fimmu-05-00518
- 格式:pdf
- 大小:1.30 MB
- 文档页数:11
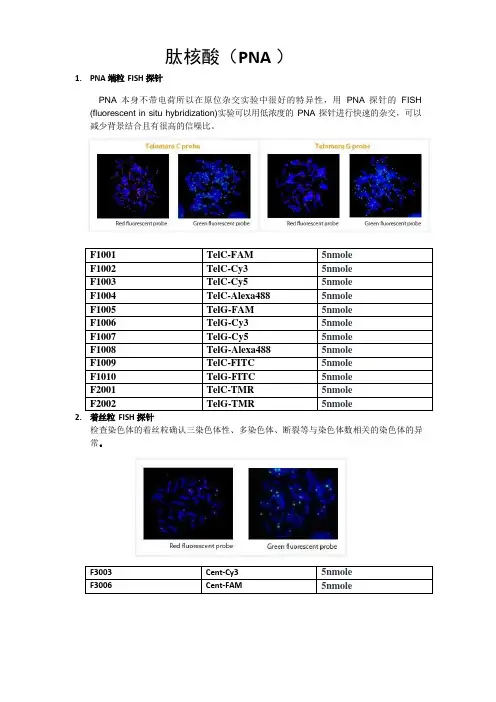
1.PNA 端粒FISH 探针肽核酸(PNA )PNA 本身不带电荷所以在原位杂交实验中很好的特异性,用PNA 探针的FISH (fluorescent in situ hybridization)实验可以用低浓度的PNA 探针进行快速的杂交,可以减少背景结合且有很高的信噪比。
F1001 TelC-FAM5nmoleF1002 TelC-Cy3 5nmoleF1003 TelC-Cy5 5nmoleF1004 TelC-Alexa488 5nmoleF1005 TelG-FAM 5nmoleF1006 TelG-Cy3 5nmoleF1007 TelG-Cy5 5nmoleF1008 TelG-Alexa488 5nmoleF1009 TelC-FITC 5nmoleF1010 TelG-FITC 5nmoleF2001 TelC-TMR 5nmoleF2002 TelG-TMR 5nmole2.着丝粒FISH 探针检查染色体的着丝粒确认三染色体性、多染色体、断裂等与染色体数相关的染色体的异常。
F3003 Cent-Cy3 5nmoleF3006 Cent-FAM 5nmole参考文献(端粒FISH 探针和着丝粒FISH 探针):1Kentaro Taemura et al., Dynamic rearrangement of telomeres during spermatogenesis in mice. Developmental Biology. 2005;281:196-207.2Won-Woo Lee et al., Age-related telomere length dynamics in peripheral blood mononuclear cells of healthy cynomolgus monkeys measured by Flow FISH. Immunology. 2002;105:458-465.3Heather Perry et al., Identification of indicator microorganisms using a standardized PNA FISH method. Journal of Microbiological Methods 2001;47:281-292.4Caifu Chen et al., Single base discrimination of CENP-B repeats on mouse and human chromosomes with PNA-FISH. Mammalian Genome. 1999;10:13-18.5M. Hultdin et al., Telomere analysis by flourescence in situ hybridization and flow cytometry. Nucleic Acids Research. 1998;26(16):3651-3656.6Peter M. Landsdorp et al., Heterogeneity in telomere length of human chromosomes. Human Molecular Genetics. 1996;5(5):685-691.3.PNA oligomers for PCR clamping 球蛋白抑制剂血液内存在的mRNA 的70%以上是球蛋白mRNA,显著减少基因的发现分析及敏感度。

fgf5基因FGF5基因是编码人体成长因子5的基因,是FGF(成纤维细胞生长因子)基因家族中的一员。
FGF5是一种重要的信号蛋白,对于细胞生长、分化和组织发育起着至关重要的作用。
本文将从FGF5基因的结构、功能以及与人类疾病的关系等方面进行探讨。
FGF5基因位于人类染色体4q21.21区域,由3个外显子和2个内含子组成。
这个基因编码了由267个氨基酸组成的FGF5蛋白。
FGF5蛋白通过与细胞表面上的受体结合,触发一系列信号传导途径,以调控细胞的生长和分化。
FGF5在人体中的功能非常重要。
它参与了许多生理过程,包括胚胎发育、器官形成和维持以及伤口愈合等。
研究发现,FGF5在毛发生长中起到了至关重要的作用。
正常情况下,FGF5的表达水平低,能够促进毛囊的生长和发育。
而当FGF5过度表达时,会抑制毛囊的生长,导致毛发停止生长,进而引起脱发。
除了与正常生理过程相关外,FGF5基因也与一些疾病的发生发展密切相关。
研究表明,FGF5基因的突变与人类先天性毛发疾病有关,如毛发稀疏症等。
此外,一些研究还发现,FGF5的异常表达与某些肿瘤的发生有关,如乳腺癌、胃癌等。
对于这些疾病,研究人员希望通过对FGF5基因的研究,找到相应的治疗方法和药物靶点。
针对FGF5基因的研究还有很多需要进一步深入探索的方向。
首先,我们需要进一步了解FGF5基因的调控机制,包括转录因子对其表达的影响以及信号通路的调节。
其次,我们需要研究FGF5与其他基因之间的相互作用,探索其在细胞信号传导网络中的具体作用。
此外,我们还需要研究FGF5基因在不同种群中的遗传变异情况,以及与个体发育和疾病易感性的关系。
FGF5基因作为编码FGF5蛋白的基因,在细胞生长、分化和组织发育中起着重要作用。
它的异常表达与一些疾病的发生发展密切相关,对于研究这些疾病的发病机制和寻找治疗方法具有重要意义。
未来的研究将进一步揭示FGF5基因的调控机制和功能,为相关疾病的防治提供理论基础和临床指导。

(本试剂盒仅供体外研究使用,不用于临床诊断!)Elabscience®游离胆固醇(FC)比色法测试盒Free Cholesterol (FC) Colorimetric Assay Kit产品货号:E-BC-K004-M产品规格:48T(44 samples)/96T(92 samples)检测仪器:酶标仪(500-520 nm)使用前请仔细阅读说明书。
如果有任何问题,请通过以下方式联系我们:销售部电话************,************技术部电话131****6790具体保质期请见试剂盒外包装标签。
请在保质期内使用试剂盒。
联系时请提供产品批号(见试剂盒标签),以便我们更高效地为您服务。
用途本试剂盒适用于检测血清、血浆、动物组织样本中的游离胆固醇含量。
检测原理游离胆固醇(Free Cholesterol,FC)在胆固醇氧化酶(Cholesterol oxidase,CO)的氧化作用下生成4-胆甾烯酮和过氧化氢。
过氧化氢在4-氨基安替吡啉和酚存在时,经过氧化物酶催化,反应生成苯醌亚胺非那腙的红色醌类化合物,其颜色深浅与游离胆固醇含量成正比。
其检测原理如下图:提供试剂和物品说明:试剂严格按上表中的保存条件保存,不同测试盒中的试剂不能混用。
对于体积较少的试剂,使用前请先离心,以免量取不到足够量的试剂。
所需自备物品仪器:酶标仪(500-520 nm,最佳检测波长510 nm)试剂:异丙醇(AR)试剂准备试剂盒中的试剂平衡至室温。
样本准备①样本处理样本要求:样本中不能添加还原性物质,如抗坏血酸、谷胱甘肽等。
组织样本:常规匀浆处理(匀浆介质为异丙醇)。
②样本的稀释在正式检测前,需选择2-3个预期差异大的样本稀释成不同浓度进行预实验,根据预实验的结果,结合本试剂盒的线性范围:0.07-24 mmol/L,请参考下表稀释(仅供参考):注:稀释液为生理盐水(0.85%)或1×PBS(0.01M,pH7.4)。
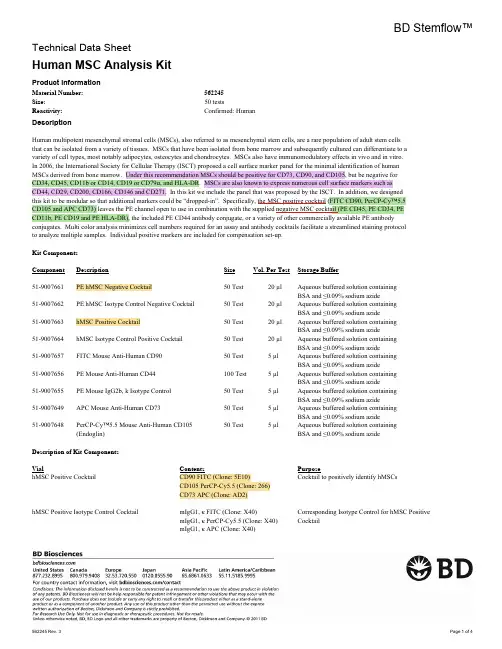
BD Stemflow™Technical Data SheetHuman MSC Analysis KitProduct InformationMaterial Number:562245Size: 50 testsConfirmed: HumanReactivity:DescriptionHuman multipotent mesenchymal stromal cells (MSCs), also referred to as mesenchymal stem cells, are a rare population of adult stem cellsthat can be isolated from a variety of tissues. MSCs that have been isolated from bone marrow and subsequently cultured can differentiate to avariety of cell types, most notably adipocytes, osteocytes and chondrocytes. MSCs also have immunomodulatory effects in vivo and in vitro.In 2006, the International Society for Cellular Therapy (ISCT) proposed a cell surface marker panel for the minimal identification of humanMSCs derived from bone marrow. Under this recommendation MSCs should be positive for CD73, CD90, and CD105, but be negative forCD34, CD45, CD11b or CD14, CD19 or CD79α, and HLA-DR. MSCs are also known to express numerous cell surface markers such asCD44, CD29, CD200, CD166, CD146 and CD271. In this kit we include the panel that was proposed by the ISCT. In addition, we designedthis kit to be modular so that additional markers could be “dropped-in”. Specifically, the MSC positive cocktail (FITC CD90, PerCP-Cy™5.5CD105 and APC CD73) leaves the PE channel open to use in combination with the supplied negative MSC cocktail (PE CD45, PE CD34, PECD11b, PE CD19 and PE HLA-DR), the included PE CD44 antibody conjugate, or a variety of other commercially available PE antibodyconjugates. Multi color analysis minimizes cell numbers required for an assay and antibody cocktails facilitate a streamlined staining protocolto analyze multiple samples. Individual