翻译草稿无线传感器网络大作业资料
- 格式:doc
- 大小:143.50 KB
- 文档页数:15

基于ZigBee的点对点通信实验一:ZigBee的简介Zigbee是IEEE 802.15.4协议的代名词。
根据这个协议规定的技术是一种短距离、低功耗的无线通信技术。
这一名称来源于蜜蜂的八字舞,由于蜜蜂(bee)是靠飞翔和“嗡嗡”(zig)地抖动翅膀的“舞蹈”来与同伴传递花粉所在方位信息,也就是说蜜蜂依靠这样的方式构成了群体中的通信网络。
其特点是近距离、低复杂度、自组织、低功耗、低数据速率、低成本。
主要适合用于自动控制和远程控制领域,可以嵌入各种设备。
简而言之,ZigBee就是一种便宜的,低功耗的近距离无线组网通讯技术。
无线传感网络的无线通信技术可以采用ZigBee技术、蓝牙、Wi-Fi和红外等技术。
ZigBee技术是一种短距离、低复杂度、低功耗、低数据速率、低成本的双向无线通信技术或无线网络技术,是一组基于IEEE802.15.4无线标准研制开发的组网、安全和应用软件方面的通信技术。
1、CC2530简介CC2530是用于IEEE802.15.4、ZigBee和RF4CE应用的一个真正的方案。
它能以非常低的总的材料成本建立强大的网络节点。
CC2530结合了领先的RF收发功能的优良性能,业界标准的增强型8051CPU,系统内可编程内存,8-KB RAM和许多其他KB的内存。
CC2530有不同的运行模式,使得它尤其适应超低功耗要求的系统。
系统模式之间的转换时间短进一步确保了低能源消耗。
2、网络结构及协议解2.1 Basic RF 简介Basic RF 由TI 公司提供,它包含了IEEE 802.15.4 标准的数据包的收发。
这个协议只是用来演示无线设备是如何进行数据传输的,不包含完整功能的协议。
但是它采用了与802.15.4 MAC 兼容的数据包结构及ACK 包结构,其功能限制如下:1. 不提供“多跳”、“设备扫描”及Beacon。
2. 不提供不同种的网络设备,如协调器、路由器等。
所有节点同级,只实现点对点传输。

Zigbee Wireless Sensor Network in Environmental MonitoringApplicationsI. ZIGBEE TECHNOLOGYZigbee is a wireless standard based on IEEE802.15.4 that was developed to address the unique needs of most wireless sensing and control applications. Technology is low cost, low power, a low data rate, highly reliable, highly secure wireless networking protocol targeted towards automation and remote control applications. It’s depicts two key performance characteristics –wireless radio range and data transmission rate of the wireless spectrum. Comparing to other wireless networking protocols such as Bluetooth, Wi-Fi, UWB and so on, shows excellent transmission ability in lower transmission rate and highly capacity of network. A. Zigbee FrameworkFramework is made up of a set of blocks called layers.Each layer performs a specific set of services for the layer above. As shown in Fig.1. The IEEE 802.15.4 standard defines the two lower layers: the physical (PHY) layer and the medium access control (MAC) layer. The Alliance builds on this foundation by providing the network and security layer and the framework for the application layer.Fig.1 FrameworkThe IEEE 802.15.4 has two PHY layers that operate in two separate frequency ranges: 868/915 MHz and 2.4GHz. Moreover, MAC sub-layer controls access to the radio channel using a CSMA-CA mechanism. Its responsibilities may also include transmitting beacon frames, synchronization, and providing a reliable transmission mechanism.B. Zigbee’s TopologyThe network layer supports star, tree, and mesh topologies, as shown in Fig.2. In a star topology, the network is controlled by one single device called coordinator. The coordinator is responsible for initiating and maintaining the devices on the network. All other devices, knownas end devices, directly communicate with the coordinator. In mesh and tree topologies, the coordinator is responsible for starting the network and for choosing certain key network parameters, but the network may be extended through the use of routers. In tree networks, routers move data and control messages through the network using a hierarchical routing strategy. Mesh networks allow full peer-to-peer communication.Fig.2 Mesh topologiesFig.3 is a network model, it shows that supports both single-hop star topology constructed with one coordinator in the center and the end devices, and mesh topology. In the network, the intelligent nodes are composed by Full Function Device (FFD) and Reduced Function Device (RFD). Only the FFN defines the full functionality and can become a network coordinator. Coordinator manages the network, it is to say that coordinator can start a network and allow other devices to join or leave it. Moreover, it can provide binding and address-table services, and save messages until they can be delivered.Fig.3 Zigbee network modelII.THE GREENHOUSE ENVIRONMENTAL MONITORINGSYSTEM DESIGNTraditional agriculture only use machinery and equipment which isolating and no communicating ability. And farmers have to monitor crops’ growth by themselves. Even if some people use electrical devices, but most of them were restricted to simple communication between control computer and end devices like sensors