曼昆宏观经济学英语课后题答案
- 格式:docx
- 大小:63.24 KB
- 文档页数:31


曼昆经济学原理英文版答案As the creator of the Baidu Wenku document "Principles of Economics by Mankiw (English Version) Answers", I would like to provide a comprehensive guide to the solutions of the questions in the book. This document aims to help students better understand the principles of economics and improve their problem-solving abilities.Chapter 1: Ten Principles of Economics。
1. People face trade-offs.2. The cost of something is what you give up to get it.3. Rational people think at the margin.4. People respond to incentives.5. Trade can make everyone better off.6. Markets are usually a good way to organize economic activity.7. Governments can sometimes improve economic outcomes.8. The standard of living depends on a country's production.9. Prices rise when the government prints too much money.10. Society faces a short-run trade-off between inflation and unemployment.Chapter 2: Thinking Like an Economist。

曼昆经济学原理英文第六版答案【篇一:曼昆经济学原理英文版文案加习题答案8章】ation a new in the news box on ―the tax debate‖ has been added.by the end of this chapter, students should understand:? how taxes reduce consumer and producer surplus.? the meaning and causes of the deadweight loss from a tax. ? why some taxes have larger deadweight losses than others. ? how tax revenue and deadweight loss vary with the size of a tax.chapter 8 is the second chapter in a three-chapter sequence dealing with welfare economics. in theprevious section on supply and demand, chapter 6 introduced taxes and demonstrated how a tax affects the price and quantity sold in a market. chapter 6 also described the factors that determine how the burden of the tax is divided between the buyers and sellers in a market. chapter 7 developed welfare economics—the study of how the allocation of resources affects economic well-being. chapter 8 combines the lessons learned in chapters 6 and 7 and addresses the effects of taxation on welfare. chapter 9 will address the effects of trade restrictions on welfare. the purpose of chapter 8 is to apply the lessons learned about welfare economics in chapter 7 to the issue of taxation that was addressed in chapter 6. students will learn that the cost of a tax to buyers and sellers in a market exceeds the revenue collected by the government. students will also learn about the factors that determine the degree by which the cost of a tax exceeds the revenue collected by the government.144? a tax on a good reduces the welfare of buyers and sellers of the good, and the reduction in consumer and producer surplus usually exceeds the revenue raised by the government. the fall in total surplus—the sum of consumer surplus, producer surplus, and tax revenue—is called thedeadweight loss of the tax.taxes have deadweight losses because they cause buyers to consume less and sellers to produce less, and these changesin behavior shrink the size of the market below the level that maximizes total surplus. because the elasticities of supply and demand measure how much market participants respond to market conditions, larger elasticities imply larger deadweight losses.as a tax grows larger, it distorts incentives more, and its deadweight loss grows larger. because a tax reduces the size of a market, however, tax revenue does not continually increase. it first rises with the size of a tax, but if the tax gets large enough, tax revenue starts to fall. ? ?i. the deadweight loss of taxationa. remember that it does not matter who a tax is levied on; buyers and sellers will likely share inthe burden of the tax.b. if there is a tax on a product, the price that a buyer pays will be greater than the price the sellerreceives. thus, there is a tax wedge between the two prices and the quantity sold will be smaller if there was no tax.c. how a tax affects market participants1. we can measure the effects of a tax on consumers by examining the change in consumersurplus. similarly, we can measure the effects of the tax on producers by looking at the change in producer surplus.then the benefit from the tax revenue must not be ignored.3. welfare without a taxa. consumer surplus is equal to: a + b + c.b. producer surplus is equal to: d + e + f.c. total surplus is equal to: a + b + c + d + e + f. 4. welfare with a tax a. consumer surplus is equal to: a.b. producer surplus is equal to: f.5. changes in welfare a. consumer surplus changes by: –(b +c). b. producer surplus changes by: –(d + e). c. tax revenue changes by: +(b + d). d. total surplus changes by: –(c + e). 6. definition of distortion, such as a tax. d. deadweight losses and the gains from tradec. tax revenue is equal to: b +d. d. total surplus is equal to: a +b + d + f.1. taxes cause deadweight losses because they prevent buyers and sellers from benefiting fromtrade.2. this occurs because the quantity of output declines; trades that would be beneficial to both the buyer and seller will nottake place because of the tax.3. the deadweight loss is equal to areas c and e (the drop intotal surplus).4. note that output levels between the equilibrium quantity without the tax and the quantitywith the tax will not be produced, yet the value of these unitsto consumers (represented by the demand curve) is larger than the cost of these units to producers (represented by the supply curve).ii. the determinants of the deadweight lossa. the price elasticities of supply and demand will determinethe size of the deadweight loss that occurs from a tax. 1. givena stable demand curve, the deadweight loss is larger when supply is relatively elastic.2. given a stable supply curve, the deadweight loss is larger when demand is relatively elastic. b. case study: the deadweight loss debate1. social security tax and federal income tax are taxes onlabor earnings. a labor tax places a tax wedge between thewage the firm pays and the wage that workers receive.2. there is considerable debate among economists concerning the size of the deadweight lossfrom this wage tax.3. the size of the deadweight loss depends on the elasticity of labor supply and demand, andthere is disagreement about the magnitude of the elasticity of supply.【篇二:曼昆经济学原理英文版文案加习题答案31章】basic conceptsthere is a new in the news feature on the changing nature of u.s. exports and an updated presentation of the u.s. trade deficit.by the end of this chapter, students should understand:??how net exports measure the international flow of goodsand services.??how net capital outflow measures the international flow of capital.??why net exports must always equal net foreign investment.??how saving, domestic investment, and net capital outflow are related.??the meaning of the nominal exchange rate and the real exchange rate.??purchasing-power parity as a theory of how exchange rates are determined.chapter 18 is the first chapter in a two-chapter sequence dealing with open-economy macroeconomics. chapter 18 develops the basic concepts and vocabulary associated with macroeconomics in an international setting: net exports, net capital outflow, real and nominal exchange rates, and purchasing-power parity. the next chapter, chapter 19, builds an open-economy macroeconomic model that shows how these variables are determined simultaneously.the purpose of chapter 18 is to develop the basic concepts macroeconomists use to study open economies. it addresses why a nation’s net exports must equal its net capital outflow. it also addresses the concepts of the real and nominal exchange rate and develops a theory of exchange ratedetermination known as purchasing-power parity.298??net exports are the value of domestic goods and services sold abroad (exports) minus the value offoreign goods and services sold domestically (imports). net capital outflow is the acquisition of foreign assets by domestic residents (capital outflow) minus the acquisition of domestic assets by foreigners (capital inflow). because every international transaction involves an exchange of an asset for a good or service, an economy’s net capital outflow always equals its net exports.an economy’s saving can be used to finance investment at home or buy assets abroad. thus, national saving equals domestic investment plus net capital outflow.the nominal exchange rate is the relative price of the currency of two countries, and the real exchange rate is the relative price of the goods and services of two countries. when the nominal exchange rate changes so that each dollar buys more foreign currency, the dollar is said to appreciate or strengthen. when the nominal exchange rate changes so that each dollarbuys less foreign currency, the dollar is said to depreciate or weaken.according to the theory of purchasing-power parity, a dollar (or a unit of any other currency) should be able to buy the same quantity of goods in all countries. this theory implies that the nominal exchange rate between the currencies of two countries should reflect the price levels in those countries. as a result, countries with relatively high inflation should have depreciating currencies, and countries with relatively low inflation should have appreciating currencies. ?? ?? ??i. we will no longer be assuming that the economy is a closed economy.a. definition of in the world.b. definition of around the world.ii. the international flows of goods and capitala. the flow of goods: exports, imports, and net exports1. definition of abroad.2. definition of domestically.imports, also called the trade balance.4. definition of : the value of a nation’s exports minus the value of its imports, also called net exports.5. definition of .6. definition of .7. definition of .8. there are several factors that influence a country’s exports, imports, and net exports:a. the tastes of consumers for domestic and foreign goods.b. the prices of goods at home and abroad.c. the exchange rates at which people can use domestic currency to buy foreign currencies.d. the incomes of consumers at home and abroad.e. the cost of transporting goods from country to country.f. government policies toward international trade.9. case study: the increasing openness of the u.s. economy a. figure 1 shows the total value of exports and imports (expressed as a percentage of gdp) for the united states since 1950. b. advances in transportation, telecommunications, and technological progress are some of the reasons why international trade has increased over time. c. policymakers around the world have also become more accepting of freetrade over time. 10. in the news: the changing nature of u.s. exports a. growing u.s. exports include entertainment royalties, tourism, travel, and services. b. this article from the wall street journal describes the growth in new exports. b. the flow of financial resources: net capital outflow1. definition of residents minus the purchase of domestic assets by foreigners.2. the flow of capital abroad takes two forms. a. foreign direct investment occurs when a capital investment is owned and operated by a foreign entity.b. foreign portfolio investment involves an investment that is financed with foreign money but operated by domestic residents.3. net capital outflow can be positive or negative.a. when net capital outflow is positive, domestic residents are buying more foreign assets than foreigners are buying domestic assets. capital is flowing out of the country.b. when net capital outflow is negative, domestic residents are buying fewer foreign assets than foreigners are buying domestic assets. the country is experiencing a capital inflow. 4. there are several factors that influence a country’s net capital outflow:a. the real interest rates being paid on foreign assets.b. the real interest rates being paid on domestic assets.c. the perceived economic and political risks of holding assets abroad.d. the government policies that affect foreign ownership of domestic assets.c. the equality of net exports and net capital outflow1. net exports and net capital outflow each measure a type of imbalance in a world market.a. net exports measure the imbalance between a country’s exports and imports in world markets for goods and services.b. net capital outflow measures the imbalance between the amount of foreign assets bought by domestic residents andthe amount of domestic assets bought by foreigners inworld financial markets.2. for an economy, net exports must be equal to net capital outflow.3. example: you are a computer programmer who sells some software to a japanese consumer for 10,000 yen. a. thesale is an export of the united states so u.s. net exports increase.b. there are several things you could do with the 10,000 yenc. you could hold the yen (which is a japanese asset) or use it to purchase another japanese asset. either way, u.s. net capital outflow rises.d. alternatively, you could use the yen to purchase a japanese good. thus, u.s. imports will rise so the net effect on net exports will be zero.e. one final possibility is that you could exchange the yen for dollars at a bank. this doesnot change the situation though, because the bank then must use the yen for something.alternative classroom example: assume that u.s. residents do not want to buy any foreign assets, but foreign residents want to purchase some stock in a u.s. firm (such as microsoft). how are the foreigners going to get the dollars to purchase the stock? they would do it the same way u.s. residents would purchase the stock—they would have to earn more than they spend. in other words, foreigners must sell the united states more goods and services than they purchase from the united states. this leads to negative net exports for the united states. the extra dollars spent by u.s. residents on foreign-produced goods and services would be used to purchase the stock in microsoft. 4. this example can be generalized to the economy as a whole.a. when a nation is running a trade surplus (nx 0), it must be using the foreign currencyto purchase foreign assets. thus, capital is flowing out of the country (nco 0).b. when a nation is running a trade deficit (nx 0), it must be financing the net purchase of these goods by selling assets abroad. thus, capital is flowing into the country (nco0).5. every international transaction involves exchange. when a seller country transfers a good orservice to a buyer country, the buyer country gives up some asset to pay for the good or service.6. thus, the net value of the goods and services sold by a country (net exports) must equal thenet value of the assets acquired (net capital outflow).d. saving, investment, and their relationship to the international flows1. recall that gdp (y ) is the sum of four components: consumption (c ), investment (i ),government purchases (g ) and net exports (nx ).【篇三:曼昆宏观经济学课后答案(英文版)】quizzes:1. gross domestic product measures two things at once: (1) the total income of everyonein the economy; and (2) the total expenditure on the economy’s output of goods and services. it can measure both of these things at once because income must equal expenditure for the economy as a whole.2. the production of a pound of caviar contributes more to gdp than the production of apound of hamburger because the contribution to gdp is measured by market value and the price of a pound of caviar is much higher than the price of a pound of hamburger.3. the four components of expenditure are: (1) consumption;(2) investment; (3)government purchases; and (4) net exports. the largest component is consumption, which accounts for more thantwo-thirds of total expenditure.4. nominal gdp is the production of goods and services valued at current prices. realgdp is the production of goods and services valued at constant prices. real gdp is a better measure of economicwell-being because it reflects the eco nomy’s ability to satisfy people’s needs and desires. thus a rise in real gdp means people have produced more goods and services, but a rise in nominal gdp could occur either because of increased production or because of higher prices.5. although gdp is not a perfect measure of well-being, policymakers should care about itbecause a larger gdp means that a nation can afford better health care, better educational systems, and more of the material necessities of life.questions for review:1.2.3.4. an economys income must equal its expenditure, since every transaction has a buyer and a seller. thus, expenditure by buyers must equal income by sellers. the production of a luxury car contributes more to gdp than the production of an economy car because the luxury car has a higher market value. the contribution to gdp is $3, the market value of the bread, which is the final good that is sold. the sale of used records does not affect gdp at all because it involves no current production.5. the four components of gdp are consumption, such as the purchase of a music cd;investment, such as the purchase of a computer by a business; government purchases, such as an order for military aircraft; and net exports, such as the sale of american wheat to russia.6. economists use real gdp rather than nominal gdp to gauge economic well-beingbecause real gdp is not affected by changes in prices, so it reflects only changes in the amounts being produced. if nominal gdp rises, you do not know if that is because of increased production or higher prices.7.the percentage change in nominal gdp is (600-200)/200 x 100 = 200%. the percentage change in real gdp is (400-200)/200 x 100 = 100%. the percentage change in the deflator is (150-100)/100 x 100 = 50%.8. it is desirable for a country to have a large gdp because people could enjoy more goodsand services. but gdp is not the only important measure of well-being. for example, laws that restrict pollution cause gdp to be lower. if laws against pollution were eliminated, gdp would be higher but the pollution might make us worse off. or, for example, an earthquake would raise gdp, as expenditures on cleanup, repair, and rebuilding increase. but an earthquake is an undesirable event that lowers our welfare.problems and applications:1. a. consumption increases because a refrigerator is a good purchased by ahousehold.b. investment increases because a house is an investment good.c. consumption increases because a car is a good purchased by a household, butinvestment decreases because the car in ford’s inventory had been counted as aninvestment good until it was sold.d. consumption increases because pizza is a good purchased by a household.e. government purchases increase because the government spent money to providea good to the public.f. consumption increases because the bottle is a good purchased by a household,but net exports decrease because the bottle was imported.g. investment increases because new structures and equipment were built.2.3. with transfer payments, nothing is produced, so there is no contribution to gdp. purchases of new housing are included in the investment portion of gdp because housingprovides services for a long time. for the same reason, purchases of new cars could be thought of as investment, but by convention, they are not. the logic could apply to any durable good, such as household appliances.if gdp included goods that are resold, it would be counting output of that particular year, plus sales of goods produced ina previous year. it would double-count goods that were sold more than once and would count goods in gdp for severalyears if they were produced in one year and resold in another. 4.5. a. 2001: ($1 per qt. of milk ? 100 qts. milk) + ($2 per qt. of honey ? 50 qts. honey)= $2002002: ($1 per qt. of milk ? 200 qts. milk) + ($2 per qt. of honey ? 100 qts.honey) = $4002003: ($2 per qt. of milk ? 200 qts. milk) + ($4 per qt. of honey ? 100 qts.honey) = $8002001: ($1 per qt. of milk ? 100 qts. milk) + ($2 per qt. ofhoney ? 50 qts. honey)= $2002002: ($1 per qt. of milk ? 200 qts. milk) + ($2 per qt. of honey ? 100 qts.honey) = $4002003: ($1 per qt. of milk ? 200 qts. milk) + ($2 per qt. of honey ? 100 qts.honey) = $4002001: ($200/$200) ? 100 = 1002002: ($400/$400) ? 100 = 1002003: ($800/$400) ? 100 = 200b. percentage change in nominal gdp in 2002 = [($400 - $200)/$200] ? 100 =100%.percentage change in nominal gdp in 2003 = [($800 -$400)/$400] ? 100 =100%.percentage change in real gdp in 2002 = [($400 - $200)/$200] ? 100 = 100%.percentage change in real gdp in 2003 = [($400 - $400)/$400] ? 100 = 0%.percentage change in the gdp deflator in 2002 = [(100 -100)/100] ? 100 = 0%.percentage change in the gdp deflator in 2003 = [(200 -100)/100] ? 100 =100%.prices did not change from 2001 to 2002. thus, thepercentage change in thegdp deflator is zero. likewise, output levels did not change from 2002 to 2003.this means that the percentage change in real gdp is zero.c. economic well-being rose more in 2002 than in 2003, since real gdp rose in2002 but not in 2003. in 2002, real gdp rose and prices didn’t. in 2003, realgdp didn’t rise and prices did.6.a.b.c.d.e.f.7. the growth rate of nominal gdp is higher than the growth rate of real gdp because of inflation. the growth rate of real gdp is ($8,367 - $8,203)/$8,203 ? 100% = 2.0%. real gdp in 2000 (in 1996 dollars) is $9,873/(118/100) = $8,367. real gdp in 1999 (in 1996 dollars) is $9,269/(113/100) = $8,203. the growth rate ofthe deflator is (118 - 113)/113 ? 100% = 4.4%. the growth rate of nominal gdp is ($9,873 - $9,269)/$9,269 ? 100% = 6.5%. economists ignore the rise in peoples incomes that is caused by higher prices becausealthough incomes are higher, the prices of the goods and services that people buy are also higher. therefore, they will not necessarily be able to purchase more goods and services. for this reason, economists prefer to look at real gdp instead of nominal gdp.many answers are possible.a. gdp equals the dollar amount barry collects, which is $400.8. 9.c.d.e.10. national income = nnp - sales taxes = $350 - $30 = $320. personal income = national income - retained earnings = $320 - $100 = $220. disposable personal income = personal income - personal income tax = $220 - $70 = $150. in countries like india, people produce and consume a fair amount of food at home that isnot included in gdp. so gdp per person in india and the united states will differ by more than their comparative economicwell-being.if the government cares about the total income of americans,it will emphasize gnp, since that measure includes the income of americans that is earned abroad and excludes the income of foreigners. if the government cares about the total amount ofeconomic activity occurring in the united states, it will emphasize gdp, which measures the level of production in the country, whether produced by domestic citizens or foreigners.a. the increased labor-force participation of women has increased gdp in theunited states, since it means more people are working and production hasincreased.if our measure of well-being included time spent working in the home and takingleisure, it wouldnt rise as much as gdp, since the rise in womens labor-forceparticipation has reduced time spent working in the home and taking leisure.other aspects of well-being that are associated with the rise in womens increasedlabor-force participation include increased self-esteem and prestige for women inthe workforce, especially at managerial levels, but decreased quality time spentwith children, whose parents have less time to spend with them. such aspectswould be quite difficult to measure. 11. 12. b. c.24章quick quizzes1. the consumer price index tries to measure the overall cost of the goods and servicesbought by a typical consumer. it is constructed by surveying consumers to fix a basket of goods and services that the typical consumer buys, finding the prices of the goods and。

