
Workability,strength and shrinkage of ?ber reinforced expansive self-consolidating
concrete
Qi Cao a ,b ,Yinliang Cheng c ,Mingli Cao a ,?,Quanqing Gao a
a
State Key Laboratory of Coastal and Offshore Engineering,Dalian University of Technology,Dalian 116024,China b
Ocean Engineering Joint Research Center of DUT-UWA,Dalian,116024,China c
Shenzhen Expressway Company Limited,Shenzhen,518026,China
h i g h l i g h t s
Effects of ?bers on properties of expansive self-consolidating concrete (ESCC)were studied. Workability of fresh concrete decreases with increased volume fraction of ?bers. Steel ?ber improves the linear load-de?ection relationship of ESCC beams. Free expansive rate of ESCC reduces with the increase of steel ?bers content.
a r t i c l e i n f o Article history:
Received 21September 2016
Received in revised form 12November 2016Accepted 14November 2016
Available online 21November 2016Keywords:Fibers
Expansive self-consolidating concrete Workability
Mechanical properties Shrinkage
a b s t r a c t
A testing program was undertaken to evaluate the effects of ?bers on properties of expansive self-consolidating concrete (ESCC).Hooked end steel ?bers and mono?lament polypropylene ?bers were used in the tests with three selected volume fractions (0.25%,0.50%and 0.75%of the total volume of concrete)for steel ?bers and one volume fraction (0.10%)for polypropylene ?bers.Workability of fresh concrete,mechanical properties and shrinkage of hardened concrete were investigated.Slump ?ow,J-ring and V funnel tests were carried out to evaluate the ?lling ability,passing ability,and viscosity of the fresh concrete.Mechanical properties including compressive strength,splitting tensile strength and ?exural strength of hardened concrete were studied.Test results indicate that workability of fresh concrete decreases with increased volume fraction of ?bers.The compressive strength of ESCC is improved at 7days with added expansive https://www.doczj.com/doc/9f1718983.html,bined addition of expansive admixture and ?bers reduces the concrete strength at 7days,while it does not in?uence the 28days strength noticeably.For ?exural performance,steel ?ber improves the linear load-de?ection relationship of ESCC beams.Steel ?ber reinforced beam specimens with ?ber content higher than 0.50%show de?ection-hardening behavior.It is also found that free expansive rate of ESCC reduces with the increase of steel ?bers content.Overall,?ber reinforced ESCC both at 0.25%and 0.50%volume content satisfy the target performance criteria.
ó2016Elsevier Ltd.All rights reserved.
1.Introduction
Self-consolidating concrete (SCC)is a highly ?owable,non seg-regating concrete that can spread into place,?ll the formwork,and encapsulate the reinforcement without any mechanical consolida-tion [1].It has excellent properties and has been widely used in engineering ?elds.Since high content cementitious materials are used in the design,self-consolidating concrete is prone to shrink-age cracks,seriously affecting the service life of SCC-made build-ings and bridges.One way to decrease shrinkage of SCC is adding expansive agent [2,3].It compensates shrinkage of self-consolidating concrete and improves the cracking resistance of SCC.It was reported that sulphoaluminate has a micro-expansion effect and it is the main component of expansive agent studied by researchers [3–4].The bene?t of using this type of expansive agent is that it can provide increased workability for SCC other than shrinkage-compensation.Meng et al.[3]reported that the shrinkage of SCC decreases with the increase of expansive agent dosage as well as increasing concrete age within a certain range.Ettringite is produced mainly at the beginning 1–7days.It also shows that curing time plays a signi?cant role on the shrinkage of SCC with expansive agent indicating that the shrinkage is smaller when curing time is longer.It is worthwhile to mention
https://www.doczj.com/doc/9f1718983.html,/10.1016/j.conbuildmat.2016.11.0760950-0618/ó2016Elsevier Ltd.All rights reserved.
?Corresponding author.
E-mail address:caomingli3502@https://www.doczj.com/doc/9f1718983.html, (M.Cao).Construction and Building Materials 131(2017)
178–185
Contents lists available at ScienceDirect
Construction and Building Materials
journal homepage:www.e l s e v i e r.c o m /l o ca t e /c o n b u i l d m a
t
that overdosage use of expansive agent could result in reduction of mechanical properties of concrete.Thus,incorporation of expan-sive agent mainly increases cracking resistance of SCC.
Fiber reinforced self-consolidating concrete(FRSCC)has gained a lot of attention and extensive research has been con-ducted.The?bers that are used in SCC include steel?ber, polypropylene(PP)?ber,aramid?ber and basalt?ber,etc.Steel ?ber has been widely employed because of its high modulus of elasticity and tensile strength.PP has low density,good adhesive properties with SCC,and it does not segregate with concrete under its own weight.Therefore,PP can be used to restrict the micro-cracks when uniformly distributed in SCC.Aslani and Nejadi[4]studied workability and deformation of four different mixtures with one SCC and three?ber reinforced SCC.Test results indicated that,in general,addition of?bers decrease workability as well as shrinkage of SCC.It also demonstrated that?bers slightly reduce the creep of SCC.Similarly,it was reported[5]that steel?bers are effective in restricting the dry-ing shrinkage of cementitious materials.As well known,incorpo-ration of?bers in SCC decreases workability of the fresh SCC and the reduction becomes larger as?ber content increases[6–11]. Fiber could increase early strength of concrete especially for steel?bers[12].Fibers have lower effect on modulus of elastic-ity of concrete in compression[12],but it can enhance the mod-ulus of elasticity in tension[13].There is no doubt that steel ?bers can improve the tensile strength of SCC,however it was reported that propylene?ber decreases the tensile strength of SCC[12–13].Flexural performance of beam specimens was improved by steel?bers and hybrid?bers when the steel?ber volume content exceeds0.50%,and the post-peak load capacity was increased[13–14].
Although the effect of expansive agent[2–3]and?bers[4–14] on properties of SCC has been studied respectively,the combined effect of?ber and expansive agent has rarely been investigated. In this paper,an experimental program is performed to evaluate the effects of?bers on properties of expansive self-consolidating concrete(ESCC).The calcium oxide-sulphoaluminate type expan-sive agent was used to produce expansive concrete with targeted expansion rate.Then?bers(single steel?bers,hybrid steel and PP?bers)were adopted to optimize ESCC and the effect of?bers on workability,mechanical properties and shrinkage was studied.
2.Research signi?cance
Fibers are usually added into concrete to improve tensile strength,impact resistance and toughness of concrete.Research [24]has indicated that,compared with single?ber,hybrid?bers present a higher crack resistance and shrinkage reduction as well as strengthening due to various scales of reinforcement in cemen-titious matrix.It is necessary to investigate how the workability and mechanical properties of SCC are affected by the incorporation of hybrid?bers and expansive admixture.Research?ndings will assist engineers to design and implement?ber reinforced expan-sive SCC in engineering?elds.3.Experimental procedure
3.1.Materials
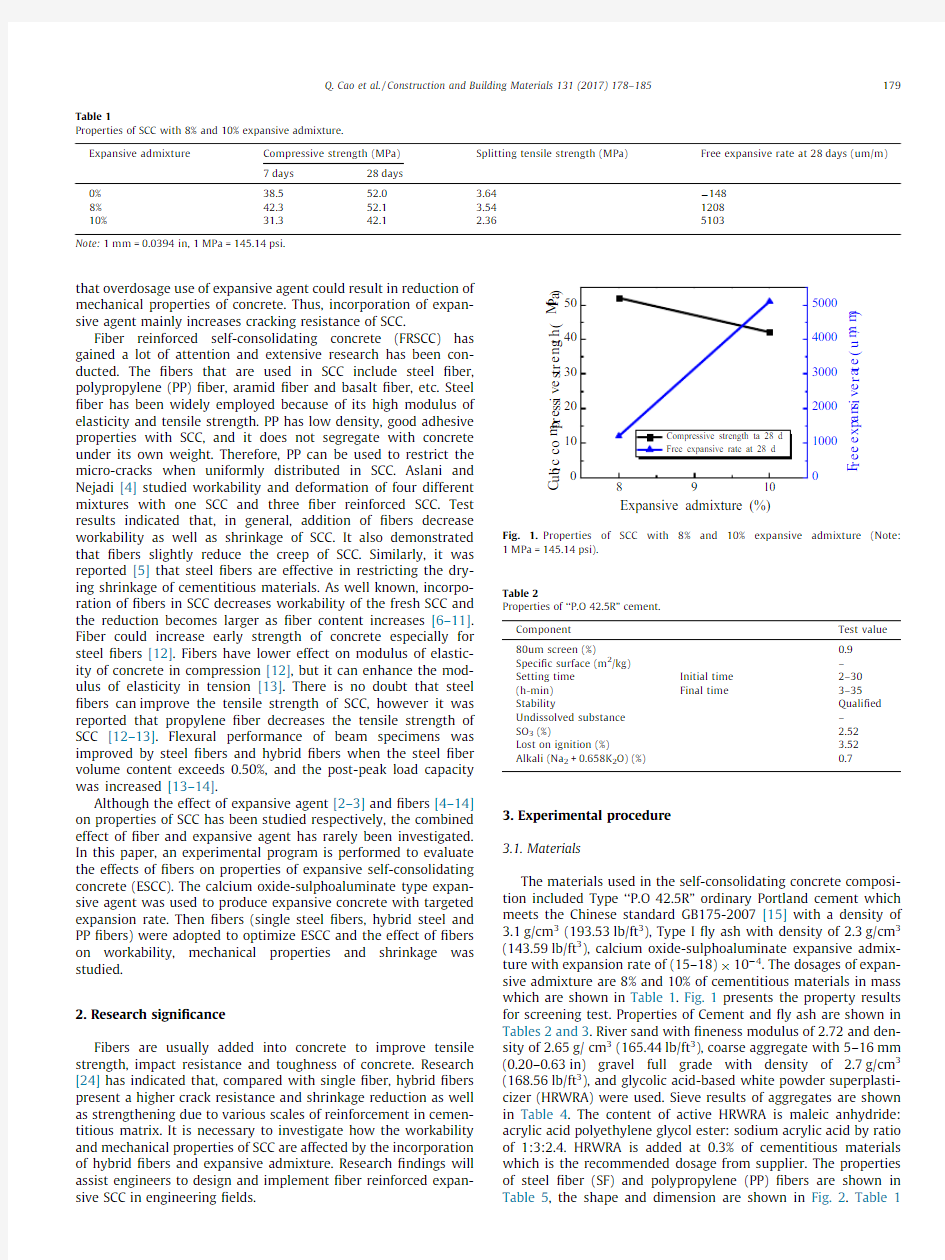
The materials used in the self-consolidating concrete composi-tion included Type‘‘P.O42.5R”ordinary Portland cement which meets the Chinese standard GB175-2007[15]with a density of 3.1g/cm3(193.53lb/ft3),Type I?y ash with density of2.3g/cm3 (143.59lb/ft3),calcium oxide-sulphoaluminate expansive admix-ture with expansion rate of(15–18)?10à4.The dosages of expan-sive admixture are8%and10%of cementitious materials in mass which are shown in Table1.Fig.1presents the property results for screening test.Properties of Cement and?y ash are shown in Tables2and3.River sand with?neness modulus of2.72and den-sity of2.65g/cm3(165.44lb/ft3),coarse aggregate with5–16mm (0.20–0.63in)gravel full grade with density of 2.7g/cm3 (168.56lb/ft3),and glycolic acid-based white powder superplasti-cizer(HRWRA)were used.Sieve results of aggregates are shown in Table4.The content of active HRWRA is maleic anhydride: acrylic acid polyethylene glycol ester:sodium acrylic acid by ratio of1:3:2.4.HRWRA is added at0.3%of cementitious materials which is the recommended dosage from supplier.The properties of steel?ber(SF)and polypropylene(PP)?bers are shown in Table5,the shape and dimension are shown in Fig.2.Table1
Table1
Properties of SCC with8%and10%expansive admixture.
