04英语语言学概论A卷及答案
- 格式:doc
- 大小:90.50 KB
- 文档页数:4

《英语语言学》练习测试题及参考答案本科I. Tick off the correct or the best possible answers:1.One of the properties of language is that a language user can understand and produce sentences he/shehas never heard before. This property of language is called ________.A. dualityB. productivityC. displacementD. arbitrarinessKey: B2.The ______ function refers to the fact that language can be used for establishing a favorable atmosphereor maintaining social contact rather than for exchanging information or ideas.A. phaticB. directiveC. evocativeD. performativeKey: A3.From a functional approach, the _______ meaning of a language use consists of what is communicatedof the feelings and attitudes of the speaker/writer.A. affectiveB. associativeC. stylisticD. collocativeKey: A4.When –ing in ‘gangling’is removed to get a verb ‘gangle’, we call this way of creating words________.A. suffixationB. back-formationC. blendingD. acronymyKey: B5.______ refers to the process by which words rise from humble beginnings to positions of importance.A. DegradationB. SpecializationC. ElevationD. ExtensionKey: C6.As we know, every speaker has his own pet words and expressions and special way of expressing hisideas in language. This language variety of individual users is called ______.A. idiolectB. regional dialectC. temporal dialectD. social dialectKey: A7.When pitch, stress and length variations are tied to the sentence rather than to the word, they arecollectively known as ________.A. intonationB. toneC. phonemeD. sentence stressKey: A8._______ refers to the change of a sound as a result of the influence of an adjacent sound.A. Addition of soundB. Loss of soundC. MetathesisD. AssimilationKey: D9.Basically, all the languages in the world can be classified in terms of language family. Vietnamese andKorean are two languages in the ______ family.A. Indo-EuropeanB. Sino-TibetanC. Hamito-SemiticD. Malayo-Polynesian Key: B10. A _______ is the minimal contrastive unit in the writing system of a language.A. morphemeB. phonemeC. graphemeD. letterKey: C11.All mono-morphemic words are constituted by free morphemes, and those poly-morphemic wordswhich consist wholly of free morphemes are called_________.A. hyponymsB. compoundsC. blendsD. allomorphsKey: B12.The requirement that the forms of two or more words of specific word classes which stand in specificsyntactic relationship with one another shall also be characterized by the same paradigmatically marked category or categories is called _______.A. concordB. governmentC. recursivenessD. cohesionKey: A13. The formation of new words by combining parts of two words or a word plus a part of another is called_____.A. blendingB. clippingC. acronymyD. compoundingKey: A14. The distinction of ‘linguistic potential’ and ‘actual linguistic behavior’ is proposed by _______.A. N. ChomskyB. F. de SaussureC. M. A. HallidayD. J. AustinKey: C15. The word meaning given in the dictionary is called _____ meaning.A. denotativeB. connotativeC. collectiveD. stylisticKey: A16. When we consider the variation relating to what a user is trying to do with language, we are dealing withaddressee relationship—continually ca tegorized as “______”.A. tenor of discourseB. mode of discourseC. field of discourseD. idiolectKey: A17. According to words’ structures, Turkish is a typical ______ language.A. isolatingB. fusionalC. analyticD. agglutinativeKey: D18. ______ refer to the fact that one type of utterance is typically followed by a special type of utterance.A. Minimal pairsB. Illocutionary actsC. Social dialectsD. Adjacency pairs Key: D19. The relation between “dead” and “alive” is labeled as ________.A. gradabilityB. complementarityC. hyponymyD. homonymyKey: B20. The words “encore” and “au pair” are loanwords from _______.A. FrenchB. GermanC. ItalianD. SpanishKey: A21. The distinction of langue and parole is proposed by______.a. N. Chomskyb. F. de Saussurec. M. A. Hallidayd. J. AustinKey: b22.Which of the following is the exception to the feature of arbitrariness of languagea. native English wordsb. borrowed wordsc. echoic wordsd. one-syllable wordsKey: c23.Which of the following feature cannot be used to describe the phone [s]a. voicelessb. oralc. alveolard. lateralKey: d24.In terms of place of articulation, the two consonants [f], [v] are ________.a. dentalb. alveolarc. palatald. labiodentalKey: d25.In terms of manner of articulation, the sounds [p], [b], [t], [d], [k], [g] are ________.a. affricatesb. fricativesc. bilabiald. oral stopsKey: d26.Which of the following statements about allophone is NOT correcta. Allophones are different forms of the same phonemeb. Allophones of the same phoneme are in complementary distribution.c. Allophones distinguish meaning.d. Allophones are language specific.Key: c27.Which of the following words is not a free morphemea. ableb. petc. changed. dustyKey: d28.How many morphemes are there in the word dischargeda. 2b. 3c. 4d. 5Key: b29.Which of the following words is made up of bound morphemes onlya. happinessb. televisionc. ecologyd. teacherKey: c30. Language is passed on from one generation to the next by teaching and learning rather than by instinct.This property of language is called_____.a. interchangeabilityb. productivityc. cultural transmissiond. arbitrarinessKey: c31.The famous quotation from Shakespeare’s play Romeo and Juliet‘A rose by any other name would smellas sweet’ well illustrates _______.A. the conventional nature of languageB. the creative nature of languageC. the universality of languageD. the big difference between human language and animal communicationKey: A32.Of the following sound combinations, only _______ is permissible according to the sequential rules inEnglish.A. kiblB. bkilC. ilkbD. ilbkKey: A33.The sentence that has a NP and a VP can be shown in a _______ formula “S→NP VP”.A. hierarchicalB. linearC. tree diagramD. verticalKey: B34.It is the _______ on Case assignment that states that a Case assignor and a Case recipient should stayadjacent to each other.A. Case ConditionB. Case ParameterC. Adjacent ConditionD. Adjacent Parameter Key: C35. Predication analysis is a way to analyze _______ meaning.A. phonemeB. wordC. phraseD. sentenceKey: D36. According to Searle, those illocutionary acts whose point is to commit the speaker to some future course of action are called _______.A. commisivesB. directivesC. expressivesD. declarativesKey: A37. The term _______ linguistics may be defined as a way of referring to the approach which studies language change over various periods of time and at various historical stages.A. synchronicB. diachronicC. comparativeD. historical comparative Key: B38. The way in which people address each other depends on their age, sex, social group, and personal relationship. The English system of address forms frequently used includes first name, last name, title+last name, _______, and kin term.A. title+first nameB. title+titleC. title aloneD. first name+last name+titleKey: C39. Language and thought may be viewed as two independent circles overlapping in some parts. When language and thought are identical or closely parallel to each other, we may regard thought as “subvocal speech,” and speech as “_______”.A. vocal thoughtB. subvocal thoughtC. covert thoughtD. overt thoughtKey: D40.Whcih of the following best states the behaviorist view of child language acquisitionA. Language acquisition is a process of habit formation.B. Language acquisition is the species-specific property of human beings.C. Children are born with an innate ability to acquire language.D. Humans are equipped with the neural prerequisites for language and language use.Key: A41. The words “kowtow” and “tea ” are loanwords from _______.A. ChineseB. GermanC. ItalianD. SpanishKey: A42. The term _______ linguistics may be defined as a way of referring to the approach which studies language change over various periods of time and at various historical stages.A. synchronicB. diachronicC. comparativeD. historical comparative Key: B43. The formation of new words by combining parts of two words or a word plus a part of another is called _____.A. blendingB. clippingC. acronymyD. compoundingKey: A44. According to words’ structures, Latin is a typical ______ language.A. isolatingB. fusionalC. analyticD. agglutinativeKey: B45. The relation between “animal” and “lamb” is labeled as ________.A. gradabilityB. complementarityC. hyponymyD. homonymyKey: C46. One of the property of language is that there is no logical connection between meaning and sounds. This property of language is called________.A. dualityB. productivityC. displacementD. arbitrarinessKey: D47. The________ function refers to the use of language to create certain feelings in the hearer.A. phaticB. directiveC. evocativeD. performativeKey: A48. The _______ meaning of a word consists of the associations it acquires on account of the meanings of words which tend to occur in its environment.A. associativeB. affectiveC. stylisticD. collocativeKey: D49. When –or in editor is removed to get a verb edit, we call this way of creating words ________.A. suffixationB. back-formationC. blendingD. acronymyKey:50. The relation between “rose” and “flower” is labeled as ________.A. gradabilityB. complementarityC. hyponymyD. homonymy Key: C51. Language can be used to refer to contexts removed from the immediate situations of the speaker. This is what we mean by __________.A. dualityB. productivityC. displacementD. arbitrarinessKey: C52. When language is used to get the hearer to do something, then it serves a _______ function.A. directiveB. informativeC. interrogativeD. expressive53. The description of a language at some point in time is a ________ study.A. diachronicB. synchronicC. descriptiveD. prescriptiveKey: B54. The distinction between “competence” and “performance” was made by______ .A. N. ChomskyB. F. de SaussureC. M. A. HallidayD. L. BloomfieldKey: A55. According to the places of articulation, sounds in English such as [t], [l], and[z] can be labeled as_______ ones.A. dentalB. bilabialC. velarD. alveolarKey: D56. According to the morphological analysis, the underlined part in the word “inter nation alism” should beregarded as a ___________ .A. rootB. stemC. prefixD. suffixKey: B57. Words such as “telex” and “workfare” are created through ___________.A. affixationB. compoundingC. conversionD. blendingKey: D58. According to the syntact ic construction analysis, simple sentence such as “John is a student.” belongs to__________construction.A. endocentricB. exocentricC. coordinateD. subordinateKey: B59. The sense relationship between “male” and “female” is _________.A. complementarityB. gradabilityC. relational oppositesD. hyponymyKey: A60. Componential analysis is a method of analyzing________ meaning.A. sentenceB. lexicalC. grammaticalD. utteranceKey: BII. Are the following statements true (T) or false (F)1. A sentence cannot be a word or a fragment in strict sense, but an utterance can be a word or a fragment ofa sentence. T/FKey: T2.It doesn’t make sense to ask what language a sentence belongs to. T/FKey: F3. A stem first of all refers to any morpheme or combination of morphemes, but an affix can be added to it.T/FKey: T4.Every word in a language can find at least one referent in the objective world. T/FKey: F5.In most cases, lexicon means vocabulary and is related to the analysis and creation of words, idioms andcollocations. T/FKey: T6.The use of the term ‘implicature’ is different from ‘implication’ in that it usually indicates a rathernarrowly defined logical relationship between two propositions. T/FKey: F7. A phrase means two or more words in sequence, intended to have meaning, that form a syntactic unit thatis less than a complete sentence. It is actually synonymous with word group. T/FKey: