16种英语时态总结
- 格式:pdf
- 大小:894.43 KB
- 文档页数:26

英语中的16种时态英语时态分为16种,下面就为大家一一列举:1、一般现在时态:表示现在的状态,或者经常反复发生的动作或习惯。
例如:I am a student.我是一名学生。
2、现在进行时态:表示正在进行的动作或存在的状态。
例如:He is studying.他在学习。
3、现在完成时态:表示过去发生的动作对现在造成的影响或结果。
例如:I have finished my homework.我已经完成了我的作业。
4、现在完成进行时态:表示从过去开始一直持续到现在的动作或状态。
例如:We have been waiting for you for hours.我们已经等了你几个小时了。
5、过去一般时态:表示过去某个时间点的状态或动作。
例如:He wasa teacher.他是一名老师。
6、过去进行时态:表示过去某个时间点正在进行的动作或存在的状态。
例如:They were playing football at that time.他们在那个时候正在踢足球。
7、过去完成时态:表示过去的过去,即过去某一时间之前发生的动作或状态。
例如:They had finished their work before we arrived.在我们到达之前,他们已经完成了他们的工作。
8、过去完成进行时态:表示过去某一时间之前一直在进行的动作或状态。
例如:We had been waiting for the bus for hours before it finally arrived.在公共汽车最终到达之前,我们已经等了好几个小时。
9、将来一般时态:表示将来某个时间点的状态或动作。
例如:She will be a doctor.她将成为一名医生。
10、将来进行时态:表示将来某个时间点正在进行的动作或存在的状态。
例如:We will be studying in the library tomorrow afternoon.我们明天下午将在图书馆学习。

英语16种时态表格总结时态是英语语法中非常重要的一部分,它们用于表示动作发生的时间、顺序和持续性等信息。
了解和掌握英语的各种时态对于学习语言的人来说至关重要。
本文将总结英语中常用的16种时态,并提供表格形式的概览,方便读者更好地理解和运用。
一、一般现在时(Simple Present)表示经常性、习惯性、客观真理形式,以及现在的动作、状态等。
肯定句:主语+动词原形否定句:主语+do/does not+动词原形疑问句:Do/Does+主语+动词原形?二、一般过去时(Simple Past)表示过去某个时间发生的动作或状态。
肯定句:主语+动词过去式否定句:主语+did not+动词原形疑问句:Did+主语+动词原形?三、一般将来时(Simple Future)表示将要发生的动作或状态。
肯定句:主语+will+动词原形否定句:主语+will not+动词原形疑问句:Will+主语+动词原形?四、现在进行时(Present Continuous)表示现在正在进行的动作或状态。
肯定句:主语+am/is/are+动词现在分进行否定句:主语+am/is/are not+动词现在分进行疑问句:Am/Is/Are+主语+动词现在分进行?五、过去进行时(Past Continuous)表示过去某个时间正在进行的动作或状态。
肯定句:主语+was/were+动词现在分进行否定句:主语+was/were not+动词现在分进行疑问句:Was/Were+主语+动词现在分进行?六、将来进行时(Future Continuous)表示将来某个时间正在进行的动作或状态。
肯定句:主语+will be+动词现在分进行否定句:主语+will not be+动词现在分进行疑问句:Will+主语+be+动词现在分进行?七、现在完成时(Present Perfect)表示过去发生的动作对现在造成的影响或结果。
肯定句:主语+have/has+动词过去分词否定句:主语+have/has not+动词过去分词疑问句:Have/Has+主语+动词过去分词?八、过去完成时(Past Perfect)表示过去某个时间之前发生的动作。
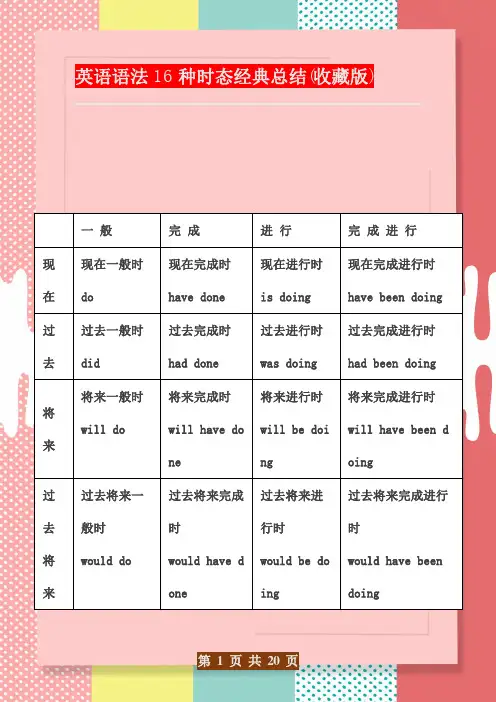
英语语法16种时态经典总结(收藏版)一般完成进行完成进行现在现在一般时do现在完成时have done现在进行时is doing现在完成进行时have been doing过去过去一般时did过去完成时had done过去进行时was doing过去完成进行时had been doing将来将来一般时will do将来完成时will have done将来进行时will be doing将来完成进行时will have been doing过去将来过去将来一般时would do过去将来完成时would have done过去将来进行时would be doing过去将来完成进行时would have beendoing16种时态形式(以do为例):注:构成时态的助动词be (is, am, are), have (has, have), shall, will 等需根据主语的变化来选择。
在这16种时态中,其中有8种时态是最重要的,也是用得最多的,是初学者必须要掌握的,它们是一般现在时(也称一般现在时)、一般过去时(也称一般过去时)、一般将来时(也称一般将来时)、现在进行时、现在完成时、过去进行时、过去完成时、过去将来一般时(也称过去将来时),其余的时态相对用得较少。
1. 一般现在时用法:A) 表示现在发生的动作、情况、状态和特征。
B) 习惯用语。
C) 经常性、习惯性动作。
例:He always helps others. (他总是帮助别人。
)D) 客观事实和普遍真理。
尤其要注意,如果前后文不是一般现在时,则无法保持主句、从句时态一致。
E) 表示一个按规定、计划或安排要发生的动作,(仅限于某些表示“来、去、动、停、开始、结束、继续”等的动词)可以与表示未来时间的状语搭配使用。
