中医词汇英汉对照
- 格式:docx
- 大小:23.57 KB
- 文档页数:3

中医词语对应的英文翻译以下是一些中医常用词语及其对应的英文翻译,供参考。
1. 中药:Chinese medicine2. 针灸:Acupuncture3. 脉象:Pulse condition4. 望、闻、问、切:Observation, listening, inquiry, palpation5. 辨证论治:Syndrome differentiation and treatment6. 气滞血瘀:Qi stagnation and blood stasis7. 气血两虚:Qi and blood deficiency8. 风寒感冒:Wind-cold感冒9. 湿热证:Damp-heat syndrome10. 脾胃虚弱:Spleen-stomach weakness11. 肝火旺盛:Liver fire flaming12. 心火旺盛:Heart fire flaming13. 肺热咳嗽:Lung heat cough14. 脾虚泄泻:Spleen deficiency diarrhea15. 肾虚腰痛:Kidney deficiency waist pain16. 湿温病:Damp-heat disease17. 风湿病:Rheumatism18. 痛经:Menstrual pain19. 月经不调:Menstrual irregularity20. 更年期综合症:Menopause syndrome21. 肥胖症:Obesity22. 高血压病:Hypertension23. 糖尿病:Diabetes24. 失眠:Insomnia25. 抑郁症:Depression26. 焦虑症:Anxiety disorder27. 自闭症:Autism28. 强迫症:OCD (Obsessive-Compulsive Disorder)29. 多动症:ADHD (Attention Deficit Hyperactivity Disorder)30. 老年痴呆症:Alzheimer's disease31. 帕金森病:Parkinson's disease32. 癌症:Cancer33. 白血病:Leukemia34. 心脏病:Heart disease35. 肝病:Liver disease36. 肾病:Kidney disease37. 肺病:Lung disease38. 高脂血症:Hyperlipidemia39. 甲亢:Hyperthyroidism40. 甲减:Hypothyroidism41. 黄褐斑:Chloasma42. 白癜风:Vitiligo43. 牛皮癣:Psoriasis44. 带状疱疹:Shingles45. 水痘:Chickenpox46. 麻疹:Measles47. 风疹:Rubella (German measles)48. 痄腮:Mumps (耳下腺炎)49. 红眼病(急性结膜炎):Red eye (acute conjunctivitis)50. 中耳炎:Otitis media (middle ear infection)请注意,这些翻译可能并不完全准确或具体,因为中医是一个非常复杂和深奥的医学系统,其概念和术语往往难以用简单的英文词汇来表达,仅供参考。

中医词汇英汉对照abdominal flatulence 中满abdominal fullness and distention 腕痛胀满abdominal retention 鼓胀accompanied symptoms 兼证activating blood and dissolving stasis 活血化瘀acuesthesia 得气acupuncture points 腧穴acupuncture therapies 针刺疗法adjuvant drugs 佐药afternoon fever 日哺发热alternate chills and fever 寒热往来anorexia 食欲不振aphtha 口疮apoplexy 中风ashi point 阿是穴associate drugs 臣药association of combination of traditional chinese medicine and western medicine中西医结合研究会association of traditional chinese medicine 中医学会asthenic cardioyang 心阳虚asthenic cardioyin 心阴虚asthma 哮证otopuncture therapy 耳针疗法auscultation-olfaction 闻诊aversion to wind and cold 畏恶风寒basis of theory of traditional chinese medicine 中医理论基础belching 嗳气blood deficiency 血虚blood heat 血热body fluid 津液calming liver wind 平肝熄风canthus 目眦carbuncle 痈cathartic method 攻里法cardiac and renal coordination 心肾相交cardiac-splenic asthenia 心脾两虚chest pain 胸痛chest stuffiness 胸闷chi pulse 尺脉chinese materia medica and preions 中药与方剂chinese medical history中国医学史chinese medicine anesthesia 中药麻醉chinese patent drugs 中成药clear abundant urine 小便清长clearing damp 利水渗湿clearing heat and expectoration 清热化痰clearing wind-damp 祛风胜湿clearing ying heat and cooling blood 清营凉血coating color 苔色cold hands and feet 手足厥冷cold-heat mixing 寒热交错cold limbs 手足厥冷cold stroke 中寒coma 神昏compendium of materia medica 本草纲目complications 并病constipation 大便不通consumptive disease 虚劳contrary treatment 反治defensive qi instability 卫气不固deficiency-excess mixing 虚实夹杂delirium 谵语diagnostic methods of traditional chinese medicine 中医诊法diaphoresis 汗法diaphoresis, pungent cold 辛凉解表diaphoresis, pungent warm 辛温解表diarrhea 泄泻different treatments for the same disease 同病异治differentiation, eight principles 八纲辨证differentiation of diseases 辨病differentiation of symptoms and signs 辨证differentiation, six meridians 六经辨证differentiation, triple energizer 三焦辨证differentiation, wei-qi-ying-xue 卫气营血辨证differentiation, zang-fu 脏腑辨证diphtheria 白喉diseases of qi-blood-fluid 气血津液病症dispersing cold and freeing bi 散寒通痹doctrines of various historical schools 中医各家学说dry heat 燥热dry stool 大便干结dysentery 痢疾dyspepsia 食滞dysphagia 噎膈dyspnea 喘证dysuria 癃闭edema 水肿eight principles 八纲electuary 冲服剂elimination 消法emesis 吐法endogenous hygrosyndrome 内湿endogenous cold 内寒endogenous dryness 内燥epilepsy 痫证epitaxis 鼻衄inspection 望诊inquiry 问诊auscultation 听诊percussion 扣诊palpation 触诊biopsy 活组织检查pathological section 病理切片endoscopy 内窥镜检查ECG(electrocardiogram) examination 心电图检查EEG(electrocardiogram) examination 脑电图检查Intravenous pyelography静脉肾盂造影术Skin-test 皮肤试验examination by centesis 穿刺检查routine analysis of blood 血常规分析urine analysis of blood 尿常规分析red blood cell count(RBC) 红细胞计数white blood cell count(WBC) 白细胞计数general check-up 全身检查routine examination 常规检查follow-up examination 随访检查consultation 会诊emergency 急诊diagnosis 诊断prognosis 预后convalescence, recovery 康复relapse 复发treatment 治疗prescribe 开药方fill a prescription 配药injecting 打针hypodermic injection 皮下注射intramuscular injection 肌肉注射intravenous injection 静脉注射inoculating 预防注射fluid infusion 点滴注射blood transfusion 输血dose 剂量tablet 药片capsule 胶囊liquid medicine 药水powder 药粉ointment 药膏(软膏)plaster 硬膏,石膏lotion 洗剂suppository 栓剂analgesics 止痛药antipyetics 退烧药antitussive 止咳药expectorant 祛痰药diuretics 利尿药hemostatic 止血药antidiarrheal 止泄药antipruritic 止痒药antidote 解毒药。
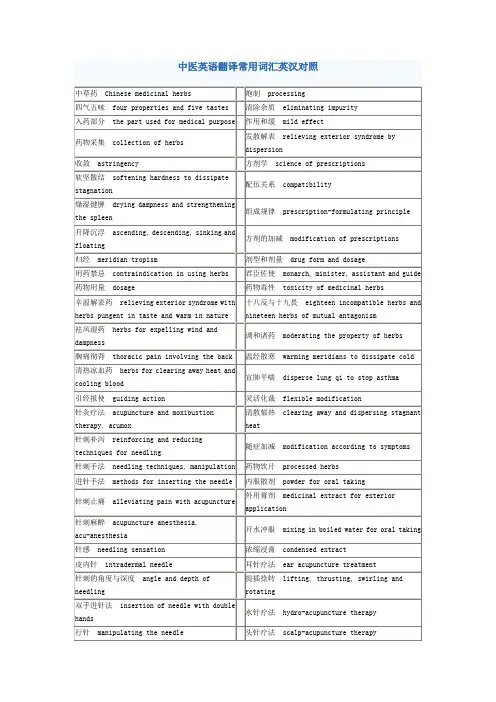

中医的专业术语英文翻译中医的专业术语英文翻译大家在写中医论文时候常常遇到一些不容易翻译的词汇,yjbys网整理了中医的专业术语英文翻译,方便大家写作。
快来点赞吧。
中国医药学:traditional Chinese medicine中医基础理论:basic theory of traditional Chinese medicine临床经验:clinical experience辨证论治:treatment based on syndrome differentiation本草:materia medica //medicinal herbs中药Chinese herbs四气五味:four properties and five tastes针灸acupuncture and moxibustion各家学说theories of different schools汗法: diaphoresis /diaphoretic therapy下法:purgative therapy吐法:emetic therapy补土派:school of invigorating the earth病因学说:theory of etiology养生:health-cultivation医疗实践medical practice治疗原则:therapeutic principles寒凉药物:herbs of cold and cool nature滋阴降火:nourishing yin to lower fire瘀血致病:disease caused by blood stasis先天之精:congenital essence气的运动变化:movement and changes of qi形与神俱:inseparability of the body and spirit神明: spirit/mental activity脏腑:zang-organs and fu-organs/viscera功能活动:functional activities形神统一:unity of the body and spirit阴阳失调:imbalance of yin and yang正邪相争:struggle between healthy qi and pathogenic factors 治未病prevention