mgmt09_tif09
- 格式:doc
- 大小:378.50 KB
- 文档页数:27

Functional changes from version 2 to version 3:●Support for DOS only systems and Windows 3.1/DOS only systems has beenterminated. The PCB and PCM IDE's have been discontinued. CCSC.EXE isnow a 32 bit application and now has a full set of command line options.PCW and CCSC fully operate on Windows 95,98,ME,NT4, and 2000. Customerswho buy or have PCB or PCM must use MPLAB as an IDE or their own editor.●All DLL files used by the compilers are in a DLL directory directly underthe directory with the EXE files. All .DLL files in the same directoryas the EXE are no longer used and may be deleted. The PC.DEF file andPCINCLUDES environment variable (in AUTOEXEC.BAT) are also no longer used.●CCSC now has the following command format:CCSC Valid Options:options cfilename options cfilename+FB Select PCB (12 bit)-D Do not create debug file +FM Select PCM (14 bit)+DS Standard .COD formatdebug file+FH Select PCH (PIC18)+DM.MAP format debug file +F7Select PC7 (PIC17)+DC Expanded .COD formatdebug file+FS Select PCS (SX)+Yx Optimization level x (0-9)+ES Standard error file+T Create call tree (.TRE) +EO Old error file format+A Create stats file (.STA)-J Do not create PJT file-M Do not create symbolfileCCSC Valid Options: (The xxx in the following are optional. If included, it sets the file extension.) options cfilename options cfilename+LNxxx Normal list file+O8xxx8 bit Intel HEX outputfile+LSxxx MPASM format list file+OWxxx16 bit Intel HEX outputfile+LOxxx Old MPASM list file+OBxxx Binary output file+LYxxx Symbolic list file-O Do not create object file -L Do not create list file+P Keep compile status window up after compile+Pxx Keep status window up for xx seconds after compile+PN Keep status window up only if there are no errors+PE Keep status window up only if there are errors+Z Keep scratch and debug files on disk after compileI="..."Set include directory search path, for example:I="c:\picc\examples;c:\picc\myincludes"If no I= appears on the command line the .PJT file willbe used to supply the include file paths.#xxx="yyy"Set a global #define for id xxx with a value of yyy, example:#debug="true"+STDOUT Outputs errors to STDOUT (for use with third party editors)+SETUP Install CCSC into MPLAB (no compile is done)+V Show compiler version (no compile is done)+Q Show all valid devices in database (no compile is done)●PCW has a new "Global Defines" window to allow compile time #defines tobe entered, saved in a separate file and loaded.● A new preprocessor directive #LOCATE has been added. #LOCATE works like#BYTE however in addition it prevents C from using the area. For example:float x;#locate x=0x50Will locate the float variable at 50-53 and C will not use this memoryfor other variables automatically located.●New byte wide I/O functions have been added that follow the normal rules formaintaining the TRIS register (unlike memory mapped port access). Examples:OUTPUT_B(3);X = INPUT_A();●New built-in function to restart the processor:RESET_CPU();Will jump to location 0 on 12 and 14 bit parts and also reset theregisters to power-up state on the PIC18.●PCW IDE changes:View Data Sheet and View Valid Fuses have moved to the View menuView|Valid Interrupts has been added to show a chips valid interrupts●The device .h file format has been updated. Information about device specificfunctions available is now in the .h file. The following defines supported forcompatibility with the old C71 compiler are no longer in the .h file. Use thenewer names:RTCC_ZERO use INT_RTCCEXT_INT use INT_EXTADC_DONE use INT_AD●#DEVICE must now be the first non-comment line in the program. Some pre-processordirectives may appear before this like #include and #define. Previous versionsof the compiler did not require a #device (it defaulted to a '71 in PCM).●The function EXT_INT_EDGE now accepts two parameter. The first parameter isthe external interrupt number (0,1 or 2) for the PIC18. If used it has no effecton 14 bit parts. If there is only one parameter the function works asit used to on external interrupt 0.●The functions SETUP_COUNTERS(), SET_RTCC() and GET_RTCC are still accepted bythe compiler however newer functions will provide better compatibility acrossfamilies. The newer functions are: SETUP_TIMER0(), SETUP_WDT(), SET_TIMER0()and GET_TIMER0(). Note that the PIC18 SETUP_WDT() only allows the WDT to beturned on or off, the time is set with #FUSES. The other PICs are the opposite.The TIMER0 is 16 bit on the PIC18 by default but can be setup to 8 bit.●For the PIC18 the READ/WRITE_PROGRAM_EEPROM accept a byte address and the readreturns a byte result. The WRITE will only work if a programming voltage isapplied to the chip.●The previously undocumented function ISAMOUNG is documented in this version.ISAMOUNG returns true if a character is one of the characters in a constantstring. For example:if( ISAMOUNG( x, "0123456789ABCDEFGHIJKLMNOPQRSTUVWXYZ") )...●Quoted strings now accept inserted hex numbers via \x. For example:printf("Hi There\x0D\x0A");●By default the compiler treats SHORT as one bit, INT as 8 bits and LONG as16 bits. The traditional C convention is to have INT defined as the mostefficient size for the target processor. This is why it is 8 bits on the PIC.In order to help with code compatibility a new directive has been added thatwill allow these types to be changed. #TYPE can redefine these keywords.For example:#TYPE SHORT=8, INT=16, LONG=32Note that the commas are optional. Since #TYPE may render some sizesinaccessible (like a one bit int in the above) four new keywords havebeen added to represent the four ints: INT1, INT8, INT16 and INT32.Be warned CCS example programs and include files may not work right ifyou use #TYPE in your program.●The ABS, LABS and FABS functions were implemented as simple C functionsin stdlib.h. ABS() is now built into the compiler and accepts any typeas a parameter. It returns the same type as the argument. For compatibilityLABS and FABS are #defined to ABS in stdlib.h.●The debug file (.COD) has been expanded from the Microchip definition toto include information to permit advanced debugging. This includes allC data types and better tracking information. CCS now provides a .DLL thatmay be used by debuggers to use this information. For example it is possibleto have a watch expression like: TABLE[I].LAST-TABLE[I].FIRSTThe new .DLL knows how to evaluate the expression and provide a properlyformatted string back to the debugger. Arrays and structures are alsoproperly formatted. The stack frame may be viewed along with the parameterspassed at each level and function return values may be traced. CCS is workingwith emulator manufactures to make use of these new capabilities.●The PCW help filename has been changed from PCW.HLP to CCSC.HLP. The samehelp file is used for PCB, PCM, and PCH.●The PCW context sensitive help has been enhanced. Placing the cursor on anyC keyword, preprocessor directive or built in function and pressing F1 willbring up help on that item. In addition pressing F1 when a red error messageis being shown will bring up additional help with that error.●The PCW IDE now allows the toolbar to be customized.● A number of internal compiler limits have been increased. For example thelimitation of a macro expansion being less than 256 characters is now 32768. Changes not documented in the May-2001 manual:●If @filename appears on the CCSC command line command line options willbe read from the specified file. Parameters may appear on multiplelines in the file.●If the file CCSC.INI exists in the same directory as CCSC.EXE then commandline parameters are read from that file before they are processed on the command line.●printf() now accepts both 16 and 32 bit variables for %LU and %LD●#define macros now accept the ANSI operators # and ##. In summary the#idx will be replaced with "paramx" and idx##idy is replaced withparamxparamy and is expanded if a new macro name is formed.●#elif is now supported. For example:#if __device__==71#define adc_pin PIN_A0#elif __device__==74#define adc_pin PIN_A2#elif __device__==874#define adc_pin PIN_E0#else#define adc_pin PIN_A1#endif●#IF directives now support: defined(id)This expression evaluates to 1 if id is a preprocessor id and0 otherwise. For example:#ifdef __PCB__#include <16c54.h>#elif defined(__PCM__)#include <16c74.h>#elif defined(__PCH__)#include <18c658.h>#endif●printf() now supports %s to insert a constant or variable string.●Three functions have been added to make manipulation of byteswithin variables easier.i8 = MAKE8(var,offset)Extracts the byte at offset from var.Same as: i8 = (((var >> (offset*8)) & 0xff)except it is done with a single byte move.i16 = MAKE16(varhigh,varlow)Makes a 16 bit number out of two 8 bit numbers.If either parameter is 16 or 32 bits only the lsbis used.Same as: i16 = (int16)(varhigh&0xff)*0x100+(varlow&0xff)except it is done with two byte moves.i32 = MAKE32(var1,var2,var3,var4)Makes a 32 bit number out of any combinationof 8 and 16 bit numbers. Note that the numberof parameters may be 1 to 4. The msb is first.If the total bits provided is less than 32 thenzeros are added at the msb.●#asm now accepts a parameter to prevent the compiler from doing automaticbank switching and optimization in the ASM code. For example:#byte x = 0xa0#asmclrf x#endasmWill generate a bank switch to bank 1 and a clear of location 20 in that bank.#asm ASISclrf x#endasmWill just generate the clear of location 20 and ignore the bank.●The READ_ADC() function always defaults to a 8 bit result. This maybe different from previous versions where the defualt was differentdepending on the chip. Use #DEVICE ADC=xx to specify the desired resolution.●Constant strings are now concatinated when they appear separated by whitespace. For example:printf("hi" "there"); is the same as printf("hithere");Changes not documented in the July-2001 manual:●Arrays may be defined with [] in many cases. For example:const char id[] = {"Hi There"}; // Same as [9]int x[]; // Same as *xint x[] = {1,2,3}; // Same as [3]●The #USE I2C option NOFORCE_SW is still accepted however the new FORCE_HWis what will appear in future documentation.●#INT_ directives now allow a NOCLEAR option to prevent the compilerfrom clearing the interrupt. For example:#INT_RTCC NOCLEARisr() {...}。


算法实现FSK来电软件解码
张俊华
【期刊名称】《电脑编程技巧与维护》
【年(卷),期】2012(000)012
【摘要】比较了来电显示硬件解码和软件解码,详细介绍了算法FSK来电解码的数学原理和程序实现,解释了在实际实现中要注意的关键环节,在实际的交换机系统中实现了理想的解码效果和高度的系统集成度,达到了预期的良好效果.
【总页数】3页(P124-126)
【作者】张俊华
【作者单位】杭州亿利通信器材有限公司,杭州310012
【正文语种】中文
【相关文献】
1.FSK制式来电信息采集器的研究与设计 [J], 赵羿然;陈玮;邹光远;刘桂红;伍子健;刘宇杰;杨海严;崔泽华;罗敏
2.FSK制式来电显示功能的FPGA实现 [J], 刘永恩;邱里鑫;刘中友
3.一种基于FSK制式的智能来电显示模块的设计与实现 [J], 赵伟;顾霞萍;王宜怀
4.FSK来电识别软解码算法研究 [J], 赵书朵;陈云生;颜恒
5.FSK与DTMF来电显示通信终端的设计 [J], 蒋晖
因版权原因,仅展示原文概要,查看原文内容请购买。
Femto设备参数设置
目录
1、参数查询 (1)
2、Femto常用参数(飞烽设备) (3)
密闭模式设置 (3)
网关地址 (3)
博威设备设置 (4)
1、参数查询
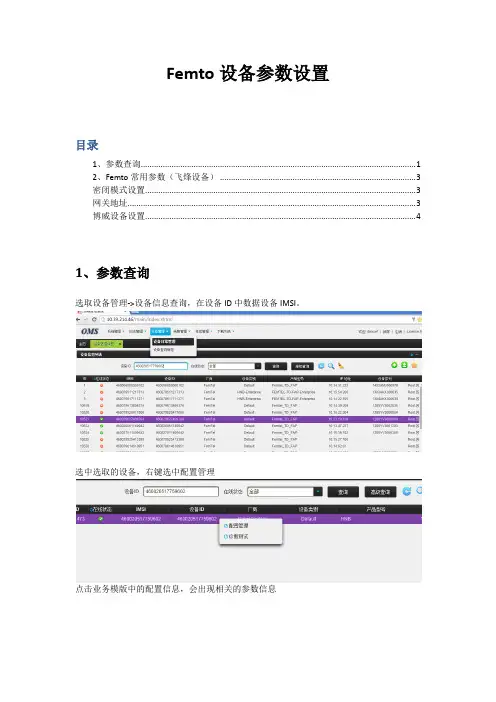
选取设备管理->设备信息查询,在设备ID中数据设备IMSI。
选中选取的设备,右键选中配置管理
点击业务模版中的配置信息,会出现相关的参数信息
在设备方法中点击获取参数值,选中编辑,并输入参数号,点击√确认
点击获取参数值,可以查看现网的配置
在参数设置中可以输入参数的值,并点击下面的参数设置,修改参数。
2、Femto常用参数(飞烽设备)
备注:
由于密闭模式博威的设备查不到相关参数,所有参数按照飞烽的进行设置,不用另外查询
3、密闭模式设置
1、将用户IMSI号加入白名单(如果有多个IMSI号,用英文逗号隔开),博威的需分别设置.