instead of wire connection, which couldn’t be strictly defined as wireless sens or network. Therefore, by through using sensor networks and, agriculture could become more automation, more networking and smarter.In this project, we should deploy five kinds of sensors in the greenhouse basement. By through these deployed sensors, the parameters such as temperature in the greenhouse, soil temperature, dew point, humidity and light intensity can be detected real time. It is key to collect different parameters from all kinds of sensors. And in the greenhouse, monitoring the vegetables growing conditions is the top issue. Therefore, longer battery life and lower data rate and less complexity are very important. From the introduction about above, we know that meet the requirements for reliability, security, low costs and low power.A. System OverviewThe overview of Greenhouse environmental monitoring system, which is made up by one sink node (coordinator), many sensor nodes, workstation and database. Mote node and sensor node together composed of each collecting node. When sensors collect parameters real time, such as temperature in the greenhouse, soil temperature, dew point, humidity and light intensity, these data will be offered to A/D converter, then by through quantizing and encoding become the digital signal that is able to transmit by wireless sensor communicating node. Each wireless sensor communicating node has ability of transmitting, receiving function.In this WSN, sensor nodes deployed in the greenhouse, which can collect real time data and transmit data to sink node (Coordinator) by the way of multi-hop. Sink node complete the task of data analysis and data storage. Meanwhile, sink node is connected with GPRS/CDMA can provide remote control and data download service. In the monitoring and controlling room, by running greenhouse management software, the sink node can periodically receives the data from the wireless sensor nodes and displays them on monitors.B. Node Hardware DesignSensor nodes are the basic units of WSN. The hardware platform is made up sensor nodes closely related to the specific application requirements. Therefore, the most important work isthe nodes design which can perfect implement the function of detecting and transmission as a WSN node, and perform its technology characteristics. Fig.4 shows the universal structure of the WSN nodes. Power module provides the necessary energy for the sensor nodes. Data collection module is used to receive and convert signals of sensors. Data processing and control module’s functions are node device control, task sche duling, and energy computing and so on. Communication module is used to send data between nodes and frequency chosen and so on.Fig.4 Universal structure of the wsn nodesIn the data transfer unit, the module is embedded to match the MAC layer and the NET layer of the protocol. We choose CC2430 as the protocol chips, which integrated the CPU, RF transceiver, net protocol and the RAM together. CC2430 uses an 8 bit MCU (8051), and has 128KB programmable flash memory and 8KB RAM. It also includes A/D converter, some Timers, AES128 Coprocessor, Watchdog Timer, 32K crystal Sleep mode Timer, Power on Reset, Brown out Detection and 21 I/Os. Based on the chips, many modules for the protocol are provided. And the transfer unit could be easily designed based on the modules.As an example of a sensor end device integrated temperature, humidity and light, the design is shown in Fig. 5.Fig.5 The hardware design of a sensor nodeThe SHT11 is a single chip relative humidity and temperature multi sensor module comprising a calibrated digital output. It can test the soil temperature and humidity. The DS18B20 is a digital temperature sensor, which has 3 pins and data pin can link MSP430 directly. It can detect temperature in greenhouse. The TCS320 is a digital light sensor. SHT11, DS18B20 and TCS320 are both digital sensors with small size and low power consumption. Other sensor nodes can be obtained by changing the sensors.The sensor nodes are powered from onboard batteries and the