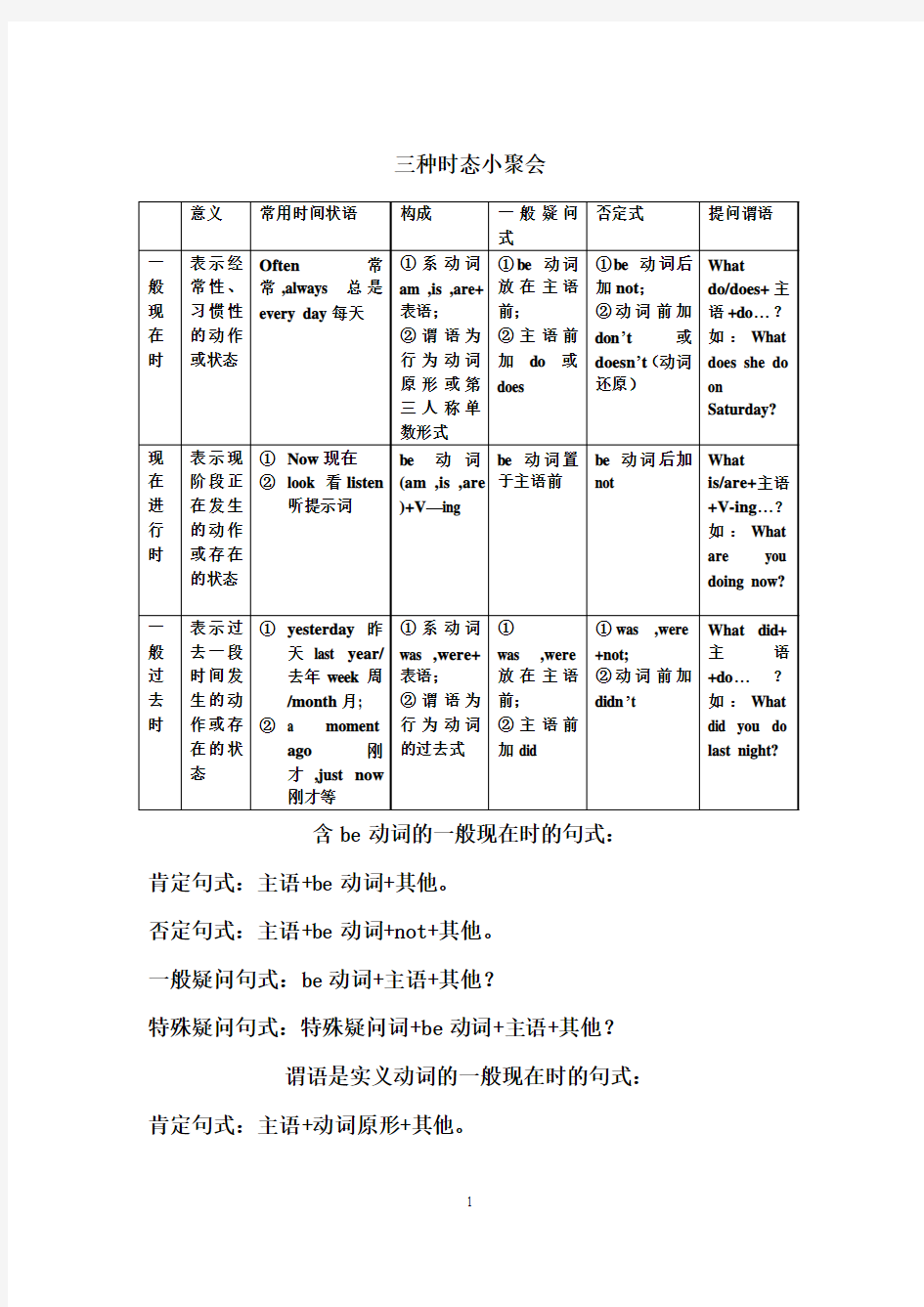

三种时态小聚会
含be动词的一般现在时的句式:
肯定句式:主语+be动词+其他。
否定句式:主语+be动词+not+其他。
一般疑问句式:be动词+主语+其他?
特殊疑问句式:特殊疑问词+be动词+主语+其他?
