vb函数大全(VBfunctionDaquan)
- 格式:doc
- 大小:36.00 KB
- 文档页数:12

返回参数的绝对值, 其类型和参数相同。
Array函数返回一个包含数组的Variant。
Asc函数返回一个Integer, 代表字符串中首字母的字符代码。
Atn函数返回一个Double, 指定一个数的反正切值。
CallByName函数执行一个对象的方法, 或者设置或返回一个对象的属性。
Choose函数从参数列表中选择并返回一个值。
Chr函数返回String, 其中包含有与指定的字符代码相关的字符。
返回一个Double, 指定一个角的余弦值。
CreateObject函数创建并返回一个对ActiveX对象的引用。
CurDir函数返回一个Variant(String), 用来代表当前的路径。
CVErr函数返回Error子类型的Variant, 其中包含指定的错误号。
Date函数返回包含系统日期的Variant(Date)。
DateAdd函数返回包含一个日期的Variant(Date), 这一日期还加上了一段时间间隔。
DateDiff函数返回Variant(Long)的值, 表示两个指定日期间的时间间隔数目。
DatePart函数返回一个包含已知日期的指定时间部分的Variant(Integer)。
DateSerial函数返回包含指定的年、月、日的Variant(Date)。
DateValue函数返回一个Variant(Date)。
Day函数返回一个Variant(Integer), 其值为1到31之间的整数, 表示一个月中的某一日。
DDB函数返回一个Double, 指定一笔资产在一特定期间内的折旧。
可使用双下落收复平衡方法或其它指定的方法进行计算。
Dir函数返回一个String, 用以表示一个文件名、目录名或文件夹名称, 它必须与指定的模式或文件属性、或磁盘卷标相匹配。
DoEvents函数转让控制权, 以便让操作系统处理其它的事件。
Environ函数返回String, 它关连于一个操作系统环境变量。
在Macintosh中不可用EOF函数返回一个Integer, 它包含Boolean值True, 表明已经到达为Random或顺序Input打开的文件的结尾。
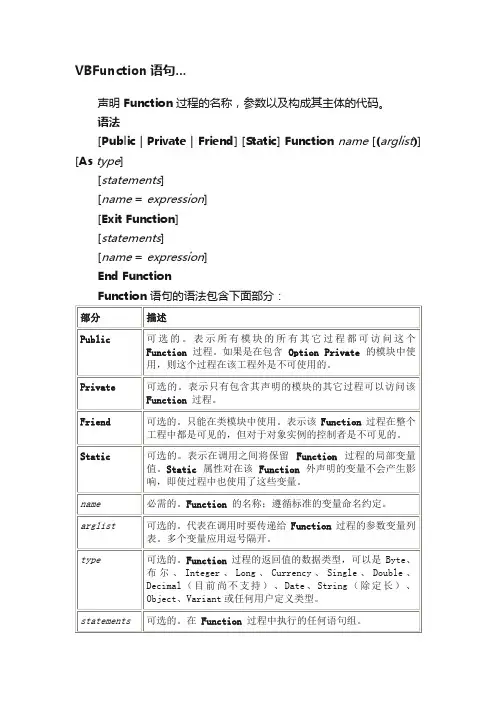
VBFunction语句...声明Function 过程的名称,参数以及构成其主体的代码。
语法[Public | Private | Friend] [Static] Function name [(arglist)] [As type][statements][name=expression][Exit Function][statements][name=expression]End FunctionFunction语句的语法包含下面部分:其中的arglist参数的语法以及语法各个部分如下:[Optional] [ByVal| ByRef] [ParamArray] varname[( )] [As type] [=defaultvalue]说明如果没有使用Public、Private 或Friend显式指定,则Function过程缺省为公用。
如果没有使用Static,则局部变量的值在调用之后不会保留。
Friend关键字只能在类模块中使用。
但Friend过程可以被工程的任何模块中的过程访问。
Friend过程不会在其父类的类型库中出现,且Friend过程不能被后期绑定。
注意Function 过程可以是递归的;也就是说,该过程可以调用自己来完成某个特定的任务。
不过,递归可能会导致堆栈上溢。
通常Static关键字和递归的Function 过程不在一起使用。
所有的可执行代码都必须属于某个过程。
不能在另外的Function、Sub 或Property 过程中定义Function 过程。
Exit Function 语句使执行立即从一个Function 过程中退出。
程序接着从调用该Function 过程的语句之后的语句执行。
在Function 过程的任何位置都可以有Exit Function语句。
Function 过程与Sub 过程的相似之处是:Function 过程是一个可以获取参数,执行一系列语句,以及改变其参数值的独立过程,而与子过程不同的是:当要使用该函数的返回值时,可以在表达式的右边使用Function 过程,这与内部函数,诸如Sqr、Cos或Chr的使用方式一样。

VB常用函数表VB常用函数表(2009-03-20 00:50:42)转载标签:asp常用函数分类:技术文章杂谈ASP纯ASPVBscript常用函数:1.数值型函数:abs(num): 返回绝对值sgn(num): num>0 1; num=0 0; num<0 -1;判断数值正负hex(num): 返回十六进制值直接表示:&Hxx 最大8位oct(num): 返回八进制值直接表示:&Oxx 最大8位sqr(num): 返回平方根 num>0int(num): 取整 int(99.8)=99; int(-99.2)=100fix(num): 取整 fix(99.8)=99; fix(-99.2)=99round(num,n): 四舍五入取小数位 round(3.14159,3)=3.142 中点数值四舍五入为近偶取整round(3.25,1)=3.2log(num): 取以e为底的对数 num>0exp(n): 取e的n次幂通常用 num^nsin(num): 三角函数,以弧度为值计算 (角度*Pai)/180=弧度 con(num); tan(num); atn(num)2.字符串函数:len(str):计算字符串长度中文字符长度也计为一!mid(str,起始字符,[读取长度]):截取字符串中间子字符串left(str,nlen):从左边起截取nlen长度子字符串right(str,nlen):从右边起截取nlen长度子字符串Lcase(str):字符串转成小写Ucase(str):字符串转成大写trim(str):去除字符串两端空格Ltrim(str):去除字符串左侧空格Rtrim(str):去除字符串右侧空格replace(str,查找字符串,替代字符串,[起始字符,替代次数,比较方法]):替换字符串注:默认值:起始字符 1;替代次数不限;比较方法区分大小写(0)InStr([起始字符,]str,查找字符串[,比较方法]):检测是否包含子字符串可选参数需同时选返回起始位置InStrRev(str,查找字符串[,起始字符][,比较方法]):反向检测是否包含子字符串返回起始位置space(n):构造n个空格的字符串string(n,str):构造由n个str第一个字符组成的字符串StrReverse(str):反转字符串split(str,分割字符串[,次数][,比较方法]):以分割字符串为分割标志将字符串转为字符数组可选参数需同时选3.数据类型转换函数:Cint(str):转换正数 True -1;False 0;日期距离1899/12/31天数;时间上午段 0;下午段 1;Cstr(str):日期输出格式 yyyy/mm/dd;时间输出格式 Am/Pm hh:mm:ssClng(str):与Cin()类似Cbool(num):num不为零 True;反之 FalseCdate(str):转换日期格式 0:#Am 12:00:00#;正数距离1899/12/31天数的日期;浮点数日期+小数时间Cbyte(num):num<255 转换为字节Csng(str):转换为单精度数值Cdbl(str):转换为双精度数值Ccur(str):转换为现金格式4.时间函数:date:取系统当前日期time:取系统当前时间now:取系统当前时间及日期值 Datetime类型timer:取当前时间距离零点秒值,计时器,可计算时间差DateAdd(间隔单位,间隔值,日期):推算相邻日期DateDiff(间隔单位,日期一,日期二):计算时间差日期二-日期一Datepart(间隔单位,日期):计算日期的间隔单位值Dateserial(date):输出日期值(按序列计算)Timeserial(time):输出时间值(按序列计算)DateValue(datetime):取出字符串中日期值Timevalue(datetime):取出字符串中时间值weekday(date):计算星期几MonthName(date):输出月分名year(datetime):截取年份month(datetime):截取月份day(datetime):截取日hour(datetime):截取小时minute(datetime):截取分钟second(datetime):截取秒5.其它函数:Array(unit,..):动态生成数组Asc(str):输出字符串第一个字符的ASCII码Chr(asc):转换ASCII为字符 Enter:Chr(13)&Chr(10)Filter(数组名称,关键字符串,[,包含][,比较方法]):将字符串数组中含有关键字符串的元素存成新的数组(默认) [包含]为false则取不包含的元素Join(ArrayName):将数组中元素连成字符串Ubound(ArrayName[,维数]):取得数组相应维数的上界Lbound(ArrayName[,维数]):取得数组相应维数的下界一般为0Randmize n:启动随机数种子Rnd(n):取得随机数,n>0或为空,取序列下一随机值,n<0,随机值相同,n=0,生产与上一随机值相同的数取介于A和B之间的随机正数C,公式:C=Int((B-A+1)*Rnd+A) 条件(B>A)子程序和自定义函数Sub StrSubName Function StrFunName(arg[1],..)