of disease调养 to cultivate health正气 healthy qi病邪 pathogenic factor疾病的防治 prevention and treatment of disease整体观念 concept of holism五脏five zang-organs六腑six fu-organs经络系统system of meridians and collaterals形神统一unity of the body and spirit有机整体organic wholeness表里关系exterior and interior relation开窍opening into生长化收藏five element function脉象pulse conditions正邪关系the states of pathogenic factors and healthy qi自然现象natural phenomena哲学概念philosophical concept对立统一unity and opposites相互消长mutual waning and waxing阴阳属性nature of yin and yang相互转化mutual transformation相互联系interrelation相互制约mutual restraint动态平衡dynamic balance阴平阳秘yin and yang in equilibrium阳消阴长 yang waning and yin waxing阴胜则阳病predominance of yin leading to disorder of yang 阳胜则热 predominance of yang generating heat寒极生热 extreme cold generating heat热极生寒extreme heat generating cold相反相成 opposite and supplementary to each other生理功能physiological functions病理变化pathological changes临床诊断clinical diagnosis有机整体organic wholeness/entirety正邪斗争struggle between healthy qi and pathogenic factors 绝对偏盛absolute predominance阳虚则寒yang deficiency leading to cold阳损及阴consumption of yang involving yin阴液不足insufficiency of yin-fluid病机pathogenesis五行学说theory of five elements运动变化motion and variation条达舒畅free development相生相克mutual generation and restriction生我我生to be generated and to generate克我我克to be restricted and to restrict生中有制restriction within generation克中有生generation within restriction木曰曲直Wood is characterized by growing freely and peripherally火曰炎上Fire is characterized by flaming up土曰稼穑Earth is characterized by cultivation and reaping金曰从革Metal is characterized by change水曰润下Water is characterized by moistening anddownward flowing方位配五行correspondence of the directions to the five elements相乘相侮over-restriction and reverse restriction土乘木The wood over-restrains the earth土虚木乘 Earth deficiency leading to over-restriction by wood 金虚木侮metal deficiency leading to counter-restriction by wood生克制化interrelationship between generation and restriction制则生化restriction ensuring generation传变transmission of disease母病及子disease of the mother-organ affecting the child-organ子病犯母disease of the child-organ affecting the mother-organ肝肾精血不足insufficiency of kidney and liver essence and blood肝阳上亢hyperactivity of liver yang藏象学说 theory of visceral manifestations五脏六腑 five zang-organs and six fu-organs奇恒之府 extraordinary fu-organs水谷精微 cereal nutrients传化水谷 transmissions and transformation of food贮藏精气 storage of essence表里关系 interior and exterior relationship治疗效应 curative effect临床实践 clinical practice藏而不泻 storage without excretion心肝血虚deficiency of heart and liver blood心肝火旺exuberance of heart and liver fire心火亢盛exuberance of heart fire滋肾养肝nourishing the kidney and liver肝阴不足insufficiency of the liver yin温肾健脾warming the kidney and strengthening the spleen 肾阳式微declination of kidney yang脾阳不振inactivation of spleen yang肝旺脾虚hyperactivity of the liver and weakness of the spleen 脾胃虚弱weakness of the spleen and stomach平肝和胃soothing the liver and harmonizing the stomach水湿停聚retention of water-dampness肾阴不足insufficiency of kidney yin心肾不交disharmony between the heart and kidney水火不济discordance between water and fire阴阳俱损simultaneous consumption of yin and yang阴阳两虚simultaneous deficiency of both yin and yang损其有余reducing excess补其不足supplementing insufficiency阴中求阳obtaining yang from yin虚寒证deficiency-cold syndrome扶阳益火strengthening yang to increasing fire祛风散寒eliminating wind to dispersing cold消导积滞promoting digestion and removing food retention 潜阳息风suppressing yang to quench wind阴阳的互根互用interdependence of yin and yang相互依存interdependence。

TCM(Traditional Chinese Medicine),Origination of TCM, 形成formation, 发展development The basic characteristic of Traditional Chinese Medicine theory整体观the whole concept, 辨证论治syndrome differentiation and treatment第一章阴阳五行学说Yin-yang , 阴阳的特性the property of yin-yangInteraction between yin and yangOpposition of yin and yangInterdependence between yin and yangWane and Wax between yin and yang Mutualtransformation between yin and yangThe applications of the theory of yin-yang in TCM说明人体的组织结构Explanation of the histological structure of the human body解释人体的生理功能Explanation of the physiology functionactivity of the human bodyExplanation of pathogenesisRelative predominance of yin or yangRelative predominance of yangRelative predominance of yinRelative decline of yin or yangRelative decline of yang阴偏衰Relative decline of yin五行the five elements,五行特性the five elements property第二章中医学的生理观藏象“ Zangxiang,”五脏five Zang-organs, 六腑six fu-organs,生理功能the physiological functions ,气qi, 血blood , 津液body fluid,气的生成、运动和分类the production ,moving and classification of qi,血的生成和运行the production and circulation of blood津液的生成、输布和排泄the production and transportation and metabolism ofbody fluid.气、血、津液的功能The physiological functions of qi, blood and body fluid心The heart,主血脉Governing blood主神志controlling the mind在体合脉governs the vessels开窍于舌opens into the tongue其华在面External manifestation on the face肝The liver,主疏泄To dredge and regulate,主藏血Storing blood在体合筋The liver governing the tendons其华在爪The external manifestation of the liver on the nails开窍于目The liver opening into the eyes脾the spleen,主运化To govern the transportation and transformation主统血To command blood, 主升elevating在体合肌肉,主四肢the spleen governing the muscles and the four limbs开窍于口The spleen opening into the mouth其华在唇The external manifestation on the lip肺The lung,主气,司呼吸Dominating qi,controlling the respiratorymovement主宣发、肃降dispersing and descending通调水道The regulation of water passage朝百脉、主治节‘ the lung is connected with all the vesse,lrsegulation the qi activity in the whole body在体合皮the lung governing the skin其华在毛Eexternal manifestation on the body hair开窍于鼻The lung opening into the nose肾The kidney,藏精store essence,主水T o