中医术语翻译英译文新10-12-21
- 格式:doc
- 大小:72.00 KB
- 文档页数:8

中医术语中英文版中医,这门古老而神奇的学问,不仅在咱们中国有着深厚的根基,如今在国际上也越来越受关注啦。
这当中,中医术语的中英文对照就显得特别重要。
先来说说“气血”这个术语吧。
在中文里,气血可是关乎着一个人的健康和活力。
英文里呢,“气血”被翻译成“Qi and Blood”。
就像我有次去参加一个国际中医交流活动,碰到一位外国友人,他对中医特别感兴趣,尤其是气血这个概念。
他一脸疑惑地问我:“这 Qi and Blood 到底是咋回事呀?为啥对身体这么重要?”我就跟他解释说:“你看啊,这 Qi 就像是身体里的一股能量,让咱们有力气、有精神;而 Blood 呢,就是咱们身体里流动的那些红色的液体,给各个器官输送营养。
要是Qi 不足,人就容易累;Blood 不够,脸色就不好看。
”他听完恍然大悟,直点头说:“原来是这样,太神奇啦!”再说说“经络”,英文是“Meridians”。
有一回,我给一个外国学生上课,讲到经络的时候,他怎么都理解不了这看不见摸不着的东西怎么能影响健康。
我就拿了根绳子在桌上比划,跟他说:“你看,这绳子就好比经络,虽然你看不到里面的纤维,但它能把力量从这一头传到那一头。
经络也是这样,把身体各个部分连接起来,让信息和能量能顺利传递。
”他眼睛一下子亮了,好像找到了打开中医神秘大门的钥匙。
还有“阴阳”,英文是“Yin and Yang”。
记得有一次,我和几个外国朋友一起喝茶聊天,说到阴阳平衡。
他们一脸懵,我就指着桌上的茶杯和茶壶说:“这茶杯好比 Yin,茶壶好比 Yang。
茶壶里的水倒进茶杯,茶杯满了,这就是一种平衡。
身体里的 Yin 和 Yang 也是这样,要相互协调,人才健康。
”他们这才有点明白了阴阳的意思。
“穴位”这个术语,英文是“Acupoints”。
曾经有个外国朋友因为头疼来找我,我给他介绍穴位按摩。
我指着他头上的几个地方说:“这几个Acupoints 你按一按,能缓解头疼。
”他半信半疑地按了按,过了一会儿,惊喜地说:“哎呀,真的不疼了!”“中药”,对应的英文是“Chinese Herbal Medicine”。

最全中医术语英文大全LT[学科]中医①traditional Chinese medicine②traditional Chinese physician ①中医学的简称。
②本学科专业职业队伍。
中药Chinese materia medica 在中医理论指导下应用的药物。
包括中药材、中药饮片和中成药等。
中医学traditional Chinesemedicine 以中医药理论与实践经验为主体,研究人类生命活动中健康与疾病转化规律及其预防、诊断、治疗、康复和保健的综合性科学。
中药学Chinese materia medica 中药学科的统称。
研究中药基本理论和各种药材饮片、中成药的来源、采制、性能、功效、临床应用等知识的学科。
中医药traditional Chinese medicine and pharmacology本草:Materia medica中药:Chinese materia medica,Chinese medicinals(包括植物药、动物药、矿物药等)中草药:Chinese HerbalMedicine,Chinese medicinal herbs中药学:Chinese pharmaceutics药材:Medicinal substance(material)中西医结合integration of traditional and western medicine中医基础理论basic theory of traditional Chinese medicine中医诊断学diagnostics of traditional Chinese medicine方剂学 prescriptions of Chinese materia medica,Traditional ChineseMedical Formulae/ prescriptions中医内科学internal medicine of traditional Chinese medicine[阴阳]The Theory of Yin and Yang阴阳对立:Opposition of yin and yang阴阳制约:Restriction of /between yin and yang阴阳互根:Interdependence of yin and yang阴阳消长:Waxing and waning of yin and yang阴阳转化:Inter-transformation of yin and yang[五行学说]The Theory of Five Elements五行:water,fire,wood,metal,soil生:promote, generate, engender克:act, restrict, restrain乘:overact, over-restrict, over-restrain, subjugate, overwhelm侮:counteract, counter-restrict, counter-restrain, rebel[整体观念] concept of organic wholeness辩证法dialectics生长化收藏sprouting, growth,transformation,ripening,storage内外环境统一性the unity between the internal and external environments机体自身整体性the integrity of the body itself古代唯物论和辩证法classic Chinese materialism and dialectics矛盾统一the contradictory unity互相联系、相互影响related to each other and influence each other标本Biao (secondary aspect) and Ben (primary aspect)本质与现象nature and phenomena矛盾的普遍性和特殊性universality and speciality of contradictions寒者热之Cold disease should be treated by warm therapy热者寒之warm disease should be treated by cold therapy虚者补之deficiency syndrome should be treated by tonifying therapy实者泻之excess syndrome should be treated by purgation therapy治病必求其本Treatment of diseases must concentrate on the root cause同病异治treatment of the same disease with different therapeutic methods异病同治treatment of different diseases with the same therapeutic method[精气神]清阳为天The lucid Yang ascends to form the heaven浊阴为地The turbid Yin descends to constitute the earth气化Qi transformation升降出入ascending, descending, going out, coming in出入废则神机化灭,升降息则气立孤危。
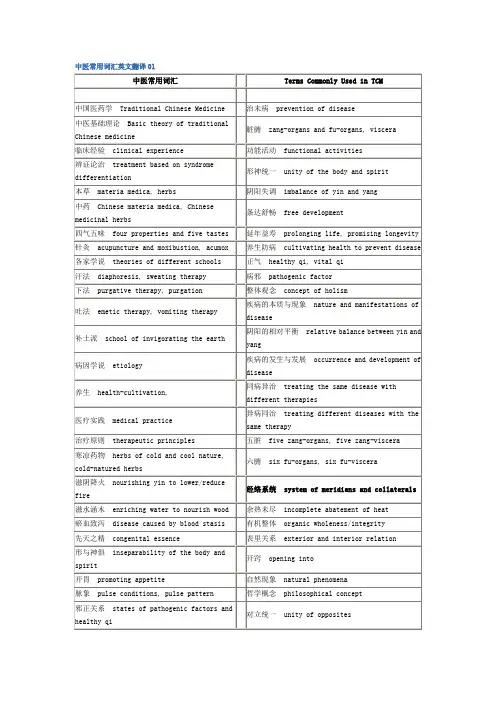
中医常用词汇英文翻译01中医英语常用词汇英文翻译02气化不利dysfunction of qi in transformation畏寒喜热aversion to cold and preference for heat 气分热盛excessive heat at qi phase气郁化热stagnation of qi transforming into heat温养脏腑warming and nourishing the viscera瘀血阻络blood stasis obstructing the collaterals清肺润燥clearing the lung and moistening dryness破瘀通经breaking blood stasis to promote menstruation 内伤头疼headache due to internal injury祛瘀eliminating stasis, expelling stasis逆传心包reverse transmission into the pericardium气不摄血failure of qi to check the blood宁心安神calming the heart and tranquilizing the mind 血液循行circulation of the blood惊悸不安palpitation due to fright气的运动形式the moving styles of qi血液生成不足insufficient production of the blood平肝止血soothing the liver to stop bleeding血液亏虚deficiency of the blood离经之血abnormal flow of the blood津液的形状、功能与分布form, function, and distribution of the body fluid气血生化之源source for the production and transformation of qi and blood脉细无力thin and weak pulse肌肤干燥dry skin肌肤甲错squamous and dry skin血脉调和流畅smooth and normal flow of the blood脏腑火热炽盛exuberant fire and heat in the viscera机体正常水液normal fluid inside the body热迫血分heat invading the blood phase气滞津停retention of fluid due to stagnation of qi寒凝气滞stagnation of cold and qi身倦乏力lassitude气滞血瘀qi stagnation and blood stasis伤津脱液consumption and loss of the body fluid津液的营养和滋润作用the nourishing and moistening functions of the body fluid津液的生成、输布和排泄production, distribution, and excretion of the body fluid腹痛拒按unpalpable abdominal pain脾的“散精”功能the function of the spleen to “dissipate essence”津液不足insufficiency of the body fluid水液停聚retention of water奇经八脉eight extraordinary vessels, eight extraordinary meridians胃的“游溢精气”the function of the stoma ch to “distribute essence”津液生化匮乏scanty production of the body fluid津液的代谢平衡the metabolic balance of the body fluid热盛耗伤津液consumption of the body fluid due to excessive heat风为百病之长wind is the leading factor in causing various diseases水液代谢障碍disturbance of water metabolism气随津脱exhaustion of qi due to loss of body fluid水湿困脾dampness encumbering the spleen濡养肌肤moistening and nourishing the skin湿邪内盛exuberance of interior dampness经脉之海sea of meridians脾虚水肿edema due to spleen deficiency滋养脏腑moistening and nourishing the viscera运行全身气血transporting qi and blood in the whole body 十二经别twelve branches of meridians联络脏腑肢节connecting with viscera, limbs and joints经别divergent meridians循行路线running route经气meridian qi十二正经twelve regular meridians十二皮部twelve skin areas, twelve skin regions/divisions 经隧阻滞blockage of meridians十二经筋twelve meridian tendons经穴meridian acupoints, Jing-River acupoint饮食劳倦improper diet and overstrain经络辨证syndrome differentiation according