高中状语从句讲解(经典打印版)
- 格式:pdf
- 大小:14.17 KB
- 文档页数:5

高中状语从句介绍1. 时间状语从句:描述主句动作发生的时间。
引导词有:when, while, as, after, before, since, until, as soon as等。
例如:I will call you as soon as I arrive. (我一到就给你打电话。
)2. 条件状语从句:描述主句动作发生的条件。
引导词有:if, unless, provided that, in case等。
例如:If it rains, we will cancel the trip. (如果下雨,我们就取消旅行。
)3. 原因状语从句:解释主句动作发生的原因。
引导词有:because, since, as, for等。
例如:I am late because I missed the bus. (我迟到了,因为我没赶上公交车。
)4. 目的状语从句:描述主句动作的目的。
引导词有:so that, in order that, in case等。
例如:I will study hard so that I can get a good job. (我会努力学习,以便找到一份好工作。
)5. 结果状语从句:描述主句动作的结果。
引导词有:so that, so...that, such...that等。
例如:He studied so hard that he passed the exam. (他努力学习,结果通过了考试。
)6. 让步状语从句:描述主句动作尽管存在某种情况或条件,但仍会发生。
引导词有:though, although, even if, even though, whether...or等。
例如:Although it was raining, we still went out. (尽管下雨,我们还是出去了。
)7. 比较状语从句:这种从句用于比较两个或多个情况或事件。
常见的引导词有:than, as...as, not as/so...as, themore...the more等。


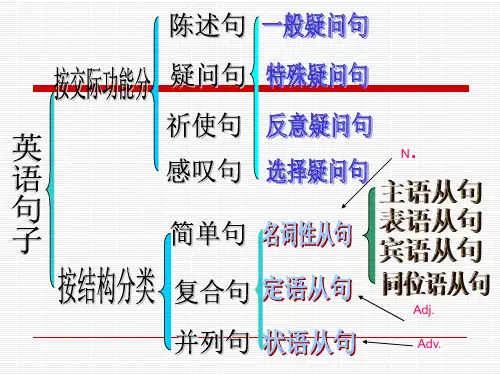
第20份高中语法讲义状语从句年月日第3章状语从句状语从句在复合句中起状语的作用,用于修饰主句中的谓语动词、形容词和副词等。
状语从句一般由连词引导,连词不充当句子成分,只起连接作用。
状语从句也可以由短语引起,也有时不需要连词而直接和主句连接起来。
状语从句多位于句首或句尾。
位于句首时,一般要用逗号与主句隔开;位于句尾时,一般不与主句隔开。
根据意义上的不同,状语从句可以表示时间、地点、原因、条件、目的、结果、让步、比较和方式等。
典型例句:1.It will not be long before we meet again.用不了多久我们会再见面的。
(时间状语从句)2.I got up early so that I caught the bus.我起得很早,所以我赶上了公共汽车。
(结果状语从句)1.表示时间的状语从句1.beforebefore的意思是“在……之前”,常用来引导时间状语从句。
句型:It is/was (not)+时间+before+从句It will (not) be+时间+before+从句It was one year before he finished his work.过了一年他才完成了他的工作。
It was not long before he finished his work.过了不久,他就完成了他的工作。
It will be three weeks before he finishes his work.要过3周,他才能完成他的工作。
It won’t be long before he finishes his work.用不了多久,他就会完成他的工作。
2.by the timeby the time的意思是“截至……(时间)”,可以引导时间状语从句。
by the time引导的从句若是一般现在时,主句要用将来完成时;若是一般过去时,主句则要用过去完成时。
By the time you receive this letter,I will have left this city for my hometown.你收到这封信时,我将已经离开这座城市回家乡了。

完整版)高中状语从句归纳状语从句是在句子中做状语的,包括时间、条件、让步、原因、目的、结果、比较、地点、方式状语从句。
时间状语从句可以由when、as、while、until、not…until、before、after、since、the minute、the moment、each (every。
next。
the first) time等引导。
在时间状语从句中,一般使用一般现在时或一般过去时来表达。
1.时间状语从句引导词当句子中有时间状语从句时,可以用when、as、while、until、not…until、before、after、since、the minute、the moment、each (every。
next。
the first) time等来引导。
这些引导词在句子中的使用有不同的侧重点和用法。
1.1 when当我们用when引导时间状语从句时,它的主语和主句的主语相同。
如果从句的谓语动词是be动词,那么从句的主语和be可以省略。
例如:When I arrived home。
I had a little rest.1.2 asas不仅可以表示“当。
的时候”,还可以表示“一面。
一面”和“随着”的意思。
例如:XXX(一面。
一面)You will XXX(随着)1.3 whileXXX表示“当。
