英语教学法(中文)
- 格式:doc
- 大小:170.50 KB
- 文档页数:26

英语五步教学法介绍一般说来,除了第一节课以外,每一节课教师所要进行教学的内容不外乎三部分:1. 复习已教过的语言材料;2. 教学新的语言项目如词汇、语音、语法或句型等;3. 进行各种形式的听、说、读、写训练活动。
为教学上述三部分内容,一般采用以下五个步骤(即五步教学法):步骤1 (Step 1): 复习(Revision)步骤2 (Step 2): 介绍(Presentation)步骤3 (Step 3): 操练(Drill)步骤4 (Step 4): 练习(Practice)步骤5 (Step 5): 巩固(Consolidation)在每一个步骤当中,教师的作用都有所不同。
一位成功的教师一定是一位“多面手”,不但会讲解、还会指挥、会导演、会组织、会表演、会监督、会评判、会记分、会帮忙、会引导,而且还是一位很好的帮助学生强化记忆的人。
教师在课堂上能够扮演上述各种角色,就能够顺利地上好一节课,完成一节课的整体教学任务。
教师在各个步骤中的作用,请看下表:教师在进行上述五个步骤的教学中,自始至终观察全班学生的反应,保证所教的内容大家都能理解。
如果相当一部分学生还没有弄懂,那么教师就需要重教。
因此,教师要随时根据情况变换自己的角色,起到不同的作用,以保证顺利完成课堂的整体教学任务。
例如,在进行第三步时,班上可能出现某种问题,教师就要从组织者或指挥者的角色再变成示范表演者,有时还要当讲解员,直到学生弄懂才能再变回第三步的角色。
下面详细分述五个教学步骤。
第一步复习(Revision)学习外语需要有个过程,需要逐步理解和吸收。
学习英语首先碰到的问题就是遗忘。
为防止遗忘,就需要复习。
复习的作用是“温故知新”,帮助学生回忆所学的语言项目,强化记忆,并对所学的知识加深理解,总结规律,发现问题及时加以解决。
此外对于练习不够、理解不深透或是疏漏的方面,及时加以弥补,以便使所学的知识和技能能更加完善和熟练。
只有帮助学生复习好、巩固好已学的知识,才能顺利地进行下一步,即介绍新的语言项目。

英语教学法的主要流派本文作者(谷金枝),请您在阅读本文时尊重作者版权。
目前,在英语教学法中起主导作用的教学法主要有语法翻译法、听说法、视听法、认知法、交际法和任务型教学法。
本文通过介绍几种主要的英语教学法的发展过程及其利弊,从而提出了如何运用某教学法才能产生更好教学效果的结论。
一、翻译法(Translation Method)语法翻译法是为培养阅读能力服务的教学法,其教学过程是先分析语法,然后把外语译成母语,主张两种语言机械对比和逐词逐句直译,在教学实践中把翻译当成教学目的,又当成教学手段。
其优点:在平时的教学中,有很多复杂的结构和抽象的概念用母语解释起来较为容易且直观,学生也易于接受,这样既能帮助学生巩固所学的规则和词汇,应用语法规则做翻译练习,也帮助教师节省时间,用于其他更为有意义的教学。
其缺点:学生只是机械地通过强化训练记忆语法规则和词汇,忽视听说能力的培养,长此以往,学生无法在交际场合将其正确、流利地运用。
他们学到的只是哑巴英语,只会读写不会听说,其结果只会是高分低能。
二、直接法(Direct Method)直接法是主张采用口语材料作为教学内容,强调模仿,主张用教儿童学习母语的方法,“通过说话学说话”的方法来学习外语,教学过程是一句话一句话地听、模仿并反复练习,直到养成语言习惯。
其优点:低年级学生活泼好学,模仿力强,老师利用直观的教具能引起学生的兴趣和注意力,让具体和抽象有利结合。
如我们教学水果的英语单词时,可以利用卡片或者挂图教学,这样既可以调动课堂气氛,又可以提高学习效率。
其缺点:教学方法过于简单化,不利于学生理解抽象复杂的概念,还有学习内容单一,词汇量少,没有拓展性。
在英语教学中教师要注重培养学生的理解能力。
三、听说法(Audiolingualism, Audiolingual Method)听说法是以句型为纲,以句型操练为中心,着重培养听说能力的外语教学法,又叫句型教学法或口语法。

英语常用交际口语教学方法(最新完整版)英语常用交际口语教学方法英语常用交际口语教学方法:1.交际法:通过教学交际,培养学生英语交际能力。
交际法是建立在语言学、心理学、人类学、社会学新学科理论上的教学法,兼收并蓄、多功能、开放式。
2.听说法:早期交际法,结构法的一种,源于美国。
以结构——功能句型教学为大纲,以听说训练为主,以培养口语能力为首要任务,重视语音语调的正确,语法知识的讲解,课堂操练和真实情景的结合。
3.全身反应法:教与学都是从身体各部位的动作开始的,学生通过全身各个部位的反应来学习英语。
4.自然法:学习者学习新的语言时,尽量在自然的环境中领悟语言知识并进行可理解性的输入。
5.全身动作反应法:它强调在理解的基础上加强身体各部分的反应,也就是在全身活动中学习。
6.合作学习法:它是指学生通过分工合作共同达成学习目标的一种学习方式。
它的关键是“合作”。
7.自主学习法:它是一种以学生为中心,强调学生“学”的内在需求,注重学生的自主学习模式。
8.情景教学法:情景是教师根据课文内容创设的情景对话。