谓语是实义动词的一般现在时的句式:肯定句式:主语+动词原形+其他。
否定句式:主语+don’t/doesn’t+动词原形+其他。
一般疑问句式:do/does+主语+动词原形+其他?
特殊疑问句式:特殊疑问词+do/does+主语+动词原形+其他?
注:当主语是第三人称单数时,一般要在动词原形后加-s或-es 。
现在进行时的句式:
肯定句式:主语+be动词+现在分词+其他。
否定句式:主语+be动词+not+现在分词+其他。
一般疑问句式:be动词+主语+现在分词+其他?
特殊疑问句式:特殊疑问词+be动词+主语+现在分词+其他?
含动词be的一般过去时的句式:
肯定句式:主语+be动词(was/were)+其他。
否定句式:主语+be动词(was/were)+not+其他。
一般疑问句式:be动词(was/were)+主语+其他?
特殊疑问句式:特殊疑问词+be动词(was/were)+主语+其他?
含行为动词的一般过去时的句式:
肯定句式:主语+动词的过去式+其他。
否定句式:主语+didn’t+动词原形+其他。
一般疑问句式:did+主语+动词原形+其他?
特殊疑问句式:特殊疑问词+did+主语+动词原形+其他?
温馨提示:辨析一般现在时和一般过去时,一定要认真看清时间状语。
4种 句动作同时发生或从句动作先于主句。(既可引导时间点又可引导时间段) I was thin when I was a child. The film had been on when w e arrived. 2. be about to do … when … be doing …when… be on o ne’s way … when … be on the point of doing …when… had done … when… “ 在那时”“这时”,表示某件事正在发生或刚刚发生,另一动作同时发生 The telephone was ringing when I got home. I was about to go to bed when he came back. W e w ere just on the point of calling you up when you came in. 3. When 还以引导条件状语从句相当于if How can I explain it to you when / if you won’t listen. How can you get good records when you don’t study? When you read it again, the meaning will become clearer to you. 4.When还可引导原因状语从句,“既然” It was foolish of you to take a taxi when you could easily walk there in five minutes. 3种 1. 必须引导持续性动作,强调在一段时间内,主句和从句动作同时发生。 My mother was cooking while I was doing my homework. Please don’t talk so loud while others are working. 2. “然而” 表示轻微转折, 两者对比。 I like watching TV while he likes reading. 3.引导让步状语从句“ 虽然,尽管” While I admit his good points, I can see his shortcomings. 1 As I left the house , I forgot the key.我离开家时,忘记了带钥匙。 As 引导时间状语从句,强调动作并行发生,不指先后。 2. As I get older, I get more optimistic. 随着年龄的增长,我变得更加乐观“随着” 表示时间的推移。 3. He hurried home, looking behind as he w ent. 他匆匆忙忙回家,边走边往后看。“一边…一边…” 4 As he was going out, it began to rain. 当他出去时开始下雨了强调两个动作紧接着发生。 5. As a boy (When he was a boy), he was hopeless at English.