govern water, 主纳气Togovern reception of qi在体合骨The kidney governing the bones开窍于耳及二阴The kidney opening into the ears, the externalgenitals and the anus其华在发External manifestation on the hair胆The gallbladder, 贮藏和排泄胆汁store and excrete the bile胃The stomach, 受纳、腐熟水谷receive and digest food主通降‘ the stomach functions to descend ’ , ‘ unobstructedcondition小肠The small intestine, 受盛化物To receive the chime and transform泌别清浊To separate the lucid from the turbid大肠The large intestine, 主传化糟粕transmitting and excreting the waste of food膀胱The bladder , storing and discharging urine气的生成The production of qi气的运动The moving of qi气的功能The physiological functions of qi推动作用Propelling function温煦作用Warming function防御作用Protecting and defencive function固摄作用Fixating function气化作用Qi-transforming function元气primordial qi, 宗气pectoral qi, 营气nutrient-qi, 卫气defensive qi第三章中医学的病理观病因Causes of disease病因的概念及分类concept, classification of causes of disease. 六淫的概念concept of six pathogenic factors,; ,六淫致病的共同特点the general pathogenic characters of six pathogenic factors;六淫各自的性质与致病特点nature, pathogenic characters and main clinic manifestations of every six pathogenicfactors(including wind, cold,Summer-heat,Dampness,Dryness,Heat(fire))风Wind其性开泄,易袭阳位Wind tend to float, disperse, go upward attack the upper andoutside parts风性善行而数变wind tends to move and change风为百病之长,易夹杂其他外感之邪Wind tends to be complicated by otherpathogenic factors寒Cold易伤阳气Cold tends t o impair yang寒性凝滞Cold tends t o coagulate寒性收引Cold tends t o contract暑Summer-heat其性炎热Summer-heat is hot暑性升散,耗气伤津Summer-heat tends to disperse and eleva,teconsume the qi andbody fluid暑多夹湿Summer-heat often complicated by dampness湿Dampness湿性重浊dampness is heavy and turbid湿易阻遏气机dampness tends to block qi湿性黏滞dampness is sticky and stagnant湿性趋下, 易袭阴位dampness tends to move downwar,dattack the lower and insideparts燥Dryness燥易伤津Dryness consume the body fluid燥性干涩Dryness is xerotic and unsmooth燥易伤肺Dryness tends to impair the lung火Heat (fire)其性炎上Heat(fire) tends to flame up易伤津耗气Heat(fire) tends to consume qi and impair body fluid易生风动血Heat(fire) tends to produce wind and disturb blood易致肿疡Heat(fire) tends to cause swelling and ulceration七情内伤的概念、The concept of internal impairment due to the seven emotions,七情致病的特点the pathogenic characters of the seven emotions痰饮、瘀血的概念、形成及致病特点The basic concept, the formation and thepathogenic characteristics of phlegm ,rheum and blood stasis痰饮phlegm ,rheum 瘀血blood stasis发病的基本原理The pathogenesis of occurrence of disease in TCM病机的概念,The concept of mechanism of pathological changes;病机the mechanism of pathological changes;邪正盛衰predomination and decline of pathogenic factors and healthy qi;阴阳失调imbalance between yin and yang;气血津液失常disorder of qi, blood and body fluid.第四章中医诊断疾病的方法中医诊法The concept of the TCM diagnostic methods中医诊断的理论依据the theory foundation of the TCM diagnostic methods.望神Inspection of spirit, 望色Inspection of complexion, 望排出物Inspection ofexcreta ,望舌Inspection of tongue,Existence of spirit (得神),Lack of spirit(少神),Loss of spirit (失神)False spirit(假神)Normal complexion 常色Morbid complexion 病色Red colour ,White colour ,Yellow colour, Bluish colour,Blackish colour临床意义clinical significance ;望舌的方法Methods for inspection of tongue问诊inquiry, 主诉chief complaint, 病史history of present illness问现在症inquiry of the present symptomsAversion to cold and fever(恶寒发热)Cold sensation without fever(但寒不热)Fever without cold sensation(但热不寒)Alternate cold and fever(寒热往来)诊脉的部位与方法The Regions and methods for taking pulse脉诊taking pulse, 正常脉象normal pulseCunkou(寸口)cun(寸), guan(关),chi(尺).辨证的概念The concept of differentiation of syndrome表里辨证External and internal differentiation of syndromes,表证External syndromes,里证internal syndromes,寒热辨证cold and heat differentiation of syndromes,寒证cold f syndromes,热证heat syndromes,虚实辨证asthenia and sthenia differentiation of Syndromes,虚证asthenia Syndromes,实证sthenia Syndromes,临床特点clinical character and difference.八纲辨证Syndromes differentiation with eight principles气血津液辨证syndrome differentiation with qi, blood and body fluid,第五章中医学的防治原则治则therapeutic principles , 治法therapeutic methods正治Routine treatment , 反治Contrary treatment,治本treat “ be(dne” al with the root cause)治标Treating biao(acute symptoms bring on great suffering to the patients, or threaten life or tend to transmit and change) in emergency ,扶正与祛邪Strengthening healthy qi and eliminating pathogenic factors,调整阴阳Regulation of yin and yang,三因制宜Abidance by individuality, locality and seasons.第六章中药基本知识中药Chinese Medicinal Herbs四气four properties、五味five flavors、升降浮沉the action of lifting, lowering,floating and sinking,、归经channel tropism、毒性toxicity中药的配伍、用药禁忌Contraindication and Compatibility of Chinese MedicinalHerbsDosage of Chinese Medicinal Herbs第七章方剂基本知识方剂的组成原则The principle of the composition of prescriptions,组成变化the modification of the composition of a prescription. 方剂的组成、用法、功效、临床应用、方解:Ingredients, administration, function,clinical application and elucidation of the prescriptions下列方剂的组成、用法、功效、应用、方解:银翘散、平胃散、藿香正气散、大承气汤、大黄附子汤第二章中医学的生理观第三节经络经络the meridians;十二经脉twelve regular meridians十二经脉走向与交接规律direction, joint law of the twelve channels、十二经脉循行分布规律distributing law of the twelve channels , 十二经脉表里络属关系exterior-interior relationship of the twelve channels ,十二经脉流注方向和次序等flowing direction and order of the twelve channels;第八章针灸学基本知识第二节刺灸方法刺法(针法) Acupuncture techniques; 进针Needling methods(insertion methods,Needling manipulation methods)得气arrival of Qi针刺意外和防治处理Management of possible accidents (emphasize晕针fainting)灸法moxibustion,第八章针灸学基本知识第一节腧穴腧穴概念;腧穴分类;腧穴定位方法;腧穴功效the points (definition, classification, location method, function)腧穴的定位、归经、基本主治功能:location, channel tropism and the basic specialtreatment function手太阴肺经:列缺;手阳明大肠经:合谷、曲池;足阳明胃经:足三里;足太阴脾经:三阴交;手少阴心经:神门;手太阳小肠经:听宫;足太阳膀胱经:委中;足少阴肾经:涌泉;手厥阴心包经:内关;手少阳三焦经:外关;足少阳胆经:风池、阳陵泉;足厥阴肝经:太冲;任脉:关元、膻中;督脉:大椎、人中;经外奇穴:印堂、太阳;。