常见的用法是:飞机、火车、轮船、汽车等定期定点运行的交通方式。
例:The next train leaves at 3 o'clock this afternoon.(下一趟火车今天下午3点开车。

英语16种时态结构及例句如下:1、一般现在时(do/does;is/am/are)。
例:He is a student.他是一个学生。
2、现在进行时(am/is/are doing)。
例:He is listning to the music now.他现在正在听音乐。
3、过去进行时(was/ were doing)。
表示在过去一个具体的时间正在发生的动作。
例:Mary was listening to light music 10 minutes ago.10分钟前,玛丽正在听轻音乐。
4、一般将来时。
基本结构是will do。
例:We will send her a glass hand-made craft as her birthday gift.我们将送给她一个玻璃的手工制品,作为给她的生日礼物。
5、将来进行时(will be doing)。
强调在将来的某个具体时间正在发生的动作或存在的状态。
例:Don't worry, you won't miss her. She will be wearing a red T-shirt and a white skirt at that time.别担心,你不会认不出她的。
她到时会穿一件红色的T恤衫和一条白色的短裙。
6、过去将来时(would do)。
表示从过去的某个时间看将要发生的事。
例:I said on Thursday I should see my friend the next day.我星期四说我将于第二天拜访我的朋友。
7、过去将来进行时(would be doing)。
强调在过去将来的某个具体时间正在发生的动作或存在的状态。
例:The government promised that a new highway would be being built next July.政府承诺说第二年7月将有一条新的高速公路正在修建。

16种时态及语态总结时态和语态是英语语法中的重要内容,它们能够帮助我们更准确、清晰地表达动作发生的时间和状态。
接下来,让我们详细了解一下英语中的 16 种时态及语态。
一、一般现在时一般现在时表示经常发生的动作、习惯性的动作或客观事实、真理。
其形式为:主语+动词原形(当主语为第三人称单数时,动词要加“s”或“es”)。
例如:“I play basketball every day”(我每天打篮球。
)“He likes music”(他喜欢音乐。
)其被动语态为:am/is/are +过去分词例如:“The book is written by him”(这本书是他写的。
)二、一般过去时一般过去时表示过去某个时间发生的动作或存在的状态。
其形式为:主语+动词的过去式。
比如:“I went to Beijing last year”(我去年去了北京。
)被动语态为:was/were +过去分词例如:“The house was built in 1980”(这座房子建于 1980 年。
)三、一般将来时一般将来时表示将来要发生的动作或存在的状态。
常见形式有:will +动词原形;be going to +动词原形。
例如:“I will visit my grandparents next week”(下周我将看望我的祖父母。
)“She is going to have a party”(她打算举办一个聚会。
)其被动语态为:will be +过去分词;be going to be +过去分词例如:“The meeting will be held tomorrow”(会议将在明天举行。
)“The sports meeting is going to be cancelled”(运动会将要被取消。
)四、过去将来时过去将来时表示从过去的某一时间来看将来要发生的动作或存在的状态。
其形式为:would +动词原形;was/were going to +动词原形。

英语十六种时态详细表1. 一般现在时 (Simple Present Tense)- 表示经常发生的动作或状态。
- 格式:主语 + 动词原形 (+ 其他成分)- 例句:I study English every day.2. 现在进行时 (Present Continuous Tense)- 表示现在正在进行的动作。
- 格式:主语 + be 动词 + 现在分词 (+ 其他成分)- 例句:She is writing a letter now.3. 一般过去时 (Simple Past Tense)- 表示过去发生的动作或状态。
- 格式:主语 + 动词过去式 (+ 其他成分)- 例句:They played soccer yesterday.4. 过去进行时 (Past Continuous Tense)- 表示过去的某个时间正在进行的动作。
- 格式:主语 + be 动词过去式 + 现在分词 (+ 其他成分)- 例句:He was studying when I called him.5. 现在完成时 (Present Perfect Tense)- 表示过去发生的动作对现在产生的影响或仍然持续的动作。
- 格式:主语 + have/has + 过去分词 (+ 其他成分)- 例句:I have visited Paris.6. 过去完成时 (Past Perfect Tense)- 表示过去某个时间或动作之前发生的动作。
- 格式:主语 + had + 过去分词 (+ 其他成分)- 例句:She had already left when I arrived.7. 将来时 (Simple Future Tense)- 表示将来要发生的动作或状态。