子程序体函数体Exit Sub 中途跳出 Exit Function 中途跳出End Sub StrFunName=Value 返回值End Function[call] StrSubName 引用子程序 Var=StrFunName(arg[1],..) 引用函数子程序和自定义函数可以递归调用;ASP六大对象常用语句示范:Response:Response.write StrVar/"String":向网页写出参数值或字符串等同于在Html标记中嵌入<%=StrVar/"String"%>Response.End:停止页面编译,并将已经编译内容输出到浏览器Response.Buffer=True|False:页面编译时是否使用缓存的设置,一般在页面头部设置Response.Flush:强制输出页面已编译部分内容Response.Clear:将缓冲区内的数据清除Response.Redirect URL:停止页面编译或输出,转载指定所需页面Response.IsClientConnected:返回True|False,检测用户是否还处于连接状态Response.Charset(CharsetName):设置页面编码类型,即<meta http-equiv="Content-Type" content="text/html; charset=gb2312">Response.ContentType [= ContentType ]:设置页面文件类型,同上Response.Expires [= number]:设置页面失效时间,单位分钟Response.ExpiresAbsolute [= [date] [time]]:设置页面失效的绝对时间Response.Status = StatusDescription:设置页面状态描述Request:Request("PassStrName"):读取网页传递值,包括表单及以?PassStrName=value&PassStrName_n=value_n形式Request[.collection|property|method](variable)Request.querystring("PassStrName"):读取Get方法传递的表单值和?PassStrName=valueRequest.QueryString(Varible)[(Index).Count]Request.form("PassStrName"):读取Post方法传递的纯表单域的值Request.Form(Parameter)[(Index).Count]Request.ServerVaribles(Server Environment Variable):读取客户端系统环境变量,详见参考Request.BinaryRead(Count):读取指定字节数的传送值Request.TotalBytes:查询体的长度,以字节为单位,只读注:同名表单如:CheckBox如有多项值,传递形式如右,StrName=value1,value2,...需要用Split函数分割各项值Multiple的Select表单与CheckBox类似,TextArea的值可包含换行字符,用Replace转为<br>,以满足格式需要Session:(用户全局变量)Session("SesName")=value:存储Session变量值,也可读取该值Session("SesName")=Empty:判断Session值是否存在的两种方法IsEmpty(Session("SesName"))=True|False:判断Session值是否存在的两种方法Session.TimeOut=num:设置Session变量的存在时效,单位分钟Session.Abandon:清除所有Session变量值Session.SessionID:Session变量的ID序列号,只读Application:(应用程序全局变量)Application("AppName")=value:存储Application变量值,也可读取该值Application("AppName")=Empty:判断Application值是否存在的两种方法IsEmpty(Application("AppName"))=True|False:判断Application值是否存在的两种方法Application.Lock:Application变量值锁定,防止同时更改变量值Application.UnLock:Application变量值解锁,允许更改变量值注:Session与Application变量都可以用来存储数组和系统对象,引用方法是变量名相当于数组名而已,但不能直接改变其值,需要借助临时数组修改值后,再赋给Session与Application变量Global.asa文件的结构:<% @language="VBscript"%><% Sub Application_OnStart ...End SubSub Application_OnEnd ... End SubSub Session_OnStart ...End SubSub Session_OnEnd ... End Sub%>Server:Server.MapPath("FileUrl"):映射文件名的服务器站点绝对地址,Path=Server.MapPath(./)可以得到虚拟目录根路径Server.HtmlEncode("string"):转换为可以直接显示带Html格式的字符串,如:<,>等Server.URLEncode( "string"):转换为浏览器地址编码set Var=Server.CreatObject("ObjName"):创建对象变量Server.ScriptTimeout = NumSeconds:ASP程序页面执行时限,以秒为单位Cookies: 存储在用户本机的临时变量,每个Cookie的最大字节4KB,最多可以有300个Cookie 1.2MBResponse.cookies("StrCookieName")=value:存储Cookie变量值,也可读取该值Response.cookies("StrCookieName")="":判断是否为空Response.cookies("StrCookieName").Expires=Date:变量有效期,以天为单位,小于当前时间立即失效Response.Cookies(Cookie[(key).Attribute]):标准语法ObjectContext 控制ASP的事务处理ObjectContext.OnTransactionAbort:由放弃的事务处理事件激发,在脚本完成处理后发生ObjectContext.OnTransactionCommit:由成功的事务处理事件激发,在脚本完成处理后发生ObjectContext.SetAbort:显式的放弃一次事务处理ObjectContext.SetComplete:覆盖前面任何调用ObjectContext.SetAbort方法的调用Msgbox "string"/StrName:VBscript提示框表单的Onsubmit事件:在同一页面写入 FunctionFormName_onsubmit()..FormName_onsubmit=True/False..end Function,页面会在提交前先执行语句,并根据返回值判断是否完成提交任务。

VB函数大全LTvbFirstFourDays 2 由新的一年中第一个至少有 4 天的星期开始。
vbFirstFullWeek 3 由一年中第一个完整的星期开始。
返回值常数值描述vbSunday 1 星期日vbMonday 2 星期一vbTuesday 3 星期二vbWednesday 4 星期三vbThursday 5 星期四vbFriday 6 星期五vbSaturday 7 星期六--------------------------------------------------------------------------------日期格式常数仅当您的工程对包含这些常数定义的相应类型库有一个显式引用时,才可以使用这些常数。
常数值描述vbGeneralDate 0 显示日期和/或时间。
对于一个实数,显示日期和时间。
如果没有小数部分,则仅显示日期。
如果没有整数部分,则仅显示时间。
日期和时间的显示由系统设置值确定。
vbLongDate 1 用计算机区域设置值指定的长日期格式显示日期。
vbShortDate 2 用计算机区域设置值指定的短日期格式显示日期。
vbLongTime 3 用计算机区域设置值指定的长时间格式显示时间。
vbShortTime 4 用计算机区域设置值指定的短时间格式显示时间。
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------Dir、GetAttr 和 SetAttr 常数可在代码中的任何地方用下列常数代替实际值:常数值描述vbNormal 0 正常的(Dir 和 SetAttr 的缺省值)vbReadOnly 1 只读的vbHidden 2 隐藏的vbSystem 4 系统文件vbVolume 8 卷标vbDirectory 16 目录或文件夹vbArchive 32 文件自上一次备份后已经改变--------------------------------------------------------------------------------驱动器类型常数仅当您的工程对包含这些常数定义的相应类型库有一个显式引用时,才可以使用这些常数。


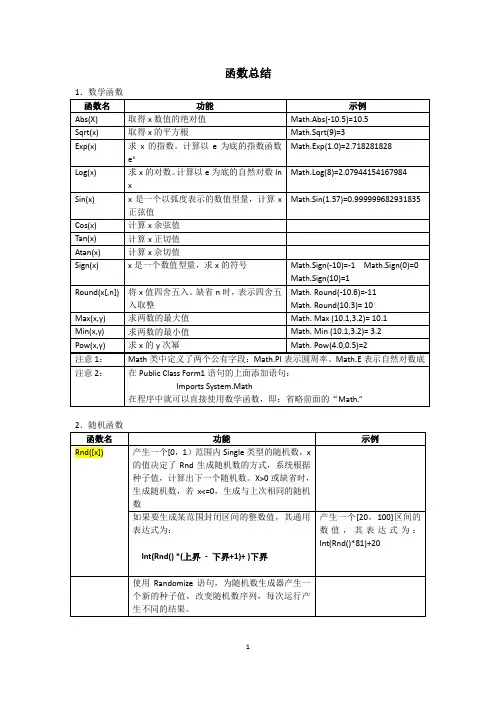
2005函數大全2009-09-21 15:53:16| 分类: 2005 |字号订阅一、数学函数函数说明Abs (num) 取绝对值。
Exp (num) 返回以e为底、以num为指数的值,如Exp(2)返回e^2值。
Log (num) 返回参数num的自然对数值,为Double类型,即以e为底的对数。