to meridians 风寒感冒common cold due to wind-cold经络感传meridian conduction, channel transmission湿热泄泻diarrhea due to damp-heat经络现象meridian phenomena内生五邪five endogenous pathogenic factors经络阻滞blockage of meridians风邪外袭pathogenic wind attacking the superficies舒筋活络relaxing tendons and activating collaterals游走性关节疼痛migratory arthralgias刺血疗法blood-pricking therapy阳气衰退decline of yang-qi外感六淫attacked by six climate pathogenic factors六淫six climatic evils感受寒邪attacked by pathogenic cold经闭发肿amenorrhea with edema虚实夹杂deficiency complicated with excess, asthenia complicated with sthenia邪正盛衰predominance or decline of pathogenic factors and healthy qi寒性凝滞cold tending to stagnate by nature病症的虚实变化asthenia and sthenia changes of disease 腠理闭塞blockage of muscular interstices机体的抗病能力body resistance经脉拘急收引contraction of tendons五心烦热feverish sensation over the five centers湿邪困脾pathogenic dampness encumbering the spleen五心five centers (palms, soles and chest)疾病的发生、发展与变化occurrence, development and changes of disease生津安神promoting the production of body fluid and tranquilizing the mind体质强弱conditions of constitution蓄血发黄jaundice due to blood accumulation气血功能紊乱dysfunction of qi and blood脾阳不振inactivation of spleen yang阴阳偏盛大relative predominance of yin and yang阴虚生内热yin deficiency generating interior heat五志过极extreme changes of emotions热极生风extreme heat producing wind精气夺则虚depletion of essence causing deficiency七情内伤internal injury due to emotional disorder阴阳互损mutual consumption of yin and yang饮食不节improper diet真热假寒true heat and false cold暴饮暴食craputence气机郁滞不畅stagnation of qi activity神昏谵语coma and delirium津液代谢失常disorder of fluid metabolism四诊合参combined use of the four diagnostic methods寒热往来alternate attacks of chill and fever精神活动mental activities津伤化燥consumption of fluid transforming into dryness 面部表情facial expressions风火胁痛hypochondriac pain due to wind-fire精充气足sufficient essence and abundant qi口眼歪斜wry mouth with distorted eyes, facial distortion 预后良好favorable prognosis湿浊内生endogenous turbid dampness表情淡漠apathetic facial expressions虚火上炎flaming of asthenia-fire精神不振dispiritedness邪气内陷internal invasion of pathogenic factors神志不清unconsciousness大肠热结retention of heat in the large intestine轻宣润燥dispersing lung qi and moistening dryness心脉瘀阻blood stasis in the heart vessels四肢抽搐convulsion of the limbs镜面舌mirror-like tongue脏腑辨证syndrome differentiation of viscera饥不欲食hunger without desire for food病位与病性location and nature of disease脉有胃气pulse with stomach qi表里同病disease involving both the exterior and interior 清里泄热clearing away heat in the interior风热眩晕vertigo due to wind-heat寒证化热cold syndrome transforming into heat syndrome寒热错杂simultaneous occurrence of cold and heat舌淡苔白而润滑light-colored tongue with white and slippery coating表邪入里invasion of the exterior pathogenic factors into the interior祛风解痉expelling wind to relieve convulsion外感胃脘痛stomachache due to exogenous pathogenic factors 医.学全.在.线网站恶寒与恶热aversion to cold and aversion to heat潮热盗汗tidal fever and night sweating口干唇裂dry mouth with cracked lips高热谵妄high fever with delirium脉数无力rapid and weak pulse和血止痛regulating blood to alleviate pain寒邪郁而化热stagnation of pathogenic cold changing into heat 寒因寒用treating pseudo-cold syndrome with herbs of cold nature未病先防preventing measures taken before the occurrence of disease热因热用treating pseudo-heat syndrome with herbs of heat nature补气健脾invigorating qi and strengthening the spleen塞因塞用treating obstructive syndrome with tonifying therapy补血养心enriching blood to nourish the heart发汗解表relieving exterior syndrome by diaphoresis水气凌心water attacking the heart风热乳蛾tonsillitis due to wind-heat心悸多梦palpitation and dreaminess痰饮咳嗽cough due to fluid retention血为气母the blood serving as the mother of qi实热蕴结accumulation of sthenia-heat调摄精神regulating mental states舒肝和胃soothing the liver and harmonizing the stomach 血脉流畅smooth circulation of blood清热泻火clearing away heat and reducing fire关节通利smooth movement of joints疏风泄热dispelling wind and reducing heat气机调畅free activity of qi行气消瘀activating qi to resolve stagnation益寿延年promoting longevity养血润肠nourishing the blood and moistening the intestine 治病求本treatment of disease must concentrate on the principle cause of disease因时、因地、因人制宜applying proper therapeutic measure in line with season, local conditions and individuality 急则治其标relieving the secondary symptoms first in treating acute disease缓则治其本relieving the primary symptoms in treating chronic disease通腑泄热purging fu-organs to eliminate heat燥湿化痰drying dampness and resolving phlegm标本兼治treatment focusing on relieving both the secondary and primary symptoms正虚邪实asthenia of healthy qi and sthenia of pathogenic factors痰湿壅肺accumulation of phlegm-dampness in the lung血枯经闭amenorrhea due to blood exhaustion祛虫消积removing parasites to eliminate accumulation 中医英语翻译常用词汇英汉对照03。
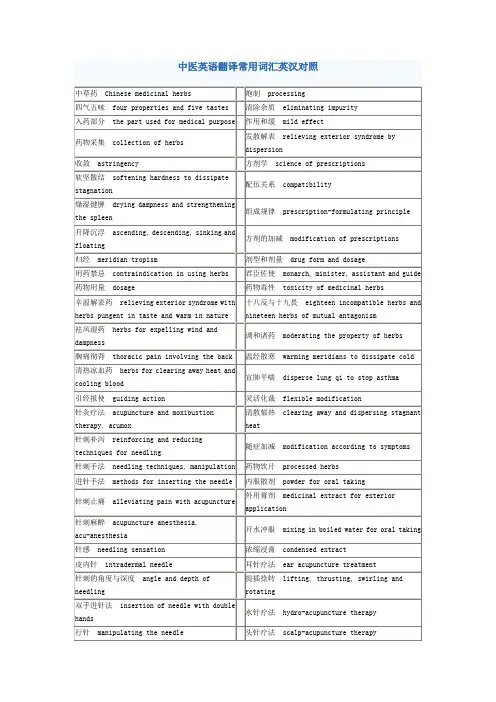

中医的专业术语英文翻译(2)中医的专业术语英文翻译阴阳离决separation of yin and yang阴阳转化transformation between yin and yang发热恶寒fever and aversion to cold头身疼痛headache and body pain感受湿邪the attack of dampness清热泄火cleaning away heat and reducing fire腠理muscular interstices水湿停滞retention of water and dampness气血运行circulation of qi and blood疾病的本质与现象:nature and manifestations of disease阴阳的相对平衡:relative balance between yin and yang疾病的发生与发展:occurrence and development of disease同病异治:treating the same disease with different therapies异病同治:treating different diseases with the same therapy1.中国医药学有数千年的历史,是中国人民长期同疾病作斗争的经验总结。
TCM, a medical system with a history of thousands years,has summarized the experience of the Chinese people accumulating in the struggle against diseases.2.中医学在古代唯物论和辩证法思想的影响和指导下,通过长期的医疗实践,逐步形成并发展为独特的医学理论体系。
Under the influence and guidance of classical Chinese materialism and dialectics,tradition Chinese medicine has eventually evolved into a medical system with unique theory through long term medical practice.3.中医学是研究人体生理病理以及疾病的诊断和防治的一门科学。

