international trade and foreign manufacturing but also encompasses the growing services industry in areas such as transportation, tourism, banking, advertising, construction, retailing, wholesaling, and mass communications. It includes all business transactions that involve two or more countries. Such business relationship may be private or governmental.2. Sales expansion, resource acquisition and diversification of sales and supplies.3. To gain profit.4. To seej out foreign markets and procurement.5. There are four major forms which are the following:Merchandise exports and Imports, Service Exports and Imports, Investment and Multinational Enterprise.6. It is the account which is a summary statement of the flow of all international economic and financial transactions between one nation (eg.the United States ) and the rest of the world over some period of time, usually one year.7. Merchandise Exporting and Importing.8. Yes. There are great differences between them.1) direct investment takes place when control follows the investment. It usually means high commitment of capital, personnel, and technology abroad. It aims at gaining of foreign resources and foreign markets. Direct investment may often gethigher foreign sales than exporting. And sometimes it involves two or more parties.2) While portfolio investments are not under control. And they are used primarilyfor financial purposes. Treasures of companies, for example, routinely more funds from one country to another to get a higher yield on short term investments.9. MNE is the abbreviation of the multinational enterprise. Its synonyms are NNC (the multinational corporation) and TNC (transnational corporation).10. Examples are travel, transport, fee, royalties, dividends and interest.11. The choice of forms is influenced by the objective being pursued and the environments in which the company must operate.12. It is limited by the number of people interested in a firm’s products and services and by customers’ capacity to make purchase.13. This is because at an early stage of international involvement these operations usually take the least commitme nt and least risk of a firm’s resources.14. Royalties means the payment for use of assets from abroad, such as for trademarks patens, copyrights, or other expertise under contract known as licencing agreements.Royalties are also paid franchising.15. It is a way of doing business in which one party (the franchiser) the use of a trademark that is an essential asset for the franchisers’ business.II Match each one on the left with its correct meaning on the right1. J2.A3.E4.B5.C6.D7.I8.G9.F 10.HIII Translate the following terms and phrases into Chinese1 购买力11 经济复苏;恢复2 潜在销售量12 经济衰退3 加价,涨价13 间接投资4 国内市场14 有形货物5 制成品15 有形进出口6 边际利润16 收入及支出;岁入及岁出7 市场占有率17 超额能力8 贸易歧视18 贸易中间人(商);经纪人9 时机选择19 全部包建的工程承包方式10 经销周期20 许可证协定IV Translate the following into English1. Trade is often the ‘engine’ of growth. However oversimplified this metaphormay be, it does serve to underline the importance of foreign trade in the process of growth. A healthy expansion of exports may not always be sufficient condition for rapid and sustained growth, but a strong positive association between the two is clearly undeniable. Trade expansion contributes to economic growth in many ways. Among them are the benefits of specialization; the favorable effects of international competitionon domestic economic efficiency; the increased capacity to pay for the imports required in development and more generally the stimulus to investment.2. International trade is the exchange of goods and services produced in one country for goods and services produced in another country. In addition to visible trade, which involves the import and export of goods and merchandise, there is also invisible trade, which involves the exchange of services between nations. Nations such as Greece and Norway have large maritime fleets and provide transportation service. This is a kind of invisible trade. Invisible trade can be as important to some nations as the export of raw materials or commodities is to others. In both cases, the nations earn the money to buy necessities.3. There exist different ways of conducting international business. Exclusive sale means the seller gives the overseas client the exclusive right of selling a particular product in a designated area within a specified period of time. In this kind of business transaction, the product is bought by the exclusive seller and therefore he should sell the product by himself, assuming sole responsibilities for his profit and loss. Exclusive