英语语法精华
- 格式:doc
- 大小:394.50 KB
- 文档页数:29
定语从句在复合句中充当定语的从句叫定语从句。
定语从句的作用相当于形容词,用来修饰主句中的某一名词或代词或整个主句,所以,也称作形容词性从句。
被定语从句修饰的词叫先行词,定语从句一般紧跟在它所修饰的先行词之后。
在先行词和定语从句之间起连接作用的词叫关系词。
一、关系词有关系代词和关系副词两种(一)关系代词引导的定语从句引导定语从句的关系代词主要有who, whom, whose, which, that,as等。
它们分别代替前面的先行词,并在定语从句中作主语、宾语、表语或定语。
1.who指人,在定语从句中作主语。
What was the name of the man who lent you the money?借钱给你的那人叫什么名字?(定语从句修饰先行词the man)He who laughs last laughs best.谁笑到最后谁笑得最好。
(定语从句修饰先行词he)The chairman of the meeting, who spoke first, sat on my right.会议主席坐在我右边,他先发言。
(定语从句修饰先行词the chairman)2.whom指人,在定语从句中做宾语。
在口语或非正式文体中,whom可省略或可用who来代替,但在介词后面以及在非限制性定语从句中只能用whom。
There are some people (whom/who)we like and others (whom/who) we dislike.有些人我们是喜欢的,有些人则是我们讨厌的。
(定语从句分别修饰先行词people, others)The people whom I work with are all friendly.和我一起工作的人都很友好。
(定语从句修饰先行词the people,介词后)Mr Carter, whom I spoke to on the phone last night, is very interested in our plan.昨晚我在电话里和卡特先生交谈过,他对我们的计划很感兴趣。
中考英语语法总复习(精华版)Ⅰ词类.专有名词:表示人名、月份、日期、地名等。
如China,John, London,the USA,Harbin .个体名词:表示单个的人或事物。
如boat, chair, desk, apple 。
集体名词:表示一群人或一些事物的总称。
如family,people, class, police . 可数名词普通名词物质名词:表示无法分为个体的物质。
如water,air, tea, sea,money,cotton 。
抽象名词:表示抽象概念的词。
如health,help, work,friendship 。
不可数名词 2.名词的数。
可数名词有单复数,不可数名词没有单复数。
3.名词的格:名词有三个格:主格(作主语)、宾格(作宾语)、和所有格。
其中只有名词的所有格有形式变化。
(二)冠词1.定冠词-the 。
错误!特指某(些)人或某(些)事物。
The students are very good。
错误!说话人与听话人都知道的人或事物。
Where is the toilet ?○3重复提到上文的人或事物。
I have a cat , the cat is white and black 。
错误!表示世界上独一无二的事物。
The moon moves around the earth .错误!形容词最高级和序数词前和表示方位的名词前。
I am the oldest 。
He is the first to school . I live in the south 。
○,6乐器的名称前常用定冠词-the 。
I like playing the piano / violin .○,7和某些形容词连用,使形容词名词化,代表某一类人.We should help the poor .错误!放在某些专有名词前。
We will go to visit the Great Wall next week . the people’s Republic of China .错误!放在姓氏的复数形式前,表示全家人或夫妇两人。
初中英语语法大全语法网络图一.名词II. 名词的数:1. 规则名词的复数形式:名词的复数形式,一般在单数形式后面加-s或-es。
现将构成方法与读音规则列表如下:2. 不规则名词复数:英语里有些名词的复数形式是不规则的,现归纳如下:名词在句中表示所有关系的语法形式叫做名词所有格。
所有格分两种:一是名词词尾加’s 构成,二是由介词of加名词构成。
前者多表示有生命的东西,后者多表示无生命的东西。
3. of所有格的用法:用于无生命的东西:the legs of the chair, the cover of the book用于有生命的东西,尤其是有较长定语时:the classrooms of the first-year students 用于名词化的词:the struggle of the oppressed二.冠词冠词分为不定冠词(a, an),定冠词(the),和零冠词。
三.代词:II. 不定代词用法注意点:1. one, some与any:1) one可以泛指任何人,也可特指,复数为ones。
some多用于肯定句,any多用于疑问句和否定句。
One should learn to think of others.Have you any bookmarks? No, I don’t have any bookmarks.I have some questions to ask.2) some可用于疑问句中,表示盼望得到肯定的答复,或者表示建议,请求等。
Would you like some bananas?Could you give me some money?3) some 和any修饰可数名词单数时,some表示某个,any表示任何一个。
I have read this article in some magazine.Please correct the mistakes, if any.4) some和数词连用表示“大约”,any可与比较级连用表示程度。

名词性从句
1.引导词、时态和语序:
①引导词选定:what/which/who/whom/whose/when/where/why/how等在从句中作成份;
whether/if不在句中作成份,但有“是否”之意;
that既不作成份也无意义。
②时态的选定:主现从随便,主过从过关。
③语序:陈述语序
2.that与what用法辨析:
①that在名词性从句中只起连接作用,不作成份,没有意义;