F8.Collocation is a term in lexicology used by some linguists to refer to the habitual co-occurrences ofindividual lexical items, or collocates. This relation of co-occurrence usually cannot be accounted for. T/F Key: T9.In order to understand how conversational principles work, we may consider how each maxim actuallyworks and how people observe these maxims in daily communication. T/FKey: T10.Syntax studies the rules which govern the ways words, word groups and phrases are combined to makegrammatical sentences in a language, i.e. it deals with the relationships between elements in sentence structures. T/FKey: T11.Even in modern society, the primary medium is sound for all languages, and the fact that childrenacquire spoken language first before they can read or write also indicates that language is primarily vocal. Key: T12.The defining properties of human language that distinguish it from any animal system ofcommunication are termed design features.Key: T13.There are other channels, besides language, for communicating our thoughts, so language is only oneaspect of semiotics.Key: T14.Modern linguistics regards the spoken language as primary, written language as secondary.Key: T15.Descriptive linguistics aims to lay down rules for ‘correct’ language use, i.e., to tell people what theyshould say and what should not say.Key: F16.Phonology is the branch of linguistics which studies the characteristics of speech sounds and theirpatterns.Key: F17.The case category is used in the analysis of word classes to identify the syntactic relationship betweenwords in a sentence.Key: Tnguage is genetically transmitted.Key: F19.The grammar taught today to language learners is still basically descriptive.Key: F20.All the sounds produced by human are speech sounds.Key: F21.Generally speaking, pragmatics can be understood as a branch of linguistic study that deals with thefactors that govern our choice of language in social interaction and the effects of our choice on others. Key: T22.[f], [v], [s], [z], [?] and [?] are all fricative in English, but [?] and [?] are alveolar while [f] and [v] aredental.Key: F23.In most cases, sentence is synonymous with utterance.Key: F24.Syntax exclusively deals with the study of the interrelationships between elements in sentence structure,and it has nothing to do with exploring the syntactic relation beyond sentence boundary.Key: F25.The London School proposed a functional approach towards the concept of phoneme, and N.Trubetzkoy made the greatest contribution to the related study.Key: F26.A phoneme in a language is a distinctive sound which is capable of distinguishing one word or oneshape of a word from another.Key: T27.Every language is part of a culture, and it cannot but serve and reflect cultural needs.Key: T28.Sentence can be extended either by conjoining or embedding, and a construction where constituentshave been linked through the use of conjunction indicates a paratactic relation.Key: F29.Both Chinese and English are tone languages.Key: F30.Words are the smallest meaningful units of language.Key: F31.Derivation changes always result in change of the word class of the original words.Key: T32.Pitch variations may be distinctive like phonemes, and in this function they are called tones. Languagesusing tones, like Chinese, are called tone language.Key: T33.The notion of inflection just indicates the manifestation of grammatical relationships, rather than lexicalones, through the addition of inflectional affixes.Key: T34.The same morpheme always takes different forms in different contexts.Key: T35. According to P. Grice, whether a speaker follows or violates the Maxims of the Cooperative Principle, he produces some implicature, i.e. a kind of extra meaning that is not contained in the utterance.Key: T36.In the history of any language the writing system always came into being before the spoken form.T/FKey: F37.In English, long vowels are also tense vowels because when we pronounce a long vowel such as/i:/, the larynx is in a state of tension. T/FKey: T38.A compound is the combination of only two words. T/FKey: F39.“The student” in the sentence “The student liked the linguistic lecture”, and “The linguistic lecture” in the sentence “The linguistic lecture liked the student.” belong to the same syntactic category. T/FKey: T40.Linguistic forms having the same sense may have different references in different situations while linguistic forms with the same reference always have the same sense. T/FKey: F41.An important difference between presupposition and entailment is that presupposition, unlike entailment, is not vulnerable to negation. That is to say, if a sentence is negated, the original presupposition is still true. T/FKey: T42.The division of English into Old English, Middle English, and Modern English is non-conventional and not arbitrary. T/FKey: Fnguage reflects sexism in society. Language itself is not sexist, just as it is not obscene; but it can connote sexist attitudes as well as attitudes about social taboos or racism. T/FKey: T44.If a child is deprived of linguistic environment, he or she is unlikely to learn a language successfully later on. T/FKey: T45.When children learn to distinguish between the sounds of their language and the sounds that are not part of the language, they can acquire any sounds in their native language once their parents teach them. T/F Key: F46. Leonard Bloomfield maintained that linguistics should describe instead of prescribe what people actually say and should take a deductive approach in analyzing data.Key: F47. Chomsky believes that linguistic study and research can help explain what happens in the mind, and linguistics should be regarded as a branch of psychology.Key: F48. Halliday claims that if we are given an adequate specification of the semantic properties of the context in terms of field, tenor and mode, we should be able to predict the syntactic properties of texts.Key: F49. Onomatopoeia indicates a non-arbitrary relationship between form and meaning.Key: F50. Traffic light system has the feature of duality.Key: F51. The distinction of ‘linguistic potential’ and ‘actual linguistic behavior’ is proposed by N. Chomsky. Key: F52. In English there are three nasal sounds. They are [m], [n], and [l].Key: T53. A morpheme is the minimal contrastive unit in the writing system of a language.Key: F54. According to the functions of affixes, we can put them into groups: inflectional affixes and derivational affixes.Key: T55. Compounding is the formation of new words by joining two or more stems.Key: T56. Metathesis refers to the change of a sound as a result of the influence of an adjacent sound.Key: F57. The requirement that the forms of two or more words of specific word classes which stand in specificsyntactic relationship with one another shall also be characterized by the same paradigmatically marked category or categories is called concord.Key: T58. According to Searle, those illocutionary acts whose point is to commit the speaker to some future course of action are called directivesKey: F59. The term synchronic linguistics may be defined as a way of referring to the approach which studies language change over various periods of time and at various historical stages.Key: F60. In terms of manner of articulation, the sounds [p], [b], [t], [d], [k], [g] are affricatesKey: FIII.Fill in the blanks:1.It is generally believed that J. Austin and _______ made the greatest contribution to the proposition ofSpeech Act Theory, an important theory in pragmatic study.Key: J. Searle2.According to the positions affixes occupy in words, __________ falls into prefixation and suffixation.Key: affixation3.The signs “&”, “@”, “%” and “$” widely used today are examples of ______ writing.Key: word4.Two methods can be used to reconstruct an older form of a language: internal reconstruction and the_______ reconstruction.Key: external5.The Sapir-Whorf hypothesis has two major thrusts: linguistic determinism and linguistic _______ .Key: relativity6.In the course of communication, a speaker may change from the standard language to the non-standardlanguage, may shift his subject matter, or may move from one point on the formality scale to another point. This linguistic behavior is referred to as ______.Key: code switch7.The different types of a language as different forms to realize a mere generalization of the language arecalled “sub-languages” or _______.Key: (language) varieties8._________ construction refers to a construction in which the distribution of words is functionallyequivalent to that of one or more of its constituents.Key: Endocentric_9.It’s commonly believed that the basic function of language is that it’s used for _________.Key: human communication10.The degree to which a test measures what it is meant to measure is termed _________ in languagetesting, and that is an important index used to evaluate the quality of a test.Key: validity11.By _______ is meant that language can refer to contexts removed from the immediate situation of thespeaker.Key: displacementnguage is a system of two sets of structures, the structure of sound and the structure of ___________. Key: meaning13.The three branches of phonetics are articulatory phonetics, auditory phonetics, and _________phonetics. Key: acoustic14.There are two kinds of stress in English. They are word stress and ________ stress.Key: sentence15.In English there are three nasal sounds. They are [m], [n], and ________.Key: [ ];16.Morphology is divided in two branches: __________ morphology and derivational morphology. Key: .inflectional17.According to H. Paul Grice’s Cooperative Principle, that one should avoid obscurity and ambiguityaccords with the ________ Maxim.Key: Manner18.The speech sounds in the production of which there is an obstruction of the airstream at some point ofthe vocal tract are called_______.Key: consonants19.A linguistic study is ______ if it tries to lay down rules for the correct use of language.Key: prescriptive20.The sentence “H e married a blonde heiress.” ______ the sentence “He married a blonde.”Key: entaills21.In the course of time, the study of language has come to establish close links with other branchesof ________ studies, such as sociology and psychology.Key: social22. Clear[1]and dark[1]are allophones of the same one phoneme /1/.They never take the same position in sound combinations, thus they are said to be in ________ distribution.Key: complementary23.A ________ is often seen as part of a word, but it can never stand by itself although it bears clear, definite meaning.Key: root24.A ________ sentence contains two or more clauses, one of which is incorporated in the other.Key: complex25.That the denial of one member of two words implies the assertion of the other is the characteristic of________ antonyms.Key: complementary26.While the meaning of a sentence is abstract and decontextualized, that of an ________ is concrete and context-dependent.Key: utterance27.Phonological rules may move phonemes from one place in the string to another. For example, Modern English verb ask was Old English askian, with the /k/ preceding the/s/. Sound change as a result of sound movement is known as ________.Key: metathesis28.In many societies of the world, we find a large number of people who speak more than one language. Asa characteristic of societies, ________ inevitably results from the coming into contact of people with different cultures and different languages.Key: bilingualism29.The brain’s neurological specialization for language is called linguistic ________, which is specific to human beings.Key: lateralization30.In order to acquire a second language, learners will subconsciously use their first language knowledge in learning a second language. This is known as language ________.Key: transfer31. _______ phonetics studies the physical properties of speech sounds when they are transmitted between mouth and ear.Key: Acoustic32. The function of establishing a set of vowels is to facilitate the_______ of vowels of languages.Key: description33. If two sounds occurring in the same environment do not contrast, that is, the substitution of one for the other does not produce a different word form, but merely a different pronunciation of the same word, then the two sounds are in ________variation.Key: free34. The principal _________features are stress, length, pitch and intonation, as all of them can be used to distinguish meaning.Key: suprasegmental35.