Hex (num)` 将参数num转换为16进制。
Oct (num) 将参数num转换为8进制Sign (num) 返回参数的正负符号,若num大于0,则返回值为1;若num等于0,则返回值为0;若num小于0,则返回值为-1。
Sqrt (num) 返回参数平方根为,Double类型。
Atan (num) 反正切函数Sin (num) 正弦函数Cos (num) 余弦函数Tan (num) 正切函数Rand (num,[int]) 将参数num四舍五入,若要指定四舍五入到哪位小数,可以加上第二个参数int。
如:Round (12. 456 )返回值为12;Round (12 . 4567,3 ) 返回值为12. 457。
Rnd [(nun)] 产生一个小于1,大于或等于0的随机数,类型为Single。
若参数num小于0,那么每次都会返回相同的随机数;若没有提供参数或参数大于0,那么会依序产生下一个随机数,此为默认值;若参数num等于0,那么会返回最近一次产生的随机数。
为了每次产生不同的随机数,在使用Rand ()函数之前,最好使用Randomize语句。
若要随机产生一个N到M的整数,可利用如下公式:Int (Rand ()*M-N+1)+N。
Pow (x,y) 求x的y次方。
Val (str) 将字符串内的数字转换成Integer或Double类型返回。
Str (num) 将数值类型参数转换成字符串返回。
Fix (num) 参数大于0时,去掉小数部分;参数小于0时,返回大于或等于该参数值。
Int (num) 参数大于0时,去掉小数部分;数小于0时,返回小于或等于该参数值。

vb函数大全(VBfunctionDaquan)vb函数大全(VB function Daquan)vb函数大全(VB function Daquan)VB commonly used function Daquan 2008-03-08 19:39, now programming software, such as VB, C++, etc., mostly with a powerful library of functions, you can save effort to complete a variety of functions. Most of the time, you can't remember the function or function format that implements a function, which results in a lot of trouble in programming. As a programmer, I have a deep understanding of this. Therefore, specially prepared several VB common function introduction, for your study or reference. There are inappropriate places to say, but also welcome in the Forum on this web site, we study.(I) type conversion class functions1. CType (X)[format]:P=CBool ("X") converts X to "Boolean" (Boolean) typeP=CByte ("X") converts X to "Byte" typeP=CCur (X) 'converts X to the' Currency 'typeP=CDate ("X") converts X to "Date" typeP=CDbl ("X") converts X to "double precision" (Double) type P=CInt (X) converts the X to an integer (Integer) typeP=CLng ("X") converts X to "long integer" (Long) typeP=CSng (X) converts X to a single precision (Single) typeP=CStr (X) converts the X to a string (String) typeP=Cvar (X) converts the X to a variant (Variant) typeP=CVErr (X) 'converts X to a Error value[paradigm]:(1) CStr (13) +CStr (23) after the value is converted into astring, and is connected with "+" number, and the result is: 1323(2) CInt ("12") +12'strings are converted into integers and then summed up with 12. Results: 24(3) P=CInt (True) ', the output is -1"Boolean and numeric conversions should be noted, Boolean values are only True and False, in which True is -1 in memory, and False is 0(4) CBool (-0.001) ', the output is TrueWhen the value is converted to Boolean, the value equal to 0 will be False, and the value not equal to 0 will be True.2. Int (X), Fix (X): take the integer value of X[format]:P=Int (X) 'takes the maximum integer value of <=XP=Fix ("X") takes the integer part of X and removes the decimal directly[paradigm]:(1) Int (-54.6) ', the result is -55, take the maximum integer of<=-54.6(2) Fix (54.6) ', the result is 54, take an integer and remove the decimal directly(two) commonly used mathematical functions[format]:1. Abs (N) takes absolute valueExample: Abs (-3.5) results: 3.52. Cos (N) cosine functionExample: Cos (0): 13. Exp (N) e is the exponential function at the bottom Example: Exp (3): 20.0684. Log (N) the natural logarithm based on eExample: Log (10): 2.35. Rnd[(N)] generates random numbersExample: Rnd result: the number between 0--16. Sin (N) sine functionExample: Sin (0): 07. Sgn (N) signed functionExplanation: take the plus sign. Y=Sgn (X) is both X>0 and Y=1; X=0 is Y=0; X<0 is Y=; -18. Sqr (N) square rootExample: Sqr (9): 39. Tan (N) tangent functionExample: Tan (0): 010.Atn (N) reverse functionExample: Atn (0): 0[note] in trigonometric functions, expressed in radians. (string) class function of string:1., ASC (X), Chr (X): conversion character, character code[format]:P=Asc (X) returns the character code of the first character of string XP=Chr (X) returns characters equal to X characters[paradigm]:(1) P=Chr (65);'output character' A 'because the ASCII of A is equal to 65(2) P=Asc ("A")Output 652. Len (X): calculate the length of the string X[format]:P=Len (X)[instructions]:The empty string length is 0, and the space character is alsoa character. A Chinese text occupies 2 Bytes, but is also counted as a character.