劳顿管理信息系统第1章 当今全球商业中的信息系统习题集
- 格式:doc
- 大小:64.50 KB
- 文档页数:33
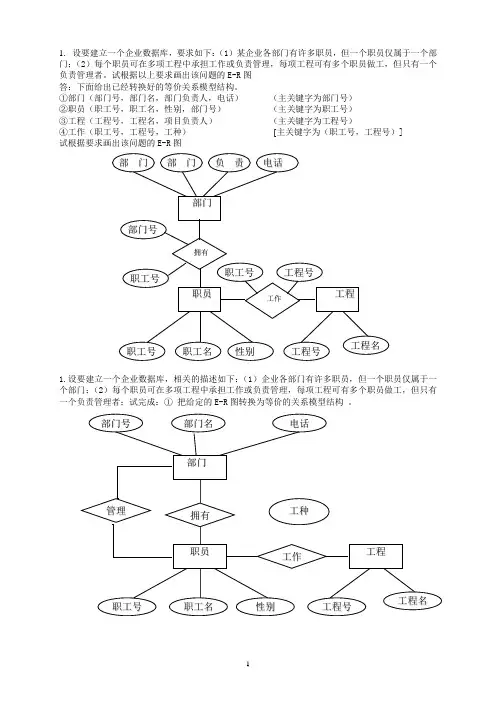
1. 设要建立一个企业数据库,要求如下:(1)某企业各部门有许多职员,但一个职员仅属于一个部门;(2)每个职员可在多项工程中承担工作或负责管理,每项工程可有多个职员做工,但只有一个负责管理者。
试根据以上要求画出该问题的E-R 图 答:下面给出已经转换好的等价关系模型结构。
①部门(部门号,部门名,部门负责人,电话) (主关键字为部门号) ②职员(职工号,职工名,性别,部门号) (主关键字为职工号) ③工程(工程号,工程名,项目负责人) (主关键字为工程号)④工作(职工号,工程号,工种) [主关键字为(职工号,工程号)] 试根据要求画出该问题的E-R 图1.设要建立一个企业数据库,相关的描述如下:(1)企业各部门有许多职员,但一个职员仅属于一个部门;(2)每个职员可在多项工程中承担工作或负责管理,每项工程可有多个职员做工,但只有一个负责管理者;试完成:① 把给定的E-R 图转换为等价的关系模型结构 。
部门号 部门名 电话部门拥有职员工作工程工程号性别 职工名 职工号 工程名管理工种部门号 部门名 负责人电话部门拥有职员 工作工程部门号职工号工程号性别 职工名 职工号 工程名工程号职工号2.下列是运算完毕的UC 矩阵,①在矩阵上划分子系统需要注意哪三个方面?②请在矩阵上划分子系统① 答案要点:A. 沿对角线一个接一个地画,既不能重叠,又不能漏掉任何一个数据或功能。
B. 小方块的划分是任意的,但必须将所有的“C ”元素都包含在小方块之内。
C. 划分的子系统要与企业组织功能结构划分基本相符。
②答案要点:功能结构图要与子系统划分的结果一致MRPII 的基本思想和特点是什么?答:基本思想:将企业作为有机整体,从全局最优的角度出发,运用科学方法有效地计划、组织和控制企业的各种制造资源,以及产、供、销、财等各个环节,使其协调发展并充分地发挥作用。
特点:遵循计划主导的管理模式。
还是企业管理的信息系统---确保资源共享。

管理信息系统习题第一章信息系统和管理(一)单项选择题1.管理的职能主要包括()A、计划、控制、监督、协调B、计划、组织、领导、控制C、组织、领导、监督、控制D、组织、领导、协调、控制2.在企业环境中,高、中层管理决策问题具有的特点是()A.结构化和非结构化B.结构化和半结构化C.半结构化和非结构化D.结构化、半结构化和非结构化3.关于计算机辅助管理,以下不正确的叙述是()A.事务处理的目的是提高工作效率B.事务处理是管理信息系统的一部分C.决策支持系统一般嵌入到管理信息系统中D.决策支持系统一般比管理信息系统规模大4.企业组织中不包括以下哪个子系统()A.管理决策系统B.管理信息系统C.作业系统D.市场环境系统5.ERP的基础是()A.控制技术B.生产技术C.工程技术D.信息技术6.集成制造系统(CIMS)是将 CAD、CAM、MIS和OA等联成一个集成系统,为使整个系统和谐地运行,必须采用()A.统一的数据库B.统一的操作系统C.统一的接口规定D.以上各项都需要(二)填空题1.管理系统是分等级的,信息也是分级的,一般分为____战略级____、____战术级_____和作业级。
2.应用电子计算机进行信息加工,根据处理功能的深浅程度不同,可把加工分为预加工、业务处理和________。
3.信息使用深度大体上可分为三个阶段,即提高效率阶段,及时转化阶段以及________。
4.系统的一般模型由输入、处理和________组成。
(三)名词解释1.管理2.业务流程再造3.信息4.数据5.系统6.系统集成(四)简答题1.信息有哪些基本性质?2.信息的价值如何衡量?如何才能正确的实现其价值?3.信息管理有什么内容?试述我国企业在信息管理上的问题?4.衡量系统好坏的指标是什么5.管理信息系统是什么样的系统?它有哪些特点?6.信息系统有几种分类方式?每种方式的长处和问题是什么?当前系统集成分类还存在什么问题?7.系统集成的策略应当包括什么内容?如何检验系统集成的成功与否?第二章管理信息系统概述(一)单项选择题1.按照系统论的一般原理,系统具有()A.目的性、整体性、相关性、环境适用性等特征B.目的性、整体性、有效性、环境适用性等特征C.目的性、有效性、相关性、环境适用性等特征D.有效性、整体性、相关性、环境适用性等特征2.管理信息系统服务的对象是()A.控制工作B.预测工作C.决策工作D.管理工作3.管理信息系统通常可分为多个子系统,整体系统的结构为()A.网状结构B.关系结构C.层次结构D.串行结构4.系统开发工作的目的和出发点是()A.满足技术指标B.满足设计者要求C.满足用户要求D.技术规范5.按管理职能部门和结构来建立的管理信息系统,其结构是()A.职能结构B.层次结构C.管理阶段结构D.综合结构6.管理信息的特点是()A.信息量小B.信息来源面窄C.信息资源的消耗性D.信息处理方式与手段的多样性7.决策的基础是()A.管理者B.客户C.信息D.规章制度8.信息存储子系统中不包括()A.数据库系统B.模型库系统C.知识库系统D.程序库系统9.以下叙述正确的是()A.MIS是一个人机系统B.信息与载体性质有关C.信息化就是计算机化加网络化D.MIS的目标就是提高工作效率节省人力10.为缩短用户与开发人员的距离,取得共同语言,最好的信息收集方法是()A.面谈B.发调查表C.查阅文献D.实地观察与实践11.管理信息系统的层次结构中,最高层是()A.事务处理B.业务信息处理C.战术信息处理D.战略信息处理12.关于MIS的建设,下面哪一项的叙述正确()A.由于MIS建设采用计算机,所以该项目并不是劳动密集型的B.MIS建设可以采用交钥匙的办法承包给有经验的单位C.用户单位领导不懂计算机,没有必要领导该单位的MIS建设工作D.系统规划与开发费用是可预见的,但系统运行的维护费用是难预见的13.用户单位建设管理信息系统的途径一般不包括()A.购买商品化的MIS系统B.根据本企业的要求修改商品化的MIS系统C.自己用第四代工具(语言)来开发D.外聘专家来开发14.现代管理信息系统是()A.计算机系统B.手工管理系统C.人和计算机等组成的系统D.通信网络系统15.管理信息系统科学的三要素是()A.物理的观点,数学的方法,计算机的技术B.数学的观点,计算机的方法,信息的技术C.系统的观点,数学的方法,计算机的应用D.、信息的观点,数学的方法,计算机的技术(二)填空题1.管理信息系统绝不只是一个技术系统,而是把人包括在内的人机系统,因而它是一个________系统。

第4章信息系统中的商业伦理和社会问题目录第4章信息系统中的商业伦理和社会问题 (1)单项选择题(一) (1)对错题(一) (5)简答题(一) (6)单项选择题(二) (7)对错题(二) (12)简答题(二) (13)单项选择题(三) (14)对错题(三) (26)简答题(三) (29)单项选择题(四) (32)对错题(四) (36)简答题(四) (37)单项选择题(一)1.下列哪句话描述了新的信息系统会导致法律灰色地带?A)新的信息系统用网络和数字化数据来工作,这比人工存储的信息更加难以控制。
B)新的信息系统出现了旧的法律体系无法覆盖的情况。
C)新的信息系统由技术人员实施的,而不是管理人员实施的。
D)新的信息系统是按照一系列逻辑和技术规则创建的,而不是根据社会和组织道德而建的。
E)新的信息系统很少被政治家或律师所理解。
Answer: BDifficulty: Moderate2.下列哪一项最好地描述了新的信息技术对社会的影响?A)它对商业伦理具有抑制作用。
B)它带来了连锁反应,引发了新的伦理、社会和政治问题。
C)这对整个社会是有益的,但为消费者带来了困境。
D)它引发了越来越复杂的伦理问题,具有瀑布效应。
E)它具有放大效应,引发了越来越多的伦理问题。
Answer: BDifficulty: Moderate3.在信息时代,在下列道德层面的哪个方面谈论的是个人和组织在知识产权的义务?A)产权与义务B)系统质量C)责任与控制D)信息权利和义务E)生活质量Answer: ADifficulty: Easy4.在信息时代,在下列道德层面的哪个方面是个人和组织在维护现有价值和制度方面所需承担的义务?A)家庭B)财产权利与义务C)系统质量D)责任与控制E)生活质量Answer: EDifficulty: Moderate5.下列哪一个不是当前引起伦理问题的关键技术趋势之一?A)数据存储技术的改进B)数据分析技术的发展C)数据质量的提高D)增加移动设备的使用E)网络技术的发展Answer: CDifficulty: Easy6.在信息时代,DoubleClick(一家广告服务平台)的核心商业活动涉及到五个道德维度中的哪一个?A)产权和义务B)系统质量C)责任与控制D)生活质量E)信息权利和义务Answer: EDifficulty: Challenging7.利用计算机收集到的不同来源的数据来创建关于个人详细信息的数字档案,属于下列哪一种?A)个人画像B)钓鱼C)垃圾邮件D)靶向E)间谍软件Answer: ADifficulty: Easy8.发现不同来源的数据之间的隐藏连接,是属于下列哪一项数据分析技术?A)HIPAAB)FIPC)NORAD)COPPAE)间谍软件Answer: CDifficulty: Easy9.下列哪一个不是大数据的潜在阴暗面的例子?A)警察通过计算机系统来分析识别将来可能会犯罪的人。

《管理信息系统》练习题一、单项选择题1. 系统实施阶段的主要内容之一是()。
A.系统物理配置方案的设计B.输入设计C.程序设计D.输出设计2. 结构化方法中,自顶向下原则的确切含义是()A 先处理上级机关事务,再处理下级机关事务B 先进行总体设计,后进行详细设计C 先把握系统的总体目标与功能,然后逐级分解,逐步细化D 先实施上级领导机关的系统后实施下属部门的系统3. 信息系统的折旧率取决于其生命周期。
由于信息技术发展迅速,信息系统的生命周期较短,一般在()。
A. 2~3年B. 5~8年C. 10~15年D. 20~30年4. 在公路运输管理中,若车辆通过道路时是免费的,公路的建设、维护费用依靠税收和财政拨款,这种管理控制称()。
A.反馈控制B.前馈控制C.输人控制D.运行控制5. 关于项目工作计划的说法中,不正确的是()A.甘特图主要从宏观的角度,对各项活动进行计划调度与控制。
B.网络计划法主要从微观的角度,用网状图表安排与控制各项活动。
C.针对开发中的不确定性问题,可以通过经常性地与用户交换意见来解决。
D.编制项目工作计划时,要确定开发阶段.子项目与工作步骤的划分。
6. 系统实施的主要活动包括()。