coordinator also allows to be powered from an external power supply determined by a jumper.C. Node Software DesignThe application system consists of a coordinator and several end devices. The general structure of the code in each is the same, with an initialization followed by a main loop.The software flow of coordinator, upon the coordinator being started, the first action of the application is the initialization of the hardware, liquid crystal, stack and application variables and opening the interrupt. Then a network will be formatted. If this net has been formatted successfully, some network information, such as physical address, net ID, channel number will be shown on the LCD. Then program will step into application layer and monitor signal. If there is end device or router want to join in this net, LCD will shown this information, and show the physical address of applying node, and the coordinator will allocate a net address to this node. If the node has been joined in this network, the data transmitted by this node will be received by coordinator and shown in the LCD.The software flow of a sensor node, as each sensor node is switched on, it scans all channelsand, after seeing any beacons, checks that the coordinator is the one that it is looking for. It then performs a synchronization and association. Once association is complete, the sensor node enters a regular loop of reading its sensors and putting out a frame containing the sensor data. If sending successfully, end device will step into idle state; by contrast, it will collect data once again and send to coordinator until sending successfully.D. Greenhouse Monitoring Software DesignWe use VB language to build an interface for the test and this greenhouse sensor network software can be installed and launched on any Windows-based operating system. It has 4 dialog box selections: setting controlling conditions, setting Timer, setting relevant parameters and showing current status. By setting some parameters, it can perform the functions of communicating with port, data collection and data viewing。

传感器技术论文中英文对照资料外文翻译文献Development of New Sensor TechnologiesSensors are devices that can convert physical。
chemical。
logical quantities。
etc。
into electrical signals。
The output signals can take different forms。
such as voltage。
current。
frequency。
pulse。
etc。
and can meet the requirements of n n。
processing。
recording。
display。
and control。
They are indispensable components in automatic n systems and automatic control systems。
If computers are compared to brains。
then sensors are like the five senses。
Sensors can correctly sense the measured quantity and convert it into a corresponding output。
playing a decisive role in the quality of the system。
The higher the degree of n。
the higher the requirements for sensors。
In today's n age。
the n industry includes three parts: sensing technology。
n technology。
and computer technology。

无线传感器作业无线传感器网络,基础支撑技术及应用无线传感器网络是当前在国际上备受关注的、涉及多学科高度交叉、知识高度集成的前沿热点研究领域.它综合了传感器技术、嵌入式计算技术、现代网络及无线通信技术、分布式信息处理技术等,能够通过各类集成化的微型传感器协作地实时监测、感知和采集各种环境或监测对象的信息,这些信息通过无线方式被发送,并以自组多跳的网络方式传送到用户终端,从而实现物理世界、计算世界以及人类社会三元世界的连通.传感器网络具有十分广阔的应用前景,在军事国防、工农业、城市管理、生物医疗、环境监测、抢险救灾、防恐反恐、危险区域远程控制等许多重要领域都有潜在的实用价值,已经引起了许多国家学术界和工业界的高度重视,被认为是对21世纪产生巨大影响力的技术之一.1.无线传感网络的基本概念无线传感器网络的系统结构包括分布式传感器节点(群)、接收发送器、互联网和用户界面等。
其中,传感器网络节点的基本组成包括如下4个基本单元:传感单元(由传感器和模数转换功能模块组成)、处理单元(包括CPU、存储器、嵌入式操作系统等)、通信单元(由无线通信模块组成)以及电源.此外,可以选择的其他功能单元包括:定位系统、移动系统以及电源自供电系统等.在传感器网络中,节点可以通过飞机布撒或人工布置等方式,大量部署在被感知对象内部或者附近.这些节点通过自组织方式构成无线网络,以协作的方式实时感知、采集和处理网络覆盖区域中的信息,并通过多跳网络将数据经由Sink节点(接收发送器)链路将整个区域内的信息传送到远程控制管理中心.反之,远程管理中心也可以对网络节点进行实时控制和操纵.传感器网络节点为一个微型化的嵌入式系统,构成了无线传感器网络的基础层支持平台.目前国内外已经出现了许多种网络节点的设计,它们在实现原理上是相似的,只是分别采用了不同的微处理器或者不同的通信或协议方式,比如采用自定义协议、802.11协议、ZigBee协议、蓝牙协议以及UwB通信方式等.典型的节点包括Berkeley Motes,Sensoria WINS,Berkeley Piconodes,MIT肛AMPs,SmartMesh Dust mote,Intel iMote以及IntelXScale nodes,ICTCAS/HKUST的BUDSl 等.传感器网络有着巨大的应用前景,建筑在各类传感网络节点平台上的、面向海陆空全方位应用需求的各类研究项目更是层出不穷.以下仅列出其中几个代表典型应用的项目为例,比如用于环境监测、气象现象的观测和天气预报、生物群落的微观观测、洪灾的预警、农田管理、智能家居、智能交通、辐射监测的研究,用于定位的Cricket和Echo,以及用于医疗的SSIM项目等.相信随着研究工作的不断深入和发展,各种传感器网络将最终遍布我们的生活环境,从而真正实现“无处不在的计算”.2.无线传感器网络的关键问题(1)系统节能无线传感器网络节点多,覆盖范围大,工作环境复杂,能源无法替代,设计有效的策略延长网络的生命周期成为无线传感器网络的核心问题。