的时候”,强调主句的动作和从句的动作同时发生。
从句一般使用进行时,动词必须是延续性动词。
例如:While we were working。
they were having a rest.While they were having a n。
they got very confused.注意:while也有对比的含义,可以解释为“然而”。
例如:XXX。
XXX.2.until和not。
untiluntil和not。
until都表示“直到。
才”。
在肯定句中,主句常用延续性动词;在否定句中,主句常用短暂性动词。

高中英语状语从句用法详解文档四维教育状语从句用法详解在主从复合句中修饰主句的动词、形容词、副词等的从句叫状语从句。
一般可分为:时间状语从句、地点状语从句、原因状语从句、目的状语从句、结果状语从句、条件状语从句、让步状语从句、比较状语从句、方式状语从句。
I时间状语从句:起时间状语作用的从句。
(时间状语从句位置灵活,可以在句首,也可在句末)常用来引导时间状语从句的引导词有:when, while, as, after, before,until/till, since, as soon as, immediately, the moment, every time, whenever等。
1.when, while, asI was very happy when I heard from you.收到你的时我非常兴奋。
When you deal with them, you should be cautious.跟他们打交道时,你应当郑重。
when指导时间状语从句中的谓语动词能够用非延续性动词,也可用延续性动词。
When I was young, I went to town myself.当我还年青时,我本人独自去城里。
(延续性动词)When I lived in country, I used to carry some water for him.我住在农村时,常常为他担水。
(延续性动词)When he received the letter, he'll tell us.当他接到后,他会告诉我们的。
(非延续性动词)When the fire broke out, all the students were sleeping soundly.火灾发生时,所有的学生正在熟睡。
(非延续性动词)注意:当when引导的时间状语从句为系表结构,而且其主语和主句的主语一致,其表语又是一个名词时,就能够用由as指导的省略句来代替when指导的从句。

状语从句2.在复合句中作状语,位置灵活。
3.状语从句可分为时间状语从句,目的状语从句,条件状语从句,让步状语从句,地点状语从句,原因状语从句,方式状语从句,结果状语从句。
4.〔一〕时间状语从句5. 1. when,as,while6. a. when表时间,从句既可以用延续性动词,又可以用瞬间动词。
7.Eg:WhenIgetthereIwillcallyou.8.如果when引导的时状的主语与主句的主语相同,而从句的谓语又是 be动词时,那么从句中的主语与b e9.可省。
10.Eg:When〔youare〕introuble,youcanaskherforhelp.11.如果when引导的时状的主语与主句的主语相同时,往往可以用“when+分词〞的形式代替该状从。
12.Eg:WhenIcameintotheroom(Whencomingintotheroom),Ifoundthelightwasoff.13.while表时间,从句需用延续性动词,或者主句的动作发生在从句的动作进行过程中。
主句的谓语动词通常是非延续性动词。
14.Eg:HecameinwhileIwasreadingabook.15.ImetherwhileIwasinschool.16. c.as表时间,与when相似,但侧重强调主从句动作同在时间点或同时间段进行。
同时可表示主句的动作随着从句的动作的变化而变化。
17.Eg:Hejumpsashesings.18.Asthewindrose,thenoiseincreased.19.before(在之前)与after〔在之后〕Eg:Seemebeforeyouleave.20.IsawthemafterIarrived.21.till与until肯定形式表示的意思是"做某事直至某时 "。
否认形式表达的意思是 "直至某时才做某事 "。
Eg:Waittill/untillIcallyou.等着直到我叫你。

状语从句(高中语法)状语从句状语从句概述状语从句是主谓结构,在句子中起副词的作用。
用来修饰动词、形容词、副词等。
在主句中。
引导状语从句的相关词是从属连词。
状语从句使用陈述性语序,通常位于复合句的开头或结尾。
当一个从句在一个句子的开头时,它通常用逗号与主句分开。
状语从句表示时间、地点、原因、目的、结果、条件、让步、行为等。
根据它们在句子中的不同功能,总共有九种。
当时间来临时,当时间来临时,当时间来临时,当时间来临时,当时间来临时,当时间来临时,当时间来临时,当时间来临时,当时间来临时,当时间来临时,当时间来临时,当时间来临时,当时间来临时,时间来临时。
当.的时候.当.的时候.当.的时候.因为.直到.直到.以前.在.之后.一…就….一…就….一…就….一…就….一…就….一…就….一…就….一…就….一…就….一…就….一…就….一…就….一…就….一…就….一…就….一…就….一…就….一…就….(那)一天/渴望更早.那很难.当一次.每次.每次.到.现在/什么时候.在.如果,如果,如果,如果,如果,如果,如果,如果,如果,如果,如果,如果,如果,如果,如果,如果,如果,如果,如果,如果,如果,如果,如果,如果,如果,如果,如果,如果,如果,如果,如果,如果,如果,如果,如果,如果,如果,如果,如果,如果,如果,如果,如果,如果,如果,如果,如果,如果,如果,如果条件是条件,如果原因是因为,如果原因原因不是……而是不是因为,而是因为既然它被考虑了。