各时态常用时间状语 一般现在时 1 every day/week/month/hour/ten minutes, every other day(每隔一天)=every second day=every two days; every three days(第三天,即每隔两天),every few days 2 in the morning/afternoon/evening, at night 3 once a week, twice a year… 4 often, usually, frequently, always(也会出现于现在进行时,表示过于频繁), sometimes, at times(时不时), from time to time, every now and then(时不时), frequently, once in a while(时不时) never(它也会出现于现在完成时),seldom(很少),hardly 5 on Sundays(=every Sunday) 6 right now(此刻, 目前) 现在进行时: now, at the moment, at present, for the time being(现在) right now(此刻, 目前)(也可用于一般现在时) always(表示过于频繁发生) 现在完成时: 1 for + 段时间(可用于各种时态), since+点时间(表示段时间)(ever since, since then) (注意这两个时间状语要求句中谓语动词是可延续性的) 2 in/over the past 30 years(注意只用in the past是一般过去时) 3 lately, recently, just (刚刚), these days(根据情况有时也可用于一般现在时) 4 so far, by now, up to now; up until now(直到现在) 5 ever(肯,疑); never(否); 6 already(肯); yet(否,疑) 一般过去时: 1 现在+过去,(即一般现在时的时间状语+一个过去的时间, 如every day last year, on Sundays last year) 2 yesterday, ...ago, just now(刚才), the other day(前几天) 3 last year/night/month... 4 in the past 5 由when 引起的时间状语从句中.(I was watching TV when he came in)(见后常用句型) 过去进行时: 1 一点时间+过去(3 o'clock yesterday; this time last month) 2 由when 引起的句中.(I was watching TV when he came in)(见后常用句型) 3 参照上下文 4 while两端都用进行时
【英语】状语从句知识点总结 一、初中英语状语从句 1.---Can students go online during lessons? ---They can’t ________ it is for that lesson. A.if B.unless C.until D.while 【答案】B 【解析】 【详解】 句意:——学生上课时能上网吗?他们不可以,除非为了上那堂课。本题考查连词辨析,A.如果;B.除非;C.直到;D.当……时候。答语是条件状语从句,根据句意结构可知,需要unless连接,故选B。 2.Tony has had to cook by himself ________ his mother went on business to Guangzhou. A.since B.after C.during D.when 【答案】A 【解析】 【详解】 句意:自从妈妈去广州出差以来,托尼不得不自己做饭。A. since从……以来;B. after在……之后;C. during 在……期间;D. when当……时候。since后跟时间状语从句时,表示的是到目前为止的时间段,从句时态为一般过去时,而主句的时态为现在完成时,故正确答案为A。 3.—____ the workers are very tired, _____they keep on working. — They are great. We must learn from them. A.Because; / B.Though; / C.Because; so D.Though; but 【答案】B 【解析】 试题分析:句意:尽管工人们很累了,但他们仍然继续工作。——他们太伟大了,我们应该向他们学习。本题考查连词的用法。Because用于表示因果关系,不能与so同时使用;Though用于表示转折关系,不能与but同时使用。结合句意,故选B. 考点:考查连词的用法。 4.Chen Wei isn’t at school today ________ he is taking a robot competition in Shanghai. A.so B.because C.before D.if
高考It +be+ 时间+ 从句”结构 总结一 在“It +be+ 时间+ 从句”结构中,引导从句的从属连词有before, that, since, until (till ), when 等。这一结构是近几年高考常考的知识点,现将它们的用法小结如下: 一、It +be (not )+ 时间段+before 从句。 其中的主句是肯定式时,意为“过多长时间才……”;主句是否定式时,意为“没过多久就……”。例如: 1. It was not long before the whole country rose and drove the Austrian soldiers from their homeland. 不久,全国人民便奋起反抗,把奥地利军队从他们的国土上赶了出去。 2. It may be five or six years before the new medicine is tested on human beings. 要过五六年时间这种新药才能在人身上做试验。 3. It was two months before he designed the bridge. 过了两个月,他设计出了这座桥梁。 二、It +will be (was )+ 时间段+until 从句 若主句中用一般将来时,则从句中用一般现在时,意思是从现在起到从句中谓语动词表示的动作发生时还有多长时间;若主句中用一般过去时,则从句中也用一般过去时,意思是从过去某一时间起到从句中谓语动词表示的动作发生还有多长时间。例如: 1. It will be ten days until my birthday comes. 到我生日还有十天。 2. It was only five minutes until her husband came back from work. 当时离她丈夫下班只有五分钟了。 注意:结构“一”与结构“二”在肯定句中几乎可以通用。但是,若从句中谓语动词表示的将来动作一定或预期肯定会发生,则多用until 引导从句;若从句中谓语动词表示的将来动作在客观上并非一定要发生时,则多用before 引导从句。 三、It +is / has been (was )+ 时间段+since 从句 在这一结构中,主句常用一般现在时、现在完成时或一般过去时。如果since 引导的状语从句中的谓语动词为非延续性动词,则表示“自从状语从句中的动作发生以后,时间过不了多久”。例如: 1. It is two years since Jim came to China. 吉姆来中国两年了。 2. It has been three years since they got married. 他们结婚已经三年了。 如果since 从句中的谓语动词为延续性动词,则表示“自从从句谓语动词表示的动作结束以来,时间已过了多久”。例如: 3. It is / has been a year since he smoked. 他戒烟已经一年了。 四、It +is / was + 时间点+when 从句 在这一结构中,时间之前没有介词,从句为when 引导的时间状语从句。从句常用一般过去时,意为“当某事发生时,时间是……”。例如: 1. It was October 1st, 1949 when the People's Republic of China was founded. 中华人民共和国成立于1949 年10 月1 日。 2. What time was it when you got to school 你几点到的学校。 五. It is /was + 时间状语+that 从句