无线传感器网络应用文章(英文) Wireless Sensor Network ApplicationsIntroduction:Wireless Sensor Networks (WSNs) have gained significant attention in recent years due to their potential for numerous applications in various fields. A WSN consists of a large number of small, low-cost sensor nodes that are wirelessly connected to monitor physical or environmental conditions. These nodes can collect, process, and transmit data to a central base station for further analysis. This article aims to explore some of the most promising applications of WSNs.Environmental Monitoring:One of the most common applications of WSNs is environmental monitoring. These networks can be deployed in remote or hazardous areas to monitor parameters such as temperature, humidity, air pollution, and water quality. For instance, in forest fire detection, sensor nodes can detect abnormal temperature increases and transmit an alert to authorities, enabling timely intervention. In agriculture, WSNs can monitor soil moisture levels and provide farmers with real-time data to optimize irrigation.Healthcare:WSNs have also found applications in the healthcare industry. They can be used to monitor vital signs of patients, such as heart rate, blood pressure, and body temperature. Sensor nodes attached to patients can wirelessly transmit data to healthcare professionals, enabling continuous monitoring and early detection of any abnormalities. WSNs areparticularly useful in remote patient monitoring, allowing patients to receive medical attention from the comfort of their homes.Smart Homes and Buildings:WSNs can play a crucial role in creating smart homes and buildings. By deploying sensor nodes throughout a building, various parameters such as temperature, lighting, occupancy, and energy consumption can be monitored and controlled. This enables energy-efficient operations by optimizing heating, cooling, and lighting systems based on real-time data. Additionally, WSNs can enhance security by detecting unauthorized access or unusual activities within a building.Industrial Automation:WSNs are widely used in industrial automation to monitor and control different processes. For example, in manufacturing plants, sensor nodes can collect data on machine performance, temperature, and vibration levels, allowing for preventive maintenance and reducing downtime. WSNs can also be used for inventory management, tracking the movement of goods within a warehouse, and ensuring timely restocking.Traffic Management:WSNs can significantly contribute to improving traffic management in urban areas. By deploying sensor nodes along roads, real-time traffic data, such as vehicle density and speed, can be collected. This information can be used to optimize traffic signal timings, detect congestion, and provide drivers with alternative routes, reducingoverall travel time and fuel consumption. WSNs also enable the implementation of intelligent transportation systems, enhancing safety and reducing accidents.Conclusion:Wireless Sensor Networks have found numerous applications in various fields, ranging from environmental monitoring to healthcare, smart homes, industrial automation, and traffic management. These networks offer a cost-effective and scalable solution for collecting and analyzing datain real-time. As technology continues to advance, it is expected thatthe applications of WSNs will continue to expand, revolutionizing different industries and improving the quality of life for people around the world.。

安阳工学院无线网络技术课程大作业课题名称 Zigbee技术的智能家居无线传感网络应用专业姓名学号日期 2013年12月12号Zigbee技术的智能家居无线传感网络应用一:前言随着21世纪的到来,特别是近年来现代高科技和信息技术正在由智能大厦走向智能化住宅小区,进而走进家庭。
人们对家居生活环境的要求也越来越高,并将注意力越来越多的放在了生活环境的安全性、舒适性和便利性上。
家居无线监控问题是当今国际建筑智能化领域的前沿性研究课题。
无线传感网络的出现克服了家庭中布线的烦琐,充分体现了智能家居系统的灵活、方便、高效。
本项目研究开发了基于ZigBee技术和hitemet技术的智能家居监控系统,将hitemet的远程监控与ZigBee短距离控制相结合,实现系统的家居无线控制和数据采集,避免了综合布线,可扩展性好。
本文首先进行系统总体设计,结合底层ZigBee无线传感网络的特点和系统总体网络监控的要求,将该系统设计分为四部分:无线传输模块、数据处理模块、以太网传输模块、上位机显示界面。
然后对ZigBee协议标准做了全面地研究分析,同时给出了基于CC2430的无线传输模块的软硬件设计和星型网络搭建,并给出了测试结果。
