
C 语言程序设计(第三版)习题库 1、设圆半径r=,圆柱高h=3,求圆周长、圆面积、圆球表面积、圆球体积、圆柱体积。用scanf 输入数据,输出计算结果,输出时要求文字说明,取小数点后两位数字。请编程序。 #include<> main(){ floatr,h,C1,Sa,Sb,Va,Vb; scanf(__”%f ”__,&r); scanf(”%d ”,__&h _);; C1=2**r; Sa=*r*r; Sb=4*Sa; Va=4**r*r*r/3; Vb=Sa*h; printf(___”Cl=%.2fSa=%.2fSb=%.2fVa=%.2fVb=%.2f ”,Cl,Sa,Sb,Va,Vb ); } 2、输入一个华氏温度,要求输出摄氏温度。公式为c=5(F-32)/9 输出要求有文字说明,取位2小数。 #include<> main(){ floatF,c; scanf("%f",&F); ____c=5*(F-32)/9______; printf("c=%.2f",c); } 3、有一函数:?? ???≥-<≤-<=10113101121x x x x x x y 写一程序,输入x 值,输出y 值。 #include<> main(){ intx,y; printf("输入x :"); scanf("%d",&x); if(x<1){/*x<1*/ y=x; printf("x=%3d,y=x=%d\n",x,y);
}elseif(____x<10_______){/*1≤x-10*/ _____y=2*x-1_______; printf("x=%3d,y=2*x-1=%d\n",x,y); }else{/*x≥10*/ y=3*x-11; printf("x=%3d,y=3*x-11=%d\n",x#include"" main() { intx,y; scanf("%d",&x); if(x<1) {y=x;} elseif(x>=1&&x<10) {y=2*x-1;} else {y=3*x-11;} printf("%d",y); }#include"" main() { intx,y; scanf("%d",&x); if(x<1) {y=x;} elseif(x>=1&&x<10) {y=2*x-1;} else {y=3*x-11;} printf("%d\n",y); }#include"" main() { intx,y; scanf("%d",&x); if(x<1) {y=x;} elseif(x>=1&&x<10) {y=2*x-1;} else {y=3*x-11;} printf("%d",y); }scanf("%d",&x);
01. 她连水都不愿喝一口,更别提留下来吃饭了。 She wouldn't take a drink, much less would she stay for dinner. 02. 他认为我在对他说谎,但实际上我讲的是实话。 He thought I was lying to him, whereas I was telling the truth. 03. 这个星期你每天都迟到,对此你怎么解释? How do you account for the fact that you have been late every day this week? 04. 他们利润增长,部分原因是采用了新的市场策略。 The increase in their profits is due partly to their new market strategy. 05. 这样的措施很可能会带来工作效率的提高。 Such measures are likely to result in the improvement of work efficiency. 06. 我们已经在这个项目上投入了大量时间和精力,所以我们只能继续。 We have already poured a lot of time and energy into the project, so we have to carry on. 07. 尽管她是家里的独生女,她父母也从不溺爱她。 Despite the fact that she is the only child in her family, she is never babied by her parents. 08. 迈克没来参加昨晚的聚会,也没给我打电话作任何解释。 Mike didn't come to the party last night, nor did he call me to give an explanation. 09. 坐在他旁边的那个人确实发表过一些小说,但决不是什么大作家。 The person sitting next to him did publish some novels, but he is by no means a great writer. 10. 他对足球不感兴趣,也从不关心谁输谁赢。 He has no interest in football and is indifferent to who wins or loses. 11. 经理需要一个可以信赖的助手,在他外出时,由助手负责处理问题。 The manager needs an assistant that he can count on to take care of problems in his absence. 12. 这是他第一次当着那么多观众演讲。 This is the first time that he has made a speech in the presence of so large an audience. 13. 你再怎么有经验,也得学习新技术。 You are never too experienced to learn new techniques. 14. 还存在一个问题,那就是派谁去带领那里的研究工作。(Use an appositional structure.) There remains one problem, namely, who should be sent to head the research there. 15. 由于文化的不同,他们的关系在开始确实遇到了一些困难。 Their relationship did meet with some difficulty at the beginning because of cultural differences. 16. 虽然他历经沉浮,但我始终相信他总有一天会成功的。 Though he has had ups and downs, I believed all along that he would succeed someday. 17. 我对你的说法的真实性有些保留看法。 I have some reservations about the truth of your claim. 18. 她长得并不特别高,但是她身材瘦,给人一种个子高的错觉。 She isn't particularly tall, but her slim figure gives an illusion of height. 19. 有朋自远方来,不亦乐乎?(Use "it" as the formal subject.) It is a great pleasure to meet friends from afar. 20. 不管黑猫白猫,能抓住老鼠就是好猫。(as long as) It doesn't matter whether the cat is black or white as long as it catches mice. 21. 你必须明天上午十点之前把那笔钱还给我。 You must let me have the money back without fail by ten o'clock tomorrow morning. 22. 请允许我参加这个项目,我对这个项目非常感兴趣。 Allow me to take part in this project: I am more than a little interested in it. 23. 人人都知道他比较特殊:他来去随意。(be free to do sth.) Everyone knows that he is special: He is free to come and go as he pleases. 24. 看她脸上不悦的神色,我似乎觉得她有什么话想跟我说。 Watching the unhappy look on her face, I felt as though she wished to say something to me. 25. 他说话很自信,给我留下了很深的印象。(Use "which" to refer back to an idea or situation.)