positive markers are included for compensation set-up.Kit ComponentsComponent Description Size Vol. Per Test Storage Buffer51-9007661PE hMSC Negative Cocktail50 Test20 µl Aqueous buffered solution containingBSA and ≤0.09% sodium azide51-9007662PE hMSC Isotype Control Negative Cocktail50 Test20 µl Aqueous buffered solution containingBSA and ≤0.09% sodium azide51-9007663hMSC Positive Cocktail50 Test20 µl Aqueous buffered solution containingBSA and ≤0.09% sodium azide51-9007664hMSC Isotype Control Positive Cocktail50 Test20 µl Aqueous buffered solution containingBSA and ≤0.09% sodium azide51-9007657FITC Mouse Anti-Human CD9050 Test 5 µl Aqueous buffered solution containingBSA and ≤0.09% sodium azide51-9007656PE Mouse Anti-Human CD44100 Test 5 µl Aqueous buffered solution containingBSA and ≤0.09% sodium azide51-9007655PE Mouse IgG2b, k Isotype Control50 Test 5 µl Aqueous buffered solution containingBSA and ≤0.09% sodium azide51-9007649APC Mouse Anti-Human CD7350 Test 5 µl Aqueous buffered solution containingBSA and ≤0.09% sodium azide51-9007648PerCP-Cy™5.5 Mouse Anti-Human CD10550 Test 5 µl Aqueous buffered solution containing(Endoglin)BSA and ≤0.09% sodium azideDescription of Kit ComponentsVial Contents PurposehMSC Positive Cocktail CD90 FITC (Clone: 5E10)Cocktail to positively identify hMSCsCD105 PerCP-Cy5.5 (Clone: 266)CD73 APC (Clone: AD2)hMSC Positive Isotype Control Cocktail mIgG1, κ FITC (Clone: X40)Corresponding Isotype Control for hMSC PositivemIgG1, κ PerCP-Cy5.5 (Clone: X40)CocktailmIgG1, κ APC (Clone: X40)PE hMSC Negative Cocktail CD34 PE (Clone:581)Cocktail to identify potential contaminantsCD11b PE (Clone: ICRF44)CD19 PE (Clone: HIB19)CD45 PE (Clone: HI30)HLA-DR PE (Clone: G46-6)PE hMSC Negative Isotype Control Cocktail mIgG1, κ PE (Clone: X40)Corresponding isotype control for PE hMSCmIgG2a, κ PE (Clone:G155-178)Negative CocktailFITC Mouse Anti-human CD90CD90 FITC (Clone: 5E10)Compensation controlPE Mouse Anti-Human CD44CD44 PE (Clone: G44-26)Compensation control/MSC positive drop-in PerCP-Cy™5.5 Mouse Anti-Human CD105CD105 PerCP-Cy™5.5 (Clone: 266)Compensation controlAPC Mouse Anti-Human CD73CD73 APC (Clone:AD2)Compensation controlPE Mouse IgG2b, κ Isotype Control mIgG2b, κ (Clone: 27-35)Corresponding Isotype Control for PE MouseAnti-Human CD44, when used as a drop in Preparation and StorageStore undiluted at 4°C and protected from prolonged exposure to light. Do not freeze.The antibody was conjugated with R-PE under optimum conditions, and unconjugated antibody and free PE were removed.The antibody was conjugated with PerCP-Cy5.5 under optimum conditions, and unconjugated antibody and free PerCP-Cy5.5 were removed. Storage of PerCP-Cy5.5 conjugates in unoptimized diluent is not recommended and may result in loss of signal intensity.The antibody was conjugated with FITC under optimum conditions, and unreacted FITC was removed.The antibody was conjugated to APC under optimum conditions, and unconjugated antibody and free APC were removed.Application NotesApplicationFlow cytometry Tested During DevelopmentRecommended Assay Procedure:(1) Detach cells using BD™ Accutase™ Cell Detachment Solution (Cat. No 561527) or similar detachment solution, wash cells and resuspend ata concentration of 1x10^7 cells/ml in BD Pharmingen™ Stain Buffer (Cat. No. 554656) or other appropriate staining buffer.(a) Cells can also be resuspended at a concentration of 5x10^6 cells/ml if cell number is a limiting factor.(2) Label tubes and add antibodies as shown below:Tube Add (1 test size)(1)FITC Mouse Anti-Human CD90 (5µl)(2)PE Mouse Anti-Human CD44 (5µl)(3)PerCP-Cy™5.5 Mouse Anti-Human CD105 (5µl)(4)APC Mouse Anti-Human CD73 (5µl)(5)Nothing(6)hMSC Positive Isotype Control Cocktail (20µl)PE hMSC Negative Isotype Control Cocktail (20µl)(7)hMSC Positive Cocktail (20µl)PE hMSC Negative Cocktail (20µl)And/or(8)hMSC Positive Isotype Control Cocktail (20µl)Drop in isotype control (i.e. PE Mouse IgG2b, κ) (5 µl)(9)hMSC Positive Cocktail (20µl)PE Drop in (i.e. PE Mouse Anti-Human CD44) (5µl)(3) Repeat tubes 5-7 and/or 8-9 for each additional cell sample.(4) Add 100 µl of prepared cell suspension to tubes 1 through 9.(5) Incubate tubes in the dark for 30 minutes (May be done on ice or at room temp)(6) Wash the cells twice with BD Pharmingen™ Stain Buffer (FBS) and resuspend at 300-500 µl in BD Pharmingen™ Stain Buffer (FBS) . Alternatively, 1X Washing/Staining Solution (1 x PBS,1% FCS, and 0.09% sodium azide) may be used.