- 格式:主语 + will/shall + 动词原形 (+ 其他成分)- 例句:We will visit our grandparents tomorrow.8. 现在完成进行时 (Present Perfect Continuous Tense)- 表示过去某个时间开始的动作一直持续到现在,并可能继续下去。

英语中16种时态总结English tenses are crucial for expressing time and action in sentences. Here's a concise summary of the 16 tenses 英文版:1. Simple Present: Used for habitual actions or general truths, as in "She walks to school every day."2. Present Continuous: Indicates an ongoing action happening now, like "They are playing soccer."3. Present Perfect: Connects past actions to the present, as seen in "She has visited Paris."4. Present Perfect Continuous: Describes an action that started in the past and continues to the present, such as "He has been studying for hours."5. Simple Past: Refers to completed actions in the past,e.g., "He ran a marathon last year."6. Past Continuous: Used for actions happening at a specific time in the past, like "She was reading when the phone rang."7. Past Perfect: Indicates an action completed before another past action, for example, "Before I left, I had finished my homework."8. Past Perfect Continuous: Describes an action that was ongoing before another past action, as in "She had beenwaiting for an hour when the bus arrived."9. Simple Future: Predicts future actions, such as "Iwill start a new job next week."10. Future Continuous: Suggests an ongoing action in the future, e.g., "They will be traveling next summer."11. Future Perfect: Indicates an action that will be completed by a certain point in the future, like "By next month, she will have finished her degree."12. Future Perfect Continuous: Describes an action thatwill have been ongoing for a certain period by a future time, for example, "He will have been working for ten years by 2025."13. Present Perfect vs. Past Perfect: The present perfect is used for actions with an unspecified time, while the past perfect is used for actions before another past action.14. Active vs. Passive Voice: Tenses can be in active voice, where the subject performs the action, or passive voice, where the subject receives the action.15. Conditional Tenses: These include zero, first, second, and third conditionals, used to express hypotheticalsituations or conditions, such as "If I had a chance, I wouldtravel the world."16. Modal Verbs: Tenses can be combined with modal verbs like 'can', 'could', 'should', 'would', and 'might' to express ability, permission, advice, or hypothetical situations, e.g., "She could have been a great scientist."Understanding these tenses allows for precise and nuanced communication in English.。

16种时态及语态总结在英语学习中,时态和语态是非常重要的语法点。
掌握好这 16 种时态及语态,对于准确表达意思、理解英语句子的含义至关重要。
下面我们就来详细了解一下这 16 种时态及语态。
