英语学习(肯定句与否定句词义的差别)
- 格式:wps
- 大小:15.00 KB
- 文档页数:2

小学英语语法详解陈述句——肯定句什么是陈述句?陈述句陈述一个事实或者说话人的看法。
它包括肯定句(The Affirmative Sentence)和否定句(The Negative Sentence)两种。
陈述句在书写时句末用句号,在明读时用降调。
一.肯定句基本结构为“主+谓"结构以及它的补充结构,以下是常用的几种肯定句。
1.主语+be动词(am/is/are)+表语He is tall.他很高。
They are honest.他们是诚实的。
Aaron老师的小提醒这里的be动词(am/is/are)也可变成其他的系动词。
I feel better.我感觉好多了。
The leaves turned yellow.叶子变黄了。
2.主语+谓语(不及物动词)The bell rang.铃声响了。
The match begins.比赛开始了。
Linda老师的小提醒当谓语动词是不及物动词的时候,虽然后面不可以跟宾语,但是可以跟状语用来修饰。
The car goes fast.车子跑得很快。
My grandpa walks slowly.我爷爷走路很慢。
3.主语+谓语(及物动词)+宾语+(状语)He wrote a letter yesterday.他昨天写了一封信。
They are playing football in the playground.他们正在操场器足球。
4.主语+谓语(及物动词)+间接宾语+直接宾语She psseds me a ball.她传给我一个球。
I give him a hug.我给他一个拥抱。
5.主语+谓语(及物动词)+宾语+宾语补足语I painted it yellow.我把它涂成黄色。
I made her cry.我把她弄哭了。
Aaron老师的小提醒这五种基本句式结构只限于简单句,也就是只包含一个谓语结构,而不包括并列句和复合句。
小学英语语法详解陈述句——否定句什么是陈述句?陈述句陈述一个事实或者说话人的看法。
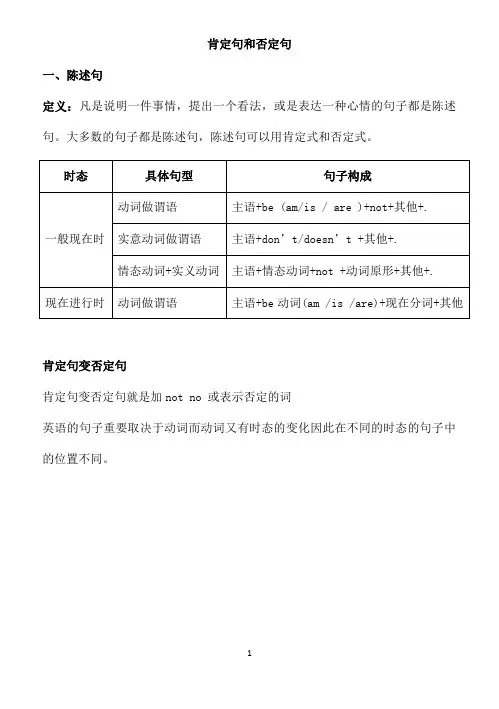
肯定句和否定句一、陈述句定义:凡是说明一件事情,提出一个看法,或是表达一种心情的句子都是陈述句。
大多数的句子都是陈述句,陈述句可以用肯定式和否定式。
肯定句变否定句肯定句变否定句就是加not no 或表示否定的词英语的句子重要取决于动词而动词又有时态的变化因此在不同的时态的句子中的位置不同。
陈述句练习把下列陈述句变成否定句。
1.My father watches TV every day . My father _____ ____ TV every day .2.Kate often does her homework at six . Kate __ often ___ her homework at six.3.I go to school at seven . I ___ ____ to school at seven .4.She usually goes home by bus . She ____ usually ____ home by bus .5.They are good students . They ____ ____ good students .6.He is clever . He ____ ____ clever .7.He has some bread for breakfast every morning .He ____ ____ ____ bread for breakfast every morning .8.I often drink some tea in the afternoon . I ___ often ____ ____ tea in the afternoon .9.He has some eggs . He ____ ____ ____ eggs .10.Kim likes his new bike .Kim ____ ____ his new bike.小升初语法之疑问句疑问句是用来提出问题的,疑问句又包括:一般疑问句、特殊疑问句、反义疑问句和选择疑问句。
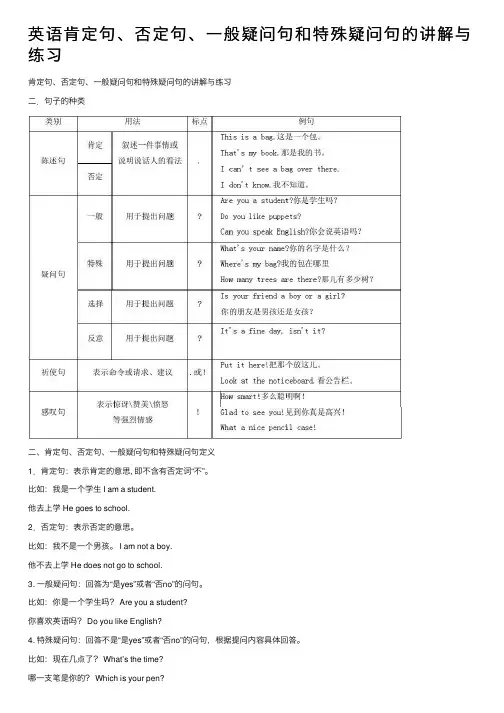
英语肯定句、否定句、⼀般疑问句和特殊疑问句的讲解与练习肯定句、否定句、⼀般疑问句和特殊疑问句的讲解与练习⼆.句⼦的种类⼆、肯定句、否定句、⼀般疑问句和特殊疑问句定义1.肯定句:表⽰肯定的意思, 即不含有否定词“不”。
⽐如:我是⼀个学⽣ I am a student.他去上学 He goes to school.2.否定句:表⽰否定的意思。
⽐如:我不是⼀个男孩。
I am not a boy.他不去上学 He does not go to school.3. ⼀般疑问句:回答为“是yes”或者“否no”的问句。
⽐如:你是⼀个学⽣吗? Are you a student?你喜欢英语吗? Do you like English?4. 特殊疑问句:回答不是“是yes”或者“否no”的问句,根据提问内容具体回答。
⽐如:现在⼏点了? What’s the time?哪⼀⽀笔是你的? Which is your pen?三、肯定句、否定句、⼀般疑问句和特殊疑问句的相互转换肯定句变否定句:在am, is, are 后⾯加上not,其余按顺序照抄。
肯定句变⼀般疑问句:把am, is, are 提前放到句⾸并⼤写Am, Is, Are,其余照抄。
肯定句变特殊疑问句(就划线部分提问):分3步骤第⼀步:先变⼀般疑问句。
第⼆步:找合适的特殊疑问词代替划线部分。
第三步:特殊疑问词提前放到句⾸,并⼤写,其余按顺序照抄,省略划线部分。
注意:1.如:Liming 's not here today. Who's not here today? 今天谁没来?2.划线部分不能在特殊疑问句中出现。
1.肯定句、否定句和⼀般疑问句的互换肯定句:否定句:⼀般疑问句:肯定回答:Yes, it is.否定回答:No, it isn’t.2.就划线部分提问(变特殊疑问句)This is a book.第⼀步:变⼀般疑问句 Is this a book?第⼆步:找合适的特殊疑问词 Is this what ?What is this?do not或者does not,其余按顺序照抄动词⽤原形。