(7) Analyze cells on flow cytometer(a) tubes 1-5 are to be used as controls to set up cytometer (i.e Compensation)Suggested Companion ProductsSizeCatalog Number Name Clone 554656Stain Buffer (FBS)500 ml(none)(none)561527Accutase™ Cell Detachment Solution100 mlTop: Schematic workflow of the human MSC analysis kit.Bottom: Cells grown in BD Mosaic™ hMSC SF Cell Culture Environment (Cat. No. 355700) were detached using BD™ Accutase™ CellDetachment Solution (Cat. No 561527) and then stained with the positive and negative cocktails (solid lines) or the positive and negativeisotype control cocktails (dashed lines). The plots were derived from gated events based on light scattering characteristics of the MSCs.Cells were analyzed using a BD™ LSRII flow cytometry system.Product Notices1.Accutase is a registered trademark of Innovative Cell Technologies, Inc.2.Please observe the following precautions: Absorption of visible light can significantly alter the energy transfer occurring in any tandem fluorochrome conjugate; therefore, we recommend that special precautions be taken (such as wrapping vials, tubes, or racks in aluminum foil) to prevent exposure of conjugated reagents, including cells stained with those reagents, to room illumination.3.This APC-conjugated reagent can be used in any flow cytometer equipped with a dye, HeNe, or red diode laser.PerCP-Cy5.5 is optimized for use with a single argon ion laser emitting 488-nm light. Because of the broad absorption spectrum of the4.tandem fluorochrome, extra care must be taken when using dual-laser cytometers, which may directly excite both PerCP and Cy5.5™. We recommend the use of cross-beam compensation during data acquisition or software compensation during data analysis.PerCP-Cy5.5–labelled antibodies can be used with FITC- and R-PE–labelled reagents in single-laser flow cytometers with no significant5.spectral overlap of PerCP-Cy5.5, FITC, and R-PE fluorescence.Cy is a trademark of Amersham Biosciences Limited. This conjugated product is sold under license to the following patents: US Patent Nos.6.5,486,616; 5,569,587; 5,569,766; 5,627,027.This product is subject to proprietary rights of Amersham Biosciences Corp. and Carnegie Mellon University and made and sold under7.license from Amersham Biosciences Corp. This product is licensed for sale only for research. It is not licensed for any other use. If you require a commercial license to use this product and do not have one return this material, unopened to BD Biosciences, 10975 Torreyana Rd, San Diego, CA 92121 and any money paid for the material will be refunded.8.Source of all serum proteins is from USDA inspected abattoirs located in the United States.9.Caution: Sodium azide yields highly toxic hydrazoic acid under acidic conditions. Dilute azide compounds in running water beforediscarding to avoid accumulation of potentially explosive deposits in plumbing.10.For fluorochrome spectra and suitable instrument settings, please refer to our Multicolor Flow Cytometry web page at/colors.11.Please refer to /pharmingen/protocols for technical protocols.ReferencesBühring HJ, Battula VL, Treml S, Schewe B, Kanz L, Vogel W. Novel markers for the prospective isolation of human MSC. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 2007;1106:262-271. (Biology: Flow cytometry)Dominici M, Le Blanc K, Mueller I, et. al. Minimal criteria for defining multipotent mesenchymal stromal cells. The International Society for Cellular Therapy position statement. Cytotherapy. 2006; 8(4):315-317. (Biology: Flow cytometry)Horwitz EM, Le Blanc K, Dominici M, et. al. Clarification of the nomenclature for MSC: The International Society for Cellular Therapy position statement.Cytotherapy. 2005; 7(5):393-395. (Biology)Kern S, Eichler H, Stoeve J, Klüter H, Bieback K. Comparative analysis of mesenchymal stem cells from bone marrow, umbilical cord blood, or adipose tissue.Stem Cells. 2006; 24(5):1294-1301. (Biology: Flow cytometry)Sánchez L, Gutierrez-Aranda I, Ligero G, et al. Enrichment of Human ESC-Derived Multipotent Mesenchymal Stem Cells with Immunosuppressive andAnti-Inflammatory Properties Capable to Protect Against Experimental Inflammatory Bowel Disease. Stem Cells. 2010; 29(2):251-262. (Biology: Cell differentiation)。
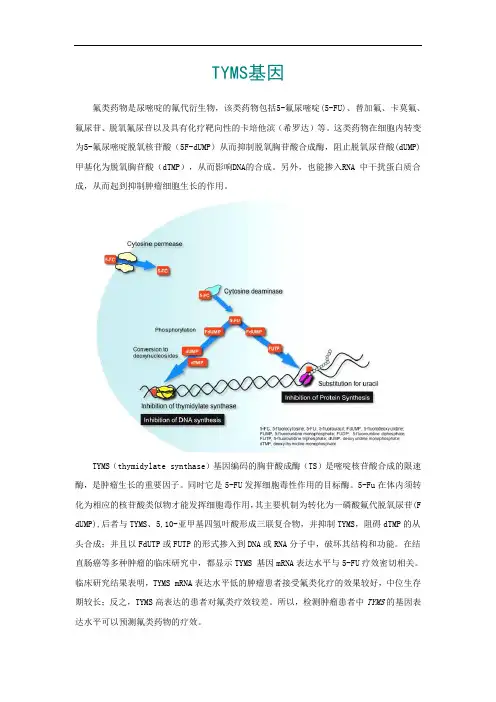
TYMS基因氟类药物是尿嘧啶的氟代衍生物,该类药物包括5-氟尿嘧啶(5-FU)、替加氟、卡莫氟、氟尿苷、脱氧氟尿苷以及具有化疗靶向性的卡培他滨(希罗达)等。
这类药物在细胞内转变为5-氟尿嘧啶脱氧核苷酸(5F-dUMP)从而抑制脱氧胸苷酸合成酶,阻止脱氧尿苷酸(dUMP)甲基化为脱氧胸苷酸(dTMP),从而影响DNA的合成。
另外,也能掺入RNA 中干扰蛋白质合成,从而起到抑制肿瘤细胞生长的作用。
TYMS(thymidylate synthase)基因编码的胸苷酸成酶(TS)是嘧啶核苷酸合成的限速酶,是肿瘤生长的重要因子。
同时它是5-FU发挥细胞毒性作用的目标酶。
5-Fu在体内须转化为相应的核苷酸类似物才能发挥细胞毒作用,其主要机制为转化为一磷酸氟代脱氧尿苷(F dUMP),后者与TYMS、5,10-亚甲基四氢叶酸形成三联复合物,并抑制TYMS,阻碍dTMP的从头合成;并且以FdUTP或FUTP的形式掺入到DNA或RNA分子中,破坏其结构和功能。
在结直肠癌等多种肿瘤的临床研究中,都显示TYMS 基因mRNA表达水平与5-FU疗效密切相关。
临床研究结果表明,TYMS mRNA表达水平低的肿瘤患者接受氟类化疗的效果较好,中位生存期较长;反之,TYMS高表达的患者对氟类疗效较差。
所以,检测肿瘤患者中TYMS的基因表达水平可以预测氟类药物的疗效。
TYMS的mRNA表达水平与5-FU/奥沙利铂治疗的疗效相关。