sale is different from agency where only commission is involved. And difference exists between general contract and exclusive sales because the exclusive seller enjoys exclusive right in a particular area.4. There is no country in the world that can produce all the products it needs.Thus countries join in international division of labor for effective production and reproduction. Sometimes a country can buy goods and services from abroad on a barter basis. Barter means doing business by exchanging goods of one sort for goods of another sort without using money. Barter trade itself isnot enough to meat a country’s import needs. But as a form of international trade, it is still attractive in developing countries where foreign exchange is in short supply and inflow of foreign funds is far from sufficient to meet their obligations in external trade.Chapter2。
作业一一、名词解释样品买方样卖方样复样对等样参考样品定牌中性无牌中性商品品质商品数量商品包装中性包装指示性标志警告性标志二、选择题1. 在国际贸易中,对于某些品质变化较大而难以规定统一标准的农副产品,其表示品质的方法常用。
( A )A. 良好平均品质B. 看货买卖C. 上好可销品质D. 凭说明书买卖2. 在国际上,对冷冻鱼或冻虾等没有公认规格和等级的商品,其交货时规定品质的方法常用。
( B )A. 良好平均品质B. 上好可销品质C. 看货买卖D. 凭样品买卖3. 对工业制成品交易,一般在品质条款中灵活制定品质指标,通常使用。
( A )A. 品质公差B. 品质机动幅度C. 交货品质与样品大体相等D.规定一个约量4. 以实物表示商品品质的方法有( AB )A. 看货买卖B. 凭样品买卖C. 凭规格买卖D. 凭等级买卖E. 凭标准买卖5. 在国际贸易中,按样品提供者的不同凭样品成交可分为。
( ABC )A. 凭买方样品买卖B. 凭卖方样品买卖C. 凭对等样品买卖D. 凭图样买卖E. 凭参考样品买卖6. 对等样品也称之为( BC )A. 复样B. 回样C. 确认样D. 卖方样品E. 买方样品7. 在国际贸易中最常见的计量办法。
( B )A. 毛重B. 净重C. 理论重理D. 法定重量8. 根据国际商会《跟单信用证统一惯例》500号出版物之规定,对于“约量”允许其增减幅度不超过。
( C )A. 3%B. 5%C. 10%D. 15%9. 根据国际商会《跟单信用证统一惯例》500号出版物之规定,在以信用证支付方式进行散装货物的买卖,若合同中未明确规定机动幅度,其交货数量可有的增减幅度为。
( B )A. 3%B. 5%C. 10%D. 15%10. 目前,国际贸易中通常使用的度量衡制度有。
( ABCD )A. 公制B. 英制C. 美制D. 国际单位制E. 法制11. 在货物买卖合同中,数量机动幅度的选择权可由( ABC )A. 船方行使B. 卖方行使C. 买方行使D. 保险公司行使E. 开证银选择12. 数量条款主要涉及( ABCD )A. 成交数量确定B.计量单位确定C. 计量方法确定D. 数量机动幅度的掌握E. 品质公差确定13. 根据包装程度的不同,目前绝大多数商品采用( A )A. 全部包装B. 局部包装C. 软性包装D. 硬性包装14. 直接接触商品并随商品进入零售网点与消费者见面的包装叫( B )A. 运输包装B. 销售包装C. 中性包装D. 定牌15. “唛头”是运输标志中的( A )A. 主要标志B. 目的地标志C. 原产地标志D. 件号标志16. 按照国际贸易惯例,在合同中不作规定时运输标志的提供方一般是( B )A. 开证行B. 卖方C. 买方D. 船方17. 运输包装的主要作用在于( AB )A. 保护商品B. 防止货损货差C. 促进销售D. 宣传商品E. 吸引客户18. 销售包装的标志和说明主要有( ABCD )A. 包装的装潢画面B. 包装上的文字说明C. 包装上的标签D. 条形码E. 唛头19. 按国际标准化组织的建议和推荐,标准运输标志的内容包括( ABCD )A. 收货人的英文缩写字母或简称B. 参考号C. 目的地D. 件数号码E. 条形码20. 包装条款的内容主要包括( ABCDE )A. 包装材料B. 包装方式C. 包装规格D. 包装标志E. 包装费用21. 在卖方同意接受买方提供包装时,合同中包括条款除一般内容外还要订明( ABCD )A. 寄送包装的方法B. 包装送达的日期C. 送交包装迟延的责任D. 运费包括费用的负担E. 包装的技术性能三、判断题1. 国际贷物买卖合同中,品名条款是合同中的次要条款。
UNIT 11. Why did the mercantilists encourage export and restrict import?Because their basic argument was that it was in a country’s best interests to maintain a trade surplus, to export more than it imported. By doing so, a country would accumulate gold and silver and, consequently, increase its national wealth and prestige.2.What do the theory of absolute advantage and that of comparative advantage have in common? 答题紧扣以下三点:specialization positive-sum game encourage由于此题涉及面较多,要求大家自己找supporting details3. According to Rocardo, would a country purchase good that it could produce more efficiently at home than in other countries? Why or why not?此题答题点在于阐述comparative advantage,需要大家从p.3 comparative advantage 下面两段抽取有用信息。
5.How does the explanation of comparative advantage put forward by Heckscher and Bertil Ohlin differ from that offered by David Ricardo?Ricardo himself placed particular stress on labor productivity and argued that differences in labor productivity between nations underlie the notion of comparative advantage.Heckscher and Bertil Ohlin argued that comparative advantage arises from differences in national factor endowments.6.According to product life-cycle theory, in what circumstances does a country tend to switch from being an exporter of a product to an importer of a particular product ?Answer:As the market in the advanced countries matures, the product becomes more standardized, and price becomes the main competitive weapon. As this occurs, cost considerations start to play a greater role in the competitive process. To take the US as an example, one result is that producers based in advanced countries where labor costs are lower than in the United States might now be able to export to the US.10.Why are the theories of international trade important to an individual business firm in its international marketing activities?Location implications:From a profit perspective, it makes sense for a firm to disperse its various productive activities to those countries where, according to the theory of international trade, they can be performed most efficiently.First-mover implications:According to the new trade theory, firms that establish