________is the method of creating words by removing the supposed suffixes.Key: Back-formation36. Pronouns and prepositions are two kinds of ________ words to which new members are not regularly added.Key: closed-class37. The sentence “I promise to come here earlier tomorrow morning.” can be used as an example to indicate the ________ function of language.Key: performative38. A linguistic study is ________ if it tries to lay down rules for the correct use of language.Key: perspective39. The sounds in the production of which no articulators come very close together and the air-stream passes through the vocal tract without _________are called vowels.Key: obstruction40. The word “gentlemanly” consists of 4 syllables an d ________morphemes.Key: 341. Positional ______, or word order, refers to the sequential arrangement of words in a language.Key: relation42. English gender contrast can only be observed in pronouns and a small number of nouns, and they are mainly of the _________gender type.Key: natural43. Componential analysis defines the meaning of a lexical element in terms of _______ components. Key: semantic44. ________refers to the process of construction where one clause is included in the sentence (main clause) in syntactic subordination.Key: subordination45. ________ construction refers to a group of syntactically related words where none of the words is functionally equivalent to the group as a whole.Key: exocentric46. The _______function is the use of language to reveal something about the emotions and attitudes of the speaker.Key: expressive47. As language is a product and capacity of the human brain, many psychologists and linguists have tried to examine the relation between language and the brain, developing a new branch of science called________.Key: psycholinguistics48. The production of any speech sound involves the movement of an airstream. The majority of sounds used in languages of the world are produced by ______ egressive airstream mechanism.Key: oral49. Some speech sounds involves the simultaneous use of two places of articulation. For example, the English [w] has both an approximation of the two lips and that of the back of the tongue and the soft palate, and may be termed______.Key: labial-velar50. ________ is used to mean sameness or close similarity of meaning.Key: synonymy51. The ________family includes most of the European languages and marry languages spoken in North India and in the two Americas and Australia.Key: Indo-European52. _________or analytic languages refer to those which depend on invariable roots or stems and word order to indicate their grammatical relations.Key: Isolating53. When we consider the variation relating to what the user is trying to do with language, whether teaching, persuading, advertising or instructing, we are dealing with addressee relationship, contextually categorized as __________.Key: tenor of discourse54. ________means that any human being can be both a producer and a receiver of messages, but the communication systems of certain animals do not have this feature. For instance, some male birds posses calls which female birds do not have.Key: Interchangeability55. ________ refers to the influence exercised by one sound segment upon the articulation of another sound, so that the sounds become less alike.Key: dissimilation56. The __________ is the smallest unit in terms of relationship between expression and content, a unit which cannot be divided without destroying or drastically altering the meaning, whether it is lexical or grammatical.Key: morpheme57. In English, prepositions and verbs determine particular forms of pronouns according to their syntactic relation with them. This requirement is called _______ in linguistics.Key: collocation58. The _______ meaning of a word consists of the associations it acquires on account of the meanings of。

ExercisesI.Multiple Choice1. __________ studies language change over time in contrast to looking at language as it is used at a given moment.A. Diachronic linguisticsB. Synchronic linguisticsC. Prescriptive linguisticsD. Comparative linguistics2. Of all the speech organs, the ______ is/are the most flexible.A. mouthB. lipsC. tongueD. vocal cords3. In terms of place of articulation, the following sounds [p], [b], [m] and [w]share the feature of ______.A. palatalB. alveolarC. bilabialD. dental4. A(n) ______ is a unit that is of distinctive value. It is an abstract unit, a collection of distinctive phonetic features.A. phoneB. soundC. allophoneD. phoneme5. Which of the following sound description is for [d]?A. voiced labiodental fricativeB. voiced alveolar stopC. voiceless labiodental fricativeD. voiceless alveolar stop6. What is the phonetic feature of the sound [u]?A. close back shortB. semi-close front shortC. semi-open central shortD. open front short7. Which of the following sentences contain a derivational affix?A. The cows escaped.B. It was raining.C. Those socks are inexpensive.D. She closed the book.8. The morpheme “ed” in the word “worked” is known as a(n) ______.A. derivational morphemeB. lexical morphemeC. inflectional morphemeD. functional morpheme9. “en-” in “enlarge” is a(n) ______.A. derivational affixB. inflectional affixC. free rootD. bound root10. ______ is the smallest unit of language that carries information about meaning or function.A. SyntaxB. GrammarC. MorphologyD. Morpheme11. Which of the following forms is possible word of English?A. sprokeB. bsarnC. mboodD. coofp12. Which pair of words below shows the relation of antonymy. ______A. flourish—thriveB. intelligent—stupidC. casual—informalD. flog—whip13. We call the relation between “furniture” and “wardrobe” as ______.A. hyponymyB. meronymyC. homophonyD. homonymy14. Most of the violations of the maxims of the CP give rise to ______.A. breakdown of conversationB. confusion of one’s intentionC. hostility between speakers and the listenersD. conversational implicatures15. In the phrase structure rule “S——>NP VP”, the arrow can be read as______.A.is equal toB.consists ofC.hasD.generates16. The meaning carried by the inflectional morpheme is ______.A. lexicalB. morphemeC. grammaticalD. semantic17. The pair of words “hot” and “cold” are ______.A. gradable antonymsB. relational antonymsC. complementary antonymsD. co-hyponyms18. Which pair of the following are complementary antonyms?A. alive / deadB. above / belowC. poor / richD. doctor / patient19. What is the relation between the pair of sentences:He likes seafood.He likes crabsA. synonymyB. inconsistencyC. entailmentD. presupposition20. Which pair of the following are homographs?A. piece n. / peace n.B. tear v. / tear n.C. fast adj. / fast v.D. flower n. / rose n.21. Which pair of the following are dialectal synonyms?A. lorry, truckB. kid, childC. collaborator, accompliceD. amaze, astound22. “Lift” and “elevator” form a pair of ______ synonyms.A. stylisticB. dialecticalC. collocationalD. connotative15. All syllables must have a ______.A. onsetB. codaC. nucleusD. consonant23. ______ studies language and speech as they are used at a given moment and not in terms of how they have evolved over time.A. Diachronic linguisticsB. Synchronic linguisticsC. Prescriptive linguisticsD. Comparative linguistics24. ______ deals with language application to other fields, particularly education.A. PsycholinguisticsB. SociolinguisticsC. Applied linguisticsD. Comparative linguistics25. Of the following sound combination, only ______ is permissible in English.A. iblkB. ilbkC. ilkbD. blik26. Which pair of words below shows the relation of synonymy. ______A. drunk—soberB. uncle—auntC. young—oldD. casual—informal27. The sense relationship between “He has been to France” and “He has been to Europe” is ______.A. hyponymyB. antonymyC. presuppositionD. entailment28. In the phrase structure rule “NP—>(Det) N (PP)…”, the arrow can be readas______.A. is equal toB. branches intoC. transformsD. generates29. In terms of the place of articulation, the following sounds [t][r][s][l][z][n] share the feature of ______.A. palatalB. alveolarC. bilabialD. dental30. Y’s utterance in the following conversation violates the maxim of ______.X: When is Su san’s farewell party?Y: Sometime next month.A.qualityB.quantityC.relationD.manner31. Of the three speech acts, linguists are most interested in the ______because this kind of speech act is identical with the speaker’s intention.A. locutionary actB. constative actC. perlocutionary actD. illocutionary act32. We call the relation between “vehicle” and “car” as ______.A. hyponymyB. synonymyC. polysemyD. homonymy33. Which of the following pairs differs from the others in the sense relation? ______A. good, badB. long, shortC. big, smallD. innocent, guilty34. As far as manners of articulation are concerned, which of the followingdiffers from the others? ______A.[p]B. [b]C. [t]D. [f]35. Which pair of the following belong to meronymy?A. animal, tigerB. hand, fingerC. livestock, dogD. furniture, dresser36. “-En” in “blacken” is a(n) ______.A. derivational affixB. inflectional affixC. free rootD. bound root37. Transformational rules do not change the basic ______ of sentences.A. formB. structureC. meaningD. sound pattern38. According to Searle, those illocutionary acts whose point is to commit the speaker to some future course of action are called____.missivesB. directivesB.expressivesD. declaratives39. The illocutionary point of the____ is to express the psychological state specified in the utterance.A. declarationsB. expressivesmissivesD. directives40. Y’s utterance in the following conversation exchange violates the maxim of______.X: Who was that you were with last night?Y: Did you know that you were wearing odd socks?A. qualityB. quantityC. relationD. mannerII. Blank filling1.Productivityor___ refers to man’s linguistic ability which enables him to produceand understand an infinitely large number of sentences in our native language, including the sentences which were never heard before.2.Some antonyms are g radable_ because there are often intermediate forms betweenthe two members of a pair.3.Duality is the way meaningless elements of language at one level (sounds andletters) combine to form meaningful units (words) at another level.4.According to its position in the new word, affixes are divided into two kinds:prefixes and suffixes.5.Phonological rules that govern the combination of sounds in a particular languageare called sequential rules.6.Root_ constitutes the core of the word and carries the major component of itsmeaning.7.A suffix is added to the end of stems to modify the meaning of the original wordand it may change its part of speech.8.In terms of morphemic analysis, derivation can be viewed as the addition ofaffixes to stems to form new words.9.Some morphemes cannot normally stand alone, but function only as parts ofwords, e.g. –s, -er, -ed and –ing, which are called bound______ morphemes. 