一般将来时时间状语归纳总结 1含next的短语next week/day/month/term 2 含tomorrow的短语the day after tomorrow 后天tomorrow morning/evening/afternoon 3 含in的短语,后跟一段时间,表示“以现在为起点,多长时间后”。In two days/years 4 含this 的短语,表示与现在相比较,将来的某个时候,this wednesday/Saturday/weekday/weekend 5 when 引导的时间状语从句when he grows up 6 单个的短语。Soon(不久)tonight(今晚)some day(将来的某一天)one day(将来的某一天)in the future(在未来)before long (不久后)from now on (从现在开始) 有些时间状语可用在不同的时态中,各有其意: now:1)I am speaking English now. 2)We have finished our homework now. 3)He's in the classroom now. this afternoon:1)We had a class meeting this afternoon. 2)We're going to see a film this afternoon. today:1)I've got two letters today. 2)We will learn a new lesson today. 3)She's cleaning her room today.
状语从句知识点总结(word) 一、初中英语状语从句 1.一What will you do then? 一I will telephone the police and complain about it the noise stops soon. A.unless B.though C.because D.if 【答案】A 【解析】 【详解】 句意:----那么你会怎么做?-----我会给警察打电话投诉,除非噪音很快停止。考查连词辨析。A. unless除非,如果不,引导否定的条件状语从句;B. though虽然,尽管,引导让步状语从句;C. because因为,引导原因状语从句;D. if如果,引导条件状语从句。根据句意可知后句表示否定条件,填unless;选A。 2.—I’m afraid the class has begun.—Don’t worry. It ________ until the bell ________. A.doesn’t begin; rings B.won’t begin; will ring C.won’t begin; rings D.doesn’t begin; will ring 【答案】C 【解析】 试题分析:句意:-恐怕课已经开始了。一不要担心。直到铃声响了才会开始。前面是主句,会议还没开始,所以用一般将来时;后面是until引导的时间状语从句,所以要用一般现在时代替一般将来时。所以选C。 考点:考查动词时态。 3.______ Mike didn’t win the race , he was still wearing a smile on his face. A.If B.Since C.Although D.Because 【答案】C 【解析】 【详解】 句意:虽然迈克没有赢了比赛,但是他脸上仍然带着笑容。A. If 如果,引导条件状语从句;B. Since 由于,引导原因状语从句;C. Although 尽管,虽然,引导让步状语从句;D. Because 因为,引导原因状语从句。根据句意,故选C。 4.---Could you give me some advice on travelling? ---Take a map with you _______ you have a guide or you know the city very well. A.if B.unless C.although D.because 【答案】B
英语现在完成时惯用时间状语小结 在英语中,常与现在完成时连用的词语有许多,常见的有如下划线部分: I have been very busy of late/recently. 我最近很忙。 Have you seen Li Ming lately?你近来见过李明吗? I have just had my breakfast.我刚吃过早饭。 So far, we have been very successful.到现在为止,我们是成功的。 Since the People’s Repubic of Ch ina was founded in 1949, great changes have taken place in our home town.自从1949年中华人民共和国成立以来,我们家乡发生了巨大的变化。 He has learned a lot(much/a great deal)since his arrival(=since he arrived)他自从到这里以来就学到了许多东西。 Since seeing you, I have had good news.自从遇到你以后,我就得到了好消息。 I haven’t seen you for long(for a long time/for an age/for ages)我很久没有看见你了。 He left the city in 1955 and I haven’t seen him since. 他在1955年离开这个城市,后来我从没看见过他。 He came to Beijing in 1955 and has lived here ever since.他在1955年到北京,以后一直住在这里。 Bows and arrows have long since been out of use.弓箭久已不用了。 He has already started for Europe.他已经动身去欧洲。 We haven’t heard the things yet.我们还没有听到过这些情况。 I have heard this piece of news before.我从前听到过这条消息。 Never before have I met him.以前我没见过他。 Have you ever been to Changsha?你到过长沙吗?-Y es. I have been there once.我到过一次。 I have seen the film many times.这部电影我看过多次了。 I haven’t seen much of him. 这些天我不大见到他。 We haven’t reached an agreement as yet.我们还没有达成协议。 I have eaten there only once.我在那里只吃过一次。 Now that you have done your work, you can go home now.你既然把事情做完了,你就可以回家。 Up to/till now/the present,we have finished part of the work.到现在为止,我已完成了部分工作。Where have you been all the while?你一直在那里?
