中医学英文词汇汇总
- 格式:pdf
- 大小:16.07 KB
- 文档页数:10

英⽂写作翻译频道为⼤家整理的英⽂翻译⼝译分类词汇:TCM 中医类词汇,供⼤家参考:) TCM 中医中医名著 famous TCM work《黄帝内经》 Huang Di’s Classic of Internal Medicine / Yellow Emperor's Canon of Traditional Chinese Medicine 《神农本草经》 Shennong’s Herbal Classic《本草纲⽬》 Compendium of Materia Medica《易经》 I Ching; Book of Change万物⼈为贵 nothing compares to a human life救死扶伤 healing the sick and saving the dying阴阳 yin-yang, the two opposing and complementary principles in nature相⽣相克 mutual generation and restriction对⽴制约 mutually opposing and constraining互根互⽤interdependent and mutually promoting相互转化mutually transformational新陈代谢 metabolism针灸 acupuncture针刺疗法acupuncture艾炙疗法 moxibustion推拿 medical massage⽳位acupuncture point针刺⿇醉 acupuncture anesthesia综合医院 general hospital中医部 TCM section/ department拔⽕罐疗法 (Chinese) cupping therapy刮痧疗法skin scraping therapy with water, liquor or vegetable oil理疗 physical therapy切脉 feeling the pulse偏⽅folk prescription秘⽅ secret prescription (normally of excellent curative effect)祖传秘⽅ secret prescription handed down from one's ancestors阴阳五⾏学说 the theory of yin-yang and five elements (metal, wood, water, fire and earth)⼼ heart肝 liver脾spleen胃stomach肺 lung肾 kidney内伤七情(喜、怒、忧、思、悲、恐、惊) internal causes (joy, anger, worry, thought, grief, fear and surprise)外感六* (风、寒、暑、湿、燥、⽕) external causes (wind, cold, heat, wetness, dryness and fire)中药四性 four properties of medicinal herb寒cold热hot温warm凉cool中药五味five tastes of medicinal herb酸sour苦bitter甜sweet辣spicy咸salty按摩message therapy减肥 lose weight经络 main and collateral channels inside human body; meridian⾷补保健maintain good health through the intake of nourishing food太极拳 Tai chi quan; Tai chi Chuan; Taijiquan boxing延缓衰⽼ to defer senility药典pharmacopoeia有机整体 an organic whole瑜珈 yoga中国古代药王神农⽒ Shennong, herbal medicine master of ancient China中华医学会 Chinese Medical Association安全第⼀,预防为主 safety first, precaution crucial.。

附录二:中医英语水平考试词汇表(讨论稿)中华中医药学会翻译分会Ⅰ 医学英语词汇 (约440 条)n. 腹;腹部n. 流产, 堕胎, 早产. 急性的, 剧烈n. 服用n.允许入住(医院). 使恶化, 加重n.极度痛苦n. 疾病(尤指微恙)n. 蛋白n.酒精,乙醇n. 酒精中毒. 食物的, 营养的. 碱性的n. 过敏氨基酸n. 健忘症n. 止痛剂n. 解剖学n. 贫血, 贫血症n. 麻醉n. 食欲减退, 厌食n. 缺氧n. 抗生素n. 抗体 n. 抗抑郁药n. 抗原n. 主动脉n. 阑尾炎, 盲肠炎n. 阑尾n.食欲,胃口n. 心律不齐, 心律失常n. 动脉硬化n. 动脉n. 关节痛n. 关节炎n. 腹水n. 阿斯匹林(解热镇痛药), 乙酰水杨酸 n. 哮喘n. 心房n. 听诊. 腋下的钡餐. 双侧的,两边的n. 胆汁n. 活组织检查, 活组织切片检查n. 膀胱n. 肠n. 支气管炎n. 钙n. 小腿n. 毛细血管n. 包囊;胶囊n. 碳水化合物n. 癌,腺癌n. 心电图. 心脏血管的n. 携带者,带菌者n. 软骨(组织)n. 白内障n. 导管. 脑的, 大脑的. 脑血管的n.药剂师n. 化学疗法n. 水痘n. 胆固醇. 慢性的n. 肝硬化n.绞痛n. 结肠n. 昏迷n. 并发症. 天生的, 先天的n. 充血结缔组织n. 便秘. 传染性的, 会感染的n. 污染, 污染物n. 禁忌证冠状动脉心脏病(冠心病) n. 皮层n. 危象. 危急的, 临界的n. 紫绀n. 耳聋n. 残废;畸形. 退化性的n. 脱水n. 分娩n. 痴呆. 牙齿的n. 抑郁(症)n. 皮炎n. 皮肤学v. [病情等]恶化,变坏v. 解毒n. 糖尿病n. 诊断,诊断结果n. 渗析,透析n. 横膈膜n. 腹泻舒张压n. 消化v. 允许..离开;n. 排泄物,出院 . 远侧的. 利尿的; n. 利尿剂n. 头昏眼花() n. 供体, 捐赠者. 背側的,后面的n. 剂量n. 痢疾n.呼吸困难n. 水肿n. 心电图 (略作)n. 栓塞n. 胚胎n. 脑炎n. 内分泌n. 内窥镜n. 肠炎n. 酶n. . 流行病;流行性的n. 上腹部n. 表皮组织, 上皮组织n. 爆发;出疹n. 红血球n. 食道n. 病因学, 病源论v. 排泄n. 呼出, 呼气n. (生命)期望值n. 手足,末端n.视力,目力n. 衰竭输卵管n. . 禁食;禁食的,空腹的 n. 粪, 屎n. 胎儿n.流行性感冒n. 病灶由食物传播的n. 镊子, 钳子n. 骨折;挫伤n. 胆囊n. 胆石n. 胃切除术n. 胃炎. 胃肠的. 遗传的, 起源的n. 腺体n. 球蛋白葡萄糖液输注n. 腹股沟n. 齿龈n. 妇科医学心力衰竭n. 心痛n. 血尿(症)n. 血液透析n. 血色素, 血红蛋白 n. 出血n. 肝炎n. 肝肿大n. 遗传n. 疝气n. 荨麻疹n. 荷尔蒙, 激素n. 主人;宿主n. 卫生, 卫生学n. 高血压. 免疫的n. 发病率n. 切口, 切开n. 失禁,不能自制n. 指征,适应证n. 消化不良n. 梗塞形成, 梗死形成 n. 传染, 感染. 有传染性的, 易传染的 n. 不生育,不育症n. 炎症, 发炎n. 输注n. 摄食; 摄取n. 吸入n. 精神错乱n. 失眠, 失眠症n. 吸〔气〕n. 胰岛素n. 干预,介入肠梗阻n. 肠. 肌肉内的 . 静脉内的. [检查等]进入体内的. 非随意的n. 碘n. 刺激n. 局部缺血n. 隔绝,隔离. 痒的n. 黄疸n.颌,颚n. 分娩n. 喉. 侧面的n. 损害, 身体上的伤害. 致死的n. 白血病n. 白细胞, 白血球n. 白带n. 肢(臂、腿)n. 脂质;油脂 [脂肪;乳酪]大叶性肺炎n. [肺、肝等的]叶v. (使)局限化n. 腰神经, 腰椎n. 淋巴腺, 淋巴淋巴结n. 淋巴细胞磁共振显像()n. 疟疾. 恶性的n. 营养失调, 营养不良 n. 治疗失当,医疗差错 n. 表现,显示n. 髓, 骨髓v. & n. 按摩n. . 母性; 产科病房 n. 麻疹, 风疹n. 药物,药物治疗n. 黑便n. 膜, 隔膜n. 脑膜炎n. 绝经期, 更年期n. 月经n. 新陈代谢n. (癌肿的)转移n. 微生物n. 偏头痛n. 吗啡n. 死亡率晕车(船等)n. 黏膜n. 黏液n. 腮腺炎. 肌肉的n. 心肌梗死n. 近视 n. 恶心, 反胃,晕船n. 坏疽, 坏死. 阴性的. 新生儿的n. 神经学, 神经科n. 神经细胞, 神经元n. 烟碱, 尼古丁n. 乳头. n. 生理盐水n. 营养品,食物n. 营养(学)n. 肥胖n. 产科医生n. 产科n. 药膏n. 肿瘤学n. 发作n. 眼科学. 眼的, 视力的, 光学的 n. 生物体, 有机体n. 整形外科n. 卵巢n. 超剂量n. 卵n. 起搏器n. (医生诊断时等) 摸, 触 n. 心悸n. 胰腺n. 胰腺炎n.气喘n. 瘫痪,麻痹n. 寄生虫n. 病原体n. 病理学n. 小儿科n. 骨盆;骨盘n. 阴茎n. 叩诊n. 穿孔n. 心包. 围产期的n. 蠕动n. 汗;出汗n. 药剂师n. 药理学;药物学n. 药房,药剂学n. 咽n. 痰n. 色素n. 安慰剂,安慰治疗n. 胎盘n. 血浆n. 血小板n. 肺炎n. 气胸n..小儿麻痹症, 急性骨髓灰质炎 n. 息肉. 阳性的. [位置上]后面的. 手术后的n. 钾n. 怀孕a. 产前的n.预防n. 预后俯卧位. 前列腺的 n. 前列腺n. 蛋白尿. 精神病学的, 精神病治疗的 .心理的,心理学的. 肺部的n. 脓, 脓汁狂犬病n. X 光线学, 放射医学n. 水泡音,啰音n. 皮疹n. 反跳痛n. 接受者,受体n. 直肠. 复发的,周期性发作的n. 养生法n. 康复n. 排异作用,拒绝n.(疾病)复发n.(疾病)缓解(期) . 肾脏的, 肾的n. 呼吸. 有反应的a.不安的,焦虑的n. 复苏n. 保持, 潴留n. 视网膜. 风湿的n. 唾液n. 公共卫生n. 手术刀, 解剖刀 . 继发性的n. 分泌物,隐藏n. 切开术n. 镇静剂. 久坐的n. 发作, 癫痫发作 . 感觉的,感觉器官的 n. 后遗症n. 血清() 非典型肺炎n. 休克n. 窦n. (动物之)骨架, 骨骼 n. 头骨,颅骨,脑壳 n. 天花 n. 钠. 疼痛的 n. 疮,(皮肉的)伤 n. (感情等)一阵发作, 痉挛n. 精子n. 括约肌n. 血压计, 血压测量计n. 脊柱n. 脾n. 夹板n. 海绵体 (外科用的)棉球, 纱布 v. n. 扭伤n. 唾液, 痰n. (器官)狭窄. 消过毒的,无菌n. 杀菌; 绝育n. 类固醇n. 听诊器n. 兴奋剂n. 缝n. 大便n. 脑卒中. 皮下的n. 吸引. 表浅的,表层的. 仰卧的n. 补充;补充剂n. 易感性,易受影响性. 肿胀的a.交感的n. 症状, 征兆n. 昏厥n. 综合症. 合成的n. 梅毒收缩压n. 压痛n. 腱n. 绷紧;张力;紧张,焦虑 . 晚期的n. 睾丸n. 破伤风. 治疗的n. 治疗剂, 治疗学家 n. 治疗, 疗法n. 体温计n. 大腿. 胸的n. 胸, 胸腔n. 血栓症n. 扁桃腺n. 毒素n. 气管切开术n. 镇静剂n. 输血, 输液v. 移植, 移种n. 移植. 横向的 n. 外伤. 肺结核, 结核病n. 肿块,肿瘤B 超n. 溃疡n. 溃疡形成n. 尿毒症n. 输尿管. 泌尿的n. 泌尿学n. 子宫n. 疫苗n. 阴道n.(心脏)瓣膜n. 血管扩张剂n. 静脉. 静脉的n. 呼吸机n. 脑室, 心室n. 囊,泡;水疱n. 脉管;导管. 内脏的v. & n. 呕吐. 喘息, 很困难地呼吸n. 喘息 n. 子宫Ⅱ 中医英语词汇 (约1330 条)阿是穴嗳气艾灸艾条安神安神定志安胎按摩按诊八法八纲八纲辨证八会穴拔罐疗法拔针白睛白苔百日咳斑疹瘢痕灸半表半里半表半里证半身不遂膀胱膀胱经膀胱气化膀胱湿热膀胱虚寒包煎胞宫胞睑胞络悲悲则气消本本草纲目本虚标实崩漏鼻衄鼻塞鼻翼煽动鼻渊鼻准闭经闭证痹证砭石便秘便溏变证辨病论治辨证论治标标本同治表寒表寒里热表里表里俱实表里配穴表里双解表里同病表气不固表实表实里虚表邪表邪入里表虚表证别络禀赋不足并病病变病机 ()病脉病色病性病因病因辨证病证薄苔补 1.补不足 (广义) ; 2.(偏阳气) ; 3. 滋养 ( 偏阴血) ; 4. 强壮; 5.壮阳 ; 6. 针刺手法补法补火助阳补脾益气补气补气固表补气摄血补肾固精补肾纳气补肾阳补肾滋阴补泻补血补血调经补血药补阳补益剂补益心脾补阴补阴剂补中益气不得眠不寐不内外因不通则痛不育不孕仓廪之官藏 1.同"脏" ; 2.脏器总称 ; 3产科产门 ()长夏肠鸣肠澼肠痈常脉常色朝食暮吐潮红潮热炒制沉脉乘痴呆迟脉齿痕舌冲剂冲脉冲任不调冲任不固冲任虚寒抽搐抽筋处方传变传导之官传经喘鸣喘息疮疡春温纯阳之体刺络拔罐刺手刺痛从治法腠理催乳寸口搓针大便不通大便失禁大肠寒结大肠津亏大肠经大肠湿热大汗大络带脉带下病 's 丹剂丹田单方单煎单手进针法胆经胆虚气怯胆郁痰扰但寒不热但热不寒淡渗利湿导便导引盗汗得气得神地支电针电针麻醉调和肝脾调和气血调和营卫调经调理冲任跌打损伤督脉短气顿服多汗 ()多梦多尿鹅口疮呃逆恶风恶寒恶露恶色恶心耳聋耳轮耳鸣耳穴耳针发病发汗解表发散风寒药烦渴烦闷烦热烦躁易怒反胃泛酸方剂房室不节肥胖肺朝百脉肺合大肠肺津不布肺经肺痨肺脾两虚肺气不利肺气不宣肺气上逆肺气虚肺热炽盛肺肾阴虚肺司呼吸肺痿肺阴虚证肺主皮毛肺主气肺主治节风关风寒表证风寒感冒风寒束表风轮风热证风湿相搏风痰风温风疹伏脉伏痰伏邪伏饮扶正固本扶正祛邪浮络浮脉浮肿复方腹满腹痛拒按腹痛喜温腹泄腹胀干咳干咳无痰肝肝藏血肝胆火旺肝胆气郁肝胆湿热肝风内动肝火犯肺肝火上炎肝脾不调肝脾两虚肝气不舒肝气犯胃肝气横逆肝气郁结肝肾不足肝肾同源肝肾阴虚肝胃不和肝血亏虚肝阳化风肝阳上亢肝郁气滞肝主筋肝主疏泄膏药隔物灸攻补兼施骨蒸潮热固崩止带固表止汗固冲止带固经止血固涩药固肾涩精刮痧疗法归经鬼门滚法寒化寒积寒极生热寒凝气滞寒热往来寒湿困脾寒痰寒邪寒者热之毫针和解表里和胃降逆黑睛洪脉后天之本后天之精后下滑脉滑苔化湿药化痰开窍化痰止咳黄带黄疸黄帝内经’s 黄苔回阳救逆魂活血调经活血化瘀活血通络火克金火生土霍乱饥不欲食急下存阴煎药法健脾健脾和胃健脾化湿健忘交通心肾绞痛结胸解表剂金克木金匮要略金水相生津津血同源津液筋紧脉近血进针经别经方经络经络辨证经脉 ; 经外奇穴经穴惊风惊悸精气精神精血颈椎病九针灸法厥逆 1. ; 2. 厥阴厥证君臣佐使, , 君火开窍剂开胃咳嗽咳血克客邪恐芤脉口臭口疮口淡口干口渴口苦口眼歪斜苦寒清气宽胸散结髋狂言劳倦冷汗冷秘离经之血里寒里寒证里急后重里热里实里虚理法方药 , , , 理气理气化痰理气健脾理气药理气止痛理中利水渗湿利水消肿利咽痢疾敛肺止咳凉肝熄风凉血止血淋证另煎留针六经辨证六经病六气六淫咯痰癃闭络脉络穴落枕麻疹脉 1. ; 2. ; 3. 脉合四时脉静脉象脉诊脉证合参梅花针梦遗泌别清浊秘方面色面色不华面色苍白面瘫命关命门摩法母病及子母气木火刑金木克土木生火木郁化火目系目痒募穴暮食朝吐内服内伤发热内因内眦纳呆纳气纳气平喘脑脑髓逆传逆传心包逆证腻苔尿闭尿黄尿急尿频尿少尿痛尿血尿浊捏法扭伤浓缩丸脓弄舌怒怒伤肝怒则气上女子胞呕逆呕吐呕血排便排脓排石胖大舌炮制培土生金 () 培土抑木 () 配伍配伍禁忌配穴皮肤针皮毛疲乏脾不统血脾合胃脾经脾气脾气不升脾气不舒脾气亏虚证脾气下陷脾气郁结脾肾阳虚脾失健运脾统血脾胃不和脾胃湿热脾胃虚寒脾虚脾虚湿困脾虚水泛证脾阳不振脾主升清脾主运化痞满偏瘫平补平泻平刺平旦服平肝潜阳平肝息风平脉破血七怪脉七窍七情七情内伤奇方奇恒之腑奇经奇经八脉脐起针气气闭气不摄血气分气分证气功气化气化不利气机气机不畅气机失调气轮气门气逆气随血脱气脱气陷气虚气虚血瘀气虚证气血气血辨证气血不足气血两燔气血两虚气血失调气血双补气阴两伤气阴两虚气营两燔气郁气郁化火气滞气滞血瘀切脉轻剂轻证清法清肺清气泄热清热化痰清热剂清热解毒清热利湿清热凉血清热药清热燥湿清暑益气清胃降逆清泻肝胆清心清心泻火清虚热清阳不升清营凉血清营泄热情志内伤情志郁结驱虫药祛风祛风剂祛风通络祛痰剂祛邪扶正雀啄灸热 1. 抽象义; 2. 外感病症状热闭热毒内陷热伏冲任热化热极生寒热结阳明热秘热迫大肠热扰心神证热入心包热入血分热邪热因热用热者寒之热证任脉 ()妊娠腹痛妊娠呕吐日晡潮热 3-5 .柔肝揉法濡脉乳痈褥疮软膏软坚散结锐眦润肠通便润肺润肺化痰润肺止咳润下弱脉三部九候三关三焦三焦辨证三焦经三焦虚寒三因散寒解表散寒祛湿散寒止痛散剂散瘀散瘀消肿色脉合参涩肠止泻涩剂涩脉痧证闪罐疝善色伤风伤寒伤津伤食伤暑上寒下热上焦上热下寒上实下虚上脘上虚下实少腹硬满少火少气少神少阳少阴少阴寒化舌红少津舌尖红舌强舌苔舌苔白腻舌态舌下络脉舌象舌诊舌质摄生身热身痛身痒身重神神昏神倦神明神疲乏力神气神志神志不清审证求因肾不纳气肾藏精肾经肾精肾精不足肾气肾气不固肾气不足肾气虚肾水肾司二便肾虚水泛肾阳不足肾阳衰微肾阴肾主纳气肾主水渗湿渗湿利水升降出入 , , 升降浮沉 , , 升清升清降浊生化之源生津止渴生药失音 ()湿湿痹湿毒湿化湿困脾阳湿气湿热湿热下注湿邪十二经脉十二皮部十五络时方时气时疫实实喘实寒实火实脉实热实邪实者泻之食积食入即吐食少手法手厥阴心包经手少阳三焦经手少阴心经手太阳小肠经手太阴肺经手阳明大肠经手足汗出手足厥冷手足心热受盛之官疏风解表疏风透疹疏肝和胃疏肝解郁疏肝理气疏肝利胆疏肝泻火疏散风热疏通经络舒肝理气暑邪数脉腧穴水不涵木 () 水道水谷不化水谷精微水寒射肺水火不济水火相济水煎水气凌心水热互结水饮水饮内停顺传顺证思则气结四气四诊四肢倦怠四肢厥冷宿食宿痰酸甘化阴酸痛随证加减髓海不足孙络胎动不安胎息痰 1. ; 2. 痰多痰火痰火扰心痰蒙心包痰迷心窍痰气互结痰热痰热内扰痰热壅肺痰热阻肺痰湿痰饮痰瘀互结痰中带血汤剂特定穴体倦体倦乏力体质天干天癸天人相应停经通便通调水道通经通经活络通利关节通利小便通络通窍通阳化气通因通用同病异治痛风痛经痛无定处痛有定处头痛头项强痛头晕头重脚轻透热转气透营转气吐法吐故纳新吐舌吐酸吐血推拿退黄退虚热吞酸吞咽困难脱证外感发热外感风寒外感风热外感热病外邪外因外治法丸剂完谷不化脘腹胀满脘痞脘痛亡阳亡阴望色望诊危候微脉萎黄痿软舌痿证卫表卫表不固卫气卫气同病卫气营血 , , 卫阳畏寒肢冷胃不和胃寒胃寒呕吐胃寒证胃火胃火炽盛胃火上升胃经胃纳不佳胃气不和胃气上逆胃热消谷胃失和降胃实胃阳胃阳虚胃阴胃阴不足胃主降浊胃主受纳温病温补脾胃温补脾阳温肺温肺化痰温肺化饮温肺散寒温经活血温经散寒温经止痛温经止血温里温里散寒温里药温疟温肾健脾温肾纳气温胃止呕温邪犯肺温阳利水温运脾阳温针灸温中和胃温中健脾温中降逆温中散寒温中止呕瘟疫文火闻诊问寒热问汗问诊无汗 ()无尿五迟五更泄五积五劳五淋五禽戏五心烦热五行五行学说五运五脏五志午后潮热武火熄风熄风止痉喜按喜则气缓细脉下法下焦下焦湿热下利清谷下脘先煎先天先天不足先天之本先天之精弦脉涎相乘相火相火妄动相克相生相侮消导消渴消痞化积消食导滞消食化痰消食剂消肿解毒小便不利小便浑浊小便涩痛小便失禁小便自利小肠经小肠实热小肠虚寒小腹哮病哮喘哮鸣邪气邪正消长胁斜刺泄泻泻法泻肺泻火泻火解毒泻南补北泻下药泻下逐水心包心包经心藏神心烦心烦不寐心肺气虚心肝火旺心肝血虚心火亢盛心火上炎心悸心脾两虚心气不宁心气血两虚心窍心肾不交心痛彻背心血虚心阴阳两虚心主神明心主血脉辛辛凉解表新感行气宽中行气止痛形寒肢冷胸闷胸痞胸胁胸胁苦满虚虚喘虚烦虚寒虚火虚火上炎虚劳虚实夹杂虚阳上浮虚则补之虚证宣肺宣肺化痰宣肺平喘宣肺止咳悬灸眩晕穴血不归经血不循经血分血分热毒血分瘀热血分证血海血脉血热血热妄行血热证血脱血虚血瘀血郁血燥血燥生风血证血肿押手牙关紧闭牙痛牙龈肿痛咽喉不利咽喉肿痛咽痒岩羊癫风阳明阳气阳跷脉阳胜则热阳盛阳盛阴衰阳损及阴阳维脉阳痿阳邪阳虚阳虚阴盛阳证阳中求阴疡养生养胎养胃阴养心安神养血养血安神养血柔肝养血息风养血药养阴养阴润燥腰酸腰痛腰膝酸软药膏药酒药膳夜盲夜寐不安夜啼液遗尿以毒攻毒以右治左异病同治疫毒疫疠益气益气安神益气和胃益气养阴益胃意因地制宜因人制宜因时制宜阴阴寒凝结阴竭阳脱阴经阴络阴气阴跷脉阴胜则寒阴盛阴盛格阳证阴盛阳衰阴损及阳阴维脉阴邪阴虚阴虚动风阴虚火旺阴虚阳亢阴阳对立阴阳格拒阴阳互根阴阳两虚阴阳偏盛阴阳偏衰阴阳失调阴阳消长阴阳学说阴阳转化阴液阴液不足阴证阴中求阳引火归原饮饮留胃肠饮食不振饮停胸胁饮邪隐痛营分 () 营分证营气营卫不和营血痈忧游走痛有汗有神瘀血瘀血证瘀血阻络瘀阻胞宫语声低微语声重浊郁证预后元气元气不足原气远血月经月经不调月经过多月经过少月经后期月经先期运化运化失职晕厥脏脏病及腑脏腑脏腑辨证脏腑学说脏寒脏气脏象燥热犯肺燥湿化痰燥湿健脾燥湿止痒燥邪燥邪犯肺证躁动不安痄腮谵语战汗胀痛针刺麻醉针灸真寒假热真气真实假虚真心痛真阳真阴真阴耗损诊籍疹镇肝熄风镇惊镇惊安神镇咳怔忡癥瘕正骨正气正气大虚正邪相争正治证 1. ; 2. (亚型)证候证型症状支饮肢倦乏力肢体困重肢体麻木直刺直中止痉止咳化痰止痛止血药止痒志治本治标治病求本治未病治则痔滞针中风中风闭证中风脱证中腑中寒中焦中焦湿热中经中络中气中气下陷中暑中脘中阳不足中药中药学中医 1. ();2.中医学中脏肿胀重镇安神逐水逐水药主色主证助阳解表爪甲不荣壮热壮阳灼痛滋肾养肝滋肾益阴滋水涵木滋阴滋阴安神滋阴潜阳子病犯母子气自汗走罐足厥阴肝经足少阳胆经足少阴肾经足太阳膀胱经足太阴脾经足阳明胃经卒中。
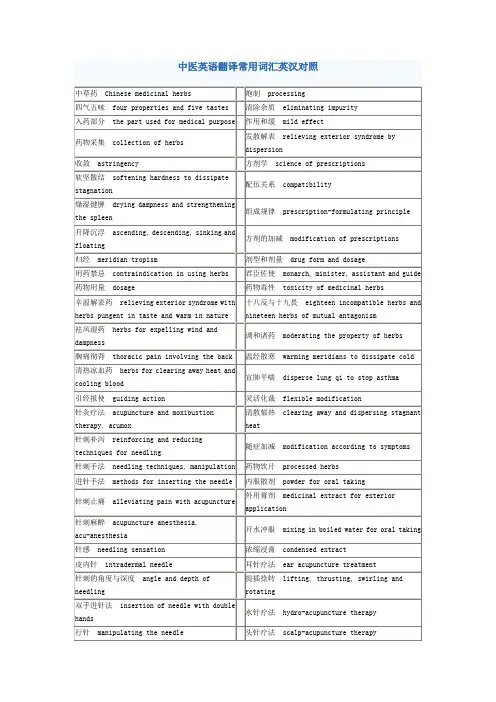

中医的专业术语英文翻译大家在写中医论文时候常常遇到一些不容易翻译的词汇,yjbys 网整理了中医的专业术语英文翻译,方便大家写作。
快来点赞吧。
中国医药学:traditional Chinese medicine中医基础理论:basic theory of traditional Chinese medicine临床经验:clinical experience辨证论治:treatment based on syndrome differentiation本草:materia medica //medicinal herbs中药Chinese herbs四气五味:four properties and five tastes针灸acupuncture and moxibustion各家学说theories of different schools汗法: diaphoresis /diaphoretic therapy下法:purgative therapy吐法:emetic therapy补土派:school of invigorating the earth病因学说:theory of etiology养生:health-cultivation医疗实践medical practice治疗原则:therapeutic principles寒凉药物:herbs of cold and cool nature滋阴降火:nourishing yin to lower fire瘀血致病:disease caused by blood stasis先天之精:congenital essence气的运动变化:movement and changes of qi。

基础中医英语汇总Unit1tumor:肿瘤;肿块;赘生物a mass of diseased cells in the body which divide and increased too quiklyailment:小病,不安an illness that is not very seriousrevival:恢复精神;苏醒;再生效a process in which something becomes active or strong againintegration:综合;集成the combining of two or more things so that they work effectivelynormalize:使正常化;使规格化,使标准化standardizewell-deserved :;理应的;当之无愧的well-earned because of good or bad behavior, skill, work,anesthesia:麻醉;麻木the state of unable to feel paintherapeutic:治疗的;治疗学的;有益于健康的relating to the treatment or cure of an illness debilitate:使衰弱;使虚弱make one ill or weakformula:公式,准则;配方;婴儿食品a prescription of ingredients in fixed proportion turmoil:混乱,骚动a state of confusion, excitement of anxietyderide:嘲笑;嘲弄treat sb. Or sth. As funny and not worthy of serious attention pharmacological:药理学的related to the scientific study of drugs and medicines treatise:论文;论述;专著a serious of book or article about a particular subject nontoxic:无毒的not poisonous to one’s healthstagnation:停滞;滞止a state of in activeforebear:祖先;祖宗ancestorphysique:体格,体形the form, size, and development of a person’s bodycirculation:流通,传播;循环;发行量the movement of blood around the bodydehydration:脱水loss of water from the body or from an organ or body partinfection:感染;传染;传染病;影响being ill through contact with bacteriadigestion:消化;领悟the process of digesting foodhyperactive:极度活跃的;活动过度的abnormally or extremely activeinadequacy:state of lacking the quality or quantity required stressful:紧张的;有压力的causing mental or emotional stresslibido:性欲;生命力emotional energy or urge, esp sexualunit3physiology:生理学;生理机能the branch of biology that deals with the normal functions of living organism and their partsinduce:引诱;[电]感应;[医]诱导;引起bring about or giving rise tointerfere:干涉;打扰;妨碍prevent continuing or being carried out properlyfluid:流动的;不固定的;流畅的substance that has no fixed shape and yields easily to external pressureascending:上升;登高;追溯sloping or leading upwardsimpair:削弱;损害;减少weaken or damageexcretion: 排泄,排泄物;分泌,分泌物the process of eliminating or expelling waste waterrot:腐烂;腐败;堕落cause to decaynausea:恶心,晕船;极端的憎恶feeling of sickness with an inclination to vomitpalpitation:可触知性;明白 a noticeably rapid, strong, or irregular heartbeat due to agitation, exertion, or illnesstrait:特性,特点;品质;少许distinguish quality or characteristictimidity:胆怯,胆小;羞怯showing a lack of courage or confidence amenorrhoea: an abnormal absence of menstruation tinnitus: ringing r buzzing in the earsirritability:兴奋性;易怒;过敏性having or showing a tendency to be easily annoyed or made angrytextBcorrespondence:一致;相当;通信a close similarity, connection, or equivalence deficiency:缺乏;不足的数额;缺陷,缺点a lack of shortageprevalence: . 流行;普遍;广泛being widespread in a particular area or at a particular time pallid:苍白的;暗淡的;无生气的pale, typically because of poor healthretention:扣留,滞留;保留;记忆力;[医]闭尿the continued possession, use, or control of poor healthgroan:呻吟;抱怨;发吱嘎声make a deep inarticulate sound in response to pain despair husky:声音沙哑的;有壳的;强壮的sounding low-pitched and slightly hoarse rancid:腐臭的;令人作呕的,讨厌的smelling or tasting unpleasant as a result of being old and stalefragrant:芳香的;愉快的having a pleasant or sweet smellsubdue:征服;抑制;减轻overcome. Quieten, or bring under control repressed:被抑制的;被压抑的restrained, inhibited, or oppressedatrophy:萎缩,萎缩症;发育停止(of body tissue or an organ)wasting awaytrigger:触发;引发,引起cause to happen or existpurplish: rather purple in colortinge:淡色;些许味道;风味, 微染;使带气息a tendency towards or trace of some colorunit4essence:本质,实质;精华;香精the most basic and important quality of something transmute:使变形;使变质change one substance or type of thing into another sufficient:足够的;充分的as much as needed for a particular purposetemper: make something less sever or extremedynamic:动力的;动力学的;动态的;有活力的force that produces change, action, or effect ambience:气氛,布景;周围环境the special atmosphere or mood created by particular environmentunfolding:伸展;解折叠;演变spreading outprimordial:原始的;根本的;[生]原生的being or happening first in sequence of time bestow:授予;使用;放置;留宿give someone something of great value or important underlying:在下面的;优先的;根本的;潜在的basicepisode:插曲;插话;一段情节;有趣的事件an event or short period of time during which something happensinhalation:吸入;吸入药剂breathe in air, smoke, or gasvolition: 意志,意志力;决断力the power to choose or decide something without being forced to do itthrive:繁荣,兴旺;茁壮成长become and continue to be, successful, strong , heathy,etc. disseminate:散布;宣传,传播scatter widelydisposition:性情;倾向;处置;部署particular type of charactertextBchoke:使窒息;呛;阻塞;扑灭;抑制be unable to breathe proper because sth. Is in throat or there Is not enough airlethargy:死气沉沉;昏睡;嗜眠(症)felling as if one has no energy and no interest in doing anythingdistention:膨胀,扩张swelling or being swollenwade:跋涉;可涉水而过的地方walk through water that is not deepscanty:缺乏的;吝啬的;仅有的;稀疏的not enoughretention:扣留,滞留;保留;记忆力;[医]闭尿action of holding sth in position or containing itwheeze:喘息;呼哧呼哧地响breathe with difficultysyndrome:医]综合征;[医]综合症状;[医]并发症状;[计]校验子;[计]并发位an illness which consist of a set of physical or mental problemsexertion:努力;发挥;运用a lot of physical or mental effortcomplexion:面色;肤色;情况;局面the nature color or appearance of the skin on face coarse:粗糙的;下等的;粗俗的having a rough surface that feels slightly hard not smoothunit5physiology:生理学;生理机能the branch of biological sciences dealing with the functioning of organsdeficient:不足的;有缺陷的;不充分的inadequate in amount ordegreestagnant:停滞的;污浊的;不景气的;迟钝的nor circulating or floatingstasis:郁积,停滞;血行停滞a stoppage of the flow of the blood or body fluids in any part abdomen:腹部;下腹;腹腔a part of the body below the chest that includes the stomach and bowsbleed:流血;渗出;悲痛loose blood from one’s bodyfeeble:微弱的,无力的;虚弱的;薄弱的very weakimpair:削弱;损害;减少make worse or less effectivesecrete:藏匿;私下侵吞;[生]分泌produce a liquid substance either as a waste mateialor for use within the bodyexcrete:分泌;排泄eliminate by a normal dischargedisperse:使散开;分散;传播separate and fo in different directionsexpulsion:开除;驱逐the act of sending or driving a substance out of body and bowels occlude:使闭塞;封闭;挡住obstructsuffuse:充满;弥漫spread all over or through sthdiarrhea:腹泻,痢疾abdominal frequency and liquidity of fecal discharges impede:阻止;妨碍;阻碍delay or stop the progress of sthquote:引述;举证;报价a passage or expression that is citedtextBtenuous:纤细的;稀薄的;贫乏的extremely thinrarefield:稀薄的;纯化的subtle and refinedextremities:四肢,骨端;末端,极限(extremity复数形式);手足the parts of the body that is farthest from the centre, esp the hands and feetgauge:计量器;标准尺寸;容量规格make a judgment about sthcatalytic:接触反应的;起催化作用的, 催化剂;刺激因素causing the process of speeding up a chemical reaction with a catalystpathogenic:致病的;病原的;发病的able to cause diseasediffuse:散开的;弥漫的spread sth in all directionsspontaneous:自发的;自然的;无意识的happening naturally, without being made happenprone:有…倾向的,易于…的;俯卧的likely to do sthnourish:滋养;怀有;使健壮keep a person an animal or a plantpectoral: relating to or connecting with chest simultaneously: at the same timedefensive:自卫的;防御用的projectivepore:细想;凝视;熟读hole in the skin that sweat can pass throughassume:假定;承担;呈现;采取take on a certain form, attribute or aspectunit6acupuncture:针刺疗法;针刺method of p ricking the tissues of human body with fine needles in order to cure disease, to relieve pain or as a local anestheticcutaneous:皮肤的;侵犯皮肤的of or relating to or affecting the skinacupoint:穴道,[中医] 穴位locations on the body that are the focus of acupuncture tendon:腱a band of tough, inelastic fibrous tissue that connects a muscle with its bone attachmentsuperficial:表面的;肤浅的being on or near the surfacesymmetrical:匀称的,对称的having similarity in size, shape, and elative position or corresponding partsscapular:肩胛的;肩胛骨的of or relating to the shoulder or scapulavertex:顶点;头顶;天顶the top of the headdorsal:背的,背侧的;背部的of, toward on, in , or near the back or upper surface of an organ, a part or an organismmalleolus:解剖] 踝either of the two rounded protuberances on each side to the ankle by recurring inner formed by a projection of the tibia and the outer by a projection of the fibula ventral:腹部的;腹侧的relating to or situated on or close to the abdomencongestion:充血;拥塞;拥挤excessive accumulation of blood or other fluid in a body part psoriasis: [皮肤] 牛皮癣;银屑癣a noncontagious in flammatory skin disease characterized by recurring reddish patches covered with silvery scalesfossa: [解剖] 凹;小窝a small cavity of depression , as in a boneocciput:枕骨部;后头部the back part of the head or skulleczema: [医]湿疹a noncontagious inflammation of the skin, characterized chiefly by redness itching and the outbreak or lesions that may discharge serous matter and become encrusted and scalyhomeostasis: [生理] 体内平衡;[自] 内稳态the ability or tendency of an organism or a cell to maintain internal equilibrium by adjusting its physiological processaxilla: [解剖] 腋窝,[解剖] 腋下;咯肢窝the armpitmeridian:子午线,经线;顶点any of the channels through which vital energy is believed to circulate round the bodymetabolism:新陈代谢the complex of physical and chemical process accruing within a living cell or organism that are necessary for the maintenance of lifepernicious:有害的;恶性的;致命的;险恶的exceeding harmful causing grave harm complication:混乱;复杂;复杂化;[医]并发症any disease or disorder that occurs during the course of another diseaseresume: . 