
第六章动词的时态与语态
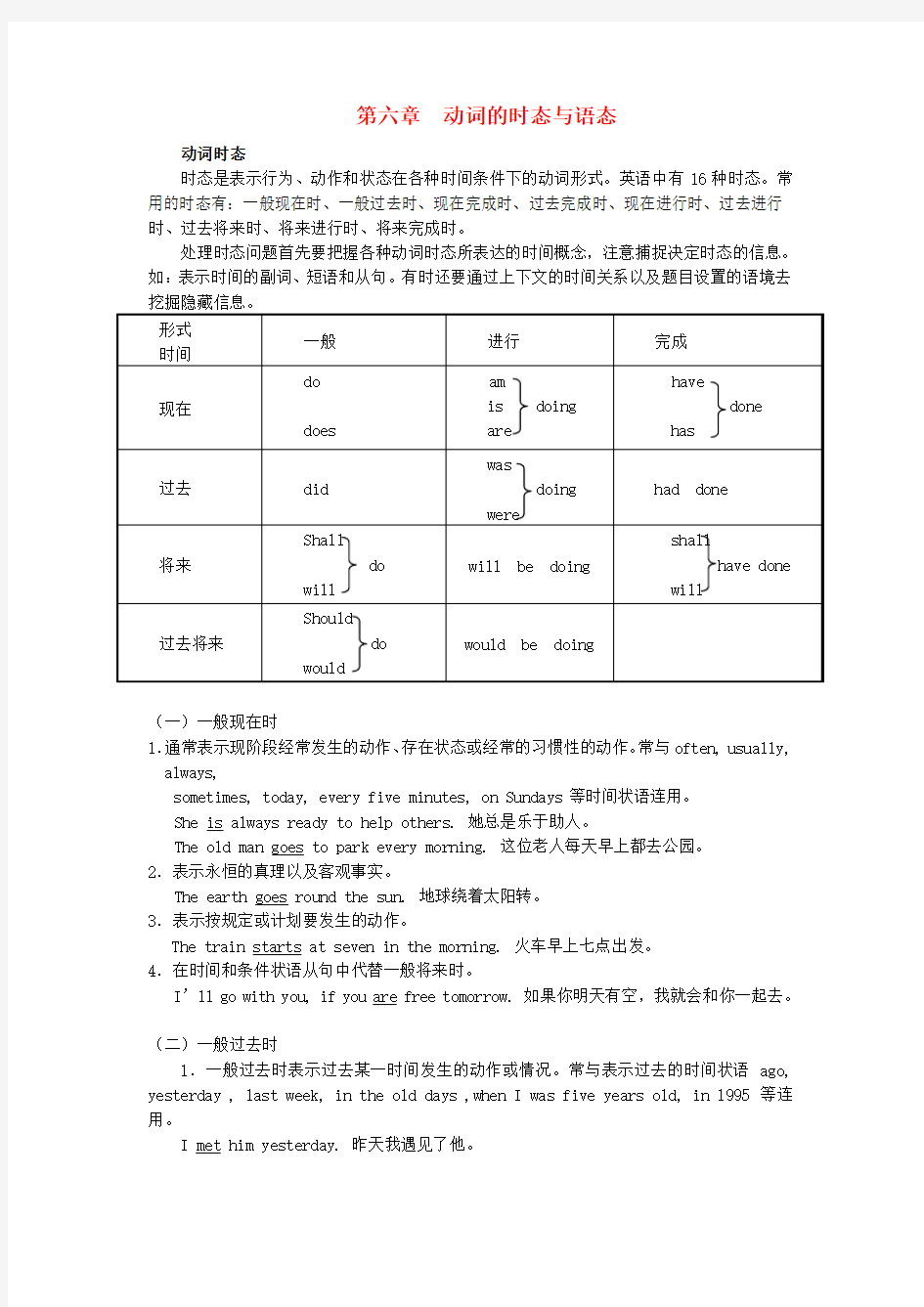
动词时态
时态是表示行为、动作和状态在各种时间条件下的动词形式。英语中有16种时态。常用的时态有:一般现在时、一般过去时、现在完成时、过去完成时、现在进行时、过去进行时、过去将来时、将来进行时、将来完成时。
处理时态问题首先要把握各种动词时态所表达的时间概念,注意捕捉决定时态的信息。如:表示时间的副词、短语和从句。有时还要通过上下文的时间关系以及题目设置的语境去
(一)一般现在时
1.通常表示现阶段经常发生的动作、存在状态或经常的习惯性的动作。常与often, usually, always,
sometimes, today, every five minutes, on Sundays等时间状语连用。
She is always ready to help others. 她总是乐于助人。
The old man goes to park every morning. 这位老人每天早上都去公园。
2.表示永恒的真理以及客观事实。
The earth goes round the sun. 地球绕着太阳转。
3.表示按规定或计划要发生的动作。
The train starts at seven in the morning. 火车早上七点出发。
4.在时间和条件状语从句中代替一般将来时。
I’ll go with you, if you are free tomorrow. 如果你明天有空,我就会和你一起去。
(二)一般过去时
1.一般过去时表示过去某一时间发生的动作或情况。常与表示过去的时间状语ago, yesterday , last week, in the old days ,when I was five years old, in 1995 等连用。
I met him yesterday. 昨天我遇见了他。
They began to work two months ago. 两个月前他们开始工作。
2.一般过去时多和表示过去了的时间状语连用。但是有时候句子并没有过去的时间状语,这时就要通过语境、说话人的口气来判断。
He wrote a novel. 他写了一部小说。
I didn’t expect you were waiting for us. 我没预料到你正在等我们。
3.used to do sth. 意为“过去常常做某事”,暗含“现在不做了”之意。be used to do sth. 意为“被用于做某事”,不定式表示目的,可用于多种时态。be used to doing sth. 习惯做某事。
He used to get up early . 过去他总是早起。(现在不这样了)
He will be used to getting up early . 他将会习惯早起。
Wood is used to make paper. 木材被用来造纸。
(三)一般将来时
1、表示将要发生的动作或存在的状态,常用的时间状语有later(on), soon, in a month, next time, from now on, tomorrow等。
I shall be eighteen years old next year. 明年我就十八岁了。
He will not go to the airport to meet her this afternoon. 今天下午他不去机场接她。
2、一般将来时的其它表示形式
(1)一般现在时表将来
①按照计划或时刻表要发生的事情。
The new library opens next month. 新图书馆下月开放。
The plane takes off at 3:00 P.m. 飞机于下午三点起飞。
②在条件状语从句和时间状语从句中用一般现在时表将来。
If you leave tomorrow , I’ll see you at the airport. 如果你明天走,我到机场送你。
When she comes, I’ll tell her about it. 她来时我将把这件事告诉她。
(2)现在进行时表将来
现在进行时表示将来,往往是指计划好或准备要做的事。一些表示动作转换的终止性动词,如go, come, leave, start, begin,stay,take off,arrive等,或者也称为位移性动词,其进行时表示马上要做某事。
I’m taking the kids to the zoo this Sunday. 这个周日我将带孩子们去动物园。
He is leaving school in one year’s time.他一年后就要毕业了。
(3)be to do sth结构表示计划中约定的或按职责、义务和要求必须去做的事或即将发生的动作。
The president is to visit Japan in May.主席将于五月访问日本。
I’m to get married next year. 我明年结婚。
(4)be about to do. 结构表示“刚要做某事,马上要做某事,正要做某事”,强调动作即将发生(不跟表将来的时间状语连用)。
We are about to discuss this problem.我们将马上讨论这个问题。
They were about to leave when the telephone rang. 他们正要离开时电话响了。
3、will和be going to的区别。
(1)will多表示带意愿色彩的将来或客观上将来要发生的事,也可表示临时做出决定
将要做的事。
I will stay with you and help you. 我会和你一起并且帮助你。
—You have left the light on. 你还开着灯呢。
— Oh, so I have. I will go and turn it off. 哦,确实是的。我马上去关掉它。
(2)be going to常用于口语中,主要用来表示将发生的动作或存在的状态、打算或准备要做的事或根据某种迹象判断可能将要发生的事。
There’s going to be an English film this evening. 今晚有一场英文电影。
Look at those clouds. It’s going to rain. 看那些乌云,要下雨了。
(四)现在完成时
1、表示过去发生或已经完成的某一动作对现在造成的影响或结果。常与already, ever, never, just ,yet等副词连用。
