各向异性介质中频率相关横波分裂参数的提取算法_英文_
- 格式:pdf
- 大小:1.16 MB
- 文档页数:8

第一章:声波测井物理基础1、描述声波的基本参数频率f :声音传播过程中,介质震动的频率即介质质点每秒钟振动的次数就是声波的频率周期T :指介质完成一次振动所需要的时间速度c或v:指声波的传播速度波长λ:声音在介质中传播时,相位相同的两点在空间上的距离称为声波的波长2、声速(时差)的影响因素以及如何影响,流体、压力、岩性、密度等等(一)岩性<最主要的影响因素,灰质含量↑声速↑>(二)孔隙和流体<孔隙性岩层声速<非孔隙性、含气饱和度↑纵波速度↓横波速度↑> (三)压力<压力↑波速↑极大值后基本保持不变,压力对声速影响可达35%+>(四)温度<相对压力而言,影响很小可忽略、温度↑纵波速度稍许↓>(五)岩石生成的地质条件<老地层的声速>新地层、构造顶部的声速>构造翼部>(六)埋藏深度<深度↑声速↑>3、泥浆对超声的衰减因素泥浆对超声波的衰减包括吸收衰减和固相颗粒散射衰减两部分(一)泥浆对超声波的吸收衰减:主要有泥浆的粘滞、热传导以及泥浆的微观过程引起的弛豫效应(二)泥浆固相颗粒对超声波的散射衰减:泥浆中含有的固相颗粒引起的散射衰减、泥浆添加剂引起的散射衰减、声频散4、声阻抗的概念及其对反射波和透射波的影响声阻抗:地震波在介质中传播时,作用于某个面积上的压力与单位时间内垂直通过此面积的指点流量之比,其数值等于介质密度ρ与波速v的乘积,即Z=ρ.v。
影响:声波发生反射和折射的能量分配取决于泥浆和井壁两种介质的声阻抗值大小、入射角和折射角的关系。
当声波垂直井壁入射时,θ1θ2p=0,从右式可以看出,介质1和介质2声阻抗分别为Z1、Z2Β为反射系数α为折射系数,系数越大,越易进行Z1Z2声阻抗差越大,声耦合越差,声能量传递就越差,通过界面传播的折射波能量就小,若两介质声阻抗相近,声耦合率较好,声波都形成折射波通过界面传播到介质2,这时反射波能量就非常小,当Z1<<Z2时,声阻抗差异明显,声耦合差,不利于声音传递。

1.1 时频脊线提取算法的重要性1.2 Veterbi算法的应用领域1.3 研究现状和存在问题2. Veterbi 时频脊线提取算法原理2.1 Veterbi算法概述2.2 时频脊线提取算法原理及其与Veterbi算法的关系 2.3 算法优势和局限性3. 算法实现与性能分析3.1 算法实现步骤3.2 时频脊线提取算法在实际应用中的性能表现3.3 算法的改进和优化方向4. 应用案例和展望4.1 时频脊线提取算法在通信领域的应用案例4.2 算法未来发展方向及潜在应用领域5. 结语---1.1 时频脊线提取算法的重要性时频分析是信号处理领域的重要研究内容,对于时变信号的分析和处理具有重要意义。
时频脊线提取算法作为一种主要的时频分析方法,在音频处理、通信领域等有着广泛的应用。
1.2 Veterbi算法的应用领域Veterbi算法是一种动态规划算法,最早应用于语音识别领域,后来被广泛应用于其他领域,如密码学、生物信息学等。
其优势在于能够在大数据量下高效地搜索最优路径。
1.3 研究现状和存在问题当前,时频脊线提取算法在实际应用中面临着一些问题,例如在处理非线性和非平稳信号时,提取效果不佳。
如何结合Veterbi算法的优势来改进时频脊线提取算法成为了一个研究热点。
2. Veterbi 时频脊线提取算法原理2.1 Veterbi算法概述Veterbi算法是一种动态规划算法,主要用于寻找隐藏马尔可夫模型中最有可能的状态序列。
其基本思想是通过递推的方式,计算出每一时刻的最优状态,并最终确定全局最优状态序列。
2.2 时频脊线提取算法原理及其与Veterbi算法的关系时频脊线提取算法是一种在时频域中找到具有连续变化频率和幅度的最能代表时频局部特征的子信号的方法。
在其实现过程中,可以借鉴Veterbi算法的思想,通过动态规划的方式寻找时频局部特征点。
3. 算法实现与性能分析3.1 算法实现步骤时频脊线提取算法的实现步骤包括信号预处理、时频分析、特征点提取等。
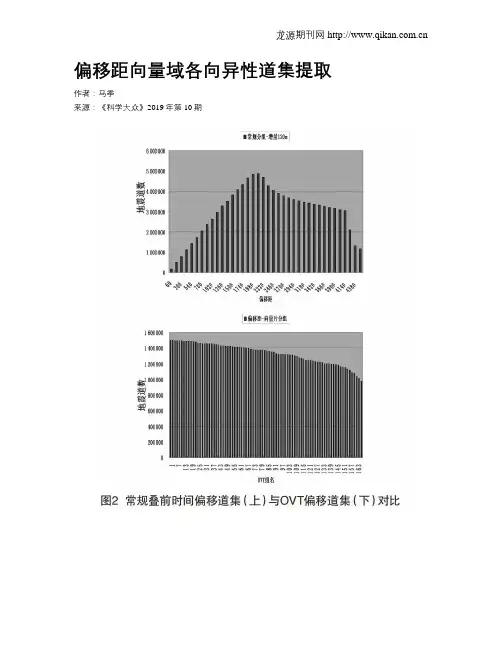
偏移距向量域各向异性道集提取作者:马季来源:《科学大众》2019年第10期摘; ;要:近几年地震勘探技术发展迅速,宽方位采集的地震资料已经非常普遍,并成为今后的发展方向。
文章利用某地区的实际宽方位资料,采用宽方位角信息采集资料的针对性处理技术,在偏移距向量域进行了叠前道集的划分,得到更加均匀的含有不同方位角和偏移距的叠前道集资料,从而为地层各向异性的研究提供丰富可靠的信息。
关键词:各向异性;宽方位;偏移距向量域;叠前属性道集随着油气藏勘探的不断深入,储集层变得愈加复杂,具有很强非均质性和各向异性的储层成为当前油气勘探的重要目标,并成为近期研究的热点,但是研究力度远远不够。
通过宽方位角信息采集资料的针对性处理,得到含有不同方位角信息的叠前道集资料,从而为地层各向异性的研究提供丰富的信息。
1; ; 偏移距向量片技术偏移距向量片技术是当前比较好的分方位的处理技术,同时考虑方位角和偏移距两个方面的特性,其得到的地震属性能更好地反应地下真实情况,同时很好地保留方位角和偏移距的信息,也为五维内插技术的应用奠定了一定的基础。
作为当前为数不多的面向宽方位地震资料的处理方法之一,炮检距向量片(Offset Vector Tile,OVT)技术近年来成为处理中的一大热点。
图1是一个十字排列地震数据的分布情况,从该十字排列的数据分布情况来看,实心圆圈(竖向)为炮点,实心三角形(横向)为检波点。
按照方位角理论,把图中一个十字排列的地震数据以炮线检波线交点为中心,按照炮线与检波线间隔大小的矩形(矩形)进行划分单元,每个单元按照顺序给固定的编号,所有相同位置的编号的矩形对地下形成一次覆盖,对于每个固定的矩形地震资料来说,其方位角和偏移距是在一定的范围内变化的,因此其偏移后属性也是在一定方位角和偏移距范围内的。
2; ; 应用实例选取某地区宽方位采集地震资料,如图2所示,按照常规叠前时间偏移,对地震数据按照120 m的偏移距进行划分,偏移后每个偏移距组里面的地震导数差别极大,这样的道集得到的地震属性受到覆盖次数不均匀的影响,不能真实反映地下地质体属性。

各向异性高分辨率Radon变换压制多次波范景文;李振春;宋翔宇;张凯;周隶华【期刊名称】《石油地球物理勘探》【年(卷),期】2016(051)004【摘要】针对VTI介质和海洋大炮检距地震数据反射波同相轴不能严格满足双曲时距关系,一次波和多次波能量在Radon域中聚焦性较差,多次波的压制效果不理想的问题,通过在双曲Radon变换积分路径中引入各向异性参数η,描述VTI介质和海洋大炮检距地震数据的时距曲线关系,在Radon域中有效聚焦一次波和多次波能量.同时,引入基于共轭导向梯度(CGG)算法的各向异性高分辨率Radon变换,基于L1范数对模型空间进行稀疏约束,提高Radon变换的分辨率.模型数据和海上大炮检距实际资料测试表明,该方法能够很好地压制多次波.【总页数】5页(P665-669)【作者】范景文;李振春;宋翔宇;张凯;周隶华【作者单位】中国石油大学(华东)地球科学与技术学院,山东青岛266580;中国石油大学(华东)地球科学与技术学院,山东青岛266580;中海油研究总院,北京100028;中国石油大学(华东)地球科学与技术学院,山东青岛266580;新疆油田分公司采油一厂地质研究所,新疆克拉玛依834000【正文语种】中文【中图分类】P631【相关文献】1.混合域高分辨率双曲Radon变换及其在多次波压制中的应用 [J], 巩向博;韩立国;王升超2.各向异性Radon变换及其在多次波压制中的应用 [J], 巩向博;韩立国;李洪建3.各向异性Radon变换在深水地震多次波压制中的应用 [J], 梁全有;韩立国;巩向博4.基于低频约束的高分辨率Radon变换多次波压制方法研究 [J], 刘仕友;马继涛;孙万元;应明雄5.基于SLA范数的高阶高分辨率λ-f域Radon变换多次波压制方法(英文) [J], 孙文之;李振春;曲英铭;李志娜因版权原因,仅展示原文概要,查看原文内容请购买。

VTI介质多波速度分析方法及应用摘要:在地层存在广泛各向异性的基础上,常规的速度分析已经不再适用。
本文以VTI介质为研究对象,对影响速度分析的各向异性参数进行了综合分析,且在提高速度分析的精度方面有了自己的见解。
首先研究了各向异性介质的基础理论和地震波传播特点,其次研究了各向异性介质下时距曲线的拟合公式,得出地层参数与速度的关系,再次研究转换波速度分析引入单平方根方程法。
利用交互式速度分析方法对模型进行了计算处理,结果表明该方法的正确性。
关键词:各向异性;VTI介质;速度分析;非双曲线时距曲线随着地震勘探技术的发展需求,各向异性逐渐成为地震勘探的前沿课题之一。
地震波在地下介质中的传播速度是地震数据处理和解释中非常重要的参数。
在早期求取这一参数的过程中,人们把地球介质假想成为各向同性,推动了石油地震勘探的发展。
但从理论和实际角度出发,各向异性广泛存在于地球地层中。
基于各向同性的地震勘探处理方法就不再适用于各向异性介质。
