
Available online at https://www.doczj.com/doc/d93548135.html,
Cellular and nuclear degradation during apoptosis
Bin He,Nan Lu and Zheng Zhou
Apoptosis ensures quick death and quiet clearance of
unwanted or damaged cells,without inducing much,if any,immunological responses from the organism.In metazoan organisms,apoptotic cells are swiftly engulfed by other cells.The degradation of cellular content is initiated in apoptotic cells and completed within engul?ng cells.In apoptotic cells,
caspase-mediated proteolysis cleaves protein substrates into fragments;nuclear DNA is partially degraded into nucleosomal units;and autophagy potentially contributes to apoptotic cell removal.In engul?ng cells,speci?c signaling pathways promote the sequential fusion of intracellular vesicles with phagosomes and lead to the complete degradation of
apoptotic cells in an acidic environment.Phagocytic receptors that initiate the engulfment of apoptotic cells play an additional and crucial role in initiating phagosome maturation through activating these signaling pathways.Here we highlight recent discoveries made in invertebrate models and mammalian systems,focusing on the molecular mechanisms that regulate the ef?cient degradation of apoptotic cells.
Address
Verna and Marrs McLean Department of Biochemistry and Molecular Biology,Baylor College of Medicine,Houston,TX 77030,USA Corresponding author:Zhou,Zheng (zhengz@https://www.doczj.com/doc/d93548135.html, )
Current Opinion in Cell Biology 2009,21:900–912This review comes from a themed issue on Cell division,growth and death
Edited by Angelika Amon and Mike Tyers Available online 24th September 20090955-0674/$–see front matter
#2009Elsevier Ltd.All rights reserved.DOI 10.1016/j.ceb.2009.08.008
Introduction
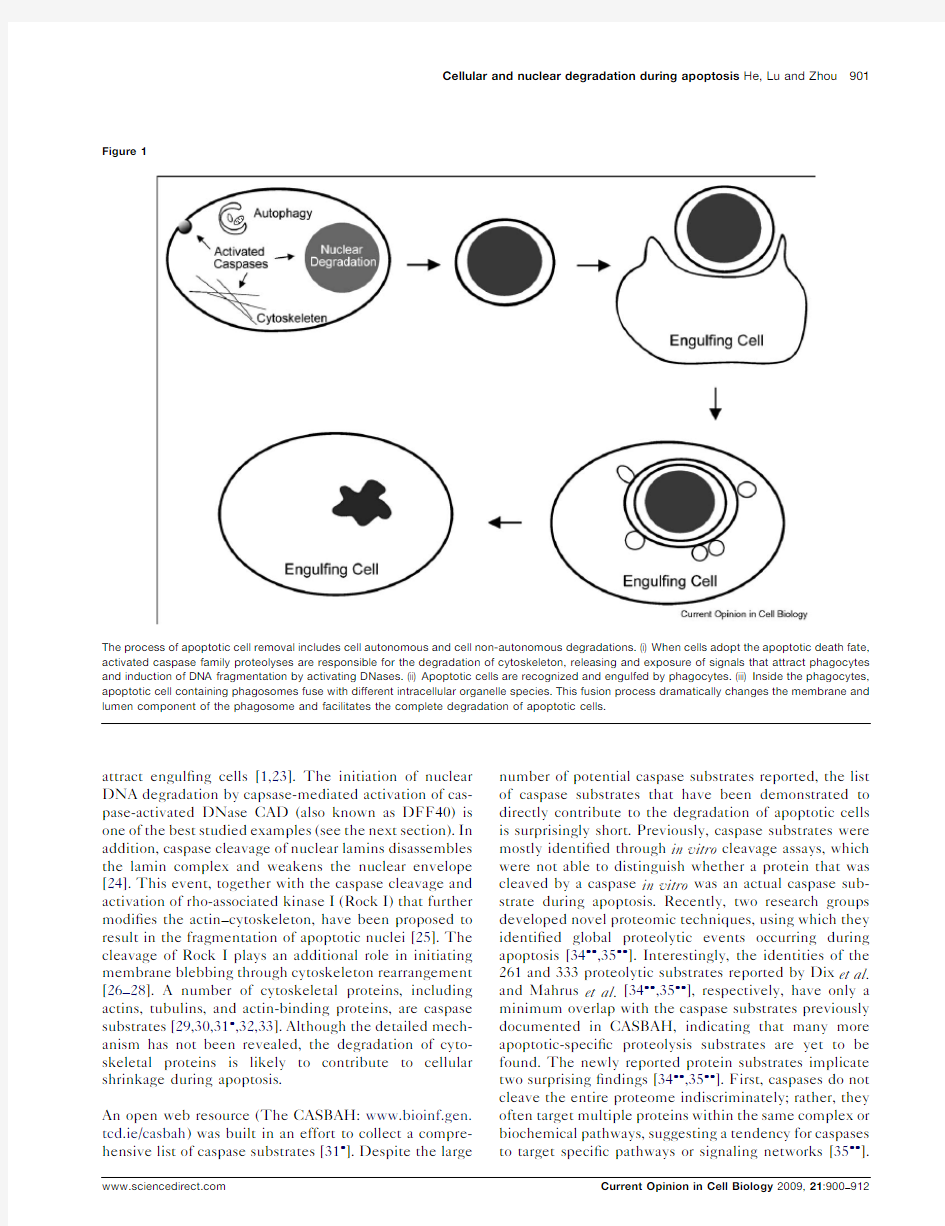
Among multiple types of cell deaths that have been identi?ed,apoptosis stands out as a distinct type that is executed swiftly and quietly,without inducing much,if any,immunological responses in the organism.During an animal’s life,a larger number of unwanted cells undergo apoptosis,a genetically programmed cell suicide process;these cells display several morphological changes in-cluding cellular shrinkage,chromatin condensation,nuclear fragmentation,and plasma membrane blebbing,yet retain their plasma membrane integrity and are rapidly internalized by other cells (Figure 1).The ef?-cient demolition of apoptotic cells is a result of the degradation activities provided by both apoptotic cells
and their phagocytes.Cell autonomous degradation is initiated and executed by caspases,a family of cysteine-dependent aspartate-directed proteases that play determinant roles in apoptosis,and by caspase-acti-vated proteases and nucleases [1].After being swiftly engulfed by their neighboring cells or professional pha-gocytes through phagocytosis,an actin-based cell intern-alization process,apoptotic cells are sequestered in intracellular vacuoles referred to as ‘phagosomes’where they are degraded by a lysosome-mediated digestive activities (Figure 1)[2–4].
The ef?cient removal of apoptotic cells plays important roles in sculpting structures,maintaining homeostasis,and eliminating abnormal,non-functional,or harmful cells [5,6].It is also an ef?cient tool for cell competition [7].Moreover,this process prevents potentially harmful in?ammatory and auto-immune responses that could occur if contents from apoptotic cells had leaked out [8].Macrophages that engulf apoptotic cells even elicit anti-in?ammatory responses that facilitate the resolution of regional in?ammation [9–12].Inef?cient engulfment or degradation of apoptotic cells is associated with numerous chronicle in?ammatory and auto-immune diseases [13–17,18 ].In this review,we describe recent advances in our understanding of apoptotic cell degradation,focusing on four major topics:(1)caspase-mediated proteolysis and cell autonomous degradation,(2)the multi-step degra-dation of nuclear DNA,(3)the role of autophagy in the removal of apoptotic cells,and (4)signaling pathways that regulate the maturation of phagosomes.This review does not cover many related topics such as the mechanisms that control the initiation of apoptosis,the exposure of ‘eat me’signals,the recognition and engulfment of apoptotic cells,cross-presentation of apoptotic cell anti-gens,and the fate of cells undergoing caspase-indepen-dent apoptosis,which are covered by other excellent reviews [4,19–21].
Caspase-mediated proteolysis initiates cell autonomous degradation of apoptotic cell contents
The activation of initiator caspases by ‘intrinsic’or ‘extrinsic’apoptotic signals marks the beginning of apop-tosis [22].Initiator caspases further cleave and activate effector caspases,which subsequently process a large number of cellular substrates proteolytically [22].These cleavage events are believed to lead to the signature cellular changes observed from apoptotic cells,which include cellular retraction,degradation of the nuclear envelope,chromatin condensation,degradation of nuclear DNA,and the release of signaling molecules that
attract engul?ng cells[1,23].The initiation of nuclear DNA degradation by capsase-mediated activation of cas-pase-activated DNase CAD(also known as DFF40)is one of the best studied examples(see the next section).In addition,caspase cleavage of nuclear lamins disassembles the lamin complex and weakens the nuclear envelope [24].This event,together with the caspase cleavage and activation of rho-associated kinase I(Rock I)that further modi?es the actin–cytoskeleton,have been proposed to result in the fragmentation of apoptotic nuclei[25].The cleavage of Rock I plays an additional role in initiating membrane blebbing through cytoskeleton rearrangement [26–28].A number of cytoskeletal proteins,including actins,tubulins,and actin-binding proteins,are caspase substrates[29,30,31 ,32,33].Although the detailed mech-anism has not been revealed,the degradation of cyto-skeletal proteins is likely to contribute to cellular shrinkage during apoptosis.
An open web resource(The CASBAH:www.bioinf.gen. tcd.ie/casbah)was built in an effort to collect a compre-hensive list of caspase substrates[31 ].Despite the large number of potential caspase substrates reported,the list of caspase substrates that have been demonstrated to directly contribute to the degradation of apoptotic cells is surprisingly short.Previously,caspase substrates were mostly identi?ed through in vitro cleavage assays,which were not able to distinguish whether a protein that was cleaved by a caspase in vitro was an actual caspase sub-strate during apoptosis.Recently,two research groups developed novel proteomic techniques,using which they identi?ed global proteolytic events occurring during apoptosis[34 ,35 ].Interestingly,the identities of the 261and333proteolytic substrates reported by Dix et al. and Mahrus et al.[34 ,35 ],respectively,have only a minimum overlap with the caspase substrates previously documented in CASBAH,indicating that many more apoptotic-speci?c proteolysis substrates are yet to be found.The newly reported protein substrates implicate two surprising?ndings[34 ,35 ].First,caspases do not cleave the entire proteome indiscriminately;rather,they often target multiple proteins within the same complex or biochemical pathways,suggesting a tendency for caspases to target speci?c pathways or signaling networks[35 ].
Cellular and nuclear degradation during apoptosis He,Lu and Zhou901 Figure
1
The process of apoptotic cell removal includes cell autonomous and cell non-autonomous degradations.(i)When cells adopt the apoptotic death fate, activated caspase family proteolyses are responsible for the degradation of cytoskeleton,releasing and exposure of signals that attract phagocytes and induction of DNA fragmentation by activating DNases.(ii)Apoptotic cells are recognized and engulfed by phagocytes.(iii)Inside the phagocytes, apoptotic cell containing phagosomes fuse with different intracellular organelle species.This fusion process dramatically changes the membrane and lumen component of the phagosome and facilitates the complete degradation of apoptotic cells.
Secondly,many of the cleavage products are mapped to stably folded functional domains,suggesting that rather than complete degradation of proteins,the apoptotic proteolytic cascades primarily generate new forms of proteins that may adapt new functions that further con-tribute to the self-killing event[34 ].Future challenge resides at understanding the functional signi?cance of the cleavage of the newly identi?ed caspase targets in vivo. The degradation of apoptotic nuclear DNA is a multi-step process
The degradation of nuclear DNA into oligonucleosomal fragments is a hallmark of apoptosis[36].The massive cleavage of genetic materials irreversibly compromises DNA replication and gene transcription.Early in apop-tosis,accompanied by chromatin condensation,chromo-somal DNA is?rst cleaved into high molecular weight (HMW)fragments of50–300kb,which are subsequently processed into low molecular weight(LMW)fragments, the characteristic180-bp DNA[37].DNA fragments are readily detected in situ by the TUNEL(terminal deox-ynucleotidyl transferase dUTP-mediated nick end labeling)assay,which labels30-OH end of DNA breaks [38].After dying,cells are engulfed by phagocytes,the partially digested DNA molecules are completely degraded into nucleotides in phagosomes[37].A num-ber of nucleases have been proposed to degrade apop-totic DNA,some of which act in apoptotic nuclei, whereas others in phagosomal lumen(Figure2) [37,39–43].
902Cell division,growth and death
Figure
2
In living cells,the activity of CAD is inhibited by ICAD and the EndoG is sequestered in mitochondrial intermembrane space.(A)During apoptosis,the activated caspases cleave ICAD and release CAD,which forms homodimer and cleaves linker DNA between necleosomes.The activation of caspases also triggers the release of EndoG from mitochondria into nucleus to cleave chromosomal DNA.(B)After being engulfed by phagocytes,the apoptotic cell resides in phagosome.Through phagosomal maturation,the phagosome acquires different digestive enzymes including DNase II a from lysosomes and its lumen is gradually acidified.Under acidic condition,the active DNase II a further degrades nucleosomal DNA into nucleotides.
CAD/DFF40is the major cell autonomous nuclease that accounts for most if not all activities for the generation of LMW DNA in apoptotic mammalian cells[44 ,45 ].In cells in which CAD is deleted or inactive,internucleo-somal DNA fragmentation is either completely abolished or greatly reduced[18 ,46,47].In living cells,CAD is in a complex with inhibitor of CAD(ICAD,as known as DFF45),which acts as CAD’s folding chaperon during protein synthesis and subsequently inhibits its DNA cleavage activity[44 ,45 ,48,49].During apoptosis,cas-pase3cleaves ICAD and releases CAD[44 ,45 ,50 ]. Initially,it was proposed that caspase cleavage of ICAD allowed CAD to enter the nucleus[44 ].Subsequent evidence indicates that the endogenous ICAD/CAD complex resides in the nucleus of living cells;further-more,the cleavage of ICAD that releases CAD appears to occur inside the nucleus[51,52].The released CAD forms a scissor-like homodimer and cleaves double-strand DNA at nucleosomal linkers[53 ,54].In addition,histone H1 might stimulate the enzymatic activity of CAD and also contribute to CAD’s substrate speci?city[55,56].
The residual DNA degradation activity detected in CAD-de?cient cells suggests the existence of additional nuclease(s)during apoptosis[46,57 ].Mammalian endo-nuclease G(EndoG)is such a nuclease[57 ].In living cells,EndoG resides in mitochondrial intermembrane space;upon apoptotic stimuli,it is released from mito-chondria and translocated to nucleus,where it cleaves nucleic acids[57 ,58].EndoGI,a recently identi?ed EndoG inhibitor in Drosophila,is present in the nuclei of living cells and acts as a guardian for the accidental leakage of EndoG from mitochondria[59].EndoGI is translocated to the cytoplasm upon apoptotic stimuli[59]. Additional CAD-independent DNases activities detected in apoptotic cells include L-DNase II,apoptosis-enhan-cing nuclease(AEN),and DNase g,which can be acti-vated by different apoptotic stimuli[60–63].
The C.elegans genome does not encode any close sequence homolog of CAD.C.elegans NUC-1(nuclease abnormal),a homolog of mammalian DNase II,is the?rst nuclease identi?ed that drives the degradation of nuclear DNA in apoptotic cells[64,65].In nuc-1mutant embryos, many apoptotic cells remain TUNEL-positive,whereas in wild-type embryos TUNEL-positive apoptotic cells are hardly detectable[65].Genetic and cellular charac-terizations of nuc-1and nuc-1’s functional relationship with genes involved in the engulfment of apoptotic cells indicate the presence of at least three steps of apoptotic DNA degradation:the initial digestion that generates TUNEL-positive DNA ends,the conversion of TUNEL-positive to TUNEL-negative DNA ends, which depends on NUC-1activity,and the complete digestion of nuclei DNA into free nucleotides[65]. Although the expression pattern of NUC-1has not been determined,genetic evidence suggests that NUC-1is likely to act in apoptotic cells to mediate DNA degra-dation[65].In addition,the C.elegans EndoG homolog CPS-6and several other exonucleases and endonucleases form a DNA degradation complex named‘degradosome’that acts in parallel to NUC-1to promote DNA degra-dation[42,66,67].