2、将接入模式由Open Access 修改为Close Access(注意首字母大写,中间有空格)
4、网关地址
femto网管地址: 10.39.214.46
用户名:daixuef 密码daixuef
5、博威设备设置
1、封闭模式:由Open Access 改为Close Access,在Close和Access之间有一个空格,
首写字母均需大写。
2、封闭模式IMIS添加:将对应的IMSI添加到detail IMSI里,且对应的Enable都修改为1,然后提交.。


DALSTAR DS-1x-01M15 November 25, 2002 Basics about thecameraCamera Descriptions§ 1024 × 1024 × 12-bit @ 15 fps.§ Single channel RS-422 digital video output.§ Progressive scan.§ Internal (separate) sync.§ Internal and external exposure control.§ 20 MHz pixel clock rate.Mode of operations as per Matrox Imaging (in parentheses as per camera manufacturer)Interface Modes§ Continuous (no binning, binning)§ Asynchronous reset (no binning, binning)Basics about theinterface modesCamera Interface BriefsMode 1: Continuous (no binning)§ 1024 × 1024 × 12-bit @ 15 fps.§ Single channel RS-422 digital video.§ Progressive scan.§ Matrox Meteor-II/Digital receiving HSYNC, VSYNC, PIXEL CLOCK (@ 20MHz) and video signals from camera.§DCF: 1M15C1.DCFMode 2: Continuous (Binning)§ Up to 512 × 512 × 12-bit @ 30 fps.§ Single channel RS-422 digital video.§ Progressive scan.§ Matrox Meteor-II/Digital receiving HSYNC, VSYNC, PIXEL CLOCK (@ 10MHz) and video signals from camera.§DCF used: 1M15C2.DCFDALSTAR DS-1x-01M15 November 25, 2002 Basics about theCamera Interface Briefs (cont.)interface modesMode 3: Asynchronous reset (no binning)§ 1024 × 1024 × 12-bit.§ Single channel RS-422 digital video.§ Progressive scan.§ Matrox Meteor-II/Digital receiving TTL external trigger signal.§ Matrox Meteor-II/Digital sending EXPOSURE2 (TRIGGER IN) signal tocamera to initiate and control exposure time.§ Matrox Meteor-II/Digital receiving HSYNC, VSYNC, PIXEL CLOCK (@ 20MHz) and video signals from camera.§ DCF used: 1M15A1.DCFMode 4: Asynchronous reset (binning)§ 512 × 512 × 12-bit.§ Single channel RS-422 digital video.§ Progressive scan.§ Matrox Meteor-II/Digital receiving TTL external trigger signal.§ Matrox Meteor-II/Digital sending EXPOSURE2 (TRIGGER IN) signal tocamera to initiate and control exposure time.§ Matrox Meteor-II/Digital receiving HSYNC, VSYNC, PIXEL CLOCK (@ 10MHz) and video signals from camera.§ DCF used: 1M15A2.DCFDALSTAR DS-1x-01M15 November 25, 2002 Specifics about theCamera Interface Detailsinterface modesModes 1 and 2: Continuous§Frame Rate: Matrox Meteor-II/Digital receives the continuous video fromthe camera at 15/30 frames per second (no binning/binning).§Exposure time: Exposure time is inversely proportionate to the framerate or determined by the shutter setting. Refer to the camera manual formore information.§Camera Control: Camera control settings are made using DALSA’scontrol software. Contact DALSA for more information.Modes 3 and 4: Asynchronous Reset§Frame rate: The frame rate is determined by the frequency of theexternal trigger signal.§Exposure time: The width (rising edge to falling edge) of theEXPOSURE2 (TRIGGER IN)* signal is the exposure time. The exposuretime can be modified in the DCF using Matrox Intellicam or with the MILMdigControl() function. Refer to the respective manual for moreinformation.§Camera Control: External Trigger Mode/Integrate checkbox must bechecked in DALSA’s control software. Refer to the camera manual formore information.§Timing diagram:*SMA ConnectorDALSTAR DS-1x-01M15 November 25, 2002 Cabling details for thisinterface modeCabling Requirements – PCI VersionModes 1 and 2: Continuous§Cable: DBHD100-TO-OPEN (open ended) cable required for video,synchronization and control signals.§Connection: Connections between the 60-pin quad row connectors(DATA1) of the camera and the 100-pin connector of the Matrox Meteor-II/Digital are as follows:DALSTAR D1-1x-01M15(60-pin quad row connector- DATA 1) METEOR2-DIG/4/R (100-pin connector)Pin name Pin no.Pin name Pin no. D1A0+ 01 →DATA, INPUT, 0+ 01D1A0- 02 →DATA, INPUT, 0- 02D1A1+ 03 →DATA, INPUT, 1+ 03D1A1- 04 →DATA, INPUT, 1- 04D1A2+ 05 →DATA, INPUT, 2+ 05D1A2- 06 →DATA, INPUT, 2- 06D1A3+ 07 →DATA, INPUT, 3+ 07D1A3- 08 →DATA, INPUT, 3- 08D1A4+ 09 →DATA, INPUT, 4+ 09D1A4- 10 →DATA, INPUT, 4- 10D1A5+ 11 →DATA, INPUT, 5+ 11D1A5- 12 →DATA, INPUT, 5- 12D1A6+ 13 →DATA, INPUT, 6+ 13D1A6- 14 →DATA, INPUT, 6- 14D1A7+ 17 →DATA, INPUT, 7+ 15D1A7- 18 →DATA, INPUT, 7- 16D1A8+ 19 →DATA, INPUT, 8+ 17D1A8- 20 →DATA, INPUT, 8- 18D1A9+ 21 →DATA, INPUT, 9+ 19D1A9- 22 →DATA, INPUT, 9- 20D1A10+ 23 →DATA, INPUT, 10+ 21D1A10- 24 →DATA, INPUT, 10- 22D1A11+ 25 →DATA, INPUT, 11+ 23D1A11- 26 →DATA, INPUT, 11- 24D1HSYNC+ 58 →HSYNC, INPUT, + 33D1HSYNC - 57 →HSYNC, INPUT, - 34D1VSYNC+ 56 →VSYNC, INPUT, + 35D1VSYNC - 55 →VSYNC, INPUT, - 36D1GND 45 →GROUND 37D1GND 46 →GROUND 38D1PCLK- 59 →CLOCK, INPUT, + 39D1PCLK + 60 →CLOCK, INPUT, - 40 Continued…DALSTAR DS-1x-01M15 November 25, 2002 Cabling details for thisinterface modeCabling Requirements – PCI version (cont.)Modes 3 and 4: Asynchronous Reset§Cable: DBHD100-TO-OPEN (open ended) cable required for video,synchronization and control signals.§External Trigger: TTL external trigger source should be connected to thepin 2 and 7 (OPTO TRIG+/-) of the 9-pin Trigger Input connector locatedon the Matrox Meteor-II/Digital secondary RS-232/Trigger Input bracket.§Connection: Connections between the SMA/BNC connector of thecamera and the 100-pin connector of the Matrox Meteor-II/Digital are asin Modes 1 and 2: Continuous including the following:DALSTAR D1-1x-01M15 (SMA/BNC connector) METEOR2-DIG/4/R (100-pin connector)Pin name Pin no.Pin name Pin no. SMA or BNC -- ←EXPOSURE2, OUTPUT, TTL 88GND -- -- GROUND 38Cabling Requirements – PC/104-PLUS versionModes 1 and 2: Continuous§Cable:(A)* For a Matrox Meteor-II/Digital PC/104-PLUS frame grabber installed in a Matrox 4Sight-II, the VHDCI-TO-OPEN (open ended) cable is required to connect to the Matrox 4Sight-II’s expanded video input connectors. (B)* For connecting directly to a Matrox Meteor-II/DigitalPC/104-PLUS frame grabber, a custom ribbon cable can be built using the included low profile IDC mating connectors included with the board. §Connections: Connections between the 60-pin quad row connectors (DATA1) of the camera and the 68-pin connector of the Matrox Meteor-II/Digital are as follows.DALSTAR D1-1x-01M15(60-pin quad row connector- DATA 1) MET2-DIG+/L(68-pin connector)(A)* (B)*Pin name Pin no.Pin name Pin no.Pin no. D1A0+ 01 →DATA, INPUT, 0+ 34 01 D1A0- 02 →DATA, INPUT, 0- 68 02 D1A1+ 03 →DATA, INPUT, 1+ 33 03 D1A1- 04 →DATA, INPUT, 1- 67 04 D1A2+ 05 →DATA, INPUT, 2+ 32 05 D1A2- 06 →DATA, INPUT, 2- 66 06 D1A3+ 07 →DATA, INPUT, 3+ 31 07 D1A3- 08 →DATA, INPUT, 3- 65 08 D1A4+ 09 →DATA, INPUT, 4+ 30 09 D1A4- 10 →DATA, INPUT, 4- 64 10 Continued…*Note: column A represents connections via the Matrox 4Sight-II’s expanded video input connector and column B represents connections directly to the Matrox Meteor-II/Digital PC/104-Plus low profile IDC video input connector.DALSTAR DS-1x-01M15 November 25, 2002 Cabling details for thisinterface modeCabling Requirements – PC/104-PLUS version (cont.)Modes 1 and 2: ContinuousDALSTAR D1-1x-01M15(60-pin quad row connector- DATA 1) MET2-DIG+/L(68-pin connector)(A)* (B)*Pin name Pin no.Pin name Pin no.Pin no. D1A5+ 11 →DATA, INPUT, 5+ 29 11 D1A5- 12 →DATA, INPUT, 5- 63 12 D1A6+ 13 →DATA, INPUT, 6+ 28 13 D1A6- 14 →DATA, INPUT, 6- 62 14 D1A7+ 17 →DATA, INPUT, 7+ 27 15 D1A7- 18 →DATA, INPUT, 7- 61 16 D1A8+ 19 →DATA, INPUT, 8+ 08 53 D1A8- 20 →DATA, INPUT, 8- 42 54 D1A9+ 21 →DATA, INPUT, 9+ 07 55 D1A9- 22 →DATA, INPUT, 9- 41 56 D1A10+ 23 →DATA, INPUT, 10+ 06 57 D1A10- 24 →DATA, INPUT, 10- 40 58 D1A11+ 25 →DATA, INPUT, 11+ 05 59 D1A11- 26 →DATA, INPUT, 11- 39 60 D1HSYNC+ 58 →HSYNC, INPUT, + 26 17 D1HSYNC - 57 →HSYNC, INPUT, - 60 18 D1VSYNC+ 56 →VSYNC, INPUT, + 24 21 D1VSYNC - 55 →VSYNC, INPUT, - 58 22 D1GND 45 →GROUND 43 52 D1GND 46 →GROUND 43 52 D1PCLK- 59 →CLOCK, INPUT, + 22 25 D1PCLK + 60 →CLOCK, INPUT, - 56 26 *Note: column A represents connections via the Matrox 4Sight-II’s expanded video input connector and column B represents connections directly to the Matrox Meteor-II/Digital PC/104-Plus low profile IDC video input connector.Modes 3 and 4: Asynchronous Reset§Cable:(A)* For a Matrox Meteor-II/Digital PC/104-PLUS frame grabber installed in a Matrox 4Sight-II, the VHDCI-TO-OPEN (open ended) cable is required to connect to the Matrox 4Sight-II’s expanded video input connectors. (B)* For connecting directly to a Matrox Meteor-II/DigitalPC/104-PLUS frame grabber, a custom ribbon cable can be built using the included low profile IDC mating connectors included with the board. §External Trigger: TTL external trigger source should be connected to OPTOTRIG, INPUT pin 11 (A)* or pin 47 (B)* and OPTOTRIG COM (Ground) pin 10 (A)* or pin 49 (B)*.Continued…DALSTAR DS-1x-01M15 November 25, 2002Cabling details for thisinterface mode Cabling Requirements – PC/104-PLUS version (cont.)Modes 3 and 4: Asynchronous Reset§ Connection: Connections between the two 60-pin quad row connectors(DATA1) of the camera and the 68-pin connector of the Matrox Meteor-II/Digital are as in Modes 1 and 2: Continuous (PC/104-PLUS version )including the following:DALSTAR D1-1x-01M15 (SMA connector)MET2-DIG+/L (68-pin connector) (A)* (B)*Pin name Pin no. Pin name Pin no. Pin no.SMA or BNC -- ← EXPOSURE2, OUTPUT, TTL 46 88GND -- -- GROUND 43 38 *Note: column A represents connections via the Matrox 4Sight-II’s expanded video inputconnector and column B represents connections directly to the Matrox Meteor-II/DigitalPC/104-Plus low profile IDC video input connector.The DCF(s) mentioned in this application note can be found on the MIL CD or our FTP site (). The information furnished by Matrox Electronics System, Ltd. is believed to be accurate and reliable. Please verify all interface connections with camera documentation or manual. Contact your local sales representative or Matrox Sales office or Matrox Imaging Applications at 514-822-6061 for assistance. Corporate headquarters:Canada and U.S.A.Matrox Electronic Systems Ltd.1055 St. Regis Blvd.Dorval, Quebec H9P 2T4CanadaTel: (514) 685-2630Fax: (514) 822-6273。


UEFI Awareness Manual TianoCoreRelease 09.2023UEFI Awareness Manual TianoCoreTRACE32 Online HelpTRACE32 DirectoryTRACE32 IndexTRACE32 Documents ......................................................................................................................UEFI Awareness Manuals .............................................................................................................UEFI Awareness Manual TianoCore (1)History (4)Overview (4)Brief Overview of Documents for New Users5 Supported Versions5Configuration (6)ARM 32-Bit6 ARM 64-Bit7 Hooks & Internals in TianoCore7Features (8)Display of UEFI Resources8 Symbol Autoloader9 Autoloader Configuration9 Scan the UEFI Module Table10 Display the Autoloader Table11 TianoCore Specific Menu12Debugging UEFI Phases of TianoCore (13)Debugging from Reset Vector13 SEC Phase13 PEI Phase13 DXE Phase13 BDS Phase14TianoCore Commands (15)EXTension.ConfigTab Display DXE configuration table15 EXTension.DXEDRiVer Display loaded DXE drivers15 EXTension.DXEModule Display DXE modules16 EXTension.FV Display firmware volumes17 EXTension.HOB Display HOBs17 EXTension.Option Set awareness options18 EXTension.PEIModule Display PEI modules19 EXTension.PEISvc Display PEI services19EXTension.POST Display POST code20 EXTension.PROTocol Display installed protocols20TianoCore PRACTICE Functions (21)EXT.DXEDRV.ENTRY()Entry address for DXE driver21 EXT.DXEDRV.MAGIC()Magic of DXE driver21 EXT.DXEDRV.PATH()Build path for DXE driver21 EXT.DXEFILE.PATH()Build path for DXE module22 EXT.PEIM.ENTRY()Entry address for PEI module22 EXT.PEIM.MAGIC()Magic of PEI module22 EXT.PEIM.PATH()Build path for PEI module22UEFI Awareness Manual TianoCoreVersion 09-Oct-2023 History28-Aug-18The title of the manual was changed from “UEFI <x> Debugger” to “UEFI Awareness Manual <x>”.OverviewThe UEFI Awareness for TianoCore contains special extensions to the TRACE32 Debugger. This chapter describes the additional features, such as additional commands and debugging approaches.Brief Overview of Documents for New UsersArchitecture-independent information:•“Training Basic Debugging” (training_debugger.pdf): Get familiar with the basic features of a TRACE32 debugger.•“T32Start” (app_t32start.pdf): T32Start assists you in starting TRACE32 PowerView instances for different configurations of the debugger. T32Start is only available for Windows.•“General Commands” (general_ref_<x>.pdf): Alphabetic list of debug commands.Architecture-specific information:•“Processor Architecture Manuals”: These manuals describe commands that are specific for the processor architecture supported by your Debug Cable. T o access the manual for your processorarchitecture, proceed as follows:-Choose Help menu > Processor Architecture Manual.•“OS Awareness Manuals” (rtos_<os>.pdf): TRACE32 PowerView can be extended for operating system-aware debugging. The appropriate OS Awareness manual informs you how to enable theOS-aware debugging.