[paradigm]:(1) make X= "" (empty string)The output of Len (X) is 0(2) make X= "ABCD""The output of Len (X) is 4(3) make X= VB tutorial"The output of Len (X) is 43. Mid (X) function: read the string X characters in the middle [format]:P=Mid (X, n)Read by the N character of X, read all the characters behind.P=Mid (X, N, m)Read by the N character of X, read the M characters behind. [paradigm]:(1) X= "ABCDEFG""P=Mid (X, 5)The result is: "P=" efg"(2) X= "ABCDEFG""P=Mid (X, 2,4)The result is P= "BCDE""4. Replace: replaces some of the string in a string with another string[format]:P=Replace (X, S, R)[explanation]: replace the string S in string X with string R, and then return.[paradigm]:X=, VB, is, very, good"P=Replace (X, good, nice)The output is: P=, VB, is, very, nice"5. StrReverse: inverted string[format]:P=StrReverse (X)[instructions]:Returns the string after the X parameter is reversed[paradigm]:(1) X= "ABC""P=StrReverse (X)Output: P= "CBA""6., Ucase (X), Lcase (X): convert English letters to uppercase and lowercase[format]:P=Lcase (X)Convert uppercase characters from X strings to lowercaseP=Ucase (X)"Convert lowercase letters from X strings to uppercase."[instructions] no other characters or Chinese characters will be affected except English letters.[paradigm]:(1) make X=, VB, and, VC"The result of Lcase (X) is "VB, and, VC", and Ucase (X) is "VB AND VC""7. InStr function: finding strings[format]:P=InStr (X, Y)Locate the position of the Y from the first character of the X P=InStr (n, X, Y)Find the position of the Y from the X n character[instructions]:(1) if the Y is found in X, the return value is the place where the first character of the Y appears in X.(2) InStr (X, Y) is equivalent to InStr (1, X, Y).(3) if the string length, or X is an empty string, or Y is not found in X, 0 is returned.(4) if Y is an empty string, returns 0.Date time class function:1., Year (X), Month (X), Day (X): take out year, month, day[format]:P=Year (X)Take out the value of the X "year" sectionP=Month (X)Take out the value of the X "month" sectionP=Day (X)Take out the value of the X "day" section[description]:Year returns in AD, and if X has only time and no date, the date is #1899/12/30#2., Hour, Minute, Second function: take out, divide, or second[format]:P=Hour (X)Take the value of the "X" part of the "when"P=Minute (X)Take out the value of the "X" partP=Second (X)Take out the value of the X "seconds" section[indicates that the return value of]:Hour is between 0---23 [paradigm]:X=10:34:23P=Hour (X)Q=Minute (X)R=Second (X)Output results: P=10, Q=34, R=233., DateSerial function: merge year, month, date, become date[format]:DateSerial (Y, M, D)Where Y is the year, M is the month, and D is the date[instructions]:(1) if the value of M is greater than 12, the month will beextrapolated from December to M-12 months; if less than 1, the month will be extrapolated from January to 1-M months.(2) if the date D is greater than the number of days in that month, the date from the date of the month, the number of D- months later; if less than 1, then the date from 1 days forward projections 1-D days.[paradigm]:P=DateSerial (2000,02,02)The result is P=2000/02/024.TimeSerial function: when merging, minutes and seconds become time[format]:P=TimeSerial (H, M, S)H is the number of hours, M is minutes, and S is seconds[explanation]: the principle of calculation is the same as that of DateSerial above[paradigm]:P=TimeSerial (6,32,45)The result was: P=6:32:455.Date, Time, Now function: read the date and time of the system[format]:P=Date ()P=Time ()P=Now ()[explanation]: none of these three functions have arguments [paradigm]:If the current time is 19:26 on August 29, 2003 evening, 45 seconds, thenP=Now ()The result is: P=2003-08-29 19:26:456.MonthName: returns the name of the month[format]:P=MonthName (X)[to indicate that the]:X parameter can be passed in to 1---12, returns the value of "month" and "February""...... But in English Windows, the return is "January", "February""......[paradigm]:P=MonthName (1)"P=" one month"7.WeekdayName: returns the name of the week[format]:P=WeekdayName (X)[shows that the]:X parameter can be passed in 1 - 7, and returns the value "Sunday", Monday"...... But in English windows, the return is "Sunday", "Monday""......