Notes on A-infinity algebras, A-infinity categories and non-commutative geometry. I
- 格式:pdf
- 大小:632.81 KB
- 文档页数:70
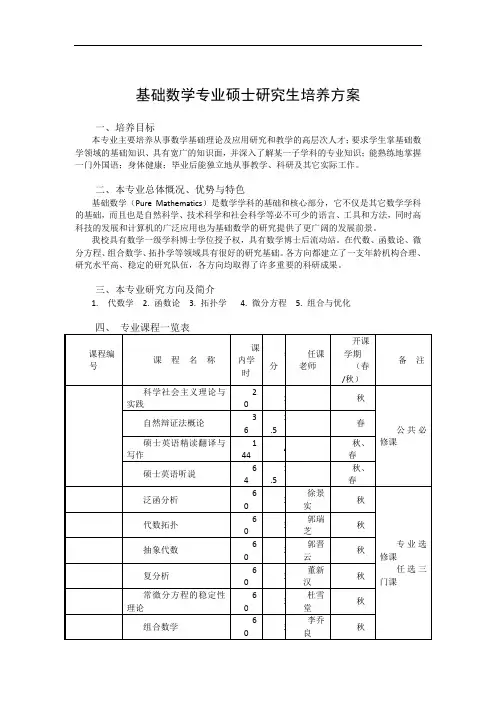
基础数学专业硕士研究生培养方案一、培养目标本专业主要培养从事数学基础理论及应用研究和教学的高层次人才;要求学生掌基础数学领域的基础知识、具有宽广的知识面,并深入了解某一子学科的专业知识;能熟练地掌握一门外国语;身体健康;毕业后能独立地从事教学、科研及其它实际工作。
二、本专业总体慨况、优势与特色基础数学(Pure Mathematics)是数学学科的基础和核心部分,它不仅是其它数学学科的基础,而且也是自然科学、技术科学和社会科学等必不可少的语言、工具和方法,同时高科技的发展和计算机的广泛应用也为基础数学的研究提供了更广阔的发展前景。
我校具有数学一级学科博士学位授予权,具有数学博士后流动站。
在代数、函数论、微分方程、组合数学、拓扑学等领域具有很好的研究基础。
各方向都建立了一支年龄机构合理、研究水平高、稳定的研究队伍,各方向均取得了许多重要的科研成果。
三、本专业研究方向及简介1. 代数学2. 函数论3. 拓扑学4. 微分方程5. 组合与优化五、专业课程开设具体要求课程编号:课程名称:泛函分析英文名称:Functional Analysis任课教师:徐景实适应学科、方向:基础数学、计算数学、概率论与数理统计、应用数学、运筹学与控制论预修课程:数学分析、实变函数主要内容:熟悉距离空间、赋范线性空间、Banach空间、Hilbert空间的基本定理,熟练掌握线性算子和线性泛函的表示、弱收敛性和线性算子的谱等。
了解广义函数的概念和运算。
主要教材及参考文献:1、张恭庆.泛函分析讲义(上、下册)[M].科学出版社.*****2、夏道衍.实变函数论与泛函分析[M].高等教育出版社.3.、定光桂.巴那赫空间引论[M].科学出版社,1999.4、J.B.Conway.A Course in Functional Analysis (2nd Ed.)[M].GTM. 96 Springer-Verlag,1990.C-algebras and Operator theory[M].Academic Press,1990.**********5、G.J.Murphy.课程编号:课程名称:代数拓扑英文名称:Algebraic Topology任课教师:郭瑞芝适应学科、方向:基础数学、应用数学预修课程:点集拓扑、近世代数主要内容:商空间、基本群、多面体及其单纯同调、奇异同调、范畴与函子、奇异同调群相对奇异同调、正合同调序列、切除定理、多面体的同调群及其应用、CW-复形、上同调群。

双指标非交换鞅的一些不等式尹磾;马聪变【摘要】In this paper, we discuss the inequalities of two-parameter noncommutative martingales. By using the inequalities of one-parameter noncommutative martingales methods, we obtain the relation betweenk · kHp(M) and k · khp(M) of two-parameter noncommutative martingales (2 ≤ p < ∞), which generalize the equivalence relation between k · kLp(M) and k · khp(M) of two-parameter noncommutative martingales (2≤p≤4) .%本文研究了双指标非交换鞅的一些不等式问题.利用单指标非交换鞅不等式的方法,获得了双指标非交换鞅的k·kHp(M)和k·khp(M)之间的关系(2≤p<∞).推广了双指标非交换鞅的k·kLp(M)和k·khp(M)之间的等价关系(2≤p≤4).【期刊名称】《数学杂志》【年(卷),期】2017(037)004【总页数】8页(P851-858)【关键词】von Neumann代数;双指标鞅;Burkholder不等式;鞅 Hardy空间【作者】尹磾;马聪变【作者单位】武汉大学数学与统计学院,湖北武汉 430072;武汉大学数学与统计学院,湖北武汉 430072【正文语种】中文【中图分类】O177.5非交换鞅空间理论是非交换数学中分析理论的有机组成部分,是当前泛函分析领域的前沿研究方向.从20世纪70年代,人们开始研究非交换鞅.为了研究非交换鞅空间,需要引进新的思想和方法.1971年Cuculescu[1]研究了非交换鞅的弱(1,1)型不等式并提出了著名Cuculescu构造以取代停时的方法.1997年Pisier和Xu[2]取得重大突破,他通过引进列均方函数与行均方函数对p<2与p≥2分别定义了恰当的非交换鞅的Hardy空间Hp(M),并由此证明Burkholder-Gundy鞅不等式的非交换类比.随后经过众多数学家的努力,非交换鞅取得重要进展.到目前为止,绝大多数经典鞅的不等式都成功过渡到了非交换情形,例如条件均方函数的Burkholder不等式[3],Doob极大不等式[4],Stein不等式[2]等.双指标鞅是单指标鞅的自然推广.在交换的情形,Weisz对双指标鞅做了许多工作(见文[5]).Weisz的工作表明,从单指标到双指标绝不是简单的推广,实际上很多在单指标鞅研究中常用的方法不能够适用于双指标鞅的情形.因此常常需要一些新的技巧和方法.关于双指标非交换鞅的研究目前尚属起步阶段.本文研究双指标非交换鞅,证明了双指标非交换鞅的一些不等式.包括双指标非交换鞅的‖·‖Hp(M)和‖·‖hp(M)之间的关系,双指标非交换序列的Stein不等式以及‖·‖Lp(M)和‖·‖hp(M)之间的等价关系. 首先回顾一下关于非交换Lp-空间的一些基本定义与记号.设(M,τ)是一个非交换概率空间,这里M是Hilbert空间H上的von Neumann代数,τ为M上的正规忠实的迹,满足τ(1)=1.记L0(M)为关于(M,τ)的可测算子全体组成的拓扑∗-代数.设1≤p <∞,令其中表示x的模.定义则(Lp(M),‖·‖p)是Banach空间,称之为关于(M,τ)的非交换Lp-空间.当p=∞时,规定L∞(M)=M,且L∞(M)上的范数‖·‖∞为算子范数.设(Mn)n≥0是M的一列单调增加的子von Neumann代数,用En表示M到Mn的条件期望算子.Lp(M)中的序列x=(xn)n≥0称为是关于(Mn)n≥0的鞅,若对任意的m≥n,有En(xm)=xn.关于非交换Lp-空间与非交换鞅的更详细的介绍可参见文献[6].设N是非负整数的集合,N2={ (n1,n2):n1,n2∈N}.在N2上定义半序如下:对任意的n=(n1,n2),m=(m1,m2)∈N2,定义n≤m当且仅当n1≤m1,n2≤m2以及n<m若n≤m且n/m.设(Mn;n∈N2)是M的一列关于N2偏序单调增加的子von Neumann代数,并且在M中w∗-稠密.对任意的n=(n1,n2)∈N2,用En或者En1,n2表示M到Mn的条件期望算子.一般地,对于M的任意一列子von Neumann代数(Nn;n≥0),令表示包含的最小的von Neumann代数.对每个(n1,n2)∈N2,定义以后总是设(Mn;n∈N2)满足(F4)条件:对任意的x∈M和任意的n=(n1,n2)∈N2,有为了方便起见,规定对任意的x∈L1(M),当n1=0或者n2=0时,En1,n2(x)=0.定义2.1 设x=(xn,n∈N2)是L1(M)中的序列.称x为关于(Mn)n∈N2的鞅,如果满足若进一步对每个n∈N2,有xn∈Lp(M)(1≤p≤∞),则称x为关于(Mn)n∈N2的Lp-鞅.此时,令若‖x‖p<∞,则称x为Lp-有界鞅.设x=(xn,n∈N2)是关于(Mn)n∈N2的鞅,n=(n1,n2).令约定当n1=0或者n2=0时,dxn=0,称dx=(dxn)为x的鞅差序列.容易证明当(Mn)n∈N2满足(F4)条件时,若(dxn,n∈N2)是鞅差序列,则En(dxm)=0(∀nm). 为了定义关于双指标非交换鞅的Hardy空间,先回顾一下非交换列空间与行空间的定义(详见文[6]).设1≤p<∞,x=(xn)是Lp(M)中的有限序列.令则‖·‖Lp(M,lc2)和‖·‖Lp(M,lr2)在Lp(M)的有限序列上定义了范数.相应的完备化空间分别记为.注意到对于Lp(M)中的一个序列(xn),如果在Lp(M)中有界,则极限存在.用表示这个极限,则当1≤p<∞时,CRp[Lp(M)]空间定义如下.(i)当p≥2时,定义,赋予范数(ii)当1≤p<2时,定义,赋予范数下面定义双指标非交换鞅的Hardy空间Hp(M).设x=(xn,n∈N2)是一个鞅,令如果(Sc,(n,n)(x))n≥1和(Sr,(n,n)(x))n≥1在Lp(M)中有界,令称Sc(x)和Sr(x)分别为鞅x=(xn,n∈N2)的列均方函数与行均方函数.定义2.2 (i)设1≤p<∞.定义双指标非交换鞅的列Hardy空间,类似地,定义双指标非交换鞅的行Hardy空间.(ii)定义非交换鞅Hardy空间如下.当1≤p≤2时,定义,赋予范数当2≤p<∞时,定义,赋予范数注对一个双指标鞅x=(xn,n∈N2)的鞅差序列dx=(dxn)n∈N2,把它重新编号变成一个单指标的序列,则可以把它视为一个单指标序列dx=(xn)(但是要注意的是xn)一般不是单指标的鞅差序列).因此,无论x=(xn)是单指标鞅还是双指标鞅都有下面定义双指标非交换鞅Hardy空间hp(M).由于这里需要考虑双指标有限鞅,为此先给出双指标有限鞅的知识.设x=(xn,n∈N2)是一个鞅,k∈N,称形如x(k)=(xn1∧k,n2∧k,(n1,n2)∈N2)为停止于k的有限鞅.设1≤p<∞,对Lp(M)中的有限鞅x=(xn),定义记分别为按上述范数完备化的Banach空间.对L2(M)中任意的有限鞅x=(xn),令则‖x‖hcp(M)=‖sc(x)‖p,‖x‖hrp(M)=‖sr(x)‖p.还需要考虑lp(Lp(M)),定义记为lp(Lp(M))中由所有鞅差序列构成的子空间,并且定义‖x‖hdp(M)=‖dx‖lp(Lp(M)).定义2.3 (i)设1≤p<2.定义,赋予范数(ii)设2≤p<∞.定义,赋予范数在这一部分研究双指标非交换鞅Hardy空间的一些不等式,包括双指标非交换鞅的‖·‖Hp(M)和‖·‖hp(M)之间的关系,双指标非交换序列的Stein不等式以及‖·‖Lp(M)和‖·‖hp(M)之间的等价关系.这些结果是关于单指标鞅相应的结果在双指标鞅相应的推广(见文[3]).下面的定理3.1是这一节的主要结果.定理3.1 设x=(xn)n∈N2是Lp(M)中的鞅.则(i) 当1≤p≤2 时,有‖x‖Hp(M)≤Cp‖x‖hp(M);(ii)当2≤p<∞ 时,有‖x‖hp(M)≤p‖x‖Hp(M),其中Cp和p是只依赖于p的常数. 为证明上述定理,需要用到下面的一系列引理.引理3.2[3,4]设(Mn)n≥1是M的一列单调递增的子von Neumann代数,En表示M到Mn的条件期望算子.则对任意的有限序列,有这里Cp是只依赖于p的正常数.下面把引理3.2推广到双指标的情形.引理3.3 设(Mn)n∈N2是M的一列关于N2偏序单调递增的子von Neumann 代数,En表示M到Mn的条件期望算子,则对任意的有限双指标序列,有这里Cp与引理3.2中的Cp一致.证 (i)利用(F4)条件和引理3.2,有(ii)证明方法与(i)的证明是类似的.证毕.推论3.4 (双指标序列的Stein不等式)设2≤p<∞,则对Lp(M)中任意的有限双指标序列(an),有这里Cp与引理3.3中的Cp一致.证利用引理3.3和不等式E(x)∗E(x)≤E(|x|2),得到定理证毕.引理3.5 设1≤p<∞.则对任意的有限双指标序列(xn)⊂Lp(M),有(i)当2≤p<∞时,(ii)当1≤p≤2时,证(i)将(xn)n∈N2进行重新编号为一个单指标的序列,再利用非交换单指标的结论(见文[7]),就得到所要证明的不等式.(ii)证明方法与(i)的证明是类似的.引理证毕.定理3.1的证明(i)先考虑有限鞅的情形.设x=(xn)为hp(M)中停止于k的有限鞅.设x=y+z+w是x的一个分解,其中y,z分别为中的有限鞅,,满足dwk=0,∀k(n,n).由于,由引理3.3(i),有类似地,可以证明接下来证明由定义知道利用引理3.5(ii),得到令,则对x的所有分解取下确界,得到‖x‖Hp(M)≤Cp‖x‖hp(M).一般情形,设x=(xn)n∈N2∈hp(M).对任意的k∈N,令x(k)=(xn1∧k,n2∧k)n∈N2.由上面证明得到‖x(k)‖Hp(M)≤Cp‖x(k)‖hp(M).再令k→∞得到‖x‖Hp(M)≤Cp‖x‖hp(M).(ii)与(i)的证明类似,也先考虑有限鞅的情形.设x=(xn)为Hp(M)中停止于k的有限鞅.由引理3.3(ii)得到通过取伴随得到其次证明由引理 3.5(i) 得到令,由上面的证明得到一般情形,先考虑有限鞅,再取极限即得到所要的结论.定理证毕.下面转到双指标非交换鞅的Burkholder不等式.要用到下面的双指标非交换鞅的Burkholder-Gundy不等式.引理3.6 [7]设1<p<∞.x=(xn,n∈N2)是Lp(M)中的鞅,则x是Lp-有界鞅当且仅当x∈Hp(M).更确切地说,有这里的αp,βp是只与p有关的正常数.定理3.7 设2≤p≤4,x=(xn,n∈N2)是Lp(M)中的鞅,则x是Lp-有界鞅当且仅当x∈hp(M).更确切地说,有这里的αp,βp为引理3.6中的常数,为定理3.1(ii)中的常数.证首先证明第一个不等式.事实上,由定理3.1(ii)和引理3.6可知接下来证明第二个不等式.由引理3.6知‖x‖p≤βp‖x‖Hp(M).下面只需再证明不妨设‖x‖hp(M)≤1.有令|dxn|2=En-1|dxn|2+dyn(n∈N2),这里dyn=|dxn|2-En-1|dxn|2.注意到,有这里y是一个鞅.注意到,利用引理3.5(ii)和引理3.6,得到因此通过取伴随可证因此定理证毕.由定理3.7和定理3.1(ii)得到如下推论.推论3.8 设2≤p≤4,对任意的Lp-有限鞅x=(xn,n∈N2),有证第二个不等式直接由定理3.1得到.对于第一个不等式,由引理3.6和定理3.7得到.证毕.【相关文献】[1]Cuculescu I.Martingales on von Neumann algebras[J].J.Multi.Anal.,1971,1:17-27.[2]Pisier G,Xu Quanhua.Non-commutative martingaleinequalities[J].Comm.Math.Phys.,1997,189:667-698.[3]Junge M,Xu Q.Noncommutative Burkholder/Rosenthal inequalities[J].Ann.Prob.,2003,31:948-995.[4]Junge M.Doob’s inequalities for non-commutative martingales[J].J.ReineAngew.Math.,2002,549:149-190.[5]Weisz F.Martingale Hardy spaces and their application in Fourier analysis[M].Berlin:Springer-Verlag.1994.[6]Pisier G,Xu Quanhua.Non-commutativeLp-spaces[M].Vol.II,Holland:Elsevier,2003.[7]曹芳.双指标非交换鞅的收敛性和不等式[J].数学杂志,2015,35(6):1511-1520.。
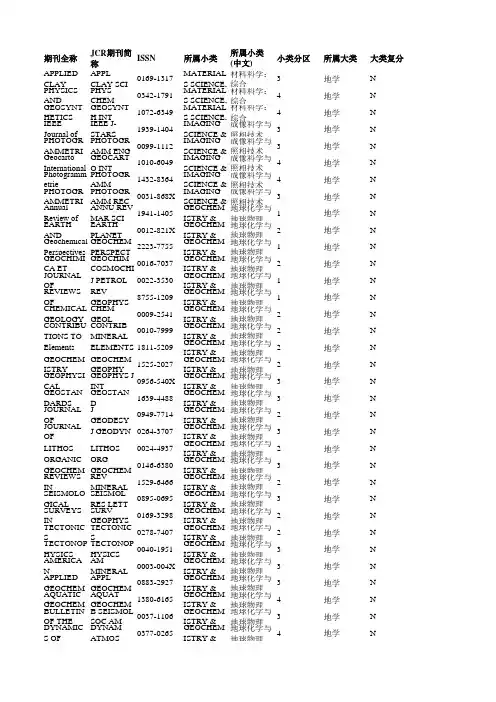
期刊全称JCR期刊简称ISSN所属小类所属小类(中文)小类分区所属大类大类复分APPLIED CLAYAPPL CLAY SC0169-1317MATERIALS S材料科学:综合3地学N PHYSICS AND PHYS CHEM M0342-1791MATERIALS S材料科学:综合4地学N GEOSYNTHET GEOSYNTH IN1072-6349MATERIALS S材料科学:综合4地学N IEEE Journal of IEEE J-STARS1939-1404IMAGING SCIE成像科学与照相3地学N PHOTOGRAMMPHOTOGRAMM0099-1112IMAGING SCIE成像科学与照相3地学N Geocarto Intern GEOCARTO IN1010-6049IMAGING SCIE成像科学与照相4地学N Photogrammetri PHOTOGRAMM1432-8364IMAGING SCIE成像科学与照相4地学N PHOTOGRAMMPHOTOGRAMM0031-868X IMAGING SCIE成像科学与照相3地学N Annual Review ANNU REV MA1941-1405GEOCHEMIST地球化学与地球1地学N EARTH AND P EARTH PLANE0012-821X GEOCHEMIST地球化学与地球2地学N Geochemical Pe GEOCHEM PE2223-7755GEOCHEMIST地球化学与地球1地学N GEOCHIMICA G EOCHIM COS0016-7037GEOCHEMIST地球化学与地球2地学N JOURNAL OF PJ PETROL0022-3530GEOCHEMIST地球化学与地球1地学N REVIEWS OF GREV GEOPHYS8755-1209GEOCHEMIST地球化学与地球1地学N CHEMICAL GECHEM GEOL0009-2541GEOCHEMIST地球化学与地球2地学N CONTRIBUTIOCONTRIB MIN0010-7999GEOCHEMIST地球化学与地球2地学N Elements ELEMENTS1811-5209GEOCHEMIST地球化学与地球2地学N GEOCHEMIST GEOCHEM GE1525-2027GEOCHEMIST地球化学与地球2地学N GEOPHYSICALGEOPHYS J IN0956-540X GEOCHEMIST地球化学与地球3地学N GEOSTANDARGEOSTAND G1639-4488GEOCHEMIST地球化学与地球3地学N JOURNAL OF GJ GEODESY0949-7714GEOCHEMIST地球化学与地球2地学N JOURNAL OF GJ GEODYN0264-3707GEOCHEMIST地球化学与地球3地学N LITHOS LITHOS0024-4937GEOCHEMIST地球化学与地球2地学N ORGANIC GEOORG GEOCHE0146-6380GEOCHEMIST地球化学与地球3地学N REVIEWS IN MREV MINERAL1529-6466GEOCHEMIST地球化学与地球2地学N SEISMOLOGICSEISMOL RES 0895-0695GEOCHEMIST地球化学与地球3地学N SURVEYS IN GSURV GEOPHY0169-3298GEOCHEMIST地球化学与地球2地学N TECTONICSTECTONICS0278-7407GEOCHEMIST地球化学与地球2地学N TECTONOPHY TECTONOPHY0040-1951GEOCHEMIST地球化学与地球3地学N AMERICAN M A M MINERAL0003-004X GEOCHEMIST地球化学与地球3地学N APPLIED GEO APPL GEOCHE0883-2927GEOCHEMIST地球化学与地球3地学N AQUATIC GEOAQUAT GEOC1380-6165GEOCHEMIST地球化学与地球4地学N BULLETIN OF B SEISMOL SO0037-1106GEOCHEMIST地球化学与地球3地学N DYNAMICS OFDYNAM ATMO0377-0265GEOCHEMIST地球化学与地球4地学NGEOCHEMICA GEOCHEM T1467-4866GEOCHEMIST地球化学与地球3地学N3地学N GEOFLUIDSGEOFLUIDS1468-8115GEOCHEMIST地球化学与地球4地学N GEOPHYSICS G EOPHYSICS0016-8033GEOCHEMIST地球化学与地球4地学N J ATMOS SOL-1364-6826GEOCHEMIST地球化学与地球JOURNAL OF A3地学N J GEOCHEM E0375-6742GEOCHEMIST地球化学与地球JOURNAL OF G3地学N Lithosphere LITHOSPHERE1941-8264GEOCHEMIST地球化学与地球3地学N MINERALIUM M INER DEPOS0026-4598GEOCHEMIST地球化学与地球4地学N MINERALOGYMINER PETRO0930-0708GEOCHEMIST地球化学与地球4地学N NONLINEAR P NONLINEAR P1023-5809GEOCHEMIST地球化学与地球0033-4553GEOCHEMIST地球化学与地球4地学N PURE AND AP PURE APPL GE4地学N RADIOCARBO RADIOCARBO0033-8222GEOCHEMIST地球化学与地球4地学N Solid Earth SOLID EARTH1869-9510GEOCHEMIST地球化学与地球4地学N Acta Geodaetica ACTA GEOD G2213-5812GEOCHEMIST地球化学与地球4地学N Acta Geodynam ACTA GEODY1214-9705GEOCHEMIST地球化学与地球4地学N1895-6572GEOCHEMIST地球化学与地球Acta Geophysic ACTA GEOPHY4地学N ANNALS OF G ANN GEOPHY1593-5213GEOCHEMIST地球化学与地球1672-7975GEOCHEMIST地球化学与地球4地学N Applied Geophy APPL GEOPHY1982-2170GEOCHEMIST地球化学与地球4地学N Boletim de Cien B CIENC GEOD4地学N Bollettino di Ge B GEOFIS TEO0006-6729GEOCHEMIST地球化学与地球4地学N0009-2819GEOCHEMIST地球化学与地球CHEM ERDE-GCHEMIE DER E4地学N CHINESE J GE0001-5733GEOCHEMIST地球化学与地球CHINESE JOUR4地学N0812-3985GEOCHEMIST地球化学与地球EXPLOR GEOPExploration Geo4地学N0016-7029GEOCHEMIST地球化学与地球GEOCHEMIST GEOCHEM INT4地学N GEOCHEMICA GEOCHEM J0016-7002GEOCHEMIST地球化学与地球GEOCHEMIST GEOCHEM-EX1467-7873GEOCHEMIST地球化学与地球4地学N4地学N Geofisica Intern GEOFIS INT0016-7169GEOCHEMIST地球化学与地球4地学N Geofizika GEOFIZIKA0352-3659GEOCHEMIST地球化学与地球4地学N0016-7932GEOCHEMIST地球化学与地球GEOMAGN AEGEOMAGNETI4地学N0016-8025GEOCHEMIST地球化学与地球GEOPHYSICALGEOPHYS PRO4地学N GEOTECTONI GEOTECTONI0016-8521GEOCHEMIST地球化学与地球4地学N IZV-PHYS SOL1069-3513GEOCHEMIST地球化学与地球IZVESTIYA-PH4地学N1793-4311GEOCHEMIST地球化学与地球Journal of Earth J EARTHQ TSU4地学N1083-1363GEOCHEMIST地球化学与地球J ENVIRON ENJOURNAL OF E0963-0651GEOCHEMIST地球化学与地球4地学N J SEISM EXPLOJOURNAL OF S4地学N J SEISMOL1383-4649GEOCHEMIST地球化学与地球JOURNAL OF S4地学N Journal of VolcaJ VOLCANOL 0742-0463GEOCHEMIST地球化学与地球LITHOLOGY A4地学N LITHOL MINE0024-4902GEOCHEMIST地球化学与地球4地学N MAR GEOD0149-0419GEOCHEMIST地球化学与地球MARINE GEOD4地学N MAR GEOPHY0025-3235GEOCHEMIST地球化学与地球MARINE GEOPNEAR SURF G1569-4445GEOCHEMIST地球化学与地球4地学N Near Surface Ge4地学N PERIOD MINE0369-8963GEOCHEMIST地球化学与地球Periodico di Min1529-9074GEOCHEMIST地球化学与地球4地学N Petrophysics PETROPHYSIC0039-3169GEOCHEMIST地球化学与地球4地学N STUDIA GEOP STUD GEOPHY0012-8252GEOSCIENCESEARTH-SCIEN EARTH-SCI RE地球科学综合1地学N0016-7606GEOSCIENCESGEOLOGICAL GEOL SOC AM地球科学综合1地学N1991-959X GEOSCIENCESGeoscientific M G EOSCI MODE地球科学综合1地学N1342-937X GEOSCIENCESGONDWANA RGONDWANA R地球科学综合1地学N NAT GEOSCI1752-0894GEOSCIENCESNature Geoscien地球科学综合1地学N PRECAMBRIA PRECAMBRIA0301-9268GEOSCIENCES地球科学综合1地学N QUATERNARY0277-3791GEOSCIENCESQUATERNARY地球科学综合1地学N AM J SCI0002-9599GEOSCIENCESAMERICAN JO地球科学综合2地学N BULLETIN OF B VOLCANOL0258-8900GEOSCIENCES地球科学综合3地学N BASIN RESEA B ASIN RES0950-091X GEOSCIENCES地球科学综合2地学N Climate of the P CLIM PAST1814-9324GEOSCIENCES地球科学综合2地学N Cryosphere CRYOSPHERE1994-0416GEOSCIENCES地球科学综合2地学N0197-9337GEOSCIENCESEARTH SURF PEARTH SURFA地球科学综合2地学N2190-4979GEOSCIENCESEarth System D E ARTH SYST D地球科学综合2地学N0169-555X GEOSCIENCESGEOMORPHOLGEOMORPHOL地球科学综合2地学N GEOPHYS RES0094-8276GEOSCIENCESGEOPHYSICAL地球科学综合2地学N HOLOCENE HOLOCENE0959-6836GEOSCIENCES地球科学综合2地学N1027-5606GEOSCIENCESHYDROLOGY HYDROL EART地球科学综合2地学N J GEOL SOC L0016-7649GEOSCIENCESJOURNAL OF T地球科学综合2地学N0148-0227GEOSCIENCESJ GEOPHYS REJOURNAL OF G地球科学综合2地学N J GLACIOL0022-1430GEOSCIENCESJOURNAL OF G地球科学综合2地学N J HYDROL0022-1694GEOSCIENCESJOURNAL OF H地球科学综合2地学N JOURNAL OF Q0267-8179GEOSCIENCESJ QUATERNAR地球科学综合2地学N PALAEOGEOG0031-0182GEOSCIENCESPALAEOGEOG地球科学综合2地学N PALEOCEANO PALEOCEANO0883-8305GEOSCIENCES地球科学综合2地学N PROGRESS IN PROG PHYS G0309-1333GEOSCIENCES地球科学综合2地学N Quaternary Geo QUAT GEOCH1871-1014GEOSCIENCES地球科学综合2地学N ADV GEOPHY0065-2687GEOSCIENCESADVANCES IN地球科学综合4地学N ANNALES GEOANN GEOPHY0992-7689GEOSCIENCES地球科学综合3地学N0260-3055GEOSCIENCESANNALS OF G ANN GLACIOL地球科学综合3地学N ANTARCTIC S ANTARCT SCI0954-1020GEOSCIENCES地球科学综合3地学N1075-2196GEOSCIENCESArchaeological ARCHAEOL PR地球科学综合3地学N BOREAS BOREAS0300-9483GEOSCIENCES地球科学综合3地学N COMPUT GEO0098-3004GEOSCIENCESCOMPUTERS &地球科学综合3地学N CR GEOSCI1631-0713GEOSCIENCESCOMPTES REN地球科学综合3地学N Earth Interactio EARTH INTER1087-3562GEOSCIENCES地球科学综合3地学N ENG GEOL0013-7952GEOSCIENCESENGINEERING地球科学综合4地学N Geoheritage GEOHERITAG1867-2477GEOSCIENCES地球科学综合3地学N GEOLOGICAL GEOL J0072-1050GEOSCIENCES地球科学综合3地学N GEOLOGICAL GEOL MAG0016-7568GEOSCIENCES地球科学综合3地学N0276-0460GEOSCIENCESGEO-MARINE GEO-MAR LET地球科学综合3地学N Geosphere GEOSPHERE1553-040X GEOSCIENCES地球科学综合3地学N GEOTEXTILES0266-1144GEOSCIENCESGEOTEXT GEO地球科学综合3地学N HYDROGEOL 1431-2174GEOSCIENCESHYDROGEOLO地球科学综合3地学N INTERNATION1437-3254GEOSCIENCESINT J EARTH S地球科学综合3地学N INT J SPELEOL0392-6672GEOSCIENCESINTERNATION地球科学综合3地学N0305-4403GEOSCIENCESJ ARCHAEOL SJOURNAL OF A地球科学综合3地学N J ASIAN EART1367-9120GEOSCIENCESJOURNAL OF A地球科学综合3地学N J MARINE SYS0924-7963GEOSCIENCESJOURNAL OF M地球科学综合3地学N J PALEOLIMN0921-2728GEOSCIENCESJOURNAL OF P地球科学综合3地学N J S AM EARTH0895-9811GEOSCIENCESJOURNAL OF S地球科学综合3地学N0191-8141GEOSCIENCESJ STRUCT GEOJOURNAL OF S地球科学综合3地学N J VOLCANOL 0377-0273GEOSCIENCESJOURNAL OF V地球科学综合3地学N Landslides LANDSLIDES1612-510X GEOSCIENCES地球科学综合3地学N MAR GEOL0025-3227GEOSCIENCESMARINE GEOL地球科学综合3地学N MARINE AND MAR PETROL 0264-8172GEOSCIENCES地球科学综合3地学N Mathematical G MATH GEOSC1874-8961GEOSCIENCES地球科学综合4地学N NATURAL HA N AT HAZARD1561-8633GEOSCIENCES地球科学综合3地学N PHOTOGRAMM0099-1112GEOSCIENCESPHOTOGRAMM地球科学综合3地学N POLAR RESEA POLAR RES0800-0395GEOSCIENCES地球科学综合3地学N1040-6182GEOSCIENCESQUATERN INTQUATERNARY地球科学综合3地学N QUATERNARY0033-5894GEOSCIENCESQUATERNARY地球科学综合3地学N TERRA NOVA T ERRA NOVA0954-4879GEOSCIENCES地球科学综合3地学N ACTA CARSOL0583-6050GEOSCIENCESACTA CARSOL地球科学综合4地学N ACTA GEOLO A CTA GEOL S1000-9515GEOSCIENCES地球科学综合4地学NActa Montanisti ACTA MONTA1335-1788GEOSCIENCES地球科学综合4地学N1866-7511GEOSCIENCESArabian Journal ARAB J GEOSC地球科学综合4地学N Archaeological ARCHAEOL A1866-9557GEOSCIENCES地球科学综合4地学N0003-813X GEOSCIENCESARCHAEOMETARCHAEOMET地球科学综合4地学N0812-0099GEOSCIENCESAUSTRALIAN AUST J EARTH地球科学综合4地学N Austrian Journa AUSTRIAN J E2072-7151GEOSCIENCES地球科学综合4地学N0011-6297GEOSCIENCESBULLETIN OF B GEOL SOC D地球科学综合4地学N BULLETIN OF B GEOSCI1214-1119GEOSCIENCES地球科学综合4地学N BULLETIN DE B SOC GEOL F0037-9409GEOSCIENCES地球科学综合4地学N0008-3674GEOSCIENCESCAN GEOTECHCANADIAN GE地球科学综合4地学N CAN J EARTH 0008-4077GEOSCIENCESCANADIAN JO地球科学综合4地学N Central Europea CENT EUR J G2081-9900GEOSCIENCES地球科学综合4地学N0009-8604GEOSCIENCESCLAYS AND C CLAY CLAY M地球科学综合4地学N CLAY MINER0009-8558GEOSCIENCESCLAY MINERA地球科学综合4地学N COMPUT GEO0266-352X GEOSCIENCESCOMPUTERS A地球科学综合4地学N COMPUTATIO COMPUTAT G1420-0597GEOSCIENCES地球科学综合4地学N DOKLADY EA DOKL EARTH 1028-334X GEOSCIENCES地球科学综合4地学N Earth and Envir EARTH ENV S1755-6910GEOSCIENCES地球科学综合4地学N EARTH SCIEN EARTH SCI HI0736-623X GEOSCIENCES地球科学综合4地学N EARTH SCI IN1865-0473GEOSCIENCESEarth Science In地球科学综合4地学N EARTH SCI RE1794-6190GEOSCIENCESEarth Sciences R地球科学综合4地学N ENVIRON ENG1078-7275GEOSCIENCESENVIRONMEN地球科学综合4地学N EPISODES EPISODES0705-3797GEOSCIENCES地球科学综合4地学N ERDE ERDE0013-9998GEOSCIENCES地球科学综合4地学N1736-4728GEOSCIENCESEstonian Journa EST J EARTH S地球科学综合4地学N2095-0195GEOSCIENCESFrontiers of Ear FRONT EARTH地球科学综合4地学N GEOARABIA GEOARABIA1025-6059GEOSCIENCES地球科学综合4地学N GEOARCHAEO0883-6353GEOSCIENCESGEOARCHAEO地球科学综合4地学N1010-6049GEOSCIENCESGeocarto Intern GEOCARTO IN地球科学综合4地学N1733-8387GEOSCIENCESGEOCHRONOMGEOCHRONOM地球科学综合4地学N0985-3111GEOSCIENCESGEODINAMIC GEODIN ACTA地球科学综合4地学N1335-0552GEOSCIENCESGEOLOGICA CGEOL CARPAT地球科学综合4地学N GEOL CROAT1330-030X GEOSCIENCESGEOLOGIA CR地球科学综合4地学N Geomatics Natu GEOMAT NAT1947-5705GEOSCIENCES地球科学综合4地学N1266-5304GEOSCIENCESGeomorphologieGEOMORPHOL地球科学综合4地学N GEOSCIENCE GEOSCI CAN0315-0941GEOSCIENCES地球科学综合4地学NGEOSCI J1226-4806GEOSCIENCESGEOSCIENCES地球科学综合4地学N1072-6349GEOSCIENCESGEOSYNTHET GEOSYNTH IN地球科学综合4地学N ISLAND ARC ISL ARC1038-4871GEOSCIENCES地球科学综合4地学N Italian Journal o ITAL J GEOSC2038-1719GEOSCIENCES地球科学综合4地学N J AFR EARTH 1464-343X GEOSCIENCESJOURNAL OF A地球科学综合4地学N JOURNAL OF AJ APPL GEOPH0926-9851GEOSCIENCES地球科学综合4地学N J CAVE KARST1090-6924GEOSCIENCESJOURNAL OF C地球科学综合4地学N0749-0208GEOSCIENCESJ COASTAL REJOURNAL OF C地球科学综合4地学N1674-487X GEOSCIENCESJournal of Earth J EARTH SCI-C地球科学综合4地学N Journal of Earth J EARTH SYST0253-4126GEOSCIENCES地球科学综合4地学N J GEOL SOC IN0016-7622GEOSCIENCESJOURNAL OF T地球科学综合4地学N J GEOSCI-CZE1802-6222GEOSCIENCESJournal of Geosc地球科学综合4地学N0141-6421GEOSCIENCESJ PETROL GEOJOURNAL OF P地球科学综合4地学N Jokull JOKULL0449-0576GEOSCIENCES地球科学综合4地学N0016-7746GEOSCIENCESNETH