•“UEFI Awareness Manuals” (uefi_<x>.pdf): TRACE32 PowerView can be extended for UEFI-aware debugging. The appropriate UEFI manual informs you how to enable the UEFI-awaredebugging.Supported VersionsCurrently TianoCore is supported for the following versions:•TianoCore on ARM32 and ARM64 architecturesConfigurationThe UEFI Awareness for TianoCore is configured by loading an extension definition file called “tiano.t32”from the demo directory with the EXTension.CONFIG command. The command takes two parameters that specify the memory base address and size of the UEFI package. See the file <board>Pkg/<board>Pkg.dsc of your UEFI implementation. “PcdSystemMemoryBase” rsp. “PcdSystemMemorySize” are the needed values.Additionally, load the “tiano.men” menu file (see “TianoCore specific Menu”) and configure the Symbol Autoloader.ARM 32-BitA full configuration for ARM 32-bit can look like this (the path prefix ~~ expands to the system directory ofTRACE32.):; Specify the memory base address and size,; see <board>Pkg/<board>Pkg.dsc:; PcdSystemMemoryBase = 0x80000000; PcdSystemMemorySize = 0x08000000; Load the TianoCore Awareness:EXTension.CONFIG ~~/demo/arm/bootloader/uefi/tiano/tiano.t32 \0x80000000 0x08000000; In a TrustZone/Hypervisor environment, you may need to; specify the access class where the UEFI BIOS runs.; E.g. if TianoCore runs in hypervisor zone:EXTension.ACCESS H:; Load the additional menu:MENU.ReProgram ~~/demo/arm/bootloader/uefi/tiano/tiano.men; Configure symbol autoloader:sYmbol.AutoLOAD.CHECKUEFI "do ~~/demo/arm/bootloader/uefi/tiano/autoload "See also the example scripts in ~~/demo/arm/bootloader/uefi/tianoARM 64-BitA full configuration for ARM 64-bit can look like this (the path prefix ~~ expands to the system directory ofTRACE32.):; Specify the memory base address and size,; see <board>Pkg/<board>Pkg.dsc:; PcdSystemMemoryBase = 0x80000000; PcdSystemMemorySize = 0x08000000; Load the TianoCore Awareness:EXTension.CONFIG ~~/demo/arm/bootloader/uefi/tiano/tiano.t32 \0x80000000 0x08000000; In a TrustZone/Hypervisor environment, you may need to; specify the access class where the UEFI BIOS runs.; E.g. if TianoCore runs in hypervisor zone:EXTension.ACCESS H:; Load the additional menu:MENU.ReProgram ~~/demo/arm/bootloader/uefi/tiano/tiano.men; Configure symbol autoloader:sYmbol.AutoLOAD.CHECKUEFI "do ~~/demo/arm/bootloader/uefi/tiano/autoload "See also the example scripts in ~~/demo/arm/bootloader/uefi/tianoHooks & Internals in TianoCoreIMPORTANT:When using GCC on ARM:The ELF->COFF converter (GenFw) may spoil the debug information when using several text/data sections (check with "-v"). The linker must combine all sections into one text section and one data section. The edk2/BaseT ools/Scripts directory contains a suitable linker script (GccBase.lds or previously gcc4.4-ld-script). Please ensure that this script is used when linking a module, e.g. by adding it to the linker flags in the edk2/BaseT ools/Conf/tools_def.template:--script=$(EDK_TOOLS_PATH)/Scripts/GccBase.ldsFeaturesThe UEFI Awareness for TianoCore supports the following features.Display of UEFI ResourcesThe extension defines new commands to display various UEFI resources. Information on the following UEFI components can be displayed:PEI phase:EXTension.FV PEI PEI firmware volumesEXTension.PEIModule PEI modules in FVsEXTension.HOB PEI PEI HOBsDXE phase:EXTension.FV DXE DXE firmware volumesEXTension.DXEModule DXE modules in FVsEXTension.DXEDRiVer Loaded DXE driversEXTension.HOB DXE DXE HOBsEXTension.PROTocol DXE Installed DXE protocolsEXTension.ConfigTab DXE configuration tableFor a description of the commands, refer to chapter “TianoCore Commands”.If you want to display the UEFI objects “On The Fly” while the target is running, you need to have access to memory while the target is running. Enable SYStem.MemAccess or SYStem.CpuAccess (CPUdependent), but be aware of the limitations (no cache reading, real-time intrusion).Symbol AutoloaderThe UEFI code is provided by the boot FLASH, but debugging becomes more comfortable when debug symbols are available.TRACE32 contains an “Autoloader”, which can be set up for automatic loading of symbol files. TheAutoloader maintains a list of address ranges, corresponding UEFI components and the appropriate load command. Whenever the user accesses an address within an address range known to the Autoloader, the debugger invokes the load associated command. The command is usually a call to a PRACTICE script, that handles loading the symbol file.The TRACE32 Autoloader has to be set up. This includes the following steps:1.Autoloader configuration.2.Scan of the UEFI module table to the Autoloader table.3.Display of the Autoloader table.Autoloader ConfigurationThe command sYmbol.AutoLOAD.CHECKUEFI <load_command> specifies the command that isautomatically used by the Autoloader to load the symbol information. T ypically the script autoload.cmm provided by Lauterbach is called.The command sYmbol.AutoLOAD.CHECKUEFI implicitly also defines the parameters that TRACE32 uses internally for the Autoloader.The script is provided in the TRACE32 demo directory:•32-bit: ~~/demo/arm/bootloader/uefi/tiano/autoload.cmm.•64-bit: ~~/demo/arm/bootloader/uefi/tiano/autoload.cmm.Example:; Configure symbol Autoloader for 32-bit TianoCoresYmbol.AutoLOAD.CHECKUEFI "DO ~~/demo/arm/bootloader/uefi/tiano/autoload.cmm"Scan the UEFI Module TableWhen the Autoloader is configured, the command sYmbol.AutoLOAD.CHECK can be used to scan the UEFI module table into the Autoloader table and to activate the Autoloader.Since the UEFI module table is updated by UEFI a re-scan might be necessary.The point of time at which the UEFI module table is re-scanned can be set very flexibly: sYmbol.AutoLOAD.CHECK [ON | OFF | ONGO]The default setting is sYmbol.AutoLOAD CHECK OFF. With this setting TRACE32 re-scans the UEFI module table only on request by using the sYmbol.AutoLOAD.CHECK command.With sYmbol.AutoLOAD.CHECK ON, TRACE32 re-scans the UEFI module table after every single step and whenever the program execution is stopped. This significantly slows down the speed of TRACE32.With sYmbol.AutoLOAD.CHECK ONGO, TRACE32 re-scans the UEFI module table whenever the program execution is stopped.NOTE:The Autoloader can load the symbol information for the SecCore, the PeiCore, allPEI modules and the DXE core as soon as the memory mode (e.g. 32-bit protectedmode) used by UEFI is activated.The Autoloader can only load symbol information for DXE modules that arealready loaded.Display the Autoloader TableThe command “sYmbol.AutoLOAD.List ” shows a list of all known address ranges/components and their symbol load commands.Autoload context menu Touch Advise TRACE32 to load the symbols for the selected module now.Set Mark selected module as loaded.ClearDelete symbols for the selected module in TRACE32.Module address range Module nameModule status dyn: (no meaning)load: symbols for module are loadedLoad command Parameters for load commandTianoCore Specific MenuThe menu file “tiano.men” contains a menu with TianoCore specific menu items. Load this menu with the MENU.ReProgram command.Y ou will find a new menu called TianoCore.•Use the PEI submenu to launch windows displaying PEI specific resources.•Use the DXE submenu to launch windows displaying DXE specific resources.•Use the Symbol Autoloader submenu to configure the symbol autoloader.See also chapter “Symbol Autoloader”.-List Components opens a sYmbol.AutoLOAD.List window showing all components currently active in the autoloader.-Check Now! performs a sYmbol.AutoLOAD.CHECK and reloads the autoloader list.-Set Loader Script allows you to specify the script that is called when a symbol file load is required. Y ou may also set the automatic autoloader check.Debugging UEFI Phases of TianoCoreUEFI runs in several “phases”. It starts with the “Security” (SEC) phase which immediately switches to the “Pre-EFI Initialization Environment” (PEI) phase. After this phase ended, control is given to the “Driver Exe-cution Environment” (DXE) phase. Shortly, before the OS is booted, the “Boot Device Selection” (BDS) phase is running.Each of this phases needs a different debugging environment. See below for a detailed description of each phase.Debugging from Reset VectorTRACE32 is a JT AG-based debugging tool and, as such, allows the user to start debugging their system right from the reset vector. It is possible to walk through the very first steps of the start-up to detect FLASH problems or faulty reset behavior.Shortly after reset, the system switches into the SEC phase.SEC PhaseTianoCore itself does not provide an SEC phase. It is up to the developer to implement a custom SEC phase, and as such out of the scope of this documentPEI PhaseIf you want to debug the PEI phase right from the start, halt the system at the reset vector. Then load the symbols of your PEI core module with the symbol autoloader, and go until the desired entry point, e.g: sYmbol.AutoLOAD.CHECKsYmbol.AutoLOAD.Touch "ArmPlatformPrePiUniCore"Go PrePiMainInspect the PEI resources with the menu items in the “PEI” submenu.DXE PhaseAfter PEI phase completed, it hands off control to the DXE core. T o debug the DxeCore from start, load the symbols of “DxeCore” just before PEI jumps into the DxeCore and set a breakpoint at “DxeMain”. DxeMain then starts the DXE dispatcher.For debugging a DXE driver from its entry point, a special script “go_dxedrv” is available in the ~~/demo directory. Call this script with the name of the DXE module before the module is started. E.g. to debug the DXE driver “Metronome”:DO go_dxedrv MetronomeThis script sets a breakpoint in the DXE core code and waits until the specified DXE module is loaded. Then it sets a breakpoint onto the module entry point and halts there. Y ou can then start debugging the module from scratch.BDS PhaseTianoCore implements the BDS phase as DXE driver. T o debug the BDS phase, debug the “ArmPlat-formBds” module like shown in “DXE Phase”.TianoCore CommandsEXTension.ConfigTabDisplay DXE configuration tableDisplays the DXE configuration table.EXTension.DXEDRiVerDisplay loaded DXE driversDisplays a table with all DXE drivers that DxeCore already loaded into the system.Y ou can sort the window to the entries of a column by clicking on the column header.“magic” is a unique ID, used by the UEFI Awareness to identify a specific driver.Format:EXTension.ConfigTabFormat:EXTension.DXEDRiVerEXTension.DXEModuleDisplay DXE modulesDisplays a table with all DXE modules found in the system (firmware volumes or HOBs).Y ou can sort the window to the entries of a column by clicking on the column header.“magic” is a unique ID, used by the UEFI Awareness to identify a specific module.The “magic” fields are mouse sensitive. Right-click on them to get a local menu. Double-clicking on them opens appropriate windows.Format:EXTension.DXEModuleEXTension.FVDisplay firmware volumesDisplays a table with the firmware volumes of the PEI or DXE phase.If an address of a firmware volume is specified, the command displays the contents of this FV .“magic” is a unique ID used by the UEFI Debugger to identify a specific firmware volume or file.The “magic” fields are mouse sensitive, double clicking on them opens appropriate windows. Right-clickingon them will show a context menu.The debugger tries to detect the address of the boot firmware volume automatically . If this fails, specify the address of the boot FV manually with the EXTension.Option BOOTFV command.EXTension.HOBDisplay HOBsDisplays a table with the hand off blocks of the PEI or DXE phase.Format:EXTension.FV [PEI | DXE [<fv_address >]]Format:EXTension.HOB [PEI | DXE ]The “address” fields are mouse sensitive, double-clicking them opens appropriate windows. Right-clicking on them will show a context menu.EXTension.OptionSet awareness optionsSets various options to the awareness. Format:EXTension.Option<option> <option>:BOOTFV <address>PEIHOBS <address>SYSTABLE <address>UCODE <address>BOOTFV Set the base address of the boot firmware volume.PEIHOBS Set the base address of the HOB list in PEI phase.SYSTABLE Set the base address of the EFI System Table UCODESet the base address of the microcode table.EXTension.PEIModuleDisplay PEI modulesDisplays a table with all PEI modules found in the system.Y ou can sort the window to the entries of a column by clicking on the column header.“magic” is a unique ID, used by the UEFI Awareness to identify a specific module.The “magic” fields are mouse sensitive. Right-click on them to get a local menu. Double-clicking on them opens appropriate windows.EXTension.PEISvcDisplay PEI servicesDisplays a table with all available PEI services.Format:EXTension.PEIModuleFormat:EXTension.PEISvcEXTension.POSTDisplay POST code(Only available on x86/x64 targets.)Displays the Power-On Self-Test code.EXTension.PROTocolDisplay installed protocolsDisplays the list of installed DXE protocols.Format:EXTension.POSTFormat:EXTension.PROTocolTianoCore PRACTICE FunctionsThere are special definitions for TianoCore specific PRACTICE functions.EXT.DXEDRV.ENTRY()Entry address for DXE driver Syntax:EXT.DXEDRV.ENTRY(<dxedrv_magic>)Returns the entry address for the specified DXE driver.Parameter Type: Decimal or hex or binary value.Return Value Type: Hex value.EXT.DXEDRV.MAGIC()Magic of DXE driver Syntax:EXT.DXEDRV.MAGIC("<dxedrv_name>")Returns the “magic” of the specified loaded DXE driver.Parameter Type: String (with quotation marks).Return Value Type: Hex value.EXT.DXEDRV.PATH()Build path for DXE driver Syntax:EXT.DXEDRV.PATH(<dxedrv_magic>)Returns the build path for the specified DXE driver.Parameter Type: Decimal or hex or binary value.Return Value Type: String.EXT.DXEFILE.PATH()Build path for DXE module Syntax:EXT.DXEFILE.PATH(<dxem_magic>)Returns the build path for the specified DXE module.Parameter Type: Decimal or hex or binary value.Return Value Type: String.EXT.PEIM.ENTRY()Entry address for PEI module Syntax:EXT.PEIM.ENTRY(<peim_magic>)Returns the entry address for the specified PEI module.Parameter Type: Decimal or hex or binary value.Return Value Type: Hex value.EXT.PEIM.MAGIC()Magic of PEI module Syntax:EXT.PEIM.MAGIC("<peim_name>")Returns the “magic” of the specified PEI module.Parameter Type: String (with quotation marks).Return Value Type: Hex value.EXT.PEIM.P ATH()Build path for PEI module Syntax:EXT.PEIM.PATH(<peim_magic>)Returns the build path for the specified PEI module.Parameter Type: Decimal or hex or binary value.Return Value Type: String.。