TYMS低表达的患者生存期显著长于TYMS高表达的患者[参考文献][1] Rho JK, Choi YJ, Jeon BS, Choi SJ, Cheon GJ, Woo SK, Kim HR, Kim CH, Choi CM, Lee JC (2010) Combined treatment with silibinin and epidermal growth factor receptor tyrosine kinase inhibitors overcomes drug resistance caused by T790M mutation. Mol Cancer Ther 9: 3233-3243.[2] Rosell R, Moran T, Cardenal F, Porta R, Viteri S, Molina MA, Benlloch S, Taron M (2010) Predictive biomarkers in the management of EGFR mutant lung cancer. Ann N Y Acad Sci 1210: 45-52.[3] Taus A, V ollmer I, Arriola E (2011) Activating and resistance mutations of the epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR) gene and non-small cell lung cancer: a clinical reality. Arch Bronconeumol 47: 103-105.[4] Xu Y, Liu H, Chen J, Zhou Q (2010) Acquired resistance of lung adenocarcinoma to EGFR-tyrosine kinase inhibitors gefitinib and erlotinib. Cancer Biol Ther 9: 572-582.[5] De Luca A, Normanno N (2010) Predictive biomarkers to tyrosine kinase inhibitors for the epidermal growth factor receptor in non-small-cell lung cancer. Curr Drug Targets 11: 851-864.。

Human IFN gamma ELISPOT Catalog Number 88-7386Pub. No. MAN0017483 Rev.A.0 (30)WARNING! Read the Safety Data Sheets (SDSs) and follow thehandling instructions. Wear appropriate protective eyewear,clothing, and gloves. Safety Data Sheets (SDSs) are availablefrom /support.Product informationDescriptionThis Human IFN gamma ELISPOT reagent set contains the necessary reagents for performing enzyme-linked immunosorbent spot (ELISPOT) assays for high-resolution frequency analysis of IFN gamma-secreting cells. This ELISPOT reagent set is pre-titrated for optimal spot development.Time requirements• 1 overnight incubation•1−2 days cell activation•3−5 hours washing, antibody incubations, and color development Components•Capture Antibody: Pre-titrated, functional grade (low endotoxin) purified antibody•Detection Antibody: Pre-titrated, biotin-conjugated antibody •ELISA/ELISPOT Coating BufferELISA/ELISPOT Coating Buffer Powder or 10X PBS ELISPOTCoating Buffer•5X ELISA/ELISASPOT Diluent•EnzymePre-titrated Avidin-HRP Concentrate•Certificate of Analysis: Lot-specific instructions for dilution ofantibodies and enzymeOther materials needed•Reagents:–96-Well PVDF Membrane ELISPOT Plates (Milipore,Cat. No. MAIPS4510)–AEC (3-amino-9-ethyl carbazole) Substrate (Sigma,Cat. No. A-5754–Distilled water (dH2O)–ELISPOT Wash Buffer: ELISA/ELISPOT Wash Buffer Powder(Cat. No. 00-0400) or 1X PBS with 0.05% Tween™ 20–Complete RPMI-1640–1X PBS•Instruments:–Pipettes and pipettors–Refrigerator–Incubator–Laminar flow hood–Plate washer: Wash bottle or automated wash machine–ELISPOT plate reader or dissecting microscope for visualinspectionReagent preparation•ELISA/ELISPOT Coating Buffer (1X)Make a 1:10 dilution of 10X PBS ELISPOT Coating Buffer in dH2O or reconstitute ELISA/ELISPOT Coating Buffer Powder to 1L indH2O and sterilize by filtering using a 0.22-µM filter.•Complete RPMI-1640Complete RPMI-1640 with 10% Fetal Bovine Serum and 1%Penicillin/Streptomycin/L-Glutamine.•5X ELISA/ELISPOT DiluentDilute 5X ELISA/ELISPOT Diluent 1:5 in dH2O.•ELISA/ELISPOT Wash BufferReconstituted ELISA/ELISPOT Wash Buffer Powder(Cat. No. 00-0400) or 1X PBS with 0.05% Tween™ 20 (0.5 mLTween™ 20 in 1 L PBS).•0.1M Acetate Solution (pH 5.0)bine 148 mL of 0.2 M acetic acid (11.55 mL glacial aceticacid per 1 L of dH2O) with 352 mL of 0.2 M sodium acetate (27.2g sodium acetate per 1 L of dH2O).b.QS to 1 L with dH2O, then adjust pH to 5.0.•AEC (3-amino-9-ethyl carbazole) Substrate Solutiona.Prepare AEC Stock Solution by dissolving 100 mg of AEC in10 mL of N, N Dimethylformamide (DMF; Cat. No. 20672).b.Add 333 µL of AEC Stock Solution to 10 mL of 0.1M AcetateSolution (pH 5.0), then filter through a 0.45-µm filter.c.Add 5 µL of 30% H2O2 just before use. Mix and useimmediately.Experimental proceduresAseptic stepsNote: Use sterile buffers and aseptic techniques and perform all steps in a laminar flow hood.1.Dilute Functional Grade purified capture antibody in sterileELISA/ELISPOT Coating Buffer, as noted on the Certificate ofAnalysis.2.Coat ELISPOT plate with 100 µL/well of capture antibodysolution, then incubate at 2-8°C overnight.3.Decant or aspirate coating antibody from plate.4.Wash plates 2 times with 200 µL/well of sterile ELISA/ELISPOTCoating Buffer, then decant.5.Block plate with 200 µL/well of complete RPMI-1640 at roomtemperature for 1 hour, then decant or aspirate plate.6.Aliquot mitogen, antigen, or controls diluted in completeRPMI-1640 to appropriate wells at 100 µL/well.For Research Use Only. Not for use in diagnostic procedures.7.Aliquot cells at desired densities (e.g., 1x105–2x106 cells/mL) at100 µL/well and incubate at 37°C, in a 5% CO2 humidifiedincubator for 24-48 hours.Note: Optimal kinetics and cell densities vary with targetcytokine, treatment, and cell type and must be empiricallydetermined. Cells can be diluted in a sterile tissue culture platestarting at 2x106 cells/well in triplicate wells with a series of 1:3 or 1:4 serial dilutions down the plate, and then transferred to theELISPOT plate.Non-aseptic steps1.Decant cells and medium from plates.2.Wash plate 3 times with ELISA/ELISPOT Wash Buffer.3.Dilute biotinylated detection antibody in Assay Diluent accordingto instructions on the Certificate of Analysis.4.Add 100 µL/well of detection antibody solution, then incubate atroom temperature for 2 hr (or at 2-8°C overnight).5.Decant