I have just finished my homework. 我刚刚完成我的家庭作业。
He has been to Germany. 他去过德国。
2、表示从过去某时刻开始,持续到现在的动作或情况,并且有可能会继续持续下去,此时经常用延续性动词。时间状语常用since加一个过去的时间点,或for加一段时间,或加一个现在时间。
I have known him for three years. 我认识他三年了。
He has lived here since 1995.他自1995年以来就住在这儿。
【注意】(1)因为含有for加一段时间或since加一时间点这样的时间状语的完成时,有延续性的特点,所以不能使用瞬间动词。
My sister has been married for 5 years.我姐姐结婚五年了。
My sister has married. Don’t disturb her. 我姐姐已经结婚了。不要打扰她。
(2)在This/That/It is the first/second/third/..time that..句型里,从句要用现在完成时。
This is the second time that the products of our company have been shown in the International Exhibition. 这是我公司产品第二次参加国际展览会。
(3)句型It is/has been...since..所使用的两种时态都正确。
It is/has been 10 years since I last saw him. 从我上次见到他以来已经有10年了。
(五)过去完成时
1、过去完成时是一个相对时态,表示过去的过去,只有在两个过去发生的动作相比较时才可显示出来。
When we got to the station, the train had left.
2、过去完成时表示截止到过去某一时间已经完成的动作。
By the end of last month, we had reviewed four books. 截止到上个月末,我们已经复习了四本书。
3、表示思维的动词用过去完成时,意为“原本······(但事与愿违)”。
I had thought that he would win. 我原以为他能赢。
We had believed that he could tell the truth. 我们原本相信他能够说实话。
(六)现在进行时
1、现在进行时表示说话时或现阶段正在进行的动作。
Listen, someone is crying. 听,有人在哭。
What are you doing these days? 这些天你们在干什么?
2、有时,现在进行时也与always等副词连用,表示反复出现的习惯性动作,用以表达说话人赞扬、讨厌等情绪。
He is always asking the same question. 他总是问同一个问题。(厌烦)
3、动词go, come, leave, arrive, start, begin, end等表将要发生的动作时也用现在进行时。
They are leaving for Shanghai. 他们将动身去上海。
4、状态动词be, have, belong to, remember, know, love, like, prefer, remember, forget, hope, wish, want, see, hear, find, feel等一般不用于进行时。
Do you know where he is? 你知道他在哪儿吗?
(七)过去进行时
1、表示在过去某一时刻或过去一段时间内正在发生的动作。
I was doing my homework at this time yesterday. 昨天的这个时候我正在做作业。
2、如果when, while这样的时间状语引导词所引导的主从句之一是一般过去时,则另一个句子常用过去进行时。
I was washing my hair when you knocked at the door. 你敲门的时候我正在洗头发。【辨析】现在完成时与一般过去时
现在完成时是联系过去和现在的纽带,它强调过去的动作对现在的影响;一般过去时只表示过去的某个具体时间里发生的动作,与现在没有联系。试比较:
He has worked in that hospital for 8 years. (表示他从过去开始工作,一直工作到现在,可能现在仍在那家医院工作。)
他已经在那家医院里工作了8年。
He worked in that hospital for 8 years. (这只是讲述一个过去的事实,表示他现在已经不在那家医院了。)
他曾经在那家医院工作了8年。
Have you had your lunch? 你吃午饭了吗?
What did you have for lunch? 你午饭吃的是什么?
I have ever been to the Great Wall, and I went there last summer. 我去过长城,我去年夏天去的。
Exercises:
1. —I took a photo of you just now.
—Really? I with attention.
A. didn’t look
B. wasn’t looking
C. am not looking
D. have’t looked
2. —You haven’t said a word about my new hair-style. What do you think of it? —I’m sorry I anything about it sooner. I certainly think it’s pretty.
A. don't say
B. wasn’t saying
C. didn’t say
D. haven’t said
3. —Can I help you, Madam.
— No, thanks, I .
A. have just looked around
B. just look around
C. am just looking around
D. just looked around
4. —That famous cherry tree because of pollution.
—Yes, we have to do something to save it.
