
被动语态用法详解
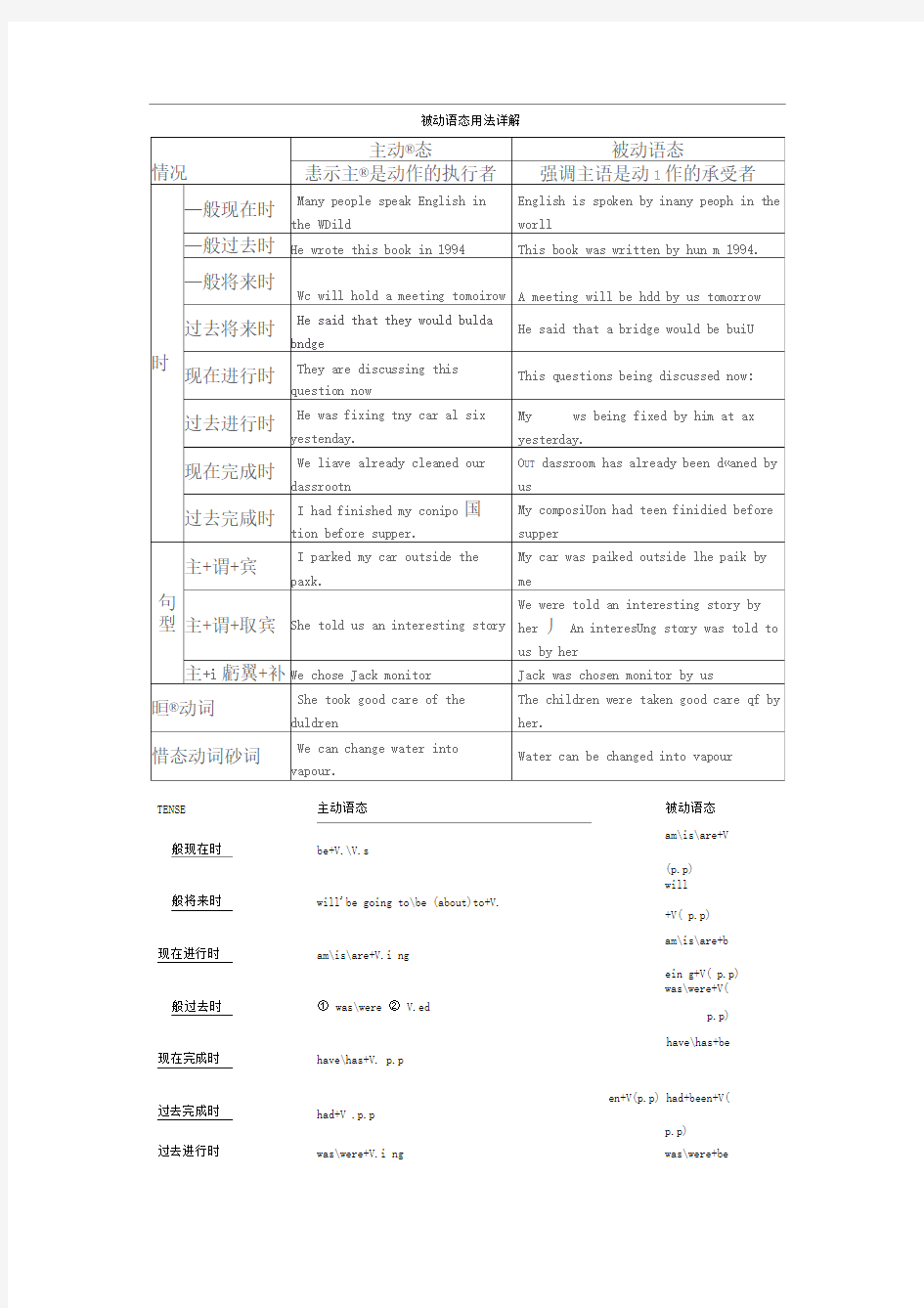
TENSE
般现在时
般将来时现在进行时般过去时现在完成时过去完成时过去进行时主动语态被动语态
am\is\are+V be+V.\V.s
(p.p)
will
will'be going to\be (about)to+V.
+V( p.p)
am\is\are+b am\is\are+V.i ng
ein g+V( p.p) ① was\were ② V.ed
was\were+V(
p.p)
have\has+be have\has+V. p.p
en+V(p.p) had+been+V( had+V .p.p
p.p)
was\were+V.i ng was\were+be
情态动词 情态动词+V.
in g+V ( p.p )
情态动词
被动语态牢记一点,
+be+V ( p.p ) be 加动词过去分词。 分析句中主和谓, 承受者作主语即被动。 短语动词不可忘介、 副词。 另有不及物动词, 只有主动无被动。 还要注意其时态, 与主动语态全相同。 不用被动语态的情况 (即多数的瞬间动词): 亡) ,disaPPear (消失),end (vi. 结束),fail, happen, last, lie, asleep, keep silenee, lose heart, take place. 比较: rise, fall, happen 1)不及物动词或动词短语无被动语态 app ear, die (死
rema in, sit, sp read, break out, come true, fall After the fire, very little rema ined of my house.