一、一般现在时(Simple Present Tense)一般现在时表示经常发生的动作、习惯性的动作或者客观事实、真理等。
其结构为:主语+动词原形(当主语为第三人称单数时,动词要加“s”或“es”)。
例如:“I play football every weekend”(我每个周末踢足球。
)“He likes music”(他喜欢音乐。
)一般现在时的被动语态(Simple Present Passive Voice)结构为:am/is/are +过去分词。
例如:“The room is cleaned every day”(这个房间每天都被打扫。
)二、一般过去时(Simple Past Tense)一般过去时表示过去某个时间发生的动作或存在的状态。
其结构为:主语+动词的过去式。
例如:“I went to Beijing last year”(我去年去了北京。
)一般过去时的被动语态(Simple Past Passive Voice)结构为:was/were +过去分词。
例如:“The book was written by him”(这本书是他写的。
)三、一般将来时(Simple Future Tense)一般将来时表示将来要发生的动作或存在的状态。
其结构有多种,常见的有:will +动词原形、be going to +动词原形。
例如:“I will visit my grandparents tomorrow”(我明天将去看望我的祖父母。
)“She is going to have a party next week”(她下周要举办一个派对。
)一般将来时的被动语态(Simple Future Passive Voice)结构为:will be +过去分词、be going to be +过去分词。

16种英语时态总结归纳英语时态分为16种:一般现在、一般过去、一般将来、过去将来时,以及这四者的进行时、完成时和完成进行时。
1. 一般现在时用法:A) 表示现在发生的动作、情况、状态和特征。
B) 习惯用语。
C) 经常性、习惯性动作。
例:He always helps others. (他总是帮助别人。
)D) 客观事实和普遍真理。
尤其要注意,如果前后文不是一般现在时,则无法保持主句、从句时态一致。
E) 表示一个按规定、计划或安排要发生的动作,(仅限于某些表示“来、去、动、停、开始、结束、继续”等的动词)可以与表示未来时间的状语搭配使用。
常见的用法是:飞机、火车、轮船、汽车等定期定点运行的交通方式。
例:The next train leaves at 3 o'clock this afternoon.(下一趟火车今天下午3点开车。
)How often does this shuttle bus run? (这班车多久一趟?)F) 在时间和条件状语从句里经常用一般现在(有时也用现在完成时)表示将来事情。
例:When you have finished the report, I will have waited for about 3 hours.(等你完成这份报告的时候,我就已经等了将近3个小时了。
)2. 现在进行时(be doing)用法:现在正在进行的动作。
3. 现在完成时(have done)用法:A) 表示动作到现在为止已经完成或刚刚完成。
例:I bought a new house, but I _________ my old one yet, so at the moment I have two houses.A) didn't sell B) sold C) haven't sold D) would sell答案是C) haven't sold。
B) 表示从过去某时刻开始,持续到现在的动作或情况,并且有可能会继续延续下去。

16种时态及语态总结在英语学习中,时态和语态是非常重要的语法知识点。
掌握好时态和语态,能够让我们更准确、清晰地表达自己的想法和描述各种情况。
接下来,就让我们一起详细了解一下英语中的 16 种时态及语态。
一、一般现在时(Simple Present Tense)一般现在时表示经常发生的动作、习惯性的行为或客观事实、真理等。
其结构为:主语+动词原形(当主语为第三人称单数时,动词要加“s”或“es”)例如:I go to school every day (我每天上学。
)He likes playing football (他喜欢踢足球。
)主动语态:主语+动词原形/动词第三人称单数形式被动语态:am/is/are +过去分词二、一般过去时(Simple Past Tense)一般过去时用于表示过去某个时间发生的动作或存在的状态。
结构:主语+动词的过去式例如:I played basketball yesterday (我昨天打篮球了。
)主动语态:主语+动词的过去式被动语态:was/were +过去分词三、一般将来时(Simple Future Tense)一般将来时表示将来要发生的动作或存在的状态。
结构:will +动词原形或者 be going to +动词原形例如:I will visit my grandparents next week (我下周要去看望我的祖父母。
)主动语态:will +动词原形或者 be going to +动词原形被动语态:will be +过去分词或者 be going to be +过去分词四、过去将来时(Past Future Tense)过去将来时主要用于描述过去某个时间点看来将要发生的动作或存在的状态。
结构:would +动词原形或者 was/were going to +动词原形例如:He said he would come the next day (他说他第二天会来。

时态(Tense)是表示行为、动作和状态在各种时间条件下的动词形式.因此,当我们说时态结构的时候,指的是相应时态下的动词形式。
英语时态分为16种,如下表所示:各时态结构及用法1. 一般现在时(do/does; is/am/are)①表示现在的情况、状态和特征。
