专题一名词主要考查三个方面: 1、联系上下文,考查同义词、近义词辨析; 2、可数名词的单复数、不可数名词、抽象名词、名词词 组的意义和用法; 3、名词的固定搭配和习惯用语。 ◆名词的数 规则名词的复数形式
a block of一块; a bottle of一瓶 a group of一群; a pile of一堆 a pair of一组/双/对; a piece of一片/张/块既可作可数名词又可作不可数名词的词
The broken ______may cut into your hand if you touch it, you should be careful. A. glass B. glasses C. candle D. candles 【2016广西来宾】 —There are many ____ about this farm. —Yes, lots of ____ are planted on it. A. photo; potato B. photos; potatos C. photos; potatoes D. photoes; potatoes 1. Help yourself to some_______. There are lots of vitamins in them. A. tomato B. tomatoes C. tomatos D. potatos 2.if you take a plane, you cannot take ______ onto the plane with you. A. knife B. knifes C. knives D. a knives 3. The _______ have caught the two_______ already. A. policeman; thief B. policemen; thiefs C. policemen; thieves D. policeman; thieves 【2016重庆】It’s sports time. Most students in Class 1 are playing football on the playground. A. boy B. boys C. boy’s D. boys’ 【2015攀枝花】All the are from . A. men doctors; Germany B. men doctors; German C. man doctors; Germany D. man doctor; German 【2015广安】 —How many can you see in the picture? —Two.
小学英语中常见不可数名词 小学英语中常见不可数名词water(水)milk(牛奶)tea(茶)juice(果汁)hair(头发)coffee (咖啡)bread(面包)rice(米饭)chocolate(巧克力)grass(草)paper(纸)money(钱)film(胶卷)rain(雨)cheese(奶酪)meat(肉)soup(汤)food(食物)fish(鱼肉) 可数名词有bag pen apple book pencil picture photo bus dog cat… 可数名词有单数和复数两种形式。指一个人或一件事物时,用单数形式;指两个或多个人或事物时用复数形式。名词由单数形式变成复数形式的规则如下: 1. 一般的名词词尾直接加-s 。如: book →books room →rooms house →houses day →days 2. 以s, ss, ch, sh, x 结尾的名词,在词尾加-es 。如: bus →buses glass →glasses watch →watches dish →dishes box →boxes 3. 以辅音字母+y 结尾的名词,要先将y改为i再加-es。如: city →cities body →bodies factory →factories等等。 4. 以f 或fe 结尾的名词,要将f或fe改为v再加-es。如: half →halves leaf →leaves knife →knives wife →wives 5. 特例[悄悄话:特例常常考,要记住。] ①child →children ②man →men woman →women policeman →policemen (规律:man →men) ③tomato →tomatoes potato →potatoes [悄悄话:初中英语以o 结尾的名词变复数时只有这两个词加-es,其余的当然加-s喽!如:photo →photos ] ④foot →feet tooth →teeth [悄悄话:oo变成ee。] ⑤sheep, Chinese, Japanese单、复数同形[悄悄话:变复数时词形不变。] ⑥people单数形式表示复数意义,要求谓语动词用复数;people的复数形式peoples通常指多个民族。