Expansive admixture Compressive strength(MPa)Splitting tensile strength(MPa)Free expansive rate at28days(um/m) 7days28days
0% 8%38.5
42.3
52.0
52.1
3.64
3.54
à148
1208
10%31.342.1 2.365103
Note:1mm=0.0394in,1MPa=145.14psi.
Table2
Properties of‘‘P.O42.5R”cement.
Component Test value
80um screen(%)0.9
Speci?c surface(m2/kg)–
Setting time Initial time2–30
(h-min)Final time3–35
Stability Quali?ed
Undissolved substance–
SO3(%) 2.52
Lost on ignition(%) 3.52
Alkali(Na2+0.658K2O)(%)0.7
Q.Cao et al./Construction and Building Materials131(2017)178–185179
shows mechanical and shrinkage properties of SCC with 8%and 10%expansive admixture.8%expansive admixture dosage was selected for the next step by taking into account of both mechan-ical and shrinkage properties.
3.2.Specimen production
Expansive self-consolidating concrete was ?rst made with tar-get workability performance shown in Table 6,which is employed for this study according to EFNARC (European Federation of National Associations Representing for Concrete)[16,17]and ASTM (American Society for Testing and Materials)C1621[18].Then steel ?ber and hybrid steel ?ber-polypropylene ?ber were added respectively into the mix to make ?ber reinforced expansive self-consolidating concrete.To keep ?ber distributed in concrete homo-geneously without any bundles,the following mixing procedure was undertaken.Coarse aggregate,?ne aggregate and ?bers were added and mixed with half water for 2min (4min for hybrid ?bers).Then cementitious materials including cement,?y ash and expansive agent were added and mixed for another 2min,followed by adding remaining water with 1min mixing and adding HRWRA with 3min mixing.Then the mixture was rested for 2min,followed by 3min mixing.During the mixing,no bundles or nonuniformity of ?bers were observed indicating the good quality of ?ber distribution in expansive self-consolidating concrete (ESCC).
Compressive strength and splitting tensile strength test speci-mens were 150?150?150mm (5.91?5.91?5.91in)cubes according to CECS 18:89)[19]and GB /T50081-2002[20].Flexural strength and drying shrinkage test were conducted according to ASTM C1609[21]and ASTM C157[22],and specimen dimension was 100?100?400mm (3.94?3.94?15.76in).One stainless steel probe was embedded at each end of the specimen with depth of 10mm (0.39in)in the center of cross section for expansion-shrinkage test.All specimens were demolded at 24h after casting and cured in a standard curing room (temperature:23±2°C
[73±3°F],humidity P 95%)until the age of testing at 28days.The expansion-shrinkage test was conducted by using a length comparator outside the curing room and putting back into curing room immediately.Table 7shows the test matrix.Please note that ‘‘NSCC”represents control (normal)self-consolidating concrete group,ESCC represents self-consolidating concrete with expansive agent at 8%of cementitious materials which is the selected dosage.In this study,all of the ?ber-reinforced SCC is mixed with 8%of the expansive agent.Fiber volume fractions and mixture code are also listed in Table 7.In Table 7,‘‘ESF”indicates the expansive SCC with single steel ?ber (SF),the number 1,2,3represents volume ratios of 0.25%,0.50%and 0.75%,respectively (percentage of total con-crete volume).‘‘EHY”indicates ESCC with hybrid ?bers.Fiber factor V f L f /d f [9]is used,where V f ,L f and d f are ?ber volume ratio,?ber length and ?ber diameter,respectively.3.3.Test methods
In this study,referring to EFNARC [16–17]and the US speci?ca-tion ASTM C1621[18],three tests including slump ?ow,J-ring and V-funnel were conducted.Five indexes consisting of slump ?ow,T 50,J-ring spread distance,J-ring height difference (D h)and V-funnel time (T V )were chosen to evaluate ?owability,passing ability,and viscosity of tested mixtures.
The mechanical properties consist of compressive strength,splitting tensile strength,and ?exural properties of SCC.In accor-dance with speci?cations [19–20],three specimens were tested for each mixture at 7days and 28days for compressive strength respectively.For ?exural test,by using third-point loading setup,specimens were turned over 90°from casting top surface.LVDTs were installed on both sides symmetrically at mid-span of beams to monitor middle-span de?ection.Three specimens were tested and test results were averaged.In addition,drying shrinkage test was conducted following ASTM C157[22]and concrete prisms were measured vertically by length comparator.4.Experimental results and discussion 4.1.Workability performance
In general,incorporation and increase of ?bers content in SCC show a negative impact on ?owability and passing ability of SCC [6–12].To study the effect of ?bers content on expansive SCC,workability tests were conducted for 6mixtures.Test results are shown in Tables 8and 9and Fig.3.It can be derived from Table 8that,ESCC mixture presents signi?cant low T 50and T V
Table 4
Sieve results of aggregates.Sieve size (mm)<0.150.150.300.60 1.18 2.36 4.75Sand
Retained percentage (%)
7.4012.917.231.922.87.60Accumulated retained percentage (%)
99.892.479.562.330.47.60
Sieve size (mm)<2.36 2.36 4.59.51619Coarse aggregate
Retained percentage (%)
0.04 1.1256.8441.70.320Accumulated retained percentage (%)100.02
99.98
98.86
42.02
0.32
Table 5
Properties of ?bers.Fiber type Shape Length L/mm Diameter d/mm Aspect ratio L/d Tensile strength/MPa Elastic modulus/GPa Speci?c gravity/g ácm à3ST Hooked 350.5564>11502007.85PP
Straight
19
0.07
271
568
4.35
0.91
Note:1mm =0.0394in,1MPa =145.14psi,1kg/m 3=0.0624lb/ft 3.
Table 3
Properties of ?y ash.Number Index
Test value 1Fineness (45um square hole sieve %)8.92Water demand ratio %843Lost on ignition % 4.84Water content %0.35
SO 3%
1
180
Q.Cao et al./Construction and Building Materials 131(2017)178–185
values compared to control group SCC.It is inferred that by adding 8%expansive agent to SCC,the ?owability of SCC was improved and viscosity of SCC was decreased.Static segregation and bleeding were not observed in the test.In all,?owability of all six mixtures meets the criteria of 600mm (2.64in)and higher.The data in Table 8shows that the slump ?ow ranges between 620and 760mm (24.43and 29.94in),in which EHY exhibit the lowest val-ues.It indicated that addition of hybrid ?bers decreases the ?owa-bility of ESCC.Slump ?ow of hybrid ?bers reinforced concrete decreases 140mm and 110mm (5.52and 4.33in)compared with ESCC group and single ?ber group ESF-1respectively.This is also reported in Gencel et al.[8]and He et al.’s [6]study that,at certain water reducing agent content,polypropylene ?ber shows a more signi?cant impact on slump ?ow than that of steel ?bers.When both ?bers are mixed and incorporated,the reduction of slump ?ow is higher than that of single ?ber.For T 50,all tested mixtures are in the range of 2.3–4.8s,meeting the requirement of EFNARC which is between 2and 5s.This re?ects the desirable viscosity of concrete mixtures.When expan-sive admixture added in the NSCC,it reduces the viscosity of con-crete as it can be seen that,V-funnel time decreases from 12.2s to 7.4s,reducing by 39.3%.In the same time,T 50reduces about 25.8%.With the incorporation of the ?bers,the viscosity of fresh concrete increases.When the steel ?bers volume content reached 0.75%,clogging phenomenon was observed in V-funnel test.It is specu-lated that high content of steel ?bers in the funnel exit impeded the ?ow of concrete other than the high viscosity of https://www.doczj.com/doc/9f1718983.html,pared with ESCC mixture,T 50’s of all ?ber reinforced con-crete mixtures increase by 35–109%,while increase of T V ’s is between 32%and 347%as shown in Table 9.Obviously,compared with T 50,T V is more sensitive to the effect of ?ber dosage without considering the blocking case for ESF-3.In addition,compared
with
Fig.2.Fibers:(a)Steel ?ber and (b)PP ?ber.
Table 6
Performance requirements for SCC and initial target performance criteria for current study.Property
EFNARC2002EFNARC2005Initial target values of current study
Range
Class Range Slump ?ow(mm)
650–800
SF1550–650P 650
SF2660–750SF3760–850T 50(s)2–5VS1622–5VS2>2V funnel(s)
6–12VF168625VF19–25J-ring(mm)
0–10––0–20Compressive strength (MPa)–––>40Free expansive rate (um/m)
–
–
–
>300
Note:1mm =0.0394in,1MPa =145.14psi.
Table 7
Mixture proportions.Mixture code Expansive Cement (kg/m 3)FA
(kg/m 3)Sand (kg/m 3)Coarse Water (kg/m 3)HRWRA (kg/m 3)SF (%)
PP (%)
V f L f /d f
Admixture (kg/m 3)Aggregate (kg/m 3)w/c
NSCC
–398170795770200 1.8650.3500–ESCC (8%)45366157795770200 1.8400.3500–ESCC (10%)57354157795770200 1.8250.3500–ESF-145366157795770200 1.8400.350.25015.9ESF-245366157795770200 1.8600.350.50031.8ESF-345366157795770200 2.0000.350.75047.7EHY
45
366
157
795
770
200
1.850
0.350.250.1043.1
Note:‘‘ESF”presents Expansive Steel Fiber reinforced SCC.‘‘EHY”presents Expansive Hybrid ?ber reinforced SCC.1kg/m 3=0.0624lb/ft 3.1kg =2.2lb.
Q.Cao et al./Construction and Building Materials 131(2017)178–185181
single steel?bers,hybrid?bers reinforced SCC show higher T50and T V.