A n s w e r s t o T e x t b o o k Q u e s t i o n s a n d P r o b l e m s CHAPTER 7?Unemployment and the Labor MarketQuestions for Review1. The rates of job separation and job finding determine the natural rate of unemployment. The rate of jobseparation is the fraction of people who lose their job each month. The higher the rate of job separation, the higher the natural rate of unemployment. The rate of job finding is the fraction of unemployed people who find a job each month. The higher the rate of job finding, the lower the natural rate ofunemployment.2. Frictional unemployment is the unemployment caused by the time it takes to match workers and jobs.Finding an appropriate job takes time because the flow of information about job candidates and job vacancies is not instantaneous. Because different jobs require different skills and pay different wages, unemployed workers may not accept the first job offer they receive.In contrast, structural unemployment is the unemployment resulting from wage rigidity and job rationing. These workers are unemployed not because they are actively searching for a job that best suits their skills (as in the case of frictional unemployment), but because at the prevailing real wage the quantity of labor supplied exceeds the quantity of labor demanded. If the wage does not adjust to clear the labor market, then these workers must wait for jobs to become available. Structural unemployment thus arises because firms fail to reduce wages despite an excess supply of labor.3. The real wage may remain above the level that equilibrates labor supply and labor demand because ofminimum wage laws, the monopoly power of unions, and efficiency wages.Minimum-wage laws cause wage rigidity when they prevent wages from falling to equilibrium levels. Although most workers are paid a wage above the minimum level, for some workers, especially the unskilled and inexperienced, the minimum wage raises their wage above the equilibrium level. It therefore reduces the quantity of their labor that firms demand, and creates an excess supply ofworkers, which increases unemployment.The monopoly power of unions causes wage rigidity because the wages of unionized workers are determined not by the equilibrium of supply and demand but by collective bargaining between union leaders and firm management. The wage agreement often raises the wage above the equilibrium level and allows the firm to decide how many workers to employ. These high wages cause firms to hire fewer workers than at the market-clearing wage, so structural unemployment increases.Efficiency-wage theories suggest that high wages make workers more productive. The influence of wages on worker efficiency may explain why firms do not cut wages despite an excess supply of labor. Even though a wage reduction decreases th e firm’s wage bill, it may also lower workerproductivity and therefore the firm’s profits.4. Depending on how one looks at the data, most unemployment can appear to be either short term orlong term. Most spells of unemployment are short; that is, most of those who became unemployed find jobs quickly. On the other hand, most weeks of unemployment are attributable to the small number of long-term unemployed. By definition, the long-term unemployed do not find jobs quickly, so they appear on unemployment rolls for many weeks or months.5. Europeans work fewer hours than Americans. One explanation is that the higher income tax rates inEurope reduce the incentive to work. A second explanation is a larger underground economy in Europe as a result of more people attempting to evade the high tax rates. A third explanation is the greater importance of unions in Europe and their ability to bargain for reduced work hours. A final explanation is based on preferences, whereby Europeans value leisure more than Americans do, and therefore elect to work fewer hours.Problems and Applications1. a. In the example that follows, we assume that during the school year you look for a part-time job,and that, on average, it takes 2 weeks to find one. We also assume that the typical job lasts 1semester, or 12 weeks.b. If it takes 2 weeks to find a job, then the rate of job finding in weeks isf = (1 job/2 weeks) = 0.5 jobs/week.If the job lasts for 12 weeks, then the rate of job separation in weeks iss = (1 job/12 weeks) = 0.083 jobs/week.c. From the text, we know that the formula for the natural rate of unemployment is(U/L) = [s/(s + f )],where U is the number of people unemployed, and L is the number of people in the labor force.Plugging in the values for f and s that were calculated in part (b), we find(U/L) = [0.083/(0.083 + 0.5)] = 0.14.Thus, if on average it takes 2 weeks to find a job that lasts 12 weeks, the natural rate ofunemployment for this population of college students seeking part-time employment is 14 percent.2. Call the number of residents of the dorm who are involved I, the number who are uninvolved U, and thetotal number of students T = I + U. In steady state the total number of involved students is constant.For this to happen we need the number of newly uninvolved students, (0.10)I, to be equal to thenumber of students who just became involved, (0.05)U. Following a few substitutions:(0.05)U = (0.10)I= (0.10)(T – U),soWe find that two-thirds of the students are uninvolved.3. To show that the unemployment rate evolves over time to the steady-state rate, let’s begin by defininghow the number of people unemployed changes over time. The change in the number of unemployed equals the number of people losing jobs (sE) minus the number finding jobs (fU). In equation form, we can express this as:U t + 1–U t= ΔU t + 1 = sE t–fU t.Recall from the text that L = E t + U t, or E t = L –U t, where L is the total labor force (we will assume that L is constant). Substituting for E t in the above equation, we findΔU t + 1 = s(L –U t) –fU t.Dividing by L, we get an expression for the change in the unemployment rate from t to t + 1:ΔU t + 1/L = (U t + 1/L) – (U t/L) = Δ[U/L]t + 1 = s(1 –U t/L) –fU t/L.Rearranging terms on the right side of the equation above, we end up with line 1 below. Now take line1 below, multiply the right side by (s + f)/(s + f) and rearrange terms to end up with line2 below:Δ[U/L]t + 1= s – (s + f)U t/L= (s + f)[s/(s + f) – U t/L].The first point to note about this equation is that in steady state, when the unemployment rate equals its natural rate, the left-hand side of this expression equals zero. This tells us that, as we found in the text, the natural rate of unemployment (U/L)n equals s/(s + f). We can now rewrite the above expression, substituting (U/L)n for s/(s + f), to get an equation that is easier to interpret:Δ[U/L]t + 1 = (s + f)[(U/L)n–U t/L].This expression shows the following:? If U t/L > (U/L)n (that is, the unemployment rate is above its natural rate), then Δ[U/L]t + 1 is negative: the unemployment rate falls.? If U t/L < (U/L)n (that is, the unemployment rate is below its natural rate), then Δ[U/L]t + 1 is positive: the unemployment rate rises.This process continues until the unemployment rate U/L reaches the steady-state rate (U/L)n.4. Consider the formula for the natural rate of unemployment,If the new law lowers the chance of separation s, but has no effect on the rate of job finding f, then the natural rate of unemployment falls.For several reasons, however, the new law might tend to reduce f. First, raising the cost of firing might make firms more careful about hiring workers, since firms have a harder time firing workers who turn out to be a poor match. Second, if job searchers think that the new legislation will lead them to spend a longer period of time on a particular job, then they might weigh more carefully whether or not to take that job. If the reduction in f is large enough, then the new policy may even increase the natural rate of unemployment.5. a. The demand for labor is determined by the amount of labor that a profit-maximizing firm wants tohire at a given real wage. The profit-maximizing condition is that the firm hire labor until themarginal product of labor equals the real wage,The marginal product of labor is found by differentiating the production function with respect tolabor (see Chapter 3 for more discussion),In order to solve for labor demand, we set the MPL equal to the real wage and solve for L:Notice that this expression has the intuitively desirable feature that increases in the real wagereduce the demand for labor.b. We assume that the 27,000 units of capital and the 1,000 units of labor are supplied inelastically (i.e., they will work at any price). In this case we know that all 1,000 units of labor and 27,000 units of capital will be used in equilibrium, so we can substitute these values into the above labor demand function and solve for W P .In equilibrium, employment will be 1,000, and multiplying this by 10 we find that the workers earn 10,000 units of output. The total output is given by the production function: Y =5K 13L 23Y =5(27,00013)(1,00023)Y =15,000.Notice that workers get two-thirds of output, which is consistent with what we know about theCobb –Douglas production function from Chapter 3.c. The real wage is now equal to 11 (10% above the equilibrium level of 10).Firms will use their labor demand function to decide how many workers to hire at the given realwage of 11 and capital stock of 27,000:So 751 workers will be hired for a total compensation of 8,261 units of output. To find the newlevel of output, plug the new value for labor and the value for capital into the production function and you will find Y = 12,393.d. The policy redistributes output from the 249 workers who become involuntarily unemployed tothe 751 workers who get paid more than before. The lucky workers benefit less than the losers lose as the total compensation to the working class falls from 10,000 to 8,261 units of output.e. This problem does focus on the analysis of two effects of the minimum-wage laws: they raise thewage for some workers while downward-sloping labor demand reduces the total number of jobs. Note, however, that if labor demand is less elastic than in this example, then the loss ofemployment may be smaller, and the change in worker income might be positive.6. a. The labor demand curve is given by the marginal product of labor schedule faced by firms. If acountry experiences a reduction in productivity, then the labor demand curve shifts to the left as in Figure 7-1. If labor becomes less productive, then at any given real wage, firms demand less labor. b. If the labor market is always in equilibrium, then, assuming a fixed labor supply, an adverseproductivity shock causes a decrease in the real wage but has no effect on employment orunemployment, as in Figure 7-2.c. If unions constrain real wages to remain unaltered, then as illustrated in Figure 7-3, employment falls to L 1 and unemployment equals L – L 1.This example shows that the effect of a productivity shock on an economy depends on the role ofunions and the response of collective bargaining to such a change.7. a. If workers are free to move between sectors, then the wage in each sector will be equal. If the wages were not equal then workers would have an incentive to move to the sector with the higher wage and this would cause the higher wage to fall, and the lower wage to rise until they were equal.b. Since there are 100 workers in total, L S = 100 – L M . We can substitute this expression into thelabor demand for services equation, and call the wage w since it is the same in both sectors:L S = 100 – L M = 100 – 4wL M = 4w.Now set this equal to the labor demand for manufacturing equation and solve for w:4w = 200 – 6ww = $20.Substitute the wage into the two labor demand equations to find L M is 80 and L S is 20.c. If the wage in manufacturing is equal to $25 then L M is equal to 50.d. There are now 50 workers employed in the service sector and the wage w S is equal to $12.50.e. The wage in manufacturing will remain at $25 and employment will remain at 50. If thereservation wage for the service sector is $15 then employment in the service sector will be 40. Therefore, 10 people are unemployed and the unemployment rate is 10 percent.8. Real wages have risen over time in both the United States and Europe, increasing the reward forworking (the substitution effect) but also making people richer, so they want to “buy” more leisure (the income effect). If the income effect dominates, then people want to work less as real wages go up. This could explain the European experience, in which hours worked per employed person have fallen over time. If the income and substitution effects approximately cancel, then this could explain the U.S.experience, in which hours worked per person have stayed about constant. Economists do not have good theories for why tastes might differ, so they disagree on whether it is reasonable to think that Europeans have a larger income effect than do Americans.9. The vacant office space problem is similar to the unemployment problem; we can apply the sameconcepts we used in analyzing unemployed labor to analyze why vacant office space exists. There is a rate of office separation: firms that occupy offices leave, either to move to different offices or because they go out of business. There is a rate of office finding: firms that need office space (either to start up or expand) find empty offices. It takes time to match firms with available space. Different types of firms require spaces with different attributes depending on what their specific needs are. Also, because demand for different goods fluctuates, there are “sectoral shifts”—changes in the composition ofdemand among industries and regions that affect the profitability and office needs of different firms.。

曼昆宏观经济经济学第九版英文原版答案3(总13页)--本页仅作为文档封面,使用时请直接删除即可----内页可以根据需求调整合适字体及大小--Answers to Textbook Questions and ProblemsCHAPTER3?National Income: Where It Comes From and Where It Goes Questions for Review1. The factors of production and the production technology determine theamount of output an economy can produce. The factors of production are the inputs used to produce goods and services: the most important factors are capital and labor. The production technology determines how much output can be produced from any given amounts of theseinputs. An increase in one of the factors of production or animprovement in technology leads to an increase in the economy’soutput.2. When a firm decides how much of a factor of production to hire ordemand, it considers how this decision affects profits. For example, hiring an extra unit of labor increases output and thereforeincreases revenue; the firm compares this additional revenue to the additional cost from the higher wage bill. The additional revenue the firm receives depends on the marginal product of labor (MPL) and the price of the good produced (P). An additional unit of labor produces MPL units of additional output, which sells for P dollars per unit.Therefore, the additional revenue to the firm is P ? MPL. The cost of hiring the additional unit of labor is the wage W. Thus, this hiring decision has the following effect on profits:ΔProfit= ΔRevenue –ΔCost= (P ? MPL) –W.If the additional revenue, P ? MPL, exceeds the cost (W) of hiring the additional unit of labor, then profit increases. The firm will hire labor until it is no longer profitable to do so—that is, until the MPL falls to the point where the change in profit is zero. In the equation abov e, the firm hires labor until ΔP rofit = 0, which is when (P ? MPL) = W.This condition can be rewritten as:MPL = W/P.Therefore, a competitive profit-maximizing firm hires labor until the marginal product of labor equals the real wage. The same logicapplies to the firm’s decision regarding how much capital to hire:the firm will hire capital until the marginal product of capitalequals the real rental price.3. A production function has constant returns to scale if an equalpercentage increase in all factors of production causes an increase in output of the same percentage. For example, if a firm increases its use of capital and labor by 50 percent, and output increases by50 percent, then the production function has constant returns toscale.If the production function has constant returns to scale, then total income (or equivalently, total output) in an economy ofcompetitive profit-maximizing firms is divided between the return to labor, MPL ? L, and the return to capital, MPK ? K. That is, under constant returns to scale, economic profit is zero.4. A Cobb–Douglas production function has the form F(K,L) = AKαL1–α.The text showed that the parameter αgives capital’s share ofincome. So if capital earns one-fourth of total income, then ? = .Hence, F(K,L) = Consumption depends positively on disposable income—. the amount of income after all taxes have been paid. Higher disposable income means higher consumption.The quantity of investment goods demanded depends negatively on the real interest rate. For an investment to be profitable, itsreturn must be greater than its cost. Because the real interest rate measures the cost of funds, a higher real interest rate makes it more costly to invest, so the demand for investment goods falls.6. Government purchases are a measure of the value of goods and servicespurchased directly by the government. For example, the government buys missiles and tanks, builds roads, and provides services such as air traffic control. All of these activities are part of GDP.Transfer payments are government payments to individuals that are not in exchange for goods or services. They are the opposite of taxes: taxes reduce household disposable income, whereas transfer payments increase it. Examples of transfer payments include Social Security payments to the elderly, unemployment insurance, and veterans’benefits.7. Consumption, investment, and government purchases determine demandfor the economy’s output, whereas the factors of production and the production function determine the supply of output. The real interest rate adjusts to ensure that the deman d for the economy’s goodsequals the supply. At the equilibrium interest rate, the demand for goods and services equals the supply.8. When the government increases taxes, disposable income falls, andtherefore consumption falls as well. The decrease in consumptionequals the amount that taxes increase multiplied by the marginalpropensity to consume (MPC). The higher the MPC is, the greater is the negative effect of the tax increase on consumption. Becauseoutput is fixed by the factors of production and the productiontechnology, and government purchases have not changed, the decrease in consumption must be offset by an increase in investment. Forinvestment to rise, the real interest rate must fall. Therefore, a tax increase leads to a decrease in consumption, an increase ininvestment, and a fall in the real interest rate.Problems and Applications1. a. According to the neoclassical theory of distribution, the realwage equals the marginal product of labor. Because of diminishing returns to labor, an increase in the labor force causes themarginal product of labor to fall. Hence, the real wage falls.Given a Cobb–Douglas production function, the increase in the labor force will increase the marginal product of capital and will increase the real rental price of capital. With more workers, the capital will be used more intensively and will be more productive.b. The real rental price equals the marginal product of capital. Ifan earthquake destroys some of the capital stock (yet miraculously does not kill anyone and lower the labor force), the marginalproduct of capital rises and, hence, the real rental price rises.Given a Cobb–Douglas production function, the decrease in the capital stock will decrease the marginal product of labor and will decrease the real wage. With less capital, each worker becomesless productive.c. If a technological advance improves the production function, thisis likely to increase the marginal products of both capital andlabor. Hence, the real wage and the real rental price bothincrease.d. High inflation that doubles the nominal wage and the price levelwill have no impact on the real wage. Similarly, high inflationthat doubles the nominal rental price of capital and the pricelevel will have no impact on the real rental price of capital.2. a. To find the amount of output produced, substitute the given valuesfor labor and land into the production function:Y = = 100.b. According to the text, the formulas for the marginal product oflabor and the marginal product of capital (land) are:MPL = (1 –α)AKαL–α.MPK = αAKα–1L1–α.In this problem, α is and A is 1. Substitute in the given values for labor and land to find the marginal product of labor is andmarginal product of capital (land) is . We know that the real wage equals the marginal product of labor and the real rental price of land equals the marginal product of capital (land).c. Labor’s share of the output is given by the marginal product oflabor times the quantity of labor, or 50.d. The new level of output is .e. The new wage is . The new rental price of land is .f. Labor now receives .3. A production function has decreasing returns to scale if an equalpercentage increase in all factors of production leads to a smaller percentage increase in output. For example, if we double the amounts of capital and labor output increases by less than double, then the production function has decreasing returns to scale. This may happen if there is a fixed factor such as land in the production function, and this fixed factor becomes scarce as the economy grows larger.A production function has increasing returns to scale if an equalpercentage increase in all factors of production leads to a larger percentage increase in output. For example, if doubling the amount of capital and labor increases the output by more than double, then the production function has increasing returns to scale. This may happen if specialization of labor becomes greater as the population grows.For example, if only one worker builds a car, then it takes him a long time because he has to learn many different skills, and he must constantly change tasks and tools. But if many workers build a car, then each one can specialize in a particular task and become more productive.4. a. A Cobb–Douglas production function has the form Y = AKαL1–α. Thetext showed that the marginal products for the Cobb–Douglasproduction function are:MPL = (1 –α)Y/L.MPK = αY/K.Competitive profit-maximizing firms hire labor until its marginal product equals the real wage, and hire capital until its marginal product equals the real rental rate. Using these factsand the above marginal products for the Cobb–Douglas productionfunction, we find:W/P = MPL = (1 –α)Y/L.R/P = MPK = αY/K.Rewriting this:(W/P)L = MPL ? L = (1 –α)Y.