因为由于让步,即使无论什么无论什么无论什么无论什么授予/授予尽管事实是,尽管事实是,尽管事实是,尽管事实是,尽管事实是,尽管事实是,尽管事实是,尽管事实是,尽管事实是,尽管事实是,尽管事实是尽管事实上它无处不在。
状语从句概述状语从句是主谓结构,在句子中起副词的作用。
用来修饰动词、形容词、副词等。
在主句中。
引导状语从句的相关词是从属连词。
状语从句使用陈述性语序,通常位于复合句的开头或结尾。

状语从句Adverbial ClauseI 定义和分类一、定义在复合句中充当状语的从句叫状语从句。
状语从句通常由从属连词或起连词作用的词组引导。
试比较下列两句句子:1.I will return the book to him tomorrow. 我明天会把书还给他。
2.I will return the book to him when I meet him. 我见到他时会把书还给他。
分析在句1中,副词tomorrow作为时间状语在修饰动词return。
在句2中出现了两个谓语动词,分别是return和meet,表示有两句句子存在。
句2中的when I meet him取代了句1中tomorrow的位置。
when作为状语从句的引导词(即从属连词)连接起了主句I will return the book和从句I meet him两部分。
在分析主从句时,可以通过确定谓语动词和连词来将长句变为短句,从而便于理解句子的意思。
二、分类状语从句根据它表达的意思不同,可以分为以下基本的九类:1.时间状语从句,例如:When he arrived home last night, it was just nine o'clock. 昨晚他到家时恰好九点。
2.地点状语从句,例如:I put the book back where it had been. 我把书放回了原处。
3.原因状语从句,例如:It is inexpensive to produce because it is made from corn.由于是玉米做成的,它的生产成本不高。
4.目的状语从句,例如:They took a subway in order that they might not be held up in the traffic.为了不被堵在路上,他们搭乘了地铁。
5.结果状语从句,例如:The village is so small that it cannot be shown in the map.这个村庄太小了以致于在地图上都找不到。
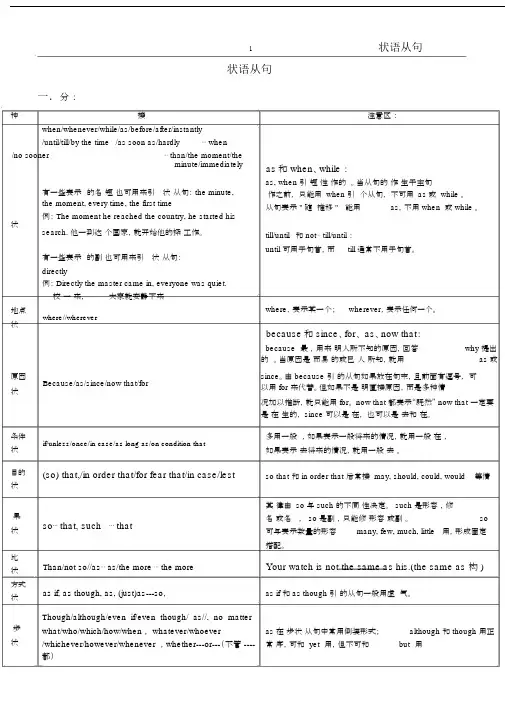
1状语从句状语从句一.分:种接when/whenever/while/as/before/after/instantly/until/till/by the time /as soon as/hardly⋯when/no sooner⋯than/the moment/theminute/immediately有一些表示的名短也可用来引状从句: the minute,the moment, every time, the first time例: The moment he reached the country, he started his 状search. 他一到达个国家,就开始他的探工作。
有一些表示的副也可用来引状从句:directly例: Directly the master came in, everyone was quiet.校一来,大家就安静下来地点where//wherever状原因Because/as/since/now that/for状注意区:as和 when、while :as, when 引短性作的。
当从句的作生于主句作之前,只能用 when 引个从句,不可用 as 或 while 。
从句表示 " 随推移 " 能用as,不用 when 或 while 。
till/until和not⋯till/until:until 可用于句首,而till 通常不用于句首。
where,表示某一个;wherever,表示任何一个。
because和 since、for、 as、now that:because最,用来明人所不知的原因,回答why 提出的。
当原因是而易的或已人所知,就用as 或since。
由 because 引的从句如果放在句末,且前面有逗号,可以用 for 来代替。
但如果不是明直接原因,而是多种情况加以推断,就只能用 for。
now that 都表示“既然” now that 一定要是在生的, since 可以是在,也可以是去和在。

状语从句状语从句在句中作状语,可分为:时间、条件、让步、原因、目的、结果、比较、地点、方式状语从句。
一、时间状语从句弓丨导时间状语从句的连词有:whe n, as, while, un til, not …un til, before, after, sin ce, the minute, the mome nt, each (every, next, the first) time等。
时间状语从句中一般用一般现在时或一般过去时。