因此,发展各向异性的地震勘探处理方法是非常必要的。
由于地层存在各向异性,速度的提取就与地层各向异性有关,这个特点就是速度各向异性。
如果忽略速度各向异性就会造成地层速度提取不准确,进而影响以地层速度为基础的后续处理步骤[3]。
综上所述,各向异性地震勘探处理方法不仅是对理论研究的完善,更是实际应用迫切的需要[4]。
本文以VTI介质为理论为基础,研究了各向异性介质非零偏多波时距曲线公式,在此基础上将速度谱技术引入到非零偏多波速度分析中,研究了各向异性多波速度分析方法和步骤,建立了各向异性介质叠加速度模型。
一、各向异性介质速度分析原理1.各向异性介质基本定义在各向同性弹性体中,介质内任意一点沿不同方向弹性性质都一样,但也有许多物体其弹性性质在各个方向上不尽相同,因而是各向异性的,这种不同是材料本身的性质决定的,由介质的本构方程来描述。
各向同性材料中地震波的传播规律和各向异性材料中地震波的传播规律是不同的。

应用遗传算法进行地震各向异性反演
Horne,S;金晓雷
【期刊名称】《石油物探译丛》
【年(卷),期】1995(000)003
【摘要】我们以遗传算法为基础,研究了一种用于求取地震测量数据各向异性参数的一般反演方法。
我们将这种技术应用于Conoco公司在俄克拉荷马试验场,得到了两组方位VSP数据集,进行了横波观测数据的反演。
对六方和斜方晶系求取了水平极化方向和时间延迟。
模型求解结果与过去应用全波型合成数据的试验和误差匹配得到的研究结果相一致。
横波分裂观测结果表明了横波线性奇异性的存在,并且与试验场已知的倾斜裂缝体系相一致。
在全波型模拟之前应用了该反演方法,结果表明,在保持相同精度的同时可以大大节省计算时间。
【总页数】14页(P68-80,54)
【作者】Horne,S;金晓雷
【作者单位】不详;不详
【正文语种】中文
【中图分类】P631.443
【相关文献】
1.用改进的遗传算法进行地震波阻抗反演研究 [J], 王宝珍;杨文采
2.用退火遗传算法进行地震波阻抗反演 [J], 李晶;陈裕明;唐湘蓉
3.用改进的遗传算法进行地震波阻抗反演 [J], 李晶;陈裕明;王振国
4.用遗传算法进行瑞利波反演 [J], 赵东;王光杰;王兴泰;孙仁国
5.用遗传算法进行AVO数据反演 [J], Subhashi;严建文
因版权原因,仅展示原文概要,查看原文内容请购买。

amplitude spectrum 振幅谱abnormal events:异常同相轴absorption:吸收作用acoustic:声学的,声的alias 假频anisotropy 各向异性acoustic impedance声阻抗,波阻抗acoustic wave:声波,地震波:air gun:空气枪:air wave空气波angle of incidence:入射角apparent velocity:视速度apparent wavelength:视波长arrival波至arrival time:波至时间attenuation:衰减:average velocity:平均速度azimuth方位角binary gain二进制增益blind zone:盲区:body waves体波break波跳coefficient of anisotropy各向异性系数coherence:相干性coherent:相关的common-depth-point共深度点common-depth-point stack共深度点叠加common-offset gather共偏移距道集common-offset stack共炮检距叠加(同距叠加)common-range gather共炮检距道集(选排)Common reflection point共反射点compressional wave压缩波converted wave转换波critical angle临界角:critical reflection临界反射curved path弯曲射线路径deconvolution反褶积diffraction绕射diffraction stack绕射叠加dispersion扩散,频散display:显示:diving waves:弓形射线波:dynamic corrections动校正elastic弹性的elastic constants:弹性常数:elastic impedance弹性阻抗elastic wave弹性波epicenter震中event:同相轴first arrival初至first break初至波focus:震源fold覆盖次数format数据格式gather道集geophone:地震检波器geophone interval检波距ground roll地滚波group interval组合间距group velocity群速度guided wave导波head wave首波horizontal stacking:水平叠加impedance:阻抗:incident angle入射角interval velocity层速度long-path multiple全程多次反射波low-velocity layer低速层marker bed.标准层migration偏移,运移minimum-phase:最小相位:multiple:多次波:multiple coverage多次覆盖multiplexed format:多路编排格式mute:切除:NMO正常时差。

二维电导率各向异性介质电磁感应效应的有限元算法李予国摘要二维电性各向异性大地电磁场通过有限元方法计算获得。
模型由包含各向异性块的层状介质构造组成。
每个块或者层可能是由3×3的电导率张量限定。
正演问题可以归结为两个耦合的关于垂直-平行于场分量的x E 和x H 。
它们由有限元法数值地解出。
线性有限元的解系是用预条件共轭梯度法求取的。
之后,地表垂直-平行的场分量y E 和y H ,利用样条插值通过对x E 和x H 进行数值微分得到。
二维有限元算法通过对比二维有限差分的解证明是正确的。
三个类型的模型的大地电磁响应用来证明各向异性的影响:水平,垂直,倾斜各向异性。
第四个模型用来模拟在剪切和俯冲带各向异性的影响。
这些模型的响应模拟了电阻率曲线在长周期和具有明显的主对角线元素的张量主抗存在室的分离,正如以前观测到的。
1、简介近些年来,越来越多的关注投入到了对电性各向异性的电磁感应方面上的研究,尤其是为了试图完全理解对更长周期的大地电磁的观测数据。
加拿大地区的大地电磁测量显示了电性的各向异性在下地壳和上地幔(Kellett 等,1992;Mareschal 等1995)。
大的来自围绕德国深钻点(KTB )各向异性大地电磁曲线解释为上地壳高度的电各向异性(Eisel 和 Haak 1999)。
Rasmussen (1988)使用一个深地壳层内的各向异性模型来解释瑞典南部的大地电磁横断面数据。
层状构造的各向异性效应首先被O’Brien 和Morrison (1967)研究。
Reddy 和 Rankin (1975)首先开始研究二维各向异性模型,他们只考虑水平各向异性的工作。
最近,Osella 和Martinelli (1993)计算了一些圆滑不规则边界有一定的主轴旋转角的大地电磁响应。
Schmucker (1994)提出一个计算不均匀薄的覆盖体在层状半空间的电磁感应效应,其中可以含有一个或者两个各向异性的电导层。

机械振动常用英语词汇Aacceleration 加速度acceleration mobility 加速度导纳accelerometer加速度计adjoint matrix 伴随矩阵admittance 导纳algebraic 代数的algorithm 算法alignment 对中amplifier 放大器amplitude 振幅,幅度amplitude-frequency characteristics 幅频特性amplitude-frequency curve幅频特性曲线amplitude spectrum 幅值谱angular velocity 角速度aperiodic 非周期的appendix 附录argument 自变量autocorrelation 自相关auto-correlation function自相关函数auto-covariance function自协方差函数auto-spectral density自功率谱密度average value 均值axis 轴BBack substitution回代back-to-back mounting背靠背安装backward precession 反进动backward whirl 反向涡动balancing machine平衡机barium钡beam 梁bearing轴承beating 拍belt皮带Bode plot波德图boundary condition 边界条件burst random excitation 猝发随机激励Ccalibrate 校准,标定calibration 校准,标定cantilever 悬臂central difference