A.编码.系统测试B.系统安装C.新旧系统转换D.以上都是7. 系统转换最重要并且工作量最大的是()。
A.组织准备和系统初始化工作B.物质准备和系统初始化工作C.数据准备和系统初化工作D.人员培训和系统初始工作8. 用户使用Internet Explorer的企业信息系统的模式是()A.主从结构B. 文件服务器/工作站C.客户机/服务器D. 浏览器/WeB服务器9. 数据字典产生在哪个阶段()。
A 系统规划B 系统分析C 系统设计D 系统实施10. 管理控制属于()。
A. 中期计划范围B. 长远计划范围C. 战略计划范围D. 作业计划范围二、填空题1. 工资系统中的职工姓名和基本工资属数据动态特性分类中的属性数据。


第一章管理信息系统概论P22本章思考题:1、信息有哪些特性?(P3)答:信息具有很多重要的特性,包括真伪性、层次性、可传输性与可变换性、共享性等等。
(1) 真伪性。
信息有真伪之分,客观反映现实世界事物的程度是信息的准确性。
(2) 层次性。
信息是分等级的。
信息和管理层一样,一般分为战略层、策略层和执行层三个层次。
(3) 可传输性。
信息的可传输性是指信息可以通过各种局域网络、互联网等媒介快速传输和扩展的特性。
(4) 可变换性。
可变换性是指信息可以转化成不同的形态,也可以由不同的载体来存储。
(5) 共享性。
从共享的角度来讲,信息不同于其他资源,它不具有独占性。
2、信息流在企业中有什么作用?(P4)答:在企业中信息流起着至关重要的作用,具体表现在:(1)伴随着物流等其他流的产生,都有与之对应的信息流产生;(2)信息流反映其他流的状态,并且对其他流具有控制和调节作用。
3、信息系统由哪几部分组成?(P12)答:信息系统的基本构造是由输入、处理、输出和反馈四个部分组成。
(1)系统输入:是一个获取原始数据的活动。
通过输入,系统捕获或收集来自企业内部或外部环境的原始数据。
(2)处理:部分将原始输入的数据转换成更具有意义的形式。
(3)输出部分:将经过处理的信息传递给人或用于生产活动。
(4)反馈:是指描述系统运行状况的数据,它将信息返回给组织的有关人员以便帮助他们评价或校正输入。
4、理解管理信息系统的层次与管理层次性的关系?(P15)答:5、说说你对系统方法的理解?(P12)答:系统的方法不仅仅是一种认识方法,同时也是一种实践的方法,是一条行动的指南。
如果人们在实践中遵循系统方法,使用系统的方法做指导,就应该处处从系统的整体角度来考虑问题。
相反的,人们如果违背系统方法,做事不从整体来看,过分注重局部是无法认识问题的,成语中所谓一叶障目、管中窥豹就说的是这种行为。
6、如何理解MIS的战略作用与面临的挑战?(P20-P21)答:MIS的战略作用:由于经济全球化和市场国际化的发展趋势,企业所面临的竞争更趋激烈。
Essentials of Business Information Systems, 7ELaudon & LaudonLecture Files, Barbara J. EllestadChapter 8 Achieving Operational Excellence and Customer Intimacy: Enterprise ApplicationsOver the last decade businesses have come to realize how important it is to totally integrate business processes across the enterprise. We’ve spoken about “islands of information” many times. In today’s fast-paced world, managing information assets is more important than ever before. In this chapter we’ll look at how important it is for information to be available in every nook and cranny in the enterprise.8.1 Enterprise SystemsWe’ve look at enterprise resource planning systems in previous chapters and also discovered the importance of efficiently and effectively maintaining data that businesses can develop into useful information. As we’ve seen, it can be disastrous for an organization to have more than one set of data for customers, employees, and suppliers. The best idea is to have one database that supplies information where and when necessary across functional lines. Everyone from employees to managers, from customers to suppliers, would have the necessary tools to extract the data that they need and present it in the format that fits them best. That’s where enterprise systems come in.What are Enterprise Systems?Enterprise systems aim to correct the problem of firms not having integrated information. Also known as enterprise resource planning (ERP) systems, their main goal is to bridge the communication gap among all departments and all users of information within a company. If production enters information about its processes, the data are available to accounting, sales, and human resources. If sales and marketing is planning a new advertising campaign, anyone anywhere within the organization will have access to that information. Enterprise systems truly allow a company to use information as a vital resource and enhance the bottom line.Data integration throughout the firm is the key. Consolidated data from divisions and departments throughout the business, including key business processes, are immediately available to any authorized user.The greatest enticement of enterprise systems is the chance to cut costs firm-wide and enhance the ability to pass information throughout the organization. Take the success of Oracle Corporation as an example. “The company now has an enterprise-wide system for managing customer contacts. Previously, the salesforce used a network that was different from the fulfillment and shipping network. By unifying these networks, salespeople don’t have to duplicate the efforts of others in the organization, and thereby save time and money. At the beginning of the year, the company said that it expected the changeover to save $1.2 billion over the next four quarters. Just three months later, Chief Financial Officer Jeff Henley told analysts that Oracle will save nearly twice that by year-end.” (BusinessWeek, April 6, 2000)How Enterprise Systems WorkMany businesses assume that their operations are totally integrated across functional lines. After all, Manufacturing responds to an order from Sales and produces a product for which Accounting and Finance sends an invoice. A Production manager sends an email to the Human Resources Department requesting five new employees. When the Marketing department decides on a new advertising campaign, a copy of