J ring test was employed to measure the passing ability of tested mixtures.The slump spread distance through J-ring as well as the height difference(D h)inside and outside of vertical bars were both measured.Table8shows that D h is in the range of4–40mm (0.16–1.58in)for?ber reinforced SCC.They are higher than EFNARC acceptable range of0–10mm(0–0.39in).However it should be noticed that the limits suggested by EFNARC are for plain SCC.The reasons for high D h can be explained as following:the comparable length between clear distance among reinforcement in J ring and steel?bers(43mm and35mm)(1.69and1.38in) hinders the?ow of?ber reinforced SCC.It can be seen that, compared with ESF-1group,the D h of group EHY increases about 400%.It is demonstrated that PP plays an important role in affect-ing the viscosity of the SCC mixture.It can be seen that as steel ?ber content increases,J-ring spread distance D J decreases.Also it is shown that the difference between slump?ow distance and J-ring spread distance(D-D J)increases as steel?ber content increases.It is demonstrated that addition of steel?ber impedes the passing ability of tested SCC mixtures signi?cantly.According to blocking assessment criteria in ASTM C1621[18],SCC mixture with0.50%steel?ber content is in the range of minimal to notice-able blocking(20–50mm(0.79–1.97in)difference between slump ?ow and J-ring).However,SCC mixture with0.75%steel?ber con-tent can be de?ned as noticeable to extreme blocking(P50mm (1.97in)difference between slump?ow and J-ring?ow).
https://www.doczj.com/doc/9f1718983.html,pressive strength(Cubic specimens)
Strength test results are shown in Table10,in which f cu,7,f cu,28 and f st represent compressive strength at7days,28days and split-ting tensile strength at28days,respectively.As can be seen from Table10and Fig.4,compressive strength of ESCC is10%higher than that of NSCC at7days and it does not shown signi?cant difference at28days.It can be seen that,the incorporation of?bers reduces the compressive strength from42.3MPa(ESCC)to 35.5MPa(average of ESF-1,ESF-2,ESF-3and EHY)(6.13ksi to 5.16ksi)at18.8%or so at7days.While Aslani and Nejadi[12]test data indicated that the?ber improved the regular SCC compressive
strength at7days.This suggests that?ber does not improve compressive strength of expansive SCC at early age of7days.
For28days compressive strength,f cu,28of single steel?ber spec-imens(ESF-)?uctuated around52MPa(7.54ksi)which does not
Table8
Workability of tested mixtures.
Mixture code Slump?ow J-ring/mm V-funnel Slump?ow-J-ring/mm D/mm T50/s D J D h T v/s D-D J
NSCC750 3.1750212.20
ESCC760 2.376027.40
ESF-1730 3.170049.830
ESF-2700 3.56601613.940
ESF-3670 4.847040Blocking200
EHY620 4.45652033.155
Note:1mm=0.0394in.
Table9
Ratio of slump?ow,J-ring and V-funnel of?ber reinforced-ESCC to ESCC. Mixture code D T50D J D h Tv
ESCC11111 ESF-10.96 1.350.922 1.32 ESF-20.92 1.520.878 1.88 ESF-30.88 2.090.7420–EHY0.82 1.910.6210 4.47
182Q.Cao et al./Construction and Building Materials131(2017)178–185
by the following two factors (1)the different physical parameters of mono?lament polypropylene ?bers,and (2)the compatibility effect between expansive agent and ?bers which might lead to the internal structural changes of concrete and reduce the com-pressive strength after 28days curing.4.3.Splitting tensile strength
Form Table 10and Fig.4,it shows that addition of steel ?bers improve splitting tensile strength of NSCC and ESCC.However,incorporation of expansive agent decreases the splitting tensile Table 10
Strength properties of hardened concrete.Property NSCC ESCC ESF-1ESF-2ESF-3EHY f cu,7(MPa)38.542.336.635.535.134.7f cu,28(MPa)52.052.153.952.752.549.9f st (MPa)
3.64
3.54
3.65
4.10
4.61
3.90
Note:1MPa
=145.14psi.
Q.Cao et al./Construction and Building Materials 131(2017)178–185
183
the steel?bers content reaches at0.50%and0.75%(40kg and60kg (88.2and132.3lb)in mass).But in Ding et al.’s[23]study,steel ?ber reinforced beam(40kg(88.2lb)mass content)did not show de?ection-hardening behavior.It is speculated that addition of ?ber limits the free expansion of concrete,causing the concrete to produce a self-stressing and strengthen the bond between steel ?bers and concrete matrix.Importantly,this proves the bene?t of combined addition of expansive agent and steel?bers.
The de?ection at peak load P p for ESF-3and ESF-2are0.83mm and0.66mm(0.033and0.026lb),https://www.doczj.com/doc/9f1718983.html,pared with the ?rst peak load P1,P p increases27.1%and9.0%for ESF-3and ESF-2, respectively.This demonstrates that de?ection hardening is more signi?cant when steel?ber content is higher.However,for speci-men ESF-1and EHY,in which steel?bers content is less than 0.50%,the de?ection hardening behavior was not observed.
Table11lists the beam bending test results for six mixtures.For ?rst peak load P1,it shows that the?rst-peak loads of?ber-reinforced SCC beams are greater than that of NSCC beam when the steel?ber content is equal to or greater than0.50%.The?rst-peak load of ESF-3is18.1%and37.1%higher than that of NSCC and ESCC,respectively.
In general,for d1(?rst peak de?ection),f600(residual load at net de?ection of L/600),f150(residual load at net de?ection of L/150), T150(toughness of beam specimen at net de?ection of L/150)and R T,150(equivalent?exural strength ratio),they all increase as steel ?ber content increases for single?bers cases.For hybrid?bers scenarios,the above parameters are between those of ESF-1and ESF-2.It indicates that0.1%PP helps to improve the mechanical performance and de?ection of steel?ber reinforced ESCC beam specimens.
4.5.Drying shrinkage
Fig.6shows the expansion-shrinkage curves of all six tested mix-tures.Generally,NSCC and ESCC show shrinkage behavior and expansion with shrinkage over-compensation behavior,respec-tively.Four out of?ve ESCC specimens meet the shrinkage performance criteria(>300microstrain)in Table6except specimen ESF-3.It illustrates that adding8%expansive agent could over-compensate the shrinkage of concrete.It can also be seen from the Fig.6that,at7-days and28-days time point,expansive rate of ESCC is about12times and8times of the shrinkage of NSCC respectively. In general,the addition of?bers reduces concrete expansion for all ?ber reinforced concrete specimens.It can be seen that steel?bers content is the dominant factor that affects expansive rate of?ber reinforced concrete.With increase of steel?bers content,expansion of?ber reinforced concrete reduces gradually.In all,specimens with steel?bers content of0.75%show the lowest expansion rate.As shown,the difference of expansion rate between ESF-1and ESF-2 and between ESF-2and ESF-3were175micro-strain and335 micro-strain,respectively,i.e.,the decrease range of expansion rate increases as steel?ber content increases.It can be revealed that restraining effect of steel?ber on expansion increases as steel?ber content increases.Also,it illustrates that addition of PP does not impact the expansion rate signi?cantly as the two curves from ESF-1and EHY are in line with each other closely.
5.Conclusions
From the experiments and analysis conducted above,the following conclusions can be drawn:
1.For workability,8%expansive agent(ESCC)reduces the viscos-
ity of ordinary NSCC.Hybrid steel and polypropylene?bers reinforced mixture(EHY)decreases workability compared with
ESCC and single steel?bers reinforced SCC mixture(ESF).It can be inferred that,based on the test results,addition of PP has an adverse effect impact on workability of fresh ESCC.
2.For compressive strength,it does not show signi?cant differ-
ence between ESCC and NSCC at28days.But the compressive strength of ESCC is improved https://www.doczj.com/doc/9f1718983.html,bined addition of expansive admixture and?bers reduces the concrete strength at7days,while it does not in?uence the28days strength noticeably.
3.Flexural test results show that?exural stiffness of ESCC beam
specimens is lower than that of NSCC.The incorporation of?ber enhances the cracking load of ESCC beams.Self prestress gener-ated in?ber reinforced concrete enables de?ection hardening of
0.50%and0.75%SF reinforced ESCC beam specimens.With the
increase of?ber content,the deformation and?exural capacity of beam specimens enhance.
4.The drying shrinkage test show that expansion of?ber rein-
forced ESCC mixtures decreases as SF content increases.Addi-tion of PP does not impact the expansive rate signi?cantly. https://www.doczj.com/doc/9f1718983.html,prehensively,the incorporation of?ber into expansive SCC
could improve splitting tensile strength and?exural properties signi?cantly while maintaining the decent expansive rate to achieve self-prestress in structural application.In all,?ber reinforced ESCC at both0.25%and0.50%volume content satisfy all the target performance criteria.
Acknowledgments
The?nancial support provided by the National Natural Science Foundation of China under the grants of NSFC51208077, 51421064,and51678111,and the National Basic Research Program of China(973Program,Grant No.2015CB057703)are gratefully acknowledged.
References
[1]ACI237,Self-Consolidating Concrete,American Concrete Institute,Farmington
Hills,MI,2007.
[2]Q.Cao,S.Hwang,K.Khayat,G.Morcous,Design and implementation of self-
consolidating concrete for connecting precast concrete deck panels to bridge girders,J.Mater.Civ.Eng.ASCE(2016).0416058-1-12..
[3]Z.L.Meng,J.Zhou,X.W.Ma,Y.S.Xue,G.Y.Li,In?uences of U-expansion agent
on the shrinkage properties of self-compacting concrete,Concrete8(2013) 79–82(In Chinese).
[4]F.Aslani,S.Nejadi,Creep and shrinkage of self-compacting concrete with and
without?bers,J.Adv.Concr.Technol.11(2003)251–265.
[5]M.Cao,C.Zhang,H.Lv,Mechanical response and shrinkage performance of
cementitious composites with a new?ber hybridization,Constr.Build.Mater.
57(2014)45–52.
[6]X.B.He,Y.Bo,J.Y.Gu,Q.Shen,Combined impacts of polypropylene?bres on
workability,strength and permeability of SCC,Mag.Concr.Res.66(2014) 127–140.
[7]B.Akcay,M.A.Tasdemir,Mechanical behaviour and?bre dispersion of hybrid
steel?bre reinforced self-compacting concrete,Constr.Build.Mater.28(2012) 287–293.
[8]O.Gencel,C.Ozel,W.Brostow,G.Martínez-Barrera,Mechanical properties of
self-compacting concrete reinforced with polypropylene?bres,Mater.Res.15 (2011)216–225.
[9]K.H.Khayat,F.Kassimi,P.Ghoddousi,Mixture design and testing of?ber-
reinforced self-consolidating concrete,ACI Mater.J.111(2014)143–151. [10]M.Yakhlaf,Md.Sa?uddin,K.A.Soudki,Properties of freshly mixed carbon?bre
reinforced self-consolidating concrete,Constr.Build.Mater.46(2013) 224–231.
[11]M.Sahmaran,A.Yurtseven,I.O.Yaman,Workability of hybrid?ber reinforced
self-compacting concrete,Build.Environ.40(2005)1672–1677.
[12]F.Aslani,S.Nejadi,Self-compacting concrete incorporating steel and
polypropylene?bers:compressive and tensile strengths,moduli of elasticity and rupture,compressive stress–strain curve,and energy dissipated under compression,Compos.B53(2013)121–133.