英语常见中医术语绪论introduction中医学traditional Chinese medicine (TCM)中医学理论体系theory system of TCM中医基础理论basic theory of TCM整体观念holism concept五脏一体观holism of five ogans形神一体观holism of body and spirit天人一体观holism of human beings and universe医学模式medical pattern辨证syndrome differentiation论治treatment variation疾病disease证候syndrome症状symptom体征physical sign辨病disease diagnosing同病异治different treament for the same disease异病同治the same treatment for the different disease第一章中医学的哲学基础Ancient philosophic basis of TCM精jing(as the world origin in ancient philosophy)气qi(as the world origin in the ancient philosophy) 精气学说theory of jingqi生命life中介medium气机 qi activity气化qi transformation感应induction水地说hypothesis of jing originating from water and earth 云气说hypothesis of qi originating from cloud and air气一元论monism of qi元气一元论monism of qi阴阳yinyang; yin and yang阴阳学说theory of yinyang阴阳对立inter-opposition between yin and yang阴阳互根inter-dependence between yin and yang阴阳消长wane and wax between yin and yang阴阳交感inter-induction between yin and yang阴阳互藏inter-containing between yin and yang阴阳转化inter-transformation between yin and yang阴阳自和reestablishment to yin-yang equilibrium阴阳平衡both yin and yang in equilibrium五行five elements五行学说theory of five elements五行相生inter-promotion of five elements五行相克inter-inhibition of five elements五行制化relationship of promotion and restriction of five elements五行相乘inter-invasion of five elements五行相侮reverse restriction in five elements五行胜复resistance of oppressed elements母病及子mother-organ diorder involving its child-organ子病及母child-organ disorder involving its mother-organ滋水涵木replenishing water to nourish wood培土生金reinforcing earth to generate metal益火补土tonifying fire to supplement earth金水相生mutual generation between metal and water抑木扶土inhibiting wood and strengthening earth培土治水cultivating earth to control water佐金平木assisting metal and calming wood泻南补北purging the south (fire) and nourishing the north (water)宏观观察obsevation on macroscopic level中和golden mean类比analogy第二章藏象Viscera state藏象viscera state藏象学说doctrine of viscera state脏腑viscera; zangfu organs五脏five zang organs心heart肺lung脾spleen肝liver肾kidney六腑six fu organs胆gall baldder胃stomach小肠small intestin大肠large intestine三焦tri-jiao; sanjiao膀胱urinary blader奇恒之腑extraordinary fu organs脑brain髓marrow骨bone脉vessel女子胞uterus满而不实full of essence without foodstuff实而不满full of foodstuff without essence心主神明heart controlling mental activities心主血脉heart controlling blood circulation心藏神heart storing spirit肺主气lun governing qi肺主呼吸之气lung governing respiratory qi肺主一身之气lung governing physical qi肺朝百脉convergence of vessels in the lung肺主行水lung governing water metabolism肺主治节lung governing coordinative activities of viscera肺为华盖lung being the canopy肺为娇脏lung being the delicate organ肺主宣发肃降lung controlling dispersing outward and inwards气门pore后天之本source of acquired constitution脾主运化spleen governing transportation and transformation脾气主升spleen governing ascending脾主统血spleen governing blood脾喜燥恶湿spleen preferring dryness to dampness肝主疏泄liver govering regulating肝主藏血liver storing blood肝体因而用阳liver of yin nature with yang functioning肝为刚脏liver being the resolute viscera罢极之本source of endurance先天之本congenital foundation肾藏精kidney storing essence肾阴kidney yin肾阳kidney yang肾精kidney essence肾气kidney qi天癸tiangui肾主水液kidney governing water肾主纳气kidney receiving respiratory qi命门vital gate七冲门seven important portals胆主决断gallbladder governing deciding胃主通降stomach managing downward transportation of food喜润恶燥preferring moisture to dryness受盛化物containing and digesting泌别清浊separating the clear from the turbid上焦如雾upper-jiao resembling mist中焦如沤middle-jiao resembling fermenter下焦如渎lower-jiao rezembling drainage元神之府mentality house脑为髓海brain being the marrow sea心肾相交coordination between heart and kidney水火相济regulation between water and fire肺为气之主lung being the governor of qi肾为气之根kidney being the root of qi肝肾同源liver and kidney sharing the same origin乙癸同源Yi and Gui sharing the same origin (liver and kidney sharing the same origin)精血同源essence and blood sharing the ame origin藏泄互用interdependence between storing and discharging纳运相得inter-promotion between containing and digestion 升降相因inerdependence between ascending and descending燥湿相济interdependence between drying and moistening 胃润喜恶燥stomach preferring moisture to dryness第三章精气血津液神Essence, qi, blood, body fluid and,spirit气qi元气primordial qi元阴primordial yin元阳primordial yang气机qi activity气化qi transformation气海qi sea卫气defensive qi宗气thoracic qi营气nutrient qi原气primordial qi气能生血qi promoting blood production气为血之帅qi being the governor of blood气主升之qi promoting气能生津qi promoting body fluid production气能行血qi promtoting blood circulation血为气之母blood being the mother of qi血主濡之blood nourishing气能行津qi promoting body fluid circulation气能摄血qi governing blood津能载气body fluid conveying qi血能载气blood conveying qi气能摄津qi governing body fluid津停气滞body fluid retention causing qi stagnation血blood精essence神spirit精能化气essence transforming into qi先天之精congenital essence后天之精acquired essence水谷之精foodstuff essence气能生精qi promoting esssence production津血同源body fluid and blood sharing the same source血汗同源bloood and sweat sharing the same source膻中danzhong虚里heart apex津液body fluid第四章经络Meridians and collaterals经络meridians and collaterals经络学说theory of meridian and collateral; meridian doctrine 经气meridian qi经脉meridian; channel络脉collateral十二经脉twelve meridians十二正经twelve regular channels手太阴肺经lung channel of hand taiyin(L)手阳明大肠经large intestine channel of hand yangming(LI) 足阳明胃经stomach channel of foot yangming(St)足太阴脾经spleen channel of foot tayin(Sp)手少阴心经heart channel of hand shaoyin(H)手太阳小肠经small intestine channel of hand taiyang(SI) 足太阳膀胱经urinary bladder channel of foot taiyang(U足少阴肾经kidney channel of foot shaoyin(K)手厥阴心包经pericadium channel of hand jueyin(P)手少阳三焦经tri-jiao channel of hand shaoyang(TJ)足少阳胆经gall bladder channel of foot shaoyang(G足厥阴肝经liver channel of foot jueyin(Liv)奇经八脉eight extra channels督脉governor vesesl; Du meridian任脉conception vessel; Ren meridian冲脉flush vessel; Chong meridian带脉belt vessel; Dai meridian阴跷脉yinqiao meridian阳跷脉yangqiao meridian阴维脉yinwei meridian阳维脉yangwei meridan十二经别twelve divergent channels十五别络fifteen large collaterals孙络minute collateral浮络superficial collateral十二经筋twelve meridian musculatures十二皮部twelve