[paradigm]:P=WeekdayName (1)The result is: P=, Sunday"Mathematical function of /doc/c57f7c690229bd64783e0912a21614 7916117e29.html function DaquanAbs (Num) takes absolute value.Exp (Num) returns the value of e at the bottom and num asan exponent, such as Exp (2) returning the e^2 value.Log (Num) returns the natural pair value of parameter num, which is the Double type, that is, the logarithm based on E.Hex (Num) converts the parameter num to 16.Oct (Num) converts the parameter num to 8Sign (Num) returns the positive and negative sign of the parameter. If num is greater than 0, the return value is 1; if num equals 0, thenthe return value is 0; if num is less than 0, then the return value is -1.Sqrt (Num) returns the square root of the argument, Double type.Atan (Num) tangent functionSin (Num) sine functionCos (Num) cosine functionTan (Num) tangent functionRand (Num, [int]) will enter the parameter num four, five, to specify four to five into which decimal, you can add second parameters int. For example, Round (12.456) returns the value of 12 Round (12.4567,3) returns 12.457.Rnd [[nun]] produces a random number less than 1, greater than or equal to 0, of type Single. If num is less than 0, then each will return the same number; if you don't provide the parameters or parameter is greater than 0, so in order to generate a random number next, this is the default value; if the parameter num is equal to 0, then returns the last generated random number. In order to generate different random numbers each time, it is better to use the Randomize statement before using the Rand () function. To randomly generate an integer from N to M, you can use the following formula: Int (Rand ()) *M-N+1, +N.Pow (x, y) seeks the Y power of X.Val (STR) converts the number in a string to Integer or Double type.Str (Num) converts a numeric type parameter into a string to return.When the Fix (Num) parameter is greater than 0, the decimal part is removed; when the parameter is less than 0, the value returned is greater than or equal to the parameter value.When the Int (Num) parameter is greater than 0, the decimal part is removed; when the number is less than 0, the parameter is returned less than or equal to the parameter value.。
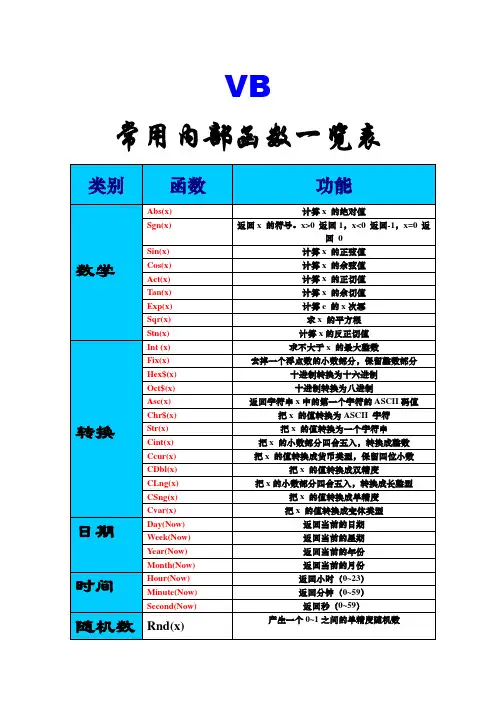
Abs 函数返回数的绝对值。
And 运算符执行两个表达式的逻辑连接。
Array 函数返回含一数组的变体。
Asc 函数返回字符串首字母的ANSI 字符代码。
赋值运算符(=) 给变量或属性赋值。
Atn 函数返回数的反正切值。
调用语句将控制移交Sub 或Function 过程。
CBool 函数返回已被转换为Boolean 子类型的变体的表达式。
CByte 函数返回已被转换为字节子类型的变体的表达式。
CCur 函数返回已被转换为货币子类型的变体的表达式。
CDate 函数返回已被转换为日期子类型的变体的表达式。
CDbl 函数返回已被转换为双精度子类型的变体的表达式。
Chr 函数返回指定ANSI 字符码的字符。
CInt 函数返回已被转换为整数子类型的变体的表达式。
Class 对象提供对已创建的类的事件的访问。
Class 语句声明类名Clear 方法清除Err 对象的所有属性设置。
CLng 函数返回已被转换为Long 子类型的变体的表达式。
颜色常数颜色常数列表。
比较常数用于比较运算的常数列表。
连接运算符(&) 强制两个表达式的字符串连接。
Const 语句声明用于字母值的常数。
Cos 函数返回角度的余弦值。
CreateObject 函数创建并返回对“自动”对象的引用。
CSng 函数返回已被转换为单精度子类型的变体的表达式。
CStr 函数返回已被转换为字符串子类型的变体的表达式。
日期和时间常数在日期和时间运算中用来定义星期几和其他常数的常数列表。
日期格式常数用于日期和时间格式的常数列表。
Date 函数返回当前系统日期。
DateAdd 函数返回加上了指定的时间间隔的日期。
DateDiff 函数返回两个日期之间的间隔。
DatePart 函数返回给定日期的指定部分。
DateSerial 函数返回指定年月日的日期子类型的变体。
DateValue 函数返回日期子类型的变体。
Day 函数返回日期,取值范围为1 至31。
VB函数大全vbFirstFourDays 2 由新的一年中第一个至少有 4 天的星期开始。
vbFirstFullWeek 3 由一年中第一个完整的星期开始。
返回值常数值描述vbSunday 1 星期日vbMonday 2 星期一vbTuesday 3 星期二vbWednesday 4 星期三vbThursday 5 星期四vbFriday 6 星期五vbSaturday 7 星期六--------------------------------------------------------------------------------日期格式常数仅当您的工程对包含这些常数定义的相应类型库有一个显式引用时,才可以使用这些常数。
常数值描述vbGeneralDate 0 显示日期和/或时间。
对于一个实数,显示日期和时间。
如果没有小数部分,则仅显示日期。
如果没有整数部分,则仅显示时间。
日期和时间的显示由系统设置值确定。
vbLongDate 1 用计算机区域设置值指定的长日期格式显示日期。
vbShortDate 2 用计算机区域设置值指定的短日期格式显示日期。
vbLongTime 3 用计算机区域设置值指定的长时间格式显示时间。
vbShortTime 4 用计算机区域设置值指定的短时间格式显示时间。
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------Dir、GetAttr 和 SetAttr 常数可在代码中的任何地方用下列常数代替实际值:常数值描述vbNormal 0 正常的(Dir 和 SetAttr 的缺省值)vbReadOnly 1 只读的vbHidden 2 隐藏的vbSystem 4 系统文件vbVolume 8 卷标vbDirectory 16 目录或文件夹vbArchive 32 文件自上一次备份后已经改变--------------------------------------------------------------------------------驱动器类型常数仅当您的工程对包含这些常数定义的相应类型库有一个显式引用时,才可以使用这些常数。