中医术语的中英文参考对照治则principle of treatment 在对临床的具体立法、处方、用药等具有普遍的指导意义,因而在治疗疾病时必须遵循的基本原则。
治病求本treatment aiming at its pathogenesis 针对产生疾病的根本原因进行治疗的原则。
急则治标symptomatic treatment in acute condition 与缓则治本相对而言,在大出血、暴泻、剧痛等标症甚急的情况,及时救治标病。
缓则治本radical treatment in chronic case 与急则治标相对而言,针对病势缓和、病情缓慢的情况,从本病的病机出发,采取调理、补益为主的治疗原则。
标本兼治treating both manifestation and root cause of disease 针对病证出现的标本并重的情况,采用治标与治本相结合的治疗原则。
治未病preventive treatment of disease 采取一定的措施防止疾病产生和发展的治疗原则,包括未病先防和既病防变两个方面。
同病异治treating same disease with different methods 表现相同的病证,可因人、因时、因地的不同,或由于病情的发展、病机的变化、病型的各异、正邪消长等差异,采取不同治法的治疗原则。
异病同治treating different diseases with same method 表现不同的病证,由于发病机理相同,采取相同治法的治疗原则。
因时制宜treatment in accordance with seasonal conditions 考虑到时令气候寒热燥湿的不同而选择适宜的治法、方药的治疗原则。
因地制宜treatment in accordance with local conditions 考虑到地域环境的不同而选择适宜的治法、方药的治疗原则。

中医常用术语英文翻译[学科]中医①traditional Chinese medicine②traditional Chinesephysician ①中医学的简称。
②本学科专业职业队伍。
中药Chinesemateria medica 在中医理论指导下应用的药物。
包括中药材、中药饮片和中成药等。
中医学 traditionalChinese medicine 以中医药理论与实践经验为主体,研究人类生命活动中健康与疾病转化规律及其预防、诊断、治疗、康复和保健的综合性科学。
中药学Chinese materiamedica 中药学科的统称。
研究中药基本理论和各种药材饮片、中成药的来源、采制、性能、功效、临床应用等知识的学科。
中医药 traditionalChinese medicine and pharmacology本草:Materia medica中药:Chinese materiamedica,Chinese medicinals(包括植物药、动物药、矿物药等)中草药:Chinese HerbalMedicine,Chinese medicinal herbs中药学:Chinese pharmaceutics药材:Medicinalsubstance(material)中西医结合 integration of traditional and western medicine 中医基础理论 basictheory of traditional Chinese medicine 中医诊断学 diagnostics of traditional Chinese medicine 方剂学 prescriptions of Chinese materia medica,Traditional Chinese Medical Formulae/ prescriptions中医内科学 internal medicine of traditional Chinese medicine[阴阳]The Theory of Yinand Yang阴阳对立:Opposition of yin andyang阴阳制约:Restriction of/between yin and yang阴阳互根:Interdependence ofyin and yang阴阳消长:Waxing and waning ofyin and yang阴阳转化:Inter-transformationof yin and yang[五行学说]The Theory of FiveElements五行:water,fire,wood,metal,soil生:promote, generate,engender克: act, restrict,restrain乘:overact,over-restrict, over-restrain, subjugate, overwhelm侮:counteract,counter-restrict, counter-restrain, rebel[整体观念] concept of organicwholeness辩证法 dialectics生长化收藏 sprouting, growth,transformation,ripening,storage内外环境统一性 the unity betweenthe internal and external environments机体自身整体性 the integrity of thebody itself古代唯物论和辩证法 classic Chinesematerialism and dialectics 矛盾统一the contradictoryunity互相联系、相互影响related to each otherand influence each other标本 Biao (secondaryaspect) and Ben (primary aspect)本质与现象nature and phenomena矛盾的普遍性和特殊性universality andspeciality of contradictions寒者热之Cold disease shouldbe treated by warm therapy热者寒之warm disease shouldbe treated by cold therapy虚者补之deficiency syndromeshould be treated by tonifyingtherapy实者泻之excess syndromeshould be treated by purgation therapy治病必求其本 Treatment ofdiseases must concentrate on the root cause同病异治treatment ofthe same disease with different therapeutic methods异病同治treatment ofdifferent diseases with the same therapeutic method[精气神]清阳为天 The lucid Yangascends to form the heaven浊阴为地 The turbid Yindescends to constitute the earth气化 Qitransformation升降出入 ascending,descending, going out, coming in出入废则神机化灭,升降息则气立孤危。

中医诊断常用词汇的中英对照中医作为中国传统医学的重要组成部分,拥有悠久的历史和丰富的诊治经验。
在中医诊断过程中,医生会使用一系列特定的术语来描述症状和疾病。
本文将介绍一些中医诊断常用词汇的中英对照,以便更好地理解和学习中医理论。
一、症状描述1. 舌苔(Tongue Coating)中医诊断中,医生会仔细观察患者舌苔的颜色、质地和厚薄程度等。
常见的舌苔表现包括白色、黄色、薄白、薄黄等。
2. 脉象(Pulse)中医通过触摸患者脉搏来判断体内脏腑的功能和疾病情况。
常见的脉象包括弦脉、滑脉、实脉、虚脉等。
3. 咳嗽(Cough)咳嗽是中医常见的症状之一,可分为干咳、湿咳、痰多、痰黄等不同类型。
4. 发热(Fever)体温升高是常见的中医症状,可用于判断病证的性质及严重程度。
5. 头晕(Dizziness)中医将头晕分为眩晕、头昏、头眩等不同类型,以辅助诊断病因和辨证。
二、疾病诊断1. 冠心病(Coronary Heart Disease)冠心病是指冠状动脉血液供应不足引发的心脏病,常见症状包括胸痛、气短等。
2. 高血压(Hypertension)高血压是中医常见疾病,可引发头痛、头晕、眼花等症状。
3. 糖尿病(Diabetes)糖尿病是一种代谢性疾病,主要特征是血糖浓度增高。
中医将糖尿病分为三型,即上、中、下三焦糖尿病。
4. 高血脂(Hyperlipidemia)高血脂是指血液中脂质含量过高的病症,中医观点认为高血脂与体内湿气过盛有关。
5. 慢性胃炎(Chronic Gastritis)慢性胃炎是胃粘膜长期受损引起的一种炎症,中医常用‘胃气郁结’来描述其病因。
三、中医治疗方法1. 针灸(Acupuncture)针灸是中医常用的治疗方法之一,通过刺激人体穴位来调节气血,达到治疗疾病的目的。
2. 中药疗法(Chinese Herbal Medicine)中药疗法是中医的核心治疗方法,通过使用植物的根、茎、叶、花等部位制成的药材来疗效疾病。

中医药常用名词术语英译1. 嘿,你知道“阴阳”在中医药里怎么英译不?“Yin - Yang”呀。
就好比白天和黑夜,一个是阳,一个是阴,它们相互对立又相互依存呢。
比如说,一个人身体太“阳”了,可能就容易上火,就像夏天太阳太猛,大地都干涸了。
2. 咱来聊聊“气”这个词的英译,“Qi”。
这“气”啊,就像身体里的小发动机。
我有个朋友,老是没精打采的,中医就说他“气”不足。
这“气”在身体里到处跑,推动着身体各个机能运转呢。
3. “经络”的英译是“Meridian”。
这经络就像身体里的高速公路网哦。
我上次去看中医,医生说经络不通会导致很多毛病。
就像高速公路堵了,车就没法顺畅地跑,身体里的气血也一样。
4. “穴位”的英语是“Acupoint”。
穴位就像身体上的一个个小开关。
有次我头疼,中医在我头上的一个穴位按了几下,哎呀,就像打开了止痛的开关一样,立马感觉好多了。
5. “中药”的英译是“Chinese materia medica”。
这中药可神奇啦,就像大自然赐给我们的医药宝藏。
我奶奶生病就爱喝中药,那些草药熬出来的汤,感觉就像把大自然的力量都喝进肚子里了。
6. 你了解“方剂”的英译吗?是“Prescription”。
方剂就像是一个医药团队。
比如说一个治疗感冒的方剂,里面有好几味中药,就像团队里不同的成员,各自发挥着作用,一起把感冒这个“敌人”打败。
7. “炮制”的英语是“Processing”。
这炮制就像给中药做一场精心的改造。
我见过中药师傅炮制药材,把原本普普通通的药材,经过各种工序,就像把一个灰姑娘变成公主一样,药效都变得更厉害了。
8. “辨证论治”的英译是“Treatment based on syndrome differentiation”。
这就像医生当侦探呢。
我去看中医,医生又是看舌头,又是把脉,然后判断我的“证”,再根据这个来治疗。
就像侦探根据线索破案一样精准。
9. “四气五味”的英语是“Four natures and five flavors”。

