
Study on an Evaluating Model of Forestry Carbon Sequestration Capacity by Using GIS
Quan Li Xu,Kun Yang*,Shuang Yun Peng,Jia Sheng
Wang,Jian Hong Xiong
Faculty of Tourism and Geographic Science Yunnan Normal University, No.298, Dec.1st Street,650091
Kunming, P.R.China
Go2happiness@https://www.doczj.com/doc/b417650579.html,
*Corresponding author: Kmdcynu@https://www.doczj.com/doc/b417650579.html,
Jun Hua Yi
The Institute of Potogrammetry and Remote Sense of
Yunnan Province
Kunming, P.R.China
Yjh2ok@https://www.doczj.com/doc/b417650579.html,
Abstract—At the age of post-Kyoto Protocol, international forestry carbon sequestration project not only has strongly achieved the form of harmoniously developing between economy and environment conservancy in developing countries, but also is promoting the relative research on theory and technology in Forestry Carbon Sequestration. And this paper has discussed that how to establish the Geo-Spatial Model of Evaluating for Forestry Carbon Sequestration Capacity, as well as the principle, method and the result of it’s integrating with GIS. In any case, this study mainly concentrates on how to find the optimistic trees and land blocks for forestation, and estimating the economic benefit and the invested risk of planting in the selected land block with the selected tree, so that the GIS software based on this model could offer some reasonable and scientific evidences for decision-making supporting in forestation, furthermore, in forestry carbon trade. An experiment with ArcObjects for the models has been given in the end. And as a result, we also analyses the result, as well as make a research conclusion.
Keywords- Forest Carbon Sequestration, Geo-spatial Model, Modeling, ArcGIS, ArcObjects, ArcSDE
I.I NTRODUCTION
The pollution which is leading a warmer weather in climate on the earth due to letting Greenhouse atmosphere (such as CO2) has been a common and international challenge to whole the human. United Nations Framework Convention on Climate Change(UNFCCC) has been in effect since March 1994,and it is the first convention that whole controls the emission of greenhouse atmosphere like CO2 against changing warmer of climate in globe, as well as a basic framework for cooperating in facing the common problem of climate changing. It is only a standard, however, the convention has no any sanction in law for all the world. Therefore, the third conference COP3 taking in Kyoto come into being Kyoto Protocol, which main aim is to give a concrete limitation with the law on emission of CO2 for developed industry countries. In order to help those countries to complete their mission, there are three implement mechanisms in this protocol, which are JI, EI and CDM. And the forest carbon sequestration project under CDM is the only tight collaboration between developed county and developing country to confront with the change of climate globally.
At the same time, the relative technologies and theories on forest carbon sequestration are increasing rapidly, which include geo-spatial modeling of evaluation for forest carbon sequestration Capacity. And this aim of modeling is to find what land is suitable for which trees each other ,and furthermore how to obtain a maximum carbon or economic benefit under the minimum cost. These models are much helpful in decision making for carbon trade.
II.T HE S UMMARIZATION ON G EO-SPATIAL M ODEL OF
E VALUATING FOR
F OREST C ARBON S EQUESTRATION
C APACITY
A.The Structure and Correlation of Models
The models discussed in this paper include three submodels, which are optimistic selecting between Trees and Land-Blocks, estimating of carbon sequestration, and economic calculating on carbon trade. And the first model is the most important and complex one in these submodels, which also has two parts that are tree-selecting model and land-blocks-selecting model. The second model and the third model will be implemented based on the first model. The correlation of those models is shown in Figure 1.
Figure 1. The general structure of whole model and the correlation of
submodels
B.The Parameters and Output for Models
The ensuring of parameters and output of those models is affected by many aspects, which include tree’s formula of growth, tree’s condition of growth and level of carbon trade in market, ect. Thereby, how to select those parameters and make an output for model’s result has no universal standard. At the much time, that is always distinguishing in the different carbon sequestration projects. According to the status of Yunnan
This work is supported by the National High Technology Research and Development Program of China (Grant No. 2007AA12Z231), the National Basic Research Program of China (Grant No. 2007AA12Z231) , the Yunnan Science Fund (Grant No.2009FXW001) and the Youth Fund of Kunming University of Technology and Science (Grant No. KKZ2200804031).
province, we define the basic parameters and output for above models, which is shown as follows.