J GEOSCNETHERLAND地球科学综合4地学N0028-8306GEOSCIENCESNEW ZEALAN NEW ZEAL J G地球科学综合4地学N NORWEGIAN NORW J GEOL0029-196X GEOSCIENCES地球科学综合4地学N PETROL GEOS1354-0793GEOSCIENCESPETROLEUM G地球科学综合4地学N PETROLOGY PETROLOGY+0869-5911GEOSCIENCES地球科学综合4地学N0031-868X GEOSCIENCESPHOTOGRAMMPHOTOGRAMM地球科学综合4地学N PHYSICS AND PHYS CHEM E1474-7065GEOSCIENCES地球科学综合4地学N PHYSICAL GE PHYS GEOGR0272-3646GEOSCIENCES地球科学综合4地学N POLISH POLAR0138-0338GEOSCIENCESPOL POLAR RE地球科学综合4地学N QUARTERLY J Q J ENG GEOL1470-9236GEOSCIENCES地球科学综合4地学N QUATERNAIR QUATERNAIR1142-2904GEOSCIENCES地球科学综合4地学N REV MEX CIE1026-8774GEOSCIENCESREVISTA MEX地球科学综合4地学N1068-7971GEOSCIENCESRussian GeologyRUSS GEOL GE地球科学综合4地学N1819-7140GEOSCIENCESRussian Journal RUSS J PAC GE地球科学综合4地学N SCI CHINA EA1674-7313GEOSCIENCESScience China-E地球科学综合4地学N SURVEY REVI SURV REV0039-6265GEOSCIENCES地球科学综合4地学N Swiss Journal of SWISS J GEOS1661-8726GEOSCIENCES地球科学综合4地学N TERRESTRIAL TERR ATMOS 1017-0839GEOSCIENCES地球科学综合4地学N1300-0985GEOSCIENCESTURKISH JOURTURK J EARTH地球科学综合4地学N Z DTSCH GES 1860-1804GEOSCIENCESZeitschrift der D地球科学综合4地学N ZEITSCHRIFT Z GEOMORPH0372-8854GEOSCIENCES地球科学综合4地学N GEOLOGY GEOLOGY0091-7613GEOLOGY地质学1地学NINTERNATION0020-6814GEOLOGY地质学2地学N INT GEOL REVJ GEOL0022-1376GEOLOGY地质学2地学N JOURNAL OF G0263-4929GEOLOGY地质学1地学N J METAMORPHJOURNAL OF MORE GEOL RE0169-1368GEOLOGY地质学2地学N ORE GEOLOGYPERMAFROST PERMAFROST1045-6740GEOLOGY地质学2地学N SEDIMENTOL SEDIMENTOL0037-0746GEOLOGY地质学2地学N CRETACEOUS CRETACEOUS0195-6671GEOLOGY地质学3地学N FACIES FACIES0172-9179GEOLOGY地质学3地学N GEOFLUIDSGEOFLUIDS1468-8115GEOLOGY地质学3地学N GEOL ACTA1695-6133GEOLOGY地质学3地学N GEOLOGICA AJ SEDIMENT R1527-1404GEOLOGY地质学3地学N JOURNAL OF SLithosphere LITHOSPHERE1941-8264GEOLOGY地质学2地学N0078-0421GEOLOGY地质学2地学N NEWSLETTER NEWSL STRATPALAIOS PALAIOS0883-1351GEOLOGY地质学3地学N0037-0738GEOLOGY地质学3地学N SEDIMENTAR SEDIMENT GEACTA GEOLO A CTA GEOL P0001-5709GEOLOGY地质学4地学N ACTA PETROL1000-0569GEOLOGY地质学4地学N ACTA PETROLANDEAN GEO0718-7106GEOLOGY地质学3地学N Andean Geology0208-9068GEOLOGY地质学4地学N ANNALES SOCANN SOC GEOATLANTIC GE ATL GEOL0843-5561GEOLOGY地质学4地学N BULLETIN OF B GEOL SOC F0367-5211GEOLOGY地质学4地学N Baltica BALTICA0067-3064GEOLOGY地质学4地学N0891-2556GEOLOGY地质学4地学N CARBONATES CARBONATE E1634-0744GEOLOGY地质学4地学N CARNETS DE CARNETS GEOESTUDIOS GE ESTUD GEOL-0367-0449GEOLOGY地质学4地学N0435-3676GEOLOGY地质学3地学N GEOGRAFISKAGEOGR ANN AGEOL BELG1374-8505GEOLOGY地质学4地学N GEOLOGICA BGEOLOGY OF GEOL ORE DE1075-7015GEOLOGY地质学4地学N GEOLOGICAL GEOL Q1641-7291GEOLOGY地质学4地学N GEOLOGICAL GEOL SURV D1604-8156GEOLOGY地质学4地学N GFF GFF1103-5897GEOLOGY地质学4地学N HIMALAYAN HIMAL GEOL0971-8966GEOLOGY地质学4地学N JOURNAL OF I J IBER GEOL1698-6180GEOLOGY地质学4地学N LITHOL MINE0024-4902GEOLOGY地质学4地学N LITHOLOGY A0028-8306GEOLOGY地质学4地学N NEW ZEALAN NEW ZEAL J GOFIOLITI OFIOLITI0391-2612GEOLOGY地质学3地学NPROCEEDINGSP GEOLOGIST0016-7878GEOLOGY地质学4地学NP YORKS GEO0044-0604GEOLOGY地质学4地学N PROCEEDINGS1344-1698GEOLOGY地质学4地学N RESOURCE GERESOUR GEOLRIVISTA ITAL RIV ITAL PAL0035-6883GEOLOGY地质学4地学NSCOT J GEOL0036-9276GEOLOGY地质学4地学N SCOTTISH JOUSTRATIGR GE0869-5938GEOLOGY地质学4地学N STRATIGRAPH1547-139X GEOLOGY地质学4地学N Stratigraphy STRATIGRAPHARCHAEOMET0003-813X CHEMISTRY, AARCHAEOMET分析化学4地学N J ATMOS OCE0739-0572ENGINEERINGJOURNAL OF A工程:大洋2地学N APPLIED OCE APPL OCEAN 0141-1187ENGINEERING工程:大洋3地学N ENG GEOL0013-7952ENGINEERINGENGINEERING工程:地质2地学N2049-825X ENGINEERINGGeotechnique L GEOTECH LET工程:地质2地学N0266-1144ENGINEERINGGEOTEXTILESGEOTEXT GEO工程:地质1地学N Landslides LANDSLIDES1612-510X ENGINEERING工程:地质1地学N1854-0171ENGINEERINGACTA GEOTECActa Geotechnic工程:地质4地学N0008-3674ENGINEERINGCANADIAN GECAN GEOTECH工程:地质4地学N COMPUT GEO0266-352X ENGINEERINGCOMPUTERS A工程:地质3地学N2092-7614ENGINEERINGEARTHQ STRUEarthquakes and工程:地质3地学N1078-7275ENGINEERINGENVIRON ENGENVIRONMEN工程:地质4地学N1072-6349ENGINEERINGGEOSYNTHET GEOSYNTH IN工程:地质4地学N1532-3641ENGINEERINGInternational Jo INT J GEOMEC工程:地质3地学N1083-1363ENGINEERINGJ ENVIRON ENJOURNAL OF E工程:地质4地学N QUARTERLY J Q J ENG GEOL1470-9236ENGINEERING工程:地质4地学N2地学N IEEE Journal of IEEE J-STARS1939-1404ENGINEERING工程:电子与电ENVIRONMEN1078-7275ENGINEERINGENVIRON ENG工程:环境4地学N Petroleum Scien PETROL SCI1672-5107ENGINEERING工程:石油3地学N Petrophysics PETROPHYSIC1529-9074ENGINEERING工程:石油4地学N J HYDROL0022-1694ENGINEERINGJOURNAL OF H工程:土木1地学N2092-7614ENGINEERINGEarthquakes andEARTHQ STRU工程:土木3地学N SURVEY REVI SURV REV0039-6265ENGINEERING工程:土木4地学N J SYST PALAE1477-2019PALEONTOLO古生物学2地学N JOURNAL OF SPALAEOGEOG0031-0182PALEONTOLO古生物学2地学N PALAEOGEOGPALEOBIOLOG0094-8373PALEONTOLO古生物学1地学N PALEOBIOLOGPALEOCEANO PALEOCEANO0883-8305PALEONTOLO古生物学1地学N0567-7920PALEONTOLO古生物学3地学N ACTA PALAEOACTA PALAEOCRETACEOUS CRETACEOUS0195-6671PALEONTOLO古生物学2地学NFACIES FACIES0172-9179PALEONTOLO古生物学3地学N J FORAMIN RE0096-1191PALEONTOLO古生物学2地学N JOURNAL OF F0272-4634PALEONTOLO古生物学2地学N JOURNAL OF VJ VERTEBR PALETHAIA LETHAIA0024-1164PALEONTOLO古生物学2地学N0377-8398PALEONTOLO古生物学2地学N MAR MICROPAMARINE MICRPALAEONTOL PALAEONTOL0031-0239PALEONTOLO古生物学3地学N PALAIOS PALAIOS0883-1351PALEONTOLO古生物学2地学N0034-6667PALEONTOLO古生物学3地学N REVIEW OF PAREV PALAEOBALCHERINGA ALCHERINGA0311-5518PALEONTOLO古生物学4地学N AMEGHINIAN AMEGHINIAN0002-7014PALEONTOLO古生物学4地学N0753-3969PALEONTOLO古生物学4地学N ANNALES DE ANN PALEONTBULLETIN OF B GEOSCI1214-1119PALEONTOLO古生物学3地学N0375-7633PALEONTOLO古生物学4地学N BOLLETTINO B SOC PALEONCARNETS DE CARNETS GEO1634-0744PALEONTOLO古生物学4地学N CR PALEVOL1631-0683PALEONTOLO古生物学4地学N COMPTES RENEarth and Envir EARTH ENV S1755-6910PALEONTOLO古生物学4地学N0016-6995PALEONTOLO古生物学4地学N GEOBIOS GEOBIOS-LYO1733-8387PALEONTOLO古生物学3地学N GEOCHRONOMGEOCHRONOMGEODIVERSIT GEODIVERSIT1280-9659PALEONTOLO古生物学4地学N GFF GFF1103-5897PALEONTOLO古生物学4地学N J PALAEONTO0552-9360PALEONTOLO古生物学4地学N JOURNAL OF TJ PALEONTOL0022-3360PALEONTOLO古生物学3地学N JOURNAL OF PNEUES JAHRB NEUES JAHRB0077-7749PALEONTOLO古生物学4地学N P GEOLOGIST0016-7878PALEONTOLO古生物学3地学N PROCEEDINGS0375-0442PALEONTOLO古生物学3地学N PALAEONTOGPALAEONTOGPALAEONTOG0375-0299PALEONTOLO古生物学4地学N PALAEONTOGPALAEONTOL PALAEONTOL1935-3952PALEONTOLO古生物学3地学N PALAEONTOL0031-0220PALEONTOLO古生物学3地学N PalaeontologischPALEONTOLO PALEONTOL J0031-0301PALEONTOLO古生物学4地学N PALYNOLOGY0191-6122PALEONTOLO古生物学4地学N PALYNOLOGYRIVISTA ITAL RIV ITAL PAL0035-6883PALEONTOLO古生物学4地学N SPEC PAP PAL0038-6804PALEONTOLO古生物学3地学N SPECIAL PAPESTRATIGRAPHSTRATIGR GE0869-5938PALEONTOLO古生物学4地学N1547-139X PALEONTOLO古生物学3地学N Stratigraphy STRATIGRAPHAnnual Review ANNU REV MA1941-1405OCEANOGRAP海洋学1地学N0967-0637OCEANOGRAPDEEP-SEA RESDEEP-SEA RES海洋学2地学NJOURNAL OF P0022-3670OCEANOGRAPJ PHYS OCEAN海洋学2地学N0024-3590OCEANOGRAPLIMNOL OCEALIMNOLOGY A海洋学2地学N OCEAN MODE OCEAN MODE1463-5003OCEANOGRAP海洋学2地学N OCEANOGRAP1042-8275OCEANOGRAPOCEANOGRAP海洋学2地学N PALEOCEANO PALEOCEANO0883-8305OCEANOGRAP海洋学2地学N0079-6611OCEANOGRAPPROGRESS IN PROG OCEANO海洋学1地学N ATMOSPHERE ATMOS OCEA0705-5900OCEANOGRAP海洋学4地学N0278-4343OCEANOGRAPCONTINENTA CONT SHELF R海洋学3地学N0967-0645OCEANOGRAPDEEP-SEA RESDEEP-SEA RES海洋学2地学N0377-0265OCEANOGRAPDYNAM ATMODYNAMICS OF海洋学4地学N0272-7714OCEANOGRAPESTUARINE C ESTUAR COAS海洋学3地学N0276-0460OCEANOGRAPGEO-MARINE GEO-MAR LET海洋学3地学N J MARINE SYS0924-7963OCEANOGRAPJOURNAL OF M海洋学3地学N J SEA RES1385-1101OCEANOGRAPJOURNAL OF S海洋学3地学N1541-5856OCEANOGRAPLIMNOL OCEALIMNOLOGY A海洋学3地学N MAR GEOL0025-3227OCEANOGRAPMARINE GEOL海洋学3地学N OCEAN DYNA OCEAN DYNA1616-7341OCEANOGRAP海洋学3地学N Ocean Science OCEAN SCI1812-0784OCEANOGRAP海洋学3地学N POLAR RESEA POLAR RES0800-0395OCEANOGRAP海洋学3地学N TELLUS A0280-6495OCEANOGRAPTELLUS SERIE海洋学2地学N ACTA OCEAN ACTA OCEAN0253-505X OCEANOGRAP海洋学4地学N APPLIED OCE APPL OCEAN 0141-1187OCEANOGRAP海洋学4地学N1836-716X OCEANOGRAPAustralian Mete AUST METEOR海洋学4地学N BULLETIN OF B MAR SCI0007-4977OCEANOGRAP海洋学4地学N BRAZ J OCEAN1679-8759OCEANOGRAPBRAZILIAN JO海洋学4地学N0254-4059OCEANOGRAPCHIN J OCEANCHINESE JOUR海洋学4地学N HELGOLAND HELGOLAND 1438-387X OCEANOGRAP海洋学4地学N Indian Journal o INDIAN J GEO0379-5136OCEANOGRAP海洋学4地学N IZV ATMOS O0001-4338OCEANOGRAPIZVESTIYA AT海洋学4地学N J MAR RES0022-2402OCEANOGRAPJOURNAL OF M海洋学4地学N1672-5182OCEANOGRAPJournal of OceanJ OCEAN U CH海洋学4地学N J OCEANOGR0916-8370OCEANOGRAPJOURNAL OF O海洋学4地学N1755-876X OCEANOGRAPJ OPER OCEANJournal of Opera海洋学4地学N MAR GEOD0149-0419OCEANOGRAPMARINE GEOD海洋学4地学N MAR GEOPHY0025-3235OCEANOGRAPMARINE GEOP海洋学4地学N OCEANOLOGI OCEANOL HY1730-413X OCEANOGRAP海洋学4地学NOCEANOLOGI OCEANOLOGI0078-3234OCEANOGRAP海洋学4地学N0001-4370OCEANOGRAPOCEANOLOGYOCEANOLOGY海洋学4地学N TERRESTRIAL TERR ATMOS 1017-0839OCEANOGRAP海洋学4地学N1地学N Annual Review ANNU REV MA1941-1405MARINE & FR海洋与淡水生物3地学N ESTUARINE C ESTUAR COAS0272-7714MARINE & FR海洋与淡水生物2地学N J MARINE SYS0924-7963MARINE & FR海洋与淡水生物JOURNAL OF M3地学N JOURNAL OF SJ SEA RES1385-1101MARINE & FR海洋与淡水生物4地学N BULLETIN OF B MAR SCI0007-4977MARINE & FR海洋与淡水生物4地学N1679-8759MARINE & FR海洋与淡水生物BRAZ J OCEANBRAZILIAN JO4地学N Fundamental an FUND APPL LI1863-9135MARINE & FR海洋与淡水生物4地学N HELGOLAND HELGOLAND 1438-387X MARINE & FR海洋与淡水生物LIMNOL OCEA0024-3590LIMNOLOGY湖沼学1地学N LIMNOLOGY AJ PALEOLIMN0921-2728LIMNOLOGY湖沼学2地学N JOURNAL OF P1541-5856LIMNOLOGY湖沼学3地学N LIMNOL OCEALIMNOLOGY AANNALES DE ANN LIMNOL-0003-4088LIMNOLOGY湖沼学4地学N0254-4059LIMNOLOGY湖沼学4地学N CHINESE JOURCHIN J OCEANFundamental an FUND APPL LI1863-9135LIMNOLOGY湖沼学4地学N J LIMNOL1129-5767LIMNOLOGY湖沼学4地学N JOURNAL OF LLIMNOLOGY LIMNOLOGY1439-8621LIMNOLOGY湖沼学4地学N ANTARCTIC S ANTARCT SCI0954-1020ENVIRONMEN环境科学4地学N CLIMATE RES CLIM RES0936-577X ENVIRONMEN环境科学3地学N INT J BIOMET0020-7128ENVIRONMENINTERNATION环境科学3地学N J PALEOLIMN0921-2728ENVIRONMENJOURNAL OF P环境科学3地学N ARCTIC ANTA1523-0430ENVIRONMENARCT ANTARC环境科学4地学N ARCTIC ARCTIC0004-0843ENVIRONMEN环境科学4地学N1010-6049ENVIRONMENGeocarto Intern GEOCARTO IN环境科学4地学N J ATMOS CHE0167-7764ENVIRONMENJOURNAL OF A环境科学4地学N JOURNAL OF C0749-0208ENVIRONMENJ COASTAL RE环境科学4地学N MT RES DEV0276-4741ENVIRONMENMOUNTAIN RE环境科学4地学N PHYSICAL GE PHYS GEOGR0272-3646ENVIRONMEN环境科学4地学N COMPUT GEO0098-3004COMPUTER SC3地学N COMPUTERS &计算机:跨学科4地学N COMPUT GEO0266-352X COMPUTER SCCOMPUTERS A计算机:跨学科3地学N COMPUTATIO COMPUTAT G1420-0597COMPUTER SC计算机:跨学科Earth Science InEARTH SCI IN1865-0473COMPUTER SC4地学N计算机:跨学科3地学N INT J GEOGR I1365-8816COMPUTER SCINTERNATION计算机:信息系3地学N GEOINFORMA GEOINFORMA1384-6175COMPUTER SC计算机:信息系JOURNAL OF SJ SYST PALAE1477-2019EVOLUTIONA进化生物学4地学N0094-8373EVOLUTIONA进化生物学4地学N PALEOBIOLOGPALEOBIOLOGEARTH SCIEN EARTH SCI HI0736-623X HISTORY & PH4地学N科学史与科学哲APPLIED CLAY0169-1317MINERALOGYAPPL CLAY SC矿物学3地学N CONTRIB MIN0010-7999MINERALOGYCONTRIBUTIO矿物学2地学N Elements ELEMENTS1811-5209MINERALOGY矿物学2地学N LITHOS LITHOS0024-4937MINERALOGY矿物学1地学N ORE GEOL RE0169-1368MINERALOGYORE GEOLOGY矿物学2地学N1529-6466MINERALOGYREV MINERALREVIEWS IN M矿物学2地学N AMERICAN M A M MINERAL0003-004X MINERALOGY矿物学3地学N MINERALIUM M INER DEPOS0026-4598MINERALOGY矿物学3地学N MINER PETRO0930-0708MINERALOGYMINERALOGY矿物学3地学N MINERAL MA0026-461X MINERALOGYMINERALOGIC矿物学3地学N0342-1791MINERALOGYPHYSICS AND PHYS CHEM M矿物学3地学N0008-4476MINERALOGYCANADIAN M C AN MINERAL矿物学4地学N0009-8604MINERALOGYCLAYS AND C CLAY CLAY M矿物学4地学N CLAY MINER0009-8558MINERALOGYCLAY MINERA矿物学4地学N0935-1221MINERALOGYEUROPEAN JO EUR J MINERA矿物学4地学N GEMS GEMOL0016-626X MINERALOGYGEMS & GEMO矿物学4地学N GEOLOGY OF GEOL ORE DE1075-7015MINERALOGY矿物学4地学N Journal of Mine J MINER PETR1345-6296MINERALOGY矿物学4地学N LITHOL MINE0024-4902MINERALOGYLITHOLOGY A矿物学4地学N0077-7757MINERALOGYNEUES JAHRB NEUES JB MIN矿物学4地学N Periodico di MinPERIOD MINE0369-8963MINERALOGY矿物学4地学N PETROLOGY PETROLOGY+0869-5911MINERALOGY矿物学4地学N1344-1698MINERALOGYRESOUR GEOLRESOURCE GE矿物学4地学N1地学N ORE GEOL RE0169-1368MINING & MINORE GEOLOGY矿业与矿物加工4地学N Acta Geodynam ACTA GEODY1214-9705MINING & MIN矿业与矿物加工4地学N Acta Montanisti ACTA MONTA1335-1788MINING & MIN矿业与矿物加工J APPL GEOPH0926-9851MINING & MINJOURNAL OF A3地学N矿业与矿物加工Petroleum Scien PETROL SCI1672-5107ENERGY & FU能源与燃料4地学N1地学N ATMOSPHERICATMOS CHEM1680-7316METEOROLOG气象与大气科学1地学N BULLETIN OF B AM METEOR0003-0007METEOROLOG气象与大气科学CLIMATE DYNCLIM DYNAM0930-7575METEOROLOG2地学N气象与大气科学2地学N Journal of Adva J ADV MODEL1942-2466METEOROLOG气象与大气科学2地学N J CLIMATE0894-8755METEOROLOGJOURNAL OF C气象与大气科学Atmospheric Me2地学N ATMOS MEAS1867-1381METEOROLOG气象与大气科学2地学N Climate of the P CLIM PAST1814-9324METEOROLOG气象与大气科学3地学N INT J CLIMAT0899-8418METEOROLOGINTERNATION气象与大气科学3地学N J ATMOS SCI0022-4928METEOROLOGJOURNAL OF T气象与大气科学2地学N1525-755X METEOROLOGJ HYDROMETEJOURNAL OF H气象与大气科学3地学N0027-0644METEOROLOGMON WEATHEMONTHLY WE气象与大气科学3地学N OCEAN MODE OCEAN MODE1463-5003METEOROLOG气象与大气科学2地学N0035-9009METEOROLOGQUARTERLY J Q J ROY METE气象与大气科学2地学N TELLUS B0280-6509METEOROLOGTELLUS SERIE气象与大气科学4地学N ANN GEOPHY0992-7689METEOROLOGANNALES GEO气象与大气科学4地学N ATMOSPHERE ATMOS OCEA0705-5900METEOROLOG气象与大气科学3地学N ATMOS RES0169-8095METEOROLOGATMOSPHERIC气象与大气科学1530-261X METEOROLOG4地学N Atmospheric Sc ATMOS SCI LE气象与大气科学0006-8314METEOROLOG3地学N BOUNDARY-L BOUND-LAY M气象与大气科学CLIMATE RES CLIM RES0936-577X METEOROLOG3地学N气象与大气科学4地学N0377-0265METEOROLOGDYNAMICS OFDYNAM ATMO气象与大气科学3地学N INT J BIOMET0020-7128METEOROLOGINTERNATION气象与大气科学3地学N Journal of Appli J APPL METEO1558-8424METEOROLOG气象与大气科学J ATMOS OCE0739-0572METEOROLOGJOURNAL OF A3地学N气象与大气科学4地学N J ATMOS SOL-1364-6826METEOROLOGJOURNAL OF A气象与大气科学NATURAL HA N AT HAZARD1561-8633METEOROLOG3地学N气象与大气科学4地学N NONLINEAR P NONLINEAR P1023-5809METEOROLOG气象与大气科学3地学N Ocean Science OCEAN SCI1812-0784METEOROLOG气象与大气科学3地学N TELLUS A0280-6495METEOROLOGTELLUS SERIE气象与大气科学4地学N0177-798X METEOROLOGTHEOR APPL CTHEORETICAL气象与大气科学WEATHER AN WEATHER FO0882-8156METEOROLOG3地学N气象与大气科学4地学N ACTA METEO0894-0525METEOROLOGActa Meteorolog气象与大气科学4地学N ADVANCES IN0256-1530METEOROLOGADV ATMOS S气象与大气科学4地学N Advances in Me ADV METEOR1687-9309METEOROLOG气象与大气科学1976-7633METEOROLOGAsia-Pacific Jou ASIA-PAC J AT4地学N气象与大气科学ATMOSFERA ATMOSFERA0187-6236METEOROLOG4地学N气象与大气科学4地学N Atmosphere ATMOSPHERE2073-4433METEOROLOG气象与大气科学4地学N1836-716X METEOROLOGAustralian Mete AUST METEOR气象与大气科学4地学N Geomatics Natu GEOMAT NAT1947-5705METEOROLOG气象与大气科学4地学N Idojaras IDOJARAS0324-6329METEOROLOG气象与大气科学4地学N IZVESTIYA ATIZV ATMOS O0001-4338METEOROLOG气象与大气科学JOURNAL OF AJ ATMOS CHE0167-7764METEOROLOG4地学N气象与大气科学4地学N0026-1165METEOROLOGJOURNAL OF TJ METEOROL S气象与大气科学1755-876X METEOROLOGJournal of Opera4地学N J OPER OCEAN气象与大气科学Journal of Tropi J TROP METEO1006-8775METEOROLOG4地学N气象与大气科学4地学N Mausam MAUSAM0252-9416METEOROLOG气象与大气科学METEOROLOGMETEOROL A1350-4827METEOROLOG4地学N气象与大气科学METEOROL A0177-7971METEOROLOG4地学N METEOROLOG气象与大气科学4地学N METEOROL Z0941-2948METEOROLOGMETEOROLOG气象与大气科学4地学N PHYSICS AND PHYS CHEM E1474-7065METEOROLOG气象与大气科学PHYSICAL GE PHYS GEOGR0272-3646METEOROLOG4地学N气象与大气科学4地学N1068-3739METEOROLOGRUSS METEORRussian Meteoro气象与大气科学4地学N SOLA SOLA1349-6476METEOROLOG气象与大气科学4地学N TERRESTRIAL TERR ATMOS 1017-0839METEOROLOG气象与大气科学Weather WEATHER0043-1656METEOROLOG4地学N气象与大气科学4地学N Weather Climat WEATHER CL1948-8327METEOROLOG气象与大气科学INT J BIOMET0020-7128PHYSIOLOGY生理学3地学N INTERNATIONPALEOBIOLOG0094-8373ECOLOGY生态学3地学N PALEOBIOLOGPOLAR RESEA POLAR RES0800-0395ECOLOGY生态学4地学N0138-0338ECOLOGY生态学4地学N POL POLAR REPOLISH POLAR3地学N0094-8373BIODIVERSITYPALEOBIOLOGPALEOBIOLOG生物多样性保护INT J BIOMET0020-7128BIOPHYSICS生物物理4地学N INTERNATIONMathematical G MATH GEOSC1874-8961MATHEMATIC3地学N数学跨学科应用1027-5606WATER RESOUHYDROLOGY HYDROL EART水资源1地学N JOURNAL OF HJ HYDROL0022-1694WATER RESOU水资源2地学N HYDROGEOL 1431-2174WATER RESOUHYDROGEOLO水资源3地学N NATURAL HA N AT HAZARD1561-8633WATER RESOU水资源3地学N Geomatics Natu GEOMAT NAT1947-5705WATER RESOU水资源4地学N PHYSICS AND PHYS CHEM E1474-7065WATER RESOU水资源4地学N ANN GEOPHY0992-7689ASTRONOMY 天文与天体物理4地学N ANNALES GEO0009-8604SOIL SCIENCE土壤科学4地学N CLAYS AND C CLAY CLAY M4地学N0003-813X CHEMISTRY, I无机化学与核化ARCHAEOMETARCHAEOMET0169-1317CHEMISTRY, PAPPLIED CLAYAPPL CLAY SC物理化学3地学N0009-8604CHEMISTRY, PCLAYS AND C CLAY CLAY M物理化学4地学N CLAY MINER0009-8558CHEMISTRY, PCLAY MINERA物理化学4地学N J GEODESY0949-7714REMOTE SENSJOURNAL OF G遥感2地学N IEEE Journal of IEEE J-STARS1939-1404REMOTE SENS遥感2地学N。