A. has died
B. had died
C. is died
D. is dying
5. She ought to stop reading; she has a headache because she too long.
A. had read
B. read
C. is reading
D. has been reading
6. —You’re talking too much.
—Only at home. No one me but you.
A. is hearing
B. had heard
C. hears
D. heard
7. —What have you been doing? I asked you a question. Why didn’t you answer? —Sorry, I to the news on the radio.
A. listened
B. have listened
C. was listening
D. had listened
8. —You should have told him the date earlier.
—I , but he forgot about it.
A. did
B. have
C. had
D. should have
9. —You could have asked Tom for help, for he is good at physics.
—Really? Oh, a whole night ,Why didn’t you tell me earlier?
A. is wasted
B. was wasted
C. had wasted
D. has wasted
10. The thief tried to break away from the policeman who him but failed.
A. held
B. had held
C. would hold
D. was holding
11. You exercises at your desk! Why not take some exercise?
A. always do
B. are always doing
C. have always done
D. have always been doing
12. —What were you up to when she dropped in?
—I for a while and some reading.
A. was playing; was going to go
B. played; did
C. had played; was going to go
D. had played; did
用括号中动词的适当形式填空。
1.It is the fourth time that Mike (travel) to China.
2.He (not finish)the work by the end of last month.
3.LiMing (know) him since then.
4.I (receive) a letter from my brother last night.
5.We (be ) to London many times before we left England.
6.How long you (learn) English by the end of this term?
7.—He (live) in this city since he (leave) his hometown..
—When did he (leave) there?
—He there three years ago.
8.—His father (be) in the Party for years.
—When he (join) the Party?
—He (join) the Party in 1996.
9.—It (rain )for such a long time!
—When it (rain)?
—It (rain) 3 hours ago.
10.I (hope)to be back last night, but I (not catch) the train.
11.—Hello, may I speak to John?
— (speak).
动词的语态
语态有两种:主动语态和被动语态。
主语是动作的发出者为主动语态;主语是动作的接受者为被动语态。
(1)被动语态
1)用法
A.不知道动作的执行者是谁。
B.没有必要指出动作的执行者
C.强调动作的承受着。
(2)被动语态的构成及用法
1) 被动语态最基本的句型结构是: be +及物动词过去分词
一般现在时:is/am/are+done
一般过去时:was/were+done
现在进行时:is/am/are+being+done
过去进行时:was/were+being+done
一般将来时:will+be+done
过去将来时:would+be+done
现在完成时:have/has+been+done
过去完成时:had+been +done
2) 被动语态中的谓语动词一定要是及物动词
因为被动句中的主语是动作的承受者,某些短语动词如look after, think of, take care of, work out, laugh at等,也可用于被动语态。
The children were taken good care of by her.
【注意】
短语动词中的介词或副词变成被动语态时不可遗漏。
3) 主动语态变为被动语态要加“to”的情况
若宾语补足语是不带to 的不定式,变为被动语态时,该不定式前要加“to”。此类动词为感官动词,如:feel, hear, help, listen to, look at, make, observe, see, notice, watch等。例如:
The teacher made me go out of the classroom.
I was made to go out of the classroom (by the teacher).
4) 主动形式表示被动意义
1)如wash, clean, cut, read, wear, draw, write, sell等动词虽然用做主动形式却表示被动的意义。例如:
The pen writes smoothly.
2)感官动词如feel,look,smell,taste,sound等直接跟形容词作表语。
The food tastes good.
非谓语动词(只简要介绍初中部分内容,在高中阶段非谓语动词是重要语法项目,同学们要努力掌握)
对非谓语动词的考点是:感官动词后不定式作宾语补足语和动词ing形式作宾
语补足语的用法;一些特殊动词的动词不定式作宾语补足语时不带to,但变为
被动语态时就要带to;有些动词既可接不定式也可接动词ing形式作宾语,但
表达的意思不同。这些都是历年中考的重点。
(1)非谓语动词的形式
非谓语动词指的是在句中起名词,形容词或副词作用的动词形式,而不是作谓
语的动词形式。动词的非谓语形式分为动名词,分词,动词不定式。
(2)不定式作宾语补足语
Father will not allow us to play on the street.
(3)不定式作目的状语
He ran so fast as to catch the first bus.
(4)用不定式和分词作补足语都可以的动词
这样的动词有感官动词如:see, hear, look, notice, observe, feel等,使
役动词如:have, make, leave, keep, get等。接不定式表示动作的完整性,
真实性;+doing 表示动作的连续性,进行性。
I saw him work in the garden yesterday.
昨天我看见他在花园里干活了。(强调“我看见了”这个事实)
I saw him working in the garden yesterday.(强调“我见他正干活”这个
动作)
昨天我见他正在花园里干活。
(5)用不带to不定式的情况
使役动词如: let, have, make等和感官动词如: see, watch, hear, listen to, smell, feel, find 等后作宾补,省略to。在被动语态中则to不能省掉。(6)接动名词与不定式意义不同
1) stop to do 停止,中断做某事后去做另一件事。
stop doing 停止做某事。
2) forget to do 忘记要去做某事。 (未做)
forget doing 忘记做过某事。 (已做)
3) remember to do 记得去做某事。 (未做)
remember doing 记得做过某事。 (已做)
4) try to do 努力,企图做某事。
try doing 试验,试着做某事。
5) go on to do 做了一件事后,接着做另一件事。
go on doing 继续做原来做的事。
6) mean to do 打算、想
mean doing 意味着
4. 容易混淆的常用动词的辨析
(1) say, speak, talk, tell的用法。
1) say表示讲话,作为及物动词使用,后跟宾语或宾语从句。
He said he would go there.
It's time to leave. We have to say goodbye to you.
2)speak表示“讲话”,一般作为不及物动词使用,而有时作为及物动词后面跟上各种语言作为宾语。
Do you speak English?
May I speak to Mr Pope, please?
3) talk表示“谈话”,是不及物动词,与to , about, with等连用,才可宾语。What are you talking about?
Mr Jackson is talking with my father in the office now.
4) tell 表示“告诉,讲述”是及物动词,可以带双宾语或复合宾语。
She told us an interesting story yesterday.
My teacher told me that we would have an English exam the next month.
(2) look, see, watch和watch的用法。
1) look强调“看”这个动作,是不及物动词,常与at连用,然后接宾语。Look! The girl is swimming in the lake.