以上就是一些英语常用交际口语教学方法,您可以根据您的需求和环境进行选择。
英语口语教学方法现状目前,英语口语教学方法呈现多样化的趋势,其中包括语法-翻译法、交际法、社团戏剧法和会话法等。
其中,语法-翻译法作为一种最简单的方法,适用于学习时间不长的英语学习者;交际法则是一种较为高级的方法,要求学生在模拟真实的场景中使用英语进行交流。
另外,交际法也是现阶段我国中学英语课堂使用得最广泛的一种方法。
该方法在本质上是互动的、交际的。
此外,多媒体教学也日益成为一种重要的辅助手段,能够通过声音、图像等多种形式展示教学内容,提高学生的学习兴趣和效率。
但是,多媒体教学也存在一定的局限性,如课件容易流于形式,效果上乘但操作上乘的课件价格昂贵等。
在口语教学方面,教师还需要注重培养学生的语感,通过大量的听力和口语练习来提高他们的表达能力。

英语情景教学法的应用情景教学法是在课堂上设置一些真实性和准真实性的情景来学习和使用知识, 在教学过程中,教师有目的引入和创设具有一定情感色彩的,以形象为主体具体的场景,以引起学生一定的态度体验, 从而帮助学生理解知识和技能,并使学生心理机能得到发展, 达到教学目的的一种教学方法。
捷克教育家夸美纽斯曾说:“一切知识都是从感官开始的”。
情景教学法能使学生身临其境或如临其境,给学生展示鲜明具体的形象,使学生从形象的感知达到抽象的理性思维和顿悟,从而激发学生的学习兴趣,使学习活动成为学生自觉活动。
著名教育家陶行知先生说:“教学艺术就在于设法引起学生的兴味,有了兴味就肯用全副的精力去做事体。
”情景教学法,可激发学生的学习兴趣,英语教学中,巧用情境教学法不失为一条锦囊妙计。
正如布鲁姆所说:“成功的外语课堂教学应当在课内创设更多的情境,让学生有机会运用已学到的语言材料。
”现行的中学英语教学由于缺乏语言环境,课堂40分钟的利用率如何,直接影响学生语言能力的提高和智力的开发。
因此,应在初中英语的课堂教学中主动应用“情景教学法”,激发学生学习英语的兴趣,消除他们因为缺乏语言环境而产生的畏难情绪,发挥他们学习的主动性。
可以提高学生的学习积极性,增强英语课堂教学的有效性.在平时的课堂教学中,我们可以尝试采用以下几种创设情景境的教学策略:第一、运用游戏创设情景,有利于激发学生的学习兴趣游戏是人类从儿童成长为成人的过程,是极自然的事,游戏注重过程的体验,在赋予儿童娱乐体验的同时,也促进儿童认知、情感和生活技能的发展,使学生在笑声中更有效地学习,更快地吸收知识,它作为英语教学的重要辅助手段,备受学生欢迎。
因此,在英语教学中巧妙运用游戏,能有效地激发和培养学生的学习兴趣,树立学习自信心并促进学生的全面发展。
英语课堂教学中创设游戏情境能使学生达到乐、学、练的结合及思维与想像的发挥。
在适宜的情境中,用较短的时间达到最佳的效果,可以激发学习动机,发展多种能力,启发思维和想像力,对培养情感与个性都有很大的作用。

18种最实用的少儿英语教学法少儿英语学习的最好方式是找个外教一对一教学,在真正的英语环境中快速学会英语,目前比较流行的外教一对一教学的方式有类似UIABC这样的平台,外教选择性多,且每节最低也只要15元,整体在学员中口碑还是比较高的。
我们都知道少儿时期是学英语的最好时光,所以这个阶段的英语学习很重要,作为少儿英语老师来说最重要的无非就是英语教学方法!1.童话剧教学法教学内容直接决定了学生的学习欲望和制约着语言教师对教学方法的选用。
学生用书主体部分为经典的英美英语童话故事。
在英语课堂上,当孩子们遨游在光怪陆离的童话故事中,他们学习的英语积极性被充分地调动了起来,当他们和一个个栩栩如生的童话人物交上好朋友的时候,他们的英语也会取得长足的进步。
2.情景教学法Fresh English 新鲜美语是我们英语日常用语专题部分。
在英语课堂上,老师们为学生们模拟各种各样生活中的真实场景,以生动活泼的方式来呈现学生们感兴趣的单元主体,组织学生们在情景中不断地反复地操练新知,达到学以致用的学习效果。
3.音乐,律动教学法Happy Melody 和 Motion Chant是我们课本里的英语歌曲和小诗歌。
英语教学蕴含在“说,唱”英语中。
以韵律式的“说,唱”形式,配合科学编排的韵律动作,全方位地调动视觉、听觉、言语能力和肢体动作,让孩子真正“懂得”英语,真正“脱口而出”纯正的英语,真正“学”会英语。
昂立幼,少儿的学生用书中的英文歌曲和儿歌是一套真正为孩子设计的“看了就想学,一学就能跳”的英语韵律操。
它充分考虑到孩子的动作特点,有机地与英语发音和节奏配合起来,易学易跳,协调的动作使孩子深深的感受到英语的优美和学英语的乐趣4.直拼教学法Funny phonics是一套根据英文字母本身的音源,总结出的一套,学生不学就能“看单词能读,听单词能写”的英语词汇教学方法。
它用最简单、最实用、最直接的字母以及字母组合的基本发音,让学生们能很快地掌握陌生单词的认读技巧,并能迅速记忆单词和朗读文章。

五步教学法1.教学目标(Teaching aims)教学目标要简单化,解决教什么的问题。
教师要先分析教学内容,然后确定教学目标。
教学目标可以包括如下内容:a.语音,列出学生需要掌握的语音项目;b.词汇,对不同要求的词汇制定不同的教学目标;c.主题句的熟练应用,做替换练习,使功能与交际结合练习。