Mice de?cient in either CAD or EndoG are viable and develop normally[47,68–70].Apoptotic events such as phosphatidylserine exposure,caspase activation and early-stage chromatin condensation are also normal in CAD-de?cient cells,indicating that the degradation of apoptotic DNA per se is largely dispensable for the initiation and execution of apoptosis[46].Several reports, however,indicate active roles of cell autonomous nucleases in the progression of apoptosis,especially in sensitive genetic backgrounds[67,71,72].In addition,in certain cases the fragmented DNA was detected on the surface of apoptotic cells and was proposed to act as one type of the‘eat me’signals that attract phagocytes[73,74]. The partially digested nucleosomal DNA is further degraded into nucleotides by other types of nucleases, primarily DNase II a,in the phagosomes of mammalian and Drosophila engul?ng cells(Figure2).DNase II a activity is optimal in acidic compartments such as lyso-somes and phagolysomes[41,75].In DNase II-de?cient ?ies and mice,a large number of undegraded DNA accumulated inside phagocytes[18 ,76 ,77].The degra-dation of apoptotic cell DNA plays active roles in pre-venting antigenic DNA from eliciting improper immune responses[78].Undegraded apoptotic cell DNA in the macrophages of DNase II-de?cient mice induces an IFN regulatory factor3/7-dependent production of IFN b, which is cytotoxic and contributes to the lethal anemia in DNase II null mice[18 ,79,80,81 ].Conditional knockout of DNase II gene after birth causes adult mice to develop chronic polyarthritis that resembles human rheumatoid arthritis[82].In mice that lack both CAD and DNase II activities,the undegraded DNA induces innate immunity and impairs thymic development[18 ].Sim-ilarly,the innate immunity is induced by undegraded DNA in CAD(à/à)DNase II(à/à)?ies[76].In C.ele-gans,other than NUC-1,the DNase II homolog that probably acts in apoptotic cells,there must be additional functional counterparts of DNase II that act in phago-somal lumen to conduct cell non-autonomous DNA degradation.
In summary,the nuclear DNA inside apoptotic cells is degraded in multiple steps by both cell autonomous and non-autonomous means.Cell autonomous DNA degra-dation is dispensable for animal development since dying cells are subsequently engulfed by phagocytes and their DNA is effectively degraded by nucleases in phagosomes [68].However,when massive apoptosis occurs and the degradation system is overloaded,the pre-cleavage by
Cellular and nuclear degradation during apoptosis He,Lu and Zhou903
CAD may become essential[68].Although the role of DNA degradation in apoptotic execution is largely elu-sive,the resulted DNA waste needs to be properly dis-posed to avoid the activation of innate immunity.
The contribution of autophagy to the clearance of apoptotic cells
Autophagy is a speci?c cellular event in which a portion of intracellular organelles and cytosolic components are engulfed by intracellular membranes and con?ned in a double membrane vacuolar structure named autophago-somes,and are subsequently degraded by lysosomes that fuse with autophagosomes[83].Autophagy is a stress adaptation process that generates energy and nutrients by degrading macromolecules.Its relationship with apop-tosis is complex.In many cases autophagy acts to save cells from the fate of apoptosis[84–88];in other cases, when the swift apoptosis machinery is inhibited,starved cells or cells receiving death stimuli undergo an alterna-tive form of cell death via autophagy[89,90].In addition, during animal development,autophagic cell death has been observed to act as an independent form of pro-grammed cell death[91–93].Autophagy was also reported to potentiate caspase-dependent death[94].The role of autophagy in the execution of cell death thus appears to be heavily dependent on the cellular and tissue context. The question most relevant to this review,namely, whether autophagy contributes to the cell autonomous degradation of cellular contents during apoptosis,how-ever,has not been answered.Interestingly,recently a new function of autophagy relevant to the ultimate degra-dation of apoptotic cells has been reported.In an in vitro system that mimics the cavitation of early mouse embryos,Qu et al.found that autophagy that occurred in apoptotic inner ectodermal cells contributed to the generation of ATP,which further promoted the exposure of phosphatidylserine,the‘eat me’signal,on the surface of apoptotic cells,as well as the secretion of lysopho-sphatidylcholine,the‘come-get-me’signal,to the neigh-borhood[95 ].In this example,autophagy enables apoptotic cells to attract phagocytes,and thus indirectly facilitates their cell non-autonomous degradation.A similar role played by autophagy has also been reported in chick retina[96].On the contrary,ES cells in culture do not seem to rely on autophagy for the exposure of phos-phatidylserine in response to apoptotic stimuli[95 ]. Whether the mechanism described above is commonly used by many kinds of apoptotic cells awaits further investigation.
Novel signaling pathways that control the maturation of phagosomes containing apoptotic cells
General knowledge about phagosome maturation
The maturation of phagosomes,a process that involves extensive remodeling of phagosomal membrane and con-tents and results in the eventual degradation of the engulfed particle,has been well characterized in mam-malian phagocytes such as macrophages that ingest latex beads,opsonized microbes or red blood cells[97].Once created,nascent phagosomes undergo sequential fusion events with intracellular organelles in the endocytic path-way,including early endosomes,late endosomes and lysosomes[97].These fusion events promote the acid-i?cation of phagosomal lumen and deliver acid hydrolyses to phagosomes,which,in an acidic environment (pH<5.0),actively digest the protein,nucleic acid, and lipids con?ned in the phagosomal lumen[97].A number of molecules,including phosphatidylinositol-3-phosphate(PI-3P)and Class III PI3kinase Vps34,small RAB GTPases Rab5and Rab7,V-type ATPase,and membrane fusion machinery components,were found to be recruited to phagosomal surfaces and drive phago-some maturation.The synthesis of PI-3P on phagosomal surfaces,primarily conducted by Vps34,is believed to attract downstream effectors that are PI-3P-binding proteins[98,99].Rab5and Rab7act as membrane tether-ing factors for vesicles of different identities:Rab5facili-tates the early endosomes/phagosome fusion,whereas Rab7facilitates the fusion of late endosomes and lyso-somes to phagosomes[100–105].V-type ATPase cata-lyzes the acidi?cation of phagosomal lumen[106–109]. Special features of the maturation of phagosomes containing apoptotic cells
Until recently,little is known about how apoptotic cell are degraded inside phagosomes.Unlike macrophages that ingest bacteria,macrophages that engulf apoptotic cells secrete anti-in?ammatory signals and actively suppress the secretion of the proin?ammatory cytokines[9–12]. Further more,recent studies revealed that phagosomes containing apoptotic cells and opsonized-living cells matured at different rates[110 ].These observations indicate the existence of mechanisms speci?c to the degradation of apoptotic cells.Recent research conducted in invertebrate model organisms and mammalian system revealed shared and unique mechanisms employed for the degradation of apoptotic cells.
The small nematode C.elegans has been a successful model for studying apoptotic cell death and apoptotic cell engulfment[111,112].Recently,owing to the estab-lishment of multiple novel techniques,including the live-cell imaging in developing embryos and the genome-wide RNAi screen,and through the combined usage of these techniques with traditional genetic approaches,research-ers have described in detail the different steps of the maturation process of phagosomes that contain apoptotic cells and identi?ed a novel signaling pathway controlling phagosome maturation(Figure3).It has been observed that the degradation of apoptotic cells in C.elegans also requires fusions of endosomes and lysosomes to phago-somes[113 ,114 ].The recruitment of a series of key
904Cell division,growth and death
molecules,some of which previously unknown to be involved in phagosome maturation,to phagosomal sur-faces drives these fusion events [113 ,114 –116 ,117 ].Below we summarize these new ?ndings made in C.elegans as well as in other systems.
New executors of phagosome maturation that drive lysosomes/phagosome fusion
The RAB family small GTPases and their protein com-plexes are known to act as tethering factors that bring vesicles together for fusion [118].Three C.elegans RAB GTPases,RAB-5,RAB-7,and RAB-2,have been found to play distinct roles during the degradation of apoptotic cells (Figure 3)[114 –116 ,117 ].Knocking out or down the activity of each of the three results in the accumu-lation of undegraded apoptotic cells.C.elegans RAB-7is speci?cally required for the incorporation of lysosomes to phagosomes [114 ].It mediates the extension of lipid tubules from phagosomes to recruit lysosomes,like mam-malian Rab7[105,114 ],and further promotes the fusion between these two compartments after docking of lyso-somes on phagosomal surfaces [114 ].In rab-7(RNAi)treated worms,phagosomes containing apoptotic germ cells are arrested as RAB-5-labeled phagosomes,
suggesting that RAB-7may act downstream or indepen-dent of RAB-5[115 ].The homotypic fusion and vacuole protein sorting (HOPS)complex is known to act as both an exchange factor and an effector for RAB-7during yeast endocytosis [119].RNAi knockdown of each of all seven HOPS complex components causes persist-ent apoptotic cells in C.elegans gonads;furthermore,phagosomes are arrested at a RAB-7-positive stage,suggesting that the HOPS complex is likely to act down-stream of RAB-7[115 ].In a separate study,Xiao et al.independently discovered the function of the HOPS complex component VPS-18in the degradation of engulfed apoptotic cells [120 ].However,Xiao et al.proposed that the major cause of the observed phago-some maturation defect is due to defects in lysosomal biogenesis caused by the vps-18mutations [120 ].Whether and how the HOPS complex plays a direct role on phagosomal surfaces for lysosomes/phagosome fusion needs to be further investigated.
Unlike RAB-5or RAB-7,RAB-2is a less studied RAB GTPase whose function in phagosome maturation has not been revealed previously.C.elegans RAB-2was identi?ed from genetic screens for mutants that contain un-removed
Cellular and nuclear degradation during apoptosis He,Lu and Zhou 905
Figure
3
Cell non-autonomous degradation of apoptotic cells.In C.elegans ,the signaling cascade of apoptotic cell degradation starts from phagocytic receptor CED-1and is followed by CED-6,large GTPase DYN-1,small GTPases (RAB-5,RAB-7and RAB-2),Class III PI-3kinase VPS-34and members of HOPS complex.DYN-1and RAB GTPase localize on phagocytic cup or phagosome surface to regulate the sequential fusion of
intracellular organelles,including early and late endosomes and lysosomes,to phagosome.PI-3P is synthesized on the phagosome surface mainly by VPS-34and serves to recruit downstream effectors.Members of HOPS complex are RAB-7effectors and function mainly downstream of RAB-7.It is not known whether VPS-34and HOPS complex also localize on phagosome surface.During phagosome maturation,its lumen pH level drops from near neural to below 5,which activates the capthesin family proteases and DNase II to completely degrade phagosome contents.
apoptotic cells[116 ,117 ].Like RAB-7,RAB-2plays an important role in the recruitment and fusion of lysosomes to phagosomes;however,unlike RAB-7,RAB-2is also required for the acidi?cation of phagosomal lumen [116 ].RAB-2and RAB-7may control lysosome–phago-some fusions in parallel;alternatively,they may each contribute to a different subset of events.Proteomic studies in Drosophila and mammals have identi?ed Rab2as a component of phagosomes[121,122].It remains to be elucidated whether mammalian or Drosophila Rab2 plays a conserved role in the maturation of phagosomes. In addition to RAB GTPases,a novel function of the V0-ATPase in lysosomal/phagosomal fusion during the clear-ance of zebra?sh apoptotic neurons has been identi?ed through in vivo imaging[123].This fusion activity is separate from the proton pump activity of the V-type ATPase[123],and is consistent with the membrane fusion activity reported for the fusion of yeast vacuoles [124].In the near future,components of the membrane fusion machinery such as the SNARE complex and the regulators of this machinery are likely to show up on the list of novel apoptotic cell degradation factors.
Key factors that regulate the phagosome maturation executors
Dynamins are conserved large GTPases that play pivotal roles in multiple membrane traf?cking processes[125]. Dynamin’s membrane?ssion activity underlines its essential function in driving endocytosis[125].In other cellular context,dynamin and dynamin-related proteins are also known to promote membrane fusion[126–130]. In a genetic screen for mutants that are defective in both embryonic development and apoptotic cell removal, fourteen loss-of-function alleles of dyn-1,the C.elegans dynamin gene,were identi?ed[113 ].Subsequent characterizations indicate that the function of DYN-1is essential for both the engulfment and degradation of apoptotic cells[113 ,114 ].DYN-1drives the recruit-ment and fusion of early endosomes to phagocytic cups, an event that provides membrane material to support pseudopod extension around apoptotic cells[113 ].More-over,DYN-1controls the recruitment and fusion of both endosomes and lysosomes to maturing phagosomes,a process crucial for the delivery of multiple digestive enzymes and the V-type ATPase to phagosomes [113 ,114 ].Speci?cally,DYN-1acts as a mediator in a signaling pathway leading to phagosome maturation—it promotes the recruitment of RAB-7to phagosomal sur-faces and the synthesis of PI-3P on phagosomal mem-branes[114 ].DYN-1thus acts as an upstream regulator of phagosome maturation effectors(Figure3).In a gen-ome-wide RNAi screen,Kinchen et al.also identi?ed the function of dyn-1in phagosome maturation[115 ].
PI-3P is generated on the phagosomal surfaces primarily owing to the activity of Class III PI-3kinase Vps34and functions there to recruit downstream factors,such as proteins with Phox homology(PX)or Fab1–YOTB–Vac1–EEA1(FYVE)domains[97].In C.elegans engul?ng cells,PI-3P is synthesized on nascent phagosome surfaces immediately after the internalization of apoptotic cells and remains present throughout phagosome maturation [114 ].RNAi-mediated inactivation of C.elegans vps-34 results in a mild increase in the number of apoptotic germ cells and vps-34was proposed to function under the control of DYN-1to synthesize PI-3P[115 ].Given that vps-34 RNAi,unlike dyn-1mutations or RNAi,only causes mild apoptotic cell retention phenotype,there might be additional PI3kinases that act in parallel to generate phagosome-speci?c PI-3P in response to DYN-1.
The role of Rab5GTPase appears to be more complex. During the maturation of phagosomes containing microbes or opsonized particles,Rab5is proposed to act as a tethering factor between early endosomes and phagosomes[102,131,132].In both C.elegans and mam-malian cells,recent studies found that RAB-5also pro-motes the maturation of phagosomes containing apoptotic cells[115 ,133].Since the incorporation of early endo-somes to phagosomes is a crucial step during the degra-dation of apoptotic cells[113 ],it is likely,although proof is still needed that the tethering factor function of RAB-5 is conserved during apoptotic cell degradation.Besides this executor function,RAB-5also regulates downstream signaling events.In the endocytic pathway,Rab5was known to activate Vps34and promote PI-3P synthesis on the target membranes[134–136].Recently,Kinchen et al. proposed a different model in which Vps34activates Rab5 by mediating the interaction between Rab5and dynamin 2,on the basis of protein–protein interaction studies in mammalian cells and genetic studies in C.elegans[115 ]. Whether this model can be reconciled with the obser-vations made in the endocytic pathway and the model proposed by Kitano et al.[133]in RAB-5activation requires further investigation.