(知识点)肯定句否定句和一般疑问句的转换肯定句、否定句和一般疑问句是英语语法中的基本概念,它们在日常交流以及英语学习中起着重要的作用。
本文将详细探讨这三种句子结构的转换方法,并且给出一些实例以帮助读者更好地理解和运用。
一、肯定句的转换在转换肯定句时,我们一般使用否定词"not"来实现。
将肯定句转换为否定句的方法可以分为两种情况:1. 当肯定句中没有助动词时,我们在句子中加入助动词"do",并在"do"后面加上否定词"not"。
例如:肯定句:She speaks English.否定句:She does not speak English.2. 当肯定句中已经包含助动词时,我们直接在助动词后面加上否定词"not"即可。
例如:肯定句:He can swim.否定句:He cannot swim.需要注意的是,在口语中,人们常常使用缩略形式来表示否定形式。
例如,"does not"缩写为"doesn't","cannot"缩写为"can't"。
二、否定句的转换与肯定句相反,我们要将否定句转换为肯定句时,需要去掉否定词"not"。
1. 当否定句中含有助动词时,我们直接去掉否定词"not"即可。
例如:否定句:I am not interested in sports.肯定句:I am interested in sports.2. 当否定句中没有助动词时,我们需要添加助动词"do",并将助动词变为肯定形式。
例如:否定句:They don't like spicy food.肯定句:They do like spicy food.需要注意的是,一些动词本身已经具有否定意义,如"nobody"(没有人)、"nothing"(没有什么)等。

理解句型肯定句否定句与疑问句的用法理解句型肯定句、否定句与疑问句的用法句子是语言表达的基本单位,而句型则是句子的组织形式和结构。
在英语中,句型的构造可以使用肯定句、否定句和疑问句等形式。
肯定句用于陈述事实或表达肯定的观点,否定句则表示相反的意思,而疑问句则用于提问和寻求信息。
下面将详细探讨这些句型的用法。
一、肯定句肯定句是最常见的句型,用于陈述或表达事实、观点或描述。
肯定句的基本结构是主语 + 动词 + 宾语(SVO)。
在肯定句中,主语通常是一个名词、代词或名词性短语,动词则根据主语的人称和数进行变化,宾语则是动作的接受者或影响的对象。
例如:- I love cats.(我喜欢猫。
)- She plays the piano beautifully.(她弹钢琴弹得很好。
)- They have a big house.(他们有一所大房子。
)肯定句还可以通过添加修饰词、状语、从句等来提供更多的细节和信息:例如:- Peter is a talented musician who plays multiple instruments.(彼得是一个多才多艺的音乐家,他会演奏多种乐器。
)- The cake tastes delicious and looks beautiful.(这个蛋糕味道美味,外观漂亮。
)二、否定句否定句用于表示相反或拒绝的意思。
构成否定句的方法是在助动词或情态动词之前加上not。
有些动词本身就是否定意义的,如can't(不能)、won't(不愿意)等。
例如:- He does not like spicy food.(他不喜欢辣食。
)- I can't swim.(我不会游泳。
)- They won't go to the party.(他们不打算去聚会。
)在一般现在时和一般过去时中,动词be的否定形式是在be动词之后加not。
例如:- She is not a doctor.(她不是医生。

(知识点)掌握句子的肯定否定和疑问形式句子是语言中最基本的表达单位,我们在日常交流和写作中经常使用句子来表达观点、传达信息。
而句子的肯定否定和疑问形式是句子的常见变化形式,是我们必须掌握的语法知识点。
本文将从肯定句、否定句和疑问句三个方面详细介绍句子的肯定否定和疑问形式的正确运用。
一、肯定句(Affirmative Sentence)1. 在句子中,我们通常使用主语+谓语+宾语的结构来构成肯定句。
主语通常是句子的主要主题,谓语是句子表达某种动作或状态的动词,宾语是动作的承受者或受事者。
例如:- I love reading books.(我喜欢阅读书籍。
)- They are playing football in the park.(他们正在公园里踢足球。
)2. 肯定句中的谓语动词一般是用基本形式(原形动词)。
例如:- She sings beautifully.(她唱得很美。
)- We eat lunch at noon.(我们在中午吃午餐。
)3. 肯定句中可以使用副词或副词短语来修饰谓语动词,增加句子的细节和修饰。
例如:- He speaks English fluently.(他英语说得很流利。
)- They usually go to the movie theater on weekends.(他们通常在周末去电影院。
)二、否定句(Negative Sentence)1. 否定句是通过在谓语动词前加上否定副词或助动词的方式来表示的。
否定副词包括"not"、"never"等。
例如:- I do not like swimming.(我不喜欢游泳。
)- He has never been to Japan.(他从未去过日本。
)2. 在一般现在时和一般过去时中,我们可以使用助动词来构成否定句,助动词和主语之间需要加上"do not"(don't)或"did not"(didn't)。