凌华科技发布ATCA刀片服务器
佚名
【期刊名称】《测控技术》
【年(卷),期】2009(28)12
【摘要】2009年11月17日,凌华科技发布ATCA服务器等级产品aTCA-6100,此款产品搭载双英特尔64位四核Xeon处理器L5518、英特尔5520芯片组、支持6个DDR3-1066 VLP RDIMM内存插槽,最高容量达48GB、并可选配PICMG标准规范AdvancedMC(AMC)卡扩展槽。
【总页数】1页(P96-96)
【关键词】凌华科技;刀片服务器;ATCA;Xeon处理器;CA服务器;PICMG;内存插槽;标准规范
【正文语种】中文
【中图分类】TP273;TP368.5
【相关文献】
1.凌华科技发布首款双四核、双AMC插槽的ATCA刀片服务器——aTCA-6900
提供电信和网通设备绝佳运算性能、10Gigabit网络整合型解决方案 [J], 无
2.凌华科技发布首款双四核、双AMC插槽的ATCA刀片服务器 [J],
3.凌华科技领先发布支持双英特尔XeonL5518处理器与AMC插槽的ATCA刀片服务器 [J],
4.凌华科技领先发布支持双英特尔Xeon~L5518处理器与AMC插槽的ATCA
刀片服务器 [J],
5.凌华科技发布电信与网络设备专用的高端ATCA刀片服务器 [J],
因版权原因,仅展示原文概要,查看原文内容请购买。

H3C 防火墙多插卡高性能组网典型配置举例Copyright © 2013 杭州华三通信技术有限公司版权所有,保留一切权利。
非经本公司书面许可,任何单位和个人不得擅自摘抄、复制本文档内容的部分或全部,并不得以任何形式传播。
本文档中的信息可能变动,恕不另行通知。
目录1 使用版本 (1)2 特性简介 (1)3 应用场合 (1)4 注意事项 (1)5 配置前提 (2)6 路由模式配置举例 (2)6.1 组网需求 (2)6.2 配置思路 (3)6.3 配置步骤 (3)6.3.1 S9508E的配置 (3)6.3.2 SecBlade FW1的配置 (7)6.3.3 SecBlade FW2的配置 (9)6.3.4 SecBlade FW3的配置 (9)6.3.5 SecBlade FW4的配置 (10)6.4 配置文件 (11)6.4.1 S9508E (11)6.4.2 SecBlade FW1的配置 (14)6.4.3 SecBlade FW2的配置 (14)6.4.4 SecBlade FW3的配置 (15)6.4.5 SecBlade FW4的配置 (15)6.5 注意事项 (15)7 NAT模式配置举例 (16)7.1 组网需求 (16)7.2 配置思路 (16)7.3 配置步骤 (17)7.3.1 S9508E的配置 (17)7.3.2 SecBlade FW1的配置 (21)7.3.3 SecBlade FW2的配置 (23)7.3.4 SecBlade FW3的配置 (24)7.3.5 SecBlade FW4的配置 (24)7.4 注意事项 (25)7.5 配置文件 (25)7.5.1 S9508E的配置 (25)7.5.3 SecBlade FW2的配置 (26)7.5.4 SecBlade FW3的配置 (27)7.5.5 SecBlade FW4的配置 (27)8 透明模式配置举例 (28)8.1 组网需求 (28)8.2 配置思路 (28)8.3 配置步骤 (29)8.3.1 S9508E的配置 (29)8.3.2 SecBlade FW1的配置 (31)8.3.3 SecBlade FW2的配置 (32)8.3.4 SecBlade FW3的配置 (32)8.3.5 SecBlade FW4的配置 (33)8.4 配置文件 (33)8.4.1 S9508E (33)8.4.2 SecBlade FW1的配置 (34)8.4.3 SecBlade FW2的配置 (35)8.4.4 SecBlade FW3的配置 (35)8.4.5 SecBlade FW4的配置 (35)9 双机IRF组网路由/NAT模式配置举例 (35)9.1 组网需求 (35)9.2 配置思路 (36)9.3 配置步骤 (37)9.3.1 S12500的配置 (37)9.3.2 宿主交换机 1的SecBlade FW1的配置 (42)9.3.3 宿主交换机 1的SecBlade FW2的配置 (44)9.3.4 宿主交换机 1的SecBlade FW3的配置 (45)9.3.5 宿主交换机 2的SecBlade FW1的配置 (46)9.3.6 宿主交换机 2的SecBlade FW2的配置 (48)9.3.7 宿主交换机 2的SecBlade FW3的配置 (49)9.4 配置文件 (50)9.4.1 S12500的配置 (50)9.4.2 宿主交换机1的SecBlade FW1的配置 (55)9.4.3 宿主交换机1的SecBlade FW2的配置 (56)9.4.4 宿主交换机1的SecBlade FW3的配置 (57)9.4.5 宿主交换机2的SecBlade FW1的配置 (58)9.4.7 宿主交换机2的SecBlade FW3的配置 (60)10 双机IRF组网透明模式配置举例 (61)10.1 组网需求 (61)10.2 配置思路 (61)10.3 配置前提 (62)10.4 配置步骤 (62)10.4.1 S9508E的配置 (62)10.4.2 宿主交换机1的SecBlade FW1的配置 (65)10.4.3 宿主交换机1的SecBlade FW2的配置 (66)10.4.4 宿主交换机1的SecBlade FW3的配置 (67)10.4.5 宿主交换机2的SecBlade FW1的配置 (67)10.4.6 宿主交换机2的SecBlade FW2的配置 (68)10.4.7 宿主交换机2的SecBlade FW3的配置 (69)10.5 验证配置 (70)10.6 配置文件 (73)10.6.1 S9508E的配置 (73)10.6.2 宿主交换机1的SecBlade FW1的配置 (76)10.6.3 宿主交换机1的SecBlade FW2的配置 (77)10.6.4 宿主交换机1的SecBlade FW3的配置 (77)10.6.5 宿主交换机2的SecBlade FW1的配置 (78)10.6.6 宿主交换机2的SecBlade FW2的配置 (79)10.6.7 宿主交换机2的SecBlade FW3的配置 (79)10.7 注意事项 (80)11 FAQ (80)11.1 路由交换机如何实现流量负载分担? (80)11.2 目前路由交换机最大支持多少条等价路由? (80)11.3 路由交换机等价路由负载分发算法是否可以修改? (81)11.4 S9500E、S12500路由交换机的等价路由是如何选择下一跳地址的? (81)11.5 S5800、S7500E、S10500路由交换机的等价路由是如何选择下一跳地址的? (82)11.6 S5800、S7500E、S10500链路聚合的具体算法是什么?在什么情况下会有限制? (83)11.7 S9500E、S12500链路聚合是如何选择转发链路的? (83)11.8 各个系列交换机可以配置的链路聚合的流量分担方式: (83)11.9 目前S9500E GRE Tunnel有哪些使用限制? (83)11.10 多SecBlade FW插卡组网,是否适用于VRRPE部署? (84)11.11 路由交换机是否已经支持带vpn-instance的策略路由? (84)11.12 IRF方案中,IRF-Port要求最少几条链路连接(链路聚合方式),以增加IRF可靠性、避免IRF单链路故障和避免IRF单链路性能瓶颈? (84)11.13 当组网采用多SecBlade FW插卡时,出接口做NAT Outbound,是否要求每个SecBlade FW插卡出接口配置不重叠的NAT地址池? (84)11.14 当组网采用多SecBlade FW插卡负载分担N+1备份方式时,当其中有一块SecBalde FW故障时,网络是否会重新收敛,排除故障的SecBalde FW插卡,所有会话重新建立? (84)11.15 IRF方案中,由于路由交换机存在本地链路优先转发的特性,故在组网中,有什么需要注意的地方? (84)12 相关资料 (84)1 使用版本本举例是在H3C SecBladeII-CMW5.20-F3171P17版本上进行配置和验证的。

ISP1100 System Boot Copyright 2002-2004 Nortel Networks, Inc.CPU: PC PENTIUMVersion: 5.4.2BSP version: 1.2/0Creation date: Jan 31 2005, 09:14:02ataDrv 1.0: ATAPI Drive FoundController 1 drive 0Controller 1 drive 1ATAPI Controller 1 #drives found = 1Reading boot parameters from /cd0/nvram.sysPress any key to stop auto-boot...1auto-booting...boot device : ata=1,0unit number : 0processor number : 0file name : /cd0/mainos.sysflags (f) : 0x100aLoading /cd0/mainos.sys...1714304 + 137192 + 80756 Starting at 0x3000000...ataDrv 1.0: ATAPI Drive FoundController 1 drive 0Controller 1 drive 1ATAPI Controller 1 #drives found = 1Attaching network interface lo0... done.NFS client support not included.Loading symbol table from /cd0/mainos.sym ...donefsck: verifying msdos file system on /dev/hda5Copyright (c) 1993-1996 RST Software Industries Ltd. All rights reserved ver: 2.6 FCSDisk Check In Progress ...total disk space (bytes) : 2,147,155,968bytes in each allocation unit : 32,768total allocation units on disk : 65,526bad allocation units : 0available bytes on disk : 2,146,959,360available clusters on disk : 65,520maximum available contiguous chain (bytes) : 2,146,959,360available space fragmentation (%) : 0clusters allocated : 6Done Checking Disk.fsck: verifying msdos file system on /dev/hda1Copyright (c) 1993-1996 RST Software Industries Ltd. All rights reserved ver: 2.6 FCSDisk Check In Progress ...total disk space (bytes) : 2,147,155,968bytes in each allocation unit : 32,768total allocation units on disk : 65,526bad allocation units : 0available bytes on disk : 2,147,155,968available clusters on disk : 65,526maximum available contiguous chain (bytes) : 2,147,155,968available space fragmentation (%) : 0clusters allocated : 0Done Checking Disk.03/08/05 16:10:38 SRPT0730 OS 0: Cold StartRelease: sse-4.00.55Created: Monday January 31 2005 09:14:54 ESTomlInit: Can't open oml.cfg file03/08/05 16:11:05 LOG0001 tRootTask: Error reading system configuration file Loading /cd0/load/inst.out03/08/05 16:11:18 LOG0003 tRootTask: Failed to Create file: /u/config/misc.dat.CS 1000 Signaling Server Software Install Tool (sse-4.00.55)============================================================############## ################`` `##################### `` `####################` ######```########### ######`` `########## #####`` #### NORTEL NETWORKS####### #####` ####`#########` ####` Communication Server 1000 Software#######` #####`####### #####` Copyright 2002 - 2004########## `###`##``########## ### `########################`# `###################################################``````````` ````####````Please press <CR> when ready ...Verifying filesystems ...Filesystems verification succeeded.Copying "/cd0/disk.sys" to "/u/disk.sys".CS 1000 Signaling Server Software Install Tool (sse-4.00.55)============================================================You should ensure that the system date and time are correct prior to installation, since all files copied or created during install willbe time-stamped.You can press <CR> to accept the current values.Current date is: WEDNESDAY 03-08-2005Enter new date (dd mm yyyy): 03-08-2005Date is set to: WEDNESDAY 03-08-2005Current time is: 16:12:19Enter new time (hh mm ss): 16:07:00Time is set to: 16:07:00Current date and time is:WEDNESDAY 03-08-2005, 16:07:00CS 1000 Signaling Server Software Install Tool (sse-4.00.55)============================================================The Install Tool cannot determine when the hard disk was last tested.The hard disk must be tested before installation can continue. This test will take approximately 14 minutes.Please enter:<CR> -> <a> - Test the hard disk.Enter Choice> aTesting hard disk ...Testing partition /u (4194241 blocks) ...0% complete1% complete2% complete3% complete4% complete5% complete6% complete7% complete8% complete9% complete10% complete11% complete12% complete13% complete14% complete16% complete 17% complete 18% complete 19% complete 20% complete 21% complete 22% complete 23% complete 24% complete 25% complete 26% complete 27% complete 28% complete 29% complete 30% complete 31% complete 32% complete 33% complete 34% complete 35% complete 36% complete 37% complete 38% complete 39% complete 40% complete 41% complete 42% complete 43% complete 44% complete 45% complete 46% complete 47% complete 48% complete 49% complete 50% complete 51% complete 52% complete 53% complete 54% complete 55% complete 56% complete 57% complete 58% complete60% complete61% complete62% complete63% complete64% complete65% complete66% complete67% complete68% complete69% complete70% complete71% complete72% complete73% complete74% complete75% complete76% complete77% complete78% complete79% complete80% complete81% complete82% complete83% complete84% complete85% complete86% complete87% complete88% complete89% complete90% complete91% complete92% complete93% complete94% complete95% complete96% complete97% complete98% complete99% complete100% completeTesting partition /p (4194241 blocks) ...1% complete 2% complete 3% complete 4% complete 5% complete 6% complete 7% complete 8% complete 9% complete 10% complete 11% complete 12% complete 13% complete 14% complete 15% complete 16% complete 17% complete 18% complete 19% complete 20% complete 21% complete 22% complete 23% complete 24% complete 25% complete 26% complete 27% complete 28% complete 29% complete 30% complete 31% complete 32% complete 33% complete 34% complete 35% complete 36% complete 37% complete 38% complete 39% complete 40% complete 41% complete 42% complete 43% complete45% complete 46% complete 47% complete 48% complete 49% complete 50% complete 51% complete 52% complete 53% complete 54% complete 55% complete 56% complete 57% complete 58% complete 59% complete 60% complete 61% complete 62% complete 63% complete 64% complete 65% complete 66% complete 67% complete 68% complete 69% complete 70% complete 71% complete 72% complete 73% complete 74% complete 75% complete 76% complete 77% complete 78% complete 79% complete 80% complete 81% complete 82% complete 83% complete 84% complete 85% complete 86% complete 87% complete89% complete90% complete91% complete92% complete93% complete94% complete95% complete96% complete97% complete98% complete99% complete100% completeHard disk testing succeeded.CS 1000 Signaling Server Software Install Tool (sse-4.00.55)============================================================M A I N M E N UThe Install Tool will install Signaling Server software and related files. You will be prompted throughout the installation.Please enter:<CR> -> <a> - To perform a complete installation/upgrade (Signaling Server s/w, Internet Telephone f/w, Voice Gateway Media Card l/w, basic Signaling Server configuration).<b> - To install/upgrade Signaling Server software only.<c> - To copy Internet Telephone firmware only.<d> - To copy Voice Gateway Media Card loadware only.<e> - To perform basic Signaling Server configuration only.<t> - To go to the Tools Menu.<q> - Quit.Enter Choice> aCopying "/cd0/sse40055.p3/disk.sys" to "/u/disk.sys".Processing the install control file ..."/cd0/sse40055.p3/install.dat" parsed.CS 1000 Signaling Server Software Install Tool (sse-4.00.55)============================================================---------------------------------------------------INSTALLATION STATUS SUMMARY---------------------------------------------------+=================+========+========+==============================+ | Option | Choice | Status | Comment | +=================+========+========+==============================+ | software | yes | | new install 4.00.55 | +-----------------+--------+--------+------------------------------+ | firmware | yes | | copy ALL | +-----------------+--------+--------+------------------------------+ | loadware | yes | | copy ALL | +-----------------+--------+--------+------------------------------+ | configuration | yes | | | +-----------------+--------+--------+------------------------------+Please enter:<CR> -> <y> - Yes, start complete installation.<n> - No, cancel complete installation and return to the Main Menu.Enter Choice> yCS 1000 Signaling Server Software Install Tool (sse-4.00.55)============================================================You have selected to install version 4.00.55 on the system. As this is a new install, all necessary directories and files will becreated on the hard disk.Starting new install of version 4.00.55.Initializing protected partition ..."