cutaneous areas阳脉之海sea of yang meridian (governor vessel)阴脉之海sea of yin meridian (conception vessel)任主胞胎conception vessel govening uterus and gestation 十二经脉之海sea of the twelve meridians (flush vessel)血海blood sea (flush vessel)第四章体质Body constitution体质body constitution形神合一harmonization between soma and spirit体格physique体型body type人格personality气质temperament性格character素质heredity理想体质ideal body constitutions病势disease tendency质化(从化)property transformation第六章病因Pathogeny病因pathogeny病因学说etiology辨症求因pathogeny differentiation from symptoms and signs 六淫six exopathogens六气six climates六邪six exopathogen*伤寒**ogenous febrile disease中寒cold stroke风性轻扬wind tending to drift善行数变migrant and variable风性主动wind tending to migrate百病之长guide of various disease寒性凝滞cold tending to coagulate and stagnate寒性收引cold tending to contract寒则气收cold retarding qi circulation暑性升散summer heat tending to ascend and disperse炅则气泄heat causing qi exhaustion暑多夹湿summer heat usually accompanied with dampness 湿性重浊dampness being heavy and turbid湿性黏滞dampneee being viscous and lingering湿性趋下sampness tending to descend燥性干涩dryness tending to desiccate火性趋上fire tending to flare up火易生风动血fire causing wind and bleeding疠气epidemic pathogens瘟疫pestilence七情seven emotions七情内伤inernal injuries caused by seven emotions怒则气上rage causing qi to flow upwards喜则气缓joy causing qi slack悲则气消grief causing qi depression思则气结contemplation causing qi stagnation惊则气乱terror causing qi disorder恐则气下fear causing qi collapse饮食不节improper diet饮食不洁dirty diet饮食偏嗜diet preference形劳physical overstrain劳则气耗overstrain causing qi exhausetion心劳heart overstrain神劳psychological ovrestrain肾劳kidney overstrain房劳***ual overstrain有形之痰visible phlegm无形之痰invisible phlegm瘀血blood stasis结石calculus药邪medicine abuse医过therapist fault胎弱congenital deficiency胎毒fetus toxin第七章发病Invasion正气healthy qi邪气pathogenic factors遗传病genetic disease感邪即发acute onset after affected徐发chronic onset伏而后发latent onset继发secondary onset合病simultaneous onset并病following onset复病recurrence后遗症sequela重感致复re-affected causing recurrence 食复diet recurrence劳复overstrain recurrence药复medicine recurrence情志致复emotion recurrence第八章病机Pathogenesis病机pathogenesis病机学pathology病机层次pathological level基本病机basic pathogenesis实sthenia实证sthenic syndrome虚asthenia虚证asthenia syndrome虚实错杂mixture of asthenia and sthenia虚中夹实asthenia with sthenia实中夹虚sthenia with asthenia虚实转化inter-transformation between asthenia and sthenia 由实转虚sthenia transforming into asthenia因虚致实sthenia symptoms caused by asthenia虚实真假pseudo or true manifestation of asthenia and sthenia真实假虚sthenia with pseudo asthenia大实有羸状excessive sthenia manifesting a* **cessive asthenia真虚假实asthenia with pseudo sthenia至虚有盛候excessive asthenia manifesting a* **cessive sthenia正胜邪退healthy qi expelling pathogen邪去正虚pathogen retreating with asthenia healthy qi邪盛正衰prosperous pathogen with asthenia healthy qi邪正相持struggle between healthy qi and pathogen正虚邪恋asthenic healthy qi with pathogen lingering阴阳失调imbalance between yin and yang阴阳偏盛excess of yin or yang阳偏盛yang excess阳盛yang excess阴偏盛yin excess阴盛yin excess阴阳偏衰deficiency of yin or yang阳偏衰yang deficiency阳虚yang deficiency阴偏衰yin dificiency阴虚yin deficiency阴阳互损inter-impairment between yin and yang 阴损及阳yin impairment involving yang阳损及阴yang impairment involving yin阴阳格拒repellence between yin and yang阴盛格阳predominant yin rejecting yang格阳rejecting yang阳盛格阴predominant yang rejecting yin格阴rejecting yin阴阳亡失exhaustion of yin or yang亡阴yin exhaustion亡阳阳yang exhaustion精虚essence asthenia精瘀essence stasis气虚qi asthenia气机失调disorder of qi activity气滞qi stagnation气逆qi adverseness气陷qi collapse上气不足qi failing to transport upward中气下陷qi failing to lift气闭qi blockage气脱qi exhaustion血虚blood asthenia血瘀blood stasis出血haemorrhage血寒blood cold血热blood heat精气两虚asthenia of essence and qi精血不足asthenia of essence and blood气滞精瘀qi stagnation and essence stasis血瘀精阻blood stasis and essence obstruction气滞血瘀qi stagnation and blood stasis气虚血瘀qi asthenia causing blood stasis气不摄血qi failing to control blood气随血脱qi exhaustion resulting from hemorrhage 气血两虚asthenia of qi and blood津液不足body fluid asthenia伤津body fluid impairment脱液body fluid exhausetion津液输布障碍dysfunction of body fluid distribution 津液排泄障碍dysfuncion of body fluid excretion水停气阻water retention causing qi stagnation气随津脱qi exhaustion resulting from body fluid loss 津枯血燥body fluid depletion causing blood stasis 津亏血瘀body fluid depletion causing blood stasis 血瘀水停blood stasis causing water retention内风endogenous wind风气内动disturbance of endogenous wind肝风liver wind肝阳化风liver yang causing wind热极生风extreme heat causing wind阴虚风动yin asthenia causing wind血虚生风blood asthenia causing wind寒从中生cold originating from interior内寒endogenous cold湿浊内生dampness originating from interior内湿endogenous dampness津伤化燥body fluid impairment causing dryness内燥endogenous dryness火热内生heat or fire originatin from interior内热endogenous heat内火endogenous fire少火junior fire壮火excessive fire阳亢化火excessive yang causing fire气有余便是火excessive qi causing fire邪郁化火pathogen accumulation causing fire五志化火five emotions causing fire阴虚火旺yin asthenia causing fire疾病传变pathogenesis transmission病位传变focus transmission表里传变transmission between interior and exterior表病入里exogenous disease invading interior里病出表endogenous disease retreating to exterior半表半里semi-interior and semi-exterior直中direct attack六经传变six merdians transmission三焦传变tri-jiao transmission卫气营血传变transmission of wei, qi, ying and xue顺传sequential transmission逆传adverse transmission脏腑传变viscera transmission脏与脏的传变transmission among zang organs脏与腑的传变transmission among zang organs and fu organs 腑与腑的传变transmission among fu organs形脏内外传变transmission between interior and exterior寒热转化inter-transformation between cold and heat 寒化热cold transforming into heat热化寒heat transforming into cold第九章防治原则Principle of prevention and therapy预防prevention养生health promotion未病先防prevention before disease onset既病防变preventing disease from exacerbating治则therapeutic principle治法therapeutic method治病求本treating disease from the root标本branch and root正治routine treatment反治contrary treatment寒者热之cold treated with warm热者寒之heat