[13]D.A.S.Rambo,F.A.de Silva,R.D.T.Filho,Mechanical behavior of hybrid steel-
?ber self-consolidating concrete:materials and structural aspects,Mater.Des.
54(2014)32–42.
184Q.Cao et al./Construction and Building Materials131(2017)178–185
[14]M.Pajak,T.Ponikiewski,Flexural behavior of self-compacting concrete
reinforced with different types of steel?bers,Constr.Build.Mater.47(2013) 397–408.
[15]GB175-2007,Common Portland Cement,Standards Press of China,Beijing,
2008(In Chinese).
[16]EFNARC,Speci?cation and guidelines for self-compacting concrete,European
Federation for Specialist Construction Chemicals and Concrete Systems, Norfolk,UK,2002.
[17]EFNARC,The European Guidelines for Self-Compacting Concrete,Self-
Compacting Concrete European Project Group,UK,2005.
[18]ASTM C1621/C1621M-14,Standard Test Method for Passing Ability of Self-
Consolidating Concrete by J-Ring,ASTM International,West Conshohocken, PA,2014.
[19]CECS13:1989,Test Methods Used for Steel Fiber Reinforced Concrete,
Standards Press of China,Beijing,2000(In Chinese).[20]GB/T50081-2002,Standard for Test Method of Mechanical Properties on
Ordinary Concrete,China Architecture&Building Press,Beijing,2003(In Chinese).
[21]ASTM C1609/C1609M-07,Standard Test Method for Flexural Performance of
Fiber-Reinforced Concrete(Using Beam With Third-Point Loading),ASTM International,West Conshohocken,PA,2007.
[22]ASTM C157/C157M,Standard Test Method for Length Change of Hardened
Hydraulic-Cement Mortar and Concrete,ASTM International,West Conshohocken,PA,2008.
[23]Y.L.Ding,X.J.Dong,Y.H.Wang,Testing methods and evaluating standards of
?exural toughness for steel?ber reinforced concrete,J.Build.Mater.8(2005) 660–664(in Chinese).
[24]W.Sun,H.Qian,H.Chen,The effect of the combination of hybrid?bers and
expansive agent on the physical properties of cementitious composites,J.Chin.
Ceram.Soc.28(2)(2013).95–99,104.(In Chinese).
Q.Cao et al./Construction and Building Materials131(2017)178–185185
(一)总论 1.寄生虫的中间宿主是指 B A.寄生虫的成虫或无性生殖阶段寄生的宿主B.寄生虫的幼虫或无性生殖阶段寄生的宿主 C.寄生虫成虫或有性生殖阶段寄生的宿主 D.寄生虫的幼虫或有性生殖寄生的宿主 E.寄生虫的储蓄宿主 2.不是机会致病寄生虫的是D A.刚地弓形虫 B.蓝氏贾第鞭毛虫 C.粪类圆线虫D.蛔虫 E.隐孢子虫 3.有些寄生虫的成虫除能寄生于人体外,还可寄生于某些脊椎动物体内,这些动物可成为人体寄生虫病传播的来源,故称为C A.终宿主 B.中间宿主C.保虫宿主 D.转续宿主 E.异位寄生 4.寄生虫的转续宿主是指A A.寄生虫幼虫寄生的非正常宿主 B.寄生虫的适宜中间宿主 C.寄生虫成虫寄生的不适宜宿主 D.寄生虫成虫寄生的适宜的脊椎动物 E.寄生虫适宜的终宿主 5.寄生虫的生活史是指C A.寄生虫的繁殖方式 B.寄生虫的感染方式、途径 C.寄生虫生长、发育、繁殖的过程及环境 D.寄生虫生长繁殖的影响因素 E.寄生虫的生长的环境 6.寄生虫感染期的定义是C A.寄生虫感染宿主的阶段 B.寄生虫感染终宿主的阶段C.寄生虫感染人体的阶段 D.寄生虫感染中间宿主的阶段 E.寄生虫所有的生活史阶段 7.寄生虫对宿主的损伤作用不包括A A.非消除性免疫 B.夺取营养 C.机械性损伤 D.毒性作用 E.过敏反应 8.医学原虫感染的宿主,免疫类型多属于C A.消除性免疫 B.寄生虫适应性免疫C.带虫免疫 D.伴随免疫 E.寄生虫固有免疫 9.寄生虫病的传染源包括A A.病人、带虫者、保虫宿主 B.病人和保虫宿主 C.带虫者和保虫宿主或储存宿主 D.病人和带虫者 E.病人、储蓄宿主 10.人兽共患寄生虫病是指C
浅谈混凝土表面干缩裂缝成因及防治办法 发表时间:2018-10-17T16:37:41.003Z 来源:《防护工程》2018年第12期作者:邵明安 [导读] 基础不均匀沉降;拆模过早;结构性破坏;临时放置位置不当(如箱梁、空心梁板的支座不在永久支座处);施加预应力时混凝土强度不足。限于篇幅等原因,本文仅从温度和湿度变化引起的混凝土干缩裂缝进行分析探讨。 邵明安 临沂市建设工程监理公司山东省 276000 混凝土表面裂缝几乎无处不在,或呈线形分布或成网状分布,或者有规律分布,或者无规则分布。从混凝土浇筑成型至构件的使用期,混凝土的裂缝几乎伴随其终生。就其产生的原因,无外乎以下几点:温度和湿度的变化;混凝土的脆性和不均匀性;结构不合理;碱骨料反应;模板变形;基础不均匀沉降;拆模过早;结构性破坏;临时放置位置不当(如箱梁、空心梁板的支座不在永久支座处);施加预应力时混凝土强度不足。 限于篇幅等原因,本文仅从温度和湿度变化引起的混凝土干缩裂缝进行分析探讨。 1干缩裂缝产生的原因 混凝土初期硬化期间水泥放出大量的水化热,内部温度不断上升,在混凝土表面形成拉应力,后期降温过程中,由于受到其他混凝土构件的约束,又会在混凝土内部出现拉应力。同时,气温(或者混凝土表面温度)也会在混凝土表面引起很大的拉应力。当这些拉应力超出混凝土的抗裂能力时,便会出现裂缝。 绝大多数混凝土内部湿度变化很小,同时变化也很慢,但表面湿度变化较大而剧烈。这主要是因为养护不到位、时干时湿,表面干缩变形受到内部混凝土的约束,使表面混凝土受到拉力,导致表面出现裂缝。 众所周知,混凝土是一种脆性的不均匀性的材料,抗拉强度只有抗压强度的1/10左右。加之,原材料的不均匀性、集料级配的不合理性、水灰比的不稳定性。运输和浇筑过程的离析现象,振捣过程中出现漏振或者过振的现象,形成一个一个层面,在同一个混凝土构件中,其抗拉强度也不均匀,存在很多抗拉能力很低、易于出现裂缝的薄弱部位。在钢筋混凝土中,拉应力主要由钢筋承担,混凝土只承受压应力。如果在其边缘部位出现拉应力,那么只能依靠混凝土自身来承担。如果产生的拉应力大于混凝土的抗拉强度。便形成了裂缝。 2通过温度的控制减少裂缝产生的措施 根据前面的分析,混凝土表面的裂缝是因温度变化形成的拉应力引起的。那么就从控制温度和改善约束条件两方面着手解决。而温度的控制我们又从减少混凝土内部的水化温度和外环境的气温剧变两方面考虑。具体办法有:(1)改善骨料级配。严禁使用单粒级配,采用2种甚至3种粒径段的集料(碎石),进行科学合理的掺配。骨料级配合理可减少水泥用量,而减少水泥用量便可以减少水泥的水化热。同时,改善混凝土的不均匀性,提高混凝土的抗拉强度。 (2)严格控制混凝土的坍落度,通过减少用水量和水泥用量,来控制混凝土的温度应力。 (3)避开高温浇筑混凝土,如果气温高于30℃尽量不要浇筑混凝土,条件实在不允许,可采用对模板降温,给碎石降温,减少混凝土浇筑层等办法。 (4)确定合理的拆摸时间,气温骤降时进行表面保温,以免混凝土表面发生急剧的温度梯度。 (5)施工中长期暴露的混凝土,在寒冷季节采取保温措施。 (6)冬期施工时,如果采用蒸汽养护,需要注意3点,慢升温,慢降温,避高温,以免混凝土表面形成急剧的温度梯度。 (7)拆模后,混凝土一定要做好保温养护,严防常期暴露在高温、干燥、风多的自然环境中,也要杜绝干湿循环,应当覆盖洒水养护,使混凝土表面处于长期湿润状态。