肯定句、否定句、肯定句、否定句、一般疑问句和特殊疑问句的详解Positive sentence, negative sentence, positive sentence, negative sentence, general questions and special questions, explain a verb: am, is, be, are two positive sentence, negative sentence, interrogative sentence and special interrogative sentence: definition 1. sure that surely means, which does not contain negative words "". For example: I am a student, I am a student., he goes to school He goes to school. 2. negative sentence: means negative. For example: I'm not a boy. I am nota boy. He doesn't go to school. He does not go to school. yes3. general question: answer "yes" or "no no" question. For example: are you a student? Are, you, a, student? Do you like English? Do you like English? The special interrogative sentence with an interrogative word: at the beginning, a component of a sentence question sentence is a special question. The commonly used interrogative words are: special questions, what, who, whose, which, when, where, how, why, etc.. There are two kinds of special interrogative word order: special interrogative sentence has two kinds of order: 1. as interrogative words as the subject or subject attribute, namely the subject or the subject attribute question, the word order is a sentence word order: interrogative words (+ subject + Verb +) other ingredients? Such as: who, is, singing, in, the, room? Whose, bike, is, broken? 2., if interrogative words are made up of other elements, i.e., ask questions of other elements, their word order is: interrogative word + general interrogative sentence order Such as: what, class, are, you, in? What, does, she, look, like? Where, are, you, from? What, time, does, he, get, up, every, morning? How, do, you, know? Specialinterrogative word + auxiliary verb + subject + verb prototype + other? Special interrogative word + auxiliary verb + subject + verb prototype + other? Eg:Where, do, you, do, study, English, special interrogative word, +be verb + subject + other? Special question word "+be verb + subject + other"? Eg:Why, is, your, Mum, so, angry, special interrogative word + modal verb + subject + verb prototype + other? Special interrogative word + modal verb + subject + verb prototype + other? Eg:What, can, I, for, you, do, note: 1., when answering a particular question, do not use yes / no, that is, what to ask, what to answer, especially the brief answer. What time is it now? What, s, the, time. Which pen is yours? Which is your pen? Three, positive sentence, negative sentence, wh questions the mutual conversion of am, is, are sentence, surely sentence negative sentence: in am, is, are followed by not, in order to copy the rest. Make sure you change the sentence "am", "is", "are" in front of the sentence and capitalize "Am", "Is", "Are", and the rest copy. Surely sentence special interrogative sentence (underlined part questions): divided into 