中医英语术语翻译重点天人相应Correspondence of human body and natural environment辨证论治treatment based onsyndrome differentiation针灸acupuncture and moxibustion寒凉药物herbs cold and cool in nature滋阴降火nourishing yin and reducing fire整体观念concept of holism开窍(of the five zang-organs) open into生长化收藏sprout, grow, transform, ripen and store同病异治different therapeutic methods used to treat the same disease 异病同治same therapeutic method used to treating different diseases 从阴引阳drawing yang from yin阴平阳秘balance of yin and yang寒极生热extreme cold generating heat热极生寒 extreme heat gernerating cold病机总纲general rule of pathogenesis祛风散寒eliminating wind and dispersing cold实则泻之treating excess syndromes with reduction虚寒证deficiency cold syndrome实热症 excess heat syndrome潜阳熄风suppressing yang and eliminating wind补其不足 supplement insufficiency泻其有余 reduce excess五行学说the theory of five elements木曰曲直wood characterized by bending and straightening火曰炎上fire characterized by flaring up土爰稼穑earth characterized by sowing and reaping金曰从革metal characterized by clearing and changing水曰润下water characterized by moistening and descending母病及子illness of mother viscera affecting the child one子病及母illness of child viscera affecting the mother one相乘相侮over restriction and counter-restriction心火亢盛exuberant fire in the heart肾阳式微declination of kidney yang平肝和胃soothing the liver and harmonizing the stomach水火不济between water and fire奇恒之腑extraordinary fu-organs藏象学说the theory of visceral manifestation藏而不泻storage without discharge泻而不藏discharge without storage形体诸窍physical build and various orifices其华在面the luster manifesting upon the face满而不实 full but not to be solid实而不满solid but not to be full心主血脉heart governing blood and vessels肺司呼吸lung controlling breathing脾主运化spleen governing transportation and transformation肝主疏泄liver controlling conveyance and dispersion肾主藏精kidney governing storing essence面色无华lusterless complexion汗血同源sweat and blood sharing the same origin升降出入ascending, descending, going out and going in宣发肃降dispersion, purification and descent后天之本acquired base of life肝气逆上upward adverse flow of liver qi先天之精innate essence奇恒之腑extraordinary fu-organs孤俯isolated fu-organ腐熟水谷digest water and food七冲门the seven important portals胆主决断The gallbladder is responsible for making judgment泌别清浊separating the lucid from the turbid大肠主津The large intestine governs thin body fluid小肠主液The small intestine governs thick body fluid先天禀赋innateness温养腑脏warming and nourishing the viscera津血同源body fluid and blood sharing the same origin气为血帅,血为气母Qi commands the blood and the blood carries qi.益气固脱nourishing qi to stop collapse奇经八脉eight extraordinary vessels十二经筋tendons of the twelve regular meridians舒经活络soothing meridians and activating collaterals刺络拔罐collateral pricking and cupping therapy腠理闭塞stagnation of interstitial space湿邪困脾pathogenic dampness obstructing the spleen外感六淫six excesses pathogenic factors饮食劳倦mproper diet and overstrain阳常有余,阴常不足Yang is usually excessive while yin is frequently deficient. 四大经典Four GreatClassic:Huangdi s Canon of Medicine黄帝内经Classic of Difficulties难经Shennong s Classic of Materia Medica神农本草经Rreatise on Cold Damage and Miscellaneous Diseases伤寒杂病论四气four properties:cold,,hot,warm,cool五味five flavors:sour,bitter,sweet,pungent,salty(中药)七情seven conditions of ingredients in prescriptionsSingle effect,mutual reinforcement,mutual assistance,mutual restraint,mutual inhibition,mutual antagonism,mutual suppression寒凉派Liu Wansu-School of Cold and Cool攻下派Zhang Congzheng-School of Purgation补土派Li Gao-School of Reinforcing the Earth滋阴派Zhu Zhenheng-School of Nourishing Yin辛温中药herbs pungent in taste and warm in nature辛凉中药herbs pungent in taste and cool in narure向日为阳,背日为阴The side facing the sun belongs to yang and the reverse side to yin,血液常行的前提条件:心气充沛,血液充盈,脉道通利Normal circulation of blood:abundance of heart qi,sufficiency of blood,vessels are prerequisite.四气;元气primordial qi,宗气pectoral qi,营气nutrient qi,卫气defensive qi 内生五邪;内风,内寒,内湿,内燥,内火Five internal excesses;internal wind.internal cold,internal dampness,inrenal dryness,internal fire内伤七情Internal injury due to sevenemotions;joy,anger,anxiety,thought,sorrow,fear,fright怒则气上,喜则气缓,悲则气消,恐则气下,惊则气乱。

中医中英文对照一览表一、绪论中医学TCM(Traditional Chinese Medicine),中医学理论体系的形成Origination of TCM, 形成formation, 发展development中医学理论体系的基本特点The basic characteristic of Traditional Chinese Medicine theory整体观the whole concept, 辨证论治syndrome differentiation and treatment第一章阴阳五行学说阴阳Yin-yang , 阴阳的特性the property of yin-yang阴阳之间的相互关系Interaction between yin and yang阴阳对立制约Opposition of yin and yang阴阳互根互用Interdependence between yin and yang阴阳消长平衡Wane and Wax between yin and yang阴阳相互转化Mutual transformation between yin and yang阴阳学说在中医学中的应用The applications of the theory of yin-yang in TCM说明人体的组织结构Explanation of the histological structure of the human body解释人体的生理功能Explanation of the physiology function activity of the human body阐释病理变化Explanation of pathogenesis阴阳偏盛Relative predominance of yin or yang阳偏盛Relative predominance of yang阴偏盛Relative predominance of yin阴阳偏衰Relative decline of yin or yang阳偏衰Relative decline of yang阴偏衰Relative decline of yin五行the five elements,五行特性the five elements property第二章中医学的生理观藏象“Zangxiang” ,五脏five Zang-organs, 六腑six fu-organs,生理功能the physiological functions ,气qi, 血blood , 津液body fluid,气的生成、运动和分类the production ,moving and classification of qi,血的生成和运行the production and circulation of blood津液的生成、输布和排泄the production and transportation and metabolism of body fluid.气、血、津液的功能The physiological functions of qi, blood and body fluid心The heart,主血脉Governing blood主神志controlling the mind在体合脉governs the vessels开窍于舌opens into the tongue其华在面External manifestation on the face肝The liver,主疏泄To dredge and regulate, 主藏血Storing blood在体合筋The liver governing the tendons其华在爪The external manifestation of the liver on the nails开窍于目The liver opening into the eyes脾the spleen,主运化To govern the transportation and transformation主统血To command blood, 主升elevating在体合肌肉,主四肢the spleen governing the muscles and the four limbs开窍于口The spleen opening into the mouth其华在唇The external manifestation on the lip肺The lung,主气,司呼吸Dominating qi,controlling the respiratory movement主宣发、肃降dispersing and descending通调水道The regulation of water passage朝百脉、主治节‘the lung is connected with all the vessels, regulation the qi activity in the whole body在体合皮the lung governing the skin其华在毛Eexternal manifestation on the body hair开窍于鼻The lung opening into the nose肾The kidney,藏精store essence, 