method中心插分法centrifugal 离心的centrifugal force 离心力characteristic determinant特征行列式characteristic equation 特征方程characteristic matrix 特征矩阵circular frequency 圆频率clamped 固支clamped-hinged 固支-铰支clockwise 顺时针的coefficient系数cofactor 余因子column matrix 列矩阵comparison calibration 比较校准complex frequency response复频响应complex stiffness 复刚度complex amplitude 复数振幅complex modal shape 复振型complex plane 复平面complex vibration 复数振动condition monitoring 状态监测conjugate 共扼converge 收敛converged 收敛的convolution 卷曲,卷积convolution integral 卷积积分convolution theorem 卷积定理column 列coordinate 坐标coulomb damping 库仑阻尼counterclockwise 逆时针的coupling 耦合covariance 协方差crankshaft 曲轴critical speed 临界转速critically damped 临界阻尼的cross correlation 互相关cross-covariance function互协方差函数cross-spectral density 互谱密度cushion 软垫,垫子DDC 直流damper 阻尼器damped natural frequency有阻尼固有频率damping 阻尼damping factor 阻尼系数damping ratio 阻尼比dashpot 阻尼器,缓冲器decay 衰减decibel 分贝decompose 分解deflection 位移,挠度degree of freedom 自由度denominator 分母density 密度deviation 偏差derivative 导数descend order 降阶determinant 行列式diagonal matrix对角矩阵differential 微分的dimensionless 无量纲的discrete 离散的discrete spectrum 离散谱disk 盘displacement 位移dissipate 耗散divide 除DOF 自由度Duhamel’s Integral杜哈美积分Dunkerley’s method 邓克利法dynamic coupling 动力耦合dynamic matrix 动力矩阵Eeccentric mass 偏心质量eccentricity 偏心距effective mass有效质量effective value,RMS value 有效值eigenvalue 特征值eigenvalue matrix 特征值矩阵eigenvector 特征向量elastic body 弹性体element 元素,单元ensemble average 集合平均equal root 等根equilibrium 平衡equivalent viscous damping等效粘性阻尼ergodic process 各态历经过程excursion 行程Expansion Theorem展开定理exponential 指数的Euler equation 欧拉方程even 偶数Ffast Fourier transform快速傅立叶变换factorize 分解因式factorial 阶乘的finite difference method有限差分法finite element method 有限元方法flexibility 柔度flexibility matrix 柔度矩阵flexure-torsion vibration弯-扭振动flexural rigidity 抗弯刚度flutter 颤振flywheel 飞轮forced harmonic vibration强迫简谐振动forced vibration 强迫振动foregoing 在前的, 前述的forward precession正进动forward whirl正向涡动Fourier Series傅里叶级数Fourier spectrum傅立叶谱Fourier transform傅立叶变换free vibration自由振动free-damped vibration有阻尼自由振动free response自由响应frequency ratio频率比frequency response function 频响函数fundamental frequency 基频fundamental frequency vibration基频振动fundamental mode 第一阶模态GGauss elimination高斯消去法Gaussian distribution高斯分布,正态分布general solution 通解generalized coordinates 广义坐标generalized force 广义力generalized mass 广义量generalized stiffness 广义度gravitational force 重力gyroscopic 陀螺的gyroscope 陀螺仪Hhalf-power 半功率half-power bandwidth 半功率带宽half power points 半功率点harmonic 简谐的harmonic force 简谐激振力harmonic motion 简谐运动homogeneous 齐次的homogeneous equation 齐次方程Hooke’s law 虎克定律Holzer Method 霍尔兹法hysteresis damping 迟滞阻尼hysteresis loop 迟滞回线,滞后环Iimpact exciting calibration冲击校准impact hammer 冲击力锤impedance matrix 阻抗矩阵impedance transform 阻抗变换impulse excitation 脉冲激励impulse response function冲击响应函数inch 英寸independent coordinate 独立坐标inertia force 惯性力infinitesimal无穷小的initial condition 初始条件initial phase 初相位initial shock response spectrum初始冲击响应谱in-phase component 同相分量integral 积分的intermediate 中间的interpolation 插值inverse 逆inverse matrix 逆矩阵isotropic 各向同性的iteration 迭代Jjump phenomenon 跃变现象Jacobi diagonalization雅可比对角化Kkinetic energy 动能LLagrange's equation 拉格朗日方程LaPlace transformation拉普拉斯变换Linear 线性的Lissojous Curve 李萨茹图logarithm 对数logarithmic decrement 对数衰减率longitudinal 纵向的lower limit amplitude 幅值下限lumped mass 集中质量Mmagnetic tape recorder 磁带记录仪magnetic pulling exciter磁吸式激振器mass matrix 质量矩阵matrix of transfer function传递函数矩阵matrix iteration 矩阵迭代法maximum shock response spectrum冲击最大响应谱mean square value 均方值mechanical exciter 机械式激振器mechanical shaker 机械式振动台mechanical impedance 机械阻抗mechanical mobility 机械导纳midspan 跨中modal coordinates 模态坐标modal damping ratio 模态阻尼比modal impedance 模态阻抗modal mass 模态质量modal matrix 正则振型矩阵modal mobility 模态导纳modal stiffness 模态刚度modal testing 模态试验mode shape 振型(模态)modulus of elasticity 弹性模量moment 弯矩multi-degree-mf- freedom system 多自由度系统multiply 乘Nnatural frequency 