是不及物动词;raise, seat 是及物动词。 (错)The accident was happened last week. (对)The accident happened last week.
要想正确地使用被动语态,就须注意哪些动词是及物的, 哪些是不及物的。特别是一词 多义的动词往往有两种用法。解决这一问题唯有在学习过程中多留意积累。 2) 不能用于被动语态的及物动词或动词短语 :
wish, cost, notice, watch agree with, arrive at suffer from, happen to, take part in, walk in to, bel ong to the lock. 3) 系动词无被动语态(“ keep ”除外): grow, look, remain, seem, smell, sound, stay, taste, turn It sounds good. 4) 带同源宾语的及物动词,反身代词,相互代词, live, life She dreamed a bad dream last ni ght. 5) 当宾语是不定式时,很少用于被动语态。 (对)She likes to swim.
(错)To swim is liked by her. sta nd fit, have, hold, marry, own, / in, shake hands with, succeed in, This key just fits appear, be become, fall, feel, get, 不能用于被动语态:die, death, dream, 有些动词可以带双宾语。在这种情况下, 有些动词可以带双宾语 在用于被动结构时, 主动结构中的间接宾语变为主语时,直接宾语仍然保留在谓语后面;直接宾语变为主语时, 间接宾语前通常加上介词 for/to, etc. 。 即: S+V+0+D3 I0+ be done +D3 DO be done + prep. + 10 We often hear him play guitar Heis often heard
td
1]
play guitar.
T It is often heard from him to play guitar.
新被动语态
Get+过去分词也可以构成被动语态,用这种结构的句子侧重于动作的结果而不是动作本
怎样把主动语态改成被动语态? 把主动语态改为被动语态非常简单,
1. 将主动语态的宾语作被动语态的主
语;
2. 谓语动词变为“be+及物动词的过去分词”,并通过be 的变化来表达出不同的时态;
3. 主动语态的主语变为介词“ by ”的宾语,组成介词短语放在被动结构中的谓语动词 之后。(有时
“ by ”的短语可以省略);
例: 1. Bruce writes a letter every week. week.
被动语态的几种特殊用法
(1)主动形式表示被动意义
1) 常见的这类动词有:“ act , add up , clean , compare , count , cook , draw , fill iron , keep , let , look , make up , milk , kill , open , photograph , smoke, spoil ”等。
The window won ' t open .(这扇窗户打不开。 The cow milks well .(这头牛出奶率很高。 Damp wood will not fire .(湿木不易燃烧。
It turned out fine that day
.(结果那天天气很好。
)
How did his coat catch on a n ail?(
他的衣服怎么钩到钉子上了
2) 实用动词“ need /want /deserve / require +V-ing ( 动名词)” My hair n eeds cutt ing 。.
The bike wants rep airi ng It doesn ‘ t deserve mentioning
Hamlet is required readi ng for the course 3) 一些固定句型如:"be worth doing sth un der (i n )+抽象名词等表示被动意义:
身。如:The mangot hurt on his way home.那个男人在回家的路上受伤了。 glass get broke n? 杯子怎么破了? 注意: 有些动词后跟不带to 的不定式作宾语补足语,但改为被动结构后要加上“ Weheard him sing in his room just now. 刚才听到他在房间中唱歌。 now. ---He was heard to si ng in n eed doing someth ing
也表示被动
How did the
to ”。例如 his room just
可以遵循以下几个步骤:
T A letter is written by Bruce every
2. Li Lei men ded the broke n bike this morning. Li Lei this morni ng.
3. He has writte n two no vels so far. far.
4. They will plant ten trees tomorrow. tomorrow.
5. Lucy is writi ng a letter now.
6. You must lock the door when you
T The broke n bike was men ded by
T Two no vels have bee n writte n by him so
T Ten trees will be plan ted by them
T A letter is being writte n by Lucy now. leave. T the door must be locked when you leave.
prove ,read ,sell ,
?)
形式表示被动意义。 .(《哈姆雷特》为本课程指定读物。 )
. have/get sth . (sb.)done",以及 to be
Beiji ng is a big city in Chi na and worth visit ing
值得浏览。)
Mr. . Wils on had his wallet stole n the day before yesterday 丢了一个钱包)。 The bike is under (in )repair .(自行车正在修理中。) This tape recorder is in use
.(这种录音机正在使用中。
)
4) 一些不定式的主动态表示被动意义:
①There be 句型:
There are a lot of things to do . There is nothing to worry about
.
②不定式修饰want, have 等动词的宾语,而句中的主语同时又不是不定式的逻辑主语 时:
I want some clothes to wash .
Do you have anything to say for yourself?
③不定式修饰buy , get , give 等动词的直接宾语,而句中的间接宾语又是不定式的逻 辑主语时:
);It is believed that" …(据信);It is reported
…(人们希望);It is gen erally con sidered that" …
…(由此可以看出);It must be admitted that …(必 …(必须指
出)”等。
/ thought that this medici ne works well
.
It is estimated that a flight to Shan ghai would take more tha n one hour .
It is ofte n realized that wome n held a high social p ositi on in the Souther n European societies in the 10th and llth cen turies
.