treated with cool虚则补之asthenia requiring tonification实则泻之sthenia requiring purgation热因热用heat treated with warm寒因寒用cold treated with cool通因通用diarrhea treated with purgation塞因塞用obstruction treated with tonification扶正strengthening healthy qi祛邪eliminating pathogens因时制宜climate-concerned treatment因地制宜environment-concerned treatment因人制宜individuality-concerned treatment中医诊断英语阴阳五行1 五行 fie phases2 阴阳 yin and yang;yin-yang3 五志 fie minds4 五味 fie flaors5 辨证论治 syndrome differentiation and treatment;identify patterns and determine treatment脏腑6 脏腑 zang-fu organs; bowels and iscera7 心藏神 The heart stores the spirit.8 神明 spirit; mind; mental actiity9 肺主宣发 The lung goerns diffusion.10 肺主肃降 The lung goerns descent.The lung goerns purification and descent.11 通调水道 regulate the waterways12 肺主行水 The lung goerns the moement of water13 脾主运化The spleen goerns transportation and transformation.14 脾为后天之本The spleen is the root of acquired constitution.15 脾主升清 The spleen goerns ascent of the clear.16 脾统血 The spleen controls the blood.17 脾恶湿 The spleen is aerse to dampness.18 肝主疏泄 The lier goerns free coursing.19 肝主升发 The lier goerns ascent and dispersion20 肝主身之筋膜The lier goerns the body’s sinews.21 命门①ming men; life gate ②ming men (DU 4)22 肾精 kidney essence23 天癸 tian gui24 肾为先天之本The kidney is the root of congenital constitution.25 泌别清浊 separation of the clear and turbid26 三焦 triple burner27 心肾不交 failure of the heart and kidney to communicate形体官窍28 筋 sinew29 脉①essel;②pulse30 七窍 seen orifices气血津液精神31 气机 qi dynamic32 正气 right qi33 邪气 eil qi34气分 qi leel35 原气 source qi36 元气 original qi37 宗气 gathering qi38 中气 middle qi39 卫气 defensie qi40 营气 nutritie qi41 营血 nutrient-blood42 津液 fluid43 精①essence ②semen44 精气 essential qi45 神 spirit46 气为血帅 qi as commander of blood经络47 经络 channels and collaterals48 经脉 channel49 穴位 acupuncture point; point50 背俞穴 back-shu point51 耳穴 ear point; auricular point52 手太阴肺经 The hand greater yin lung channel; LU (WHO)53 手阳明大肠经The hand yang brightness large intestine channel; LI (WHO)54 足阳明胃经 The foot yang brightness stomach channel; ST (WHO)55 足太阴脾经 The foot greater yin spleen channel; SP (WHO)56 手少阴心经 The hand lesser yin heart channel; HT (WHO)57 手太阳小肠经The hand greater yang small intestine channel; SI (WHO)58 足太阳膀胱经 The foot greater yang bladder channel; BL (WHO)59 足少阴肾经 The foot lesser yin kidney channel; KI (WHO)60 手厥阴心包经 The hand reerting yin pericardium channel; PC (WHO)61 手少阳三焦经 The hand lesser yang triple burner channel; TB (WHO)62 足少阳胆经 The foot lesser yang gallbladder channel; GB (WHO)63 足厥阴肝经 The foot reerting yin lier channel; L (WHO)病因64 病因 etiology;etiologic factor;cause of disease65 实邪 excess eil66 表邪 exterior eil67 外感 external contraction68 七情 seen affects69 痰 phlegm70 饮①rheum ;fluid retention ②drink③ decoction71 瘀血 static blood72 血瘀 blood stasis病机73 病机 pathomechanism74 虚 deficiency75 实 excess76 亏虚,亏损 depletion77 不足 insufficient78 阴虚火旺 hyperactiity of fire due to yin deficiency79 气滞 qi stagnation80 气郁 qi constraint81 气逆 qi counterflow82 气陷 sinking of qi83 气闭 qi blockage84 气滞血瘀 qi stagnation and blood stasis85 内风 internal wind86 寒凝气滞 qi stagnation due to congealing cold87 心火上扰 flaring up of heart fire88 痰火扰心 phlegm-fire disturbing the heart89 痰蒙心包 phlegm clouding the pericardium90 痰浊阻肺 turbid phlegm obstructing the lung91 脾虚湿困 spleen deficiency leading to damp encumbrance ; damp encumbrance due to spleen deficiency92 脾失健运 spleen failing to transform and transport; failure of the spleen to transform and transport93 肝阳上亢 ascendant hyperactiity of lier yang94 肝郁 lier constraint95 肝气郁结 binding constraint of lier qi96 肝风内动 lier wind stirring internally97 肾不纳气 kidney failing to grasp qi98 胃纳呆滞 poor appetite and digestion99 热入心包 heat entering the pericardium诊法100 四诊 four examinations101 舌象 tongue manifestation; tongue appearance 102 舌神 tongue spirit103 舌色 tongue color104 淡红舌 light red tongue105 淡白舌 pale tongue106 红舌 red tongue107 绛舌 crimson tongue108 紫舌 purple tongue109 青舌 blue tongue110 舌形 tongue shape111 舌质 tongue body112 胖大舌 enlarged tongue113 齿痕舌 tooth-marked tongue114 肿胀舌 swollen tongue115 瘦薄舌 thin tongue116 点刺舌 spotted tongue117 芒刺舌 prickly tongue118 裂纹舌 cracked tongue119 (舌上)瘀斑 stasis maculae120 (舌上)瘀点 stasis spots121 舌态 tongue condition122 痿软舌 flaccid tongue123 强硬舌 stiff tongue124 吐舌 protruding tongue125 弄舌 waggling tongue126 舌苔 tongue coating127 厚苔 thick coating128 薄苔 thin coating129 润苔 moist coating130 燥苔 dry coating131 糙苔 rough coating132 燥裂苔 dry cracked coating133 瓣晕苔 petalled coating134 滑苔 glossy coating135 腻苔 greasy coating136 腐苔 curd-like coating137 粘腻苔 sticky greasy coating138 剥苔 peeled coating139 类剥苔 peeled-like coating140 地图舌 geographic tongue141 镜面舌 mirror-like coating142 无根苔 rootless coating143 有根苔 rooted coating144 苔色 color of coating145 脉诊 pulse examination; pulse diagnosis 146 切脉,把脉 pulse taking147 平脉 normal pulse148 寸口 radial pulse; cun kou149 寸关尺 cun, guan and chi; inch, bar and cubit 150 浮脉 floating pulse151 散脉 scattered pulse152 芤脉 hollow pulse153 伏脉 hidden pulse154 牢脉 firm pulse155 迟脉 slow pulse156 缓脉 moderate pulse157 数脉 rapid pulse158 疾脉 racing pulse159 沉脉 deep pulse160 细脉 thready pulse161 长脉 long pulse162 短脉 short pulse163 虚脉 deficient pulse164 实脉 excess pulse165 弱脉 weak pulse166 微脉 faint pulse167 洪脉 surging pulse168 滑脉 slippery pulse169 涩脉 rough pulse170 弦脉 wiry pulse171 动脉 bouncing pulse172 紧脉 tight pulse173 革脉 drumskin pulse174 濡脉 soggy pulse175 歇止脉 pausing pulse176 结脉 knotted pulse; irregularly intermittent pulse 177 代脉 intermittent pulse ; regularly intermittent pulse 178 促脉 hasty pulse; rapid-irregular pulse179 恶寒 aersion to cold180 畏寒 fear to cold181 潮热 tidal feer182 五心烦热 exing heat in the fie hearts183 骨蒸 steaming bone184 寒战 shiering185 性 nature186 味 flaour187 性味 nature and flaour188 四气 four nature189 寒 cold190 热 hot191 温 warm192 凉 cool193 平 neutral194 五味 fie flaours195 辛 acrid196 甘 sweet197 酸 sour198 苦 bitter199 咸 salty200 淡 bland201 涩 astringent202 升降浮沉 ascending and descending, floating and sinking 203 归经 channel entered204 