?Trees-Blocks selecting Model
Function: find the suitable trees or land blocks in the given situation in order to obtain the maximum
carbon sequestration or lower cost
Parameter
Terrain: Aspect, Slope, Land-position, Altitude;
Climate: The average(Min and Max)rainfall in
month or year, the average(Min and
Max)temperature in month or year and those
difference in temperature or rainfall;
Soil: The type of soil ,the fertilizer in soil and
the deepness of soil;
Growth: The average growth ratio in month or
year
Carbon Capacity: The average carbon sequestration for single tree at it’s grown
period.
Output
Output the trees sorted by the suitable degree
for the given land block.
Output visually the land blocks sorted by the
suitable degree for the given tree.
?Estimating Model for carbon sequestration
Function: according the selecting block and tree, convert the growth Capacity to carbon sequestration
and estimate it.
Parameter
Land Block: Include the all parameters
described above
Time: the period of estimating
Output: The sum of carbon sequestration for every tree during the estimating period, and be sorted
ascending
?Model of evaluating for economic benefit
Function: Give a whole evaluation at the economic benefit of carbon sequestration with the selecting
block and tree.
Parameter
Price of carbon trade: according to the current
price in international market
cost: the cost of forestations
Output
The whole benefit: includes cost and profit
Risk: analysis in economy for investment in a
carbon sequestration project
C.Methodology of Modeling with Mathematics for Models
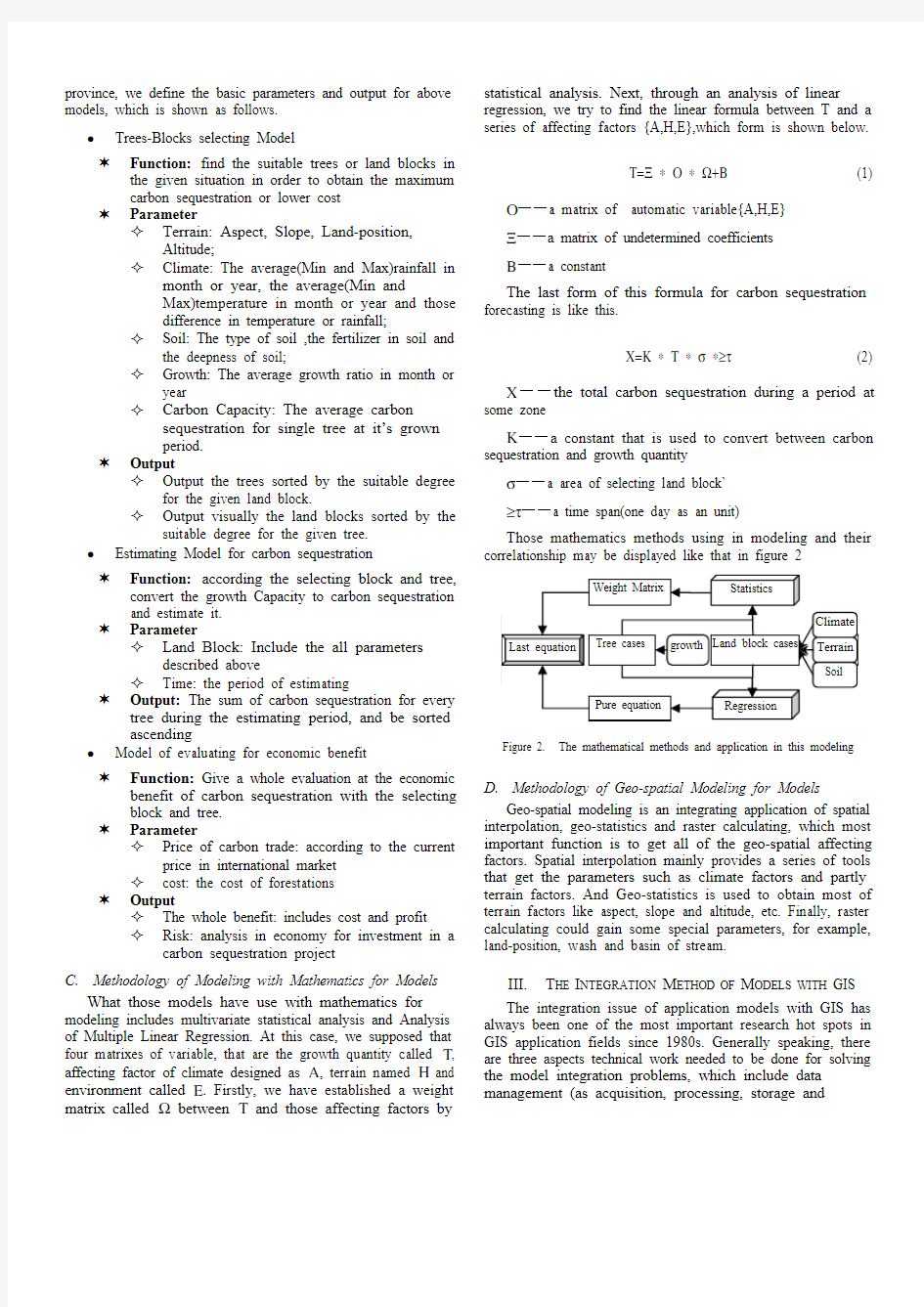
What those models have use with mathematics for modeling includes multivariate statistical analysis and Analysis of Multiple Linear Regression. At this case, we supposed that four matrixes of variable, that are the growth quantity called Τ, affecting factor of climate designed as Α, terrain named Η and environment called Ε. Firstly, we have established a weight matrix called Ω between Τ and those affecting factors by statistical analysis. Next, through an analysis of linear regression, we try to find the linear formula between T and a series of affecting factors {A,H,E},which form is shown below.
Τ=Ξ ? Ο ? Ω+Β (1) Ο——a matrix of automatic variable{A,H,E}
Ξ——a matrix of undetermined coefficients
Β——a constant
The last form of this formula for carbon sequestration forecasting is like this.
Χ=Κ ? Τ ? σ ?≥τ (2) Χ——the total carbon sequestration during a period at some zone
Κ——a constant that is used to convert between carbon sequestration and growth quantity
σ——a area of selecting land block`
≥τ——a time span(one day as an unit)
Those mathematics methods using in modeling and their correlationship may be displayed like that in figure 2
Figure 2. The mathematical methods and application in this modeling
D.Methodology of Geo-spatial Modeling for Models