(3) “get + p.p.( 动词的过去分词)"表示被动:
这种结构往往用来强调动作的结果, 也可用来表示突然发生的事态, 或最终出现的某种
事实,是一种非正式语体。
The house is getti ng pain ted / rep aired . The buildi ng got damaged in the flood .
Thousa nds of soldiers got killed in the war . As I p assed by, my coat got caught on a n ail .
[注]在下列句子中,不能使用“
get + p.p.(
动词的过去分词)”结构。
.(北京是中国的一个大城市,
.(威尔逊先生前天 His sister gave him a bike to ride .
My father get me a book to read . 5)少数动词的进行时,有时表示被动意义 :
Her works are prin ti ng The drum is beati ng My new house is build ing (2) “It is+V-ed+that-??"
结构表示被动
常用的这类结构有:"it is said that …”(据说);It is supposed that …(据推测); It is well known that"
…(众所周知
that"…(据报导);It is hoped that" (有人认为);1twill be seen that" 须承认);It must be pointed out that
It is believed
误:The stow got written by him . 正: The story Was writ . ten by him .
误: 正: The conference got being held in London The conference is being held in London
注意以下被动语态的几种情况
⑷
1)短语动词变为被动语态后,其后的介词或副词应紧随其后。 Frank was brought up by his aunt The babies are well looked after .
The meeti ng Was put off . The salesma n was put out by Mr.
. Wils on ‘ s questio n
(威尔逊先生的问题把那位售货员惹火了。
)
2) “Verb+宾语+宾补”变为被动语态后,宾语转化为主语,宾补转化为主补。 The wall Was pain ted white
. (We pain ted the wal1 white .)
He is regarded as smart (We regarded him as smart .)
The house was found empty . (We found the house empty .)
1 〃
表现在的或 一般的能力:
can 或 be able to , can 比 be able to 使用得更普遍。can
able to 更强调通过努力、克服困难做成呆事。 for
itself ; it must be
told
what to do.
sr of En glish
sp eak En glish
quite well.
考点一: 情态动词表示能力 表示现在的或一般的能力用 侧重指有能力做某事;而 be A computer can't think He is a native speake so he can of course 2〃表示将来的能力: 表示将来能力用 will be If you have a good you will be able to
道题。 3〃表示过去的能力: could 表示过去一般的能力,即不表示做或未做某事;而 示过去有能力并且成功地 man aged to do someth in g/succeeded in doing
考点二: 情态动词表示推测(可能性) 可能性可分为客观的(理论的)可能性和具体事情实际发生的可能性。 1〃客观的(理论的)可能性指并不涉及具体某事是否会发生,此种用法常常可以说明人或事 物的特征。can 用于肯定句中表示客观的(理论的)可能性,can 用于疑问及否定句中则表示 实际发生的可能性。 The World Wide Web able slee p work
to 。
out this P roblem.
如果你睡个好觉,你就能做出这
was (were) able to do 贝 U 表 了 某事,相当于 something 。 because it
A left-luggage t can be office is sometimes jok in gly called the World Wide Wait very slow.
is a p lace where bags can be left for a shor time , especially 2〃表示具体事情实际发生的可能性: 表示具体事情实际发生的可能性的层次比较见下表 in a railway stati on. (依次递减):
这些词后接动词原形是对现在事情的推测,后接完成式则表示对过去事情的推测;其中can,may/might,should,ought to,must有时还可接进行时表示对现在正在进行的事情的推测。
另外,can还可用于否定句、疑问句或感叹句中,表示疑惑、惊讶或不相信等意思;
既可用于肯定句又可用于否定句、疑问句中;ought
示过去,而表示可能性弱于他们相应的现在时形式。
She might not be in the company .She told
ai.
她可能不在公司,她告诉过我要去上海。
去武汉了吗?
What can he be doing at 么?She can't be telling
Your mother may be waiting
回家呢。
They must be follow ing us
远处尾随着我们。
You should be doing your
作业而不是看电视。
考点三:情态动词表示请求、允许、允诺
1 〃表示征求对方的意见或提出建议时,would用于第二人称的疑问句。Will(Would)you( pl ease) . ..?
—What's the
—Khulaifi.Shall 而could
to和might表示推测时,并不一定表me she would go to Shangh
this
a
for
lie. just Can he have gone to Wuhan?他有可能
mome nt?
. 她不可能在说谎。you to return home. 他会在做什
你妈妈可能正等着你
exercises
n ame?
I spell that little beh ind us. 他们肯定在离我们不in stead of
可以用于第一、
shall
分别构成:Shall 2 〃could/would
watchi ng TV. 现在你该做
第三人称的疑问句,will和
I/we/he/she/they... ? 或
for you?