接着设计了基于TMS320F2812的数据处理模块,给出了硬件电路和外围辅助电路设计方案,并为其移植了实时操作系统。
本设计实现了从底层ZigBee无线传感网络的数据采集最终到监控机的数据传输并测试成功。
最后在VC6.0环境下,应用 WindowsSockets套件接口开发显示界面对底层采集的数据分类显示。
整个智能家居监控系统能够对家用电器的完成开关量的控制,还能够对三表进行无线抄表最重要的是可监测来自家庭安防传感器的数据,以备物业等部门监控。
测试后,证实了设计方案的正确性,结果满足系统设计要求,该设计具有一定的新颖性和实用性二:ZigBee协议简介无线传感器网络节点要进行相互的数据交流就要有相应的无线网络协议(包括MAC层、路由、网络层、应用层等),传统的无线协议很难适应无线传感器的低花费、低能量、高容错性等的要求,这种情况下,ZigBee协议应运而生。

Wireless sensor networksNowadays,the use of wireless communication is more and more widely.Now I will talk about one of the most widely used wireless communication--Blue Tooth.What is Blue Tooth?Blue Tooth is a kind of technology that support short distance wireless communication. It is divided into two kinds.One is class 1 that the transmission distance is 100 meters ,the other is class2 that the transmission distance is 10 meters.Blue Tooth standard is the IEEE802.15.Bluetooth works at 2.4GHz and its bandwidth up to 3 Mb/s.The convenience of bluetooth are as follows:First of all,the use of Blue Tooth makes the transmission very convenient.W e can transmit data wen and where.Secondly,Blue Tooth is wireless.This make us no need to carry data line anymore.Thirdly,the use of greatly convenient the drivers by using the vehicle Blue Tooth system so that they can make calls when drive a car.Blue Tooth also has many advantages over other style of wireless communication. Above all,Blue Tooth has the on-off function and the state of can be found.Secondly,Blue Tooth has security Settings.Bluetooth need to match, after the success of the pairs can transmit data.Thirdly, Blue Tooth transmit very fast. Transmissionrate can reach 2.4GHz.On the other hand,Blue Tooth also has some shortages.In the home automation and industrial telemetry remote sensing, Bluetooth seems too complex, power consumption, from the past, network size is too small.Otherwise,the high price of Bluetooth impact the using will of customers.Bluetooth is widely used in our daily life. As is known to us all,most of the mobile phones,notebooks and some cars have the function of Blue Tooth. I believe most of the youth must have the experience of using Blue Tooth.Every coin has its two sides,Blue Tooth also has its advantages and its disadvantage,too.Bluetooth is most used on mobile phone,computer and other digital devices these years.I think there are many places where Bluetooth can be used.I believe Bluetooth has a broad application prospect.First,Bluetooth can be used on a wireless electronic locks.This kind of lock has a higher security and applicability.I think this kind lock is very suit for cars.People can use Bluetooth remote control to lock or unlock the car. Bluetooth remote control will be more powerful than other remote controls,for exsample infrared remote control.Second,we can use Bluetooth to build our electronic purses.Whenwe go shopping we can pay the bill without pulling out our purses.The cashier desk will detect your credit card and deducted your bill automatically.In this way we can go to a shop,a hotel,a airline company or a restaurant with ease.Third,Bluetooth system can be used in our household electrics.W e can put Bluetooth system into microwave oven's system,washing machine's system,refrigerator's and air-condition's systems.In this way,we can use a remote control to control all the household electrics.And the Bluetooth system of every electric can feedback its information to network at anytime.The mast can know the running state and control his electrics when and where.In summary,Bluetooth has been widely used in our life.And I believe the use of Bluetooth will be more and more widely. I also believe Bluetooth has a broad prospect.Maybe some of us can devoting themselves to study Bluetooth technology in the near future.。