功能 actions205 主治 indications206 用量 dosage207 使用注意 caution208 禁忌症 contraindication表寒里热 biao han li re exterior cold ,interior heat表热里寒 biao re li han exterior heat,interior cold冲任不补 chong ren bu bu chong&ren not securing任不调 chong ren bu tiao chong&ren not regulated冲任失调chong ren shi tiao loss of regulation of the chong&ren冲任损伤chong ren sun shang chong&ren detriment and damage大肠寒结 da chang han jie large intestine cold binding大肠湿热 da chang shi re large intestine damp heat大肠虚 da chang xu large intestine vacuity大肠虚寒 da chang xu han large intestine vacuity cold大肠液亏 da chang ye kui large intestine humor depletion胆热 dan re gallbladder heat胆虚 dan xu gallbladder vacuity肺火 fei huo lung fire肺津不布 fei jin bu bu lung fluids not distributed肺络损伤fei luo sun shang lung network vessel detriment&damage肺气不利 fei qi bu li inhibition of the lung qi肺气不宣 fei qi bu xuan lung qi not diffusing肺气虚 fei qi xu lung qi vacuity肺热 fei re lung heat肺肾两虚 fei shen liang xu lung-kidney dual vacuity肺肾气虚 fei shen qi xu lung-kidney qi vacuity肺肾阴虚 fei shen yin xu lung-kidney yin vacuity肺实 fei shi lung repletion肺失清肃 fei shi qing su lung loss of clearing &depurating肺虚 fei xu lung vacuity肺阴虚 fei yin xu lung yin vacuity肺阴虚燥 feiyin xu zao lung yin vacuity dryness肺燥 fei zao lung dryness伏热在里 fu re zai li deep-lying heat in the interior肝胆气虚 gan dan qi xu liver-gallbladder qi vacuity肝胆湿热 gan dan shi re liver-gallbladder damp heat肝风内动 gan feng nei dong liver wind stirring internally肝寒 gan han liver cold肝火 gan huo liver fire肝火上炎 gan huo shang yan liver fire flaring upward肝气犯脾 gan qi fan pi liver qi assails the spleen肝气犯胃 fan qi fan wei liver qi assails the stomach肝气上逆 gan qi shang ni liver qi counterflowing upward肝热 gan re liver fire肝肾亏损 gan shen kui sun liver-kidney depletion&detriment 肝肾两虚 gan shen liang xu liver-kidney dual vacuity肝血虚 gan xue xu liver blood vacuity肝阳上亢 gang yang shang kang ascendant hyperactivity of liver yang肝阴虚 gan yin xu liver yin vacuity肝郁脾虚 gan yu pi xu liver depression,spleen vacuity肝郁气滞 gan yu qi zhi liver depression qi stagnation寒极生热 han ji sheng re extreme cold engenders heat寒凝肝脉 han ning gan mai cold congelation in the liver vessel 寒凝气滞 han ning qi zhi cold congelation qi stagnation寒痰阻肺 han tan zu fei cold phlegm obstructing the lungs久热伤阴 jiu re shang yin enduring heat damages yin龙火内燔 long huo nei fan dragon fire internally blazing命门火旺 ming men huo wang life gate fire effulgence膀胱气闭 pang guang qi bi bladder qi block膀胱湿热 pang guang shi re bladder damp heat膀胱虚寒 pang gang xu han bladder vacuity cold脬气不固 pao qi bu gu bladder qi not securing脾不统血pi bu tong xue spleen not managing(i.e.,restraining)the blood脾肺两虚 pi fei liang xu spleen-lung dual vacuity脾气不升 pi qi bu sheng spleen qi not upbearing脾气虚 pi qu xu spleen qi vacuity脾热 pi re spleen heat脾肾阳虚 pi shen yang xu spleen-kidney yang vacuity脾失健运pi shi jian yun spleen loss of fortification &movement脾失运化pi shi yun hua spleen loss of movement&transformation脾胃湿热 pi wei shi re spleen-stomach damp heat脾胃虚弱 pi we xu ruo spleen-stomach vacuity weakness脾虚 pi xu spleen vacuity脾虚湿困 pi xu shi kun spleen vacuity,damp encumbrance脾阳虚 pi yang xu spleen yang vacuity脾阴虚 pi yin xu spleen yin vacuiry气化不利 qi hua bu li inhibition of qi transformation气机不利 qi ji bu li inhibition of the qi mechanism气髓血脱 qi sui xue tuo qi follows blood desertion气虚中满 qi xu zhong man qi vacuity central fullness气血两虚 qi xue liang xu qi&blood dual vacuity气血失调 qi xue shi tiao qi&blood loss of regulation气阴两虚 qi yin liang xu qi &yin dual vacuiry气滞血瘀 qi zhi xue yu qi stagnation &blood stasis热伏冲任 re fu chong ren heat deep-lying or hidden in the chong &ren热极生寒 re ji sheng han extreme heat engenders cold热结膀胱 re jie pang guang heat bound in the bladder热入心包 re ru xin bao heat entering the pericardium热入血分 re ru xue fen heat entering the blood phase热入血室 re ru xin shi heat entering the blood chamber热伤肺络 re shang fei luo heat damaging the lung network vessels热伤筋脉re shang jin mai heat damaging the sinews and vessles(or sinew vessels)热伤神明re shang shen ming heat damaging the spirit brightness热盛气分 re sheng qi fen heat exuberance in the qi division 热邪阻肺 re xie zu fei heat evils obstructing the lungs热灼肾阴 re zhuo shen yin heat buring kidney yin三蕉湿热 san jiao shi re triple burner damp heat三蕉虚寒 san jiao xu han triple burner vacuity cold上寒下热 shang han xia re above cold ,below heat上热下寒 shang re xia han above heat ,below cold伤损及下 shang sun ji xia detriment above reaching below少阴寒化 shao yin han hua shao yin cold transformation少阴热化 shao yin re hua shao yin heat transformation肾气不固 shen qi bu gu kidney qi not securing肾虚 shen xu kidney vacuity肾溆水泛 shen xu shui fan kidney vacuity,water flooding肾阳虚 shen yang xu kidney yang vacuity肾阳虚衰 shen yang xu shuai kidney yang vacuity and debility 肾阴虚 shen yin xu kidney yin vacuity升降失常sheng jiang shi chang upbearing&downbearing lose their normalcy湿热内熏 shi re nei xun dampness&heat internally brewing 湿热小蕉 shi re xiao jiao damp heat in the lower burner湿热瘀滞 shi re yu zhi damp heat stasis&stagnation湿胜阳微shi sheng yang wei dampness prevailing ,yang becoming slight湿郁热伏 shi yu re fu damp depression,heat deeply lying食滞胃腕shi zhi wei wan food stagnating in the stomach venter湿阻气分 shi zu qi fen dampness obstructing the qi division 湿阻中蕉 shi zu zhong jiao dampness obstructing the middle burner水不化气 shui bu hua qi water not transforming the qi痰火扰心 tan huo rao xin phlegm fire harassing the heart痰密心窍 tan mi xin qiao phlegm confounding ghe portals of the heart痰热阻肺 tan re zu fei phlegm heat obstructs the lungs痰湿阻肺tan shi zu fei phlegm dampness obstructing the lungs痰阻肺络 tan zu fei luo phlegm obstructing the lung network vessels胃寒 wei han stomach cold胃火上升 we huo shang sheng stomach fire borne upward胃气不固 wei qi bu gu defensive qi not securing胃气不和 wei qi bu he stomach qi disharmony胃气虚 wei qi xu stomach qi vacuity胃热 wei re stomach heat胃热壅盛wei re yong sheng stomach heat congesting&exuberant胃失和降wei shi he jiang stomach loss of harmony&downbearing胃虚 wei xu stomach vacuity胃阴虚 wei yin xu stomach yin vacuity温邪犯肺 wen