Kitano et al.observed that the activation of mammalian Rab5on the surface of nascent phagosomes containing apoptotic cells is dependent on EB1,a microtubule-tip-associating protein that also interacts with Gapex-5,a guanine nucleotide exchange factor(GEF)for Rab5 [133].Kitano et al.thus propose that the recruitment of Gapex-5to phagosomes through the microtubule network leads to the subsequent recruitment and activation of Rab5[133].The identi?cation of Gapex-5and EB1as essential factors provides a molecular mechanism that involves the novel and crucial role of microtubules for the regulation of Rab5.
Phagocytic receptors acting as the initiators of phagosome maturation
As an essential regulator of phagosome maturation that controls the recruitment and activity of multiple
906Cell division,growth and death
downstream regulators and executors,how is DYN-1 regulated?First of all,the association of DYN-1to extending pseudopods and nascent phagosomes is crucial for its function in the removal of apoptotic cells[113 ]. Furthermore,the recruitment of DYN-1to pseudopods and nascent phagosomes is dependent on the phagocytic receptor CED-1and its adaptor protein CED-6[113 ]. Lack of DYN-1enrichment to the surfaces of pseudopods and nascent phagosomes,as a consequence of ced-1or ced-6mutations,causes severe defects in engulfment and degradation of cell corpses[113 ,114 ].Consistent with this mechanism,epistasis analysis places dyn-1in the signaling pathway composed of ced-1and ced-6[113 ]. These results indicate that vesicle traf?cking is a novel event regulated by the CED-1pathway;they further imply that CED-1,by controlling DYN-1activity,also regulates phagosome maturation[113 ,114 ].
CED-1and CED-6are members of one of the two previously identi?ed C.elegans signaling pathways that are believed to speci?cally control the engulfment of apoptotic cells[137–139].The novel functions of CED-1and CED-6in phagosome maturation were over-looked previously because strategies that distinguish engulfed vs.unengulfed apoptotic cells in real time were not established[114 ].With the aid of the newly devel-oped live-cell imaging technique,Yu et al.discovered that like dyn-1mutations,ced-1mutations not only greatly reduce the ef?ciency of engulfment but also impair the degradation of those apoptotic cells that are engulfed inside phagosomes[114 ].Signaling events that require CED-1activity,including the recruitment of DYN-1and RAB-7to and the synthesis of PI-3P on the surface of phagosomes,also require CED-6[114 ].As a con-sequence,ced-1and ced-6mutants are both defective in the recruitment and fusion of early endosomes and lyso-somes to phagosomes[113 ,114 ].Although CED-1is only transiently localized to phagosomal surfaces,it co-exists with DYN-1for a period of time[113 ,114 ].Thus, through CED-6,CED-1recruits DYN-1to phagosomes, which promotes a downstream signaling cascade that leads to apoptotic cell degradation(Figure3)[113 ,114 ]. Previously,phagocytic receptors were only known to recognize phagocytic targets and initiate their engulf-ment.The above?nding reveals that in addition to this well-known function,CED-1plays a novel role in phago-some maturation.It further indicates that phagosome maturation is not a process that occurs spontaneously once a phagosome forms,rather,signaling from the pha-gocytic receptor is needed to initiate this process.More-over,this?nding suggests that different phagocytic receptors may promote different phagosome maturation modes and subsequently induce phagocytes to elicit different responses,including different immune responses.CED-1belongs to a family of transmembrane proteins whose extracellular domains are of large sizes and contain an N-terminal emilin(EMI)-like domain followed by tandem repeats of an atypical EGF like repeat motif[140].Draper,the Drosophila ortholog of CED-1,like CED-1,is known to be essential for the engulfment of apoptotic cells as well as pruned axon fragments[141–144].Interestingly,Kurant et al.[145 ] recently observed that in draper mutants,apoptotic cells are retained inside phagosomes for a prolonged period of time.On the basis of their genetic and cell biological characterizations of single mutants of draper and simu, which encodes another EMI domain and EGF repeats containing transmembrane protein,and of draper;simu double mutants,Kurant et al.further propose that SIMU is primarily involved in the recognition and uptake of apoptotic cells whereas Draper is primarily required for the degradation of apoptotic cells[145 ].These?ndings indicate a conserved role of the CED-1family of phago-cytic receptors in phagosome degradation in worms and ?ies.It remains to be elucidated whether mammalian homologs of CED-1,such as human mEGF10[138,146], and other phagocytic receptors for apoptotic cells also provide the initiation signal for phagosome maturation in addition to promoting the engulfment of apoptotic cells, and furthermore,whether the initiation of phagosome maturation is a common function performed by all pha-gocytic receptors.
Cytoskeleton reorganization might also play a role in the degradation of apoptotic cells
CED-5,the C.elegans homolog of mammalian protein Dock180,is a component of a bipartite nuclear exchange factor for CED-10/Rac1GTPase,and acts in a signaling pathway together with CED-10but in parallel to CED-1 to promote the engulfment of apoptotic cells[112]. Recently,it was observed that CED-5acted in a distinct pathway to control phagolysosome formation during the degradation of apoptotic cells[114 ].During engulf-ment,the pathway led by CED-5was known to regulate cytoskeletal reorganization[112].Cytoskeletal reorgani-zation also plays an active role in phagosome maturation in mammalian cells[110 ,147].CED-5and other mem-bers of its pathway thus might contribute to phagosome maturation through remodeling the cytoskeleton. Concluding remarks
Studies focusing on the degradation of apoptotic cells provide a wonderful platform for investigating a number of fundamental biological processes,including,but not limited to,how apoptotic execution machinery coordi-nates the multiple cellular demolishing events,whether and how autophagy,another fundamental cellular activity,is involved in the clearance of apoptotic cells, how the initiation and completion of apoptotic cell degra-dation in two different cell types are coordinated,and the identity of the components and organization of the sig-naling pathway(s)for recruiting intracellular vesicles to support phagosome maturation.The usage of model
Cellular and nuclear degradation during apoptosis He,Lu and Zhou907
organisms further places the clearance of apoptotic cells in a whole animal context.However,what we know currently,as summarized in this review,is only the tip of an iceberg.Without repeating the questions for future exploration that have already been spelled out in the text, here I would like to list several interesting questions that have not been well explored.First,what is the exact role of cell autonomous degradation of apoptotic cells?It seems that the caspase-initiated DNA degradation is dispensable under physiological conditions since DNA degradation occurring inside phagosomes provides a backup activity.However,other events,such as the exposure of‘eat me’signals,cell retraction and detach-ment from the surrounding tissue,which are essential for ensuring that apoptotic cells are to be engulfed by pha-gocytes,may rely on caspase-mediated cleavage of multiple substrates.Exploring this aspect will lead us to further understand the relationship between apoptotic cells and there neighbors.Secondly,autophagy was associated with phagosome maturation in recent studies [148,149].A comprehensive study of the contribution of autophagy in both apoptotic cells and phagocytes to the degradation of apoptotic cells will shed light on the relationship between autophagy and https://www.doczj.com/doc/d93548135.html,st but not the least,the cell non-autonomous degradation of apoptotic cells has established a new model for study-ing the mechanism of phagosome maturation.The?nd-ing that phagocytic receptors for apoptotic cells are crucial in initiating phagosome maturation provides a new clue to understand the distinct immune responses phagocytes generated against different phagocytic targets.The detailed molecular mechanisms behind each step of pha-gosome maturation,such as how dynamin serves as a mediator of phagosome maturation,what the PI-3P effec-tors are,and the functional relationship among RAB GTPases2,5,and7all await to be explored in worms,?ies and mammals.
Acknowledgements
We apologize to all authors whose relevant work was not cited owing to page limit.We thank E.Baehrecke for comments.This work was supported by NIH GM067848.
References and recommended reading
Papers of particular interest,published within the period of review, have been highlighted as:
of special interest
of outstanding interest
1.Taylor RC,Cullen SP,Martin SJ:Apoptosis:controlled
demolition at the cellular level.Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol2008,
9:231-241.
2.Zhou Z,Yu X:Phagosome maturation during the removal of
apoptotic cells:receptors lead the way.Trends Cell Biol2008, 18:474-485.
3.Kinchen JM,Ravichandran KS:Phagosome maturation:going
through the acid test.Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol2008,9:781-795. 4.Erwig LP,Henson PM:Clearance of apoptotic cells by
phagocytes.Cell Death Differ2008,15:243-250.5.Vaux DL,Korsmeyer SJ:Cell death in development.Cell1999,
96:245-254.
6.Henson PM,Hume DA:Apoptotic cell removal in development
and tissue homeostasis.Trends Immunol2006,27:244-250.
7.Li W,Baker NE:Engulfment is required for cell competition.Cell
2007,129:1215-1225.
8.Savill J,Fadok V:Corpse clearance de?nes the meaning of cell
death.Nature2000,407:784-788.
9.Fadok VA,Bratton DL,Konowal A,Freed PW,Westcott JY,
Henson PM:Macrophages that have ingested apoptotic cells in vitro inhibit proin?ammatory cytokine production through
autocrine/paracrine mechanisms involving TGF-beta,PGE2,
and PAF.J Clin Invest1998,101:890-898.
10.Voll RE,Herrmann M,Roth EA,Stach C,Kalden JR,Girkontaite I:
Immunosuppressive effects of apoptotic cells.Nature1997,
390:350-351.
11.Serhan CN,Savill J:Resolution of in?ammation:the beginning
programs the end.Nat Immunol2005,6:1191-1197.
12.Freire-de-Lima CG,Xiao YQ,Gardai SJ,Bratton DL,
Schiemann WP,Henson PM:Apoptotic cells,through
transforming growth factor-beta,coordinately induce anti-
in?ammatory and suppress pro-in?ammatory eicosanoid and NO synthesis in murine macrophages.J Biol Chem2006,
281:38376-38384.
13.Botto M,Dell’Agnola C,Bygrave AE,Thompson EM,Cook HT,
Petry F,Loos M,Pandol?PP,Walport MJ:Homozygous C1q
de?ciency causes glomerulonephritis associated with
multiple apoptotic bodies.Nat Genet1998,19:56-59.
14.Scott RS,McMahon EJ,Pop SM,Reap EA,Caricchio R,Cohen PL,
Earp HS,Matsushima GK:Phagocytosis and clearance of
apoptotic cells is mediated by MER.Nature2001,411:207-211.
15.Kawane K,Fukuyama H,Kondoh G,Takeda J,Ohsawa Y,
Uchiyama Y,Nagata S:Requirement of DNase II for de?nitive erythropoiesis in the mouse fetal liver.Science2001,
292:1546-1549.
16.Hanayama R,Tanaka M,Miyasaka K,Aozasa K,Koike M,
Uchiyama Y,Nagata S:Autoimmune disease and impaired
uptake of apoptotic cells in MFG-E8-de?cient mice.Science
2004,304:1147-1150.
17.Kawane K,Ohtani M,Miwa K,Kizawa T,Kanbara Y,Yoshioka Y,
Yoshikawa H,Nagata S:Chronic polyarthritis caused by
mammalian DNA that escapes from degradation in
macrophages.Nature2007,446:102.
18.
Kawane K,Fukuyama H,Yoshida H,Nagase H,Ohsawa Y,
Uchiyama Y,Okada K,Iida T,Nagata S:Impaired thymic
development in mouse embryos de?cient in apoptotic DNA
degradation.Nat Immunol2003,4:138-144.
This paper and references[76,81,82]characterized CAD and/or DNase II knockout aminals and demonstrated that the failure of apoptotic DNA degredation could improperly activate innate immunity,and results in auto-immune diseases and lethal anemia in animal models.These studies highlight the essential roles of DNA degradation in animal development and in the regulation of innate immnue system.
19.Danial NN,Korsmeyer SJ:Cell death:critical control points.Cell
2004,116:205-219.
20.Tait SW,Green DR:Caspase-independent cell death:leaving
the set without the?nal cut.Oncogene2008,27:6452-6461. 21.Trombetta ES,Mellman I:Cell biology of antigen processing in
vitro and in vivo.Annu Rev Immunol2005,23:975-1028.
22.Hengartner MO:The biochemistry of apoptosis.Nature2000,
407:770-776.
https://www.doczj.com/doc/d93548135.html,uber K,Bohn E,Krober SM,Xiao YJ,Blumenthal SG,
Lindemann RK,Marini P,Wiedig C,Zobywalski A,Baksh S et al.: Apoptotic cells induce migration of phagocytes via caspase-3-mediated release of a lipid attraction signal.Cell2003,
113:717-730.
24.Rao L,Perez D,White E:Lamin proteolysis facilitates nuclear
events during apoptosis.J Cell Biol1996,135:1441-1455.
908Cell division,growth and death
25.Croft DR,Coleman ML,Li S,Robertson D,Sullivan T,Stewart CL,
Olson MF:Actin–myosin-based contraction is responsible for apoptotic nuclear disintegration.J Cell Biol2005,168:245-255.
26.Coleman ML,Sahai EA,Yeo M,Bosch M,Dewar A,Olson MF:
Membrane blebbing during apoptosis results from caspase-mediated activation of ROCK I.Nat Cell Biol2001,3:339-345.
27.Sebbagh M,Renvoize C,Hamelin J,Riche N,Bertoglio J,Breard J:
Caspase-3-mediated cleavage of ROCK I induces MLC
phosphorylation and apoptotic membrane blebbing.Nat Cell Biol2001,3:346-352.
https://www.doczj.com/doc/d93548135.html,ls JC,Stone NL,Erhardt J,Pittman RN:Apoptotic membrane
blebbing is regulated by myosin light chain phosphorylation.J Cell Biol1998,140:627-636.
29.Martin SJ,O’Brien GA,Nishioka WK,McGahon AJ,Mahboubi A,
Saido TC,Green DR:Proteolysis of fodrin(non-erythroid
spectrin)during apoptosis.J Biol Chem1995,270:6425-6428.
30.Taylor RC,Brumatti G,Ito S,Hengartner MO,Derry WB,Martin SJ:
Establishing a blueprint for CED-3-dependent killing through identi?cation of multiple substrates for this protease.J Biol Chem2007,282:15011-15021.
31. Luthi AU,Martin SJ:The CASBAH:a searchable database of caspase substrates.Cell Death Differ2007,14:641-650.
32.Byun Y,Chen F,Chang R,Trivedi M,Green KJ,Cryns VL:Caspase
cleavage of vimentin disrupts intermediate?laments and
promotes apoptosis.Cell Death Differ2001,8:443-450.
33.Gerner C,Frohwein U,Gotzmann J,Bayer E,Gelbmann D,
Bursch W,Schulte-Hermann R:The Fas-induced apoptosis
analyzed by high throughput proteome analysis.J Biol Chem 2000,275:39018-39026.
34. Dix MM,Simon GM,Cravatt BF:Global mapping of the topography and magnitude of proteolytic events in apoptosis. Cell2008,134:679-691.
35. Mahrus S,Trinidad JC,Barkan DT,Sali A,Burlingame AL, Wells JA:Global sequencing of proteolytic cleavage sites in apoptosis by speci?c labeling of protein N termini.Cell2008, 134:866-876.
In the above two papers new techniques were used to identify protease
substrates in vivo.The?rst paper introduced a new high-content pro-teomic platform called PROTOMAP to pro?le proteolytic events occurring
in natural biological systems.The second paper labeled N-terminus of
newly cleaved polypeptides with biotin.Applying these methods to cells undergo apoptosis,authors were able to identify proteins not previously documented as caspase substrate and provide a topographic map of proteolytic events during apoptosis.