Geo-spatial modeling is an integrating application of spatial interpolation, geo-statistics and raster calculating, which most important function is to get all of the geo-spatial affecting factors. Spatial interpolation mainly provides a series of tools that get the parameters such as climate factors and partly terrain factors. And Geo-statistics is used to obtain most of terrain factors like aspect, slope and altitude, etc. Finally, raster calculating could gain some special parameters, for example, land-position, wash and basin of stream.
III.T HE I NTEGRATION M ETHOD OF M ODELS WITH GIS
The integration issue of application models with GIS has always been one of the most important research hot spots in GIS application fields since 1980s. Generally speaking, there are three aspects technical work needed to be done for solving the model integration problems, which include data management (as acquisition, processing, storage and
organization) work, model computing (as application analysis) work, as well as model output (mainly focused on the simulated results display and express spatially and graphically) work. In the practices of application model integration with GIS, the method of integration is usually selected by specific application requirements due to different integration application environments. There is still not an unified way of integration in the practical spatial analysis tasks. Because of the flexibility of COM GIS technology, COM based integration method of GIS with carbon sequestration models has become the present popular and feasible way of model integration in spatial decision support system development although model base is the more idea scheme for model management and intelligent processing. Based on the analysis for the parameters of carbon sequestration model equations, It is easily to note that the parameters of these models are not directly related to the geographical locations, which has resulted in the problems for model integration with GIS. By using the COM Integration method of model with GIS, the model data management, model computing and modeling result output functions may be well integrated in a flexible software framework. In the model data management aspect, not only the high resolution remote sensing images and vector graphic data may be effectively stored uniformly, but also the model input parameters may also be stored in the spatial database in attribute data form, which can offer a better data interface for model computing by using the spatial data management technology of GIS. In model computing aspect, the mathematical model may be integrated into GIS platform by using COM technology from which the forest spatial information systems will be of decision support functions. The model computing resulting will then be stored into the same forest spatial database with graphic data and the modeling analysis results will be easily connected to geographical locations. Meanwhile, the modeling simulated results may also be spatially visualized in geographic distribution patterns. The system integration principles may be displayed as that in Figure 3.