/p" initialized.Creating directory "/p/data".Creating directory "/p/etc".Creating directory "/p/gk".Creating directory "/p/gk/webfiles".Creating directory "/p/gk/webfiles/cdp".Creating directory "/p/gk/webfiles/endpoint".Creating directory "/p/gk/webfiles/doc".Creating directory "/p/gk/webfiles/entry".Creating directory "/p/gk/webfiles/database". Creating directory "/p/gk/webfiles/oos".Creating directory "/p/gk/webfiles/images". Creating directory "/p/gk/webfiles/css".Creating directory "/p/gk/webfiles/user".Creating directory "/p/gk/webfiles/file".Creating directory "/p/gk/webfiles/system". Creating directory "/p/install".Creating directory "/p/load".Creating directory "/p/tools".Creating directory "/p/web".Creating directory "/p/web/nrsm".Creating directory "/p/web/nrsm/css".Creating directory "/p/web/nrsm/des".Creating directory "/p/web/nrsm/des/en".Creating directory "/p/web/nrsm/help".Creating directory "/p/web/nrsm/help/en".Creating directory "/p/web/nrsm/images".Creating directory "/p/web/nrsm/js".Creating directory "/p/web/iplpd".Creating directory "/p/web/iplpd/locale".Creating directory "/p/web/iplpd/locale/czech". Creating directory "/p/web/iplpd/locale/danish". Creating directory "/p/web/iplpd/locale/dutch". Creating directory "/p/web/iplpd/locale/english". Creating directory "/p/web/iplpd/locale/finnish". Creating directory "/p/web/iplpd/locale/french". Creating directory "/p/web/iplpd/locale/german". Creating directory "/p/web/iplpd/locale/hungaria". Creating directory "/p/web/iplpd/locale/italian". Creating directory "/p/web/iplpd/locale/japanese". Creating directory "/p/web/iplpd/locale/latvian". Creating directory "/p/web/iplpd/locale/norwegia". Creating directory "/p/web/iplpd/locale/polish". Creating directory "/p/web/iplpd/locale/portugue". Creating directory "/p/web/iplpd/locale/russian". Creating directory "/p/web/iplpd/locale/spanish". Creating directory "/p/web/iplpd/locale/swedish". Creating directory "/p/web/iplpd/locale/turkish". Creating directory "/p/web/context".Creating directory "/p/web/context/admin". Creating directory "/p/web/context/callsvr". Creating directory "/p/web/context/doc".Creating directory "/p/web/context/support". Creating directory "/p/web/context/utility". Creating directory "/p/web/context/voipsvr". Creating directory "/p/web/context/btools". Creating directory "/p/web/css".Creating directory "/p/web/des".Creating directory "/p/web/des/cn".Creating directory "/p/web/des/de".Creating directory "/p/web/des/en".Creating directory "/p/web/des/en/lang". Creating directory "/p/web/des/en/ld14". Creating directory "/p/web/des/en/ld15". Creating directory "/p/web/des/en/ld16". Creating directory "/p/web/des/en/ld17". Creating directory "/p/web/des/en/ld32". Creating directory "/p/web/des/en/ld36". Creating directory "/p/web/des/en/ld49". Creating directory "/p/web/des/en/ld73". Creating directory "/p/web/des/en/ld86". Creating directory "/p/web/des/en/ld87". Creating directory "/p/web/des/en/ld90". Creating directory "/p/web/des/en/voipsvr". Creating directory "/p/web/des/en/ld117". Creating directory "/p/web/des/en/ld135". Creating directory "/p/web/des/en/ld137". Creating directory "/p/web/des/en/ld30". Creating directory "/p/web/des/en/ld34". Creating directory "/p/web/des/en/ld37". Creating directory "/p/web/des/en/ld39". Creating directory "/p/web/des/en/ld45". Creating directory "/p/web/des/en/ld46". Creating directory "/p/web/des/en/ld48". Creating directory "/p/web/des/en/ld54". Creating directory "/p/web/des/en/ld75". Creating directory "/p/web/des/en/ld80". Creating directory "/p/web/des/en/ld96". Creating directory "/p/web/des/fr".Creating directory "/p/web/des/voipsvr". Creating directory "/p/web/error".Creating directory "/p/web/error/en". Creating directory "/p/web/help".Creating directory "/p/web/help/cn". Creating directory "/p/web/help/en".Creating directory "/p/web/help/fn".Creating directory "/p/web/images".Creating directory "/p/web/js".Creating directory "/p/web/nav".Creating directory "/p/web/xml".Creating directory "/u/config".Creating directory "/u/db".Creating directory "/u/fw".Creating directory "/u/gk".Creating directory "/u/gk/database".Creating directory "/u/log".Creating directory "/u/patch/pch_tmp".Creating directory "/u/rpt".Creating directory "/u/tmp".Creating directory "/u/trace".Creating directory "/u/web".Creating directory "/u/web/xml".Copying "/cd0/sse40055.p3/install.dat" to "/p/install/install.dat"....Copying "/cd0/sse40055.p3/disk0001.dat" to "/p/install/disk0001.dat".Copying "/cd0/sse40055.p3/disk.sys" to "/p/disk.sys".Copying "/cd0/sse40055.p3/target/p/mainos.sym" to "/p/mainos.sym"......Copying "/cd0/sse40055.p3/target/p/mainos.sys" to "/p/mainos.sys"....................................Copying "/cd0/sse40055.p3/target/p/nvram.sys" to "/p/nvram.sys".Copying "/cd0/sse40055.p3/target/p/renfile.sys" to "/p/renfile.sys".Copying "/cd0/sse40055.p3/target/p/resfile.sys" to "/p/resfile.sys".Copying "/cd0/sse40055.p3/target/p/data/version.dat" to "/p/data/version.dat". Copying "/cd0/sse40055.p3/target/p/etc/debug.bat" to "/p/etc/debug.bat". Copying "/cd0/sse40055.p3/target/p/etc/tools.bat" to "/p/etc/tools.bat". Copying "/cd0/sse40055.p3/target/p/gk/webfiles/cdp/Create.htm" to "/p/gk/webfiles/cdp/create.htm".Copying "/cd0/sse40055.p3/target/p/gk/webfiles/cdp/ModDel.htm" to "/p/gk/webfiles/cdp/moddel.htm".Copying "/cd0/sse40055.p3/target/p/gk/webfiles/cdp/Select.htm" to "/p/gk/webfiles/cdp/select.htm".Copying "/cd0/sse40055.p3/target/p/gk/webfiles/cdp/VwCdpAct.htm" to "/p/gk/webfiles/cdp/vwcdpact.htm".Copying "/cd0/sse40055.p3/target/p/gk/webfiles/cdp/VwCdpStb.htm" to "/p/gk/webfiles/cdp/vwcdpstb.htm".Copying "/cd0/sse40055.p3/target/p/gk/webfiles/endpoint/ModDel.htm" to "/p/gk/webfiles/endpoint/moddel.htm".Copying "/cd0/sse40055.p3/target/p/gk/webfiles/endpoint/Select.htm" to "/p/gk/webfiles/endpoint/select.htm"."/p/gk/webfiles/endpoint/viewact.htm".Copying "/cd0/sse40055.p3/target/p/gk/webfiles/endpoint/ViewStdb.htm" to "/p/gk/webfiles/endpoint/viewstdb.htm".Copying "/cd0/sse40055.p3/target/p/gk/webfiles/endpoint/VwEndEnA.htm" to "/p/gk/webfiles/endpoint/vwendena.htm".Copying "/cd0/sse40055.p3/target/p/gk/webfiles/endpoint/VwEndEnS.htm" to "/p/gk/webfiles/endpoint/vwendens.htm".Copying "/cd0/sse40055.p3/target/p/gk/webfiles/endpoint/hCreate.htm" to "/p/gk/webfiles/endpoint/hcreate.htm".Copying "/cd0/sse40055.p3/target/p/gk/webfiles/endpoint/lCreate.htm" to "/p/gk/webfiles/endpoint/lcreate.htm".Copying "/cd0/sse40055.p3/target/p/gk/webfiles/endpoint/numPrefx.htm" to "/p/gk/webfiles/endpoint/numprefx.htm".Copying "/cd0/sse40055.p3/target/p/gk/webfiles/endpoint/sEpNumPx.htm" to "/p/gk/webfiles/endpoint/sepnumpx.htm".Copying "/cd0/sse40055.p3/target/p/gk/webfiles/doc/_blank.htm" to "/p/gk/webfiles/doc/_blank.htm".Copying "/cd0/sse40055.p3/target/p/gk/webfiles/doc/bsscdhtm.js" to "/p/gk/webfiles/doc/bsscdhtm.js"..Copying "/cd0/sse40055.p3/target/p/gk/webfiles/doc/bsscnbar.js" to "/p/gk/webfiles/doc/bsscnbar.js".Copying "/cd0/sse40055.p3/target/p/gk/webfiles/doc/bssctab0.gif" to "/p/gk/webfiles/doc/bssctab0.gif".Copying "/cd0/sse40055.p3/target/p/gk/webfiles/doc/bssctab1.gif" to "/p/gk/webfiles/doc/bssctab1.gif".Copying "/cd0/sse40055.p3/target/p/gk/webfiles/doc/bssctab2.gif" to "/p/gk/webfiles/doc/bssctab2.gif".Copying "/cd0/sse40055.p3/target/p/gk/webfiles/doc/bssctab3.gif" to "/p/gk/webfiles/doc/bssctab3.gif".Copying "/cd0/sse40055.p3/target/p/gk/webfiles/doc/bssctab4.gif" to "/p/gk/webfiles/doc/bssctab4.gif".Copying "/cd0/sse40055.p3/target/p/gk/webfiles/doc/bssctab5.gif" to "/p/gk/webfiles/doc/bssctab5.gif".Copying "/cd0/sse40055.p3/target/p/gk/webfiles/doc/bssctab6.gif" to "/p/gk/webfiles/doc/bssctab6.gif".Copying "/cd0/sse40055.p3/target/p/gk/webfiles/doc/bssctoc1.gif" to "/p/gk/webfiles/doc/bssctoc1.gif".Copying "/cd0/sse40055.p3/target/p/gk/webfiles/doc/bssctoc2.gif" to "/p/gk/webfiles/doc/bssctoc2.gif".Copying "/cd0/sse40055.p3/target/p/gk/webfiles/doc/bssctoc3.gif" to "/p/gk/webfiles/doc/bssctoc3.gif".Copying "/cd0/sse40055.p3/target/p/gk/webfiles/doc/bssctoc4.gif" to "/p/gk/webfiles/doc/bssctoc4.gif"."/p/gk/webfiles/doc/ehlpdht1.js".Copying "/cd0/sse40055.p3/target/p/gk/webfiles/doc/ehlpdht2.js" to "/p/gk/webfiles/doc/ehlpdht2.js"..Copying "/cd0/sse40055.p3/target/p/gk/webfiles/doc/ehlpdhtm.js" to "/p/gk/webfiles/doc/ehlpdhtm.js"..Copying "/cd0/sse40055.p3/target/p/gk/webfiles/doc/ftsbody.htm" to "/p/gk/webfiles/doc/ftsbody.htm".Copying "/cd0/sse40055.p3/target/p/gk/webfiles/doc/ftsdhtml.htm" to "/p/gk/webfiles/doc/ftsdhtml.htm".Copying "/cd0/sse40055.p3/target/p/gk/webfiles/doc/ftsform.htm" to "/p/gk/webfiles/doc/ftsform.htm".Copying "/cd0/sse40055.p3/target/p/gk/webfiles/doc/gk.ali" to "/p/gk/webfiles/doc/gk.ali".Copying "/cd0/sse40055.p3/target/p/gk/webfiles/doc/gk.ftp" to "/p/gk/webfiles/doc/gk.ftp".Copying "/cd0/sse40055.p3/target/p/gk/webfiles/doc/gk.hhc" to "/p/gk/webfiles/doc/gk.hhc".Copying "/cd0/sse40055.p3/target/p/gk/webfiles/doc/gk.hhk" to "/p/gk/webfiles/doc/gk.hhk".Copying "/cd0/sse40055.p3/target/p/gk/webfiles/doc/gk.hhs" to "/p/gk/webfiles/doc/gk.hhs".Copying "/cd0/sse40055.p3/target/p/gk/webfiles/doc/gk.htm" to "/p/gk/webfiles/doc/gk.htm".Copying "/cd0/sse40055.p3/target/p/gk/webfiles/doc/gk_csh.htm" to "/p/gk/webfiles/doc/gk_csh.htm".Copying "/cd0/sse40055.p3/target/p/gk/webfiles/doc/gk_hhc.zip" to "/p/gk/webfiles/doc/gk_hhc.zip".Copying "/cd0/sse40055.p3/target/p/gk/webfiles/doc/gk_hhk.zip" to "/p/gk/webfiles/doc/gk_hhk.zip".Copying "/cd0/sse40055.p3/target/p/gk/webfiles/doc/gk_hhs.zip" to "/p/gk/webfiles/doc/gk_hhs.zip".Copying "/cd0/sse40055.p3/target/p/gk/webfiles/doc/gkadmpwd.htm" to "/p/gk/webfiles/doc/gkadmpwd.htm".Copying "/cd0/sse40055.p3/target/p/gk/webfiles/doc/gkaltser.htm" to "/p/gk/webfiles/doc/gkaltser.htm".Copying "/cd0/sse40055.p3/target/p/gk/webfiles/doc/gkaubkvi.htm" to "/p/gk/webfiles/doc/gkaubkvi.htm".Copying "/cd0/sse40055.p3/target/p/gk/webfiles/doc/gkautobk.htm" to "/p/gk/webfiles/doc/gkautobk.htm".Copying "/cd0/sse40055.p3/target/p/gk/webfiles/doc/gkbackup.htm" to "/p/gk/webfiles/doc/gkbackup.htm".Copying "/cd0/sse40055.p3/target/p/gk/webfiles/doc/gkbkupre.htm" to "/p/gk/webfiles/doc/gkbkupre.htm"."/p/gk/webfiles/doc/gkcdpcre.htm".Copying "/cd0/sse40055.p3/target/p/gk/webfiles/doc/gkcdpmd.htm" to "/p/gk/webfiles/doc/gkcdpmd.htm".Copying "/cd0/sse40055.p3/target/p/gk/webfiles/doc/gkcdpmds.htm" to "/p/gk/webfiles/doc/gkcdpmds.htm".Copying "/cd0/sse40055.p3/target/p/gk/webfiles/doc/gkcdpvia.htm" to "/p/gk/webfiles/doc/gkcdpvia.htm".Copying "/cd0/sse40055.p3/target/p/gk/webfiles/doc/gkcdpvie.htm" to "/p/gk/webfiles/doc/gkcdpvie.htm".Copying "/cd0/sse40055.p3/target/p/gk/webfiles/doc/gkcfgsua.htm" to "/p/gk/webfiles/doc/gkcfgsua.htm".Copying "/cd0/sse40055.p3/target/p/gk/webfiles/doc/gkcfgsus.htm" to "/p/gk/webfiles/doc/gkcfgsus.htm".Copying "/cd0/sse40055.p3/target/p/gk/webfiles/doc/gkdb.htm" to "/p/gk/webfiles/doc/gkdb.htm".Copying "/cd0/sse40055.p3/target/p/gk/webfiles/doc/gkdbatit.htm" to "/p/gk/webfiles/doc/gkdbatit.htm".Copying "/cd0/sse40055.p3/target/p/gk/webfiles/doc/gkdbrest.htm" to "/p/gk/webfiles/doc/gkdbrest.htm".Copying "/cd0/sse40055.p3/target/p/gk/webfiles/doc/gkdbsymp.htm" to "/p/gk/webfiles/doc/gkdbsymp.htm".Copying "/cd0/sse40055.p3/target/p/gk/webfiles/doc/gkdrcrea.htm" to "/p/gk/webfiles/doc/gkdrcrea.htm".Copying "/cd0/sse40055.p3/target/p/gk/webfiles/doc/gkdrmd.htm" to "/p/gk/webfiles/doc/gkdrmd.htm".Copying "/cd0/sse40055.p3/target/p/gk/webfiles/doc/gkdrmdse.htm" to "/p/gk/webfiles/doc/gkdrmdse.htm".Copying "/cd0/sse40055.p3/target/p/gk/webfiles/doc/gkdrtnva.htm" to "/p/gk/webfiles/doc/gkdrtnva.htm".Copying "/cd0/sse40055.p3/target/p/gk/webfiles/doc/gkdrtnvs.htm" to "/p/gk/webfiles/doc/gkdrtnvs.htm".Copying "/cd0/sse40055.p3/target/p/gk/webfiles/doc/gkdrtpva.htm" to "/p/gk/webfiles/doc/gkdrtpva.htm".Copying "/cd0/sse40055.p3/target/p/gk/webfiles/doc/gkdrtpvs.htm" to "/p/gk/webfiles/doc/gkdrtpvs.htm".Copying "/cd0/sse40055.p3/target/p/gk/webfiles/doc/gkdrtymd.htm" to "/p/gk/webfiles/doc/gkdrtymd.htm".Copying "/cd0/sse40055.p3/target/p/gk/webfiles/doc/gkdrtyva.htm" to "/p/gk/webfiles/doc/gkdrtyva.htm".Copying "/cd0/sse40055.p3/target/p/gk/webfiles/doc/gkdrtyvs.htm" to "/p/gk/webfiles/doc/gkdrtyvs.htm".Copying "/cd0/sse40055.p3/target/p/gk/webfiles/doc/gkdrviac.htm" to "/p/gk/webfiles/doc/gkdrviac.htm"."/p/gk/webfiles/doc/gkdrvisb.htm".Copying "/cd0/sse40055.p3/target/p/gk/webfiles/doc/gkenmdsi.htm" to "/p/gk/webfiles/doc/gkenmdsi.htm".Copying "/cd0/sse40055.p3/target/p/gk/webfiles/doc/gkenmdst.htm" to "/p/gk/webfiles/doc/gkenmdst.htm".Copying "/cd0/sse40055.p3/target/p/gk/webfiles/doc/gkentcre.htm" to "/p/gk/webfiles/doc/gkentcre.htm".Copying "/cd0/sse40055.p3/target/p/gk/webfiles/doc/gkentrmd.htm" to "/p/gk/webfiles/doc/gkentrmd.htm".Copying "/cd0/sse40055.p3/target/p/gk/webfiles/doc/gkentvia.htm" to "/p/gk/webfiles/doc/gkentvia.htm".Copying "/cd0/sse40055.p3/target/p/gk/webfiles/doc/gkentvsb.htm" to "/p/gk/webfiles/doc/gkentvsb.htm".Copying "/cd0/sse40055.p3/target/p/gk/webfiles/doc/gkentyva.htm" to "/p/gk/webfiles/doc/gkentyva.htm".Copying "/cd0/sse40055.p3/target/p/gk/webfiles/doc/gkentyvs.htm" to "/p/gk/webfiles/doc/gkentyvs.htm".Copying "/cd0/sse40055.p3/target/p/gk/webfiles/doc/gkenviac.htm" to "/p/gk/webfiles/doc/gkenviac.htm".Copying "/cd0/sse40055.p3/target/p/gk/webfiles/doc/gkenvsb.htm" to "/p/gk/webfiles/doc/gkenvsb.htm".Copying "/cd0/sse40055.p3/target/p/gk/webfiles/doc/gkepcrea.htm" to "/p/gk/webfiles/doc/gkepcrea.htm".Copying "/cd0/sse40055.p3/target/p/gk/webfiles/doc/gkepcrlg.htm" to "/p/gk/webfiles/doc/gkepcrlg.htm".Copying "/cd0/sse40055.p3/target/p/gk/webfiles/doc/gkepenad.htm" to "/p/gk/webfiles/doc/gkepenad.htm".Copying "/cd0/sse40055.p3/target/p/gk/webfiles/doc/gkepense.htm" to "/p/gk/webfiles/doc/gkepense.htm".Copying "/cd0/sse40055.p3/target/p/gk/webfiles/doc/gkepenva.htm" to "/p/gk/webfiles/doc/gkepenva.htm".Copying "/cd0/sse40055.p3/target/p/gk/webfiles/doc/gkepenvs.htm" to "/p/gk/webfiles/doc/gkepenvs.htm".Copying "/cd0/sse40055.p3/target/p/gk/webfiles/doc/gkepmdse.htm" to "/p/gk/webfiles/doc/gkepmdse.htm".Copying "/cd0/sse40055.p3/target/p/gk/webfiles/doc/gkeptmd.htm" to "/p/gk/webfiles/doc/gkeptmd.htm".Copying "/cd0/sse40055.p3/target/p/gk/webfiles/doc/gkepviac.htm" to "/p/gk/webfiles/doc/gkepviac.htm".Copying "/cd0/sse40055.p3/target/p/gk/webfiles/doc/gkepvisb.htm" to "/p/gk/webfiles/doc/gkepvisb.htm".Copying "/cd0/sse40055.p3/target/p/gk/webfiles/doc/gkftppwd.htm" to "/p/gk/webfiles/doc/gkftppwd.htm"."