36.Wyllie AH:Glucocorticoid-induced thymocyte apoptosis is
associated with endogenous endonuclease activation.Nature 1980,284:555-556.
37.Samejima K,Earnshaw WC:Trashing the genome:the role of
nucleases during apoptosis.Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol2005,
6:677-688.
38.Kaufmann SH,Mesner PW Jr,Samejima K,Tone S,
Earnshaw WC:Detection of DNA cleavage in apoptotic cells.
Methods Enzymol2000,322:3-15.
39.Widlak P,Garrard WT:Discovery,regulation,and action of the
major apoptotic nucleases DFF40/CAD and endonuclease G.J Cell Biochem2005,94:1078-1087.
40.Widlak P,Garrard WT:Roles of the major apoptotic nuclease-
DNA fragmentation factor-in biology and disease.Cell Mol Life Sci2009,66:263-274.
41.Counis MF,Torriglia A:Acid DNases and their interest among
apoptotic endonucleases.Biochimie2006,88:1851-1858.
42.Parrish JZ,Xue D:Cuts can kill:the roles of apoptotic nucleases
in cell death and animal development.Chromosoma2006,
115:89-97.
43.Nagata S:DNA degradation in development and programmed
cell death.Annu Rev Immunol2005,23:853-875.
44. Enari M,Sakahira H,Yokoyama H,Okawa K,Iwamatsu A,
Nagata S:A caspase-activated DNase that degrades DNA
during apoptosis,and its inhibitor ICAD.Nature1998,
391:43-50.
Together with references[45,50 ],these are the original papers that
described the biochemical puri?cation and characterization of CAD/
DFF40as a major apoptotic DNase and clearly showed that DNase activity
of CAD is always inhibited by ICAD until ICAD is cleaved by activated
caspase3at two sites and its inhibitory effect on CAD is released.
45.
Liu X,Zou H,Slaughter C,Wang X:DFF,a heterodimeric protein
that functions downstream of caspase-3to trigger DNA
fragmentation during apoptosis.Cell1997,89:175-184.
46.Samejima K,Tone S,Earnshaw WC:CAD/DFF40nuclease is
dispensable for high molecular weight DNA cleavage and
stage I chromatin condensation in apoptosis.J Biol Chem
2001,276:45427-45432.
47.Zhang J,Liu X,Scherer DC,van Kaer L,Wang X,Xu M:Resistance
to DNA fragmentation and chromatin condensation in mice
lacking the DNA fragmentation factor45.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S
A1998,95:12480-12485.
48.Sakahira H,Iwamatsu A,Nagata S:Speci?c chaperone-like
activity of inhibitor of caspase-activated DNase for caspase-
activated DNase.J Biol Chem2000,275:8091-8096.
49.Gu J,Dong RP,Zhang C,McLaughlin DF,Wu MX,Schlossman SF:
Functional interaction of DFF35and DFF45with caspase-
activated DNA fragmentation nuclease DFF40.J Biol Chem
1999,274:20759-20762.
50.
Sakahira H,Enari M,Nagata S:Cleavage of CAD inhibitor in CAD
activation and DNA degradation during apoptosis.Nature
1998,391:96-99.
51.Lechardeur D,Drzymala L,Sharma M,Zylka D,Kinach R,Pacia J,
Hicks C,Usmani N,Rommens JM,Lukacs GL:Determinants of
the nuclear localization of the heterodimeric DNA
fragmentation factor(ICAD/CAD).J Cell Biol2000,150:321-334.
52.Samejima K,Earnshaw WC:ICAD/DFF regulator of apoptotic
nuclease is nuclear.Exp Cell Res1998,243:453-459.
53.
Woo EJ,Kim YG,Kim MS,Han WD,Shin S,Robinson H,Park SY,
Oh BH:Structural mechanism for inactivation and activation of
CAD/DFF40in the apoptotic pathway.Mol Cell2004,14:531-539.
The crystal structure of activated CAD/DFF40revealed that CAD acts as
dimer to cleave DNA.The deeply buried active site in the scissors-like
structure explains how CAD distinguishes the internucleosomal DNA from
nucleosomal DNA as its substrate.
54.Hanus J,Kalinowska-Herok M,Widlak P:The major apoptotic
endonuclease DFF40/CAD is a deoxyribose-speci?c and
double-strand-speci?c enzyme.Apoptosis2008,13:377-382.
55.Widlak P,Kalinowska M,Parseghian MH,Lu X,Hansen JC,
Garrard WT:The histone H1C-terminal domain binds to the
apoptotic nuclease,DNA fragmentation factor(DFF40/CAD)
and stimulates DNA cleavage.Biochemistry2005,44:7871-7878.
56.Liu X,Li P,Widlak P,Zou H,Luo X,Garrard WT,Wang X:The40-
kDa subunit of DNA fragmentation factor induces DNA
fragmentation and chromatin condensation during apoptosis.
Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A1998,95:8461-8466.
57.
Li LY,Luo X,Wang X:Endonuclease G is an apoptotic DNase
when released from mitochondria.Nature2001,412:95-99.
This paper and reference[71]used biochemical and genetic approach
and independently identi?ed mammalian endonuclease G(EndoG)and its
C.elegans homolog cps-6(CED-3protease suppressor)as a cell-auton-
omous nuclease in addition to CAD.
58.Arnoult D,Gaume B,Karbowski M,Sharpe JC,Cecconi F,
Youle RJ:Mitochondrial release of AIF and EndoG requires
caspase activation downstream of Bax/Bak-mediated
permeabilization.EMBO J2003,22:4385-4399.
59.Temme C,Weissbach R,Lilie H,Wilson C,Meinhart A,Meyer S,
Golbik R,Schierhorn A,Wahle E:The Drosophila melanogaster
gene cg4930encodes a high af?nity inhibitor for
endonuclease G.J Biol Chem2009,284:8337-8348.
60.Torriglia A,Lepretre C,Padron-Barthe L,Chahory S,Martin E:
Molecular mechanism of L-D Nase II activation and function as
a molecular switch in apoptosis.Biochem Pharmacol2008,
76:1490-1502.
Cellular and nuclear degradation during apoptosis He,Lu and Zhou909
61.Kawase T,Ichikawa H,Ohta T,Nozaki N,Tashiro F,Ohki R,Taya Y:
p53target gene AEN is a nuclear exonuclease required for p53-dependent apoptosis.Oncogene2008,27:3797-3810. 62.Shiokawa D,Kobayashi T,Tanuma S:Involvement of DNase
gamma in apoptosis associated with myogenic differentiation of C2C12cells.J Biol Chem2002,277:31031-31037.
63.Shiokawa D,Shika Y,Araki S,Sunaga S,Mizuta R,Kitamura D,
Tanuma S:Stage-speci?c expression of DNasegamma during B-cell development and its role in B-cell receptor-mediated apoptosis in WEHI-231cells.Cell Death Differ2007,
14:992-1000.
64.Sulston JE:Post-embryonic development in the ventral cord of
Caenorhabditis elegans.Philos Trans R Soc Lond B Biol Sci
1976,275:287-297.
65.Wu YC,Stan?eld GM,Horvitz HR:NUC-1,a Caenorhabditis
elegans DNase II homolog,functions in an intermediate
step of DNA degradation during apoptosis.Genes Dev2000, 14:536-548.
66.Hsiao YY,Nakagawa A,Shi Z,Mitani S,Xue D,Yuan HS:Crystal
structure of CRN-4:implications for domain function in
apoptotic DNA degradation.Mol Cell Biol2009,29:448-457. 67.Parrish JZ,Xue D:Functional genomic analysis of apoptotic
DNA degradation in C.elegans.Mol Cell2003,11:987-996. 68.McIlroy D,Tanaka M,Sakahira H,Fukuyama H,Suzuki M,
Yamamura K,Ohsawa Y,Uchiyama Y,Nagata S:An auxiliary
mode of apoptotic DNA fragmentation provided by
phagocytes.Genes Dev2000,14:549-558.
69.Irvine RA,Adachi N,Shibata DK,Cassell GD,Yu K,
Karanjawala ZE,Hsieh CL,Lieber MR:Generation and
characterization of endonuclease G null mice.Mol Cell Biol
2005,25:294-302.
70.David KK,Sasaki M,Yu SW,Dawson TM,Dawson VL:EndoG is
dispensable in embryogenesis and apoptosis.Cell Death Differ 2006,13:1147-1155.
71.Parrish J,Li L,Klotz K,Ledwich D,Wang X,Xue D:Mitochondrial
endonuclease G is important for apoptosis in C.elegans.
Nature2001,412:90-94.
72.Zhang J,Wang X,Bove KE,Xu M:DNA fragmentation factor45-
de?cient cells are more resistant to apoptosis and exhibit
different dying morphology than wild-type control cells.J Biol Chem1999,274:37450-37454.
73.Radic M,Marion T,Monestier M:Nucleosomes are exposed at
the cell surface in apoptosis.J Immunol2004,172:6692-6700.
74.Frisoni L,McPhie L,Colonna L,Sriram U,Monestier M,Gallucci S,
Caricchio R:Nuclear autoantigen translocation and
autoantibody opsonization lead to increased dendritic cell
phagocytosis and presentation of nuclear antigens:a novel pathogenic pathway for autoimmunity?J Immunol2005,
175:2692-2701.
75.Evans CJ,Aguilera RJ:DNase II:genes,enzymes and function.
Gene2003,322:1-15.
76. Mukae N,Yokoyama H,Yokokura T,Sakoyama Y,Nagata S: Activation of the innate immunity in Drosophila by endogenous chromosomal DNA that escaped apoptotic degradation.Genes Dev2002,16:2662-2671.
77.Krieser RJ,MacLea KS,Longnecker DS,Fields JL,Fiering S,
Eastman A:Deoxyribonuclease IIalpha is required during the phagocytic phase of apoptosis and its loss causes perinatal lethality.Cell Death Differ2002,9:956-962.
78.Nagata S:Autoimmune diseases caused by defects in clearing
dead cells and nuclei expelled from erythroid precursors.
Immunol Rev2007,220:237-250.
79.Okabe Y,Kawane K,Akira S,Taniguchi T,Nagata S:Toll-like
receptor-independent gene induction program activated by mammalian DNA escaped from apoptotic DNA degradation.J Exp Med2005,202:1333-1339.
80.Okabe Y,Kawane K,Nagata S:IFN regulatory factor(IRF)3/7-
dependent and-independent gene induction by mammalian
DNA that escapes degradation.Eur J Immunol2008,
38:3150-3158.
81.
Yoshida H,Okabe Y,Kawane K,Fukuyama H,Nagata S:Lethal anemia caused by interferon-beta produced in mouse
embryos carrying undigested DNA.Nat Immunol2005,6:49-56.
82.Kawane K,Ohtani M,Miwa K,Kizawa T,Kanbara Y,Yoshioka Y,
Yoshikawa H,Nagata S:Chronic polyarthritis caused by
mammalian DNA that escapes from degradation in
macrophages.Nature2006,443:998-1002.
83.Maiuri MC,Zalckvar E,Kimchi A,Kroemer G:Self-eating and self-
killing:crosstalk between autophagy and apoptosis.Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol2007,8:741-752.
84.Gonzalez-Polo RA,Boya P,Pauleau AL,Jalil A,Larochette N,
Souquere S,Eskelinen EL,Pierron G,Saftig P,Kroemer G:The
apoptosis/autophagy paradox:autophagic vacuolization
before apoptotic death.J Cell Sci2005,118:3091-3102.
85.Boya P,Gonzalez-Polo RA,Casares N,Perfettini JL,Dessen P,
Larochette N,Metivier D,Meley D,Souquere S,Yoshimori T et al.: Inhibition of macroautophagy triggers apoptosis.Mol Cell Biol 2005,25:1025-1040.
86.Hara T,Nakamura K,Matsui M,Yamamoto A,Nakahara Y,Suzuki-
Migishima R,Yokoyama M,Mishima K,Saito I,Okano H et al.:
Suppression of basal autophagy in neural cells causes
neurodegenerative disease in mice.Nature2006,441:885-889.
87.Komatsu M,Waguri S,Chiba T,Murata S,Iwata J,Tanida I,
Ueno T,Koike M,Uchiyama Y,Kominami E et al.:Loss of
autophagy in the central nervous system causes
neurodegeneration in mice.Nature2006,441:880-884.
88.Pua HH,Dzhagalov I,Chuck M,Mizushima N,He YW:A critical
role for the autophagy gene Atg5in T cell survival and
proliferation.J Exp Med2007,204:25-31.
89.Shimizu S,Kanaseki T,Mizushima N,Mizuta T,Arakawa-
Kobayashi S,Thompson CB,Tsujimoto Y:Role of Bcl-2family
proteins in a non-apoptotic programmed cell death dependent on autophagy genes.Nat Cell Biol2004,6:1221-1228.
90.Lum JJ,Bauer DE,Kong M,Harris MH,Li C,Lindsten T,
Thompson CB:Growth factor regulation of autophagy and cell survival in the absence of apoptosis.Cell2005,120:237-248. 91.Berry DL,Baehrecke EH:Growth arrest and autophagy are
required for salivary gland cell degradation in Drosophila.Cell 2007,131:1137-1148.
92.Berry DL,Baehrecke EH:Autophagy functions in programmed
cell death.Autophagy2008,4:359-360.
93.Nezis IP,Lamark T,Velentzas AD,Rusten TE,Bjorkoy G,
Johansen T,Papassideri IS,Stravopodis DJ,Margaritis LH,
Stenmark H et al.:Cell death during Drosophila melanogaster early oogenesis is mediated through autophagy.Autophagy
2009,5:298-302.
94.Mohseni N,McMillan SC,Chaudhary R,Mok J,Reed BH:
Autophagy promotes caspase-dependent cell death during
Drosophila development.Autophagy2009,5:329-338.
95.
Qu X,Zou Z,Sun Q,Luby-Phelps K,Cheng P,Hogan RN,Gilpin C, Levine B:Autophagy gene-dependent clearance of apoptotic cells during embryonic development.Cell2007,128:931-946. This paper discovered a role of autophagy activity in apoptotic cells using in vitro cultured mouse embryonic cells.Although autophagy genes are dispensable for apoptosis but are essential for providing the dying cell suf?cient ATP to generate the engulfment signals that are required for the apoptotic cells to be removed by phagocytes.
96.Mellen MA,de la Rosa EJ,Boya P:The autophagic machinery is
necessary for removal of cell corpses from the developing
retinal neuroepithelium.Cell Death Differ2008,15:1279-1290. 97.Vieira OV,Botelho RJ,Grinstein S:Phagosome maturation:
aging gracefully.Biochem J2002,366:689-704.
98.Vieira OV,Botelho RJ,Rameh L,Brachmann SM,Matsuo T,
Davidson HW,Schreiber A,Backer JM,Cantley LC,Grinstein S: Distinct roles of Class I and Class III phosphatidylinositol3-
kinases in phagosome formation and maturation.J Cell Biol
2001,155:19-25.
910Cell division,growth and death
99.Botelho RJ,Scott CC,Grinstein S:Phosphoinositide
involvement in phagocytosis and phagosome maturation.Curr Top Microbiol Immunol2004,282:1-30.
100.Scott CC,Botelho RJ,Grinstein S:Phagosome maturation:a few bugs in the system.J Membr Biol2003,193:137-152.
101.Zerial M,McBride H:Rab proteins as membrane organizers.Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol2001,2:107-117.