Look at the picture carefully. Can you find something unusual?
2) see 指“看见”某物,强调的是结果。
They can't see the words on the blackboard.
Does Lily often go to see a film on Sunday?
3) watch 指的是“观看”,“注视”之意。
The twins are watching TV now.
He will go to watch a volleyball match.
4) read指“看书”、“看报”、“阅读”之意。
Don't read in the sun.
I like to read newspapers when I am free.
(3) borrow, lend和keep的区别。
1) borrow意思为“借入”,常常与from连用,是非延续性动词,表示瞬间即能完成的动作。
Meimei borrowed a book from the library just now.
May I borrow your dictionary?
2) lend 是“借出”之意,常常与to连用,同borrow一样,是非延续性动词,只表示瞬间即能完成的动作。
Uncle Wany has lent his car to Mr Li.
Could you lend us your radio, please?
3) keep是“保存”的意思,动作可以延续。
How long can the recorder be kept?
The farmer kept the pat for two weeks.
(4) bring, take, carry 和get的用法。
1) bring意思为“拿来”、“带来”。指将某物或某人从别处“带来”。
Bring me the book, please.
May I bring Jim to see you next Saturday?
2) take意思是“拿走”,“带走”,把某物或某人从这里“带来”或“拿到”某处之意。
It looks like rain. Take a raincoat with you.
Mother took the little girl to the next room.
3) carry 是“带着、搬运、携带”的意思,指随身携带,有背着、扛着、抱着、提着的含义,不表明来去的方向。
Do you always carry a handbag?
The box is heavy. Can you carry it?
4) get是去某处将某物拿回来。
Please go to my office to get some chalk.
There is no water in the bottle. Why not get some?
(5) wear, put on和dress的区别
1) wear是“穿着”“戴着”的意思,可以用于穿衣服、穿鞋、戴帽子、戴手套、佩戴首饰等,强调“穿着”的状态。
Tom always wears black shoes.
He wears a raincoat even when it is fine.
She doesn't like to wear a red flowers in her hair.
2) put on是“穿上”“戴上”的意思,可以用于穿衣服、穿鞋、戴帽等。着重于穿戴的动作。
It's cold. You'd better put on your coat.
He put on his hat and went out of the room.
3) dress可以作及物动词和不及物动词,有“穿着”“打扮”的意思。作“穿着”解时,只用于穿衣服,不用于穿鞋、戴帽、戴手套。作为及物动词用时,它的宾语是人,不是衣服。dress sb. (给某人穿衣服),而wear作“穿着”用时,也是及物动词,但它的宾语是物,不是人,即wear sth.(穿着衣物)。
She always dresses well.
Get up and dress quickly.
Mary is dressing her child.
(6) take, spend 和use的用法。
1) take指做某事用多少时间,句型是:It takes/took/ will take + sb. +some time + to do sth.
It took me three days to finish the work.
It will take you a while week to travel thought the forest.
It takes only one hour to fly to Shanghai.
2) spend指某人在某事(物)上花费时间或钱。句型是:
Someone spends + money/time + on something(in) doing sth.
She spent more than 500 yuan on that coat.
He didn't spend much time on his lessons.
He spent much time (in) correcting students' exercises.
Mother spent her evenings (in) washing clothes.
3) use表示使用工具、手段等。
Do you know how to use the computer?
Shall we use your car?
(7)reach, get 和arrive的区别。
1) reach是及物动词,后面要直接跟表示地点的名词作宾语。
After the train had left, they reached the station
We reached the top of the mountain at last.
2) get是不及动词,常与to连用,再接名词,后面接表示地点的副词时,不用
to,get to常用于口语中。
When the students got to the cinema, the film had begun.
My sister was cooking when mother got home.
3) arrive是不及物动词,表示到达一个小地方时,用arrive at, 到达一个大地方时用arrive in。
The soldiers arrived at a small village
The foreigners will arrive in Shanghai tomorrow.
【演练】
1. Listen! Some of the girls ________ about Harry Potter. Let’s join them.
A. are talking
B. talk
C. will talk
D. talked
2. Our teacher, Miss Chen, ________English on the radio the day before yesterday.
A. teaches
B. taught
C. will teach
D. had taught
3. I don’t think I _________ you in that dress before.
A. have seen
B. was seeing
C. saw
D. see
4. Susan’s parents have bought a large house with a swimming pool. It _______ be very expensive.
A. must
B. can
C. mustn’t
D. can’t
5. Coffee is ready. How nice it ________ ! Would you like some?
A. looks
B. smells
C. sounds
D. feels
6. “ Mr. Zhu, you’d better _______ too much meat. You are already over weight,” said the doctor.
A. not to eat
B. to eat
C. not eat
D. eat
7. “Don’t always make Michael ________ this or that. He is already a big boy, dear,” Mr. Bush said to his wife.
A. do
B. to do
C. does
D. did
8. Sorry, I can’t hear you clearly. Will you please ________ your E-mail address? I’ll write it down.
A. review
B. recite
C. report
D. repeat
9. Don’t ________your coat, Tom! It’s easy to catch cold in spring.
A. take away
B. take off
C. take down
D. take out
10. You _______ go and ask Meimei. She _______ know the answer.
A. must; can
B. must; may
C. need; can
D. can; may
11. I’m sorry you’ve missed the t rain. It ________ 10 minutes ago.
A. left
B. has left
C. had left
D. has been left
12. I bought a new dictionary and it ________ me 30 yuan.
A. paid
B. spent
C. took
D. cost
13. ---Mum, may I go out and play basketball?
---_______ you _______ your homework yet?
A. Do; finish
B. Are; finishing
C. Did; finishing
D. Have; finished
14. I have to go now. Please remember to ________ the lights when you leave.
A. turn off
B. turn down
C. turn up
D. turn on
15. A talk on Chinese history ________ in the school next week.
A. be given
B. has been given
C. will be given
D. will give
16. Look! How heavy the rain is! You’d better ________.
A. don’t go now
B. stay here when it stops
C. not leave until it stops
D. not to leave at once
17. You may go fishing if your work ________.
A. is done
B. will be done
C. has done
D. have done
18. Cotton _______ nice and soft.
A. is felt
B. is feeling
C. feel
D. feels
19. ---Who cleaned the blackboard yesterday, Dick?