/p/gk/webfiles/doc/gkid.htm".Copying "/cd0/sse40055.p3/target/p/gk/webfiles/doc/gklogout.htm" to "/p/gk/webfiles/doc/gklogout.htm".Copying "/cd0/sse40055.p3/target/p/gk/webfiles/doc/gkmonpwd.htm" to "/p/gk/webfiles/doc/gkmonpwd.htm".Copying "/cd0/sse40055.p3/target/p/gk/webfiles/doc/gknnpxsi.htm" to "/p/gk/webfiles/doc/gknnpxsi.htm".Copying "/cd0/sse40055.p3/target/p/gk/webfiles/doc/gknptrac.htm" to "/p/gk/webfiles/doc/gknptrac.htm".Copying "/cd0/sse40055.p3/target/p/gk/webfiles/doc/gknptrrt.htm" to "/p/gk/webfiles/doc/gknptrrt.htm".Copying "/cd0/sse40055.p3/target/p/gk/webfiles/doc/gknptrsb.htm" to "/p/gk/webfiles/doc/gknptrsb.htm".Copying "/cd0/sse40055.p3/target/p/gk/webfiles/doc/gknuprfx.htm" to "/p/gk/webfiles/doc/gknuprfx.htm".Copying "/cd0/sse40055.p3/target/p/gk/webfiles/doc/gknwlpad.htm" to "/p/gk/webfiles/doc/gknwlpad.htm".Copying "/cd0/sse40055.p3/target/p/gk/webfiles/doc/gknwlpde.htm" to "/p/gk/webfiles/doc/gknwlpde.htm".Copying "/cd0/sse40055.p3/target/p/gk/webfiles/doc/gknwlpva.htm" to "/p/gk/webfiles/doc/gknwlpva.htm".Copying "/cd0/sse40055.p3/target/p/gk/webfiles/doc/gknwlpvs.htm" to "/p/gk/webfiles/doc/gknwlpvs.htm".Copying "/cd0/sse40055.p3/target/p/gk/webfiles/doc/gkommave.htm" to "/p/gk/webfiles/doc/gkommave.htm".Copying "/cd0/sse40055.p3/target/p/gk/webfiles/doc/gkoomhou.htm" to "/p/gk/webfiles/doc/gkoomhou.htm".Copying "/cd0/sse40055.p3/target/p/gk/webfiles/doc/gkoostit.htm" to "/p/gk/webfiles/doc/gkoostit.htm".Copying "/cd0/sse40055.p3/target/p/gk/webfiles/doc/gkrerelt.htm" to "/p/gk/webfiles/doc/gkrerelt.htm".Copying "/cd0/sse40055.p3/target/p/gk/webfiles/doc/gkresflo.htm" to "/p/gk/webfiles/doc/gkresflo.htm".Copying "/cd0/sse40055.p3/target/p/gk/webfiles/doc/gkresftp.htm" to "/p/gk/webfiles/doc/gkresftp.htm".Copying "/cd0/sse40055.p3/target/p/gk/webfiles/doc/gkressel.htm" to "/p/gk/webfiles/doc/gkressel.htm".Copying "/cd0/sse40055.p3/target/p/gk/webfiles/doc/gkstatus.htm" to "/p/gk/webfiles/doc/gkstatus.htm".Copying "/cd0/sse40055.p3/target/p/gk/webfiles/doc/gksynupx.htm" to "/p/gk/webfiles/doc/gksynupx.htm".Copying "/cd0/sse40055.p3/target/p/gk/webfiles/doc/gksyrqtl.htm" to "/p/gk/webfiles/doc/gksyrqtl.htm".。
精心整理页脚内容此文档为自行整理,非官方提供资料,仅供参考。
疏漏之处敬请反馈。
对RAID 进行操作很可能会导致数据丢失,请在操作之前务必将重要数据妥善备份,以防万一。
名称解释:Disk?Group :磁盘组,这里相当于是阵列,例如配置了一个RAID5,就是一个磁盘组VD(Virtual?Disk):?虚拟磁盘,虚拟磁盘可以不使用阵列的全部容量,也就是说一个磁盘组可以分为多个VDHS :Mgmt1建菜单23、在4、确认RAID 个虚拟磁盘中。
如果这个虚拟磁盘没有使用我们所配置的RAID5阵列所有的容量,剩余的空间可以配置为另外的一个虚拟磁盘,但是配置下一个虚拟磁盘时必须返回VD?Mgmt 创建(可以参考第13步,会有详细说明)。
VD?Name 根据需要设置,也可为空。
????????????????????????????????????????????????????????????????????????????????????????????????????????????????????注:各RAID 级别最少需要的硬盘数量,RAID0=1??RAID1=2??RAID5=3??RAID10=4??RAID50=65、修改高级设置,选择完VD?Size 后,可以按向下方向键,或者Tab 键,将光标移至Advanced?Settings 处,按空格键开启(禁用)高级设置。
如果开启后(红框处有X 标志为开启),可以修改Stripe?Element?Size 大小,以及阵列的Read?Policy 与Write?Policy ,Initialize 处可以选择是否在阵列配置的同时进行初始化。
精心整理页脚内容高级设置默认为关闭(不可修改),如果没有特殊要求,建议不要修改此处的设置。
6、上述的配置确认完成后,按Tab键,将光标移至OK处,按回车,会出现如下的提示,如果是一个全新的阵列,建议进行初始化操作,如果配置阵列的目的是为了恢复之前的数据,则不要进行初始化。
Windows 部署服务更新循序渐进指南Microsoft Corporation发布日期:2006 年 8 月作者:Shawn Webb编辑:Susan Sarrafan摘要本指南介绍了 Windows Server 2003 的 Windows 部署服务。
它概述了可用于测试Windows 部署服务的功能和任务,并详细介绍了此技术。
本文档支持软件产品的预发布,在最终的商业发布前,此预发布可能会有重大变更,并且是归 Microsoft Corporation 所有的机密信息。
文档的披露依照接受方和 Microsoft 间的保密协议进行。
本文档仅用于提供信息,Microsoft 在此文档中不进行任何明确的或暗示的担保。
本文档中的信息,包含 URL 及其他 Internet 网站引用,若有更改,恕不另行通知。
使用本文档的全部风险或使用本文档造成的后果均由用户承担。
除非另行说明,此处提及的示例公司、组织、产品、域名、电子邮件地址、徽标、人员、地点和事件实数虚构,并非有意联想或暗指任何真实的公司、组织、产品、域名、电子邮件地址、徽标、个人、地点或事件。
用户有责任遵守所有适用的版权法。
没有版权法的权利限制,未经Microsoft Corporation 的书面许可,对本文档的任何部分不得以任何形式、通过任何途径(电子、机械、影印、录音或其他)或出于任何目的进行复制、存储或转入检索系统或传输。
对于本文档中有关的事项,Microsoft 可能有对应的专利、专利申请、商标、版权或其他知识产权。
除非经 Microsoft 的任何书面许可协议明确提供,本文档的提供并不赋予您对这些专利、商标、版权或其他知识产权的任何许可证。
© 2006 Microsoft Corporation。
保留所有权利。
Active Directory、Microsoft、MS-DOS、Visual Basic、Visual Studio、Windows、Windows NT 和 Windows Server 是 Microsoft Corporation 在美国和/或其他国家或地区的注册商标或商标。
AMPCI-9110 通用数据采集控制板一、概述AMPCI-9110板是PCI总线通用采集控制板,该板可直接插入具备PCI插槽的工控机或个人微机,构成模拟量电压信号、数字量电压信号采集、监视输入和模拟量电压信号输出、数字量电压信号输出及计数定时系统。
AMPCI-9110板为用户提供了单端32路模拟量数据采集输入通道, 模拟量输入通道具有程控放大功能,2路12Bit模拟量电压信号输出,16Bit TTL数字量输入和16Bit TTL数字量输出,配接AMPCD821光隔端子板实现光隔I/O,可直接驱动继电器, 3路16位计数定时通道(一片82C54),基准时钟2M,它的1、2通道级连使用,用来产生定时触发A/D转换的时钟信号,其通道0保留给用户自行使用,构成脉冲计数、频率测量、脉冲信号发生器等电路。
对AMPCI-9110板的所有读写操作均为16Bit即D00~D15,当对82C54进行读写时只有D00~D07有效,同样A/D转换数据一次读入的为B00~B11。
二、性能和技术指标2.1 性能•模拟信号输入A/D分辩率12Bit• 32路模拟信号通道•模拟信号输入具有程控放大•模拟信号输出D/A分辩率12Bit (A型不具备该功能)•模拟信号输出通道2路 (A型不具备该功能)• 16Bit DI/16Bit DO TTL兼容数字量输入/输出• 1路计数定时通道(留给用户自行使用) (A型不具备该功能)• A/D转换触发工作方式:软件触发• A/D转换数据传输方式:查询方式、等待方式2.2 技术指标•输入电压范围: ±5V、0-10V•输入阻抗: > 100 MΩ• A/D转换时间: 8.5uS• A/D转换精度: 优于±0.1%(10V满量程)•模拟信号输入程控放大倍数: 1/2/4/8/16(AD526) (A型不具备该功能)•输出电压范围: ±5V、0-5V、0-10V (A型不具备该功能)•计数定时部分: 0通道留给用户使用,1通道和2通道级联用做板内定时触发,内部时钟基准2MHz(A型不具备该功能)三、使用3.1 寄存器功能描述①: 模拟输入通道选择、增益选择、D/A和82C54地址选择寄存器(写操作)Offset=00H,Offset:相对地址的偏移量,即该写操作的I/O地址(详细操作见软件说明书)D15 D14 D13 D12 D11 D10 D09 D08 D07 D06 D05 D04 D03 D02 D01 D00X X X X GT2 GT1 A1 A0 G2 G1 G0 C4 C3 C2 C1 C0C4~C0: 模拟信号输入通道选择位,C4 C3 C2 C1 C00 0 0 0 0 CH00 通道00 0 0 0 1 CH010 0 0 1 0 CH02...... .1 1 1 1 0 CH1E1 1 1 1 1 CH1F 通道31A1/A0: 82C54、D/A转换器的地址选择位(A型不具备该功能,此时无意义)a: A1 A0 8254内部寄存器0 0 #0通道数据寄存器地址0 1 #1通道数据寄存器地址1 0 #2通道数据寄存器地址1 1 控制寄存器地址b: A1 A0 D/A转换器地址选择位(A型不具备)0 0 D/A1通道低8数据寄存器地址0 1 D/A1通道高4数据寄存器地址1 0 D/A2通道低8数据寄存器地址1 1 D/A2通道高4数据寄存器地址G2~G0:程控放大增益选择位(A型不具备该功能,此时无意义)G2 G1 G0 程控放大增益倍数0 0 0 10 0 1 20 1 0 40 1 1 81 0 0 16GT1/GT2:82C54的1和2通道的GATE1/GATE2控制位(A型不具备该功能,此时无意义)GT1:计数定时器1的GATE1控制端GT2:计数定时器2的GATE2控制端(详细操作见8254操作手册)②启动A/D转换 (写操作)Offset=02H,Offset是相对地址的偏移量,该写操作的I/O地址,(详细操作见软件说明书)D15~D00 此时无意义③计数定时器8254片选 (读操作+写操作)Offset=04H,Offset是相对地址的偏移量,该读写操作的I/O地址(详细操作见软件说明书) 此时只有D7~D0 有意义④ D/A转换器片选 (写操作)Offset=06H Offset:相对地址的偏移量,该写操作的I/O地址(详细操作见软件说明书) 此时只有D7~D0 有意义,具体写操作意义由A1/A0决定,D/A转换器地址选择位见①:A1/A0a:写D/A(D/A1或D/A2)低8数据寄存器数据格式D7 D6 D5 D4 D3 D2 D1 D0B07 B06 B05 B04 B03 B02 B01 B00此时只有D7~D0 有意义,注意B07-B00在D15-D00的D07-D00上,D15-D08无意义b:写D/A(D/A1或D/A2)高4位数据寄存器数据格式D7 D6 D5 D4 D3 D2 D1 D0X X X X B11 B10 B09 B08此时只有D3~D0 有意义, 注意B11-B08在D15-D00的D03-D00上,D15-D04无意义B11~B00:D/A转换12Bit数据,X:未用位⑤启动D/A转换器 (写操作)Offset=08H Offset:相对地址的偏移量,该写操作的I/O地址(详细操作见软件说明书) 此时D15~D00 无意义,12BIT的DA转换数据写入D/A转换器后,必须执行启动D/A转换⑤输出电压才会变化⑥查询A/D 转换状态位+A/D转换数据 (读操作)Offset=0AH Offset:相对地址的偏移量,该读操作的I/O地址(详细操作见软件说明书)D15 D14 D13 D12 D11 D10 D09 D08 D07 D06 D05 D04 D03 D02 D01 D00Z X X X B11 B10 B9 B8 B7 B6 B5 B4 B3 B2 B1 B0B11~B0 : A/D转换数据Z: A/D 转换状态位 Z=1, A/D转换器正在进行转换Z=0, 转换结束,可以读取A/D转换数据⑦: 16位TTL数据输出寄存器数据格式(写操作)Offset=0CH Offset:相对地址的偏移量,该写操作的I/O地址(详细操作见软件说明书)D15 D14 D13 D12 D11 D10 D09 D08 D07 D06 D05 D04 D03 D02 D01 D00O15 O14 O13 O12 O11 O10 O9 O8 O7 O6 O5 O4 O3 O2 O1 O0 O15~O00 : 16Bit数字量输出,对应J2的DO15~DO00⑧: 16位TTL数据输入寄存器数据格式 (读操作)Offset=0EH Offset:相对地址的偏移量,该读操作的I/O地址(详细操作见软件说明书)D15 D14 D13 D12 D11 D10 D09 D08 D07 D06 D05 D04 D03 D02 D01 D00I15 I14 I13 I12 I11 I10 I9 I8 I7 I6 I5 I4 I3 I2 I1 I0 I15~I0 : 16Bit数字量输入, I15~I0对应DI15~DI0AMPCI-9110读写I/O操作命令表:OFFSET = 操作操作意义00H 写操作模拟信号输入通道选择寄存器、命令字寄存器,见(1) 02H 写操作启动A/D转换,见(2)04H 读操作/写操作计数定时器8254片选,见(3)06H 写操作D/A转换器片选,见(4)08H 写操作启动D/A转换器,见(5)0AH 读操作查询A/D 转换状态位+A/D转换数据,见(6) 0CH 写操作16位TTL数据量输出寄存器,见(7)OEH 读操作16位TTL数据量输入寄存器,见(8)3.2 工作方式3.2.1A/D部分转换触发方式①软件触发方式:执行Offset=02H写命令,触发A/D转换②定时触发方式:初始化8254的#1#2计数器,CLK2输入为2MHZ,CLK1输入为OUT2,OUT1输出的下降沿触发A/D 转换,需短接JP53.2.2 A/D部分的数据传输: 查询方式A/D转换开始后,执行Offset=0AH读命令,Z=0说明A/D转换完成可读数据3.2.2A/D转换工作过程AMPCI-9110板的A/D转换是通过软件编程来控制和启动A/D转换的<1>使用时首先应程序设定要进行A/D转换的通道号,即要对哪一通道进行A/D转换,该写操作见前面《3.1寄存器功能描述》的(1)节: “模拟输入通道选择、增益选择、D/A和82C54地址选择寄存器”,该寄存器I/O地址Offset=00H ,“Offset”是相对地址的偏移量,可理解为该寄存器的I/O地址(详细对“Offset”的读写操作见软件说明书部分)<2>程序设定完要进行A/D转换的通道号和放大倍数后,需执行程序启动A/D转换操作,A/D 转换器才开始转换,即再执行《3.1寄存器功能描述》的(2)节,“启动A/D转换”,该写操作的I/O地址 Offset=02H,“Offset”是相对地址的偏移量,(详细对“Offset”的读写操作见软件说明书部分),该操作为软件触发启动一个周期的A/D转换,若A/D转换的放大倍数不是1倍,应在设定“模拟输入通道选择、增益选择、D/A和82C54地址选择寄存器”操作后,适当加几个μS的延时以给程控放大器足够的建立时间,再执行程序启动A/D转换操作,以保证精度<3>启动A/D转换后,应通过软件查询A/D转换完成状态标志位,见前面《3.1寄存器功能描述》的(6)节,“查询A/D 转换状态位+A/D转换数据”,“Z”该位为1,说明A/D转换器正在进行转换,不可读取A/D转换数据,继续查询该位,若该位为0,说明A/D转换已完成,可读取A/D转换数据,该读操作的I/O地址 Offset=0AH,“Offset”相对地址的偏移量(详细操作见软件说明书),标志位Z对应该标志寄存器数据线D15-D00的D15<4>当执行上述“<3>查询A/D转换完成状态标志位”且“Z”位为0时,即可读取A/D转换数据,该读操作的I/O地址同样为Offset=0AH,“Offset”相对地址的偏移量(详细操作见软件说明书)3.3 调整电位器定义PR1: 程控放大器零偏移调整电位器PR2: A/D转换单极性零偏移调整电位器PR3: A/D转换双极性零偏移调整电位器PR4: A/D转换满量程调整电位器PR5: D/A基准源+5V调整电位器PR6: D/A2零偏移调整电位器PR7: D/A2满量程调整电位器PR8: D/A1零偏移调整电位器PR9: D/A1满量程调整电位器3.4 信号输入/输出插座定义:a: J1模拟输入/模拟输出定义:19 1 序号⊙⊙⊙⊙⊙⊙⊙⊙⊙⊙⊙⊙⊙⊙⊙⊙⊙⊙□⊙⊙⊙⊙⊙⊙⊙⊙⊙⊙⊙⊙⊙⊙⊙⊙⊙⊙37 20 序号37芯孔式D型插头J1 印制板插头序号 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 引脚定义 CH00 CH01 CH02 CH03 CH04 CH05 CH06 CH07 CH08 CH09插头序号 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19引脚定义 CH0A CH0B CH0C CH0D CH0E CH0F GND D/A1 D/A2插头序号 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 引脚定义 CH10 CH11 CH12 CH13 CH14 CH15 CH16 CH17 CH18 CH19插头序号 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37引脚定义 CH1A CH1B CH1C CH1D CH1E CH1F GND GNDCH00~CH1F: 对应模拟输入通道00~31共32个通道,对应通道代码00~1FD/A1,D/A2: 模拟输出通道1,2GND: 模拟输入/输出地b:数字量和计数定时器#0输出插座J2定义:插座J2定义见下页图示其中:DO0~DO15: TTL/COMS兼容数字量输出DI0~DI15: TTL/COMS兼容数字量输入+5V: 机内PCI总线+5VGND: 机内地GATE0: 计数器0门控GATEOUT0: 计数器0输出CLK0: 计数器0外部时钟输入40 39OUT0 ⊙⊙ CLK0(外)GATE0 ⊙⊙ GNDGND ⊙⊙ GND+5V ⊙⊙ +5VDI7 ⊙⊙ DI6DI5 ⊙⊙ DI4DI3 ⊙⊙ DI2DI1 ⊙⊙ DI0DI8 ⊙⊙ DI9DI10 ⊙⊙ DI11DI12 ⊙⊙ DI13DI14 ⊙⊙ DI15DO7 ⊙⊙ DO6DO5 ⊙⊙ DO4DO3 ⊙⊙ DO2DO1 ⊙⊙ DO0DO8 ⊙⊙ DO9DO10 ⊙⊙ DO11DO12 ⊙⊙ DO13DO14 ⊙□ DO152 1 J23.5跨接线选择定义:JP1: 1,2短接,模拟输入选择单极性;2,3短接,模拟输入选择双极性(出品状态) JP2: 1,2短接,8254的CLK0接2MHZ时钟输入; 2,3短接,接外部输入(出品状态); JP3: D/A2输出选择: ①1,2短接,-5V~+5V(出品状态)②2,3短接,0~+10V③3,4短接,0~+5VJP4: D/A1输出选择: 跨接方式与D/A2相同JP5:短接时定时器触发A/D转换允许;反之,禁止(出品状态);3.5 校准①A/D部分校准a.程控放大器调整:软件设置放大倍数16倍,任一通道接地,调整PR1 使AD526的8脚输出为0.0000V(出品时已调整) (AMPCI-9110A无此)b.单极性输入0~+10V:任一通道对地短接,调整PR2,使转换值为001H;输入任一通道接7.5V,调整PR4,使转换值为C00H;c.双极性输入-5V~+5V:任一通道对地短接,调整PR3,使转换值为800H;输入任一通道4.997V调整PR4使转换值为FFEH;② D/A部分校准(AMPCI-9110A无此)基准源调整: 调整PR5使336-5V输出+5.000V,出厂时已调整。
NBU备份系统操作手册目录第1章维护 (6)1.1NBU中添加环境变量的方法 (6)1.2NBU服务自启动、停止脚本位置 (9)1.3NBU启动、关闭的方法 (10)1.4日常维护健康检查的内容和示例运行结果 (11)第2章安装 (19)2.1WINDOWS平台软件安装 (19)2.1.1安装NBU Master Server (19)2.1.2装NBU Media Server (29)2.1.3安装NBU Client (41)2.1.4安装NBU补丁 (48)2.2L INUX/UNIX平台软件安装 (51)2.2.1安装Media Server (51)2.2.2安装Media Server补丁 (54)2.2.3安装Client (59)2.2.4安装Client 补丁 (61)第3章配置NBU (65)3.1配置S TORAGE U NIT (65)3.1.1新建storage Unit (65)3.1.2storage unit 属性 (65)3.2配置带库 (67)3.2.1配置设备 (67)3.2.2配置磁带 (73)3.3配置D EDUPLICATION S TORAGE P OOL (76)3.3.1建立storage server (76)3.3.2设置存储池 (81)第4章NBU灾难恢复 (84)4.1配置CATALOG备份策略 (84)4.1.1新建policy (84)4.1.2修改Attributes (85)4.1.3修改schedule (85)4.1.4指定catalog备份日志存放 (86)4.2C ATALOG的灾难恢复 (88)4.2.1导入catalog备份 (88)4.2.2恢复catalog日志文件 (88)4.2.3执行恢复 (89)第5章文件备份与恢复 (93)5.1W INDOWS系统的文件备份 (93)5.1.1打开管理界面 (93)5.1.2新建策略 (93)5.1.3attributes设置 (94)5.1.4Schedules设置 (95)5.1.5client设置 (99)5.1.6Backup Seclection设置 (100)5.2L INUX/UNIX系统的文件备份 (102)5.2.1打开管理界面 (102)5.2.2新建策略 (103)5.2.3attributes 属性设置 (104)5.2.4Schedules设置 (105)5.2.5client设置 (108)5.2.6Backup Seclection设置 (109)5.3文件恢复 (111)5.3.1打开管理界面 (111)5.3.2选择恢复选项 (111)5.3.3选择需要恢复的文件 (115)第6章ORACLE备份与恢复 (116)6.1使用模板创建备份脚本 (116)6.2修改备份脚本 (116)6.2.1全库备份脚本 (116)6.2.2归档备份脚本 (123)6.3创建P OLICY (129)6.3.1新建policy (129)6.3.2修改Attributes (131)6.3.3修改schedule (131)6.3.4指定备份的Client (133)6.3.5指定备份脚本 (134)6.4恢复O RACLE (135)6.4.1本机恢复 (135)6.4.2异机恢复 (136)6.4.3图形界面恢复 (139)第7章MS-SQL备份与恢复 (143)7.1确认主机访问 (143)7.2创建备份脚本 (144)7.2.1全备份脚本 (144)7.2.2增量备份脚本 (146)7.3创建P OLICY (147)7.3.1新建policy (147)7.3.2修改Attributes (148)7.3.3修改schedule (149)7.3.4指定备份的Client (151)7.3.5指定备份脚本 (152)7.4MS-SQL恢复 (153)7.4.1创建权限 (153)7.4.2创建脚本 (153)7.4.3修改脚本 (155)第8章虚拟机备份与恢复 (157)8.1安装MEDIA SERVER (157)8.2配置虚拟机备份 (170)8.3虚拟机备份 (174)8.3.1策略建立 (174)8.3.2执行备份 (178)8.4虚拟机恢复 (180)第9章系统备份与恢复 (186)9.1建立BMR主服务器 (186)9.1.1windows安装BMR主服务器 (186)9.1.2Linux/Unix安装BMR主服务器 (188)9.2配置资源树 (189)9.2.1windows配置 (189)9.2.2Linux/Unix配置 (200)9.3配置系统备份策略 (207)9.3.1新建policy (207)9.3.2修改Attributes (208)9.3.3修改schedule (208)9.3.4指定备份的Client (210)9.3.5指定备份选项 (211)9.3.6查看备份信息 (211)9.4系统恢复 (212)9.4.1windows BMR恢复 (212)9.4.2aix BMR恢复 (220)9.4.3linux BMR恢复 (229)第10章INFORMIX备份与恢复 (232)10.1I NFORMIX配置 (232)10.2I NFORMIX脚本配置 (232)10.3策略制定 (234)10.3.1数据库备份 (234)10.3.2配置文件备份 (238)10.3.3日志备份 (242)10.4I NFORMIX恢复 (246)10.4.1本机恢复 (246)10.4.2异机恢复 (247)第11章DB2备份与恢复 (249)11.1参数设置 (249)11.2第一种策略 (250)11.3第二种策略 (259)11.4第三种策略 (261)11.5DB恢复 (268)第12章EXCHANGE备份与恢复 (269)12.1配置NBU客户机服务登陆帐户 (269)12.2配置E XCHANGE备份策略 (271)12.2.1全库备份 (271)12.2.2单邮箱的备份 (273)12.2.3GTR备份 (275)12.2.4Exchange的恢复 (279)第13章LOTUSNOTES备份 (289)13.1W INDOWS环境变量设置 (289)13.2U NIX&L INUX环境变量设置 (290)13.3 (290)第1章维护对于一个关键业务系统而言,数据资料是整个系统运作的核心。
Fanuc 0M 参数2008-02-20 17:27250与251设定参数I/O是2与3时有效波特率552与553设定参数I/O是0与1时有效波特率518~521:依序为X,Y,Z和第4轴的快速进给速度。
设定值:30~24000MM/MIN522~525:依序为X,Y,Z和第4轴的线性加减速的时间常数。
设定值:8~4000(单位:MSEC)527设定切削进给速度的上限速度(X,Y,Z轴)设定值:6~15000mm/min529:在切削进给和手动进给指数加速/减速之时间常数。
设定值:0~4000msec。
当不用时此参数设0530:在指数加速/减速时进给率之最低极限(FL)设定值:6~15000。
通常此值设0531:设定在循环切削G73(高速钻孔循环)中之后退量。
设定值:0~32767MM532:在循环切削G73(钻深孔循环)中,切削开始点之设定。
设定值:0~32767MM533设定快速移动调整率的最低进给速度(F0)设定值:6~15000MM/MIN534设定在原点复归时之最低进给速度(FL)设定值:6~15000MM/MIN535,536,537,538在X,Y,Z与第4轴各轴的背隙量,设定值:0~2550MM539:在高速主轴的最大转数(为主轴机能的类比输出使用),(在3段变速情形下之中间速度)(主轴速度电压10V时主轴速度)设定值:1~19999RPM546:设定Cs轴的伺服环路内发生的漂移量。
设定值:0~+或-8192(VELO)自动补正时此值会自动变化(T系列)548:在指数加速/减速中手动进给的最低极限速度(FL)设定值:6~15000MM/MIN(米制)6~6000INCH/MIN(英制)549:在自动模式中打开电源后之切削进给速度550:在自动插入顺序号码中,号码之增量值551:在周速一定控制(G96)中量低的主轴转数555:在3段变速选择中,高速档之主轴转数最大设定值(S类比输出用)556:在3段变速选择中,高速档之主轴转数最低设定值(为S类比输出B类使用)557:在刀尖半径补正(T系)或刀具补正(M系)时,当刀具沿着接近于90度的锐角外围移动时,设定可忽略的小移动量之极限值。