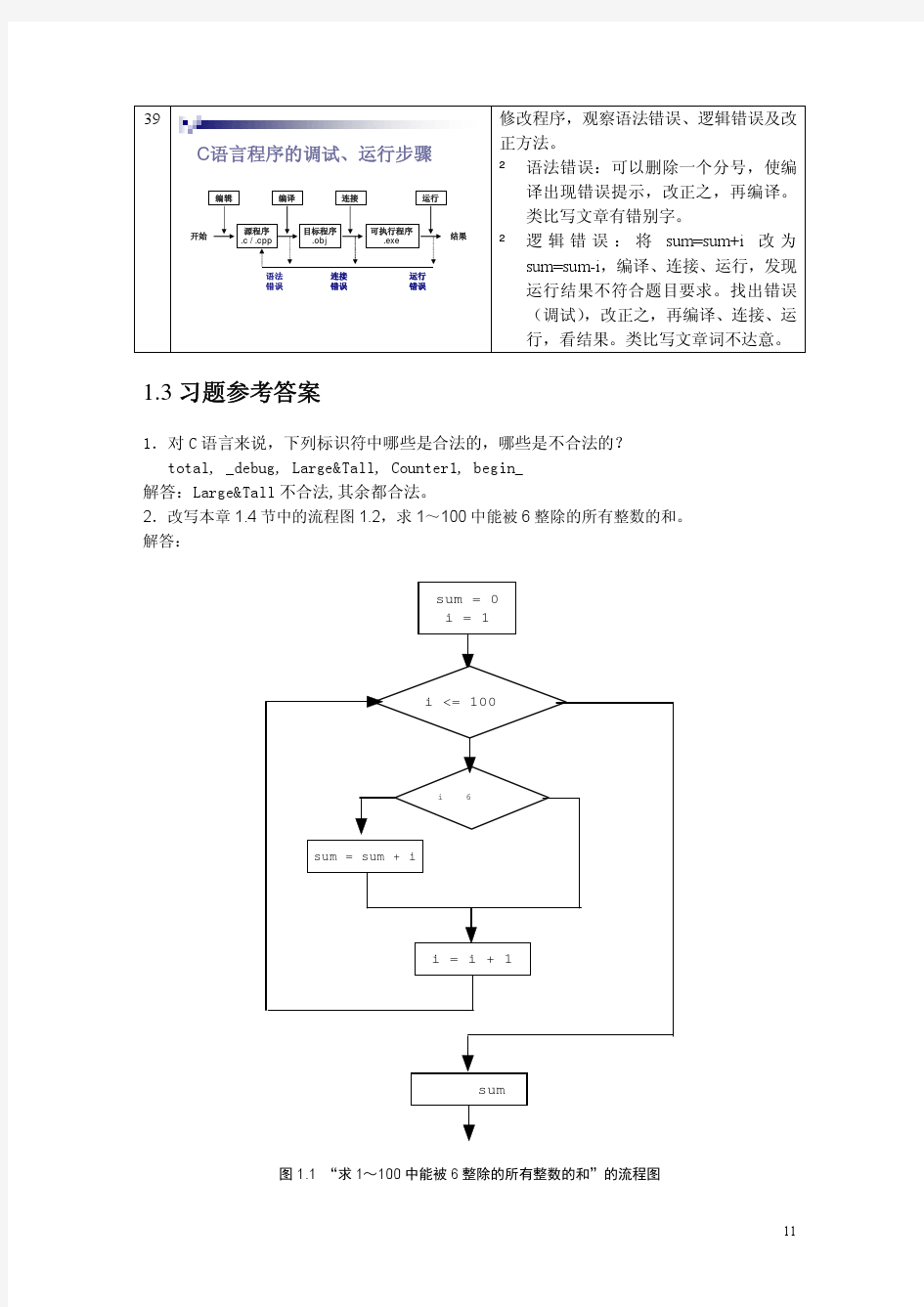
第1章程序设计和C语言1 1.1什么是计算机程序1 1.2什么是计算机语言1 1.3C语言的发展及其特点3 1.4最简单的C语言程序5 1.4.1最简单的C语言程序举例6 1.4.2C语言程序的结构10 1.5运行C程序的步骤与方法12 1.6程序设计的任务14 1-5 #include 2.1什么是算法16 2.2简单的算法举例17 2.3算法的特性21 2.4怎样表示一个算法22 2.4.1用自然语言表示算法22 2.4.2用流程图表示算法22 2.4.3三种基本结构和改进的流程图26 2.4.4用N S流程图表示算法28 2.4.5用伪代码表示算法31 2.4.6用计算机语言表示算法32 2.5结构化程序设计方法34 习题36 第章最简单的C程序设计——顺序程序设计37 3.1顺序程序设计举例37 3.2数据的表现形式及其运算39 3.2.1常量和变量39 3.2.2数据类型42 3.2.3整型数据44 3.2.4字符型数据47 3.2.5浮点型数据49 3.2.6怎样确定常量的类型51 3.2.7运算符和表达式52 3.3C语句57 3.3.1C语句的作用和分类57 3.3.2最基本的语句——赋值语句59 3.4数据的输入输出65 3.4.1输入输出举例65 3.4.2有关数据输入输出的概念67 一.填空 1. 每个C程序都必须有且仅有一个________ 函数。 2. C语言程序开发到执行通常要经过6个阶段即编辑、预处理、________、链接、加载和执行。 3. 软件是程序,以及______、使用和维护所需要的所有文档。 4. 国标中规定:“计算机程序是按照具体要求产生的适合于计算机处理的_________”。 5. 程序设计语言按照书写形式,以及思维方式的不同一般分为低级语言和________两大类。 6. C语言是由________组成的。 7. C语言的函数可分为主函数main、标准库函数和_________。 8. 一个函数是由两部分组成的,即:________和函数体。 9. 编译是将C语言所编写的源程序________成机器代码,也称为建立目标代码程序的过程。 10. 程序是由某种程序设计语言编制出来,体现了编程者的控制思想和对计算机执行操作 的要求。不同的任务功能,就会需求不同的软件程序,如:控制计算机本身软硬件协调工作,并使其设备充分发挥效力,方便用户使用的系统软件程序,称为操作系统;而为办公自动化(OA)、管理信息系统(MIS)、人工智能、电子商务、网络互联等等应用而开发的软件程序,统称为_________。 11. 机器语言是以__________形式表示的机器基本指令的集合,是计算机系统唯一不需要翻译可以直接识别和执行的程序设计语言。 12. 与机器语言相比,使用汇编语言来编写程序可以用_______来表示指令的操作码和操作对 象,也可以用标号和符号来代替地址、常量和变量。 13. 在编译程序之前,凡以____开头的代码行都先由预处理程序预处理。 14. C程序的执行均是由执行_________开始。 15. 函数体即为包含在{}内的部分。它分为________和为完成功能任务由若干个C 语句 组成的执行部分。 16. C语言程序中一条简单语句是以________字符作为结束符的。 17. C语言是结构化、________的程序设计语言。 18. 由于计算机硬件不能直接识别高级语言中的语句,因此,必须经过“_______程序”,将用高级语言编写的程序翻译成计算机硬件所能识别的机器语言程序方可执行。 19. 用高级语言编写的程序需翻译成计算机硬件所能识别的机器语言程序方可执行。所以 说,用高级语言进行程序设计,其编程效率高,方便易用,但_______没有低级语言高。 20. 新视野大学英语(第2版)第4册Unit 1答案 III. 1. idle 2. justify 3. discount 4. distinct 5. minute 6.accused 7. object 8. contaminate 9. sustain 10. worship IV. 1. accusing... of 2. end up 3. came upon 4. at her worst 5. pa: 6. run a risk of 7. participate in 8. other than 9. object to/objected V 1. K 2. G 3. C 4. E 5. N 6.0 7.1 8. L 9. A 10. D Collocation VI. 1. delay 2. pain 3. hardship 4. suffering 5. fever 6. defeat 7. poverty 