(R/P)K = MPK ? K = αY.Note that the terms (W/P)L and (R/P)K are the wage bill and total return to capital, respectively. Given that the value of α = ,then the above formulas indicate that labor receives 70 percent of total output (or income) and capital receives 30 percent of total output (or income).b. To determine what happens to total output when the labor forceincreases by 10 percent, consider the formula for the Cobb–Douglas production function:Y = AKαL1–α.Let Y1 equal the initial value of output and Y2 equal final output.We know that α = . We also know that labor L increases by 10percent:Y 1 = Y 2 = .Note that we multiplied L by to reflect the 10-percent increase in the labor force.To calculate the percentage change in output, divide Y 2 by Y 1:Y 2Y 1=AK 0.31.1L ()0.7AK 0.3L 0.7=1.1()0.7=1.069.That is, output increases by percent. To determine how the increase in the labor force affects therental price of capital, consider the formula for the real rental price of capital R/P :R/P = MPK = αAK α–1L 1–α.We know that α = . We also know that labor (L ) increases by 10percent. Let (R/P )1 equal the initial value of the rental price ofcapital, and let (R/P )2 equal the final rental price of capitalafter the labor force increases by 10 percent. To find (R/P )2,multiply L by to reflect the 10-percent increase in the laborforce:(R/P )1 = – (R/P )2 = –.The rental price increases by the ratioR /P ()2R /P ()1=0.3AK -0.71.1L ()0.70.3AK -0.7L 0.7=1.1()0.7=1.069So the rental price increases by percent. To determine how the increase in the labor forceaffects the real wage, consider the formula for the real wage W/P :W/P = MPL = (1 – α)AK αL –α.We know that α = . We also know that labor (L ) increases by 10percent. Let (W/P )1 equal the initial value of the real wage, andlet (W/P )2 equal the final value of the real wage. To find (W/P )2, multiply L by to reflect the 10-percent increase in the laborforce:(W/P )1 = (1 – –. (W/P )2 = (1 – –.To calculate the percentage change in the real wage, divide (W/P )2 by (W/P )1:W /P ()2W /P ()1=1-0.3()AK 0.31.1L ()-0.31-0.3()AK 0.3L -0.3=1.1()-0.3=0.972That is, the real wage falls by percent.c. We can use the same logic as in part (b) to setY 1 = Y 2 = A Therefore, we have:Y 2Y 1=A 1.1K ()0.3L 0.7AK 0.3L 0.7=1.1()0.3=1.029This equation shows that output increases by about 3 percent. Notice that α < means that proportional increases to capital will increase output by less than the same proportional increase to labor.Again using the same logic as in part (b) for the change in the real rental price of capital:R /P ()2R /P ()1=0.3A 1.1K ()-0.7L 0.70.3AK -0.7L 0.7=1.1()-0.7=0.935The real rental price of capital falls by percent because there are diminishing returns to capital; that is, when capital increases, its marginal product falls.Finally, the change in the real wage is:W /P ()2W /P ()1=0.7A 1.1K ()0.3L -0.30.7AK 0.3L -0.3=1.1()0.3=1.029Hence, real wages increase by percent because the added capitalincreases the marginal productivity of the existing workers.(Notice that the wage and output have both increased by the same amount, leaving the labor share unchanged —a feature of Cobb –Douglas technologies.)d. Using the same formula, we find that the change in output is:Y 2Y 1= 1.1A ()K 0.3L 0.7AK 0.3L 0.7=1.1This equation shows that output increases by 10 percent. Similarly,the rental price of capital and the real wage also increase by 10 percent:R /P ()2R /P ()1=0.31.1A ()K -0.7L 0.70.3AK -0.7L 0.7=1.1W /P ()2W /P ()1=0.71.1A ()K 0.3L -0.30.7AK 0.3L -0.3=1.15. Labor income is defined asW P ´L =WL PLabor’s share of income is defined asWL P æèççöø÷÷/Y =WL PYFor example, if this ratio is about constant at a value of , then the value of W/P = *Y/L. This means that the real wage is roughlyproportional to labor productivity. Hence, any trend in laborproductivity must be matched by an equal trend in real wages.O therwise, labor’s share would deviate from . T hus, the first fact(a constant labor share) implies the second fact (the trend in realwages closely tracks the trend in labor productivity).6. a. Nominal wages are measured as dollars per hour worked. Prices aremeasured as dollars per unit produced (either a haircut or a unit of farm output). Marginal productivity is measured as units ofoutput produced per hour worked.b. According to the neoclassical theory, technical progress thatincreases the marginal product of farmers causes their real wageto rise. The real wage for farmers is measured as units of farmoutput per hour worked. The real wage is W/P F, and this is equalto ($/hour worked)/($/unit of farm output).c. If the marginal productivity of barbers is unchanged, then theirreal wage is unchanged. The real wage for barbers is measured ashaircuts per hour worked. The real wage is W/P B, and this is equal to ($/hour worked)/($/haircut).d.If workers can move freely between being farmers and being barbers,then they must be paid the same wage W in each sector.e. If the nominal wage W is the same in both sectors, but the realwage in terms of farm goods is greater than the real wage in terms of haircuts, then the price of haircuts must have risen relativeto the price of farm goods. We know that W/P = MPL so that W = P ?MPL. This means that PF MPLF= P H MPL B, given that the nominal wagesare the same. Since the marginal product of labor for barbers has not changed and the marginal product of labor for farmers hasrisen, the price of a haircut must have risen relative to theprice of the farm output. If we express this in growth rate terms, then the growth of the farm price + the growth of the marginalproduct of the farm labor = the growth of the haircut price.f. The farmers and the barbers are equally well off after the technological progress in farming, giventhe assumption that labor is freely mobile between the two sectorsand both types of people consume the same basket of goods. Given that the nominal wage ends up equal for each type of worker andthat they pay the same prices for final goods, they are equallywell off in terms of what they can buy with their nominal income.The real wage is a measure of how many units of output areproduced per worker. Technological progress in farming increased the units of farm output produced per hour worked. Movement oflabor between sectors then equalized the nominal wage.7. a. The marginal product of labor (MPL)is found by differentiatingthe production function with respect to labor:MPL=dY dL=13K1/3H1/3L-2/3An increase in human capital will increase the marginal product of labor because more human capital makes all the existing labor more productive.b. The marginal product of human capital (MPH)is found bydifferentiating the production function with respect to humancapital:MPH=dY dH=13K1/3L1/3H-2/3An increase in human capital will decrease the marginal product of human capital because there are diminishing returns.c. The labor share of output is the proportion of output that goes tolabor. The total amount of output that goes to labor is the real wage (which, under perfect competition, equals the marginalproduct of labor) times the quantity of labor. This quantity is divided by the total amount of output to compute the labor share:Labor Share=(13K1/3H1/3L-2/3)LK1/3H1/3L1/3=1 3We can use the same logic to find the human capital share:Human Capital Share=(13K1/3L1/3H-2/3)HK1/3H1/3L1/3=1 3so labor gets one-third of the output, and human capital gets one-third of the output. Since workers own their human capital (we hope!), it will appear that labor gets two-thirds of output.d. The ratio of the skilled wage to the unskilled wage is:Wskilled Wunskilled =MPL+MPHMPL=13K1/3L-2/3H1/3+13K1/3L1/3H-2/313K1/3L-2/3H1/3=1+LHNotice that the ratio is always greater than 1 because skilledworkers get paid more than unskilled workers. Also, when Hincreases this ratio falls because the diminishing returns tohuman capital lower its return, while at the same time increasing the marginal product of unskilled workers.e. If more colleges provide scholarships, it will increase H, and itdoes lead to a more egalitarian society. The policy lowers thereturns to education, decreasing the gap between the wages of more and less educated workers. More importantly, the policy evenraises the absolute wage of unskilled workers because theirmarginal product rises when the number of skilled workers rises.8. The effect of a government tax increase of $100 billion on (a) publicsaving, (b) private saving, and (c) national saving can be analyzed by using the following relationships:National Saving = [Private Saving] + [Public Saving]= [Y –T –C(Y –T)] + [T –G]= Y –C(Y –T) –G.a. Public Saving—The tax increase causes a 1-for-1 increase inpublic saving. T increases by $100 billion and, therefore, publicsaving increases by $100 billion.b.Private Saving—The increase in taxes decreases disposable income,Y –T, by $100 billion. Since the marginal propensity to consume (MPC) is , consumption falls by ? $100 billion, or $60 billion.Hence,ΔPrivate Saving = –$100b – (–$100b) = –$40b.Private saving falls $40 billion.c. National Saving—Because national saving is the sum of privateand public saving, we can conclude that the $100 billion taxincrease leads to a $60 billion increase in national saving.Another way to see this is by using the third equation for national saving expressed above, that national saving equals Y –C(Y –T) –G. The $100 billion tax increase reduces disposable income and causes consumption to fall by $60 billion. Sinceneither G nor Y changes, national saving thus rises by $60 billion.d. Investment—To determine the effect of the tax increase oninvestment, recall the national accounts identity:Y = C(Y –T) + I(r) + G.Rearranging, we findY –C(Y –T) –G = I(r).The left side of this equation is national saving, so the equation just says that national saving equals investment. Since national saving increases by $60 billion, investment must also increase by $60 billion.How does this increase in investment take place We know that investment depends on the real interest rate. For investment to rise, the real interest rate must fall. Figure 3-1 illustrates saving and investment as a function of the real interest rate.The tax increase causes national saving to rise, so the supply curve for loanable funds shifts to the right. The equilibrium real interest rate falls, and investment rises.9. If consumers increase the amount that they consume today, thenprivate saving and, therefore, national saving will fall. We know this from the definition of national saving:National Saving = [Private Saving] + [Public Saving]= [Y –T –C(Y –T)] + [T –G].An increase in consumption decreases private saving, so national saving falls.Figure 3-2 illustrates saving and investment as a function of the real interest rate. If national saving decreases, the supply curve for loanable funds shifts to the left, thereby raising the realinterest rate and reducing investment.10. a. Private saving is the amount of disposable income, Y – T,that is not consumed:S private= Y – T – C= 8,000 – 2,000 – [1,000 + (2/3)(8,000 –2,000)]= 1,000.Public saving is the amount of taxes the government has left over after it makes its purchases:S public= T – G= 2,000 – 2,500= –500.National saving is the sum of private saving and public saving:S national= S private+ S public= 1,000 + (500)= 500.b. The equilibrium interest rate is the value of r that clears themarket for loanable funds. We already know that national saving is 500, so we just need to set it equal to investment:S national= I500 = 1,200 – 100rSolving this equation for r, we find:r = or 7%.c. When the government increases its spending, private saving remainsthe same as before (notice that G does not appear in the S privateequation above) while government saving decreases. Putting the newG into the equations above:S private= 1,000S public= T – G= 2,000 – 2,000= 0.Thus,S national= S private+ S public= 1,000 + (0)= 1,000.d. Once again the equilibrium interest rate clears the market for loanable funds:S national= I1,000 = 1,200 – 100rSolving this equation for r, we find:r = or 2%.11. To determine the effect on investment of an equal increase in bothtaxes and government spending, consider the national income accounts identity for national saving:National Saving = [Private Saving] + [Public Saving]= [Y –T –C(Y –T)] + [T –G].We know that Y is fixed by the factors of production. We also know that the change in consumption equals the marginal propensity toconsume (MPC) times the change in disposable income. This tells us thatΔNational Saving = {–ΔT – [MPC ? (–ΔT)]} + [ΔT –ΔG]= [–ΔT + (MPC ? ΔT)] + 0= (MPC –1) ΔT.The above expression tells us that the impact on national saving of an equal increase in T and G depends on the size of the marginal propensity to consume. The closer the MPC is to 1, the smaller is the fall in saving. For example, if the MPC equals 1, then the fall in consumption equals the rise in government purchases, so nationalsaving [Y –C(Y –T) –G] is unchanged. The closer the MPC is to 0 (and therefore the larger is the amount saved rather than spent for a one-dollar change in disposable income), the greater is the impact on saving. Because we assume that the MPC is less than 1, we expect that national saving falls in response to an equal increase in taxes and government spending.The reduction in saving means that the supply of loanable funds curve will shift to the left in Figure 3-3. The real interest rate rises, and investment falls.12. a. The demand curve for business investment shifts out to theright because the subsidy increases the number of profitableinvestment opportunities for any given interest rate. The demandcurve for residential investment remains unchanged.b. The total demand curve for investment in the economy shifts out tothe right since it represents the sum of business investment,which shifts out to the right, and residential investment, whichis unchanged. As a result the real interest rate rises as inFigure 3-4.c. The total quantity of investment does not change because it isconstrained by the inelastic supply of savings. The investment tax credit leads to a rise in business investment, but an offsettingfall in residential investment. That is, the higher interest rate means that residential investment falls (a movement along thecurve), whereas the rightward shift of the business investmentcurve leads business investment to rise by an equal amount. Figure3-5 shows this change. Note thatI 1B +I 1R +I 2B +I 2R =S .13. In this chapter, we concluded that an increase in governmentexpenditures reduces national saving and raises the interest rate. The increase in government expenditure therefore crowds outinvestment by the full amount of the increase. Similarly, a tax cut increases disposable income and hence consumption. This increase in consumption translates into a fall in national saving, and theincrease in consumption crowds out investment by the full amount of the increase.If consumption depends on the interest rate, then saving will also depend on it. The higher the interest rate, the greater the return to saving. Hence, it seems reasonable to think that an increase in the interest rate might increase saving and reduce consumption. Figure 3-6 shows saving as an increasing function of the interest rate.Consider what happens when government purchases increase. At anygiven level of the interest rate, national saving falls by the change in government purchases, as shown in Figure 3-7. The figure shows that if the saving function slopes upward, investment falls by less than the amount that government purchases rises by. This happens because consumption falls and saving increases in response to the higher interest rate. Hence, the more responsive consumption is tothe interest rate, the less investment is crowded out by government purchases.14. a. Figure 3-8 shows the case where the demand for loanablefunds is stable but the supply of funds (the saving schedule)fluctuates perhaps reflecting temporary shocks to income, changes in government spending, or changes in consumer confidence. In this case, when interest rates fall, investment rises; when interestrates rise, investment falls. We would expect a negativecorrelation between investment and interest rates.b. Figure 3-9 shows the case where the supply of loanable funds(saving) is stable, whereas the demand for loanable fundsfluctuates, perhaps reflecting changes in firms’ expectationsabout the marginal product of capital. We would now find apositive correlation between investment and the interest rate—when demand for funds rises, it pushes up the interest rate, so we observe that investment and the real interest rate increase at the same time.c. If both curves shift, we might generate a scatter plot as inFigure 3-10, where the economy fluctuates among points A, B, C, and D. Depending on how often the economy is at each of thesepoints, we might find little clear relationship between investment and interest rates.d. Situation (c) seems fairly reasonable—as both the supply of anddemand for loanable funds fluctuate over time in response tochanges in the economy.。

22FRONTIERS OFMICROECONOMICSWHAT’S NEW IN THE S EVENTH EDITION:A new Case Study on Left-Digit Bias has been added and a new In the News feature on "Can Brain Science Improve Economics" has been added.LEARNING OBJECTIVES:By the end of this chapter, students should understand:how to examine problems caused by asymmetric information.the market solutions to asymmetric information.why democratic voting systems may not represent the preferences of society.why people may not always behave as rational maximizers.CONTEXT AND PURPOSE:Chapter 22 is the last chapter in the microeconomics portion of the text. It is the second of two unrelated chapters that introduce students to advanced topics in microeconomics. These two chapters are intended to whet their appetites for further study in economics.The purpose of Chapter 22 is to give students a taste of three topics on the frontier of microeconomic research. The first topic addressed is asymmetric information, a situation when one person in an economic relationship has more relevant knowledge than the other person does. The second topic is political economy, the application of economic tools to the understanding of the functioning of government. The third topic addressed is behavioral economics, the introduction of psychology into the study of economic issues.KEY POINTS:In many economic transactions, information is asymmetric. When there are hidden actions, principals may be concerned that agents suffer from the problem of moral hazard. When there are hidden characteristics, buyers may be concerned about the problem of adverse selection among the sellers. Private markets sometimes deal with asymmetric information with signaling and screening.Although government policy can sometimes improve market outcomes, governments arethemselves imperfect institutions. The Condorcet paradox shows that the majority rulefails to produce transitive preferences for society, and Arrow's impossibility theorem shows that no voting system will be perfect. In many situations, democratic institutions will produce the outcome desired by the median voter, regardless of the preferences of the rest of the electorate. Moreover, the individuals who set government policy may bemotivated by self-interest rather than national interest.The study of psychology and economics reveals that human decision making is more complex than is assumed in conventional economic theory. People are not always rational, they care about the fairness of economic outcomes (even to their own detriment), and they can be inconsistent over time.CHAPTER OUTLINE:I. Asymmetric InformationA. Many times in life, one person holds more knowledge about what is going on thananother. Such a difference in access to relevant information is known as aninformation asymmetry.B. Examples1. A worker knows more than his employer about the level of his work effort. This isan example of a hidden action.2. A seller of a used car knows more than the buyer does about the car's condition.This is an example of a hidden characteristic.C. When there is asymmetric information, the party without the relevant knowledge wouldlike to have such knowledge, but the other party may have an incentive to conceal it.D. Hidden Actions: Principals, Agents, and Moral Hazard1. Important Definitionsa. Definition of moral hazard: the tendency of a person who is imperfectlymonitored to engage in dishonest or otherwise undesirable behavior.b. Definition of agent: a