《无线传感器网络》 实验指导书机械与电气工程学院郑晖编广州大学 2011年目录1实验一、处理器基础实验 (4)1.1 实验目的 (4)1.2 参考资料 (4)1.3 实验内容及步骤 (4)1.3.1开发环境搭建 (4)1.3.2了解开发环境的使用 (4)1.3.3基本I/O读写 (6)1.3.4简单A/D转换 (7)1.3.5基本定时 (8)1.3.6PWM输出 (8)2实验二、点到点无线通信实验 (9)2.1 实验目的 (9)2.2 参考资料 (9)2.3 实验内容及步骤 (9)2.3.1发送模块代码分析 (9)2.3.2接收模块代码分析 (9)2.3.3运行示例项目 (9)2.3.4应用设计 (10)3实验三、无线传感器组网实验 (11)3.1 实验目的 (11)3.2 参考资料 (11)3.3 实验内容及步骤 (11)3.3.1协调器模块代码分析 (11)3.3.2路由器模块代码分析 (12)3.3.3终端模块代码分析 (12)3.3.4运行示例项目 (14)3.3.5修改示例项目 (14)4大作业 (15)4.1 目的 (15)4.2 任务 (15)4.2.1题目1:LED跑马灯控制 (15)4.2.2题目2:超声波测距 (15)4.2.3题目3:语音通信 (15)4.2.4题目4:其它经老师同意的题目 (15)实验课时安排建议实验名称 课时实验一处理器基础实验 2实验二点到点无线通信实验 24实验三无线传感器组网实验1 实验一、处理器基础实验实验目的1.11. 掌握开发环境的搭建方法;2. 掌握基本调试步骤及方法;3. 掌握基本I/O、定时器、A/D的编程方法;1.2 参考资料1. IAR安装步骤说明:“C51RF-CC2530系统使用说明书\ IAR安装与使用.pdf”;2. 无线龙CC2530模块说明书:“C51RF-CC2530-PK使用说明书\C51RF-CC2530-PK使用说明书V1.01.pdf”;3. IAR开发环境使用方法:“C51RF-CC2530系统使用说明书\ IAR IDE用户手册.pdf”;4. CC2530芯片说明书:“C51RF-CC2530数据手册\CC253x.pdf”;5. 本实验指导书所附例程;“C51RF-CC2530-PK使用说明书\CC25306. 无线龙CC2530模块基础实验说明:基础实验V1.00.pdf”;7. 无线龙CC2530模块基础实验例程:“C51RF-CC2530演示程序\CC2530单片机基础实验”;1.3 实验内容及步骤1.3.1 开发环境搭建按照参考资料[1]、[2]的指导,安装IAR软件,安装仿真器驱动程序。
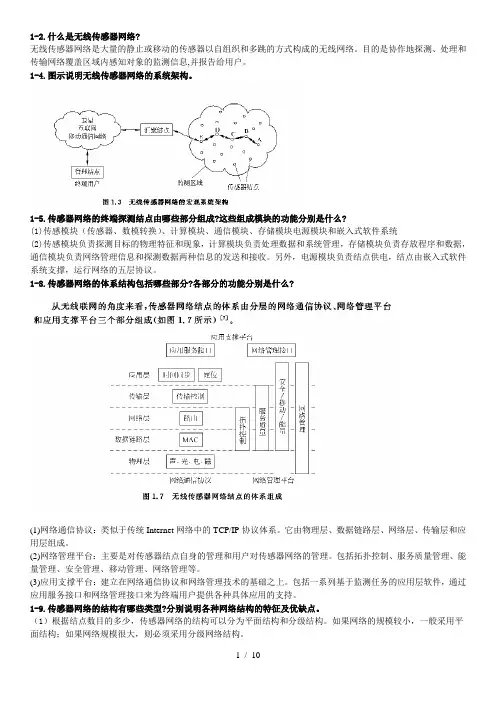
1-2.什么是无线传感器网络?无线传感器网络是大量的静止或移动的传感器以自组织和多跳的方式构成的无线网络。
目的是协作地探测、处理和传输网络覆盖区域内感知对象的监测信息,并报告给用户。
1-4.图示说明无线传感器网络的系统架构。
1-5.传感器网络的终端探测结点由哪些部分组成?这些组成模块的功能分别是什么?(1)传感模块(传感器、数模转换)、计算模块、通信模块、存储模块电源模块和嵌入式软件系统(2)传感模块负责探测目标的物理特征和现象,计算模块负责处理数据和系统管理,存储模块负责存放程序和数据,通信模块负责网络管理信息和探测数据两种信息的发送和接收。
另外,电源模块负责结点供电,结点由嵌入式软件系统支撑,运行网络的五层协议。
1-8.传感器网络的体系结构包括哪些部分?各部分的功能分别是什么?(1)网络通信协议:类似于传统Internet网络中的TCP/IP协议体系。
它由物理层、数据链路层、网络层、传输层和应用层组成。
(2)网络管理平台:主要是对传感器结点自身的管理和用户对传感器网络的管理。
包括拓扑控制、服务质量管理、能量管理、安全管理、移动管理、网络管理等。
(3)应用支撑平台:建立在网络通信协议和网络管理技术的基础之上。
包括一系列基于监测任务的应用层软件,通过应用服务接口和网络管理接口来为终端用户提供各种具体应用的支持。
1-9.传感器网络的结构有哪些类型?分别说明各种网络结构的特征及优缺点。
(1)根据结点数目的多少,传感器网络的结构可以分为平面结构和分级结构。
如果网络的规模较小,一般采用平面结构;如果网络规模很大,则必须采用分级网络结构。
(2)平面结构:特征:平面结构的网络比较简单,所有结点的地位平等,所以又可以称为对等式结构。
优点:源结点和目的结点之间一般存在多条路径,网络负荷由这些路径共同承担。
一般情况下不存在瓶颈,网络比较健壮。
缺点:①影响网络数据的传输速率,甚至造成网络崩溃。
②整个系统宏观上会损耗巨大能量。

无线传感器网络作业(总5页)--本页仅作为文档封面,使用时请直接删除即可----内页可以根据需求调整合适字体及大小--无线传感器作业:传感器网络节点使用的限制因素有哪些?1.电源能量有限传感器节点体积微小通常只携带能量十分有限的电池。
2.通信能力有限3.计算和存储能力有限,传感器节点是一种微型嵌入式设备,要求他价格低功耗小,这些限制必然导致其携带的处理器能力比较弱,存储器容量比较小。
:网络传感器有哪些特点?1.自组织性2.数据为中心3.应用相关性4.动态性5.网络规模6.可靠性:按照节点功能和结构层次划分,将传感器网络的结构有哪几种各有什么特点答:1.平面网络结构拓扑结构简单,易维护具有较好的健壮性事实上就是一种,a d h o c网络结构的形成。
由于没有中心管理节点,故采用自组织协同算法组成网络,其组网算法比较复杂。
2.分级网络结构:网络拓扑结构扩展性好,便于集中管理,可以降低系统的建设成本,提高网络覆盖率和可靠性。
3.混合网络结构:同级网络结构相比较,支持功能更强大,但所需要的硬件成本更高。
4.m e s h网络结构:由无线节点构成网络,按mes h拓扑结构部署,网内有个节点至少可以和一个其他节点通信支持多跳路由,功耗限制和移动性取决于节点类型及应用的特点,存在多种网络接入方式。
:传感器半径r,被监测区域面积为A,要求达到概率为p的覆盖率,确定传感器数目。
:WSN数据链路层中的媒体访问控制和误差控制的基本思想是什么?媒体访问控制:①对于感知区域内密集布置节点的多跳无线通信,需要建立数据通信链路以获得基本的网络基础设施。
②为了使无线传感器节点公平有效的共享通信资源,需要对共享媒体的访问进行管理。
误差控制:一般基于ARQ的误差控制,主要采用重新传送发费和管理发费。
具有低复杂的编码与解码方式的简单误差控制码可能是无线传感器网络中误差控制的最佳解决方案。
:传输层中的Event-to-sink传输和Sink-to-Sensors传说的基本思想是什么?Event-to-sink由于无线传感网络中存在大量的数据流,Sink节点需要获得一定精度,Event-to-sink 的可靠度是必要的,包括了事件特征到Sink’节点的可靠通信,而不是针对区域内各节点生成的单个传感报告/数据包进行基于数据包的可靠传递。

中英文资料对照外文翻译基于网络共享的无线传感网络设计摘要:无线传感器网络是近年来的一种新兴发展技术,它在环境监测、农业和公众健康等方面有着广泛的应用。
在发展中国家,无线传感器网络技术是一种常用的技术模型。
由于无线传感网络的在线监测和高效率的网络传送,使其具有很大的发展前景,然而无线传感网络的发展仍然面临着很大的挑战。
其主要挑战包括传感器的可携性、快速性。
我们首先讨论了传感器网络的可行性然后描述在解决各种技术性挑战时传感器应产生的便携性。
我们还讨论了关于孟加拉国和加利尼亚州基于无线传感网络的水质的开发和监测。
关键词:无线传感网络、在线监测1.简介无线传感器网络,是计算机设备和传感器之间的桥梁,在公共卫生、环境和农业等领域发挥着巨大的作用。
一个单一的设备应该有一个处理器,一个无线电和多个传感器。
当这些设备在一个领域部署时,传感装置测量这一领域的特殊环境。
然后将监测到的数据通过无线电进行传输,再由计算机进行数据分析。
这样,无线传感器网络可以对环境中各种变化进行详细的观察。
无线传感器网络是能够测量各种现象如在水中的污染物含量,水灌溉流量。
比如,最近发生的污染涌流进中国松花江,而松花江又是饮用水的主要来源。
通过测定水流量和速度,通过传感器对江水进行实时监测,就能够确定污染桶的数量和流动方向。
不幸的是,人们只是在资源相对丰富这个条件下做文章,无线传感器网络的潜力在很大程度上仍未开发,费用对无线传感器网络是几个主要障碍之一,阻止了其更广阔的发展前景。
许多无线传感器网络组件正在趋于便宜化(例如有关计算能力的组件),而传感器本身仍是最昂贵的。
正如在在文献[5]中所指出的,成功的技术依赖于共享技术的原因是个人设备的大量花费。
然而,大多数传感器网络研究是基于一个单一的拥有长期部署的用户,模式不利于分享。
该技术管理的复杂性是另一个障碍。
大多数传感器的应用,有利于这样的共享模型。
我们立足本声明认为传感器可能不需要在一个长时间单一位置的原因包括:(1)一些现象可能出现变化速度缓慢,因此小批量传感器可进行可移动部署,通过测量信号,充分捕捉物理现象(2)可能是过于密集,因此多余的传感器可被删除。
基于ZigBee技术的室内环境监控系统目录1 研究背景与意义 (12 研究内容 (13 ZigBee技术综述 (23.1 ZigBee特点 (23.2 ZigBee协议栈 (33.3 节点类型 (63.4 拓扑结构 (63.5 地址类型及ZigBee寻址 (74 室内环境监测系统设计 (84.1 系统架构 (84.2 硬件设计 (94.3 软件设计 (104.4 系统功能定义 (115 室内环境监控系统的特点 (126 总结 (137 参考文献 (13基于ZigBee技术的室内环境监控系统1 研究背景与意义随着人类进入信息时代,计算机技术、通信技术及网络技术都得到了迅猛的发展与提高,人们对居住环境也提出了更高的要求,希望自己能居住在一个生活现代化、居住环境安全化和舒适化的生活空间。
与此同时,生活节奏的不断加快,实时掌握大量信息和进行高效工作的需求日益凸显,但是繁重的家务和繁琐的家电操作占用人们大量的时间,这时就需要有一个方便快捷的智能化家居管理平台协助人们处理家居事务,将人们从家务和家电操作中解放出来。
在这种需求的驱动下,智能家居的概念也就应运而生。
人们希望通过这种技术将家庭中各种与信息相关的通讯设备、家用电器和家庭安防等装置连接到一个家庭智能化系统上进行集中或异地监视、控制和管理,保持这些家庭设施与住宅环境的和谐与协调一致,从而满足用户对居住环境的需求。