a first-mover advantage with regard to the production of a particular new product may subsequently dominate global trade in that product. This is particularly true in those industries where the global market can only profitably support a handful of firms. For the individual firm, the clear message is that it pays to invest substantial financial resources in trying to build a first-mover advantage , even if that means several years of substantial losses before a new venture becomes profitable .Policy implications:Business firms can and do exert a strong influence on government trade policy. By lobbying government, business firms can help promote free trade, or they can promote trade restrictions. Finally, Porter's theory of national competitive advantage also contains important policy implications. Thus, according to Porter, businesses should urge government to increase itsinvestment in education, infrastructure, and basic research and to adopt policies that promote strong competition within domestic markets.Unit 28. To which kind of exporters is countertrade less attractive? Small and medium-sized or large diverse multinational enterprises? And why?The option of countertrade is most attractive to large, diverse, multinational enterprises that can use their worldwide network of contracts to dispose of goods acquired in countertrading. On the other hand, unless there is no alternative, small and medium-sized exporters should probably try to avoid countertrade deals if possible, since they lack the worldwide network of operations that may be required to profitably utilize or dispose of goods acquired through them.9. How dose offset differ from counterpurchase?Offset is similar to counterpurchase insofar as one party agrees to purchase goods and services with a specified percentage of the proceeds from the original sale. The difference is that this party can fulfill the obligation with any firm in the country to which the sale is being made.10. What are the drawbacks of countertrade arrangements?Other things being equal, all firms would prefer to be paid in hard currency. Countertrade contracts may involve the exchange of unusable or poor-quality goods that the firm cannot dispose of profitably. In addition, even if the goods it receives are of high quality, the firm still needs to dispose of them profitably. To do this, countertrade requires the firm to invest in an in-house trading and department dedicated deals. This in itself can be expensive and time consuming.Unit 31. What are the major non-export modes of entry into foreign markets?Licensing, contracting and joint venture8. What are the advantages of contract manufacturing?1.It requires minimum investment of cash, time and executive talent ---particularly desirablewhere the market is risky---and permits rapid entry into a new market.2.It gives control over marketing and after-sales service and protects a trademark3.It avoids currency risks and financing problems4.It is particularly desirable where a local production base is needed (that is , insidetight controls or high tariff barriers, or where the government requires local manufacturer)but the size of the market does not warrant an investment.5.It allows labeling a produ ct as “locally made”, which is beneficial wherenationalistic feelings are strong.It avoids intracorporate pricing problems that can arise with a subsidiary, foreign branch, or joint venture.Unit 44.Why do many firms prefer horizontal FDI or licensing over exporting?Transportation CostFor the aspect of exporting, the transportation cost need to be added to production cost, it becomesunprofitable to ship some products over a large distance. This is particularly true of produces that have a low value to weight ratio and which can be production in almost any location(e.g. cement ,soft drinks, etc).For such products, relative to either FDI or licensing, the attractiveness of exporting decreases.Impediments to ExportingGovernment are the main sources of impediment to the free flow of products between nations .By placing tariffs on imported goods , governments can increase the cost of exporting relative to FDI and licensing. Similarly, by limiting imports through the imposition of quotas , governments increase the attractiveness of FDI and licensing.Following CompetitorsMany firms prefer FDI because during the process of doing business, there would be a situation—oligopoly. In such oligopoly industries a critical competitive feature is interdependence of the major players: what one firm does can have an immediate impact on the major competitors, forcing