xie fan fei warm evils assailing the lungs温邪上受 wen xie shang shou warm evils affect above下损及上 xia sun ji shang lower detriment reaches above相火妄动xiang huo wang dong ministerial fire frenetically stirring小肠湿热 xiao chang shi re small intestine damp heat小肠虚寒 xiao chang xu han small intestine vacuity cold邪留三蕉 xie liu san jiao evils retained in the three burners心火亢盛xin huo kang sheng heart fire hyperactivity &exuberance心火内炽 xin huo nei chi heart fire blazing internally心火上炎 xin huo shang yan heart fire flares upward心脾两虚 xin pi liang xu heart-spleen dual vacuity心气不宁 xin qi bu ning heart qi not quiet心气不绶 xin qi bu shou heart qi not restraining心肾不交 xin shen bu jiao heart&kidneys not interacting心虚胆怯 xin xu dan qie heart vacuity ,gallbladder timidity心血虚 xin xue xu heart blood vacuity心阳虚 xin yang xu heart yang vacuity心阴虚 xin yin xu heart yin vacuity虚风内动 xu feng nei dong vacuity wind stirring internally虚热上炎 xu re shang yan vacuity heat flares upward虚阳上浮 xu yang shang fu vacuous yang floats upward血不归经 xue bu gui jing blood not returning to the channels 血分热毒 xue fen re du blood division heat toxins血分瘀热 xue fen yu re blood division static heat血随气陷 xue sui qi xian blood follows qi fall阳盛阴伤yang sheng yin shang yang exuberance damages yin阴虚肺燥 yin xu fei zao yin vacuity lung dryness阴虚阳亢 yin xu yang kang yin vacuity yang hyperactivity。

中医常用名词术语英译与中医保健知识(宣传)Commonly Used Terminologies of Chinese Medicine&Health Preservationof Chinese Medicine(Pamphlet)杭州市外文学会编印浙江中医药大学外国语学院By Hangzhou Association of ForeignLanguages and Literaturesand College of Foreign Languages,Zhejiang Chinese Medical University2010.10杭州市外文学会&浙江中医药大学外国语学院联合编制Compiled by Hangzhou Association of Foreign Languages and Literatures And College of ForeignLanguages, Zhejiang Chinese Medical University- 1 -内 容CONTENTS中医常用名词术语英译 2-12页 Commonly Used Terminologiesof Chinese Medicine Page 2-12中医的四季养生 13-19页 Health Preservation in FourSeasons Based on Chinese Medicine Page 13-19一天里的“四季”养生 20页 Health Preservationin Four-Season a Day Page 20杭州市外文学会&浙江中医药大学外国语学院联合编制Compiled by Hangzhou Association of Foreign Languages and Literatures And College of Foreign Languages, Zhejiang Chinese Medical University- 2 -杭州市外文学会&浙江中医药大学外国语学院联合编制Compiled by Hangzhou Association of Foreign Languages and Literatures And College of Foreign Languages, Zhejiang Chinese Medical University- 12 -杭州市外文学会&浙江中医药大学外国语学院联合编制Compiled by Hangzhou Association of Foreign Languages and Literatures And College of Foreign Languages, Zhejiang Chinese Medical University- 13 -。

中医英文词汇1. 中医学(Traditional Chinese Medicine, TCM)2. 经络学(Meridianology)3. 气(Qi)4. 血(Xue)5. 阴阳(Yin-Yang)6. 五行(Five Elements)7. 经络(Meridian)8. 穴位(Acupoint)9. 针灸(Acupuncture)10. 拔罐疗法(Cupping Therapy)11. 刮痧疗法(Gua Sha Therapy)12. 中草药(Chinese Herbal Medicine)13. 草药学(Herbology)14. 方剂(Prescription)15. 药膳(Medicated Diet)16. 气功(Qigong)17. 太极拳(Tai Chi)18. 推拿按摩(Tui Na Massage)19. 中医诊断(TCM Diagnosis)20. 脉诊(Pulse Diagnosis)21. 舌诊(Tongue Diagnosis)22. 中医治疗(TCM Treatment)23. 经络按摩(Meridian Massage)24. 中医保健(TCM Wellness)25. 中医病因学(TCM Pathology)26. 中风(Stroke)27. 心血管疾病(Cardiovascular Disease)28. 消化系统疾病(Digestive System Disorders)29. 呼吸系统疾病(Respiratory System Disorders)30. 神经系统疾病(Neurological Disorders)31. 内分泌系统疾病(Endocrine Disorders)32. 妇科疾病(Gynecological Disorders)33. 男科疾病(Andrology)34. 儿科疾病(Pediatrics)35. 皮肤病(Dermatological Disorders)36. 风湿病(Rheumatological Disorders)37. 肿瘤学(Oncology)38. 精神疾病(Psychiatric Disorders)39. 疼痛管理(Pain Management)40. 康复医学(Rehabilitation Medicine)41. 中医养生(TCM Health Preservation)42. 养生学(Health Cultivation)43. 中医美容(TCM Beauty Therapy)44. 中医理疗(TCM Physical Therapy)45. 中医药化学(TCM Medicinal Chemistry)46. 中医药制剂学(TCM Pharmaceutical Preparations)47. 中医药法学(TCM Jurisprudence)48. 中医药教育(TCM Education)49. 中医药研究(TCM Research)50. 中医药文化(TCM Culture)。

中医相关英语词汇中医是我们的文化遗产,在外国也是很有名的。
下面是我整理的中医相关英语词汇,仅供参照。
中国医药学Traditional Chinese Medicine治未病prevention of disease脏腑zang-organs and fu-organs, viscera中医基础理论Basic theory of traditionalChinese medicine临床经验clinical experience功能活动functional activities形神统一unity of the body and spirit辨证论治treatment based on syndromedifferentiation本草materia medica, herbs阴阳失调imbalance of yin and yang中药Chinese materia medica, Chinese条达舒畅free developmentmedicinal herbs四气五味four properties and five tastes延年益寿prolonging life, promising longevity针灸acupuncture and moxibustion, acumox养生防病cultivating health to prevent disease各家学说theories of different schools正气healthy qi, vital qi汗法diaphoresis, sweating therapy病邪pathogenic factor下法purgative therapy, purgation整体观念concept of holism3中医英语词汇有哪些生理功能physiological functions阳消阴长yang waning and yin waxing 病理变化pathological changes阴胜则阳病predominance of yin leading todisorder of yang临床诊断clinical diagnosis阴胜则阳病an excess of yin leads to deficiency of yang 阳胜生外热exuberance of yang leading to exterior heat 阳胜则热predominance of yang generatingheat阳中求阴obtaining yang from yin寒极生热extreme cold generating heat 绝对偏盛absolute predominance热极生寒extreme heat generating cold 阳虚则寒yang deficiency leading to cold阳损及阴impairment of yang involving yin 阴阳俱损simultaneous consumption of yin andyang阴液不够insufficiency of yin-fluid 阴阳两虚simultaneous deficiency of both yin andyang病机总纲general principle of pathogenesis 阳虚发热fever due to yang deficiency病机pathomechanism, pathologicalmechanism阴阳自和natural harmony between yin and yang 阴阳胜复alternative predominance of yinand yang木乘土the wood over-restrains the earth虚寒证deficiency-cold syndrome 木火刑金wood-fireimpairs the metal扶阳退阴strengthening yang to reduce yin 金水相生generation between the metal andwater祛风散寒expelling/eliminating wind to dispersing cold 生克制化interrelationship between generation and restriction 消导积滞promoting digestion and removingfood retention制则生化restriction ensuring generation。
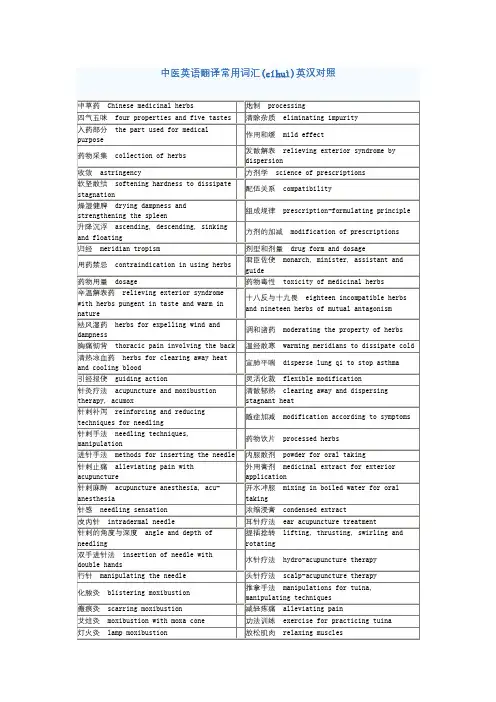