the brochure is included in all employees’ pay envelope at the end of the month. Once a week all department managers meet with the executive staff and review statistics from last month’s business.What’s the problem? Many times, departments will fail to fully communicate with all the other departments about every process that is taking place in a company. They don’t do it on purpose but forget how important total communication about every process and every piece of data is. Sales sends an order to Manufacturing with a shipment date that can’t possibly be met. Accounting and Finance bills for supplies that Production never order. Human Resources holds a training class that interferes with a rush production job. What’s the solution? Enterprise software allows every functional area to share every process and every piece of data. A business can select specific processes in specific areas but eventually everything the company does will be shared across all lines. The software uses predefined processes and requires the company to adapt itself to the software. While many companies may balk at having to change, the software is designed around the best practices for that particular function. The company can benefit from using the most successful solutions in a particular industry to help achieve its objectives. The software helps the organization automate many of the steps in the best practices instead of having to do everything manually. And best of all, the software will help employees remember all of the necessary steps in a process and provide the data to all who need it.While enterprise software can be somewhat modified, it is very expensive and very difficult to do so. Because the software is so complex, changing just one of the processes may disrupt some of the other interdependent modules. However, manufacturers of the enterprise software programs are modifying the software to envelope Internet services andmake the data available to external sources such as suppliers, governmental agencies, and customers.Business Value of Enterprise SystemsDone correctly, enterprise systems can offer big rewards. Conversely, done incorrectly can cause a firm huge headaches, loss of business, employee turmoil, and wasted dollars. The changes in the enterprise will be tremendous:• A more uniform organization: a more disciplined approach to business throughout the entire firm, regardless of physical location and/or organizationalstructure•More efficient operations and customer-driven business processes: all functional areas can focus more on the customer and respond to product demand more efficiently•Management: improved management decision making, with a comprehensive view of performance across all functional areas8.2 Supply Chain Management SystemsOh, for the days when the old saying “the customer is king” was just a catch phrase. Now, it’s an absolute reality and companies that don’t live up to the phrase will get creamed in the marketplace. There are no more separate entities or distinct lines in the sand when it comes to integrating supply chains. It’s more like shifting sand.The Supply ChainA supply chain is similar to a spider’s web. It includes all of the internal functions of an organization, along with suppliers, distributors, retailers, and customers. They are allintertwined and rely on information from each other to effectively meet the business’s objectives.Exactly what are all the activities involved in getting a product from conception to delivery? There are probably many more than you can easily think. And there are many more people involved than you might imagine. It may be helpful to break the supply chain into three distinct groups:•Upstream: suppliers that deal directly with the manufacturer and their suppliers •Downstream: distributors and those that deliver the products to the customers •Internally: the employees that transform the materials, components, and services into the actual productsThink of a mountain stream that starts very small, flows downhill, gathers more water as it combines with other streams, feeds into a river that continues to flow and eventually meets up with other rivers, and on into the ocean. The mountain stream is analogous to the suppliers, the river represents the manufacturer, and the ocean can be compared to the customers.Information and Supply Chain ManagementAs with other functional areas, information is the glue that holds the supply chain together. Lack of or faulty information can wreak havoc on the entire chain from getting supplies into the manufacturing process and getting the final product to the customer.In a perfect world, just-in-time strategies for ordering and delivering supplies would be an ordinary process. Unfortunately, we don’t live in a perfect world. Natural disasters, dock worker strikes, and terrorist activities such as September 11, 2001, can disrupt even the most carefully planned supply chains in an instant. Businesses have to plan as best they can around these kinds of events but they can’t foresee every problem. The bull-whip effect on the supply chain is more natural than you might think and happens in virtually every industry.