8. treatment 9. noise 10. agony Word building VII. 1. justify 2. glorify 3. exemplifies 4. classified 5. purified 6. intensify 7. identify 8. terrified VIII. 1. bravery 2. jewelry 3. delivery 4. machinery 5. robbery 6. nursery 7. scenery 8. discovery sentence Structure IX. 1. other than for funerals and weddings 2. other than to live an independent life 3. other than that they appealed to his eye . . ` 4. but other than that, he'll eat just about everything . 5. other than that it's somewhere in the town center X. 1. shouldn't have been to the cinema last night 2. would have; told him the answer 3. they needn't have gone at all 4. must have had too much work to do 5. might have been injured seriously XIII. 1 .B 2.A 3.C 4.D 5. B 6.A 7.B 8.A 9. C 10.A II.D 12.C 13. D 14.A 15. C 16.D 17.B 18.C I9. A 20.D 新视野大学英语(第2版)第4册Unit 2答案 Section A Comprehension o f the text 1. He lived a poor and miserable life during his childhood. 2. Because no one in Britain appeared to appreciate his talent for comedy. His comic figures did not conform to British standards. 3. Because his dress and behavior didn't seem that English. 4. It was the first movie in which Chaplin spoke. 5. He used his physical senses to invent his art as he went along without a prepared script. 6. His transformation of lifeless objects into other kinds of objects, plus the skill with which he executed it again and again. 7. She brought stability and happiness to him and became a center of calm in his family. 8. Comic. Vocabulary III. 1. coarse 2. betrayed 3. incident 4. postponed 5. execute 6. surrounding 7. applause 8. extraordinary 9. clumsy 10. sparked IV. 1. for 2. against 3. up 4. about 5. up 6. to 7. down 8. down 9. in 10. on V. l. I 2.J 3.B 4.D 5.E 6.G 7.F 8.L 9.N 10.A Collocation 第0章习题 1. 将下列十进制数分别转化为二进制数、八进制数和十六进制数: (1)128 (2)511 (3)1024 (4)65535 (5)1048575 答: (1)10000000、200、80 (2)111111111、777、1FF (3)10000000000、2000、400 (4)1111111111111111、177777、FFFF (5)11111111111111111111、3777777、FFFFF 2. 将下列二进制数转化为十进制数和十六进制数: (1)1100110101B (2)101101.1011B 答: (1)821、335 (2)45.6875、2D.B 3. 