10.When pitch, stress and sound length are tied to the sentence rather than the wordin isolation, they are collectively known as intonation.nuguge _is a system of arbitrary vocal symbols used for humancommunication.12.Saussure put forward two important concepts. Langue_ refers to the abstractlinguistic system shared by all members of a speech community.13.Broad transcription is normally used in dictionary and teachingtextbooks for general purposes.14.The root _ constitutes the core of the word and carries the majorcomponent of its meaning.15.Prefixes modify the meaning of the stem, but usually do not change thepart of speech of the original word.16. Displacement is a design feature of human language that enables speakersto talk about a wide range of things, free from barriers caused by separation in time and space.17. An independent unit of meaning that can be used freely by itself is calleda free _ morpheme.18.Clear [l] and dark [l] are allophones of the same one phoneme /l/. They nevertake the same position in sound combinations; thus they are said to be incomplementary distribution.19.Stem is the base to which one or more affixes are attached to create amore complex form that may be another stem or a word.20.Morpheme is the smallest meaningful unit of language.21.The two sounds [p] and [p h] are in complementary distribution, and they areknown as allophones of the phoneme /p/.22. _Syntax_______ is a branch of linguistics that studies how words are combinedto form sentences and the rules that govern the formation of sentences.23. Cooperative Principle (CP) is proposed by Paul Grice .24. “Words are names or labels for things.” This view is called naming theory insemantic studies.25. The sentence “My unmarried sister is married to a bachelor” is a contradition.III. True or false questions.( T ) 1. “Where did he buy the beer” presupposes “He bought the beer”.( F) 2. Sense and reference are the same aspects of meaning.( F ) 3. A word’s category can be told straightforward from its meaning.( T ) 4. The smallest meaningful units that can be used freely all by themselves are free morphemes.(T ) 5. The meaning carried by the inflectional morpheme is grammatical.( T ) 6. “The student’’ in the sentence ‘The student liked the linguistic lecture” and “The linguistic lecture” in the sentence “The linguistic lecture liked thestudent” belong to the same syntactic category.( F ) 7. Compounds with a preposition are in the category of the prepositional part of the compound.(T ) 8. Like other phrases, Infl takes an NP as its specifier and a VP category as its complement.( T ) 9. Linguistic context is concerned with the probability of words or expressions co-occurring or collocating with each other.( T ) 10. When the two words are in the same grammatical category, the compound will be in this category.( F ) 11. Linguistics is the course of language.( F ) 12.In the history of any language the writing system always came into beingbefore the spoken form.( T ) 13. Articulatory phonetics is concerned about how a speaker uses his speech organs to articulate the sounds.( F ) 14. Language system is genetically transmitted.( T) 15. Phonology is the study of the rules governing the structure, distribution, and sequencing of speech sounds and the shape of syllables.(T) 16. Sentences are not formed by randomly combining lexical items, but by following a set of syntactic rules that arrange linguistic elements in aparticular order.( T) 17. Stress has two main semantic functions: distinguish between two words and emphasize the syllable or word.( T) 18. Nouns, verbs, adjectives, and adverbs are closed class words.( T) 19. Linguistic forms with the same reference might differ in sense.(T) 20. The more commonly used a word is, the more likely it has acquired more than one meaning.( T ) 21. Utterance is based on sentence meaning; it is the realization of the Abstract meaning of a sentence in a real situation of communication or simply incontext.( F ) 22.Inviting, suggesting, warning, ordering are instances of commissives.( T ) 23. When performing an illocutionary act of representative, the speaker is making a statement or giving a description which he himself believes to betrue.(T) 24. Coordination refers top the process or result of linking linguistic units so that they have different syntactic status, one being dependent upon the other, and usually a constituent of the other.(T ) 25. Traditionally,sentence is the minimum part of language that express meaning.请浏览后下载,资料供参考,期待您的好评与关注!。

外文学院2006—2007学年度第(一)学期期末考试2004级英本《语言学概论》(必)试卷(A)班别姓名学号说明:1、期考分笔试与论文写作(IV)两部分,这仅为笔试部分,占40%。
2、测试形式:开卷。
3、考试时间:90分钟。
Part A (30%; 40 minutes)I. Multiple choice: Choose the best answer to each of the following items. Put your response (the corresponding letter) on the Answer Sheet. (20%, 0.5 x 40 items)1. The sentence "A rose by any other name would smell as sweet." illustrates the _____ nature of language.A. symbolicB. conventionalC. metaphoricalD. flower2. Which of the following is NOT one of the design features of human language?A. double articulationB. creativityC. displacementD. genetics3. Which of the following is a front, close and short vowel?A.[u:]B. [a]C. [i]D. [u]4. Which of the following forms a minimal pair?A.fear, pearB. tip, pitC. food, footD. heat, hit5. In English, if three consonants should cluster together at the beginning of a word, thecombination should obey the following rules except _____:A. The first phoneme must be /s/.B. The second phoneme must be /p/ or /t/ or /k/.C. The third phoneme must be /l/ or /r/ or /w/.D. The phoneme /h/ can replace the second phoneme if it is followed by /w/.6. Which of the following underlined parts is a bound morpheme?A. scholarshipB. classroomC. policemanD. childlike7. Which of the following words does NOT belong to the open classes?A. enjoyB. happyC. asD. beautifully8. The word impossibility consists of _____ syllables as against _____ morphemes.A. six/threeB. five/twoC. six/fourD. five/five9. For the word "to" in "It is necessary to know yourself.", we can say _____.A. it has a lexical meaningB. it is an inflectional morphemeC. it is a derivational morphemeD. it has a grammatical meaning as an infinitive marker10. In TG, 'S-structure' represents _____ structure.A. surfaceB. sentenceC. specifierD. syntactic11. The words “elevator” and “lift” are ______ synonyms.A. nearB. dialectalC. collocationally-restrictedD. stylistic12. The words “literate” and “illiterate” are ______ opposites.A. gradableB. ungradableC. relationalD. complementary13. Whi ch of the following is the correct componential analysis of the word “cake”?A.[+FOOD-SOLID+COUNTABLE]B.[+FOOD+SOLID+COUNTABLE]C.[+DRINKS-LIQUID-COUNTABLE]D.[+DRINKS+LIQUID-COUNTABLE]14. “It‟s foggy today.” is a _____-place predication.A. noB. oneC. twoD. three15. A predication consists of _____.A. argumentsB. predicatesC. argument(s) and predicatesD. argument(s) and predicate16. _____ is often regarded as a high-status marker.A. sociolectB. idiolectC. registerD. accent17. Which of the following best describes the relation between “He is alone” and “He has no oneto talk to”?A. The former is synonymous with the latter.B. The former is inconsistent with the latter.C. The former entails the latter.D. The former presupposes the latter.18. Which of the following best describes the relation between “He paid a visit to Sydney.” and“He paid a visit to Australia.”?A. The former is synonymous with the latter.B. The former is inconsistent with the latter.C. The former entails the latter.D. The former presupposes the latter.19. Which of the following best describes the relation between “Her sister is coming.” and “Shehas a sister.”?A.The former is synonymous with the latter.B.The former is inconsistent with the latter.C.The former entails the latter.D.The former presupposes the latter.20. …Statesman‟ and …politician‟ are ___.A. dialectal synonymsB. collocational synonymsC. stylistic synonymsD. synonyms that differ in their emotive meaning21. The relation between …furniture‟ and …desk‟ is ___.A. homophonyB. homographyC. polysemyD. hyponymy22. …Mother‟ and …daughter‟ are ___.A. gradable antonymsB. relational oppositesC. ungradable oppositesD. complementary synonyms23. According to Searle, acts bringing about immediate changes by saying something are _____.A. representativesB. directivesC. expressivesD. declarations24. Which of the following is a commissive?A.I‟m really sorry to hear that.B.I will see you without fail.C.You‟d better have dinner at once.D.I now declare the meeting open.25. “Why not offer him a lift?” is an instance of ____.A.representativesB.expressivesC. directivesD. commissives26. Which of the following is a declaration?A. Close the window, please.B. Would you like to go to the movie with me?C. I‟ve never seen him before.D. I appoint you monitor of the class.27. The word “mike” is a(n) ____.A.acronymB. blendC. clipped wordD. coined word28. The pronoun "our" was once spelt as "ure/urum" in Old English and "oure" in Middle English.It is the result of going through _____.A. a change in "agreement" ruleB. a change in negation ruleC. a process of simplificationD. the loss of inflections29. The word “motel” is a(n) ____.A. acronymB. blendC. clipped wordD. coined word30. “Down you come, chaps!” belongs to ____ language.A. intimateB. frozenC. consultativeD. casual31. The linguist____ is the one who distinguishes three social variables (Field, Mode, Tenor) thatdetermine the register.A. ChomskyB. HallidayC. BloomfieldD. Skinner32. The Eiffel Tower belongs to ____ culture.A. spiritualB. materialC. folkD. none of the above33. Langua ge acquisition refers to the child‟s acquisition of his ____.A. second languageB. foreign languageC. target languageD. mother tongue34. The first consonants the child can make are made with the lips and they are ____.A. [p, b, d]B. [t, d, k]C. [t, d, m]D. [p, b, m]35. If the child calls all wo men “Aunt”, then we may say the child has ____ the meaning of theword “Aunt”.A. overgeneralizedB. overextendedC. overusedD. overstressed36. The chief exponent of the behaviorist view of language acquisition is ____.A. BloomfieldB. ChomskyC. FirthD. Skinner37. It has been claimed that the garden path effect results from two principles of parsing: _____.A. minimal attachment and late closureB. word and sentence ambiguityC. selectional restrictions and hierarchical structureD. lateralization and aphasia38. Instances of mother tongue interference can be found at the level of ____.A. pronunciationB. syntaxC. lexisD. all of the above39. Which of the following sentences is an example of overgeneralization?A. Jane told me to give up smoking.B. Jane asked me to give up smoking.C. Jane hoped me to give up smoking.D. Jane advised me to give up smoking.40. Which of the following is an example of overgeneralization?A. sheepB. storiesC. booksD. footsII. True or False: Decide whether the following statements are true or false (A for True, andB for False). Put your response on the Answer Sheet. (10%, 0.5 x 20 items)41. The difference between langue and parole was made in the early 20th century.42. Cultural transmission means that the details of the language system are genetically transmittedfrom generation to generation.43. The transcription normally used in dictionaries and textbooks is narrow transcription.44. Spectrographs are used in acoustic phonetics.45. In English, pronouns belong to open class words.46. Some derivational morphemes do not change the grammatical class of its root.47. Category refers to a group of linguistic items which fulfill the same or similar functions in aparticular language such as a sentence, a noun phrase or a verb.48. Phrases that are formed of more than one word usually contain the elements of head, specifierand complement.49. When a word becomes a new word by means of functional shift, it means that there is noaddition of any affix.50. The word "holiday" we use today has gone through a process of narrowing of meaning.51. One of the most important features of diglossia is the specialization of function of the twovarieties.52. As a result of increasing immigration in the world, bilingualism is spreading.53. Language helps perpetuate the culture, and the changes in language uses reflect the culturalchanges in return.54. Each culture presents to its members the ideas and concepts that culture transmits fromgeneration to generation.55. Not all the children achieve the same level of language development.56. Children tend to learn to acquire the sound of [t] before [p].57. Second language acquisition established itself as a discipline around the 1970s.58. According to the Input Hypothesis, there is a formula: i + 1, where i represents learner'scurrent state of knowledge, and the next stage is "i + 1".59. Language processing involves either bottom-up or top-down processing.60. It is found that left-handers are generally less lateralized for language.班别姓名学号Introduction to Linguistics Final Exam, Jan. 30th, 2007.Part B (10%; 50 minutes)III. Explain each of the following linguistic phenomena, indicating (a) the relevant theory or approach in brackets at the end of the text, (b) your understanding of it, and (c) its implication or your conclusion. Write your response (in English) in the blanks given.(10%, 5x2 items)61. A: Did you ask Uncle and Auntie to come, John?B: I asked Uncle to come, Mum. (Cooperative Principle)62. Alexander Pope puts his poem entitled An Empty House in a form as follows:You beat your pate, and fancy wit willcome:knock as you please, there is nobody athome.(language change)。