3 steps the first step: the first variable general question second step: to find the special questions right replace the underlined part third: special interrogative sentence in advance, and other capitals, in order to copy, omit the underlined part. Note: 1. must change the general interrogative sentence first. However, if the subject or subject's attribute is asked, the word order remains the same as "special interrogative" (+ subject) + declarative sentence". For example: Li Ming's not here today. Who's not here today? Who did not come today? Happy progress 1 avoid detours 2. underlined part can not appear in special questions.What time when (Q time) who (people who ask) where whose whoasked the owner where asked the location which which one asked why why ask why what asked what time what things what time asked what color what color what about colour asked the time... How to ask opinions, what, day weeks, weeks, what, date, what date, ask specific dates, what, place, what location, specific address, how... How to ask the situation, how, old ask how old, how, many, ask how many, how, much, ask how much, the price how about... How to ask how far how long asked how far the way how fast time How soon, How often asked how long time to ask how long the frequency for example: 1. positive sentence, negative sentence and interrogative sentence affirmative sentence: This is a exchange book. This is not a it book. Is this a is book? Answer: Yes, it positive is. negative answer: No, isn 'it t. underlined part 2. questions (variable special questions) This is a book. the first step: Is this a Book general questions? The second step: to find the special questions Is this right what? The third step: the special questions in advance the first sentence, and other capitals, in order to copy, omit the underlined part. What is this am is are? No, surely sentence sentence, negative sentence: with do not or does not in the subject behind the rest according to the order of the verb copying sentence prototype certainly general question: at the beginning of the sentence with do or does and the rest of the capital, copy. Note: the verb prototype surely sentence special interrogative sentence (underlined part questions): divided into 3 steps the first step: the first variable general question second step: to find the special questions right replace the underlined part third: special interrogative sentence in advance, and the rest of capital, in order to copy, omit the underlined part. Note: 1. must change the general interrogative sentence first. However, if the subject or subject's attributeis asked, the word order remains the same as "special interrogative" (+ subject) + declarative sentence". 