l. when , while, as都可解释为“当'、' 的时候”但侧重点有所不同(1) whenEg: When I arrived home , I had a little rest.when从句的主语与主句主语相同,谓语动词是be动词时,从句主语和be可以省略Eg: When (she was) walking along the street, she met her class teacher.(2) as 除了表示“当'''的时候” ,还可表示为“一面'''一面”,“随着”Eg: He sang as he dan ced 一面''' 一面)You will grow wiser as you grow older. (随着)(3) while 表示“当...的时候”强调主句的动作和从句的动作同时发生,从句一般用进行时,从句动词必须是延续性动词。
Eg: While we were working, they were having a rest.While (they were) having a discussion, they got very confused.、I •、、+ :注意:while 有对比的含义,解释为“然而” 。
Eg: I prefer black tee, while he likes coffee.2. until, not …u表表示“直到'、'才”,在肯定句中主句常用延续性动词;在否定句中主句常用短暂性动词。
状语从句(思维导图)可打印(1页)1. 时间状语从句:时间状语从句用于表达句子中的时间关系,常用的引导词有:when, while, as, before, after, since, until等。
例如:When I wake up, I will have breakfast.2. 地点状语从句:地点状语从句用于表达句子中的地点关系,常用的引导词有:where, wherever等。
例如:Wherever you go, I will follow you.3. 原因状语从句:原因状语从句用于表达句子中的原因关系,常用的引导词有:because, since, as等。
例如:Because it was raining, we stayed at home.4. 条件状语从句:条件状语从句用于表达句子中的条件关系,常用的引导词有:if, unless, in case等。
例如:If you study hard, you will pass the exam.5. 结果状语从句:结果状语从句用于表达句子中的结果关系,常用的引导词有:so, that等。
例如:I was so tired that I couldn't move.状语从句(思维导图)可打印(1页)1. 目的状语从句:目的状语从句用于表达句子中的目的关系,常用的引导词有:in order to, so that, that等。
例如:I went to the library in order to study for the exam.2. 让步状语从句:让步状语从句用于表达句子中的让步关系,常用的引导词有:although, though, even though, despite等。
例如:Although it was raining, we went for a walk.3. 比较状语从句:比较状语从句用于表达句子中的比较关系,常用的引导词有:than, asas, morethan等。
高中英语状语从句讲解汇总状语从句.概念状语从句修饰主句中的动词,形容词,副词等,在复合句中作状语.引导状语从句的关联词是从属连词.状语从句用陈述句语序,一般位于复合句的句首或句末.当从句在句首时,从句后常用逗号和主句相隔.状语是句子谓语动词的重要组成部分。
它的主要语法功能是说明谓语动词,在时间、地点、方式、原因、结果,条件等方面对谓语动词作细节上的描述这些状语经常由副词、短语和从句表示。
起状语作用的从句就是状语从句。
状语从句可分为1时间2地点3目的4原因5结果6方式7条件8让步9比较九个种类。
考点分析:1. 状语从句虽然有完整的主谓结构,却是不能独立的从句。
2. 状语从句它由从属连词引导成为整个句子一个不可缺少的部分。
3. 考查的热点有条件、时间、地点、让步等状语从句的连接词词义辨析.4. 动词的时态呼应、状语从句的省略等。
5. 题干结构呈交叉和综合特征,选项设计多从定语从句和名词性从句的角度进行思维干扰。
引导状语从句的连接词列表★★★★第一讲:时间状语从句★★★★1.表示“一…就…”的连接词引导的时间状语从句:1由“as soon as, the instant/ the moment, the minute, instantly, directly, once, immediately”等引导的时间状语从句:The moment he saw me, he ran away. 他一看见我,就跑了。
My sister came directly she got my message. 我妹妹一收到我的信息就来了。
Once printed, this book will be very popular.一印刷,这本书就将非常流行。
Instantly the button is pressed, the mine explodes.这个扭一按下去,这矿就爆炸了。
They told me the news immediately they got the message.他一得到信息就马上把消息告诉了我。