“PC makers insist their inventories are in good shape. But there are signsof trouble further down the supply chain. Analysts were taken aback tolearn that the Taiwan companies that make the guts of notebooks formarket leaders Hewlett-Packard Co. and Dell Inc. saw February salesplunge 10% to 15%.What’s going on? PC makers, encouraged by robust 35% growth in third-quarter notebook unit sales and signs of even stronger holiday demand,ramped up their orders from Taiwan by a staggering 68%, according to theTaipei-based Market Intelligence Center. But while the sales surge keptgoing through the fourth quarter, analysts fear that the sudden drop insupplier orders means that the pace has slipped in the first quarter of thisyear. Analysts add that PC makers incorrectly assumed that laptops wereso hot that they were immune from the post-Christmas sales slump thathas traditionally afflicted desktop s.” (BusinessWeek, March 15, 2004)In the example of the bull-whip effect explained above, if the PC makers had been able to pass timely and accurate information to their parts suppliers, perhaps the sudden swing in supplying computer parts could have been avoided. Many companies don’t want to give up too much of their information because they fear that outsiders will compromise the information. Unfortunately this way of old-style thinking costs too much money in terms of lost opportunities, overstocked and underused parts, and overpriced products. Supply Chain Management ApplicationsSupply chain planning systems can provide information up and down the chain and help everyone involved do a better forecasting job. In the example above, the information could pass more easily between the PC retailers and the parts suppliers. While the retailers were still remiss in accurately forecasting PC sales for the first quarter, the parts suppliers could have altered their manufacturing schedules quicker and avoided the huge inventory build-up.Supply chain planning systems enable firms to•Generate demand forecasts•Develop sourcing and manufacturing plans•Share information about changes easier and faster so work can be better coordinated•Develop better demand planning•Manage the flow of products through distribution centers and warehouses by using supply chain execution systems•Coordinate activities with supply chain partners•Handle complex interdependencies among various supply chain processes•Allow users to balance the costs of transportation, delivery, and handlingSupply Chain Management and the InternetThe islands of information that we’ve frequently mentioned don’t exist just inside the corporation but also exist all up and down the supply chain. Adapting the supply chain software to the Internet and opening up the information to suppliers, logistical experts, and distributors can greatly help a company reduce costs and ensure products are delivered when needed to the right location. It won’t help a company’s bottom line tohave 1000 parkas delivered to Arizona in March when upstate New York is suffering through a difficult winter.The same type of internal collaboration that organizations can generate through intranets can be extended to supply chain partners through extranets. Suppliers can log on to a company’s extranet site and review next week’s production schedule. The supplier can ensure enough production supplies are on hand by the manufacturer without over- or under-extending itself. Changes to the production schedule can be communicated easier to the supplier through Internet-enabled applications. Long-term forecasts can be posted to the extranet and schedules adjusted. No expensive proprietary systems are necessary since all the information is transmitted through ordinary Web-based applications. Anyone internal or external to the organization can view delivery schedules or determine the optimal logistics for moving products through online applications.Figure 8-4 demonstrates how intranets and extranet provide the communication channels necessary to improve