可数名词与不可数名词 名词分可数名词与不可数名词。 1.有些名词总是用作可数名词的,如: leg,dog,pen.有些名词总是用作不可数名词,如: pork,gold,honesty.有些则有时用作可数名词,有时用作不可数名词,如:It is made of glass.(不可数) He held a glass.(可数) 与5类名词的关系 区分5类名词对决定一个名词是可数还是不可数有极其重要的意义。C代表可数(Countable),用U代表不可数(Uncountable)。1.大多数普通名词为可数名词,如: a chair,another car,dogs. 2.多数集体名词也是可数名词,如:(a)family,(each)class,(all) parties,(different) nations。 3.专有名词,多数作不可数名词,如:London,China,Ham-bet,Neptune;但有些为可数名词,如 Communists,English-men。4.物质名词一般不可数,如:milk,gold,coffee,beer.但有些可用作可数名词,表示特殊意义,如:an ice-cream(一份冰淇淋),a light rain(一阵小雨)。 5.多数的抽象名词既可作不可数名词,也可作可数名词(这时意思有些变化),如: 不可数可数beauty 美 a beauty 美人 disappointment 失望 a disappointment 失望的事 C.普通名词和物质名词 不过一个名词的可数与不可数问题最终还是靠习惯决定,习惯用法是自然形成的,不能靠简单的条文来推断。虽说表示可数的东西为可数名词,否则为不可数名词,但总有些特殊情况。在表示定形之物时,物质名词也可用作可数名词,在强调某种特性时,普通名词也可变成不可数名词。 1.气体名称通常作不可数名词,如:oxygen(氧气),hydrogen(氢气)。但odour(气味),flavor(味道),cloud(云)是可数名词;而fire则既可作不可数名词,也可作可数名词。 2.液体名称一般为不可数名词,如:milk,water;但beverage(饮料),cocktail(鸡尾酒)为可数名词,而juice(汁)、sauce (调味液)、liquor(酒)既可作可数名词,也可作不可数名词。 3.药品名称通常不可数,如: codeine;但antibiotic(抗生素),insecticide(杀虫剂),vitamin(维生素)都是可数的。4.植物中有些的名称既作可数名词,也可作不可数名词,如: 可数不可数 a pine 松树 pine 松木 a pepper 青椒 pepper 胡椒粉 5.表示天气的名词多作不可数名词,如:lightning(闪电),thunder(雷),snow,但有些为可数名词,如: comet(慧星),sunbean(阳光),ray(光线)。有些可用作两类,如: mist(浓雾),dew(露水),rain。 6.表示动物的名词一般为可数名词,如: monkey,elephant,shrimp(虾),但有些可用于两类情况,如: 可数不可数 a chicken鸡 chicken鸡肉 a duck 鸭 duck鸭肉 a fish鱼 fish 鱼(肉) 7.物质名词一般不可数,如: iron,plaster(石膏),mercury(水银)。有些两者都可以,如:chalk(粉笔),brick(砖),coal(煤)。 D.集体名词 26 有个别集体名词可用作不可数名词,如: police(警察总称),cattle(牲口),produce(农产品),vegetation(植物),clothing(衣服),furniture(家具),pottery(陶器)。 E.抽象名词 27 1.在一万个抽象名词中约有 72%(约7 200字)常常或有时既作不可数名词,又作可数名词,如: belief,beliefs; birth,births; hope,hopes;fear,fears。
选择填空: 1.The deer has four ______. A. foot B. feet C. feets D. foots 2.Her two brothers are both ______. A. policeman B. policemans C. policemen D. policemens 3.There are four _____ and two ______ in the group. A. Japanese, Germen B. Japaneses, Germen C. Japanese, Germans 4.Two ______ would come to the village. A. woman-doctors B. women doctor C. women doctors D. woman doctors 5.Can you see nine _____ in the picture? A. sheep B. dog C. pig D. horse 6.The _____ has two ______. A. boys, watches B. boy, watch C. boy, watches D. boys, watch 7.The boy often brushes his _____ before he goes to bed. A. tooth B. tooths C. teeth D. teeths 8.The Japanese ____ will not leave China until she finishes her study. A. woman B. women C. man D. men 9.There are lots of _____ in the basket on the table. A. tomatos B. tomato C. tomatoes D. tomatoss 10. The cat caught two ______ last night. A. mouses B. mice C. mouse D. mices 用所给名词的适当形式填空: 1. How many________(sheep) are there on the hill? 2. There is some________(food) in the basket. 3. The baby has only two________(tooth) now. 4. There is a lot of________(water) in the bottle. 5. There are five________(people ) in his family. 6. Let's take________(photo), OK? 7. I have lots of________(tomato) here.