写出下列数的原码、反码、补码:15、-20、-27/32 答: (1)00001111、00000000、00001111 (2)10010100、11101011、11101100 (3)1.1101100、1.0010011、1.0010100 4. 16位无符号定点整数的数值表示范围为多少?8位补码的表示范围是多少?16位补码的表示范围是多少? 答: 0~65535、-128~127、-32768~32767 5.1968年Dijkstra提出结构化程序设计的思想的原因是什么?简要回答结构化程序设计的经典定义。 答: 结构化程序设计概念的提出主要是源于程序结构的层次性与模块化使得构造出来的软件具有良好的可理解性和可维护性,随着软件规模的扩大与复杂性的提高,程序的可维护性成为程序设计者们关注的重要问题之一。 如果一个程序的代码块仅仅通过顺序、选择和循环这3种基本控制结构进行连接,并且每个代码块只有一个入口和一个出口,则称这个程序是结构化的。 6.C程序在内存中存储在哪儿?计算机的内存空间是如何分区的?分区存放不同类型的数据的目的是什么? 答: 习题解析与答案 第1章C语言概述 一.简答题 1.概述C语言的主要特点。 【解答】 (1)语言简洁、紧凑,使用方便、灵活。 (2)数据类型丰富,表达能力强。 (3)运算符多样。C语言中的运算符包含的范围非常广泛。 (4)具有结构化的控制语句。如if…else语句、while语句、do while语句、switch 语句、for语句。 (5)允许直接访问物理地址。C语言中含有的位和指针运算,能够直接对内存地址进行访问操作。 (6)所生成的目标代码质量高,可移植性好。 2.构成C语言程序的基本单位是什么?它由哪几部分组成? 【解答】函数是构成C语言程序的基本单位。一个完整的C程序一般由文件包含、宏定义、函数说明、变量和一个或若干个函数组成。 3.C语言程序的运行一般要经过哪几个步骤? 【解答】(1)编辑;(2)编译;(3)连接,生成EXE文件;(4)执行。 二.运行程序写结果 1.输入下面程序并运行。 main() { int a1,a2,x; a1=100; a2=50; x=a1-a2; printf(″x=%d\n″,x); } 【解答】运行结果为:x=50 2.输入下面程序并运行。 main() { int a1,a2,x; a1=10; a2=20; x=a1*a2; printf(″a1=%d,a2=%d\n″,a1,a2); printf(″x=%d\n″,x); } 【解答】运行结果为:a1=10,a2=20 x=200 3.输入下面程序并运行。 #include Unit 1答案2版)第4册新视野大学英语(第4. but other than that, he'll eat just about everything . 5. other than that it's somewhere in the town center III. X. 1. idle 2. justify 3. discount 4. distinct 5. minute 1. shouldn't have been to the cinema last night 6.accused 7. object 8. contaminate 9. sustain 10. worship told him the answer 。2. would haveIV. 3. they needn't have gone at all 1. accusing... of 2. end up 3. came upon 4. at her worst 5. pa: 4. must have had too much work to do 6. run a risk of 7. participate in 8. other than 9. object to/objected 5. might have been injured seriously 1. 这种植物只有在培育它的土壤中才能很好地成长。Collocation The plant does not grow well in soils other than the one in which it has been VI. developed. 1. delay 2. pain 3. hardship 4. suffering 5. fever 研究结果表明,无论我们白天做了什么事情,晚上都会做大约两个小时2. 6. defeat 7. poverty 8. treatment 9. noise 10. agony 的梦。