VB API 函数大全Show the "Save File" CommonDialog 显示“保存文件”对话框Show the "Browse Folder" Common Dialog 显示“浏览文件夹”对话框 Suspend a Computer 挂起计算机Test if an application is responding and terminate application 测定一个应用程序是响应还是终止(以IE 为例)。
Test if an application is responding and terminate application (续:)测定一个应用程序是响应还是终止Format a floppy disk 格式化软盘Zero a portion of an array 清零一个数组Determine the free space on a drive 测定驱动器上的空闲空间Edit the files stored in the "Documents" menu 编辑保存在文档菜单的文件 Copy files using the File Copy Shell 使用File Copy Shell ,拷贝文件 Show the "File Open" Common Dialog 显示“文件打开”对话框Converting Class IDs to a Prog IDs and back 转变class ID 到一个prog ID Obtaining the current user name 获得当前用户名Return the path of the temporary directory 返回临时目录的路径 Return the path of the windows directory 返回windows 目录的路径 Return the path of the system directory 返回system 目录的路径 Create a GUID 创建一个GUIDEnable and Disable the windows task bar 激活和禁止windows 任务条 Determining the system folder locations 设定system 文件夹的位置 Obtaining information about the operating system 获得操作系统的信息 Find the path of the executable associated with a file 找到文件的完整路径Locking the application screen area 锁住应用程序客户区。
Abs 函数返回数的绝对值。
And 运算符执行两个表达式的逻辑连接。
Array 函数返回含一数组的变体。
Asc 函数返回字符串首字母的ANSI 字符代码。
赋值运算符(=) 给变量或属性赋值。
Atn 函数返回数的反正切值。
调用语句将控制移交Sub 或Function 过程。
CBool 函数返回已被转换为Boolean 子类型的变体的表达式。
CByte 函数返回已被转换为字节子类型的变体的表达式。
CCur 函数返回已被转换为货币子类型的变体的表达式。
CDate 函数返回已被转换为日期子类型的变体的表达式。
CDbl 函数返回已被转换为双精度子类型的变体的表达式。
Chr 函数返回指定ANSI 字符码的字符。
CInt 函数返回已被转换为整数子类型的变体的表达式。
Clas 对象提供对已创建的类的事件的访问。
Class 语句声明类名Clear 方法清除Err 对象的所有属性设置。
CLng 函数返回已被转换为Long 子类型的变体的表达式。
颜色常数颜色常数列表。
比较常数用于比较运算的常数列表。
连接运算符(&)强制两个表达式的字符串连接。
Const 语句声明用于字母值的常数。
Cos 函数返回角度的余弦值。
CreateObject 函数创建并返回对“自动”对象的引用。
CSng 函数返回已被转换为单精度子类型的变体的表达式。
CStr 函数返回已被转换为字符串子类型的变体的表达式。
日期和时间常数在日期和时间运算中用来定义星期几和其他常数的常数列表。
日期格式常数用于日期和时间格式的常数列表。
Date 函数返回当前系统日期。
DateAdd 函数返回加上了指定的时间间隔的日期。
DateDiff 函数返回两个日期之间的间隔。
DatePart 函数返回给定日期的指定部分。
DateSerial 函数返回指定年月日的日期子类型的变体。
DateValue 函数返回日期子类型的变体。
Day 函数返回日期,取值范围为1 至31。
Description 属性返回或者设置说明某个错误的字符串。
VB数学函数1.Abs 函数返回数字的绝对值。
Abs(number)number 参数可以是任意有效的数值表达式。
如果 number 包含 Null,则返回 Null;如果是未初始化变量,则返回 0。
说明数字的绝对值是其无符号的数值大小。
例如,Abs(-1) 和 Abs(1) 都返回 1。
下面示例利用 Abs 函数计算数字的绝对值:Dim MyNumberMyNumber = Abs(50.3 ) '返回 50.3。
MyNumber = Abs(-50.3) '返回 50.3。
2.Atn 函数返回数值的反正切值。
Atn(number)number 参数可以是任意有效的数值表达式。
说明Atn 函数计算直角三角形两个边的比值 (number) 并返回对应角的弧度值。
此比值是该角对边的长度与邻边长度之比。
结果的范围是从 -pi/2 到 pi/2 弧度。
弧度变换为角度的方法是将弧度乘以 pi/180。
反之,角度变换为弧度的方法是将角度乘以180/pi 。
下面的示例利用 Atn 来计算 pi 的值:Dim pipi = 4 * Atn(1) ' 计算 pi 的值。
注意 Atn 是 Tan(将角作为参数返回直角三角形两边的比值)的反三角函数。
不要混淆 Atn 与余切(正切的倒数 (1/tangent))函数。
3.Cos 函数返回某个角的余弦值。
Cos(number)number 参数可以是任何将某个角表示为弧度的有效数值表达式。
说明Cos 函数取某个角并返回直角三角形两边的比值。
此比值是直角三角形中该角的邻边长度与斜边长度之比。
结果范围在 -1 到 1 之间。
角度转化成弧度方法是用角度乘以 pi/180。
反之,弧度转化成角度的方法是用弧度乘以180/pi。
下面的示例利用 Cos 函数返回一个角的余弦值:Dim MyAngle, MySecantMyAngle = 1.3 ' 用弧度定义一个角。
vb函数大全(VB function Daquan)vb函数大全(VB function Daquan)VB commonly used function Daquan 2008-03-08 19:39, now programming software, such as VB, C++, etc., mostly with a powerful library of functions, you can save effort to complete a variety of functions. Most of the time, you can't remember the function or function format that implements a function, which results in a lot of trouble in programming. As a programmer, I have a deep understanding of this. Therefore, specially prepared several VB common function introduction, for your study or reference. There are inappropriate places to say, but also welcome in the Forum on this web site, we study.(I) type conversion class functions1. CType (X)[format]:P=CBool ("X") converts X to "Boolean" (Boolean) typeP=CByte ("X") converts X to "Byte" typeP=CCur (X) 'converts X to the' Currency 'typeP=CDate ("X") converts X to "Date" typeP=CDbl ("X") converts X to "double precision" (Double) typeP=CInt (X) converts the X to an integer (Integer) typeP=CLng ("X") converts X to "long integer" (Long) typeP=CSng (X) converts X to a single precision (Single) typeP=CStr (X) converts the X to a string (String) typeP=Cvar (X) converts the X to a variant (Variant) typeP=CVErr (X) 'converts X to a Error value[paradigm]:(1) CStr (13) +CStr (23) after the value is converted into a string, and is connected with "+" number, and the result is: 1323(2) CInt ("12") +12'strings are converted into integers and then summed up with 12. Results: 