可数名词和不可数名词 一、可数名词与不可数名词的区别 普通名词所表示的人或事物是可以按个数计算的,这类名词叫可数名词。可数名词分为个体名词(表示某类人或事物中的个体,如worker, farmer, desk, factory等)和集体名词(表示作为一个整体来看的一群人或一些事物,如people, family 等)。如果普通名词所表示的事物是不能按个数来计算的,这类名词就叫不可数名词。不可数名词分为物质名词(表示无法分为个体的物质,如meat, rice, water, milk, orange 等)和抽象名词(表示动作、状态、情况、品质等抽象概念,如work, homework, time, health, friendship等)。 二、关于可数名词 可数名词有单数和复数两种形式。指一个人或一件事物时,用单数形式;指两个或多个人或事物时用复数形式。名词由单数形式变成复数形式的规则如下: 1. 一般的名词词尾直接加-s 。 如:book → books room → rooms house → houses day → days 2. 以s, ss, ch, sh, x 结尾的名词,在词尾加-es 。如: bus → buses glass → glasses watch → watches dish → dishes box → boxes 3. 以"辅音字母+y"结尾的名词,要先将y改为i再加-es。如: city → cities body → bodies factory → factories等等。 4. 以f 或fe 结尾的名词,要将f或fe改为v再加-es。如: half → halves leaf → leaves knife → knives wife → wives 5. 特例[悄悄话:特例常常考,要记住。] ① child → children ② man → men woman → women policeman → policemen(规律:man → men) ③ tomato → tomatoes potato → potatoes
英语语法 1.名词 1.1名词复数的规则变化 1.2其他名词复数的规则变化 1.3名词复数的不规则变化 1.4不可数名词量的表示 1.5定语名词的复数 1.6不同国家的人的单复数 1.7名词的格 2.冠词和数词 2.1不定冠词的用法 2.2定冠词的用法 2.3零冠词的用法 2.4冠词与形容词+名词结构 2.5冠词位置 2.6数词 3.代词 3.1人称代词的用法 3.2人称代词之主、宾格的替换 3.3代词的指代问题 3.4并列人称代词的排列顺序 3.5物主代词 3.6双重所有格 3.7反身代词 3.8相互代词 3.9指示代词 3.10疑问代词 3.11关系代词 3.12every , no, all, both, neither, nor 3.13none, few, some, any, one, ones 3.14代词比较辩异 one,that 和it 3.15one/another/the other 3.16“the”的妙用 3.17anyone/any one;no one/none;every/each 3.18both, either, neither, all, any, none 3.19many, much 3.20few, little, a few, a little 4.形容词和副词 4.1形容词及其用法 4.2以-ly结尾的形容词 4.3用形容词表示类别和整体 4.4多个形容词修饰名词的顺序 4.5副词及其基本用法 4.6兼有两种形式的副词
4.7形容词与副词的比较级 4.8as + 形容词或副词原级 + as 4.9比较级形容词或副词 + than 4.10可修饰比较级的词 4.11many,old 和 far 4.12the + 最高级 + 比较范围 4.13和more有关的词组 5.动词 5.1系动词 5.2什么是助动词 5.3助动词be的用法 5.4助动词have的用法 5.5助动词do的用法 5.6助动词shall和will的用法5.7助动词should和would的用法5.8短语动词 5.9非谓语动词 6.动名词 6.1动名词作主语、宾语和表语6.2Worth的用法 7动词不定式 7.1不定式作宾语 7.2不定式作补语 7.3不定式主语 7.4It's for sb.和 It's of sb. 7.5不定式作表语 7.6不定式作定语 7.7不定式作状语 7.8用作介词的to 7.9省to 的动词不定式 7.10动词不定式的否定式 7.11不定式的特殊句型too…to… 7.12不定式的特殊句型so as to 7.13不定式的特殊句型Why not 7.147不定式的时态和语态 7.15动名词与不定式 8.特殊词精讲 8.1stop doing/to do 8.2forget doing/to do 8.3remember doing/to do 8.4regret doing/to do 8.5cease doing/to do 8.6try doing/to do 8.7go on doing/to do
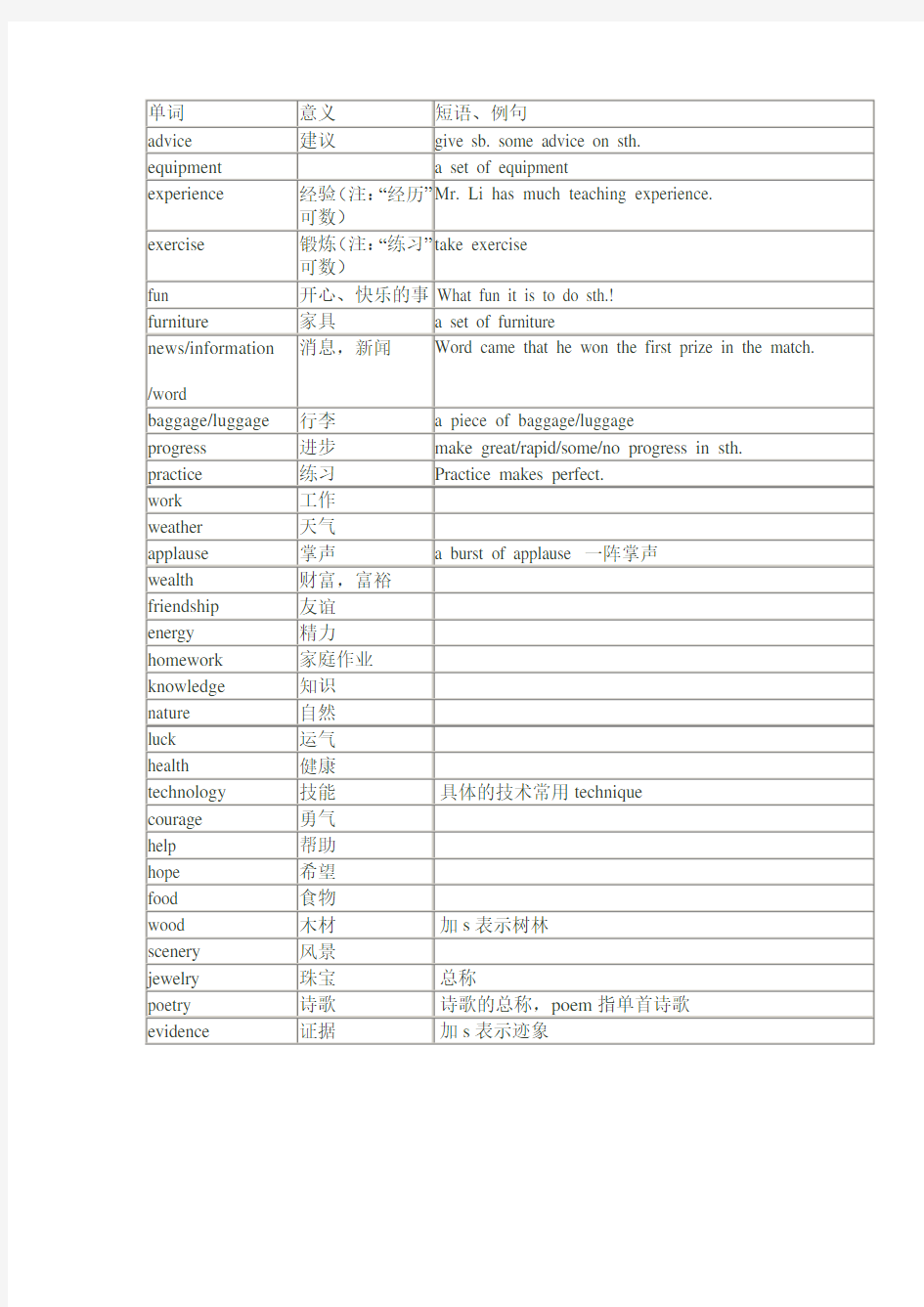
最常见的不可数名词 Non-Countable Nouns 英语不可数名词很多,很难一一列出。有时又一词多义,在一种情况下可数,而在另一种情况下又不可数。需要我们注意区别。 总体来讲,词义属抽象、物质、属类、学科时,多为不可数,一旦实指物体,则必可数。 A. Abstract 抽象名词 advice 建议 age 年老 beauty 美丽capitalism 资本主义communism 共产主义democracy 民主energy 能源 fun 乐趣 happiness 幸福 help 帮助 honesty 诚实knowledge 知识laughter 笑声 liberty 自由 life 生命、生物、活力play 玩 recreation 娱乐strength 实力trouble 麻烦 truth 真理 virtue 美德 wisdom 智慧