Figure 3. The Integration Framework of COM GIS with Carbon
Sequestration Models
IV.D ESIGN AND E XPERIMENT
A.The General Structure of Systems
As what has been discussed in the context, there are many geo-spatial factors that will be used in modeling. Therefore, how to get those factors easily and efficiently is a big problem. We are very lucky ,whereas, that GIS software like ArcGIS is advantageous to carry out that work. ArcGIS is a powerful GIS software developed by ESRI, which functions include geo-spatial data management, map displaying and controlling, especially spatial analysis such as 3D Analysis, Georeference and raster calculating, ect. As a result, ArcGIS software have supported the functions of the confirming tool of models in this case. The structure of systems is shown as follows in figure 4.
Figure 4. The general structure of systems for model tool We can learn from the below graph that ArcSDE is responsible for the geo-spatial data management, which also could be accessed by ADO or ODBC. And furthermore, the client is developed with ArcObjects, which is a COM package of ArcGIS for second developing that has the same function as ArcGIS desktop. All the structure is popular and strong when using in this modeling. Figure 5 and Figure 6 are the capturing pictures of experiment for this case.
B.The Technology for Implement
TABLE I. T HE M AJOR T ECHNOLOGIES U SED TO I MPLEMENT
C ONFIRMING T OOL
Alias Technology Explanation Developing
Framework
C/S
General structure
for developing
Developing
Method
COM/DCOM,ActiveX Implementing Developing
Tool
Visual Basic6.0
The software used
to implement COM Supporting
Platform
ArcObjects9.2
GIS Service
software
Running
Platform
ArcGIS9.2 or
ArcEngine Runtime
Client Service
software
Database
Service
MS SQL Server20
00 + ArcSDE9.2
Database manager
software
Forest GDB
SQL Server
Other DB
SQL Server
ArcGIS9.2
ArcView
ArcEdit
ArcInfo
Database Service
ArcSDE9.2
ODBC/ADO Carbon Trade
Display,Query
Statistics,Analysis
Model Calculate
Decision
Client:
Data Management
LAN
Figure 5. Getting land-position for models
Figure 6. Implement and result of model
V.C ONCLUSION
In this text, we have discussed the conception of geo-spatial model of evaluating for carbon sequestration Capacity, as well as it’s modeling method. How to establish the mathematical model and how to integrate with GIS are also expounded. And as a result, a validating tool based on ArcGIS and it’s COM library ArcObjects has been given as an experiment for this geo-spatial modeling. However, this experiment is just a practice in theory of modeling, it’s result has no stronger evidence to prove the validity of those models in modeling with Geo-spatial method, because that has to expend a much long time to find a real and feasible carbon sequestration
project to practice the models and simulate the modeling.
A CKNOWLEDGMENT.
I would like to express my gratitude to all those who help
me during the writing of this thesis. A special acknowledgement should be shown to my tutor professor Kun Yang, from whom I benefited greatly. I am particularly indebted to my wife Junhua Yi, who gave me kind encouragement and useful instructions all through my writing. Finally I wish to extend my thanks to the library assistants who supplied me with reference materials of great value.