再开始return to previous location or conditionreplenish:把…装满;补充,再装满;给…添加燃料make full of complete again by suppling what has been used up or is lackingproximal:最接近的,邻近的;近身体中央的situated close to centre , median line, or joint of attachment or origininfluenza: [医]流行性感冒(简写flu);[兽医]家畜流行性感冒an acute febrile highly contagious viral diseasedyspepsia:. [内科] 消化不良;胃弱 a disorder of digestive function characterized by discomfort or heartburn or nauseadorsum:腹股沟;交叉拱the posterior part of a human body from the neck to the end of thespinemoxibustion:艾灸a method of treatment, originally I Chinese medicine in which a moxa is burned on the skinformulation:公式化;简洁陈述;构想,规划list of ingredient of sets of instructions for making sth esp medicines and fuelsgroin:腹股沟;交叉拱the depression or fold where the legs join the abdomen the genital esp the testiclestibia:解]胫骨;胫节(昆虫)the inner and thicker of the two bones of the human legs between the knee and the anklemassage:按摩;揉kneading and rubbing parts of the body to increase circulation and promote relaxationtextBetiology: [病理] 病因学;[基医] 病原学;致病源the study of what causes the disease pathogenesis:发病机理;发病原the occurrence development of a disease exogenous:外生的;外因的;外成的derived or originating externally hemorrhoids:痔疮;痔疾swollen veins in the anorectal passagespasm:痉挛;抽搐;一阵发作a painful and involuntary muscular contraction hematuria:泌尿] 血尿;血尿症the presence of blood in urinemenorrhagia:妇产] 月经过多abnormally heavy or prolonged menstruation hypochondrium:季肋部;忧郁症;疑病症the upper region of the abcomen just below the lowest ribs on either side of the epigastriumregurgitation:回流;反刍;流回gushing backcarbuncle: [中医] 痈;红宝石a large inflamed swelling under skindizziness:头晕;头昏眼花a feeling of one is about to fallgum:使…有粘性;用胶粘,涂以树胶the tissue of the jaws that surrounds the bases of the teeth palpitation: [内科] 心悸;跳动;颤动a rapid and irregular heart beatmalnutrition:营养失调,营养不良a state of poor nutritionpuffiness:虚胖,虚肿abnormal protuberance or localized enlargement congestion:充血;拥塞;拥挤excessive accumulation of blood or other fluid in a body part suffocate:窒息;受阻,受扼制impair the respiration of or obstruct the air passage of phlegm: . 痰;粘液;粘液质abnormal thick mucus secreted by the mucosa of the respiratory passages during certain infectious prcesstendon: . 腱a thick strong string-like part of your body that connects a muscle to bone ulcer: 溃疡;腐烂物;道德败坏open sore containing poisonous matter on the outside of the body or on he surface of an internal organtextBendogenous: [生物] 内生的;内因性的derived or originating internallyblotch:污点;疙瘩;斑点an irregular shaped spotpallor:青白;灰白;苍白(尤指脸色)unnatural lack of color in skinlump:块,块状;肿块;瘤;很多;笨人abnormal protuberance or localized enlargement menstruation:生理] 月经;月经期间;有月经the discharge of the menses breathlessness:呼吸急促,气喘吁吁breathing with difficultyincontinence:失禁;无节制;不能自制involuntary urination or defecation feebleness:微弱的,无力的;虚弱的;薄弱的the state of being weak in health or body cystitis: [泌尿] 膀胱炎inflammation of the urinary bladderanorexia:厌食;神经性厌食症loss of appetite esp as a result of disease hypoglycemia:低血糖症;血糖过低an abnormal low level of glucose in the blood psoriasis:皮肤] 牛皮癣;银屑癣a chronic skin disease marked by dry red patches coveredwith scalesfatigue:疲劳,疲乏;杂役physical or mental weariness resulting from exertion listlessness:精神萎靡;无精打采the state of lacking energy or disinclined to exert effort emaciation:憔悴;消瘦,瘦弱a waste condition of the bodytinnitus:[耳鼻喉] 耳鸣a nonspecific symptom of hearting disorder characterized bu the sensation of buzzing ringing and other noises in the earsolitude:孤独;隐居;荒僻的地方the state of quality of being alone or remote from others lethargy:死气沉沉;昏睡;嗜眠(症)extreme lack of energy or vitality hypotension:低血压,血压过低low blood pressurechaotic:混乱的,无秩序的;混沌的complete unordered and unpredictable and confusingunit8discriminate:区别;辨别;歧视make a differenceinsomnia:失眠症,失眠inability to sleepdullness:迟钝,钝度mental slownesscorporal:肉体的,身体的of the human bodyblue:蓝色的;忧郁的,沮丧的;下流的feeling of deep sadness or depression grumpy:脾气暴躁的;性情乖戾的bad-temperedmechanism:机械装置;机制;技巧;原理,途径;进程the way that something works pinpoint:查明;精确地找到;准确描述locate or identify with precisionpool:联营;水塘;撞球;共同资金combine intofull-blown:花)盛开的;成熟的;(帆等)张满的fully deveopedprolapse: a condition in which an organ of the body hasslipped forward or downstamina:精力;活力;毅力;持久力ability to endure much physical or mental strain scarlet:罪孽深重的;淫荡的;鲜红色的;深红的bright redafflict:折磨;使痛苦;使苦恼cause trouble, pain or distress to sb. Or sthapathy:冷漠,无兴趣,漠不关心;无感情lack of interestirritability:兴奋性;易怒;过敏性the state of becoming annoyed very easily rebellious:反抗的;造反的;难控制的showing a desire to rebelimbibe:喝;吸收,接受;吸入drinktextBstifling:沉闷的;令人窒息的very hot or stuffy almost to the point of being suffocating disrupt:使分裂;使瓦解;使中断;使陷于混乱;破坏cause disorder in sth purulent:脓;化脓;含脓;流脓containing pusviscous:粘性的;黏的thick and stickyaberration:离开正路,越轨;失常deviation from what is accepted as normal or right pensiveness:沉思的,忧郁的;悲伤的,哀愁的deep serious thoughtfulness scrofula:[内科] 淋巴结核 a disease causing swelling of the glands, probably a form of tuberculosispuffy:一阵阵吹的;胀大的;喘气的looking swollenintractable:倔强的;棘手的;不听话的;[医]难治的very difficult to deal with congeal:凝结;凝固become thick or solid esp by coolingeffusion:泻出;渗出;[医]渗漏物pouring out esp of liquidhumidity:湿度;湿气the amount of water in the airadrenal:肾上腺的at, near, or on the kidneysmelancholy:忧郁的;使人悲伤的deep sadness which last for some timegreasy:油腻的;含脂肪多的;谄媚的covered in grease or oilunit1食疗:dietary therapy湿病:damp ailment保健:maintain wellness/ keep fit民间医药:folk medicine中西医结合:integration of TCM and western medicine内经记载,寒病需热药来医。

温补脾阳,warmly invigorating spleen yang温补肾阳,warming and recuperating kidney yang温补心肺,warmly invigorating heart and lung温补脾胃,warmly invigorating spleen and stomach温阳行气,warming yang for activating qi flowing补气养血,benefiting qi and nourishing blood补益肝脾,invigorating liver and spleen补益心脾,invigorating heart and spleen补益心肺,invigorating heart and lung补益脾肾,invigorating spleen and kidney补益心肝,invigorating heart and liver滋阴补阳, nourishing yin and tonifying yang温阳益气, warming yang and benefiting qi益气滋阴, benefiting qi and nourishing yin补益精髓,strengthening and nourishing marrow and essence补肾调精, invigorating kidney for regulating menstruation滋补肾精,replenishing kidney essence补益心肾invigorating heart and kidney滋阴补血,nourishing yin and supplementing blood温里法,method of warming interior回阳救逆,restoring yang [and rescuing the patient from collapse!温阳散寒,warmins vans for dispelling cold温阳散寒,warming yang for dispelling cold温中散寒,warming spleen and stomach for dispelling cold温肺散寒,warming lung for dispelling cold温肾散寒,warming kidney for dispelling cold温肝散寒,warming liver for dispelling cold温胃散寒,warming stomach for dispelling cold温通小肠,warmly dredging small intestine温经散寒,warming channel for dispelling cold暖宫散寒,warming uterus for dispelling cold温经活血,warming channel and activating blood circulation温经止血,warming the channel for stopping bleeding治风法,method of expelling wind疏散风邪,dispelling wind pathogens袪风解肌,dispelling pathogenic wind from muscles平肝息风,suppressing hyperactive liver for calming endogenous wind 清热息风,clearing heat for calming endogenous wind凉血息风,cooling blood for calming endogenous wind清肝息风,clearing liver-fire for calming endogenous wind解毒息风,removing toxic substance and calming endogenous wind柔肝息风,softening liver for calming endogenous wind滋阴息风,nourishing yin for calming endogenous wind养血息风,nourishing blood for calming endogenous wind温中散寒,warming spleen and stomach for dispelling cold温肺散寒,warming lung for dispelling cold温肾散寒,warming kidney for dispelling cold暖肝散寒,warming liver for dispelling cold温胃散寒,warming stomach for dispelling cold温通小肠,warmly dredging small intestine温经散寒,warming channel for dispelling cold暖宫散寒,warming uterus for dispelling cold温经活血,warming channel and activating blood circulation温经止血,warming the channel for stopping bleeding治风法,method of expelling wind疏散风邪,dispelling wind pathogens祛风解痉,dispelling pathogenic wind from muscles平肝熄风,suppressing hyperactive liver for calming endogenous wind清热熄风,clearing heat for calming endogenous wind cooling blood for calming endogenous wind清肝息风,clearing liver-fire for calming endogenous wind解毒祛风,removing toxic substance and calming endogenous wind柔肝息风,softening liver for calming endogenous wind滋阴熄风,nourishing yin for calming endogenous wind养血息风,nourishing blood for calming endogenous wind豁痰熄风,eliminating phlegm for calming endogenous wind平肝潜阳,suppressing hyperactive liver and subsiding yang息风解痉,relieving spasm by calming endogenous wind熄风定痫,arresting epilepsy by calming endogenous wind祛风解痉,dispelling pathogenic wind for resolving convulsion祛痰法,method of expelling phlegm宣肺化痰,dispersing lung qi and dissipating phlegm燥湿化痰,eliminating dampness and phlegm渗湿化痰,eliminating dampness and resolving phlegm祛痰化浊,eliminating phlegm and resolving turbidity清热化痰,removing heat-phlegm润燥化痰,moistening dryness for removing phlegm温化寒痰,warming for resolving cold-phlegm祛风化痰,dispelling pathogenic wind and eliminating phlegm涤痰熄风,clearing phlegm for calming endogenous wind理气化痰,regulating qi-flowing for eliminating phlegm散寒化饮,dispelling cold and resolving fluid-retention泻肺逐饮,eliminating pathogens from lung for expelling fluid-retention温阳化饮,warming yang for resolving fluid-retention化痰消瘀,dissipating phlegm and eliminating blood stasis化痰散结,dissipating phlegm and resolving masses化痰消瘿,dissipating phlegm for eliminating goiter祛痰宣痹,eliminating phlegm and dredging blockage of channel 开窍法,method of inducing resuscitation清热开窍,clearing away for resuscitation宁心开窍,calming heart for resuscitation芳香开窍,causing resuscitation with aromatics化痰开窍,eliminating phlegm for resuscitation辛温开窍,resuscitation with pungent and warm drug驱虫法,method of expelling intestinal parasites驱蛔杀虫, expelling and killing ascarid温脏安蛔, calming intestinal ascaris by warming method驱虫攻下,expelling intestinal parasites by purgation健脾驱虫,strengthening spleen for expelling intestinal parasites 杀虫消疳,destroying parasites for curing malnutrition安神法, tranquillization重镇安神,tranquillization with heavy prescription养心安神,nourishing blood for tranquillization益气安神,benefiting qi for tranquillizing滋阴安神,nourishing yin for tranquillization解郁安神,resolving stagnation for tranquilization消导法,method of promoting digestion消食化滞,resolving food-stagnancy消热导滞,clearing heat and removing stagnation of food消痞化积,relieving oppression and masses软坚散结,softening and resolving hard mass固涩法,astringing method固表止汗,consolidating exterior for arresting sweating益气固表,invigorating qi and consolidation of superficies敛阴固表,astringing yin and consolidation of superficies敛肺止咳,astringing lung for relieving cough涩肠止咳,relieving diarrhea with astringents益气摄精,benefiting qi for protecting semen补肾摄精,invigorating kidney for protecting semen固经止血,consolidating channel for hemostasis固涩止血,astringing for hemostasis固冲止带,consolidating Chong Vessel for stopping leukorrhagia 补肾安胎,tonifying kidney for preventing miscarriage固涩敛乳,astringing for arresting lactation缩尿止遗,reducing urination for preventing enuresis治痈疡法,method for treating sores and carbuncles疮疡消法,resolving method for ulcer and sore疮疡托法,method of expelling pathogens by strengthening vital qi 疮疡补法,benefiting method for sore and ulcer解毒消痈,removing toxic substance for eliminating carbuncles活血解毒,promoting blood circulation and detoxication解毒护阴,removing toxic substance for protecting yin解毒消肿,removing toxic substance for detumescence清热排脓,clearing heat and discharging pus通腑排脓,catharsis and expelling pus祛瘀排脓,removing blood stasis and expelling pus托里排脓,expelling pathogens by strengthening vital qi and expelling pus提脓拔毒,elminating pus and toxin提脓去腐,eliminating pus and slough活血去腐,promoting blood circulation and eliminating necrosis去腐消肿,eliminating slough and detumescence去腐生肌,eliminating slough and promoting granulation透脓生肌,promoting pus-drainage and granulation生肌收口,promoting granulation and wound healing养阴生肌,nourishing yin and promoting granulation益气生肌,benefiting qi and promoting granulation养血生肌,nourishing blood and promoting granulation回阳生肌,restoring yang and promoting granulation去毒生肌,detoxication and promoting granulation消肿生肌,detumescence and promoting granulation生肌定痛,promoting granulation and relieving pain消痈散疖,resolving carbuncle and expulsing boil通乳消肿,promoting lactation for resolving carbuncle燥湿敛疮,eliminating dampness and astringing sores消解余毒,expelling retained toxin敛疮止痛,healing sore and rlieving pain明目,improving eyesight祛风明目,dispelling pathogenic wind for improving eyesight清肝明目,removing liver-fire for improving eyesight凉血明目,cooling blood for improving eyesight化瘀明目,expelling blood stasis for improving eyesight补肾明目,tonifying kidney for improving eyesight滋肝明目,nourishing liver for improving eyesight养血明目,nourishing blood for improving eyesight补气明目,benefiting qi for improving eyesight退翳明目,removing nebula for improving eyesight通耳,improving hearing通鼻,relieving stuffy nose利咽,relieving sore throat清咽,clearing heat from throat开音,sound producing固齿,strengthening teeth壮水制阳,strengthening governor of water for restraining hyperactivity of yang益火消阴,boosting source of fire for eliminating abundance of yin 引火归原,conducting fire back to its origin交通心肾,restoring normal coordination between heart and kidney 续经接骨,reunion of fractured tendons and bones强筋壮骨,strengthening tendons and bones通络下乳,dredging collateral for promoting lactation外治法,external tretment掺药法,method of dusting powder drug吹药法,method of blowing drug导药法,guiding medicinal method滴药法,dripping method割治法,cutting method药熨疗法,therapy of hot medicinal compress热敷疗法,hot compress therapy敷贴疗法,application therapy膏药疗法,plaster therapy药膏疗法,ointment therapy发疱疗法,vesiculation therapy箍围疗法,therapy of encircling lesion with drugs湿敷疗法,moisten-compress therapy敷脐疗法,umbilical compress therapy药浴疗法,medicinal bath therapy熏洗疗法,fumigation and wash therapy熏蒸疗法,fumigation and steaming therapy冲洗疗法,irrigation therapy腐蚀疗法,immersion and wash therapy缠缚疗法,eroding method binding therapy切开疗法,incision therapy引流疗法,drainage therapy放血疗法,blood letting therapy活烙疗法,cauterization threapy烧蚀疗法,burning-eroding therapy刮痧疗法,scrapping therapy神灯照疗法,lamp lighting up therapy点眼法,eye dripping therapy敷眼疗法,eye compress therapy金针拔障疗法,therapy of cataractopiesis with mental needle勾割疗法,hook-cutting therapy滴耳疗法,ear-dripping therapy吹耳疗法,Ear insufflation therapy塞耳疗法,ear-plugging therapy洗耳疗法,ear-washing therapy鼻嗅疗法,smelling therapy塞鼻法,nostril plugging therapy吹鼻疗法,nasal insufflation therapy滴鼻疗法,nasal dripping therapy鼻腔填塞疗法,therapy of plugging into nasal cavity 取嚏疗法,sneezing therapy喷雾疗法,spraying therapy蒸汽吸入疗法,steam-inhaling therapy吹喉疗法,lanynx-blowing therapy药栓疗法,medicinal suppository therapy药线疗法,medicated thread therapy挂线疗法,ligation therapy结扎疗法,ligating therapy灌肠了法,enema therapy包扎固定疗法,bandage-fixing therapy夹板固定疗法,splint-fixing