102.Duclos S,Diez R,Garin J,Papadopoulou B,Descoteaux A, Stenmark H,Desjardins M:Rab5regulates the kiss and run
fusion between phagosomes and endosomes and the
acquisition of phagosome leishmanicidal properties in RAW 264.7macrophages.J Cell Sci2000,113(Pt19):3531-3541. 103.Desjardins M,Huber LA,Parton RG,Grif?ths G:Biogenesis of phagolysosomes proceeds through a sequential series of
interactions with the endocytic apparatus.J Cell Biol1994,
124:677-688.
104.Vieira OV,Bucci C,Harrison RE,Trimble WS,Lanzetti L, Gruenberg J,Schreiber AD,Stahl PD,Grinstein S:Modulation of Rab5and Rab7recruitment to phagosomes by
phosphatidylinositol3-kinase.Mol Cell Biol2003,
23:2501-2514.
105.Harrison RE,Bucci C,Vieira OV,Schroer TA,Grinstein S: Phagosomes fuse with late endosomes and/or lysosomes by extension of membrane protrusions along microtubules:role of Rab7and RILP.Mol Cell Biol2003,23:6494-6506.
106.Nishi T,Forgac M:The vacuolar(H+)-ATPases–nature’s most versatile proton pumps.Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol2002,3:94-103. 107.Kawasaki-Nishi S,Nishi T,Forgac M:Proton translocation driven by ATP hydrolysis in V-ATPases.FEBS Lett2003,545:76-85. 108.Hackam DJ,Rotstein OD,Zhang WJ,Demaurex N,Woodside M, Tsai O,Grinstein S:Regulation of phagosomal acidi?cation.
Differential targeting of Na+/H+exchangers,Na+/K+-
ATPases,and vacuolar-type H+-atpases.J Biol Chem1997, 272:29810-29820.
109.Lukacs GL,Rotstein OD,Grinstein S:Phagosomal acidi?cation is mediated by a vacuolar-type H(+)-ATPase in murine
macrophages.J Biol Chem1990,265:21099-21107.
110 .Erwig LP,McPhilips KA,Wynes MW,Ivetic A,Ridley AJ, Henson PM:Differential regulation of phagosome maturation in macrophages and dendritic cells mediated by Rho GTPases and ezrin-radixin-moesin(ERM)proteins.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A2006,103:12825-12830.
This paper compared the different phagosome maturation rates in macro-phagy and the role of Rho kinase in early maturation process.Phago-somes containing apoptotic cells in macrophagy mature faster than those containing Ig-opsonized target cells.These evidences suggest the exis-tence of different cellular regulatory processes in degradation of apop-totic cells verses other engulfed objects.
111.Metzstein MM,Stan?eld GM,Horvitz HR:Genetics of programmed cell death in C.elegans:past,present and future.
Trends Genet1998,14:410-416.
112.Reddien PW,Horvitz HR:The engulfment process of programmed cell death in Caenorhabditis elegans.Annu Rev Cell Dev Biol2004,20:193-221.
113 .Yu X,Odera S,Chuang CH,Lu N,Zhou Z:C.elegans dynamin mediates the signaling of phagocytic receptor CED-1for the engulfment and degradation of apoptotic cells.Dev Cell2006, 10:743-757.
The?rst paper that discovered the function of C.elegans dynamin,DYN-1,in apoptotic cell removal.Not like its canonical?ssion activity in endocytosis,dynamin function to mediate fusion of endocytic vesicles to the phagocytic cup and phagosome surface during phagocytosis. Although DYN-1only localizes on phagosome for a short period of time, its activity is important for both engulfment and degradation of apoptotic cells.This paper?rst showed the major downstream events of CED-1 signaling pathway,that is recruiting intracellular vesicles to fuse with nascent phagosome providing membrane material and proteins that are necessary for apoptotic cell degradation.
114 .Yu X,Lu N,Zhou Z:Phagocytic receptor CED-1initiates a
signaling pathway for degrading engulfed apoptotic cells.
PLoS Biol2008,6:e61.
This paper reported the function of CED-1as a phagocytic receptor in
phagosome maturation.CED-1not only promotes the engulfment of
apoptotic cells but also controls the recruitment of downstream factors
that are important for phagosome maturation.This paper also provides a
detailed characterization of RAB-7,one of the down stream effectors,
RAB-7localizes on phagosome surface shortly after engulfment to
mediate the fusion of lysosome to phagosome and its function is crucial
for degradation of apoptotic cells.
115
.Kinchen JM,Doukoumetzidis K,Almendinger J,Stergiou L,
Tosello-Trampont A,Sifri CD,Hengartner MO,Ravichandran KS:A
pathway for phagosome maturation during engulfment of
apoptotic cells.Nat Cell Biol2008,10:556-566.
In this paper,a genome-wise RNAi screen was performed to identify
genes that are involved in apoptotic cell removal in C.elegans.The work
provides the evidence that C.elegans VPS-34and HOPS complex are
required for phagosome maturation.A genetic pathway leads to degra-
dation of apoptotic cell was built starting from DYN-1.Authors also
compared the functions of several protein homologues of worm and
mammalian,showing that the phagosome degradation pathway is high
conserved in different species.
116
.Mangahas PM,Yu X,Miller KG,Zhou Z:The small GTPase Rab2
functions in the removal of apoptotic cells in Caenorhabditis
elegans.J Cell Biol2008,180:357-373.
Together with[117 ]showed the function of small GTPase RAB-2in
phagosome maturation.RAB-2mediates the fusion of lysosomes to
phagosomes.However,con?ict results were reported regarding whether
the fusion events lead phagosome acidi?cation.
117
.Lu Q,Zhang Y,Hu T,Guo P,Li W,Wang X:C.elegans Rab
GTPase2is required for the degradation of apoptotic cells.
Development2008,135:1069-1080.
118.Cai H,Reinisch K,Ferro-Novick S:Coats,tethers,Rabs,and
SNAREs work together to mediate the intracellular destination
of a transport vesicle.Dev Cell2007,12:671-682.
119.Grosshans BL,Ortiz D,Novick P:Rabs and their effectors:
achieving speci?city in membrane traf?c.Proc Natl Acad Sci U
S A2006,103:11821-11827.
120
.Xiao H,Chen D,Fang Z,Xu J,Sun X,Song S,Liu J,Yang C:
Lysosome biogenesis mediated by vps-18affects apoptotic
cell degradation in Caenorhabditis elegans.Mol Biol Cell2009,
20:21-32.
This paper disscused the important role of VPS-18,a worm homolog of
yeast HOPS complex subunit Vps18p,in phagosome degradation and
biogenesis of endosomes and lysosomes.Mutation in vps-18was shown
to affect endosome and lysosome biogenesis and block phagosomes
fuse to lysosomes.
121.Garin J,Diez R,Kieffer S,Dermine JF,Duclos S,Gagnon E,
Sadoul R,Rondeau C,Desjardins M:The phagosome proteome:
insight into phagosome functions.J Cell Biol2001,152:165-180.
122.Stuart LM,Boulais J,Charriere GM,Hennessy EJ,Brunet S,
Jutras I,Goyette G,Rondeau C,Letarte S,Huang H et al.:A
systems biology analysis of the Drosophila phagosome.Nature
2007,445:95-101.
123.Peri F,Nusslein-Volhard C:Live imaging of neuronal
degradation by microglia reveals a role for v0-ATPase a1in
phagosomal fusion in vivo.Cell2008,133:916-927.
124.Bayer MJ,Reese C,Buhler S,Peters C,Mayer A:Vacuole
membrane fusion:V0functions after trans-SNARE pairing and
is coupled to the Ca2+-releasing channel.J Cell Biol2003,
162:211-222.
125.Hinshaw JE:Dynamin and its role in membrane?ssion.Annu
Rev Cell Dev Biol2000,16:483-519.
126.Peters C,Baars TL,Buhler S,Mayer A:Mutual control of
membrane?ssion and fusion proteins.Cell2004,119:667-678.
127.Miyauchi K,Kim Y,Latinovic O,Morozov V,Melikyan GB:HIV
enters cells via endocytosis and dynamin-dependent fusion
with endosomes.Cell2009,137:433-444.
128.Hoppins S,Nunnari J:The molecular mechanism of
mitochondrial fusion.Biochim Biophys Acta2009,1793:20-26.
129.Di A,Nelson DJ,Bindokas V,Brown ME,Libunao F,Palfrey HC:
Dynamin regulates focal exocytosis in phagocytosing
macrophages.Mol Biol Cell2003,14:2016-2028.
Cellular and nuclear degradation during apoptosis He,Lu and Zhou911
130.Gold ES,Underhill DM,Morrissette NS,Guo J,McNiven MA, Aderem A:Dynamin2is required for phagocytosis in
macrophages.J Exp Med1999,190:1849-1856.
131.Perskvist N,Roberg K,Kulyte A,Stendahl O:Rab5a GTPase regulates fusion between pathogen-containing phagosomes and cytoplasmic organelles in human neutrophils.J Cell Sci 2002,115:1321-1330.
132.Fratti RA,Backer JM,Gruenberg J,Corvera S,Deretic V:Role of phosphatidylinositol3-kinase and Rab5effectors in
phagosomal biogenesis and mycobacterial phagosome
maturation arrest.J Cell Biol2001,154:631-644.
133.Kitano M,Nakaya M,Nakamura T,Nagata S,Matsuda M:Imaging of Rab5activity identi?es essential regulators for phagosome maturation.Nature2008,453:241-245.
134.Christoforidis S,Miaczynska M,Ashman K,Wilm M,Zhao L, Yip SC,Water?eld MD,Backer JM,Zerial M:
Phosphatidylinositol-3-OH kinases are Rab5effectors.Nat
Cell Biol1999,1:249-252.
135.Murray JT,Panaretou C,Stenmark H,Miaczynska M,Backer JM: Role of Rab5in the recruitment of hVps34/p150to the early endosome.Traf?c2002,3:416-427.
136.Shin HW,Hayashi M,Christoforidis S,Lacas-Gervais S, Hoepfner S,Wenk MR,Modregger J,Uttenweiler-Joseph S,
Wilm M,Nystuen A et al.:An enzymatic cascade of Rab5
effectors regulates phosphoinositide turnover in the
endocytic pathway.J Cell Biol2005,170:607-618.
137.Liu QA,Hengartner MO:Candidate adaptor protein CED-6 promotes the engulfment of apoptotic cells in C.elegans.Cell 1998,93:961-972.
138.Zhou Z,Hartwieg E,Horvitz HR:CED-1is a transmembrane receptor that mediates cell corpse engulfment in C.elegans.
Cell2001,104:43-56.
139.Ellis RE,Jacobson DM,Horvitz HR:Genes required for the engulfment of cell corpses during programmed cell death in Caenorhabditis elegans.Genetics1991,129:79-94.
140.Callebaut I,Mignotte V,Souchet M,Mornon JP:EMI domains are widespread and reveal the probable orthologs of the
Caenorhabditis elegans CED-1protein.Biochem Biophys Res Commun2003,300:619-623.141.MacDonald JM,Beach MG,Porpiglia E,Sheehan AE,Watts RJ, Freeman MR:The Drosophila cell corpse engulfment receptor Draper mediates glial clearance of severed axons.Neuron
2006,50:869-881.
142.Awasaki T,Tatsumi R,Takahashi K,Arai K,Nakanishi Y,Ueda R, Ito K:Essential role of the apoptotic cell engulfment genes
draper and ced-6in programmed axon pruning during
Drosophila metamorphosis.Neuron2006,50:855-867.
143.Manaka J,Kuraishi T,Shiratsuchi A,Nakai Y,Higashida H, Henson P,Nakanishi Y:Draper-mediated and
phosphatidylserine-independent phagocytosis of apoptotic
cells by Drosophila hemocytes/macrophages.J Biol Chem
2004,279:48466-48476.
144.Ziegenfuss JS,Biswas R,Avery MA,Hong K,Sheehan AE, Yeung YG,Stanley ER,Freeman MR:Draper-dependent glial
phagocytic activity is mediated by Src and Syk family kinase signalling.Nature2008,453:935-939.
145
.Kurant E,Axelrod S,Leaman D,Gaul U:Six-microns-under acts upstream of Draper in the glial phagocytosis of apoptotic
neurons.Cell2008,133:498-509.
This paper reveal the functions of two Drosophila phagoctosis receptors, SIMU and DRPR in?y https://www.doczj.com/doc/d93548135.html,paring with SIMU,DRPR mainly functions in controling phagosome maturation rather than the recognition and engulfment of apoptotic neurons.
146.Hamon Y,Trompier D,Ma Z,Venegas V,Pophillat M,Mignotte V, Zhou Z,Chimini G:Cooperation between engulfment
receptors:the case of ABCA1and MEGF10.PLoS ONE2006, 1:e120.
147.Lerm M,Brodin VP,Ruishalme I,Stendahl O,Sarndahl E: Inactivation of Cdc42is necessary for depolymerization of
phagosomal F-actin and subsequent phagosomal maturation.
J Immunol2007,178:7357-7365.
148.Sanjuan MA,Dillon CP,Tait SW,Moshiach S,Dorsey F,Connell S, Komatsu M,Tanaka K,Cleveland JL,Withoff S et al.:Toll-like
receptor signalling in macrophages links the autophagy
pathway to phagocytosis.Nature2007,450:1253-1257.
149.Shui W,Sheu L,Liu J,Smart B,Petzold CJ,Hsieh TY,Pitcher A, Keasling JD,Bertozzi CR:Membrane proteomics of
phagosomes suggests a connection to autophagy.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A2008,105:16952-16957.