257ISSN: 1749-3889 ( print ) 1749-3897 (online)BimonthlyVol.7 (2009) No.3JuneEngland, UK ***************************.uk International Journal ofN o n l i n e a r S c i e n c e Edited by International Committee for Nonlinear Science, WAUPublished by World Academic Union (World Academic Press)CONTENTS259.New Exact Travelling Wave Solutions for Some Nonlinear Evolution EquationsA. Hendi268.A New Hierarchy of Generalized Fisher Equations and Its Bi- Hamiltonian StructuresLu Sun274.New Exact Solutions of Nonlinear Variants of the RLW, the PHI-four and Boussinesq Equations Based on Modified Extended Direct Algebraic MethodA. A. Soliman, H. A. Abdo283. Monotone Methods in Nonlinear Elliptic Boundary Value ProblemG.A.Afrouzi, Z.Naghizadeh, S.Mahdavi290. Influence of Solvents Polarity on NLO Properties of Fluorone Dye Ahmad Y. Nooraldeen1, M. Palanichant, P. K. Palanisamy301.Projective Synchronization of Chaotic Systems with Different Dimensions via Backstepping DesignXuerong Shi, Zhongxian Wang307.Adaptive Control and Synchronization of a Four-Dimensional Energy Resources System of JiangSu ProvinceLin Jia , Huanchao Tang312.Optimal Control of the Viscous KdV-Burgers Equation Using an Equivalent Index MethodAnna Gao, Chunyu Shen,Xinghua Fan319.Adaptive Control of Generalized Viscous Burgers’ Equation Xiaoyan Deng, Wenxia Chen, Jianmei Zhang327. Wavelet Density Degree of a Class of Wiener Processes Xuewen Xia, Ting Dai332.Niches’ Similarity Degree Based on Type-2 Fuzzy Niches’ Model Jing Hua, Yimin Li340.Full Process Nonlinear Analysis the Fatigue Behavior of the Crane Beam Strengthened with CFRPHuaming Zhu, Peigang Gu, Jinlong Wang, Qiyin Shi345.The Infinite Propagation Speed and the Limit Behavior for the B-family Equation with Dispersive TermXiuming Li353.The Classification of all Single Traveling Wave Solutions to Fornberg-Whitham EquationChunxiang Feng, Changxing Wu360.New Jacobi Elliptic Functions Solutions for the Higher-orderNonlinear Schrodinger EquationBaojian Hong, Dianchen Lu368.A Counterexample on Gap Property of Bi-Lipschitz Constants Ying Xiong, Lifeng Xi371.A Method for Recovering the Shape for Inverse Scattering Problem of Acoustic WavesLihua Cheng, Tieyan Lian, Ping Li379.An Approach of Image Hiding and Encryption Based on a New Hyper-chaotic SystemHongxing Yao, Meng Li258International Journal of Nonlinear Science (IJNS)BibliographicISSN: 1749-3889 (print), 1749-3897 (online), BimonthlyEdited by International Editorial Committee of Nonlinear Science, WAUPublished by World Academic Union (World Academic Press)Publisher Contact:Academic House, 113 Mill LaneWavertree Technology Park, Liverpool L13 4AH, England, UKEmail:******************.uk,*********************************URL: www. World Academic Union .comContribution enquiries and submittingThe paper(s) could be submitted to the managing editor ***************************.uk. Author also can contact our editorial offices by mail or email at addresses below directly.For more detail to submit papers please visit Editorial BoardEditor in Chief: Boling Guo, Institute of Applied Physics and Computational Mathematics, Beijing, 100088, China;************.cnCo-Editor in Chief: Lixin Tian, Nonlinear Scientific Research Center, Faculty of Science, Jiangsu University, Zhenjiang, Jiangsu,212013;China;**************.cn,************.cnStanding Members of Editorial Board:Ghasem Alizahdeh Afrouzi, Department ofMathematics, Faculty of Basic Sciences, Mazandaran University,Babolsar,Iran;**************.ir Stephen Anco, Department of Mathematics, Brock University, 500 Glenridge Avenue St. Catharines, ON L2S3A1,Canada;***************Adrian Constantin ,Department of Mathematics, Lund University,22100Lund,****************.seSweden;*************************.se,Ying Fan, Department of Management Science, Institute of Policy and Management, ChineseAcademy of Sciences, Beijing 100080,China,**************.cn.Juergen Garloff, University of Applied Sciences/ HTWG Konstanz, Faculty of Computer Science, Postfach100543, D-78405 Konstanz, Germany;************************Tasawar Hayat, Department of mathematics,Quaid-I-AzamUniversity,Pakistan,*****************Y Jiang, William Lee Innovation Center, University of Manchester, Manchester, M60 1QD UK;*******************Zhujun Jing,Institute of Mathematics, Academy of Mathematics and Systems Sciences, ChineseAcademy of Science, Beijing, 100080,China;******************Yue Liu,Department of Mathematics, University of Texas, Arlington,TX76019,USA;************Zengrong Liu,Department of Mathematics, Shanghai University, Shanghai, 201800,China;******************.cnNorio Okada, Disaster Prevention Research Institute, KyotoUniversity,****************.kyoto-u.ac.jp Jacques Peyriere,Université Paris-Sud, Mathématique, bˆa t. 42591405 ORSAY Cedex , France;************************,****************************.frWeiyi Su, Department of Mathematics, NanjingUniversity, Nanjing,Jiangsu, 210093,China;*************.cnKonstantina Trivisa ,Department of Mathematics, University of Maryland College Park,MD20472-4015,USA;****************.eduYaguang Wang,Department of Mathematics, Shanghai Jiao Tong University, Shanghai, 200240,China;***************.cnAbdul-Majid Wazwaz, 3700 W. 103rd Street Department of Mathematics and Computer Science, Saint Xavier University, Chicago, IL 60655 ,USA;**************Yiming Wei, Institute of Policy and management, Chinese Academy of Science, Beijing, 100080,China;*****************Zhiying Wen,Department of Mathematics, Tsinghua University, Beijing, 100084, China;*******************Zhenyuan Xu, Faculty of Science, Southern Yangtze University, Wuxi , Jiangsu 214063 ,China;*********************Huicheng Yi n, Department of Mathematics, Nanjing University, Nanjing, Jiangsu, 210093, China;****************.cnPingwen Zhang, School of Mathematic Sciences, Peking University, Beijing, 100871, China;**************.cnSecretary: Xuedi Wang, Xinghua FanEditorial office:Academic House, 113 Mill Lane Wavertree Technology Park Liverpool L13 4AH, England, UK Email:***************************.uk **************************.uk ************.cn。

期刊全称ACM Transactions on Intelligent Systems and TechnologyACM Transactions on Intelligent Systems and TechnologyIEEE Communications Surveys and TutorialsIEEE Communications Surveys and TutorialsIEEE TRANSACTIONS ON FUZZY SYSTEMSIEEE TRANSACTIONS ON PATTERN ANALYSIS AND MACHINE INTELLIGENCE International Journal of Neural SystemsIEEE Transactions on Industrial InformaticsMIS QUARTERLYIEEE TRANSACTIONS ON EVOLUTIONARY COMPUTATIONIEEE TRANSACTIONS ON EVOLUTIONARY COMPUTATIONCOMPUTER-AIDED CIVIL AND INFRASTRUCTURE ENGINEERINGIEEE WIRELESS COMMUNICATIONSIEEE WIRELESS COMMUNICATIONSIEEE WIRELESS COMMUNICATIONSJournal of Statistical SoftwareIEEE Transactions on Neural Networks and Learning SystemsIEEE Transactions on Neural Networks and Learning SystemsIEEE Transactions on Neural Networks and Learning SystemsMEDICAL IMAGE ANALYSISMEDICAL IMAGE ANALYSISACM COMPUTING SURVEYSIEEE COMMUNICATIONS MAGAZINEINTEGRATED COMPUTER-AIDED ENGINEERINGINTEGRATED COMPUTER-AIDED ENGINEERINGENVIRONMENTAL MODELLING & SOFTWAREINTERNATIONAL JOURNAL OF COMPUTER VISIONIEEE Computational Intelligence MagazineIEEE JOURNAL ON SELECTED AREAS IN COMMUNICATIONSACM TRANSACTIONS ON GRAPHICSSIAM Journal on Imaging SciencesSIAM Journal on Imaging SciencesIEEE Transactions on Affective ComputingIEEE Transactions on Affective ComputingINFORMATION SCIENCESIEEE Transactions on CyberneticsIEEE Transactions on CyberneticsARCHIVES OF COMPUTATIONAL METHODS IN ENGINEERING JOURNAL OF INFORMATION TECHNOLOGYKNOWLEDGE-BASED SYSTEMSIEEE TRANSACTIONS ON IMAGE PROCESSINGJOURNAL OF MACHINE LEARNING RESEARCHIEEE NETWORKIEEE NETWORKIEEE NETWORKIEEE TRANSACTIONS ON INFORMATION THEORY JOURNAL OF LIGHTWAVE TECHNOLOGYCOMPUTERS & EDUCATIONKNOWLEDGE AND INFORMATION SYSTEMSKNOWLEDGE AND INFORMATION SYSTEMSIEEE TRANSACTIONS ON WIRELESS COMMUNICATIONS JOURNAL OF THE ACMJOURNAL OF THE ACMJOURNAL OF THE ACMJOURNAL OF THE ACMIEEE TRANSACTIONS ON MOBILE COMPUTINGIEEE TRANSACTIONS ON MOBILE COMPUTINGPATTERN RECOGNITIONAPPLIED SOFT COMPUTINGAPPLIED SOFT COMPUTINGCOMMUNICATIONS OF THE ACMCOMMUNICATIONS OF THE ACMCOMMUNICATIONS OF THE ACMInformation FusionInformation FusionARTIFICIAL INTELLIGENCEACM TRANSACTIONS ON MATHEMATICAL SOFTWAREIEEE TRANSACTIONS ON ANTENNAS AND PROPAGATION EVOLUTIONARY COMPUTATIONEVOLUTIONARY COMPUTATIONCOMPUTERS & CHEMICAL ENGINEERINGIEEE TRANSACTIONS ON SOFTWARE ENGINEERINGANNUAL REVIEW OF INFORMATION SCIENCE AND TECHNOLOGYIEEE TRANSACTIONS ON VEHICULAR TECHNOLOGYCHEMOMETRICS AND INTELLIGENT LABORATORY SYSTEMSIEEE Transactions on Systems Man Cybernetics-SystemsFUTURE GENERATION COMPUTER SYSTEMSIEEE TRANSACTIONS ON BROADCASTINGJOURNAL OF THE AMERICAN SOCIETY FOR INFORMATION SCIENCE AND TE NEURAL NETWORKSDATA MINING AND KNOWLEDGE DISCOVERYDATA MINING AND KNOWLEDGE DISCOVERYIEEE Transactions on Human-Machine SystemsIEEE Transactions on Human-Machine SystemsHUMAN-COMPUTER INTERACTIONHUMAN-COMPUTER INTERACTIONIEEE INTERNET COMPUTINGIEEE-ACM TRANSACTIONS ON NETWORKINGIEEE-ACM TRANSACTIONS ON NETWORKINGIEEE-ACM TRANSACTIONS ON NETWORKINGIEEE TRANSACTIONS ON VISUALIZATION AND COMPUTER GRAPHICS EXPERT SYSTEMS WITH APPLICATIONSIEEE INTELLIGENT SYSTEMSIEEE MICROIEEE MICRODECISION SUPPORT SYSTEMSDECISION SUPPORT SYSTEMSIEEE Transactions on Services ComputingIEEE Transactions on Services ComputingIEEE Transactions on Autonomous Mental DevelopmentARTIFICIAL LIFEARTIFICIAL LIFEIEEE Journal of Biomedical and Health InformaticsIEEE Journal of Biomedical and Health InformaticsIEEE PERVASIVE COMPUTINGIEEE PERVASIVE COMPUTINGINTERNATIONAL JOURNAL OF INFORMATION TECHNOLOGY & DECISION MA INTERNATIONAL JOURNAL OF INFORMATION TECHNOLOGY & DECISION MA INTERNATIONAL JOURNAL OF INFORMATION TECHNOLOGY & DECISION MA INFORMATION & MANAGEMENTINTERNATIONAL JOURNAL OF APPROXIMATE REASONINGBIOLOGICAL CYBERNETICSCOMPUTERS & STRUCTURESJOURNAL OF STRATEGIC INFORMATION SYSTEMSAd Hoc NetworksAd Hoc NetworksJOURNAL OF MATHEMATICAL IMAGING AND VISIONJOURNAL OF MATHEMATICAL IMAGING AND VISIONIEEE TRANSACTIONS ON MULTIMEDIAIEEE TRANSACTIONS ON MULTIMEDIAIEEE TRANSACTIONS ON MULTIMEDIAIEEE TRANSACTIONS ON COMMUNICATIONSIEEE TRANSACTIONS ON PARALLEL AND DISTRIBUTED SYSTEMSMobile Information SystemsMobile Information SystemsIEEE TRANSACTIONS ON KNOWLEDGE AND DATA ENGINEERINGIEEE TRANSACTIONS ON KNOWLEDGE AND DATA ENGINEERING COMPUTERS & OPERATIONS RESEARCHNEURAL COMPUTATIONIEEE Transactions on Information Forensics and SecurityIEEE MICROWAVE MAGAZINEIMAGE AND VISION COMPUTINGIMAGE AND VISION COMPUTINGIMAGE AND VISION COMPUTINGENGINEERING APPLICATIONS OF ARTIFICIAL INTELLIGENCEIEEE TRANSACTIONS ON RELIABILITYIEEE TRANSACTIONS ON RELIABILITYNEUROCOMPUTINGAUTONOMOUS ROBOTSADVANCED ENGINEERING INFORMATICSINTERNATIONAL JOURNAL OF ELECTRONIC COMMERCEInternational Journal of Web and Grid ServicesInternational Journal of Web and Grid ServicesCOMPUTERS AND ELECTRONICS IN AGRICULTUREIEEE Antennas and Wireless Propagation LettersUSER MODELING AND USER-ADAPTED INTERACTIONIEEE Transactions on HapticsSTRUCTURAL AND MULTIDISCIPLINARY OPTIMIZATIONCOMPUTER GRAPHICS FORUMJournal of Optical Communications and NetworkingJournal of Optical Communications and NetworkingJournal of Optical Communications and NetworkingCOMPUTERS & INDUSTRIAL ENGINEERINGMACHINE LEARNINGACM Transactions on Sensor NetworksACM Transactions on Sensor NetworksEUROPEAN JOURNAL OF INFORMATION SYSTEMSJournal of Computational ScienceJournal of Computational ScienceCOMPUTERS IN INDUSTRYIEEE-ACM Transactions on Computational Biology and BioinformaticsEMPIRICAL SOFTWARE ENGINEERINGVLDB JOURNALVLDB JOURNALJOURNAL OF MANAGEMENT INFORMATION SYSTEMSCOMPUTER SPEECH AND LANGUAGECOMPUTERCOMPUTERJournal of Grid ComputingJournal of Grid ComputingInternational Journal of Bio-Inspired ComputationInternational Journal of Bio-Inspired ComputationPervasive and Mobile ComputingPervasive and Mobile ComputingINDUSTRIAL MANAGEMENT & DATA SYSTEMSINTERNATIONAL JOURNAL OF INTELLIGENT SYSTEMSIEEE Transactions on Computational Intelligence and AI in GamesIEEE Transactions on Computational Intelligence and AI in GamesDATA & KNOWLEDGE ENGINEERINGDATA & KNOWLEDGE ENGINEERINGPARALLEL COMPUTINGCOMPUTING IN SCIENCE & ENGINEERINGMECHATRONICSCOMPUTER METHODS IN BIOMECHANICS AND BIOMEDICAL ENGINEERING IEEE SOFTWARESOFT COMPUTINGSOFT COMPUTINGJOURNAL OF NETWORK AND COMPUTER APPLICATIONSJOURNAL OF NETWORK AND COMPUTER APPLICATIONSJOURNAL OF NETWORK AND COMPUTER APPLICATIONSACM TRANSACTIONS ON SOFTWARE ENGINEERING AND METHODOLOGY TELECOMMUNICATIONS POLICYElectronic Commerce Research and ApplicationsElectronic Commerce Research and ApplicationsINTERNET RESEARCH-ELECTRONIC NETWORKING APPLICATIONS AND POLI INTERNET RESEARCH-ELECTRONIC NETWORKING APPLICATIONS AND POLIACM Transactions on Knowledge Discovery from DataACM Transactions on Knowledge Discovery from DataROBOTICS AND COMPUTER-INTEGRATED MANUFACTURING INFORMATION SYSTEMSWiley Interdisciplinary Reviews-Data Mining and Knowledge DiscoveryWiley Interdisciplinary Reviews-Data Mining and Knowledge DiscoveryCOMPUTER METHODS AND PROGRAMS IN BIOMEDICINECOMPUTER METHODS AND PROGRAMS IN BIOMEDICINEINFORMATION AND SOFTWARE TECHNOLOGYINFORMATION AND SOFTWARE TECHNOLOGYSPEECH COMMUNICATIONJOURNAL OF HEURISTICSJOURNAL OF HEURISTICSARTIFICIAL INTELLIGENCE IN MEDICINECOMPUTER-AIDED DESIGNJOURNAL OF COMPUTING IN CIVIL ENGINEERINGFuzzy Optimization and Decision MakingJournal of the Association for Information SystemsIEEE TRANSACTIONS ON COMPUTERSIEEE Systems JournalIEEE Systems JournalCOMPUTER VISION AND IMAGE UNDERSTANDINGOPTICAL FIBER TECHNOLOGYJournal of Web SemanticsJournal of Web SemanticsJournal of Web SemanticsIEEE Vehicular Technology MagazineINTERNATIONAL JOURNAL OF SYSTEMS SCIENCEACM Transactions on the WebACM Transactions on the WebIEEE TRANSACTIONS ON ELECTROMAGNETIC COMPATIBILITYIEEE TRANSACTIONS ON AEROSPACE AND ELECTRONIC SYSTEMSIEEE COMPUTER GRAPHICS AND APPLICATIONSINTERNATIONAL JOURNAL OF HUMAN-COMPUTER STUDIESADVANCES IN ENGINEERING SOFTWAREADVANCES IN ENGINEERING SOFTWARECOMPUTERS IN BIOLOGY AND MEDICINECOMPUTER NETWORKS-THE INTERNATIONAL JOURNAL OF COMPUTER AND COMPUTER NETWORKS-THE INTERNATIONAL JOURNAL OF COMPUTER AND COMPUTER NETWORKS-THE INTERNATIONAL JOURNAL OF COMPUTER AND Swarm IntelligenceInternational Journal of Fuzzy SystemsPersonal and Ubiquitous ComputingPersonal and Ubiquitous ComputingJOURNAL OF VISUAL COMMUNICATION AND IMAGE REPRESENTATION JOURNAL OF VISUAL COMMUNICATION AND IMAGE REPRESENTATION ARTIFICIAL INTELLIGENCE REVIEWINFORMATICANEURAL COMPUTING & APPLICATIONSJOURNAL OF INFORMATION SCIENCECOMPUTATIONAL LINGUISTICSCOMPUTATIONAL LINGUISTICSIEEE COMMUNICATIONS LETTERSIEEE TRANSACTIONS ON VERY LARGE SCALE INTEGRATION (VLSI) SYSTEM IEEE TRANSACTIONS ON COMPUTER-AIDED DESIGN OF INTEGRATED CIRCU IEEE TRANSACTIONS ON COMPUTER-AIDED DESIGN OF INTEGRATED CIRCU INFORMS JOURNAL ON COMPUTINGINTERNATIONAL JOURNAL OF HIGH PERFORMANCE COMPUTING APPLICAT INTERNATIONAL JOURNAL OF HIGH PERFORMANCE COMPUTING APPLICAT INTERNATIONAL JOURNAL OF HIGH PERFORMANCE COMPUTING APPLICAT MACHINE VISION AND APPLICATIONSMACHINE VISION AND APPLICATIONSJOURNAL OF HYDROINFORMATICSRADIO SCIENCEJOURNAL OF COMPLEXITYAutomated Software EngineeringENGINEERING COMPUTATIONSCOMPUTER COMMUNICATIONSCOMPUTER COMMUNICATIONSACM TRANSACTIONS ON INFORMATION SYSTEMSMOBILE NETWORKS & APPLICATIONSMOBILE NETWORKS & APPLICATIONSMOBILE NETWORKS & APPLICATIONSIEEE Design & TestCOMPUTER STANDARDS & INTERFACESCOMPUTER STANDARDS & INTERFACESGenetic Programming and Evolvable MachinesGenetic Programming and Evolvable MachinesMULTIDIMENSIONAL SYSTEMS AND SIGNAL PROCESSINGPATTERN RECOGNITION LETTERSIEEE Transactions on Dependable and Secure ComputingIEEE Transactions on Dependable and Secure ComputingIEEE Transactions on Dependable and Secure ComputingWORLD WIDE WEB-INTERNET AND WEB INFORMATION SYSTEMSWORLD WIDE WEB-INTERNET AND WEB INFORMATION SYSTEMSONLINE INFORMATION REVIEWROBOTICS AND AUTONOMOUS SYSTEMSJournal of Real-Time Image ProcessingINTERNATIONAL JOURNAL OF UNCERTAINTY FUZZINESS AND KNOWLEDGE ADAPTIVE BEHAVIORJOURNAL OF INTELLIGENT MANUFACTURINGJOURNAL OF COMPUTER AND SYSTEM SCIENCESJOURNAL OF COMPUTER AND SYSTEM SCIENCESNEURAL PROCESSING LETTERSJOURNAL OF SYSTEMS AND SOFTWAREJOURNAL OF SYSTEMS AND SOFTWARESOFTWARE TESTING VERIFICATION & RELIABILITYCOMPUTERS & SECURITYACM Transactions on Applied PerceptionIEEE MULTIMEDIAIEEE MULTIMEDIAIEEE MULTIMEDIAIEEE MULTIMEDIAIEEE TRANSACTIONS ON CONSUMER ELECTRONICSSIMULATION MODELLING PRACTICE AND THEORYSIMULATION MODELLING PRACTICE AND THEORYREQUIREMENTS ENGINEERINGREQUIREMENTS ENGINEERINGComputer Supported Cooperative Work-The Journal of Collaborative Computing DISPLAYSSoftware and Systems ModelingINTERACTING WITH COMPUTERSAUTONOMOUS AGENTS AND MULTI-AGENT SYSTEMSBusiness & Information Systems EngineeringJOURNAL OF ARTIFICIAL INTELLIGENCE RESEARCHINTERNATIONAL JOURNAL OF SATELLITE COMMUNICATIONS AND NETWOR ACM Transactions on Autonomous and Adaptive SystemsACM Transactions on Autonomous and Adaptive SystemsACM Transactions on Autonomous and Adaptive SystemsWIRELESS COMMUNICATIONS & MOBILE COMPUTINGWIRELESS COMMUNICATIONS & MOBILE COMPUTINGINTERNATIONAL JOURNAL OF COMPUTER INTEGRATED MANUFACTURING JOURNAL OF PARALLEL AND DISTRIBUTED COMPUTINGApplied OntologyApplied OntologyApplied OntologyJournal of Ambient Intelligence and Smart EnvironmentsJournal of Ambient Intelligence and Smart EnvironmentsJournal of Ambient Intelligence and Smart EnvironmentsINFORMATION PROCESSING & MANAGEMENTInternational Journal on Semantic Web and Information SystemsInternational Journal on Semantic Web and Information SystemsInternational Journal of Applied Mathematics and Computer Science TELECOMMUNICATION SYSTEMSOPEN SYSTEMS & INFORMATION DYNAMICSJOURNAL OF CRYPTOLOGYSIAM JOURNAL ON COMPUTINGJournal of Software-Evolution and ProcessIET OptoelectronicsCOMPUTATIONAL INTELLIGENCEIET Radar Sonar and NavigationCOMPUTERS & GRAPHICS-UKINTERNATIONAL JOURNAL OF HUMAN-COMPUTER INTERACTIONIEEE Transactions on Learning TechnologiesAPPLIED COMPUTATIONAL ELECTROMAGNETICS SOCIETY JOURNALACM TRANSACTIONS ON PROGRAMMING LANGUAGES AND SYSTEMS COMPUTER AIDED GEOMETRIC DESIGNCOMPUTERS & ELECTRICAL ENGINEERINGCOMPUTERS & ELECTRICAL ENGINEERINGJOURNAL OF DATABASE MANAGEMENTJOURNAL OF DATABASE MANAGEMENTBEHAVIOUR & INFORMATION TECHNOLOGYACM Transactions on Multimedia Computing Communications and ApplicationsACM Transactions on Multimedia Computing Communications and ApplicationsACM Transactions on Multimedia Computing Communications and Applications MULTIMEDIA TOOLS AND APPLICATIONSMULTIMEDIA TOOLS AND APPLICATIONSMULTIMEDIA TOOLS AND APPLICATIONSIEEE