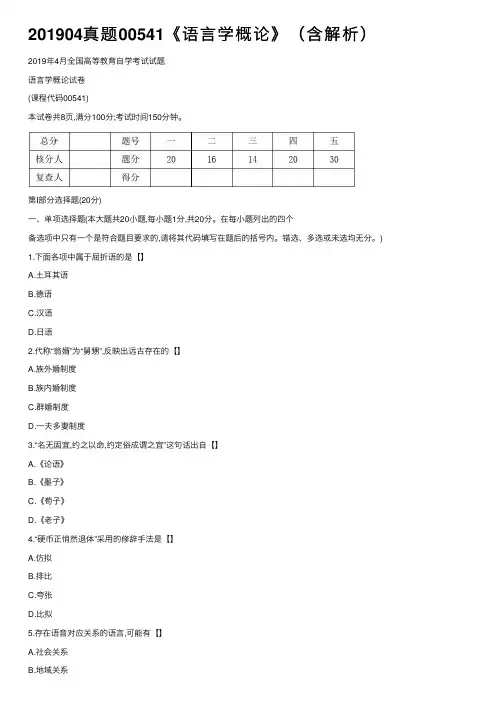
201904真题00541《语⾔学概论》(含解析)2019年4⽉全国⾼等教育⾃学考试试题语⾔学概论试卷(课程代码00541)本试卷共8页,满分100分;考试时间150分钟。
第I部分选择题(20分)⼀、单项选择题(本⼤题共20⼩题,每⼩题1分,共20分。
在每⼩题列出的四个备选项中只有⼀个是符合题⽬要求的,请将其代码填写在题后的括号内。
错选、多选或未选均⽆分。
)1.下⾯各项中属于屈折语的是【】A.⼟⽿其语B.德语C.汉语D.⽇语2.代称“翁婿”为“舅甥”,反映出远古存在的【】A.族外婚制度B.族内婚制度C.群婚制度D.⼀夫多妻制度3.“名⽆固宜,约之以命,约定俗成谓之宜”这句话出⾃【】A.《论语》B.《墨⼦》C.《荀⼦》D.《⽼⼦》4.“硬币正悄然退体”采⽤的修辞⼿法是【】A.仿拟B.排⽐C.夸张D.⽐拟5.存在语⾳对应关系的语⾔,可能有【】A.社会关系B.地域关系6.下⾯各项中采⽤了夸张修辞⼿法的是【】A.当官不与民做主,不如回家卖红薯B.危楼⾼百尺,⼿可摘星⾠C.天空好像⼀盏乏了油的灯D.东边⽇出西边⾬7.萨不尔和沃尔夫主张的观点是【】A.语⾔不同但思维⽅式可以相同B.思维决定语⾔C.语⾔与思维⽆关D.语⾔决定思维8.下⾯各项中属于惯⽤语的是【】A.并蒂莲B.⼤花脸C.⼀线天D.主⼼⾻9.隐语是⼀种特殊的社会⽅⾔,其最突出的特征是【】A.具有排他性B.发⾳特殊C.没有书写形式D.不出声10.下⾯各项中属于中国传统“⼩学”的是【】A.⾳系学B.⾳韵学C.⾳响学D.⾳位学11.论⽂属于书⾯语体中的【】A.宣传体B.应⽤体C.科学体D.⽂学体12.发⽣语⾔转⽤必然经历的阶段是【】A.克⾥奥尔阶段B.语⾔混同阶段13.我国第⼀部完备的字典是【】A.《说⽂解字》B.《⽟篇》C.《康熙字典》D.《释名》14.在秦简、汉印等⽂献中,“医”字写作“醫”,字形从“⾣”(盛酒器),这表明古代【】A.⽣病与喝酒有关 B.酒由医⽣酿制C.医⽣好酒D.药与酒有关15.下⾯各项中属于借词的是【】A.葡萄B.给⼒C.红粉D.萌宠16.“客⼈来了”中的“客⼈”的指称类型是【】A.不定指B.定指C.⽆指D.任指17.吃饭时如果筷⼦掉落,⼈们往往会说“筷落,快乐,快快乐乐”,这是通过词语谐⾳来【】A.讨⼝彩 B.避讳C.表达⾼兴之意D.表达不⾼兴之意18.索绪尔的代表作是【】A.《普遍语法》B.《普通语⾔学教程》C.《结构主义语⾔学》D.《语⾔论》19.下⾯各项中属于清⾳的是【】A.[m]B.[a]C.[b]D.[??]20.⼉童语⾔发展进⼊复杂句阶段的时间⼀般是【】A.2岁左右D.7岁左右第Ⅱ部分⾮选择题(80分)⼆、名词解释题(本⼤题共4⼩题,每⼩题4分,共16分。

ExercisesI.Multiple Choice1. __________ studies language change over time in contrast to looking at language as it is used at a given moment.A. Diachronic linguisticsB. Synchronic linguisticsC. Prescriptive linguisticsD. Comparative linguistics2. Of all the speech organs, the ______ is/are the most flexible.A. mouthB. lipsC. tongueD. vocal cords3. In terms of place of articulation, the following sounds [p], [b], [m] and [w]share the feature of ______.A. palatalB. alveolarC. bilabialD. dental4. A(n) ______ is a unit that is of distinctive value. It is an abstract unit, a collection of distinctive phonetic features.A. phoneB. soundC. allophoneD. phoneme5. Which of the following sound description is for [d]A. voiced labiodental fricativeB. voiced alveolar stopC. voiceless labiodental fricativeD. voiceless alveolar stop6. What is the phonetic feature of the sound [u]A. close back shortB. semi-close front shortC. semi-open central shortD. open front short7. Which of the following sentences contain a derivational affixA. The cows escaped.B. It was raining.C. Those socks are inexpensive.D. She closed the book.8. The morpheme “ed” in the word “worked” is known as a(n) ______.A. derivational morphemeB. lexical morphemeC. inflectional morphemeD. functional morpheme9. “en-” in “enlarge” is a(n) ______.A. derivational affixB. inflectional affixC. free rootD. bound root10. ______ is the smallest unit of language that carries information about meaning or function.A. SyntaxB. GrammarC. MorphologyD. Morpheme11. Which of the following forms is possible word of EnglishA. sprokeB. bsarnC. mboodD. coofp12. Which pair of words below shows the relation of antonymy. ______A. flourish—thriveB. intelligent—stupidC. casual—informalD. flog—whip13. We call the relation between “furniture” and “wardrobe” as ______.A. hyponymyB. meronymyC. homophonyD. homonymy14. Most of the violations of the maxims of the CP give rise to ______.A. breakdown of conversationB. confusion of one’s intentionC. hostility between speakers and the listenersD. conversational implicatures15. In t he phrase structure rule “S——>NP VP”, the arrow can be read as______.A.is equal toB.consists ofC.hasD.generates16. The meaning carried by the inflectional morpheme is ______.A. lexicalB. morphemeC. grammaticalD. semantic17. The pair of words “hot” and “cold” are ______.A. gradable antonymsB. relational antonymsC. complementary antonymsD. co-hyponyms18. Which pair of the following are complementary antonymsA. alive / deadB. above / belowC. poor / richD. doctor / patient19. What is the relation between the pair of sentences:He likes seafood.He likes crabsA. synonymyB. inconsistencyC. entailmentD. presupposition20. Which pair of the following are homographsA. piece n. / peace n.B. tear v. / tear n.C. fast adj. / fast v.D. flower n. / rose n.21. Which pair of the following are dialectal synonymsA. lorry, truckB. kid, childC. collaborator, accompliceD. amaze, astound22. “Lift” and “elevator” form a pair of ______ synonyms.A. stylisticB. dialecticalC. collocationalD. connotative15. All syllables must have a ______.A. onsetB. codaC. nucleusD. consonant23. ______ studies language and speech as they are used at a given moment and not in terms of how they have evolved over time.A. Diachronic linguisticsB. Synchronic linguisticsC. Prescriptive linguisticsD. Comparative linguistics24. ______ deals with language application to other fields, particularly education.A. PsycholinguisticsB. SociolinguisticsC. Applied linguisticsD. Comparative linguistics25. Of the following sound combination, only ______ is permissible in English.A. iblkB. ilbkC. ilkbD. blik26. Which pair of words below shows the relation of synonymy. ______A. drunk—soberB. uncle—auntC. young—oldD. casual—informal27. The sense relationship between “He has been to France” and “He has been to Europe” is ______.A. hyponymyB. antonymyC. presuppositionD. entailment28. In the phrase structure rule “NP—>(Det) N (PP)…”, the arrowcan be read as______.A. is equal toB. branches intoC. transformsD. generates29. In terms of the place of articulation, the following sounds [t][r][s][l][z][n] share the feature of ______.A. palatalB. alveolarC. bilabialD. dental30. Y’s utterance in the following conversation violates themaxim of ______.X: When is Susan’s f arewell partyY: Sometime next month.A.qualityB.quantityC.relationD.manner31. Of the three speech acts, linguists are most interested in the ______because this kind of speech act is identical with the speaker’s intention.A. locutionary actB. constative actC. perlocutionary actD. illocutionary act32. We call the relation between “vehicle” and “car” as ______.A. hyponymyB. synonymyC. polysemyD. homonymy33. Which of the following pairs differs from the others in thesense relation ______A. good, badB. long, shortC. big, smallD. innocent, guilty34. As far as manners of articulation are concerned, which of the followingdiffers from the others ______A.[p]B. [b]C. [t]D. [f]35. Which pair of the following belong to meronymyA. animal, tigerB. hand, fingerC. livestock, dogD. furniture, dresser36. “-En” in “blacken” is a(n) ______.A. derivational affixB. inflectional affixC. free rootD. bound root37. Transformational rules do not change the basic ______ ofsentences.A. formB. structureC. meaningD. sound pattern38. According to Searle, those illocutionary acts whose point is to commit the speaker to some future course of action are called____.missivesB. directivesB.expressivesD. declaratives39. The illocutionary point of the____ is to express the psychological state specified in the utterance.A. declarationsB. expressivesmissivesD. directives40. Y’s utterance in the following conversation exchange viola tes the maxim of ______.X: Who was that you were with last night?Y: Did you know that you were wearing odd socks?A. qualityB. quantityC. relationD. mannerII. Blank filling1.Productivityor___ refers to man’s linguistic ability which enables him to produce and understand an infinitely large number of sentences in our native language, including the sentences which were never heard before.2.Some antonyms are g radable_ because there are often intermediate forms between the two members of a pair.3.Duality is the way meaningless elements of language at one level (sounds and letters) combine to form meaningful units (words) at another level.4.According to its position in the new word, affixes are divided into two kinds: prefixes and suffixes.5.Phonological rules that govern the combination of sounds ina particular language are called sequential rules.6.Root_ constitutes the core of the word and carries the major component of its meaning.7. A suffix is added to the end of stems to modify the meaning of the original word and it may change its part of speech.8.In terms of morphemic analysis, derivation can be viewed as the addition of affixes to stems to form new words.9.Some morphemes cannot normally stand alone, but function only as parts of words, . –s, -er, -ed and –ing, which are called bound______ morphemes.10.When pitch, stress and sound length are tied to the sentence rather than the word in isolation, they are collectively known asintonation.nuguge _is a system of arbitrary vocal symbols used for human communication.12.Saussure put forward two important concepts. Langue_ refers to the abstract linguistic system shared by all members of a speech community.13.Broad transcription is normally used in dictionary and teachingtextbooks for general purposes.14.The root _ constitutes the core of the word and carries the majorcomponent of its meaning.15.Prefixes modify the meaning of the stem, but usually do not change thepart of speech of the original word.16. Displacement is a design feature of human language that enables speakersto talk about a wide range of things, free from barriers caused by separationin time and space.17. An independent unit of meaning that can be used freely by itself is calleda free _ morpheme.18.Clear [l] and dark [l] are allophones of the same one phoneme /l/. They nevertake the same position in sound combinations; thus they are said to be incomplementary distribution.19.Stem is the base to which one or more affixes are attached tocreate amore complex form that may be another stem or a word.20.Morpheme is the smallest meaningful unit of language.two sounds [p] and [p h] are in complementary distribution, and they are known as allophones of the phoneme /p/.22. _Syntax_______ is a branch of linguistics that studies how words are combined to form sentences and the rules that govern the formation of sentences.23. Cooperative Principle (CP) is proposed by Paul Grice .24. “Words are names or labels for things.” This view is called naming theory in semantic studies.25. The sentence “My unmarried sister is married to a bachelor” is a contradition.III. True or false questions.( T ) 1. “Where did he buy the beer” presupposes “He bought the beer”.( F) 2. Sense and reference are the same aspects of meaning.( F ) 3. A word’s category can be told straightforward from its meaning.