therapy整复疗法,reduction therapy泥疗法,mud therapy蜡疗法,wax therapy食疗,dietetic therapy药枕疗法,medicinal pillow therapy药兜疗法,medicinal bag therapy蜂毒疗法,bee-toxin therapy鳝血疗法,eel-blood therapy草药,medicinal herb药材,medicinal material: crude medicinal地道药材,famous-region drug鲜药,fresh medicine天然药物,natural medicine采制,collection and manufacturing采收期,collection period产地加工,processing in situ萌发期,germination period枯萎期,withering period贮藏,storage干燥,drying晾干,drying in the sun阴干,drying in the shade烘干,drying by baking虫蛀,bitten by insect霉变,milden and rot泛油,oily调制,compounding霉变,milden and rot泛油,oily原植物鉴定,identification of original plant原动物鉴定,identification of original animal 原矿物鉴定,identification of original mineral 基源鉴定,identification of original根,root根茎,rhizome皮,bark, peel叶,leaf花,flower果实,fruit种子,seed全草,whole herb性状鉴定,macroscopical identification形状,shape,form大小,size表面特征,surface character色泽,color and luster质地,texture折断面,fracture surface断面特征,cut surface character菊花心,radial striations朱砂点,spot of oil cavity气(嗅)odor,smell味,taste显微鉴定,microscopical identification理化鉴定,physical and chemical identification 生化鉴定,biological identification质量分析,quality analysis质量标准,quality standard质量控制,quality control炮制,processing饮片,decoction pieces净制,cleansing挑选,selection筛选,screening风选,selection in the wind水选,selection in the water洗漂,washing and blanching润,moistening浸润,immersion洗润,rinsing moistening淋润,showering moistening泡润,soaking moistening切片,slice切段,section切片,piece切丝,sliver炒制,stir-frying清炒,simple stir-frying加辅料炒,fried with adjuvant material 辅料,adjuvant material麸炒,stir-frying with bran土炒,fried with earth烫,scalding烫制,scalding砂烫,heated with sand锻制,calcining明煅,calcining openly煅淬,calcining and quenching制碳,carbonizing炒碳,carbonizing by stir-frying煅碳,carbonizing by calcining制炭存性,burn as charcoal with nature 煨制,roasting in ashes蒸制,steaming煮制,boiling炖制,stewing酒制,processing with wine酒炙,stir-frying with wine酒炖,stewing with wine酒蒸,steaming with wine醋制,processing with vinegar醋灸,stir-frying with vinegar醋煮,boiling with vinegar醋蒸,steaming with vinegar盐制,processing with salt-water盐灸,stir-frying with salt-water盐蒸,steaming with salt-water姜汁制,stir-frying with ginger juice蜜制,stir-frying with honey油制,processed with oil制霜,frost-like powder水飞,levigating性味,nature and flavour四气,four nature of drugs寒cold热hot温warm凉cool平,calm, plain五味,five flavours辛,pungent甘sweet酸,sour苦,bitter咸,salty淡,tasteless涩,astringent升降浮沉,ascending and descending,floating and sinking 归经,channel entry引经,channel affinity,channel ushering配伍,concerted application of drugs七情,seven relations单行,drug used singly相使,mutual enhancement相须,mutual promotion相畏,incompatibility相杀,counteract the toxicity of another drug相恶,mutual inhibition相反,clashing,antagonism十八反,eighteen clashes十九畏,nineteen fears禁忌,contraindications配伍禁忌,incompatibility of drugs in a prescription证候禁忌,incompatibility of drugs in pattern妊娠禁忌(药),contraindications during pregnanacy服药食忌,food taboo (dietetic restraint) in drug application 剂量,dosage克,gram毫升,millilitre丁公藤,Caulis Erycibes(拉); obtuseleaf erycibe stem丁香,Flos Caryophylli(拉'); clove八角茴香,Fructus Anisi Stellati(拉); Chinese star anise人参,Radix Ginseng(拉); ginseng野山参,Radix Ginseng Indici (拉); wild ginseng红参,Radix Ginseng Rubra(拉); red ginseng生晒参,Radix Ginseng (拉)fresh ginseng人参叶,Folium Ginseng(拉); ginseng leaf儿茶,Catechu(拉); cutch,black catechu九里香,Folium et Cacumen Murrayae(拉); murraya jasminorage九香虫,Aspongopus(拉); stink-bug刀豆,Semen Canavaliae(拉); jack bean三七,Radix Notoginseng(拉); sanchi三棱,Rhizoma Sparganii(拉): common burreed rubber生姜,Rhizoma Zingiberis Recens(拉); fresh ginger干姜,Rhizoma Zingiberis(拉); zingiber(dried ginger)干漆,ResinaToxicodendri(拉); dried lacquer土木香,Radix Inulac(拉): inula root土贝母,Rhizoma Bolbostematis(拉); paniculate bolbostemma土荆皮,Cortex Pseudolaricis(拉); golden larch bark土茯苓,Rhizoma Smilacis Glabrae(拉); glabrous greenbrier rhizome土鳖虫,Eupolyphaga Seu Steleophaga(拉); ground beetle大血藤,Caulis Sargentodoxae(拉); sargentgloryvine stem大青叶,Folium Isatidis(拉); dyers woad leaf大枣,Fructus Jujubae(拉); Chinese date红大戟,Radix Knoxiae(拉); knoxia root京大戟,Radix Euphorbiae Pekinensis(拉); peking euphorbia root大黄,Radix et Rhizoma Rhei(拉); rhubarb大蓟,Herba seu Radix Cirsii Japonici (拉); Japanese thistle herb Japanese大腹皮,Pericarpium Arecae(拉): areca peel山麦冬,Radix Liriopes(拉): liriope roottuber山豆根,Radix Sophorae Tonkinensis(拉); Vietnamese sophora root北豆根,Rhizoma Menispermi(拉): asiatic moonseed rhizome北沙参,Radix Glehniae(拉); coastal glehnia root山茱萸,Fructus Corni(拉); asiatic cornelian cherry fruit山药,Rhizoma Dioscoreae(拉); common yam rhizome山柰,Rhizoma Kaempferiae(拉): galanga resurrectionlily rhizome山楂,Fructus Crataegi(拉): hawthorn fruit山慈菇,Pseudobulbus Cremastrae seu Pleiones(拉): appendiculate cremastra pseudobulb or common pleiine pseudobulb千年健,Rhizoma Homalomenae(拉); obscured homalomena rhizome千金子,Semen Euphorbiae(拉); caper euphorbia seed川乌,Radix Aconiti(拉): common monkshood mother root制川乌,Radix Aconiti Preparata(拉): prepared common monkshood mother川芎,Rhizoma Ligustici Chuanxiong(拉); szechwan lovage rhizome川楝子,Fructus Meliae Toosendan(拉); szechwan chinaberry fruit广藿香,Herba Pogostemonis(拉): cablin patchouli herb小茴香,Fructus Ligustri Lucidi(拉): glossy privet fruit女贞子,Fructus Foeniculi(拉); fennel小蓟HerbaCirsii(拉); field thistle herb马齿苋,Herba Portulacae(拉); purslane herb马勃,Lasiosphaera seu Calvatiae(拉); puff-ball马钱子,Semen Strychni(拉); nux vomica马兜铃,, Fructus Aristolochiae(拉); dutohmanspipe fruit马鞭草,Herba Verbenae(拉); european verbena herb土牛膝,Radix et Rhizome Achyranthes(拉); native achyranthes王不留行,Semen Vaccariae(拉); cowherb seed天仙子,Semen Hyoscyami(拉): henbane seed天仙藤,Herba Aristolochiae(拉): dutchmanspipe vine天冬,Radix Asparagi(拉); cochinchinese asparagus root天花粉,Radix Trichosanthis(拉); snakegourd root天竹黄,Concretio Silicea Bambusae(拉); tabasheer天南星,Rhizoma Arisaematis(拉); jackinthepulpit tuber胆南星,Rhizoma Arisaematis Cum bile(拉); bile arisaema天麻,Rhizoma Gastrodiae(拉); tall gastrodia tuber天葵子,Radix Semiaquilegiae(拉): muskroot-like semiaquilgia root木瓜,Fructus Chaenomelis(拉); common floweringqince fruit木香,Radix Aucklandiae(拉); common aucklandia root木贼,Herba Equiseti Hiemalis(拉): common scouring rush herb木通,Caulis Akebiae(拉),akebia stem川木通,Caulis Clematis armanoii(拉); armand clematis stem关木通,Caulis Aristolochiae Manshuriensis(拉); manchurian dutchmanspipe stem 木蝴蝶,Semen Oroxyli(拉); indian trumpetflower seed木鳖子,Semen Momordicae(拉); cochinchina momordica seed五加皮,Corlex Acanthopanax Radicis (拉),acanthopanax [root bark]香加皮,Cortex Periplocae(拉); Chinese silkvine root-bark五味子,Fructus Schisandrae Chinensis(拉); Chinese magnoliavine fruit五倍子,Galla Chinensis(拉); Chinese gall五灵脂,Faeces Togopteri(拉); flying squirrel's droppings太子参,Radix Pseudostellariae(拉); heterophylly lalsestarwort root车前子,Semen Plantaginis(拉): plantain seed车前草,Herba Plantaginis(拉); plantain herb瓦楞子,ConchaArcae(拉); are shell牛黄,Calculus Bovis(拉); cow-bezor牛蒡子,Fructus Arctii(拉); great burdock achene牛膝,Radix Achyranthis Bidentatae(拉); twotoothed achyranthes root川牛膝,Radix Cyathulae (拉); medicinal cyathula toot贝母,Bulbus Fritillaria (拉);fritillaria [bulb],川贝母,Bulbus Fritillariae Cirrhosae(拉); tendrilleaf fritillary bulb浙贝母,Bulbus Fritillariae Thunbergii(拉); thunberb fritillary bulb升麻,Rhizoma Cimicifugae(拉); largetrifoliolious bugbane rhizome化橘红,Exocarpium Citri Grandis(拉); pummelo peel月季花,Flos Rosae Chinensis(拉); Chinese rose flower乌药,Radix Linderae(拉),combined spicebush root乌梢蛇,Zaocys(拉); black-tail snake乌梅,Fructus Mume(拉); smoked plum火麻仁,Fructus Cannabis(拉); hemp seed巴豆,Fructus Crotonis(拉): croton fruit巴戟天,Radix Morindae Officinalis(拉); morinda root水牛角,Cornu Bubali(拉): buffalo horn水红花子,Fructus Polygoni Orientalis(拉); pirnce's-teather fruit水蛭,Hirudo(拉); leech玉竹,Rhizoma Polygonati Odorati(拉); fragrant solomonseal rhizome功劳木,Caulis Mahoniae(拉); Chinese mahonia stem功劳叶,Folium Ilex(拉); mahonia [leaf]甘松,Radix et Rhizoma Nardostachyos(拉): nardostachys root甘草,Radix Glycyrrhizae(拉); liquorice root甘遂,Radix Euphorbiae Kansui(拉): gansui root艾叶,Folium Artemisiae Argyi(拉); argy wormwood leaf石韦,Folium Pyrrosiae(拉); shearer's pyrrosia leaf石决明,Concha Ha1iotidis(拉); abalone shell石菖蒲,Rhizoma Acori Tatarinowii(拉); grassleaf sweetflag rhizome石斛,Herba Dendrobii(拉); dendrobiurn石榴皮,Pericarpium Granati(拉); pomegranate rind石膏,Gypsum Fibrosum (拉): gypsum龙胆,Radix Geniianae(拉): Chinese gentian龙骨,Os Draconis(拉);dragon bone龙眼肉,Arillus Longan(拉); longan aril仙茅,Rhizoma Curculigins(拉): common curculigo rhizome仙鹤草,Herba Agrimoniae(拉); hairyvein agrimonia herb白及,Rhizoma Blelillae(拉); common bletilla rubber白术,Rhizoma Atractylodis Macrocephalae(拉); largehead alractylodes rhizome白头翁,Radix Pulsatillae(拉): Chinese Pulsatilla root白豆蔻,Fructus Ammomi Rotundus (拉); white cardamon fruit白毛藤,Herba Solani (拉);dimbing nightshade白花蛇舌草,Herba Hedyotis (拉); hedyotis白芷,Radix Angelicae Dahuricae(拉): dahurian angelica root白附子,Rhizoma Typhonii(拉); giant typhonium rhizome白茅根,Rhizoma Imperatae(拉); lalang grass rhizome白矾,Alumen(拉); alum白果,Semen Ginkgo(拉); ginkgo seed白前,Rhizoma Cynanchi Stauntonii(拉): willowleaf swallowwort rhizome白白扁豆,Semen Dalichoris Album(拉): white hyacinth bean白蔹,Radix Ampelopsis(拉): Japanese ampelopsis root白鲜皮,Cortex Dictamni(拉); densefruit pittany root-bark白薇,Radix Cynanchi Atrati(拉); blackend swallowwort root瓜蒌,Fructus Trichosanthis(拉); snakegourd fruit瓜蒌子,Semen Trichosanthis(拉); trichosanthes seed瓜蒌皮,Pericarpium Trichosanthis(拉): snakegourd peel冬瓜皮,Exocarpium Benincasae(拉),Chinese waxgourd peel冬瓜子,Semen Benincasae(拉);wax gourd seed冬虫夏草Cordyceps(拉); Chinese caterpillar fungus冬葵果,Fructus Malvae(拉); cluster mallow fruit玄明粉,Natrii Sulfas Exsiccatus(拉); exsiccated sodium sulfate玄参,Radix Scrophulariae(拉); figwort root半边莲,Herba Lobeliae Chinensis(拉): Chinese lobelia herb半枝莲,Herba Scutellariae Barbatae(拉); barbated skullcup herb半夏,Rhizoma Pinelliae(拉): pinellia tuber法半夏,Rhizoma Pinelliae Preparatum(拉); prepared pinellia tuber清半夏,Rhizoma Pinelliae Preparata(拉)purified pinellia [tuber]姜半夏,Rhizome Pinelliae Preparata (拉);ginger[-processed] pinellia [tuber]半夏曲,Rhizoma Pinelliae Fermentata(拉); fermented pinellia丝瓜络,Retinervus Luffae Fructus(拉): luffa vegetable sponge老鹤草,1.Herba Erodii2.Herba Geranii(拉): common heron's bill herb.wilford granesbill herb 白芍,Radix Paeoniae Alba(拉); white peony root赤芍,Radix Paeoniae Rubra(拉); red peony root地龙,Lumbricus(拉); earthworm地肤子,Fructus Kochiae(拉): belvedere fruit地骨皮,Cortex Lycii(拉); Chinese wolfberry root-bark地黄,Radix Rehmanniae(拉); rehmannia root生地黄,Radix Rehmaniae Recens(拉);dried/fresh rehmannia [root]熟地黄,Radix Rehmanniae Preparata(拉); prepared rehmannia root地榆,Radix Sanguisorbae(拉); garden burnet root地锦草,Herba Euphorbiae Humifusae(拉); creeping euphorbia芒硝,Natrii Sulfas(拉); sodium sulfate胡麻子,Semen Lini(拉): linseed西红花,Stigma Croci(拉); saffron西河柳,Cacumen Tamaricis(拉); Chinese tamarisk twig西洋参,Radix Panacis Quinquefolii(拉); american ginseng百合,Bulbus Lilii(拉); lily bulb百部,Radix Stemonae(拉); stemona root当归,Radix Angelicae Sinensis(拉); Chinese angelica肉豆蔻,Semen Myristicae(拉): nutmeg肉苁蓉,Herba Cistanches(拉); desertliving cistanche肉桂,Cortex Cinnamomi(拉); cassia bark朱砂,Cinnabaris(拉); cinnabar竹节参,Rhizoma Panacis Japonici(拉): Japanese ginseng竹茹,Caulis Bambusae in Taenia(拉); bamboo shavings延胡索,Rhizoma Corydalis(拉); yanhusuo自然铜,Pyritum(拉); pyrite血余炭,Crinis Carbonisatus(拉); carbonized hair血竭,Sanguis Draconis(拉): dragon's blood全蝎,Scorpio(拉); scorpion合欢皮,Cortex Albiziae(拉); silktree albizia bark合欢花,Flos Albiziae(拉); albizia flower决明子,Semen Cassiae(拉); cassia seed冰片,Bomcolum Syntheticum(拉): borneol灯芯草,Medulla Junci(拉): common rush安息香,Benzoinum(拉); benzoin广防己,Radix aristolochiae fangchii (拉);southern fangchi root防己,radix Stephaniae Tetrandrae (li);mealy fangji [root]u防风,Radix Saposhnikoviae(拉); divaricate saposhnikovia root红豆蔻,Fructus Alpiniae Galangae(拉): galanga galangal fruit红花,Flos Carthami(拉); safflower红芪,Radix Hedysari(拉); manyinflorescenced sweetvetch root红景天,Radix Rhodiolae (拉); folium seu Herba Rhodiola麦冬,Radix Ophiopogonis(拉); dwarf lilyturf tuber麦芽,Fructus Hordei Germinatus(拉); germinated barley远志,Radix Polygalae(拉); thinleaf milkwort root赤小豆,Semen Phaseoli(拉); rice bean赤石脂,Halloysitum Rubrum(拉); red halloysite芫花,Flos Genkwa(拉); lilac daphne flower花椒,Pericarpium Zanthoxyli(拉): pricklyash peel花蕊石,Ophicalcitum(拉); ophicalcite芥子,Semen Sinapis Albae(拉): ustard [seed]苍术,Rhizoma Atractylodis(拉): atractylodes rhizome苍耳子,Fructus Xanthii(拉): Siberian cocklebur fruit芡实,Ssemen Euryales(拉); gordon euryale seed芦荟,Aaloe(拉); aloes芦根,Rhizoma Phragmitis(拉); reed rhizome芦笋,Cacumen Asparagi (拉); asparagus苏木,Lignum Sappan(拉): sappan wood苏合香,styrax(拉),storax杜仲,Cortex Eucommiae(拉); eucommia bark豆蔻,Fructus Amomi Rotundus(拉);两面针,Radix Zanthoxyli(拉): shiny leaf pricklyash root连钱草,Herba Glechomae(拉); longtube ground ivy herb连翘,Fructus Forsythia(拉); weeping forsythia capsule吴茱萸,Fructus Evodiae(拉); medicinal evodia牡丹皮,Cortex Moutan Radicis(拉); tree peony bark牡荆叶,Folium Viticis Negundo(拉); hempleaf negundo chastetree leaf牡蛎,Concha Ostreae(拉): oyster shell何首乌,Radix Polygoni Multiflori(拉); fleeceflower root制何首乌,Radix Polygoni Multiflori Preparata(拉); prepared fleeceflower root伸筋草,Herba Lycopodii(拉); common clubmoss herb佛手,Fructus Citri Sarcodactylis(拉): finger citron皂角刺,Spina Gleditsiae(拉); Chinese honeylocust spine谷芽,Fructus Setariae Germinatus(拉); millet sprout谷精草,Flos Eriocauli(拉); pipewort flower龟甲,Carapax et Plastrum Testudinis(拉); tortoise carapace and plastron辛夷,Flos Magnoliae(拉): biond magnolia flower羌活,Rhizoma et Radix Notopterygii(拉): incised notopterygium rhizome or root沙苑子,Semen Astragali Complanari(拉); flatstem milkvetch seed沙棘,Fructus Hippophae(拉); seabuckthorn fruit沉香,Lignum Aquilariae Resinatum(拉): Chinese eaglewood wood诃子,Fructus Chebulae(拉); medicine terminalia fruit补骨脂,Fructus Psoraleae(拉): malaytea scurfpea fruit灵芝,Ganoderma(拉): glossy ganoderma阿胶,Colla Coni Asini (拉);ass hide glue阿魏,Resina Ferulae(拉); Chinese asafetida陈皮,Pericarpium Citri Reticulatae(拉): dried tangerine peel附子,Radix Aconiti Lateralis Preparata(拉): prepared common monkshood daughter root 忍冬藤,Gaulis Lonicerae(拉); honeysuckle stem鸡内金,Endothelium Corneum Gigeriae Galli(拉): chicken's gizzard-skin鸡血藤,Gaulis Spatholobi(拉); suberect spatholobus stem鸡骨草,Herba Abri(拉): canton love-pea vine鸡冠花,Flos Celosiae Cristatae(拉): cockcomb flower玫瑰花,Flos Rosae Rugosae(拉); rose flower青木香,Radix Aristolochiae(拉): slender dutchmanspipe root青风藤,Gaulis Sinomenii(拉); orientvine stem青叶胆,Herba Swertiae Mileensis(拉); mile swertia herb青皮,Pericarpium Citri Reticulatae Viride(拉); green tangerine peel青果,Fructus Canarii(拉); Chinese white olive青葙子,Semen Celosiae(拉); feather cockscomb seed青蒿,Herba Artemisiae Annuae(拉): sweet wormwood herb青黛,Indigo Naturalis(拉); natural indigo青礞石,Lapis Chloriti(拉); chlorite schist杏仁,Semen Armeniacae Amarum(拉); bitter apricot seed苦参,Radix Sophorae Flavescentis(拉); lightyellow sophora root苦楝皮,Cortex Meliae(拉); szechwan chinaberry bark枇杷叶,Folium Eriobotryae(拉); loquat leaf板蓝根,Radix Isatidis(拉); isatis root松花粉,Pollen Pini(拉); pine pollen枫香脂,Resina Liquidambaris(拉): beautiful sweetgum resin刺五加,Radix et Gaulis Acanthopanacis Senticosi(拉);manyprickle acanthopanax郁李仁,Semen Pruni(拉); Chinese dwarf cherry seed郁金,Radix Curcumae(拉),: turmeric root tuber虎杖,Rhizoma Polygoni Cuspidati(拉); giant knotweed rhizome昆布,1.Thallus Laminariac,2.Thallus Eckloniacf;kelp or tangle明党参,Radix Changii(拉); medicinal changium root败酱草,Herba Patriniae(拉); atrina glass罗布麻叶,Foliun Apocyni Veneti;dogbane leaf罗汉果,Fructus Momordicae(拉): grosvenor momordica fruit知母,Rhizoma Anemarrhenae(拉); common anemarrhena rhizome委陵菜,Herba Potentillae Chinensis(拉): Chinese cinquefoil垂盆草,Herba Sedi(拉); stringy stonecrop herb使君子,Fructus Quisquali(拉): rangooncreeper fruit侧柏叶,Cacumen Platycladi(拉); Chinese arborvitae twig and leaf佩兰,Herba Eupatorii(拉): fortune eupatorium herb金果榄,Radix Tinosporae(拉): tinospora root金沸草,Herba Inulae(拉)inula herb金芥麦,Rhizoma Fagopyri Dibotryis(拉); golden buckwheat rhizome金钱白花蛇,Bungarus Parvus(拉); coin-like white-banded snake金钱草,Herba Lysimachiae(拉); Christina loosestrife广金钱草,Herba Desmodii(拉)snowbellleaf tickclover herb金银花,Flos Lonicerae(拉): honeysuckle flower金樱子,Fructus Rosae Laevigatae(拉); Cherokee rose fruit金礞石,Lapis Micae Aureus(拉); mica-schist狗脊,Rhizoma Cibotii(拉): cibot rhizome肿节风,Herba Sarcandrae (拉)arcandra [twig and leaf|鱼腥草,Herba Houttuyniae(拉); houttuynia炉甘石,Ga1aniina(拉): calamine卷柏,Herba Selaginellae(拉): spikemoss泽兰,Herba Lycopi(拉); hirsute shiny bugleweed herb泽泻,Rhizoma Alismatis;oriental waterplantain rhizome降香,Lignum Dalbergiae Odoriferae(拉),; rosewood细辛,Herba Asari(拉); manchurian wildginger珍珠,Margarita(拉): pearl珍珠母,Concha Margarititera(拉): nacre荆芥,Herba Schizonepetae(拉); fìneleaf schizonepeta herb茜草,Radix Rubiae(拉); india madder root荜茇,Fructus Piperis Longi(拉); long pepper荜澄茄,Fructus Litseae(拉); mountain spicy fruit草乌,Radix Aconiti Kusnezoffii(拉): kusnezoff monkshood root制草乌,Radix Aconiti Kusnezoffii Preparata(拉): prepared kusnezoff monkshood root 草豆蔻,Ssemen Alpiniae Katsumadai(拉); katsumada galangal seed草果,Fructus Tsaoko(拉); caoguo茵陈,Herba Artemisiae Scopariae(拉); virgate wormwood herb茯苓,Poria(拉); indian bread茺蔚子,Fructus Leonuri(拉); motherwort fruit胡芦巴,Semen Trigonellae(拉); common fenugreek seed胡黄连,Rhizoma Picrorhizae(拉); figwortflower picrorhiza rhizome胡椒,Fructus Piperis Nigri(拉); pepper fruit。