a response in kind. There is some evidence that these imitative behaviors lead to FDI. Product Life CycleVernon’s view is that firms undertake FDI at pa rticular stages in the life cycle of a product they have pioneered. They invest in other advanced countries when local demand in those countries grows large enough to support local production( as Xerox did ).They subsequently invest in developing countries when product standardization and market saturation give rise to price competition and cost pressures.8. What is backward vertical FDI?Backward vertical FDI is an investment into an industry abroad that provides inputs for a firm’s domestic production processes.Q9: According to the market power arguments, why do firms go all the trouble and expense of setting up operations in foreign countries?1 one aspect of market power argument is that firms undertake vertical FDI to limit competition and strengthen their control over the market. The most common argument is that by vertically integrating backward to gain control over the source of raw-material inputs, a firm can effectively shut new competitor out of an industry. Such a strategy involves FDI only because the raw-material inputs are found abroad.2 Another strand of market power explanation of vertical FDI sees such investment not as an attempt to build entry barriers, but as an attempt to circumvent the barriers established by firms already doing business in a country.Q10: What are the two explanations for vertical FDI offered by the market imperfections argument?1 however, as we saw in the case of horizontal FDI, licensing can be self-defeating as a mechanism for the sale of know-how. If the oil refining firms had licensed their prospecting and extraction know-how to Saudi Arabian or Kuwaiti firms, they would have risked giving away their technological know-how to those firms, creating future competitors in the process.2 Another strand of the market imperfections argument predicts that vertical FDI will occur when a firm must undertake investment in specialized assets whose value is dependent uponinputs provided by a foreign supplier. In this context, a specialized asset is an asset designed to perform a specific task, and whose value is significantly reduced in its next-best use.Unit 65.What are the points in favor of a floating exchange rate claim?The case for floating exchange rates has two main elements: monetary policy autonomy and trade balance adjustment.I think that a floating exchange rate regime gives countries monetary policy autonomy which will give monetary control to a government. A government could use monetary policy to contract or expand the economy to deal with the problems it faces without worrying about the need to maintain parity.The adjustment mechanism works much more smoothly under a floating exchange rate regime because if a country is running a trade deficit, the imbalance between the supply and demand of that country’s currency in the foreign exchange markets will lead to depreciation in its exchange rate. In turn, by making its exports cheaper and its imports more expensive, an exchange rate depreciation should ultimately correct the trade deficit.6. List the four arguments that the case for a fixed exchange rate regime claims.1) Monetary DisciplineIt maintains a fixed exchange rate parity ensures that governments do mot expand their money supplies at inflationary rates. And it advocates of fixed rates argue that governments all too often give in to political pressures and expand the monetary supply far too rapidly, causing unacceptably high price inflation. A fixed exchange rate regime will ensure that this does not occur.2) SpeculationCritics of floating exchange rate regime also argue that speculation can cause fluctuations in exchange rates. They point to the dollar's rapid rise and fall during the 1980s,which they claim had nothing to do with comparative inflation rates and the U.S. Trade deficit, but everything to do with speculation. Thus, advocates of fixed exchange rate regime argue that such a system will limit the destabilizing effects of speculation.3) UncertaintySpeculation also adds to the uncertainty surrounding future currency movements that characterizes floating exchange rate regimes. They argue that a fixed exchange rate, by eliminating such uncertainty, promotes the growth of international trade and investment.4) Trade Balance AdjustmentsThose in favor of floating exchange rates argue that floating rates help adjust trade imbalances. Critics question the closeness of the link between the exchange