( T ) 4. The smallest meaningful units that can be used freely all by themselves are free morphemes.(T ) 5. The meaning carried by the inflectional morpheme is grammatical.( T ) 6. “The student’’ in the sentence ‘The student liked the linguistic lecture” and “The linguistic lecture”in the sentence “The linguistic lecture liked the student”belong to the same syntactic category.( F ) 7. Compounds with a preposition are in the categoryof the prepositional part of the compound.(T ) 8. Like other phrases, Infl takes an NP as its specifier and a VP category as its complement.( T ) 9. Linguistic context is concerned with the probability of words or expressions co-occurring orcollocating with each other.( T ) 10. When the two words are in the same grammatical category, the compound will be in this category.( F ) 11. Linguistics is the course of language.( F ) the history of any language the writing system always came into being before the spoken form.( T ) 13. Articulatory phonetics is concerned about how a speaker uses his speech organs to articulate the sounds.( F ) 14. Language system is genetically transmitted.( T) 15. Phonology is the study of the rules governing the structure, distribution,and sequencing of speech sounds and the shape of syllables.(T) 16. Sentences are not formed by randomly combining lexical items, but by following a set of syntactic rules thatarrange linguistic elements in a particular order.( T) 17. Stress has two main semantic functions: distinguish between two words and emphasize the syllable or word.( T) 18. Nouns, verbs, adjectives, and adverbs are closed class words.( T) 19. Linguistic forms with the same reference might differ in sense.(T) 20. The more commonly used a word is, the more likely it has acquired more than one meaning.( T ) 21. Utterance is based on sentence meaning; it is the realization of the Abstract meaning of a sentence in a realsituation of communication or simply in context.( F ) , suggesting, warning, ordering are instances of commissives.( T ) 23. When performing an illocutionary act of representative, the speaker is making a statement or giving a description which he himself believes to be true.(T) 24. Coordination refers top the process or result of linking linguistic units so that they have different syntactic status, one being dependent upon the other, and usually a constituent of the other.(T ) 25. Traditionally,sentence is the minimum part of language that express meaning.。

英语语言学概论 A卷普通用卷学习方式: 业余时间:无限制考试科目:《英语语言学概论》(总分) 100分一单选题 (共20题,总分值60分 )1. 判断两种话是不同语言还是同一种语言的不同方言应该主要参考__________________ (3 分)A. 相互理解程度B. 语言结构的差异程度C. 共同的历史文化传统和民族认同感D. 地域临近程度2. 关于语言获得的原因,下列学说中偏重于内部条件解释的一项是(3 分)A. 天赋说B. 摹仿说C. 强化说D. 刺激反应说3. 语言符号具有可变性的根本原因在于语言符号的(3分)A. 任意性B. 强制性C. 离散性D. 系统性4. 构形语素属于(3 分)A. 虚词语素B. 词根语素C. 自由语素D. 黏着语素5. 从语音的社会功能角度划分出来的最小语音单位是________________ (3 分)A. 音位B. 音素C. 音节D. 音渡6. 下列各组辅音中,发音部位相同的一组是__________________ (3 分)A. [k, η]B. [m, n]C. [n, η]D. [k,p]7. “汽车”和“卡车”是__________ (3 分)A. 上下位词B. 同义词C. 等义词D. 近义词8. 机器翻译可以分为四个层级,从低到高的排序是(3分)A. 单词、句子、话语、篇章B. 单词、句子、句群、篇章C. 单词、句法、语义、语境D. 语音、语法、语义、语用9. 英语动词“去”的原形是“go”,过去时的形式是“went”,这在语法手段的词形变化中叫作________________ (3 分)A. 附加B. 屈折C. 异根D. 零形式10. 英语“students”中的“-s”是_________ (3 分)A. 虚词语素B. 词根语素C. 构形语素D. 构词语素11. 下列各项中,谓词和变元之间属于动作与结果关系的是(3 分)A. 写黑板B. 打篮球C. 织毛衣D. 寄包裹12. 从词的构造类型上看,汉语“动人”一词属于(3 分)A. 单纯词B. 复合词C. 派生词D. 简缩词13. 首先提出“能指”和“所指”这对概念的语言学家是(3 分)A. 洪堡特B. 索绪尔C. 乔姆斯基D. 萨丕尔14. 最早的表音文字是(3 分)A. 拉丁文字B. 腓尼基文字C. 古希腊文字D. 古埃及文字15. 在语言谱系分类的层级体系中,最大的类别是__________ (3 分)A. 语族B. 语支C. 语系D. 语群16. 根据字符跟什么样的语言单位相联系的标准来分类,已知自源文字都属于_________ (3 分)A. 词文字B. 语素文字C. 音节文字D. 音位文字17. 认为“思维和语言各自发展,二者没有关系”的学者不包括(3 分)A. 古希腊哲学家柏拉图B. 法国哲学家迪卡尔C. 英国哲学家霍布斯D. 苏联语言学家马尔18. 下列各组中,三个复合词构词类型不一致的一组是_________________ (3 分)A. 席卷耳鸣地震B. 打倒切断推翻C. 发光散热出气D. 天地欢乐爱好19. 听觉上最自然、最容易分辨的最小语音单位是(3分)A. 音素B. 重音C. 音位D. 音节20. 关于语音四要素,下列说法不正确的一项是________________ (3 分)A. 音高变化是语调的主要构成要素B. 能起区别语言意义作用的是绝对的音高、音强和音长C. 音长是由发音体振动的持续时间决定的D. 音强是由发音体振动的振幅大小决定的21. 目前对于语言和思维的关系,比较一致的观点是(3分)A. 有什么样的思维,就有什么样的语言B. 有什么样的语言,就有什么样的思维C. 思维对语言有一定影响,但更重要的是语言决定思维D. 语言对思维有一定影响,但更重要的是思维决定语言22. 以下不属于语言学的三大发源地的是________________ (3 分)A. 中国B. 埃及C. 印度D. 希腊-罗马二多选题 (共5题,总分值20分 )1. 对发音器官功能的描述,不正确的是_________________ (4 分)A. 声带在发音中的作用是次要的B. 被动发音器官是不能自主运动的C. 口腔中最为灵活的部位是上腭D. 口腔中最为灵活的部位是上腭2. 下列关于虚词的表述,正确的是_________________(4 分)A. 虚词可以分为辅助词和功能词两个小类B. 虚词包括助动词、介词、连词和语气词等C. 虚词是没有词汇意义只有语法意义的词D. 虚词不稳固,发展变化比较快3. 下列各组词语中,可以构成最小语义场的有(4 分)A. 毛笔电笔眉笔B. 银河黄河海河C. 南瓜黄瓜冬瓜D. 山头线头桥头E. 货车客车军车4. 下列对“你把这本书好好读一遍!”这个句子类型的分析,正确的是_________________ (4 分)A. 主谓句B. 把字句C. 陈述句D. 单句5. 下列关于基本语汇的表述,正确的是__________ (4分)A. 基本语汇是整个语汇系统的核心和基础B. 基本语汇使用范围广、构词能力强C. 基本语汇大部分是相当稳定的D. 基本语汇也包括大部分新造词和古语词6. 下列关于“地域方言”的表述中,正确的有(4 分)A. 地域方言随社群分化而形成B. 地域方言是语言内部的变体C. 地域方言有独立的结构系统D. 语音差异是方言分区的主要依据E. 地域方言间的差异一定小于语言三简答题 (共1题,总分值20分 )1. 举例说明语言符号的任意性表现在哪些方面? (20分)参考答案一单选题 (共20题,总分值60分 ) 1. 答案:C解析过程:2. 答案:A解析过程:3. 答案:A解析过程:4. 答案:D解析过程:5. 答案:B解析过程:6. 答案:A解析过程:7. 答案:A 解析过程:8. 答案:C 解析过程:9. 答案:C 解析过程:10. 答案:C 解析过程:11. 答案:C 解析过程:12. 答案:D 解析过程:13. 答案:B 解析过程:14. 答案:B 解析过程:15. 答案:C 解析过程:16. 答案:A 解析过程:17. 答案:D 解析过程:18. 答案:A 解析过程:19. 答案:D 解析过程:20. 答案:B 解析过程:1 21. 答案:D解析过程:22. 答案:B解析过程:二多选题 (共5题,总分值20分 ) 1. 答案:A,B,C解析过程:2. 答案:A,B,C解析过程:3. 答案:A,C,E解析过程:4. 答案:A,B,D解析过程:5. 答案:A,B,C解析过程:6. 答案:A,B,D,E解析过程:三简答题 (共1题,总分值20分 )1. 答案:答:语言符号的任意性是指语言符号的音义联系并非是本质的,必然的,而是由社会成员共同约定的,一种意义为什么要用这个声音形式,而不用那种声音形式,这中间没有什么道理可言,完全是偶然的、任意的。


语言学概论04任务一、判断题(共 10 道试题,共 20 分。
)1. 基本词具有很强的构词能力,而像“我、他、啊、吗、从”这类词都没有能产性特点,所以不是基本词。
A. 错误B. 正确2. 书面语是在口语的基础上产生的,对口语的规范发展有积极作用。
A. 错误B. 正确3. 语言发展变化的根本原因是语言中的各种因素相互影响。
A. 错误B. 正确4. 语言的分化和统一都与社会的发展密切相关。
A. 错误B. 正确5. 任何一种语言的共同语,都是在某一种方言的基础上形成的。
A. 错误B. 正确6. 一种语言与另一种语言融合,主要取决于操这种语言的民族是否居于统治地位。
A. 错误B. 正确7. 洋泾浜不同于克里奥耳语,二者的使用范围和发展结果都不一样。
A. 错误B. 正确8. “江”古代专指长江,今天泛指所有的江河,这种变化就是词义的转移。
A. 错误B. 正确9. 多义词有多项意义,但是在一个具体的句子中一般只有一项意义。
A. 错误B. 正确10. 语言发展具有渐变性特点,所以产生了地域方言和社会方言。
A. 错误B. 正确二、单项选择题(共 15 道试题,共 30 分。
)1. “上帝”“天堂”“妖怪”“神仙”等词的词义是()。
A. 不反映现实现象B. 反映现实现象C. 没有现实根据D. 对现实现象的歪曲反映2. 下列反义词之间属于非此即彼的一组是()。
A. 白—黑B. 大—小C. 高—低D. 生—死3. 就下列词语来看,只有()组中的汉字全都能独立地表示语素。
A. 山峰音乐事理委员B. 沙发吉它卡片罗马C. 葡萄玻璃枇杷纱门D. 蜘蛛窈窕逍遥逃遁4. 语言发展变化的基本条件是()。
A. 自然的发展变化B. 语言内部的因素C. 社会的发展变化D. 个人生活经历的变化5. 在一种语言内部划分地域方言时的依据主要是()。
A. 语法B. 词汇C. 词义D. 语音6. 下列各组词只有()是意译词。
A. 雷达马达咖啡B. 啤酒苜蓿哈密C. 西装篮球胡瓜D. 槟榔浪漫坦克7. 下列说法只有______不正确。


《英语语言学概论》题与答案-CAL-FENGHAI.-(YICAI)-Company One1ExercisesI.Multiple Choice1. __________ studies language change over time in contrast to looking at language as it is used at a given moment.A. Diachronic linguisticsB. Synchronic linguisticsC. Prescriptive linguisticsD. Comparative linguistics2. Of all the speech organs, the ______ is/are the most flexible.A. mouthB. lipsC. tongueD. vocal cords3. In terms of place of articulation, the following sounds [p], [b], [m] and [w]share the feature of ______.A. palatalB. alveolarC. bilabialD. dental4. A(n) ______ is a unit that is of distinctive value. It is an abstract unit, a collection of distinctive phonetic features.A. phoneB. soundC. allophoneD. phoneme5. Which of the following sound description is for [d]A. voiced labiodental fricativeB. voiced alveolar stopC. voiceless labiodental fricativeD. voiceless alveolar stop6. What is the phonetic feature of the sound [u]A. close back shortB. semi-close front shortC. semi-open central shortD. open front short7. Which of the following sentences contain a derivational affixA. The cows escaped.B. It was raining.C. Those socks are inexpensive.D. She closed the book.8. The morpheme “ed” in the word “worked” is known as a(n) ______.A. derivational morphemeB. lexical morphemeC. inflectional morphemeD. functional morpheme9. “en-” in “enlarge” is a(n) ______.A. derivational affixB. inflectional affixC. free rootD. bound root10. ______ is the smallest unit of language that carries information about meaning or function.A. SyntaxB. GrammarC. MorphologyD. Morpheme11. Which of the following forms is possible word of EnglishA. sprokeB. bsarnC. mboodD. coofp12. Which pair of words below shows the relation of antonymy. ______A. flourish—thriveB. intelligent—stupidC. casual—informalD. flog—whip13. We call the relation between “furniture” and “wardrobe” as ______.A. hyponymyB. meronymyC. homophonyD. homonymy14. Most of the violations of the maxims of the CP give rise to ______.A. breakdown of conversationB. confusion of one’s intentionC. hostility between speakers and the listenersD. conversational implicatures15. In the phrase structure rule “S——>NP VP”, the arrow can be read as______.A.is equal toB.consists ofC.hasD.generates16. The meaning carried by the inflectional morpheme is ______.A. lexicalB. morphemeC. grammaticalD. semantic17. The pair of words “hot” and “cold” are ______.A. gradable antonymsB. relational antonymsC. complementary antonymsD. co-hyponyms18. Which pair of the following are complementary antonymsA. alive / deadB. above / belowC. poor / richD. doctor / patient19. What is the relation between the pair of sentences:He likes seafood.He likes crabsA. synonymyB. inconsistencyC. entailmentD. presupposition20. Which pair of the following are homographsA. piece n. / peace n.B. tear v. / tear n.C. fast adj. / fast v.D. flower n. / rose n.21. Which pair of the following are dialectal synonymsA. lorry, truckB. kid, childC. collaborator, accompliceD. amaze, astound22. “Lift” and “elevator” fo rm a pair of ______ synonyms.A. stylisticB. dialecticalC. collocationalD. connotative15. All syllables must have a ______.A. onsetB. codaC. nucleusD. consonant23. ______ studies language and speech as they are used at a given moment and not in terms of how they have evolved over time.A. Diachronic linguisticsB. Synchronic linguisticsC. Prescriptive linguisticsD. Comparative linguistics24. ______ deals with language application to other fields, particularly education.A. PsycholinguisticsB. SociolinguisticsC. Applied linguisticsD. Comparative linguistics25. Of the following sound combination, only ______ is permissible in English.A. iblkB. ilbkC. ilkbD. blik26. Which pair of words below shows the relation of synonymy. ______A. drunk—soberB. uncle—auntC. young—oldD. casual—informal27. The sense relationship between “He has been to France” and “He has been to Europe” is ______.A. hyponymyB. antonymyC. presuppositionD. entailment28. In the phrase structure rule “NP—>(Det) N (PP)…”, the arrow can be readas______.A. is equal toB. branches intoC. transformsD. generates29. In terms of the place of articulation, the following sounds [t][r][s][l][z][n] share the feature of ______.A. palatalB. alveolarC. bilabialD. dental30. Y’s utterance in the following conversation violates the maxim of ______.X: When is Susan’s farewell partyY: Sometime next month.A.qualityB.quantityC.relationD.manner31. Of the three speech acts, linguists are most interested in the ______because this kind of speech act is identical with the speaker’s inte ntion.A. locutionary actB. constative actC. perlocutionary actD. illocutionary act32. We call the relation between “vehicle” and “car” as ______.A. hyponymyB. synonymyC. polysemyD. homonymy33. Which of the following pairs differs from the others in the sense relation ______A. good, badB. long, shortC. big, smallD. innocent, guilty34. As far as manners of articulation are concerned, which of the followingdiffers from the others ______A.