information 信息justice 正义kindness 善良work 工作youth 青年 B. Matter, material 物质名词 air 空气 beer 啤酒blood 血液bread 面包butter 黄油cake 蛋糕chalk 粉笔cheese 奶酪coal 煤coffee 咖啡electricity 电力fog 雾 fish 鱼 gold 黄金grass 草 hair 头发 ice 冰juice 果汁lumber 木材meat 肉milk 牛奶oil 油oxygen 氧气paper 纸rain 雨 rice 水稻smoke 烟雾snow 雪soap 肥皂soup 汤sugar 糖tea 茶water 水wine 葡萄酒
Money Chicken Fish Water Bread Paper News Meat Cake Coffee Snow, Tea, Milk, Rice, Traffic, Homework, Housework Age Hair Time Weather Wind World Moon Sleep Luck Music Nature Ice Food Glass Gold Help Hope People Soap a piece of bread [ cake,paper(纸),thread(线)cloth(布)furniture(家具)coal(煤)news(新闻)advice(意见)information(信息)work(工作)meat(肉) ] 一块面包[ 一块蛋糕、一张纸、一根线、…… ] an item of information (一则情报) a burst of applause (一阵掌声) a fit of anger(一顿脾气)
a slip of paper (一张纸条) a length of cloth(一段布料) a cake of soap (一块肥皂) a tube of tooth-paste (一条牙膏 ) a bottle of ink( 一瓶墨水) 它在句子中作主语时句子的谓语也只用单数形式。 例如: Water is a liquid .水是液体。 Wealthdoesn't mean happiness .富有并不意味幸福。 常见的物质名词 如:snow(雪) rain(雨) water(水) coffee(咖啡) tea(茶) meat (肉) milk(牛奶) rice(米饭) bread(面包) orange (桔汁)等; 抽象名词是指表示动作、状态、品质、感情等抽象概念的词常见的抽象名词 如: work(工作) study(学习) love(爱) friendship (友谊)等。 最常见的不可数名词有: Advice, Baggage, change(零钱) furniture(家具) bread面包 beer啤酒 cloth布 coffee咖啡 cream奶油 dust尘土 gin杜松子酒
初中英语重点知识:不可数名词和名词的格 不可数名词 不可数名词没有复数形式。专有名词、物质名词、抽象名词一般为不可数名词。 常见的不可数名词 专有名词: BBC英国广播公司 Mark Twain马可·吐温 the West Lake西湖 物质名词: milk 牛奶 gas 汽油 light 光 wind 风 抽象名词: fun 乐事 kindness 善良
happiness 幸福 progress 进步 不可数名词表达不同意义 1)有些物质名词因词义发生变化而被用作可数名词,其复数形式的含义也发生了变化。 tea茶a tea 一杯茶 two teas两杯茶 beer啤酒. a beer 一杯啤酒two beers两杯啤酒 glass 玻璃a glass一个璃杯 glasses眼镜,玻璃杯 初中英语重点知识:不可数名词和名词的格 2)有些物质名词的复数形式有特殊的否义。 rains大量的雨水,多场雨snows大量的雪,雪堆,多场雪 winds多场风 sands沙堆,沙丘 woods树林
waters 大片水域 专有名词 专有名词一般视为不可数名词,有时也可用作可数名词,前面可用a /an ,也可有复数形式。 He wishes to be Liu Dehua. 他想成为一个刘德华式的人物。 A Bob is asking to see you.一个叫Bob 的人要求见你。 抽象名词 抽象名词表示具体事物时,变为可数名词,前面可用a /an,也可有复数形式,表示“某种人或事”。常见的这类名词有: pleasure令人感到高兴的人或事 suecess成功的人或事failure失败的人或事 worry令人感到烦恼的人或事 beauty美人或美丽的事物wonder奇迹 巧学妙记 ★不可数名词很特殊,六点用法要记清。 一是没有复数形式;(milk) 二是作主语,谓语须用单;(The water is clenn.The air is fresh.)