状语从句1. 时间状语从句(1) when引导的时间状语从句①when引导的时间状语从句,其动词既可以是延续性动作的动词,也可以是瞬间性动作的动词,可以表示主句的动作和从句的动作同时发生,或从句的动作发生在主句的动作之前。when you apply for a job, you must present your credentials. 当你申请工作时,你必须递交你的有关证件。(同时)when the students heard the teacher’s footsteps, they all adopted talking. 当学生们听到老师的脚步声时,他们都停止了讲话。(从句动作发生在前)② when还可表示just then(正在那时)的意思,此时其所引导的从句只放在主句之后。we were about to start when it began to rain. 我们正要动身,突然天下起雨来。The game had hardly/scarcely/barely begun when it started raining. 比赛刚刚开始就下起雨来。(2) as引导的时间状语从句as侧重表示主句和从句的动作并相发生,翻译成一边,一边。We were having breakfast as she was combing her hair. 她梳头时我们在吃早饭。(3) while引导的时间状语从句while或“在……期间”,所引导的从句的动作是延续性的,并表示和主句的动作同时发生。When the teacher paraphrased the text in English, the students listened attentively and took notes. 当老师用英语解释课文时,学生们聚精会神地听并做着笔记。I can learn while I work. 我可以边工作边学习。(4) before引导的时间状语从句① before“在……之前”I’ll be back before you have left.你离开之前我就会回来。② before“……之后才”It may be many years before we meet again. 可能要过许多年我们才能再见了。It was three days before I came back. 他三天后才回来。(5) as soon as/once/directly/the instant等引导的时间状语从句as soon as 是最常见的表示“一……就”的从属连词,其他连词还有immediately,instantly,the instant (that),the minute(that) ,the moment(that)等,它们通常都可与as soon as换用。As soon as we got home, the telephone rang. 我们一到家,电话就响了。I recognized her immediately I saw her. 我一看见她就认出她来了。Directly the teacher came in everyone was quiet. 老师一进来,大家就静了下来。(6) hardly...when/no sooner...than引导的时间状语从句关联从属连词hardly/barely/scarcely...when和no sooner...than的意思是“刚……就”,它们所引导的从句中的谓语动词通常为过去完成时。如:He had no sooner (no sooner had he)arrived home than he was asked to start on another journey. 他刚一到家,就又要他出另一次差。No sooner had the words been spoken than he realized that he should have remained silent. 这些话刚一出口,他就意识到自己应该保持沉默。(7) since引导的时间状语从句在含有since引导的时间状语从句的复合句中,从句的谓语动词通常为一般过去时,主句的谓语动词通常为现在完成时、过去完成时和一般现在时:We’ve never met since we graduated from the college. 大学毕业后我们就再没见过面。Great changes have taken place since you left. 你走了以后,这里发生了巨大变化。(8) till/until引导的时间状语从句till和until同义,作“直到……时(为止)”解,till多口语话,until多用于句首。如:Donald will remain in college until(till) he finishes his Ph.D course. 唐纳德将留在学校直到完成他的博士学位课程。I won’t go with you until(till) I finished my homework. 等我做完作业我才和你一起去。
2. 地点状语从句(1) where引导的地点状语从句,很简单,最基础的。从属连词where“在(或到)……的地方”Where there is a will, there is a way. 有志者事竟成。Put it where you found it. 把它放在原来的地方。① where 在地点状语从句中,除指地点外,还可指处境等。就看句子翻译了。如:He said he was happy where he was. 他说他对自己的处境很满意。It’s your fault that she is where she is.她今天落到这个地步都怪你。(2) wherever引导的地点状语从句wherever=no matter where,后者只能放句首。从属连词wherever“在(或到)……的各个地方”:You can go wherever(anywhere) you like these days. 这些天你可以去你想去的地方。Where (no matter where) they went, the experts were warmly welcomed. 专家每到一处,都受到热烈的欢迎。