Computer Architecture LettersCognitive Systems ResearchSOFTWARE-PRACTICE & EXPERIENCEScientific ProgrammingGRAPHICAL MODELSCYBERNETICS AND SYSTEMSACM SIGCOMM Computer Communication ReviewInformation VisualizationPRESENCE-TELEOPERATORS AND VIRTUAL ENVIRONMENTSPRESENCE-TELEOPERATORS AND VIRTUAL ENVIRONMENTSACM TRANSACTIONS ON DATABASE SYSTEMSACM TRANSACTIONS ON DATABASE SYSTEMSOptical Switching and NetworkingOptical Switching and NetworkingJOURNAL OF FUNCTIONAL PROGRAMMINGACM TRANSACTIONS ON COMPUTER SYSTEMSACM Transactions on Computer-Human InteractionACM Transactions on Computer-Human InteractionComputers and ConcreteETRI JOURNALIEEE SECURITY & PRIVACYIEEE SECURITY & PRIVACYR JournalCOMPUTINGVISUAL COMPUTERACM Transactions on StorageACM Transactions on StorageCONSTRAINTSCONSTRAINTSOPTIMIZATION METHODS & SOFTWAREINFORMATION SYSTEMS FRONTIERSINFORMATION SYSTEMS FRONTIERSEUROPEAN TRANSACTIONS ON TELECOMMUNICATIONS PERFORMANCE EVALUATIONPERFORMANCE EVALUATIONIET Microwaves Antennas & PropagationACM Transactions on Modeling and Computer SimulationJOURNAL OF INTELLIGENT & ROBOTIC SYSTEMSACM Transactions on Embedded Computing SystemsACM Transactions on Embedded Computing SystemsCIN-COMPUTERS INFORMATICS NURSINGCOMPUTER JOURNALCOMPUTER JOURNALCOMPUTER JOURNALCOMPUTER JOURNALENGINEERING WITH COMPUTERSDESIGNS CODES AND CRYPTOGRAPHYNETWORKSNETWORK-COMPUTATION IN NEURAL SYSTEMSInformation Technology and ControlInformation Technology and ControlIETE TECHNICAL REVIEWInternational Journal of Data Warehousing and MiningJOURNAL OF SUPERCOMPUTINGJOURNAL OF SUPERCOMPUTINGNEW GENERATION COMPUTINGNEW GENERATION COMPUTINGWIRELESS NETWORKSWIRELESS NETWORKSPATTERN ANALYSIS AND APPLICATIONSJOURNAL OF INTELLIGENT & FUZZY SYSTEMS CONCURRENCY AND COMPUTATION-PRACTICE & EXPERIENCE CONCURRENCY AND COMPUTATION-PRACTICE & EXPERIENCE ACM Transactions on Internet TechnologyACM Transactions on Internet TechnologyInternational Journal of Ad Hoc and Ubiquitous ComputingInternational Journal of Ad Hoc and Ubiquitous ComputingACM Transactions on Computational LogicACM Transactions on Information and System SecurityCluster Computing-The Journal of Networks Software Tools and ApplicationsCluster Computing-The Journal of Networks Software Tools and Applications INTERNATIONAL JOURNAL OF COMMUNICATION SYSTEMSEURASIP Journal on Wireless Communications and NetworkingEXPERT SYSTEMSEXPERT SYSTEMSINTERNATIONAL JOURNAL OF RF AND MICROWAVE COMPUTER-AIDED ENG INTERNATIONAL JOURNAL OF GENERAL SYSTEMSINFORMATION RETRIEVALMODELING IDENTIFICATION AND CONTROLCONNECTION SCIENCECONNECTION SCIENCESOFTWARE QUALITY JOURNALSIMULATION-TRANSACTIONS OF THE SOCIETY FOR MODELING AND SIMULA SIMULATION-TRANSACTIONS OF THE SOCIETY FOR MODELING AND SIMULA Digital InvestigationDigital InvestigationDISTRIBUTED AND PARALLEL DATABASESDISTRIBUTED AND PARALLEL DATABASESKNOWLEDGE ENGINEERING REVIEWSIGMOD RECORDSIGMOD RECORDJOURNAL OF INTELLIGENT INFORMATION SYSTEMSJOURNAL OF INTELLIGENT INFORMATION SYSTEMSInternational Journal of Wavelets Multiresolution and Information Processing International Journal on Document Analysis and RecognitionJOURNAL OF COMPUTER INFORMATION SYSTEMSINTERNATIONAL JOURNAL OF COOPERATIVE INFORMATION SYSTEMSAI MAGAZINEIET Computer VisionACM Journal on Emerging Technologies in Computing SystemsDISTRIBUTED COMPUTINGInternational Journal of Antennas and PropagationJOURNAL OF MULTIPLE-VALUED LOGIC AND SOFT COMPUTINGJOURNAL OF MULTIPLE-VALUED LOGIC AND SOFT COMPUTINGBELL LABS TECHNICAL JOURNALBELL LABS TECHNICAL JOURNALJournal on Multimodal User InterfacesJournal on Multimodal User InterfacesCryptography and Communications-Discrete-Structures Boolean Functions and Sequences Science China-Information SciencesAPPLICABLE ALGEBRA IN ENGINEERING COMMUNICATION AND COMPUTIN APPLICABLE ALGEBRA IN ENGINEERING COMMUNICATION AND COMPUTIN IBM JOURNAL OF RESEARCH AND DEVELOPMENTIBM JOURNAL OF RESEARCH AND DEVELOPMENTIBM JOURNAL OF RESEARCH AND DEVELOPMENTIBM JOURNAL OF RESEARCH AND DEVELOPMENTREAL-TIME SYSTEMSCOMPUTER MUSIC JOURNALWIRELESS PERSONAL COMMUNICATIONSINFORMATION AND COMPUTATIONJOURNAL OF SYSTEMS ARCHITECTUREJOURNAL OF SYSTEMS ARCHITECTUREACM TRANSACTIONS ON DESIGN AUTOMATION OF ELECTRONIC SYSTEMS ACM TRANSACTIONS ON DESIGN AUTOMATION OF ELECTRONIC SYSTEMS International Journal of Distributed Sensor NetworksInternational Journal of Distributed Sensor NetworksTHEORY AND PRACTICE OF LOGIC PROGRAMMINGTHEORY AND PRACTICE OF LOGIC PROGRAMMINGACM Transactions on Architecture and Code OptimizationACM Transactions on Architecture and Code OptimizationInternational Journal of Information SecurityInternational Journal of Information SecurityInternational Journal of Information SecurityAEU-INTERNATIONAL JOURNAL OF ELECTRONICS AND COMMUNICATIONS Natural ComputingNatural ComputingJOURNAL OF SYMBOLIC COMPUTATIONJournal of Signal Processing Systems for Signal Image and Video Technology MULTIMEDIA SYSTEMSMULTIMEDIA SYSTEMSMATHEMATICAL STRUCTURES IN COMPUTER SCIENCEJOURNAL OF LOGIC AND COMPUTATIONINFORMATION SYSTEMS MANAGEMENTAdvances in Electrical and Computer EngineeringComputer Science and Information SystemsComputer Science and Information SystemsJOURNAL OF AUTOMATED REASONINGAI EDAM-ARTIFICIAL INTELLIGENCE FOR ENGINEERING DESIGN ANALYSIS AI EDAM-ARTIFICIAL INTELLIGENCE FOR ENGINEERING DESIGN ANALYSIS INTERNATIONAL JOURNAL OF PATTERN RECOGNITION AND ARTIFICIAL INT SCIENCE OF COMPUTER PROGRAMMINGComputational and Mathematical Organization TheoryMICROPROCESSORS AND MICROSYSTEMSMICROPROCESSORS AND MICROSYSTEMSAdvances in Mathematics of CommunicationsJOURNAL OF VISUAL LANGUAGES AND COMPUTINGJournal of SimulationJOURNAL OF COMPUTER SCIENCE AND TECHNOLOGYJOURNAL OF COMPUTER SCIENCE AND TECHNOLOGYPHOTONIC NETWORK COMMUNICATIONSPHOTONIC NETWORK COMMUNICATIONSDISCRETE MATHEMATICS AND THEORETICAL COMPUTER SCIENCE THEORETICAL COMPUTER SCIENCEALGORITHMICAASLIB PROCEEDINGSKYBERNETIKAANNALES DES TELECOMMUNICATIONS-ANNALS OF TELECOMMUNICATION INTEGRATION-THE VLSI JOURNALInternational Journal of Critical Infrastructure ProtectionACM Transactions on AlgorithmsInternational Journal of Computers Communications & ControlFORMAL ASPECTS OF COMPUTINGJOURNAL OF UNIVERSAL COMPUTER SCIENCEJOURNAL OF UNIVERSAL COMPUTER SCIENCECONCURRENT ENGINEERING-RESEARCH AND APPLICATIONSANALOG INTEGRATED CIRCUITS AND SIGNAL PROCESSINGInternational Journal of Microwave and Wireless TechnologiesJOURNAL OF COMPUTING AND INFORMATION SCIENCE IN ENGINEERING JOURNAL OF VISUALIZATIONIET SoftwareInternational Journal of Unconventional ComputingTurkish Journal of Electrical Engineering and Computer SciencesLanguage Resources and EvaluationIEEE ANNALS OF THE HISTORY OF COMPUTINGINTERNATIONAL JOURNAL OF PARALLEL PROGRAMMINGIT ProfessionalIT ProfessionalIT ProfessionalJOURNAL OF NEW MUSIC RESEARCHINFORMATION PROCESSING LETTERSIntelligent Data AnalysisNeural Network WorldJOURNAL OF LOGIC AND ALGEBRAIC PROGRAMMINGACM SIGPLAN NOTICESAI COMMUNICATIONSJournal of Internet TechnologyJournal of Internet TechnologyIET Information SecurityIET Information SecurityJournal of Applied LogicJournal of Applied LogicFORMAL METHODS IN SYSTEM DESIGNTHEORY OF COMPUTING SYSTEMSNatural Language EngineeringVIRTUAL REALITYVIRTUAL REALITYInternational Journal of Computational Intelligence SystemsInternational Journal of Computational Intelligence SystemsJOURNAL OF COMMUNICATIONS AND NETWORKSJOURNAL OF COMMUNICATIONS AND NETWORKSMINDS AND MACHINESACTA INFORMATICAJournal of Network and Systems ManagementJournal of Network and Systems ManagementAd Hoc & Sensor Wireless NetworksAd Hoc & Sensor Wireless NetworksKSII Transactions on Internet and Information SystemsKSII Transactions on Internet and Information SystemsLogical Methods in Computer ScienceUniversal Access in the Information SocietyCOMPUTER ANIMATION AND VIRTUAL WORLDSInternational Journal of Network ManagementInternational Journal of Network ManagementJOURNAL OF ORGANIZATIONAL COMPUTING AND ELECTRONIC COMMERCE JOURNAL OF ORGANIZATIONAL COMPUTING AND ELECTRONIC COMMERCE FUNDAMENTA INFORMATICAEADVANCES IN COMPUTERSADVANCES IN COMPUTERSAPPLIED ARTIFICIAL INTELLIGENCEJOURNAL OF EXPERIMENTAL & THEORETICAL ARTIFICIAL INTELLIGENCE PROGRAM-ELECTRONIC LIBRARY AND INFORMATION SYSTEMSSecurity and Communication NetworksSecurity and Communication NetworksProblems of Information TransmissionNew Review of Hypermedia and MultimediaINTERNATIONAL JOURNAL OF FOUNDATIONS OF COMPUTER SCIENCE COMPUTER APPLICATIONS IN ENGINEERING EDUCATIONIET Computers and Digital TechniquesIET Computers and Digital TechniquesJOURNAL OF COMMUNICATIONS TECHNOLOGY AND ELECTRONICS Frontiers of Computer ScienceFrontiers of Computer ScienceFrontiers of Computer SciencePeer-to-Peer Networking and ApplicationsPeer-to-Peer Networking and ApplicationsANNALS OF MATHEMATICS AND ARTIFICIAL INTELLIGENCEChina CommunicationsCOMPUTER LANGUAGES SYSTEMS & STRUCTURESCOMPEL-THE INTERNATIONAL JOURNAL FOR COMPUTATION AND MATHEM International Journal of Web Services ResearchInternational Journal of Web Services ResearchJournal of Organizational and End User ComputingJournal of Zhejiang University-SCIENCE C-Computers & ElectronicsJournal of Zhejiang University-SCIENCE C-Computers & ElectronicsKYBERNETESJournal of Cellular AutomataIEICE TRANSACTIONS ON COMMUNICATIONSRomanian Journal of Information Science and TechnologyInternational Arab Journal of InformationInternational Arab Journal of InformationCANADIAN JOURNAL OF ELECTRICAL AND COMPUTER ENGINEERING-REVU JOURNAL OF CIRCUITS SYSTEMS AND COMPUTERSMalaysian Journal of Computer ScienceMalaysian Journal of Computer ScienceCOMPUTING AND INFORMATICSJOURNAL OF INFORMATION SCIENCE AND ENGINEERINGJournal of Web EngineeringJournal of Web EngineeringInternational Journal on Artificial Intelligence ToolsInternational Journal on Artificial Intelligence ToolsRAIRO-THEORETICAL INFORMATICS AND APPLICATIONSIEEE Latin America TransactionsDESIGN AUTOMATION FOR EMBEDDED SYSTEMSDESIGN AUTOMATION FOR EMBEDDED SYSTEMSIEICE TRANSACTIONS ON FUNDAMENTALS OF ELECTRONICS COMMUNICAT IEICE TRANSACTIONS ON FUNDAMENTALS OF ELECTRONICS COMMUNICAT INTERNATIONAL JOURNAL OF SOFTWARE ENGINEERING AND KNOWLEDGE INTERNATIONAL JOURNAL OF SOFTWARE ENGINEERING AND KNOWLEDGE COMPUTER SYSTEMS SCIENCE AND ENGINEERINGCOMPUTER SYSTEMS SCIENCE AND ENGINEERINGJOURNAL OF COMPUTER AND SYSTEMS SCIENCES INTERNATIONAL JOURNAL OF COMPUTER AND SYSTEMS SCIENCES INTERNATIONAL JOURNAL OF COMPUTER AND SYSTEMS SCIENCES INTERNATIONALIETE JOURNAL OF RESEARCHMICROWAVE JOURNALIEICE TRANSACTIONS ON INFORMATION AND SYSTEMSIEICE TRANSACTIONS ON INFORMATION AND SYSTEMSCRYPTOLOGIAINTELLIGENT AUTOMATION AND SOFT COMPUTINGPROGRAMMING AND COMPUTER SOFTWARETraitement du SignalJournal of the Institute of Telecommunications ProfessionalsMICROWAVES & RFELECTRONICS WORLDCOMPUTER GRAPHICS WORLDJCR期刊简称ISSN所属小类所属小类(中文)小类分区大类复分大类分区ACM T INTEL SYST TEC2157-6904C OMPUTER SCIENCE, ARTI计算机:人工智能1N1 ACM T INTEL SYST TEC2157-6904C OMPUTER SCIENCE, INFO计算机:信息系统1N1 IEEE COMMUN SURV TUT1553-877X T ELECOMMUNICATIONS电信学1N1 IEEE COMMUN SURV TUT1553-877X C OMPUTER SCIENCE, INFO计算机:信息系统1N1 IEEE T FUZZY SYST1063-6706C OMPUTER SCIENCE, ARTI计算机:人工智能1N1 IEEE T PATTERN ANAL0162-8828C OMPUTER SCIENCE, ARTI计算机:人工智能1N1 INT J NEURAL SYST0129-0657C OMPUTER SCIENCE, ARTI计算机:人工智能1N1 IEEE T IND INFORM1551-3203C OMPUTER SCIENCE, INTE计算机:跨学科应1N1 MIS QUART0276-7783C OMPUTER SCIENCE, INFO计算机:信息系统1N1 IEEE T EVOLUT COMPUT1089-778X C OMPUTER SCIENCE, THEO计算机:理论方法1N1 IEEE T EVOLUT COMPUT1089-778X C OMPUTER SCIENCE, ARTI计算机:人工智能1N1 COMPUT-AIDED CIV INF1093-9687C OMPUTER SCIENCE, INTE计算机:跨学科应1N1 IEEE WIREL COMMUN1536-1284T ELECOMMUNICATIONS电信学1N1 IEEE WIREL COMMUN1536-1284C OMPUTER SCIENCE, INFO计算机:信息系统1N1 IEEE WIREL COMMUN1536-1284C OMPUTER SCIENCE, HAR计算机:硬件1N1 J STAT SOFTW1548-7660C OMPUTER SCIENCE, INTE计算机:跨学科应1N1 IEEE T NEUR NET LEAR2162-237X C OMPUTER SCIENCE, THEO计算机:理论方法1N1 IEEE T NEUR NET LEAR2162-237X C OMPUTER SCIENCE, ARTI计算机:人工智能1N1 IEEE T NEUR NET LEAR2162-237X C OMPUTER SCIENCE, HAR计算机:硬件1N1 MED IMAGE ANAL1361-8415C OMPUTER SCIENCE, INTE计算机:跨学科应1N1 MED IMAGE ANAL1361-8415C OMPUTER SCIENCE, ARTI计算机:人工智能2N1 ACM COMPUT SURV0360-0300C OMPUTER SCIENCE, THEO计算机:理论方法1N1 IEEE COMMUN MAG0163-6804T ELECOMMUNICATIONS电信学1N2 INTEGR COMPUT-AID E1069-2509C OMPUTER SCIENCE, INTE计算机:跨学科应2N2 INTEGR COMPUT-AID E1069-2509C OMPUTER SCIENCE, ARTI计算机:人工智能2N2 ENVIRON MODELL SOFTW1364-8152C OMPUTER SCIENCE, INTE计算机:跨学科应2N2 INT J COMPUT VISION0920-5691C OMPUTER SCIENCE, ARTI计算机:人工智能2N2 IEEE COMPUT INTELL M1556-603X C OMPUTER SCIENCE, ARTI计算机:人工智能2N2 IEEE J SEL AREA COMM0733-8716T ELECOMMUNICATIONS电信学1N2 ACM T GRAPHIC0730-0301C OMPUTER SCIENCE, SOFT计算机:软件工程1N2 SIAM J IMAGING SCI1936-4954C OMPUTER SCIENCE, ARTI计算机:人工智能2N2 SIAM J IMAGING SCI1936-4954C OMPUTER SCIENCE, SOFT计算机:软件工程1N2 IEEE T AFFECT COMPUT1949-3045C OMPUTER SCIENCE, CYB计算机:控制论1N2。



(0,2) 插值||(0,2) interpolation0#||zero-sharp; 读作零井或零开。
0+||zero-dagger; 读作零正。
1-因子||1-factor3-流形||3-manifold; 又称“三维流形”。
AIC准则||AIC criterion, Akaike information criterionAp 权||Ap-weightA稳定性||A-stability, absolute stabilityA最优设计||A-optimal designBCH 码||BCH code, Bose-Chaudhuri-Hocquenghem codeBIC准则||BIC criterion, Bayesian modification of the AICBMOA函数||analytic function of bounded mean oscillation; 全称“有界平均振动解析函数”。
BMO鞅||BMO martingaleBSD猜想||Birch and Swinnerton-Dyer conjecture; 全称“伯奇与斯温纳顿-戴尔猜想”。
B样条||B-splineC*代数||C*-algebra; 读作“C星代数”。
C0 类函数||function of class C0; 又称“连续函数类”。
CA T准则||CAT criterion, criterion for autoregressiveCM域||CM fieldCN 群||CN-groupCW 复形的同调||homology of CW complexCW复形||CW complexCW复形的同伦群||homotopy group of CW complexesCW剖分||CW decompositionCn 类函数||function of class Cn; 又称“n次连续可微函数类”。
Cp统计量||Cp-statisticC。

Quasi-Normal Modes of Stars and Black HolesKostas D.KokkotasDepartment of Physics,Aristotle University of Thessaloniki,Thessaloniki54006,Greece.kokkotas@astro.auth.grhttp://www.astro.auth.gr/˜kokkotasandBernd G.SchmidtMax Planck Institute for Gravitational Physics,Albert Einstein Institute,D-14476Golm,Germany.bernd@aei-potsdam.mpg.dePublished16September1999/Articles/Volume2/1999-2kokkotasLiving Reviews in RelativityPublished by the Max Planck Institute for Gravitational PhysicsAlbert Einstein Institute,GermanyAbstractPerturbations of stars and black holes have been one of the main topics of relativistic astrophysics for the last few decades.They are of partic-ular importance today,because of their relevance to gravitational waveastronomy.In this review we present the theory of quasi-normal modes ofcompact objects from both the mathematical and astrophysical points ofview.The discussion includes perturbations of black holes(Schwarzschild,Reissner-Nordstr¨o m,Kerr and Kerr-Newman)and relativistic stars(non-rotating and slowly-rotating).The properties of the various families ofquasi-normal modes are described,and numerical techniques for calculat-ing quasi-normal modes reviewed.The successes,as well as the limits,of perturbation theory are presented,and its role in the emerging era ofnumerical relativity and supercomputers is discussed.c 1999Max-Planck-Gesellschaft and the authors.Further information on copyright is given at /Info/Copyright/.For permission to reproduce the article please contact livrev@aei-potsdam.mpg.de.Article AmendmentsOn author request a Living Reviews article can be amended to include errata and small additions to ensure that the most accurate and up-to-date infor-mation possible is provided.For detailed documentation of amendments, please go to the article’s online version at/Articles/Volume2/1999-2kokkotas/. Owing to the fact that a Living Reviews article can evolve over time,we recommend to cite the article as follows:Kokkotas,K.D.,and Schmidt,B.G.,“Quasi-Normal Modes of Stars and Black Holes”,Living Rev.Relativity,2,(1999),2.