person who is performing an act for another person,called the principal.c. Definition of principal: a person for whom another person, called the agent, isperforming some act.2. The employment relationship is the classic example.a. Workers (agents) may be tempted to shirk their work-related responsibilitiesbecause their employers (the principals) do not monitor their behavior closely.b. Employers can respond by providing better monitoring, paying higher wages, ordelaying part of the worker's pay until later in the worker's life.3. FYI: Corporate Managementa. From an economic standpoint, the most important feature of the corporate formof organization is the separation of ownership and control.b. This creates a principal–agent problem where the shareholders are theprincipals and the managers are the agents.c. Managers’ goals may not always coincide with shareholders' goal of profitmaximization.d. As a result, many managers are provided compensation packages that provideincentives to act in the best interest of corporate profits.E. Hidden Characteristics: Adverse Selection and the Lemons Problem1. Definition of adverse selection: the tendency for the mix of unobserved attributesto become undesirable from the standpoint of an uninformed party.2. Examples include the used car market, the labor market, and the market forinsurance.3. When markets suffer from adverse selection, the invisible hand does notnecessarily work well.a. In the used car market, owners of "cherry" or "plum" cars may choose to keepthem rather than sell them at a low price.b. In the labor market, wages may be stuck at a level above the equilibrium wage,resulting in unemployment.c. In insurance markets, buyers with low risk may decline to purchase insurancebecause the price is too high.F. Signaling to Convey Private Information1. Definition of signaling: an action taken by an informed party to reveal privateinformation to an uninformed party.2. Examples of Signalinga. Firms may spend money on advertising to signal the high quality of theirproducts.b. Students may spend time in school to signal that they are high-abilityindividuals.3. For a signal to be effective, it must be costly. However, it must be less costly(or more beneficial) to the person or firm with the higher-quality product.4. Case Study: Gifts as Signalsa. Because people know their own preferences better than anyone else, we wouldexpect that they would prefer cash gifts.b. However, the ability to choose the right gift for someone may serve as a signalof an individual's love.c. Note that choosing the right gift is costly and the cost depends on how wellthe giver knows the recipient (which may be determined as a measure of thegiver's level of interest in the recipient).G. Screening to Uncover Private Information1. Definition of screening: an action taken by an uninformed party to induce aninformed party to reveal information.2. Examples of Screeninga. A buyer of a used car may ask to have the car examined by a mechanic prior topurchase.b. An insurance company may offer different policies that would lead safe or riskydrivers to reveal themselves. Safe drivers are likely to prefer policies withlow premiums and high deductibles. Risky drivers are more likely to preferpolicies with higher premiums and low deductibles.H. Asymmetric Information and Public Policy1. Market failures such as externalities, public goods, imperfect competition, andpoverty show that governments can sometimes improve market outcomes.2. Asymmetric information is another reason why market outcomes may be inefficient.3. However, three factors make it difficult for the government to improve the outcomein some cases.a. The private market can sometimes deal with information asymmetries on its ownusing a combination of signaling and screening.b. The government rarely has more information than the private parties do.c. The government is itself an imperfect institution.II. Political EconomyA. Definition of political economy: the study of government using the analytic methods ofeconomics.B. The Condorcet Voting Paradox1. Most advanced societies rely on democratic principles, allowing the majority toset government policy.2. For most policy issues, the number of possible outcomes exceeds two.3. Example: Three possible outcomes (A, B, and C) and three voter types (Type 1, Type2, and Type 3). The mayor of a town wishes to aggregate the individual preferences into preferences for society as a whole.a. In pairwise majority voting, A would beat B, B would beat C, and C would beat A.b. This violates transitivity. We generally expect that if A is preferred to B andB is preferred to C, then A would be preferred to C.c. Definition of Condorcet paradox: the failure of majority rule to producetransitive preferences for society.d. This implies that the order on which things are voted can determine the result.C. Arrow's Impossibility Theorem1. In a 1951 book, economist Kenneth Arrow examined if a perfect voting system exists.2. He assumes that society wants a voting scheme that satisfies social properties.a. Unanimity.b. Transitivity.c. Independence of irrelevant alternatives.d. No dictators.3. Arrow proved that no voting system could have all of these properties.4. Definition of Arrow impossibility theorem: a mathematical result showing that,under certain assumed conditions, there is no scheme for aggregating individual preferences into a valid set of social preferences.5. Arrow’s impossibility theorem implies that no matter what voting scheme societyadopts for aggregating the preferences of its members, in some way it will be flawed as a mechanism for social choice.D. The Median Voter Is King1. Example: A society is deciding how much money to spend on a public good. Eachvoter has a most-preferred budget and prefers outcomes closer to his preferredbudget.Figure 12. Definition of median voter theorem: a mathematical result showing that if votersare choosing a point along a line and each voter wants the point closest to his preferred point, then majority rule will pick the most preferred point of themedian voter.a. The median voter is the voter exactly in the middle of the distribution.b. On Figure 1, the median voter wants a budget of $10 billion.3. One implication of the median voter theorem is that if two political candidatesare each trying to maximize their chance of election, they will both move their positions toward the median voter.4. Another implication of the median voter theorem is that minority views are notgiven much weight.E. Politicians Are People Too1. Politicians may be self-interested.2. Some politicians may be motivated by desire for reelection and others may bemotivated by greed.III. Behavioral EconomicsA. Definition of behavioral economics: the subfield of economics that integrates theinsights of psychology..B. Behavioral economics is a relatively new field in economics where economists make useof basic psychological insights into human behavior.C. People Aren’t Always Rational1. Economists assume that human beings are always rational.a. Firm owners maximize profit.b. Consumers maximize utility.c. Given constraints that they face, these individuals make decisions byrationally weighing all costs and benefits.2. Real people are often more complex than economists assume.a. They can be forgetful, impulsive, confused, emotional, and shortsighted.b. These imperfections suggest that humans should not be viewed as rationalmaximizers but as “satisficers,” where they choose options that are simply“good enough.”3. Studies of human decision making have found several systematic mistakes thatpeople make.a. People are overconfident.b. People give too much weight to a small number of vivid observations.c. People are reluctant to change their minds.4. Case Study: Left-Digit Biasa. Studies suggest that buyers are excessively sensitive to a price's left-mostdigit.b. An irrational focus on the left-most digit is called left-digit bias.D. People Care about Fairness1. Example: the ultimatum game.a. Two volunteers are told they are going to play a game and could win a total of$100.b. The game begins with a coin toss, which is used to assign the volunteers to theroles of Player A and Player B.c. Player A’s job is to propose a division of the prize between himself and theother player.d. After Player A makes his proposal, Player B decides whether to accept or rejectit.e. If Player B accepts the proposal, both players are paid according to theproposal. If Player B rejects the proposal, both players receive nothing.2. Conventional economic theory suggests that Player A should know that if he offers$1 to Player B and keeps $99 for himself, Player B should accept it ($1 is greater than $0).3. In reality, when the offer made to Player B is small, Player B often rejects it.4. Knowing this, people in the role of Player A often offer a more substantialportion of the money to Player B.5. This implies that people may be driven by a sense of fairness.E. People Are Inconsistent over Time1. Many times in life, people make plans for themselves but then fail to followthrough.2. The desire for instant gratification can induce a decisionmaker to abandon hispast plan.3. An important implication is that people will try to find ways to commit theirfuture selves to following through on their plans.F. In the News: Can Brain Science Improve Economics1. A new branch of economics examines the biology of the brain to understand economicbehavior.2. This article from Project Syndicate discusses neuroeconomics, the study of how thephysical structures that underlie brain functioning affect economic decision-making.SOLUTIONS TO TEXT PROBLEMS:Quick Quizzes1. Buyers of life insurance will likely have higher than the average death rates.Two reasons for this are moral hazard and adverse selection.Moral hazard is the tendency of a person who is imperfectly monitored to engage indishonest or otherwise undesirable behavior. After purchasing insurance, aninsured person may engage in riskier behavior than do people who are not insured.Adverse selection is the tendency for the mix of unobserved attributes to becomeundesirable from the standpoint of an uninformed party. In this case, those withhigher risk of death are more likely to want to buy insurance. As a result, theprice of life insurance will reflect the costs of a riskier-than-average person.Buyers with low risk of death may find the price of life insurance too high andmay choose not to purchase it.A life insurance company can mitigate moral hazard by trying to monitor behaviorbetter and charging higher rates to those who engage in risky behavior (such assmoking). It can mitigate adverse selection by trying to collect betterinformation on applicants; for example, it may require that all applicants submitto a medical examination before issuing insurance.2. According to the median voter theorem, if each voter chooses a point closest tohis preferred point, the district vote will reflect the preferences of the medianvoter. Therefore, the district will end up with a student-teacher ratio of 11:1.3. Human decision making can differ from the rational human being of conventionaleconomic theory in three important ways: (1) people aren’t always rational, (2)people care about fairness, and (3) people are inconsistent over time.Questions for Review1. Moral hazard is the tendency of a person who is imperfectly monitored to engage indishonest or otherwise undesirable behavior. To reduce the severity of thisproblem, an employer may respond with (1) better monitoring, (2) paying efficiencywages, or (3) delaying part of a worker’s compensation to later in his work life.2. Adverse selection is the tendency for the mix of unobserved attributes to becomeundesirable from the standpoint of an uninformed party. Examples of markets inwhich adverse selection might be a problem include the market for used cars andthe market for insurance.3. Signaling is an action taken by an informed party to reveal private information toan uninformed party. Job applicants may use a college diploma as a signal ofability. Screening is an action taken by an uninformed party to induce an informedparty to reveal information. A life insurance company may require applicants tosubmit to a health examination so that the company will have more information onthe person’s risk of death.4. Condorcet noticed that the majority rule will fail to produce transitiveproperties for society.5. The median voter’s preferences will beat out any other proposal in a two-way racebecause the median voter will have more than half of the voters on his side.6. Two volunteers are chosen and a coin toss determines which volunteer is Player Aand which is Player B. Player A proposes a split of a sum of money and then PlayerB decides whether to accept or reject the proposal. If Player B accepts, the sumof money is divided as outlined in the proposal. If Player B rejects the proposal,each player gets nothing.Conventional economic theory predicts that Player A will offer only $1 to Player Band keep the remainder for himself. This is predicted to occur because Player Aknows that Player B will be better off with $1 than with $0. However, in reality,Player B generally rejects small proposals that he considers unfair. If Player Aconsiders this, he will likely offer Player B a more substantial amount.Quick Check Multiple Choice1. b2. a3. d4. b5. a6. cProblems and Applications1. a. The landlord is the principal and the tenant is the agent. There is asymmetricinformation because the landlord does not know how well the tenant will takecare of the property. Having a tenant pay a security deposit increases thelikelihood that the tenant will take care of the property in order to receivehis deposit back when he vacates the property.b. The stockholders of the firm (the owners) are the principals and the topexecutives are the agents. The firm’s owners do not know in advance how wellthe top executives will perform their duties. Tying some of the executives’compensation to the value of the firm provides incentive for the executives towork hard to increase the value of the firm.c. The insurance company is the principal and the customer is the agent. Insurancecompanies do not know whether the car owner is likely to leave the vehicleparked with the keys in it or park it in a high crime area. Individuals whowill go to the trouble of installing anti-theft equipment are more likely totake good care of their vehicles. Offering a discount on insurance premiumswill induce car owners to install such devices.2. Individuals who are relatively healthy may decide to forgo purchasing the policyif the premium rises. Thus, the insurance company is left with only thosepolicyholders who are relatively unhealthy. This means that the firm’s revenue smay in fact fall, but its costs could remain the same. Therefore, the firm’sprofits could fall.3. Saying "I love you" is likely not a good signal. To be an effective signal, thesignal must be costly. In fact, the signal must be less costly, or more beneficial, to the person with the higher-quality product. Simply professing one's love does not meet this requirement.4. If insurance companies were not allowed to determine if applicants are HIV-positive, more individuals who are HIV-positive would be able to purchaseinsurance, but that insurance would be very expensive. Covering these individuals would raise the cost of providing health insurance and the company would have to raise premiums for all. Thus, individuals who are not HIV-positive would be forced to pay more for health insurance and may drop coverage. Insurance companies would be left insuring only those who are ill (including those who are HIV-positive), increasing the adverse selection problem. The number of individuals without health insurance would likely rise as a result.5. Ken is violating the property of independence of irrelevant alternatives. Adding achoice of strawberry after he chooses vanilla over chocolate should not induce him to change his mind and prefer chocolate.6. a. If the three friends use a Borda count, the Chinese restaurant gets the mostvotes (10); the Italian restaurant gets 9 votes; the Mexican restaurant gets 7votes; and the French restaurant gets 4 votes.b. In this scenario, the Italian restaurant gets 5 votes and the Chineserestaurant gets 4 votes. Thus, they will choose to eat at the Italianrestaurant.c. This voting violates the assumption of independence of irrelevant alternatives.The presence of the Mexican and French restaurants should not alter thegroup’s preferences between the Italian and Chinese restaurants.7. a. There would be a tie between the three television shows, with 6 votes each.b. In a vote between NCIS and Glee, NCIS would win. In a vote between NCIS andHomeland, Homeland would wi n. Thus, Monica’s first choice (Homeland) would win.c. No. He will want to vote between Glee and Homeland first, with the winner thencompeting in a second vote with NCIS. That way, his preferred choice (NCIS)would win.d. If Chandler says he prefers Glee over NCIS, Glee will then compete in a voteagainst Homeland (which it will win). This way, Chandler will not have to watch his least preferred show (Homeland).8. a. The efficient number of DVDs is three. Total surplus would be the sum of theroommat es’ willingness to pay (38 + 26 + 18 = 82) minus the cost of the DVDs(15 + 15 + 15 = 45) which is 37.b. Quentin would want 4 DVDs; Spike would prefer 3; Ridley wants 2; Martin wants 1;and Steven does not want to buy a DVD.c. The preference of the median roommate (Ridley) is 2 DVDs.d. Quentin and Spike would vote for 3 DVDs, but the other three roommates wouldvote for 2 DVDs.e. No. Any other option besides 2 DVDs would get fewer votes.f. No. The provision of the public good will likely be determined by thepreferences of the median voter. This may or may not be the efficient outcome.9. More than likely, the two stands will locate at the center of the beach. Thus,they will always be closest for at least half of the beach goers. This is related to the median voter theorem.10. a. Assuming the needy person is a rational consumer, he would use the cash tomaximize his utility and purchase what he needs most.b. The soup kitchen may be better than the cash handout if the government does nothave complete information about how the needy person will spend the cash. That is, rather than the possibility of the needy person spending the cash on drugs or alcohol, the government can be certain the needy person is getting food from the soup kitchen.c. The soup kitchen may be better than the cash handout based on behavioraleconomics because people aren't always rational and the needy person may spend the cash on something he doesn't need as much as food.。

曼昆《宏观经济学》(第6、7版)第10章总需求Ⅰ:建立IS LM-模型课后习题详解跨考网独家整理最全经济学考研真题,经济学考研课后习题解析资料库,您可以在这里查阅历年经济学考研真题,经济学考研课后习题,经济学考研参考书等内容,更有跨考考研历年辅导的经济学学哥学姐的经济学考研经验,从前辈中获得的经验对初学者来说是宝贵的财富,这或许能帮你少走弯路,躲开一些陷阱。
以下内容为跨考网独家整理,如您还需更多考研资料,可选择经济学一对一在线咨询进行咨询。
一、概念题1.IS LM- model)-模型(IS LM答:IS LM-模型是描述产品市场和货币市场之间相互联系的理论结构。
在产品市场上,国民收入取决于消费、投资、政府购买和净出口加起来的总支出或者说总需求水平,而总需求尤其是投资需求要受到利率影响,利率则由货币市场供求情况决定,就是说,货币市场要影响产品市场;另一方面,产品市场上所决定的国民收入又会影响货币需求,从而影响利率,这又是产品市场对货币市场的影响。
可见,产品市场和货币市场是相互联系、相互作用的,而收入和利率也只有在这种相互联系、相互作用中才能决定。
IS曲线是描述产品市场达到均衡时,国民收入与利率之间存在着反向变动关系的曲线。
LM曲线是描述货币市场达到均衡时,国民收入和利率之间存在着同向变动关系的曲线。
把IS曲线和LM曲线放在同一个图上,就可以得出说明两个市场同时均衡时,国民收入与利率决定的IS LM-模型。
2.IS曲线(IS curve)答:IS曲线指将满足产品市场均衡条件的收入和利率的各种组合点连接起来而形成的曲线。
它反映产品市场均衡状态,表示的是在任何一个给定的利率水平上都有与之对应的国民收入水平。
由于利率上升引起计划投资减少,计划投资减少又引起收入减少,所以IS曲线一般是一条向右下方倾斜的曲线。
一般来说,在产品市场上,位于IS曲线右边的收入和利率的组合,都是投资小于储蓄的非均衡组合,即产品市场上存在着过剩的供给;位于IS曲线左边的收入和利率的组合,都是投资大于储蓄的非均衡组合,即产品市场上存在着过度的需求。
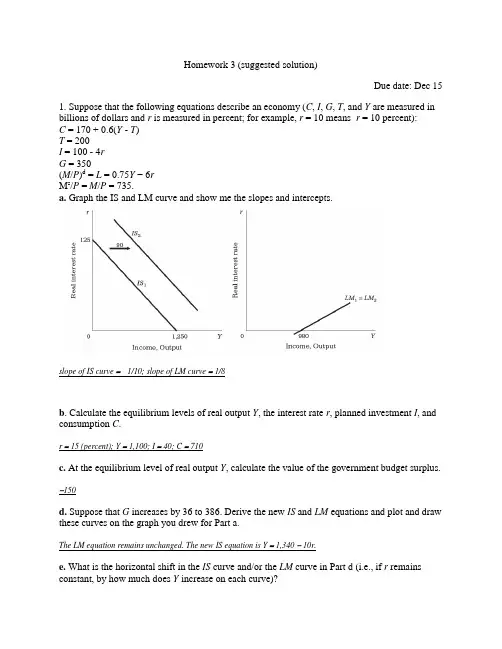