可以用于疑问句表示请求,使语气更加委婉,但其回答语不能再用
初中英语情态动词用法详解 【情态动词知识梳理】 情态动词有具体的词义,但也同助动词一样,需要与其他词语一起构成句子的谓语,另外情态动词没有人称和数的变化,情态动词后必须跟动词原形。 考点一:can,may,must等情态动词在陈述句中的用法: 1. can的用法: (1).表示能力、许可、可能性。表示能力时一般译为“能、会”,即有种能力,尤其是生来具备的能力,此时may和must均不可代替它。如:She can swim fast, but I can’t . 她能游得很快,但我不能。I can see with my eyes.我用眼睛看。 (2).表示许可,常在口语中。如:You can use my dictionary. 你可以用我的字典。(3).表示推测,意为“可能”,常用于否定句和疑问句中,此时can’t译为“不可能”。如:Can the news be true?这个消息会是真的吗?—Can it be our teacher?那个人有可能是我们老师吗?—No, it can’t be our teacher. He is on a visit to the Great Wal l.不可能。咱们老师正在游览长城呢。 【例题】—I think Miss Gao must be in the library. She said she would go there.—No. She __be there, I have just been there. 【解析】根据下文“我刚去过那儿”可知,应为“不可能”,can’t表示推测[答案] 2. could的用法: (1).can的过去式,意为“能、会”,表示过去的能力。如:He could write poems when he was 10. 他十岁时就会写诗。 (2). could在疑问句中,表示委婉的语气,此时could没有过去式的意思。如:Could you do me 你能帮我个忙吗?—Could I use your pen?我能用一下你的钢笔吗?—Yes, you can.可以。(注意回答) 3. may的用法: (1).表示请求、许可,比can正式,如:May I borrow your bike?我可以借你的自行车吗?You may go home now.现在你可以回家了。 【例题】—_______ I borrow your MP3?—Sure . Here you are. A. May B.Should C.Must D.
初中英语情态动词的基本用法讲解 1. can (could) 1)表示能力,could 主要指过去时间。 Two eyes can see more than one. 两只眼比一只眼看得清。 Could the girl read before she went to school? 这女孩上学前能识字吗? 2)表示可能(理论上或是逻辑判断上)。 The temperature can fall to —60 °C , that is 60 °C below freezing. 气温可降至一60 C,也就是零下60 C。 He can't (couldn't) have enough money for a new car. 他不可能有足够的钱买新车。 You mustn't smoke while you're walking around in the wood. You could start a fire. 在林子里走时勿吸烟,那样可能会引起火灾。 3)表示允许。 Can I have a look at your new pen? 我可以看一看你的新钢笔吗? He asked whether he could take the book out of the reading-room. 他问他可不可以把书带出阅览室。 4)表惊异、怀疑、不相信等态度。主要用于否定句、疑问句或感叹句中。 Where can (could) they have gone to? 他们会去哪儿了呢? He can't (couldn't) be over sixty. 他不可能超过六十岁。 How can you be so careless? 你怎么这么粗心? 5)比较委婉客气地提出问题或陈述看法。 Can (Could) you lend me a hand? 帮我一把好吗? I' m afraid we couldn 't give you an answer today. 恐怕我们今天不能给你答复。 2. may (might) 1)表允许,might 可以指过去时间,也可指现在时间,语气更委婉。 You may take whatever you like. 你喜欢什么就拿什么。 He told me that I might smoke in the room. 他告诉我可以在房间里抽烟。 May (Might) I ask for a photo of your baby? 我可以要一张你宝宝的照片吗? 在回答以may引起的问句时,多避免用这个词,而用其它方式,如Yes, please. / Certainly. / Please don' t ./ You' d better not. / No, you mustn ' t.等,以免显得太严峻或不客气。 2)表可能(事实上)。可以指过去时间,也可以指现在时间,但语气更加不肯定。 He may be at home. 他可能在家。 She may not know about it. 她可能不知道这件事。 He was afraid they might not agree with him. 他担心他们可能不同意他的意见。 They might be having a meeting, but I ' m not sure. 他们有可能在开会,不过我不肯定。 3. must 1)表示义务。意为“必须” (主观意志)。 We must do everything step by step. 我们一切都必须循序渐进地做。 You mustn' t talk to her like that. 你不可能那样对她说话。 --Must we hand in our exercise —books now? 我们现在就要交练习本吗? --No, you needn' t. / No, you don' t have to. 不必。(这种情况下,一般不用mustn' t)2)表示揣测。意为“想必、准是、一定”等,只用于肯定句。
情态动词must用法详解 (1) 表示“必须” 此时可用于肯定句、否定句或疑问句,用于否定句时,mustn’t的意思是“一定不要”“不能”,而不表示“不必”。如: Water must be pure if it is to be drunk. 水如供饮用必须净化。 Must I finish the work tonight? 我必须今晚完成这项工作吗? Adverbs mustn’t be put between the verb and the object. 副词不能放在动词和宾语之间。 must主要表示现在或将来,但在间接引语中也可表过去(=had to)。如: She asked her boss if she must (had to) work overtime. 她请示上司她是否要加班。 对于must开头的一般疑问句,若作否定回答,可以用needn’t,不能用mustn’t。如:“Must I clean all the rooms?” “No, you needn’t.” “这些房间我都得清扫吗?”“不必。” (2) 表示推测 意为“准是”“一定是”,通常只用于肯定句。若用于否定句或疑问句,则用can 代之。如: That can’t be the only way. There must be other ways of solving the problem. 那不可能是解决问题的唯一办法,肯定有另外的办法。 Jane’s light is on. She must be at home. She can’t be out. 简的房间里开着灯。她一定在家,不会出去的。 若要谈论过去或完成的情况,必须用“must+have+过去分词”。如: You must have mistaken my intention. 你一定是误会了我的意图。 She must have been very young when she got married. 她结婚时一定很年轻。 