[Online Article]:cited on<date>, /Articles/Volume2/1999-2kokkotas/. The date in’cited on<date>’then uniquely identifies the version of the article you are referring to.3Quasi-Normal Modes of Stars and Black HolesContents1Introduction4 2Normal Modes–Quasi-Normal Modes–Resonances7 3Quasi-Normal Modes of Black Holes123.1Schwarzschild Black Holes (12)3.2Kerr Black Holes (17)3.3Stability and Completeness of Quasi-Normal Modes (20)4Quasi-Normal Modes of Relativistic Stars234.1Stellar Pulsations:The Theoretical Minimum (23)4.2Mode Analysis (26)4.2.1Families of Fluid Modes (26)4.2.2Families of Spacetime or w-Modes (30)4.3Stability (31)5Excitation and Detection of QNMs325.1Studies of Black Hole QNM Excitation (33)5.2Studies of Stellar QNM Excitation (34)5.3Detection of the QNM Ringing (37)5.4Parameter Estimation (39)6Numerical Techniques426.1Black Holes (42)6.1.1Evolving the Time Dependent Wave Equation (42)6.1.2Integration of the Time Independent Wave Equation (43)6.1.3WKB Methods (44)6.1.4The Method of Continued Fractions (44)6.2Relativistic Stars (45)7Where Are We Going?487.1Synergism Between Perturbation Theory and Numerical Relativity487.2Second Order Perturbations (48)7.3Mode Calculations (49)7.4The Detectors (49)8Acknowledgments50 9Appendix:Schr¨o dinger Equation Versus Wave Equation51Living Reviews in Relativity(1999-2)K.D.Kokkotas and B.G.Schmidt41IntroductionHelioseismology and asteroseismology are well known terms in classical astro-physics.From the beginning of the century the variability of Cepheids has been used for the accurate measurement of cosmic distances,while the variability of a number of stellar objects(RR Lyrae,Mira)has been associated with stel-lar oscillations.Observations of solar oscillations(with thousands of nonradial modes)have also revealed a wealth of information about the internal structure of the Sun[204].Practically every stellar object oscillates radially or nonradi-ally,and although there is great difficulty in observing such oscillations there are already results for various types of stars(O,B,...).All these types of pulsations of normal main sequence stars can be studied via Newtonian theory and they are of no importance for the forthcoming era of gravitational wave astronomy.The gravitational waves emitted by these stars are extremely weak and have very low frequencies(cf.for a discussion of the sun[70],and an im-portant new measurement of the sun’s quadrupole moment and its application in the measurement of the anomalous precession of Mercury’s perihelion[163]). This is not the case when we consider very compact stellar objects i.e.neutron stars and black holes.Their oscillations,produced mainly during the formation phase,can be strong enough to be detected by the gravitational wave detectors (LIGO,VIRGO,GEO600,SPHERE)which are under construction.In the framework of general relativity(GR)quasi-normal modes(QNM) arise,as perturbations(electromagnetic or gravitational)of stellar or black hole spacetimes.Due to the emission of gravitational waves there are no normal mode oscillations but instead the frequencies become“quasi-normal”(complex), with the real part representing the actual frequency of the oscillation and the imaginary part representing the damping.In this review we shall discuss the oscillations of neutron stars and black holes.The natural way to study these oscillations is by considering the linearized Einstein equations.Nevertheless,there has been recent work on nonlinear black hole perturbations[101,102,103,104,100]while,as yet nothing is known for nonlinear stellar oscillations in general relativity.The study of black hole perturbations was initiated by the pioneering work of Regge and Wheeler[173]in the late50s and was continued by Zerilli[212]. The perturbations of relativistic stars in GR werefirst studied in the late60s by Kip Thorne and his collaborators[202,198,199,200].The initial aim of Regge and Wheeler was to study the stability of a black hole to small perturbations and they did not try to connect these perturbations to astrophysics.In con-trast,for the case of relativistic stars,Thorne’s aim was to extend the known properties of Newtonian oscillation theory to general relativity,and to estimate the frequencies and the energy radiated as gravitational waves.QNMs werefirst pointed out by Vishveshwara[207]in calculations of the scattering of gravitational waves by a Schwarzschild black hole,while Press[164] coined the term quasi-normal frequencies.QNM oscillations have been found in perturbation calculations of particles falling into Schwarzschild[73]and Kerr black holes[76,80]and in the collapse of a star to form a black hole[66,67,68]. Living Reviews in Relativity(1999-2)5Quasi-Normal Modes of Stars and Black Holes Numerical investigations of the fully nonlinear equations of general relativity have provided results which agree with the results of perturbation calculations;in particular numerical studies of the head-on collision of two black holes [30,29](cf.Figure 1)and gravitational collapse to a Kerr hole [191].Recently,Price,Pullin and collaborators [170,31,101,28]have pushed forward the agreement between full nonlinear numerical results and results from perturbation theory for the collision of two black holes.This proves the power of the perturbation approach even in highly nonlinear problems while at the same time indicating its limits.In the concluding remarks of their pioneering paper on nonradial oscillations of neutron stars Thorne and Campollataro [202]described it as “just a modest introduction to a story which promises to be long,complicated and fascinating ”.The story has undoubtedly proved to be intriguing,and many authors have contributed to our present understanding of the pulsations of both black holes and neutron stars.Thirty years after these prophetic words by Thorne and Campollataro hundreds of papers have been written in an attempt to understand the stability,the characteristic frequencies and the mechanisms of excitation of these oscillations.Their relevance to the emission of gravitational waves was always the basic underlying reason of each study.An account of all this work will be attempted in the next sections hoping that the interested reader will find this review useful both as a guide to the literature and as an inspiration for future work on the open problems of the field.020406080100Time (M ADM )-0.3-0.2-0.10.00.10.20.3(l =2) Z e r i l l i F u n c t i o n Numerical solutionQNM fit Figure 1:QNM ringing after the head-on collision of two unequal mass black holes [29].The continuous line corresponds to the full nonlinear numerical calculation while the dotted line is a fit to the fundamental and first overtone QNM.In the next section we attempt to give a mathematical definition of QNMs.Living Reviews in Relativity (1999-2)K.D.Kokkotas and B.G.Schmidt6 The third and fourth section will be devoted to the study of the black hole and stellar QNMs.In thefifth section we discuss the excitation and observation of QNMs andfinally in the sixth section we will mention the more significant numerical techniques used in the study of QNMs.Living Reviews in Relativity(1999-2)7Quasi-Normal Modes of Stars and Black Holes 2Normal Modes–Quasi-Normal Modes–Res-onancesBefore discussing quasi-normal modes it is useful to remember what normal modes are!Compact classical linear oscillating systems such asfinite strings,mem-branes,or cavitiesfilled with electromagnetic radiation have preferred time harmonic states of motion(ωis real):χn(t,x)=e iωn tχn(x),n=1,2,3...,(1) if dissipation is neglected.(We assumeχto be some complex valuedfield.) There is generally an infinite collection of such periodic solutions,and the“gen-eral solution”can be expressed as a superposition,χ(t,x)=∞n=1a n e iωn tχn(x),(2)of such normal modes.The simplest example is a string of length L which isfixed at its ends.All such systems can be described by systems of partial differential equations of the type(χmay be a vector)∂χ∂t=Aχ,(3)where A is a linear operator acting only on the spatial variables.Because of thefiniteness of the system the time evolution is only determined if some boundary conditions are prescribed.The search for solutions periodic in time leads to a boundary value problem in the spatial variables.In simple cases it is of the Sturm-Liouville type.The treatment of such boundary value problems for differential equations played an important role in the development of Hilbert space techniques.A Hilbert space is chosen such that the differential operator becomes sym-metric.Due to the boundary conditions dictated by the physical problem,A becomes a self-adjoint operator on the appropriate Hilbert space and has a pure point spectrum.The eigenfunctions and eigenvalues determine the periodic solutions(1).The definition of self-adjointness is rather subtle from a physicist’s point of view since fairly complicated“domain issues”play an essential role.(See[43] where a mathematical exposition for physicists is given.)The wave equation modeling thefinite string has solutions of various degrees of differentiability. To describe all“realistic situations”,clearly C∞functions should be sufficient. Sometimes it may,however,also be convenient to consider more general solu-tions.From the mathematical point of view the collection of all smooth functions is not a natural setting to study the wave equation because sequences of solutionsLiving Reviews in Relativity(1999-2)K.D.Kokkotas and B.G.Schmidt8 exist which converge to non-smooth solutions.To establish such powerful state-ments like(2)one has to study the equation on certain subsets of the Hilbert space of square integrable functions.For“nice”equations it usually happens that the eigenfunctions are in fact analytic.They can then be used to gen-erate,for example,all smooth solutions by a pointwise converging series(2). The key point is that we need some mathematical sophistication to obtain the “completeness property”of the eigenfunctions.This picture of“normal modes”changes when we consider“open systems”which can lose energy to infinity.The simplest case are waves on an infinite string.The general solution of this problem isχ(t,x)=A(t−x)+B(t+x)(4) with“arbitrary”functions A and B.Which solutions should we study?Since we have all solutions,this is not a serious question.In more general cases, however,in which the general solution is not known,we have to select a certain class of solutions which we consider as relevant for the physical problem.Let us consider for the following discussion,as an example,a wave equation with a potential on the real line,∂2∂t2χ+ −∂2∂x2+V(x)χ=0.(5)Cauchy dataχ(0,x),∂tχ(0,x)which have two derivatives determine a unique twice differentiable solution.No boundary condition is needed at infinity to determine the time evolution of the data!This can be established by fairly simple PDE theory[116].There exist solutions for which the support of thefields are spatially compact, or–the other extreme–solutions with infinite total energy for which thefields grow at spatial infinity in a quite arbitrary way!From the point of view of physics smooth solutions with spatially compact support should be the relevant class–who cares what happens near infinity! Again it turns out that mathematically it is more convenient to study all solu-tions offinite total energy.Then the relevant operator is again self-adjoint,but now its spectrum is purely“continuous”.There are no eigenfunctions which are square integrable.Only“improper eigenfunctions”like plane waves exist.This expresses the fact that wefind a solution of the form(1)for any realωand by forming appropriate superpositions one can construct solutions which are “almost eigenfunctions”.(In the case V(x)≡0these are wave packets formed from plane waves.)These solutions are the analogs of normal modes for infinite systems.Let us now turn to the discussion of“quasi-normal modes”which are concep-tually different to normal modes.To define quasi-normal modes let us consider the wave equation(5)for potentials with V≥0which vanish for|x|>x0.Then in this case all solutions determined by data of compact support are bounded: |χ(t,x)|<C.We can use Laplace transformation techniques to represent such Living Reviews in Relativity(1999-2)9Quasi-Normal Modes of Stars and Black Holes solutions.The Laplace transformˆχ(s,x)(s>0real)of a solutionχ(t,x)isˆχ(s,x)= ∞0e−stχ(t,x)dt,(6) and satisfies the ordinary differential equations2ˆχ−ˆχ +Vˆχ=+sχ(0,x)+∂tχ(0,x),(7) wheres2ˆχ−ˆχ +Vˆχ=0(8) is the homogeneous equation.The boundedness ofχimplies thatˆχis analytic for positive,real s,and has an analytic continuation onto the complex half plane Re(s)>0.Which solutionˆχof this inhomogeneous equation gives the unique solution in spacetime determined by the data?There is no arbitrariness;only one of the Green functions for the inhomogeneous equation is correct!All Green functions can be constructed by the following well known method. Choose any two linearly independent solutions of the homogeneous equation f−(s,x)and f+(s,x),and defineG(s,x,x )=1W(s)f−(s,x )f+(s,x)(x <x),f−(s,x)f+(s,x )(x >x),(9)where W(s)is the Wronskian of f−and f+.If we denote the inhomogeneity of(7)by j,a solution of(7)isˆχ(s,x)= ∞−∞G(s,x,x )j(s,x )dx .(10) We still have to select a unique pair of solutions f−,f+.Here the information that the solution in spacetime is bounded can be used.The definition of the Laplace transform implies thatˆχis bounded as a function of x.Because the potential V vanishes for|x|>x0,the solutions of the homogeneous equation(8) for|x|>x0aref=e±sx.(11) The following pair of solutionsf+=e−sx for x>x0,f−=e+sx for x<−x0,(12) which is linearly independent for Re(s)>0,gives the unique Green function which defines a bounded solution for j of compact support.Note that for Re(s)>0the solution f+is exponentially decaying for large x and f−is expo-nentially decaying for small x.For small x however,f+will be a linear com-bination a(s)e−sx+b(s)e sx which will in general grow exponentially.Similar behavior is found for f−.Living Reviews in Relativity(1999-2)K.D.Kokkotas and B.G.Schmidt 10Quasi-Normal mode frequencies s n can be defined as those complex numbers for whichf +(s n ,x )=c (s n )f −(s n ,x ),(13)that is the two functions become linearly dependent,the Wronskian vanishes and the Green function is singular!The corresponding solutions f +(s n ,x )are called quasi eigenfunctions.Are there such numbers s n ?From the boundedness of the solution in space-time we know that the unique Green function must exist for Re (s )>0.Hence f +,f −are linearly independent for those values of s .However,as solutions f +,f −of the homogeneous equation (8)they have a unique continuation to the complex s plane.In [35]it is shown that for positive potentials with compact support there is always a countable number of zeros of the Wronskian with Re (s )<0.What is the mathematical and physical significance of the quasi-normal fre-quencies s n and the corresponding quasi-normal functions f +?First of all we should note that because of Re (s )<0the function f +grows exponentially for small and large x !The corresponding spacetime solution e s n t f +(s n ,x )is therefore not a physically relevant solution,unlike the normal modes.If one studies the inverse Laplace transformation and expresses χas a com-plex line integral (a >0),χ(t,x )=12πi +∞−∞e (a +is )t ˆχ(a +is,x )ds,(14)one can deform the path of the complex integration and show that the late time behavior of solutions can be approximated in finite parts of the space by a finite sum of the form χ(t,x )∼N n =1a n e (αn +iβn )t f +(s n ,x ).(15)Here we assume that Re (s n +1)<Re (s n )<0,s n =αn +iβn .The approxi-mation ∼means that if we choose x 0,x 1, and t 0then there exists a constant C (t 0,x 0,x 1, )such that χ(t,x )−N n =1a n e (αn +iβn )t f +(s n ,x ) ≤Ce (−|αN +1|+ )t (16)holds for t >t 0,x 0<x <x 1, >0with C (t 0,x 0,x 1, )independent of t .The constants a n depend only on the data [35]!This implies in particular that all solutions defined by data of compact support decay exponentially in time on spatially bounded regions.The generic leading order decay is determined by the quasi-normal mode frequency with the largest real part s 1,i.e.slowest damping.On finite intervals and for late times the solution is approximated by a finite sum of quasi eigenfunctions (15).It is presently unclear whether one can strengthen (16)to a statement like (2),a pointwise expansion of the late time solution in terms of quasi-normal Living Reviews in Relativity (1999-2)11Quasi-Normal Modes of Stars and Black Holes modes.For one particular potential(P¨o schl-Teller)this has been shown by Beyer[42].Let us now consider the case where the potential is positive for all x,but decays near infinity as happens for example for the wave equation on the static Schwarzschild spacetime.Data of compact support determine again solutions which are bounded[117].Hence we can proceed as before.Thefirst new point concerns the definitions of f±.It can be shown that the homogeneous equation(8)has for each real positive s a unique solution f+(s,x)such that lim x→∞(e sx f+(s,x))=1holds and correspondingly for f−.These functions are uniquely determined,define the correct Green function and have analytic continuations onto the complex half plane Re(s)>0.It is however quite complicated to get a good representation of these func-tions.If the point at infinity is not a regular singular point,we do not even get converging series expansions for f±.