Homework 3 (suggested solution)Due date: Dec 15 1. Suppose that the following equations describe an economy (C, I, G, T, and Y are measured in billions of dollars and r is measured in percent; for example, r = 10 means r = 10 percent):C = 170 + 0.6(Y - T)T = 200I = 100 - 4rG = 350(M/P)d= L = 0.75Y − 6rM s/P = M/P = 735.a. Graph the IS and LM curve and show me the slopes and intercepts.slope of IS curve = 1/10; slope of LM curve = 1/8b. Calculate the equilibrium levels of real output Y, the interest rate r, planned investment I, and consumption C.r = 15 (percent); Y = 1,100; I = 40; C = 710c. At the equilibrium level of real output Y, calculate the value of the government budget surplus. -150d. Suppose that G increases by 36 to 386. Derive the new IS and LM equations and plot and draw these curves on the graph you drew for Part a.The LM equation remains unchanged. The new IS equation is Y = 1,340 - 10r.e. What is the horizontal shift in the IS curve and/or the LM curve in Part d (i.e., if r remains constant, by how much does Y increase on each curve)?The shift in the IS curve is equal to 90. The LM curve does not shift.f. Refer to the IS and LM equations you derived in Part d. With Y on the left-hand side of the equations, calculate the new equilibrium levels of real output Y, the interest rate r, planned investment I, and consumption C.Y = 1,140; r = 20; I = 20; C = 734g. Instead of increasing G, suppose that the Fed sought to achieve the equilibrium level of real output Y in Part h through expansionary monetary policy alone. By how much would the Fed have to increase the money supply?54h. Compare the equilibrium levels of consumption C, government spending G, and planned investment I in Parts f and g. Based on this comparison, why might some economists prefer expansionary fiscal policy while others prefer expansionary monetary policy?Government purchases are higher in Part f. Since taxes and output are the same as Parts f and g, consumption is also the same. Since the interest rate is lower in Part g, investment is higher. Advocates of expansionary fiscal policy may argue that the United States is badly in need of public spending in areas like education, defense, and infrastructure. Advocates of expansionary monetary policy, on the other hand, would tout its effect on investment, which might spur economic growth as the capital stock grows.2. a. In 2009, President Obama increased government spending and cut net taxes. Draw the appropriate graphs to indicate what would happen to the IS, LM, aggregate demand, and short-run aggregate supply curves, and indicate any short-run changes in the equilibrium levels of r, I, C, G, Y, and P if the Fed had not changed any of its policies.An increase in G and cut in net taxes T shift the IS and AD curves to the right (or IS and AD curves shift upward). The SRAS and LM curves do not shift in the short run.The equilibrium levels of Y, r, and C all rise. The equilibrium level of I falls, and G and P do not change in the short run (given the horizontal SRAS curve of Chapter 9)b. During this period, the Fed actually pursued expansionary monetary policy and kept interest rates nearly constant. Redraw your diagrams from Part a and indicate what actually happened to the IS curve, LM curve, aggregate demand curve, short-run aggregate supply curve, and the levels of r, I, C, G, Y, and P. How do they compare with the levels in Part a?The Federal Reserve increased the money supply at the same time as government spending rose and taxes fell. Consequently, both the IS and LM curves shifted to the right. This shifted the AD curve even farther to the right.The levels of Y and C rise by more in Part b than in Part a. The remaining variables, r, I, G, and P remain constant.3. The Fed is considering two alternative monetary policies:holding the money supply constant and letting the interest rate adjust, or• adjusting the money supply to hold the interest rate constant.In the IS–LM model, which policy will better stabilize output under the following conditions? a. All shocks to the economy arise from exogenous changes in the demand for goods and services.Figure 11–25(A) shows what the IS–LM model looks like for the case in which the Fed holds the money supply constant. Figure 11–25(B) shows what the model looks like if the Fed adjusts the money supply to hold the interest rate constant; this policy makes the effective LM curve horizontal.If all shocks to the economy arise from exogenous changes in the demand for goods and services, this means that all shocks are to the IS curve. Suppose a shock causes the IS curve to shift from IS1 to IS2. Figures 11–26(A) and (B) show what effect this has on output under the two policies. It is clear that output fluctuates less if the Fed follows a policy of keeping the money supply constant. Thus, if all shocks are to the IS curve, then the Fed should follow a policy of keeping the money supply constant.b. All shocks to the economy arise from exogenous changes in the demand for money.If all shocks in the economy arise from exogenous changes in the demand for money, this means that all shocks are to the LM curve. If the Fed follows a policy of adjusting the money supply to keep the interest rate constant, then the LM curve does not shift in response to these shocks—the Fed immediately adjusts the money supply to keep the money market in equilibrium. Figures 11–27(A) and (B) show the effects of the two policies. It is clear that output fluctuates less if the Fed holds the interest rate constant, as in Figure 11–27(B). If the Fed holds the interest rate constant and offsets shocks to money demand by changing the money supply, then all variability in output is eliminated. Thus, if all shocks are to the LM curve, then the Fed should adjust the money supply to hold the interest rate conconstant,thereby stabilizing output.。

221WHAT’S NEW IN THE SEVENTH EDITION:There are no major changes to this chapter.LEARNING OBJECTIVES:By the end of this chapter, students should understand:what items are included in a firm’s costs of production. the link between a firm’s production process and its total costs.the meaning of average total cost and marginal cost and how they are related. the shape of a typical firm’s cost curves.the relationship between short-run and long-run costs.CONTEXT AND PURPOSE:Chapter 13 is the first chapter in a five-chapter sequence dealing with firm behavior and the organization of industry. It is important that students become comfortable with the material in Chapter 13 because Chapters 14 through 17 are based on the concepts developed in Chapter 13. To be more specific, Chapter 13 develops the cost curves on which firm behavior is based. The remaining chapters in thissection (Chapters 14-17) utilize these cost curves to develop the behavior of firms in a variety of different market structures—competitive, monopolistic, monopolistically competitive, and oligopolistic.The purpose of Chapter 13 is to address the costs of production and develop the firm’s cost curves. These cost curves underlie the firm’s supply curve. In previous chapters, we summarized the firm’s production decisions by starting with the supply curve. While this is suitable for answering manyquestions, it is now necessary to address the costs that underlie the supply curve in order to address the part of economics known as industrial organization —the study of how firms’ decisions about prices and quantities depend on the market conditions they face.KEY POINTS:The goal of firms is to maximize profit, which equals total revenue minus total cost.THE COSTS OF PRODUCTION222 ❖ Chapter 13/The Costs of Production∙When analyzing a firm’s behavior, it is important to include all the opportunity costs of production. Some of the opportunity costs, such as the wages a firm pays its workers, are explicit. Other opportunity costs, such as the wages the firm owner gives up by working at the firm rather than taking another job, are implicit. Economic profit takes both explicit and implicit costs into account, whereas accounting profits consider only explicit costs.∙A firm’s costs reflect its production process. A typical firm’s production function gets flatter as the quantity of an input increases, displaying the property of diminishing marginal product. As a result, a firm’s total-cost curve gets steeper as the quantity produced rises.∙A firm’s total costs can be divided between fixed costs and variable costs. Fixed costs are costs that do not change when the firm alters the quantity of output produced. Variable costs are costs that change when the firm alters the quantity of output produced.∙From a firm’s total cost, two related measures of cost are derived. Average total cost is total cost divided by the quantity of output. Marginal cost is the amount by which total cost rises if output increases by one unit.∙When analyzing firm behavior, it is often useful to graph average total cost and marginal cost. For a typical firm, marginal cost rises with the quantity of output. Average total cost first falls as output increases and then rises as output increases further. The marginal-cost curve always crosses the average-total-cost curve at the minimum of average total cost.∙A firm’s costs often depend on the time horizon considered. In particular, many costs are fixed in the short run but variable in the long run. As a result, when the firm changes its level of production, average total cost may rise more in the short run than in the long run.CHAPTER OUTLINE:I.What Are Costs?A.Total Revenue, Total Cost, and Profit1.The goal of a firm is to maximize profit.Chapter 13/The Costs of Production ❖ 2232.Definition oftotal revenue: the amount a firm receives for the sale of its output.3.Definition of total cost: the market value of the inputs a firm uses in production.4.Definition of profit: total revenue minus total cost.B.Costs as Opportunity Costs1.Principle #2: The cost of something is what you give up to get it.2.The costs of producing an item must include all of the opportunity costs of inputs used inproduction.3.Total opportunity costs include both implicit and explicit costs.a.Definition of explicit costs: input costs that require an outlay of money by thefirm.b.Definition of implicit costs: input costs that do not require an outlay of moneyby the firm.c.The total cost of a business is the sum of explicit costs and implicit costs.d.This is the major way in which accountants and economists differ in analyzing theperformance of a business.e.Accountants focus on explicit costs, while economists examine both explicit and implicitcosts.C.The Cost of Capital as an Opportunity Cost1.The opportunity cost of financial capital is an important cost to include in any analysis of firmperformance.2.Example: Caroline uses $300,000 of her savings to start her firm. It was in a savings accountpaying 5% interest.3.Because Caroline could have earned $15,000 per year on this savings, we must include thisopportunity cost. (Note that an accountant would not count this $15,000 as part of the firm'scosts.)224 ❖ Chapter 13/The Costs of Production4.If Caroline had instead borrowed $200,000 from a bank and used $100,000 from her savings,the opportunity cost would not change if the interest rate stayed the same (according to the economist). But the accountant would now count the $10,000 in interest paid for the bank loan.D.Economic Profit versus Accounting Profit1.Figure 1 highlights the differences in the ways in which economists and accountants calculateprofit.2.Definition of economic profit: total revenue minus total cost, including both explicitand implicit costs .a.Economic profit is what motivates firms to supply goods and services.b.To understand how industries evolve, we need to examine economic profit.3.Definition of accounting profit: total revenue minus total explicit cost .4.If implicit costs are greater than zero, accounting profit will always exceed economic profit.II.Production and CostsA.The Production Function1.Definition of production function: the relationship between quantity of inputs usedto make a good and the quantity of output of that good.2.Example: Caroline's cookie factory. The size of the factory is assumed to be fixed; Carolinecan vary her output (cookies) only by varying the labor used.Number ofWorkersOutputMarginal Productof LaborCost of Factory Cost of WorkersTotal Cost of Inputs 00---$30$0$30150503010402904030205031203030306041402030407051501030508061555306090Chapter 13/The Costs of Production ❖ 2253.Definition of marginal product: the increase in output that arises from an additionalunit of input.a.As the amount of labor used increases, the marginal product of labor falls.b.Definition of diminishing marginal product: the property whereby the marginalproduct of an input declines as the quantity of the input increases.4.We can draw a graph of the firm's production function by plotting the level of labor (x -axis)against the level of output (y -axis).226 ❖ Chapter 13/The Costs of Productiona.The slope of the production function measures marginal product.b.Diminishing marginal product can be seen from the fact that the slope falls as theamount of labor used increases.B.From the Production Function to the Total-Cost Curve1.We can draw a graph of the firm's total cost curve by plotting the level of output (x-axis)against the total cost of producing that output (y-axis).a.The total cost curve gets steeper and steeper as output rises.b.This increase in the slope of the total cost curve is also due to diminishing marginalproduct: As Caroline increases the production of cookies, her kitchen becomesovercrowded, and she needs a lot more labor.Chapter 13/The Costs of Production ❖ 227III.The Various Measures of CostA.Example: Conrad’s Coffee ShopOutputTotal Cost Fixed Cost Variable Cost Average Fixed Cost Average Variable Cost AverageTotalCostMarginal Cost 0 $3.00 $3.00 $0------------1 3.30 3.000.30$3.00$0.30$3.30$0.302 3.80 3.000.80 1.500.40 1.900.503 4.50 3.00 1.50 1.000.50 1.500.704 5.40 3.00 2.400.750.60 1.350.905 6.50 3.00 3.500.600.70 1.30 1.1067.80 3.00 4.800.500.80 1.30 1.3079.30 3.00 6.300.430.901.33 1.50228 ❖ Chapter 13/The Costs of Production811.00 3.008.000.38 1.00 1.38 1.70912.90 3.009.900.33 1.10 1.43 1.901015.003.0012.000.301.201.502.10B.Fixed and Variable Costs1.Definition of fixed costs: costs that do not vary with the quantity of outputproduced.2.Definition ofvariable costs: costs that do vary with the quantity of outputproduced.3.Total cost is equal to fixed cost plus variable cost.C.Average and Marginal Cost1.Definition of average total cost: total cost divided by the quantity of output.2.Definition ofaverage fixed cost: fixed costs divided by the quantity of output.3.Definition of average variable cost: variable costs divided by the quantity of output.4.Definition of marginal cost: the increase in total cost that arises from an extra unitof production.Chapter 13/The Costs of Production ❖ 2295.Average total cost tells us the cost of a typical unit of output and marginal cost tells us thecost of an additional unit of output.D.Cost Curves and Their Shapes1.Rising Marginal Costa.This occurs because of diminishing marginal product.b.At a low level of output, there are few workers and a lot of idle equipment. But as outputincreases, the coffee shop gets crowded and the cost of producing another unit of outputbecomes high.2.U-Shaped Average Total Costa.Average total cost is the sum of average fixed cost and average variable cost.b.AFC declines as output expands and AVC typically increases as output expands. AFC ishigh when output levels are low. As output expands, AFC declines pulling ATC down. Asfixed costs get spread over a large number of units, the effect of AFC on ATC falls andATC begins to rise because of diminishing marginal product.c.Definition of efficient scale: the quantity of output that minimizes average totalcost.3.The Relationship between Marginal Cost and Average Total Costa.Whenever marginal cost is less than average total cost, average total cost is falling.Whenever marginal cost is greater than average total cost, average total cost is rising.b.The marginal-cost curve crosses the average-total-cost curve at minimum average totalcost (the efficient scale).230 ❖ Chapter 13/The Costs of Production4.Typical Cost Curvesa.Marginal cost eventually rises with output.b.The average-total-cost curve is U-shaped.c.Marginal cost crosses average total cost at the minimum of average total cost.IV.Costs in the Short Run and in the Long RunA.The division of total costs into fixed and variable costs will vary from firm to firm.B.Some costs are fixed in the short run, but all are variable in the long run.1.For example, in the long run a firm could choose the size of its factory.2.Once a factory is chosen, the firm must deal with the short-run costs associated with thatplant size.C.The long-run average-total-cost curve lies along the lowest points of the short-run average-total-cost curves because the firm has more flexibility in the long run to deal with changes in production.D.The long-run average-total-cost curve is typically U-shaped, but is much flatter than a typicalshort-run average-total-cost curve.E.The length of time for a firm to get to the long run will depend on the firm involved.F.Economies and Diseconomies of Scale1.Definition of economies of scale: the property whereby long-run average total costfalls as the quantity of output increases.2.Definition of diseconomies of scale: the property whereby long-run average totalcost rises as the quantity of output increases.3.Definition of constant returns to scale: the property whereby long-run average totalcost stays the same as the quantity of output changes.4.FYI: Lessons from a Pin Factorya.In The Wealth of Nations, Adam Smith described how specialization in a pin factoryallowed output to be greater than it would have been if each worker attempted toperform many different tasks.b.The use of specialization allows firms to achieve economies of scale.V.Table 3 provides a summary of all of the various cost definitions used throughout this chapter.SOLUTIONS TO TEXT PROBLEMS:Quick Quizzes1.Farmer McDonald’s opportunity cost is $300, consisting of 10 hours of lessons at $20 an hourthat he could have been earning plus $100 in seeds. His accountant would only count theexplicit cost of the seeds ($100). If McDonald earns $200 from selling the crops, thenMcDonald earns a $100 accounting profit ($200 sales minus $100 cost of seeds) but incursan economic loss of $100 ($200 sales minus $300 opportunity cost).2.Farmer Jones’s production function is shown in Figure 1 and his total-cost curve is shown inFigure 2. The production function becomes flatter as the number of bags of seeds increasesbecause of the diminishing marginal product of seeds. The total-cost curve gets steeper asthe amount of production increases. This feature is also due to the diminishing marginalproduct of seeds, since each additional bag of seeds generates a lower marginal product, andthus, the cost of producing additional bushels of wheat rises.Figure 1Figure 23.The average total cost of producing 5 cars is $250,000/5 = $50,000. Since total cost rosefrom $225,000 to $250,000 when output increased from 4 to 5, the marginal cost of the fifthcar is $25,000.The marginal-cost curve and the average-total-cost curve for a typical firm are shown inFigure 3. They cross at the efficient scale because at low levels of output, marginal cost isbelow average total cost, so average total cost is falling. But after the two curves cross,marginal cost rises above average total cost, and average total cost starts to rise. So thepoint of intersection must be the minimum of average total cost.Figure 34.The long-run average total cost of producing 9 planes is $9 million/9 = $1 million. The long-run average total cost of producing 10 planes is $9.5 million/10 = $0.95 million. Since thelong-run average total cost declines as the number of planes increases, Boeing exhibitseconomies of scale.Questions for Review1.The relationship between a firm's total revenue, profit, and total cost is profit equals totalrevenue minus total costs.2.An accountant would not count the owner’s opportunity cost of alternative employment as anaccounting cost. An example is given in the text in which Caroline runs a cookie business, butshe could instead work as a computer programmer. Because she's working in her cookiefactory, she gives up the opportunity to earn $100 per hour as a computer programmer. Theaccountant ignores this opportunity cost because money does not flow into or out of thefirm. But the cost is relevant to Caroline’s decision to run the cookie factory.3.Marginal product is the increase in output that arises from an additional unit of input.Diminishing marginal product means that the marginal product of an input declines as thequantity of the input increases.4.Figure 4 shows a production function that exhibits diminishing marginal product of labor.Figure 5 shows the associated total-cost curve. The production function is concave becauseof diminishing marginal product, while the total-cost curve is convex for the same reason.Figure 4Figure 55.Total cost consists of the costs of all inputs needed to produce a given quantity of output. Itincludes fixed costs and variable costs. Average total cost is the cost of a typical unit of output and is equal to total cost divided by the quantity produced. Marginal cost is the cost of producing an additional unit of output and is equal to the change in total cost divided by the change in quantity. An additional relation between average total cost and marginal cost is that whenever marginal cost is less than average total cost, average total cost is declining; whenever marginal cost is greater than average total cost, average total cost is rising.Figure 66.Figure 6 shows the marginal-cost curve and the average-total-cost curve for a typical firm.There are three main features of these curves: (1) marginal cost is U-shaped but risessharply as output increases; (2) average total cost is U-shaped; and (3) whenever marginal cost is less than average total cost, average total cost is declining; whenever marginal cost is greater than average total cost, average total cost is rising. Marginal cost is increasing for output greater than a certain quantity because of diminishing returns. The average-total-cost curve is downward-sloping initially because the firm is able to spread out fixed costs over additional units. The average-total-cost curve is increasing beyond some output levelbecause as quantity increases, the demand for important variable inputs increases; therefore, the cost of these inputs increases. The marginal-cost and average-total-cost curves intersect at the minimum of average total cost; that quantity is the efficient scale.7.In the long run, a firm can adjust the factors of production that are fixed in the short run; forexample, it can increase the size of its factory. As a result, the long-run average-total-costcurve has a much flatter U-shape than the short-run average-total-cost curve. In addition,the long-run curve lies along the lower envelope of the short-run curves.8.Economies of scale exist when long-run average total cost decreases as the quantity ofoutput increases, which occurs because of specialization among workers. Diseconomies ofscale exist when long-run average total cost rises as the quantity of output increases, whichoccurs because of the coordination problems inherent in a large organization.Quick Check Multiple Choice1. a2. d3. d4. c5. b6. aProblems and Applications1. a.opportunity cost; b. average total cost; c. fixed cost; d. variable cost; e. total cost; f.marginal cost.2. a.The opportunity cost of something is what must be given up to acquire it.b.The opportunity cost of running the hardware store is $550,000, consisting of $500,000to rent the store and buy the stock and a $50,000 implicit cost, because your aunt wouldquit her job as an accountant to run the store. Because the total opportunity cost of$550,000 exceeds the projected revenue of $510,000, your aunt should not open thestore, as her economic profit would be negative.3. a.The following table shows the marginal product of each hour spent fishing:Hours Fish Fixed Cost Variable Cost Total Cost Marginal Product 00$10$0$10---11010515102181010208324101525642810203045301025352b.Figure 7 graphs the fisherman's production function. The production function becomesflatter as the number of hours spent fishing increases, illustrating diminishing marginalproduct.Figure 7c.The table shows the fixed cost, variable cost, and total cost of fishing. Figure 8 shows the fisherman's total-cost curve. It has an upward slope because catching additional fish takes additional time. The curve is convex because there are diminishing returns to fishing time because each additional hour spent fishing yields fewer additional fish.Figure 84.Here is the completed table:WorkersOutputMarginal Product Total Cost Average Total Cost Marginal Cost00---$200------12020300$15.00$5.00250304008.00 