固有频率natural logarithm 自然对数nondimensional 无量纲的nonlinear 非线性的non-proportional viscous damping 非比例粘性阻尼normal force 法向力normalization 正则化normal mode 主振型numerator 分子Ooctave 倍频程odd 奇数off-diagonal element非对角元素oil whirl 油膜涡动oil whip 油膜振荡orientation 方位orthogonal 正交的orthogonal matrix 正交矩阵orthogonality 正交性orthonormal mode 正则振型oscillatory 振动的,摆动的oscillatory motion 振荡运动overdamped 过阻尼的Pparallel 并联,平行Parseval's Theorem 帕斯瓦尔定理partial differential 偏微分particular solution 特解partitioned matrix 分块矩阵peak value 峰值pendulum (钟)摆periodic 周期的periodic motion 周期运动phase 相位phase distortion 相位失真[畸变]phase frequency characteristics相频特性phase frequency characteristics相频特性曲线phase shift 相移phase spectrum 相位谱piezoelectric crystal accelerometer压电晶体加速度计piezoelectric effect 压电效应piezoresistive effect 压阻效应pipe 管道polar moment of inertia极转动惯量polarization 极化polygon 多边形,多角形polynomial 多项式portable vibrometer 便携式测振仪potential energy 势能power 冥(次方),功率power spectral density 功率谱密度premultiply 左乘principal coordinate 主坐标principal frequency 主频率principal mass 主质量principal vibration 主振动principal stiffness 主刚度principle of superposition叠加原理probability 概率probability distribution 概率分布probability density function概率密度函数product 乘积propagation(声波, 电磁辐射等)传播proportional damping 比例阻尼proportional phase shift 比例相移proportional viscous damping比例粘性阻尼pulley 皮带轮,滑轮pulse excitation 脉冲激励Qquasi-periodic vibration准周期振动QR decomposition QR分解quefrency 倒频率quotient 商Rramp 斜面,斜道radial 径向的radial vibration 径向振动radian 弧度random vibration 随机振动Rayleigh method 瑞利法Rayleigh quotient 瑞利商Rayleigh-Ritz Method瑞利-里兹法real symmetric matrix 实对称矩阵recast 改动reciprocal 倒数的reciprocity calibration 互易校准法rectangular pulse 矩形脉冲recurrence formula递推公式, 循环residual amplitude 残余振幅residual shock response spectrum剩余冲击响应谱resolution 分辨率resonance 共振rigid body 刚体rise time 上升时间Ritz method 李兹法rms 均方根rod 杆root mean square 均方根root solving 求根rotation matrix 旋转矩阵rotatingmachine 旋转机械rotor 转子rotor-support system转子支承系统row 行row matrix 行矩阵rudder 舵Ssampling frequency 采样频率sampling interval 采样间隔sampling theorem 采样定理scaling 比例运算seismic 地震的seismometer 地震仪self-excitation vibration 自激振动sensitivity 灵敏度series 串联shaft 轴shaft vibration 轴振动shear 剪力shear modulus of elasticity剪切弹性模量shock excitation 冲击激励shock isolation 振动隔离shock response 冲击响应shock response spectrum击响应谱shock response spectrum analysis 冲击响应谱分析shock testing machine 冲击试验台SI 国际(单位)制sideband 边(频)带signal conditioner 信号处理器simply support 简支singular matrix 降秩(矩)阵single-DOF 单自由度slender 细长的slope 转角,斜率spin 旋转spring 弹簧square root 平方根stabilize 稳定standard deviation 标准偏差standard vibration exciter标准振动台state vector 状态向量static calibration 静态校准static coupling 静力耦合static equilibrium position静平衡位置steady state 稳态step function 阶跃函数stiffness 刚度stiffness influence coefficient刚度影响系数stiffness matrix 刚度矩阵strain 应变stress 应力string 线, 细绳stroboscope 闪光测速仪structural damping 结构阻尼subdiagonal 子对角subscript 下标subsidiary 附属的,次要的successive 接连不断的support motion 支承运动suspend 悬挂suspension 悬挂synthesis 综合,合成synchronous forward precession同步正进动synchronous whirl 同步涡动symmetric matrix 对称矩阵Ttabulate 将列成表tangent 切线,正切tangential 切向的tensile 拉力的,张力的tension 张力,拉力terminology 术语time delay 延时torque 扭矩, 转矩torsion 扭转torsional 扭转的torsional stiffness 抗扭刚度torsional vibration扭转振动TR 传递率trace of the matrix 矩阵的迹transducer 传感器transfer function 传递函数transfer matrix method 传递矩阵法transient response 瞬态响应transient vibration 瞬态振动transmissibility 隔振系数transpose 转置trial 测试,试验triangular matrix 三角矩阵truncation error 截断误差,舍位误差twist 扭,转Uunbalance 不平衡unbalance response 不平衡响应underdamped 欠阻尼的uniformization 归一化unit impulse 单位脉冲unit matrix 单位矩阵unit vector 单位向量unsymmetric 非对称upper limit amplitude 幅值上限upper triangular matrix 上三角阵Vvariance 方差velocity 速度velometer 速度计vertical vibration 垂直振动vibration 振动vibration absorber 吸振器vibration isolation 隔振vibration nomogram 振动诺模图vicinity 在附近virtual work 虚功viscous damping 粘性阻尼Wwaveform 波形wavelength 波长wave reproduction 波形再现wave-shape distortion 波形畸变wedge劈,尖劈,楔子whirl 旋转,涡动,进动Wiener-Khinchin formula维纳-辛钦公式window function 窗函数。