rate and the trade balance. They claim trade deficits are determined by the balance between savings and investment in a country, not by the external value of its currency. Moreover, they argue that a depreciation in a currency will lead to inflation.10. Under present managed-float system, how would a company responds to the volatility of exchange rates?1) Currency ManagementAn obvious implication with regard to currency management is that the current system is a managed-float system in which government intervention can help drive the foreign exchange market. Companies engaged in significant foreign exchange activities need to be aware of this andto adjust their foreign exchange transactions accordingly.A second message contained in this chapter is that under the present system speculative buying and selling of currencies can create very volatile movements in exchange rates.2) Business StrategyThe volatility of the present floating exchange rate regime suggests that one response might be to build strategic flexibility.Disperse production to different locations around the globe as a hedge against currency fluctuations.Anther way of building strategic flexibility involves contracting out manufacturing. This allows a company to shift suppliers from country to country in response to shifts in relative costs brought about by exchange rate movements.The role of the IMF and the World Bank in the present international monetary system also has implications for business strategy. International businesses selling or producing in such countries need to be aware of this and plan accordingly.3) Corporate-Government RelationsBusinesses can influence government policy toward the international monetary system. Business can and should use its influence to promote an international monetary system that facilitates the growth of international trade and investment.Unit 71. What are the importance of demand chain thinking?The importance of demand chain thinking is that it believes that the company would be more effective by considering its target market’s requirement first and then plan, implement, and control the physical flows of materials and final goods from points of origin to points of use to meet customer requirements as a profit.4. What does the just-in-time production methods expect of supplies? Why?Just-in-time production consists of arranging for supplies to come into the factory the rate that they are needed. If the supplies are dependable, then the manufacturer can carry much lower level of inventory and still meet customer-order-fulfillment standards.5. What are the remarkable differences between storage warehouses and distribution warehouses? Storage warehouses store goods for moderate-to-long periods of time. Distribution warehouses receive goods from various company plants and suppliers and move them out as soon as possible.7. In what way can a company achieve market-logistics efficiency?①The starting point is to study what customers required and what competitors are offering .Customers are interested in on-time delivery ,supplier willingness to meet emergency needs, careful handling of merchandise, supplier willingness to take back defected goods and resupply them quickly.②The company must then research the relative importance of these service outputs.③The company must also consider competitors’ service standard.④The company ultimately has to establish some promise to the market.Unit 81. What are the bases for the legal systems of the countries of the world?The bases for common law is tradition ,past practices ,and legal practices ,and legal precedent set by the courts through interpretations of statutes , legal legislation ,and past rulings. Common law seeks “interpretations through the past decisions of higher courts which interpret the same statutes or apply established and customary principles of law to a similar set of fact.Code law is bases on an all-inclusive system of written rules(codes) of law, Under code law, the legal system is generally divided into three separate codes: commercial ,civil ,and criminal .While common law is recognized as not being all inclusive, code law is considered complete as a result of “catchall” provisions found in most code-law systems.3.Define the term “act of God”. How is this term interpreted and applied in different countries? The “act of God” refers to some extraordinary happenings of nature not reasonably anticipated by either party of a contract. Floods, lightning, earthquake, and similar occurrences are generally considered acts of God.Under common law, acts of God are confined