②what在名词性从句中是连接代词,在从句中作主、宾、表,有意义;
③that引导作动宾的宾从时可以省略。
④reason作主句主语时,从句的引导词只能用that,不能用why或because。
⑤that可引导定语从句,是关系代词,what不引导定语从句。
3. whether与if用法辨析:
①在引导作动宾的宾从时可以用if ;
②引导主从,it作形式主语时可以用if ;
③和to do,or not连用时以及引导作介宾的宾从时只能用whether ;
④其余时亦只可用whether。
4.-ever与no matter用法辨析:
①-ever可引导让步状语从句和名词性从句;
②no matter只可引导让步状语从句。
5.that引导定从和同位从的用法辨析:
①that引导的同位从成分完整,对抽象名词fact/suggestion/hope/promise/idea等补充说明;
②that引导的定从成分不完整,对现行次做修饰限定。

一般将来时◆一般将来时主要有以下几种表现形式由助动词 shall 或 will 加动词原形构成, shall 用于第一人称, will 用于二、三人称。
除英国外的说英语的国家,在陈述句中,即使在第一人称一般也用 will,在英国也有这种趋势。
在口语中,常用 shall, will的缩写形式为’ll,如:I ’ ll, you等。
’Shall not的缩写式为 :shan ’ t, willnot 的缩写式为: won’ t.肯定句: I/We shall/will go.You/He/She/They Will go.否认句: I/We shall/will not go.You/He/She/They Will not go.疑问句: Shall I/we go?Will you/he/she/they go?◆一般将来时用法(1〕一般将来时表示将要发生的动作或情况。
例如: I will(shall) arrive tomorrow. 我明天到。
Will you be free tonight? 你今晚有空吗?We won’ t (shan’ t) be busy this evening我们今.晚不忙。
(2〕在一般将来时的句子中,有时有表示将来时间的状语,有时没有时间状语,这时要从意思上判断是否指未来的动作或情况。
例如:We’ ll only stay for two weeks. 我们只待两星期。
The meeting won’ t last long会开.不了多久。
1 / 10〔 3〕在以第一人称 I 或 we 作主语的问句中,一般使用助动词 shall,这时或是征求对方的意见 (a),或是询问一个情况 (b):a. Where shall we meet? 我们在哪儿碰头?b. Shall we have any classes tomorrow?明天我们有课吗?在这类问句中,近年来也有不少人用will,特别是在美国。

高中英语精华浓缩语法分册(第四版)第一章定语从句1.1定语从句(一)1.1.1关系代词:which、who、that、whoseThis is a shop that/which sells personal computers.The watch that/which I bought yesterday works well.An architect is a person who/that designs houses and buildings.The player who/that I beat in the table tennis game was a seed player.On the hill were maple trees whose leaves had turned red.(I had a meeting whose purpose was completely unclear.I had a meeting the purpose of which was completely unclear.I had a meeting of which the purpose was completely unclear.)The hero whose left leg he lost in the war is well looked after.1.1.2关系副词:where、when、whyI still remember the day when we first met.The city where I was born is on the new railway line.This is the reason why he left the company.1.1.3介词+关系代词=关系副词句中的when = on which where = in which why = for which1.1.4关系代词与关系副词的区别:I like to take my vocation in the mountain which is quiet and beautiful.I like to take my vocation in the mountain where(in which)there are many plants.We will never forget the day which we spent together.We will never forget the day when(on which)we worked.That is the reason which he gave us for his action.That is the reason why (for which) he did that thing.1.1.5介词提前The man with whom you shook hands just now is head of our department.The room in which my family live used to be a garage.Last night I had a dream in which I became a Nobel Prize winner.The palace to which I often pay a visit was built in the 17th century.The teacher in whose class my daughter is studying is a kindhearted man.1.1.6 限定与非限定的区别:A.This is a shop that sells personal computers.Shakespeare,whose plays are popular,was a