在复合句中修饰主句或主句中的某一成分的从句 叫状语从句。状语从句通常由从属连词或起连词作用的词组引导,有时甚至不需要连词直接和主句连接起来。状语从句根据它表达的意思不同,可分为时间、地点、原因、目的、结果、条件、方式、比较、让步等九类。 一、时间状语从句 时间状语从句是表示时间关系的从句。可以引导时间状语从句的连词很多,根据意义和主从句之间的时间关系,通常可分为以下几种情况:A.when, while, as, whenever when, while, as表示主句谓语作和从句的谓语动作同时发生或几乎同时发生。 1.when ①when表示点时间时,从句中用短暂性动词;表 示段时间时,用持续性动词。 When I got home, my family were already having dinner. 我到家的时候,全家已在吃晚饭。 (when表示点时间) When they were still talking and laughing, the
teacher came in. 表示段when(当他们还在说笑的时候,老师进来了。时间) He waved a hello when he saw her. 当他看见她的时候,就挥手打了个招呼。(when 表示点时间) When you think you know nothing, you begin to know something. 当你认为自己一无所知的时候,就开始知道一些事情了。(when表示段时间) 注意: 当when意思是正当……时候(and at that moment)时,when只能跟在前一分句之后。 He was about to go to bed when the doorbel rang. 他正要上床,忽然门铃响了。 They were watching the World Cup when suddenly the lights went out. 他们正看着世界杯比赛,突然灯灭了。 They had just arrived home when it began to rain. 他们刚到家,天就开始下雨了。
英语中八种常见时态常用时间状语归纳 一、一般现在时 1. 概念:表示现阶段经常发生的动作或现在的某种状况,也表示客观事实、客观规律或客观真理。谓语动词要用原形,主语是第三人称时,谓语动词要用第三人称单数形式。 2. 常见时间状语标志:always, often, sometimes, usually, every day, on Sundays, once a day / week / month等。 例如: I do some exercise every day. 我每天做一些锻炼。 She knows French and German besides English.除英语外,她还懂法语和德语。 The sun rises in the east. 太阳从东边升起。 二、一般将来时 1. 概念:表示将来发生的动作或存在的状态,以及打算、计划或准备做某事。 2. 常见时间状语标志:tomorrow, the day after tomorrow, next day / week / month / year…, this week / month / year, soon, in + 时间状语(如in one hour / in a few minutes等),in the future, in future等。 例如: I’ll take you there tomorrow. 我明天带你去那儿。 Next month we will have our school open day. 下个月我们将迎来学校开放日。 The Talent Show is coming in two weeks’ time. 新秀选拔演出还有两周时间就要到了。 三、一般过去时 1. 概念:表示在过去的某个时间发生的动作或存在的状态,也表示过去习惯性、经常性的动作。谓语动词要用过去时。 2. 常见时间状语标志:yesterday, the day before yesterday, last night / week / month, 时间词+ ago (如three days ago), in / on + 过去的时间词(如in 2010), just now, at that time, in those days, one day, long long time ago, once upon a time等。 例如: Two years ago she bought an expensive mountain bike.两年前,她买了一辆昂贵的山地自行车。 Last year, however, nearly twenty billion tons of rice was produced. 然而,去年的稻谷产量接 近200亿吨。
概念:表示现阶段经常发生的动作或现在的某种状况, 也表示客观事实、客观规律或客观真 理。谓语动词要用原形,主语是第三人称时,谓语动词要用第三人称单数形式。 2. 常见时间状语标志 :always, often, sometimes, usually, every day, on Sun days, once a day / week / month 等。 例如: I do some exercise every day. 我每天做一些锻炼。 She knows French and German besides English.除英语外,她还懂法语和德语。 The sun rises in the east.太阳从东边升起。 般将来时 过去 现在 将来 __________ ? ..一 ........... 1?概念:表示将来发生的动作或存在的状态,以及打算、计划或准备做某事。 2. 