Chapter 9 Planning Tools and TechniquesTRUE/FALSE QUESTIONSTECHNIQUES FOR ASSESSING THE ENVIRONMENT1.Benchmarking is a form of environmental scanning.(False; easy; p. 238)petitor intelligence chiefly involves corporate spying.(False; easy; p. 239; AACSB: Ethics)petitor’s advertisements, want-ad placements, and corporate Web sites can all serve as goodsources of competitive intelligence.(True; moderate; p. 239)4.Buying a competitor’s product for evaluation is a form of environmental scannin g.(True; easy; p. 239)petitor intelligence becomes illegal corporate spying when it involves the theft of proprietary ornonproprietary materials.(False; easy; p. 240; AACSB: Ethics)6.Time series analysis, substitution effect, and economic indicators are all examples of quantitativeforecasting techniques.(True; moderate; p. 241)7. A manager who wanted to predict next quarter’s sales on the basis of 4 years of previous sales datawould probably use time series analysis.(True; moderate; p. 241)8.The more dynamic the environment, the more likely managers are to forecast effectively. (False; difficult; p. 242)9.Benchmarking involves evaluating company effectiveness against its own standards.(False; moderate; p. 243)10.To be most useful, benchmarking should involve companies in the same industry.(False; moderate; p. 243)TECHNIQUES FOR ALLOCATING RESOURCES11.Before managers can organize and lead in order to implement the goals, they must have a budget. (False; moderate; p. 244)12.It is not unusual for budgets to be used for improving time, space, and use of material resources. (True; easy; p. 244)13.A cash budget lists primary activities and allocates a dollar amount to each.(False; easy; p. 244)14.Profit budgets combine revenue and expense budgets into one.(True; moderate; p. 244)15.We live in a world in which almost everything is expressed in monetary units.(True; moderate; p. 245)16.Scheduling involves allocating resources by detailing what activities have to be done, the order inwhich they are to be completed, who is to do each, and when they are to be completed.(True; easy; p. 246)17.The bars of a Gantt chart show input, both planned and actual, over a period of time.(False; moderate; p. 246)18.The Gantt chart can serve as a control tool because the manager can see deviations from the plan. (True; moderate; p. 246)19.Events, activities, and critical paths are all parts of PERT network analysis.(True; easy; p. 247)20.Resource allocation problems can be solved with breakeven analysis.(False; difficult; p. 249)21.Fixed costs are expenses that do not change, regardless of volume.(True; easy; p. 249)22.To compute a breakeven point, a manager needs to know the unit price of the product being sold, thefixed cost per unit, and the total variable cost.(False; moderate; p. 249)CONTEMPORARY PLANNING TECHNIQUES23.Two planning techniques that are appropriate for a dynamic and complex environment are projectmanagement and forecasting.(False; easy; p. 252)24.In a typical project, all of the work is done by a project manager who reports to the projectcoordinator.(False; moderate; p. 253)25.The project planning process begins by clearly defining the project’s goals.(True; easy; p. 253)26.Project management is a management technique that emphasizes flexibility and rapid response tomarket opportunities.(True; easy; p. 253)27.Project management differs from managing a production line based mainly on the temporary natureof most projects and project teams.(True; moderate; p. 254)28.One of the challenges of being a project manager is managing their full-time employees.(True; easy; p. 254)29.Scenario planning is useful in forecasting events such as terrorist attacks and natural disasters. (False; moderate; p. 255)30.One suggestion that has been identified by risk experts as particularly important for preparing forunexpected events is to have an early warning system in place.(True; moderate; p. 255)MULTIPLE-CHOICE QUESTIONSFor each of the following choose the answer that most completely answers the question. TECHNIQUES FOR ASSESSING THE ENVIRONMENT31.What are three tools that managers can use to analyze their organization’s environment?a.strategic planning, environmental scanning, and TQMb.forecasting, budgeting, and time managementc.environmental scanning, forecasting, and benchmarkingd.benchmarking, planning, and evaluating(c; moderate; p. 238)32.Environmental scanning is the screening of large amounts of information to anticipate and____________.a.follow new legislation that is being passed by Congressb.interpret changes in the environmentc.correct failure in pollution equipmentd.forecast climatic changes that will affect materials used(b; moderate; p. 238)33.Research has shown that companies with advanced environmental scanning systems _____________.a.increased their profits and revenue growthb.collect more data, but do not see much difference in their profits and revenue growthc.improved their ability to compete in the market placed.decreased their profits and revenue growth(a; moderate; p. 238)34.One of the fastest growing areas of environmental scanning is _______________.a.regression analysispetitor intelligencec.reengineeringd.forecasting(b; moderate; p. 239)petitor intelligence allows managers to _______________.a.react to competitor actionsb.cut cost below the competitionc.increase market diversificationd.anticipate competitor actions(d; difficult; p. 239)petitor intelligence experts suggest that 80 percent of what a manager needs to know aboutcompetitors can be found out from ______________.panies such as Dun & Bradstreetb.their competitors’ employees, suppliers, and customersc.their competitors’ products, suppliers, and customersd.their own employees, suppliers, and customers(d; moderate; p. 239)37.Many firms regularly buy competitors’ products and have their own engineers study them to learnabout new technical innovations. This process is called ______________.petitor engineeringpetition engineeringc.strategic engineeringd.reverse engineering(d; moderate; p. 239)38.When seeking competitor intelli gence, there is often a fine line between what’s considered legal andethical and what’s considered ____________.a.illegal and ethicalb.illegal and unethicalc.legal and unethicald.practical and legal(c; moderate; p. 240; AACSB: Ethics)39.The value of global scanning is largely dependent on the ____________.a.extent of foreign competition activities in the marketb.price that foreign competition charges in the marketc.extent of government regulation activities in the foreign marketd.extent of the organization’s globa l activities(d; moderate; p. 240; AACSB: Globalizations)40.Managers need forecasts that will allow them to predict future events effectively and ___________.a.accuratelyb.efficientlyc.specificallyd.in a timely manner(d; moderate; p. 241)41.Environmental scanning creates the basis for ____________.a.project managementb.forecastsc.benchmarkingd.budgeting(b; difficult; p. 241)42.What is defined as a prediction of outcomes?a. a forecastb. a benchmarkc. a budgetd. a resource(a; easy; p. 241)43.Virtually any component in the organization’s __________ environments can be forecasted.a.general and specificb.internal and externalc.externald.general(c; difficult; p. 241)44.Forecasting techniques fall into what two categories?a.fixed asset and human capitalb.predictive and confirmatoryc.quantitative and qualitatived.empirical and conceptual(c; moderate; p. 241)45.Quantitative forecasting applies a set of mathematical rules to ____________.a.develop predictions of outcomes from customers’ opinionsb. a series of past data to predict outcomesc.analyze what has happened in the past and determine when it will occur againd.estimate the number of products that should be produced at a given time(b; moderate; p. 241)46.What type of forecasting technique relies on the judgment and opinion of knowledgeable individuals?a.qualitativeb.short termc.confirmatoryd.predictive(a; moderate; p. 241)47.If General Motors plans on changing their truck paint color scheme because they believe that in thefuture more women will be interested in purchasing these vehicles, this is an example of what kind of environmental scanning?a.scenariob.forecastingc.benchmarkingd.anticipating(b; moderate; p. 241)48.What forecasting technique uses a mathematical formula to predict how, when, and under whatcircumstances a new product or technology will replace an existing one?a.econometric modelsb.economic indicatorsc.substitution effectd.regression models(c; moderate; p. 241; AACSB: Technology)49.What forecasting technique combines and averages the opinions of experts?a.sales force compositionb.customer evaluationc.substitution effectd.jury of opinion(d; moderate; p. 241)50.CPFR®, Internet-based software, offers a standardized way for retailers and manufacturers to use theInternet to ____________.a.collaboratively benchmarkb.collaboratively forecastc.perform environmental scanningd.perform global scanning(b; difficult; p. 242; AACSB: Technology)51.The goal of forecasting is to provide managers with ____________.a.accurate predictions of trends and eventsb.decisions as to what customers will be demanding and whenrmation about the dynamics of environmental changermation that will facilitate decision making(d; difficult; p. 242)52.Forecasting techniques are most accurate when the environment is __________.a.changing inverselyb.dynamic on the long term, so turning points can be identifiedc.not rapidly changingd.seasonal, but not cyclical(c; moderate; p. 242)53.One suggestion for improving forecasting effectiveness is to _____________.e complex forecasting sequencesb.gather as much data as possiblec.always employ global forecastinge simple forecasting techniques(d; moderate; p. 242)54.When comparing every forecast with a no-change (in an environment) forecast, the no-changeforecast is accurate approximately __________.a.half of the timeb.three-fourths of the timec.two-thirds of the timed.80 percent of the time(a; difficult; p. 242)55.Managers should use _______________ that look 12 to 18 months ahead, instead of using a single,static forecast.a.no-change forecastsb.rolling forecastsc.quantitative forecastsd.qualitative forecasts(b; moderate; p. 242)56.Which of the following is a suggestion for improving forecasting effectiveness?a.do not utilize a “no change” scenariob.base forecasts beyond the next 2 yearsc.utilize the “half-life” estimation modeld.employ multiple forecasting methods(d; moderate; p. 242)57.Benchmarking is the search for the best practices among competitors or noncompetitors that lead totheir ____________.a.ability to achieve such a large market shareb.ability to so accurately predict the environmentc.superior performanced.ability to identify new market niches(c; difficult; p. 243)58.Which of the following is true concerning benchmarking?a.Benchmarking always involves analyzing a competitor.b.Benchmarking is most effective when analyzing within your own industry.c.Benchmarking may involve analyzing a company with a completely different product.d.Benchmarking foreign companies is not suggested due to cultural differences.(c; moderate; p. 243)59.Some companies have chosen some pretty unusual benchmarking partners. Southwest Airlinesstudied ____________.a.package handling at FedEx hubsb.UPS package-handling hubsc.Indy pit crewsd.tire changers at Goodyear stores(c; moderate; p. 243)TECHNIQUES FOR ALLOCATING RESOURCES60.A budget is a numerical plan for allocating resources _____________.a.to specific activitiesb.dedicated to special projectsc.to areas of productiond.to developing new products(a; difficult; p. 244)61.What type of budget projects future sales?a.cash budgetb.expense budgetc.profit budgetd.revenue budget(d; easy; p. 244)62.What type of budget takes into account the costs that vary with volume?a.cash budgetb.expense budgetc.fixed budgetd.variable budget(d; easy; p. 244)63.What type of budget assumes a fixed level of sales or production?a.fixed budgetb.profit budgetc.revenue budgetd.variable budget(a; easy; p. 244)64.Budgets are popular most likely because they’re applicable to a wide variety of organizations and___________.a.define how much money will be spentb.specify how much money the organizations will receivec.work activities within organizationsd.estimate the number of units that will be produced(c; difficult; p. 245)65.Which of the following is an accurate statement about budgets?a.They are typically not used for time estimating.b.By nature, they are only financially based.c.They are a useful tool for allocating resources and guiding work in diverse departments.d.They are typically used for large and small capital expenditures.