例:He is a student.他是一个学生.②表示经常性、习惯性动作。
例:He always helps others.他总是帮助别人.③客观事实和普遍真理。
例:The earth moves the sun.地球绕着太阳转.④表示一个按规定、计划或安排要发生的动作.(常用于列车、客车、飞机或轮船时刻表)例:The next train leaves at 3 o’clock this afternoon。
下一趟火车今天下午3点开车。
⑤主将从现:在时间、条件和让步状语从句中经常用一般现在表示将的来事情。
例:If it rains tomorrow, we will stay at home.如果明天下雨,我们会待在家里。
2。
现在进行时(am/is/are doing)①表示此时此刻正在发生的事情。
例:He is listning to the music now。
他现在正在听音乐。
②表示目前一段时间内一直在做的事情,但不一定此时此刻正在做。
例:I am studying by using Qisu English APP this term.这个学期我一直在使用奇速英语APP学习。
③现在进行时可以表示将来的含义。
瞬时动词的进行一定表将来。
例:I am leaving。
我要离开了。
持续动词的进行只有有将来的时间状语或有将来语境中才表将来。
例: I am travelling next month。
下个月我要去旅行。
④现在进行时与频度副词连用,表示说话者或褒义或贬义的感情色彩。
例: He is always helping others.他总是帮助别人。
英语16种时态表格总结各时态结构及具体用法:1.一般现在时(do/does; is/am/are)①表示现在的情况、状态和特征。
例:He is a student.他是一个学生。
②表示经常性、习惯性动作。
例:He always helps others.他总是帮助别人。
③客观事实和普遍真理。
例:The earth moves the sun.地球绕着太阳转。
④表示一个按规定、计划或安排要发生的动作。
(常用于列车、客车、飞机或轮船时刻表)例:The next train leaves at 3 o'clock this afternoon.下一趟火车今天下午3点开车。
⑤主将从现:在时间、条件和让步状语从句中经常用一般现在表示将的来事情。
例:If it rains tomorrow, we will stay at home.如果明天下雨,我们会待在家里。
2.现在进行时(am/is/are doing)①表示此时此刻正在发生的事情。
例:He is listning to the music now.他现在正在听音乐。
②表示目前一段时间内一直在做的事情,但不一定此时此刻正在做。
例:I am studying computer this term.这个学期我一直在学习计算机。
③现在进行时可以表示将来的含义。
瞬时动词的进行一定表将来。
例:I am leaving.我要离开了。
持续动词的进行只有有将来的时间状语或有将来语境中才表将来。
例:I am travelling next month.下个月我要去旅行。
④现在进行时与频度副词连用,表示说话者或褒义或贬义的感情色彩。
例:He is always helping others.他总是帮助别人。
(褒义)3.过去进行时(was/ were doing)①表示在过去一个具体的时间正在发生的动作。
例:Mary was listening to light music 10 minutes ago.10分钟前,玛丽正在听轻音乐。
时态语态总结说明:1. 英语有16种时态,其中常见的有10种;2. 一般现在时、一般过去时、一般将来时、过去将来时四种基本时态均有被动语态。
3. 现在进行时、过去进行时有被动语态,而将来进行时和过去将来进行时没有被动语态。
4. 现在完成时、过去完成时有被动语态,将来完成时和过去将来完成时很少用于被动结构。
5. 完成进行时均没有被动语态(包括现在完成进行时、过去完成进行时、将来完成进行时、过去将来完成进行时)。
注意:填充单元格为不常用时态。
▲用法及举例:1. 一般时态的被动语态一般时态的被动形式都由“助动词be+过去分词”构成(动作发生时间由be表现出来) (1) 一般现在时的被动语态In China, the railways are owned by the state. 在中国,铁路是国有的。
They are asked to shoulder the costs of the repair. 要求他们承担这笔修理费。
The new drug began to operate not long after it is taken. 这种新药服用后不久就会开始见效。
(2) 一般过去时的被动语态:Each couple was asked to complete a form. 要求每对夫妇填一张表。
The thief was handed over to the police. 这个小偷已经送交派出所了。
He was admitted into the club as a member. 他被接纳为俱乐部的会员。
(3) 一般将来时的被动语态:The hotel will be closed during repairs. 那家饭店在整修期间将停业。
Light refreshments will be served after the meeting. 会议之后有简单茶点招待。
If you don’t give care to your work, you will be fired. 如果你不细心工作,你会被解聘的。
英语语法16种时态总结咱们学英语啊,这语法里的时态就像一个个性格各异的小伙伴,各有各的特点。
今天咱们就来好好认识认识这 16 个“小伙伴”!先来说说一般现在时,这就好比是我们每天的日常生活,平平淡淡但又稳定不变。
比如说,“I play basketball every weekend”(我每个周末都打篮球。