英文汉译Unconformity不整合2D-seismic二维地震3D-seismic三维地震4D-seismic四维地震Abnormal events异常波Absolute permeability绝对渗透率Absorption吸收Absorption coefficient吸收系数Acceleration of gravity重力加速度Accumulate error累计误差Acoustic impedance波阻抗Acoustic logging声波测井Acoustic impedance声阻抗Acoustic impedance section波阻抗剖面Acoustic impedance section声阻抗剖面Acoustic log声波测井Acoustic variable density logging声波变密度测井Acoustic velocity log声速测井Acoustic wave声波Adachi formulas阿达奇公式Adaptive Deconvolution自适应反褶积Adjacent-bed effect围岩影响Adjugate伴随矩阵Aeolotropy各向异性Aerated layer风化层AGC(automatic gain control)自动增益控制Aggradation加积作用Algorithm算法Alias假频Amplitude振幅Amplitude anomaly振幅异常Amplitude distortion振幅失真Amplitude equalization振幅平衡Amplitude log声波幅度测井Amplitude modulation振幅调制Amplitude of the envelope振幅包络Amplitude recovery真振幅恢复AMT(audiomagnetotelluric method)音频大地电磁法Analog模拟Angle of incidence入射角Angular frequency 角频率Anisotropy各向异性Anticipation function 期望函数anticline背斜构造Aperture time时窗时间API unitAPI单位Apparent表观值Apparent density视密度Apparent dip视倾角Apparent polarity视极性Apparent resistivity视电阻率Apparent velocity视速度Apparent wavelength视波长Apparent wavenumber视波数Applied geophysics应用地球物理学Archie’s formulas阿尔奇经验公式Areal heterogeneity平面非均质Array排列,组合Arrival波至Asynchronous异步的Attenuation衰减Attribute属性,品质Autoconvolution自褶积Autocorrelation自相关Autocovariancet自协方差Auxiliary key horizon辅助标准层Average平均Average velocity平均速度Average velocity平均速度AVO technique AVO技术Axis轴Azimuth方位角,方位Background背景Balanced section平衡剖面Balancing a survey平差Band频带Band-pass通频带Bandwidth带宽Barrier layer隔层Base lap底超Base line基线Base map草图,底图Base station基点Base-line shift基线偏移Basin盆地bedding层理Bias偏差;偏流;偏压;偏磁Bimodal双峰的Bin面元Binary二进制Binate重采样bipole双极bland zone盲区block数据块borehole televiewer井下电视bouguer anomaly布格异常Bouguer correction布格校正boundary conditionBright spot亮点Bulk porosity总孔隙度caprock盖层Chemical sedimentary rock化学沉积岩Clastic sedimentary rock碎屑沉积岩Clay mineral粘土矿物Clean sandstone model纯砂岩模型CMS(chemical remanent magnetization)化学剩磁Compensate neutron log补偿中子测井Complex cycle复合旋回Comprehensive log interpretation测井资料综合解释Concentric folding同心褶皱Connectivity砂体连通性continuation延拓contour等值线convergence收敛Converted wave转换波convolution褶积Core岩芯corer取芯器,取样器correction校正correlation对比;相关;匹配Correlation coefficient相关系数Correlation filter相关滤波COS (common offset stack)共炮检距叠加Cosine law余弦定理coupling耦合Covariance协方差creep蠕变Critical angle临界角Critical damping临界阻尼Crooked line弯曲线测量Cross十字Cross bedding交错层理Crosscorrelation filter互相关滤波crossplot交会图Cross-section剖面;截面Curie point居里点curl旋度Curvature曲率Curve fitting曲线拟合Cycle skip周波跳跃Cylindrical divergence圆柱状发散datum基准面Decay constant衰减常数Decay curve衰减曲线decimate重采样Decimate重采样Declination磁偏角Decollement滑脱面Decomposition分辨Deconvolution反褶积Delay time延迟时间Demodulation解调Density logging密度测井Density contrast密度差Depositional remanent magnetism沉积剩余磁性Depositional sequence沉积层序Depth map深度图Depth migration深度偏移Depth of investigation勘探深度Development seismic开发地震Development well logging开发测井Diaper底避构造Dielectric log介电常数测井Dielectric consist介电常数Differential差异;差分Differential compaction差异压实作用Diffraction绕射Diffraction stack绕射叠加Digital数字Dim spot暗点Dip倾角Dip angle地层倾角Dip direction地层倾向Dip line倾斜测线Dip moveout倾角时差Dipole偶极Direct detection直接检测Direct problem正问题Direct wave直达波Dirichlet condition狄利赫来条件Discrete fourier transform离散傅里叶变换Disharmonic folding不谐和褶皱Dispersion curve频散曲线Displacement偏离Displacement current位移电流Dissertation Abstracts International国际学位论文文摘Distortion畸变Distributed分布Divergence发散;散度Domain域Dome丘,穹隆Dominant frequency主频Doppler effect多普勒效应Downdip下降,下倾,Downlap下超Drape披盖Drift漂移Drill钻机Dual water model双水模型Dynamic correction动校正Dynamic memory动态存储器Dynamic range动态范围Dynamite烈性硝甘炸药Effective permeability有效渗透率Effective porosity有效孔隙度Eigenvalue特征值Eigenvector特征向量Elastic弹性的Elastic constants弹性常数Elastic deformation弹性常数Elastic impedance波阻抗Elastic limit弹性限度Elastic moduli弹性模量Elastic wave弹性波Electromagnetic propagation