Word building Research findings show that we spend about two hours dreaming every night, VII. no matter what we may have done during the day. 1. justify 2. glorify 3. exemplifies 4. classified 有些人往往责怪别人没有尽最大努力,以此来为自己的失败辩护。3. 5. purified 6. intensify 7. identify 8. terrified Some people tend to justify their failure by blaming others for not trying their VIII. best. 1. bravery 2. jewelry 3. delivery 4. machinery 我们忠于我们的承诺:凡是答应做的,我们都会做到。4. 5. robbery 6. nursery 7. scenery 8. discovery We remain true to our commitment: Whatever we promised to do, we would sentence Structure do it. 连贝多芬的父亲都不相信自己儿子日后有一天可能成为世界上最伟大的5. IX. 音乐家。爱迪生也同样如此,他的老师觉得他似乎过于迟钝。1. other than for funerals and weddings Even Beethoven's father discounted the possibility that his son would one day 2. other than to live an independent life become the greatest musician in the world. The same is true of Edison, who 3. other than that they appealed to his eye . . ` 1 / 7 seemed to his teacher to be quite dull. sentence structure 当局控告他们威胁国家安全。6. They were accused by the authorities of threatening the state security. X. 1. it is a wonder to find c语言课后习题答案 第二章习题 2.什么叫做结构化算法?为什么要提倡结构化算法? 答:结构化算法是由一些基本结构顺序组成的。在基本结构之间不存在向前或向后的跳转,流程的转移只存在于一个基本的结构范围内。一个非结构化的算法可以用一个等价的结构化算法代替,其功能不变。 跟结构化算法比较起来,非结构化算法有以下缺点: 流程不受限制的随意转来转去,使流程图豪无规律使人在阅读的时候难以理解算法的逻辑.难以阅读,也难以修改,从而使算法的可靠性和可维护性难以保证。 4. 第三章习题 1.#include float p,p1,r=0.09; scanf("%u",&n); p=pow(1+r,n); p1=(p-1)*100; printf("%5.2f%%\n",p1); } 运行结果:输入,回车,见结果: 2.#include 《C语言程序设计》练习及答案 得分评卷人复查人 一、单选题,每小题1分,共60分(将正确答案的序号写在题目的括号中)。 1、结构化程序设计的三种基本控制结构是(D )。 A、主程序、子程序、函数 B、输入、处理、输出 C、调用,返回,转移 D、顺序、选择、循环 2、下列关于C程序变量的叙述, ( D )是错误的。 A、变量名必须由字母或下划线开头。 B、程序中的变量必须在被使用之前定义。 C、不同的基本类型的变量之间可以混合运算。 D、变量的数据类型决定变量的"作用域"。 3、能将C语言编写的源程序转换为目标程序的软件是(C )。 A、编辑程序 B、汇编程序 C、编译程序 D、解释程序 4、以下符号中,合法的用户标识符是( D )。 A、-p B、int C、3ab D、_xt_ 5、以下选项中,与m=n++完全等价的表达式是( C )。 A、m=++n B、m+=n+1 C、m=n, n=n+1 D、n=n+1,m=n 6、若有定义:int aa[8];。则以下表达式中不能代表数组元aa[1]的地址的是(C )。 A、&aa[0]+1 B、&aa[1] C、&aa[0]++ D、aa+1 7、表达式!5&(7+3)&&(4+5)的值是(A)。 A、0 B、1 C、5 D、9 8、以下选项中非法的C语言表达式是(A )。 