常见时间状语标志 :tomorrow, the day after tomorrow, next day / week / month / year week / month / year, soon, in + 时间状语 (如 in one hour / in a few minutes 等),in the future, in future 等。 例如: I 'take you there tomorrow.我明天带你去那儿。 Next mon th we will have our school ope n day.下个月我们将迎来学校开放日。 The Tale nt Show is comi ng in two weeks ' time.新秀选拔演出还有两周时间就要到了。 1?概念:表示在过去的某个时间发生的动作或存在的状态,也表示过去习惯性、经常性的 动作。谓语动词要用过去时。 2.常见时间状语标志 :yesterday, the day before yesterday, last ni ght / week / mon th,时间词 + ago (如 three days ago), in / on + 过去的时间词 (如 in 2010), just now, at that time, in those days, one day, long long time ago, once upon a time 等。 例如: Two years ago she bought an expensive mountain bike. 两年前,她买了一辆昂贵的山地自行 车。 Last year, however, n early twenty billio n tons of rice was produced. 然而,去年的稻谷产量接 近200亿吨。 英语中八种常见时态常用时间状语归纳 —、一般现在时 … ,this 三、一般过去时 过去 现在 將來
时间状语从句 一. 概念:在复合句中,由时间连接词引导的状语从句叫做时间状语从句。 二.种类: 1.由when, while, as引导的时间状语从句。 (1).when引导的从句的谓语动词可以是延续性的动词,又可以是瞬时动词。动作既可和主句的动作同时发生又可在主句的动作之前或之后发生,并且when有时表示“就在那时”。 When she came in, I stopped eating.她进来时,我停止吃饭。(瞬时动词) When I lived in the countryside, I used to carry some water for him. 当我住在农村时,我常常为他担水。(延续性的动词) (2)while强调主句的动作与从句的动作同时持续地进行,用于这一用法时while引导的时间状语从句和主句中的谓语动词必须是延续性动词,或者主句的动作发生在从句动作的进行过程中,主句中的谓语动词通常是非延续性动词。并且while有时还可以表示对比While my wife was reading the newspaper, I was watching TV. I met her while I was at school. I like playing football while you like playing basketball. (3)as引导时间状语从句时表示“当……时,一边……一边……”,侧重表示两个动作同时发生(包括一个主语同时进行两个动作),或者一种动作随着另一种动作的变化而变化。He jumps as he goes along. 他边走边跳。 As we was going out, it began to snow.当我们出门时,开始下雪了。(as强调句中两个动作紧接着先后发生,而不强调开始下雪的特定时间) 2.由before和after引导的时间状语从句。 before引导的时间状语从句表示主句动作发生在从句动作之前。从句不用否定的谓语形式。从句位于主句之后时,before有时译成“才;就”。还要注意主句和从句的时间关系。当主句用将来时,从句总是用现在时;从句用过去时,则主句多用过去完成时,以此来体现动作发生的先后顺序。 after表示主句动作发生在从句动作之后,主句和从句的时间关系正好与before相反。如:It will be four days before they come back.他们要过四天才能回来。 My father had left for Canada just before the letter arrived. 我父亲恰好在信到达之前去加拿大了。 After we had finished the work, we went home.完成工作之后,我们回家了。 3.由till或until引导的时间状语从句。till和until一般情况下两者可以互换,但是在强调句型中多用until。并且要注意的是:如果主句中的谓语动词是瞬时动词时,必须用否定形式;如果主句中的谓语动词是延续性动词时,用肯定或否定形式都可以,但表达的意思不同。till不可以用在句首,而until可以放在句首。 I didn't go to bed until(till) my father came back.直到我父亲回来我才 上床睡觉。 I worked until he came back.我工作到他回来为止。 I didn't work until he came back.他回来我这才开始工作。 4.由since引导的时间状语从句。“自从……以来”,或“自从……以后”, since引导的从句的谓语动词可以是延续性的动词,又可以是瞬时动词。主句通常用现在完成时态,从句谓语动词用一般过去时,。但在It is +时间+since从句的句型中,主句多用一般现在时。 I have been in Beijing since you left. 自从你离开以来,我一直在北京了。