d. 设计好活动形式或是游戏形式。
2.教学步骤(Teaching procedures)五步教学法的五步之间前后联系、环环相扣的。
Step 1 Warm-up activities (Revision—复习)五步教学法的第一步是复习,主要讲两个问题,复习的作用和复习的方法。
1)复习的作用:温故知新(Gain the new insight through restudying the old materials)建立起新旧知识之间的联系,以旧引新,减小教学的难度。
2)复习的主要方法:a. Objects(实物)b. Pictures(图片)c. Simple blackboard drawings (简笔画)d. Charts (列表)e. Demonstration (表演)f. Summary (总结)g. Questions (设问)教师可以依据教学内容灵活选用这些复习的方法,激活课堂教学。
Step 2 The presentation of the new material(讲授新课)新课主要讲结构和功能(Structure and function),如何将新授的内容展示给学生,我们介绍五种导入的方法:1)自问自答导入法2)手指木偶导入法3)角色表演导入法4)简笔画导入法5)实物图片导入法教师依据教学内容,灵活选用适当的导入方法进行导入,使我们的教学从一开始就抓住学生的注意力。
如何讲授结构的方法有两种:1)Examples and structure (通过例句讲结构)2)Real or unreal situation (真实或非真实情景)Step 3 Drill(操练)(Oral repetition)第三步是操练,主要对新课中的结构进行操练。

英语阅读课运用的教学方法(精选)英语阅读课运用的教学方法英语阅读课的教学方法有以下几种:1.导入(Pre-reading):通过提问、讨论、看视频、读*等方式导入新课,让学生产生兴趣并集中注意力。
2.速读(Fastreading):快速浏览全文,读懂*主旨和结构。
3.细读(Slowreading):仔细阅读全文,理解*细节和内涵。
4.讨论(Discussion):就*中的某个话题或问题展开讨论,培养学生批判性思维和团队合作精神。
5.笔记(Note-taking):让学生边阅读边做笔记,锻炼学生归纳、概括和总结能力。
6.回答问题(Questionanswering):回答教师提出的问题或学生自问自答,培养学生分析和解决问题的能力。
7.角色扮演(Roleplaying):让学生扮演*中的角色进行对话演练,增强学生口语表达能力。
8.复述(Retelling):让学生用自己的语言复述*内容,锻炼学生记忆、概括和表达能力。
9.写作(Writing):让学生根据*内容进行写作练习,培养学生书面表达能力。
10.课堂练习(Classexercises):让学生在课堂上完成相关的练习题,检测学生对*的理解程度。
以上教学方法可根据具体的教学目标和学生水平进行调整和组合,以适应不同的教学需求。
英语阅读中有什么教学方法英语阅读的教学方法有以下几种:1.略读(Skimming)略读又称跳读或浏览,是一种非常实用的阅读方法。
略读时,需要快速浏览全文,对*的主要内容有个大致的了解,不需要细嚼慢咽地阅读。
2.查读(Scanning)查读是快速阅读的一种。
与略读不同,查读带有明确的目的性,有针对性地寻找关键词,如时间、地点、人物、事件等。
3.细读(Readingforfullunderstanding)细读需要全面了解*内容,并对*中的一些细节部分进行反复思考和研究。
细读的任务是理解和消化*,以便能够在实际中正确地使用所学的语言知识。

七年级英语教案教学方法(精选)七年级英语教案教学方法以下是七年级英语教案的教学方法:1.课堂游戏法:在游戏中学习,掌握并运用英语。
2.交际训练法:通过日常交际训练,培养学生英语运用能力。
3.英语思维法:让学生用英语思考,摆脱中文翻译的困扰。
4.课文整体教学法:通过整体教学,培养学生英语阅读理解能力。
5.歌谣法:利用歌谣教学,培养学生的语感和美感。
6.故事法:利用故事教学,培养学生的英语兴趣和阅读能力。
7.多媒体辅助教学法:利用多媒体教学,提高学生的学习兴趣和效果。
8.合作学习法:通过小组合作学习,培养学生合作精神和团队意识。
9.互动参与法:通过师生互动、生生互动,让学生积极参与英语学习。
10.语境教学法:通过创设真实的语境,让学生在语境中学习、掌握和运用英语。
以上是七年级英语教案的教学方法,应根据具体的教学目标和教学内容来选择合适的教学方法,以达到最佳的教学效果。
初中英语书写教学方法研究初中英语书写教学是培养学生英语表达能力和语言思维的重要环节,下面是一些教学方法,可以帮助学生提高英语书写能力:1.基础训练:在初中英语书写教学中,基础训练是必不可少的。
教师可以从字母、单词、句子等方面入手,逐步提高学生的书写能力。
例如,教师可以通过字母书写练习,让学生掌握正确的书写姿势和笔画顺序,逐步提高书写质量。
2.模仿练习:在基础训练的基础上,教师可以引导学生进行模仿练习。