(c; difficult; p. 245)66.Budgeting is an important managerial activity because it forces financial discipline and structure__________.a.with the cash part of the organizationb.throughout the organizationc.in the areas of the organization that need it the mostd.especially with start-up companies(b; difficult; p. 245)67.Many managers don’t lik e preparing budgets because they feel the process is time consuming,inflexible, inefficient, and ____________.a.infallibleb.inflationaryc.insignificantd.ineffective(d; difficult; p. 245)68.Which of the following is not a scheduling device used by managers?a.benchmarkingb.Gantt chartsc.load chartsd.PERT network analysis(a; easy; p. 246)69.The Gantt chart was developed during the early 1900s by Henry Gantt, an associate of the scientificmanagement leader ________________.a.Henri Fayolb.Fredrich Traylorc.Henry Fordd.Frederick Taylor(d; moderate; p. 246)70.A Gantt chart is essentially a bar graph with __________ axis and __________ axis.a.time on the vertical; the activities to be scheduled on the horizontalb.time on either; the activities to be scheduled on the otherc.time on the vertical; project completion on the horizontald.time on the horizontal; the activities to be scheduled on the vertical(d; moderate; p. 246)71.The Gantt chart visually shows when tasks are supposed to be done and compares that with the____________.a.supervisors’ estimate of completionb.actual progress on eachc.scheduled delivery of materialsd.customer’s requested date of delivery(b; difficult; p. 246)72.Load charts list on the vertical axis either departments or _____________.a.functional areasb.specific resourcesc.budgetsd.product weights(b; moderate; p. 246)73.Load charts schedule capacity by _____________.a.goalsb.activityc.work aread.time(c; easy; p. 246)74.The Program Evaluation and Review Technique (PERT) is especially useful in scheduling_____________.rge projectsb.programsc.processesd.planning(a; difficult; p. 247)75.A PERT network depicts the sequence of activities needed to complete a project and the __________each activity.a.estimated day ofb.time or costs associated withc.amount of money needed ford.step of(b; difficult; p. 247)76.The four terms that are required to construct a PERT network are: events, activities, ____________,and ____________.a.crucial path; slack timeb.critical path; estimated timec.crucial path; earliest dated.slack time; critical path(d; moderate; p. 247)77.In a PERT network, events are __________.a.end points that represent the completion of major activitiesb.the longest or the most time-consuming sequence of events in a PERT networkc.the amount of time an individual activity can be delayed without delaying the whole projectd.all key activities needed to complete a project(a; moderate; p. 247)78.Which of the PERT steps represent the time or resources required to progress from one event toanother?a.eventsb.critical pathsc.checkpointsd.activities(d; moderate; p. 247)79.In the PERT process, what is the critical path?a.the central guideline that other activities feed intob.the checkpoint for comparing standards of completionc.the most time-consuming sequence of events and activitiesd.the most costly path in a scheduling outline(c; moderate; p. 247)80.The first step in developing a PERT network is to _______________.a.determine the order in which events must be completedb.identify every significant activity that must be achieved for a project to be completedc.diagram the flow of activities from start to finishpute a time estimate for completing each activity(b; easy; p. 248)81.A manager who needed to cut the completion time of a project would want to concentrate on_______________ that could be completed faster.a.those activities along the critical pathb.those activities that allow for slack timec.activitiesd.events(a; moderate; p. 249)82.What type of technique is widely used to help managers make profit projections?a.factor analysisb.cost accountingc.breakeven analysisd.PERT network analysis(c; easy; p. 249)83.An organization breaks even when its total revenue is just enough to equal its __________.a.fixed costb.breakeven costsc.variable costsd.total cost(d; moderate; p. 249)84.Examples of fixed costs include ______________.a.property taxesb.energy costsbor costsd.raw materials(a; easy; p. 249)85.If a retail sales manager wants to know how many denim jackets must be sold in order to reach aspecified profit objective, he or she is employing what type of planning tool?a.breakeven analysisb.PERT network analysisc.Gantt chartd.cost accounting(a; difficult; p. 249)86.What is a mathematical technique that solves resource allocation problems?a.breakeven analysisb.linear programmingc.PERT network analysisd. a Gantt chart(b; easy; p. 250)87.Because linear programming requires that there be limited resources and outcome optimization, it____________.a.cannot be applied to all resource allocation problemsb.cannot have many constraintsc.can be applied to all resource allocation problemsd.calculates lost time(a; difficult; p. 250)88.Some applications for linear programming include ______________.a.scheduling a few activities that are independent of each otherb.planning a large projectc.coordinating hundreds of activities, some of which must be done simultaneouslyd.selecting transportation routes that minimize shipping costs(d; moderate; p. 250)89.What is a mathematical equation that can predict the outcome of all proposed alternatives?a. a constraintb. a linear programc.an objective functiond. a feasibility region(c; moderate; p. 251)90.Constraints imposed by capacity limits establish the _______________.a.objective functionb.feasibility regionc.subjective regiond.linear program(b; moderate; p. 252)CONTEMPORARY PLANNING TECHNIQUES91.A project is considered to be a one-time set of activities that has _______________.a.definitive assessment stages across timeb.significant points to be analyzedc. a definite beginning and ending point in timed.an estimated start and finish date(c; difficult; p. 253)92.Proj ect management is the task of getting a project’s activities done on time, within budget, and__________.a.of following directionsb.of making adjustments in plansc.according to specificationsd.within the limits of city engineering(c; difficult; p. 253)93.To plan a project, all activities in the project and the resources needed to do them must be____________.a.satisfiedb.on handc.identifiedd.trained(c; difficult; p. 253)94.What step often uses flowchart diagrams such as a Gantt chart, a load chart, or a PERT network?pare with objectivesb.determine project completion datec.establish sequencesd.estimate time for activities(c; moderate; p. 253)95.The role of project manager remains difficult because she or he is managing people who______________.a.will make mistakes during the projectb.might not show up for work on the day of an important presentationc.are not skilled enough to participate in the projectd.are still linked to their permanent work areas(d; difficult; p. 254)96.The only real influence project managers have is __________.a.their ability to keep the project moving forwardb.their communication skills and their power of persuasionc.the ability of the supplier to deliverd.their ability to insist that the project be finished according to plans(b; moderate; p. 254; AACSB: Communication)97.As managers assess the environment, issues and concerns that could affect their organization’scurrent or planned operations are likely to be revealed, and they __________.a.won’t be equally importantb.won’t be equally associatedc.will be equally importantd.will be as important as others, but not equal in value(a; difficult; p. 254)98.What is a consistent view of what the future is likely to be?a. a critical pathb. a projectc. a resourced. a scenario(d; easy; p. 254)99.Developing scenarios can be described as ______________.a.planningb.thinking about what has happenedc.guessing as to what will changed.contingency planning(d; moderate; p. 254)100.Different assumptions in a scenario can lead to ________________.a.different outcomesb.the same estimatesc.disputes over which is correctd.divergent ideas into results(a; difficult; p. 255)101.The intent of scenario planning is not to try to predict the future, but to reduce uncertainty by __________.a.calculating the potential profits from different specified conditionsb.pretending that the customer needs are different from those forecastedc.supposing that a different market mix existedd.playing out potential situations under different specified conditions(d; moderate; p. 255)102.Although scenario planning is useful in anticipating events that can be anticipated, it is difficult to ____________.a.establish datelinesb.prepare for increased sales of outputc.present the fact when they occurd.forecast random events(d; moderate; p. 255)103.Planning tools and techniques can help managers prepare __________.a.confidently for the futureb.future eventsc.better budgetsrger projects(a; difficult; p. 256)104.Planning tools and techniques will never replace the manager’s __________ in using the information gained to develop effective and efficient plans.a.knowledge and expertiseb.skills and capabilitiesc.motivation and leadershipd.time and efforts(b; difficult; p. 256)SCENARIO QUESTIONSFor each of the following choose the answer that most completely answers the question. TECHNIQUES FOR ASSESSING THE ENVIRONMENTDollars to Donuts (Scenario)Ralph Friedgrin is the owner of a chain of five donut shops in Smalltown, MD. Smalltown is located along the Interstate 95, about half-way between Lost and Nowhere.105.Mr. Friedgrin demands that the five store managers during their weekly meeting discuss what the customers in their stores are requesting. Mr. Friedgrin always reads the monthly donut-industry magazine, Holey Mazole. He always attends the Annual National Conference of Donut Makers and updates his managers when he returns. These activities are examples of __________.petitor intelligenceb.boundary spanningc.environmental scanningd.intellectual exercise(c; difficult; p. 238)106.On occasion, Mr. Friedgrin goes to nearby, larger towns such as Lost and Nowhere to visit big chain donut shops. Mr. Friedgrin purchases donuts and chats with these customers about their donut likes and dislikes. He also will “peek” into the kitchen to view the equipment, or when he can, he will watch through the customer observation window to see the whole process. Mr. Friedgrin is performing which planning technique?petitor intelligenceb.environmental scanningc.intellectual exercised.boundary spanning(a; difficult; p. 239)107.Mr. Friedgrin went to donut shops in Lost and Nowhere so he could talk with his competitor’s customers, peek at their equipment, and evaluate their donut-making process. These acts were __________.a.legalb.legal and ethicalc.ethicald.neither legal nor ethical(b; easy; p. 240; AACSB: Ethics)108.Mr. Friedgrin’s largest supplier recently approached him about implementing a Web-based software that will utilize data about past sales trends promotions and other factors to jointly calculatea demand forecast for particular products. His supplier referred to this system as a __________.a.JIT systemb.CPFR systemc.RFID systemd.SCM system(b; moderate; p. 241; AACSB: Technology)109.If Mr. Friedgrin knew the average number of donuts that Smalltown adults bought per week and the number of Smalltown adults, he could then use which planning tool?a.environmental scanningb.qualitative forecasting techniquec.quantitative forecasting techniqued.scenario projection technique(c; difficult; p. 241)110.Mr. Friedgrin recently had three selected stores experiment with three new frying oils. Customers were then asked to take a taste-preference test of three sample donuts, one for each of the oils: N, O, and W. Based upon the results of this test, it was concluded that oil N in the test was favored. Which planning tool was Mr. Friedgrin using in this instance?a.quantitative forecasting techniqueb.Delphi techniquec.focus group techniqued.qualitative forecasting technique(d; moderate; p. 241)111.Mr. Friedgrin contacted the owner of a NASCAR racing team to see if he could spend time with its pit crew to study their teamwork. This is an example of __________.a.qualitative forecastingb.benchmarkingc.quantitative forecastingd.scanning(b; easy; p. 243)112. Mr. Friedgrin recently went on a well-deserved vacation. While at the beachfront resort, Mr.Friedgrin took many notes regarding the excellent service he received. On the flight home, he reviewed his notes to see what lessons he could apply to his donut shops. When Mr. Friedgrin is out looking at the “best practices” of the other donut stores in these town s, he is performing which of the following?a.qualitative forecastingb.benchmarkingc.environmental scanningd.scenario planning(b; easy; p. 243)TECHNIQUES FOR ALLOCATING RESOURCESDonut Expansion (Scenario)Ralph Friedgrin, owner of five donut shops in Smalltown, MD, located half the way between Lost and Nowhere, recently began development of expansion plans based on analyses conducted with his planning tools and techniques. His management team concluded that it was time to expand his donut business to a whole new market niche. Fred, the project manager, has asked that an estimated time of construction and estimated costs be provided. Fred approved construction of two stores in Littleville and recently contracted with the engineering-manufacturing firm from Nowhere, Planning Plus, Inc. (PPI), to build the stores. Fred informs PPI of other nearby donut stores’“best practices” and tells them that he wants them incorporated into his new stores.113.Fred has planned the opening day activities. The donut store will be open for 24 hours. He has planned who will work which hours and who will perform which duties during the time the store is open. Fred has also planned which type of donut is to be made at what time. What Fred did in making these plans is known as _______________.a.Gantt chartb.PERTc.linear programmingd.scheduling(d; easy; p. 246)114.PPI developed a diagram similar to a flowchart to estimate the probable time required to complete construction of the two stores. This flowchart-like diagram is known as _______________.a. a program evaluation and review techniqueb. a Gantt chartc.linear programmingd.scheduling(b; moderate; p. 246)。