英语名词复数的规则变化 英语中名词可分为可数名词和不可数名词。可数名词在应用时有单数和复数形式。表示一个用单数,表示两个或两个以上用复数。复数名词的构成分为规则变化和不规则变化。 一、规则变化: 1、一般在名词词尾加s, ①map—maps地图,bird—birds鸟, orange—oranges 桔子, bike—bikes自行车; 2、以s, x, ch, sh结尾的名词加es, ①box—boxes盒子,class—classes班级,watch—watches手表,dish-dishes盘,碟子,餐具; 3、以O结尾的名词后面加s或es ①photo—photos相片radio—radios收音机zoo—zoos动物园tomato—tomatoes西红柿potato—potatoes土豆 4、以辅音字母加y结尾的名词,变y为i+es ①baby—babies婴儿family—families家庭; 以元音字母加y结尾的名词直接加s ①boy—boys男孩toy—toys 玩具; 5、以fe或f结尾的名词,把fe或f变为ves ①knife—knives小刀 wife—wives妻子 leaf—leaves树叶。 二、名词复数的不规则变化 1、child---children foot---feet tooth---teeth mouse---mice man---men woman---women 注意:与man 和woman构成的合成词,其复数形式也是-men 和-women。 如:an Englishman,two Englishmen. 但German不是合成词,故复数形式为Germans;Bowman是姓,其复数是the Bowmans。2、单复同形如:
名词的用法 可数名词 (一) 定义:能以数目来计算,可以分成个体的人或东西。可数名词变成复数形式规则变化 一般情况下,直接在词尾+s: book→books, pencil→pencils. man — men 男人woman — women 妇女tooth — teeth 牙齿foot — feet 脚 有些名词的单复数形式相同 deer — deer 鹿sheep — sheep绵羊 Chinese — Chinese 中国人Japanese — Japanese 日本人 (四) 特殊的复数形式的名词 由两部分构成的东西的名词,总以复数形式出现,如:glasses眼镜,trousers裤子,socks 袜子,clothes衣服等。若表达具体数目,要借助量词pair对/双,suit套等。 a pair of glasses, two pairs of socks (五)可数名词的特点 (1) 有单复数:one desk, two chairs, many birds。 (2) 可以用不定冠词a/an、数词、many, some, any, a lot of, lots of等词修饰:an apple, three pictures, some students。 (3) 单数名词做主语,谓语动词用单数形式;复数名词做主语,谓语动词要用复数形式。 ①There is a pen on the desk. 桌子上有一支笔。 ②There are some students in the classroom. 教室里有一些学生。
(4) 在特殊疑问句中,用how many修饰可数名词 There are three pens on the desk. (对划线部分提问) →How many pens are there on the desk? 不可数名词 (一)定义:不能以数目计算,不可以分成个体的概念、状态、品质、感情或表示物质材料的 东西,如water, tea, bread等。它没有复数概念,它的前面不能用补丁冠词a/an. 表特指时可用定冠词the修饰。 ①Water is very important to life. 水对生命来说十分重要。 ②The bread on the table is Mark’s. 桌子上的面包师Mark的。 (二)特点 (1) 不可数名词前面可以有much, a little, a lot of等修饰词:much bread, a little tea (2) 不可数名词不能用数词修饰,需要借助单位词来表示数量: a piece of paper 一张纸,a piece of bread一片面包,a cup of tea一杯茶 (3) 不可数名词变复数:量词变复数形式,作主语时谓语动词用复数 two pieces of bread 两片面包,three cups of tea 三杯茶 (4) 对不可数名词的修饰词提问,疑问词用how much. There is some milk in the glass. (对划线部分提问) →How much milk is there in the glass? 练习: 一、根据句意及所给单词填空。 1. ________(this) are my English books. 2. My aunt Jane and my mother are ___________(sister). 3. I have two ___________(watch). They are on the desk. 4. I have some __________(photo) of my family. 5. Do you like these ____________(dictionary)? 6. Those are _________(bus). 7. I have lots of________(tomato) here. 8. The________(leaf) on the tree turn-yellow. 二、选择填空: 1. —Mom, I want___. ——Here you are. A. a bread B. a piece of bread C. some breads D.breads 2. The _____ has two ______. A. boys, watches B. boy, watch C. boy, watches D. boys, watch 3. There are lots of _____ in the basket on the table. A. tomatos B. tomato C. tomatoes D. tomatoss 4. —_____apples do we need to make fruit salad? —Let me think...We need three apples. A. How long B. How often C. How much D. How many 5. "Lily, Let's make vegetable salad. How many _____ do we need?" "One is enough." A. oranges B. potato C. tomatoes. 