第一课1.中国中医药traditional Chinese medicine; TCM中医基础理论basic theory of traditional Chinese medicine临床经验clinical experience辨证论治treatment based on syndrome differentiation 杂病miscellaneous diseases中药学Chinese pharmacy 四气五味four properties and five tastes针灸acupuncture and moxibustion; acumox古代中国哲学classical Chinese philosophy汗法sweating therapy; diaphoresis 下法purgation吐法vomiting therapy; emetic therapy补土派the School of Reinforcing the Earth方剂prescription; formula 医疗实践medical practice治疗原则therapeutic principles寒凉药herbs cold and cool in nature滋阴降火nourishing yin and reducing fire瘀血致病diseases caused by blood stagnation第二课1 ve zang-organs; five zang-viscera五脏six fu-organs六腑system of meridians and collaterals经络系统holism整体观念organic wholenss有机整体social attribute社会属性(of the five zang-organs) open into开窍sprout, grow, transform, ripen and store生长化收藏diagnostics诊断学relationship between pathogenic factors and healthy qi邪正关系therapeutics治疗学common cold due to wind and cold风寒感冒different therapeutic methods used to treat the same disease同病异治the same therapeutic method used to treat different diseases异病同治balance of water metabolism水液代谢平衡clearing away heart fire清心火nature of disease疾病本质treating the left side for curing diseases located on the right side以左治右drawing yang from yin从阴引阳treating the lower part for curing diseases located on the upper part病在上者下取之第三课1 philosophical concept哲学概念mutual transformation相互转化balance of yin and yang阴平阳秘transformation between yin and yang阴阳转化extreme cold turning into heat寒极生热pathological changes病理变化absolute predominance 绝对偏盛general rule of pathogenesis病机总纲supplementing what it lacks of补其不足eliminating wind and dispersing cold祛风散寒mutually inhibiting and promoting相互消长mutually inhibiting and restraining相互制约interdependence相互依存excess of yin leading to decline of yang阴胜则阳病contrary and supplementary to each other相反相成organic whole有机整体impairment of yang involving yin阳损及阴deficiency of both yin and yang阴阳两虚deficiency cold syndrome虚寒证suppressing yang and eliminating wind熄风潜阳第四课1.the doctrine of five elements; the theory of five phases五行学说free development 条达舒畅to be generated and togenerate生我我生restraint in generation生中有制Wood is characterized by growing freely and peripherally.木曰曲直Earth is characterized by cultivation and reaping.土元稼穑Water is characterized by moistening and downward flowing.水曰润下over restriction and counter-restriction相乘相侮Wood over restricts earth because it is deficient.土虚木乘promotion, restriction, inhibition and transformation生克制化disorder of a mother-organ involving its child-organ母病及子insufficiency of essence and blood in the liver and kidney肝肾精血不足blood deficiency in the heart and liver心肝血虚exuberant fire in the heart心火亢盛insufficiency of liver yin肝肾不足declination of kidney yang肾阳衰微weakness of the spleen and stomach脾胃虚弱soothing the liver and harmonizing the stomach平肝和胃insufficiency of kidney yin肾阴不足balance between water and fire水火不济第五课doctrine of visceral manifestations脏象学说five zang-organs and six fu-organs五脏六腑extraordinary fu-organs齐桓之府nutrients of water and food水谷精微ransmitting and transforming water and food传化水谷storing essence贮藏精气internal and external relationship表里关系therapeutic effects治疗效应clinical practice临床实践storage without discharge藏而不写discharge without storage泻而不藏physical build and various orifices形体诸窍(of five zang-organs) open into开窍spirit and emotions精神情志the heart storing spirit心藏神the lung storing corporeal soul肺藏魄the liver storing ethereal soul肝藏魂the spleen storing consciousness 脾藏意the kidney storing will肾藏志the luster manifesting upon the face其华在面第六课the heart governing blood and vessels心主血脉sufficiency of heart qi心气充沛rosy complexion面色红润sufficiency of blood血液充盈unsmooth vessels脉道不利lusterless complexion面色无华thin and weak pulse脉象细弱the heart storing spirit心藏神sweat and blood sharing the same origin汗血同源ascending, descending, going out and going in升降出入dispersion,purification and descent宣发肃降regulating water passage通调水道the spleen governing transportation and transformation 脾主运化nutrients of water and food水谷精微stoppage of water and fluid水液停滞acquired base of life后天之本regulating qi activity调畅气机upward adverse flow of liver qi肝气上逆innate essence先天之精the kidney receiving qi肾主纳气第七课extraordinary fu-organs齐桓之府isolated fu-organ孤府digest water and food腐熟水谷anus破门remaining part of liver qi肝之余气upper energizer上焦separating the lucid from the turbid泌别清浊residue of foods食物残渣The large intestine governs thin body fluid大肠主津bile精汁The small intestine governs thick body fluid小肠主液primary digestion 初步消化essential qi精气the seven important portals七冲门The gallbladder is responsible for making judgment胆主决断discharge waste排泄糟粕occurrence of menstruation月经来潮epiglottis 吸门morphological hollowness形态中空transporting and transforming water and food传化水谷第八课innateness先天禀赋nutrients; refined substance精微物质blood circulation血液循环water metabolism水液代谢way of qi movement气的运动形式ascending, descending, exiting and entering movements of qi的升降出入运动normal function of qi activity气机条畅primary motive force of life生命的原动力warming and nourishing the viscera温养脏腑qi of the viscera and meridians脏腑经络之气qi activity气机qi transformation气化innate qi先天之气acquired qi后天之气healthy qi正气pathogenic factors邪气primordial qi元气thoracic qi宗气nutritive qi营气defensive qi卫气第九课qi promoting the production of blood气生血qi promoting the flow of blood气行血qi commanding blood气摄血blood carrying qi血载气blood generating qi血生气qi promoting the production of body fluid气生津液qi promoting the flow of body fluid气行津液qi commanding body fluid气摄津液body fluid carrying qi津液载气body fluid generating qi津液生气body fluid and blood sharing the same origin津血同源exhaustion of qi due to loss of body fluid气随液脱exhaustion of qi due to hemorrhage气随血脱loss of qi due to profuse sweating气随津泄Normal flow of qi ensures normal flow of blood while stagnation of qi causes stagnation of blood.气行则血行气滞则血瘀Qi commands the blood and the blood carries qi.气为血帅血为气母Normal flow of qi ensures normal flow of body fluid while stagnation of qi causes stagnation of body fluid.气行则水行气滞则水滞nourishing qi to stop collapse益气固脱Sweating therapy should be not be used to treat patients suffering from hemorrhage.亡血家不可发汗Sweating therapy should not be used to treat hemorrhage.夺血者无汗第十课theory of meridians and collaterals经络学说system of meridians and collaterals经络系统transporting qi and blood to the whole body运行全身气血being connected with the viscera and limbs联络脏腑肢节running routes循行路线twelve regular meridians十二正经the regions through or along which the meridians run and the order by which the meridians are connected with each other循行部位和交接顺序(of a collateral) pertaining to a certain meridian络属关系eight extraordinary vessels (meridians)奇经八脉branches of the twelve regular meridians十二经别divergent collaterals别络skin divisions of the twelve regular meridians十二皮部tendons of the twelve regular meridians十二经筋qi of meridians经络之气syndrome differentiation of meridians and collaterals经络辨证meridian conduction经络感传meridian manifestations经络现象blockage of meridians经络阻滞soothing meridians and activating collaterals舒筋活络collateral pricking and cupping therapy刺络拔罐第十课theory of meridians and collaterals经络学说system of meridians and collaterals经络系统transporting qi and blood to the whole body运行全身气血being connected with the viscera and limbs联络脏腑肢节running routes循行路线twelve regular meridians十二正经the regions through or along which the meridians run and the order by which the meridians are connected with each other循行部位和交接顺序(of a collateral) pertaining to a certain meridian络属关系eight extraordinary vessels (meridians)奇经八脉branches of the twelve regular meridians十二经别divergent collaterals别络skin divisions of the twelve regular meridians十二皮部tendons of the twelve regular meridians十二经筋qi of meridians经络之气14 syndrome differentiation of meridians and collaterals经络辨证meridian conduction经络感传meridian manifestations经络现象blockage of meridians经络阻滞soothing meridians and activating collaterals舒筋活络collateral pricking and cupping therapy刺络拔罐Lesson 11six exogenous pathogenic factors外感六淫improper diet and overstrain 饮食劳倦common cold due to wind-cold风寒感冒diarrhea due to damp-heat/damp-heat diarrhea 湿热泄泻five endogenous pathogenic factors内生五邪pathogenic wind attacking the exterior 风邪外袭migratory arthralgia/joint pain游走性关节痛wind being the leading pathogenic factor风为百病之长attacked/invaded by pathogenic cold感受寒邪decline of yang qi阳气衰退cold tending to stagnate by nature寒性凝滞stagnation of interstitial space 腠理闭塞spasm and contraction of muscles and tendons经脉拘急收引pathogenic dampness obstructing the spleen湿邪困脾inactivation of spleen-yang脾阳不振production of endogenous heat due to yin deficiency阴虚生内热extreme heat producing wind热极生风internal impairment due to yin deficiency 七情内伤improper diet饮食不节engorgement 暴饮暴食Lesson 12occurrence, development, and changes of disease疾病的发生发展变化(body )constitutional state 体质强弱dysfunction of qi and blood气血功能紊乱various pathological changes多种多样的病理变化exuberance or decline of pathogenic factors and healthy qi/ strength contrast between pathogenic factors and healthy qi邪正盛衰deficiency or excess changes of disease /transformation between deficiency and excess during a disease病症的虚实变化the human body’resistance against diseases 人体的抗病能力feverish sensation over the five centers (palms, soles, and chest)五心烦热deficiency complicated with excess虚实夹杂turnover of disease/prognosis of disease疾病转归relative predominance of yin or yang阴阳偏盛extreme changes of five emotions五志过极depletion of essence causing deficiency精气夺则虚mutual consumption of yin and yang阴阳互损true heat and false cold; false cold and true heat真热假寒或假寒真热stagnation of qi activity气机瘀滞不畅disorder of fluid metabolism津液代谢失常endogenous cold/ cold originating from the interior 寒从中生fluid consumption producing dryness津伤化燥stirring of endogenous wind/disturbance of endogenous wind风气内动Lesson 13spirit, complexion, and physical conditions 神色形态mental activities 精神活动sufficient essence and abundant qi精气充足apathetic facial expressions表情淡漠normal complexion and varied normal complexion 主色与客色convulsion of the limbs四肢抽搐stirring of wind due to damp-heat 湿热风动interior sinking of pathogenic toxin邪毒内陷scaly skin/ squamous and dry skin肌肤甲错hunger without appetite 饥不欲食combined use of the four diagnostic methods四诊合参facial expressions面部表情favorable prognosis预后良好dispiritedness 精神不振five colors indicating diseases / diagnostic significance of five colors五色主病facial distortion口角歪斜flaming of deficient fire虚火上炎retention of heat in the large intestine大肠热结mirror-like tongue光剥舌pulse manifestations脉象Lesson 14prevention before occurrence未病先防harmony between qi and blood气血平和regulating mental conditions调摄精神smooth circulation of blood血脉流畅smooth movement of joints关节通利smooth flow of qi/ free activity of qi气机条畅prolonging life and promoting longevity益寿延年preventive and therapeutic principles防治原则treatment should focus on the root of diseases治病求本treating secondary symptoms in acute disease急则治其标treating primary symptoms in chronic disease缓则治其本simultaneous treatment of primary and secondary symptoms 标本兼治deficiency of healthy qi and excess of pathogenic factors正虚邪实removing parasites to eliminate accumulation驱虫消积accumulation of phlegm-dampness in the lung痰湿壅盛blood serving as the mother of qi血为气母treatment in accordance with seasons, locality and individuality.因时因地因人制宜avoiding cold herbs in cold weather用寒远寒exogenous dry disease in autumn 外感秋燥moistening dryness with pungent and cool herbs辛凉润燥Lesson 15ⅰ.treatment with syndrome differentiation/ 辨证论治disease involving both exterior and interior表里同病simultaneous occurrence of cold and heat/ mixture of cold and heat寒热错杂regression of interior pathogenic factors to the exterior 里邪出表true cold and false heat 真寒假热aversion to cold and aversion to heat恶寒与恶热tasteless sensation in the mouth without thirst 口淡不渴transformation of stagnated pathogenic cold into heat 寒邪郁而化热exterior-deficiency syndrome due to exogenous pathogens外感表虚feverish sensation over five centers五心烦热location and nature of disease病位与病性mixture of deficiency and excess虚实夹杂invasion of exterior pathogenic factors into the interior表邪入里cold syndrome transforming into heat syndrome寒症化热true heat and false cold真热假寒heat syndrome transforming into cold syndrome热证转寒pale tongue with white, moist and slippery fur舌淡苔白而润滑rapid and weak pulse脉数无力tidal fever and night sweating 潮热盗汗coma with delirium神昏谵语Lesson 16Chinese medicinal herbs 中草药four properties and five flavors 四气五味the part used for medical purpose入药部分collection of herbs药物采集processing of herbs 炮制eliminating impurity清除杂质mild effect作用和缓relieving exterior syndrome by dispersion发散解表astringing and checking收敛固涩lubricant purgation by softening hardness 软坚润下drying dampness to invigorate the spleen燥湿健脾ascending, descending, sinking and floating升降沉浮channel tropism/channel distribution of medicines归经medication contraindication用药禁忌dosage 药物剂量pungent and warm herbs with the function of relieving exterior syndrome 辛温解表药herbs for expelling wind and dampness祛风湿药eighteen incompatible herbs and nineteen herbs of mutual antagonism十八反十九畏herbs for clearing away heat and cooling blood清热凉血药herbs for eliminating phlegm and stopping cough祛痰止咳药Lesson 17Science of prescription方剂学compatibility配伍关系prescription-formulating principle组成规律modification of prescriptions方剂的加减drug form and dosage 剂型与剂量monarch, minister, assistant and guide君臣佐使toxicity of medicinal herbs药物毒性moderating the property of herbs 缓和药性guiding action引经报使mediating all herbs in a prescription调和诸药warming channels to dissipate cold温经散寒dispersing lung to relieve asthma宣肺平喘flexible modification灵活化裁clearing away and dispersing stagnated heat清散郁热modification according to symptoms随症加减processed herbs药物饮片power for oral taking内服散剂medicinal extract for external application 外用膏剂mixed in boiled water for oral taking 开水冲服condensed extract浓缩浸膏Lesson 18acupuncture and moxibustion therapy针灸疗法reinforcing and reducing techniques for needling针刺补泻needling techniques针刺手法methods for needle-inserting进针手法alleviating pain with acupuncture针刺止痛acupuncture anesthesia针刺麻醉needling sensation 针感intradermal needle皮内针angle and depth ofneedling针刺的角度和深度insertion of needle with double hands双手进针manipulation of needle行针ear acupuncture therapy耳针疗法lifting, thrusting, twisting and rotating 提插捻转water-acupuncture therapy水针疗法scalp-acupuncture therapy头针疗法blistering moxibustion 化脓灸scarring moxibustion瘢痕灸moxibustion with moxa cone艾炷灸lamp moxibustion灯火灸needle-warming moxibustion温针灸Lesson 19tuina manipulations推拿手法alleviating pain减轻疼痛exercise for practicing tuina功法训练relaxing muscles放松肌肉relieving muscular tension解除肌肉紧张restricted activity 活动受限dislocation of joint关节脱位protrusion of lumbar vertebral disc腰椎间盘突出rotating reduction旋转复位injury of soft tissue软组织损伤adhesion and stiffness of joint 关节粘连僵硬lubricating joint滑利关节reinforcing and reducing manipulation手法补写horizontal pushing with the thumb拇指平推法pushing manipulation with one finger一指禅推法point-pressing manipulation点按法kneading manipulation with the large thenar大鱼际揉法alternated rubbing and kneading 交替搓揉injury of lumbar muscles腰肌劳损vertical exertion of force 垂直用力Lesson 20differentiation of tongue manifestations辨舌象differentiation of pulse manifestations辨脉象balancing expelling pathogenic factors with strengthening healthy qi 正邪兼顾thoracic retention of fluid支饮chills in the back/aversion to cold in the back背部恶寒dark complexion/black complexion面色黧黑slippery tongue coating/ moist and glossy tongue coating舌苔水滑taut pulse/wiry pulse 弦脉dispelling pathogenic cold发散寒邪invigorating the stomach to resolve fluid健胃化饮nourishing kidney water to astringe lung qi滋肾水以敛肺气nourishing yin blood to protect liver yin养阴血以护肝阴expelling pathogenic factors without impairing the healthy qi祛邪而不伤正invigorating qi to harmonize the middle-jiao益气和中mediating all herbs in a prescription调和诸药prescriptions for drastic diaphoresis发汗峻剂cold in the exterior and fluid in the interior表寒里饮cold water attacking the stomach水寒犯胃effective prescriptions有效方剂cold limbs in syncope 手足厥冷Lesson 21complementary therapy补充疗法alternative medicine 替代医学rehabilitation process康复过程side-effects副作用active ingredients 有效成分evidence-based data 询证数据double-blind randomized trial双盲随机试验stroke onset中风发病hyper-acute stage超急性期proprietary medicine 专利药品animal models动物模型risk of bleeding出血的危险因素mechanism of action作用机制low-quality medical treatments医疗质量低下physiotherapy物理疗法neuroplasticity 神经可塑性mainstream medicine 主流药物antiplatelet agent抗血小板剂microbial analysis微生物分析heavy metal research 重金属研究。