---John _________.
A. cleaned
B. does
C. did
D. is
20. ---Linda had nothing for breakfast this morning, _______?
---No. She got up too late.
A. had she
B. hadn’t she
C. did she
D. didn’t she
【练习答案】
1.A
2.B
3.A
4.A
5.B
6.C
7.A
8.D
9.B 10.D 11.A 12.D 13.D 14.A 15.C 16.C 17.A 18.D 19.C 20.C
1. Please do me a favor — ______ my friend Mr. Smith to Youth Theater at 7:30 tonight. A. to invite B. inviting C. invite D. invited 2. —I called you last night,but nobody answered. —Oh,I usually________ off my cell phone by 8:00 pm. A. switched B. have switched C. switch D. had switched 3. I _________ping-pong quite well, but I haven’t had time to play since the new year. A. will play B. have played C. played D. play 4. The house belongs to my aunt but she D. doesn’t live 5. The father as well as his three children skating on the frozen river every Sunday A. is going B. go C. goes D. are going 6. Months ago we sailed ten thousand miles across this open sea, which _____ the Pacific, and we met no storms. A. was called B. is called C. had been called D. has been called 7. In many parts of the world, tea ________ milk mild and sugar. A. is serving B. is served C. serves D. served 8 The fact that so many people still smoke in public places ___ that we may need a nationwide campaign to raise awareness of the risks of smoking. A. suggest B. suggests C. suggested D. suggesting 9. Around two o’clock every night, Sue will start talking in her dream. It somewhat ______ us. A. bothers B. had bothered C. would bother D. bothered 10. The palace caught fire three times in the last century, and little of the original building _______now. A. remains B. is remained C. is remaining D. has been remained 11. Look at the pride on Tom’s face. He_______ to have been praised by the manager just now. A. seemed B. seems C. had seemed D. is seeming 12. In the spoken English of some areas in the US, the "r" sounds at the end of the words . A. are dropped B. Drop C. are being dropped D. have dropped 13. —Do you have any problems if you —Well, A. offer C. are offered D. will be offered 14. The wet weather will continue tomorrow,when a cold front A. is expected C. expects D. will be expected 15. —How long do you want me to heat the oil? —Heat it till it ________ to smoke. A. would begin B. begins C. will begin D. began 16. The number of deaths from heart disease will be reduced greatly if people ___to eat more fruit and vegetables. A. persuade B. will persuade C. be persuaded D. are persuaded 17. — When will you come to see me, Dad? — I will go to see you when you the training course. A. will have finished B. will finish C. are finishing D. finish 18. Come and see me whenever _______. A. you are convenient B. you will be convenient C. it is convenient to you D. it will be convenient
高中英语教案时态总结 一、时态的内涵 Tense翻译为时态,包含时间+状态两个方面。 时间的划分:过去,现在,将来 状态的划分:一般,进行,完成 状态——实意动词: 四种形式例:go, went, gone, going 四种形式各有分工一般:go, went 进行:going 完成:gone 例: 一般 I go to school every day. I went to school yesterday. 进行 we are learning English. I was learning English when you called me yesterday. 完成 We have had breakfast. I had had breakfast by 8 this morning. 时间——助动词 那接下来又有新的问题了。比如说,现在分词,它只有一种形式,如going ,或者learning, 那我们时间又不一样,有过去进行的,现在进行的,比如刚才的两个例句,we are learning English, 我们用的是are. I was learning English yesterday when you called me. 用的是was. 所以我们发现,learning是没有变化的,但前面这个are, was是变化的。它们的变化就把这个时间讲清楚了。而它呢,位于learning实意动词之前的这个,叫助动词。也就是说,be,是个助动词。如果我问be是什么词很多同学肯定会说be是系动词,其实be又是助动词,又是系动词,这里的be就是助动词。大家该如何理解呢,看这里,一个实意动词,只能把状态讲清楚,但因为一个状态里面,有不同的时间,比如进行,有过去进行,现在进行,和将来进行,而实意动词本身不能把这个时间讲清楚,于是就借助于,求助于,助动词来帮忙,
高中英语语法(时态和语态) 一.动词的时态 时态是谓语动词所表示的动作或情况发生时间的各种形式。英语动词有16种时态,但是常见的只有九种:一般现在时、一般过去时、一般将来时、现在进行时、过去进行时、现在完成时、过去完成时、过去将来时、现在完成进行时。 (一)一般现在时(do / does) 1.具体用法 1) 表示经常性或习惯性动作 We always care for each other and help each other. 我们总是互相关心互相帮助。 He goes to school every day. 2)表示现在的特征或状态 He is very happy. Do you sing? ----A little. 3)表示普遍真理 Light travels faster than sound. 光速比声速快。 Actions speak louder than words. 行动胜过言语。 * 常与一般现在时态连用的词或短语主要有:often, usually, sometimes, every day, every morning/afternoon, on Sundays/weekends等等。 I often go to the cinema on Sundays. 我经常星期天去看电影。 He goes to work early every day. 他每天上班很早。 (二)一般过去时( did ) (1)表示过去某一特定时间所发生的、可完成的动作或状态,常与表示确切过去时间的词、短语或从句连用。例如: We went to the pictures last night and saw a very interesting film. (2)表示过去习惯性动作。例如: He always went to class last. I used to do my homework in the library. (三)一般将来时( will / shall do) 1)表示将来打算进行或期待发生的动作或状态。例如: I shall graduate next year. 2)一般将来时有时可以表示一种倾向或习惯性动作。如 Crops will die without water. You won’t succeed with out their support. 3) 几种替代形式: *be going to +v在口语中广泛使用,表示准备做或将发生的事情。例如: I'm going to buy a house when we've saved enough money. *be to +v表示计划安排要做的事,具有"必要"的强制性意义。例如: I am to play tennis this afternoon. *be about to +v表示即将发生的事情。例如: He was about to start. *be due to +v表示预先确定了的事,必定发生的事。例如: The train is due to depart in ten minutes. 5)少数动词如:begin, come, leave, go, arrive, start, stop, return, open, close等的一般现在时可用来表示将来的动作。(多用来表示按计划事先安排好即将发生的动作,句中通常还有一个表示将来的时间状语)。例如: The meeting begins at seven.