supply chain management.Figure 8-4: Intranets and Extranets for Supply Chain Management.Demand-Driven Supply ChainsTraditionally, customers purchase whatever products are available. While the colors, sizes, and prices may have varied somewhat, generally the manufacturer decided what to produce by forecasting what the potential demand would be through a push-based model. That is quickly changing to a pull-based model in which the customer tells the manufacturer ahead of time what he/she wants to buy. One of the best examples of this new pull-based model is Dell Computer’s build-to-order business model. Dell doesn’t build a computer until it receives a customer order. Then it builds the computer to the customer’s specifications. Granted, the customer must choose from a pre-determined list of options, but Dell doesn’t have a huge stock of unsold inventory based on faulty demand forecasting that no one wants.Figure 8-5 below shows the differences between the push-based and pull-based supply chain models.Figure 8-5: Push- Versus Pull-based Supply Chain ModelsAutomobile manufacturers are also adopting pull-based modeling for their customers. A customer in Des Moines can log onto a Web site and select the color, engine, options and kind of tires for his/her new car. The order is sent to the factory in Detroit and the manufacturer’s suppliers simultaneously. While the customer must wait for delivery, at least he/she will get exactly the car they wanted. Figure 8-6 diagrams an Internet-driven supply chain.Figure 8-6: The Future Internet Driven Supply Chain.Business Value of Supply Chain Management SystemsThe benefits of implementing an integrated, networked supply chain management system include:•Match supply to demand•Reduce inventory levels•Improve delivery service•Speed product time to market•Use assets more effectivelyIn turn a company can•Improve customer service and responsiveness•Reduce costs•Utilize cash betterThese last three benefits of implementing a supply chain management system point directly to improving the bottom line for the company. By making the supply chain more efficient a company can save millions of dollars and improve its relationships with its customers.8.3 Customer Relationship Management Systems“Arun Jain, chairman of the marketing department at the Uni versity atBuffalo School of Management, said preserving relationships with existingcustomers is important for businesses because acquiring new ones isexpensive. Once you build a relationship with a customer, then you cansell additional products to them, they recommend you to others, cost ofserving goes down, they become less sensitive to price,” Jain said. “In thebeginning, you may end up paying to acquire them, but if you haveselected the right type of customer, they become profitable.” (USATodayOnline, March 14, 2004)While many companies strive to be “customer-centric” very few have been able to completely focus every functional area on the customer. Largely due to the new avenues of information customers have through the Internet, organizations must fight harder to keep the customers they work so hard to get in the first place.What Is Customer Relationship Management?The goals of customer relationship management systems are to optimize •revenue•profitability•customer satisfaction•customer retention“Since the mid-1990s, companies have been trying to make their enterpriseand customer data pay off. They know this data has value, but they don’tknow how to effectively extract it. In their mining efforts, companies havebuilt huge data warehouses, sunk millions of dollars into CRM systemsand endured painful change management initiatives—often with lacklusterresults.[Four companies were successful in implementing CRM systems: AceHardware, Academic Management Services, Continental Airlines, andKorn/Ferry International.]These companies’ investments succeeded because they first analyzed theirbusiness needs and goals, reengineered existing business processes to takeadvantage of the data they were capturing, and put technology in placethat’s both easy to use and supports the needs of users as well as thecompany’s business objectives. And they haven’t forgotten that it’s thecustomer-facing employee who can make all the difference in whether ornot a customer feels well served—and that no technology, howeversuperior, can make up for that human touch.” (CIO Magazine, Feb 15,2004)Many companies are overloaded with data about customers. Unfortunately, the companies don’t have any useful information that can help them increase customer satisfaction and