6. Would you like _____ to eat now? A. some B. anything C. something D. thing 7. I'm so hungry. Please give me _____ to eat.
A、不可数名词,初中阶段常见的不可数名词有:water ; meat ; rice ; bread ; milk ; tea ; orange(桔汁) ; fruit ; air ; snow ; chalk; work ; paper(纸) ; time(时间); music ; weather ; grass ; news ; food ; fish(鱼 江西泰和康俊民 进入中考英语总复习阶段,不少学生难以从心理和生理上适应紧张的学习节奏和繁重的学业负担,尤其是原本在英语学习上有困难的学生,更是无从下手,把课余时间几乎都花在大量的题海练习中,事倍功半,收效甚微。那么,该如何调整复习策略呢? 同学们进入中考复习时应注意抽出一些时间把所学的初中英语知识梳理一下,通过比较和归类,找出规律,从而找到解决困难的切入口,提高自己学习英语的信心。 [词汇]多总结、多联想、多比较、多运用 很多学生花大量的时间去单纯地抄单词,背单词,却记不住拼写,也记不准汉语意思。你说“工人”,他会熟练地拼出“worker”,但你说“worker”,他就不知何物,关键在于他忽视了英语是音形结合的文字。会拼写的学生却能灵活地掌握单词的读音规则和字母组合。比如:学了bike,他就会拼读like, side, five, nine;反之,别人读出这些单词的时候,他也可以根据读音规则拼写出这些单词。 拼写过关后,就要学会运用这些词汇。首先,要分清每个单词的词性,如名词、形容词、副词、动词、代词以及介词等。最好是词不离句,词组结合,搭配使用。比如:名词care加上后缀-ful变成形容词,那么use, help, colour, wonder后加上后缀-ful也变成形容词了。再如:学了mind doing sth你就要联系到finish doing sth, keep doing sth, practise doing sth等等。坚持多归纳,多联想,多比较,多运用,你的词汇量一定会增加,运用能力也一定会有所提高。 [语法]运用中学会发现和归纳 中国人学英语,在语法上花的精力远比外国人多。实际上,语言的最大功能是交际和沟通,学会语法是为了更好地表达和运用。 在复习时态时,先把时态的结构搞清楚,然后加上不同的时间状语进行改写,并改成否定句和疑问句。比如:He does his homework every day.把划线部分改成yesterday, tomorrow,now, at this time yesterday, for two hours, by two yesterday afternoon,再确定时态的变化。先机械,后灵活,还可以加上不同的人称和其它的动词词组进行操练。关键要学会学习,学会归纳。 [阅读]通过上下文整体把握 好的文章要多读、细读,最好把关键的短语和词语搭配记录下来。要注意语篇的整体理解,遇到生词先不要急着查词典,而是应该通过上下文去理解和把握,同时要注意同一词汇在不同句子中的不同释义。比如free既可以表示“免费的”,也可以表示“有空的”或“自由的”,遇到实在不能理解的关键词才去查词典。要多阅读不同体裁和题材的文章,了解欧美的文化背
英语常用词组4249个 (详细版) 薛建菠 A 1.a fraction of 一部分 2.a matter of concern 焦点 3.a series of 一系列, 一连串 4.abandon sb to sth (不顾责任、义务等)抛弃,离弃 5.abandon sth to sb 不得已而放弃 辨析 abandon:迫于不得已而停止(支持,帮助);放弃义务,信念,责任 stop:停止某行为 give up doing:放弃做某种行为 6.ability to do sth(注:不加of doing)有能力做某事 7.to the best of one’s ability 尽其所能 辨析 ability:具备做某事的能力(用法:ability to do sth(注:不加of doing)) capability:具备做某事所需的能力或素质(用法:capability to do sth/也可加of doing)) 8.be able to do sth 能够 辨析 able:强调通过努力而获得的能力(用法:be able to do sth) can:表示本身具有的一般能力 capable:(用法:capable of doing) 9.be about to do …when… 打算 10.abound with/in 富于、充满… 11.above all 近义词:especially 尤其是, 最重要的 12.be absent from 缺席 13.absence of mind 近义词:being absent-minded 心不在焉 14.absent oneself from sth 不在 15.absolve sb from 赦免某人… 16.be absorbed in 近义词:be engrossed in;be lost in;be rapt in;be concentrated on be focused on;be centered on 全神贯注于… 17.abstain from 避开(免)… 18.be abundant in 近义词:be rich in;be well supplied with 富于,富有 19.abundant in 富于 20.accept sth 同意某事 21.accept sb into sth/ accept sb as sth 接纳某人 22.accept that… 相信/认为… 23.access to (不可数名词) 能接近,进入 辨析 accept:表示主观意愿 receive:表示客观事实(用法:receive sth from sb/sth) 24.by accident 偶然 辨析