antibody solution, then wash 4 times withELISA/ELISPOT Wash Buffer allowing wells to soak for 1 minute for each wash.6.Dilute Avidin-HRP reagent in Assay Diluent according toinstructions on the Certificate of Analysis.7.Add 100 µL/well of Avidin-HRP solution, then incubate at roomtemperature for 45 minutes.8.Decant Avidin-HRP solution.9.Wash plate 3 times with ELISA/ELISPOT Wash Buffer.10.Wash 2 times with 1X PBS without Tween™ 20.11.Add 100 µL/well of freshly-prepared AEC Substrate Solution,then develop at room temperature for 10-60 minutes monitoring development of spots.12.Stop the substrate reaction by washing wells 3 times with 200µL/well of dH2O.13.Air-dry the plate, then count spots using a dissecting microscopeor automated ELISPOT plate reader.Store plates in the dark prior to reading.Customer and technical supportVisit /support for the latest in services and support, including:•Worldwide contact telephone numbers•Product support, including:–Product FAQs–Software, patches, and updates–Training for many applications and instruments•Order and web support•Product documentation, including:–User guides, manuals, and protocols–Certificates of Analysis–Safety Data Sheets (SDSs; also known as MSDSs)Note: For SDSs for reagents and chemicals from othermanufacturers, contact the manufacturer.Limited product warrantyLife Technologies Corporation and/or its affiliate(s) warrant their products as set forth in the Life Technologies' General Terms and Conditions of Sale found on Life Technologies' website at/us/en/home/global/terms-and-conditions.html. If you have any questions, please contact Life Technologies at /support.Manufacturer: Bender MedSystems GmbH | Campus Vienna Biocenter 2 | 1030 Vienna, AustriaThe information in this guide is subject to change without notice.DISCLAIMER: TO THE EXTENT ALLOWED BY LAW, LIFE TECHNOLOGIES AND/OR ITS AFFILIATE(S) WILL NOT BE LIABLE FOR SPECIAL, INCIDENTAL, INDIRECT, PUNITIVE, MULTIPLE, OR CONSEQUENTIAL DAMAGES IN CONNECTION WITH OR ARISING FROM THIS DOCUMENT, INCLUDING YOUR USE OF IT.Important Licensing Information: This product may be covered by one or more Limited Use Label Licenses. By use of this product, you accept the terms and conditions of all applicable Limited Use Label Licenses.©2017 Thermo Fisher Scientific Inc. All rights reserved. All trademarks are the property of Thermo Fisher Scientific and its subsidiaries unless otherwise specified./support | /askaquestion23 November 2017。
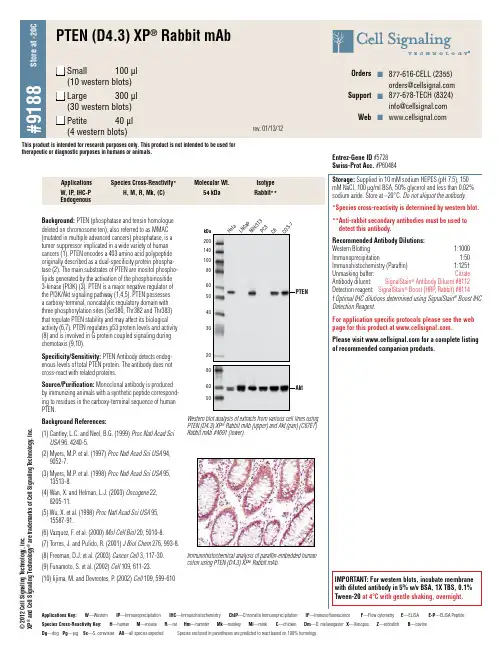
Background: PTEN (phosphatase and tensin homologue deleted on chromosome ten), also referred to as MMAC (mutated in multiple advanced cancers) phosphatase, is a tumor suppressor implicated in a wide variety of human cancers (1). PTEN encodes a 403 amino acid polypeptide originally described as a dual-specificity protein phospha-tase (2). The main substrates of PTEN are inositol phospho-lipids generated by the activation of the phosphoinositide 3-kinase (PI3K) (3). PTEN is a major negative regulator of the PI3K/Akt signaling pathway (1,4,5). PTEN possesses a carboxy-terminal, noncatalytic regulatory domain with three phosphorylation sites (Ser380, Thr382 and Thr383) that regulate PTEN stability and may affect its biological activity (6,7). PTEN regulates p53 protein levels and activity (8) and is involved in G protein coupled signaling during chemotaxis (9,10).Specificity/Sensitivity: PTEN Antibody detects endog-enous levels of total PTEN protein. The antibody does not cross-react with related proteins.Source/Purification: Monoclonal antibody is produced by immunizing animals with a synthetic peptide correspond-ing to residues in the carboxy-terminal sequence of human PTEN.Background References:(1) C antley, L.C. and Neel, B.G. (1999) Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 96, 4240-5.(2) M yers, M.P . et al. (1997) Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 94, 9052-7.(3) M yers, M.P . et al. (1998) Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 95, 13513-8.(4) W an, X. and Helman, L.J. (2003) Oncogene 22, 8205-11.(5) W u, X. et al. (1998) Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 95, 15587-91.(6) V azquez, F. et al. (2000) Mol Cell Biol 20, 5010-8.(7) T orres, J. and Pulido, R. (2001) J Biol Chem 276, 993-8.(8) F reeman, D.J. et al. (2003) Cancer Cell 3, 117-30.(9) F unamoto, S. et al. (2002) Cell 109, 611-23.(10) I ijima, M. and Devreotes, P . (2002) Cell 109, 599-610kDa PTENAktL N C a P N I H /3T 3P C 3C 6C O S -7200140100806050403020806050H e L aWestern blot analysis of extracts from various cell lines usingPTEN (D4.3) XP ® Rabbit mAb (upper) and Akt (pan) (C67E7) Rabbit mAb #4691 (lower).W, IP , IHC-P EndogenousH, M, R, Mk, (C)54 kDaRabbit**Storage: Supplied in 10 mM sodium HEPES (pH 7.5), 150 mM NaCl, 100 µg/ml BSA, 50% glycerol and less than 0.02% sodium azide. Store at –20°C. Do not aliquot the antibody.*Species cross-reactivity is determined by western blot.