Unit1Test A1.differentiating syndromes and treatment 辨证论治2.syndrome differentiation with eight principles 八纲辨证3.location of diseases 病变部位4.tendency of pathological changes 病势5.external disease factors 外感病邪6.duration of a disease 病程7.aversion to cold 恶寒8.nasal congestion 鼻塞9.sore,itchy throat 喉痒咽痛10.penetrate from the superficial layers to the interior of the body 由表传里11.changes in tongue coating 舌苔变化12.cold limbs 四肢厥冷13.pallor/pale face 面色苍白14.clear and copious urine 小便清长15.absence of thirst 口不渴16.primary disease 原发病17.pale tongue with white coating 舌淡苔白18.malar flush 颧红19.struggle between the anti-pathogenic factors and pathogenic factors 正邪相争20.yang/yin depletion/collapse 亡阳/亡阴21.reduced appetite 食欲减退22.abdominal distention 腹部胀满23.qi transformation 气化24.pseudo-cold and real heat 真寒假热二句子翻译1.The clinical manifestations of diseases, though intricate, can be analyzed with the eight principles according to the category, location and nature of disease as well as the conflict between the anti-pathogenic factors and pathogenic factors.疾病的临床表现尽管错综复杂,但基本上都可以用八纲从疾病的类别、病性、邪正盛衰方面进行分析。
中医①traditional Chinese medicine②traditional Chinese physician①中医学的简称。
②本学科专业职业队伍。
中药Chinese materia medica 在中医理论指导下应用的药物。
包括中药材、中药饮片和中成药等。
中医学traditional Chinese medicine 以中医药理论与实践经验为主体,研究人类生命活动中健康与疾病转化规律及其预防、诊断、治疗、康复和保健的综合性科学。
中药学Chinese materia medica 中药学科的统称。
研究中药基本理论和各种药材饮片、中成药的来源、采制、性能、功效、临床应用等知识的学科。
中医药traditional Chinese medicine and pharmacology 中医与中药的合称。
中医药学traditional Chinese medicine and pharmacology 中医学与中药学的合称,侧重反映中医与中药两者共同发展,密不可分。
中西医结合integration of traditional and western medicine 现代医学等现代科学知识及手段来继承和发展中医药,中西医学相互补充,取长补短,诊治疾病的医学形式。
中医基础理论basic theory of traditional Chinese medicine 研究和阐明中医学的基本概念、基本理论、基本规律、基本原则的学科。
中医诊断学diagnostics of traditional Chinese medicine 根据中医学的理论体系,研究诊察病情、判断病种、辨别证候的基础理论、基本知识和基本技能的学科。
方剂学prescriptions of Chinese materia medica 研究治法与方剂配伍规律及其临床运用的学科。
中医内科学internal medicine of traditional Chinese medicine 研究外感温病、内伤杂病等内科疾病诊治与预防的临床中医学。
1 English Translation of TCM Medical Terms Unit 1 A brief introduction to traditional Chinese medicine 1. traditional Chinese medicine 2 .syndrome differentiation and treatment 3. holism 4. correspondence between man and nature 5. returning to the original purity and simplicity/ returning to nature 6. symptoms and signs 7. syndrome 8. dialectical materialism and historical materialism 9. side-effect/ adverse-effect 10. therapeutic effect/ efficacy/curative effect 11. diagnosis and treatment 12. symptomatology 13. integrated/ combined traditional Chinese and Western medicine 14.Miraculous Pivot 15. Plain Questions 16. Huangdi’s Internal Classic 17. Treatise on Cold-damage and Miscellaneous diseases 18. Compendium of Materia Medica 19. A-B Classic of Acupuncture and Moxibustion 20.Essential Prescriptions for Emergencies 21 Supplement to Essential Prescriptions for Emergencies 22 Classic on Difficult Issues of Medicine Unit Two Yin-yang Theory 1. the opposition and unity of yin and yang 2. restriction and transformation of yin and yang 3. excess/ predominance of yin leading to/ causing disorder of yang and excess /predominance of yang causing disorder of yin 4. interdependence of yin and yang 5. There would be impossible survival with solitary yin and vice versa. 6. waning and waxing of yin and yang 7. dynamic change 8. quantitative change 9. qualitative change 10. yin-yang figure/ Taiji figure 11. Excess of yin leading to deficiency of yang, or excess of yang leading to deficiency of yin. 12. yin within yang, and yang within yin 13. materialism 14. dynamic balance 15. inter-transformation between yin and yang/mutual transformation of yin and yang 16. infinite divisibility of yin and yang 17. tissues and structure 18. physiological function 19. the opposition and restriction of yin and yang 20. Severe cold will give birth to heat, and severe heat will give birth to cold.
Unit 3 Ying -yang Theory in TCM 1. The lung has the function of dominating qi and controlling breath. 2. the balance/ equilibrium between yin and yang 2
3. The harmony of yin and yang ensures the harmonious life activities while the disassociation of yin and yang will exhaust essence, and eventually, death occurs. 4. healthy qi 5. pathogenic qi / pathogen/ pathogenic factor 6. cold deficiency syndrome /cold syndrome of deficiency 7. dry-heat syndrome 8. mutual impairment of yin and yang / mutual detriment to yin and yang 9. deficiency of yin affecting yang or deficiency of yang affecting yin 10. Yin deficiency fails to control yin. 11. differentiation according to the eight principles Unit 4 Five Phase Theory 1. five phase theory / five elements theory 2. generating, generate /engendering 3. restraining , restrict , restriction 4 . restriction and transformation 5. overwhelming/ over-restriction /over-acting /subjugation 6. rebellion / counter-restriction/ reverse-restriction 7. Fire is characterized by flaming (up). 8. Wood is characterized by growing freely. 9. Water is characterized by moistening and flowing downward. 10. Earth is characterized by cultivation and reaping. 11. Metal is characterized by change. 12. five flavors, five colors, five growth and development , five seasons and five notes 13. five sense organs, five body constituents, five emotions and five voices 14. generated/ being generated generating/ to generate 15. restricted/ being restricted restricting/ to restrict 16 .The “generating” element is thought of as the “mother”. 17. The “generated’ element is as the “child”. 18. The disorder of mother-organ affecting/involving the child-organ; the disorder of child-organ affecting/ involving mother-organ 19. ecological equilibrium 20. mother-child relationship Unit 5 Five Phase Theory in TCM 1 The kidney stores vital essence. 2. The kidney controls water metabolism. 3. The heart-yang has warming function. 4.The liver has the function of smoothing and regulating flow of qi and blood. 5. transmission and change 6. The liver-fire impairs the lung. 7. excessive heart-fire 8.exuberance/excess of the heart and liver fire 9. nourishing the kidney and liver 10. the failure of the spleen in transportation and transformation (脾失运化) 11.flushed face and blood-shot ( red) eyes