great writer.Football,which is a very interesting game, is played all over the world.B.The cab drivers who knew about the traffic jam took another road.The cab drivers,who knew about the traffic jam,took another road.C.The wine which was in the cellar was all ruined.The wine,which was in the cellar, was all ruined.1.1.7The teachers speak highly of the workbooks,all of which have come out.The audience,most of whom were college students, enjoyed the concert.These books,two of which I have read,are interesting.1.1.8School will break up on July 1,by which time we will have got our school reports.He may be late,in which case we ought to wait for him.He lost his temper,at which point I decided to go home.They bribed the officials,which practice was very common there.He believes in students’ doing more homework,which idea I am quite opposed to.1.1.9He is a teacher,as/which is clear from his manner.As we know,water resources are very limited on the earth.(as was expected/as is natural)She has married again,as was expected.She has married again,which was unexpected.Most devices of the integrated circuit,as are manufactured, are ruggedlypacked.(名词短语或句子)The meeting,which was held in the park,was a success.(可以单个名词)He was late for school,as/which was usual with him.He saw the girl,as/which he had hoped(he would).He saw the girl,which delighted him.Bamboo is hollow,which makes it very light.David is tall,as are my brothers.David works hard,as do my brothers.1.1.10先行词被形容词最高级、序数词、the only、the last、the same、the very、any、all等所修饰This is the best film that has ever been made.The first place that we visited was the Great Wall.The only furniture that he had in the room was a bed and a small desk.all the words that I've learnedThose were the very words that he said at the meeting.all、anything、nothing、little、much等不定代词That is all that I want to say.Is there anything that I can do for you?There’s still much that is to be done.人与物的名词词组They talked of persons and things that they remembered in the school.1.1.1 1What’s that which he refused to accept?That which was bitter to endure may be sweet to remember.曾经艰辛回味甜。

一般将来时◆一般将来时主要有以下几种表现形式由助动词shall或will加动词原形构成,shall 用于第一人称,will用于第二、三人称。
除英国外的说英语的国家,在陈述句中,即使在第一人称一般也用will,在英国也有这种趋势。
在口语中,常用shall, will的缩写形式为’ll, 如:I’ll, you’ll等。
Shall not的缩写式为:shan’t, will not 的缩写式为:won’t.肯定句:I/We shall/will go.You/He/She/They Will go.否定句:I/We shall/will not go.You/He/She/They Will not go.疑问句:Shall I/we go?Will you/he/she/they go?◆一般将来时用法(1)一般将来时表示将要发生的动作或情况。
例如:I will(shall) arrive tomorrow.我明天到。
Will you be free tonight? 你今晚有空吗We won’t (shan’t) be busy this evening. 我们今晚不忙。
(2)在一般将来时的句子中,有时有表示将来时间的状语,有时没有时间状语,这时要从意思上判断是否指未来的动作或情况。
例如:Will she come? 她(会)来吗We’ll only stay for two weeks. 我们只待两星期。
The meeting won’t last long. 会开不了多久。
(3)在以第一人称I或we作主语的问句中,一般使用助动词shall,这时或是征求对方的意见(a),或是询问一个情况(b):a. Where shall we meet? 我们在哪儿碰头b. Shall we have any classes tomorrow?明天我们有课吗在这类问句中,近年来也有不少人用will,特别是在美国。