2. the underlined part should not appear in the particular question. Non single three do, three does single non single sentence: I like English. three must have general questions: Do you like English? I do not like negative sentences: English. single sentence: He likes English. three must have general questions: Does he like English? He does not like negative sentence: English. happy progress in 2 detours the underlined part question: I like English. the first step: the first variable Do you like English general questions? The second step: to find the special questions right Do you like what to replace the underlined part? The third step: the special questions in advance in the first sentence, and other capitals, in order to copy, omit marking part. What do you like? A statement to the general interrogative sentence, declarative sentence to general questions, then special interrogative statements to the general interrogative sentence formulas to easily suspect Chen Chen, a suspect is easy, I sentence: be verb sentences: in advance. (the first two words are reversed) if there is be, move be ahead of time. I, am, a, girl., I, you, Are, you, a, girl? Yes, I, am./No, I, am, not., You, are,, clever., Are, you, clever? He, is, a, pupil., Is, he, a, pupil? II sentence: verb sentence: sentence: verb sentence: (with auxiliary, without changing the original sentence order, before verbs (words) after (verb) before verbs (verb) and no be (auxiliary word Do, Does, Did),) the auxiliary reduction. Restore I, go, to, school, every, day, Do,, you, go, to, school, everyday? You, swim, every, day., Do, you, swim, every, day? The auxiliary (verb) reduction,Refers to the following: moving. Before (words) after (verb) reduction, refers to the following: the original verb plus s/es is reduced to get rid of the tail, which is the prototype of the verb in the word list. Note: has, have, do. Does restored. Such as does my homework, He goes to bed at 9:00 every day. Does he go to bed at 9:00 every day? She reads book Does she read. Book He does his homework at? 6:00 every afternoon. Does he do his homework at 6:00 every afternoon? 'in the past tense verb sentence, the past, before the did He wanted a cake. prototype is reduced to Did he want a cake? Ask you, out of their own.I (I, my) sentences into you (You, your) to ask you out of their own. Don't forget to add the question mark at the end of the sentence. The sentence becomes you, jumping out of yourself and asking you. Don't forget to add the question mark at the end of the sentence. Class III sentences: modal verbs, sentence types, sentences: modal verbs can also