912Cell division,growth and death
关于感恩的演讲稿:心存感恩,回馈人生敬爱的老师,亲爱的同学们: 大家好! 我是来自六年五班的李嘉龙,我演讲的题目是《心存感恩,回馈人生》。 一滴水,要感谢大海,让它汇聚成了无尽的水流;一朵花,要感谢雨露,滋润它在阳光下茁壮成长;一只鹰,要感谢长空,赐予了它前进远方的力量;一座山,要感谢大地,用自己的臂膀,给了她高耸的方向;一个人,要学会感恩,才能托起世界的脊梁!学会感恩,不仅是报答,更是心存感激的表示。 “羊有跪乳之恩,鸦有反哺之义”,世界的主宰——人,更要充满感恩之情。一颗感恩之心,化干戈为玉帛;一颗感恩之心,化腐朽为神奇;一颗感恩之心,化冰峰为春暖。学会了感恩,才会在生活中发现美好。一次,美国前总统罗斯福家失窃,被偷去了许多东西,一位朋友闻讯后,忙写信安慰他,劝他不必太在意。罗斯福给朋友写了一封回信:“亲爱的朋友,谢谢你来信安慰我,我现在很平安。感谢上帝,因为第一,贼偷去的是我的东西,而没有伤害我的生命;第二,贼只偷去我部分东西,而不是全部;第三,最值得庆幸的是,做贼的是他,而不是我。”对任何一个人来说,失窃绝对是不幸的事,而罗斯福却能在失窃中找到美好,因为他拥有了茁壮成长的感恩之树。 在人生的路上,缺少了感恩,就缺少了阳光雨露。这种人生的哲理,让我们不断地面临生命的挑战,人生的巅峰。感恩沟通了人的心灵,让他人的帮助铭记在心。在这个时代,如果人与人之间不存在感恩,那么人与人之间的关系就不复存在,社会也将成为一片大沙漠。 感恩是人与生俱来的本性,是生活美好的基础。我们心怀感恩,就能回报社会,报答自然。马斯洛曾说,心若改变,态度就跟着改变;态度若改变,习惯就跟着改变;习惯若改变,性格就跟着改变;性格若改变,人生就跟着改变。我们若播种感恩的心,就收获诚恳的态度;若播种诚恳的态度,就带动良好的习惯;若播种良好的习惯,就升华为健康的性格;若播种健康的性格,才收获成功的人生! 我的演讲完毕,谢谢大家。 第1 页共3 页
乡村学校少年宫辅导员工作职责 一、认真备课、讲课,合理制定教学进度,在教学实践中,注重基础知识与基本技能的传授,充分调动学生的学习积极性与主观能动性,认真开展教研活动,不断提高教育教学质量。 二、艺术类教师可以有组织、有计划地选择开展声乐、舞蹈、器乐、语言与形象表演等活动,组织各类特色班。 三、有组织、有制度搞好学员民主管理,注重思想品德与行为规范教育,做到教书育人,使学生身心都能健康成长。 四、按时并有质量地完成乡村学校少年宫的活动任务。在教学中把教学任务与特色活动合理结合,使更多的未成年人在活动中得到锻炼与提高。 五、遵守劳动纪律,讲究职业道德与师容教态,负责管理好教室卫生及安全,建造良好整洁的教学环境。 六、按时完成少年宫领导交给的其它工作。
少年宫安全管理制度 1、所有参加活动的学员必须由家长负责接送,并与少年宫签订《安全管理协议书》。 2、教师应加强与学员监护人的密切联系,掌握家长的通讯联系方式。 3、教师必须在所有学员安全离开教学活动区域后,关闭所有用电设备,并关好门窗后方可离开。 4、教师负责教学时间(包括课前、课后、课间)教学场所的全程安全管理。 5、门卫管理人员负责管理门前停车与师生进出,保证少年宫门前安全无事故。 6、所有教职员工,如发现安全隐患或事故,必须零时间报告,并进行恰当处理,不得离开事发现场。 7、教师未经同意,不得擅自组织学员外出活动,组织集体活动实行报批制度,并实行安全责任制,采取必要的安全防护措施。
少年宫组织机构 芝阳学校少年宫工作小组 组长:同庆社 副组长:高效忠孙凯武 成员:何亚利吴朝辉马永健屈娟平卫晶星赵院芳 芝阳学校少年宫辅导员队伍 办公室主任:同庆社 办公室副主任:高效忠 成员:卫晶星王东峰黎万民 专职辅导员 董燕刘玲高连侠王艳 强菲张延张会贤郭勤学 少年宫副主任工作职责 乡村少年宫副主任协助少年宫主任工作,全面完成少年宫的教育教学任务,不断提高教育教学质量,其主要职责就是: 1、组织与管理教学工作,有计划地组织教师进行教研活动,认真学
心存感恩演讲稿【三篇】 心存【一】 尊敬的老师,亲爱的同学们: 我今天演讲的题目是“心怀感恩,快乐工作”。感谢明月照亮了夜空;感谢朝霞捧出的黎明;感谢春光融化了冰雪;感谢大地哺育了生灵;感谢母亲赐予生命;感谢生活赠友谊爱情。感谢生活中所发生的一切,幸运与不幸,快乐与痛苦,富有与贫穷,伴我们一起成长,让我们感受生活的真谛——做人要怀有一颗感恩的心! 怀着感恩的心,孔繁森呕心沥血,鞠躬尽瘁,造福 ___人民,魂洒青藏高原;怀着感恩的心,唐山“十三义士”在第一时间奔赴四川灾区,不分昼夜地运送物资,抗震救灾;怀着感恩的心,我们身边的英模艾前文,烈火中冒着生命危险勇救他人,有人问他为什么,他动情地说:“不能让烈火吞噬他人生命!”;怀着感恩的心,我们身边的征税楷模姚淑云,对纳税人总是晓之理,动之以情,被纳税人誉为“微笑天使”。 但是,随着经济社会的发展,物质不断丰富,物欲也开始泛滥,人们的心变得越来越浮躁。攀比收入,攀比享受,攀比潇洒。我们的工作和生活,不正受着这种思潮的影响和冲击吗?我们经常谈论的
话题是别人薪水多高,股票涨啦跌啦,你今天泡吧了吗?牌场手气好吗?如果我们都抱着这样的心态去工作去生活,那么我们的社会将变得怎样呢?当你遭受灾难的时候,有谁能够挺身而出;你困苦的时候,有谁伸出温暖之手?国难当头的时候,有谁能够为之献身?许多人的心灵都蒙上了一层灰尘,变得麻木,甚至冷酷,埋怨工作,埋怨生活,剩下永无休止的抱怨。其实,只要我们冷静地想想,非洲的难民,依拉克的战争,就会深感作为中 ___自豪;想想下岗职工的艰辛,生意人的忙碌,就会深感作为税务干部的幸运;想想父母的操劳和含辛茹苦,就会深感受作为儿女的幸福。让我们学会感恩吧,铭记感恩,感恩革命前辈为祖国创下的伟业;感恩国税大家庭,为我们营造宽松舒适的工作生活环境;感恩纳税人艰辛地付出,才使得国富民强;感恩身边的同事和朋友,烦恼一起分担,快乐一起分享。让我们抚去心灵上的尘埃,用心感恩,抱着一颗童真的心,善于发现事物的美好,感受平凡中的美丽,以坦荡的心境、开阔的胸怀来应对生活中的酸甜酸苦辣,让原本平淡的生活焕发出迷人的光彩! 亲爱的同仁,让我们用感恩的心去学习吧,学习前人宝贵的经验和知识,充实自己的头脑,用敏锐的眼光捕捉现代知识信息,紧跟时代的步伐,用钻研的精神学习税务专业知识,在业务上做行家里手,勇争第一。
防火墙设备技术要求 一、防火墙参数要求: 1.性能方面: 1.1网络吞吐量>10Gbps,应用层吞吐率>2Gbps,最大并发连接数>400万(性能要求真实可靠,必须在设备界面显示最大并发连接数不少于400万),每秒新建连接>15万。 1.2万兆级防火墙,网络接口数量不少于12个接口,其中千兆光口不少于4个、千兆电口不少于6个、万兆光接口不少于2个,另外具有不少于2个通用扩展插槽。 1.3冗余双电源,支持HA、冗余或热备特性。 1.4具备外挂日志存储系统,用于存储防火墙日志文件等相关信息,另外支持不同品牌网络设备、服务器等符合标准协议的日志格式,日志存储数量无限制。 1.5内置硬盘,不小于600G,用于日志存储。 2.功能方面(包含并不仅限于以下功能): 2.1具有静态路由功能,包括基于接口、网关、下一跳IP地址的静态路由功能。 2.2具有OSPF动态路由功能,符合行业通用的OSPF协议标准。 2.3具有网络地址转换功能,支持一对一、多对一、多对多的网络地址转换功能。
2.4具有OSI网络模型三层至七层访问控制功能,可基于IP、端口号、应用特征、数据包大小、URL、文件格式、内容、时间段等进行安全访问控制和过滤。 2.5具有基于资源和对象的流量分配功能,包括基于单个IP、网段、IP组、访问源地址及目标地址、应用等的流量管理、分配。 2.6完善的日志及审计系统,防火墙内所有功能均具备相应的日志可供查看和审计。 2.7具有内置或第三方CA证书生成、下发及管理功能。 2.8具有身份认证、身份审计功能,支持用户ID与用户IP 地址、MAC地址的绑定,支持基于CA证书、AD域、短信、微信等多种身份认证方式。 2.9具有入侵检测模块,支持入侵防护、DoS/DDoS防护,包含5年特征库升级服务。 2.10具有上网行为管理模块,支持上网行为检测、内容过滤等功能,包含5年应用特征库升级服务。 2.11具有病毒防护模块,可包含5年病毒库升级服务。 2.12具备基于WEB页面的管理、配置功能,可通过WEB 页面实现所有功能的配置、管理和实时状态查看。 2.13具有SSL VPN模块,含不低于50人的并发在线数。针对手机和电脑,有专门的SSL VPN客户端。 3.质保和服务
2019年专项督查工作总结 根据惠阳安委办《转发关于开展安全生产重点工作专项督查的通知》的文件要求,我局全面开展安全生产重点工作专项安全隐患督查治理工作,落实好安全生产各项工作,坚决防范和坚决遏制重特大事故的发生,确保我区交通运输安全形势持续稳定。现将有关情况总结如下: 一、主要做法 (一)加强组织领导,确保工作扎实有效地开展。为切实开展安全生产重点工作专项督查活动,我局成立工作领导小组,制定了工作方案,并及时下文到局属各单位、各交管所及交通运输企业,督促企业法定代表人落实安全生产主体责任,建立健全安全生产管理机构,严格执行“一岗双责”管理制度,同时,对检查内容进行全面的工作布置,强调工作重点,落实具体措施,确保安全生产大检查扎实有效地开展。 (二)开展安全督查,抓好安全生产的源头管理。重点督查运输企业安全安全产“回头看”的工作情况,进一步认清当前安全生产的严峻形势,深入行业重点和领域督促企业隐患排查治理工作到底到边,针对前一段时间,开展的隐患排查整改行动中存在问题、薄弱环节及事故暴露出来的问题,继续深入开展隐患排查治理的再检查,再督促,再落实,做到隐患排查治理全覆盖。一是督促各运输企业认真落实行业安全生产主体责任,进一步完善安全生产目标管理体系,企业负责人认真履行“一岗双责”制度,安全生产的制度、措施、人员及经费都能按规定落到实处。二是在道路客运安全方面,以组织开展“道路客运安全年”和“百日大检查”为主线,以认真落实客运行业“三关一监督”、“三不进站、六不出站”及“三品”检查制度为抓手,全面加强了对超速、超员、超范围经营及疲劳驾驶违法行为的查处力度,严格落实客运车辆凌晨2-5时停车落地休息制度,充分发挥GPS动态监控系统的作用。三是在危险货物运输方面,强化了行业源头管理,对全区的20
年终总结述职报告 大家好,我是XXX,是学院人力资源部人事专员,同时也是学院管 理系人力资源、市场营销专业的班级辅导员。时间如白驹过隙,转眼间 一年即将过去,2013年新年的钟声又在耳边敲响,面对朝夕相处并给予 自己工作极大支持的同事与各位领导的关怀,下面我从三方面汇报自己 这一年来的工作。 要得到爱首先得付出爱。我的付出换来了孩子们的信任和肯定,在 学校对班主任工作的测评中,学生们对我的满意率几乎每项都为100%。 不要让时间白白的从身边溜走,给自己留下些美好的回忆,把精力 放到工作上,端正工作态度,我们时刻要用感恩的心去工作,要热爱自 己所从事的工作。只有在感恩、热爱自己工作的情况下,才能把工作做 到最好。一个人在工作时,如果能以饱满的精神,满腔的热情,充分发 挥自己的特长,那么即使是做最平凡的工作,也能成为最有用的人;如 果以冷淡的态度去做哪怕是最高尚的工作,也不过是个平庸的人。所以 我们要把心沉下来,兢兢业业做好本职工作。 (一)年上半年,公司已制定了完善的规程及考勤制度年下半年,行 政部组织召开了年的工作安排布置会议年底实行工作目标完成情况考评,将考评结果列入各部门管理人员的年终绩效。在工作目标落实过程中宿 舍管理完善工作制度,有力地促进了管理水平的整体提升。 三要对本办公室的同志进行经常性思想沟通,及时把握本部门廉政 建设执行情况。深入基层,听取群众和企业意见,针对存在的实际问题,
及时改正,切实转变工作作风。同时,自己也要虚心接受群众监督,倾听下属意见,对照廉洁自律规定和有关规章制度,经常性对照检查。要严格按照财经纪律,执行有关开支制度,身先士卒,发挥好模范带头作用。以上述廉,不当之处,敬请各位领导、同志们批评指正。 年终总结述职报告 XX年即将过去,回顾这一年来我科在院领导的正确领导下,坚持“以病人为中心,提高医疗服务质量为主题”.以邓小平理论和“三个代表”重要思想为指导。我科全体医务人员努力学习,钻研业务,使各级人员的自身素质和业务水平都上了一个台阶。全科人员同心同德圆满完成医院下达的各项工作任务,现将本年度的工作总结如下: 一.加强科室管理 科室不断完善标准化的操作规程,全体人员严格按照标准化操作,并有严格的奖惩制度。 科室各种资料管理有条有序.资料完整。各项设备仪器均有专人负责保养并定期检查。 二.努力钻研业务 科室全体员工积极参加院内.外的业务学习,努力提高自己的业务素质和业务水平。不断更新知识,提高技术水平。 坚持每天早读片的制度,着重讨论疑难片的诊断,不断提高全科人员的诊断水平。 三.树立良好的医德医风 树立良好的医德医风,大力弘扬白求恩精神,加强职业道德和行业
心存感恩演讲稿10篇 尊敬的老师,亲爱的同学们: 大家好!今天我在国旗下讲话的主题是《温馨五月,心存感恩》。 有一个人,她永远占据在你心中最柔软的地方,你愿用自己的 一生去爱她;有一种爱,它让你肆意的索取、享用,却不要你任何的 回报——这个人,叫“母亲”,这种爱,叫“母爱”! 母爱是世界上最平凡而又最伟大的情感,她伴我们成长,为我 们遮风挡雨,我们一切的荣耀,都于这平凡而伟大的母爱。天下的母亲们需要的不是物质上的满足,而是希望自己的子女们,都能有一个好的未来,拥有一颗感恩的心,将来能回报社会,回报关爱自己的人。 母亲是一切,是母亲给了我们一切!没有母亲就没有我们,就没有我们的一切。无论我们在哪,母亲纤长的爱始终牵挂着我们。无论我们走了多远,永远也走不出母亲爱的心房。因此,我们都应感恩母亲,感恩母爱。 记得在一则广告中曾出现过小男孩为自己母亲洗脚的感人片断,可在现实的生活中,每个儿女是否都能够做得到的呢?“滴水之恩当 以涌泉相报”我们或许有时会对一个生疏人的一点关怀念念不忘,却对母亲的大爱熟视无睹:嫌她唠叨,或因一些小事就大发雷霆……然而,母亲却永远在一旁默默地支持我们,耐心的开导教育我们,给予我们支持和鼓励。母亲如玉一般纯洁,受母爱浇灌的生命会酝酿出纯美和芬芳。我们应该怀着一颗感恩的心去聆听母亲的唠叨,诚恳面对母亲的严厉,感悟母亲阳光般的心灵世界……