2010高考二轮复习英语学案 专题六动词时态和语态 【典例精析】1.(2008全国I卷,27)—Have you known Dr. Jackson for a long time? —Yes, since she ______ the Chinese Society. A. has joined B. joins C. had joined D. joined 【解析】D句意:—你认识Dr. Jackson好久时间了吗? —是的,自从她加入汉语协会我就认识她。Since 自从......以来,引导时间状语从句,强调过去认识时的时间,第一句话所用的现在完成时是判断该句子时态的重要依据。 2.(2008辽宁卷,23)We first met on a train in 2000. We both felt immediately that we ______ each other for years. A. knew B. have known C. have known D. know 【解析】C句意:在2000年我们第一次在火车上相遇。我俩同时立刻赶到彼此认识多年了。根据题干第二句可知主句为过去时,而that 引导的宾语从句的谓语动词又发生在主句动词之前,即为过去的过去,故用过去完成时来表示。 3.(2008天津卷,14)He _____ football regularly for many years when he was young. A. was playing B. played C. has played D. had played 【解析】D句意:他年轻的时候踢了多年的足球。句中的when he was young是表示过去的时间状语。题干中没有强调在过去的某个时间段正在发生某事,故排除A项;句中也没有信息词强调对现在造成的影响或与现在的联系,故排除C项;句中也没有以过去的某个时间点或动作点作为参照,故排除D项。 4.(09北京)27. The way the guests ___ in the hotel influenced their evaluation of the service. A. treated B. were treated C. would treat D. would be treated 【解析】B考查时态和语态的用法。The guests 与treat之间是被动的关系,并且动作已经发生,所以用一般过去时的被动形式。 5.(09天津)2. My parents _____ in Hong Kong. They were born there and have never lived anywhere else. A. live B. lived C. were living D. will live 【解析】A考查时态。后句意思“他们出生在香港,从来没有去过别的地方”,由此可知前句“一直在香港住”,时态用一般现在时,说明事实,故选A。 6.(09福建)6 -Why does the Lake smell terrible? -Because large quantities of water . A. have polluted B. is being polluted C. has been polluted D. have been polluted 【解析】D考查动词时态,语态和主谓语一致。根据前一分句可知所填动词表示过去发生的动作对现在产生的影响,时态用现在完成时,动词与主语是被动关系,用被动语态。主语是large quantities of water,其中心词是quantities,是复数,谓语动词用复数,选D。
高三英语语法教案:时态和语态 分类说明 高考中对动词的时态和语态的命题不可少,每年都有两、三分。然而,命题一般都是以基础知识为主,把时态与语境结合起来,在复习动词时态和语态时,应特别注意下面一些问题:1.动词的八种基本时态的形式和意义:一般现在时;一般过去时;一般将来时;现任进行时;过去进行时;现在完成时;过去完成时;现在完成进行时。并且,由此扩充了解将来完成时;将来进行时,将来完成进行时;过去将来完成时等。 2.掌握各种时态的时间状语要求,特别是上下文中所暗含的时间。 3.注意并掌握句子中时态一致性的要求,如:宾语从句中的时态要求:主句若为过去时,从句必须用相应的过去时,但当从句表示客观真理时,又可只用一般现在时;时间、条件状语中的时态要求:当主句为将来时时,从句片j一般现在时;虚拟语气中的时态要求:(见虚拟语气)。 4,掌握各种时态及含情态动词中的被动语态的形式和应用。 (1)分清动词的词性,熟悉并掌握常见的不及物动词happen,take place,occur,exist等,它们不能用被动语态; (2)分清主语与谓语之间的关系; (3)变被动语态的动词一般为及物动词,但有些不及物动词与介词所形成的短语动词也可有被动形式,此时,变被动语态后介词不能丢; (4)熟悉并掌握主动形式表被动意义的情况,如: A.及物动词read,write,sell,wash等,用作不及物动词,如:. The pen _________well. A.writes B.wrote C.is written D.has written B.做定语不定式的逻辑主语是句子的主语或宾语时。如: I have much work ________. A.to do B.to be done C.to be doing D.to have done 但当不定的式的逻辑主语不是句子的主语或宾语时,则须用被动语态.如: Do you have any work ________now? I’m free. A.to do B.to be done C.to be doing D.to have done C.形容词hard,difficult,interesting,exciting,surprising等后的不定式作语及worth后面的doing。 回放真题 真题1(2004甘肃、青海卷29) --Thank goodness,you’re here! What _________you?
高中英语时态语态讲解 1、一般现在时主要用来表示人、事物的现在状况和特点;表示经常或习惯性的动作;表示客观规律和永恒真理;按照计划安排好了将要发生的动作(一般指时 刻表)等 He usually goes to w ork at 7 o’clock every morning. The train to Shanghai leaves at 7am. 考点一:表示永恒的真理,即使出现在过去的语境中,仍用一般现在时。如:I learned that the earth goes around the sun when I was in primary school. 考点二:在时间、方式、让步和条件状语从句中,代替一般将来时;常用的引导词有:时间:when, until, after, before, as soon as, once, the moment/the minute, the day; 条件:if, unless, provided. If he accepts the job, he will get more money soon. 只要他努力工作,我不介意他什么时候做完试验。 2、现在进行时 表说话时或目前一段时间内正在进行的活动;或表感情色彩,加强语气。与频率副词,如always,constantly,continually,again等连用表示说话人的某种感情色彩(赞叹、厌烦、埋怨等)。 We are having English class. The house is being built these days. The little boy is always making trouble. 考点一:在时间状语或条件状语从句中表示将来正在进行的动作。Look out when you are crossing the street. Don't wake him up if he is still sleeping at 7 tomorrow morning. 考点二:表示在最近按计划或安排要进行的动作(这时多有表示将来的时间状语)。 Marry is leaving on Friday. 3、现在完成时 (1)非延续动作:动作发生在过去,对现在有影响。(2)延续性动作:动作和状态的持续。现在完成时有一些标志性的时间状语: 考点一:for + 时间段;since + 时间点 They have lived in Beijing for five years. They have lived in Beijing since 1995. 考点二:常见的不确定的时间状语:lately; recently, just, already, yet, up to now; till now; so far, these days, Has it stopped raining yet ? 考点三:在表示“最近几世纪/ 年/ 月以来……”时间状语中,谓语动词用现在完成时。 in the past;over the past; during the last等 考点四:表示“第几次做某事,”或在“It is the best (worst, most interesting ) +名词+that” 后面,主句是一般现在时态时,从句用现在完成时。 This is my first time that I have visited China. This is the most interesting film I have ever seen. 4.一般过去时 表在过去某个特定时间发生且完成的动作,或过去习惯性动作,不强调对现在的影响,只说明过去。常跟明确的过去时间连用, 注意: 考点一:used to + do,表示过去经常但现在已不再维持的习惯动作。 be/become/get used to + doing,表示习惯于 He used to smoke a lot. He has got used to getting up early. 考点二:在时间和条件状语从句中,代替过去将来时。 He promised to buy me a computer if he got a raise 5. 过去进行时