通过模仿课本中的范本,学生可以逐渐掌握英语书法的规范和标准,提高书写水平。
3.创造练习:模仿练习之后,教师可以鼓励学生进行创造练习。
学生可以自己创作单词、句子、段落等,通过创造练习,学生可以更好地掌握英语书法的技巧和特点,提高书写能力。
4.评价和反馈:在英语书写教学中,评价和反馈是非常重要的。
教师可以定期对学生的书写进行评估,指出学生的不足之处,并给出改进建议。
同时,学生也可以自我评价和反思自己的书写,发现自己的不足之处,并加以改进。
5.多样化教学:为了激发学生的兴趣和积极性,教师可以采用多样化的教学方式。

英语教学方法与策略有哪些1、演示法演示法是教师把实物或实物的模象展示给同学观察,或通过示范性的实验,通过现代教学手段,使同学获得知识更新的一种教学方法。
它是辅助的教学方法,常常与讲授、谈话、讨论等方法配合一起使用。
2、参观法参观法是依据教学目的要求,组织同学到一定的校外场所自然界、生产现场和其他社会生活场所,使同学通过对实际事物和现象的观察、研究获得新知识的方法。
3、学习法学习法是在教师指导下同学巩固知识和培养各种学习技能垢基本方法,也是同学学习过程中的一种主要的施行活动。
4、实验法实验法是同学在教师指导下,使用一定的设备和材料,通过控制条伯的操作,引起实验对象的某些变化,并从观察这些变化中获得新知识或验证知识的一种教学方法,它也是自然科学学科常用的一种方法。
5、实习法(或称实习作业法)实习法是同学在教师纽上,利用一定实习场所,参加一定实习工作,以掌握一定的技能和有关的直接知识,或验证间接知识,综合运用所学知识的一种教学方法6、读书指导法读书指导法是教师目的、有计划地指导同学通过独立阅读教材和参照资料获得知识的一种教学方法。
2英语教学方法有哪些1、情景教学法:情景是教师创设或模拟的生活场景,应具有真实、生动、有用的特点,便于同学将所学语言材料进行综合、创造性地进行表达交流。
这种学习方法,有接近生活的交际功能,而且能变单调、机械的句型操练为活泼、生动的交际性学习。
2、动作教学法:在低年级英语教学中,用具体形象的手势、动作来辅助英语学习,激发同学学习兴趣,提升学习效果。
3、活动教学法:就是按照同学身心发展过程中的不同阶段来〔制定〕、布置情境,提供材料,让同学积极参加自由操作、观察思索。
通过活动让同学自己熟悉事物、发现问题,得出答案,发掘同学潜能。
4、三位一体教学法:是依据字母、音素、音标三者的内在联系业务和交叉关系将三者融为一体进行教学的方法。
5、自然法:这种方法同意同学依据自己对已学知识的熟练程度来参加活动。

英语听说课的教学方法(最新)英语听说课的教学方法英语听说课旨在提高学生的听力理解与口语表达技能,以下是一些可能的教学方法:1.听力训练:听力训练是提高学生听力理解能力的重要手段。
教师可以通过播放录音、电影、电视剧等音频材料,让学生听懂不同的口音、语速和语调,同时要求他们记录关键信息。
2.口语练习:口语练习是提高学生口语表达能力的关键。
教师可以组织学生开展对话、讨论、演讲等活动,让学生进行口语表达。
教师还可以引导学生使用英语进行思维,培养他们的语言感知能力。
3.互动交流:互动交流是提高英语听说能力的有效方式。
教师可以组织学生开展小组讨论、角色扮演等活动,让学生在互动交流中提高听说能力。
4.多媒体教学:多媒体教学可以提供丰富的教学资源,让学生接触到更多的英语材料。
教师可以利用多媒体教学,让学生观看英语电影、听英语歌曲、阅读英语*等,提高他们的听说能力。
5.语言实践:语言实践是提高学生听说能力的必要环节。
教师可以组织学生参加英语角、英语俱乐部等活动,让学生在真实的语言环境中进行听说练习。
总之,英语听说课的教学方法应该注重学生的参与和实践,让学生在互动交流中提高听说能力,同时注重多媒体教学和语言实践,让学生接触到更多的英语材料和真实的语言环境。
英语听说常用的教学方法英语听说常用的教学方法有:1.直接法:直接法是美国语言学者戴尔·道格拉斯倡导的一种语言教学法。
这种方法的基本精神是:语言教学必须以现实中的语言交际为目的,教学内容应该是真实自然的,课堂上的教学活动应该模仿现实生活中的真实情景。
2.分解法:这是一种传统的听说法,源于英国。
这种方法的优点是:语言知识讲解得比较系统,语言技能训练比较规范,教学程序井井有条,学生便于系统地学习英语语音、词汇、语法等知识,便于掌握连读、失去爆破、同化、不完全爆破、弱化、浊化、重音、语调等语音知识和语流音变规律。
3.情景法:情景法强调语言功能,重视创造真实的生活情景,使课堂活动生动有趣。
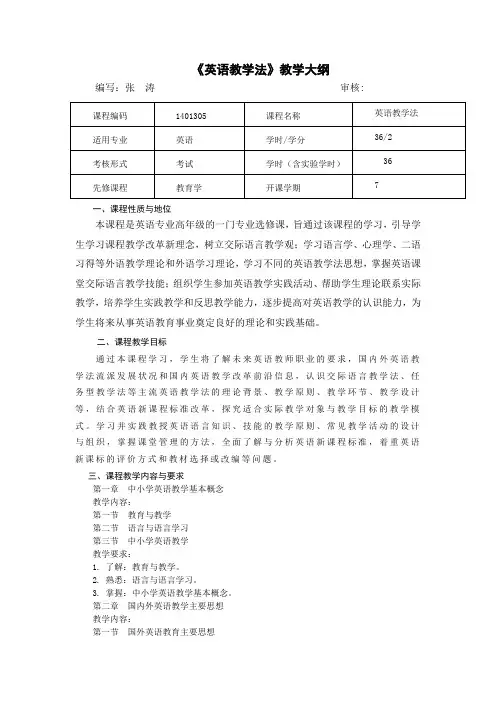
《英语教学法》教学大纲编写:张涛审核:一、课程性质与地位本课程是英语专业高年级的一门专业选修课,旨通过该课程的学习,引导学生学习课程教学改革新理念,树立交际语言教学观;学习语言学、心理学、二语习得等外语教学理论和外语学习理论,学习不同的英语教学法思想,掌握英语课堂交际语言教学技能;组织学生参加英语教学实践活动、帮助学生理论联系实际教学,培养学生实践教学和反思教学能力,逐步提高对英语教学的认识能力,为学生将来从事英语教育事业奠定良好的理论和实践基础。