retention, thereby increasing revenues and profitability. The ability to turn raw data into useful information is where CRM systems shine. CRM systems can gather customer information from all corners of a business, consolidate the information and then provide it to the customer touch points. By offering a consolidated viewpoint of the customer to these touch points, a company can cater to the customer that offers the most profitability.Financial institutions are a prime example of how effective CRM systems can be to help identify the customers that offer the most “bang for the buck.” Most of the larger banks offer more than just checking and savings accounts. They provide investment services, insurance policies, and loans. It’s much cheaper for Wells Fargo bank for instance, to provide its current customers with all of these financial products, rather than trying to attract new customers for each of the product lines. Information gleaned from a CRM system can provide Wells Fargo with information about which customers are more likely to purchase these products and the sales force can target that market better.CRM SoftwareCRM application software ranges in size and complexity making it possible for an organization to select the type of software it needs the most. Modules focusing on partner relationship management or employee relationship management can be integrated into the customer relationship management software at a later date.Partner relationship management systems are a reflection of internal customer relationship management systems but extend past the immediate borders of a firm to its selling partners. For instance, Levi Jeans doesn’t sell directly to its customer but rather through other retail outlets. How Levi’s partners cater to the customer directly affects itsprofitability. Therefore, Levi is very interested in sharing information about its customers with its partners to increase sales of its products. Using partner relationship management systems not only helps Levi but also its retailers.Employee relationship management modules associated with CRM focus more on how employees perform and interact with customers. These modules help a company manage •Employee objectives•Employee performance•Performance-based compensation•Employee trainingSome of the more common capabilities of CRM software are:•Sales force automation: allows the sales force to focus on the most profitable customer. It also reduces the cost per sale for acquiring new customers andretaining old ones•Customer service: gathers information from a variety of sources and makes it available across organizational functions so that data is input only once •Marketing: Allows companies to engage in cross-selling, up-selling, and bundling through better analysis of customer dataFigure 8-9 shows how customer data feeds into these three functions.Figure 8-9: CRM Software Capabilities.Operational and Analytical CRMIt’s important to understand the difference between the operational and analytical aspects of CRM systems. Operational CRM includes everything a company should provide those employees who interface directly or indirectly with the customer: the sales force, call centers, and support activities. Managers and decision makers would use the analytical CRM to help them improve business performance. The analytical CRM uses data from the operational CRM and provides managers with the opportunity to target smaller, specific customer groups or market segmentation. Rather than trying to blanket a huge group of potential customers, many of whom are not interested, managers use the analytical CRM to focus their efforts on those customers who can offer the most profit at the least cost. Table 8.3 will help you differentiate between operational and analytical CRM examples.One of the most important benefits of analytical CRM is the ability to determine the customer lifetime value (CLTV). The text mention that it costs six times more to gain a new customer than to keep an old one. By measuring the CLTV of customers, organizations can calculate customer profitability and determine which customers they should cater to.Business Value of Customer Relationship Management SystemsAs the old saying goes, “We’re wasting half of our advertising budget; we just don’t know which half.” CRM software will help managers better understand their customers thereby helping them make better decisions about product lines and marketing campaigns. CRM systems can also help reduce the customer churn rate and identify which customers are most profitable. Hopefully CRM will help them