log电磁波传播测井Elevation correction高程校正emulate仿真End-on端点放炮Engineering geophysics工程地球物理enthalpy焓entropy熵envelope包络equalization均衡Equipotential surface等位面Event同相轴Expectation期望Exponential decay指数衰减Factor analysis因子分析Fade切除Fan-filter扇形滤波Fast fourier transform快速傅里叶变换fault断层Fault断层Fault bench断阶构造Fault drop落差Fault line断层线Fault surface断层面Fault throw断距feedback反馈Fence diagram栅状图Fence effect栅栏效应Fermat’s principle费马原理Filter滤波器Finite-difference method有限差分法Finite-element method有限元法Firing引爆First break初至Flat spot平点Flattened section已拉平的剖面Flexural-slip folding挠曲滑动褶皱Floating datum浮动基准面Flow chart流程图Flushed zone冲洗带flute切除flux通量Flyer检波器串fold地层褶曲folding褶皱format格式formation地层Formation occurrence地层产状Formation sensitivity储层敏感性Formation strike地层走向Formation evaluation地层评价Formation resistivity factor地层电阻率因子Formation-density log地层密度测井Forward solution正演解four-property relationship四性关系fracture裂缝Fresnel diffraction菲涅尔衍射Gas hydrate天然气水合物geochronology地质年代学geodesy大地测量学Geodetic latitude大地纬度Geodetic reference system大地参考系统Geodynamics project地球动力学研究计划Geographic latitude大地纬度geoid大地水准面Geomagnetic pole地磁极Geomagnetic reversal地磁反转Geometric factor几何因子Geometric spreading几何扩散Geophone检波器Geophone检波器组合Geophone array检波器组合Geophone interval检波距Geophone pattern检波器组合geophysicist地球物理学家Geophysics survey地球物理测量geosyncline地槽Geothermal gradient地热梯度ghost虚反射graben地堑graben地堑gradient梯度gravimeter重力仪Gravitational folding重力褶皱Gravitational potential重力位gravity重力Gravity anomaly 重力异常Gravity reduction重力改正Gravity survey重力测量Grid网格Ground roll地滚波Group interval组距Group velocity群速度Guided wave导波hammer重锤Handshake信息交换harmonic谐波Harmonic function调和函数Head wave首波Heat conductivity热导率high-resolution seismic高分辨率地震Horizontal bedding水平层理Horizontal slice水平切片Horizontal spot平点horst地垒horst地垒Igneous rock火成岩Index bed标准层Induced polarization激发极化Inductance电感induction感应Induction electrical survey感应电测井Induction logging感应测井inductivity磁导率Information extracted信息提取Innerbeded heterogeneity层内非均质Instantaneous frequency瞬时频率Instantaneous phase瞬时相位instruction指令insulator绝缘体Integrated circuit集成电路Integrated geophysics综合地球物理Integration混波Intelligent terminal智能终端intensity强度Intensity of magnetization磁化强度Interactive人机联作Interbed夹层Interbed multiple层间多次波Interbeded heterogeneity层间非均质Intercept distortion截断失真Interpretation解释Invaded zone冲洗带Inverse cycle反旋回Inverse draw逆牵引Inversion problem反问题Key bed标志层Laterolog侧向测井Layer velocity section层速度剖面Layer velocity层速度Level calibration层位标定litho-density log岩性密度测井Log interpretation model测井解释模型Log response equation测井响应方程Logging tool standardization测井仪器标准化logging-constrained reversion测井约束地震反演Logs测井曲线Material balance equation物质平衡方程Metamorphic rock变质岩Microelectrode log微电极测井microfacies沉积微相migrated-stacked section偏移叠加剖面Model of bulk-volume rock岩石体积模型Monoclinal strata单斜层mute切除Natural gamma-ray logging自然伽马测井Natural gamma ray spectral log自然伽马能谱测井normal正断层Normal cycle正旋回Normal draw正牵引Normal fault正断层Normal-moveout corrections正常时差校正Nosing structure鼻状构造Oil layer group油层组Oil sandbody油砂体one-step 3D-migration一步三维偏移Parameter参数permeability渗透率Permeability max-mean ratio渗透率突进系数permeability max-min ratio渗透率级差permeability variation coefficient渗透率变异系数Petrophysical property油层物性phase spectrum相位谱Pinch out地层尖灭Polarity reversal极性反转Pore throat孔隙喉道potential势能Primary pore原生孔隙prospect勘探工区,勘探远景区Prospecting seismology勘探地震学Random随机的Ray tracing射线追踪Reciprocity principle互换定理Reconnaissance踏勘,Recover恢复,还原Recovery收获率Recursive filter递归滤波Reef礁Reflecting point反射点Reflection反射Reflection factor反射系数Reflection character analysis反射波特征分析Reflection coefficient反射系数Reflection polarity反射波极性Reflection strength反射波强度Reflection survey反射波勘探Reflector反射界面Refraction折射Refraction wave折射波Refractive index折射系数,折射率Refractor折射界面,折射层Regression海退Regression analysis回归分析Relative permeability相对渗透率Relaxation time驰豫时间Reserving space储集空间reservoir储集层Reservoir fundamental parameter储集层基本参数Resistivity logging电阻率测井Resistivity index电阻率指数resolution分辨率Resolution分辨率Resonance共振Reverberation鸣震reverse逆断层Reverse