strictly to these happenings of nature.However, under code law, acts of God are not limited solely to acts of natures but are extended to include “unavoidable interferences with performance, whether resulting from the elements, forces of nature, or unforeseeable human acts”, including such things as labor strikes and riots.6. What are the factors that must be taken into account of in determining the governing law in case of commercial disputes?International legal disputes are generally determined in one of the three ways:1)on the basis of jurisdictional clauses included in contracts2)on the basis of where a contract was entered into3)on the basis of where the provisions of the contract were performed10. Why is it always necessary to include an arbitration clause in an international contract? Unless a provision for arbitration of any dispute is incorporated as part of a contract, the likelihood of securing agreement for arbitration after a dispute arises is somewhat reduced. In fact, attempts to refer a dispute to arbitration after disagreement arises frequently fail since one party or the other is unwilling to agree on the form or place of arbitration.。
UNIT ONE Ⅰ. 1. 世界贸易组织2.国际商会3. 联合国贸易和发展会议4. 世界银行5.国际货币基金组织6. 中华人民共和国商务部7. 中国国际贸易促进委员会8. 中华人民共和国海关总署9. 国家质量监督检验检疫总局Ⅱ.(F)(T)(T)(F)(F)(T)Ⅲ. ( 4 ) A. Gree air conditioner( 6 ) B. Dengcun Green Tea( 3 ) C. soy bean( 2 ) D. mineral (F)Ⅱ. .(F)(F)(T)ore ( 5 ) E. paintings( 7 ) F. construction equipment( 8 ) G. medicine( 1 ) H. T-shirt Ⅳ. 1.AC2009 is our newly developed product, it is of superior quality, fashionable design and reasonable price. 2. 500 metric tons is the biggest amount we can supply at present. 3. We have received the sample which you sent to us last Friday and we are satisfied with the sample quality. 4. If the quality of the first consignment is satisfactory,we will place a repeat order in large quantity. 5. The landed quantity instead of the shipping quantity shall govern.Ⅱ.1.用铁桶装,每桶净重190公斤。
《国际贸易概论》课后习题与答案第一章导论一、填空题1.社会分工的扩大和具有可供交换的剩余产品的出现、国家的产生是国际贸易得以产生的两个基本前提。
2.一些海岛国家,如英国、日本的对外贸易常被称为海外贸易。
3.一国或地区的对外贸易可以分为出口和进口两个组成部分。
4.一个国家或地区其出口总值与进口总值的差额就是净出口,也可称为贸易余额。
5.大多数国家(地区)在统计有形商品时,出口额以 FOB价格(离岸价格) 价格计算,进口额以 CIF价格(到岸价格)价格计算。
6.剔除了价格变动的影响计算出来的对外贸易额称为对外贸易量。
7.对外贸易依存度是指一国对外贸易总额与国内生产总值(GDP)的比值所占的比重。
8.国际贸易商品结构指一定时期内各大类商品或某种商品在国际贸易中的构成。
9.国际贸易地理方向通常用各洲、各国或各地区的出口贸易额占世界出口贸易总额的比重来表示。
二、单项选择题1.国际贸易额指用货币表示的一定时期内世界各国的(C)的总和。
A.对外贸易额B.商品贸易额C.进口贸易额D.出口贸易额2.我国商品进出口总额是指实际进出我国( D )的商品总金额。
A.关境B.保税区C.自由贸易区D.国境3.商品生产国与消费国通过第三国进行交易,对第三国来说这属于( B )。
A.三边贸易B.转口贸易C.易货贸易D.直接贸易4.贸易逆差是指一个国家或地区(B )。
A.本年度进口额高于上年度进口额B.出口总额小于进口总额C.进口总额小于出口总额D.外汇流入小于外汇流出5.对外贸易的地理方向反映( D )。
A.各国或各地区的出口贸易额占世界出口总额的比重B.各国或各地区的进口贸易额占世界进口总额的比重C.一国各类出口商品在世界出口总额中所占的比重D.一国的出口商品去想和进口商品来源6.国际贸易商品结构指( C )。
A.各种商品在一国进口总额或出口总额中所占的比重B.各国或各地区的出口贸易额或进口贸易额占世界出口总额或进口总额的比重C.各类商品在世界出口总额中所占的比重D.一国的出口商品去向和进口商品来源7.对外贸易依存度指一国在一定时期内的(A)的比重。
Unit 1各种贸易壁垒主要来源于政府干预Various trade barriers mainly come from government intervention.近年来中国经济迅速增长,贸易结构也相应改变很大。
In recent years,Chinese economy has been growing rapidly and the trade structure has beem changed a lot.当前国际贸易中最大的困难是非关税壁垒,如进口配额,出口管制等。
Nowadays the biggest difficulty in international trade is non-tariff barriers such as import quota and export control.大多数贸易协定是多边贸易协定,而非双边贸易协定。
Most of the trade agreements are multilateral instead of bilateral one.Unit 2我方对产品质量很满意,想知道它们是怎么包装的。
We are very satisfied with the quality of your products and we would like to know how they are packed.豆子是以散装回尼龙袋供应的。
Beans are supplied in bulk or in nylon bags.我方采用纸箱而非木箱,因为纸箱同样适用于海上运输,但成本更少,质量更轻。
We use cartons instead of wooden cases because the further is just as sea worthy as the later and less in cost as well as lighter in weight.每罐装330毫升零度可口可乐,每24罐装一纸箱。
Multiple-choice questions 1.The sale o particular goods such as ornaments, jewels, paintings, artworks ,etc. is usually made by___ a. sale as seen b. sale by buyer’s sample c. sale by seller’s sample d. sale by specification 2.The sample reproduced by the seller according to the buyer’s sample for the buyer’s confirmation is called___ a. duplicate sample b. confirming sample c. reference sample d. buyer’s sample 3.The mostly adopted method of sale is___ a. sale by sample b. sale as seen c. sale by specification d. sale by trade mark and brand 4.According to the CISG, if the quantity of goods the seller delivers is greater than the contracted quantity,___ a .the buyer must accept the exceed quantity b. the buyer is entitled to reject all the goods c. the buyer is entitled to reject the excess quantity d. all of the above are not correct 5. Which of the