既降低混凝土环境温度,又防止表面干缩出现裂缝。特别是混凝土早期的前7天,水化热大,混凝土强度及弹性模量急剧变化。内部产生残余应力,与温度应力进行迭加,而混凝土本身抗拉抗裂性就差,这个时期则更低。因此养护不好更容易出现裂缝。 (8)合理进行分缝分块。 (9)对于地下工程可采用早回填早覆盖。 (10)在混凝土终凝前用木抹子压抹一次,混凝土表面形成微膜并把细小裂缝处理掉。 (11)严格控制钢筋的保护层,若钢筋保护层不足,因收缩沿钢筋位置出现裂缝。 (12)混凝土拆模后应即时覆盖,防止因风吹,减少混凝土表面的水分。 3减水剂的使用对减少混凝土表面裂缝的重要作用 (1)由于混凝土中存在大量的毛细孔道,水分蒸发后毛细管中产生毛细管张力,导致混凝土出现干缩变形。因此,掺合减水剂可以减少水分,从而减少毛细管张力,起到减少于缩变形的可能性。 (2)水灰比是影响混凝土收缩的重要因素,使用减水剂可使混凝土用水量减少25%左右。 (3)水泥用量也是混凝土收缩率的重要影响因素,掺加减水剂的混凝土在保持强度不变的情况下,可减少15%左右的水泥用量。 (4)掺加减水剂还可以改善水泥浆的稠度,减少混凝土的泌水,从而减少混凝土的沉缩变形。 (5)由于减少了用水量,因此减少了水分蒸发后形成的空穴,从而提高了水泥浆与骨料的黏结力,进而提高混凝土的抗裂性能,减少裂缝。 (6)掺加减水剂可使混凝土的密实性提高,从而有效地提高混凝土的抗碳化性,减少碳化收缩。 (7)减水剂一般对混凝土有缓凝作用。但时间恰当,因此在有效防止水泥迅速水化放热基础上,避免因水泥长期不凝造成塑性收缩增加。 (8)减水剂可以改善混凝土的和易性,表面容易抹平,形成微膜,减少水分蒸发,从而减少干缩。 4结束语
吸虫(trematode) 扁形动物门Phylum Platyhelminthes 吸虫纲Class Trematoda 复殖目Order Digenea 吸虫形态 背腹扁平,两侧对称 具口、腹吸盘 无体腔 雌雄同体 消化道:肠盲管 吸虫对寄生生活的适应 特殊的附着器官:吸盘等 消化系统退化 高度发达的生殖能力 有无性增殖世代 吸虫的雌性生殖系统 卵巢(1个)→输卵管(卵黄腺通过卵黄总管,受精囊注入)→卵模(梅氏腺)→子宫(盘曲)→生殖腔→生殖孔 吸虫的雄性生殖系统 睾丸(1-2个)→输出管(2根)→输精管→储精囊→射精管→阴茎(阴茎袋)→生殖腔→生殖孔 吸虫卵特点 卵圆形,大小差异大 多数具卵盖 卵内含卵细胞+卵黄细胞 或毛蚴 吸虫生活史阶段 虫卵(Egg)毛蚴(Miracidium)胞蚴(Sporocyst) 雷蚴(Redia) 尾蚴(Cercaria) 囊蚴(Metacercaria)童虫(Preadult) 成虫(Adult worm) 吸虫的无性世代 虫卵(水中或螺内孵化)→毛蚴(螺宿主淋巴系统内发育)→胞蚴(螺内无性增殖)→雷蚴(螺内无性增殖)→尾蚴(逸出螺体)→囊蚴(第二中间宿主)→ 常见医学吸虫 华支睾吸虫(肝吸虫)卫氏并殖吸虫(肺吸虫) 布氏姜片吸虫(姜片虫)日本裂体吸虫(血吸虫) 华支睾吸虫Clonorchis sinensis 概述 寄生肝胆管 致肝吸虫病,主要分布远东地区 人体感染与饮食习惯有关 人体首例1874;国内1908上海 成虫形态 为吸虫的模式形态大小、体形似葵花子口吸盘略大于腹吸盘睾丸分支,卵巢分叶虫卵形态 蠕虫卵中之最小者形似芝麻,具卵盖、肩峰,另一端有小棘,内含毛蚴
大体积混凝土干缩裂缝的原因与预防 现代工程整浇混凝土都具有不同程度的大体积混凝土的性质,尤其C50以上混凝土水泥用量大,水灰比较小,对干燥收缩有利(过低水灰比对早期塑性收缩和自生收缩不利),但由于水泥浆量较多以及高效减水剂的作用,总收缩可比中低强度混凝土大,并且拉压强度比降低,徐变小,应力松弛低,脆性高容易引起开裂。本文对高强混凝土施工过程中容易产生收缩裂缝的原因进行分析: 一、含水量,含水量越高,表现为水泥浆量或含胶浆量越大,坍落度大,收缩越大。收缩越大的混凝土拆模过早,表面早期大量失水易产生裂缝。施工过程中应严格控制坍落度,避免雨中浇筑混凝土,严禁现场加水。 二、原材料质量,粗细骨料中含泥量越大收缩越大,骨料粒径越细,砂率越高,收缩越大,水泥活性越高,颗粒越细比表面积越大,收缩越大,超细掺合料具有相同性质。混凝土近代发展高效化学外加剂和矿物掺合料作为第五、第六组分掺入,有利于提高混凝土的耐久性,但是应当注意原材料的用量和质量。大掺量高性能混凝土的早期塑性收缩和自生收缩较大,易引起开裂。必须严格控制原材料质量,不宜采用吸水率大的骨料及掺合料(骨料可以预先水洗)。重视外加剂掺量(要检测称量装置的可靠性)的准确性和敏感性,掺量过多过少会造成质量事故。
三、早期养护,养护时间过短,收缩大易产生裂缝。应适当延长早期养护时间,拆模后宜覆盖塑料薄膜,加强潮湿养护对控制早期塑性裂缝很有益处。 四、注意振捣,特别是在交接处,超振会造成混凝土离析和大量泌水,表面失水过快,早期收缩越大,表面容易产生裂缝。 五、环境,施工过程中如果风速较大,收缩就越大,封闭或开敞环境中的裂缝程度取决于环境温湿度变化,水化温升,里表温差及降温速率相差大易产生裂缝。应当控制较低的入模温度,在天气好的情况下施工,尽量避免中午高温时段进行浇筑。 混凝土工程是桥梁的重要组成部分,施工过程中现场技术人员、拌合站、试验室应相互配合,及时沟通,保证混凝土施工过程中的连续稳定,才能造就完美工程。
第三章吸虫 一、选择题 【A型题】 3001.下列哪项不是吸虫的形态结构特点() A.外观呈叶状或长舌状 B.腹背扁平 C.多为雌雄同体 D.具口,腹吸盘 E.有体腔 3002.吸虫的受精过程一般可以是() A.自体受精 B.异体受精 C.自体及异体受精 D.精子和卵子在体外受精 E.以上都不是 3003.寄生人体吸虫的繁殖方式() A.幼虫进行有性生殖,成虫进行无性生殖 B.幼虫进行无性生殖,成虫进行有性生殖 C.幼虫和成虫均进行无性生殖 D.幼虫和成虫均进行有性生殖 E.幼虫不繁殖,成虫进行有性生殖 3004.需要一个中间宿主即可完成生活史的吸虫() A.华支睾吸虫 B.日本血吸虫 C.卫氏并殖吸虫 D.斯氏狸殖吸虫 E.异形吸虫 3005.华支睾吸虫的主要保虫宿主为() A.纹沼螺 B.淡水鱼及淡水虾 C.猫,狗 D.牛,羊 E.家禽3006.华支睾吸虫对宿主的特异性要求不严格,表现在()
A.可寄生于螺,也可寄生于鱼,虾 B.所寄生的鱼类繁多(包括大型食用鱼和小杂鱼) C.我国各地吃鱼习惯不同,但均有病例报告 D.终宿主除人体,还可寄生于肉食性哺乳动物 E.幼虫和成虫所寄生的宿主种类较多及地区都较广泛 3007.布氏姜片虫的中间宿主() A.纹沼螺 B.赤豆螺 C.拟钉螺 D.扁卷螺 E.川卷螺 3008.我国布氏姜片虫的最主要保虫宿主是() A.家鼠及野鼠 B.鸡,鸭 C.猪 D.狗,猫 E.牛,羊 3009.影响布氏姜片吸虫囊蚴在自然界生存的最重要因素为() A.温度 B.水的酸碱度(PH) C.干燥 D.光线 E.水的深度3010.肝片形吸虫的重要性在于() A.人体感染范围广泛 B.保虫宿主种类多 C.虫体较大,引起症状严重 D.使牛,羊致病,影响畜牧业发展 E.椎实螺分布广泛,致本虫易于散播3011.并殖类吸虫的形态特征是() A.卵巢与子宫并列 B.两个睾丸并列 C.两侧卵黄腺并列分布 D.卵巢与子宫并列和两个睾丸并列 E.生殖孔与排泄孔并列 3012.斯氏狸殖吸虫的第一中间宿主是() A.纹沼螺 B.长角涵螺 C.川卷螺 D.扁卷螺 E.拟钉螺3013.感染肺吸虫是由于: A.食入未煮熟的淡水鱼 B.生食水红菱,荸荠(马蹄) C.生食或食入未煮熟的溪蟹 D.食入未煮熟的淡水螺 E.吸入感染性虫卵
浅谈混凝土表面干缩裂缝防治措施 发表时间:2012-08-27T10:18:40.887Z 来源:《赤子》2012年第6期作者:谢贰军 [导读] 当这些拉应力超出混凝土的抗裂能力时,便会出现裂缝。 谢贰军(广西富林劳务有限公司,广西南宁 530022) 摘要:混凝土是当前建筑工程施工中主要的施工原材料之一,随着当前社会的不断发展,人们对混凝土认识日益增加,在混凝土施工中对其各种施工缺陷的管理和控制方式手段不断的增加。在混凝土施工中,表面干缩裂缝的形成是其主要的质量隐患和缺陷。结合本人的多年实践,针对混凝土表面出现的干缩裂缝,通过在施工中的各种原理和缺陷因素进行综合分析,提出其在施工中的主要处理手段和处理方法。 关键词:混凝土;干缩裂缝;防治办法 混凝土是当前建筑工程施工中主要的施工形式,由于其物美价廉,取材方便,施工技术简单和耐久性能高成为当前建筑工程应用的主要方式。混凝土表面裂缝几乎无处不在,或呈线形分布或成网状分布,其裂缝出现的过程中是一种无规律的分布状况和分布方法,其在施工的过程中如何解决和提高其裂缝的出现措施和出现方法是当前建筑工程在施工中探讨的重点。从混凝土浇筑成型至构件的使用期,混凝土的裂缝几乎伴随其终生。其混凝土裂缝的产生原因主要是有以下几点:温度和湿度的变化;混凝土的脆性和不均匀性;在施工中构造结构的不合理,以及在混凝土配合中各种原材料应用的不够准确和完善,在施工的时候由于施工环节控制不严谨,模板变形;基础不均匀沉降;拆模过早;结构性破坏,临时放置的时候选用放置的位置不恰当,造成混凝土在施工中出现了诸多的裂缝因素和产生方式。 1 干缩裂缝产生的原因 混凝土初期硬化期间水泥放出大量的水化热,使得在混凝土凝结的过程中内部温度不断的提高和上升,造成混凝土在干缩的时候其表面温度不断的提高,其在发展中出现了诸多的裂缝和制约影响因素是当前混凝土表面应拉力出现了巨大的变化。后期降温过程中,由于受到其他混凝土构件的约束,又会在混凝土内部出现拉应力。