中医常用词汇01中医常用词Terms Commonly Used inTCM中国医药Traditional Chinese Medicin治未prevention of diseas脏zang-organs and fu-organs, viscer中医基础理Basic theory of traditionalChinese medicin功能活clinical experiencfunctional activitie临床经unity of the body and spiri辨证论treatment based on syndrome形神统differentiatio imbalance of yin and yan本materia medica, herb阴阳失条达舒free developmen中Chinese materia medica, Chinese medicinalherb延年益prolonging life, promising longevit四气五four properties and five tastecultivating health to prevent diseasacupuncture and moxibustion, acumo养生防针各家学正theories of different schoolhealthy qi, vital q汗diaphoresis, sweating therappathogenic facto病下purgative therapy, purgatio整体观concept of holisnature and manifestations of疾病的本质与现吐emetic therapy, vomiting therapdiseasrelative balance between yin and补土school of invigorating the eart阴阳的相对平yanoccurrence and development of病因学疾病的发生与发etiologdiseastreating the same disease with differenthealth-cultivation,同病异养therapietreating different diseases with the same异病同医疗实medical practictherap治疗原therapeutic principlefive zang-organs, five zang-viscer五寒凉药六herbs of cold and cool nature,six fu-organs, six fu-viscercold-natured herbsystem of meridians and collateralnourishing yin to lower/reduce fir滋阴降经络系incomplete abatement of hea余热未enriching water to nourish woo滋水涵有机整disease caused by blood stasi瘀血致organic wholeness/integritcongenital essenc先天之exterior and interior relatio表里关opening int开inseparability of the body and spiri形与神natural phenomenpromoting appetit开自然现philosophical concep哲学概pulse conditions, pulse patter脉states of pathogenic factors and邪正关对立统unity of oppositehealthy qmutual waning and waxin相互消fever and aversion to col发热恶寒.头身疼痛headache and body pain相互转化mutual transformation阴阳属性nature of yin and yang久痢脱肛proctoptosis due to prolongeddysenter相互联nourishing yin and clearing away heainterrelatio养阴清相互制清肺clear away lung-heamutual restraint, mutualrestriction/interactio动态平dynamic equilibriu湿邪犯pathogenic dampness invading thelun阴平阳clearing away heat and reducing firyin and yang in equilibriu清热泻阴阳的互根互腠muscular interstices, striae, interstitialinterdependence of yin and yanspac相互依interdependenc水湿停retention of water and dampness,water retentio阴阳离separation of yin and yan癃retention of urin相反相circulation/flow of qi and blooopposite and supplementary to eac气血运生理功阴阳转transformation between yin and yanphysiological function病理变阳消阴yang waning and yin waxinpathological change临床诊clinical diagnosi阴胜则阳predominance of yin leading todisorder of yan阳胜生外exuberance of yang leading to exterioran excess of yin leads to deficiency阴胜则阳heaof yan阳中求obtaining yang from yi阳胜则predominance of yang generatinghea绝对偏absolute predominancextreme cold generating hea寒极生阳虚则yang deficiency leading to col热极生extreme heat generating col阴阳俱simultaneous consumption of yin and yanimpairment of yang involving yi阳损及阴阳两insufficiency of yin-flui阴液不simultaneous deficiency of both yin andyan阳虚发general principle of pathogenesi病机总fever due to yang deficienc阴阳自natural harmony between yin and yanpathomechanism, pathological mechanis病木乘the wood over-restrains the eartalternative predominance of yin and阴阳胜yan木火刑虚寒deficiency-cold syndromwood-fire impairs the meta金水相generation between the metal and wate扶阳退strengthening yang to reduce yi生克制interrelationship between generation and祛风散expelling/eliminating wind torestrictiodispersing col制则生消导积restriction ensuring generatiopromoting digestion and removingfood retentio母病及suppressing yang to quench win潜阳熄disease of the mother-organ affecting thechild-orga传theory of five element五行学transmission of disease, progress of diseas子病犯motion and variatio运动变disease of the child-organ affecting themother-orgainsufficiency of liver and kidney肝肾精血不struggle/combat between healthy qi正邪相争.and pathogenic factors essence and blood肝阳上亢hyperactivity of liver yang mutual generation and restriction相生相心肝血asthenia / deficiency of heart and liver生我,我to be generated and to generatbloo心肝火exuberance of heart and liver fir克我,我to be restricted and to restric心火亢hyperactivity/exuberance of heart fir生中有restriction within generatio滋肾养克中有generation within restrictionourishing the kidney and live方位配五木曰曲wood is characterized by growingcorrespondence of the directions to thefive elementfreely and peripherall温肾健warming the kidney and strengthening the火曰炎fire is characterized by flaming u splee肾阳土爰稼earth is characterized by cultivationof kidney yanand reapin脾阳不inactivation of spleen yan金曰从metal is characterized by chang脾胃虚gradual onset of diseashypofunction/weakness of the spleen and病缓stomac地道不menopaus肝阴不insufficiency of liver yi平肝和相乘相over-restriction and reversesoothing the liver and harmonizing thestomacrestrictio水火不retention of water-dampnes水湿停discordance between water and fir藏象学theory of visceral manifestationinsufficiency of kidney yi肾阴不奇恒之extraordinary fu-organdisharmony between the heart and心肾不kidne水谷dredging water passagnutrients, essence of water and foo宣通水传化水通调水transmission and transformation offoodredging and regulating waterpassag贮藏精storage of essencactivating qi to excrete wate行气利治疗效水液停retention of fluicurative / therapeutic effec 藏而不postnatal / acquired base of lif后天之storage without excretio泻而不regulating qi activit调畅气excretion without storag表热里exterior heat and interior colupward flow of liver q肝气上肝旺脾水曰润water is characterized by moisteninghyperfunction of the liver and weakness ofthe spleeand downward flowin大肉陷obvious emaciation and muscular atrophy,脾主运the spleen governing transportationextreme emaciatioand transformatio面色红stagnation of liver qruddy complexion, rosy cheek肝气郁胆虚不得insomnia due to gallbladder asthenigallbladder deficiency syndrom胆虚导便laxatiodigesting foo腐熟水跌打损poor appetit食欲不traumatic injur动静结integration of motion andepigastric distension and depressio脘腹胀quietness/stillnes定eructation with fetid odo嗳气酸relieving asthm心主血the heart controlling blood and vesselseparating the clear from the turbi泌别清abundance of heart q心气充residue of foo食物残渣.。

英语常见中医术语绪论introduction中医学traditional Chinese medicine (TCM)中医学理论体系theory system of TCM中医基础理论basic theory of TCM整体观念holism concept五脏一体观holism of five ogans形神一体观holism of body and spirit天人一体观holism of human beings and universe医学模式medical pattern辨证syndrome differentiation论治treatment variation疾病disease证候syndrome症状symptom体征physical sign辨病disease diagnosing同病异治different treament for the same disease异病同治the same treatment for the different disease第一章中医学的哲学基础Ancient philosophic basis of TCM精jing(as the world origin in ancient philosophy)气qi(as the world origin in the ancient philosophy)精气学说theory of jingqi生命life中介medium气机qi activity气化qi transformation感应induction水地说hypothesis of jing originating from water and earth 云气说hypothesis of qi originating from cloud and air气一元论monism of qi元气一元论monism of qi阴阳yinyang; yin and yang阴阳学说theory of yinyang阴阳对立inter-opposition between yin and yang阴阳互根inter-dependence between yin and yang阴阳消长wane and wax between yin and yang阴阳交感inter-induction between yin and yang阴阳互藏inter-containing between yin and yang阴阳转化inter-transformation between yin and yang阴阳自和reestablishment to yin-yang equilibrium阴阳平衡both yin and yang in equilibrium五行five elements五行学说theory of five elements五行相生inter-promotion of five elements五行相克inter-inhibition of five elements五行制化relationship of promotion and restriction of five elements 五行相乘inter-invasion of five elements五行相侮reverse restriction in five elements五行胜复resistance of oppressed elements母病及子mother-organ diorder involving its child-organ子病及母child-organ disorder involving its mother-organ滋水涵木replenishing water to nourish wood培土生金reinforcing earth to generate metal益火补土tonifying fire to supplement earth金水相生mutual generation between metal and water抑木扶土inhibiting wood and strengthening earth培土治水cultivating earth to control water佐金平木assisting metal and calming wood泻南补北purging the south (fire) and nourishing the north (water)宏观观察obsevation on macroscopic level中和golden mean类比analogy第二章藏象Viscera state藏象viscera state藏象学说doctrine of viscera state脏腑viscera; zangfu organs五脏five zang organs心heart肺lung脾spleen肝liver肾kidney六腑six fu organs胆gall baldder胃stomach小肠small intestin大肠large intestine三焦tri-jiao; sanjiao膀胱urinary blader奇恒之腑extraordinary fu organs脑brain髓marrow骨bone脉vessel女子胞uterus满而不实full of essence without foodstuff实而不满full of foodstuff without essence 心主神明heart controlling mental activities心主血脉heart controlling blood circulation心藏神heart storing spirit肺主气lun governing qi肺主呼吸之气lung governing respiratory qi肺主一身之气lung governing physical qi肺朝百脉convergence of vessels in the lung肺主行水lung governing water metabolism肺主治节lung governing coordinative activities of viscera肺为华盖lung being the canopy肺为娇脏lung being the delicate organ肺主宣发肃降lung controlling dispersing outward and inwards气门pore后天之本source of acquired constitution脾主运化spleen governing transportation and transformation脾气主升spleen governing ascending脾主统血spleen governing blood脾喜燥恶湿spleen preferring dryness to dampness肝主疏泄liver govering regulating肝主藏血liver storing blood肝体因而用阳liver of yin nature with yang functioning肝为刚脏liver being the resolute viscera罢极之本source of endurance先天之本congenital foundation肾藏精kidney storing essence肾阴kidney yin肾阳kidney yang肾精kidney essence肾气kidney qi天癸tiangui肾主水液kidney governing water肾主纳气kidney receiving respiratory qi命门vital gate七冲门seven important portals胆主决断gallbladder governing deciding胃主通降stomach managing downward transportation of food喜润恶燥preferring moisture to dryness受盛化物containing and digesting泌别清浊separating the clear from the turbid上焦如雾upper-jiao resembling mist中焦如沤middle-jiao resembling fermenter下焦如渎lower-jiao rezembling drainage元神之府mentality house脑为髓海brain being the marrow sea心肾相交coordination between heart and kidney水火相济regulation between water and fire肺为气之主lung being the governor of qi肾为气之根kidney being the root of qi肝肾同源liver and kidney sharing the same origin乙癸同源Yi and Gui sharing the same origin (liver and kidney sharing the same origin)精血同源essence and blood sharing the ame origin藏泄互用interdependence between storing and discharging纳运相得inter-promotion between containing and digestion升降相因inerdependence between ascending and descending燥湿相济interdependence between drying and moistening胃润喜恶燥stomach preferring moisture to dryness第三章精气血津液神Essence, qi, blood, body fluid and,spirit气qi元气primordial qi元阴primordial yin元阳primordial yang气机qi activity气化qi transformation气海qi sea卫气defensive qi宗气thoracic qi营气nutrient qi原气primordial qi气能生血qi promoting blood production气为血之帅qi being the governor of blood气主升之qi promoting气能生津qi promoting body fluid production气能行血qi promtoting blood circulation血为气之母blood being the mother of qi血主濡之blood nourishing气能行津qi promoting body fluid circulation气能摄血qi governing blood津能载气body fluid conveying qi血能载气blood conveying qi气能摄津qi governing body fluid津停气滞body fluid retention causing qi stagnation血blood精essence神spirit精能化气essence transforming into qi先天之精congenital essence后天之精acquired essence水谷之精foodstuff essence气能生精qi promoting esssence production津血同源body fluid and blood sharing the same source血汗同源bloood and sweat sharing the same source膻中danzhong虚里heart apex津液body fluid第四章经络Meridians and collaterals经络meridians and collaterals经络学说theory of meridian and collateral; meridian doctrine 经气meridian qi经脉meridian; channel络脉collateral十二经脉twelve meridians十二正经twelve regular channels手太阴肺经lung channel of hand taiyin(L)手阳明大肠经large intestine channel of hand yangming(LI)足阳明胃经stomach channel of foot yangming(St)足太阴脾经spleen channel of foot tayin(Sp)手少阴心经heart channel of hand shaoyin(H)手太阳小肠经small intestine channel of hand taiyang(SI)足太阳膀胱经urinary bladder channel of foot taiyang(U足少阴肾经kidney channel of foot shaoyin(K)手厥阴心包经pericadium channel of hand jueyin(P)手少阳三焦经tri-jiao channel of hand shaoyang(TJ)足少阳胆经gall bladder channel of foot shaoyang(G足厥阴肝经liver channel of foot jueyin(Liv)奇经八脉eight extra channels督脉governor vesesl; Du meridian任脉conception vessel; Ren meridian冲脉flush vessel; Chong meridian带脉belt vessel; Dai meridian阴跷脉yinqiao meridian阳跷脉yangqiao meridian阴维脉yinwei meridian阳维脉yangwei meridan十二经别twelve divergent channels十五别络fifteen large collaterals孙络minute collateral浮络superficial collateral十二经筋twelve meridian musculatures十二皮部twelve cutaneous areas阳脉之海sea of yang meridian (governor vessel)阴脉之海sea of yin meridian (conception vessel)任主胞胎conception vessel govening uterus and gestation十二经脉之海sea of the twelve meridians (flush vessel)血海blood sea (flush vessel)第四章体质Body constitution体质body constitution形神合一harmonization between soma and spirit体格physique体型body type人格personality气质temperament性格character素质heredity理想体质ideal body constitutions病势disease tendency质化(从化)property transformation第六章病因Pathogeny病因pathogeny病因学说etiology辨症求因pathogeny differentiation from symptoms and signs 六淫six exopathogens六气six climates六邪six exopathogen*伤寒**ogenous febrile disease中寒cold stroke风性轻扬wind tending to drift善行数变migrant and variable风性主动wind tending to migrate百病之长guide of various disease寒性凝滞cold tending to coagulate and stagnate寒性收引cold tending to contract寒则气收cold retarding qi circulation暑性升散summer heat tending to ascend and disperse炅则气泄heat causing qi exhaustion暑多夹湿summer heat usually accompanied with dampness 湿性重浊dampness being heavy and turbid湿性黏滞dampneee being viscous and lingering湿性趋下sampness tending to descend燥性干涩dryness tending to desiccate火性趋上fire tending to flare up火易生风动血fire causing wind and bleeding疠气epidemic pathogens瘟疫pestilence七情seven emotions七情内伤inernal injuries caused by seven emotions怒则气上rage causing qi to flow upwards喜则气缓joy causing qi slack悲则气消grief causing qi depression思则气结contemplation causing qi stagnation惊则气乱terror causing qi disorder恐则气下fear causing qi collapse饮食不节improper diet饮食不洁dirty diet饮食偏嗜diet preference形劳physical overstrain劳则气耗overstrain causing qi exhausetion心劳heart overstrain神劳psychological ovrestrain肾劳kidney overstrain房劳***ual overstrain有形之痰visible phlegm无形之痰invisible phlegm瘀血blood stasis结石calculus药邪medicine abuse医过therapist fault胎弱congenital deficiency胎毒fetus toxin第七章发病Invasion正气healthy qi邪气pathogenic factors遗传病genetic disease感邪即发acute onset after affected徐发chronic onset伏而后发latent onset继发secondary onset合病simultaneous onset并病following onset复病recurrence后遗症sequela重感致复re-affected causing recurrence食复diet recurrence劳复overstrain recurrence药复medicine recurrence情志致复emotion recurrence第八章病机Pathogenesis病机pathogenesis病机学pathology病机层次pathological level基本病机basic pathogenesis实sthenia实证sthenic syndrome虚asthenia虚证asthenia syndrome虚实错杂mixture of asthenia and sthenia虚中夹实asthenia with sthenia实中夹虚sthenia with asthenia虚实转化inter-transformation between asthenia and sthenia由实转虚sthenia transforming into asthenia因虚致实sthenia symptoms caused by asthenia虚实真假pseudo or true manifestation of asthenia and sthenia 真实假虚sthenia with pseudo asthenia大实有羸状excessive sthenia manifesting a* **cessive asthenia 真虚假实asthenia with pseudo sthenia至虚有盛候excessive asthenia manifesting a* **cessive sthenia 正胜邪退healthy qi expelling pathogen邪去正虚pathogen retreating with asthenia healthy qi邪盛正衰prosperous pathogen with asthenia healthy qi 邪正相持struggle between healthy qi and pathogen正虚邪恋asthenic healthy qi with pathogen lingering 阴阳失调imbalance between yin and yang阴阳偏盛excess of yin or yang阳偏盛yang excess阳盛yang excess阴偏盛yin excess阴盛yin excess阴阳偏衰deficiency of yin or yang阳偏衰yang deficiency阳虚yang deficiency阴偏衰yin dificiency阴虚yin deficiency阴阳互损inter-impairment between yin and yang阴损及阳yin impairment involving yang阳损及阴yang impairment involving yin阴阳格拒repellence between yin and yang阴盛格阳predominant yin rejecting yang格阳rejecting yang阳盛格阴predominant yang rejecting yin格阴rejecting yin阴阳亡失exhaustion of yin or yang亡阴yin exhaustion亡阳阳yang exhaustion精虚essence asthenia精瘀essence stasis气虚qi asthenia气机失调disorder of qi activity气滞qi stagnation气逆qi adverseness气陷qi collapse上气不足qi failing to transport upward中气下陷qi failing to lift气闭qi blockage气脱qi exhaustion血虚blood asthenia血瘀blood stasis出血haemorrhage血寒blood cold血热blood heat精气两虚asthenia of essence and qi精血不足asthenia of essence and blood气滞精瘀qi stagnation and essence stasis血瘀精阻blood stasis and essence obstruction气滞血瘀qi stagnation and blood stasis气虚血瘀qi asthenia causing blood stasis气不摄血qi failing to control blood气随血脱qi exhaustion resulting from hemorrhage 气血两虚asthenia of qi and blood津液不足body fluid asthenia伤津body fluid impairment脱液body fluid exhausetion津液输布障碍dysfunction of body fluid distribution 津液排泄障碍dysfuncion of body fluid excretion水停气阻water retention causing qi stagnation气随津脱qi exhaustion resulting from body fluid loss 津枯血燥body fluid depletion causing blood stasis 津亏血瘀body fluid depletion causing blood stasis 血瘀水停blood stasis causing water retention内风endogenous wind风气内动disturbance of endogenous wind肝风liver wind肝阳化风liver yang causing wind热极生风extreme heat causing wind阴虚风动yin asthenia causing wind血虚生风blood asthenia causing wind寒从中生cold originating from interior内寒endogenous cold湿浊内生dampness originating from interior内湿endogenous dampness津伤化燥body fluid impairment causing dryness内燥endogenous dryness火热内生heat or fire originatin from interior内热endogenous heat内火endogenous fire少火junior fire壮火excessive fire阳亢化火excessive yang causing fire气有余便是火excessive qi causing fire邪郁化火pathogen accumulation causing fire五志化火five emotions causing fire阴虚火旺yin asthenia causing fire疾病传变pathogenesis transmission病位传变focus