discover which half of the ad budget is wasted.Once again, the benefits of using CRM systems are worth the challenges you’ll face. Benefits:•Increased customer satisfaction•Reduced marketing costs•More effective marketing•Lower costs for customer acquisition and retention•Increased sales revenue•Better response to customer needs8.4 Enterprise Applications: New Opportunities and Challenges Before implementing enterprise application systems, organizations need a very clear picture of where they are now and where they want to go. Organizations must decide which processes provide the most value and which processes need the most improvement. And, the firm must allocate the organization resources where they are most needed.Challenges and OpportunitiesThe return on investment to companies that implement enterprise systems can be enormous in terms of enhanced information between suppliers, employees, customers, and business partners. The better the information is, the better the decisions. The better the information is, the better the products and services are for the customer. The more customers there are, the higher profits for the company.Hang on for a rough ride:•Daunting Implementation: technological and fundamental changes will pervade every corner of the organization. The organizational structure and culture willchange. The most daunting task will be retraining thousands of workers andconvincing them the change is good. It will be easier to fail than to succeed.•High Up-Front Costs and Future Benefits: There is no such thing as an overnight success when implementing an enterprise system. On average, it takesthree to five years to fully implement an enterprise system. Keeping the firm ontrack and focused on the end result is more difficult than most firms comprehend.•Data Management: It’s more important than ever before. Now that one database serves the entire organization, if data are mismanaged, it will affect the everybusiness function and process.•Inflexibility: Make a change in one area of the business is much more difficult after implementing an enterprise system. The software is just too complex toeasily change.•Realizing Strategic Value: Businesses that rely on unique or cutting-edge processes to gain a competitive advantage will lose that edge with enterprisesystem software. Enterprise systems are not the answer for every firm.Extending Enterprise SoftwareAs companies get more comfortable with supply chain management and customer relationship management programs they realize the importance of branching out to enterprise solutions, enterprise suites, or e-business suites. Software manufacturers are creating these programs and ensuring firms can integrate more easily with customers, suppliers, and business partners.。
第15章管理全球系统单项选择题(一)1.苹果iPhone最终组装是在哪个地方?A)美国B)日本C)韩国D)中国E)德国Answer: DDifficulty: Easy2.国际系统架构的主要维度包括以下各项,除了:A)全球环境B)企业全球战略C)技术平台D)跨境数据流E)管理和业务流程Answer: DDifficulty: Challenging3.下列哪一个不是推动全球商业的一般文化因素?A)全球通信和运输技术B)政治不稳定C)全球知识库D)全球文化E)全球社会规范Answer: DDifficulty: Challenging4.所有主要业务功能的全球协调新水平允许经营活动的位置按照:A)比较优势。
B)社会规范和价值观。
C)竞争威胁。
D)知识库。
E)人工成本。
Answer: ADifficulty: Challenging15.下列哪一项是国际信息系统的最佳定义?A)使用全球互联网互相交谈的系统B)国际业务使用的系统C)跨越全球的业务流程D)组织协调世界贸易和其他活动所必需的基本信息系统E)由全球公司开发的系统Answer: DDifficulty: Easy6.当你想建立一个国际信息系统时,首先要考虑的是什么?A)世界政治状况B)帮助你实现目标的新技术C)你的业务运行的国际环境,并能识别你的企业和行业的业务驱动因素D)全球环境下你面临的商业挑战E)世界上不同的计算和通信标准Answer: CDifficulty: Moderate7.下列哪个行业最受全球化影响?A)电信B)制造C)法律D)娱乐E)运输Answer: BDifficulty: Moderate8.跨境数据流是指:A)国际系统中的信息流。
B)国家法律改变数据流从一个国家流向另一个国家的方式。
C)把信息从一个国家转移到另一个国家的业务。
D)跨越国际边界的信息流动。
E)协调来自不同国家信息的业务流程。
Answer: DDifficulty: Challenging9.下列哪个不是全球业务的商业驱动力?A)全球通信和运输技术B)全球文化的发展2C)全球社会规范的出现D)政治稳定E)全球系统的发展Answer: EDifficulty: Easy10.在狭隘或个人特征的基础上作出判断和采取行动称为:A)本地化。
管理信息系统第三版课后答案【篇一:管理信息系统课后习题答案】t>1、请阐述信息管理和管理信息系统的区别和联系2、结合一个实例,说明管理信息系统是人机一体化的系统。
3、从管理层次分类看,不同层次的管理信息系统在目的和功能上有何不同?4、什么是crm?结合实例说明它有哪些应用。
5、什么是电子商务?它和管理信息系统有何联系?6、管理信息系统发展历经了哪些阶段?各个阶段的典型应用技术是什么?7、决策支持系统的基本特征是什么?四、简答题1、答:区别:信息管理的对象是信息以及与之相关的信息活动,信息活动包括信息的收集、存储、加工、传递和运用等,信息管理是管理的一种;而管理信息则是指经过加工处理后对企业生产经营活动产生影响的数据,是信息的一种。
联系:管理信息是信息的一种,因此管理信息时信息管理的对象,是信息管理重要的资源,是科学决策的基础以及实施信息管理控制的依据。
2、略3、答:管理信息系统按照管理任务的层次由高到低进行划分可分为战略管理层、战术管理层和作业管理层。
战略层的目的是支持企业的战略性的决策,系统的功能表现为全局性、方向性,或关系到企业竞争能力的重要问题的分析与决策。
战术层和作业层管理的主要目的则是提高工作效用和工作效率,管理信息系统为战术层提供资源配置、运作绩效等经营状态的分析评估和计划落实的控制优化等功能,为作业层提供准确便捷的数据收集处理功能。
4、答:crm (customer relationship management )客户关系管理,客户关系管理包括企业识别、挑选、获取、发展和保持客户的整个商业过程。
其核心是客户价值管理,它将客户价值分为既成价值、潜在价值和模型价值,通过一对一营销原则,满足不同价值客户的个性化需求,提高客户忠诚度和保有率,实现客户价值持续贡献,从而全面提升企业盈利能力。
crm目前在银行、通信、商贸等大型服务企业中得到较为理想的应用。
5、答:电子商务就是企业利用现代信息技术,特别是互连网技术来改变商务活动中的信息流程,从而改变业务流程,提高企业竞争力的一切商务活动。