** A nti-rabbit secondary antibodies must be used to detect this antibody.Recommended Antibody Dilutions: Western Blotting 1:1000 Immunoprecipitation 1:50 Immunohistochemistry (Paraffin) 1:125† Unmasking buffer: CitrateAntibody diluent: SignalStain ®Antibody Diluent #8112 Detection reagent: SignalStain ® Boost (HRP , Rabbit) #8114 †Optimal IHC dilutions determined using SignalStain ® Boost IHC Detection Reagent.For application specific protocols please see the web page for this product at .Please visit for a complete listing of recommended companion products.Applications Species Cross-Reactivity*Molecular Wt.Isotype IMPORTANT: For western blots, incubate membrane with diluted antibody in 5% w/v BSA, 1X TBS, 0.1% Tween-20 at 4°C with gentle shaking, overnight.Entrez-Gene ID #5728 Swiss-Prot Acc. #P60484Species Cross-Reactivity Key:H —humanM —mouseR —ratHm —hamsterMk —monkey Mi —minkC —chickenDm —D. melanogaster X —XenopusZ —zebrafishB —bovineDg —dog Pg —pig Sc —S. cerevisiae All —all species expected Species enclosed in parentheses are predicted to react based on 100% homology.Applications Key:W —Western IP —Immunoprecipitation IHC —Immunohistochemistry ChIP —Chromatin ImmunoprecipitationIF —ImmunofluorescenceF —Flow cytometryE —ELISA E-P —ELISA PeptideImmunohistochemical analysis of paraffin-embedded human colon using PTEN (D4.3) XP ® Rabbit mAb.© 2012 C e l l S i g n a l i n g T e c h n o l o g y , I n c .X P ® a n d C e l l S i g n a l i n g T e c h n o l o g y ® a r e t r a d e m a r k s o f C e l l S i g n a l i n g T e c h n o l o g y , I n c .This product is intended for research purposes only. This product is not intended to be used for therapeutic or diagnostic purposes in humans or animals.Orders n 877-616-CELL (2355) orders@ Support n 877-678-TECH (8324) info@ Web n © 2009 C e l l S i g n a l i n g T e c h n o l o g y , I n c .Immunohistochemical analysis using PTEN (D4.3) XP ® Rabbit mAb on SignalSlide(TM) PTEN IHC Controls#8106 (paraffin-embedded LNCaP (left) and NIH/3T3 (right) cells).。

Inhibitors, Agonists, Screening Libraries Data SheetBIOLOGICAL ACTIVITY:WEHI–345 is a potent and selective inhibitor of RIPK2, with IC50 of 0.13 μM.IC50 value: 0.13 μMTarget: RIPK2in vitro: WEHI–345 is a selective RIPK2 kinase inhibitor, which delays RIPK2 ubiquitylation and NF–κB activation downstream of NOD engagement. WEHI–345 is an ATP analogue and was therefore predicted to bind in the ATP–binding pocket of RIPK2. WEHI–345proved to be highly specific for RIPK2(Kd=46 nM) and displayed negligible activity (>10 μM) against RIPK1, RIPK4 and RIPK5.in vivo: WEHI–345 inhibits NOD signalling and has a beneficial effect on an EAE model. WEHI–345 blocks MDP–induced cytokine production. WEHI–345 ameliorates experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis in mice. WEHI–345 also potently inhibited MDP–induced cytokine and chemokine secretion in the mouse macrophage Raw 264.7 cell line.PROTOCOL (Extracted from published papers and Only for reference)Cell assay [1]THP–1 cells were stably transfected with an NF–κB GFP reporter (pTRH NF–κB). Cells were left untreated or stimulated with either WEHI–345 or WEHI–450, followed by stimulation with L18–MDP or C12–iE–DAP for different time points. NF–κB activity was assessed by the mean fluorescence intensity of green cells using Weasel software (WEHI).Animal administration [1]Six–10–week–old C57Bl/6 female mice were injected intraperitoneally with WEHI–345 or vehicle control (40% polyethyleneglycol 400,20% Koliphor HS15, 0.83% benzylalcohol) in a 100 μl inoculum. After 30 min, mice were challenged with 100 μg MDP or with PBS control by another intraperitoneal injection (100 μl). The mice were killed by CO2asphyxiation 4 h after MDP treatment and the blood was harvested by heart puncture.References:[1]. Nachbur U, et al. A RIPK2 inhibitor delays NOD signalling events yet prevents inflammatory cytokine production. Nat Commun. 2015 Mar 17;6:6442.Product Name:WEHI–345Cat. No.:HY-18937CAS No.:1354825-58-3Molecular Formula:C 22H 23N 7O Molecular Weight:401.46Target:RIP kinase Pathway:Apoptosis Solubility:DMSO: ≥ 32 mg/mLCaution: Product has not been fully validated for medical applications. For research use only.Tel: 609-228-6898 Fax: 609-228-5909 E-mail: tech@ Address: 1 Deer Park Dr, Suite Q, Monmouth Junction, NJ 08852, USA。