二、课程教学目标通过本课程学习,学生将了解未来英语教师职业的要求,国内外英语教学法流派发展状况和国内英语教学改革前沿信息,认识交际语言教学法、任务型教学法等主流英语教学法的理论背景、教学原则、教学环节、教学设计等,结合英语新课程标准改革,探究适合实际教学对象与教学目标的教学模式。
学习并实践教授英语语言知识、技能的教学原则、常见教学活动的设计与组织,掌握课堂管理的方法,全面了解与分析英语新课程标准,着重英语新课标的评价方式和教材选择或改编等问题。
三、课程教学内容与要求第一章中小学英语教学基本概念教学内容:第一节教育与教学第二节语言与语言学习第三节中小学英语教学教学要求:1. 了解:教育与教学。
2. 熟悉:语言与语言学习。
3. 掌握:中小学英语教学基本概念。
第二章国内外英语教学主要思想教学内容:第一节国外英语教育主要思想第二节我国英语教学主要思想教学要求:1. 了解:国外英语教育主要思想。
2. 熟悉:我国英语教学主要思想。
3. 掌握:我国英语教学主要思想、国外英语教学主要思想。
第三章中小学英语教学要素教学内容:第一节学生第二节教师第三节教学内容第四节教学环境教学要求:1. 了解:中小学英语教学要素。
2. 熟悉:教学内容。
3. 掌握:中小学英语教学要素之间的关系。
第四章中小学英语教学原则教学内容:第一节学生中心原则第二节合理目标原则第三节有效原则第四节真实原则教学要求:1. 了解:中小学英语教学原则。
正确学习英语的教学方法有哪些?有哪些方法可以直接帮助小学、初中的学生学英语?这是现在除了学生本身,众多家长都会考虑的问题,就是因为传统的英语教学方式已经完全不能满足孩子学习英语的需求,所以为了提高孩子的英语综合能力,家长们都绞尽脑汁,现在就让店铺给大家带来有关学习英语的教学方法,供大家参考!小学学习英语的教学方法1、分析孩子的心理孩子学习英语是需要动力的,不要跟他讲未来和国家大义,孩子能够直观感受到的东西就是有关英语学习这件事自己到底感不感兴趣,学习英语就目前而言能给他带来什么好处,这些都是最直观的东西,需要给到孩子。
比如说有些孩子可以比较喜欢表现,英文学好英语可能可以受到老师的表扬和关注,同学艳羡的目光,这也算是比较正向的引导,再者有些孩子学习能力比较强,对世界的好奇心和探索欲比较浓厚,因为了解到了英语这门语言的多元化,认识到世界各种各样有趣的故事和绘本都是英文原著,那么求知欲会促使孩子学习,英文原版动画片和电影同理,知道孩子的学习需求,投其所好,那样孩子就能全身心的去学习。
2、教学方法语言环境对英语学习的作用不容忽视,每天一节课几十分钟其实能起到的作用就是教授知识,孩子想要真正学会掌握英语需要不断的使用,就像我们学习汉语一样,要经历过多少锻炼才能造就一个能说会道的我们,英语也一样,每天要保证给孩子提供固定的英语输入和输出,让英语融入到小学生的方方面面。
选择的机构要能够激发孩子学习英语的热情,因为一昧的知识输入和输出很容易让孩子的学习造成厌倦,采用比赛的模式,可以提升课堂的趣味性,激发孩子的好胜心,在回答问题的过程中,如果一个孩子答对了,那么外教可以通过给孩子发奖杯的形式激发已经回答问孩子的学习欲望,激发没有回答问题孩子的竞争意识,那么下一次,孩子就会很主动积极的去回答问题,有竞争当然就会有合作!初中学习英语的教学方法1、自然教学法在学习英语中,用习得的方式比学习的效果好得多。
因此,英语课堂环境创设得接近学生的实际生活。
交际法介绍、描述与评析一.交际法的背景和理论依据交际法( the Communicative Approach),又称功能法(Functional Approach)或意念法(Notional Approach), 是以语言的“功能——意念”项目为纲,培养交际能力的外语教学法。
交际法是20世纪70年代根据语言学家海姆斯(Hymes)和韩礼德(Halliday)的理论形成的,是全世界影响较大的外语教学法流派。
交际学派认为:语言教学的目的是培养学生使用目的语进行交际的能力,语言教学的内容不仅要包括语言结构,还要包括表达各种意念和功能的常用语句。
交际法重视培养学生的语言能力,采用真实、地道的语言材料,主张句型加情景来学习语言,鼓励学生多多接触和使用外语。
交际法的代表人物有荷兰的范埃克 Ek),英国的语言学家威尔金斯( D. A. Wiklin) ,威多森( H. G. Widdowson)等。
交际法从诞生起就明确地把目标定位于使学生获得交际能力, 它强调语言的交际功能和语言的形式同等重要。
交际法针对传统教学法的弊端, 提出了重视语言交际功能的观点, 坚持以语言功能项目为纲来培养学生的交际能力, 打破传统语言教学死气沉沉的课堂教学局面。
因此, 交际教学法一经产生就风靡全球, 成为世界上影响最大的语言教学流派之一.长期以来,语言学界围绕语言的“形式一功能”争论不休,对它们的研究几乎涵盖了语言学研究的所有内容,而这些争论必然又反映在与之相对应的教学法理论和实践上。
交际法的流行反映出功能主义者在这场论战中取得胜利。
他们认为语言的本质在于它是用于人类交际的一种工具,外语教学应体现这一本质;能用外语进行成功的交际,就说明外语教学是基本成功的。
交际法对于语言本质的描述抓住了外语教学的关键所在,第一次为外语教学指明了方向。