动词时态语态及动词辨析练习100题 1. Once environmental damage ___, it will take many years for the system to recover. A has done B is to do C does D is done 2 --- When are you leaving? ---- My plane ___ at 10:45. A takes off B took off C is about to take off D will take off 3 I didn't like Aunt Lucy, who ___ without warning and bringing us presents. A always turned up B has always turned up C had always turned up D was always turning up 4 --- ____ my English book? I want to look up a word in it. ---- Yes, I ___ it lying on your desk a few minutes ago. A Had you seen, saw B Did you see , have seen C Have you seen,saw D Do you see, saw 5 He will phone ___ he ___ his work. A for the moment ,sets about B the moment,sets about C the moment, will set about D for the moment, will set about 6 That tree looked as if it ___ for a long time. A hasn't watered B didn't water C hadn't been watered D wasn't watered 7 --- Was Tom there when you arrived? --- Yes, but he ___ home soon afterwards. A had gone B has gone C is going D went 8 ---Would you mind if I __ here? --- Certainly not. Please go ahead. A will smoke B did smoke C smoked D am smoking 9 I should have written to you earlier, but ___ rather busy recently. A I've been B I'd been C I'm being D I were 10 --- Why weren't you at the meeting yesterday/ ---- I __ for a long-distance call from my aunt in America then. A waited B was waiting C had been waiting D had waited 11 Before the first non-stop flight made in 1949, it ___ necessary for all planes to land for refueling. A would be B has been C had been D would have been 12 ---Was that the first time ___ you ___ England's coast? --- Yes, it was. A /, left B when, have left C when, had left D /, had left 13 The car ran down the hill,and the driver ___ , according to the newspaper,to have been killed. A said B was saying C was said D had been said 14 --- He promised to come on time. --- What do you imagine ___ to him then? A has happpened B was happening C happening D was happened 15 --- Kate returned home yesterday. ---Really? Where ___ ? A has she been B had she gone C has she gone D had she been 16 ---Let's hurry.The President is coming. --- Oh, really? I ___ afraid that we ___ him. A was , had already missed B am, have already missed C am, will miss D was, was missing 17 --- Are you a visitor here? ---That's right..I ___ round the world and now my dream of coming to China ___ true. A am travelling,has come B was travelling,had come C have travelled, has come D had travelled, is coming
动词的时态和语态 时态 一般现在时 (1)可表示客观真理、科学事实。 The sun rises in the east and sets in the west. 太阳从东方升起,从西方落下。 (2)可用在由if,unless引导的条件状语从句,由even/if/though引导的让步状语从句,由when,before,until/till,as soon as,the moment引导的时间状语从句,由no matter what/who/when/where/how或whatever,whoever等引导的让步状语从句中,这时主句往往表将来或主句是祈使句。 I’ll go with you as soon as I finish it. 我一做完,就与你一同去。 Whatever you say,I will not change my mind. 无论你说什么,我都不会改变主意。 一般过去时 表示“刚才,在过去”之意,暗示现在已“不再这样”。 —Your phone number again?I didn’t quite catch it. ——再重述一下你的电话码好吗?我没记下来。 —It’s 9568686. ——是9568686。 一般将来时 (1)“will+动词原形”表示事物的固有属性与必然趋势。 Fish will die without water.离开水,鱼就会死。 (2)“be going to+动词原形”可表示根据迹象对未来进行推断。 Look at the dark clouds.It is going to rain. 看那乌云,要下雨了。 (3)“be about to+动词原形”表示立即的将来,很少与时间状语连用。 The train is about to start.火车就要开了。 (4)位移动词如e,go,arrive等,其一般现在时表按时间表将要发生的事,现在进行时可表计划、安排要做的事。
英语中的动词有时态(Tense)要求。所谓“时”,即动作发生的时间;“态”, 即动作的方式状态。“时”有四种:现在时,过去时,将来时,过去将来时; “态”也有四种:一般式,进行式,完成式,完成进行式。因此,英语中一共有 二.新课讲解 1.一般过去时(the Past Simple) (1)用法(uses) 表示过去某时发生的动作或存在的情况。如: He worked in a bank all his life. He discovered a desert island in the Pcific. The safari was exciting but dangerous. I knew what he meant. They always interviewed new employees on Fridays. (2)形式(form) 即动词的过去式,分两种情况,一种是在动词结尾加ed或ied,这种动词 称为规则动词,另一种不能加,形式多样,称为不规则动词。 规则动词: a.一般情况下,动词词尾加 -ed ,如: work-worked play-played want-wanted act-acted b.以不发音的 -e 结尾动词,动词词尾加 -d,如: live-lived move-moved decide-decided decline-declined hope-hoped judge-judged raise-raised wipe-wiped c.以辅音字母 + y结尾的动词,把-y变为-i 再加-ed,如: study-studied try-tried copy-copied justify-justified cry-cried carry-carried embody-embodied empty-emptied d.以一个辅音字母结尾的重读闭音节动词,双写词尾辅音字母,再加 -ed,如: stop-stopped beg-begged drag-dragged drop-dropped plan-planned drip-dripped