3.3339040500 5.56 2.50412030600 5.00 3.33514020700 5.00 5.00615010800 5.3310.0071555900 5.8120.00a.See the table for marginal product. Marginal product rises at first, then declines becauseof diminishing marginal product.b.See the table for total cost.c.See the table for average total cost. Average total cost is U-shaped. When quantity islow, average total cost declines as quantity rises; when quantity is high, average totalcost rises as quantity rises.d.See the table for marginal cost. Marginal cost is also U-shaped, but rises steeply asoutput increases. This is due to diminishing marginal product.e.When marginal product is rising, marginal cost is falling, and vice versa.f.When marginal cost is less than average total cost, average total cost is falling; the costof the last unit produced pulls the average down. When marginal cost is greater thanaverage total cost, average total cost is rising; the cost of the last unit produced pushes the average up.5.At an output level of 600 players, total cost is $180,000 (600 × $300). The total cost ofproducing 601 players is $180,901. Therefore, you should not accept the offer of $550, because the marginal cost of the 601st player is $901.6. a.The fixed cost is $300, because fixed cost equals total cost minus variable cost. At anoutput of zero, the only costs are fixed cost.b.Quantity TotalCost VariableCostMarginal Cost(using total cost)Marginal Cost(using variable cost)0$300$0------135050$50$50239090404034201203030445015030305490190404065402405050Marginal cost equals the change in total cost for each additional unit of output. It is also equal to the change in variable cost for each additional unit of output. This relationship occurs because total cost equals the sum of variable cost and fixed cost and fixed costdoes not change as the quantity changes. Thus, as quantity increases, the increase intotal cost equals the increase in variable cost.7.The following table illustrates average fixed cost (AFC), average variable cost (AVC), andaverage total cost (ATC) for each quantity. The efficient scale is 4 houses per month,because that minimizes average total cost.Quantity VariableCost FixedCostTotalCostAverageFixed CostAverageVariable CostAverageTotal Cost0$0.00$200.00$200.00---------110.00200.00210.00$200.00$10.00$210.00220.00200.00220.00100.0010.00110.00340.00200.00240.0066.6713.3380.00480.00200.00280.0050.0020.0070.005160.00200.00360.0040.0032.0072.006320.00200.00520.0033.3353.3386.677640.00200.00840.0028.5791.43120.008. a.The lump-sum tax causes an increase in fixed cost. Therefore, as Figure 10 shows, onlyaverage fixed cost and average total cost will be affected.Figure 10b.Refer to Figure 11. Average variable cost, average total cost, and marginal cost will all begreater. Average fixed cost will be unaffected.Figure 119. a.The following table shows average variable cost (AVC), average total cost (ATC), andmarginal cost (MC) for each quantity.Quantity VariableCost TotalCostAverageVariable CostAverageTotal CostMarginalCost0$0.00$30.00---------110.0040.00$10.00$40.00$10.00225.0055.0012.5027.5015.00345.0075.0015.0025.0020.00470.00100.0017.5025.0025.005100.00130.0020.0026.0030.006135.00165.0022.5027.5035.00b.Figure 12 shows the three curves. The marginal-cost curve is below the average-total-cost curve when output is less than four and average total cost is declining. Themarginal-cost curve is above the average-total-cost curve when output is above four and average total cost is rising. The marginal-cost curve lies above the average-variable-cost curve.Figure 1210.The following table shows quantity (Q), total cost (TC), and average total cost (ATC) for thethree firms:Firm A Firm B Firm CQuantity TC ATC TC ATC TC ATC1$60.00$60.00$11.00$11.00$21.00$21.00270.0035.0024.0012.0034.0017.00380.0026.6739.0013.0049.0016.33490.0022.5056.0014.0066.0016.505100.0020.0075.0015.0085.0017.006110.0018.3396.0016.00106.0017.677120.0017.14119.0017.00129.0018.43Firm A has economies of scale because average total cost declines as output increases. Firm B has diseconomies of scale because average total cost rises as output rises. Firm C has economies of scale from one to three units of output and diseconomies of scale for levels of output beyond three units.。

曼昆经济学原理答案英文版一、选择题1、在经济学中,什么是GDP?A.国内生产总值B.国民生产总值C.国内总收入D.国民总收入答案:A.国内生产总值(Gross Domestic Product,GDP)是指一个国家在一定时期内所有常住单位的生产活动的最终成果。
2、GDP的计算方法是什么?A.收入法B.支出法C.生产法D.混合法答案:B.支出法。
GDP可以通过对一国所有常住单位的商品和服务的最终消费支出、资本形成总额和货物与服务净出口进行计算,这种计算方法被称为支出法。
3、在经济学中,什么是通货膨胀?A.货币贬值B.物价上涨C.货币供应增加D.以上都不是答案:A.通货膨胀是指商品和服务的总体价格水平上升,导致货币购买力下降。
4、什么是货币政策?A.政府调节货币供应量的政策B.政府调节利率的政策C.政府调节汇率的政策D.以上都不是答案:A.货币政策是指中央银行通过控制货币供应量来调节利率和影响经济活动的政策。
二、简答题1、请简述GDP的概念及作用。
答案:GDP是指一个国家在一定时期内所有常住单位的生产活动的最终成果。
GDP是国民经济核算的核心指标,也是衡量一个国家经济状况和发展水平的重要指标。
它反映了整个国家经济运行的有效性,以及国民收入分配的公平性。
2、请简述通货膨胀的原因及影响。
答案:通货膨胀的原因有多种,包括货币供应量增加、需求拉动、成本推动等。
其中,货币供应量增加是最主要的原因。
当货币供应量增加时,物价上涨,导致货币购买力下降。
通货膨胀会对经济产生负面影响,包括降低消费者购买力、增加企业成本、扭曲价格信号等。
通货膨胀还会导致社会不稳定和政治风险。
曼昆的经济学原理课件是经济学教育中的重要资源,它以深入浅出的方式解释了经济学的基本原理和概念。
本文将对这些原理进行概述,并解释它们在现实生活中的应用。
曼昆的经济学原理主要包括微观经济学和宏观经济学两个部分。
微观经济学主要研究个体经济单位的行为和决策,如消费者、企业和政府。

曼昆经济学原理英⽂版⽂案加习题答案30章281WHAT’S NEW IN THE SEVENTH EDITION:There are no major changes to this chapter.LEARNING OBJECTIVES:By the end of this chapter, students should understand:why inflation results from rapid growth in the money supply.the meaning of the classical dichotomy and monetary neutrality.why some countries print so much money that they experience hyperinflation.how the nominal interest rate responds to the inflation rate.the various costs that inflation imposes on society.CONTEXT AND PURPOSE:Chapter 17 is the second chapter in a two-chapter sequence dealing with money and prices in the long run. Chapter 16 explained what money is and how the Federal Reserve controls the quantity of money. Chapter 17 establishes the relationship between the rate of growth of money and the inflation rate. The purpose of this chapter is to acquaint students with the causes and costs of inflation. Students will find that, in the long run, there is a strong relationship between the growth rate of money and inflation. Students will also find that there are numerous costs to the economy from high inflation, but that there is not a consensus on the importance of these costs when inflation is moderate.KEY POINTS:The overall level of prices in an economy adjusts to bring money supply and money demand into balance. When the central bank increases the supply of money, it causes the price level to rise. Persistent growth in the quantity of money supplied leads to continuing inflation.MONEY GROWTH ANDINFLATION282?Chapter 17/Money Growth and InflationThe principle of monetary neutrality asserts that changes in the quantity of money influence nominal variables but not real variables. Most economists believe that monetary neutrality approximately describes the behavior of the economy in the long run.A government can pay for some of its spending simply by printing money. When countries rely heavily on this “inflation tax,” the result is hyperinflation.One application of the principle of monetary neutrality is the Fisher effect. According to the Fisher effect, when the inflation rate rises, the nominal interest rate rises by the same amount, so that the real interest rate remains the same.Many people think that inflation makes them poorer because it raises the cost of what they buy. This view is a fallacy, however, because inflation also raises nominal incomes.Economists have identified six costs of inflation: shoeleather costs associated with reduced money holdings, menu costs associated with more frequent adjustment of prices, increased variability of relative prices, unintended changes in tax liabilities due to nonindexation of the tax code, confusion and inconvenience resulting from a changing unit of account, and arbitrary redistributions of wealth between debtors and creditors. Many of these costs are large during hyperinflation, but the size ofthese costs for moderate inflation is less clear.CHAPTER OUTLINE:I. The inflation rate is measured as the percentage change in the Consumer Price Index, the GDPdeflator, or some other index of the overall price level.A. Over the past 80 years, prices have risen on average 3.6% per year in the United States.1. There has been substantial variation in the rate of price changes over time.2. From 2002 to 2012, prices rose at an average rate of 2.5% per year, while prices rose by7.8% per year during the 1970s.B. International data shows an even broader range of inflation experiences. In 2012, inflation was0.1% in Japan, 5.1% in Russia, 9.3% in India, and 21.1% in Venezuela.II. The Classical Theory of InflationChapter 17/Money Growth and Inflation?283A. The Level of Prices and the Value of Money1. When the price level rises, people have to pay more for the goods and services they buy.2. A rise in the price level also means that the value of money is now lower because each dollarnow buys a smaller quantity of goods and services.3. If P is the price level, then the quantity of goods and services that can be purchased with $1 is equal to 1/P.4. Suppose you live in a country with one good (ice cream cones).a. When the price of an ice cream cone is $2, the value of a dollar is 1/2 cone.b. When the price of an ice cream cone rises to $3, the value of a dollar is 1/3 cone.B. Money Supply, Money Demand, and Monetary Equilibrium1. The value of money is determined by the supply and demand for money.2. For the most part, the supply of money is determined by the Fed.3. The demand for money reflects how much wealth people want to hold in liquid form.a. One variable that is very important in determining the demand for money is the price level.b. The higher prices are, the more money that is needed to perform transactions.c. Thus, a higher price level (and a lower value of money) leads to a higher quantity of money demanded.4. In the long run, money supply and money demand are brought into equilibrium by the overall level of prices.a. If the price level is above the equilibrium level, people will want to hold more moneythan is available and prices will have to decline.b. If the price level is below equilibrium, people will want to hold less money than that available and the price level will rise.5. We can show the supply and demand for money using a graph.a. The horizontal axis shows the quantity of money.b. The left-hand vertical axis is the value of money, measured by 1/P.c. The right-hand vertical axis is the price level (P). Note that it is inverted—a high value of money means a low price level and vice versa.284?Chapter 17/Money Growth and Inflationd. The supply curve is vertical because the Fed has fixed the quantity of money available.e. The demand curve for money is downward sloping. When the value of money is low, people demand a larger quantity of it to buy goods and services.f. At the equilibrium, the quantity of money demanded is equal to the quantity of money supplied.C. The Effects of a Monetary Injection1. Assume that the economy is currently in equilibrium and the Fed suddenly increases the supply of money.2. The supply of money shifts to the right.3. The equilibrium value of money falls and the price level rises.4. When an increase in the money supply makes dollars more plentiful, the result is an increasein the price level that makes each dollar less valuable.5. Definition of quantity theory of money: a theory asserting that the quantity ofmoney available determines the price level and that the growth rate in thequantity of money available determines the inflation rate.D. A Brief Look at the Adjustment Process1. The immediate effect of an increase in the money supply is to create an excess supply ofmoney.2. People try to get rid of this excess supply in a variety of ways.a. They may buy goods and services with the excess funds.b. They may use these excess funds to make loans to others by buying bonds or depositingthe money in a bank account. These loans will then be used by others to buy goods andservices.Chapter 17/Money Growth and Inflation ? 285c. In either case, the increase in the money supply leads to an increase in the demand forgoods and services.d. Because the supply of goods and services has not changed, the result of an increase inthe demand for goods and services will be higher prices.E. The Classical Dichotomy and Monetary Neutrality1. In the 18th century, David Hume and other economists wrote about the relationship betweenmonetary changes and important macroeconomic variables such as production, employment, real wages, and real interest rates. 2. They suggested that economic variables should be divided into two groups: nominal variablesand real variables.a. Definition of nominal variables: variables measured in monetary units .b. Definition of real variables: variables measured in physical units .3. Definition of classical dichotomy: the theoretical separation of nominal and realvariables . 4. Prices in the economy are nominal (because they are quoted in units of money), but relativeprices are real (because they are not measured in money terms).5. Classical analysis suggested that different forces influence real and nominal variables.a. Changes in the money supply affect nominal variables but not real variables.b. Definition of monetary neutrality: the proposition that changes in the moneysupply do not affect real variables .F. Velocity and the Quantity Equation1. Definition of velocity of money: the rate at which money changes hands .2. To calculate velocity, we divide nominal GDP by the quantity of money.3. If P is the price level (the GDP deflator), Y is real GDP, and M is the quantity of money:4. Rearranging, we get the quantity equation:286 ? Chapter 17/Money Growth and Inflation5. Definition of quantity equation: the equation M × V = P × Y , which relates thequantity of money, the velocity of money, and the dollar value of the economy’s output of goods and services .a. The quantity equation shows that an increase in the quantity of money must be reflectedin one of the other three variables.b. Specifically, the price level must rise, output must rise, or velocity must fall.c. Figure 3 shows nominal GDP, the quantity of money (as measured by M2) and thevelocity of money for the United States since 1960. It appears that velocity is fairly stable, while nominal GDP and the money supply have grown dramatically.6. We can now explain how an increase in the quantity of money affects the price level usingthe quantity equation.a. The velocity of money is relatively stable over time.b. When the central bank changes the quantity of money (M ), it will proportionately changethe nominal value of output (P × Y ).c. The economy’s output of goods and services (Y ) is determined primarily by availableresources and technology. Because money is neutral, changes in the money supply do not affect output.d. This must mean that P increases proportionately with the change in M .e. Thus, when the central bank increases the money supply rapidly, the result is a high rateof inflation.G. Case Study: Money and Prices during Four Hyperinflations1. Hyperinflation is generally defined as inflation that exceeds 50% per month.ALTERNATIVE CLASSROOM EXAMPLE: Suppose that: Real GDP = $5,000Velocity = 5Money supply = $2,000Price level = 2We can show that: M x V = P x Y$2,000 x 5 = 2 x $5,000$10,000 = $10,000Chapter 17/Money Growth and Inflation ? 2872. Figure 4 shows data from four classic periods of hyperinflation during the 1920s in Austria,Hungary, Germany, and Poland.3. We can see that, in each graph, the quantity of money and the price level are almost parallel.4. These episodes illustrate Principle #9: Prices rise when the government prints too muchmoney.H. The Inflation Tax1. Some countries use money creation to pay for spending instead of using tax revenue.2. Definition of inflation tax: the revenue the government raises by creating money .3. The inflation tax is like a tax on everyone who holds money.4. Almost all hyperinflations follow the same pattern.a. The government has a high level of spending and inadequate tax revenue to pay for itsspending.b. The government’s ability to borrow funds is limited.c. As a result, it turns to printing money to pay for its spending.d. The large increases in the money supply lead to large amounts of inflation.e. The hyperinflation ends when the government cuts its spending and eliminates the needto create new money. 5. FYI: Hyperinflation in Zimbabwea. In the 2000s, Zimbabwe faced one of history’s most extreme examples of hyperinflation.b. Before the period of hyperinflation, one Zimbabwe dollar was worth a bit more than oneU.S. dollar.c. By 2009, the Zimbabwe government was issuing notes with denominations as large as 10 trillion Zimbabwe dollars (which were worth about three U.S. dollars).I. The Fisher Effect1. Recall that the real interest rate is equal to the nominal interest rate minus the inflation rate.2. This, of course, means that:288 ? Chapter 17/Money Growth and Inflationa. The supply and demand for loanable funds determines the real interest rate.b. Growth in the money supply determines the inflation rate.3. When the Fed increases the rate of growth of the money supply, the inflation rate increases. This in turn will lead to an increase in the nominal interest rate.4. Definition of Fisher effect: the one-for-one adjustment of the nominal interest rateto the inflation rate .a. The Fisher effect does not hold in the short run to the extent that inflation is unanticipated.b. If inflation catches borrowers and lenders by surprise, the nominal interest rate will fail to reflect the rise in prices.5. Figure 5 shows the nominal interest rate and the inflation rate in the U.S. economy since 1960.III. The Costs of InflationA. A Fall in Purchasing Power? The Inflation Fallacy1. Most individuals believe that the major problem caused by inflation is that inflation lowers the purchasing power of a person’s income.2. However, as prices rise, so do incomes. Thus, inflation does not in itself reduce the purchasing power of incomes.B. Shoeleather Costs1. Because inflation erodes the value of money that you carry in your pocket, you can avoid this drop in value by holding less money.ALTERNATIVE CLASSROOM EXAMPLE:Real interest rate = 5% Inflation rate = 2%This means that the nominal interest rate will be 5% + 2% = 7%.If the inflation rate rises to 3%, the nominal interest rate will rise to 5% + 3% = 8%.Chapter 17/Money Growth and Inflation?2892. However, holding less money generally means more trips to the bank.3. Definition of shoeleather costs: the resources wasted when inflation encouragespeople to reduce their money holdings.4. This cost can be considerable in countries experiencing hyperinflation.C. Menu Costs1. Definition of menu costs: the costs of changing prices.2. During periods of inflation, firms must change their prices more often.D. Relative-Price Variability and the Misallocation of Resources1. Because prices of most goods change only once in a while (instead of constantly), inflation causes relative prices to vary more than they would otherwise.2. When inflation distorts relative prices, consumer decisions are distorted and markets are less able to allocate resources to their best use.E. Inflation-Induced Tax Distortions1. Lawmakers fail to take inflation into account when they write tax laws.2. The nominal values of interest income and capital gains are taxed (not the real values).a. Table 1 shows a hypothetical example of two individuals, living in two countries earning the same real interest rate, and paying the same tax rate, but one individual lives in a country without inflation and the other lives in a country with 8% inflation.b. The person living in the country with inflation ends up with a smaller after-tax real interest rate.3. This implies that higher inflation will tend to discourage saving.4. A possible solution to this problem would be to index the tax system.290?Chapter 17/Money Growth and InflationF. Confusion and Inconvenience1. Money is the yardstick that we use to measure economic transactions.2. When inflation occurs, the value of money falls. This alters the yardstick that we use to measure important variables like incomes and profit.G. A Special Cost of Unexpected Inflation: Arbitrary Redistributions of Wealth1. Example: Sam Student takes out a $20,000 loan at 7% interest (nominal). In 10 years, the loan will come due. After his debt has compounded for 10 years at 7%, Sam will owe the bank $40,000.2. The real value of this debt will depend on inflation.a. If the economy has a hyperinflation, wages and prices will rise so much that Sam may be able to pay the $40,000 out of pocket change.b. If the economy has deflation, Sam will find the $40,000 a greater burden than he anticipated.3. Because inflation is often hard to predict, it imposes risk on both Sam and the bank that the real value of the debt will differ from that expected when the loan is made.4. Inflation is especially volatile and uncertain when the average rate of inflation is high.H. Inflation Is Bad, but Deflation May Be Worse1. Although inflation has been the norm in recent U.S. history, from 1998 to 2012 Japan experienced a 4-percent decline in its overall price level.2. Deflation leads to lower shoeleather costs, but still creates menu costs and relative-price variability.Chapter 17/Money Growth and Inflation?2913. Deflation also results in the redistribution of wealth toward creditors and away from debtors.I. Case Study: The Wizard of Oz and the Free Silver Debate1. Some scholars believe that the book The Wizard of Oz was written about U.S. monetary policy in the late 19th century.2. From 1880 to 1896, the United States experienced deflation, redistributing wealth from farmers (with outstanding loans) to banks.3. Because the United States followed the gold standard at this time, one possible solution to the problem was to start to use silver as well. This would increase the supply of money, raising the price level, and reduce the real va lue of the farmers’ debts.4. There has been some debate over the interpretation assigned to each character, but it is clear that the story revolves around the monetary policy debate at that time in history.5. Even though those who wanted to use silver were defeated, the money supply in the United States increased