Inhibitors, Agonists, Screening Libraries Data SheetBIOLOGICAL ACTIVITY:Enzalutamide is an androgen–receptor (AR) antagonist with IC 50 of 36 nM in LNCaP cells.IC50 & Target: IC50: 36 nM (androgen–receptor, in LNCaP cells)[1]In Vitro: Enzalutamide has greater affinity to AR than Bicalutamide does in a competition assay with 16β–[18F]fluoro–5α–DHT (18–FDHT) in castration–resistant LNCaP/AR cells (AR–overexpressing). While Enzalutamide shows no agonism in LNCaP/AR prostate cells. Enzalutamide antagonizes induction of prostate–specific antigen (PSA) and transmembrane serine protease 2(TMPRSS2), combination with the synthetic androgen R1881 in parental LNCaP cells. Enzalutamide inhibits the transcriptional activity of a mutant AR protein (W741C, mutation of Trp741 to Cys)[1]. Enzalutamide also prevents nuclear translocation and co–activator recruitment of the ligand–receptor complex [2].In Vivo: Enzalutamide induces great tumor regression in castrate male mice bearing LNCaP/AR xenografts at a dose of 10 mg/kg [1].Enzalutamide shows dose–independent pharmacokinetics at intravenous and oral doses of 0.5–5 mg/kg [4].PROTOCOL (Extracted from published papers and Only for reference)Cell Assay: Enzalutamide is dissolved in DMSO and stored, and then diluted with appropriate medium before use [1]. [1]LNCaP cells (107 cells/condition) are grown in RPMI media supplemented with 5% charcoalstripped serum for 22 days, then treated with DMSO or 1 nM R1881, combined with an antiandrogen (DMSO, 1 μM Bicalutamide, 10 μM Bicalutamide, 1 μM RD162, 10 μM RD162, 1 μM MDV3100, or 10 μM MDV3100) for 8 hours. An aliquot of cells are harvested for qRT–PCR of PSA and TMPRSS2 mRNA. Theremaining cells are cross–linked using 1% paraformaldehyde for 10 minutes, then glycine is added and samples centrifuged (4°C,4000 rpm, 5 minutes) to stop further crosslinking. Chromatin immunoprecipitation is performed using a chromatinimmunoprecipitation assay kit. Immunoprecipitated DNA is amplified by real–time PCR. Primers are PSA enhancerforward–ATGTTCACATTAGTACACCTTGCC and reverse–TCTCAGATCCAGGCTTGCTTACTGTC and TMPRSS2 enhancerforward–TGGTCCTGGATGATAAAAAAAGTTT and reverse–GACATACGCCCCACAACAGA [1].Animal Administration: Enzalutamide is dissolved in vehicle (10 % DMSO, 45 % polyethylene glycol 400, and 45 %saline) (Rat)[4].[3][4]Mice [3]Following a 5–day acclimation period, 5– to 9–week–old male CB17SCID mice are castrated and allowed to recover for an additional 5days before inoculation with tumor cells. LNCaP cells co–expressing exogenous AR and the AR–dependent reporter construct ARR2–Pb–Luc (LNCaP–AR–Lux cells) are used to generate a xenograft model of human prostate cancer. Before implantation,LNCaP–AR–Lux cells are prepared by the addition of trypsin–EDTA, washed with complete medium, collected and resuspended at 20×106 cells/mL. Cell suspensions are diluted with Matrigel to 2×106 cells/0.2 mL and delivered subcutaneously in the suprascapularregion. Tumor growth is monitored to the volume of 100 mm 3 when treatment begins (80 days). The observed rate of tumor take with LNCaP–AR–Lux cells is between 70% and 80%. Body weight and tumor volumes (width 2×length/2) are measured two to three times per week with a digital caliper, and the average tumor volumes are determined. Test drugs are diluted in TweenProduct Name:Enzalutamide Cat. No.:HY-70002CAS No.:915087-33-1Molecular Formula:C 21H 16F 4N 4O 2S Molecular Weight:464.44Target:Androgen Receptor; Autophagy Pathway:Others; Autophagy Solubility:10 mM in DMSO80:PEG 400, and stored at 4°C until administration by oral gavage. Each group of mice (n=7) is treated daily for 28 consecutive days with 1, 10, or 50 mg/kg Enzalutamide, vehicle control, or 50 mg/kg Bicalutamide. At the end of the treatment period or when tumor volume exceeded 1,000 mm3, animals are euthanized and blood and tissue samples are collected for analysis.Rat[4]Male SD rats (n=3) are administered Enzalutamide through the tail vein (intravenous) and by oral gavage at 1 mg/kg and are kept in metabolic cages after dosing. Urine and feces samples are collected over the following time intervals after dosing: 0–2, 2–4, 4–6, 6–10, 10–24, 24–48, and 48–72 h. The metabolic cages are rinsed with distilled water, and residues are added to the urine samples at 72 h. To extract the Enzalutamide present in the feces, samples are shaken vigorously for 12 h with 50 % methanol.References:[1]. Tran C, et al. Development of a second–generation antiandrogen for treatment of advanced prostate cancer. Science, 2009, 324 (5928), 787–790.[2]. Scher HI, et al. Antitumour activity of MDV3100 in castration–resistant prostate cancer: a phase 1–2 study. Lancet, 2010, 375(9724), 1437–1446.[3]. Guerrero J, et al. Enzalutamide, an androgen receptor signaling inhibitor, induces tumor regression in a mouse model of castration–resistant prostate cancer. Prostate. 2013 Sep;73(12):1291–305.[4]. Kim TH, et al. Pharmacokinetics of enzalutamide, an anti–prostate cancer drug, in rats. Arch Pharm Res. 2015 Nov;38(11):2076–82.Caution: Product has not been fully validated for medical applications. For research use only.Tel: 609-228-6898 Fax: 609-228-5909 E-mail: tech@Address: 1 Deer Park Dr, Suite Q, Monmouth Junction, NJ 08852, USA。
REVIEWARTICLEpublished:22October2014doi:10.3389/fimmu.2014.00518
Immunotherapeuticpotentialofextracellularvesicles
BinZhang1,YijunYin1,RuennChaiLai1andSaiKiangLim1,2*1ExosomeandSecretedNano-vesicleGroup,A*STARInstituteofMedicalBiology,Singapore2DepartmentofSurgery,YongLooLinSchoolofMedicine,NationalUniversityofSingapore,Singapore