R EFERENCE
[1]Dixon R K, Brown S , Houghton R A ,etc Carbon Pools and Flux of
Global Forest Ecosystems 1Science , 1994 ,pp. 263 :185 – 1901
[2]Iverson L R, Brown S, Prasad A etc. Use of GIS for estimating potential
and actual forest biomass forcontinental south and Southeast Asia . In:
Effects of L and2use Change on Atmospheric CO2 Concentration:South
and Southeast Asia as a case study. New York: Sp ringer- Verlag, 1994.
pp. 67~ 116.
[3]Sykes M T, Prentice I C. Carbon storage and climate change in Swedish
forest: a comparison of static and dynamic modeling approaches. In:
Forest Ecosystem s, Forest Management and the Global Carbon Cycle,
NA TO A S I Series, Vo l. I40. Heidelberg: Springer-Verlag, 1995. pp.
69~ 78.
[4]fang Huang,he-ping Zhang, xia-lin Chen. A evaluating of forest carbon
sequestration and it’s economic benefit for major forest type in Hu Nan
province. GuangXi Forestry Science. 2007.3.Vol.36.No.1
[5]Cun-Jian Yang, Ji-Yuan Liu, Zeng-Xiang. Zhang A research on
estimating for tropic forest biomass based on remote sensing. Geography
and Geo-Information Science. 2004.6.Vol.20,No.6
[6]Ji-Yuan Liu, Da-Fang Zhuang, Yang-Rong Ling. A study on
classification of vegetation in Northeast of China based on GIS. Journal
of Remote Sensing. 1998 ,2(4) pp.:285 - 291.
[7]Ying He. A summarization of the estimating method for forest carbon
sequestration. World Forestry Research. 2005.2.Vol18,No1
[8]Hong-Bo Yang, Bo Wu, Jin-Tun Zhang. The development of research
on carbon sequestration and reserve of carbon in forest ecology system.
Journal of Beijing Normal University(Nature Science).2005.4.Vol.41,No.2
[9]Min Zhao, Guang-Sheng Zhou. An analysis for reserve of carbon
sequestration and it’s affecting factors in forest ecology system of China.
Geographic Science. 2004.2.Vol 24,No.1
[10]Xiao-Quan Zhang, Nu-Yun Li, Shu-Hong Wu. A analysis for the
feasibility and capacity of afforestation project with China implementing
CDM. Forestry Science. 2005.9.Vol 41,No.5
[11]Jing-Yun Fang, Guo-Hua Liu, Song-Ling Xu. The complete output and
biomass of forestry in China. Journal of Ecology. 1996, pp. 16:497~508