)这就是一种日常的、习惯性的动作。
我还记得我小时候,每天早上妈妈都会叫我起床,然后说:“Get up, honey It's time for school”(起床啦,宝贝。
该上学了。
)这就是一般现在时,简单又常见。
一般过去时呢,就像是回忆里的老照片,记录着过去发生的事情。
比如,“I went to Beijing last year”(我去年去了北京。
)有一次我翻相册,看到了小时候和小伙伴们一起在公园里玩耍的照片,那时候的快乐时光仿佛就在昨天,而描述那些过去的快乐,就得用一般过去时。
一般将来时,充满了期待和憧憬。
像“I will go to the party tomorrow”(我明天会去参加派对。
)每次快到假期,我都会满心欢喜地计划着要去哪里玩,这时候心里想的那些还没发生的事情,就要用一般将来时来表达。
现在进行时,就像正在直播的画面,动作正在进行。
“I'm reading a book now”(我现在正在读书。
)记得有一次我在家里写作业,突然听到外面传来一阵吵闹声,我忍不住往窗外看,原来是小区里的孩子们正在开心地玩耍,他们跑啊、跳啊,这就是典型的现在进行时。
过去进行时呢,是过去某个时刻正在进行的动作。
“I was watching TV when she called me”(她给我打电话的时候我正在看电视。
)有一回我正在厨房做饭,突然电话响了,等我接完电话回到厨房,发现锅里的水都快烧干了,而我刚才做饭的那个时刻,就是过去进行时。
将来进行时,想象一下未来某个时刻正在做的事。
英文学习归纳:英语语法16种时态总结1. 一般现在时(do/does; is/am/are)①表示现在的情况、状态和特征。
例:He is a student.他是一个学生。
②表示经常性、习惯性动作。
例:He always helps others.他总是帮助别人。
③客观事实和普遍真理。
例:The earth moves around the sun.地球绕着太阳转。
④表示一个按规定、计划或安排要发生的动作。
(常用于列车、客车、飞机或轮船时刻表)例:The next train leaves at 3 o'clock this afternoon.下一趟火车今天下午3点开车。
⑤主将从现:在时间、条件和让步状语从句中经常用一般现在表示将的来事情。
例:If it rains tomorrow, we will stay at home.如果明天下雨,我们会待在家里。
④现在进行时与频度副词连用,表示说话者或褒义或贬义的感情色彩。
例:He is always helping others.他总是帮助别人。
(褒义)④过去进行时和频度副词连用可以表示说话者或褒义或贬义的感情色彩。
例:When he lived in country,he was always helping the poor. 住在乡下时,他总是帮助穷人。
4. 一般将来时①基本结构是will do。
例:We will send her a glass hand-made craft as her birthday gift.我们将送给她一个玻璃的手工制品,作为给她的生日礼物。
②表示“打算…,要…”时,可用am/is/are going to do。
例:This is just what I am going to say.这正是我想说的。
③表示“即将、正要”时,可用am/is/are about to do。
强调近期内或马上要做的事。
英语时态总结表格16种时态在英语语言中非常重要,它能帮助我们准确地表达事件的发生时间。
在英语中,我们有许多不同的时态来表示过去、现在和将来的事件。
在本文中,我将为大家总结英语的16种时态,并提供每一种时态的用法和例句。
1. 现在简单时态 (Present Simple)用法:描述常规的行为、事实或普遍真理。
例句:I play football every weekend.2. 过去简单时态 (Past Simple)用法:描述发生在过去某个具体时间的行为或事实。
例句:She traveled to Europe last year.3. 将来简单时态 (Future Simple)用法:描述将来的行为或计划。
例句:They will arrive at the airport tomorrow.4. 现在进行时态 (Present Continuous)用法:描述现在正在发生的动作。
例句:He is studying for his exams at the moment.5. 过去进行时态 (Past Continuous)用法:描述过去某一特定时间正在进行的动作。
例句:They were playing football when it started raining.6. 将来进行时态 (Future Continuous)用法:描述将来某一时间正在进行的动作。
例句:I will be studying at the library tomorrow afternoon.7. 现在完成时态 (Present Perfect)用法:描述过去发生但与现在有联系的动作或经历。
例句:She has visited Paris many times.8. 过去完成时态 (Past Perfect)用法:描述过去某一时间或事件之前发生的动作。
例句:They had already eaten dinner when we arrived.9. 将来完成时态 (Future Perfect)用法:描述将来某一时间之前已经完成的动作。
英语16种时态表格总结英语是世界上使用最广泛的语言之一,掌握好英语对于我们来说非常重要。
而英语的时态是英语语法中最基础、最重要的部分之一。
掌握好英语的时态,对于我们正确地表达自己的意思至关重要。
今天,我们就来总结一下英语中的16种时态,希望对大家有所帮助。
一、一般现在时一般现在时表示经常性或习惯性的动作或状态,也可表示客观真理、科学事实等。
例如:I work in a company.(我在一家公司工作。