He must have come this way; here are his footprints. 他一定是走这条路来的,这里还有他的脚印呢。 They must have finished their homework, for they are playing happily on the playground. 他们一定是写完作业了,他们在操场上玩得多开心呢。 (3) 表示“偏偏” 有时must可表示某事发生得不早不迟,就在某个当紧的时候,多指某些不受欢迎的事情的发生。如: The car must break down just we were starting our holidays. 我们刚刚开始休假,汽车偏偏坏了。 Must you worry her with questions, just when she is busy cooking dinner? 她正忙着做饭你干吗偏偏问她问题? Just when I was busy, the neighbor must come and chatter. 正当我忙碌的时候,邻居偏偏过来聊天。 有时还可指主观上的偏执或固执,常可译为“偏”“偏要”。如: After I gave her my advice,she must go and do the opposite. 在我给她出主意之后她偏要反着干。 Must you make so much noise? 你就非得弄出这么大的声音吗? (4) must 与have to 的区别 两者都表示“必须”,但must 侧重于说话者的主观看法,认为有必要或有义务去做某事;have to 则重于客观需要,含有“不得不”“被迫”之意。如: Everyone must keep the law. 人人都要守法。 The last train has gone. We’ll have to walk home. 最后一班车已经开了,我们得走回家了。
c a n与c o u l d的用法详解及情态动词有关习题 Company Document number:WTUT-WT88Y-W8BBGB-BWYTT-19998
can与could的用法详解 一、表示能力 (1)表示现在的能力,用can: My sister can drive. 我妹妹会开车。 Everyone here can speak English. 这儿人人会说英语。 (2)表示将来的能力,通常不用can或could,而用be able to的将来时态: I’ll be able to speak French in another few months. 再过几个月我就会讲法语了。 One day people will be able to go to the moon on holiday. 总有一天人们可以到月球上去度假。 但是,若表示现在决定将来是否有能力做某事,则可用 can: Can you come to the party tomorrow 你明天能来参加我们的聚会吗 (3)表示过去的能力,有时可用could,有时不能用could,具体应注意以下几点: ①若表示过去一般的能力(即想做某事就随时可做某事的能力),可用could: Could you speak English then 那时候你会说英语吗 ②若表示过去的特定能力(即在过去特定场合做某事的能力),则不能用could,而用w as (were) able to do sth,或用 managed to do sth,或用 succeeded in doing sth 等。 He studied hard and was able to pass the exam. 他学习很努力,所以考试能及格。 At last he succeeded in solving the problem. 他终于把那个问题解决了。 【注】could 不用来表示过去特定能力通常只限于肯定句,否定句或疑问句中,它则可以表示过去特定的能力: I managed to find the street, but I couldn’t find her house. 我想法找到了那条街,但没找到她的房子。(前句为肯定句用managed to,不用could,后句为否定句,可用could)另外,could还可与表示感知的动词(如see, hear, smell, taste, feel, understand等)连用表示的特定能力: Looking down from the plane, we could see lights on the runway. 从飞机上向下看,我们可以看见机场跑道上的点点灯火。 还有在中,could也可表示: He said he could see me next week. 他说他下周能见我。 二、表示许可 (1)对于现在或将来的“许可”,要区分以下两种情况: ①表示(即请求别人允许自己做某事),两者均可用,但用could 语气更委婉: Can [Could] I come in 我可以进来吗
英语情态动词用法总结(完整) 一、单项选择情态动词 1.--- Difficulties always go with me! --- Cheer up! If God closes door in front of you, there be a window opened for you. A.must B.would C.could D.can 【答案】A 【解析】 【详解】 考查情态动词辨析。句意:——困难总是伴随着我!——高兴点! 如果上帝在你面前关上了门,一定有一扇窗户为你打开。A. must必须;B. would将要;C. could能,会;D. can能,会。must表示对现在的状态推测时,意为“一定”,表示可能性很大的推测。符合语境。故选A。 【点睛】 1) must用在肯定句中表示较有把握的推测,意为"一定"。 2) must表对现在的状态或现在正发生的事情的推测时, must 后面通常接系动词be 的原形或行为动词的进行式。 3) must 表示对已发生的事情的推测时,must 要接完成式。 4) must表示对过去某时正发生的事情的推测,must 后面要接完成进行式。 5) 否定推测用can't。 本句中的。must表示对现在的状态推测时,意为一定,表示可能性很大的推测。符合第2点用法。 2.Paul did a great job in the speech contest. He many times last week. A.need have practised B.might practise C.must have practised D.could practise 【答案】C 【解析】 【详解】 考查情态动词。句意:保罗在演讲比赛中表现得很好。他上星期一定练习了很多次。must have done是对过去发生的动作最有把握的猜测,意思是“一定”。故C选项正确。 3.He is a bad-tempered fellow, but he ________ be quite charming when he wishes. A.shall B.should C.can D.must 【答案】C 【解析】 【详解】 考查情态动词辨析。句意:他是个脾气不好的家伙,但当他希望自己有魅力的时候,他可