一般将来时◆一般将来时主要有以下几种表现形式由助动词shall或will加动词原形构成,shall 用于第一人称,will用于二、三人称。
除英国外的说英语的国家,在陈述句中,即使在第一人称一般也用will,在英国也有这种趋势。
在口语中,常用shall, will的缩写形式为’ll, 如:I’ll, you’ll等。
Shall not的缩写式为:shan’t, will not 的缩写式为:won’t.肯定句:I/We shall/will go.You/He/She/They Will go.否定句:I/We shall/will not go.You/He/She/They Will not go.疑问句:Shall I/we go?Will you/he/she/they go?◆一般将来时用法(1)一般将来时表示将要发生的动作或情况。
例如:I will(shall) arrive tomorrow.我明天到。
Will you be free tonight? 你今晚有空吗?We won’t (shan’t) be busy this evening. 我们今晚不忙。
(2)在一般将来时的句子中,有时有表示将来时间的状语,有时没有时间状语,这时要从意思上判断是否指未来的动作或情况。
例如:We’ll only stay for two weeks. 我们只待两星期。
The meeting won’t last long. 会开不了多久。
(3)在以第一人称I或we作主语的问句中,一般使用助动词shall,这时或是征求对方的意见(a),或是询问一个情况(b):a. Where shall we meet? 我们在哪儿碰头?b. Shall we have any classes tomorrow?明天我们有课吗?在这类问句中,近年来也有不少人用will,特别是在美国。
例如:How will I get there? 我怎么去?(4)be going to+动词原形a.表示打算、准备做的事。
初中英语语法大全语法网络图一.名词II. 名词的数:1. 规则名词的复数形式:名词的复数形式,一般在单数形式后面加-s或-es。
现将构成方法与读音规则列表如下:III. 名词的所有格:名词在句中表示所有关系的语法形式叫做名词所有格。
所有格分两种:一是名词词尾加’s 构成,二是由介词of加名词构成。
前者多表示有生命的东西,后者多表示无生命的东西。
3. of所有格的用法:用于无生命的东西:the legs of the chair, the cover of the book用于有生命的东西,尤其是有较长定语时:the classrooms of the first-year students 用于名词化的词:the struggle of the oppressed二.冠词冠词分为不定冠词(a, an),定冠词(the),和零冠词。
三.代词:II. 不定代词用法注意点:1. one, some与any:1) one可以泛指任何人,也可特指,复数为ones。
some多用于肯定句,any多用于疑问句和否定句。
One should learn to think of others.Have you any bookmarks? No, I don’t have any bookmarks.I have some questions to ask.2) some可用于疑问句中,表示盼望得到肯定的答复,或者表示建议,请求等。
Would you like some bananas?Could you give me some money?3) some 和any修饰可数名词单数时,some表示某个,any表示任何一个。
I have read this article in some magazine.Please correct the mistakes, if any.4) some和数词连用表示“大约”,any可与比较级连用表示程度。
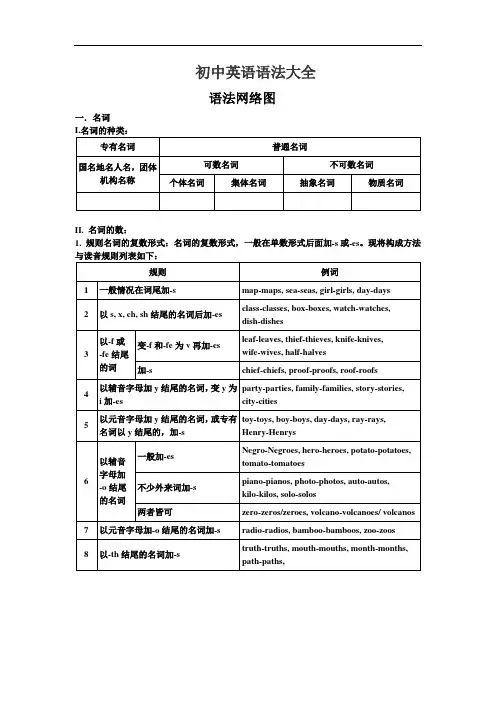
初中英语语法大全一.名词I.名词的种类:专有名词普通名词国名地名人名,团体机构名称可数名词不可数名词个体名词集体名词抽象名词物质名词II.名词的数:1.规则名词的复数形式:名词的复数形式,一般在单数形式后面加-s或-es。
现将构成方法与读音规则列表如下:规则例词1一般情况在词尾加-s map-maps,sea-seas,girl-girls,day-days2以s,x,ch,sh结尾的名词后加-es class-classes,box-boxes,watch-watches, dish-dishes3以-f或-fe结尾的词变-f和-fe为v再加-esleaf-leaves,thief-thieves,knife-knives,wife-wives,half-halves加-s chief-chiefs,proof-proofs,roof-roofs4以辅音字母加y结尾的名词,变y为i加-es party-parties,family-families,story-stories, city-cities5以元音字母加y结尾的名词,或专有名词以y结尾的,加-s toy-toys,boy-boys,day-days,ray-rays, Henry-Henrys6以辅音字母加-o结尾的名词一般加-esNegro-Negroes,hero-heroes,potato-potatoes,tomato-tomatoes不少外来词加-spiano-pianos,photo-photos,auto-autos,kilo-kilos,solo-solos两者皆可zero-zeros/zeroes,volcano-volcanoes/volcanos7以元音字母加-o结尾的名词加-s radio-radios,bamboo-bamboos,zoo-zoos8以-th结尾的名词加-s truth-truths,mouth-mouths,month-months, path-paths,2.