每年5月的第二个星期日定为母亲节,这已经成为国际性的一个庆祝节日了。它是为歌颂世间伟大的母亲,纪念母亲的恩情,发扬孝敬母亲的道德而定立的。同学们,为了母亲的微笑,为了明天的收获,就让你我在这温馨五月,从今天开始,从孝顺母亲开始,学会感恩吧!让我们记住这天下母亲共同的生日吧,为母亲洗一次脚,为她捶一次背。给母亲一个暖暖的拥抱,一脸感恩的笑容吧!一句“妈妈,您辛苦了!”就能让母亲的脸颊重绽灿烂的笑容!让我们多给母亲一点体贴与关怀,让母亲和我们的家充盈着幸福与和谐,那么我们就迎来了真正的长大!正如一首诗所说的:孩儿的成长,是母亲再生的希望;孩儿的失败,是母亲酸楚的泪水;孩儿的成功,是母亲幸福的微笑。 让我们时刻怀着一颗感恩的心,让我们一起成为懂得感恩的人,感谢我们的父母,感谢所有爱我们的人。我的国旗下讲话完毕,谢谢大家! 尊敬的老师,亲爱的同学们: 大家好! 没有亲情,友情和爱情,世界将是一片孤独,一片黑暗。所以,为了摆脱它,就要学会感恩。学会感恩,会使我们的心胸更加宽广,会让我们的生活更加快乐,美好。 “唉,我真是倒霉!又要做题,又要补课。”我开始发起了牢骚,不过就是因为一次考试没有考好,妈妈就让我天天做题,补课。这种教育,属于典型的“题海战术”。因为它们,我变成了井底之蛙,笼中之鸟,没有半点自由,因此我感到非常不满。
华为USG6000系列下一代防火墙详细性能参数表
能,与Agile Controller配合可以实现微信认证。 应用安全●6000+应用协议识别、识别粒度细化到具体动作,自定义协议类型,可与阻断、限流、审计、统计等多种手段自由结合在线协议库升 级。注:USG6320可识别1600+应用。 ●应用识别与病毒扫描结合,发现隐藏于应用中的病毒,木马和恶意软件,可检出超过500多万种病毒。 ●应用识别与内容检测结合,发现应用中的文件类型和敏感信息,防范敏感信息泄露。 入侵防御●基于特征检测,支持超过3500漏洞特征的攻击检测和防御。 ●基于协议检测,支持协议自识别,基于协议异常检测。 ●支持自定义IPS签名。 APT防御与沙箱联动,对恶意文件进行检测和阻断。 Web安全●基于云的URL分类过滤,支持8500万URL库,80+分类。 ●提供专业的安全URL分类,包括钓鱼网站库分类和恶意URL库分类。 ●基于Web的防攻击支持,如跨站脚本攻击、SQL注入攻击。 ●提供URL关键字过滤,和URL黑白名单。 邮件安全●实时反垃圾邮件功能,在线检测,防范钓鱼邮件。 ●本地黑、白名单,远程实时黑名单、内容过滤、关键字过滤、附件类型、大小、数量。 ●支持对邮件附件进行病毒检查和安全性提醒。 数据安全●基于内容感知数据防泄露,对邮件,HTTP,FTP,IM、SNS等传输的文件和文本内容进行识别过滤。 ●20+文件还原和内容过滤,如Word、Excel、PPT、PDF等),60+文件类型过滤。 安全虚拟化安全全特性虚拟化,转发虚拟化、用户虚拟化、管理虚拟化、视图虚拟化、资源虚拟化(带宽、会话等)。 网络安全●DDoS攻击防护,防范多种类型DDoS攻击,如SYN flood、UDP flood、ICMP flood、HTTP flood、DNS flood、ARP flood和ARP 欺骗等。 ●丰富的VPN特性,IPSec VPN、SSL VPN、L2TP VPN、MPLS VPN、GRE等。 路由特性●IPv4:静态路由、RIP、OSPF、BGP、IS-IS。 ●IPv6:RIPng、OSPFv3、BGP4+、IPv6 IS-IS、IPv6RD、ACL6。 部署及可靠性透明、路由、混合部署模式,支持主/主、主/备HA特性。 智能管理●支持根据应用场景模板生成安全策略,智能对安全策略进行优化,自动发现冗余和长期不使用的策略。 ●全局配置视图和一体化策略管理,配置可在一个页面中完成。 ●可视化多维度报表呈现,支持用户、应用、内容、时间、流量、威胁、URL等多维度呈现报表。 标准服务●USG6300-AC:SSL VPN 100用户。 ●USG6300-BDL-AC:IPS-AV-URL功能集升级服务时间12个月,SSL VPN 100用户。 可选服务●IPS升级服务:12个月/36个月 ●URL过滤升级服务:12个月/36个月●反病毒升级服务:12个月/36个月 ●IPS-AV-URL功能集:12个月/36个月 注:√表示为支持此项功能,—表示为不支持此项功能。
督导工作总结范文通用版2篇 General version of supervision work summary model 汇报人:JinTai College
督导工作总结范文通用版2篇 前言:工作总结是将一个时间段的工作进行一次全面系统的总检查、总评价、总分析,并分析不足。通过总结,可以把零散的、肤浅的感性认识上升为系统、深刻的 理性认识,从而得出科学的结论,以便改正缺点,吸取经验教训,指引下一步工作 顺利展开。本文档根据工作总结的书写内容要求,带有自我性、回顾性、客观性和 经验性的特点全面复盘,具有实践指导意义。便于学习和使用,本文档下载后内容 可按需编辑修改及打印。 本文简要目录如下:【下载该文档后使用Word打开,按住键盘 Ctrl键且鼠标单击目录内容即可跳转到对应篇章】 1、篇章1:督导工作总结样本(最新版) 2、篇章2:督导工作总结范文 篇章1:督导工作总结样本(最新版) XX年10月份我校接受区督导办的督导教学工作。 作为我校体育教研组长,我感到压力还是很大的。首先 是《学校体育工作条例》这一块儿,要把三年的材料整理归类出来。因为这次督导的检查要求和以往不同,所以很多材料要重新准备补充完善,还要把以前遗失的缺少的材料补充完整,还不能耽误正常的教学工作,所有的一切都只能利用课余时间,甚至加班到凌晨。在开始之前,首先我先给自己明确了要做什
么、从哪里下手、准备什么、如何能按要求完成,然后给组内的教师分工好他们的任务。由于组内成员都是刚毕业的新教师,很多工作他们根本无从下手,所以只能安排一些简单的能够快速上手的任务,而大部分材料的整理都要依靠我来独自完成,但是我们没有畏惧困难,都是认认真真的努力完成着。尤其是这几位年轻教师,不懂就问不会就学,非常配合我的工作,从而使这部分工作能够顺利的完成。 为了迎接督导检查,我按照学校要求认真设计了一节展 示课:一年级的《滚动与爬行》。其实挺不愿意用一年级做展示课的,因为一年级新生刚入学不到两个月,很多的课堂训练还不到位,孩子们还不能完全进入到学生的角色中,还不明确自己在课堂上应该做什么,怎么做。真是要用一年级做课,我都不敢想象会出什么乱子,尤其是在户外,但是领导安排了,尤其是学校领导希望我作为一名老教师能够起到带头作用,也为学校的督导课安排解决一些实际困难。我接受了并开始认真准备。 滚动与爬行是一年级刚开学的入门教材之一,内容安排 比较简单,主要是激发学生对体育锻炼的兴趣,我选择这个教材,即针对于此,又因为这种教材只要教师引导得体,就能够
辞职信 尊敬的队领导: 我现在正式申请辞退现在班长职务,此决定已经过长时间深刻思考,并非一时冲动之举。刚任班长之初,我信心十足,真是想好好干下去,事实上我也确实如此,我原来有很多抱负,希望能够把班级带的更好,但是车队的很多事情、以及队领导的一些行为,让我感到十分失望,让我在好好干工作时心理却没有组织可以依靠。我认为拥有一个好的环境创造一个良好的适合的氛围,跟随一个英明果断、有人格魅力的领导工作,工作才有更大的动力的积极性。在这个岗位上任职期间,我非常了解领导的辛苦,领导也很难,所以我有工作上和个人利益上的不满从来也不说。但是现在我无法一直忍受,所以我提出辞职。 我所做的工作与我预期想象的很不一样,我不想再这样继续下去,作为一个班长,夹在队领导和战士之间,做了很多受累不讨好的工作,我想队领导可能至今也不知道我有什么困难,我需要什么,我在想什么。我现在工作激情全无,对班级管理没有负责,所以我不认为我还能干好这个班长。 其实,我一直都很喜欢这份工作,也十分感谢各位领导的信任、栽培及包容,也感谢各位战友给予的帮助和关心,我对这段时间的照顾表示真心的感谢。当然,我也自认为自己在任职期间的工作中做出了自己的最大努力。但因为某些原因,我最终选择了辞职,并希望能够尽早正式离职。希望队领导能早日找到合适的人手接替我的工作,我会尽力配合做好交接工作,保证班级管理工作的正常运作,对班级、对战友尽好最后的责任。在递交这份辞呈时,我的心情十分沉重。现在班级的管理和发展需要大家竭尽全力,由于我状态不佳,和一些其他原因的影响,无法为班级为战友做出相应的贡献,自己心理也不能承受现在这样坐在位置上却无所作为,因此请批准我的辞职!。 此致, 敬礼篇二:班长辞职申请 班长辞职申请书 尊敬的辅导员: 很遗憾在这个时间向辅导员提出辞职。我自九月份担任班长一职务至今,正是在这里我完成了一个从高中生到大学生的转变,工作上多有疏漏,但是我必须说明,不是因为我的工作走进了死胡同所以才提出辞职,不是我无能,要留下一个烂摊子留给后来人收拾,而是我想有更多的自由时间接触社会锻炼自我,更多的时间接近同学走进同学当中,只是这是我很早的决定,已经考虑了很久也也觉得足够明智,不是我不能为同学做出多少的牺牲,而是我有我的追求,路是自己走出来的,我想去好好的走自己的路,而这里的工作着实让我受到了许多的束缚,也很抱歉辞职报告很早就已经写完,拖了很久才正式提出。心情的不稳定因素有,现在的状况您可以非常放心,我是非常理性和坦白的面对您们,面对自己的未来的。 不要觉得是我因为无能力继续管理班级而提出辞职,很多人会这样想,觉得我是扛不住了,所以才辞职了,但是对于我来说并不是,我有我的追求。无论今天的主题是什么,我的心中的却很复杂,有感激,有气愤,有无奈,有歉意,有不舍,也有成长。我想最重要的应该是自己学会了慢慢长大和成熟来到这个新环境,开始感觉还不错,真是想好好干下去。事实上也是如此,。我原来有很多抱负,希望能够在这里实现,但是学校的很多事情和同学们种种行为让我感到十分失望。我认为,拥有一个好的环境创造一个良好的适合的氛围,跟随一个英明果断、有人格魅力的领导工作,我才有发展和前途。在这个岗位上干了这么久,我非常了解领导人之辛苦,您也很难,所以我有利益上的不满从来不说。但是当我无法忍受的时候,就只有选择辞职。学生的素质是我不能预见的,本来期望自己也可以在这里展现在自己的能力魅力,可以有丰富多彩的年轻的生活,可是,却一次次的让我失望,从考勤到各项活动的参加,从平时的学习状态到周末期间的各种“准备”都让我很失望很痛心。从着装到言
心怀感恩主题演讲稿 导读:本文心怀感恩主题演讲稿,仅供参考,如果能帮助到您,欢迎点评和分享。 时常怀着感恩的心,你会看到一个不同的世界,对于心存感恩话题,我们需要怎么发言才深入人心? 下面是为大家精心整理的“心怀感恩主题演讲稿”,欢迎大家阅读,供大家参考。内容还请关注哦。 心怀感恩主题演讲稿(1)尊敬的老师们,亲爱的同学们: 你们好!新的一天带着微笑和清新在大地上降临了。 有人说,一个人最大的不幸,不是得不到别人的“恩”,而是得到了,却漠然视之。因为一个不懂得感恩的人,只会把别人的给予当作理所当然,只会一味索取,而不能给予什么。他是一个自私自利的人,更严重的是他的生活会因此而觉得缺少乐趣,体验不到相互给予的快乐和从自身为他人制造的快乐中延伸而有的一种快乐,他将无法融入社会,甚至他的生存也会受到威胁,以至产生极端心理,做出危害社会的行为。到那时,遗憾的是老师,伤心的是父母,痛心的是自己。 感恩是一种生存智慧,是做人的道德底线,感受和感激他人恩惠的能力的成长,是一个人维护自己的内心安宁感和提高幸福充裕感必不可少的心理能力。感恩,不仅是一种情感,更是一种行为表现,是以“寸草心”报“三春晖”的赤子之举。感恩有时只需要一句问候,一束鲜花,一个拥抱,甚至一句话,就能传递亲情,表达心意。我们
只有学会感恩,才能以平等的眼光看待每一个生命,尊重每一份平凡的劳动,在未来的生活中少一些怨天尤人的抱怨,而多一份发自内心的满足与快乐。只要我们心怀感恩,我们便会发现,生活原来是如此的和谐和美丽! 所以,我们要感恩时代,同过去,同上代比生活,比待遇,比条件,感念时代的赐予,在意现在的拥有,增强奉献意识和社会责任意识。我们要感恩社会,感谢大自然对生命之源的赐予,感悟社会的馈赠,学会热爱自然,回报社会。我们要感恩团队,感恩集体的每一个人给予自己的关心,帮助和支持,感念团队共建的每一份荣誉和成功。我们要感恩父母,感念父母对我们生命的赐予和生活的辛酸与沧桑,感谢父母对我们的无私付出和养育之恩,对父母长辈多一份体贴,多一份关怀,多一句问候,尽孝心,重人伦,付亲情。我们要感恩老师,感谢老师对我们心智的启迪和生命成长的关怀,感念老师对我们的辛勤付出和教诲,在感念师恩中崇德成才,奉献社会。我们还要感恩对手,感谢强大的对手给予我们的竞争压力和挑战,感谢对手给予我们学习的鞭策和成长进步的动力,用感恩的心做人做事。 同学们,如果你心存感恩,当你因没有履行学生的职责而受到老师的批评乃至训斥时,就会放下所谓的面子,不再一意孤行,因为你知道,老师是真心帮助你。如果你心存感恩,放学时哪怕肚子再饿,也不在校外小店逗留,要按时回家,因为你知道,你的家人在焦急地等你,你的停留会堵塞交通。如果你心存感恩,当同学间有了矛盾,哪怕你再委屈,也会用正确的方法去化解,不是大打出手,更不至于
2020年督导工作总结范文5篇Summary of supervision in 2020
2020年督导工作总结范文5篇 小泰温馨提示:工作总结是将一个时间段的工作进行一次全面系统的总检查、总评价、总分析,并分析不足。通过总结,可以把零散的、肤浅的感性认识上升为系统、深刻的理性认识,从而得出科学的结论,以便改正缺点,吸取经验教训,指引下一步工作顺利展开。本文档根据工作总结的书写内容要求,带有自我性、回顾性、客观性和经验性的特点全面复盘,具有实践指导意义。便于学习和使用,本文下载后内容可随意调整修改及打印。 本文简要目录如下:【下载该文档后使用Word打开,按住键盘Ctrl键且鼠标单击目录内容即可跳转到对应篇章】 1、篇章1:2020年督导工作总结范文 2、篇章2:教育督导室上文档 3、篇章3:12月政府教育督导室工作总结及工作要点 文档 4、篇章4:督导工作总结文档 5、篇章5:2020督导总结范文 篇章1:2020年督导工作总结范文 本学年我院自律会督导部的工作主要分为文明督导和出 勤统计两部分。