)二、一般过去时一般过去时表示过去某个时间发生的动作或状态。
例如:I worked in a company.(我在一家公司工作过。
)三、一般将来时一般将来时表示将来某个时间要发生的动作或状态。
例如:I will work in a company.(我将在一家公司工作。
)四、现在进行时现在进行时表示现在进行的动作或状态。
例如:I am working in a company.(我正在一家公司工作。
)五、过去进行时过去进行时表示过去某一时刻正在进行的动作。
例如:I was working in a company.(我当时正在一家公司工作。
)六、将来进行时将来进行时表示将来某个时间正在进行的动作。
例如:I will be working in acompany.(我将来会在一家公司工作。
)七、一般过去将来时一般过去将来时表示过去某个时间将来要发生的动作或状态。
例如:I would work in a company.(我过去将要在一家公司工作。
)八、现在完成时现在完成时表示过去某个时间开始,一直延续到现在的动作或状态。
例如:I have worked in a company for 5 years.(我在一家公司工作了5年了。
)九、过去完成时过去完成时表示过去某个时间之前已经完成的动作或状态。
例如:I had worked in a company before I went to college.(我在上大学之前在一家公司工作过。
英语共有十六种时态,其表现形式如下(以study为例)用动词原形, 第三人称单数变化规则是: 一般情况加“-s”, 以辅音加“y”结尾的词把“y”-“i”, 再加“-es”(但元音加“y”结尾的则直接加“-s”) , 以“o, s, x, ch, sh”结尾的词加“-es”。
be 动词的变化形式是is , am, are。
A) 经常性、习惯性或反复发生的动作(常同often , sometimes, usually, always, twice a month, every week , on Sundays, occasionally, normally , generally, weekly, now and then ,every so often , as a rule, rarely 等状语连用)。
例:He always helps others. (他总是帮助别人。
)Birds f ly . 鸟会飞。
I never sit up late into the night . 我从不迟睡。
B)客观事实和普遍真理,也在格言中用。
注意,如果前后文不是一般现在时,则无法保持主句、从句时态一致。
例:The ear th moves round the sun . 地球绕太阳转。
No man but errs. 人非圣贤, 孰能无过。
C)表示情况、特征、能力或现在发生的动作、状态和特征。
例:She loves music . 她喜欢音乐。
She lives in a villa at the foot of the hill . 她住在山脚下的一座别墅里。
He doesn’t speak French . 他不会讲法语。
Contradictions exist everywhere . 矛盾处处存在。
D) 表示一个按规定、计划或安排要发生的动作,(仅限于某些表示“来、去、动、停、开始、结束、继续”等的动词) 可以与表示未来时间的状语搭配使用。
常见的用法是:飞机、火车、轮船、汽车等定期定点运行的交通方式。
例:The next train leaves at 3 o'clock this afternoon. How often does this shuttle bus run? (这班车多久一趟?)E) 在由when,if,after,before,although,as,as soon as,the minute,the next time,whether,because,even if,in case,though, till , until , unless , so long as , where, whatever, wherever 等引导的表示时间、条件、比较等状语从句中, 用一般现在时代替一般将来时。
例:I’ll tell her when she comes tomorrow . 她明天来的时候我会告诉她的。
You will surely succeed i f you try your best. 功夫不负有心人。
F)表示现在瞬间一般现在时可以用来描述动作的完成与说话的时间几乎是同时的这种情况, 常用于体育运动的实况报道, 戏法表演, 技术操作表演等的解说词。
例:Demonstrator(示范者) : Now I put the cake mixture into this bowl and add a drop of water.I declare the meeting open . As I write, the war has broken out . ( = At the time of writing)G)表示过去时间一般现在时可以用来表示不确定的过去时间, 只限于为数不多的动词, 如: hear, tell , say,forget等; 也可穿插现在进行时等来叙述往事, 以增加描写的生动性和真实感, 亦称作历史现在时。
例:That is long, long ago . I hear he has come back from Japan . Oh , I forget what he said . 我忘了他的话了。
Julia says you told her to buy the book . 朱莉娅说你让她买这本书的。
Jane tells me you are entering college nextH)表示将来时间一般现在时可用于指将来时间, 表示按时间表将要发生的动作或事件, 或者事先安排好的动作。