主水To govern water, 主纳气To govern reception of qi在体合骨The kidney governing the bones开窍于耳及二阴The kidney opening into the ears, the external genitals and the anus 其华在发External manifestation on the hair胆The gallbladder, 贮藏和排泄胆汁store and excrete the bile胃The stomach, 受纳、腐熟水谷receive and digest food主通降‘the stomach functions to descend’,‘unobstructed condition小肠The small intestine, 受盛化物To receive the chime and transform泌别清浊To separate the lucid from the turbid大肠The large intestine, 主传化糟粕transmitting and excreting the waste of food膀胱The bladder ,storing and discharging urine气的生成The production of qi气的运动The moving of qi气的功能The physiological functions of qi推动作用Propelling function温煦作用Warming function防御作用Protecting and defencive function固摄作用Fixating function气化作用Qi-transforming function元气primordial qi, 宗气pectoral qi, 营气nutrient-qi, 卫气defensive qi第三章中医学的病理观病因 Causes of disease病因的概念及分类concept, classification of causes of disease.六淫的概念concept of six pathogenic factors;,,六淫致病的共同特点the general pathogenic characters of six pathogenic factors;六淫各自的性质与致病特点nature, pathogenic characters and main clinic manifestations of every six pathogenic factors(including wind, cold,Summer-heat,Dampness,Dryness,Heat (fire))风Wind其性开泄,易袭阳位Wind tend to float, disperse, go upward attack the upper and outside parts风性善行而数变wind tends to move and change风为百病之长,易夹杂其他外感之邪Wind tends to be complicated by other pathogenic factors寒Cold易伤阳气Cold tends to impair yang寒性凝滞Cold tends to coagulate寒性收引Cold tends to contract暑Summer-heat其性炎热Summer-heat is hot暑性升散,耗气伤津Summer-heat tends to disperse and elevate,consume the qi and body fluid暑多夹湿Summer-heat often complicated by dampness湿Dampness湿性重浊dampness is heavy and turbid湿易阻遏气机dampness tends to block qi湿性黏滞dampness is sticky and stagnant湿性趋下, 易袭阴位dampness tends to move downward,attack the lower and inside parts燥Dryness燥易伤津Dryness consume the body fluid燥性干涩Dryness is xerotic and unsmooth燥易伤肺Dryness tends to impair the lung火Heat (fire)其性炎上Heat(fire) tends to flame up易伤津耗气Heat(fire) tends to consume qi and impair body fluid易生风动血Heat(fire) tends to produce wind and disturb blood易致肿疡Heat(fire) tends to cause swelling and ulceration七情内伤的概念、The concept of internal impairment due to the seven emotions,七情致病的特点the pathogenic characters of the seven emotions痰饮、瘀血的概念、形成及致病特点The basic concept, the formation and the pathogenic characteristics of phlegm ,rheum and blood stasis痰饮phlegm ,rheum 瘀血blood stasis发病的基本原理The pathogenesis of occurrence of disease in TCM病机的概念,The concept of mechanism of pathological changes;病机the mechanism of pathological changes;邪正盛衰predomination and decline of pathogenic factors and healthy qi;阴阳失调imbalance between yin and yang;气血津液失常disorder of qi, blood and body fluid.第四章中医诊断疾病的方法中医诊法The concept of the TCM diagnostic methods中医诊断的理论依据the theory foundation of the TCM diagnostic methods.望神Inspection of spirit, 望色Inspection of complexion, 望排出物Inspection of excreta ,望舌Inspection of tongue,Existence of spirit (得神),Lack of spirit(少神),Loss of spirit (失神)False spirit(假神)Normal complexion 常色Morbid complexion 病色Red colour ,White colour ,Yellow colour, Bluish colour,Blackish colour临床意义clinical significance ;望舌的方法Methods for inspection of tongue问诊inquiry, 主诉chief complaint, 病史history of present illness问现在症inquiry of the present symptomsAversion to cold and fever(恶寒发热)Cold sensation without fever(但寒不热)Fever without cold sensation(但热不寒)Alternate cold and fever(寒热往来)诊脉的部位与方法The Regions and methods for taking pulse脉诊taking pulse, 正常脉象normal pulseCunkou(寸口)cun(寸), guan(关),chi(尺).辨证的概念The concept of differentiation of syndrome表里辨证External and internal differentiation of syndromes,表证External syndromes,里证internal syndromes,寒热辨证cold and heat differentiation of syndromes,寒证cold f syndromes,热证heat syndromes,虚实辨证asthenia and sthenia differentiation of Syndromes,虚证asthenia Syndromes,实证sthenia Syndromes,临床特点clinical character and difference.八纲辨证Syndromes differentiation with eight principles气血津液辨证syndrome differentiation with qi, blood and body fluid,第五章中医学的防治原则治则therapeutic principles , 治法therapeutic methods正治Routine treatment , 反治Contrary treatment,治本treat “ben”(deal with the root cause)治标Treating biao(acute symptoms bring on great suffering to the patients, or threaten life or tend to transmit and change) in emergency ,扶正与祛邪Strengthening healthy qi and eliminating pathogenic factors,调整阴阳Regulation of yin and yang,三因制宜Abidance by individuality, locality and seasons.第六章中药基本知识中药Chinese Medicinal Herbs四气four properties、五味five flavors、升降浮沉the action of lifting, lowering, floating and sinking,、归经channel tropism、毒性toxicity中药的配伍、用药禁忌Contraindication and Compatibility of Chinese Medicinal Herbs中药的剂量Dosage of Chinese Medicinal Herbs第七章方剂基本知识方剂的组成原则The principle of the composition of prescriptions,组成变化the modification of the composition of a prescription.方剂的组成、用法、功效、临床应用、方解:Ingredients, administration, function,clinical application and elucidation of the prescriptions下列方剂的组成、用法、功效、应用、方解:银翘散、平胃散、藿香正气散、大承气汤、大黄附子汤第二章中医学的生理观第三节经络经络the meridians;十二经脉twelve regular meridians十二经脉走向与交接规律direction, joint law of the twelve channels、十二经脉循行分布规律distributing law of the twelve channels ,十二经脉表里络属关系exterior-interior relationship of the twelve channels ,十二经脉流注方向和次序等flowing direction and order of the twelve channels;第八章针灸学基本知识第二节刺灸方法刺法(针法)Acupuncture techniques; 进针Needling methods (insertion methods, Needling manipulation methods)得气arrival of Qi针刺意外和防治处理Management of possible accidents (emphasize 晕针fainting) 灸法moxibustion,第八章针灸学基本知识第一节腧穴腧穴概念;腧穴分类;腧穴定位方法;腧穴功效the points (definition, classification, location method, function)腧穴的定位、归经、基本主治功能:location, channel tropism and the basic special treatment function下列腧穴的定位、基本主治功能:手太阴肺经:列缺;手阳明大肠经:合谷、曲池;足阳明胃经:足三里;足太阴脾经:三阴交;手少阴心经:神门;手太阳小肠经:听宫;足太阳膀胱经:委中;足少阴肾经:涌泉;手厥阴心包经:内关;手少阳三焦经:外关;足少阳胆经:风池、阳陵泉;足厥阴肝经:太冲;任脉:关元、膻中;督脉:大椎、人中;经外奇穴:印堂、太阳;。