be easy to move, subject to reverse. The modal verb (Can, Will will, May can) is also easy to move, subject to reverse, You, can, swim., Can, you, swim? You, will, go, to, Beijing, tomorrow., Will, you, go,, to, Beijing, tomorrow? General questions to special questions usually end in turn, when, what, time, why, how many, how much) usually end turn, to mention the word What (part of Gath,,,,,), the rest also copy. The rest are copied. Your, name, is, Jiahui., Is, your, name, Ren, Jiahui, What, is, your, name, happy progress,, detours, I, go, to, school, at, 7:20, every, day.:Do, you, Ren, go, to,, school, at, 7:20, every, day? :? What, time, do, you, go, to, school, every, day? Who asks the subject to keep the order, and the rest to copy the original sentence. Ask the subject to keep the order and the rest to copy the original sentence. I, go, to, school, at, 7:20, every, day.:Who, go, to, school, at, 7:20, every, day? :? I, go, to, school, every, day?Who, go, to, school, every, day? Solve the problem of sentence patterns, and ask questions about the underlined parts. The original formula, the copyright belongs to me synchronous practice general questions exercises 1. His father is an English teacher. 2. These cats are crying. 3. They can swim.4. I like to read English. go to school on5. I foot.6. He likes English.7. His father goes to work by bus. He is crying under the8. tree.9. His birthday is on the twentieth of November. Mrs. Li and Kitty are in 10. a big shop. 11. Kitty is wearing her new uniform. The boy under the tree 12. is hungry. 13. He goes to school every day. I want to have a 15. model car. 16. She wants a cup of coffee. happy 4 detours 17. Mrs. Li and Kitty watch television at night. I do my homework after 18. school.5 happy detours special questions exercises (special questions exercises (a) and fill in the blanks with the right words (who, where, when) 1._____ is that pretty girl She is my sister.2._____? Are Jack and Tom They are behind you.3._____? Do you go to school I go to school from Monday? To Friday.4.桌子上有________帽。
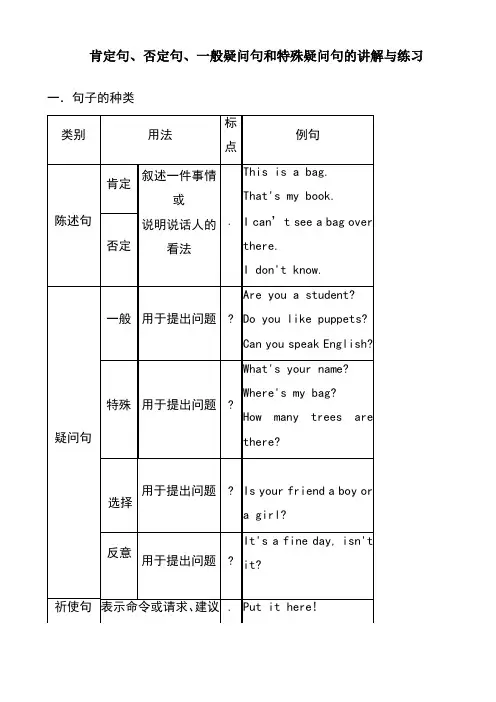
肯定句、否定句、一般疑问句和特殊疑问句的讲解与练习一.句子的种类一、be动词:am, is, are二、肯定句、否定句、一般疑问句和特殊疑问句定义1.肯定句:表示肯定的意思, 即不含有否定词“不”。
比如:我是一个学生 I am a student.他去上学 He goes to school.2.否定句:表示否定的意思。
比如:我不是一个男孩。
I am not a boy.他不去上学 He does not go to school.3. 一般疑问句:回答为“是yes”或者“否no”的问句。
比如:你是一个学生吗? Are you a student?你喜欢英语吗? Do you like English?4. 特殊疑问句:回答不是“是yes”或者“否no”的问句,根据提问内容具体回答。
比如:现在几点了?What’s the tim e?哪一支笔是你的? Which is your pen?三、肯定句、否定句、一般疑问句和特殊疑问句的相互转换有am, is, are的句子,肯定句变否定句:在am, is, are后面加上not,其余按顺序照抄。
肯定句变一般疑问句:把am, is, are提前放到句首并大写Am, Is, Are,其余照抄。
肯定句变特殊疑问句(就划线部分提问):分3步骤第一步:先变一般疑问句。