in 1898 when gold was discovered in Alaska and supplies of gold were shipped in from Canada and South Africa.6. Within 15 years, prices were back up and the farmers were better able to handle their debts.292?Chapter 17/Money Growth and InflationSOLUTIONS TO TEXT PROBLEMS:Quick Quizzes1. When the government of a country increases the growth rate of the money supply from 5 percent per year to 50 percent per year, the average level of prices will start rising very quickly, as predicted by the quantity theory of money. Nominal interest rates will increase dramatically as well, as predicted by the Fisher effect. The government may be increasing the money supply to finance its expenditures.Chapter 17/Money Growth and Inflation?2932. Six costs of inflation are: (1) shoeleather costs; (2) menu costs; (3) relative-price variability and the misallocation of resources; (4) inflation-induced tax distortions; (5) confusion and inconvenience; and (6) arbitrary redistributions of wealth. Shoeleather costs arise because inflation causes people to spend resources going to the bank more often. Menu costs occur when people spend resources changing their posted prices. Relative-price variability occurs because as general prices rise, a fixed dollar price translates into a declining relative price, so the relative prices of goods are constantly changing, causing a misallocation of resources. The combination of inflation and taxation causes distortions in incentives because people are taxed on their nominal capital gains and interest income instead of their real income fromthese sources. Inflation causes confusion and inconvenience because it reduces money’s ability to function as a unit of account. Unexpected inflation redistributes wealth between borrowers and lenders.Questions for Review1. An increase in the price level reduces the real value of money because each dollar in your wallet now buys a smaller quantity of goods and services.2. According to the quantity theory of money, an increase in the quantity of money causes a proportional increase in the price level.3. Nominal variables are those measured in monetary units, while real variables are those measured in physical units. Examples of nominal variables include the prices of goods and nominal GDP. Examples of real variables include relative prices (the price of one good in terms of another), and real wages. According to the principle of monetary neutrality, only nominal variables are affected by changes in the quantity of money.4. Inflation is like a tax because everyone who holds money loses purchasing power. In a hyperinflation, the government increases the money supply rapidly, which leads to a high rate of inflation. Thus the government uses the inflation tax, instead of taxes, to finance its spending.5. According to the Fisher effect, an increase in the inflation rate raises the nominal interest rate by the same amount that the inflation rate increases, with no effect on the real interest rate.6. The costs of inflation include shoeleather costs associated with reduced money holdings, menu costs associated with more frequent adjustment of prices, increased variability of relative prices, unintended changes in tax liabilities due to nonindexation of the tax code, confusion and inconvenience resulting from a changing unit of account, and arbitrary redistributions of wealth between debtors and creditors. With a low and stable rate of inflation like that in the United States, none of these costs are very high. Perhaps the most important one is the interaction between inflation and the tax code, which may reduce saving and investment even though the inflation rate is low.7. If inflation is less than expected, creditors benefit and debtors lose. Creditors receive dollar payments from debtors that have a higher real value than was expected.294?Chapter 17/Money Growth and InflationQuick Check Multiple Choice1. d2. d3. b4. b5. a6. dProblems and Applications1. In this problem, all amounts are shown in billions.a. Nominal GDP = P ×Y = $10,000 and Y = real GDP = $5,000, so P = (P ×Y)/Y =$10,000/$5,000 = 2.Because M ×V = P ×Y, then V = (P ×Y)/M = $10,000/$500 = 20.b. If M and V are unchanged and Y rises by 5%, then because M ×V = P ×Y, P must fallby 5%. As a result, nominal GDP is unchanged.c. To keep the price level stable, the Fed must increase the money supply by 5%, matching the increase in real GDP. Then, because velocity is unchanged, the price level will be stable.d. If the Fed wants inflation to be 10%, it will need to increase the money supply 15%.Thus M ×V will rise 15%, causing P ×Y to rise 15%, with a 10% increase in prices anda 5% rise in real GDP.2. a. If people need to hold less cash, the demand for money shifts to the left, because there will be less money demanded at any price level.b. If the Fed does not respond to this event, the shift to the left of the demand for money combined with no change in the supply of money leads to a decline in the value ofmoney (1/P), which means the price level rises, as shown in Figure 1.Figure 1Chapter 17/Money Growth and Inflation?295c. If the Fed wants to keep the price level stable, it should reduce the money supply fromS1 to S2 in Figure 2. This would cause the supply of money to shift to the left by thesame amount that the demand for money shifted, resulting in no change in the value ofmoney and the price level.Figure 23. With constant velocity, reducing the inflation rate to zero would require the money growthrate to equal the growth rate of output, according to the quantity theory of money (M ×V = P ×Y).4. If a country's inflation rate increases sharply, the inflation tax on holders of money increasessignificantly. Wealth in savings accounts is not subject to a change in the inflation taxbecause the nominal interest rate will increase with the rise in inflation. But holders ofsavings accounts are hurt by the increase in the inflation rate because they are taxed ontheir nominal interest income, so their real returns are lower.5. a. When the price of both goods doubles in a ye ar, inflation is 100%. Let’s set the marketbasket equal to one unit of each good. The cost of the market basket is initially $4 andbecomes $8 in the second year. Thus, the rate of inflation is ($8 – $4)/$4 × 100 = 100%.Because the prices of all goods rise by 100%, the farmers get a 100% increase in theirincomes to go along with the 100% increase in prices, so neither is affected by thechange in prices.b. If the price of beans rises to $2 and the price of rice rises to $4, then the cost of themarket basket in the second year is $6. This means that the inflation rate is ($6 – $4)/$4 × 100 = 50%. Bob is better off because his dollar revenues doubled (increased 100%)while inflation was only 50%. Rita is worse off because inflation was 50% percent, so the price of the good she buys rose faster than the price of the good (rice) she sells, whichrose only 33%.c. If the price of beans rises to $2 and the price of rice falls to $1.50, then the cost of themarket basket in the second year is $3.50. This means that the inflation rate is ($3.5 –$4)/$4 × 100 = -12.5%. Bob is better off because his dollar revenues doubled (increased 100%) while prices overall fell 12.5%. Rita is worse off because inflation was -12.5%, so the price of the good she buys didn't fall as fast as the price of the good (rice) she sells,which fell 50%.296?Chapter 17/Money Growth and Inflationd. The relative price of rice and beans matters more to Bob and Rita than the overallinflation rate. If the price of the good that a person produces rises more than inflation,he will be better off. If the price of the good a person produces rises less than inflation,he will be worse off.6. The following table shows the relevant calculations:Row (3) is row (1) minus row (2). Row (4) is 0.40 × row (1). Row (5) is (1 – .40) × row (1),which equals row (1) minus row (4). Row (6) is row (5) minus row (2). Note that eventhough part (a) has the highest before-tax real interest rate, it has the lowest after-tax realinterest rate. Note also that the after-tax real interest rate is much lower than the before-taxreal interest rate.7. The functions of money are to serve as a medium of exchange, a unit of account, and a storeof value. Inflation mainly affects the ability of money to serve as a store of value, becauseinflation erodes money's purchasing power, making it less attractive as a store of value.Money also is not as useful as a unit of account when there is inflation, because stores haveto change prices more often and because people are confused and inconvenienced by thechanges in the value of money. In some countries with hyperinflation, stores post prices interms of a more stable currency, such as the U.S. dollar, even when the local currency is stillused as the medium of exchange. Sometimes countries even stop using their local currencyaltogether and use a foreign currency as the medium of exchange as well.8. a. Unexpectedly high inflation helps the government by providing higher tax revenue andreducing the real value of outstanding government debt.b. Unexpectedly high inflation helps a homeowner with a fixed-rate mortgage because hepays a fixed nominal interest rate that was based on expected inflation, and thus pays alower real interest rate than was expected.c. Unexpectedly high inflation hurts a union worker in the second year of a labor contractbecause the contract probably based the worker's nominal wage on the expectedinflation rate. As a result, the worker receives a lower-than-expected real wage.d. Unexpectedly high inflation hurts a college that has invested some of its endowment ingovernment bonds because the higher inflation rate means the college is receiving alower real interest rate than it had planned. (This assumes that the college did notpurchase indexed Treasury bonds.)9. a. The statement that "Inflation hurts borrowers and helps lenders, because borrowersmust pay a higher rate of interest," is false. Higher expected inflation means borrowerspay a higher nominal rate of interest, but it is the same real rate of interest, soborrowers are not worse off and lenders are not better off. Higher unexpected inflation,on the other hand, makes borrowers better off and lenders worse off.Chapter 17/Money Growth and Inflation?297 b. The statement, "If prices change in a way that leaves the overall price level unchanged,then no one is made better or worse off," is false. Changes in relative prices can make some people better off and others worse off, even though the overall price level does not change. See problem 6 for an illustration of this.c. The statement, "Inflation does not reduce the purchasing power of most workers," istrue. Most workers' incomes keep up with inflation reasonably well.。
Note that C′is greater than C,and T1′is greater than T1, as shown. This is because in part (b), the consumer has lower consumption in the first part of life, so there are more resources left when there is no constraint—consumption will be higher. The case where people are borrowing constrained in their early working years is more realistic since it is difficult, if not impossible, to borrow against expected future income.6.The life-cycle model predicts that an important source of saving is that people savewhile they work to finance consumption after they retire. That is, the young save, and the old dissave. If the fraction of the population that is elderly will increase over the next 20 years, the life-cycle model predicts that as these elderly retire, they will begin to dissave their accumulated wealth in order to finance their retirement consumption: thus, the national saving rate should fall over the next 20 years.7.In this chapter, we discussed two explanations for why the elderly do not dissave asrapidly as the life-cycle model predicts. First, because of the possibility of unpredictable and costly events, they may keep some precautionary saving as a buffer in case they live longer than expected or have large medical bills. Second, they may want to leave bequests to their children, relatives, or charities, so again, they do not dissave all of their wealth during retirement.If the elderly who do not have children dissave at the same rate as the elderly who do have children, this seems to imply that the reason for low dissaving is the precau-tionary motive; the bequest motive is presumably stronger for people who have children than for those who don’t.An alternative interpretation is that perhaps having children does not increase desired saving. For example, having children raises the bequest motive, but it may also lower the precautionary motive: you can rely on your children in case of financial emer-gency. Perhaps the two effects on saving cancel each other.8.If you are a fully rational and time-consistent consumer, you would certainly prefer thesaving account that lets you take the money out on demand. After all, you get the same return on that account, but in unexpected circumstances (e.g., if you suffer an unex-pected, temporary decline in income), you can use the funds in the account to finance your consumption. This is the kind of consumer in the intertemporal models of Irving Fisher, Franco Modigliani, and Milton Friedman.By contrast, if you face the “pull of instant gratification,” you may prefer the account that requires a 30-day notification before withdrawals. In this way, you pre-commit yourself to not using the funds to satisfy a desire for instant gratification. This precommitment offers a way to overcome the time-inconsistency problem. That is, some people would like to save more, but at any particular moment, they face such a strong desire for instant gratification that they always choose to consume rather than save. This is the type of consumer in David Laibson’s theory.。
Answers to Textbook Questions and ProblemsCHAPTER3 National Income: Where It Comes From and Where It GoesQuestions for Review1. The factors of production and the production technology determine the amount of output an economycan produce. The factors of production are the inputs used to produce goods and services: the most important factors are capital and labor. The production technology determines how much output can be produced from any given amounts of these inputs. An increase in one of the factors of production or an improvement in technology leads to an increase in the economy’s output.2. When a firm decides how much of a factor of production to hire or demand, it considers how thisdecision affects profits. For example, hiring an extra unit of labor increases output and thereforeincreases revenue; the firm compares this additional revenue to the additional cost from the higher wage bill. The additional revenue the firm receives depends on the marginal product of labor (MPL) and the price of the good produced (P). An additional unit of labor produces MPL units of additional output, which sells for P dollars per unit. Therefore, the additional revenue to the firm is P ⨯MPL. The cost of hiring the additional unit of labor is the wage W. Thus, this hiring decision has the following effect on profits:ΔProfit= ΔRevenue –ΔCost= (P ⨯MPL) –W.If the additional revenue, P ⨯MPL, exceeds the cost (W) of hiring the additional unit of labor, then profit increases. The firm will hire labor until it is no longer profitable to do so—that is, until the MPL falls to the point where the change in profit is zero. In the equation above, the firm hires labor until ΔProfit = 0, which is when (P ⨯MPL) = W.This condition can be rewritten as:MPL = W/P.Therefore, a competitive profit-maximizing firm hires labor until the marginal product of labor equals the real wage. The same logic applies to the firm’s decision regarding how much capital to hire: the firm will hire capital until the marginal product of capital equals the real rental price.3. A production function has constant returns to scale if an equal percentage increase in all factors ofproduction causes an increase in output of the same percentage. For example, if a firm increases its use of capital and labor by 50 percent, and output increases by 50 percent, then the production function has constant returns to scale.If the production function has constant returns to scale, then total income (or equivalently, total output) in an economy of competitive profit-maximizing firms is divided between the return to labor, MPL ⨯L, and the return to capital, MPK ⨯K. That is, under constant returns to scale, economic profit is zero.4. A Cobb–Douglas production function has the form F(K,L) = AKαL1–α. The text showed that theparameter αgives capital’s share of income. So if capital earns one-fourth of total income, then α=0.25. Hence, F(K,L) = AK0.25L0.75.5. Consumption depends positively on disposable income—i.e. the amount of income after all taxes havebeen paid. Higher disposable income means higher consumption.The quantity of investment goods demanded depends negatively on the real interest rate. For an investment to be profitable, its return must be greater than its cost. Because the real interest ratemeasures the cost of funds, a higher real interest rate makes it more costly to invest, so the demand for investment goods falls.6. Government purchases are a measure of the value of goods and services purchased directly by thegovernment. For example, the government buys missiles and tanks, builds roads, and provides services such as air traffic control. All of these activities are part of GDP. Transfer payments are government payments to individuals that are not in exchange for goods or services. They are the opposite of taxes: taxes reduce household disposable income, whereas transfer payments increase it. Examples of transfer payments include Social Security payments to the elderly, unemployment insurance, and veterans’ benefits.7. Consumption, investment, and government purchases determine demand for the economy’s output,whereas the factors of production and the production function determine the supply of output. The real interest rate adjusts to ensure that the demand for t he economy’s goods equals the supply. At theequilibrium interest rate, the demand for goods and services equals the supply.8. When the government increases taxes, disposable income falls, and therefore consumption falls as well.The decrease in consumption equals the amount that taxes increase multiplied by the marginalpropensity to consume (MPC). The higher the MPC is, the greater is the negative effect of the tax increase on consumption. Because output is fixed by the factors of production and the production technology, and government purchases have not changed, the decrease in consumption must be offset by an increase in investment. For investment to rise, the real interest rate must fall. Therefore, a tax increase leads to a decrease in consumption, an increase in investment, and a fall in the real interest rate.Problems and Applications1. a. According to the neoclassical theory of distribution, the real wage equals the marginal product oflabor. Because of diminishing returns to labor, an increase in the labor force causes the marginalproduct of labor to fall. Hence, the real wage falls.Given a Cobb–Douglas production function, the increase in the labor force will increase the marginal product of capital and will increase the real rental price of capital. With more workers,the capital will be used more intensively and will be more productive.b. The real rental price equals the marginal product of capital. If an earthquake destroys some of thecapital stock (yet miraculously does not kill anyone and lower the labor force), the marginalproduct of capital rises and, hence, the real rental price rises.Given a Cobb–Douglas production function, the decrease in the capital stock will decrease the marginal product of labor and will decrease the real wage. With less capital, each worker becomes less productive.c. If a technological advance improves the production function, this is likely to increase the marginalproducts of both capital and labor. Hence, the real wage and the real rental price both increase.d. High inflation that doubles the nominal wage and the price level will have no impact on the realwage. Similarly, high inflation that doubles the nominal rental price of capital and the price levelwill have no impact on the real rental price of capital.2. a. To find the amount of output produced, substitute the given values for labor and land into theproduction function:Y = 1000.51000.5 = 100.b. According to the text, the formulas for the marginal product of labor and the marginal product ofcapital (land) are:MPL = (1 –α)AKαL–α.MPK = αAKα–1L1–α.In this problem, α is 0.5 and A is 1. Substitute in the given values for labor and land to find themarginal product of labor is 0.5 and marginal product of capital (land) is 0.5. We know that thereal wage equals the marginal product of labor and the real rental price of land equals the marginal product of capital (land).c. Labor’s share of the output is given by the marginal product of labor times the quantity of labor, o r50.d. The new level of output is 70.71.e. The new wage is 0.71. The new rental price of land is 0.35.f. Labor now receives 35.36.3. A production function has decreasing returns to scale if an equal percentage increase in all factors ofproduction leads to a smaller percentage increase in output. For example, if we double the amounts of capital and labor output increases by less than double, then the production function has decreasing returns to scale. This may happen if there is a fixed factor such as land in the production function, and this fixed factor becomes scarce as the economy grows larger.A production function has increasing returns to scale if an equal percentage increase in all factorsof production leads to a larger percentage increase in output. For example, if doubling the amount of capital and labor increases the output by more than double, then the production function has increasing returns to scale. This may happen if specialization of labor becomes greater as the population grows.For example, if only one worker builds a car, then it takes him a long time because he has to learn many different skills, and he must constantly change tasks and tools. But if many workers build a car, then each one can specialize in a particular task and become more productive.4. a. A Cobb–Douglas production function has the form Y = AKαL1–α. The text showed that the marginalproducts for the Cobb–Douglas production function are:MPL = (1 –α)Y/L.MPK = αY/K.Competitive profit-maximizing firms hire labor until its marginal product equals the real wage, and hire capital until its marginal product equals the real rental rate. Using these facts and theabove marginal products for the Cobb–Douglas production function, we find:W/P = MPL = (1 –α)Y/L.R/P = MPK = αY/K.Rewriting this:(W/P)L = MPL ⨯L = (1 –α)Y.