同时,他们设计了各自不同的教学模式,丰富了外语教学理论,促进了教学法的发展。
交际教学法的理论依据主要源于功能主义的语言学理论和心灵主义的心理学理论:146)。
小学五年级英语的学习方法和教学方法英语对很多人来说都是很难的,但这是因为缺乏相应的学习方法和技巧,而且老师需要对学生进行引导。
下面跟大家介绍一些小学五年级英语的学习方法和教学方法,希望对大家有所帮助。
怎么学好小学五年级的英语学习任何东西都可以分成两大步骤,第一步是基本功的学习,第二步是基本功的发挥和运用,且基本功的学习最为重要。
英语的基本功是语音、词汇、语法、语言风格四大基本功,英语的运用是听说读写四大能力。
表面上看,我们过去似乎也学过英语的语音、词汇、语法、语言风格四大基本功,其实大大不然,我这里所说的四大基本功,是经过多年研究后重新发现和重新定义的四个全新概念,这四大基本功不仅更科学、更完整、更系统,而且还改进了以往同类概念中存在的诸多问题。
比如语音的学习,不仅包括音标的学习,还包括发声方法学习、口腔发声部位的学习,8大语调的学习、变速发音的学习和国际音标的改进;比如词汇的学习,不仅学习单词的意思,还要学习单词的组成方法和记忆方法,特别是要学习快步英语所提出的英语单词的“发音记忆法”;再比如语法的学习,不仅要学习以往以用词为主的“微观语法”,还要学习以造句为主的“宏观语法”,学习英语句子的组成结构;语言风格则是中国人目前还不十分清楚的内容,但它却十分重要,不了解英语的语言风格,即使你认识再多的英语单词,背下了再多的英语句子,也难以了解和认识英语,难以彻底学会英语。
因此我所说的四大基本功,是全新的概念,需要从头理解和学习。
即使中国人发现了学英语基本功的问题和两大步骤的问题,下决心学会英语的四大基本功,也难以做到,因为中国人多年来所使用的学英语工具(如国际音标、语法书、英语字典等等)有十分严重的缺陷,这些缺陷导致了中国人根本就没有办法学会英语的四大基本功。
比如字典上的英语音标是近似的,用这种近似音标难以学会准确的英语发音;比如英语语法书中的很多概念是有缺陷的,用这些有缺陷的概念很难学会语法;比如国际音标不包括卷舌音,用国际音标没法学会美国英语的发音等等。
幼儿英语教学方法有哪些(经典版)编制人:__________________审核人:__________________审批人:__________________编制单位:__________________编制时间:____年____月____日序言下载提示:该文档是本店铺精心编制而成的,希望大家下载后,能够帮助大家解决实际问题。
文档下载后可定制修改,请根据实际需要进行调整和使用,谢谢!并且,本店铺为大家提供各种类型的经典范文,如演讲稿、总结报告、合同协议、方案大全、工作计划、学习计划、条据书信、致辞讲话、教学资料、作文大全、其他范文等等,想了解不同范文格式和写法,敬请关注!Download tips: This document is carefully compiled by this editor. I hope that after you download it, it can help you solve practical problems. The document can be customized and modified after downloading, please adjust and use it according to actual needs, thank you!In addition, this shop provides you with various types of classic sample essays, such as speech drafts, summary reports, contract agreements, project plans, work plans, study plans, letter letters, speeches, teaching materials, essays, other sample essays, etc. Want to know the format and writing of different sample essays, so stay tuned!幼儿英语教学方法有哪些我们都知道少儿时期是学英语的最好时光,所以这个阶段的英语学习很重要,作为少儿英语老师来说最重要的无非就是英语教学方法。
交际法介绍、描述与评析一.交际法的背景和理论依据交际法( the Communicative Approach),又称功能法(Functional Approach)或意念法(Notional Approach), 是以语言的“功能——意念”项目为纲,培养交际能力的外语教学法。
交际法是20世纪70年代根据语言学家海姆斯(Hymes)和礼德(Halliday)的理论形成的,是全世界影响较大的外语教学法流派。
交际学派认为:语言教学的目的是培养学生使用目的语进行交际的能力,语言教学的容不仅要包括语言结构,还要包括表达各种意念和功能的常用语句。