引导时间状语从句的从属连词归纳 (1) 表示“当…时候”或“每当”的时间连词。主要的?when, while, as, whenever: He jumped up when the phone rang. 电话铃响时他吓了一跳。 We listened while the teacher read. 老师朗读时我们听着。 The phone rang just as I was leaving. 我正要离开,电话铃就响了起来。 (2) 表示“在…之前?(或之后?)”的时间连词。主要的有?b efore, after: Turn the lights off before you leave. 离开前请关灯。 He started the job soon after he left the university. 他大学毕业后就开始做这份工作。 (3) 表示“自从”或“直到”的时间连词。主要的有?s ince, until, till: He has lived here since he got married. 他结婚后就一直住在这儿。 Most men worked until [till] they’re 65. 大多数男人工作到?65岁。 (4) 表示“一…就”的时间连词。主要的有?a s soon as, the moment, the minute, the second, the instant, immediately, directly, instantly, once, no sooner…than, hardly…when等: Tell him the news as soon as you see him. 你一见到他就把这消息告诉他。 I recognized her the moment (that) I saw her. 我一看到她就认出她来了。 I want to see him the minute (that) he arrives. 他一到来我就要见他。 I went home directly I had finished work. 我一干完活就回家了。 Once he arrives, we can start. 他一来我们就可以开始。 (5) 表示“上次”、“下次”、“每次”等的时间连词。主要的有?e very time(每次?),e ach time(每次?),(the) next time(下次?),a ny time(随时?),(the) last time(上次?),t he first time(第一次?):
状语从句连词总结 1时间状语从句: when当.... 时候 while当.... 时候(动词只能是延续性动词) as当 .. 时候(经常表示一边... 一边... ) after/before 在.... 之后/之前 un til/till直到……(即某一持续性行为持续到某一时间点) since/ever since自从.... (即子某一时间点以来,常用完成时态或完成进行时) 名词性短语the time the mome nt the mi nute the day the year the first/sec ond time each time 每次every time 每次next time 下次any time 在任何时候whenever 不管什么时候 by the time到..... 时候(即指到某一时间点为止,主句常用完成时态) 一... 就... as soon as once immediately directly in sta ntly 还没来得及... 就... hardly .............. w he n no sooner ........... t ha n as long as 长达... 非时间状语从句:动词ing形式;at ......... 形式;on doing/on sth形式 2地点状语从句 where在哪里,在什么地方 wherever 无论在哪里 any where 无论何处everywhere 至U处,处处no where 无处,任何地方都无 to/in/from the place (s)where 或to/in /from any place where 3原因状语从句 because (语气最强)因为,多置于主句之后 as (语气最弱)因为,多置于主句之前 since语气较弱,常表示对方已知的事实,相当于“既然” now (that)既然 for the reason that因为(that引导的是同位语从句,先行词为reason) in that由于某种原因,多用于书面语 seeing that 因为,鉴于 4目的状语从句 in order that 以便 so (that)为了 for fear that惟恐,以防 in case以防万一有某种情况发生 5结果状语从句 so (that)所以 so ..... that ........ 结构
英语状语从句归纳总结英语时间状语从句 状语从句 1.时间状语从句 (1) whenwhen用作并列连词(正在那时,突然) We were about to start when it began to rain.I was watching TV when someone knocked at the door. …on the point of doing…when… did… ……had just done when …… (2) as as与延续性动词连用,侧重两个动作伴随发生,其时态一致: As he grew older he lost interest in everything except gardening. We were having breakfast as she ________ ( watch )TV.(3) while while “在……期间”,与延续性动词连用,和主句的动作同时发生,常用三种时态。 1.While I was waiting at the bus stop, buses went by in the opposite direction.2. While in prison, he wrote his first novel. 3.Shoes were mended while you waited.