中考英语专题练习-含情态动词的被动语态(含解析) 一、单选题 1.-- When should I hand in my paper? -- Your paper must as soon as the bell . A. hand in; rings B. hand in; will ring C. be handed in; rings 2.Which things ______ by common people to protect the environment? A. can be B. can do C. can be done D. can be do 3.Children to watch thrillers. They may have a bad influence on children. A. shouldn't allow B. should allow C. shouldn't be allowed D. should be allowed 4.Your bedroom is so dirty, It should every day. A. clean B. is cleaned C. cleans D. be cleaned 5.Waste paper everywhere. It's our duty to keep the school clean. A. throws B. are thrown C. shouldn't be thrown 6.—It's difficult for village children to cross the river to school. —I think a bridge _________ over the river. A. should be built B. will build C. is built D. was built 7.Don't put off today's work for tomorrow. I mean, today's work______ today. A. may do B. must do C. may be done D. must be done 8.People who drink wine ____________ to drive after May Day. A. don't allow B. isn't allowed C. mustn't allow D. mustn't be allowed 9.It's difficult for the village children to cross the river to get to school. We think a bridge________ over the river A. was built B. should be built C. has been built D. is being built 10.Things should ________ here before you enter the library. A. keeps B. are kept C. be kept D. keep 11.The robot needs _______ once a month. And we will check it for you for free. A. to check B. checked C. checking D. to checking 12.The young mothers are told little kids can't ___________ alone at home. A. leave B. to leave C. left D. be left 13.The television ________. It doesn't work now. A. must be repaired B. was repairing C. must repair D. has repaired 14.Don't put off today's work till tomorrow. I mean, today's work today. A. must be done B. must do C. may be done 15.—Can I my hair colored, Mom? —No. As a student, you ________ do that. A. let; are allowed to B. got; should be allowed to C. get;may not D. get; shouldn't be allowed to
初一英语:情态动词can-must-may的用法
————————————————————————————————作者:————————————————————————————————日期:
学员编号:年级:初一课时数及课时进度:学员姓名:辅导科目:英语学科教师: 学科组长/带头人签名及 日期 课题情态动词 授课时间:备课时间: 情态动词can,must,may的用法 教学目标 掌握三个情态动词的用法 重点、难点 掌握情态动词的用法并能灵活运用 考点及考试要求 教学内容 Step 1: homework checking and dictation Step 2: 情态动词 一、概念:情态动词是一种本身有一定的词义,表示说话人的情绪、态度或语气的动词,但不能单独作谓语,只能和其他动词原形构成复合谓语,没有人称和数的变化。 情态动词数量不多,但用途广泛,主要有:can (could), may (might), must, need, ought to, dare (dared), shall (should), will (would) . 二、can/could 1. 表示能力(如体力和脑力方面),意为“能、会” Can you speak Chinese? Can you play basketball? 2. 表示请求或者允许,多用在口语中,意为“可以、能”等客观条件的允许。用于疑问句中用来提出要求,用于否定句中表示不允许。 Can you help me? You can’t play the computer 3. 表示可能,理论上的可能。 He can be out now. It can’t bu sunny all the time.
初三英语情态动词must 的用法总结教学案例 初三英语情态动词“must”强化训练教学设计 一、教学设计 (一)学情分析(Learning situation analysis) 进入初三我所接手的班级的情况比较复,初一、初二两年频繁调换英语教师,学生的知识不够系统化,学习方法、做题思路等都不够成熟,且基础普遍较差。英语复习课是巩固和发展知识、技能的重要课型.它的作用,就是帮助学生重温已学的知识和技能,使记忆中的痕迹得到强化,并对已获得的知识加以整理、归纳、概括,使知识条理化、系统化.因此教师必须注意引导学生多动脑、多动手、多参加课堂活动。复习课如果上得不好,往往会变成旧课的重复,或者是新课的“再版”。这样不仅不能发挥复习课的作用,而且会使学生因乏味而降低学习兴趣。此教学案例的教学对象是初三学生,整体英语水平较低,且自主学习能力有限,自主学习的习惯还没有形成;大部分学生的基础不牢固,学习习惯较差,学习兴趣不大。 (二)课标与教材分析(Curriculum and teaching material analysis) 按照《国家英语课程标准》要求,现行的英语课堂教学模式应该是以学生为主体的课堂,鼓励学生以参与的方式掌握应用英语语言知识的能力。英语教学目标中是这样描述的:“基础教育阶段英语课程的总体目标是培养学生的综合语言运用能力。综合语言运用能力的形成是建立在学生语言技能、语言知识、情感态度、学习策略和文化意识等素养整体发展的基础上。”语言知识和语言技能是综合语言运用能力的基础,文化意识是得体运用语言的保证,情感态度是影响学生学习和发展的重要因素,而学习策略则是提高学习效率、发展自主学习能力的关键。因此,这五个方面共同促进综合语言使用能力的形成。 (三)教学目标与要点分析(The teaching goal and key points of analysis) 1. The teaching goal (教学目标): 1)Knowledge objectives (知识目标):To master modal verb “must”. To understand some special cases. 2)Ability to target (能力目标):To use ”can” freely and correctly. 3)Emotional attitude goal (情感态度目标):To enjoy communicating in English. 2. Teaching important points and difficult points (教学重点和难点): 1)情态动词must在情景对话中的的用法 (The usage of the modal verbs “must” in situational dialogues ) 2)表示猜测时的must ("Must" for speculation in tone) 3)怎样回答带有“must”的问句?(How to answer a question with "must" ?) (四)教学策略设计(The teaching strategy design): 本堂课的设计着力体现出素质教育思想,以学生为主体,以“五步”教学法(读、学、点、练、悟)来指导课堂行为。 (The design of class strive to embody the thought of quality education, take the studen t as the main body, in order to "five-step" teaching method, reading, learning, practice and enlightenment, point) to guide classroom behavior.) (五)、教学过程设计(The teaching process design):