第二步:找合适的特殊疑问词代替划线部分。
第三步:特殊疑问词提前放到句首,并大写,其余按顺序照抄,省略划线部分。
注意:1.一定先变一般疑问句。
但是,如果问的是主语或主语的定语时,语序不变,为"特殊疑问词(+主语)+陈述句"。
如:Liming 's not here today. Who's not here today? 今天谁没来?2.划线部分不能在特殊疑问句中出现。
例如:1.肯定句、否定句和一般疑问句的互换肯定句:This is a book.否定句:This is not a book.一般疑问句:Is this a book?肯定回答:Yes, it is.否定回答:No, it isn’t.2.就划线部分提问(变特殊疑问句)This is a book.第一步:变一般疑问句 Is this a book?第二步:找合适的特殊疑问词 Is this what ?第三步:特殊疑问词提前放到句首,并大写,其余按顺序照抄,省略划线部分。

肯定句否定句与祈使句的区别肯定句、否定句与祈使句的区别一、引言在语法学中,肯定句、否定句和祈使句是常见的句子类型。
它们在表达方式上有明显的区别。
本文将探讨肯定句、否定句和祈使句的区别以及在实际应用中的使用规则。
二、肯定句肯定句是最常见的句子类型之一。
它用于陈述事实、表达肯定的观点或指出存在的情况。
肯定句通常使用陈述句句式,即主语在句子中充当主动角色,动词表达动作或状态,而宾语则接受动作或状态。
例如:- 我喜欢吃巧克力。
- 他每天骑自行车上学。
- 他们正在观看一部电影。
在以上例句中,每个句子都陈述了某种事实或肯定的情况。
三、否定句与肯定句相对,否定句用于否定某种情况或陈述事物不存在。
否定句通常在动词前面加上否定副词(如"不"、"没有"、"无"等),或使用其他否定形式的助动词。
例如:- 我不喜欢吃巧克力。
- 他没有骑自行车上学。
- 他们没有观看电影。
在以上例句中,通过在动词前加上"不"这个否定副词来改变句子的含义。
四、祈使句祈使句用于表达请求、命令、建议或建议。
它通常没有明确的主语,并以动词原形开头。
祈使句中的动词直接传达请求或指示。
例如:- 吃下你的蔬菜。
- 给我打电话。
- 请保持安静。
以上例句中,动词的原形直接传达命令、请求或建议的含义。
五、总结通过以上的讨论,我们可以看出肯定句、否定句和祈使句在表达方式上的明显区别。
肯定句用于陈述肯定的观点、陈述客观事实或指出存在的情况。
它通常采用陈述句的句式结构。
否定句用于否定情况、表达不愿意或陈述事物不存在。
它通常在动词前添加否定副词或使用否定形式的助动词来改变句子的含义。
祈使句用于表达请求、命令、建议或建议。
它通常没有明确的主语,并以动词原形开头。
根据具体的语境和场合,我们可以准确选择使用肯定句、否定句或祈使句来表达自己的意思。
六、结语在日常交流和书面表达中,正确运用肯定句、否定句和祈使句是至关重要的。

句型转换否定句与肯定句的转换句型转换:否定句与肯定句的转换句型的转换是英语学习中非常重要的一部分,它可以帮助我们提高语言表达的灵活性。
在句型转换中,否定句与肯定句的转换是一项常见的任务。
本文将讨论一些常见的句型转换规则,帮助您掌握如何在否定和肯定之间转换句子。
I. 变一般句为否定句在将一般句转换为否定句时,我们通常需要使用否定词(例如not, never, nobody)来改变句子的意思。
1. 否定动词将助动词do或be放在句子前面,再加上not,即可将一般句变为否定句。
例句:原句:She sings very well.否定句:She does not sing very well.原句:He is a doctor.否定句:He is not a doctor.2. 否定副词将肯定句中的肯定副词替换为否定副词,即可将一般句变为否定句。
例句:原句:I often go to the park on weekends.否定句:I never go to the park on weekends.原句:They always eat breakfast together.否定句:They never eat breakfast together.3. 否定代词将肯定句中的代词替换为否定代词,即可将一般句变为否定句。
例句:原句:Everyone is here.否定句:Nobody is here.原句:Somebody called you.否定句:Nobody called you.II. 变否定句为肯定句在将否定句转换为肯定句时,我们通常需要删除否定词或使用转折词来改变句子的意思。
1. 删除否定词将否定句中的否定词删除,即可将否定句变为肯定句。
例句:原句:You haven't finished your homework yet.肯定句:You have finished your homework.原句:He doesn't like coffee.肯定句:He likes coffee.2. 使用转折词使用转折词(例如but, yet, still)来改变句子的意思,从而将否定句转换为肯定句。
be动词的肯定句与否定句构成be动词是英语中十分常用的一类动词,可以用于构成肯定句和否定句。
本文将介绍be动词的肯定句和否定句的构成方式。
一、be动词的肯定句构成方式be动词的肯定句由主语和be动词的各种形式构成。
根据主语的单复数和人称的不同形式,be动词的形式也会相应变化。
下面是be动词在肯定句中的各种形式:1. 第一人称单数:I am2. 第二人称单数:You are3. 第三人称单数:He/She/It is4. 第一人称复数:We are5. 第二人称复数:You are6. 第三人称复数:They are肯定句的构成方式是简单直接的,主语+be动词的相应形式即可。
例如:1. I am a teacher.2. You are my friend.3. She is an engineer.4. We are students.5. They are playing football.二、be动词的否定句构成方式be动词的否定句构成方式比肯定句稍微复杂一些,需要在be动词前加上not。