同时,气温(或者混凝土表面温度)也会在混凝土表面引起很大的拉应力。当这些拉应力超出混凝土的抗裂能力时,便会出现裂缝。 绝大多数混凝土内部湿度变化很小,同时变化也很慢,但表面湿度变化较大而剧烈。这主要是因为养护不到位、时干时湿,表面干缩变形受到内部混凝土的约束,使表面混凝土受到拉力,导致表面出现裂缝。 众所周知,混凝土是一种脆性的不均匀性的材料,抗拉强度只有抗压强度的1/10左右。加之,原材料的不均匀性、集料级配的不合理性、水灰比的不稳定性。运输和浇筑过程的离析现象,振捣过程中出现漏振或者过振的现象,形成一个一个层面,在同一个混凝土构件中,其抗拉强度也不均匀,存在很多抗拉能力很低、易于出现裂缝的薄弱部位。在钢筋混凝土中,拉应力主要由钢筋承担,混凝土只承受压应力。如果在其边缘部位出现拉应力,那么只能依靠混凝土自身来承担。如果产生的拉应力大于混凝土的抗拉强度。便形成了裂缝。 2 通过温度的控制减少裂缝产生的措施 凝土是一种由砂石骨料、水泥、水及其他外加材料混合而形成的非均质脆性材料。由于混凝土施工的过程中各种施工工艺和施工方式日益完善,在施工的过程中是通过相关的技术措施技术管理手段进行分析与应用。根据前面的分析,混凝土表面的裂缝是因温度变化形成的拉应力引起的。那么就从控制温度和改善约束条件两方面着手解决。而温度的控制我们又从减少混凝土内部的水化温度和外环境的气温剧变两方面考虑。具体办法有: (1)改善骨料级配。严禁使用单粒级配,采用2种甚至3种粒径段的集料(碎石),进行科学合理的掺配。骨料级配合理可减少水泥用量,而减少水泥用量便可以减少水泥的水化热。同时,改善混凝土的不均匀性,提高混凝土的抗拉强度。(2)严格控制混凝土的坍落度,通过减少用水量和水泥用量,来控制混凝土的温度应力。 (3)避开高温浇筑混凝土,如果气温高于30℃尽量不要浇筑混凝土,条件实在不允许,可采用对模板降温,给碎石降温,减少混凝土浇筑层等办法。 (4)确定合理的拆摸时间,气温骤降时进行表面保温,以免混凝土表面发生急剧的温度梯度。(5)施工中长期暴露的混凝土,在寒冷季节采取保温措施。 (6)冬期施工时,如果采用蒸汽养护,需要注意3点,慢升温,慢降温,避高温,以免混凝土表面形成急剧的温度梯度。(7)拆模后,混凝土一定要做好保温养护,严防常期暴露在高温、干燥、风多的自然环境中,也要杜绝干湿循环,应当覆盖洒水养护,使混凝土表面处于长期湿润状态。既降低混凝土环境温度,又防止表面干缩出现裂缝。特别是混凝土早期的前7天,水化热大,混凝土强度及弹性模量急剧变化。内部产生残余应力,与温度应力进行迭加,而混凝土本身抗拉抗裂性就差,这个时期则更低。因此养护不好更容易出现裂缝。 (8)合理进行分缝分块。 (9)对于地下工程可采用早回填早覆盖。 (10)在混凝土终凝前用木抹子压抹一次,混凝土表面形成微膜并把细小裂缝处理掉。 (11)严格控制钢筋的保护层,若钢筋保护层不足,因收缩沿钢筋位置出现裂缝。 (12)混凝土拆模后应即时覆盖,防止因风吹,减少混凝土表面的水分。 3 减水剂的使用对减少混凝土表面裂缝的重要作用 (1)由于混凝土中存在大量的毛细孔道,水分蒸发后毛细管中产生毛细管张力,导致混凝土出现干缩变形。因此,掺合减水剂可以减少水分,从而减少毛细管张力,起到减少于缩变形的可能性。 (2)水灰比是影响混凝土收缩的重要因素,使用减水剂可使混凝土用水量减少25%左右。(3)水泥用量也是混凝土收缩率的重要影响因素,掺加减水剂的混凝土在保持强度不变的情况下,可减少15%左右的水泥用量。(4)掺加减水剂还可以改善水泥浆的稠度,减少混凝土的泌水,从而减少混凝土的沉缩变形。(5)由于减少了用水量,因此减少了水分蒸发后形成的空穴,从而提高了水泥浆与骨料的黏结力,进而提高混凝土的抗裂性能,减少裂缝。 (6)掺加减水剂可使混凝土的密实性提高,从而有效地提高混凝土的抗碳化性,减少碳化收缩。
造成混凝土干缩裂缝的原因有,施工单位对混凝土的养护不良,使表面水分蒸发过快,体积收缩,而楼板内部湿度变化较小。避免在混凝土施工过程中出现肝裂缝,施工单位应采取防护措施。1。混凝土水泥用量、水灰比和砂率不能过大,严格控制砂石含泥量,避免食用过量粉沙,振捣要密实,并对板面进行二次压抹,提高混凝土抗拉强度,减少干缩。2。加强混凝土早期养护,并适当延长养护时间;3。浇筑混凝土前将基层模板浇水湿透。4。混凝土浇筑后应及早进行洒水养护,楼板干缩裂缝对结构强度影响不大,但会使钢筋锈蚀,影响美观,处理意见,一般可在表面抹一层薄砂浆进行处理。 工程混凝土楼板出现裂缝的现象比较常见,现根据有关资料,对现浇混凝土楼板和砌块填充墙裂缝的原因和对策分析如下,供参考。 一、现浇混凝土楼板裂缝的类型 1.纵向裂缝:即沿建筑物纵向方向的裂缝,出现在板下皮居多,个别上下贯通。 2.横向裂缝:即在跨中1/3范围内,沿建筑物横向方向的裂缝,出现在板下皮居多,个别上下贯通。 3.角部裂缝:在房间的四角出现的斜裂缝,板上皮居多。 4.不规则裂缝:分布及走向均无规则的裂缝。 5.楼板根部的横向裂缝:距支座在30cm内产生的裂缝,位于板上皮。 6.顺着预埋电线管方向产生的裂缝。 二、楼板产生裂缝的原因 1.设计方面 1.1 设计结构时安全储备偏小,配筋不足或截面较小,使梁板成型后刚度差,整体挠度偏大,引起板四角裂缝。 1.2 设计板厚不够,又不做挠度验算,整体挠度偏大,引起板四角裂缝。 1.3 房屋较长时未设置伸缩缝,在薄弱环节产生收缩裂缝。(美国混凝土学会的资料认为混凝土有干缩和温度变形两种,干缩变形每30.48m约收缩19mm。温度变化引起的变形为,37℃的温度变化每30.48m 收缩或延长19mm 左右。国内有人认为40m 长的楼板因硬化凝固产生的纵向收缩量为8—20mm。) 1.4 基础设计处理不当,引起不均匀沉降,使上部结构产生附加应力,导致楼板裂缝。 1.5 楼板双向受力,按单向板配筋,引起裂缝。 2.商品混凝土原因 2.1 水灰比大,水泥用量大。 2.2 高效缓凝剂用量过大,在未凝固前石子下沉,产生沉缩裂缝,常发生在梁板交接处。 2.3 砂石质量不好,级配不好,含泥量大,含粉量大。 3 施工原因 3.1 养护不到位,强制性规范要求混凝土养护要苫盖并浇水,现在大多数不苫盖,浇水也不能保证经常性湿润。 3.2 施工速度过快,上荷早,特别是砖混住宅楼板,前一天浇筑完楼板,第二天即上砖、走车,造成早期混凝土受损。 3.3 冬时期间受冻。 3.4 拆模过早或模板支撑系统刚度不够。 3.5 混凝土表面浮浆过厚,表面强度不够。 3.6 施工时楼板混凝土盖筋被踩弯、踩倒,保护层过厚,承载力下降。
寄生虫学吸虫部分复习题 一、A型题:每道试题下有A、B、C、D、E 5个备选答案,从中选出1个最佳答案,并按要求答在答卷上。每题: 0.50分 01、并殖吸虫卵的颜色通常是( ) A.淡黄色 B.棕黄色 C.金黄色 D.黄褐色 E.无颜色 02、布氏姜片虫的保虫宿主主要是( ) A.牛 B.猪 C.猫 D.犬 E.羊 03、在卫氏并殖吸虫生活史中,野猪、猪、兔等可作为( ) A.终宿主 B.中间宿主 C.保虫宿主 D.转续宿主 E.第二中间宿主 04、土源性蠕虫生活史的特点是( ) A.卵在 外界环境中发育 B.幼虫在外界环境中发育 C.卵和(或)幼虫在外界环境中发育 D.仅转换宿主1次 E.需要转换宿主2次以上 05、人体寄生吸虫的繁殖方式是( ) A.幼虫行有性生殖,成虫行无性生殖 B.幼虫行无性生殖,成虫行有性生殖 C.幼虫和成虫均行无性生殖 D.幼虫和成虫均行有性生殖 E.幼虫行幼体增殖,成虫行孤雌生殖 06、生物源性蠕虫的生活史特点是( ) A.需要转换宿主在2 次以上 B.幼虫均需在中间宿主体内发育至感染期才能感染人体 C.虫卵必须入水才能继续发育 D.人经口而感染 E.虫体在人体内均能发育为成虫 07、寄生人体的吸虫繁殖方式( ) A.幼虫进行有性生殖,成虫进行无性生殖 B.幼虫进行无性生殖,成虫进行有性生殖
C.幼虫和成虫均进行无性生殖 D.幼虫和成虫均进行有性生殖 E.幼虫不繁殖,成虫进行有性生殖 08、关于吸虫生活史的特征,错误的描述是( ) A.有终宿主和保虫宿主 B.幼虫发育过程在水生动物或植物进行 C.幼虫发育至成虫需蜕皮 D.更换宿主生活史才能完成 E.生活史中有性世代与无性世代交替 09、日本血吸虫卵外壳的超微结构( ) A.表面光滑 B.有微管贯通壳内外 C.由卵黄膜、壳质层和脂层组成 D.表面有点状花纹 E.外被一层蛋白质膜 10、环卵沉淀试验是检查( ) A.血清中的血吸虫抗原 B.循环的抗血吸虫抗体 C.循环的血吸虫特异性免疫复合物 D.粪便中的虫卵 E.虫卵中孵出的毛蚴 11、直肠粘膜压片法用于诊断( ) A.旋毛虫病 B.血吸虫病 C.猪带绦虫病 D.弓形虫病 E.蛲虫病 12、日本血吸虫感染人体后产生的免疫力能杀伤再进入人体内的( ) A.雌虫 B.雄虫 C.童虫 D.虫卵 E.以上均不是 13、布氏姜片吸虫寄生在( ) A.胆囊 B.小肠 C.结肠 D.胃 E.直肠 14、日本血吸虫成虫寄生于人体的( ) A.肝脏 B.小肠 C.肠系膜动脉 D.肠系膜静脉 E.直肠、乙状结肠 15、血吸虫毛蚴最显著的向性之一是( )