(This is particularly serious for values of s with negative real part because we expect exponential growth in x).The next new feature is that the analyticity properties of f±in the complex s plane depend on the decay of the potential.To obtain information about analytic continuation,even use of analyticity properties of the potential in x is made!Branch cuts may occur.Nevertheless in a lot of cases an infinite number of quasi-normal mode frequencies exists.The fact that the potential never vanishes may,however,destroy the expo-nential decay in time of the solutions and therefore the essential properties of the quasi-normal modes.This probably happens if the potential decays slower than exponentially.There is,however,the following way out:Suppose you want to study a solution determined by data of compact support from t=0to some largefinite time t=T.Up to this time the solution is–because of domain of dependence properties–completely independent of the potential for sufficiently large x.Hence we may see an exponential decay of the form(15)in a time range t1<t<T.This is the behavior seen in numerical calculations.The situation is similar in the case ofα-decay in quantum mechanics.A comparison of quasi-normal modes of wave equations and resonances in quantum theory can be found in the appendix,see section9.Living Reviews in Relativity(1999-2)K.D.Kokkotas and B.G.Schmidt123Quasi-Normal Modes of Black HolesOne of the most interesting aspects of gravitational wave detection will be the connection with the existence of black holes[201].Although there are presently several indirect ways of identifying black holes in the universe,gravitational waves emitted by an oscillating black hole will carry a uniquefingerprint which would lead to the direct identification of their existence.As we mentioned earlier,gravitational radiation from black hole oscillations exhibits certain characteristic frequencies which are independent of the pro-cesses giving rise to these oscillations.These“quasi-normal”frequencies are directly connected to the parameters of the black hole(mass,charge and angu-lar momentum)and for stellar mass black holes are expected to be inside the bandwidth of the constructed gravitational wave detectors.The perturbations of a Schwarzschild black hole reduce to a simple wave equation which has been studied extensively.The wave equation for the case of a Reissner-Nordstr¨o m black hole is more or less similar to the Schwarzschild case,but for Kerr one has to solve a system of coupled wave equations(one for the radial part and one for the angular part).For this reason the Kerr case has been studied less thoroughly.Finally,in the case of Kerr-Newman black holes we face the problem that the perturbations cannot be separated in their angular and radial parts and thus apart from special cases[124]the problem has not been studied at all.3.1Schwarzschild Black HolesThe study of perturbations of Schwarzschild black holes assumes a small per-turbation hµνon a static spherically symmetric background metricds2=g0µνdxµdxν=−e v(r)dt2+eλ(r)dr2+r2 dθ2+sin2θdφ2 ,(17) with the perturbed metric having the formgµν=g0µν+hµν,(18) which leads to a variation of the Einstein equations i.e.δGµν=4πδTµν.(19) By assuming a decomposition into tensor spherical harmonics for each hµνof the formχ(t,r,θ,φ)= mχ m(r,t)r Y m(θ,φ),(20)the perturbation problem is reduced to a single wave equation,for the func-tionχ m(r,t)(which is a combination of the various components of hµν).It should be pointed out that equation(20)is an expansion for scalar quantities only.From the10independent components of the hµνonly h tt,h tr,and h rr transform as scalars under rotations.The h tθ,h tφ,h rθ,and h rφtransform asLiving Reviews in Relativity(1999-2)13Quasi-Normal Modes of Stars and Black Holes components of two-vectors under rotations and can be expanded in a series of vector spherical harmonics while the components hθθ,hθφ,and hφφtransform as components of a2×2tensor and can be expanded in a series of tensor spher-ical harmonics(see[202,212,152]for details).There are two classes of vector spherical harmonics(polar and axial)which are build out of combinations of the Levi-Civita volume form and the gradient operator acting on the scalar spherical harmonics.The difference between the two families is their parity. Under the parity operatorπa spherical harmonic with index transforms as (−1) ,the polar class of perturbations transform under parity in the same way, as(−1) ,and the axial perturbations as(−1) +11.Finally,since we are dealing with spherically symmetric spacetimes the solution will be independent of m, thus this subscript can be omitted.The radial component of a perturbation outside the event horizon satisfies the following wave equation,∂2∂t χ + −∂2∂r∗+V (r)χ =0,(21)where r∗is the“tortoise”radial coordinate defined byr∗=r+2M log(r/2M−1),(22) and M is the mass of the black hole.For“axial”perturbationsV (r)= 1−2M r ( +1)r+2σMr(23)is the effective potential or(as it is known in the literature)Regge-Wheeler potential[173],which is a single potential barrier with a peak around r=3M, which is the location of the unstable photon orbit.The form(23)is true even if we consider scalar or electromagnetic testfields as perturbations.The parameter σtakes the values1for scalar perturbations,0for electromagnetic perturbations, and−3for gravitational perturbations and can be expressed asσ=1−s2,where s=0,1,2is the spin of the perturbingfield.For“polar”perturbations the effective potential was derived by Zerilli[212]and has the form V (r)= 1−2M r 2n2(n+1)r3+6n2Mr2+18nM2r+18M3r3(nr+3M)2,(24)1In the literature the polar perturbations are also called even-parity because they are characterized by their behavior under parity operations as discussed earlier,and in the same way the axial perturbations are called odd-parity.We will stick to the polar/axial terminology since there is a confusion with the definition of the parity operation,the reason is that to most people,the words“even”and“odd”imply that a mode transforms underπas(−1)2n or(−1)2n+1respectively(for n some integer).However only the polar modes with even have even parity and only axial modes with even have odd parity.If is odd,then polar modes have odd parity and axial modes have even parity.Another terminology is to call the polar perturbations spheroidal and the axial ones toroidal.This definition is coming from the study of stellar pulsations in Newtonian theory and represents the type offluid motions that each type of perturbation induces.Since we are dealing both with stars and black holes we will stick to the polar/axial terminology.Living Reviews in Relativity(1999-2)K.D.Kokkotas and B.G.Schmidt14where2n=( −1)( +2).(25) Chandrasekhar[54]has shown that one can transform the equation(21)for “axial”modes to the corresponding one for“polar”modes via a transforma-tion involving differential operations.It can also be shown that both forms are connected to the Bardeen-Press[38]perturbation equation derived via the Newman-Penrose formalism.The potential V (r∗)decays exponentially near the horizon,r∗→−∞,and as r−2∗for r∗→+∞.From the form of equation(21)it is evident that the study of black hole perturbations will follow the footsteps of the theory outlined in section2.Kay and Wald[117]have shown that solutions with data of compact sup-port are bounded.Hence we know that the time independent Green function G(s,r∗,r ∗)is analytic for Re(s)>0.The essential difficulty is now to obtain the solutions f±(cf.equation(10))of the equations2ˆχ−ˆχ +Vˆχ=0,(26) (prime denotes differentiation with respect to r∗)which satisfy for real,positives:f+∼e−sr∗for r∗→∞,f−∼e+r∗x for r∗→−∞.(27) To determine the quasi-normal modes we need the analytic continuations of these functions.As the horizon(r∗→∞)is a regular singular point of(26),a representation of f−(r∗,s)as a converging series exists.For M=12it reads:f−(r,s)=(r−1)s∞n=0a n(s)(r−1)n.(28)The series converges for all complex s and|r−1|<1[162].(The analytic extension of f−is investigated in[115].)The result is that f−has an extension to the complex s plane with poles only at negative real integers.The representation of f+is more complicated:Because infinity is a singular point no power series expansion like(28)exists.A representation coming from the iteration of the defining integral equation is given by Jensen and Candelas[115],see also[159]. It turns out that the continuation of f+has a branch cut Re(s)≤0due to the decay r−2for large r[115].The most extensive mathematical investigation of quasi-normal modes of the Schwarzschild solution is contained in the paper by Bachelot and Motet-Bachelot[35].Here the existence of an infinite number of quasi-normal modes is demonstrated.Truncating the potential(23)to make it of compact support leads to the estimate(16).The decay of solutions in time is not exponential because of the weak decay of the potential for large r.At late times,the quasi-normal oscillations are swamped by the radiative tail[166,167].This tail radiation is of interest in its Living Reviews in Relativity(1999-2)。

惠昌常教授通俗报告会题目:代数的表现法报告人:惠昌常教授(北京师范大学长江学者,德国洪堡Bessel科研奖获得者)摘要:众所周知,任何有限群都是对称群的子群。
这样,对于一个抽象的群来说,它的元素我们总可以用置换来实现。
那么,对于有三个运算的一个代数而言,如何来实现它呢?在这个报告中,我们将介绍三种表现的方法:矩阵法,图表法和箭图法。
时间:2011年12月21日下午3:00地点:安徽大学磬苑校区博北D101科技处数学科学学院惠昌常教授系列学术报告会报告人:惠昌常教授(北京师范大学长江学者,德国洪堡Bessel科研奖获得者)报告一:题目:Module categories and BB-tilting modules摘要:In the first lecture, we shall talk about how to get derived equivalences from module categories. This is related to the Auslander-Reiten sequences, or more generally, to the so-called D-split sequences. Of course, basic definitions and elementary results will be recalled.时间:2011年12月22日上午9:00地点:安徽大学磬苑校区博学北楼A401报告二:Triangulated categories and Auslander-Yoneda algebras摘要:In this lecture, we shall see how to extend our result systematically from module categories to triangulated categories. Here we shall work with the so-called $\Phi$-Auslander-Yoneda algebras.时间:2011年12月23日下午2:30地点:安徽大学磬苑校区博学北楼A401举办单位:安徽大学数学科学学院∙报告人简介:∙惠昌常,北京师范大学数学科学学院长江学者特聘教授、博士生导师,德国洪堡Bessel科研奖获得者(2006)。

数学: 科学的王后和仆人Mathematics: Queen and Servant of Science北京理工大学叶其孝本文的题目是已故的美国科学院院士、著名数学家、数学史学家和科普作家Eric Temple Bell(贝尔, 1883, 02, 07 ~ 1960, 12, 21)于1951年写的一本书的书名Mathematics: Queen and Servant of Science (数学: 科学的王后和仆人). 该书主要是为大学生和非数学领域的人士写的, 介绍纯粹和应用数学的各个方面, 更着重在说明数学科学的极端重要性.The Mathematical Association of America, 1996, 463 pages实际上这是他1931年写的The Queen of the Sciences (科学的王后)和1937年写的The Handmaiden of the Sciences (科学的女仆)这两本通俗数学论著的合一修订扩大版.Eric Temple Bell Alexander Graham Bell (1847 ~ 1922) 按常识的理解, 女王是优美、高雅、无懈可击、至尊至贵的, 在科学中只有纯粹数学才具有这样的特点, 简洁明了的数学定理一经证明就是永恒的真理, 极其优美而且无懈可击;另一方面, 科学和工程的各个分支都在不同程度上大量应用数学, 这时数学科学就是仆人, 这些仆人是否强有力, 用起来是否得心应手是雇佣这些仆人的主人最为关心的事. 事实上, servant这个字本身就有“供人们利用之物, 有用的服务工具”的意思. 毫无疑问, 我们的目的不是为数学争一个好的名分, 而是想说明数学是怎样通过数学建模来解决各种实际问题的; 数学(数学建模)的极端重要性, 以及探讨正确认识和理解数学科学的作用对于发展我国科学技术、经济以及教育, 从而争取在21世纪把我国真正建设成为屹立于世界民族之林的强国,乃至个人事业发展的至关重要性. 当然, 我们也希望说明王后和仆人集于一身并不矛盾. 历史上, 很多特别受人尊敬的科学家, 不仅仅是由于他们的科学成就, 更因为他们的科学成就能够服务于人类.数学是科学的王后, 算术是数学的王后. 她常常放下架子为天文学和其他科学效劳, 但是在所有情况下, 第一位的是她(数学)应尽的责任. (高斯)Mathematics is the Queen of the Sciences, and Arithmetic the Queen of Mathematics. She often condescends to render service to astronomy and other natural sciences, but under all circumstance the first place is her due.— Carl Friedrich Gauss (卡尔·弗里德里希·高斯, 1777, 4, 30 ~ 1855, 2, 23)From: Bell, Eric T., Mathematics: Queen and Servant of Science, MAA, 1951, p.1;Men of Mathematics, Simon and Schuster, New York, 1937, p. xv.***************************************************自古以来,数学的发展始终与科学技术的发展紧密相连,反之亦然. 首先, 我们来看一下导致我们现在这个飞速发展的信息社会的19、20世纪几乎所有重大科学理论的发展和完善过程中数学(数学建模)所起到的不可勿缺的作用.数学研究的成果往往是重大科学发明的催生素(仅就19、20世纪而言, 流体力学、电磁理论、相对论、量子力学、计算机、信息论、控制论、现代经济学、万维网和互联网搜索引擎、生物学、CT、甚至社会政治学领域等). 但是20世纪上半世纪, 数学虽然也直接为工程技术提供一些工具, 但基本方式是间接的: 先促进其他科学的发展, 再由这些科学提供工程原理和设计的基础. 数学是幕后的无名英雄.现在, 数学无处不在, 数学和工程技术之间,在更广阔的范围内和更深刻的程度上, 直接地相互作用着, 极大地推动了科学和工程科学的发展, 也极大地推动了技术的发展. 数学不仅是幕后的无名英雄, 很多方面开始走向“前台”. 但是对数学的极端重要性迄今尚未有共识, 取得共识对加强一个国家的竞争力来说是至关重要的.硬能力―一位美国朋友谈及对未来中国人的看法: 20年后, 中国年轻人会丢了中国人现在的硬能力, 他们崇拜各种明星, 不愿献身科学, 不再以学术研究为荣, 聪明拔尖的学生都去学金融、法律等赚钱的专业; 而美国人因为认识到其硬能力(例如数学)不行, 进行教育改革, 20年后, 不但保持了其软实力即非专业能力的优势, 而且在硬能力上赶上中国人.‖“正在丢失的硬实力”, 鲁鸣, 《青年文摘》2011年第5期动向:美国很多州新办STEM高中, 一些大学开始开设STEM课程等.STEM = Science + Technology + Engineering + Mathematics2012年2月7日公布的美国总统科技顾问委员会给总统的报告,参与超越:培养额外的100万具有科学、技术、工程和数学学位的大学生(Engage to Excel: Producing One Million Additional College Graduates with Degrees in Science, Technology, Engineering, and Mathematics)The Mathematical Sciences in 2025, the National Academies Press, 2013人们使用的数学科学思想、概念和方法的范围在不断扩大的同时,数学科学的用途也在不断扩展. 21世纪的大部分科学与工程将建立在数学科学的基础上.This major expansion in the uses of the mathematical sciences has been paralleled by a broadening in the range of mathematical science ideas and techniques being used. Much of twenty-first century science and engineering is going to be built on a mathematical science foundation, and that foundation must continue to evolve and expand.数学科学是日常生活的几乎每个方面的组成部分.互联网搜索、医疗成像、电脑动画、数值天气预报和其他计算机模拟、所有类型的数字通信、商业和军事中的优化问题以及金融风险的分析——普通公民都从支撑这些应用功能的数学科学的各种进展中获益,这样的例子不胜枚举.The mathematical sciences are part of almost every aspect of everyday life. Internet search, medical imaging, computer animation, numerical weather predictions and othercomputer simulations, digital communications of all types, optimization in business and the military, analyses of financial risks —average citizens all benefit from the mathematical science advances that underpin these capabilities, and the list goes on and on.调查发现:数学科学研究工作正日益成为生物学、医学、社会科学、商业、先进设计、气候、金融、先进材料等许多研究领域不可或缺的重要组成部分. 这种研究工作涉及最广泛意义下数学、统计学和计算综合,以及这些领域与潜在应用领域的相互作用. 所有这些活动对于经济增长、国家竞争力和国家安全都是至关重要的,而且这种事实应该对作为整体的数学科学的资助性质和资助规模产生影响. 数学科学的教育也应该反映数学科学领域的新的状况.Finding: Mathematical sciences work is becoming an increasingly integral and essential component of a growing array of areas of investigation in biology, medicine, social sciences, business, advanced design, climate, finance, advanced materials, and many more. This work involves the integration of mathematics, statistics, and computation in the broadest sense and the interplay of these areas withareas of potential application. All of these activities are crucial to economic growth, national competitiveness, and national security, and this fact should inform both the nature and scale of funding for the mathematical sciences as a whole. Education in the mathematical sciences should also reflect this new stature of the field.****************************************************************为了以下讲述的方便, 我们先来了解一下什么是数学建模.数学模型(Mathematical Model)是用数学符号对一类实际问题或实际发生的现象的(近似的)描述.数学建模(Mathematical Modeling)则是获得该模型并对之求解、验证并得到结论的全过程.数学建模不仅是了解基本规律, 而且从应用的观点来看更重要的是预测和控制所建模的系统的行为的强有力的工具.数学建模是数学用来解决各种实际问题的桥梁.↑→→→→→→→→↓↑↓↑↓↓↑↓←←←←←通不过↓↓通过)定义:数学建模就是上述框图多次执行的过程数学建模的难点观察、分析实际问题, 作出合理的假设, 明确变量和参数, 形成明确的数学问题. 不仅仅是翻译的问题; 涉及的数学问题可能是复杂、困难的, 求解也许涉及深刻的数学方法. 如何作出正确的判断, 寻找合适、简洁的(解析或近似) 解法; 如何验证模型.简言之:合理假设、模型建立、模型求解、解释验证.记住这16个字, 将会终生受用.数学建模的重要作用:源头创新当然数学建模也有局限性, 不能单独包打天下, 因为实际问题是非常复杂的, 需要多学科协同解决.在图灵(A. M. Turing)的文章: The Chemical Basis of Morphogenesis (形态生成的化学基础), Philosophical Transactions of the Royal Society of London (伦敦皇家学会哲学公报), Series B (Biological Sciences),v.237(1952), 37-72.1. 一个胚胎的模型. 成形素本节将描述一个正在生长的胚胎的数学模型. 该模型是一种简化和理想化, 因此是对原问题的篡改. 希望本文论述中保留的一些特征, 就现今的知识状况而言, 是那些最重要的特征.1. A model of the embryo. MorphogensIn this section a mathematical model of the growing embryo will be described. This model will be asimplification and an idealization, and consequently a falsification. It is to be hoped that the features retained for discussion are those of greatest importance in the present state of knowledge.想单靠数学建模本身来解决重大的生物学问题是不可能的,另一方面,想仅仅依靠实验来获得对生物学的合理、完整的理解也是极不可能的. There is no way mathematical modeling can solve major biological problems on its own. On the other hand, it ishighly unlikely that even a reasonably complete understanding could come solely from experiment.—— J. D. Murray, Why Are There No 3-Headed Monsters? Mathematical Modeling in Biology, Notices of the AMS,v. 59 (2012), no. 6, p.793.自古以来公平、公正的竞赛都是培养、选拔人才的重要手段, 科学和数学也不例外.中学生IMO (国际数学奥林匹克(International Mathematical Olympiad), 1959 ~)北美的大学生Putnbam数学竞赛(1938 ~)全国大学生数学竞赛(2010 ~)Mathematical Contest in Modeling (MCM, 1985 ~)美国大学生数学建模竞赛Interdisciplinary Contest in Modeling (ICM, 1999~)美国大学生跨学科建模竞赛China Undergraduate Mathematical Contest in Modeling (CUMCM, 1992~) 中国大学生数学建模竞赛中国大学生参加美国大学生数学建模竞赛情况中国大学生数学建模竞赛情况在以下讲述中涉及物理方面的具体的数学模型 (问题)的叙述和初步讨论可参考《物理学与偏微分方程》, 李大潜、秦铁虎编著, (上册, 1997; 下册, 2000), 高等教育出版社.Seven equations that rule your world (主宰你生活的七个方程式), by Ian Stewart, NewScientist, 13 February 2012.Fourier transformation 2ˆ()()ix f f x e dx πξξ∞--∞=⎰Wave equation 22222u u c t x ∂∂=∂∂ Ma xwell‘s equation110, , 0, H E E E H H c t c t∂∂∇⋅=∇⨯=-∇⋅=∇⨯=∂∂Schrödinger‘s equation ˆψH ψi t∂=∂Ian Stewart, In Pursuit of the Unknown:17 Equations That Changed the World (追求对未知的认识:改变世界的17个方程), Basic Books, March 13, 2012.目录(Contents)Why Equations? /viii1. The squaw on the hippopotamus ——Pythagoras‘sTheorem/12. Shortening the proceedings —— Logarithms/213. Ghosts of departed quantities —— Calculus/354. The system of the world ——Newton‘s Law ofGravity/535. Portent of the ideal world —— The Square Root ofMinus One/736. Much ado about knotting ——Euler‘s Formula forPolyhedra/837. Patterns of chance —— Normal Distribution/1078. Good vibrations —— Wave Equation/1319. Ripples and blips —— Fourier Transform/14910. The ascent of humanity —— Navier-StokesEquation/16511. Wave in the ether ——Maxwell‘s Equations/17912. Law and disorder —— Second Law ofThermodynamics /19513. One thing is absolute —— Relativity/21714. Quantum weirdness —— Schrödinger Equation/24515. Codes, communications, and computers ——Information Theory/26516. The imbalance of nature —— Chaos Theory/28317. The Midas formula —— Black-Scholes Equation/195Where Next?/317Notes/321Illustration Credits/330Index/331相对论Albert Einstein(1879, 3, 14 ~1955, 4, 18)20世纪最伟大的科学成就莫过于Einstein(爱因斯坦)的狭义和广义相对论了, 但是如果没有Minkowski (闵可夫斯基)几何、Riemann(黎曼)于1854年发明的Riemann几何, 以及Cayley(凯莱), Sylvester(西勒维斯特)和Noether(诺特)等数学家发展的不变量理论, Einstein的广义相对论和引力理论就不可能有如此完善的数学表述. Einstein自己也不止一次地说过.早在1905年, 年仅26岁的爱因斯坦就已提出了狭义相对论. 狭义相对论推倒了牛顿力学的质量守恒、能量守恒、质量能量互不相关、时空永恒不变的基本命题. 这是一场真正的科学革命.为了导出狭义相对论,爱因斯坦作出了两个假设:运动的相对性(所有匀速运动都是相对的)和光速为常数(光的运动例外, 它是绝对的). (1)狭义相对性原理,即在所有惯性系中, 物理学定律具有相同的数学表达形式;(2)光速不变原理,真空中光沿各个方向传播的速率都相等,与光源和观察者的运动状态无关.时空不是绝对独立的.由此可以导出一些推论: 相对论坐标变换式和速度变换式, 同时的相对性, 钟慢尺缩效应和质能关系式等.他的好友物理学家P.Ehrenfest指出实际上还蕴涵着第三个假设, 即这两个假设是不矛盾的. 物体运动的相对性和光速的绝对性, 两者之间的相互制约和作用乃是相对论里一切我们不熟悉的时空特征的根源.(部分参阅李新洲:《寻找自然之律--- 20世纪物理学革命》, 上海科技教育出版社, 2001.)1907 年德国数学家H. Minkowski (1864 ~1909) 提出了―Minkowski 空间‖,即把时间和空间融合在一起的四维空间1,3R. Minkowski 几何为Einstein 狭义相对论提供了合适的数学模型.“没有任何客观合理的方法能够把四维连续统分离成三维空间连续统和一维时间连续统. 因此从逻辑上讲, 在四维时空连续统(space- time continuum)中表述自然定律会更令人满意. 相对论在方法上的巨大进步正是建立在这个基础之上的, 这种进步归功于闵可夫斯基(Minkowski).”—Albert Einstein, The Meaning of Relativity, 1922, Princeton University Press. 中译本, 阿尔伯特·爱因斯坦著, 相对论的意义, (普林斯顿科学文库(Princeton Science Library) 1), 郝建纲、刘道军译, 上海科技教育出版社, 2001, p. 27.有了Minkowski 时空模型后, Einstein 又进一步研究引力场理论以建立广义相对论. 1912 年夏他已经概括出新的引力理论的基本物理原理, 但是为了实现广义相对论的目标, 还必须寻求理论的数学结构, Einstein 为此花了 3 年的时间, 最后, 在数学家M. Grossmann 的介绍下学习掌握了发展相对论引力学说所必需的数学工具—以Riemann几何和Ricci, Levi - Civita的绝对微分学, 也就是Einstein 后来所称的张量分析.“根据前面的讨论, 很显然, 如果要表达广义相对论, 就需要对不变量理论以及张量理论加以推广. 这就产生了一个问题, 即要求方程的形式必须对于任意的点变换都是协变的. 在相对论产生以前很久, 数学家们就已经建立了推广的张量演算理论. 黎曼(Riemann)首先把高斯(Gauss)的思路推广到了任意维连续统, 他很有预见性地看到了……进行这种推广的物理意义. 随后, 这个理论以张量微积分的形式得到了发展, 对此里奇(Ricci)和莱维·齐维塔(Tulio Levi-Civita, 1873~1941)做出了重要贡献. ”—阿尔伯特·爱因斯坦著, 相对论的意义, 郝建纲、刘道军译, 上海科技教育出版社, 2001, p. 57.从数学建模的角度看, 广义相对论讨论的中心问题是引力理论, 其基础是以下两个假设: 1. (等效原理)惯性力场与引力场的动力学效应是局部不可分辨的,(或说引力和非惯性系中的惯性力等效);2. (广义相对性原理) 一切参考系都是平权的,换言之,客观的真实的物理规律应该在任意坐标变换下形式不变——广义协变性(即一切物理定律在所有参考系[无论是惯性的或非惯性的]中都具有相同的形式)。