Editedby:FrancescE.Borras,Institutd’InvestigacióenCiènciesdelaSalutGermansTriasiPujol,Spain
Reviewedby:GregoryB.Lesinski,TheOhioStateUniversityComprehensiveCancerCenter,USABegoñaPérez-Cabezas,InstitutodeBiologiaMoleculareCelular,Portugal
*Correspondence:SaiKiangLim,ExosomeandSecretedNano-vesicleGroup,A*STARInstituteofMedicalBiology,8ABiomedicalGrove,#05-05Immunos,138648Singaporee-mail:saikiang.lim@imb.a-star.edu.sg
ExtracellularvesicleorEVisatermthatencompassesallclassesofsecretedlipidmem-branevesicles.Despitebeingscientificnovelties,EVsaregainingimportanceasamediatorofimportantphysiologicalandpathologicalintercellularactivitiespossiblythroughthetrans-feroftheircargoofproteinandRNAbetweencells.Inparticular,exosomes,thecurrentlybestcharacterizedEVshavebeennotablefortheirinvitroandinvivoimmunomodula-toryactivities.Exosomesarenanometer-sizedendosome-derivedvesiclessecretedbymanycelltypesandtheirimmunomodulatorypotentialisindependentoftheircellsource.Besidesimmunecellssuchasdendriticcells,macrophages,andTcells,cancerandstemcellsalsosecreteimmunologicallyactiveexosomesthatcouldinfluencebothphysiologicalandpathologicalprocesses.Theimmunologicalactivitiesofexosomesaffectbothinnateandadaptiveimmunityandincludeantigenpresentation,Tcellactivation,TcellpolarizationtoregulatoryTcells,immunesuppression,andanti-inflammation.Assuch,exosomescarrymuchimmunotherapeuticpotentialasatherapeuticagentandatherapeutictarget.
Keywords:extracellularvesicles,exosomes,immunomodulation,innateimmunity,adaptiveimmunity,immunotherapy
INTRODUCTIONExtracellularvesicles(EVs)areincreasinglyimplicatedasamajormodeofintercellularcommunication.MostcelltypesareknowntosecreteEVswhichareessentiallybi-lipidmembranevesiclescarryingacomplexcargoofproteinsandRNAs.TheseEVscanbetakenupbyothercelltypestherebytransferringproteinsandRNAsfromonecelltoanother.TherearemanyclassesofEVssuchasexosomes,microvesi-cles,ectosomes,membraneparticles,exosome-likevesiclesandapoptoticbodies,andtheycouldbedistinguishedbytheirbio-genesispathway,size,flotationdensityonasucrosegradient,lipidcomposition,sedimentationforce,andproteincargo[reviewedinRef.(1,2)].However,manyofthesedifferentiatingparameterssuchassize,flotationdensityonasucrosegradient,lipidcom-position,sedimentationforce,andproteincargoarenotdiscretevaluesthatareexclusivetoaspecificclassofEVs.Consequently,classificationofEVshasbeenchallenging.ExosomesarepresentlythebestcharacterizedEVs.Theyaredefinedasmembranevesi-clesof50–100nmdiametercontainingproteins,RNAs,andlipids(3–8).Theyaresecretedbycellswhenendosomalmembranesinvaginateinwardtoformmultivesicularbodies(MVBs)andtheMVsfusedwiththeplasmamembrane.Thisendosomalbiogen-esisisadistinctivefeatureofexosomes,andispresentlyknowntobeuniquetoexosomesandnotanyoftheotherclassesofEVs.Asendocytosisismostactiveatspecializedmicrodomainsinplasmamembranesuchaslipidrafts,exosomessuchasmes-enchymalstemcell(MSC)exosomeshavemembranesenrichedinelementsoflipidraftssuchasGM1gangliosidesandtransferrinreceptors(9).However,ascertainingthebiogenesisofEVsistech-nicallychallengingandnotalwayspractical,andconsequently,theterm“exosomes”havebeenusedgenericallytodescribeanyEVsthatsharesomeofthebiophysicalorbiochemicalparametersofexosomeswithoutvalidatingtheirbiogenesis.Hence,thetermEVsandexosomesinthisreviewwillbeusedsynonymously.ManycelltypesareknowntosecreteEVs,andtheyincludeepithelialcells(10,11),fibroblasts(12),erythrocytes(13,14),platelets(15),mastcells(16),tumorcells(17–19),stemcells(20–22),andimmunecellssuchasdendriticcells(DCs)(23,24),monocytes(25,26),macrophages(27,28),NKcells(29,30),Blymphocytes(31,32),andTlymphocytes(33,34).However,thephysiologicalfunctionsofEVsremaintenuous.Partofthiscouldbeattributedtothelackofadefinitivecriteriontopurify,characterize,andclassifytheclassesofEVsunambiguously.Exosomeswerefirstthoughttobeacellularmeansforthedis-posalofredundantproteinsbygroupsstudyingreticulocytemat-uration(35–37),buttheyarenowgenerallyviewedasmediatorsofintercellularcommunicationthroughthetransferofbiologi-callyactivematerials.However,withthepresentlackofclarityindefiningtheclassesofEVs,theroleofEVsorexosomesasmediatorsofintercellularcommunication,andtheireffectsonbiologicalorphysiologicalprocessesremainsaconundrum.Forexample,docellssecreteorevenhavethecapacitytoproduceallclassesofEVs?DocellssecretemorethanoneclassofEVsatanyonetime?AresecretionorproductionofEVsandtheircargoregulated?ItislikelythatourpresentdayunderstandingofEVfunctionsisanamalgamofthediametricallydifferentfunctionsofdifferentEVclasses,leadingtoaconfusingandsometimescon-tradictoryperceptionofEVorexosomefunctions.Oneoftheearliestreportedphysiologicaltargetsofexosome-mediatedinter-cellularcommunicationistheimmunesystem.Blymphocyteswerethefirstimmunecelltypereportedtosecretevesiclesandthesevesiclesexpressabundantmajorhistocompatibilitycomplex(MHC)ClassIandIImolecules,B7.1(CD80)andB7.2(CD86)co-stimulatorymolecules,andICAM-1(CD54)adhesionmolecules.