智能家居系统的结构如图1所示:图1 智能家居系统结构图由图1可知,室内环境监控系统是智能家居系统中其必不可少的一部分,是实现智能家居系统功能的重要组成部分与基本条件,是给用户提供一个安全、舒适、便捷的生活环境的重要手段。
一个好的室内环境监控系统对于构建智能家居系统和提高用户的生活环境质量具有重要的意义。
2 研究内容本文以基于ZigBee技术的室内环境监控系统为研究背景,利用ZigBee技术作为支撑平台,将温湿度传感器、光照传感器、雨滴传感器、火灾传感器及人体感应传感器等传感器节点采集到的数据信息通过ZigBee 网络汇聚到网络中的网关节点,该网关节点再通过Wifi模块将处理后的数据传送给Android上位机软件,然后用户通过与上位机软件进行交互,通过显示的数据信息反馈控制诸如空调、电灯等电器,可营造一个安全、舒适、温馨的室内氛围。
毕业设计(论文)译文及原稿免费下载,免费分享。
让论文写得更简单,更舒适。
更容易……译文题目ZigBee:无线技术,低功耗传感器网络原稿题目ZigBee: Wireless Technology for Low-Power Sensor Networks原稿出处电子文献ZigBee:无线技术,低功耗传感器网络加里莱格美国东部时间2004年5月6日上午12:00技师(工程师)们在发掘无线传感器的潜在应用方面从未感到任何困难。
例如,在家庭安全系统方面,无线传感器相对于有线传感器更易安装。
而在有线传感器的装置通常占无线传感器安装的费用80%的工业环境方面同样正确(适用)。
而且相比于有线传感器的不切实际甚至是不肯能而言,无线传感器更具应用性。
虽然,无线传感器需要消耗更多能量,也就是说所需电池的数量会随之增加或改变过于频繁。
再加上对无线传感器由空气传送的数据可靠性的怀疑论,所以无线传感器看起来并不是那么吸引人。
一个低功率无线技术被称为ZigBee,它是无线传感器方程重写,但是。
一个安全的网络技术,对最近通过的IEEE 802.15.4无线标准(图1)的顶部游戏机,ZigBee的承诺,把无线传感器的一切从工厂自动化系统到家庭安全系统,消费电子产品。
与802.15.4的合作下,ZigBee提供具有电池寿命可比普通小型电池的长几年。
ZigBee设备预计也便宜,有人估计销售价格最终不到3美元每节点,。
由于价格低,他们应该是一个自然适应于在光线如无线交换机,无线自动调温器,烟雾探测器和家用产品。
(图1)虽然还没有正式的规范的ZigBee存在(由ZigBee联盟是一个贸易集团,批准应该在今年年底),但ZigBee的前景似乎一片光明。
技术研究公司In-Stat/MDR在它所谓的“谨慎进取”的预测中预测,802.15.4节点和芯片销售将从今天基本上为零,增加到2010年的165万台。
不是所有这些单位都将与ZigBee结合,但大多数可能会。
基于无线传感网络的煤矿瓦斯检测系统近年来瓦斯爆炸的安全事故频频发生,严重威胁了生产的安全,给国家和人民造成重大的损失。
其中一个很重要的原因就是瓦斯生产的安全,给国家和人民造成了重大损失。
其中,一个很重要的原因就是瓦斯监控设备不能很好地发挥作用。
传统的瓦斯监控设备,监控范围有限,并且基本采用有线模式传输信号,在矿井中使用十分不便。
而无线传感器网络存在监测区域内大量的廉价微型传感器节点,通过无线通信方式组成的一个多跳的自组织网络,其目的是采集和处理网络覆盖区域中被感知对象的信息,并通过无线模块发送给观察者。
是集数据的采集、融合、分析、传输于一体,具有展开快速、可靠稳定、可维护性好等特点,特别适用于环境恶劣、不方便人工监控和通过有线网络监控的场所。
如果将其应用于煤矿中,配上上层监控软件,可以很好地实现对煤矿内重点区域瓦斯浓度的实时监控、显示和预警,对煤矿的安全生产起着非常重要的作用。
下面就提出一种基于无线传感网络的煤矿瓦斯预警系统的设计方法。
1、系统构架设计矿井瓦斯监测系统由监测传感器、井下分站、信息传输系统和地面中心等部分组成。
井下分站和地面中心站的连接部分即是信息传输系统。
信息传输系统按结构可以分为放射状、环状和树状三种。
在同等的监控容量的情况下,减少系统的分支,井下各分站就近接入由井上中心站下来的系统电缆。
在无线通信设计中井下现有光纤通信系统相当于树的主干,井下各分站由无线通信系统中的主节点代替,各个主节点接入多个无线传感器子节点,每个主节点与其接入的子节点构成一组。
井巷瓦斯监测无线通信系统是结合井下现有光纤通信系统和无线瓦斯传感器网络提出的一种瓦斯监测系统。
利用每一个传感器均具有的检测功能,同时又具有信号的接收、处理、判断、控制检测系统开关、发送以及根据信号对检测系统开关进行控制的特点。
2、传感器节点设计传感器节点由传感器模块、处理器模块、无线通信模块及电源模块4部分组成,如图2所示。
传感器模块负责监测区内信息的采集和数据转换;处理器模块负责控制整个传感器节点的操作,接收和处理本身采集的数据以及其他节点发来的数据;无线通信模块负责与其他传感器节点进行无线通信,交换控制消息和收发采集数据;电源模块为传感器、处理器及无线模块提供运行所需的能量,并对其进行管理,以达到最大的使用效率。
传感器技术外文文献及中文翻译引言传感器是现代检测技术的重要组成部分,它能将物理量、化学量等非电信号转换为电信号,从而实现检测和控制。
传感器广泛应用于工业、医疗、军事等领域中,如温度、湿度、气压、光强度等参数检测。
随着科技的发展,传感器不断新型化、微型化和智能化,已经涵盖了人体所有的感官,开启了大规模的物联网与智能化时代。
本文将介绍几篇与传感器技术相关的外文文献,并对其中较为重要的内容进行中文翻译。
外文文献1标题“Flexible Sensors for Wearable Health: Why Materials Matter”作者Sarah O’Brien, Michal P. Mielczarek, and Fergal J. O’Brien文献概述本文主要介绍了柔性传感器在可穿戴健康监测中的应用,以及传感材料的选择对柔性传感器性能的影响。
文章先介绍了柔性传感器的基本工作原理和常见的柔性传感材料,然后重点探讨了传感材料对柔性传感器灵敏度、稳定性、响应速度等性能的影响。
最后,文章提出未来柔性传感器材料需满足的性能要求,并对可能的研究方向和应用进行了展望。
翻译摘要柔性传感器是可穿戴健康监测中重要的成分,通过将身体状态转化为电信号进行检测。
选择合适的传感材料对柔性传感器产品的成本、性能及标准化有着面向未来的影响。
本文对柔性材料的常见种类 (如: 聚合物、金属、碳复合材料等) 进行了介绍,并重点探讨了传感材料选择的影响因素,如对柔性传感器的灵敏度、特异性和响应时间等。
此外,文章还探讨了柔性传感器的性能要求和建议未来的技术方向。
外文文献2标题“Smart sensing system for precision agriculture”作者Olivier Strauss, Lucas van der Meer, and Benoit Figliuzzi文献概述本文主要介绍智能传感系统在精准农业中的应用。
2.3 Intermediate stepRegarding the GPSR protocol, the best neighbor node is the nearest node to the destination.We modify this rule in GPSR and add a restriction for selecting the best neighbors based on thelist of private keys.2.3中间步骤对于GPSR协议来说,最佳邻居节点是到目的地的最近的节点。
我们在GPSR协议中修改这个规则,并且基于私人密钥列表对选择最佳的邻居节点添加一个限制。
In other words, when node A finds the best neighbor B from its neighborhood table, the list of private keys of node A needs to be compared with the list of private keys of node B.Then, node B is selected as a next node if and only if at least one private key of node A and B is selected from the same matrix.If they have no similar matrices, node B is eliminated from the neighborhood table and this phase repeats again to find the best neighborhoods.换句话说,当节点A从它的邻居节点表中找到最好的邻居节点B时,A节点的私钥列表需要和B节点的私钥列表进行比对。
然后,节点B将会被选择作为下一跳节点当且仅当节点A和B的至少一个私钥是选自同一矩阵。
如果节点A和节点B没有相似的矩阵,那么节点B将从节点A的邻居节点列表中移除,这个相位会继续重复以找到节点A最好的邻居节点。