Abbreviations of Names of SerialsThis list gives the form of references used in Mathematical Reviews(MR).The abbreviation is followed by the complete title,the place of publication and other pertinent information.∗not previously listed E available electronically §journal reviewed cover-to-cover V videocassette series †monographic series¶bibliographic journal∗Abh.Braunschw.Wiss.Ges.Abhandlungen derBraunschweigischen Wissenschaftlichen Gesellschaft.J.Cramer Verlag,Braunschweig.(Formerly Abh.Braunschweig.Wiss.Ges.)Abh.Braunschweig.Wiss.Ges.Abhandlungen derBraunschweigischen Wissenschaftlichen Gesellschaft.Goltze,G¨o ttingen.(Continued as Abh.Braunschw.Wiss.Ges.)§Abh.Math.Sem.Univ.Hamburg Abhandlungen aus dem Mathematischen Seminar der Universit¨a t Hamburg.Vandenhoeck&Ruprecht,G¨o ttingen.ISSN0025-5858.†Abh.Math.-Naturwiss.Kl.Akad.Wiss.Lit.Mainz Abhandlungen der Mathematisch-NaturwissenschaftlichenKlasse.Akademie der Wissenschaften und der Literaturin Mainz.[Transactions of the Mathematical-ScientificSection.Academy of Sciences and Literature in Mainz]Steiner,Stuttgart.ISSN0002-2993.§Abstr.Appl.Anal.Abstract and Applied Analysis.Mancorp,Tampa,FL.ISSN1085-3375.¶Abstracts Amer.Math.Soc.Abstracts of Papers Presented to the American Mathematical Society.Amer.Math.Soc.,Providence,RI.ISSN0192-5857.Acad.Roy.Belg.Bull.Cl.Sci.(6)Acad´e mie Royale deBelgique.Bulletin de la Classe des Sciences.6e S´e rie.Acad.Roy.Belgique,Brussels.ISSN0001-4141.Acad.Roy.Belg.Cl.Sci.M´e m.Collect.8o(3)Acad´e mieRoyale de Belgique.Classe des Sciences.M´e moires.Collection in-8o.3e S´e rie.Acad.Roy.Belgique,Brussels.ISSN0365-0936.Acad.Serbe Sci.Arts Glas Acad´e mie Serbe des Scienceset des Arts.Glas.Classe des Sciences Naturelles etMath´e matiques.Srpska Akad.Nauk.i Umetnost.,Belgrade.ISSN0374-7956.†Acc`e s Sci.Acc`e s Sciences.[Access to Sciences]De Boeck Univ.,Brussels.§E ACM J.Exp.Algorithmics The ACM Journal ofExperimental Algorithmics.ACM,New York.ISSN1084-6654.E ACM Trans.Math.Software Association for ComputingMachinery.Transactions on Mathematical Software.ACM,New York.ISSN0098-3500.∗§Acta Acad.Paedagog.Agriensis Sect.Mat.(N.S.)Acta Academiae Paedagogicae Agriensis.Nova Series.SectioMatematicae.Eszterh´a zy K´a roly Coll.,Eger.∗§Acta Anal.Funct.Appl.Acta Analysis Functionalis Applicata.AAFA.Yingyong Fanhanfenxi Xuebao.SciencePress,Beijing.ISSN1009-1327.§E Acta Appl.Math.Acta Applicandae Mathematicae.An International Survey Journal on Applying Mathematics andMathematical Applications.Kluwer Acad.Publ.,Dordrecht.ISSN0167-8019.§Acta Arith.Acta Arithmetica.Polish Acad.Sci.,Warsaw.ISSN0065-1036.Acta Astronom.Sinica Acta Astronomica Sinica.TianwenXuebao.Kexue Chubanshe(Science Press),Beijing.(Translated in Chinese Astronom.Astrophys.)ISSN0001-5245.Acta Astrophys.Sinica Acta Astrophysica Sinica.TiantiWuli Xuebao.Kexue Chubanshe(Science Press),Beijing.(Translated in Chinese Astronom.Astrophys.)ISSN0253-2379.Acta Automat.Sinica Acta Automatica Sinica.ZidonghuaXuebao.Kexue Chubanshe(Science Press),Beijing.ISSN0254-4156.Acta Cienc.Indica Math.Acta Ciencia Indica.Mathematics.Pragati Prakashan,Meerut.ISSN0970-0455.Acta Cient.Venezolana Acta Cient´ıfica Venezolana.Asociaci´o n Venezolana para el Avance de la Ciencia.Asoc.Venezolana Avance Cien.,Caracas.ISSN0001-5504.Acta Comment.Univ.Tartu.Math.Acta etCommentationes Universitatis Tartuensis de Mathematica.Univ.Tartu,Fac.Math.,Tartu.ISSN1406-2283.E Acta Cryst.Sect.A Acta Crystallographica.Section A:Foundations of Crystallography.Munksgaard,Copenhagen.ISSN0108-7673.§Acta Cybernet.Acta Cybernetica.J´o zsef Attila Univ.Szeged,Szeged.ISSN0324-721X.Acta Hist.Leopold.Acta Historica Leopoldina.DeutscheAkad.Naturforscher Leopoldina,Halle an der Saale.ISSN0001-5857.§E Acta Inform.Acta Informatica.Springer,Heidelberg.ISSN0001-5903.§Acta Math.Acta Mathematica.Inst.Mittag-Leffler, Djursholm.ISSN0001-5962.§E Acta Math.Acad.Paedagog.Nyh´a zi.(N.S.)Acta Mathematica.Academiae Paedagogicae Ny´ıregyh´a ziensis.New Series.Bessenyei Gy¨o rgy Coll.,Ny´ıregyh´a za.ISSN0866-0182.§Acta Math.Appl.Sinica Acta Mathematicae Applicatae Sinica.Yingyong Shuxue Xuebao.Kexue Chubanshe(Science Press),Beijing.ISSN0254-3079.§Acta Math.Appl.Sinica(English Ser.)Acta Mathematicae Applicatae Sinica.English Series.Yingyong ShuxueXuebao.Science Press,Beijing.ISSN0168-9673.§E Acta Math.Hungar.Acta Mathematica Hungarica.Akad.Kiad´o,Budapest.ISSN0236-5294.§Acta rm.Univ.Ostraviensis Acta Mathematica et Informatica Universitatis Ostraviensis.Univ.Ostrava,Ostrava.ISSN1211-4774.§Acta Math.Sci.(Chinese)Acta Mathematica Scientia.Series A.Shuxue Wuli Xuebao.Chinese Edition.KexueChubanshe(Science Press),Beijing.(See also Acta Math.Sci.(English Ed.))ISSN1003-3998.§Acta Math.Sci.(English Ed.)Acta Mathematica Scientia.Series B.English Edition.Shuxue Wuli Xuebao.SciencePress,Beijing.(See also Acta Math.Sci.(Chinese))ISSN0252-9602.§E Acta Math.Sin.(Engl.Ser.)Acta Mathematica Sinica.English Series.Springer,Heidelberg.ISSN1000-9574.§Acta Math.Sinica Acta Mathematica Sinica.Chinese Math.Soc.,Acta Math.Sinica m.,Beijing.ISSN0583-1431.§E Acta enian.(N.S.)Acta Mathematica Universitatis Comenianae.New enius Univ.Press,Bratislava.ISSN0862-9544.§Acta Math.Vietnam.Acta Mathematica Vietnamica.Nat.Center Natur.Sci.Tech.,Hanoi.ISSN0251-4184.∗Acta Mech.Sin.Engl.Ser.Acta Mechanica Sinica.English Series.The Chinese Society of Theoretical and AppliedMechanics.Chinese J.Mech.Press,Beijing.(FormerlyActa Mech.Sinica(English Ed.))ISSN0567-7718.Acta Mech.Sinica(Beijing)Acta Mechanica Sinica.LixueXuebao.Chinese J.Mech.Press,Beijing.(See also ActaMech.Sinica(English Ed.))ISSN0459-1879.Acta Mech.Sinica(English Ed.)Acta Mechanica Sinica.English Edition.Lixue Xuebao.Kexue Chubanshe(SciencePress),Beijing.(Continued as Acta Mech.Sin.Engl.Ser.)(See also Acta Mech.Sinica(Beijing))ISSN0567-7718.∗Acta Mech.Solida Sin.Acta Mechanica Solida Sinica.Chinese Journal of Solid Mechanics.Huazhong Univ.Sci.Tech.,Wuhan.ISSN0894-9166.†Acta Numer.Acta Numerica.Cambridge Univ.Press, Cambridge.ISSN0962-4929.Acta Phys.Polon.B Jagellonian University.Institute ofPhysics and Polish Physical Society.Acta Physica PolonicaB.Jagellonian Univ.,Krak´o w.ISSN0587-4254.Acta Phys.Sinica Acta Physica Sinica.Wuli Xuebao.Chinese Phys.Soc.,Beijing.ISSN1000-3290.Acta put.Manage.Eng.Ser.Acta Polytechnica Scandinavica.Mathematics,Computingand Management in Engineering Series.Finn.Acad.Tech.,Espoo.ISSN1238-9803.§Acta Sci.Math.(Szeged)Acta Universitatis Szegediensis.Acta Scientiarum Mathematicarum.Univ.Szeged,Szeged.ISSN0001-6969.Acta Sci.Natur.Univ.Jilin.Acta Scientiarum NaturaliumUniversitatis Jilinensis.Jilin Daxue.Ziran Kexue Xuebao.Jilin University.Natural Sciences Journal.Jilin Univ.Nat.Sci.J.,Editor.Dept.,Changchun.ISSN0529-0279.Acta Sci.Natur.Univ.Norm.Hunan.Acta ScientiarumNaturalium Universitatis Normalis Hunanensis.HunanShifan Daxue Ziran Kexue Xuebao.J.Hunan Norm.Univ.,Editor.Dept.,Changsha.ISSN1000-2537.Acta Sci.Natur.Univ.Pekinensis See Beijing DaxueXuebao Ziran Kexue BanActa Sci.Natur.Univ.Sunyatseni Acta ScientiarumNaturalium Universitatis Sunyatseni.Zhongshan DaxueXuebao.Ziran Kexue Ban.Journal of Sun Yatsen University.Natural Sciences.J.Zhongshan Univ.,Editor.Dept.,Guangzhou.ISSN0529-6579.Acta Tech.CSA V Acta Technica CSA V.Acad.Sci.CzechRepub.,Prague.ISSN0001-7043.§Acta Univ.Carolin.Math.Phys.Acta Universitatis Carolinae.Mathematica et Physica.Karolinum,Prague.ISSN0001-7140.§Acta Univ.Lodz.Folia Math.Acta UniversitatisLodziensis.Folia Mathematica.Wydawn.Uniw.Ł´o dzkiego,Ł´o d´z.ISSN0208-6204.Acta Univ.Lodz.Folia Philos.Acta UniversitatisLodziensis.Folia Philosophica.Wydawn.Uniw.Ł´o dzkiego,Ł´o d´z.ISSN0208-6107.∗§Acta Univ.M.Belii Ser.Math.Acta Universitatis Matthiae Belii.Natural Science Series.Series Mathematics.MatejBel Univ.,Bansk´a Bystrica.(Formerly Acta Univ.MathaeiBelii Nat.Sci.Ser.Ser.Math.)§Acta Univ.Mathaei Belii Nat.Sci.Ser.Ser.Math.Matej Bel University.Acta.Natural Science Series.Series Mathematics.Matej Bel Univ.,Bansk´a Bystrica.(Continued as Acta Univ.M.Belii Ser.Math.)Acta Univ.Oulu.Ser.A Sci.Rerum Natur.ActaUniversitatis Ouluensis.Series A.Scientiae RerumNaturalium.Univ.Oulu,Oulu.ISSN0355-3191.§Acta Univ.Palack.Olomuc.Fac.Rerum Natur.Math.Acta Universitatis Palackianae Olomucensis.Facultas Rerum Naturalium.Mathematica.ISSN0231-9721.†Acta Univ.Ups.Stud.Philos.Ups.Acta Universitatis Upsaliensis.Studia Philosophica Upsaliensia.Uppsala Univ., Uppsala.ISSN0585-5497.†Acta Univ.Upsaliensis Skr.Uppsala Univ.C Organ.Hist.Acta Universitatis Upsaliensis.Skrifter r¨o randeUppsala anisation och Historia.[ActaUniversitatis Upsaliensis.Publications concerning Uppsalaanization and History]Uppsala Univ.,Uppsala.ISSN0502-7454.†Actualit´e s Math.Actualit´e s Math´e matiques.[Current Mathematical Topics]Hermann,Paris.†Actualit´e s Sci.Indust.Actualit´e s Scientifiques etIndustrielles.[Current Scientific and Industrial Topics]Hermann,Paris.†Adapt.Learn.Syst.Signal mun.Control Adaptive and Learning Systems for Signal Processing,Communications,and Control.Wiley,New York.Adv.Appl.Clifford Algebras Advances in Applied Clifford Algebras.Univ.Nac.Aut´o noma M´e xico,M´e xico.ISSN0188-7009.†Adv.Appl.Mech.Advances in Applied Mechanics.Academic Press,Boston,MA.ISSN0065-2165.∗†Adv.Astron.Astrophys.Advances in Astronomy andAstrophysics.Gordon and Breach,Amsterdam.ISSN1025-8206.†Adv.Book Class.Advanced Book Classics.Perseus, Reading,MA.†Adv.Bound.Elem.Ser.Advances in Boundary Elements put.Mech.,Southampton.(Continued as Int.Ser.Adv.Bound.Elem.)ISSN1368-258X.†Adv.Chem.Phys.Advances in Chemical Physics.Wiley, New York.†put.Econom.Advances in Computational Economics.Kluwer Acad.Publ.,Dordrecht.§E put.Math.Advances in ComputationalMathematics.Baltzer,Bussum.ISSN1019-7168.†put.Sci.Advances in Computing Science.Springer,Vienna.ISSN1433-0113.∗†Adv.Des.Control Advances in Design and Control.SIAM, Philadelphia,PA.§Adv.Differential Equations Advances in Differential Equations.Khayyam,Athens,OH.ISSN1079-9389.†Adv.Discrete Math.Appl.Advances in DiscreteMathematics and Applications.Gordon and Breach,Amsterdam.ISSN1028-3129.†Adv.Fluid Mech.Advances in Fluid put.Mech.,Southampton.ISSN1353-808X.†Adv.Fuzzy Systems Appl.Theory Advances in Fuzzy Systems—Applications and Theory.World Sci.Publishing,River Edge,NJ.§E Adv.in Appl.Math.Advances in Applied Mathematics.Academic Press,Orlando,FL.ISSN0196-8858.§Adv.in Appl.Probab.Advances in Applied Probability.Appl.Probab.Trust,Sheffield.ISSN0001-8678.∗†Adv.Ind.Control Advances in Industrial Control.Springer, London.†Adv.Lectures Math.Advanced Lectures in Mathematics.Vieweg,Braunschweig.ISSN0932-7134.§E Adv.Math.Advances in Mathematics.Academic Press, Orlando,FL.ISSN0001-8708.§Adv.Math.(China)Advances in Mathematics(China).Shuxue Jinzhan.Peking Univ.Press,Beijing.ISSN1000-0917.†Adv.Math.Econ.Advances in Mathematical Economics.Springer,Tokyo.†Adv.Math.Sci.Advances in the Mathematical Sciences.Amer.Math.Soc.,Providence,RI.§Adv.Math.Sci.Appl.Advances in Mathematical Sciences and Applications.An International Journal.Gakk¯o tosho,Tokyo.ISSN1343-4373.§Adv.Nonlinear Var.Inequal.Advances in Nonlinear Variational Inequalities.An International Journal.Internat.Publ.,Orlando,FL.ISSN1092-910X.†Adv.Numer.Math.Advances in Numerical Mathematics.Teubner,Stuttgart.†Adv.Partial Differ.Equ.Advances in Partial Differential Equations.Wiley-VCH,Berlin.†Adv.Partial Differential Equations Advances in Partial Differential Equations.Akademie Verlag,Berlin.†Adv.Ser.Dynam.Systems Advanced Series in Dynamical Systems.World Sci.Publishing,River Edge,NJ.†Adv.Ser.Math.Phys.Advanced Series in Mathematical Physics.World Sci.Publishing,River Edge,NJ.†Adv.Ser.Math.Sci.Eng.Advanced Series in Mathematical Science and Engineering.World Fed.Publ.,Atlanta,GA.†Adv.Ser.Neurosci.Advanced Series in Neuroscience.World Sci.Publishing,River Edge,NJ.†Adv.Ser.Nonlinear Dynam.Advanced Series in Nonlinear Dynamics.World Sci.Publishing,River Edge,NJ.†Adv.Ser.Stat.Sci.Appl.Probab.Advanced Series on Statistical Science&Applied Probability.World Sci.Publishing,River Edge,NJ.†Adv.Ser.Theoret.Phys.Sci.Advanced Series onTheoretical Physical Science.World Sci.Publishing,RiverEdge,NJ.∗†Adv.Soft Comput.Advances in Soft Computing.Physica, Heidelberg.†Adv.Spat.Sci.Advances in Spatial Science.Springer, Berlin.†Adv.Stud.Contemp.Math.Advanced Studies inContemporary Mathematics.Gordon and Breach,New York.∗§Adv.Stud.Contemp.Math.(Pusan)Advanced Studies in Contemporary Mathematics(Pusan).Adv.Stud.Contemp.Math.,m.,Saga.ISSN1229-3067.†Adv.Stud.Pure Math.Advanced Studies in PureMathematics.Kinokuniya,Tokyo.†Adv.Textb.Control Signal Process.Advanced Textbooks in Control and Signal Processing.Springer,London.∗†Adv.Texts Phys.Advanced Texts in Physics.Springer,Berlin.ISSN1439-2674.§E Adv.Theor.Math.Phys.Advances in Theoretical and Mathematical Physics.Internat.Press,Cambridge,MA.ISSN1095-0761.†Adv.Theory put.Math.Advances in the Theory of Computation and Computational Mathematics.Nova Sci.Publ.,Commack,NY.†Adv.Top.Math.Advanced Topics in Mathematics.PWN, Warsaw.§E Aequationes Math.Aequationes Mathematicae.Birkh¨a user,Basel.ISSN0001-9054.§Afrika Mat.(3)Afrika Matematika.Journal of the African Mathematical Union.Journal de l’Union Math´e matiqueAfricaine.S´e rie3.Union Math.Africaine,Caluire.†Agr´e g.Math.Agr´e gation de Math´e matiques.Masson,Paris.AI Commun.AI Communications.The European Journal onArtificial Intelligence.IOS,Amsterdam.ISSN0921-7126.†AIAA Ed.Ser.AIAA Education Series.AIAA,Washington, DC.†AIP Conf.Proc.AIP Conference Proceedings.Amer.Inst.Phys.,New York.ISSN0094-243X.†AIP Ser.Modern Acoust.Signal Process.AIP Series in Modern Acoustics and Signal Processing.Amer.Inst.Phys.,New York.†AKP Class.AKP Classics.A K Peters,Wellesley,MA.∗†Al-Furq¯a n Islam.Herit.Found.Publ.Al-Furq¯a n Islamic Heritage Foundation Publication.Al-Furq¯a n Islam.Herit.Found.,London.†Albion Math.Appl.Ser.Albion Mathematics&Applications Series.Albion,Chichester.§E Algebr.Represent.Theory Algebras and Representation Theory.Kluwer Acad.Publ.,Dordrecht.ISSN1386-923X.Algebra and Logic Algebra and Logic.Consultants Bureau,New York.(Translation of Algebra Log.and Algebra iLogika)ISSN0002-5232.†Algebra Ber.Algebra Berichte.[Algebra Reports]Fischer, Munich.ISSN0942-1270.§E Algebra Colloq.Algebra Colloquium.Springer,Singapore.ISSN1005-3867.§Algebra i Analiz Rossi˘ıskaya Akademiya Nauk.Algebrai Analiz.“Nauka”S.-Peterburg.Otdel.,St.Petersburg.(Translated in St.Petersburg Math.J.)ISSN0234-0852.§Algebra i Logika Sibirski˘ıFond Algebry i Logiki.Algebrai Logika.Izdat.NII Mat.-Inform.Osnov Obuch.NGU,Novosibirsk.(Continued as Algebra Log.)(Translatedin Algebra and Logic)ISSN0373-9252.∗§Algebra Log.Algebra i Logika.Institut Diskretno˘ıMatematiki i Informatiki.Sib.Fond Algebry Log.,Novosibirsk.(Formerly Algebra i Logika)(Translatedin Algebra and Logic)ISSN0373-9252.†Algebra Logic Appl.Algebra,Logic and Applications.Gordon and Breach,Amsterdam.ISSN1041-5394.§E Algebra Universalis Algebra Universalis.Univ.Manitoba, Winnipeg,MB.ISSN0002-5240.§Algebras Groups Geom.Algebras,Groups and Geometries.Hadronic Press,Palm Harbor,FL.ISSN0741-9937.§E Algorithmica Algorithmica.An International Journal in Computer Science.Springer,New York.ISSN0178-4617.†Algorithms Combin.Algorithms and Combinatorics.Springer,Berlin.ISSN0937-5511.†Algorithms Comput.Math.Algorithms and Computation in Mathematics.Springer,Berlin.ISSN1431-1550.§Aligarh Bull.Math.The Aligarh Bulletin of Mathematics.Aligarh Muslim Univ.,Aligarh.Aligarh J.Statist.The Aligarh Journal of Statistics.AligarhMuslim Univ.,Aligarh.ISSN0971-0388.