A、x+1=x+1 B、0<=x<100 C、i=j==0 D、(char)(65+3) 9、在TURBO C中, int类型变量所占字节数是(B )。 A、1 B、2 C、4 D、8 10、C语言中基本的数据类型包括(B)。 A、整型,实型,逻辑型 B、整型,实型,字符型 C语言课后习题答案-第四版- 谭浩强(1-7) 第一章 #include {float r5,r3,r2,r1,r0,p,p1,p2,p3,p4,p5; p=1000; r5=0.0585; r3=0.054; r2=0.0468; r1=0.0414; r0=0.0072; p1=p*((1+r5)*5); // 一次存5年期 p2=p*(1+2*r2)*(1+3*r3); // 先存2年期,到期后将本息再存3年期 p3=p*(1+3*r3)*(1+2*r2); // 先存3年期,到期后将本息再存2年期 p4=p*pow(1+r1,5); // 存1年期,到期后将本息存再存1年期,连续存5次 p5=p*pow(1+r0/4,4*5); // 存活期存款。活期利息每一季度结算一次printf("p1=%f\n",p1); // 输出按第1方案得到的本息和 printf("p2=%f\n",p2); // 输出按第2方案得到的本息和 printf("p3=%f\n",p3); // 输出按第3方案得到的本息和 printf("p4=%f\n",p4); // 输出按第4方案得到的本息和 printf("p5=%f\n",p5); // 输出按第5方案得到的本息和 return 0; } #include C语言程序设计第二版 习题参考答案 Document serial number【LGGKGB-LGG98YT-LGGT8CB-LGUT- C语言程序设计习题参考答案 习题 1 一、判断题 1.在计算机中,小数点和正负号都有专用部件来保存和表示。 2.二进制是由0和1两个数字组成的进制方式。 3.二进制数的逻辑运算是按位进行的,位与位之间没有进位和借位的关系。 4.在整数的二进制表示方法中,0的原码、反码都有两种形式。 5.有符号数有三种表示法:原码、反码和补码。 6.常用字符的ASCII码值从小到大的排列规律是:空格、阿拉伯数字、大写英文字母、小写英文字母。 解:1.F2.T 3.T 4.T 5.T 6.T 二、单选题 1.在计算机中,最适合进行数值加减运算的数值编码是。 A. 原码 B. 反码 C. 补码 D. 移码 2.已知英文小写字母m的ASCII码为十进制数109,则英文小写字母y的ASCII 码为十进制数。 A. 112 B. 120 C. 121 D. 122 3.关于ASCII码,在计算机中的表示方法准确地描述是。 A. 使用8位二进制数,最右边一位为1 B. 使用8位二进制数,最左边一位为1 C. 使用8位二进制数,最右边一位为0 D. 使用8位二进制数,最左边一位为0 4.设在机器字长4位,X=0111B,Y=1011B,则下列逻辑运算中,正确的是 ___________。 A. X∧Y=1000 B. X∨Y=1111 C. X⊕Y=0011 D. ˉY=1000 5.下列叙述中正确的是()。 A.高级语言就是机器语言 B.汇编语言程序、高级语言程序都是计算机程序,但只有机器语言程序才是计算机可以直接识别并执行的程序 C.C语言因为具有汇编语言的一些特性,所以是汇编语言的一种 D.C源程序经过编译、连接,若正确,执行后就能得到正确的运行结果6.用C语言编写的源程序经过编译后,若没有产生编译错误,则系统将()。 A.生成可执行文件B.生成目标文件 C.输出运行结果D.自动保存源文件 7.下列叙述中不正确的是()。 A.main函数在C程序中必须有且只有一个 B. C程序的执行从main函数开始,所以main函数必须放在程序最前面 C. 函数可以带参数,也可以不带参数。 新视野大学英语Book II课后练习题答案 Unit 1 Section A Language focus 3.Words in use 1.condense 2.exceed 3.deficit 4.exposure 5.asset 6.adequate https://www.doczj.com/doc/ca8127498.html,petent 8.adjusting 9.precisely 10.beneficial 4.Word building Words learned new words formed -al/ial manager managerial editor editorial substantial substance survive survival traditional tradition marginal margin -cy Consistent consistency Accurate accuracy Efficiency efficient -y Recover recovery Minister ministry assemble assembly 5. 