(4) before ① before“在……之前” I had finished my papers before my teacher went abroad.② before “过…时间之后才…”, 注意使用 ___________和 ___________时态。 They worked long hours before everything returned to normal.恢复正常 It will be a long time before we finish this dictionary. ③ 还没来得及 The bell rang off before I could answer it.(5) as soon as “一… 就….”, directly,immediately,instantly;the instant (that),the minute (that) ,the second (that) ,the moment (that)等通常都可与as soon as 换用。 I recognized her immediately I saw her. (6) … hardly...when … / … no sooner...than … “刚……就…”,从句用过去时,主句用过去完成时。注意倒装。 He had no sooner / No sooner had he arrived than he was asked to leave again. We had hardly begun / Hardly had we begun our talk when it began to rain.
在复合句中,由时间连接词引导的状语从句叫做时间状语从句。时间状语从句通常由when, while, as,after,before,since,until等词引导。 一、时间状语从句种类 1、引导的从句表示主从句的动作同时发生,或从句的动作在主句之前。when引导的从句的谓语动词可以是延续性的动词,又可以是瞬时动词。例如: When she came in, I stopped eating.她进来时,我停止吃饭。(瞬时动词) When I lived in the countryside, I used to carry some water for him.当我住在农村时,我常常为他担水。(延续性的动词) We were about to leave when he came in.我们就要离开,就在那时他进来了。 2、While引导的从句的谓语动作必须是延续性的,并强调主句和从句的动作同时发生(或者相对应)。并且while有时还可以表示对比。例如:While my wife was reading the newspaper, I was watching TV. (was reading是延续性的动词,was reading和was watching同时发生) I like playing football while you like playing basketball.我喜欢踢足球,而你喜欢打篮球。(对比) 3、As表示“一边……一边”,as引导的动作是延续性的动作,一般用于主句和从句动作同时发生;as也可以强调“一先一后。例如:We always sing as we walk.我们总是边走边唱。(as表示“一边……一边”)As we was going out, it began to snow.当我们出门时,开始下雪了。(as强调句中两个动作紧接着先后发生,而不强调开始下雪的特定时间) 4、由before和after引导的时间状语从句,表示两个动作一前一后发生。 例如:It will be four days before they come back. 他们要过四天才能回来。 After you think it over, please let me know what you decide.你仔细考虑过以后,告诉我你是怎样决定的。 5、由till或until引导的时间状语从句。till和until一般情况下两者可以互换,但是在强调句型中多用until。并且要注意的是:如果主句中的谓语动词是瞬时动词时,必须用否定形式;如果主句中的谓语动词是延续性动词时,用肯定或否定形式都可以,但表达的意思不同。till不可以用在句首,而until可以放在句首。例如: I didn't go to bed until(till)my father came back.直到我父亲回来我才上床睡觉。 I worked until he came back.我工作到他回来为止。 6、由since引导的时间状语从句表示“自从……以来”。 I have been in Beijing since you left. 自从你离开以来,我一直在北京了。 7、由as soon as引导的时间状语从句表示“一……就”。例如: As soon as I reach Canada, I will ring you up. 我一到加拿大,就给你来电话。 二、时态问题 在状语从句中,有“主将从现”的规定,即主句用一般将来时,从句用一般现在时表示将来时。例句:I will call you as soon as I arrive in Beijing. 我到北京就将给你打电话。(这是由as soon as引导的时间状语从句,从句中的谓语动词arrive是一般现在时,表示一般将来时,决不可用will arrive) 常见考法 对于时间状语从句的考查,多以单选和完形填空的形式,从连词的意义角度让大家选择连词,或从时态的角度设题,考查学生灵活运用的能力。 典型例题:I'm sure he will jump up when he the good news. A . know B will know C. knows D knowing 解析:本题考查学生时间状语从句的时态问题。时间状语从句中,主句若是一般将来时,从句应用一般现在时表示将来时。从句的主语是单三人称,所以排除A 。