24(3) P=CInt (True) ', the output is -1"Boolean and numeric conversions should be noted, Boolean values are only True and False, in which True is -1 in memory, and False is 0(4) CBool (-0.001) ', the output is TrueWhen the value is converted to Boolean, the value equal to 0 will be False, and the value not equal to 0 will be True.2. Int (X), Fix (X): take the integer value of X[format]:P=Int (X) 'takes the maximum integer value of <=XP=Fix ("X") takes the integer part of X and removes the decimal directly[paradigm]:(1) Int (-54.6) ', the result is -55, take the maximum integer of<=-54.6(2) Fix (54.6) ', the result is 54, take an integer and remove the decimal directly(two) commonly used mathematical functions[format]:1. Abs (N) takes absolute valueExample: Abs (-3.5) results: 3.52. Cos (N) cosine functionExample: Cos (0): 13. Exp (N) e is the exponential function at the bottom Example: Exp (3): 20.0684. Log (N) the natural logarithm based on eExample: Log (10): 2.35. Rnd[(N)] generates random numbersExample: Rnd result: the number between 0--16. Sin (N) sine functionExample: Sin (0): 07. Sgn (N) signed functionExplanation: take the plus sign. Y=Sgn (X) is both X>0 and Y=1; X=0 is Y=0; X<0 is Y=; -18. Sqr (N) square rootExample: Sqr (9): 39. Tan (N) tangent functionExample: Tan (0): 010.Atn (N) reverse functionExample: Atn (0): 0[note] in trigonometric functions, expressed in radians. (string) class function of string:1., ASC (X), Chr (X): conversion character, character code[format]:P=Asc (X) returns the character code of the first character of string XP=Chr (X) returns characters equal to X characters[paradigm]:(1) P=Chr (65);'output character' A 'because the ASCII of A is equal to 65(2) P=Asc ("A")Output 652. Len (X): calculate the length of the string X[format]:P=Len (X)[instructions]:The empty string length is 0, and the space character is also a character. A Chinese text occupies 2 Bytes, but is also counted as a character.[paradigm]:(1) make X= "" (empty string)The output of Len (X) is 0(2) make X= "ABCD""The output of Len (X) is 4(3) make X= VB tutorial"The output of Len (X) is 43. Mid (X) function: read the string X characters in the middle [format]:P=Mid (X, n)Read by the N character of X, read all the characters behind.P=Mid (X, N, m)Read by the N character of X, read the M characters behind. [paradigm]:(1) X= "ABCDEFG""P=Mid (X, 5)The result is: "P=" efg"(2) X= "ABCDEFG""P=Mid (X, 2,4)The result is P= "BCDE""4. Replace: replaces some of the string in a string with another string[format]:P=Replace (X, S, R)[explanation]: replace the string S in string X with string R, and then return.[paradigm]:X=, VB, is, very, good"P=Replace (X, good, nice)The output is: P=, VB, is, very, nice"5. StrReverse: inverted string[format]:P=StrReverse (X)[instructions]:Returns the string after the X parameter is reversed[paradigm]:(1) X= "ABC""P=StrReverse (X)Output: P= "CBA""6., Ucase (X), Lcase (X): convert English letters to uppercase and lowercase[format]:P=Lcase (X)Convert uppercase characters from X strings to lowercaseP=Ucase (X)"Convert lowercase letters from X strings to uppercase."[instructions] no other characters or Chinese characters will be affected except English letters.[paradigm]:(1) make X=, VB, and, VC"The result of Lcase (X) is "VB, and, VC", and Ucase (X) is "VB AND VC""7. InStr function: finding strings[format]:P=InStr (X, Y)Locate the position of the Y from the first character of the XP=InStr (n, X, Y)Find the position of the Y from the X n character[instructions]:(1) if the Y is found in X, the return value is the place where the first character of the Y appears in X.(2) InStr (X, Y) is equivalent to InStr (1, X, Y).(3) if the string length, or X is an empty string, or Y is not found in X, 0 is returned.