where the list of private keys of node B is Pr B and Pr A is the list of private keys of node A.2.3.1 Shared key generation phaseWhen the best neighbor is selected, the node needs a shared key to communicate with its neighbors securely. The shared key is created for each pair of two nodes that have a private key from the same matrix Pi.For example, if nodes i and j have a key form matrix P1, the sharedkey can be calculated by:2.3.1共享密钥生成阶段当最好的邻居节点被选中时,该节点需要一个共享的密钥来安全地与它的邻居节点进行通信。
对于每一对拥有来自同一矩阵Pi的私有密钥的两个节点,共享密钥都会被创建。
例如,如果节点i和节点j有一个来自矩阵P1的密钥,那么节点i和节点j之间的共享密钥可以通过下式进行计算:11月9日翻译至此We have mentioned it earlier that Pr is symmetric matrix,我们已经提到过它公关是对称矩阵,Then, the result of P 1 _ kP is a symmetric matrix with size N × N in which SKij = SKji is the shared key between nodes i and j .然后,结果P k *P 1是一个大小为N × N 的对称矩阵,在这个矩阵中ji ij SK SK ,并且它们是节点i 和节点j 之间的共享密钥。
After generating the shared secret key, the packet and the selected index are sent to the best neighbor by using the shared key.当产生共享密钥后,数据包和选定的索引通过使用共享密钥被送到最好的邻居节点。
It is important to mention that we assume our network is completely dense and each node has at least one neighbor with the same specification.在此有必要提到的是,我们假设我们的网络是完全致密的,并且每个节点至少有一个具有相同规格的邻居节点。
2.3.2 Verification phaseWhen the packet is received by the best neighbor (for example node B ), this node extracts the index from the packet and regenerate the shared key.2.3.2 验证阶段当数据包被最佳邻居节点(例如节点B )接收后,那么该节点将从数据包中提取索引,并且再生共享密钥。
Then, node B creates an ACK message, signs it by using a shared key, and sends it to node A .然后,节点B 创建一个ACK 消息,通过使用共享的密钥将该消息进行标记,并将其发送给节点A 。
If the ACK message is verified by node A , node B is a trusted node, otherwise node B is a malicious node. 如果这个ACK 消息通过了节点A 的验证,那么节点B 就被认为是一个可受信任的节点,否则节点B 被认为是一个恶意节点。
Therefore, Node A generates an alarm message and broadcast to the network that the node for eliminating the malicious node from their neighborhood tables.因此,节点A 将产生一个报警信息,并向网络进行广播,告知网络中其它节点应该从他们的邻居表中消除该恶意节点。
2.4 Destination StepWhen a packet is received by the destination node, the probability of wormhole attack happening is checked based on the distance between source node to the destination node and the number of hops from source to destination.A necessary condition for detecting wormhole in destination node is:2.4目标步当数据包被目标节点接收后,根据源节点到目的节点之间的距离和源节点到目的节点之间的跳数,虫洞攻击发生的概率可以被测算到。
用于检测目标节点的虫洞的必要条件是:where the location of the source node is (xs , ys ), (xd , yd ) is the location of thedestination, R is the radio range of nodes, number of hops from source to destination is shown by h .When the wormhole is detected, a request packet is sent to source node in order to send a packet again from another path.上式中,()s s y ,x 是源节点的位置,()d d y x ,是目的节点的位置。
R 是节点的无线广播范围半径,从源节点到目的节点的跳数由h 显示。
当检测到该虫洞时,一个请求数据包将被发送到源节点,以便源节点从另一个路径中再次发送一个数据包给目的节点。
3.1 Miss detection probability analysis3.1漏误检测概率分析Miss detection probability is a crucial metric to evaluate wormhole detection methods.漏误检测概率是评价虫洞检测方法的一个重要指标。
According to key distribution of this method, there are y potential private keys for N sensor nodes in the network and each sensor node randomly selects α private keys ( α≤y ).根据该方法的主要分布,在网络中的N 个传感器节点中有y 个潜在的私人密钥,并且每个传感器节点随机选择α个私人密钥(α≤y )。
Therefore, the probability of a specific key belonging to one node is equal to bay c while the malicious nodes do not have a private key. 因此,一个特定的密钥属于一个节点的概率是等于⎥⎦⎥⎢⎣⎢y α,而恶意节点没有一个私人密钥。
If the adversary is able to compromise x nodes, the probability that just m nodes from x nodes (m ≤ x ≤ N) contain the specific key (i K ) from y potential private keys is computed by:如果对手能够向x 节点妥协,仅仅是m 节点从x 节点(m ≤ x ≤ N) 包含从潜在的私人密钥y 的概率可以通过下面公式计算:Therefore, the probability of breaking one link by an adversary is calculated in below formula:因此,被对手打破一个链接的概率可以通过下面的公式来计算:Where x is the number of compromised nodes, numbers of selected nodes are shown by m, y isthe number of potential private keys and αis equal to the number of private keys for each node.其中,x是妥协节点的数目,选定的节点的数目由m表示,y是潜在私人密钥的数,α是每个节点的私钥数目To create a wormhole in geographic routing protocol necessitates two or more malicious nodes to receive packets at one point of the network and forward those packets to another location by a wireless or wired tunnel.在地理路由协议中创建一个“虫洞”,需要2个或多个恶意节点在网络的一个节点处接收这些数据包,并且通过无线或有线通道将这些数据包转发到另一个位置。