transmission表里传变transmission between interior and exterior表病入里exogenous disease invading interior里病出表endogenous disease retreating to exterior半表半里semi-interior and semi-exterior直中direct attack六经传变six merdians transmission 三焦传变tri-jiao transmission卫气营血传变transmission of wei, qi, ying and xue顺传sequential transmission逆传adverse transmission脏腑传变viscera transmission脏与脏的传变transmission among zang organs脏与腑的传变transmission among zang organs and fu organs 腑与腑的传变transmission among fu organs形脏内外传变transmission between interior and exterior寒热转化inter-transformation between cold and heat寒化热cold transforming into heat热化寒heat transforming into cold第九章防治原则Principle of prevention and therapy预防prevention养生health promotion未病先防prevention before disease onset既病防变preventing disease from exacerbating治则therapeutic principle治法therapeutic method治病求本treating disease from the root标本branch and root正治routine treatment反治contrary treatment寒者热之cold treated with warm热者寒之heat treated with cool虚则补之asthenia requiring tonification实则泻之sthenia requiring purgation热因热用heat treated with warm寒因寒用cold treated with cool通因通用diarrhea treated with purgation塞因塞用obstruction treated with tonification扶正strengthening healthy qi祛邪eliminating pathogens因时制宜climate-concerned treatment因地制宜environment-concerned treatment因人制宜individuality-concerned treatment中医诊断英语阴阳五行1 五行fie phases2 阴阳yin and yang;yin-yang3 五志fie minds4 五味fie flaors5 辨证论治syndrome differentiation and treatment;identify patterns and determine treatment脏腑6 脏腑zang-fu organs; bowels and iscera7 心藏神The heart stores the spirit.8 神明spirit; mind; mental actiity9 肺主宣发The lung goerns diffusion.10 肺主肃降The lung goerns descent.The lung goerns purification and descent.11 通调水道regulate the waterways12 肺主行水The lung goerns the moement of water13 脾主运化The spleen goerns transportation and transformation.14 脾为后天之本The spleen is the root of acquired constitution.15 脾主升清The spleen goerns ascent of the clear.16 脾统血The spleen controls the blood.17 脾恶湿The spleen is aerse to dampness.18 肝主疏泄The lier goerns free coursing.19 肝主升发The lier goerns ascent and dispersion20 肝主身之筋膜The lier goerns the body’s sinews.21 命门①ming men; life gate ②ming men (DU 4)22 肾精kidney essence23 天癸tian gui24 肾为先天之本The kidney is the root of congenital constitution.25 泌别清浊separation of the clear and turbid26 三焦triple burner27 心肾不交failure of the heart and kidney to communicate形体官窍28 筋sinew29 脉①essel;②pulse30 七窍seen orifices气血津液精神31 气机qi dynamic32 正气right qi33 邪气eil qi34气分qi leel35 原气source qi36 元气original qi37 宗气gathering qi38 中气middle qi39 卫气defensie qi40 营气nutritie qi41 营血nutrient-blood42 津液fluid43 精①essence ②semen44 精气essential qi45 神spirit46 气为血帅qi as commander of blood经络47 经络channels and collaterals48 经脉channel49 穴位acupuncture point; point50 背俞穴back-shu point51 耳穴ear point; auricular point52 手太阴肺经The hand greater yin lung channel; LU (WHO)53 手阳明大肠经The hand yang brightness large intestine channel; LI (WHO)54 足阳明胃经The foot yang brightness stomach channel; ST (WHO)55 足太阴脾经The foot greater yin spleen channel; SP (WHO)56 手少阴心经The hand lesser yin heart channel; HT (WHO)57 手太阳小肠经The hand greater yang small intestine channel; SI (WHO)58 足太阳膀胱经The foot greater yang bladder channel; BL (WHO)59 足少阴肾经The foot lesser yin kidney channel; KI (WHO)60 手厥阴心包经The hand reerting yin pericardium channel; PC (WHO)61 手少阳三焦经The hand lesser yang triple burner channel; TB (WHO)62 足少阳胆经The foot lesser yang gallbladder channel; GB (WHO)63 足厥阴肝经The foot reerting yin lier channel; L (WHO)病因64 病因etiology;etiologic factor;cause of disease65 实邪excess eil66 表邪exterior eil67 外感external contraction68 七情seen affects69 痰phlegm70 饮①rheum ;fluid retention ②drink③decoction71 瘀血static blood72 血瘀blood stasis病机73 病机pathomechanism74 虚deficiency75 实excess76 亏虚,亏损depletion77 不足insufficient78 阴虚火旺hyperactiity of fire due to yin deficiency79 气滞qi stagnation80 气郁qi constraint81 气逆qi counterflow82 气陷sinking of qi83 气闭qi blockage84 气滞血瘀qi stagnation and blood stasis85 内风internal wind86 寒凝气滞qi stagnation due to congealing cold87 心火上扰flaring up of heart fire88 痰火扰心phlegm-fire disturbing the heart89 痰蒙心包phlegm clouding the pericardium90 痰浊阻肺turbid phlegm obstructing the lung91 脾虚湿困spleen deficiency leading to damp encumbrance ; damp encumbrance due to spleen deficiency92 脾失健运spleen failing to transform and transport; failure of the spleen to transform and transport93 肝阳上亢ascendant hyperactiity of lier yang94 肝郁lier constraint95 肝气郁结binding constraint of lier qi96 肝风内动lier wind stirring internally97 肾不纳气kidney failing to grasp qi98 胃纳呆滞poor appetite and digestion99 热入心包heat entering the pericardium诊法100 四诊four examinations101 舌象tongue manifestation; tongue appearance102 舌神tongue spirit103 舌色tongue color104 淡红舌light red tongue105 淡白舌pale tongue106 红舌red tongue107 绛舌crimson tongue108 紫舌purple tongue109 青舌blue tongue110 舌形tongue shape111 舌质tongue body112 胖大舌enlarged tongue113 齿痕舌tooth-marked tongue114 肿胀舌swollen tongue115 瘦薄舌thin tongue116 点刺舌spotted tongue117 芒刺舌prickly tongue118 裂纹舌cracked tongue119 (舌上)瘀斑stasis maculae120 (舌上)瘀点stasis spots121 舌态tongue condition122 痿软舌flaccid tongue123 强硬舌stiff tongue124 吐舌protruding tongue125 弄舌waggling tongue126 舌苔tongue coating127 厚苔thick coating128 薄苔thin coating129 润苔moist coating130 燥苔dry coating131 糙苔rough coating132 燥裂苔dry cracked coating133 瓣晕苔petalled coating134 滑苔glossy coating135 腻苔greasy coating136 腐苔curd-like coating137 粘腻苔sticky greasy coating138 剥苔peeled coating139 类剥苔peeled-like coating140 地图舌geographic tongue141 镜面舌mirror-like coating142 无根苔rootless coating143 有根苔rooted coating144 苔色color of coating145 脉诊pulse examination; pulse diagnosis 146 切脉,把脉pulse taking147 平脉normal pulse148 寸口radial pulse; cun kou149 寸关尺cun, guan and chi; inch, bar and cubit150 浮脉floating pulse151 散脉scattered pulse152 芤脉hollow pulse153 伏脉hidden pulse154 牢脉firm pulse155 迟脉slow pulse156 缓脉moderate pulse157 数脉rapid pulse158 疾脉racing pulse159 沉脉deep pulse160 细脉thready pulse161 长脉long pulse162 短脉short pulse163 虚脉deficient pulse164 实脉excess pulse165 弱脉weak pulse166 微脉faint pulse167 洪脉surging pulse168 滑脉slippery pulse169 涩脉rough pulse170 弦脉wiry pulse171 动脉bouncing pulse172 紧脉tight pulse173 革脉drumskin pulse174 濡脉soggy pulse175 歇止脉pausing pulse176 结脉knotted pulse; irregularly intermittent pulse 177 代脉intermittent pulse ; regularly intermittent pulse 178 促脉hasty pulse; rapid-irregular pulse179 恶寒aersion to cold180 畏寒fear to cold181 潮热tidal feer182 五心烦热exing heat in the fie hearts183 骨蒸steaming bone184 寒战shiering中药185 性nature186 味flaour187 性味nature and flaour188 四气four nature189 寒cold190 热hot191 温warm192 凉cool193 平neutral194 五味fie flaours195 辛acrid196 甘sweet197 酸sour198 苦bitter199 咸salty200 淡bland201 涩astringent202 升降浮沉ascending and descending, floating and sinking203 归经channel entered204 功能actions205 主治indications206 用量dosage207 使用注意caution208 禁忌症contraindication表寒里热biao han li re exterior cold ,interior heat表热里寒biao re li han exterior heat,interior cold冲任不补chong ren bu bu chong&ren not securing冲任不调chong ren bu tiao chong&ren not regulated 冲任失调chong ren shi tiao loss of regulation of the chong&ren冲任损伤chong ren sun shang chong&ren detriment and damage大肠寒结da chang han jie large intestine cold binding大肠湿热da chang shi re large intestine damp heat大肠虚da chang xu large intestine vacuity大肠虚寒da chang xu han large intestine vacuity cold大肠液亏da chang ye kui large intestine humor depletion胆热dan re gallbladder heat胆虚dan xu gallbladder vacuity肺火fei huo lung fire肺津不布fei jin bu bu lung fluids not distributed肺络损伤fei luo sun shang lung network vessel detriment&damage肺气不利fei qi bu li inhibition of the lung qi肺气不宣fei qi bu xuan lung qi not diffusing肺气虚fei qi xu lung qi vacuity肺热fei re lung heat肺肾两虚fei shen liang xu lung-kidney dual vacuity肺肾气虚fei shen qi xu lung-kidney qi vacuity肺肾阴虚fei shen yin xu lung-kidney yin vacuity肺实fei shi lung repletion肺失清肃fei shi qing su lung loss of clearing &depurating肺虚fei xu lung vacuity肺阴虚fei yin xu lung yin vacuity肺阴虚燥feiyin xu zao lung yin vacuity dryness肺燥fei zao lung dryness伏热在里fu re zai li deep-lying heat in the interior肝胆气虚gan dan qi xu liver-gallbladder qi vacuity肝胆湿热gan dan shi re liver-gallbladder damp heat肝风内动gan feng nei dong liver wind stirring internally肝寒gan han liver cold肝火gan huo liver fire肝火上炎gan huo shang yan liver fire flaring upward肝气犯脾gan qi fan pi liver qi assails the spleen肝气犯胃fan qi fan wei liver qi assails the stomach肝气上逆gan qi shang ni liver qi counterflowing upward肝热gan re liver fire肝肾亏损gan shen kui sun liver-kidney depletion&detriment肝肾两虚gan shen liang xu liver-kidney dual vacuity肝血虚gan xue xu liver blood vacuity肝阳上亢gang yang shang kang ascendant hyperactivity of liver yang 肝阴虚gan yin xu liver yin vacuity肝郁脾虚gan yu pi xu liver depression,spleen vacuity肝郁气滞gan yu qi zhi liver depression qi stagnation寒极生热han ji sheng re extreme cold engenders heat寒凝肝脉han ning gan mai cold congelation in the liver vessel寒凝气滞han ning qi zhi cold congelation qi stagnation寒痰阻肺han tan zu fei cold phlegm obstructing the lungs久热伤阴jiu re shang yin enduring heat damages yin龙火内燔long huo nei fan dragon fire internally blazing命门火旺ming men huo wang life gate fire effulgence膀胱气闭pang guang qi bi bladder qi block膀胱湿热pang guang shi re bladder damp heat膀胱虚寒pang gang xu han bladder vacuity cold脬气不固pao qi bu gu bladder qi not securing脾不统血pi bu tong xue spleen not managing(i.e.,restraining)the blood 脾肺两虚pi fei liang xu spleen-lung dual vacuity脾气不升pi qi bu sheng spleen qi not upbearing脾气虚pi qu xu spleen qi vacuity脾热pi re spleen heat脾肾阳虚pi shen yang xu spleen-kidney yang vacuity脾失健运pi shi jian yun spleen loss of fortification &movement脾失运化pi shi yun hua spleen loss of movement&transformation脾胃湿热pi wei shi re spleen-stomach damp heat脾胃虚弱pi we xu ruo spleen-stomach vacuity weakness脾虚pi xu spleen vacuity脾虚湿困pi xu shi kun spleen vacuity,damp encumbrance脾阳虚pi yang xu spleen yang vacuity脾阴虚pi yin xu spleen yin vacuiry气化不利qi hua bu li inhibition of qi transformation气机不利qi ji bu li inhibition of the qi mechanism气髓血脱qi sui xue tuo qi follows blood desertion气虚中满qi xu zhong man qi vacuity central fullness气血两虚qi xue liang xu qi&blood dual vacuity气血失调qi xue shi tiao qi&blood loss of regulation气阴两虚qi yin liang xu qi &yin dual vacuiry气滞血瘀qi zhi xue yu qi stagnation &blood stasis热伏冲任re fu chong ren heat deep-lying or hidden in the chong &ren热极生寒re ji sheng han extreme heat engenders cold热结膀胱re jie pang guang heat bound in the bladder热入心包re ru xin bao heat entering the pericardium热入血分re ru xue fen heat entering the blood phase热入血室re ru xin shi heat entering the blood chamber热伤肺络re shang fei luo heat damaging the lung network vessels热伤筋脉re shang jin mai heat damaging the sinews and vessles(or sinew vessels)热伤神明re shang shen ming heat damaging the spirit brightness热盛气分re sheng qi fen heat exuberance in the qi division热邪阻肺re xie zu fei heat evils obstructing the lungs热灼肾阴re zhuo shen yin heat buring kidney yin三蕉湿热san jiao shi re triple burner damp heat三蕉虚寒san jiao xu han triple burner vacuity cold上寒下热shang han xia re above cold ,below heat上热下寒shang re xia han above heat ,below cold伤损及下shang sun ji xia detriment above reaching below少阴寒化shao yin han hua shao yin cold transformation少阴热化shao yin re hua shao yin heat transformation肾气不固shen qi bu gu kidney qi not securing肾虚shen xu kidney vacuity肾溆水泛shen xu shui fan kidney vacuity,water flooding肾阳虚shen yang xu kidney yang vacuity肾阳虚衰shen yang xu shuai kidney yang vacuity and debility肾阴虚shen yin xu kidney yin vacuity升降失常sheng jiang shi chang upbearing&downbearing lose their normalcy湿热内熏shi re nei xun dampness&heat internally brewing湿热小蕉shi re xiao jiao damp heat in the lower burner湿热瘀滞shi re yu zhi damp heat stasis&stagnation湿胜阳微shi sheng yang wei dampness prevailing ,yang becoming slight湿郁热伏shi yu re fu damp depression,heat deeply lying食滞胃腕shi zhi wei wan food stagnating in the stomach venter湿阻气分shi zu qi fen dampness obstructing the qi division湿阻中蕉shi zu zhong jiao dampness obstructing the middle burner水不化气shui bu hua qi water not transforming the qi痰火扰心tan huo rao xin phlegm fire harassing the heart痰密心窍tan mi xin qiao phlegm confounding ghe portals of the heart痰热阻肺tan re zu fei phlegm heat obstructs the lungs痰湿阻肺tan shi zu fei phlegm dampness obstructing the lungs痰阻肺络tan zu fei luo phlegm obstructing the lung network vessels胃寒wei han stomach cold胃火上升we huo shang sheng stomach fire borne upward胃气不固wei qi bu gu defensive qi not securing胃气不和wei qi bu he stomach qi disharmony胃气虚wei qi xu stomach qi vacuity胃热wei re stomach heat胃热壅盛wei re yong sheng stomach heat congesting&exuberant胃失和降wei shi he jiang stomach loss of harmony&downbearing胃虚wei xu stomach vacuity胃阴虚wei yin xu stomach yin vacuity温邪犯肺wen xie fan fei warm evils assailing the lungs温邪上受wen xie shang shou warm evils affect above下损及上xia sun ji shang lower detriment reaches above相火妄动xiang huo wang dong ministerial fire frenetically stirring小肠湿热xiao chang shi re small intestine damp heat小肠虚寒xiao chang xu han small intestine vacuity cold邪留三蕉xie liu san jiao evils retained in the three burners心火亢盛xin huo kang sheng heart fire hyperactivity &exuberance心火内炽xin huo nei chi heart fire blazing internally心火上炎xin huo shang yan heart fire flares upward心脾两虚xin pi liang xu heart-spleen dual vacuity心气不宁xin qi bu ning heart qi not quiet心气不绶xin qi bu shou heart qi not restraining心肾不交xin shen bu jiao heart&kidneys not interacting心虚胆怯xin xu dan qie heart vacuity ,gallbladder timidity心血虚xin xue xu heart blood vacuity心阳虚xin yang xu heart yang vacuity心阴虚xin yin xu heart yin vacuity虚风内动xu feng nei dong vacuity wind stirring internally虚热上炎xu re shang yan vacuity heat flares upward虚阳上浮xu yang shang fu vacuous yang floats upward血不归经xue bu gui jing blood not returning to the channels血分热毒xue fen re du blood division heat toxins血分瘀热xue fen yu re blood division static heat血随气陷xue sui qi xian blood follows qi fall阳盛阴伤yang sheng yin shang yang exuberance damages yin阴虚肺燥yin xu fei zao yin vacuity lung dryness阴虚阳亢yin xu yang kang yin vacuity yang hyperactivity阴虚阳旺yin xu yang wang yin vacuity yang effulgence阴阳两虚yin yang liang xu yin&yang dual vacuity荥卫不和ying wei bu he constructive &defensive disharmony瘀热在里yu re zai li stasis&heat located in the interior燥气伤肺zao qi shang fei dry qi damaging the lungs中气不足zhong qi bu zu central qi insufficiency中气下陷zhong qi xia xian central qi downward fall中阳不振zhong yang bu zhen central yang devitalized壮热食气zhuang re shi qi strong fire eats the qi中医英语笔画查找一阳"frist yang, Shaoyang Channel"一阴"frist yin, Jreyin Channel"一逆one mista ade in treatment一息respiration一侧的unilateral一日量daily dose一服药a dose of medicine一夫法finger breadth measurement一身痛重general pain and heaviness乙癸同源Yi(the live) and Gui)the Kidney) bejing the same source二阴"two lower orifices, ie, the external urethral orifice and the anus"二浊reddish and whitish turbid urine二十八脉twenty-eight kinds of pulse condition二阳并病Shaoyang syndrome complicated by Taiyang syndrome二便不利difficulty in urination and defecation。

中医的专业术语英文翻译大家在写中医论文时候常常遇到一些不容易翻译的词汇,yjbys网整理了中医的专业术语英文翻译,方便大家写作。
快来点赞吧。