following is China’s official metrical system? a. The metric system b. The British system c.The American system d. The international system of units(SI) 6. At present, which of the following is not the system of weights and measures commonly used in international trade? a. SI b. The French system c.The British system d. The metric system 7. The weight applicable for weighting products with unstable moisture contents such as wool, cotton ,raw silk, etc. is___ a. conditioned weight b. theoretic weight c. net weight d. dry weight 8. The use of shipping mark on the outer packing is not aimed at___ a.. promoting the sales of goods b. facilitating shipping and storing c. preventing the goods from being wrongly delivered or shipped d. facilitating the identification and count of the goods in the process of loading and unloading 1.a 2.b 3.c 4.c 5.d 6.b 7.a 8.a 1.The most commonly used mode of transport in international trade is______ a .air transport. b .road transport c.ocean transport d.railway transport 2.If an item is marked with "M" in the tariff , the the liner rate for this item is collected on ____ a. its unit. b .its weight c. its capacity d. its measurement 3.FIO in the voyage charter-party means that the shipowner is ____ a .only responsible for the charges of loading B. Only responsible for the charges of unloading C. Responsible for both the loading and unloading charges D.responsible neither for the loading charges nor for the unloading charges. 4.Liner terms in the voyage charge-party means that the shipowner is _____ a .only responsible for of loading charges B. Only responsible for unloading charges C. Responsible for both the loading and unloading charges D.responsible neither for the loading charges nor for the unloading charges. 5. In voyage charter ,theshipowner is only responsible for loading under____ a . FI b. FO c.FIO d. Liner terms 6. Lay days are commonly expressed as ____ a. Running days b. Working days c. Weather working days d. Eight hour's working days 7.Which of the following modes provides door-to-door container service or house-to-house container service? a.CY/CY container service b.CY/CFS container service c.CFS/CY container service d.CFS/CFS container service 8.Container capacity is measured in ___ A.FEU(Forty-foot Equivalent Units) b.TEU(Twenty-foot Equivalent Units) C.EEU(Eight-foot Equivalent Units) d.NEU(Nineteen-foot Equivalent Units) 9.The document which can be transferred by endorsement is ____ A.rail waybill B.Air waybill C.Sea waybill D.Order bill of lading 10.Which of the following are NOT rules governing bill of lading? a.The Hague Rules b.The Hague-Visby Rules c.The Hamburg Rules d.The New York Rules 11. In the filed of consignee of a B/L ,"To order of ABC CO.Ltd"is marked . This B/L is____ A.a straight B/L B.A blank B/L C.An order B/L D. A direct B/L 12.MarineBs/L perform a number of functions except____ A. Evidence of the contract of carriage B. Receipt for the goods shipped C. Doucment of title to the goods D. Non-negotiable document 13.Which of the following terms on the B/L shows that the Bill of Lading is a clean B/L? A. One carton short B. Insufficient packing C. In apparent good order and condituion D. Miss safety seal 14.The issuance of ___is unlawful A. Stale Bs/L B. On deck Bs/L C. Ante-date Bs/L D. Charter-party Bs/L 15. The air freight forwarder assembles a number of individual shipments into one consignment and dispatched them on one air waybill .This type of air transport service is called____ A. Consolidation B. Scheduled airline C. Chartered carrier D. Air express service 1. As a type of perils of the sea, tsunami is _ A. a natural calamity B.a fortuitous accident C.an additional risk D. a general extraneous risk 2. As a type of perils of the sea, being stranded is _ A. a natural calamity B. a fortuitous accident C. an additional risk D. a general extraneous risk 3. In ocean transit, sacrifices resulted from the jettisoning of some cargoes on a ship to keep the ship afloat during a storm are _ A. a general average B. a particular average C. a total actual loss D. a constructive total loss 4. In ocean transit, when the subject matter insured is irretrievably deprived thereof, there is_A. a constructive total loss B. an actual total loss C. a general average D. a particular average 5. a ocean transit, the subject matter insured – a precision instrument amounting to US $1000,000 was badly damaged. The cost of recovering it would be US$120,000. In such case, the loss was _ A. a constructive total loss B. an actual total loss C. a partial loss D. a total loss