不规则名词复数:英语里有些名词的复数形式是不规则的,现归纳如下:规则例词1改变名词中的元音字母或其他形式man-men,woman-women,foot-feet,goose-geese, mouse-mice2单复数相同sheep,deer,means,works,fish,yuan,jin, 3只有复数形式trousers,clothes,thanks,goods,glasses, 4一些集体名词总是用作复数people,police5部分集体名词既可以作单数(整体)也可以作复数(成员)class,family,crowd,couple,group,government, population,team,public,party6复数形式表示特别含义customs(海关),times(时代),spirits(情绪), drinks(饮料),sands(沙滩),papers(文件报纸), looks(外表),brains(头脑智力),greens(青菜)7表示“某国人”加-sAmericans,Australians,Germans,Greeks,Swedes,Europeans单复数同形Swiss,Portuguese,Chinese,Japanese以-man或-woman结尾的改为-men,-womenEnglishmen,Frenchwomen8合成名词将主体名词变为复数sons-in-law,lookers-on,passers-by,story-tellers,boy friends无主体名词时将最后一部分变为复数grown-ups,housewives,stopwatches将两部分变为复数women singers,men servantsIII.名词的所有格:名词在句中表示所有关系的语法形式叫做名词所有格。
初中英语语法大全语法网络图一.名词I.II. 名词的数:1. 规则名词的复数形式:名词的复数形式,一般在单数形式后面加 -s 或-es。
现将构成方法与读音规则列表如下:III. 名词的所有格:名词在句中表示所有关系的语法形式叫做名词所有格。
所有格分两种:一是名词词尾加 's构成,二是由介词 of 加名词构成。
前者多表示有生命的东西,后者多表示无生命的东西。
1.'所s有格的构成:the boy 's father, Jack oo'k, sh ber son-in-law's photo, 单数名词在末尾加 's复数名词般在末尾加 ' the teachers ' room, the twins ' mother, 不规则复数名词后加 's the children ' s toys, women ' s rights,以 s 结尾的人名所有格加 's或者 ' Dickens ' novels, Charles 's job, the Smiths ' house表示各自的所有关系时 ,各名词末尾均须加 's Japan ' s and America ' s problems,Jane bikes's and Mary 's表示共有的所有关系时在最后一词Japan and America ' s problems, Jane and Mary 's father 表示"某人家""店铺",所有格后名词省略the doctor ' s, the barber ' s, the tailor ' s, my uncle3. of 所有格的用法: 用于无生命的东西: the legs of the chair, the cover of the book 用于有生命的东西,尤其是有较长定语时: the classrooms of the first-year students用于名词化的词: the struggle of the oppressed 二.冠词 冠词分为不定冠词( a, an ),定冠词( the ),和零冠词。
1 英语语法精华 时态与语态 时态 语态 主动时态 被动语态
一般时态 一般现在时 do/does am/are/is done 一般过去时 did was/were done 一般将来时 will/shall do will/shall be done 一般过去将来时 would/should do would/should be done
进行时态 现在进行时 am/are/is doing am/are/is being done 过去进行时 was/were doing was/were being done 将来进行时 will/shall be doing 无 过去将来进行时 would/should be doing 无
完成时态 现在完成时 have/has done have/has been done 过去完成时 had done had been done 将来完成时 will/shall have done will/shall have been done 过去将来完成时 would/should have done would/should have been done 完成进行时态 现在完成进行时 have/has been doing 无
过去完成进行时 had been doing 无 将来完成进行时 will/shall have been doing 无 过去将来完成进行时 would/should have been doing 无 主动态:用于主动句中,它表示主语是谓语动词所表示动作的执行者。通常如果主动句中谓语动词是及物动词时,主动句可转换成被动句。 被动态:用于被动句中,它表示主语是谓语动词所表示动作的承受者。 用于被动的情况: ①、by短语(by+动作执行者); ②、不知道、不必知道或不愿说出动作的执行者; ③、用于表示“据说”、“据信”、“据报道”、“据估计”、“众所周知”、“必须指出”、等句子,使语气更加委婉。 ㈠一般现在时:动词原形或第三人称单数(复数形式) 用法:①、表示现在动作或状态 例句:1.I agree with you. 2.He works in a hospital. 3.-Are you a student? -Yes,I am. 4.There is a book on the desk. 5.This book is written by Mr.Chen.(被动) 2
6.It is said that there is plenty of oil off our coast(沿海).(被动) 7.It must be pointed out that China is a development country.(被动) ②、经常性或习惯性的动作(与频度副词always,usually,frequently,regularly,rarely,seldom,never,sometimes) 例句:1.We always care for each other and help each other. 2.I usually get up at 6:00 every morning. 3.He drinks heavily. 4.He rarely rains here. 5.Films are often shown in our university.(被动) ③、普遍真理或客观事实 例句:1.The earth move round the Sun. 2.China lies in the east of Asia. 3.Practice makes perfect.