[p]B. [b]C. [t]D. [f]35. Which pair of the following belong to meronymyA. animal, tigerB. hand, fingerC. livestock, dogD. furniture, dresser36. “-En” in “blacken” is a(n) ______.A. derivational affixB. inflectional affixC. free rootD. bound root37. Transformational rules do not change the basic ______ of sentences.A. formB. structureC. meaningD. sound pattern38. According to Searle, those illocutionary acts whose point is to commit the speaker to some future course of action are called____.missivesB. directivesB.expressivesD. declaratives39. The illocutionary point of the____ is to express the psychological state specified in the utterance.A. declarationsB. expressivesmissivesD. directives40. Y’s utterance in the following conversation exchange violates the maxim of ____ __.X: Who was that you were with last nightY: Did you know that you were wearing odd socksA. qualityB. quantityC. relationD. mannerII. Blank filling1.Productivityor___ refers to man’s linguistic ability which enables him toproduce and understand an infinitely large number of sentences in our native language, including the sentences which were never heard before.2.Some antonyms are gradable_ because there are often intermediate formsbetween the two members of a pair.3.Duality is the way meaningless elements of language at one level (sounds andletters) combine to form meaningful units (words) at another level.4.According to its position in the new word, affixes are divided into two kinds:prefixes and suffixes.5.Phonological rules that govern the combination of sounds in a particularlanguage are called sequential rules.6.Root_ constitutes the core of the word and carries the major component of itsmeaning.7. A suffix is added to the end of stems to modify the meaning of the originalword and it may change its part of speech.8.In terms of morphemic analysis, derivation can be viewed as the addition ofaffixes to stems to form new words.9.Some morphemes cannot normally stand alone, but function only as parts ofwords, . –s, -er, -ed and –ing, which are called bound______ morphemes. 10.When pitch, stress and sound length are tied to the sentence rather than theword in isolation, they are collectively known as intonation.nuguge _is a system of arbitrary vocal symbols used for humancommunication.12.Saussure put forward two important concepts. Langue_ refers to the abstractlinguistic system shared by all members of a speech community.13.Broad transcription is normally used in dictionary and teachingtextbooks for general purposes.14.The root _ constitutes the core of the word and carries the majorcomponent of its meaning.15.Prefixes modify the meaning of the stem, but usually do not change thepart of speech of the original word.16. Displacement is a design feature of human language that enables speakersto talk about a wide range of things, free from barriers caused by separationin time and space.17. An independent unit of meaning that can be used freely by itself is calleda free _ morpheme.18.Clear [l] and dark [l] are allophones of the same one phoneme /l/. They nevertake the same position in sound combinations; thus they are said to be incomplementary distribution.19.Stem is the base to which one or more affixes are attached to create amore complex form that may be another stem or a word.20.Morpheme is the smallest meaningful unit of language.two sounds [p] and [p h] are in complementary distribution, and they are known as allophones of the phoneme /p/.22. _Syntax_______ is a branch of linguistics that studies how words are combinedto form sentences and the rules that govern the formation of sentences.23. Cooperative Principle (CP) is proposed by Paul Grice .24. “Words are names or labels for things.” This view is called naming theory insemantic studies.25. The sentence “My unmarried sister is married to a bachelor” is a contradition.III. True or false questions.( T ) 1. “Where did he buy the beer” presupposes “He bought the beer”.( F) 2. Sense and reference are the same aspects of meaning.( F ) 3. A word’s category can be told straightforward from its meaning.( T ) 4. The smallest meaningful units that can be used freely all by themselves are free morphemes.(T ) 5. The meaning carried by the inflectional morpheme is grammatical.( T ) 6. “The student’’ in the sentence ‘The student liked the linguistic lecture” and “The linguistic lecture” in the sentence “The linguistic lecture liked thestudent” belong to the same syntactic category.( F ) 7. Compounds with a preposition are in the category of the prepositional part of the compound.(T ) 8. Like other phrases, Infl takes an NP as its specifier and a VP category as its complement.( T ) 9. Linguistic context is concerned with the probability of words or expressions co-occurring or collocating with each other.( T ) 10. When the two words are in the same grammatical category, the compound will be in this category.( F ) 11. Linguistics is the course of language.( F ) the history of any language the writing system always came into being before the spoken form.( T ) 13. Articulatory phonetics is concerned about how a speaker uses his speech organs to articulate the sounds.( F ) 14. Language system is genetically transmitted.( T) 15. Phonology is the study of the rules governing the structure, distribution, and sequencing of speech sounds and the shape of syllables.(T) 16. Sentences are not formed by randomly combining lexical items, but by following a set of syntactic rules that arrange linguistic elements in aparticular order.( T) 17. Stress has two main semantic functions: distinguish between two words and emphasize the syllable or word.( T) 18. Nouns, verbs, adjectives, and adverbs are closed class words.( T) 19. Linguistic forms with the same reference might differ in sense.(T) 20. The more commonly used a word is, the more likely it has acquired more than one meaning.( T ) 21. Utterance is based on sentence meaning; it is the realization of the Abstract meaning of a sentence in a real situation of communication or simply incontext.( F ) , suggesting, warning, ordering are instances of commissives.( T ) 23. When performing an illocutionary act of representative, the speaker is making a statement or giving a description which he himself believes to betrue.(T) 24. Coordination refers top the process or result of linking linguistic units so that they have different syntactic status, one being dependent upon the other,and usually a constituent of the other.(T ) 25. Traditionally,sentence is the minimum part of language that express meaning.。

语言概论考试题及答案一、选择题(每题2分,共10分)1. 语言的最小意义单位是:A. 音素B. 词C. 语素D. 句子答案:C2. 下列哪个选项不是语言的属性?A. 社会性B. 生产性C. 创造性D. 封闭性答案:D3. 语言学研究的主要对象是:A. 文学作品B. 语言C. 语言现象D. 语言规则答案:B4. 语言的词汇量随着社会的发展而:A. 减少B. 保持不变C. 增加D. 不确定答案:C5. 语言的语音系统是由哪些要素构成的?A. 音素B. 音标C. 音位D. 音节答案:C二、填空题(每题2分,共10分)1. 语言的______性是指语言是社会约定俗成的符号系统。
答案:社会2. 语言的______性是指语言能够表达无限多的思想和概念。
答案:生产3. 语言的______性是指语言能够创造新的表达方式。
答案:创造4. 语言的______性是指语言是开放的,能够不断吸收新词汇。
答案:开放5. 语言的______性是指语言在不同社会群体和地区之间存在差异。
答案:变异三、简答题(每题10分,共20分)1. 简述语言学的主要研究领域。
答案:语言学的主要研究领域包括语音学、形态学、句法学、语义学、语用学、社会语言学、心理语言学、计算语言学等。
2. 描述语言的交际功能。
答案:语言的交际功能是指语言作为交流思想、情感和信息的工具,使人们能够相互理解和沟通。
四、论述题(20分)1. 论述语言与思维的关系。
答案:语言与思维的关系是密切且复杂的。
一方面,语言是思维的表达工具,人们通过语言来组织和表达思想;另一方面,语言的结构和词汇也影响着人们的认知和思维方式。
语言不仅反映思维,也在一定程度上塑造思维。
五、翻译题(每题5分,共10分)1. 将下列句子从英语翻译成汉语。
"Language is the dress of thought."答案:语言是思想的外衣。
2. 将下列句子从汉语翻译成英语。
“语言是文化的载体。
语言学概论试题(及部分答案)2004年10月15日A语言学概论试题及答案一、填空题、(每空1分,共15分)1、()的建立,使语言学摆脱了过去的附庸地位,成为一门独立发展的科学。
2、语言符号的形式是(),语言符号的内容是()3、一个音节可以没有起音和(),但决不可缺少()。
5、附加在词根上,一般表示附加性词汇意义的语素叫()。
6、交际的基本单位是()。
7、语法手段可以分力两大类型:()和()。
8、语言发展有两个特点:()和()。
9、根据语言的亲属关系对语言的分类叫做(),也叫做()。
10、文字起源于()。
二、单选题(在本题的每一小题的备选答案中,只有一个答案是正确的,请把你认确答案的题号,填入题干的括号内。
多选不给分。
每题1分,共15分)1、社会语言学属于()①理论语言学②广义应用语言学③普通语言学④狭义应用语言学2、元音[]的名称是()①舌尖后高圆唇元音②舌尖前高圆唇元音③舌尖后高不圆唇元音④舌尖前高不圆唇元音3、下列汉字的读音中,包含有三合元音的是()①邮②欧③玩④农4、汉语普通话音节结构()①最长由三个音素组成②最长由四个音素组成③最长由五个音素组成④最短由两个音素组成5、下列词中,属于单纯词的是()①玻璃②黑扳③语言④红旗6、下列词中,属于复台词的是()①傻子②席子③天子④椅子7、下列词组中,属于多义的是()①两只学生送的花瓶②两位学生送的花瓶③两只学生送的花篮。
④两个学生送的花篮8、下列词中粗体的成分,属于同音关系的是()①杜鲁门——杜绝②负荆一负担③忽然--突然④花朵——浪花9、英语的‘foot”(脚,单数)变为“feet”(脚,复数)运用的语法手段是()①附加②异根③内部屈折④重叠10、汉语普通话中的:“卡通片”中的“卡”是一个()①语素②音节③前缀④词11、汉语中的:“了、着、过”在古代具有实实在在的词汇意义,到现代变成只表语义的助词,这属于()①异化②类化③新语法范畴的形成④实词虚化12、下列语言中属于粘着语的是()①苗语②越南语③俄语④日语13、在一种语言内部划脑言时,最主要的依据是()①语法②语义③语音④词汇14、下列词的词义,属于词义缩小的是()①“皮”原指兽皮②“涕”原指眼泪③“瓦”原指一切烧好的上器④“江”原捐“长江”15、人类几种古老文字的原始字形,都是()①象形的②会意的③表音的④形声的三、多选题(在本题的每一小题的备选答案中,正确答案有三个或三个以上多请把为正确答案的题号,填入题干的括号内。
《英语语言学概论》期末考试样卷台州学院____学年第____学期_____级英语专业《英语语言学概论》期末试卷A卷(闭卷)姓名__________ 班级___________ 学号_____________I.Decide whether the following statements are True (T) or False (F).(10 points, 1 point each)1.Articulatory Phonetics studies the physical properties of speech sounds.2.Adjectives belong to open class words.3.John Austin made the distinction between a constative and a performative.4.What essentially distinguishes semantics and pragmatics is whether in thestudy of meaning the context of use is considered.5.English is a typical intonation language.6.Phones in complementary distribution should be assigned to the same phoneme.7.Pragmatics treats the meaning of language as something intrinsic andinherent.8.There are words of more or less the same meaning used in different regional dialects.9.Transformations are the rules which can change the meaning of sentence.10.Sense and reference are two different notions of semantics, and they arerelated to each other.II. Fill in the following blanks. (10 points, 1 point each)1.The word “and” is a c____________ conjunction.2.Linguistic c__________ is a native speak er’s linguistic knowledge of hislanguage.3.The relationship between the sound and the meaning of a word is a________.4. A m________ is the smallest linguistic unit that carries meaning.5. A sentence is formed by phonological rules, m______ rules, syntactic rulesand semantic rules.6.The most recognizable difference between American English and BritishEnglish are in p________ and vocabulary.7.Speech v________refers to any distinguishable form of speech used by aspeaker or a group of speakers.8.P ____ refers to the realization of langue in actual use.9.Linguistics is generally defined as the s ____ study of language.10.As a type of linguistic system in L2 learning, i_______ is a product of L2training, mother tongue interference, overgeneralization of the target language rules, and learning and communicative strategies of the learner..III. Mark the choice that can best complete the statement. (20 points, 1 point each)1. Which of the following branch of linguistics takes the inner structure of word as its main object of study?A. Phonetics.B. Semantics.C. Morphology.D. Sociolinguistics.2. ________refers to a marginal language of few lexical items and straightforward grammatical rules, used as a medium of communication.A. DialectB. IdiolectC. PidginD. Register3. Which of the following is a voiceless bilabial stop?A.[w].B. [m].C. [b].D. [p].4. The phenomenon that words having different meanings have the same form is called ________.A. hyponymyB. synonymyC. polysemyD. homonymy5. Which of the following words is NOT formed by blending?A. Smog.B. Botel.C. Brunch.D. Edit.6. What phonetic feature distinguishes the [p] in please and the [p] in speak?A.VoicingB. AspirationC. RoundnessD. Nasality7. The word boyguard is a ______.A. compound wordB. complex wordC. derivational wordD. free morpheme8. All words contain a _________.A. rootB. bound morphemeC. prefixD. suffix9. Of the following sound combinations, only ______ is permissible.A. kiblB. hkilC. ilkbD. ilbk10. Where is the primary stress of the word phonology?A. pho.B. no.C. lo.D. gy.11. Conventionally a ________ is put in slashes.A. allophoneB. phoneC. phonemeD. morpheme12. The plural affix in the word tables is a(n) _______.A. inflectional suffixB. derivational suffixC. free morphemeD. root13. Language is tool of communication. The symbol “highway closed”serves___.A. an expressive functionB. an informative functionC. a performative functionD. a persuasive function14. Which of the following groups of words is a minimal pair?A. but/pubB. wet/whichC. cool/curlD. fail/find15. Whorf believed that speakers of different languages perceive and experienced the world differently, that is relative to their linguistic background, hence the notion of ______________.A. linguistic determinationB. linguistic relativismC. linguistic nativismD. linguistic behaviorism16. What are the dual structures of language?A. Sounds and letters.B. Sounds and meaning.C. Letters and meaning.D. Sounds and symbols.17. The meaning carried by the inflectional morpheme is _______.A. lexicalB. morphemicC. grammaticalD. semantic18. According to Krashen ______ refers to the gradual and subconscious development of ability in the first language by using it naturally in daily communication.A. learningB. competenceC. performanceD. acquisition19. Which of the following is one of the core branches of linguistics?A. Phonology.B. Psycho-linguistics.C. Sociolinguistics.D. Anthropology.20. The relationship be tween “flower” and “tulip” is _________.A. homonymyB. hyponymyC. polysemyD. synonymyIV. Translate the following linguistic terms: (10 points, 1 point each)A. From English to ChineseB. From Chinese to English1. acoustic phonetics 6. 