§pok Alkalmazott Matematikai Lapok.Magyar Tudom´a nyos Akad.,Budapest.ISSN0133-3399.∗Allg.Stat.Arch.Allgemeines Statistisches Archiv.AStA.Journal of the German Statistical Society.Physica,Heidelberg.ISSN0002-6018.†´Alxebra´Alxebra.[Algebra]Univ.Santiago deCompostela,Santiago de Compostela.†Am.Univ.Stud.Ser.IX Hist.American University Studies.Series IX:ng,New York.ISSN0740-0462.∗§E AMA Algebra Montp.Announc.AMA.AlgebraMontpellier Announcements.AMA Algebra Montp.Announc.,Montpellier.§E Amer.J.Math.American Journal of Mathematics.Johns Hopkins Univ.Press,Baltimore,MD.ISSN0002-9327.Amer.J.Math.Management Sci.American Journal ofMathematical and Management Sciences.Amer.Sci.Press,Syracuse,NY.ISSN0196-6324.E Amer.J.Phys.American Journal of Physics.Amer.Assoc.Phys.Teach.,College Park,MD.ISSN0002-9505.Amer.Math.Monthly The American MathematicalMonthly.Math.Assoc.America,Washington,DC.ISSN0002-9890.†Amer.Math.Soc.Colloq.Publ.American Mathematical Society Colloquium Publications.Amer.Math.Soc.,Providence,RI.ISSN0065-9258.†Amer.Math.Soc.Transl.Ser.2American Mathematical Society Translations,Series2.Amer.Math.Soc.,Providence,RI.(Selected translations of Russian language publications Tr.St.-Peterbg.Mat.Obshch.)ISSN0065-9290.E Amer.Statist.The American Statistician.Amer.Statist.Assoc.,Alexandria,V A.ISSN0003-1305.†Amer.Univ.Stud.Ser.V Philos.American University Studies.Series V:ng,New York.ISSN0739-6392.†AMS Progr.Math.Lecture Ser.AMS Progress in Mathematics Lecture Series.Amer.Math.Soc.,Providence,RI.†AMS Short Course Lecture Notes AMS Short Course Lecture Notes.Amer.Math.Soc.,Providence,RI.†AMS-MAA Joint Lecture Ser.AMS-MAA Joint Lecture Series.Amer.Math.Soc.,Providence,RI.†AMS/IP Stud.Adv.Math.AMS/IP Studies in Advanced Mathematics.Amer.Math.Soc.,Providence,RI.ISSN1089-3288.E An.Acad.Brasil.Ciˆe nc.Anais da Academia Brasileira deCiˆe ncias.Acad.Brasil.Ciˆe nc.,Rio de Janeiro.ISSN0001-3765.†An.F´ıs.Monogr.Anales de F´ısica.Monograf´ıas.[Annals of Physics.Monographs]CIEMAT,Madrid.§An.S¸tiint¸.Univ.Al.I.Cuza Ias¸i Inform.(N.S.)Analele S¸tiint¸ifice ale Universit˘a t¸ii“Al.I.Cuza”din Ias¸i.Informatic˘a.Serie Nou˘a.Ed.Univ.“Al.I.Cuza”,Ias¸i.ISSN1224-2268.§An.S¸tiint¸.Univ.Al.I.Cuza Ias¸i.Mat.(N.S.)Analele S¸tiint¸ifice ale Universit˘a tii“Al.I.Cuza”din Ias¸i.SerieNou˘a.Matematic˘a.Univ.Al.I.Cuza,Ias¸i.ISSN1221-8421.§An.S¸tiint¸.Univ.Ovidius Constant¸a Ser.Mat.Universit˘a t¸ii “Ovidius”Constant¸a.Analele S¸tiint¸ifice.Seria Matematic˘a.“Ovidius”Univ.Press,Constant¸a.ISSN1223-723X.§An.Univ.Bucures¸ti Mat.Analele Universit˘a t¸ii Bucures¸ti.Matematic˘a.Univ.Bucharest,Bucharest.ISSN1013-4123.An.Univ.Craiova rm.Analele Universitˇa t¸iidin Craiova.Seria Matematic˘a-Informatic˘a.Univ.Craiova,Craiova.ISSN1223-6934.∗§An.Univ.Oradea Fasc.Mat.Analele Universit˘a t¸ii din Oradea.Fascicola Matematica.Univ.Oradea,Oradea.ISSN1221-1265.§An.Univ.Timis¸oara Ser.Mat.-Inform.Universit˘a t¸ii din Timis¸oara.Analele.Seria Matematic˘a-Informatic˘a.Univ.Timis¸oara,Timis¸oara.ISSN1224-970X.An.Univ.Timis¸oara Ser.S¸tiint¸.Fiz.Analele Universit˘a t¸iidin Timis¸oara.Seria S¸tiint¸e Fizice.Univ.Vest Timis¸oara,Timis¸oara.†Anal.Appl.Analysis and its Applications.IOS,Amsterdam.ISSN1345-4240.§E Anal.Math.Analysis Mathematica.Akad.Kiad´o,Budapest.ISSN0133-3852.†Anal.Methods Spec.Funct.Analytical Methods and Special Functions.Gordon and Breach,Amsterdam.ISSN1027-0264.†Anal.Modern.Apl.Analiz˘a Modern˘a s¸i Aplicat¸ii.[Modern Analysis and Applications]Ed.Acad.Romˆa ne,Bucharest.§Analysis(Munich)Analysis.International Mathematical Journal of Analysis and its Applications.Oldenbourg,Munich.ISSN0174-4747.E Analysis(Oxford)Analysis.Blackwell,Oxford.ISSN0003-2638.†Angew.Statist.¨Okonom.Angewandte Statistik und¨Okonometrie.[Applied Statistics and Econometrics]Vandenhoeck&Ruprecht,G¨o ttingen.§E Ann.Acad.Sci.Fenn.Math.Annales AcademiæScientiarium Fennicæ.Mathematica.Acad.Sci.Fennica,Helsinki.ISSN1239-629X.§Ann.Acad.Sci.Fenn.Math.Diss.AcademiæScientiarum Fennicæ.Annales.Mathematica.Dissertationes.Acad.Sci.Fennica,Helsinki.ISSN1239-6303.§E Ann.Appl.Probab.The Annals of Applied Probability.Inst.Math.Statist.,Hayward,CA.ISSN1050-5164.§E b.Annals of Combinatorics.Springer,Singapore.(Continued as b.)ISSN0218-0006.∗§E b.Annals of Combinatorics.Birkh¨a user,Basel.(Formerly b.)ISSN0218-0006.§Ann.Differential Equations Annals of DifferentialEquations.Weifen Fangcheng Niankan.Fuzhou Univ.,Fuzhou.ISSN1002-0942.†Ann.Discrete Math.Annals of Discrete Mathematics.North-Holland,Amsterdam.Ann.´Econom.Statist.Annales d’´Economie et deStatistique.Inst.Nat.Statist.´Etud.´Econom.,Amiens.ISSN0769-489X.§Ann.Fac.Sci.Toulouse Math.(6)Annales de la Facult´e des Sciences de Toulouse.Math´e matiques.S´e rie6.Univ.Paul Sabatier,Toulouse.ISSN0240-2963.†Ann.Fac.Sci.Univ.Kinshasa Annales de la Facult´e des Sciences.Universit´e de Kinshasa.[Annals of the Facultyof Science.University of Kinshasa]Presses Univ.Kinshasa,Kinshasa.Ann.Fond.Louis de Broglie Fondation Louis de Broglie.Annales.Fond.Louis de Broglie,Paris.ISSN0182-4295.§E Ann.Global Anal.Geom.Annals of Global Analysis and Geometry.Kluwer Acad.Publ.,Dordrecht.ISSN0232-704X.∗E Ann.Henri Poincar´e Annales Henri Poincar´e.A Journal of Theoretical and Mathematical Physics.Birkh¨a user,Basel.(Merged from Ann.Inst.H.Poincar´e Phys.Th´e or.and Helv.Phys.Acta)ISSN1424-0637.∗Ann.I.S.U.P.Annales de l’I.S.U.P..Univ.Paris,Inst.Stat., Paris.§E Ann.Inst.Fourier(Grenoble)Universit´e de Grenoble.Annales de l’Institut Fourier.Univ.Grenoble I,Saint-Martin-d’H`e res.ISSN0373-0956.§E Ann.Inst.H.Poincar´e Anal.Non Lin´e aire Annales de l’Institut Henri Poincar´e.Analyse Non Lin´e aire.Gauthier-Villars,´Ed.Sci.M´e d.Elsevier,Paris.ISSN0294-1449.Ann.Inst.H.Poincar´e Phys.Th´e or.Annales de l’InstitutHenri Poincar´e.Physique Th´e orique.Gauthier-Villars,´Ed.Sci.M´e d.Elsevier,Paris.(Merged into Ann.HenriPoincar´e)ISSN0246-0211.§E Ann.Inst.H.Poincar´e Probab.Statist.Annales de l’Institut Henri Poincar´e.Probabilit´e s et Statistiques.Gauthier-Villars,´Ed.Sci.M´e d.Elsevier,Paris.ISSN0246-0203.E Ann.Inst.Statist.Math.Annals of the Institute ofStatistical Mathematics.Kluwer Acad.Publ.,Norwell,MA.ISSN0020-3157.†Ann.Internat.Soc.Dynam.Games Annals of the International Society of Dynamic Games.Birkh¨a userBoston,Boston,MA.†Ann.Israel Phys.Soc.Annals of the Israel Physical Society.IOP,Bristol.ISSN0309-8710.Ann.Japan Assoc.Philos.Sci.Annals of the JapanAssociation for Philosophy of Science.Japan Assoc.Philos.Sci.,Tokyo.ISSN0453-0691.§Ann.Mat.Pura Appl.(4)Annali di Matematica Pura ed Applicata.Serie Quarta.Zanichelli,Bologna.ISSN0003-4622.E Ann.Math.Artificial Intelligence Annals of Mathematicsand Artificial Intelligence.Baltzer,Bussum.ISSN1012-2443.§Ann.Math.Blaise Pascal Annales Math´e matiques Blaise Pascal.Univ.Blaise Pascal,Lab.Math.Pures Appl.,Aubi`e re.ISSN1259-1734.§Ann.Math.Sil.Annales Mathematicae Silesianae.Wydawn.Uniw.´Sl‘askiego,Katowice.(See also Pr.Nauk.Uniw.´Sl.Katow.)ISSN0860-2107.†Ann.New York Acad.Sci.Annals of the New York Academy of Sciences.New York Acad.Sci.,New York.ISSN0077-8923.§E Ann.of Math.(2)Annals of Mathematics.Second Series.Princeton Univ.Press,Princeton,NJ.ISSN0003-486X.†Ann.of Math.Stud.Annals of Mathematics Studies.Princeton Univ.Press,Princeton,NJ.E Ann.of Sci.Annals of Science.Taylor&Francis,London.ISSN0003-3790.E Ann.Oper.Res.Annals of Operations Research.Baltzer,Bussum.ISSN0254-5330.E Ann.Phys.(8)Annalen der Physik(8).Wiley-VCH,Berlin.ISSN0003-3804.E Ann.Physics Annals of Physics.Academic Press,Orlando,FL.ISSN0003-4916.§Ann.Polon.Math.Annales Polonici Mathematici.Polish Acad.Sci.,Warsaw.ISSN0066-2216.§Ann.Probab.The Annals of Probability.Inst.Math.Statist., Bethesda,MD.ISSN0091-1798.§E Ann.Pure Appl.Logic Annals of Pure and Applied Logic.North-Holland,Amsterdam.ISSN0168-0072.§E Ann.Sci.´Ecole Norm.Sup.(4)Annales Scientifiques de l’´Ecole Normale Sup´e rieure.Quatri`e me S´e rie.Gauthier-Villars,´Ed.Sci.M´e d.Elsevier,Paris.ISSN0012-9593.§Ann.Sci.Math.Qu´e bec Annales des SciencesMath´e matiques du Qu´e bec.Groupe Cherch.Sci.Math.,Montreal,QC.ISSN0707-9109.§Ann.Scuola Norm.Sup.Pisa Cl.Sci.(4)Annali della Scuola Normale Superiore di Pisa.Classe di Scienze.SerieIV.Scuola Norm.Sup.,Pisa.§Ann.Statist.The Annals of Statistics.Inst.Math.Statist., Hayward,CA.ISSN0090-5364.§Ann.Univ.Ferrara Sez.VII(N.S.)Annali dell’Universit`a di Ferrara.Nuova Serie.Sezione VII.Scienze Matematiche.Univ.Ferrara,Ferrara.§Ann.Univ.Mariae Curie-Skłodowska Sect.A Annales Universitatis Mariae Curie-Skłodowska.Sectio A.Mathematica.Uniw.Marii Curie-Skłodowskiej,Lublin.ISSN0365-1029.Ann.Univ.Sarav.Ser.Math.Annales UniversitatisSaraviensis.Series Mathematicae.Univ.Saarlandes,Saarbr¨u cken.ISSN0933-8268.§Ann.Univ.Sci.Budapest.E¨o tv¨o s Sect.Math.Annales Universitatis Scientiarum Budapestinensis de RolandoE¨o tv¨o s Nominatae.Sectio Mathematica.E¨o tv¨o s Lor´a ndUniv.,Budapest.ISSN0524-9007.§put.AnnalesUniversitatis Scientiarum Budapestinensis de RolandoE¨o tv¨o s Nominatae.Sectio Computatorica.E¨o tv¨o s Lor´a ndUniv.,Budapest.ISSN0138-9491.†Annu.Rev.Fluid Mech.Annual Review of FluidMechanics.Annual Reviews,Palo Alto,CA.ISSN0066-4189.Annuaire Univ.Sofia rm.Godishnik naSofi˘ıskiya Universitet“Sv.Kliment Okhridski”.Fakultetpo Matematika i Informatika.Annuaire de l’Universit´e deSofia“St.Kliment Ohridski”.Facult´e de Math´e matiques etInformatique.Presses Univ.“St.Kliment Ohridski”,Sofia.ISSN0205-0808.Annuaire Univ.Sofia Fac.Phys.Godishnik na Sofi˘ıskiyaUniversitet“Sv.Kliment Okhridski”.Fizicheski Fakultet.Annuaire de l’Universit´e de Sofia“St.Kliment Ohridski”.Facult´e de Physique.Presses Univ.“St.Kliment Ohridski”,Sofia.ISSN0584-0279.†Anu.Filol.Univ.Barc.Anuari de Filologia(Universitat de Barcelona).[Philology Yearbook(University ofBarcelona)]Univ.Barcelona,Barcelona.†Anwend.orientier.Stat.Anwendungsorientierte Statistik.[Applications-Oriented Statistics]Lang,Frankfurt am Main.ISSN1431-7982.Anz.¨Osterreich.Akad.Wiss.Math.-Natur.Kl.¨Osterreichische Akademie der Wissenschaften.Mathematisch-Naturwissenschaftliche Klasse.Anzeiger.¨Osterreich.Akad.Wissensch.,Vienna.∗§E ANZIAM J.The ANZIAM Journal.The Australian& New Zealand Industrial and Applied Mathematics Journal.Austral.Math.Soc.,Canberra.(Formerly J.Austral.Math.Soc.Ser.B)ISSN0334-2700.†Aportaciones Mat.Aportaciones Matem´a ticas.[Mathematical Contributions]Soc.Mat.Mexicana,M´e xico.†Aportaciones un.Aportaciones Matem´a ticas: Comunicaciones.[Mathematical Contributions:Communications]Soc.Mat.Mexicana,M´e xico.∗†Aportaciones Mat.Invest.Aportaciones Matem´a ticas: Investigaci´o n.[Mathematical Contributions:Research]Soc.Mat.Mexicana,M´e xico.(Formerly Aportaciones Mat.Notas Investigaci´o n)†Aportaciones Mat.Notas Investigaci´o n Aportaciones Matem´a ticas:Notas de Investigaci´o n.[MathematicalContributions:Research Notes]Soc.Mat.Mexicana,M´e xico.(Continued as Aportaciones Mat.Invest.)†Aportaciones Mat.Textos Aportaciones Matem´a ticas: Textos.[Mathematical Contributions:Texts]Soc.Mat.Mexicana,M´e xico.§E Appl.Algebra put.Applicable Algebra in Engineering,Communication and Computing.Springer,Heidelberg.ISSN0938-1279.§E Appl.Anal.Applicable Analysis.An International Journal.Gordon and Breach,Yverdon.ISSN0003-6811.§E Appl.Categ.Structures Applied Categorical Structures.A Journal Devoted to Applications of Categorical Methods inAlgebra,Analysis,Order,Topology and Computer Science.Kluwer Acad.Publ.,Dordrecht.ISSN0927-2852.†put.Control Signals Circuits Applied and Computational Control,Signals,and Circuits.Birkh¨a userBoston,Boston,MA.ISSN1522-8363.§E put.Harmon.Anal.Applied and Computational Harmonic Analysis.Time-Frequency and Time-Scale Analysis,Wavelets,Numerical Algorithms,andApplications.Academic Press,Orlando,FL.ISSN1063-5203.†Appl.Log.Ser.Applied Logic Series.Kluwer Acad.Publ., Dordrecht.†Appl.Math.Applications of Mathematics.Springer,New York.ISSN0172-4568.§Appl.Math.Applications of Mathematics.Acad.Sci.Czech Repub.,Prague.ISSN0862-7940.∗†Appl.Math.Applied Mathematics.Chapman&Hall/CRC, Boca Raton,FL.(Formerly put.)§E put.Applied Mathematics andComputation.North-Holland,New York.ISSN0096-3003.†Appl.Math.Engrg.Sci.Texts Applied Mathematics and Engineering Science Texts.CRC,Boca Raton,FL.∗rm.Applied Mathematics and Informatics.Tbilisi Univ.Press,Tbilisi.ISSN1512-0074.∗§Appl.Math.J.Chinese Univ.Ser.A Applied Mathematics.A Journal of Chinese Universities.Series A.Appl.Math.J.Chinese Univ.,m.,Hangzhou.(FormerlyGaoxiao Yingyong Shuxue Xuebao Ser.A)(See also Appl.Math.J.Chinese Univ.Ser.B)ISSN1000-4424.§Appl.Math.J.Chinese Univ.Ser.B Applied Mathematics.A Journal of Chinese Universities.Ser.B.Appl.Math.J.Chinese Univ.,m.,Hangzhou.(See also Appl.Math.J.Chinese Univ.Ser.A and Gaoxiao Yingyong Shuxue。
arXiv:math/0606241v2 [math.RA] 14 Aug 2006NotesonA∞-algebras,A∞-categoriesand
non-commutativegeometry.I
MaximKontsevichandYanSoibelmanFebruary2,2008
Contents1Introduction21.1A∞-algebrasasspaces........................21.2Someapplicationsofgeometriclanguage..............31.3Contentofthepaper.........................41.4GeneralizationtoA∞-categories..................6
IA∞-algebrasandnon-commutativedg-manifolds72Coalgebrasandnon-commutativeschemes72.1Coalgebrasasfunctors........................72.2Smooththinschemes.........................102.3InnerHom...............................11
3A∞-algebras143.1Maindefinitions...........................143.2MinimalmodelsofA∞-algebras...................163.3CentralizerofanA∞-morphism...................17
4Non-commutativedg-lineLandweakunit194.1Maindefinition............................194.2Addingaweakunit..........................20
5Modulesandbimodules205.1Modulesandvectorbundles.....................205.2OnthetensorproductofA∞-algebras...............23
6Yonedalemma236.1ExplicitformulasfortheproductanddifferentialonCentr(f)..236.2Yonedahomomorphism.......................24
1IISmoothnessandcompactness257HochschildcochainandchaincomplexesofanA∞-algebra257.1Hochschildcochaincomplex.....................257.2Hochschildchaincomplex......................267.2.1Cyclicdifferentialformsoforderzero............267.2.2Higherordercyclicdifferentialforms............267.2.3Non-commutativeCartancalculus.............277.2.4DifferentialontheHochschildchaincomplex.......287.3ThecaseofstrictlyunitalA∞-algebras...............307.4Non-unitalcase:Cuntz-Quillencomplex..............31
8HomologicallysmoothandcompactA∞-algebras328.1Homologicalsmoothness.......................328.2CompactA∞-algebras........................34
9DegenerationHodge-to-deRham369.1Mainconjecture............................369.2RelationshipwiththeclassicalHodgetheory...........38
10A∞-algebraswithscalarproduct3910.1Maindefinitions...........................3910.2Calabi-Yaustructure.........................40
11HochschildcomplexesasalgebrasoveroperadsandPROPs4311.1Configurationspacesofdiscs....................4311.2Configurationsofpointsonthecylinder..............4611.3GeneralizationofDeligne’sconjecture...............4811.4RemarkaboutGauss-Maninconnection..............5011.5Flatconnectionsandthecoloredoperad..............5011.6PROPofmarkedRiemannsurfaces.................54
12Appendix6312.1Non-commutativeschemesandind-schemes............6312.2ProofofTheorem2.1.1........................6512.3ProofofProposition2.1.2......................6612.4Formalcompletionalongasubscheme...............67
1Introduction1.1A∞-algebrasasspacesThenotionofA∞-algebraintroducedbyStasheff(orthenotionofA∞-categoryintroducedbyFukaya)hastwodifferentinterpretations.Firstoneisoperadic:anA∞-algebraisanalgebraovertheA∞-operad(oneofitsversionsistheoperadofsingularchainsoftheoperadofintervalsintherealline).Secondone
2isgeometric:anA∞-algebraisthesameasanon-commutativeformalgradedmanifoldXover,say,fieldk,havingamarkedk-pointpt,andequippedwithavectorfielddofdegree+1suchthatd|pt=0and[d,d]=0(suchvectorfieldsarecalledhomological).Bydefinitionthealgebraoffunctionsonthenon-commutativeformalpointedgradedmanifoldisisomorphictothealgebraofformalseriesn≥0i1,i2,...,in∈Iai1...inxi1...xin:=MaMxMoffreegradedvariablesxi,i∈I(thesetIcanbeinfinite).HereM=(i1,...,in),n≥0isanon-commutativemulti-index,i.e.anelementofthefreemonoidgeneratedbyI.Homologicalvectorfieldmakestheabovegradedalgebraintoacomplexofvectorspaces.Thetriple(X,pt,d)iscalledanon-commutativeformalpointeddifferential-graded(orsimplydg-)manifold.ItisaninterestingproblemtomakeadictionaryfromthepurealgebraiclanguageofA∞-algebrasandA∞-categoriestothelanguageofnon-commutativegeometry1.Onepurposeofthesenotesistomakefewstepsinthisdirection.FromthepointofviewofGrothendieck’sapproachtothenotionof“space”,ourformalpointedmanifoldsaregivenbyfunctorsongradedassociativeArtinalgebrascommutingwithfiniteprojectivelimits.Itiseasytoseethatsuchfunc-torsarerepresentedbygradedcoalgebras.Thesecoalgebrascanbethoughtofascoalgebrasofdistributionsonformalpointedmanifolds.Theabove-mentionedalgebrasofformalpowerseriesaredualtothecoalgebrasofdistributions.Inthecaseof(small)A∞-categoriesconsideredinthesubsequentpaperwewillslightlymodifytheabovedefinitions.Insteadofonemarkedpointonewillhaveaclosedsubschemeofdisjointpoints(objects)inaformalgradedmanifold,andthehomologicalvectorfielddmustbecompatiblewiththeembeddingofthissubschemeaswellaswiththeprojectionontoit.