初一可数名词和不可数名词讲解 定义:1可数名词是指能以数目来计算,可以分成个体的人或东西;因此它有复数形式,当它的复数形式在句子中作主语时,句子的谓语也应用复数形式。 2.不可数名词是指不能以数目来计算,不可以分成个体的概念、状态、品质、感情或表示物质材料的东西;它一般没有复数形式,只有单数形式,它的前面不能用不定冠词a / an 。 可数名词用法讲解 可数名词有单复数之分。 ㈠单数可数名词 1. 单数可数名词一般不会单独出现,前面通常要有限定词。 例如:She is friend(friend 前面加上my.) I have pen.(pen前面加上a) I like boy.(boy前面加上this) 限定词通常有三类。 ⑴冠词。经常用不定冠词a、an。 ⑵形容词性物主代词。 ⑶指示代词this、that 。this、that可用the代替。 2.单数可数名词做主语看作第三人称单数,谓语动词使用三单(单数)形式。 My father is (be) very tall. His brother likes (like) playing basketball.
㈡可数名词的复数形式。 1.单数变复数 规则变化 a.一般情况下,直接加-s.如:book-books, bag-bags, cat-cats, bed-beds b.如:book-books, bag-bags, cat-cats, bed-beds c.以“辅音字母+y”结尾,变y为i, 再加-es,如:family-families, strawberry-strawberries d.以“f或fe”结尾,变f或fe为v, 再加-es,如:knife-knives e.以o结尾,通常加s.初中范围只有这四个词Negro hero potato potato 这 四个词加es 如tomato -potatoes. tomato-tomatoes巧记黑人英雄种西红柿和马铃薯这四个词es 不规则变化: man-men, woman-women, policeman-policemen, policewoman-policewomen, mouse-mice child-children, foot-feet,. tooth-teeth, fish-fish, sheep-sheep people-people, Chinese-Chinese, Japanese-Japanese. 2.什么时候使用可数名词的复数形式? a.数词大于1,可数名词用复数。 b.可数名词前有Some/any、these/those 、a lot of/lots of、many、How many、a few修饰时,可数名词用复数。 Some/any+可复 a lot of/lots of+可复 Many+可复 How many+可复 A few+可复 c.复数名词表示泛指是可数名词使用复数形式。
初中英语——可数名词和不可数名词 一、可数名词与不可数名词的区别 普通名词所表示的人或事物是可以按个数计算的,这类名词叫可数名词。可数名词分为个体名词(表示某类人或事物中的个体,如 worker,farmer,desk,factory等)和集体名词(表示作为一个整体来看的一群人或一些事物,如people,family等)。如果普通名词所表示的事物是不能按个数来计算的,这类名词就叫不可数名词。不可数名词分为物质名词(表示无法分为个体的物质,如meat, rice,water, milk, orange等)和抽象名词(表示动作、状态、情况、品质等抽象概念,如work, homework, time, health, friendship等)。 二、关于可数名词 可数名词有单数和复数两种形式。指一个人或一件事物时,用单数形式;指两个或多个人或事物时用复数形式。名词由单数形式变成复数形式的规则如下: 1.一般的名词词尾直接加-s。如: book → books room → roomshouse → houses day → days 2.以s,ss, ch,sh, x结尾的名词,在词尾加-es。如: bus → buses glass → glasseswatch → watchesdish → dishes box → boxes 3.以"辅音字母+y"结尾的名词,要先将y改为i再加-es。如: city → cities body → bodiesfactory → factories等等。 4.以f或fe结尾的名词,要将f或fe改为v再加-es。如: half → halves leaf → leavesknife → kniveswife → wives 5.特例[悄悄话: 特例常常考,要记住。] ①child→children②man→menwoman→womenpoliceman→policemen