中国医药学:traditional Chinese medicine中医基础理论:basic theory of traditional Chinese medicine临床经验:clinical experience辨证论治:treatment based on syndrome differentiation本草:materia medica //medicinal herbs中药Chinese herbs四气五味:four properties and five tastesacupuncture and moxibustion各家学说theories of different schools汗法: diaphoresis /diaphoretic therapy下法:purgative therapy吐法:emetic therapy补土派:school of invigorating the earth病因学说:theory of etiology养生:health-cultivation医疗实践medical practice治疗原则:therapeutic principles寒凉药物:herbs of cold and cool nature滋阴降火:nourishing yin to lower fire瘀血致病:disease caused by blood stasis先天之精:congenital essence气的运动变化:movement and changes of qi形与神俱:inseparability of the body and spirit神明: spirit/mental activity脏腑:zang-organs and fu-organs/viscera功能活动:functional activities形神统一:unity of the body and spirit阴阳失调:imbalance of yin and yang正邪相争:struggle between healthy qi and pathogenic factors 治未病prevention of disease调养 to cultivate health正气 healthy qi病邪 pathogenic factor疾病的防治 prevention and treatment of disease整体观念 concept of holism五脏five zang-organs六腑six fu-organs经络系统system of meridians and collaterals形神统一unity of the body and spirit有机整体organic wholeness表里关系exterior and interior relation开窍opening into生长化收藏five element function脉象pulse conditions正邪关系the states of pathogenic factors and healthy qi自然现象natural phenomena哲学概念philosophical concept对立统一unity and opposites相互消长mutual waning and waxing阴阳属性nature of yin and yang相互转化mutual transformation相互联系interrelation相互制约mutual restraint动态平衡dynamic balance阴平阳秘yin and yang in equilibrium阳消阴长 yang waning and yin waxing阴胜则阳病predominance of yin leading to disorder of yang 阳胜则热 predominance of yang generating heat寒极生热 extreme cold generating heat热极生寒extreme heat generating cold相反相成 opposite and supplementary to each other生理功能physiological functions病理变化pathological changes临床诊断clinical diagnosis有机整体organic wholeness/entirety正邪斗争struggle between healthy qi and pathogenic factors 绝对偏盛absolute predominance阳虚则寒yang deficiency leading to cold阳损及阴consumption of yang involving yin阴液不足insufficiency of yin-fluid病机pathogenesis五行学说theory of five elements运动变化motion and variation条达舒畅free development相生相克mutual generation and restriction生我我生to be generated and to generate克我我克to be restricted and to restrict生中有制restriction within generation克中有生generation within restriction木曰曲直Wood is characterized by growing freely and peripherally火曰炎上Fire is characterized by flaming up土曰稼穑Earth is characterized by cultivation and reaping金曰从革Metal is characterized by change水曰润下Water is characterized by moistening and downward flowing方位配五行correspondence of the directions to the five elements相乘相侮over-restriction and reverse restriction土乘木The wood over-restrains the earth土虚木乘 Earth deficiency leading to over-restriction by wood 金虚木侮metal deficiency leading to counter-restriction by wood生克制化interrelationship between generation and restriction制则生化restriction ensuring generation传变transmission of disease母病及子disease of the mother-organ affecting the child-organ子病犯母disease of the child-organ affecting the mother-organ肝肾精血不足insufficiency of kidney and liver essence and blood肝阳上亢hyperactivity of liver yang藏象学说 theory of visceral manifestations五脏六腑 five zang-organs and six fu-organs奇恒之府 extraordinary fu-organs水谷精微 cereal nutrients传化水谷 transmissions and transformation of food贮藏精气 storage of essence表里关系 interior and exterior relationship治疗效应 curative effect临床实践 clinical practice藏而不泻 storage without excretion心肝血虚deficiency of heart and liver blood心肝火旺exuberance of heart and liver fire心火亢盛exuberance of heart fire滋肾养肝nourishing the kidney and liver肝阴不足insufficiency of the liver yin温肾健脾warming the kidney and strengthening the spleen 肾阳式微declination of kidney yang脾阳不振inactivation of spleen yang肝旺脾虚hyperactivity of the liver and weakness of the spleen 脾胃虚弱weakness of the spleen and stomach平肝和胃soothing the liver and harmonizing the stomach水湿停聚retention of water-dampness肾阴不足insufficiency of kidney yin心肾不交disharmony between the heart and kidney水火不济discordance between water and fire阴阳俱损simultaneous consumption of yin and yang阴阳两虚simultaneous deficiency of both yin and yang损其有余reducing excess补其不足supplementing insufficiency阴中求阳obtaining yang from yin虚寒证deficiency-cold syndrome扶阳益火strengthening yang to increasing fire祛风散寒eliminating wind to dispersing cold消导积滞promoting digestion and removing food retention 潜阳息风suppressing yang to quench wind阴阳的互根互用interdependence of yin and yang相互依存interdependence。

中医英语重要词汇针灸:acupuncture and moxibustion。
经络:meridian/channel and collateral。
表:exterior,里:interior。
归经:meridians tropism舌象:淡红舌:light red tongue,淡白舌:pale tongue。
薄苔:thin coating。
厚苔:thick coating,润:moist,燥dry,腻:greasy。
绛:crimson。
枯荣老嫩:flourishing,withered,tough ,tender.方剂:formula,prescription 配伍关系:compatibility/combination relationship。
方剂的加减:modification of prescription .药~medicinal 君臣佐使:sovereign,minister,assistant,guide。
症状:手足厥冷:reversal cold of hand and feet,哮:wheezing 哮喘:asthma。
恶心:nausea,痢疾:dysentery。
自汗:spontaneous sweating,尿频:frequent urination,带下:leukorrhea。
便溏:loose stool。
便秘:constipation,面色:complexion。
里急后重:tenesmus。
呕吐:vomiting,嗳气:belching.得神:presence of vitality,呃逆:hiccup,太息:sighing.小便:urine,大便:stool。
口渴:thirst。
胁痛:hypochondriac pain,咯血:hemoptysis,胸痛:chest pain,眩晕:vertigo/dizziness,心悸:palpitation,腹痛:abdominalpain。
中医临床常用英语词汇中医,一般指以中国汉族劳动人民创造的传统医学为主的医学,所以也称汉医。
是研究人体生理、病理以及疾病的诊断和防治等的一门学科。
中医①traditional Chinese medicine②traditional Chinese physician ①中医学的简称。
②本学科专业职业队伍。
中药 Chinese materia medica 在中医理论指导下应用的药物。
包括中药材、中药饮片和中成药等。
中医学 traditional Chinese medicine 以中医药理论与实践经历为主体,研究人类生命活动中安康与疾病转化规律及其预防、诊断、治疗、康复和保健的综合性科学。
中药学 Chinese materia medica 中药学科的统称。
研究中药根本理论和各种药材饮片、中成药的、采制、性能、成效、临床应用等知识的学科。
中医药 traditional Chinese medicine and pharmacology 中医与中药的合称。
中医药学 traditional Chinese medicine and pharmacology 中医学与中药学的合称,侧重反映中医与中药两者共同开展,密不可分。
中西医结合 integration of traditional and western medicine 现代医学等现代科学知识及手段来继承和开展中医药,中西医学相互补充,取长补短,诊治疾病的医学形式。
中医根底理论 basic theory of traditional Chinese medicine 研究和说明中医学的根本概念、根本理论、根本规律、根本原那么的学科。
中医诊断学 diagnostics of traditional Chinese medicine 根据中医学的理论体系,研究诊察病情、判断病种、区分证候的根底理论、根本知识和根本技能的学科。
方剂学 prescriptions of Chinese materia medica 研究治法与方剂配伍规律及其临床运用的学科。
传统中医学词汇是由诺贝笔翻译公司整理一阳"frist yang, Shaoyang Channel"一阴"frist yin, Jreyin Channel"一逆one mista ade in treatment一息 respiration一侧的 unilateral一日量 daily dose一服药 a dose of medicine一夫法 finger breadth measurement一身痛重general pain and heaviness乙癸同源Yi(the live) and Gui)the Kidney) bejing the same source二阴"two lower orifices, ie, the external urethral orifice and the anus"二浊reddish and whitish turbid urine二十八脉twenty-eight kinds of pulse condition二阳并病Shaoyang syndrome complicated by Taiyang syndrome二便不利difficulty in urination and defecation二便失禁urinary and fecal incontinence十问inquire about ten aspects of the patient十剂ten kinds of prescription十八反 eighteen incompatible medicaments十二剂twelve kinds of prescription十二节 twelve joints十二禁 twelve contraindications十二经 twelve regular channels十二时traditional twelve two-hour periods十二脏 twelve internal organs十二怪脉"ten moribund pulses, ten kinds of paradoxical pulse condition"十九畏nineteen nedicaments of nutual antagonism十三科the thirteen medical specialties十四经the fourteen channels十五络(脉)fifteen main collaterals十二节刺twelve methods of needling十二经别branches of the twelve regular channels十二经筋muscle along the twelve regular channels十二皮部 twelve skin areas十六郄穴 sixteen cleft points十四经穴"accupuncture points on the fourteen regular channels, acupoints on regular channels" 十五络穴fifteen main collaterals points十二经动脉arteries of the twelve channels十二井穴 twelve well-points十二经之海sea of the twelve channels丁痂 scar丁奚疳infantile malnutrition due to excessive feeding丁躬势 bowing丁字形骨折 T-shaped fracturre七方"seven prescriptions, Seven formulae"七恶the symtoms and signs indicating poor prognosis of suppurative infections of the exterior part of the body七窍 seven orifices七情 seven emotions七疝seven kinds of hernia七伤 1.seven kinds of impairments 2.seven symptoms suggesting consumption of the kidney-qi七冲门 seven important portals七怪脉"seven moribund pulses, seven paradoxical pulse conditions, seven fatal pulse conditions" 七日风=脐风 neonatal tetanus七星针=梅芬针 seven star needle八纲the eight principal syndromes serving as guidelines in diagnosis八法eight therapeutic methods八廓the eight regions of the white of the eye八溪 eight joints八会穴"eight hui-points, eight influential points"八片锦 different pictures of superficial venules of index finger in children as a reference for diagnosis八纲辨证 analyzing and differentiating pathological conditions in accordance with the eight principal syndromes八脉交会穴 eight confluence points人中疔 boi on philtrum人咬伤human bite; bite by man人迎脉 Renying pulse人背复位 back-carrying reduction人痘接种 human variolation人工牛黄"artificial ox gallstone, Calculus Bovis Factitius"人事不省=神昏 unconsciousness入臼 joint reduction儿风 eclampsia儿病=恶阻儿茶"catechu, blzck catechu, Catechu"儿枕痛 after-pains儿捧母心 breech presentation儿科四大要证four chief diseases in pediatrics九刺nine types of needling九气nine kinds of illness due to disturbance of qi九窍 nine orifices九脏 nine internal organs九虫病 parasitic diseases九窍出血bleeding from the nine orifices九六补泻法nini-six reinforcing-reducing method刀伤 incised wound刀晕 traumatic syncope刀创伤drug for incised wound刀斧伤wound by knife or ax三宝"three exxentialsessence, qi and configurative force"三痹three types of arthralgiz三刺=齐刺 three-stratum puncture三法 "three therapeutic methods-diaphoresis, emesis, and purgation"三伏"1.three periods of dog days, 2.the third period of dog days"三关the three passes三焦"tri-jiao, sanjiao, triple warmer, triple heater"三毛(丛,聚) clump hair三品three grades of medicines三消three types of diabetes三因three categories etiologic factors三虫病 three intestinal parasitoses三春柳=柽柳三焦病disease of tri-jiao三焦经 Tri-jiao Channel三焦咳 tri-jiao cough三棱针"three-deged needle, tri-ensiform needle"三陷证three typesof inward penetration of pyogenic agent三阳病disease of the three yang channels三阳经 three yang channels三阳络 Sanyanglo三阴病diseases of the three yin channels三阴经 three yin channels三阴痉convulsion with symptoms of three yin channels三阴疟 three-yin malaria三板疗法"tri-tabular massage, massage with three Kinds of boards"三部九候three portions and nine pulse-takings7 三焦辨证differentiation of syndrome according to the pathological changes of trijiao 三焦实热heat in tri-jiao of excess type三焦虚寒cold syndromes of deficiency type三阳合病disease involving all three yang channels三点挤压法 three-point pressure method三焦主决渎the triple warmer manages the dredging of water pathway干便 dry stool干疽cellulitis at the anterolateral aspect of the shoulder干咳"dry cough, unproductive cough"干呕 retching干陷dry type of inward penetation of pyogenic agent干癣 1.chronic eczema 2.neurodermatitis干皮 dried bark干血劳emaciation due to blood disorders干胁痛 dry hypochondriac pain干脚气 dry beriberi干霍乱 dr cholera干眼症 xerophthalmia干拔罐 1.dry cupping 2.ordinary cupping土earth(in five elements)土方"folk recipe, local recipe"土疳=针眼 hordeolum土栗infection of the heel土风疮 popular urticaria土生甘sweet flavour is attributed to earth土生金 earth generates metal土克水 earth restricts water土脯子 mantis cheeks土乘水 earth subjugates water土不制水earth fails to control water土生万物earth produces myriads of things土喜温燥earth prefers warmth and dryness土郁夺之Dampness accumulated in the spleen(earth) should be removed8 下胞 Lower eyelid下膊 forearm下法"purgation, purgative therapy"下疳 chancre下膈intake of food in the morning and vomiting in the evening下工"an inferior medical worker, an inexperienced healer"下骨sending down the fishbone下极 1.anus 2.perineum 3.area between inner canthi 4.another name for Hengku下焦"lower-jiao, lower warmer, lower heater, lower burner"下利 diarrgea下迫 tenesmus下气 "1.a therapeutic mithod to keep the adverse qi flowing downward 2.aerofluxus, breaking wind 3.qu of the lower part of the body"下窍 lower orifices下泉 urine下乳=催乳 lactogenesis下脘 1.phlorus 2.Hsiawan下陷=中气下陷 descending disorders下消"diabetes of the kindney type, diabetes incolving the lower-jiao"下搭手lower back cellulitis下丹田lower elixir field下发背"lumbar carbuncle, deep-rooted ulcer in the lumbar region"下焦病 lower-jiao syndrome下马痈acute pyogenic infection of right下石疽indurated mass of knee下牙床 mandible下注疮eczema of shank下病上取treating diseases of the lower part of the body by needling points on the upper part of the body下腹胀气flatulence in the lower abdomen下汲肾阴consumption of the kidney-yin by the excessive heart fire下焦如渎lower-jiao resembling water passages下焦主出The Lower-jiao is in charge of excretory system下厥上竭exharstion of blood with cold limbs下厥上冒 dizzeness caused by adverse flow of qi下利清谷diarrhea with undigested food in the stool下损及上dusease in the lower part affecting the upper下胎毒法dispelling toxic heat and meconium gathered at the fetus for the new born下者举之Sinking disorders should be treated with drugs of raising property; prolapse and ptosis must be treated with the lifting method to reinforce the vital function of the spleen下焦湿热downward flow of damp and heat下利赤白 dysenteric diarrhea下横骨伤fracture of public bone下行通路 descending pathway大夫"an official's title in the feudal age, now used for a doctor in northern China"大肠 large intestine大毒extremely poisonous drugs大方 heavy prescription大分distinct line between large muscles大风= 麻风大腹 upper abdomen大谷large space between muscles大汗"profuse sweating, byperhidrosis, excessive perspiration"大经 rge channels 2.the needling of points on a large channel exhibiting symptoms大厥 coma大络 large collatereals大脉"large pluse, gigantic pulse"10 大衄profuse bleeding from the mouth and nose大气 "atmosphere, air"大溲(解) "defecation, bowel movements"大泻 vigorous reduction大医 respected doctor大针 large needle大眦=内眦 great canthus大节 large joints大产 eutocia大便 feces; stool;defecation大耳 mycrotia大肉 large muscles大嘴 macrostomia大肠病disease of large intestine大肠经"Large Intestine Channel, LI"大肠虚asthenia of large intestine大肠痈 acute appendictis大肠胀flatulence of large intestine大方科speciality of internal medicine大瘕泄 dysentery大结胸large accumulation of phlegm-heat in the chest大头垫 megacaput pad大头风=大头瘟infection with swollen head大腿疽=股疽大腿痈 carbuncle of thigh大泻刺 drainage needling大指间web of great toe大周天large cirde of vital energy大眦漏=漏睛 dacryocystitis大方脉 adult's pulse大出血 "massive hemorrhage,hematorrhea"大肠气 inguinal hernia大麻风 "lepra, leprosy"大便溏 loose stool大补元气invigorating primodial qi大肠寒结constipation due to retention of cold-pathogen in large intestine 大肠滑脱prolapse of rectum大肠气滞qi stagnation of large intestine大肠热结 large intestinal11 大肠湿热 large intestinal damp-heat大肠虚寒asthenia-cold of large intestine大肠液亏deficiency of fluid in large intestine大方脉科 internal medicine大风恶疫=麻风大肉陷下 obvious emaciation and muscular atrophy大头伤寒=大头瘟大眦脓漏dacryocystitis with pyorrhea大气疗法 aerotherapy大风荷毒most dangerous pathogenic factors大肠津亏fluid deficiency in the large intestine大便干结 dry stool大便不通 constipation大便色黑 "black stool, melena"大便如漆 tarry stools大便失禁 incontinence of feces大便困难 dyschesia大便频数 frequency of bowel movement大汗淋漓 profuse perspiration大骨枯槁bones become dry and brittle大渴引饮 extreme thirst大肠主传导large intestine takes charge of transportation大实有羸状appearance of deficiency in extreme excess兀兀欲吐 intense nausea万灵药 panacea寸 a length measurement corresponding to the middle segment of one's middle finger 寸脉 cun pulse寸口脉 cunkou pulse寸白虫 proglottid of tapeworm寸白虫病 taeniasis寸、关、尺 "cun,guan,and chi,inch,bar,and cubit"上胞 upper eye lid上膊 upper arm上膈"postcibal vomiting,vomiting immediately after in gestion"12 上工 "Shang-gong,superior medical worker"上火sufering from excessive internal heat上焦 "upper-jiao,upper warmer,upper heater"上气 1.abnormal rising of qi 2.the upper qi上窍 upper orifices上脘 1.shangwan 2.episgastrium上消diabetes involving the upper-jiao上搭手cellulitis near the scapular region上丹田upper elixir field上腭痈 abscess on palate上耳背 Shangerpei上发背suppurative inflammation of the uppermost part of the back上横骨 sternal notch上马痈left buttock carbuncle上石疽upper stony mass behind the ear上水鱼abscess of the popliteal region上牙床upper dental bed上肢瘫paralysis of upper extremities上焦证upper warmer syndrome上胞下垂 "ptosis,blepharoptosis"上病下取treating diseases in the upper part by managing the lower上膈下膈upper stenosis and lower stenosis上寒下热cold in the upper and heat in the lower上焦病症syndrome of the upper-jiao上焦如雾the upper-jiao resembling a sprayer上焦主纳The upper-jiao is in charge of receiving上骱手法 reduction of dislocation上厥下竭syncope due to exhaustion below上气喘促 shortness of breath上热下寒heat in the upper and cold in the lower上实下虚excess in the upper and deficiency in the lower上损及下the upper effecting the lower上吐下泻 vomiting and diarrhea上下配穴"coordination of the acupionts of the upper with those of the lower, superior-inferior point association"上虚下实deficiency in the upper and excess in the lower上肢不遂moter impairment of the upper extremities上翘下钩势dorso-extension and ventro-flexion exercise口 "mouth,oral cavity"口臭"foul breath, halitosis"口疮 "aphthae,canker sore"口淡 tastelessness口服 "per oral,per os"口疳 aphthae in children口紧=唇紧口噤 "lockjaw, trismus"口苦 bitter taste口软flaccidity of mouth in infants口水 "saliva,spittle"口酸 sour taste口{口呙} wry mouth口咸 salty taste口吃 "stutter,stammer"口糜erosion of mucous membrance of the oral carity口渴 thirst口不仁numbness of mouth口齿科specialty of stomatology and dentistry口甘甜 sweet taste口疳风=舌头泡blisters of the tongue口丫疮"ulcer on the angle of lips,perleche"口中和normal sense of mouth口臭口烂 halitosis and aphthosis口唇发紫 cyanotic lips口唇紧缩=唇紧口干唇裂dry mouth with cracked lips口噤唇青trismus with cyanotic lips口舌糜烂 aphthous stomatitis14 口涎外溢"1.involuntary drooling 2.sialorrhea,ptyalism,sialism,excessive flow of saliva"口眼{口呙}斜"1.facia hemiparalysis deviation of the eye and mouth, wry mouth with distorted eyes"口中无味=口淡flat feeling in mouth口干唇燥 dry mouth and lips口不知谷味loss of appetite口齿咽喉科"1.Department of the Mouth, Teath and Throat 2.specialty of mouth tooth-throat"口沃沫多唾excessive salivation with froth千日疮 verruca vulgaris千岁疮=流注疮 widespread scrofula久咳 chronic cough久痢 protracted drsentery久疟 chronic malaria久痔=肛漏 recto-analfistula久泻 chronic diarrhea久热伤阴persistent fever injuring yin essence久不受孕fail to be impregnated for a long time久泻不止 chromic diarrhea丸剂 "pill,bolus"广肠 sigmoidorectum广疮=杨梅疮 syphilis广明anterosuperior part of the human body丫叉毒丫刺毒pustule in the web between the fiest and second metacarpals亡血 "hemorrhage, bleading"亡阳"yang depletion,yang exhaustion"亡阴"yin depletion,yin exhaustion"亡血家patient with hemorrhagic diathesis尸厥 corpse-like syncope尸体 "corpse,cadaver"尸咽"ophthalmo-oro-genital syndrome,Behcet's syndrome"卫 defensive function卫气 defensive energy卫分证" weifen syndrome,febrile disease at wei phase,syndrom of wei system"卫生局"health bureau, sanitary bureau"卫生学 sanitary science卫气不固=表气不固wei-energy fail to protect the body卫气同病"syndrome of both weifen and qufen,syndrome of both qi and wei systems"卫气管血辨证analysing and differentiating the development of an epidemic febrile disease by studying condition of the four systems女科 "1.women's diseases,gynecology and obster\trics 2.medical department for women,department