文明督导主要是日常督导。在日常督导方面,我部门每 周都抽选早上安排10-12个督导人员分别于教学楼的每一层、门厅和楼道口进行督导。督导的内容为:带早餐、穿拖鞋、迟到等。在日常督导过程中,督导人员都按要求带校徽和督导牌,不穿拖鞋,工作积极,能积极地记录,制止带早餐,穿拖鞋的行为。另一部门工作则是监督草坪,维护草坪工作,我部门每天安排2-3个人与各系自律会同学合作,在教学楼与食堂中间的草坪周围监督,并且能够及时阻止破坏草坪,踩草坪抄近道的同学,拍摄下同学踩草坪的不文明行为并给公布,予通报批评。通过我们的努力,使绝大部份同学的素质有了提升。 出勤统计方面,督导部每周一对班级进行抽选升旗出勤 情况进统计,并每周作一次汇报。,每月,督导部都会对每个班级进行不定期的抽点,以提高升旗出勤率。 督导部还每周进行会议,总结前一周的工作,布置下一 周的任务。 在本部门工作之余,我院督导(自,请保留此标记。) 部还参加一些公共工作。如自律会办公室值班,各活动的场地布置,现场维护。同时,我们还积极参加学院的工作,如各个晚会活动上的秩序维持,部门干事之间工作积极受到了学院领导的好评。还有积极我们积极配合其他部门顺利的举办了一系
江门职业技术学院辅导员助理管理办法 (试行) 第一章总则 第一条为充分调动学生自我教育、自我管理、自我服务的功能,为学生的成长成才提供实践平台,并进一步创新我院学生工作,特设辅导员助理。 第二条为规范辅导员助理的管理,特制订本办法。 第二章岗位职责 第三条辅导员助理的主要工作职责: 1、协助辅导员做好学生思想政治教育、日常管理、学风建设、奖贷助勤等工作,推进学生素质教育。 2、协助辅导员做好学生行为和纪律教育,深入学生宿舍,抓好学生的宿舍内务,组织开展文明宿舍等活动。 3、协助辅导员做好学生党员、团员的培养、教育、发展和考核工作,指导学生团支部、班委会开展工作,参与学生社会实践。 4、协助辅导员深入了解、掌握学生的基本情况、思想动态、心理问题、学习表现、生活现状等实际问题,及时、准确收集相关信息,传达学院、系有关文件、通知等。 5、与协助管理的年级同学交流学习方法,传授学习经验,提高同学学习自觉性。 6、协助辅导员组织学生开展丰富多彩的校园科技、文化、艺术、体育和其他课外活动。 7、协助辅导员处理学生突发事件,维护校园安全,保证学院稳定。 8、完成学生工作处、系党总支和辅导员交办的其它工作。 第三章配备与选聘 第四条根据学生工作处及各系学生工作的实际情况,各教学系配备3名辅导员学生助理,分别担任1-3年级辅导员助理工作。系辅导员老师为指导老师。 第五条每学年初开始接受学生报名,学生本人可直接向系或学生生工作处提出申请,或由班级、团支部、教学系、团委推荐,并按要求填写《江门职业技术学院辅导员助理报名表》(附一)。
第六条选聘对象:江门职业技术学院全日制二、三年级大专学生(分校区可结合实际另行考虑)。 第七条选聘条件: 1、思想政治觉悟高,政治方向正确、坚定,在思想上和行动上能自觉地同党组织、学院保持一致。中共党员优先。 2、责任心强,诚实守信,敬业奉献,热心服务同学,有较强的组织纪律性,有较强的组织、协调和管理能力,在同学中具有较高的威信。 3、能正确处理学习和工作的关系,学习成绩优良,无不合格课程。 4、工作积极主动,胆大心细,有较强的口头语言和文字表达能力。 5、具有广泛的兴趣爱好,身心健康。 第八条每学年初,进行辅导员助理推荐和选拔,学生工作处牵头,按《江门职业技术学院辅导员助理报名表》的个人志愿安排到系参加选拔,各系人员选拔由系具体组织,各系确定人选后报学生工作处审批。录用后颁发正式聘书,聘期为一学年。 第四章管理与考核 第九条受聘用的辅导员助理自受聘之日起,每月要进行月考核,每学期要进行学期考核,考核内容以工作职责为主要内容,分为优秀、良好、合格和不合格四个等次(具体标准见学期工作考核表)。 月考核安排在每月27-30日,考核时要填写《江门职业技术学院学生辅导员助理月考核表》(附二),学院根据每月的考核情况发放劳务津贴,劳务津贴合格以上的每人每月100元,不合格的发60元,连续二个月不合格的给予解聘。工作不足一个月的按比例发放,劳务津贴由学生工作处统一制表,指导老师到财务处代领。 学期考核安排在学期结束前第二个星期内完成,学期考核时辅导员助理须交个人书面工作总结,指导老师负责考核和填写《江门职业技术学院辅导员助理学期工作考核表》(附三),考核部门加具意见后交学生工作处备案。 第十条指导老师应认真负责,悉心指导辅导员助理开展工作,安排给助理的工作要有明确的要求,并要检查落实。
关于心怀感恩主题的演讲稿 尊敬的各位领导、老师,亲爱的同学们: 大家上午好! 今天我演讲的题目是“心怀感恩,励志成才”。 古有云,投之以桃,报之以李。众所周知,知恩图报,是做人之根本,德行之根本。 “滴水之恩,当涌泉相报。”中华民族作为世界上有着悠久文明历史的一个民族,不但孕育了博大精深的历史文化,更凝聚了我们炎黄子孙的传承精神——感恩奋进! 我们都应该知道,感恩的方法有很多,譬如,精忠报国,孝敬父母,尊老爱幼……而感恩的捷径却只有一种,那就是励志成才!的确,“吃得苦中苦,方为人上人”这句话一直诠释着这一信念。只有付出,才会到达理想的目的地;只有拼搏,才会收获意料中的成功;只有播种,才能够收获你想要的果实;只有奋斗,才能品味幸福精彩的人生。 感恩国家,她给了我们安逸、平和的生活学习环境,所以我们要精忠报国;感恩父母,他们养育了我们,所以我们要孝敬父母;感恩无数前辈先驱,他们为了下一代,甘愿牺牲自己,来给我们塑造一个稳定而又独立的国度,所以我们要敬老尊老。 作为一名贫困生,从大一开学,就很幸运得到国家助
学金,从而解决了我生活费的来源,让我毫无顾虑的认真 学习,除此之外,我又得到了减免学费的机会。那一刻我 感动极了,谢谢学校、学院能给我这次机会,让我不再为 学费和生活费发愁。也正因为有了国家助学金、有了减 免学费的机会,我备受鼓舞,在课余时间做各种兼职,解决了日常开支问题。也正因为这份感动,我更加激励自己, 更要刻苦学习,又很幸运地在大一学年拿到了三等奖学金,在大二学年相继得到二等奖学金、优秀班干部、优秀团员、三下乡先进个人等荣誉。但我深深地知道,这些荣誉不是属于自己一个人的,而是属于大家的,因为没有国家 助学金,我不可能专心学习;没有学校学院的帮助,我会为学费生活费不停奔波;没有老师和同学的帮助,我不可能 有那么的时间和精力参与各种实践活动。在此,我要谢谢您们的关心和帮助,感谢你们一直以来的鼓励和支持,有 您们我很幸福! 心怀感恩,励志成才,品尝着这份感动和幸福,我又申请了国家大学生创新创业训练项目,在这条路上困苦心酸自不必说,要放弃的念头不时出现,但是每每想到大家给 予我的关心和帮助,我一次次鼓足信心和勇气,擦掉汗水、擦干泪水,只管不懈努力、勇往直前,坚持到底,相信自己能够完成,并且完成得很好。很高兴刚刚得知,我参加的 生命科学竞赛进入了省赛。阳光总在风雨后,不经历风雨
( 工作总结 ) 单位:_________________________姓名:_________________________日期:_________________________ 精品文档 / Word文档 / 文字可改 督导组成员工作总结Work summary of members of the steering group
督导组成员工作总结 根据省委进行的教育活动工作的统一部署,我被抽调到省委省直督导组,参与督导124个省直机关的XXX教育活动,历时半年。期间,我下苦功夫、下真功夫、下硬功夫,以高度负责的态度、求真务实的作风、探索创新的精神,高标准、严要求,现已圆满完成了党和组织交给的督导任务。特鉴定如下: 在学习动员阶段,为了通晓上情,了解下情,确保督导质量和方向。我总是先行一步,认真学习了许多书籍和文件,研读了大量有关资料,力争学通政策,吃透文件,做到学深、学精、会用。在此基础上,按照分工,我走访了20多个省直机关,了解学习情况,检查读书笔记,并给以恰当的指导,督促各单位不打折扣地完成了学习任务。
在分析评议阶段,我到许多机关进行了调研,抽查了大量征求意见表,听取了各单位的汇报,并对其作了分析记录。同时,对各单位上报的征求意见表、党性分析材料等,认真负责-地进行了审阅,并提出了具体意见,还参加了近10个机关的民主生活会,确保了每一个环节到位,力争每一步都见到实效。 在整改提高阶段,我对一些单位进行了检查,查阅了其单位班子及个人的整改方案、整改配档表和长效机制的建立情况,并详细了解了整改进度,针对各单位的实际情况,进行了有的放矢的督促。 在整个督导过程中,我积极开动脑筋,出点子想办法,探索思路;做到上下沟通,搞好上情下达、下情上报;严格要求自己,自觉维护省委形象;并撰写了简报、散文、杂文、理论文章等几十篇,现已公开发表3篇,真正做到了“指导不领导,督促不包办,到位不越位,参与不干预,服务不添乱”,向党交上了一份合格答卷。 虽然取得了一定成绩,圆满完成了任务,但是由于长期以来失眠、腿疼,每天上下班要周转2个多小时,晚上还要加班处理本单位的工作,所以影响了精力,一些该深入总结的经验没有及时总结
成都学院(成都大学)兼职辅导员管理办法(试行) 第一章总则 第一条为深入贯彻《中共中央国务院关于进一步加强和改进大学生思想政治教育的意见》(中发[2004]16号)和《普通高等学校辅导员队伍建设规定》(中华人民共和国教育部令第24号)精神,根据学校党委《成都大学关于进一步加强学生思想政治教育工作队伍建设的实施细则》(成大委发[2009]43号),为进一步加强我校辅导员队伍建设,规范我校兼职辅导员队伍建设和管理工作,特制定本办法。 第二条兼职辅导员工作是学校思想政治工作、学生管理工作的重要组成部分;兼职辅导员是学校贯彻落实党的教育方针,促进学生德、智、体全面发展的一支重要力量,对维护学校正常教学、生活秩序具有重要作用。 第二章兼职辅导员的职责 第三条兼职辅导员的主要工作职责范围: (一)帮助学生树立正确的世界观、人生观、价值观,确立在中国共产党领导下走中国特色社会主义道路、实现中华民族伟大复兴的 共同理想和坚定信念。 (二)经常性地开展谈心活动,帮助、引导学生养成良好的道德品质、心理品质,增强学生克服困难、经受考验、承受挫折的能力。 (三)协助学校心理健康教育与咨询中心做好学生心理健康教育和咨询工作,关心学生的情感需求,有针对性地帮助学生处理好学习成才、择业交友、健康生活等方面的具体问题。 (四)了解和掌握学生思想政治状况,针对学生关心的热点、焦点问题,及时进行教育和引导,化解矛盾冲突,参与处理有关突发事件,维护好校园安全和稳定。
(五)经常深入到学生中开展工作,认真抓好学生日常教育与管理工作;协助学院学生工作办公室做好学生评奖、评优、勤工助学、申发困难补助及学生贷款等工作。 (六)协助学院学生工作办公室积极开展就业指导和服务工作,为学生提供高效优质的就业指导和信息服务,帮助学生树立正确的择 业观念。 (七)以班级为基础,以学生为主体,发挥学生班集体在大学生思想政治教育中的组织力量。 (八)指导学生开展科技、文化、体育和社会实践活动,促进学生的全面发展。 (九)做好兼职辅导员工作日记,建立学生管理档案,积累有关资料。 第四条根据实际情况,兼职辅导员的主要精力,可重点放在带班上,可协助或负责学生工作的条块工作。 第三章兼职辅导员的条件和聘任 第五条兼职辅导员必须具备以下条件: (一)德才兼备,乐于奉献,热爱大学生思想政治教育事业,具有强烈的责任心和使命感,讲求团结,顾全大局。 (二)具有相关的学科专业背景,具备较强的组织管理能力、语言文字表达能力、调查研究和解决实际问题的能力。 (三)本科及以上学历,原则上应是中共党员。 第六条兼职辅导员原则上由带班的青年专任教师、行政人员和在校研究生担任;确因工作原因需聘请校外人员担任兼职辅导员的,报学生处审批;要严格控制校外人员担任兼职辅导员的数量。 第七条聘任兼职辅导员,应由各学院申报,学生处审核,人事处备案。 聘请校外人员担任兼职辅导员,由各学院申报,学生处审核,各学
关于感恩的演讲稿:心存感恩,回馈人生 时间:2020年08月02日编稿:作者一 第一篇:关于感恩的演讲稿:心存感恩,回馈人生 关于感恩的演讲稿:心存感恩,回馈人生 敬爱的老师,友爱的同学们: 大家好! 我是来自六年五班的李嘉龙,我演讲的题目是《心存感恩,回馈人生》。 一滴水,要谢谢大海,让它汇聚成了无尽的水流;一朵花,要谢谢雨露,滋润它在阳光下健壮成长;一只鹰,要谢谢长空,赐予了它前进远方的力量;一座山,要谢谢大地,用自己的臂膀,给了她高耸的方向;一个人,要学会感恩,才干托起世界的脊梁!学会感恩,不仅是报答,更是心存感激的表示。 “羊有跪乳之恩,鸦有反哺之义”,世界的主宰——人,更要充满感恩之情。一颗感恩之心,化干戈为玉帛;一颗感恩之心,化腐朽为奇特;一颗感恩之心,化冰峰为春暖。学会了感恩,才会在生活中发觉美好。一次,美国前总统罗斯福家失窃,被偷去了许多东西,一位朋友闻讯后,忙写信安慰他,劝他不必太在意。罗斯福给朋友写了一封回信:“友爱的朋友,感谢你来信安慰我,我现在很平安。谢谢上帝,因为第一,贼偷去的是我的东西,而没有损害我的生命;第二,贼只偷去我部分东西,而不是全部;第三,最值得庆幸的是,做贼的是他,而不是我。”对任何一个人来说,失窃绝对是不幸的事,而罗
斯福却能在失窃中寻到美好,因为他拥有了健壮成长的感恩之树。 在人生的路上,缺少了感恩,就缺少了阳光雨露。这种人生的哲理,让我们不断地面临生命的挑战,人生的巅峰。感恩沟通了人的心灵,让他人的帮助铭记在心。在这个时代,假如人与人之间不存在感恩,那么人与人之间的关系就不复存在,社会也将成为一片大沙漠。 感恩是人与生俱来的本性,是生活美好的基础。我们心怀感恩,就能回报社会,报答自然。马斯洛曾说,心若改变,态度就跟着改变;态度若改变,习惯就跟着改变;习惯若改变,性格就跟着改变;性格若改变,人生就跟着改变。我们若播种感恩的心,就收获诚恳的态度;若播种诚恳的态度,就带动良好的习惯;若播种良好的习惯,就升华为健康的性格;若播种健康的性格,才收获成功的人生! 我的演讲完毕,感谢大家。第 1 页共 3 页关于感恩的演讲稿:忠孝两全,以孝为先 相信大家都一定看过一则公益广告,一位孝顺的媳妇在忙碌了一天后,还为婆婆打好洗足水,为婆婆洗足,当年幼的孩子看见妈妈正在为奶奶洗足时,自己也打好了洗足水,一簸一簸的端到妈妈的面前说:“妈妈我也为你洗足”。这一场景确实很令人感动,也让人深省,我们长这么大到底为父母都做过些什么?我们有几个人能记住父母的生日?父母最喜欢吃的东西?父母的鞋码?这些看似很微不脚到的事,却表现这我们是否对父母有一份孝心。 说起来也真够羞愧的,以上的问题,我基本上都不能回答。其实现在像我一样的人还真不少,母亲节,父亲节,父母的生日早已被各