fault逆断层RMS(root-mean-square)均方根Rock stratum岩层Rock structure岩石构造Rock texture岩石结构Rotational旋转断层Sample ratio取样间隔Sampling theorem采样定理Sand砂岩Sands group砂层组saturation饱和度scattering散射Seal rock封堵层Secondary pore次生孔隙Secondary field二次场Secondary porosity次生孔隙度Sedimentary cycle沉积旋回Sedimentary facies沉积相Sedimentary rhythm沉积韵律Sedimentary rock沉积岩Seis检波器, 地震检波器seiscrop等时切片图Seislog地震测井seisloop三维测量排列Seismic exploration地震勘探Seismic facies地震相Seismic inversion地震反演Seismic normalization地震正演Seismic wavelet地震子波Seismic datum地震基准面Seismic discontinuity地震不连续面Seismic event地震同相轴Seismic exploration地震勘探Seismic facies地震相Seismic log地震测井Seismic map地震构造图Seismic profile地震剖面Seismic pulse地震脉冲Seismic record地震记录Seismic refraction method地震折射波法Seismic section地震剖面Seismic sequence analysis地震层序分析Seismic stratigraphy地震地层学Seismic survey地震勘探Seismic tomography地震层析seismic-geologic section地震地质剖面seismic-sequent stratigraphy地震层序地层学Seismogram地震记录Seismograph地震仪Seismologist地震学家Seismology地震学sensitivity灵敏度Series of development strata开发层系Shale泥岩Shaly sandstone model泥质砂岩模型Shear wave横波Shielding屏蔽,屏蔽层Shoot爆炸,放炮,激发Signal to noise ratio信噪比Significance level显著性水平Similar folding相似褶皱simulated annealing模拟退火Single layer小层Singularity奇点,奇异点,奇异性Skin depth趋肤深度Smoothing平滑SP(spontaneous potential or self potential )自然电位Spacing电极距,源距Spatial aliasing空间假频Spectrum谱,频谱Spherical球面的Spill point溢出点Spontaneous potential log自然电位测井Spread排列,布置Spreading发散,扩散Stacked section水平叠加剖面stacked-migrated section叠偏剖面Stacking velocity叠加速度Standard标准的Static correction静校正Statistical统计的Storage存储器Storm扰动Strain应变,形变,胁变Strata overlap地层超覆Stratigraphic interpretation地层学解释Stratum loss地层缺失Streamer拖缆Strike slip走向滑动断层Stringer高速薄层Structural geology构造地质Structure构造Superposition叠加定理Supervisor野外监督Suppression压制Surface wave面波Survey测量,勘测,勘探Susceptibility磁化率Synchronous同步的syncline向斜构造Synthetic seismogram合成地震记录Synthetic seismogram合成地震记录Systematic error系统误差TAR(ture-amplitude recovery )真振幅恢复Tectonic map大地构造图Telluric current大地电流Tensor张量Terrain correction地形校正Thermal conductivity热导率Three instantaneous parameter section三瞬剖面throat eveness coefficient喉道均质系数throat mean喉道平均值throat mid-value喉道中值Thrust fault冲断层Thrust fault逆掩断层Tie-line联接测线Time-distance curve时距曲线Time-slice map等时切片Time-variant时变的Tomography层析成像技术Toplap顶超Topographic correction地形校正Total reflection全反射Trace analysis道分析Trace equalization道均衡Trace gather道集Trace integration道积分Trace inversion道反演Trace sequential道序编排transform转换断层Transform fault转换断层Transformed wave转换波Transgression海侵Transient electromagnetic method瞬变电磁法Transistor晶体管Transmission coefficient透射系数Transverse wave横波Transversely isotropic横向各向同性Trap圈闭Travel path传播路径Tree-dimensional survey三维勘探Trough波谷Truncation error截断误差Tumescence火山隆起two-step 3D-migration二步三维偏移Uncertainty不定性,不确定性,不可靠性Updip上倾放炮Uphole geophone井口检波器Upward continuation向上延拓Valley波谷Variable area变面积Variable density变密度Variance方差Vector矢量Velocity analysis速度分析Velocity inversion速度倒转Velocity layering速度分层Velocity spectrum速度谱Velocity sweeping速度扫描Vibration survey振动测量Vibrator振动器Video display视频显示Virtual memory虚拟存储器Viscoelastic粘弹性的Viscosity粘度,粘滞性Water saturation含水饱和度Wave group波组wave equation波动方程Wave equation migration波动方程偏移Wave impedance波阻抗Wave velocity波速Waveform波形Wavefront波前Wavelet地震子波Wavelet equalization子波均衡Wavelet extraction子波提取Wavelet processing子波处理Wavenumber波数Wavy bedding波状层理Weathering 风化层Weathering风化层,低速带Weathering correction低速带校正Weathering layer风化层,低速带Weathering shot低速带测定Weighted array加权平均加权组合Weighted average加权平均Well logging测井Well logging series测井系列White白噪声White noise level白噪水平Young’s modulus杨氏模量Zero-phase零相位Zoeppritz’s equation佐普里茨方程。
134Manuscript received by the Editor January 11, 2011; revised manuscript received April 25, 2011.*This research is supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 41004055).1. College of Optoelectronic Science and Engineering, National University of Defense Technology, Changsha 410073, China.