交际法重视培养学生的语言能力,采用真实、地道的语言材料,主句型加情景来学习语言,鼓励学生多多接触和使用外语。
交际法的代表人物有荷兰的埃克(J.A.Van. Ek),英国的语言学家威尔金斯( D. A. Wiklin) ,威多森( H. G. Widdowson)等。
交际法从诞生起就明确地把目标定位于使学生获得交际能力, 它强调语言的交际功能和语言的形式同等重要。
交际法针对传统教学法的弊端, 提出了重视语言交际功能的观点, 坚持以语言功能项目为纲来培养学生的交际能力, 打破传统语言教学死气沉沉的课堂教学局面。
因此, 交际教学法一经产生就风靡全球, 成为世界上影响最大的语言教学流派之一.长期以来,语言学界围绕语言的“形式一功能”争论不休,对它们的研究几乎涵盖了语言学研究的所有容,而这些争论必然又反映在与之相对应的教学法理论和实践上。
交际法的流行反映出功能主义者在这场论战中取得胜利。
他们认为语言的本质在于它是用于人类交际的一种工具,外语教学应体现这一本质;能用外语进行成功的交际,就说明外语教学是基本成功的。
交际法对于语言本质的描述抓住了外语教学的关键所在,第一次为外语教学指明了方向。
同时,他们设计了各自不同的教学模式,丰富了外语教学理论,促进了教学法的发展。
交际教学法的理论依据主要源于功能主义的语言学理论和心灵主义的心理学理论(Bell.1981:146)。
英语教学方法有哪几种1. Communicative Language Teaching (交流式教学法): 这种方法侧重于提高学生的语言交流能力,通过实际的交际活动来帮助学生掌握语言技能。
2. Task-Based Language Teaching (任务型教学法): 这种方法将语言教学与实际任务相结合,要求学生通过完成任务来实践语言运用。
3. Content-Based Instruction (以内容为基础的教学法): 这种方法将语言学习与学科知识相结合,以提高学生的学科知识和语言能力。
4. Total Physical Response (全身反应法): 这种方法通过运动、动作和身体反应来帮助学生理解和掌握语言。
5. Cooperative Learning (合作学习法): 这种方法通过学生之间的合作学习来提高语言能力,培养学生的团队合作和沟通能力。
6. Suggestopedia (暗示式教学法): 这种方法通过创造宽松、积极的学习环境,激发学生的学习兴趣和潜能。
7. The Silent Way (沉默法): 这种方法强调学生的主动参与和发现,教师在教学中保持沉默,让学生自己探索和发现语言规律。
8. Community Language Learning (社区语言学习法): 这种方法强调建立积极的、互动的学习社区,通过教师和学生的合作来帮助学生学习语言。
9. Lexical Approach (词汇法): 这种方法强调词汇的教学和运用,认为词汇是语言学习的核心。
10. Grammar-Translation Method (语法-翻译法): 这种方法侧重于教授语法知识和翻译技巧。
Grammar-translation approach 语法翻译法
语言观
语法翻译法起源于历史比较语言学(机械语言学理论),认为语言都起源于一种共同的原始
语言,语言规律是相同的,词汇的所代表的概念也是相同的,不同的只是书写和语音形式。
习得观
学习者通过互译和语法关系的替换,就能够掌握另一种语言。
教学观
1. 为了完成互译和语法关系的转换,母语所起的翻译能力很重要。因此,重视母语在教学
中的使用。
2. 注重语言规则的学习,认为语言教学就是规则的理解和教学。
代表教学步骤
1. 教师在教学中需使用“规范”的语言书面语
2. 教师在课堂上积极使用母语
3. 教学方式以母语的外语的互相翻译为主,并通过大量的书面翻译及写作来巩固和检验语
法知识
4. 重视语法教学,强调词与词之间的组合规则,讲词的形态和曲折变化,对复杂的语法现
象做详尽的解释
5. 注重书面语练习,不注重听说练习
语法教学法的典型教学流程
Tasks:
1. Share with your experiences that you were taught in this grammar-translation approach?
2. Sum up the advantage of this approach.
3. Sum up the disadvantage of this approach.
语法翻译法的优势
1. 充分利用母语的优势,协助学习者理解目的语
2. 语法教学作为中心,有利于学习者掌握语言“规范”,理解语言的结构框架知识。
3. 注重阅读能力的培养,翻译能力能得以锻炼。
4. 教学方式安全,简便易行,可操作性强。
语法翻译法的劣势
1. 过分依赖母语和翻译方法,容易造成学习者依赖母语。
2. 把语言更多当做知识而不是交际技能来锻炼
3. 过分重视学习者阅读写作能力,轻视学习者的听说能力
4. 机械翻译,大量阅读等方法较死板,容易使学习者失去主动性和兴趣,学习气氛沉闷。
Task:
When and how can we apply this approach properly?