月半小夜曲小提琴简谱及歌词 下面由为大家介绍《月半小夜曲》小提琴简谱,希望能帮到你。 《月半小夜曲》小提琴简谱【图片来源:中国曲谱网】《月半小夜曲》歌词仍然倚在失眠夜望天边星宿仍然听见小提琴如泣似诉再挑逗为何只剩一弯月留在我的天空这晚以后音讯隔绝人如天上的明月是不可拥有情如曲过只遗留无可挽救再分别为何只是失望填密我的空虚这晚夜没有吻别仍在说永久想不到是借口从未意会要分手但我的心每分每刻仍然被她占有她似这月儿仍然是不开口提琴独奏独奏着明月半倚深秋我的牵挂我的渴望直至以后仍然倚在失眠夜望天边星宿仍然听见小提琴如泣似诉再挑逗为何只剩一弯月留在我的天空这晚以后音讯隔绝人如天上的明月是不可拥有情如曲过只遗留无可挽救再分别为何只是失望填密我的空虚这晚夜没有吻别仍在说永久想不到是借口从未意会要分手但我的心每分每刻仍然被她占有她似这月儿仍然是不开口提琴独奏独奏着明月半倚深秋我的牵挂我的渴望直至以后仍在说永久想不到是借口从未意会要分手但我的心每分每刻仍然被她占有她似这月儿仍然是不开口提琴独奏独奏着明月半倚深秋我的牵挂我的渴望直至以后《月半小夜曲》创作背景在20世纪90年代初,李克勤刚进入宝丽金不久,有天听到《月半小夜曲》的日文原版河合奈保子的《ハーフムーン·セレナーデ》旋律后,被深深吸引,但被告知已被同公司的关正杰所用,让他很失望。 突然有一天,关正杰决定改编其他歌曲而放弃了这首歌,李克勤
赶紧把它拿过来重新改编,《月半小夜曲》也成为其代表作之一。 《月半小夜曲》歌曲鉴赏《月半小夜曲》用管弦乐的形式以及点缀上歌剧和声,有了一种“悲壮的形式意味,而不仅仅是小情小调的“哭诉,李克勤在音乐路上找到一些变化,更具力量感,至少给人不一样的听感。 猜你喜欢:1.let it go小提琴简谱2.爱的致意小提琴简谱3.蒲公英的约定小提琴演奏教学简谱4.See You Again小提琴演奏教学简谱5.一路向北小提琴演奏教学简谱
仍然倚在失眠夜望天边星宿 仍然听见小提琴如泣似诉再挑逗为何只剩一弯月留在我的天空 这晚以后音讯隔绝人如天上的明月是不可拥有 情如曲过只遗留无可挽救再分别为何只是失望 填密我的空虚 这晚夜没有吻别仍在说永久 想不到是借口 从未意会要分手但我的心每分每刻仍然被她占有 她似这月儿 仍然是不开口 提琴独奏独奏着明月半倚深秋 我的牵挂我的渴望直至以后ying yin yi zai sa min ye mang tin bin sing sou ying yin ting gan siu tai gan you ya ci sou zai tiu dou wei huo zi sheng ya wan yue lou zai o di tin hong ze man yi hou yan sun ga zue yan yu tin sang di ming yu si bu ho yong you cing yu ku guo zi wai lou mou ho wan lou zai fan bi wei huo zi si sa mong tin man o di hong hui ze man ye mu you man bi ying zai su wing gou sing ba dou si zie hou cong mei yi wei yiu fan sou dan o di san mui fan mui ha ying yin bei ta zin you ta ci ze yue yi ying yin si ba hoi hou tai kan dou zou dou zou ze ming yu bun yi san cou o di hin gua o di he mong zi zi yi hou
仍然倚在失眠夜望天边星宿 ying yin yi zuai sa min ye muang tin bin sing sou 淫燃以在沙绵夜望天边声兽 仍然听见小提琴如泣似诉再挑逗 ying yin tiang gin siu tei ken yu ya cyi cou zuai tiu dou 淫燃听干小提肯如因是树灾挑豆 为何只剩一弯月留在我的天空 wai huo zyi sing ya wan yu lou zuai euo dei tin hong 妹何只省亚弯韵楼在鳄的听轰 这晚以后音讯隔绝 zie man yi hao yang sun ga zue 这满以后音讯嘎绝 人如天上的明月是不可拥有 yan yu tin sang dei miang yu syi ba huo yong you 盐如听上的民韵是罢和拥有 情如曲过只遗留无可挽救再分别 cing yu quo guo zyi wai lou mou huo wan gou zuai fen bi 情如苦过只围楼魔幻晚构在分列 为何只是失望填密我的空虚 wai huo zyi syi sa muang ti ma euo dei hong hui 为何机射社莫听蛮我的红黑 这晚夜没有吻别 zie man ye mu you men bi 这莫夜木有们的 仍在说永久想不到是借口 ying zuai siu wen gou sang ba dou syi zie hou 因在岁应够射博逗射这后 从未意会要分手 cong mei yi hui you fen sou 从唯一胃药分手 但我的心每分每刻仍然被她占有 dang euo dei seng muei fen muei ha ying yin bei ta zin you 但我的声微分为哈也因为她精油 她似这月儿仍然是不开口 ta syi zie yu yi ying yin syi ba huai hou 他亲这云笛也映射吧嗨侯 提琴独奏独奏着明月半倚深秋 tei ken dou zou dou zou ze miang yu bun yi sen cou 还轰动这东这渣名誉博医生抽 我的牵挂我的渴望直至以后 euo dei hin gua euo dei ha muang zyi za yi hao 莫gi看挂蓦地看莫扯扯以后