混凝土总是开裂,原来是这个原因导致的 1、荷载引起的裂缝 混凝土在常规静、动荷载及次应力下产生的裂缝称荷载裂缝,归纳起来主要有直接应力裂缝、次应力裂缝两种。直接应力裂缝是指外荷载引起的直接应力产生的裂缝,次应力裂缝是指由外荷载引起的次生应力产生裂缝。 荷载裂缝特征依荷载不同而异呈现不同的特点。这类裂缝多出现在受拉区、受剪区或振动严重部位。但必须指出,如果受压区出现起皮或有沿受压方向的短裂缝,往往是结构达到承载力极限的标志,是结构破坏的前兆,其原因往往是截面尺寸偏小。 2、收缩引起的裂缝 混凝土具有热胀冷缩性质,当外部环境或结构内部温度发生变化,混凝土将发生变形,若变形遭到约束,则在结构内将产生应力,当应力超过混凝土抗拉强度时即产生温度裂缝。在某些大跨径桥梁中,温度应力可以达到甚至超出活载应力。温度裂缝区别其它裂缝最主要特征是将随温度变化而扩张或合拢。 3、荷载引起的裂缝 在实际工程中,混凝土因收缩所引起的裂缝是最常见的。在混凝土收缩种类中,塑性收缩和缩水收缩(干缩)是发生混凝土体积变形的主要原因,另外还有自生收缩和炭化收缩。 塑性收缩,发生在施工过程中、混凝土浇筑后4~5小时左右,此时水泥水化反应激烈,分子链逐渐形成,出现泌水和水分急剧蒸发,混凝土失水收缩,同时骨料因自重下沉,因此时混凝土尚未硬化,称为塑性收缩。塑性收缩所产生量级很大,可达1%左右。在骨料下沉过程中若受到钢筋阻挡,便形成沿钢筋方向的裂缝。在构件竖向变截面处如T梁、箱梁腹板与顶底板交接处,因硬化前
控制水灰比,避免过长时间的搅拌,下料不宜太快,振捣要密实,竖向变截面处宜分层浇筑。 缩水收缩(干缩),混凝土结硬以后,随着表层水分逐步蒸发,湿度逐步降低,混凝土体积减小,称为缩水收缩(干缩)。因混凝土表层水分损失快,内部损失慢,因此产生表面收缩大、内部收缩小的不均匀收缩,表面收缩变形受到内部混凝土的约束,致使表面混凝土承受拉力,当表面混凝土承受拉力超过其抗拉强度时,便产生收缩裂缝。混凝土硬化后收缩主要就是缩水收缩。如配筋率较大的构件(超过3%),钢筋对混凝土收缩的约束比较明显,混凝土表面容易出现龟裂裂纹。 自生收缩,自生收缩是混凝土在硬化过程中,水泥与水发生水化反应,这种收缩与外界湿度无关,且可以是正的(即收缩,如普通硅酸盐水泥混凝土),也可以是负的(即膨胀,如矿渣水泥混凝土与粉煤灰水泥混凝土)。 炭化收缩,大气中的二氧化碳与水泥的水化物发生化学反应引起的收缩变形。炭化收缩只有在湿度50%左右才能发生,且随二氧化碳的浓度的增加而加快。炭化收缩一般不做计算。 混凝土收缩裂缝的特点是大部分属表面裂缝,裂缝宽度较细,且纵横交错,成龟裂状,形状没有任何规律。 4、地基础变形引起的裂缝 由于基础竖向不均匀沉降或水平方向位移,使结构中产生附加应力,超出混凝土结构的抗拉能力,导致结构开裂。 5、钢筋锈蚀引起的裂缝 由于混凝土质量较差或保护层厚度不足,混凝土保护层受二氧化碳侵蚀炭化至钢筋表面,使钢筋周围混凝土碱度降低,或由于氯化物介入,钢筋周围氯离子
寄生虫学吸虫部分复习题 一、A型题:每道试题下有A、B、C、D、E 5个备选答案,从中选出1个最佳答案,并按要求答在答卷上。每题: 0.50分 01、并殖吸虫卵的颜色通常是( ) A.淡黄色 B.棕黄色 C.金黄色 D.黄褐色 E.无颜色 02、布氏姜片虫的保虫宿主主要是( ) A.牛 B.猪 C.猫 D.犬 E.羊 03、在卫氏并殖吸虫生活史中,野猪、猪、兔等可作为( ) A.终宿主 B.中间宿主 C.保虫宿主 D.转续宿主 E.第二中间宿主 04、土源性蠕虫生活史的特点是( ) A.卵在外界环境中发育 B.幼虫在外界环境中发育 C.卵和(或)幼虫在外界环境中发育 D.仅转换宿主1次 E.需要转换宿主2次以上 05、人体寄生吸虫的繁殖方式是( ) A.幼虫行有性生殖,成虫行无性生殖 B.幼虫行无性生殖,成虫行有性生殖 C.幼虫和成虫均行无性生殖 D.幼虫和成虫均行有性生殖 E.幼虫行幼体增殖,成虫行孤雌生殖 06、生物源性蠕虫的生活史特点是( ) A.需要转换宿主在2 次以上 B.幼虫均需在中间宿主体内发育至感染期才能感染人体 C.虫卵必须入水才能继续发育 D.人经口而感染 E.虫体在人体内均能发育为成虫 07、寄生人体的吸虫繁殖方式( ) A.幼虫进行有性生殖,成虫进行无性生殖 B.幼虫进行无性生殖,成虫进行有性生殖 C.幼虫和成虫均进行无性生殖 D.幼虫和成虫均进行有性生殖 E.幼虫不繁殖,成虫进行有性生殖 08、关于吸虫生活史的特征,错误的描述是( ) A.有终宿主和保虫宿主 B.幼虫发育过程在水生动物或植物进行 C.幼虫发育至成虫需蜕皮
D.更换宿主生活史才能完成 E.生活史中有性世代与无性世代交替 09、日本血吸虫卵外壳的超微结构( ) A.表面光滑 B.有微管贯通壳内外 C.由卵黄膜、壳质层和脂层组成 D.表面有点状花纹 E.外被一层蛋白质膜 10、环卵沉淀试验是检查( ) A.血清中的血吸虫抗原 B.循环的抗血吸虫抗体 C.循环的血吸虫特异性免疫复合物 D.粪便中的虫卵 E.虫卵中孵出的毛蚴 11、直肠粘膜压片法用于诊断( ) A.旋毛虫病 B.血吸虫病 C.猪带绦虫病 D.弓形虫病 E.蛲虫病 12、日本血吸虫感染人体后产生的免疫力能杀伤再进入人体内的( ) A.雌虫 B.雄虫 C.童虫 D.虫卵 E.以上均不是 13、布氏姜片吸虫寄生在( ) A.胆囊 B.小肠 C.结肠 D.胃 E.直肠 14、日本血吸虫成虫寄生于人体的( ) A.肝脏 B.小肠 C.肠系膜动脉 D.肠系膜静脉 E.直肠、乙状结肠 15、血吸虫毛蚴最显著的向性之一是( ) A.向湿性 B.向光性 C.向上性 D.向触性 E.向温性 16、华支睾吸虫的第一中间宿主是( ) A.钉螺 B.纹沼螺 C.川卷螺类 D.拟钉螺类 E.扁卷螺类 17、日本血吸虫的主要寄生部位是( ) A.膀胱静脉丛 B.胃底静脉丛
1.为什么混凝土在潮湿条件下养护时收缩较小,干燥条件下养护时收缩较大,而在水中养 护时却几乎不收缩? 2. 工地上为何常对强度偏低而塑性偏大的低碳盘条钢筋进行冷拉。 3. 加气混凝土砌块砌筑的墙抹砂浆层,采用于烧结普通砖的办法往墙上浇水后即抹,一 般的砂浆,往往易被加气混凝土吸去水分而容易干裂或空鼓,请分析原因。 4. 高速公路的沥青混凝土面层及抗滑表层可否使用石屑作热拌沥青混合料的细集料? 5. 吸声材料与绝热材料的气孔特征有何差别? 1. 混凝土在干燥条件下养护时,由于水化过程不能充分进行,混凝土内毛细孔隙的含量较高,因而干缩值较大;当在潮湿条件下养护时,水分较充足,毛细孔隙的数量相对较少,因而干缩值较小;当混凝土在水中养护时,毛细孔隙内的水面不会弯曲,不会引起毛细压力,所以混凝土不会产生收缩,且由于凝胶表面吸附水,增大了凝胶颗粒间的距离,使得混凝土在水中几乎不产生收缩。但将水中养护的混凝土放置于空气中时,混凝土也会产生干缩,不过干缩值小于一直处于空气中养护的混凝土。 2. 对钢筋冷拉可提高其屈服强度,但塑性变形能力有所降低,工地上常对强度偏低而塑性偏大的低碳盘条钢筋进行冷拉。 3. 加气混凝土砌块的气孔大部分是"墨水瓶"结构,只有小部分是水分蒸发形成的毛细孔,肚大口小,毛细管作用较差,故吸水导热缓慢。烧结普通砖淋水后易吸足水,而加气混凝土表面浇水不少,实则吸水不多。用一般的砂浆抹灰易被加气混凝土吸去水分,而易产生干裂或空鼓。故可分多次浇水,且采用保水性好、粘结强度高的砂浆。 4. 热拌沥青混合料的细集料宜采用优质的天然砂或人工砂,在缺砂地区,也可使用石屑。但用于高速公路、一级公路、城市快速路、主干路沥青混凝土表层及抗滑表层的石屑用量不宜超过砂的用量。 5. 吸声材料与绝热材料都是属于具有多孔结构的材料,但对材料的孔隙特征上有着完全不同的要求。绝热材料要具有封闭的不连通的气孔,这种气孔越多,其绝热性能越好;而吸声材料恰恰相反,要求具有开放的、互相连通的气孔,这种孔隙越多,其吸声性能越好。 1.某混凝土搅拌站原使用砂的细度模数为 2.5,后改用细度模数为2.1的砂。改砂后原混凝 土配方不变,发觉混凝土坍落度明显变小。请分析原因。 2. 马歇尔试验方法简便,世界各国广泛使用,其主要作用是什么?可否正确反映沥青混 合料的抗车辙能力? 3. 现在建筑工程上倾向于使用塑料管代替镀锌管,请比较塑料管与镀锌管的优缺点。 4. 木材的边材与心材有何差别。 5. 某工程队于7月份在湖南某工地施工,经现场试验确定了一个掺木质素磺酸钠的混凝 土配方,经使用一个月情况均正常。该工程后因资金问题暂停5个月,随后继续使用原混凝土配方开工。发觉混凝土的凝结时间明显延长,影响了工程进度。请分析原因,并提出解决办法。 1.因砂粒径变细后,砂的总表面积增大,当水泥浆量不变,包裹砂表面的水泥浆层变薄, 流动性就变差,即坍落度变小。 2. 从多年实践和研究总结可知,马歇尔试验可有效地用于配合比设计决定沥青用量和施 工质量控制,但它不能正确反映沥青混合料的抗车辙能力。 3. 与镀锌管相比,塑料管重量要轻的多只有镀锌管的1/8,在运输,安装方面要省工省时的 多; 塑料管不腐蚀,不生锈,镀锌管则很容易生锈; 特别是塑料管的表面光滑,表面张力小,
人体寄生虫学复习题 一、名词解释 寄生虫宿主终宿主中间宿主保虫宿主生活史感染阶段带虫者 伴随免疫夜现周期性生物源性蠕虫疟疾复发生物性传播 二、填空题 1、寄生虫对宿主的致病作用包括、、、。 2、寄生虫病流行的基本环节为、、。 3、寄生虫病的传染源有、、。 4、寄生虫病的防治原则为、、。 5、常见蠕虫卵的形态结构,有波浪状蛋白质膜的是,外形两侧不对称的是,最小的是,最大的是。 6、写出下列寄生虫的寄生部位:蛔虫,钩虫,蛲虫,丝虫,肝吸虫,片虫,日本血吸虫,猪带绦虫,牛带绦虫,疟原虫和。 7、写出下列寄生虫的感染阶段:蛔虫,钩虫,蛲虫,丝虫,肝吸虫,片虫,日本血吸虫,猪带绦虫、,牛带绦虫,疟原虫。 8、取痰液检查的寄生虫病有、、。 9、可致肝、肺、脑同时损害的寄生虫有、、、。 10、填中间宿主。肝吸虫第一中间宿主有、,卫氏肺吸虫的第一中间宿主,片虫的中间宿主。 11、典型疟疾发作的三步曲是、、。 12、人体寄生虫学容包括、、。 13、建国初期的五大寄生虫病,在长江以北流行是。 14、线虫的发育过程中有、、三个阶段。 15、蛔虫对人体最严重的危害在于成虫有乱窜、钻孔的习性,由此引起,其中最常见的症状是、。钩虫对人体的主要危害,丝虫对人体的主要危害。 16、蛔虫病常用的实验诊断方法是。饱和盐水漂浮法主要用于的检查。 17、送检标本需注意保温的原虫有与,需在晚间采集血液标本检查的寄生虫是。 18、能以引起贫血为主要临床表现的寄生虫是、、。 19、猪带绦虫感染人体的方式有、、。 20、医学节肢动物对人的主要危害是,其方式有与。