1.editorial 2.recovery 3.accuracy 4.substance 5.managerial 6.margin 7.assembly 8.Ministry 9.survival 10.tradition 11.consistency 12.efficient 6.Banked cloze 1.L 2.C 3.J 4.A 5.I 6.O 7.N 8.E 9.H 10.F 7.Expressions in use 1.feel obliged to 2.be serious about 3.run into 4.distinguish between 5.thrust upon 6.was allergic to 7.get lost 8.be attracted to 9.make sense 10.looked upon as 9.Translate the following paragraph into Chinese. 人们普遍认为英语是一种世界语言,经常被许多不以英语为第一语言的国家使用。与其他语言一样,英语也发生了很大的变化。英语的历史可以分为三个主要阶段,古英语,中古英语和现代英语。英语起源于公元5世纪,当时三个日耳曼部落入侵英国,他们对于英语语言的形成起了很大的作用。在中世纪和现代社会初期,英语的影响遍及不列颠群岛。从17世纪初,它的影响力开始在世界各地显现。欧洲几百年的探险和殖民过程导致了英语的重大变化。今天,由于美国电影,电视,音乐,贸易和技术,包括互联网的大受欢迎,美国英语的影响力尤其显著。 10.Translate the following paragraph into English Chinese calligraphy is a unique art and the unique art treasure in the world. The formation and development of the Chinese calligraphy is closely related to the emergence and evolution of Chinese characters. In this long evolutionary process,Chinese characters have not only played an important role in exchanging ideas and transmitting culture but also developed into a unique art form.Calligraphic works well reflect calligraphers’ personal feeling, knowledge, self-cultivation, personality, and so forth, thus there is an e xpression that “seeing the calligraphers’ handwriting is like seeing the person”. As one of the treasures of Chinese culture, Chinese calligraphy shines splendidly in the world’s treasure house of culture and art. Section B 4.words in use 1.mysterious 2.desperate 3.devise 4.negotiate 5.recalled 6.specifically 7.depict 8.ignorance 9.expand 10.confusion 5.Expressions in useC语言程序设计试题集与答案解析
新视野大学英语4册第二版课后习题答案.doc
VI. 1. service 2. help/hand 3. influence 4. guarantee 5. visit 6. span . 7. welcome 8. spirit 9. duties 10. buildings Word BuildingC语言课后习题答案(最终)
c语言程序设计第五版习题答案
新视野大学英语册第二版课后习题答案全解
最新c语言课后习题答案汇总
(完整版)C语言程序设计练习及答案
C语言课后习题答案(完整版)-第四版-_谭浩强
C语言程序设计第二版习题参考答案
新视野大学英语2册课后题答案