目录第1章当今全球商业中的信息系统 (1)单项选择题(一) (1)对错题(一) (11)简答题(一) (12)单项选择题(二) (13)对错题(二) (26)简答题(二) (29)第1章当今全球商业中的信息系统1单项选择题(一)1.下列哪一项不属于企业信息系统6个重要的企业业务目标?A)创造新产品、新服务和新商业模式;B)改善决策C)获得竞争优势D)提高员工的士气E)确保企业生存Answer: DDifficulty: Challenging2.威瑞森电信(Verizon)公司通过基于web的数字仪表板为管理者提供精确的实时信息,该公司的这项应用使如下哪个方面得到了改善?A)遵守规章制度1本习题集系翻译,版权Copyright©2018Pearson Education,Inc。
B)管理决策C)创造新产品的效率D)与供应商的密切关系Answer: BDifficulty: Challenging3.下列哪项可以让公司获得竞争优势?(1)新产品、新服务和商务模式(2)优质低价的产品(3)实时响应客户需求A)只有(1)B)(1)和(2)C)(2)和(3)D)(1)和(3)E)(1)、(2)和(3)Answer: EDifficulty: Challenging4.一个公司投资于信息系统,是因为该信息系统对企业开展业务而言是必需的。
这样的信息系统反映了企业是为了实现下列业务目标中的哪一个?A)卓越的运营B)改善决策C)获得竞争优势D)与客户保持亲密关系E)确保企业生存Answer: EDifficulty: Moderate5.文华东方公司利用计算机系统来跟踪客人的喜好,这体现了哪种企业业务目标?A)改善企业柔性B)改善决策C)提高效率D)与客户建立密切关系E)实现卓越的运营Answer: DDifficulty: Moderate6.在花旗银行在纽约推出第一台ATM之后,其他零售银行也转而使用ATM,这一现象表明利用信息系统获取哪类企业业务目标?A)提高效率B)与客户和供应商建立密切关系C)确保企业生存D)获得竞争优势E)改善决策Answer: CDifficulty: Moderate7.以下哪种目标较好地描述了本章开篇案例Kroger实施信息技术背后的业务战略?A)提高客户满意度水平B)确保企业生存C)提升员工士气D)改善决策E)降低采购成本Answer: ADifficulty: Moderate8.以下哪一项信息系统应用是企业利用信息系统来创造新产品的一个例子?A)沃尔玛的零售链(RetailLink)系统B)文华东方酒店(Mandarin Oriental)利用计算机追踪客户喜好C)威瑞森电信(Verizon)公司使用基于Web的数字仪表板为管理者提供实时的公司信息D)苹果公司创造 iPodE)Kroger利用传感器来监测食品冷柜的温度Answer: DDifficulty: Challenging9.沃尔玛利用信息系统及其最新的业务实践、相应的管理制度等,实现了如下哪一项企业目标?A)创造新产品与服务B)提高运营效率C)确保企业生存D)与客户建立紧密关系E)增强竞争优势Answer: BDifficulty: Challenging10.2015年美国企业在信息系统硬件、软件和通信设备上花费了多少钱?A)大约1亿美元B)大约10亿美元C)大约1000亿美元D)大约1万亿美元E)大约10万亿美元Answer: DDifficulty: Moderate11.为了弄清楚顾客将购买衣服行为,百货公司开发了一个新的应用系统,用于分析顾客在他们商店的花费水平,并与流行的衣服款式作交叉分析。
这样的信息系统是希望支持如下哪个企业目标?A)与客户建立紧密关系B)确保企业生存C)实现卓越的运营D)改善决策E)创造新产品与服务Answer: CDifficulty: Moderate12.大约有百分之多少的美国企业已经实施了某种形式的远程工作计划?A)大约15%B)大约25%C)大约35%D)大约60%E)大约70%Answer: DDifficulty: Moderate13.下列哪项不属于信息系统领域新技术的发展趋势?A)云计算B)大数据C)物联网D)移动数字化平台E)企业价值的共创Answer: EDifficulty: Moderat14.下列关于数字化公司的描述中哪项描述是不正确的?A)在数字化的公司中,时间与空间的切换是常态B)如今绝大多数公司已经完全数字化了C)数字化公司为灵活的全球化组织和管理提供了非常好的机会D)与传统企业相比,数字化公司能更快地感知和响应环境的变化E)在经济不景气时期,数字化公司有更灵活的生存机会Answer: BDifficulty: Challenging15.某个公司为了符合联邦法律的要求,必须在新的信息系统能力方面进行投资,这样的投资为了满足哪个企业目标?A)与客户建立紧密关系B)实现卓越的运营C)确保企业生存D)创造新的产品E)改善决策Answer: CDifficulty: Moderate16.互联网浏览、email、社交媒体等互联网活动产生了大量的数据,被之为A)物联网B)大数据C)数字化移动平台D)云计算E)商务智能Answer: BDifficulty: Easy17.以下哪一个不是信息系统技术当前正在发生的变化?A)大数据商业应用的不断增长B)云计算的发展C)PC平台的发展D)移动数字平台的出E)由物联网产生的数据被越来越多加以利用Answer: CDifficulty: Moderate18.托马斯·弗里德曼(Thomas Friedman)声称世界是“平的”,意思是A)发达国家的经济和文化优势正在被抹平B)用于即时通信的互联网和技术的使用C)旅行时间的缩短,以及随时随地发生的全球交易和旅行D)全球化的发展E)使用全球货币的不断增加Answer: ADifficulty: Easy19.2015年美国经济的百分之多少是源自外贸?A)10%B)25%C)30%D)50%E)66%Answer: CDifficulty: Challenging20.下列描述哪一项不属于全球化所带来的影响?A)运营成本的显著下降B)通过外包是劳动力成本得以下降C)找到低成本供应商的能力D)交易成本的上升E)商业模式在多个国家得以复制Answer: DDifficulty: Challenging21.在某个典型的一年中,有多少服务性的工作岗位被转移到低工资的国家?A)3000B)3万C)30万D)300万E)3000万Answer: CDifficulty: Challenging22.下列哪一项描述是不正确的?A)2015年,美国企业在信息系统硬件、软件和通信设备上投入了约1万亿美元B)2015年,美国企业在商业和管理咨询、信息技术服务方面投入了5000亿美元C)民营企业对信息技术的投资从1999年总投资的21%增长到2015年所有投资资本的37%D)IT投资的大部分商业价值来自于企业内部的组织、管理和文化的变革E)美国企业用于商业和管理咨询的大部分资金用于重新设计公司的业务运营,以便更好地发挥新技术的优势Answer: BDifficulty: Challenging23.大概多少美国人利用智能手机或平板电脑上网?A)1.18亿B)1.72亿C)1.94亿D)2.20亿E)2.58亿Answer: CDifficulty: Challenging24.如下哪一项描述是不正确的?A)许多美国财富500强公司的一半收入以上来自海外业务B)在中国制造的大多数PC都使用在韩国制造的微处理器芯片C)美国销售的玩具中有80%是在中国制造的D)2015年,苹果公司60%的收入来自美国以外的地区E)技术公司更加依赖于海外收入Answer: BDifficulty: Challenging对错题(一)25.互联网广告每年以大约5%的增速在发展。
Answer: FALSEDifficulty: Challenging26.制定一份市场营销计划是企业业务流程的一个例子。
Answer: TRUEDifficulty: Easy27.所有公司的重要业务关系和核心业务流程必须数字化使能,只有这样才能被认定为数字化公司。
Answer: FALSEDifficulty: Easy28.商业模式描述了一个公司如何生产、交付和销售产品或服务以创造财富。
Answer: TRUEDifficulty: Easy29.2015年私营企业对信息技术的投资占所有投资资本的37%。
Answer: TRUE简答题(一)30.你打算经营一家小规模的自行车信使公司。
鉴于公司的服务类型(在有限的地理区域内人工送包裹),你的公司能成为一家数字化公司吗?如何使它成为一家数字化公司?参考答案: 是的,您的公司可以是一家数字公司。
数字化公司不仅仅依赖于拥有数字化产品和服务。
数字化公司与客户、供应商和员工的关系大部分都是数字化使能的。
订单交付、递送分配、管理员工和任务都可以由数字化驱动;使用手机,信息系统,和手持设备连接客户、递送管理者和自行车信使。
Difficulty: Challenging31.一个组织使用信息系统以后将会发生哪些主要变革?你认为哪种变革对企业影响最大?参考答案: 发生的主要变化包括:1)企业使用社会化网络平台来连接客户和供应商;2)企业使用平板电脑和移动平台实现远程办公;3)共同创造商业价值,企业价值的来源从产品转向解决方案和经验,从内部转向供应商网络,并与客户合作。
关于最大影响,学生的参考答案会有所不同。
其中一个例子是: 协作性的增加对企业影响最大,因为客户可以获得对终端产品的更多控制;足够灵活地倾听和满足客户需求的企业会更成功。
单项选择题(二)32.组织利用信息系统中哪三类活动产生的信息来控制运营的?A)信息、研究和分析B)输入、输出和反馈C)数据、信息和反馈D)数据分析、处理和反馈E)输入、处理和输出Answer: EDifficulty: Easy33.库存食品上RFID传感器产生的如存储位置这样的数据,是下列哪一项典型的例子?A)原始输入B)原始输出C)客户与产品数据D)销售信息E)信息系统Answer: ADifficulty: Easy34.“存储温度有问题的食品总数”是以下哪一项的例子?B)原始数据C)有意义的信息D)反馈E)处理Answer: CDifficulty: Easy35.输出:A)是经过处理后产生的有意义信息的反馈B)是传递给组织中合适的人员以帮助他们评估输入的信息C)是将数据传递给需要使用的人或活动D)是将处理后的信息传递给需要使用的人或活动E)将原始输入转换成有意义的形式Answer: DDifficulty: Easy36.将原始数据转换成更加有意义的信息,被称之为A)获取B)处理C)组织D)反馈E)分析Difficulty: Easy37.以下哪一项是来自汽车制造商的原始数据的例子?A)2016年纽约每天平均售出120辆斯巴鲁(Subarus)。