名词 名词:是一些名称,表示人物、地方、国家、动物或物品等。 不用an、one,如How many sandwiches would you like?你想要多少块三明治。I would like just one sandwiches.我只要一块三明治。比较May I have a sandwiches?和May I have one sandwiches?的区别) 单数变复数的规则:
1、 Chinese中国人,sheep羊,deer鹿,fish鱼, Japanese日本人,li,jin,yuan,two li,three mu,four jin,但除人民币元、角、分外,美元、英镑、法郎等都有复数形式。如:a dollar, two dollars; a meter, two meters 2、不规则的名词 foot脚-feet mouse老鼠-mice child小孩-child goose鹅-geese man男人-men woman 女人-women tooth牙-teeth,注意:与man 和woman构成的合成词,其
复数形式也是-men 和-women。如:an Englishman,two Englishmen. 但German 不是合成词,故复数形式为Germans; 3、集体名词,以单数形式出现,但实为复数。 如:people police cattle 等本身就是复数,不能说 a people,a police,a cattle,但可以说 a person,a policeman,a head of cattle,the English,the British,the French,the Chinese,the Japanese,the Swiss 等名词,表示国民总称时,作复数用。如:The Chinese are industries and brave.中国人民是勤劳勇敢的。 4、以s结尾,仍为单数的名词,如: a). maths,politics,physics等学科名词,为不可数名词,是单数。 b). news 是不可数名词“新闻”。 c). the United States,the United Nations 应视为单数。 The United Nations was organized in 1945. 联合国是1945年组建起来的。 d). 以复数形式出现的书名,剧名,报纸,杂志名,也可视为单数。 "The Arabian Nights" is a very interesting story-book..<<一千零一夜>>是一本非常有趣的故事书。 5、没有单数形式的名词:表示由两部分构成的东西 glasses眼镜shorts短裤trousers裤子scissors剪刀 若表达具体数目,要借助数量词pair(对,双);suit(套); a pair of glasses; two pairs of trousers,His trousers are there 他的裤子在那里 6、另外还有一些名词,其复数形式有时可表示特别意思,如:goods货物,waters水域,fishes (各种)鱼,room为可数名词时为“房间”,如:I live in Room 5.而room为抽象名词时 为空间上面一句话应译为“请给老妇人在校车上留个地方。”这样的词还有:glass 玻璃glasses 眼镜stone 石头a stone 一块石头time 时间two times 两次wood 木头woods 树林。 clothes 为衣服,而cloth则是布,sand沙子,而sands是沙滩 7、不同国家的人的单复数(注:中日不变英法变,其余S加后面) 名称总称(谓语用复数)一个人两个人 中国人the Chinese a Chinese two Chinese 瑞士人the Swiss a Swiss two Swiss 澳大利亚人the Australians an Australian two Australians 俄国人the Russians a Russian two Russians 意大利人the Italians an Italian two Italians 希腊人the Greek a Greek two Greeks 法国人the French a Frenchman two Frenchmen 日本人the Japanese a Japanese two Japanese 美国人the Americans an American two Americans 印度人the Indians an Indian two Indians 加拿大人the Canadians a Canadian two Canadians 德国人the Germans a Germans two Germans 英国人the English an Englishman two Englishmen 瑞典人the Swedish a Swede two Swedes 8、复合名词的复数形式(名词+名词) 1)、通常只变后面的名词为复数,如boy student→boy student s,shoe shop→shoe shop s 2)但当前面的名词是man和woman时,两个词都变为复数,如man teacher→m e n teacher s 3)一般组合名词变为复数形式时只将中心词变为复数 daughter-in-law儿媳妇—daughters-in-law man doctor男医生-men doctor half brother—half brothers(同父异母或同母异父的兄弟),man driver—men drivers(男司机) woman doctor—women doctors(女大夫)grown up—grown ups(成年人) 4)、“数词+名词+形容词”构成的复合形容词,中间的名词不能用复数形式而须用单数形 式,She is a five-year-old girl 她是一个五岁女孩。a ten-story-high building 一幢