(熟能生巧) 4.A friend in need is a friend indeed.(患难朋友才是真正朋友) 5.Cars are driven with engines(发动机).(被动) ④、表示将来要发生的动作 I、用于陈述句(谓语动词是begin,start,come,go,arrive,leave,depart,return,retire,stay,stop,end,open,close及be动词等时,可表示规定、计划或安排要发生的事情,通常与表示将来的时间状语连用) 例句:1.The meeting begins tomorrow. 2.The train arrives at 2:30 p.m and leaves at 3:00 p.m. 3.The match takes place on Sunday. 4.He retires(退休) next month. 5.Tomorrow is Saturday. 6.Who speaks next. II、用于时间状语从句(通常由when,as,after,before,till/untill,as soon as等连词引导) 例句:1.I’ll come and see you when I have time. 2.I’ll write to you after I leave Shanghai. 3.Is mother going to leave before we get back? 4.He will stay here untill/till you come. 5.We will start as soon as you are ready. III、用于条件状语从句(通常由if,unless,in case,so long as等连词引导) 例句:1.We can catch the bus if we hurry up. 2.If the weather permits,we’ll go for a picnic tomorrow. 3.I won’t write to him unless he writes to me. 4.You will fail unless you work harder. ⑤、一般现在时还可以用于: 1. 报刊、杂志新闻标题或小说章节题目; 2. 剧情介绍或广播电视解说词; 3. 舞台表演、体育比赛等现场解说。 ㈡一般过去时(动词过去式) ①、过去某时发生的动作或存在的状态(通常与表示过去的时间状语连用) 例句:1.I met her yesterday. 3
2.He worked in that bank for five years. 3.I saw him ten minutes ago. 4.-Did you hear Mary sing just now? –No,I didn’t. 5.That bridge was built in 1980.(被动) ②、过去经常性或习惯性动作(只适用于动态供词和would,可与often,alaways等频度副词连用) 例句:1.I uesd to go to the movies when I was young. 2.We often did morning exercises when we were young. 3.She always carrled(撑着) an unbrella. 4.He never drank wine. 5.At that time this kind of work was always done by men.(被动) 6.While having breakfest,he would read newspapers in those days. ③、表示委婉语气(一般用于want,hope,think,wonder等词) 例句:1.I hope you could atend the opening ccremony(开幕式). 2. Did you want to see me? 3.I thought I might come and see you this evening. 4.I wondered if you could lend me your pen. ④、表示虚拟语气 ㈢一般将来时(will/shall+动词原形)shall用于第一人称 ①、将要发生的动作或状态(通常要与表示将来的时间状语连用) 例句:1.We will/shall arrive this afternoon. 2.-Will you be busy tonigh? -Yes,I will. 3.He won’t come to the party next week. 4.When will you be able to give us an answer? 5.Spring will come again. 6.The conference(会议) will be held tomorrow.(被动) ②、表示一种倾向或习惯性动作 例句:1.Crops(庄稼) will die without water. 2.Whenever he has time,he will come and see us. ⊿be going to+动词原形与be to+动词原形也可表示将要发生的动作或情况。 ⑴be going to+动词原形(表示打算或准备要做的事或即将肯定要发生的事) 例句:i、I am going to buy a house. ii、She isn’t going to meet him at the station. iii、Is he going to leature in English? iv、Who is going to speak first? v、She is going to have a baby. vi、Look at these clouds!It is going to rain. ⑵be to+动词原形(表示按计划安排即将发生的事或表示指示、命令、禁止或征求意见) 例句:i、This railway is to be opened to traffic next month.(被动) ii、The Prime Minister(首相) is to make a statement(声明) tomorrow. iii、You are to deliver these invitations before ten.(指示、命令) iv、You are not to tell him anything about our plans.(禁止) v、Am I to go on with the work?(征询)