三、单项选择题 1、联合国倡议重点防治的6种热带病中除麻风病外,5种是寄生虫病,它们是: A、疟疾、血吸虫病、钩虫病、丝虫病、利什曼原虫病 B、疟疾、血吸虫病、丝虫病、利什曼原虫病、锥虫病 C、疟疾、钩虫病、丝虫病、蛲虫病、蛔虫病 D、血吸虫病、钩虫病、蛔虫病、痢疾阿米巴病 2、人体寄生虫学的畴不包括: A、医学原虫学 B、医学蠕虫学 C、医学昆虫学 D、医学微生物学 3、下列哪项不是寄生虫病的流行特点: A、致病性 B、地方性 C、季节性 D、自然疫源性 4、人体抗寄生虫的免疫多表现为: A、非消除性免疫 B、消除性免疫 C、先天免疫 D、伴随免疫 5、寄生物是指: A、二种共栖生物中受益的一方 B、二种互利共生生物中受益的一方 C、寄生关系的二种生物中受益的一方 D、寄生关系二种生物中的任何一方 6、下列对寄生虫的描述,哪项不恰当: A、一生离不开宿主 B、可自宿主体表获得营养 C、可自宿主体获得营养 D、对宿主造成损害 7、专性寄生虫是指寄生虫的: A、整个生活史中均需过寄生生活 B、整个生活史中均需选择特殊宿主 C、至少一个生活史期必须过寄生生活 D、至少一个生活史期必须严格选择宿主 8、第一中间宿主是指寄生虫的: A、无性期寄生的几个宿主中最重要的一个 B、无性期寄生的几个宿主中最前的一个 C、有性期寄生的几个宿主中最重要的一个 D、有性期寄生的几个宿主中最前的一个 9、寄生虫的幼虫阶段或无性生殖阶段所寄生的宿主称: A、终宿主 B、中间宿主 C、保虫宿主 D、转续宿主
浅析混凝土的干燥收缩 摘要:干燥收缩是水泥混凝土中常见的一种变形,而干缩变形又是引起水泥混凝土材料开裂的最主要原因之一。因此研究混凝土的干燥收缩机理,对减小混凝土结构的收缩和提高混凝土结构的耐久性有非常重要的意义。 关键词:混凝土;干燥收缩;机理 中图分类号:tu528.1 文献标识码:a drying shrinkage of concrete li-jing abstract:drying shrinkage of cement concrete is a common deformation. shrinkage of concrete and other cement-based materials often are at the origin of crack formation. therefore, it is important to study the shrinkage mechanism in order to be able to minimize shrinkage. it also has the important meaning to extend service life of reinfored concrete structures. keyword: concrete; drying shrinkage; mechanism 1. 引言 干燥收缩简称干缩,是指混凝土停止养护后,在不饱和的空气中失去内部毛细孔和凝胶孔中的吸附水而发生的不可逆收缩。 近年来随着高强混凝土(hsc)的广泛应用,因干燥收缩而引起混凝土结构的裂缝更为普遍。根据国内外高强混凝土配合比研究和应
吸虫部分测试习题 一、名词解释 1.抱雌沟 2.血吸虫伴随免疫 3.尾蚴性皮炎 二、填空题 1. 吸虫(trematode)属_ 门纲。 2. 吸虫消化系统包括、、、和。 3. 吸虫的消化系统中无,未被消化吸收的废物经排出体外。 4. 复殖吸虫中除了的种类是雌雄异体外,其它均为雌雄同体。 5. 复殖吸虫的系统最为发达。 6. 复殖吸虫的生活史都需经历与的交替。 7. 复殖吸虫生活史复杂,它包括卵、、、、、、与成虫阶段。 8. 复殖吸虫离不开,虫卵必须在或被软体动物宿主吞食后才能孵出毛蚴。 9. 裂体科吸虫无期,直接侵入终宿主发育为成虫。 10. 吸虫获得能量的主要方式为和。 11. 华支睾吸虫又称,其成虫寄生在人体的。 12. 华支睾吸虫成虫寄生于、、等宿主的肝胆道内。 13. 华支睾吸虫第一中间宿主为,第二中间宿主为。 14. 华支睾吸虫病的主要危害是。 15. 华支睾吸虫感染与胆管和有一定关系。 16. 一般认为是肝吸虫病较好的影像学检查方法。 17. 在中找到是确诊肝吸虫病最主要的证据。 18. 华支睾吸虫病的传染源广泛存在,主要为感染华支睾吸虫的、、 等。 19. 华支睾吸虫病是经感染的,该病在一个地区流行的关键因素是当地人群有吃生的或未煮熟的的习惯。 20. 华支睾吸虫常见的中间宿主有:、、。 21. 治疗华支睾吸虫病的药物,目前应用最多的是与。 22. 布氏姜片吸虫是一种寄生在和小肠内的大型吸虫。 23. 姜片虫的中间宿主为。以菱角、荸荠等水生植物为。 24. 姜片虫病主要流行分布在亚洲的和地区。 25. 姜片虫病的诊断主要依赖于检查。 26.大量感染姜片虫时,虫体成团可引起。 27.肺吸虫的感染阶段是,血吸虫的感染阶段是。 28. 肺吸虫病的病理变化过程可分为、、三期。 29.肺吸虫的第一中间宿主是,第二中间宿主是和。 30.血吸虫成虫主要寄生于。 31. 血吸虫病的临床表现的不同,可分、和血吸虫病。 三、是非题 1. 寄生于人体的吸虫均属于复殖目。() 2. 吸虫的体被是合胞体结构。()
混凝土干缩裂缝成因及预防措施 钢筋混凝土结构出现裂缝的现象较为普遍,裂缝的出现将影响混凝土的耐久性和防水性能。而大多数裂缝的出现均与混凝土体积变形有关。我们知道由于混凝土中所含水分的改变、化学反应、温度变化所引起变形均称之为体积变形,在约束状态下,混凝土体积变形会由于约束状自生体积变形态下,混凝土体积变形会由于约束而产生应力,当拉应力超过混凝土抗拉强度时,则会产生裂缝。混凝土的变形主要有三种:即干缩变形、自生体积变形及温度变形,这里主要讨论干缩变形所造成的裂缝,即可称之为干缩裂缝。 1、混凝土的干缩裂缝 引起混凝土干缩裂缝的重要原因是水分的蒸发,这种蒸发干燥过程总是由表及里逐步发展的,因而湿度总是不均匀的,干缩变形也是不均匀的。 混凝土干缩机理比较复杂,最主要的原因是混凝土内部空隙水蒸发变化时引起的毛细管引力,水泥水化生成的大量微细孔隙,在干燥条件下,胶体中自由水逐渐蒸发产生毛细管引力,胶体孔隙受到压缩,胶体的体积随着水分的蒸发减少而不断收缩,从而引起混凝土体积收缩。胶体的数量及其特性随着水泥的化学成分、细度、水灰比、龄期而不同。一般来说,单位用水量和水泥用量比较多的混凝土胶体数量多,而混凝土的干缩变形也比较大。
混凝土的干缩裂缝取决于干缩、徐变、弹性性质和抗拉强度等方面的综合作用,当存在以下有三个基本条件:①混凝土发生干缩变形,②处于约束状态,③干缩应力达到混凝土抗拉强度。此时混凝土会出现干缩裂缝的主要原因。 2、影响干缩的主要因素 由于此可以看出影响混凝土干缩变形的主要因素为水泥品种、混凝土的配合比和养护条件。已有资料表明铝酸三钙含量低,细度不宜过细,矿渣含量少的水泥品种干缩较小,就混凝土的配合比来看,混凝土的干缩率主要取决于单位用水量和水泥用量以及砂率。相比之下用水量的影响较为突出。随着用水量、水泥量、砂率的增加,相应会加大混凝土的干缩率。由此可见,采用水量低的贫水泥混凝土,砂率低的干硬混凝土一般干缩率都比较小。同时还应加强湿水养护,加强混凝土的保水性,也可延缓干缩的发生。 3、预防干缩裂缝产生的措施 a、选用干缩较小的水泥品种:普通水泥的干缩要低于矿渣水泥; b、合理调整混凝土的配合比:采用低水灰比,低单方水泥和低用水量,同时还宜降低砂率,尽量采用粗砂; c、适当提高混凝土的抗拉强度。在水泥用量一定的条件下,缩小水灰比可使混凝土抗拉强度增高大于混凝土干缩应力的增加,有减少裂缝的趋势。使用早强剂可提高混凝土的早期强度,
吸虫 一、选择题 (一)A型选择题 1.吸虫的受精方式可以是 A.自体受精 B.异体受精 C.自体及异体受精 D.精子和卵子在体外受精2.寄生人体吸虫的繁殖方式是 A.幼虫进行有性生殖,成虫进行无性生殖 B.幼虫进行无性生殖,成虫进行有性生殖 C.幼虫和成虫均进行无性生殖 D.幼虫和成虫均进行有性生殖 3.吸虫在形态上具有下列共同特征,其中哪一条不全对? A.具有口、腹吸盘 B.无体腔 C.消化道不完整 D.虫体两侧对称 4.吸虫的生活史具有下列共同特征,其中哪一条不对? A.生活史阶段多 B. 有宿主更换和世代交替 C.终宿主不严格,有保虫宿主 D.感染阶段是囊蚴,均经口感染5.人体吸虫的生活史中,都必需的中间宿主是 A.淡水鱼类 B.淡水螺类 C.淡水贝类 D.水生植物 6.寄生人体吸虫的成虫繁殖方式是 A.无性生殖 B.有性生殖 C.孤雌生殖 D.接合生殖 7.吸虫生活史第一中间宿主多为 A.脊椎动物 B.哺乳动物 C. 淡水鱼类 D.淡水螺类 8.华支睾吸虫对人体的危害主要是 A. 引起内脏幼虫移行症 B. 引起胆结石 C. 引起肝脏损害 D. 引起胰腺炎 9.肝吸虫病的病原学检查以哪种方法检出率最高? A.十二指肠胆汁引流检查法 B.大便直接涂片法 C.自然沉淀法 D.饱和盐水浮聚法 10.华支睾吸虫的主要保虫宿主为 A.纹沼螺 B.淡水鱼及淡水虾 C.猫、狗 D.牛、羊 11.华支睾吸虫的第一中间宿主是 A.川卷螺 B扁卷螺 C.钉螺 D.豆螺 12.人感染肝吸虫是由于 A.生食或半生食猪肉 B.生食或半生食溪蟹 C.生食或半生食淡水鱼 D.生食或半生食牛肉