(4) if Y is an empty string, returns 0.Date time class function:1., Year (X), Month (X), Day (X): take out year, month, day[format]:P=Year (X)Take out the value of the X "year" sectionP=Month (X)Take out the value of the X "month" sectionP=Day (X)Take out the value of the X "day" section[description]:Year returns in AD, and if X has only time and no date, the date is #1899/12/30#2., Hour, Minute, Second function: take out, divide, or second[format]:P=Hour (X)Take the value of the "X" part of the "when"P=Minute (X)Take out the value of the "X" partP=Second (X)Take out the value of the X "seconds" section[indicates that the return value of]:Hour is between 0---23[paradigm]:X=10:34:23P=Hour (X)Q=Minute (X)R=Second (X)Output results: P=10, Q=34, R=233., DateSerial function: merge year, month, date, become date[format]:DateSerial (Y, M, D)Where Y is the year, M is the month, and D is the date[instructions]:(1) if the value of M is greater than 12, the month will beextrapolated from December to M-12 months; if less than 1, the month will be extrapolated from January to 1-M months.(2) if the date D is greater than the number of days in that month, the date from the date of the month, the number of D- months later; if less than 1, then the date from 1 days forward projections 1-D days.[paradigm]:P=DateSerial (2000,02,02)The result is P=2000/02/024.TimeSerial function: when merging, minutes and seconds become time[format]:P=TimeSerial (H, M, S)H is the number of hours, M is minutes, and S is seconds[explanation]: the principle of calculation is the same as that of DateSerial above[paradigm]:P=TimeSerial (6,32,45)The result was: P=6:32:455.Date, Time, Now function: read the date and time of the system[format]:P=Date ()P=Time ()P=Now ()[explanation]: none of these three functions have arguments[paradigm]:If the current time is 19:26 on August 29, 2003 evening, 45 seconds, thenP=Now ()The result is: P=2003-08-29 19:26:456.MonthName: returns the name of the month[format]:P=MonthName (X)[to indicate that the]:X parameter can be passed in to 1---12, returns the value of "month" and "February""...... But in English Windows, the return is "January", "February""......[paradigm]:P=MonthName (1)"P=" one month"7.WeekdayName: returns the name of the week[format]:P=WeekdayName (X)[shows that the]:X parameter can be passed in 1 - 7, and returns the value "Sunday", Monday"...... But in English windows, the return is "Sunday", "Monday""......[paradigm]:P=WeekdayName (1)The result is: P=, Sunday"Mathematical function of function DaquanAbs (Num) takes absolute value.Exp (Num) returns the value of e at the bottom and num as an exponent, such as Exp (2) returning the e^2 value.Log (Num) returns the natural pair value of parameter num, which is the Double type, that is, the logarithm based on E.Hex (Num) converts the parameter num to 16.Oct (Num) converts the parameter num to 8Sign (Num) returns the positive and negative sign of the parameter. If num is greater than 0, the return value is 1; if num equals 0, thenthe return value is 0; if num is less than 0, then the return value is -1.Sqrt (Num) returns the square root of the argument, Double type.Atan (Num) tangent functionSin (Num) sine functionCos (Num) cosine functionTan (Num) tangent functionRand (Num, [int]) will enter the parameter num four, five, tospecify four to five into which decimal, you can add second parameters int. For example, Round (12.456) returns the value of 12 Round (12.4567,3) returns 12.457.Rnd [[nun]] produces a random number less than 1, greater than or equal to 0, of type Single. If num is less than 0, then each will return the same number; if you don't provide the parameters or parameter is greater than 0, so in order to generate a random number next, this is the default value; if the parameter num is equal to 0, then returns the last generated random number. In order to generate different random numbers each time, it is better to use the Randomize statement before using the Rand () function. To randomly generate an integer from N to M, you canuse the following formula: Int (Rand ()) *M-N+1, +N.Pow (x, y) seeks the Y power of X.Val (STR) converts the number in a string to Integer or Double type.Str (Num) converts a numeric type parameter into a string to return.When the Fix (Num) parameter is greater than 0, the decimal part is removed; when the parameter is less than 0, the value returned is greater than or equal to the parameter value.When the Int (Num) parameter is greater than 0, the decimal part is removed; when the number is less than 0, the parameter is returned less than or equal to the parameter value.。