动词的时态和语态用法详解 在英语中,不同时间里发生的动作或存在的状态需要用动词的不同形式表示出来,动词的这种不同 形式就构成了动词的时态。 英语中的时态按动作发生时间分为现在时态、过去时态、将来时态 二、常见时态的基本用法 1. 一般现在时:一般现在时是描述现在或经常性的动作性质或状态的时态。常和表示频率、时间的副词 (短语) always, every time, now and the n, occasi on ally, often, seldom, sometimes, usually 连用。 1) 表示经常性或习惯性的动作。 We have three meals a day. 2) 表示客观事实、真理和自然现象。 Kno wledge is power. 3)表示现在的情况或状态。 I live in Beiji ng. 4)表示已经“列入日程”的将来的事件,尤其指计划中的和安排好的将来的动作,这些动词往往表示“出 发,到达”等含义 的词, 女口, arrive, begin, go, leave, start, stay 等。 The train arrives at 10:30. There's ple nty of time. 。 考点一:表示永恒的真理,即使出现在过去的语境中,仍用一般现在时。 如: I learned that the earth goes around the sun when I was in primary school. 考点二:在时间和条件状语从句中,代替一般将来时;常用的引导词有:时间:when, until, after, before, as soon as, on ce, the mome nt/the minu te, the day; 条件:if, uni ess, provided. If he accepts the job, he will get more money soon. 考点三:在 make sure (certain), see to it, mind, care, matter 替一般将来时。 So long as he works hard, I don ' t mind when he finish 考点四:在 the more …the more …(越 ..................... 越 ... )句型中 在时。 The harder you study, the better results you will get. 2. 一般过去时:一般过去时表示过去发生的动作、存在的状态,或反复发生的动作,句中一般都有表示 过去具体时间的时间 状语。 1)在确定的过去时间里所发生的动作或状态。 此时与表示过去的时间状语连用, 如yesterday, last week, an hour ago, the other day, in 1998 等。 +宾语从句,从句用一般现在时代 es the experime nt. ,若主句是一般将来时,从句通常用一般现
英语动词时态语态 1. --- Oh, dear. I forgot the air tickets. --- You ______ something. A. have left B. are always leaving C. are leaving D. always left 2. --- I ______ so busily recently that I ______ no time to help you with your math. --- That’s O K. I can manage it by myself. A. have been working; have B. have worked; had C. am working; will have D. had been working; had had 3. Remember to send me a photo of us next time you ______ to me. A. are writing B. will write
C. has written D. write 4. He ______ at the meeting, but his heart attack prevented him. A. will speak B. is going to speak C. had to speak D. was going to speak 5. --- I beg your pardon, but I didn’t quite catch you. --- Oh, I ______ myself. A. am talking to B. talked about C. have talked to D. was talking to 6. I ______ ping-pong quite well, but I haven’t had time to play since the New Year. A. will play B. have played
高中英语动词时态 时态是英语谓语动词的一种形式,表示动作发生的时间和所处的状态.英语中的时态是通过动词形式本身的变化来实现的.英语有16种时态,但中学阶段较常用的有十种:一般现在时,一般过去时,一般将来时,过去将来时,现在进行时,过去进行时,将来进行时,过去完成时, 现在完成时和现在完成进行时. 1.一般现在时 1) 经常性或习惯性的动作,常与表示频腮度的时间状语连用。时间状语:every..., sometimes,at..., on Sunday。 I leave home for school at 7 every morning. 每天早上我七点离开家。 2) 客观真理,客观存在,科学事实。 The earth moves around the sun. 地球绕太阳转动。 Shanghai lies in the east of China. 上海位于中国东部。 注意:此用法如果出现在宾语从句中,即使主句是过去时,从句谓语也要用一般现在时。 例:Columbus proved that the earth is round. 哥伦布证实了地球是圆的。 3) 表示格言或警句。 Pride goes before a fall.骄者必败。 4) 现在时刻的状态、能力、性格、个性。 I don't want so much. 我不要那么多。 Ann writes good English but does not speak well. 安英语写得不错,讲的可不行。 5) 下列动词come, go, arrive, leave, start, begin, return的一般现在时可以表示将来,主要用来表示在时间上已确定或安排好的事情。 The train leaves at six tomorrow morning. 火车明天上午六点开。 When does the bus star? It stars in ten minutes. 汽车什么时候开?十分钟后。 6) 在时间,条件,让步从句中用一般现在时表将来。 When Bill comes (不是will come), ask him to wait for me. 比尔来后,让他等我。 I'll write to you as soon as I arrive there. 我到了那里,就写信给你。 7) 以here, there等开始的倒装句,表示动作正在进行。 Here comes the bus. = The bus is coming. 车来了。 There goes the bell. = The bell is ringing. 铃响了。 2. 现在进行时 1)现在进行时表示现在(此刻)正在进行的动作和表示现阶段(此段)正在发生的动作(但说话者不一定正在进行)(即此刻,此段正发生)。 Someone is knocking at the door. Can you answer it? Maria is Britain at the moment. She’s learning English. 2)用现在进行时表示将来 a. 下列动词come, go, arrive, leave, start, begin, return等现在进行时可以表示将来。 I'm leaving tomorrow. 明天我要走了。 Are you staying here till next week? 你会在这儿呆到下周吗? b. 渐变动词,如get, run, grow, become, begin以及瞬间动词die等。 He is dying. 他要死了。 3)现在进行时常与always, constantly, continually, forever, all the time等连用表示说话人的感情色彩(厌恶,不满,赞许等)。
1、一般现在时主要用来表示人、事物的现在状况和特点;表示经常或习惯性的动作,句子中常有often, always, from time to time 等时间状语;表示客观规律和永恒真理等。He usually goes to w ork at 7 o’clock every morning. The earth goes around the sun. Guangzhou is situated in the south of China. 考点一:表示永恒的真理,即使出现在过去的语境中,仍用一般现在时。如:I learned that the earth goes around the sun when I was in primary school. 考点二:在时间和条件状语从句中,代替一般将来时;常用的引导词有:时间:when, until, after, before, as soon as, once, the moment/the minute, the day; 条件:if, unless, provided. If he accepts the job, he will get more money soon. 考点三:在make sure (certain), see to it, mind, care, matter +宾语从句,从句用一般现在时代替一般将来时。 So long as he works hard, I don’t mind when he finishes the experiment. 只要他努力工作,我不介意他什么时候做完试验。 考点四:在the more… the more … (越……越……) 句型中, 若主句是一般将来时, 从句通常用一般现在时。 The harder you study, the better results you will get. 2、现在进行时 表说话时或目前一段时间内正在进行的活动:或表感情色彩,加强语气。与频率副词,如always,constantly,continually,again等连用表示说话人的某种感情色彩(赞叹、厌烦、埋怨等)。