Sit down wherever you like. 你喜欢坐哪儿就坐哪儿wherever不可以换成no matter where 3. 原因状语从句(1) because引导的原因状语从句通常用于回答why引出的疑问句,语气最强,该从句一般位于主句后面。I didn’t go abrord with her because I couldn’t afford it.我没有和她一起出国是因为费用太高。Don’t scamp your work because you are pressed for time.不要因为时间仓促而马马虎虎。(2) as引导的原因状语从句as引导的原因状语从句多位于主句之前,通常可以和since换用。如:As I didn’t know the way,I asked a policeman. 我不认识路,因而问警察。As it is snowing, we shall not climb the mountain. 由于在下雪,我们不去爬山了。(3) since引导的原因状语从句since引导的原因状语从句多位于主句之前,通常可以和as换用。与as用法一样Since traveling by air is much faster,they decided to take a plane. 既然乘飞机旅行快得多,他们就决定坐飞机。Since you won’t help me ,I’ll ask someone else. 你既然不帮我,那我就请别人帮忙。(4) now(that)引导的原因状语从句now(that)“既然”,Now(that) you have passed your test you can drive on your own. 你既已考试合格,就可以独自开车了。(5) seeing (that)引导的原因状语从句Seeing (that)“鉴于;由于”,通常用于非正式文体。如:Seeing (that) the weather is bad,we’ll stay at home. 天气不好,我们还是呆在家里吧。4. 目的状语从句(1) in order that引导的目的状语从句in order that“为了;以便”。多用于正式文体,通常可以与so that换用。如:You stopped at Hangzhou in order that they could go around West Lake. 他们在杭州停了下来,以便游览西湖。The expert spoke slowly in order that everyone should understand. 专家讲得很慢,以便人人听得懂。(2) so (that)引导的目的状语从句so that“为了;以便”。so that通常可以与in order that换用,它所引导的目的状语从句总是放在主句之后,在非正式文体中,常省略that。如:Speak clearly so that they may understand you. 你要讲得清楚,他们才听得懂。She wanted tea ready at seven so she could be out by eight. 她要七点钟备好茶点,这样她八点以前就可以出门了。(3) in case/for fear (that)等引导的目的状语从句in case,for fear(that)这俩个从属连词都表示否定目的,意思是“以免”,“以防”。in case它所引导的从句中的谓语动词可以是陈述语气形式,也可以是虚拟语气形式;for fear(that)引导的从句中的谓语带有may,might,should等情态动词Take your umbrella in case it rains. 带上你的伞,以防下雨。He took an umbrella with him for fear that it might rain. 他带了一把伞,以防下雨。1. 结果状语从句(1) so that引导的结果状语从句① so that引导的结果状语从句只能位于主句之后,so that”引导什么从句根据句意来判断Suddenly it began to rain heavily,so that it was almost impossible to carry on driving. 突然下起了大雨,几乎无法继续开车。Linda phoned me in on arrival so that I know she was safe and sound. 琳达到达后给我打了电话,因而我知道她平安无事。(2) so...that引导的结果状语从句so...that“如此……以致”,that可以省略,so后面接形容词或副词。如:She spoke so fast that nobody could catch what she was saying. 她说话如此之快竟没有人听出来她在讲什么。There is so little time left that I have to tell you about it latter. 现在剩下的时间不多了,我只好以后再给你讲这件事。(3) such...that引导的结果状语从句引导结果状语从句的such...that的具体内容是:such+a/an+形容词+名词+that从句。such+a/an+形容词+单数名词+that=so+形容词+a/an+单数名词+that从句。The professor told us such a funny story that all the students laughed.(=The professor told us so funny a story that all the students laughed.)