能这样使用的动词有: be, arrive, begin , come, start , depart , end, leave, go, sail ,stop , return , dine, finish, open, close 等。
例: Is there a film tonight?今晚有电影吗? A:When does he leave for the city ? B: He leaves next week .Tomorrow is Christmas Day . 明天是圣诞节。
When does the ship sail ? 船什么时候起航?The meeting begins at 2: 00 in the afternoon and ends at 5: 00.会议在下午两点开始, 五点结束。
The plane takes off at eight and arrives in Beijing at eleven . 飞机八点起飞, 十一点到达北京。
I)在新闻标题、小说章节标题或小说、电影、戏剧情节介绍和幻灯、图片的说明中, 常用一般现在时U . S . President holds talks with British Prime Minister . 美国总统同英国首相举行会谈。
American Ambassador leaves Beijing. I Have a Chance(小说的章标题)At rise, the stage is dark. It is two thirty in the morning . (舞台说明)Bank Robbery: Robbers take $10 , 000 . 银行劫案: 匪徒抢走一万美金。
J)用来表示强硬语气、严厉警告或指点道路You finish the work before ten o’clock tomorrow . You mind your own business .If he does that again , he goes to prison . Either he leaves or you leave .You take the first turning ahead, then cross a bridge and you see the city library .K)代替现在完成时动词learn, hear, see, understand , read, forget 等表示“已知, 已忘”时, 可用一般现在时代替现在完成时; it be + 时间+ since . . .结构可用一般现在时代替现在完成时。
例: I forget( have forgotten) her name .I understand( = have understood) what he wants . It is( = has been) ten years since she moved here .L)用于延续性动词或静态动词, 表示持续状态、心理活动、爱憎、知觉等The cont ract holds good . 合同有效。
John loves nature .The material f eels soft. I don’t owe anything to anybody .M)表示仍旧有影响的已故人物的言行或状态, 或引用书面材料Shakespeare is the author of“Hamlet. Confucius regards sex as human . 孔子视性为人之常情。
Chaucer writes that love is blind. 乔叟写道, 爱情是盲目的。
Shelly says,“If winter comes , can spring be far behind ?”雪莱说:“冬天到了, 春天还会远吗?”N)用于定语从句或宾语从句中表示将来。
这时, 主句常用一般将来时。
例如:Let’s see who gets there first . He will give you anything you ask for .Anyone that comes will be warmly welcome. She won’t forgive anyone who steals flowers in her garden .A quar rel will arise as to who rules the country. Anyone who does it will get a gift .O)一般现在时与一般过去时的连用有时候, 在同一个复合句中, 会出现一般现在时和一般过去时连用的现象, 这是因为所取的时间点不同。
例如: As the city does not have many enter taining places to go, we treated the foreign friends tosome real Chinese food . (从句用一般现在时does not have 表示这个城市长期的客观情况, 一般过去时t reated 则表示过去的某次行为动作)现在进行时的构成是:be + 现在分词(is/ am/are+doing)特殊疑问句:特殊疑问词+相应be动词+主语+现在分词+Sth?间接引语中改为过去进行时。
变化规则1.直接+ ing(例:sleep+ing sleeping)2.去掉不发音的e+ing(例:bite-e+ing biting)3.重读闭音节,且末尾只有1个辅音字母,双写辅音字母+ing(例:sit+ t+ing sitting)4.以ie结尾变ie为y+ing (例:die-dying lie-lying)5.不规则变化6结尾为c且c读作/k/时,在结尾加k再加ing,如picnic-picnicking现在进行时的基本用法/功能:1)表示现在正在进行的动作或发生的事The kettle is boiling. Shall I make tea ? 壶开了, 沏点茶好吗?Is the sun shining ? 出太阳了吗? It’s blowing hard . 风挺大。