中医助理医师英语1.针灸:acupuncture2.中药:traditional Chinese medicine3.脉搏:pulse4.草药:herbal medicine5.推拿:tuina massage6.肾炎:nephritis7.保健:healthcare8.疫苗:vaccine9.气虚:qi deficiency10.经络:meridians11.针刺:needle insertion12.风湿病:rheumatism13.保健品:health supplements14.病因:etiology15.神经病:neurosis16.足三里穴:ST36 acupuncture point17.血糖:blood sugar18.强直性脊柱炎:ankylosing spondylitis19.中枢神经系统:central nervous system20.腰椎间盘突出:lumbar disc herniation21.血压:blood pressure22.病理:pathology23.肝炎:hepatitis24.手法:manipulation techniques25.心血管疾病:cardiovascular diseases26.中医诊断:traditional Chinese medicine diagnosis27.骨质疏松症:osteoporosis28.腹心肌梗塞:acute myocardial infarction29.推拿师:tuina therapist1. Acupuncture is commonly used in traditional Chinese medicine.2. Traditional Chinese medicine involves the use ofherbal medicine.3. The TCM practitioner checked the patient's pulse.4. Herbal medicine is prescribed to patients with various ailments.5. Tuina massage can help relieve muscle tension and pain.6. Nephritis is a common kidney disease treated in TCM.7. Healthcare plays an important role in maintaining overall well-being.8. Vaccines are used to prevent various diseases.9. Qi deficiency is a common condition treated in TCM.10. Meridians are the pathways through which energy flows in the body.11. Needle insertion is a technique used in acupuncture.12. Rheumatism is a chronic condition often treated in TCM.13. Health supplements can support overall health andwell-being.14. Etiology refers to the cause or origin of a disease.15. Neurosis is a psychological disorder treated in TCM.16. ST36 acupuncture point is commonly used for various conditions.17. Blood sugar levels are monitored in patients with diabetes.18. Ankylosing spondylitis is a type of rheumatic disease.19. The central nervous system is responsible for controlling bodily functions.20. Lumbar disc herniation is a common condition treated in TCM.21. Blood pressure is an important indicator of cardiovascular health.22. Pathology is the study of diseases and their effects on the body.23. Hepatitis is a liver disease treated in TCM.24. TCM practitioners use various manipulation techniques during treatment.25. Cardiovascular diseases are a major health concern worldwide.26. TCM diagnosis involves a comprehensive analysis of symptoms and medical history.27. Osteoporosis is a condition characterized by weak bones.28. Acute myocardial infarction is a medical emergency, often treated in TCM.29. A tuina therapist specializes in tuina massage techniques.。
中医术语英文大全以下是一些常见的中医术语及其对应的英文译名:1. 中医 (Traditional Chinese Medicine)2. 针灸 (Acupuncture and Moxibustion)3. 按摩 (Massage)4. 草药 (Herbal Medicine)5. 中药 (Traditional Chinese Medicine)6. 推拿 (Tuina)7. 食疗 (Diet Therapy)8. 气功 (Qigong)9. 气血 (Qi and Blood)10. 经络 (Meridians)11. 寒热 (Cold and Heat)12. 脉象 (Pulse Diagnosis)13. 五行 (Five Elements)14. 通脉散结 (Promoting Qi Circulation and Resolving Stagnation)15. 疏肝理气 (Soothing the Liver and Regulating Qi)16. 补肾固本 (Tonifying the Kidneys and Strengthening the Essence)17. 温阳散寒 (Warming Yang and Dispelling Cold)18. 疏风清热 (Dispelling Wind and Clearing Heat)19. 透疹退湿 (Promoting Eruption and Resolving Dampness)20. 润肺止咳 (Moistening the Lungs and Stopping Cough)这只是一小部分中医术语的英文译名,由于中医涉及的领域广泛且复杂,还有许多其他的中医术语没有在列表中列出。
术语翻译1.traditional Chinese medicine; TCM2.basic theory of traditional Chinese medicine3.clinical experience4.treatment based on syndrome differentiation5.miscellaneous diseases6.Chinese pharmacy7.four properties and five tastes8.acupuncture and moxibustion; acumox9.classical Chinese philosophy10.sweating therapy; diaphoresis11.purgation12.vomiting therapy; emetic therapy13.the School of Reinforcing the Earth14.etiology15.prescription; formula16.medical practice17.therapeutic principles18.herbs cold and cool in nature19.nourishing yin and reducing fire20.diseases caused by blood stasis1.five zang-organs; five zang-viscera2.six fu-organs3.system of meridians and collaterals4.holismanic wholeness6.social attribute7.(of the five zang-organs) open into8.sprout, grow, transform, ripen and store9.diagnostics10.relationship between pathogenic factors and healthy qi11.therapeuticsmon cold due to wind and cold13.different therapeutic methods used to treat the same disease14.the same therapeutic method used to treat different diseases15.balance of water metabolism16.clearing away heart fire17.nature of disease18.treating the left side for curing diseases located on the right side19.drawing yang from yin20.treating the lower part for curing diseases located on the upper part一.术语翻译1.philosophical concept2.mutual transformation3.balance of yin and yang4.transformation between yin and yang5.extreme cold turning into heat6.pathological changes7.absolute predominance8.general rule of pathogenesis9.supplementing what it lacks of10.eliminating wind and dispersing cold11.mutually inhibiting and promoting12.mutually inhibiting and restraining13.interdependence14.excess of yin leading to decline of yang15.contrary and supplementary to each otheranic whole17.impairment of yang involving yin18.deficiency of both yin and yang19.deficiency cold syndromesuppressing yang and eliminating wind第四课术语翻译1.the doctrine of five elements; the theory of five phases2.free development3.to be generated and to generate4.restraint in generation5.Wood is characterized by growing freely and peripherally.6.Earth is characterized by cultivation and reaping.7.Water is characterized by moistening and downward flowing.8.over restriction and counter-restriction9.Wood over restricts earth because it is deficient.10.promotion, restriction, inhibition and transformation11.disorder of a mother-organ involving its child-organ12.insufficiency of essence and blood in the liver and kidney13.blood deficiency in the heart and liver14.exuberant fire in the heart15.insufficiency of liver yin16.declination of kidney yang17.weakness of the spleen and stomach18.soothing the liver and harmonizing the stomach19.insufficiency of kidney yin20.imbalance between water and fire术语翻译1.doctrine of visceral manifestations2.five zang-organs and six fu-organs3.extraordinary fu-organs4.nutrients of water and food5.transmitting and transforming water and food6.storing essence7.internal and external relationship8.therapeutic effects9.clinical practice10.storage without discharge11.discharge without storage12.physical build and various orifices13.