(R/P)K = MPK ⨯K = αY.Note that the terms (W/P)L and (R/P)K are the wage bill and total return to capital, respectively.Given that the value of α = 0.3, then the above formulas indicate that labor receives 70 percent of total output (or income) and capital receives 30 percent of total output (or income).b. To determine what happens to total output when the labor force increases by 10 percent, considerthe formula for the Cobb–Douglas production function:Y = AKαL1–α.Let Y 1 equal the initial value of output and Y 2 equal final output. We know that α = 0.3. We also know that labor L increases by 10 percent:Y 1 = AK 0.3L 0.7. Y 2 = AK 0.3(1.1L )0.7.Note that we multiplied L by 1.1 to reflect the 10-percent increase in the labor force. To calculate the percentage change in output, divide Y 2 by Y 1:Y 2Y 1=AK 0.31.1L ()0.7AK 0.3L 0.7=1.1()0.7=1.069.That is, output increases by 6.9 percent.To determine how the increase in the labor force affects the rental price of capital, consider the formula for the real rental price of capital R/P :R/P = MPK = αAK α–1L 1–α.We know that α = 0.3. We also know that labor (L ) increases by 10 percent. Let (R/P )1 equal the initial value of the rental price of capital, and let (R/P )2 equal the final rental price of capital after the labor force increases by 10 percent. To find (R/P )2, multiply L by 1.1 to reflect the 10-percent increase in the labor force:(R/P )1 = 0.3AK –0.7L 0.7. (R/P )2 = 0.3AK –0.7(1.1L )0.7.The rental price increases by the ratioR /P ()2R /P ()1=0.3AK -0.71.1L ()0.70.3AK -0.7L 0.7=1.1()0.7=1.069So the rental price increases by 6.9 percent. To determine how the increase in the labor forceaffects the real wage, consider the formula for the real wage W/P :W/P = MPL = (1 – α)AK αL –α.We know that α = 0.3. We also know that labor (L ) increases by 10 percent. Let (W/P )1 equal the initial value of the real wage, and let (W/P )2 equal the final value of the real wage. To find (W/P )2, multiply L by 1.1 to reflect the 10-percent increase in the labor force:(W/P )1 = (1 – 0.3)AK 0.3L –0.3. (W/P )2 = (1 – 0.3)AK 0.3(1.1L )–0.3.To calculate the percentage change in the real wage, divide (W/P )2 by (W/P )1:W /P ()2W /P ()1=1-0.3()AK 0.31.1L ()-0.31-0.3()AK 0.3L-0.3=1.1()-0.3=0.972That is, the real wage falls by 2.8 percent.c. We can use the same logic as in part (b) to setY 1 = AK 0.3L 0.7. Y 2 = A (1.1K )0.3L 0.7.Therefore, we have:Y 2Y 1=A 1.1K ()0.3L 0.7AK 0.3L 0.7=1.1()0.3=1.029This equation shows that output increases by about 3 percent. Notice that α < 0.5 means thatproportional increases to capital will increase output by less than the same proportional increase to labor.Again using the same logic as in part (b) for the change in the real rental price of capital:R /P ()2R /P ()1=0.3A 1.1K ()-0.7L 0.70.3AK -0.7L 0.7=1.1()-0.7=0.935The real rental price of capital falls by 6.5 percent because there are diminishing returns to capital; that is, when capital increases, its marginal product falls.Finally, the change in the real wage is:W /P ()2W /P ()1=0.7A 1.1K ()0.3L -0.30.7AK 0.3L -0.3=1.1()0.3=1.029Hence, real wages increase by 2.9 percent because the added capital increases the marginalproductivity of the existing workers. (Notice that the wage and output have both increased by the same amount, leaving the labor share unchanged —a feature of Cobb –Douglas technologies.)d. Using the same formula, we find that the change in output is:Y 2Y 1= 1.1A ()K 0.3L 0.7AK 0.3L 0.7=1.1This equation shows that output increases by 10 percent. Similarly, the rental price of capital and the real wage also increase by 10 percent:R /P ()2R /P ()1=0.31.1A ()K -0.7L 0.70.3AK -0.7L 0.7=1.1W /P ()2W /P ()1=0.71.1A ()K 0.3L -0.30.7AK 0.3L -0.3=1.15. Labor income is defined asW P ´L =WLP Labor’s share of income is defined asWL P æèççöø÷÷/Y =WL PYFor example, if this ratio is about constant at a value of 0.7, then the value of W /P = 0.7*Y /L . Thismeans that the real wage is roughly proportional to labor productivity. Hence, any trend in laborproductivity must be matched by an equal trend in real wages. Otherwise, labor’s share would deviate from 0.7. Thus, the first fact (a constant labor share) implies the second fact (the trend in real wages closely tracks the trend in labor productivity).6. a. Nominal wages are measured as dollars per hour worked. Prices are measured as dollars per unitproduced (either a haircut or a unit of farm output). Marginal productivity is measured as units of output produced per hour worked.b. According to the neoclassical theory, technical progress that increases the marginal product offarmers causes their real wage to rise. The real wage for farmers is measured as units of farm output per hour worked. The real wage is W /P F , and this is equal to ($/hour worked)/($/unit of farm output).c. If the marginal productivity of barbers is unchanged, then their real wage is unchanged. The realwage for barbers is measured as haircuts per hour worked. The real wage is W /P B , and this is equal to ($/hour worked)/($/haircut).d. If workers can move freely between being farmers and being barbers, then they must be paid thesame wage W in each sector.e. If the nominal wage W is the same in both sectors, but the real wage in terms of farm goods isgreater than the real wage in terms of haircuts, then the price of haircuts must have risen relative to the price of farm goods. We know that W /P = MPL so that W = P MPL . This means that P F MPL F = P H MPL B , given that the nominal wages are the same. Since the marginal product of labor for barbers has not changed and the marginal product of labor for farmers has risen, the price of a haircut must have risen relative to the price of the farm output. If we express this in growth rate terms, then the growth of the farm price + the growth of the marginal product of the farm labor = the growth of the haircut price.f. The farmers and the barbers are equally well off after the technological progress in farming, giventhe assumption that labor is freely mobile between the two sectors and both types of peopleconsume the same basket of goods. Given that the nominal wage ends up equal for each type ofworker and that they pay the same prices for final goods, they are equally well off in terms of what they can buy with their nominal income. The real wage is a measure of how many units of output are produced per worker. Technological progress in farming increased the units of farm outputproduced per hour worked. Movement of labor between sectors then equalized the nominal wage.7. a. The marginal product of labor (MPL)is found by differentiating the production function withrespect to labor:MPL=dY dL=11/3H1/3L-2/3An increase in human capital will increase the marginal product of labor because more human capital makes all the existing labor more productive.b. The marginal product of human capital (MPH)is found by differentiating the production functionwith respect to human capital:MPH=dY dH=13K1/3L1/3H-2/3An increase in human capital will decrease the marginal product of human capital because there are diminishing returns.c. The labor share of output is the proportion of output that goes to labor. The total amount of outputthat goes to labor is the real wage (which, under perfect competition, equals the marginal product of labor) times the quantity of labor. This quantity is divided by the total amount of output to compute the labor share:Labor Share=(13K1/3H1/3L-2/3)LK1/3H1/3L1/3=1 3We can use the same logic to find the human capital share:Human Capital Share=(13K1/3L1/3H-2/3)HK1/3H1/3L1/3=1 3so labor gets one-third of the output, and human capital gets one-third of the output. Since workers own their human capital (we hope!), it will appear that labor gets two-thirds of output.d. The ratio of the skilled wage to the unskilled wage is:Wskilled Wunskilled =MPL+MPHMPL=13K1/3L-2/3H1/3+13K1/3L1/3H-2/313K1/3L-2/3H1/3=1+LHNotice that the ratio is always greater than 1 because skilled workers get paid more than unskilled workers. Also, when H increases this ratio falls because the diminishing returns to human capitallower its return, while at the same time increasing the marginal product of unskilled workers.e. If more colleges provide scholarships, it will increase H, and it does lead to a more egalitariansociety. The policy lowers the returns to education, decreasing the gap between the wages of more and less educated workers. More importantly, the policy even raises the absolute wage of unskilled workers because their marginal product rises when the number of skilled workers rises.8. The effect of a government tax increase of $100 billion on (a) public saving, (b) private saving, and (c)national saving can be analyzed by using the following relationships:National Saving = [Private Saving] + [Public Saving]= [Y –T –C(Y –T)] + [T –G]= Y –C(Y –T) –G.a. Public Saving—The tax increase causes a 1-for-1 increase in public saving. T increases by $100billion and, therefore, public saving increases by $100 billion.b. Private Saving—The increase in taxes decreases disposable income, Y –T, by $100 billion. Sincethe marginal propensity to consume (MPC) is 0.6, consumption falls by 0.6 $100 billion, or $60 billion. Hence,ΔPrivate Saving = –$100b – 0.6 (–$100b) = –$40b.Private saving falls $40 billion.c. National Saving—Because national saving is the sum of private and public saving, we canconclude that the $100 billion tax increase leads to a $60 billion increase in national saving.Another way to see this is by using the third equation for national saving expressed above, that national saving equals Y –C(Y –T) –G. The $100 billion tax increase reduces disposableincome and causes consumption to fall by $60 billion. Since neither G nor Y changes, nationalsaving thus rises by $60 billion.d. Investment—To determine the effect of the tax increase on investment, recall the nationalaccounts identity:Y = C(Y –T) + I(r) + G.Rearranging, we findY –C(Y –T) –G = I(r).The left side of this equation is national saving, so the equation just says that national savingequals investment. Since national saving increases by $60 billion, investment must also increaseby $60 billion.How does this increase in investment take place? We know that investment depends on thereal interest rate. For investment to rise, the real interest rate must fall. Figure 3-1 illustrates saving and investment as a function of the real interest rate.The tax increase causes national saving to rise, so the supply curve for loanable funds shifts to the right. The equilibrium real interest rate falls, and investment rises.9. If consumers increase the amount that they consume today, then private saving and, therefore, nationalsaving will fall. We know this from the definition of national saving:National Saving = [Private Saving] + [Public Saving]= [Y –T –C(Y –T)] + [T –G].An increase in consumption decreases private saving, so national saving falls.Figure 3-2 illustrates saving and investment as a function of the real interest rate. If national saving decreases, the supply curve for loanable funds shifts to the left, thereby raising the real interest rate and reducing investment.10. a. Private saving is the amount of disposable income, Y – T, that is not consumed:S private= Y – T – C= 8,000 – 2,000 – [1,000 + (2/3)(8,000 – 2,000)]= 1,000.Public saving is the amount of taxes the government has left over after it makes its purchases:S public= T – G= 2,000 – 2,500= –500.National saving is the sum of private saving and public saving:S national= S private+ S public= 1,000 + (500)= 500.b. The equilibrium interest rate is the value of r that clears the market for loanable funds. We alreadyknow that national saving is 500, so we just need to set it equal to investment:S national= I500 = 1,200 – 100rSolving this equation for r, we find:r = 0.07 or 7%.c. When the government increases its spending, private saving remains the same as before (noticethat G does not appear in the S private equation above) while government saving decreases. Puttingthe new G into the equations above:S private= 1,000S public= T – G= 2,000 – 2,000= 0.Thus,S national= S private+ S public= 1,000 + (0)= 1,000.d. Once again the equilibrium interest rate clears the market for loanable funds:S national= I1,000 = 1,200 – 100rSolving this equation for r, we find:r = 0.02 or 2%.11. To determine the effect on investment of an equal increase in both taxes and government spending,consider the national income accounts identity for national saving:National Saving = [Private Saving] + [Public Saving]= [Y –T –C(Y –T)] + [T –G].We know that Y is fixed by the factors of production. We also know that the change in consumption equals the marginal propensity to consume (MPC) times the change in disposable income. This tells us thatΔNational Saving= {–ΔT – [MPC ⨯ (–ΔT)]} + [ΔT –ΔG]= [–ΔT + (MPC ⨯ΔT)] + 0= (MPC – 1) ΔT .The above expression tells us that the impact on national saving of an equal increase in T and G depends on the size of the marginal propensity to consume. The closer the MPC is to 1, the smaller is the fall in saving. For example, if the MPC equals 1, then the fall in consumption equals the rise in government purchases, so national saving [Y – C (Y – T ) – G ] is unchanged. The closer the MPC is to 0 (and therefore the larger is the amount saved rather than spent for a one-dollar change in disposable income), the greater is the impact on saving. Because we assume that the MPC is less than 1, we expect that national saving falls in response to an equal increase in taxes and government spending.The reduction in saving means that the supply of loanable funds curve will shift to the left in Figure 3-3. The real interest rate rises, and investment falls.12. a. The demand curve for business investment shifts out to the right because the subsidy increases thenumber of profitable investment opportunities for any given interest rate. The demand curve for residential investment remains unchanged.b. The total demand curve for investment in the economy shifts out to the right since it represents thesum of business investment, which shifts out to the right, and residential investment, which isunchanged. As a result the real interest rate rises as in Figure 3-4.c. The total quantity of investment does not change because it is constrained by the inelastic supply of savings. The investment tax credit leads to a rise in business investment, but an offsetting fall in residential investment. That is, the higher interest rate means that residential investment falls (a movement along the curve), whereas the rightward shift of the business investment curve leads business investment to rise by an equal amount. Figure 3-5 shows this change. Note that I 1B +I 1R +I 2B +I 2R =S .13. In this chapter, we concluded that an increase in government expenditures reduces national saving andraises the interest rate. The increase in government expenditure therefore crowds out investment by the full amount of the increase. Similarly, a tax cut increases disposable income and hence consumption.This increase in consumption translates into a fall in national saving, and the increase in consumption crowds out investment by the full amount of the increase.If consumption depends on the interest rate, then saving will also depend on it. The higher the interest rate, the greater the return to saving. Hence, it seems reasonable to think that an increase in the interest rate might increase saving and reduce consumption. Figure 3-6 shows saving as an increasing function of the interest rate.Consider what happens when government purchases increase. At any given level of the interest rate, national saving falls by the change in government purchases, as shown in Figure 3-7. The figure shows that if the saving function slopes upward, investment falls by less than the amount thatgovernment purchases rises by. This happens because consumption falls and saving increases inresponse to the higher interest rate. Hence, the more responsive consumption is to the interest rate, the less investment is crowded out by government purchases.14. a. Figure 3-8 shows the case where the demand for loanable funds is stable but the supply of funds(the saving schedule) fluctuates perhaps reflecting temporary shocks to income, changes ingovernment spending, or changes in consumer confidence. In this case, when interest rates fall,investment rises; when interest rates rise, investment falls. We would expect a negative correlation between investment and interest rates.b. Figure 3-9 shows the case where the supply of loanable funds (saving) is stable, whereas thedemand for loanable funds fluctuates, perhaps reflecting changes in firms’ expectations about the marginal product of capital. We would now find a positive correlation between investment and the interest rate—when demand for funds rises, it pushes up the interest rate, so we observe thatinvestment and the real interest rate increase at the same time.c. If both curves shift, we might generate a scatter plot as in Figure 3-10, where the economyfluctuates among points A, B, C, and D. Depending on how often the economy is at each of these points, we might find little clear relationship between investment and interest rates.d. Situation (c) seems fairly reasonable—as both the supply of and demand for loanable fundsfluctuate over time in response to changes in the economy.。
CHAPTER 23: MEASURING A NATION’S INCOME True/False Indicate whether the statement is true or false. ?1.? The circular flow diagram describes all transactions between households and firms in a simple economy and shows the equality of expenditures and income. ANSWER:? T POINTS:? 0 / 1
?2.? Gross domestic product includes most items produced and sold illicitly. ANSWER:? F POINTS:? 0 / 1
?3.? Net national product is the total income of a nation’s residents minus losses from depreciation. ANSWER:? T POINTS:? 0 / 1
?4.? Disposable personal income is the income that households and unincorporated business have left after satisfying all their obligations to the government. It equals personal income minus personal taxes and certain non-tax payments to government. ANSWER:? T POINTS:? 0 / 1
?5.? The purchase of new houses by households is included in the calculation of personal consumption expenditures of GDP. ANSWER:? F POINTS:? 0 / 1
Multiple Choice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. ?1.? When GDP falls, a. income and expenditure must both fall. b. income and expenditure can both rise. c. income must fall, but expenditure may rise or fall. d. expenditure must fall, but income may rise or fall. ANSWER:? A POINTS:? 0 / 1
?2.? Income equals expenditure because a. firms always pay out all their revenue as income to someone. b. each time a sale is made, there is a buyer and a seller. c. households own the factors of production used to generate incomes. d. All of the above are correct. ANSWER:? B POINTS:? 0 / 1
?3.? If a province makes the production and sale of illicit drugs legal, then GDP a. must increase. b. must decrease. c. wouldn't change. d. may increase or decrease. ANSWER:? A POINTS:? 0 / 1
?4.? When a government provides subsidies to encourage growth of small businesses, the subsidies would a. be included in GDP because they are invested by businesses. b. be included in GDP because they are a form of government spending. c. not be included in GDP because they are transfer payments. d. may or may not be included in GDP, depending on how the funds are used. ANSWER:? C POINTS:? 0 / 1
?5.? Diesel fuel is a. always considered a final good. b. counted as an intermediate good if a company uses it to provide transportation services. c. counted as a final good if a farmer uses it to run a tractor to grow crops. d. Both b and c are correct. ANSWER:? B POINTS:? 0 / 1
?6.? Gross domestic product a. is the market value of all final goods and services produced within a country in a given period (usually a year) b. is the income in the hands of individuals after deducting income taxes; income available to households to spend and save c. is the value of goods and services purchased by all levels of government— federal, provincial, and local—in a given period d. is the market value of all final goods and services produced by permanent residents of a nation in a given time period ANSWER:? A POINTS:? 0 / 1
?7.? Macroeconomics is that branch of economics that studies a. the conditions of individual markets b. the influence of governments on individual markets c. economy-wide phenomena d. only the private sector of the economy ANSWER:? C POINTS:? 0 / 1
?8.? Suppose that nominal GDP is $6,000 billion and real GDP is $3,000. What is the GDP price deflator? a. 125 b. 150 c. 200 d. 250 ANSWER:? C POINTS:? 0 / 1 ?9.? The purchase of final goods and services by households is called a. investment b. public sector expenditure c. consumption d. net exports ANSWER:? C POINTS:? 0 / 1
?10.? Investment is the purchase of capital equipment, inventories, and a. structures b. non-durable goods c. depreciation d. import investment ANSWER:? A POINTS:? 0 / 1
?11.? Transfer payments a. are included in GDP because they are forms of income b. are included in GDP because goods and services have been produced in the transfer c. are NOT included in the GDP because goods and services have not been produced in the transfer d. are included in GDP because they represent the production of transfers of goods and services to foreign countries ANSWER:? C POINTS:? 0 / 1
?12.? Which of the following would be considered consumption expenditure? a. The Smiths buy a home built in 1990. b. The federal government pays the salary of a captain in the Armed Forces. c. The Hostlers buy a new car that was manufactured in Germany. d. The government buys food for its armed forces. ANSWER:? C POINTS:? 0 / 1