英语情态动词的用法大全附解析 一、初中英语情态动词 1.—We've got everything ready for the picnic. —Do you mean I __________ bring anything with me? A. can't B. mustn't C. couldn't D. needn't 【答案】 D 【解析】【分析】句意:—我们已经为野餐准备好了一切。—你的意思是我不必带任何东西吗?A. can't 不能;B. mustn't 表示禁止,一定不要;C. couldn't不能,表示过去时态;D. needn't不必。结合句意,故选D。 【点评】本题考查情态动词的用法。 2.—How amazing this robot is! —Wow, it has video cameras in its eyes, so it “see” and interact with pe ople. A. may B. can C. must D. should 【答案】 B 【解析】【分析】句意:—这个机器人多么惊人啊!—哇,在它的眼睛里有摄像机,因此它能看见和人打交道。A. may 可以,可能;表示许可,B. can 能;表示能力,C. must 必须;D. should应该;根据it has video cameras in its eyes,可知是有能力看见,故选B。 【点评】考查情态动词辨析。熟记情态动词的含义和用法。 3.—Where is George? —He _______ be here just now. His coffee is still warm. A. need B. can't C. must D. shouldn't 【答案】 C 【解析】【分析】句意:——乔治在哪里?——他刚才一定在这里,他的咖啡还是热的。A. need需要; B. can't 不能,不可能(表示推测); C. must 必须,一定(表示推测); D. shouldn't不应该;根据His coffee is still warm.可知表示肯定推测一定在这儿;故答案为C。 【点评】考查情态动词。掌握情态动词表推测时的意义和用法。 4.— Sorry, I forgot to take money with me. Maybe I can't buy the book you like. — Mum, you ______ worry about it. We can pay by Alipay (支付宝). A. can't B. needn't C. mustn't D. shouldn't 【答案】 B 【解析】【分析】句意:——对不起,我忘记带钱了。也许我不能买你喜欢的书。——妈妈,你不用担心。我们可以用支付宝支付。A. can't不能,指不允许或否定推测;B. needn't 不需,指没必要;C. mustn't不能,表禁止;D. shouldn't不应该,表建议。根据句意语境,本句是说妈妈不需要担心,故答案为B。 【点评】考查情态动词。理解句意并掌握情态动词的意义和用法区别。
情态动词练习(小测) 1.Buses and cars ______ stop when the traffic lights are right. A. can B. must C. may D. need 2. –Excuse me, Can you tell me the way to the railway station? Oh, sorry, but I don’t know.You ____ go and ask that policeman. A.may B. must C.would D. should 3. –Children all like this book. -I think it ______ very interesting. A. need be B. must be C. may be D. can be 4. To make our hometown (家乡) more beautiful , you _____ throw rubbish into the river. A. needn’t B.mustn’t C. must D. may 5. She ______ know the answer .I’m am not sure. A. maybe B.may be C.may D. must 6. –Must I go with tomorrow? –No. you ______ . A. must B. shouldn’t C.needn’t D.can’t 7.-_______ I have your name ,please? –Yes,Michael. M-I-C-H-A-E-L. A.Must B. Will C.May D. Need 8. Since(因为) the road is wet this morning,_______ last night. A. it must rain B. it must have rained C.it must be rained D.it must have been rained 9.Work _______ come first.. A. can B.may C.should D. must 10. He _____ come here tomorrow. A. don’t need B.doesn’t need to C.needn’t to D.needs not 11.In our school ,classrooms ______ cleaned every Sunday. A. will do B. shall do C.must be D.can be 12.-Please don’t use my computer.-Sorry, I _______ do it again. A. can’t B. must not C. won’t D. should 13. –Sir, you _____ sit here. It’s for women or children only. A. don’t B. can’t C. won’t D. needn’t 14.My boy, you _____ talk to your father like that. A.won’t B. don’t C. shouldn’t D.has to 15. -_______Iwatch TV now, Mum? -No, you _______ finish your homework first. A. Must, needn’t B. Can ,may C. May, must D. May,mustn’t 16. –You must be here at 5:30 tomorrow. –Sorry ,I _____be here so early. A.won’t B. don’t C. shouldn’t D.has to 17. Last Summer ,it was very dry. I ________ it every day. A. must water B. have to water C. had to water D. didn’t have to 句型转换 1.He must be a policeman.(否定句) He _______ be a policeman. 2. I’m sure he is sleeping. (同义句) He _______ be sleeping. 3.You don’t have to get up early.(同义句) You __________ get up early. 形容词的比较级和最高级 用所给词的适当形式填空 1.Summer is the ________(hot) of the four seasons. 2.Tommy’s homework is much _______(good) than it was last