The Direct method 直接法
直接法出现的历史背景
1)19世纪80年代左右,当时工业和国际贸易发展较迅速,贸易经济发展对外语学习和外
语人才特别是对口语能力提出了新要求。
2)一些不受传统思想束缚的教学改革家发起了对语法翻译法的批判运动和改革运动。
3)当时的语言学家积极对语言和语言学习本质进行了批判性思考,认为语言学习应该转化
为语言使用。
4)当时以国际语音协会建立为标志的语音学发展起来了,语音研究有了长足的发展。
语言观:
1. 语言是一种技能或习惯,习惯的养成要靠大量的重复,练习和模仿。有声语言是第一位
的,书面语言是第二性的,认为语言使用比语言学习更重要。
2. “一切有关语言的研究必须建立在语音学的基础上”---- Sweet .
习得观:
主张语言习得过程就是“通过说话学说话”,就像学习者学习母语时一样。
教学观:
主张按照幼儿习得母语的自然过程和方法来设计外语教学的过程和教法,并采用直观手段教
学。教学过程应该是一句话一句话听、模仿、反复练习,直到养成语言习惯。
教学方法和特点:
1)根据幼儿学语言的理论,直接法主张听说领先,重视语音、语调和口语教学。
2)强调模仿练习,让儿童靠直觉感知、靠直觉模仿,进行机械操练和记忆背诵,以求养成
一种语言习惯。
3)以句子为教学的基本单位,整句学、整句用,不孤立地教授单词和语法规则。
4)教学过程中完全用外语进行教学,把外语声音形式同客观表象直接联系,不经过母语这
一“中介”,不依赖母语翻译。
5)为了帮助理解,教师广泛采用各种直观手段,如实物、图画、动作、手势、表情和游戏
等来解释词义和句子,使外语语词的声音和它代表的语义直接联系起来,培养儿童把外语与
客观事物直接建立联系和直接用外语思维的能力。
典型教学过程:
1)教师口头展示句子或课文
2)学生模仿跟读
3)教师纠正错误
4)学生继续模仿,直到重复正确为止
5)一课完成后,教师提问,学生回答,或者学生提问,老师回答
直接法的优势:
1)重视语音、语调和口语教学,有利于培养学生的听说能力。
2)充分利用直观教具,促进学生调动多种感官习得外语,使形象与语义直接建立联系,有利于
活跃课堂气氛,激发学生的学习兴趣,培养学生用外语直接思维、记忆、表达的习惯。
3)注重模仿、朗读的语言实践练习,有助于培养学生的语言熟练技巧和语言习惯。
4)重视以句子为单位进行外语教学,有利于培养学生直接运用外语的能力。
直接法的缺点:
1) 忽视母语的积极作用。在讲解一些抽象语言知识的时候,完全排斥母语的中介作用,既容
易造成理解错误,又浪费时间,学习者在输出时容易产生较多错误
2) 忽视语法的作用,对语言结构的操练不充分;忽视读写能力的培养。
3) 忽视成年人和儿童学习英语的各自特点,完全照搬儿童习得母语的方法,给外语教学带来
不必要的困难,对学习者的认知能力没有合理运用。忽视语法对学习者的监控和指导作用,
片面强调机械模仿和记忆 。
Task:
1) Do you see the impact of this approach in your own learning or teaching
experiences?
2) Generally, the direct approach was not successfully applied in China, why?
3) What are the implications from this approach?
The Audio-visual method 视听法
视听法的产生背景:
1.视听法(Audio Visual Approach)于五十年代由古布里纳提出首创于法国,是当时法国对外国
成年人进行短期速成教学的一种方法。
2. 视听法发扬了直接法、听说法的长处(以外语教外语,加强模仿,口语领先,句本位原
则,以口语训练句型结构)并在此基础上进行了改良。
3. 2O世纪 5O年代结构主义语言学家对外语教学的影响是显著的,行为主义作为心理学领
域的新兴理论,也对外语学习产生了作用。
语言观
1. 结构主义语言学家认为语言首先是一种语言体系,可以把语言中的句子层层分析描写,
分析成句型,短语,音节等多层次结构,从而描绘出语言词汇句子的总貌。
2. 视听法强调听说优先于读写,口语领先原则,口语是第一位的,书面是第二位的。
3. 视听法根据结构主义语言学理论制定出语言教学的最低口语词汇量和最基本的句型。
习得观
受行为主义“刺激-反应”模式影响,视听法认为“知觉是不同类感觉相互联系和综合
的结果。”“感觉刺激必须达到一定的量才能被知觉到”。 儿童在习得母语的过程中,语言
信息经过听觉通道输入大脑的频率较高,入学后依靠视觉感受文字符号,接受远信息的机会
大大增强,相对来说视觉感知能力有所减弱。而这种母语学习过程也是在各种情景中进行的。
因此,视听法将图像和声音结合起来,充分调动潜在的听觉感知能力,利用情景教学使学生
整体感知语言,在课堂上反复联系,对学生形成 “刺激”,使其在碰到类似场景时做出 “反
应”其方法符合了行为心理学家强调通过 “刺激——反应”形成语言习惯的观点 ,也符合
人的学习和记忆原理。
教学观
1. 以最低口语词汇量和最基本的句型为基础,在具体教学中应该依照层次结构要求学习者
掌握语音、节奏、句子,反复练习,熟能生巧。
2. 在教学中,应该重视情景视觉感觉的效应,通过用幻灯片和同步录音等教学手段,将情
景视觉和录音听觉结合在一起,因为视听结合的方法比单纯依靠听觉或视觉来理解、记忆和
储存的语言材料要多得多。视觉形象为学生提供形象思维的条件,促使学生自然和牢固地掌
握外语。听觉形象有助于养成正确的语音、语调、节奏及遣词、造句的能力和习惯。