下面是be动词在否定句中的各种形式:1. 第一人称单数:I am not2. 第二人称单数:You are not3. 第三人称单数:He/She/It is not4. 第一人称复数:We are not5. 第二人称复数:You are not6. 第三人称复数:They are not否定句的构成方式是在be动词前加上not。
例如:1. I am not a teacher.2. You are not my friend.3. She is not an engineer.4. We are not students.5. They are not playing football.三、be动词的肯定句和否定句的区别be动词的肯定句和否定句在语义上存在明显的区别。
肯定句表示肯定的事实或陈述,而否定句则表示否定的事实或陈述。
肯定句、否定句、一般疑问句和特殊疑问句的讲解与练习欧阳引擎(2021.01.01)一.句子的种类一、be动词:am, is, are二、肯定句、否定句、一般疑问句和特殊疑问句定义1.肯定句:表示肯定的意思, 即不含有否定词“不”。
比如:我是一个学生 I am a student.他去上学 He goes to school.2.否定句:表示否定的意思。
比如:我不是一个男孩。
I am not a boy.他不去上学 He does not go to school.3. 一般疑问句:回答为“是yes”或者“否no”的问句。
比如:你是一个学生吗? Are you a student?你喜欢英语吗? Do you like English?4. 特殊疑问句:回答不是“是yes”或者“否no”的问句,根据提问内容具体回答。
比如:现在几点了?What’s th e time?哪一支笔是你的? Which is your pen?三、肯定句、否定句、一般疑问句和特殊疑问句的相互转换肯定句变否定句:在am, is, are后面加上not,其余按顺序照抄。
肯定句变一般疑问句:把am, is, are提前放到句首并大写Am, Is, Are,其余照抄。
肯定句变特殊疑问句(就划线部分提问):分3步骤第一步:先变一般疑问句。
第二步:找合适的特殊疑问词代替划线部分。
第三步:特殊疑问词提前放到句首,并大写,其余按顺序照抄,省略划线部分。
注意:1.如:Liming 's not here today.Who's not here today? 今天谁没来?2.划线部分不能在特殊疑问句中出现。
例如:1.肯定句、否定句和一般疑问句的互换肯定句:This is a book.否定句:一般疑问句:Is this a book?肯定回答:Yes, it is.否定回答:No, it isn’t.2.就划线部分提问(变特殊疑问句)This is a book.第一步:变一般疑问句 Is this a book?第二步:找合适的特殊疑问词 Is this what ?第三步:特殊疑问词提前放到句首,并大写,其余按顺序照抄,省略划线部分。
英语讲义:肯定句与否定句词义的差别
“We have seen everyone besides Tom's father.”
这句话是“除了汤姆的父亲外,我们还见过其他的人。
”
如果把这话误解为:“除了(没见过)汤姆的父亲,其他的人我们都见过了”,那么就大错特错了。
反面这个意思应该这样表达:
“We have seen everyone than Tom's father.”
须知介词“besides的含义等于”in addition to“或”as well as“。
连词”than“的意思有如介词”except“。
例如:
(1)John was left with no choice than to quit.
(除了离开,约翰别无其他选择。
)
再比较下列两个句子就更清楚了:
(2)Besides rice, the farmers have produced peanuts.
(3)They have gathered all the crops except / than corns.
上述(2)的意思是(除了米之外,农夫还生产花生。
)(3)的意思却是“除了玉蜀黍之外,他们把其他农作物收割了。
”
由上面几个例子看,besides和except / than是不同义的,但是besides如果出现在否定句或疑问句里,意思就和except相同了。
例如:
(4)I have no other option besides this one.
(5)Some people care for nothing besides their money.
(6)What can we do besides obeying ?
这三个句子里的“besides”都可由“except”取代之。
由此可见,同一个字词,在肯定句和否定句中的意思会有转变。
与“besides , except”一样,“until”这个字也有类似的麻烦,常常令初学英语的人感到头疼。
看看下面例子(7)的意思是(7a)还是(7b)“呢?
(7)We slept until midnight.
a.我们到半夜才睡觉。
b.我们一直睡到半夜(才醒)。
显然(7a)是错的;(7b)才正确。
(7a)的英语句子应该是:
(8)We didn't sleep until midnight.
为什么呢?原因是“until”在肯定句中表示一个动作的终结,如例(7b),又如例(9):(9)Madam Lin slept until her son came home.
“Until”在否定句中才表示一个动作的开始,如例(8),又如例(10):
(10)Madam Lin did not sleep until her son came home.
这些句子里的“until”都可以由“till”取代。
要注意的是“until”可以在句前出现,“till”就不可以了,因此(11)是对的,(12)是错的:
(11)Until last year, Peter was working for ABC Corporation.
*(12)Till last year, Peter was working for ABC Corporation.
纵上所述,我们知道,同一个词语的意思会随肯定句和否定句而改变词义。
幸好这类词语不多,巧遇时稍微留意便行了。