(of five zang-organs) open into14.spirit and emotions15.the heart storing spirit16.the lung storing corporeal soul17.the liver storing ethereal soul18.the spleen storing consciousness19.the kidney storing will20.the luster manifesting upon the face第六课术语翻译1.the heart governing blood and vessels2.sufficiency of heart qi3.rosy complexion4.sufficiency of blood5.unsmooth vessels6.lusterless complexion7.thin and weak pulse8.the heart storing spirit9.sweat and blood sharing the same origin10.ascending, descending, going out and going in11.dispersion, purification and descent12.regulating water passage13.the spleen governing transportation and transformation14.nutrients of water and food15.stoppage of water and fluid16.acquired base of life17.regulating qi activity18.upward adverse flow of liver qi19.innate essence20.the kidney receiving qi一.术语翻译1.extraordinary fu-organs2.isolated fu-organ3.digest water and food4.anus5.remaining part of liver qi6.upper energizer7.separating the lucid from the turbid8.residue of foods9.The large intestine governs thin body fluid10.bile11.The small intestine governs thick body fluid12.primary digestion13.essential qi14.the seven important portals15.The gallbladder is responsible for making judgment16.discharge waste17.occurrence of menstruation18.epiglottis19.morphological hollowness20.transporting and transforming water and food第八课术语翻译1.innateness2.nutrients; refined substance3.blood circulation4.water metabolism5.way of qi movement6.ascending, descending, exiting and entering movements of qi7.normal function of qi activity8.primary motive force of life9.warming and nourishing the viscera10.qi of the viscera and meridians11.qi activity12.qi transformation13.innate qi14.acquired qi15.healthy qi16.pathogenic factors17.primordial qi18.thoracic qi19.nutritive qi20.defensive qi术语翻译1.qi promoting the production of blood2.qi promoting the flow of blood3.qi commanding blood4.blood carrying qi5.blood generating qi6.qi promoting the production of body fluid7.qi promoting the flow of body fluid8.qi commanding body fluid9.body fluid carrying qi10.body fluid generating qi11.body fluid and blood sharing the same origin12.exhaustion of qi due to loss of body fluid13.exhaustion of qi due to hemorrhage14.loss of qi due to profuse sweating15.Normal flow of qi ensures normal flow of blood while stagnation of qi causes stagnation ofblood.16.Qi commands the blood and the blood carries qi.17.Normal flow of qi ensures normal flow of body fluid while stagnation of qi causes stagnationof body fluid.18.nourishing qi to stop collapse19.Sweating therapy should be not be used to treat patients suffering from hemorrhage.20.Sweating therapy should not be used to treat hemorrhage.第十课术语翻译1.theory of meridians and collaterals2.system of meridians and collaterals3.transporting qi and blood to the whole body4.being connected with the viscera and limbs5.running routes6.twelve regular meridians7.the regions through or along which the meridians run and the order by which the meridiansare connected with each other8.(of a collateral) pertaining to a certain meridian9.eight extraordinary vessels (meridians)10.branches of the twelve regular meridians11.divergent collaterals12.skin divisions of the twelve regular meridians13.tendons of the twelve regular meridians14.qi of meridians15.syndrome differentiation of meridians and collaterals16.meridian conduction17.meridian manifestations18.blockage of meridians19.soothing meridians and activating collaterals20.collateral pricking and cupping therapy。
中医基本名词术语中英对照国际标准一、介绍在讨论中医基本名词术语的中英对照国际标准之前,我们需要先了解一下中医的基本概念。
中医是我国传统的医学体系,其理论基础包括阴阳学说、五行学说、气血理论等。
中医强调整体观念,注重防治和调理,因此在临床实践中有着丰富的实践经验和独特的治疗方法。
二、中医基本名词术语中英对照国际标准1. Yin and Yang - 阴阳在中医理论中,阴阳是最基本的概念之一。
阴阳学说是一种辩证法,用来分析和描述事物的相对、对立和统一的关系。
阴阳不仅可以用来说明自然界和生命体的结构和运动规律,还可以用来分析和指导临床诊疗。
2. Five Elements - 五行五行学说是我国古代哲学的重要组成部分,也是中医学理论的重要组成部分。
五行学说包括金、木、水、火、土五种元素,它们之间相互克制、相生相克,体现了自然界万物之间的相互作用和联系,也被运用到了中医的临床实践中。
3. Qi and Blood - 气血气血是中医理论中的重要概念,它们是人体内最基本的物质和能量。
气血的流通和运动对人体的生命活动起着至关重要的作用。
在中医临床中,调理气血的平衡是维护健康的重要手段之一。
4. Meridian - 经络经络是中医理论中的重要概念,是人体内气血运行的通道。
中医认为,经络是连接脏腑、肢体、头面等各个部位的通道,它们的畅通与否对身体的健康起着至关重要的作用。
在中医临床中,针灸、推拿等手法的应用就是通过调理经络来治疗疾病。
5. Acupuncture - 针灸针灸是中医的重要治疗方法之一。
通过刺激人体特定穴位,调节气血运行,达到治疗疾病的目的。
针灸不仅在我国传统医学中有着悠久的历史,也受到了世界各国的广泛关注和认可。
6. Herbal Medicine - 中药中药是中医药的主要表现形式之一,利用植物、矿物、动物等天然药材制成,具有独特的药理作用。
中药以其独特的疗效和较低的副作用,在临床应用中发挥着不可替代的作用。
矿产资源开发利用方案编写内容要求及审查大纲
矿产资源开发利用方案编写内容要求及《矿产资源开发利用方案》审查大纲一、概述
㈠矿区位置、隶属关系和企业性质。
如为改扩建矿山, 应说明矿山现状、
特点及存在的主要问题。
㈡编制依据
(1简述项目前期工作进展情况及与有关方面对项目的意向性协议情况。
(2 列出开发利用方案编制所依据的主要基础性资料的名称。
如经储量管理部门认定的矿区地质勘探报告、选矿试验报告、加工利用试验报告、工程地质初评资料、矿区水文资料和供水资料等。
对改、扩建矿山应有生产实际资料, 如矿山总平面现状图、矿床开拓系统图、采场现状图和主要采选设备清单等。
二、矿产品需求现状和预测
㈠该矿产在国内需求情况和市场供应情况
1、矿产品现状及加工利用趋向。
2、国内近、远期的需求量及主要销向预测。
㈡产品价格分析
1、国内矿产品价格现状。
2、矿产品价格稳定性及变化趋势。
三、矿产资源概况
㈠矿区总体概况
1、矿区总体规划情况。
2、矿区矿产资源概况。
3、该设计与矿区总体开发的关系。
㈡该设计项目的资源概况
1、矿床地质及构造特征。
2、矿床开采技术条件及水文地质条件。