of gyhecology and obstetrics"女医 1.woman physician 2.physician who attends to women's diseases女劳疸jaundice due to sexual intemperance女劳复relapse of disease due to intemperance in sexual life女子胞 uterus女阴溃疡 ulcerative vulvitis小产 "abortion, miscarriage"小肠the small intestine小毒"d toxicity 2.drugs with a little toxicity,slightly poisonous drugs" 小方 "minor prescription,minor or mild prescription"小分small space between muscles小腹=少腹 lower abdomen小逆minor mistake in treatment小溲 urine小溪=溪谷小心=心包络=命门小眦"lateral canthus, external canthus"小耳 microtia小眼 microphthalmus小嘴 microstomia小便 "urine, urination, micturition"小肠病disorder of the small intestine16 小肠经=手太阳小肠经small intestine channel小肠咳"small intestine cough, cough accompanied by flatulence"小肠疝[气] hernia小肠痈small intestinal abscess小肠胀flatulence of the small intestine小方科 specialty of pediatrics小腹满distension of lower addomen小夹板 splintlet小结胸accumulation of phligm-heat in the chest小伤寒"common cold, common cold of wink-cold type"小舌头 uvula小腿疽=胫疽 leg cellulitis小中风 faint小周天 a small circle of the evolutive小眦漏fistula in the lateral canthus小方脉 infantile pulse小腹疽(痈)carbuncle of lower abdomen小便短赤scanty dark urine小便短小 oliguria小便黄赤 dark urine小便辣痛 ardor urine小便淋沥 dribbling urination小便涩痛difficulty and pain in micturition小便灼热burning sensation during urination小肠实热excessive heat in the small intestine小肠虚寒hypofunction of the small intestine with cold manifestations小儿暴惊sudden fright in children小儿表热exterior-heat syndrome in children小儿虫吐parasite vomiting in children小儿喘急dyspnea in children小儿卒利acute infantile diarrhea in children17 小儿扎目incessant winking of eyes in children小儿发热 fever in children小儿发痧eruptive disease in children小儿疳眼eye disorder due to malnutrition in children小儿寒吐vomiting in children due to cold小儿脚拳 1.infantile pedal spasm 2.spasm of toes in children小儿惊吐vomiting in children induced by frightening小儿咳逆choking cough in children小儿客忤convulsive seizure in duced by terror in children小儿羸瘦 emaciation in children小儿里热endopathic heat syndrowme in children小儿脉法pulse-taking in children小儿热吐vomiting in children due to heat小儿实热heat syndrome of excess type in children小儿食积infantile indigestion with food retention小儿手拳contracture of fingers in children小儿瘫痪 infantile paralysis小儿痰鸣wheezing cough in children小儿通睛"esotropia in children, convergent strabismus in children"小儿吐泻vomiting and diarrhea in children小儿哮喘asthma in children小儿虚热heat syndrome of deficiency type in children小儿遗溺(尿)"1.incontinence of urine in children 2.bed-wetting, nocturnal enuresis in children" 小儿脉科 specialty of pediatrics小户嫁痛pain in vagina小溲热赤dark urine with burning sensation小腿转筋spasm of calf小儿夜啼nocturnal fretfulness infinfants小儿疳积mallnutrition and indigestion syndrome in children18 小儿浮肿edema in children小儿痢疾dysentery in children小儿感冒common cold in children小儿痢证epilepsy in children小儿淋证infection of urinary system in children小儿风水 acute glomerular小儿血虚 anemia in children小儿自汗"spontaneous perspiration in children, hyperhidrosis in children"小儿咳嗽cough in children小儿腹痛abdominal pain in children小儿无耳 anotia小便不利"dysuria, difficulty in micturition"小便不禁=小便失禁"incontinence of urine, aconuresis"小便淋沥dripping discharge of urine小便频数frequency of micturition小儿暑热(渴)证summer fever of children小儿痰湿吐"vomiting in children, due to phlegmdampness"小肠主受盛small intestion has a function of reception小腹中痞块mass in the lower abdomen小儿涕液不收incessant running nose in children小儿推拿疗法 infantile massage小儿囟门不合non-closure of fontanels in infants小儿时行痿 poliomyelitis小儿遗毒烂斑 congenital syphilis飞痘pustules from smallpox vaccination飞法 flying method飞疡(扬)喉hematoma of uvulla飞腾八法=灵龟八法the eight magic turttle techniques飞蚊幻视 muscae volitantes叉喉风acute laryngeal disorder with compressive feeling in the throat19 马牙1.gingival cyst of mucous gland in the newborn 2.yellowish eruptions on the gum of the newborn马桶癣contact dermatitis of buttock马脾风acute asthmatic attack in children马蹄针 staple puncture马刀侠瘿sabre and beadstring scuofulae马蜞咬伤bite by leech子烦 restlessness during pregnancy子户=气穴子淋 stranguria during pregnancy子满 gestational edema子门cervical orifice of uterus子气 1.qi of the child organ 2.edema of legs in pregnancy子舌=重舌子嗽=妊娠咳嗽intractable cough during pregnancy子痫(冒) eclampsia gravidarum子悬"upward flow of fetusqi, feeling of distension in the thorax during pregnancy"子喑"gestational aphonia, aphonia during pregnancy"子痈acute or chronic orchitis and epedidymitis子脏=女子胞医学翻译子肿 edema during pregnancy子宫石 womb stone子宫痛 uterismus子母痔prolapsed internal hemorrhoids子病及母disorder of the child organ affecting the mother organ子肠不收=子宫脱(垂)出 uterine prolapse子盗母气illness of the child organ may involve the mother organ子户肿胀 swelling of vulva子死腹中=死胎不下dead foetus in the uterus子午捣臼zi wu dao jiu needli大夫"an official's title in the feudal age, now used for a doctor in northern China"大肠 large intestine大毒extremely poisonous drugs大方 heavy prescription大分distinct line between large muscles大风= 麻风大腹 upper abdomen大谷large space between muscles大汗"profuse sweating, byperhidrosis, excessive perspiration"大经 rge channels 2.the needling of points on a large channel exhibiting symptoms 大厥 coma大络 large collatereals大脉"large pluse, gigantic pulse"10 大衄profuse bleeding from the mouth and nose大气 "atmosphere, air"大溲(解) "defecation, bowel movements"大泻 vigorous reduction大医 respected doctor大针 large needle大眦=内眦 great canthus大节 large joints大产 eutocia大便 feces; stool;defecation大耳 mycrotia大肉 large muscles大嘴 macrostomia大肠病disease of large intestine大肠经"Large Intestine Channel, LI"大肠虚asthenia of large intestine大肠痈 acute appendictis寸 a length measurement corresponding to the middle segment of one's middle finger 寸脉 cun pulse寸口脉 cunkou pulse寸白虫 proglottid of tapeworm寸白虫病 taeniasis寸、关、尺 "cun,guan,and chi,inch,bar,and cubit"上胞 upper eye lid上膊 upper arm上膈"postcibal vomiting,vomiting immediately after in gestion"12 上工 "Shang-gong,superior medical worker"上火sufering from excessive internal heat上焦 "upper-jiao,upper warmer,upper heater"上气 1.abnormal rising of qi 2.the upper qi上窍 upper orifices上脘 1.shangwan 2.episgastrium上消diabetes involving the upper-jiao上搭手cellulitis near the scapular region上丹田upper elixir field上腭痈 abscess on palate上耳背 Shangerpei上发背suppurative inflammation of the uppermost part of the back上横骨 sternal notch上马痈left buttock carbuncle上石疽upper stony mass behind the ear上水鱼abscess of the popliteal region上牙床upper dental bed上肢瘫paralysis of upper extremities上焦证upper warmer syndrome上胞下垂 "ptosis,blepharoptosis"上病下取treating diseases in the upper part by managing the lower上膈下膈upper stenosis and lower stenosis上寒下热cold in the upper and heat in the lower上焦病症syndrome of the upper-jiao上焦如雾the upper-jiao resembling a sprayer上焦主纳The upper-jiao is in charge of receiving上骱手法 reduction of dislocation上厥下竭syncope due to exhaustion below上气喘促 shortness of breath上热下寒heat in the upper and cold in the lower上实下虚excess in the upper and deficiency in the lower上损及下the upper effecting the lower上吐下泻 vomiting and diarrhea上下配穴"coordination of the acupionts of the upper with those of the lower, superior-inferior point association"上虚下实deficiency in the upper and excess in the lower上肢不遂moter impairment of the upper extremities大肠胀flatulence of large intestine大方科speciality of internal medicine大瘕泄 dysentery大结胸large accumulation of phlegm-heat in the chest大头垫 megacaput pad大头风=大头瘟infection with swollen head大腿疽=股疽大腿痈 carbuncle of thigh大泻刺 drainage needling大指间web of great toe大周天large cirde of vital energy大眦漏=漏睛 dacryocystitis大方脉 adult's pulse大出血 "massive hemorrhage,hematorrhea"大肠气 inguinal hernia大麻风 "lepra, leprosy"大便溏 loose stool大补元气invigorating primodial qi大肠寒结constipation due to retention of cold-pathogen in large intestine 大肠滑脱prolapse of rectum大肠气滞qi stagnation of large intestine大肠热结 large intestinal11 大肠湿热 large intestinal damp-heat大肠虚寒asthenia-cold of large intestine大肠液亏deficiency of fluid in large intestine大方脉科 internal medicine大风恶疫=麻风大肉陷下 obvious emaciation and muscular atrophy大头伤寒=大头瘟大眦脓漏dacryocystitis with pyorrhea大气疗法 aerotherapy大风荷毒most dangerous pathogenic factors大肠津亏fluid deficiency in the large intestine大便干结 dry stool大便不通 constipation大便色黑 "black stool, melena"大便如漆 tarry stools大便失禁 incontinence of feces大便困难 dyschesia大便频数 frequency of bowel movement大汗淋漓 profuse perspiration大骨枯槁bones become dry and brittle大渴引饮 extreme thirst大肠主传导large intestine takes charge of transportation大实有羸状appearance of deficiency in extreme excess 兀兀欲吐 intense nausea万灵药 panacea上翘下钩势dorso-extension and ventro-flexion exercise传统中医学词汇是由诺贝笔翻译公司整理网站:/。
中医词汇术语下面是店铺整理的中医词汇术语,以供大家学习参考。
AAbdominal flatulence 中满Abdominal fullness and distention 腕痛胀满Abdominal retention 鼓胀Accompanied Symptoms 兼证Activating blood and dissolving stasis 活血化瘀Acuesthesia 得气Acupuncture points 腧穴Acupuncture therapies 针刺疗法Adjuvant drugs 佐药Afternoon fever 日哺发热Alternate chills and fever 寒热往来Anorexia 食欲不振Aphtha 口疮Apoplexy 中风Ashi point 阿是穴Associate drugs 臣药Association of combination of traditional Chinese medicine and western medicine 中西医结合研究会Association of traditional Chinese medicine 中医学会Asthenic cardioyang 心阳虚Asthenic cardioyin 心阴虚Asthma 哮证Otopuncture therapy 耳针疗法Auscultation-olfaction 闻诊Aversion to wind and cold 畏恶风寒BBasis of theory of traditional Chinese medicine 中医理论基础Belching 嗳气Blood deficiency 血虚Blood heat 血热Body fluid 津液CCalming liver wind 平肝熄风Canthus 目眦Carbuncle 痈Cathartic method 攻里法Cardiac and renal coordination 心肾相交Cardiac-splenic asthenia 心脾两虚Chest pain 胸痛Chest stuffiness 胸闷Chi pulse 尺脉Chinese materia medica and prescriptions 中药与方剂Chinese medical 中国医学史Chinese medicine anesthesia 中药麻醉Chinese patent drugs 中成药Clear abundant urine 小便清长Clearing damp 利水渗湿Clearing heat and expectoration 清热化痰Clearing wind-damp 祛风胜湿Clearing Ying heat and cooling blood 清营凉血Coating color 苔色Cold hands and feet 手足厥冷Cold-heat mixing 寒热交错Cold limbs 手足厥冷Cold stroke 中寒Coma 神昏Compendium of Materia Medica 本草纲目Complications 并病Constipation 大便不通Consumptive disease 虚劳Contrary treatment 反治DDefensive Qi instability 卫气不固Deficiency-excess mixing 虚实夹杂Delirium 谵语Diagnostic methods of traditional Chinese medicine 中医诊法Diaphoresis 汗法Diaphoresis, pungent cold 辛凉解表Diaphoresis, pungent warm 辛温解表Diarrhea 泄泻Different treatments for the same disease 同病异治Differentiation, eight principles 八纲辨证Differentiation of diseases 辨病Differentiation of symptoms and signs 辨证Differentiation, six meridians 六经辨证Differentiation, triple energizer 三焦辨证Differentiation, Wei-Qi-Ying-Xue 卫气营血辨证Differentiation, Zang-Fu 脏腑辨证Diphtheria 白喉Diseases of Qi-blood-fluid 气血津液病症Dispersing cold and freeing Bi 散寒通痹Doctrines of various historical schools 中医各家学说Dry heat 燥热Dry stool 大便干结Dysentery 痢疾Dyspepsia 食滞Dysphagia 噎膈Dyspnea 喘证Dysuria 癃闭EEdema 水肿Eight principles 八纲Electuary 冲服剂Elimination 消法Emesis 吐法Endogenous hygrosyndrome 内湿Endogenous cold 内寒Endogenous dryness 内燥Epilepsy 痫证Epitaxis 鼻衄Eruption 斑疹Etiology 病因Exterior syndrome 表证Exterior sthenia 表实Exterior asthenia 表虚Extremely cold limbs 手足厥逆FFacial distortion 口眼歪斜Feeling 按诊Fluid deficiency 津液不足Frequent micturition 小便频数Frequent vomiting 反胃GGastric asthenia 胃虚Gastric cavity 胃脘Gastro-Qi 胃气Generation-inhibition in five elements 五行相克Gingiva 牙龈Greyish fur 灰苔HHarmonizing liver-spleen 调和肝脾Heart fire hyperactivity 心火亢盛Heart-kidney Yang deficiency 心肾阳虚Heart Yang hypoactivity 心阳不振Healthy Qi 正气Hectic fever 潮热Hemorrhage Zheng 血证IInsomnia 失眠Inspection 望诊Intergeneration 相生Inter-restriction 相克Inter-subjuation 相乘Irregular pulse 结代脉KKidney Yang deficiency 肾阳虚Kidney Yin deficiency 肾阴虚LLarge intestine damp-heat 大肠湿热Large pulse 大脉Leukorrhea 白带Liver fire flaming 肝火上炎Liver-stomach disharmony 肝胃不和Liver wind agitation 肝风内动Liver Yang rising 肝阳上亢Liver Yin deficiency 肝阴虚Long pulse 长脉Longer menstrual interval 月经后期Loose stool 便溏Lung heart 肺热Lung Qi deficiency 肺气虚Lung Qi impairment 肺气失宣MMeasles 麻疹Menstrual irregularities 月经失调Merdian-collateral theory 经络学说Meridial distribution 归经Mutual promotion 相须NNight sweat 盗汗Nine orifices 九窍Normal pulse 平脉Nourishing blood and liver 养血柔肝PPale tongue 淡白舌Palpation 切诊Palpitation 心悸Pathogenesis 病机Peeled coating 剥脱苔Pestilence 疫疠Pharynx neurosis 梅核气Phlegm-damp obstructing lung 痰湿阻肺Pill 丸Pores 玄府Principal and subordinate 标本Pulse condition 脉象Pulse-taking 脉诊Purgation-tonifying 攻补兼施QQi-blood and fluid 气血津液Qi deficiency 气虚Qi depression 气滞Qi function 气机RRapid pulse 数脉Relaxing bowels 润肠通便Removing stasis to promote blood circulation 化瘀行血Resolving damp, aromatic 芳香化湿Resuscitation 开窍Retch 干呕Reverse restriction 相侮SSchool in favour of the doctrine of warm diseases 温病学派School of febrile diseases by cold injury 伤寒学派Scrofula 瘰疬Sighing 太息Smallpox 天花Somnolence 多寐Sore 疮Spleen Qi deficiency 脾气虚Spleen Yang deficiency 脾阳虚Spleen Yin deficiency 脾阴虚Spontaneous sweating 自汗Stranguria 小便涩痛Stomach cold 胃寒Stomach heat 胃热Strengthening healthy energy 扶正Striae 腠理Stringy pulse 弦脉Sunstroke 中暑TTenesmus 里急后重Tonifying deficiency 虚则补之Tonifying kidney and holding Qi 补肾纳气Tonifying Qi and spleen 益气健脾Treating excess with purgation 实则泻之Treatment with syndrome differentiation 辨证论治Twenty-eight pulses 二十八脉UUlcer 溃疡Urinal incontinence 小便失禁Uterus 女子胞VVitaport 命门WWhitish fur 白苔Whooping cough 百日咳YYellowish fur 黄苔Ying and Yang in balance 阴平阳秘ZZheng 证。
中医①traditional Chinese medicine②traditional Chinese physician ①中医学的简称。
②本学科专业职业队伍。
中药 Chinese materia medica 在中医理论指导下应用的药物。
包括中药材、中药饮片和中成药等。
中医学 traditional Chinese medicine 以中医药理论与实践经验为主体,研究人类生命活动中健康与疾病转化规律及其预防、诊断、治疗、康复和保健的综合性科学。
中药学 Chinese materia medica 中药学科的统称。
研究中药基本理论和各种药材饮片、中成药的来源、采制、性能、功效、临床应用等知识的学科。
中医药 traditional Chinese medicine and pharmacology 中医与中药的合称。
中医药学 traditional Chinese medicine and pharmacology 中医学与中药学的合称,侧重反映中医与中药两者共同发展,密不可分。
中西医结合 integration of traditional and western medicine 现代医学等现代科学知识及手段来继承和发展中医药,中西医学相互补充,取长补短,诊治疾病的医学形式。
中医基础理论 basic theory of traditional Chinese medicine 研究和阐明中医学的基本概念、基本理论、基本规律、基本原则的学科。
中医诊断学 diagnostics of traditional Chinese medicine 根据中医学的理论体系,研究诊察病情、判断病种、辨别证候的基础理论、基本知识和基本技能的学科。
方剂学 prescriptions of Chinese materia medica 研究治法与方剂配伍规律及其临床运用的学科。
中医内科学 internal medicine of traditional Chinese medicine 研究外感温病、内伤杂病等内科疾病诊治与预防的临床中医学。
一、绪论
中医学TCM(Traditional Chinese Medicine),
中医学理论体系的形成Origination of TCM, 形成formation, 发展development
中医学理论体系的基本特点
The basic characteristic of Traditional Chinese Medicine theory
整体观the whole concept, 辨证论治syndrome differentiation and treatment
第一章阴阳五行学说
阴阳Yin-yang , 阴阳的特性the property of yin-yang
阴阳之间的相互关系Interaction between yin and yang
阴阳对立制约Opposition of yin and yang
阴阳互根互用Interdependence between yin and yang
阴阳消长平衡Wane and Wax between yin and yang
阴阳相互转化Mutual transformation between yin and yang
阴阳学说在中医学中的应用
The applications of the theory of yin-yang in TCM
说明人体的组织结构Explanation of the histological structure of the human body
解释人体的生理功能Explanation of the physiology function activity of the human
body
阐释病理变化Explanation of pathogenesis
阴阳偏盛Relative predominance of yin or yang
阳偏盛Relative predominance of yang
阴偏盛Relative predominance of yin
阴阳偏衰Relative decline of yin or yang
阳偏衰Relative decline of yang
阴偏衰Relative decline of yin
五行the five elements,
五行特性the five elements property
第二章中医学的生理观
藏象“Zangxiang” ,
五脏five Zang-organs, 六腑six fu-organs,生理功能the physiological functions ,
气qi, 血blood , 津液body fluid,
气的生成、运动和分类the production ,moving and classification of qi,
血的生成和运行the production and circulation of blood
津液的生成、输布和排泄the production and transportation and metabolism of
body fluid.
气、血、津液的功能The physiological functions of qi, blood and body fluid
心The heart,
主血脉Governing blood
主神志controlling the mind
在体合脉governs the vessels
开窍于舌opens into the tongue
其华在面External manifestation on the face
肝The liver,
主疏泄To dredge and regulate, 主藏血Storing blood
在体合筋The liver governing the tendons
其华在爪The external manifestation of the liver on the nails
开窍于目The liver opening into the eyes
脾the spleen,
主运化To govern the transportation and transformation
主统血To command blood, 主升elevating
在体合肌肉,主四肢the spleen governing the muscles and the four limbs
开窍于口The spleen opening into the mouth
其华在唇The external manifestation on the lip
肺The lung,
主气,司呼吸Dominating qi,controlling the respiratory movement
主宣发、肃降dispersing and descending
通调水道The regulation of water passage
朝百脉、主治节,the lung is connected with all the vessels, regulation the qi activity in
the whole body
在体合皮the lung governing the skin
其华在毛Eexternal manifestation on the body hair
开窍于鼻The lung opening into the nose
肾The kidney,
藏精store essence, 主水To govern water, 主纳气To govern reception of qi
在体合骨The kidney governing the bones
开窍于耳及二阴The kidney opening into the ears, the external genitals and the anus
其华在发External manifestation on the hair
胆The gallbladder, 贮藏和排泄胆汁store and excrete the bile
胃The stomach, 受纳、腐熟水谷receive and digest food
主通降,the stomach functions to descend?,,unobstructed condition
小肠The small intestine, 受盛化物To receive the chime and transform
泌别清浊To separate the lucid from the turbid
大肠The large intestine, 主传化糟粕transmitting and excreting the waste of food
膀胱The bladder ,storing and discharging urine
气的生成The production of qi
气的运动The moving of qi
气的功能The physiological functions of qi