Algebraic processing technique for extracting frequency-dependent shear-wave splitting parameters in an anisotropic medium*
APPLIED GEOPHYSICS, Vol.8, No.2 (June 2011), P. 134 - 140, 5 Figures.DOI:10.1007/s11770-011-0276-2
Han Kai-Feng1 and Zeng Xin-Wu1
Abstract: Based on the dual source cumulative rotation technique in the time-domain proposed by Zeng and MacBeth (1993), a new algebraic processing technique for extracting shear-wave splitting parameters from multi-component VSP data in frequency-dependent medium has been developed. By using this dual source cumulative rotation technique in the frequency-domain (DCTF), anisotropic parameters, including polarization direction of the shear-waves and time-delay between the fast and slow shear-waves, can be estimated for each frequency component in the frequency domain. It avoids the possible error which comes from using a narrow-band fi lter in the current commonly used method. By using synthetic seismograms, the feasibility and validity of the technique was tested and a comparison with the currently used method was also given. The results demonstrate that the shear-wave splitting parameters frequency dependence can be extracted directly from four-component seismic data using the DCTF. In the presence of larger scale fractures, substantial frequency dependence would be found in the seismic frequency range, which implies that dispersion would occur at seismic frequencies. Our study shows that shear-wave anisotropy decreases as frequency increases. Keywords: Algebraic processing technique, anisotropy, shear-wave splitting, frequency dependence
IntroductionA successful application of seismic anisotropy is its ability to provide subsurface fracture orientations from the polarization of the faster seismic shear-waves and spatial distributions of fracture intensity from time-delays between the split fast and slow seismic shear-waves (Crampin, 1985; Li 1997; Zhang et al., 2009). Multi-component data acquired using vertically and horizontally polarized sources and three-component geophones have gained acceptance as a way of providing direct measurements of previously inaccessible physical properties of subsurface rocks (Tatham and Mccormack, 1991; Wu et al., 2010). Many techniques have been
developed in recent years to permit visualization and estimation of these shear-wave attributes. Actually, the majority of these analysis techniques rely on a convolutional equation for wave propagation through a uniform anisotropic solid (Queen and Rizer, 1990; Zeng and MacBeth, 1993). This vector convolutional model can be derived by factorizing the anisotropic refl ectivity expressions for full waves and point sources (Fryer and Frazer, 1984), keeping only the essential characteristics of the anisotropic model which affect the most salient features of the wave propagation. In this respect, estimation of the shear-wave attributes is model-based or parametric, as it is carried out using known matrix equations for anisotropic wave propagation through 135
Han and Zenga horizontal plane-layered structure. Many popular analysis techniques have been introduced to obtain the seismic anisotropy parameters, including the numerical rotation of Alford (1986), dual source cumulative rotation technique (Zeng and MacBeth, 1993), the layer stripping approach (Winterstein and Meadows, 1991), and etc. However, these algebraic processing techniques are applied in the time-domain.So far the terms ‘crack’ and ‘fracture’ have been used as synonyms in geophysics. Although both grain micro-scale cracks and macro-scale fractures are considered to cause seismic anisotropy (Liu et al., 1993). Reservoir engineers are more interested in the latter because for the prediction of permeability in many hydrocarbon reservoirs it is believed that the fluid flow in the reservoir is dominated by formation-scale fluid units (on the order of meters). If we are constrained to work within the conventional equivalent medium approach, then we can only obtain crack density and orientation from the seismic data. Unfortunately, different fracture distributions may have the same crack density because a few large cracks can give the same crack density as many smaller cracks. Thus, conventional equivalent medium theory cannot provide information about fracture sizes. In recent years, it has been proposed that multiscale fl uid interaction could cause frequency-dependent anisotropy. With a suitable model (Chapman, 2003), fracture sizes, which control the fluid flow, may potentially be predicted from frequency-dependent seismic anisotropic measurements. To obtain the anisotropic parameters which can be useful for permeability prediction, we require an effective algebraic processing technique. The current commonly used method is applying Alford rotation (or another normal shear-wave splitting algorithm) to different band-pass datasets (say, 5 to 10 Hz and 10 to 20 Hz) to obtain those parameters for different frequency bands. If considering window function effects for bandpass filters, narrow bandpass filters could possibly lead to large computing errors for time-delay calculations.The contribution of our present work is to develop a new algebraic processing technique (i.e., DCTF) for frequency-dependent shear-wave splitting, in order to estimate shear-wave splitting attributes from the multi-component medium response. This technique is based on the dual source cumulative rotation technique in the time-domain proposed by Zeng and MacBeth (1993). By using the DCTF, for a single frequency in the frequency domain, anisotropy parameters can be estimated. Then using synthetic seismograms, we investigate the possibility of using the frequency dependence of