情态动词can,must的用法:1. 不随着主语变化而变化;2.后跟动词原形; 1.Can 表示能,会。 1.不随着主语变化而变化; 后跟动词原形; 否定形式can not= can’t不能,不会 提can到句首,句末加“”,其肯否定回答:Yes,** can. No, ** can’t. Must,必须; 不随着主语变化而变化; 后跟动词原形; 否定形式must not = mustn’t 不允许,不准,禁止 提must到句首,句末加“”,其肯否定回答:Yes,** must. No, ** needn’t. (不,**不必)
练习题: 一.翻译 我能从墙上跳下来。 Sue 会骑自行车。 Sandy 和Sue 能打印这份信。 他们能看见那只鸟。 我必须回家。 Emma必须写作业。 我们必须从墙上跳下来。 他们必须写字。 不允许他们在街上玩。 禁止他们玩火。 二.改写句型。 1. I can sing. 改否定句: _____________ 改一般疑问句:________________ 作肯否定回答:______________________________ 划提:_____________________________ can ride a bike. 改否定句: ______________________
改一般疑问句:_____________________作肯否定回答:____________________ 划提:_____________________________ and Billy must do their homework. 改否定句: ______________________ 改一般疑问句:_____________________作肯否定回答:__________________ 划提:_____________________________ must stay at home. 改否定句: ______________________ 改一般疑问句:_____________________作肯否定回答:__________________ 划提:_____________________________ Sophie must read a novel. 改否定句: ______________________ 改一般疑问句:_____________________作肯否定回答:__________________ 划提:_____________________________ He can see that nest. 改否定句: ______________________ 改一般疑问句:_____________________作肯否定回答:__________________ 划提:_____________________________ They must listen to the stereo. 改否定句: ______________________ 改一般疑问句:_____________________作肯否定回答:__________________ 划提:_____________________________ 三.Must,mustn’t ,can ,can’t 填空 “________ I come at 6 o’clock””Oh no, you needn’t.” A blind man ________ judge colours. “May I go there””No,you_______.” Two eyes ________ see more than one. I _______ be off. Thank you very much for supper. You _______ be careful. You _______ be careless. ______ I stay up till mid-night, please The teacher _______ favour some children more than others.
英语情态动词用法详解 一、单项选择情态动词 1.Look! There are so many mistakes in your composition. You ________ have fixed full attention on it. A.can B.should C.need D.might 【答案】B 【解析】 【详解】 考查情态动词。句意:看!你的作文里有那么多的错误。你本应该把所有的注意力都集中在它上面的。表示“本应该做但实际上没有做”应该用should have done结构,can have done 表示可能;need表示需要;might have done表示可能做过某事;故选B。 2.---Hi, Johnson, any idea where Susan is? ---It is class time, so she __________ in the classroom now. A.can be B.must have been C.might have been D.should be 【答案】D 【解析】 考查情态动词的用法。A. can be可能,可以是;B. must have been一定(对过去事实肯定的推测);C. might have been可能(对过去事实肯定的推测);D. should be应该是。句意:—知道苏珊在哪里吗?—现在是上课时间,她应该在教室里。故答案选D。 3.The room is so clean. He ________ have cleaned it yesterday evening. A.will B.need C.can D.must 【答案】D 【解析】 【详解】 考查情态动词表推测。句意:房间如此干净,他一定是昨天晚上打扫过了。must have done 表示对过去发生的事情有把握的猜测,意思是“一定(做过)”,故D项正确。 4.— Excuse me, do you mind if I open the window? — Well, if you __________. I can put on more clothes. A.can B.may C.must D.shall 【答案】C 【解析】
情态动词的被动语态 教学设计 一、教学目标 1. 了解情态动词的被动语态结构 2. 掌握情态动词的被动语态的变换方法 二、教学准备 多媒体,微课软件,纸和笔 三、教学步骤 1.通过例句学习变换方法 Ann can take good care of the cats . The cats can be taken good care of by Ann. 2. 总结结构: S+ can/must/should等情态动词+ be+过去分词 3.练习题 ① You must clean your bedroom every day. ② Parents should encourage teenagers to do social work. ③ Can Lucy do her homework tomorrow instead? 4.更多练习
I. 用括号内所给单词的适当形式填空。 1.How many magazines ____(can borrow) in your library every week? 2.In many countries, teenagers under 18 ____(should not allow) to go into Internet bars. 3.Some people think trees ____(should plant) on Tree planting Day only. 4.The flowers ____(must water) every day. 5.A dictionary ____(can use) in the exam. II.同义句转换,每空一词。 1.Students should clean their classroom every day. Their classroom ____ _____ ____ every day. 2.Can you mend this radio? ____ this radio ____ ____? 3.We should not allow fifteen-year-olds to work at night. Fifteen-year-olds ____ ____ ____ to work at night.