应用语言学2. closed class words 7. 格语法3. componential analysis 8. 积极迁移4. distinctive features 9. 历史语言学5. Critical Period Hypothesis 10. 声调语言V. Draw a tree diagram for the following sentence by applying TGGrammar.(10 points)The man saw a horse.VI. Answer the following questions briefly. (20 points)1. Define phoneme. (4 points)2. Explain complementary distribution with an example.(5 points)3. What are the four criteria for classifying English vowels. (4 points)4. Analyze the following conversation by applying the Cooperative Principles.(7 points)A: Teheran is in Turkey, isn’t it, teacher?B: And London is in France, I suppose.VII. Do the following analysis. (20 points)1. Write the one proper description from the list under B for the underlined part of each word in A. (5 points, 1 point each)A B(1) terroriz ed a. free root(2) un civil ized b. bound root(3) terror ize c. inflectional suffix(4) luke warm d. derivational suffix(5) im possible e. inflectional prefixf. derivational prefix2. Consider the following sentences in Swahili, and anwer the questions:(15 points)mtu amelala The man has slept.mtu analala The man is sleeping.mtu atalala The man will sleep.watu wamelala The men have slept.watu wanalala The men are sleeping.watu watalala The men will sleep.visu vinaanguka The knives are falling.kikapu kimeanguka The basket has fallen.watoto watafika The children will arrive.1)toto in Swahili means ______ in English.2)The meaning of the morpheme wa- in Swahili is _______.3)______ in Swahili means “sleep” in English.4)Translate mtoto anaanguka into English.5)Translate vikapu vimefika into English.台州学院______学年第_____学期_____级___专业《英语语言学概论》期末试卷A卷(闭卷)答题卷姓名__________ 班级___________ 学号_____________I.Decide whether the following statements are True (T) or False (F).(10 points, 1 point each)II. Fill in the following blanks. (10 points, 1 point each)1._________2.__________3. __________4._________5._________6._________7.___________8.___________9._________10._________III. Mark the choice that can best complete the statement. (20 points, 1 point each)IV. Translate the following linguistic terms: (10 points, 1 point each)1._________________ 6.________________2._________________ 7._________________3. ________________ 8._________________4._________________ 9._________________5.__________________ 10.________________V. Draw a tree diagram for the following sentence by applying TG grammar.(10 points)The man saw a horse.VI. Answer the following questions. (20 points)_________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________ __________________________________________________________________________________ _____________________________________________________________________2._______________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________ _____________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________ 3._________________________________________________________________________________ ___________________________________________________________________________________ ___________________________________________________________________________________ ______________ _____________4.___________________________________________________________________ ___________________________________________________________________________________ ___________________________________________________________________________________ ________________________________________________________________________________________________ ___________________________________________________________________________________ ______________ _________________________________________VII. Do the following analysis. (20 points)1. (1) ________ (2) _________ (3) ________ (4) _______ (5) ________2. (1) _______________(2) _______________实用文档(3) _______________(4) _______________(5) _______________第11页/共11页。
《英语语言学概论》精选试题11. Which of the following statements about language is NOT true?A. Language is a systemB. Language is symbolicC. Animals also have languageD. Language is arbitrary2. Which of the following features is NOT one of the design features of language?A. SymbolicB. DualityC. ProductiveD. Arbitrary3. What is the most important function of language?A. InterpersonalB. PhaticC. InformativeD. Metalingual4. Who put forward the distinction between Langue and Parole?A. SaussureB. ChomskyC. HallidayD. Anonymous5. According to Chomsky, which is the ideal user's internalized knowledge of his language?A. competenceB. paroleC. performanceD. langue6. The function of the sentence "A nice day, isn't it?" is .A. informativeB. phaticC. directiveD. performative7. Articulatory phonetics mainly studies .A. the physical properties of the sounds produced in speechB. the perception of soundsC. the combination of soundsD. the production of sounds8. The distinction between vowels and consonants lies in .A. the place of articulationB.the obstruction of airstreamC. the position of the tongueD. the shape of the lips9. Which is the branch of linguistics which studies the characteristics of speech sounds and provides methods for their description, classification and transcription?A.PhoneticsB. PhonologyC. SemanticsD. Pragmatics10. Which studies the sound systems in a certain language?A.PhoneticsB. PhonologyC. SemanticsD. Pragmatics11. Minimal pairs are used to .A. find the distinctive features of a languageB.find the phonemes of a languageC. compare two wordsD. find the allophones of language12. Usually, suprasegmental features include ___ ,length and pitch.A. phonemeB. speech soundsC.syllablesD.stress13. Which is an indispensable part of a syllable?A. CodaB. OnsetC. StemD. Peak三、判断1.The analyst collects samples of the language as it is used, not according to some views of how it should be used. This is called the prescriptive approach. F2.Broad transcription is normally used by the phoneticians in their study of speech sounds. F台州学院考试题1. Articulatory Phonetics studies the physical properties of speech sounds.2. English is a typical intonation language.3. Phones in complementary distribution should be assigned to the same phoneme.4. Linguistic c__________ is a native speaker’s linguistic knowledge of his language.1. The relationship between the sound and the meaning of a word is a________.2. P ____ refers to the realization of langue in actual use.3. Linguistics is generally defined as the s ____ study of language.1. Which of the following branch of linguistics takes the inner structure of word as its main object of study?A. Phonetics.B. Semantics.C. Morphology.D. Sociolinguistics.3. Which of the following is a voiceless bilabial stop?A. [w].B. [m].C. [b].D. [p].6. What phonetic feature distinguishes the [p] in please and the [p] in speak?A.VoicingB. AspirationC. RoundnessD. Nasality11. Conventionally a ________ is put in slashes.A. allophoneB. phoneC. phonemeD. morpheme13. Language is tool of communication. The symbol “highway closed” serves___.A. an expressive functionB. an informative functionC. a performative functionD. a persuasive function14. Which of the following groups of words is a minimal pair?A. but/pubB. wet/whichC. cool/curlD. fail/find16. What are the dual structures of language?A. Sounds and letters.B. Sounds and meaning.C. Letters and meaning.D. Sounds and symbols.19. Which of the following is one of the core branches of linguistics?A. Phonology.B. Psycho-linguistics.C. Sociolinguistics.D. Anthropology.IV.Translate the following linguistic terms:(10points,1point each)A.From English to ChineseB.From Chinese to English1. acoustic phonetics6. 應用語言學2. closed class words4. distinctive featuresVI.Answer the following questions briefly.(20points)1. Define phoneme. (4 points)2. Explain complementary distribution with an example.(5 points)3. What are the four criteria for classifying English vowels. (4 points)问答答案 1. A contrastive phonological segment whose phonetic realizations are predictable by rules. (4 points)(or: A phoneme is a phonological unit; it is a unit that is of distinctive value.)2. The situation in which phones never occur in the same phonetic environment. (4 points) e.g. [p] and [p h] never occur in the same position. (1 point)3. the position of the tongue in the mouth(1 point), the openness of the mouth(1 point), the shape of the lips(1 point), and the length of the vowels. (1 point)Chapter 1 Introductions to LinguisticsI. Choose the best answer. (20%)1. Language is a system of arbitrary vocal symbols used for human __________A. contactB. communicationC. relationD. Community2. Which of the following words is entirely arbitrary?A. treeB. typewriterC. crashD. Bang3. The function of the sentence ―Water boils at 100 degrees Centigrade.‖ i s__________.A. interrogativeB. directiveC. informativeD. Performative4. In Chinese when someone breaks a bowl or a plate the host or the people present are likely to say―碎碎(岁岁)平安‖as a means of controlling the forces which they believes fee lmight affect their lives. Which functions does it perform?A. InterpersonalB. EmotiveC. PerformativeD. Recreational5. Which of the following property of language enables language users to overcome the barriers caused by time and place, due to this feature of language, speakers of a language are free to talk about anything in any situation?A. TransferabilityB. DualityC.DisplacementD. Arbitrariness6. Study the following dialogue. What function does it play according to the functions of language?—A nice day,isn’t it?— Right! I really enjoy the sunlight.A. EmotiveB.PhaticC. PerformativeD. Interpersonal7. __________ refers to the actual realization of the ideal language user’s knowledge of the rules of his language in utterances.A. PerformanceB. CompetenceC. LangueD. Parole8. When a dog is barking, you assume it is barking for something or at someone thatexists hear and now. It couldn’t be sorrowful for some lost love or lost bone. This indicates the design feature of __________.A. cultural transmissionB. productivityC.displacementD. Duality9. __________ answers such questions as how we as infants acquire our first language.A.PsycholinguisticsB.Anthropological linguisticsC. SociolinguisticsD. Applied linguistics10. __________ deals with language application to other fields, particularly education.A. Linguistic theoryB. Practical linguisticsC. Applied linguisticsD. Comparative linguisticsII. Decide whether the following statements are true or false. (10%)11. Language is a means of verbal communication. Therefore, the communication way used by the deaf-mute is not language. F13. Speaking is the quickest and most efficient way of the human communication systems.14. Language is written because writing is the primary medium for all languages. F15. We were all born with the ability to acquire language, which means the details of any language system can be genetically transmitted. F16. Only human beings are able to communicate. F17. F. de Saussure, who made the distinction between langue and parole in the early 20th century, was a French linguist. F18. A study of the features of the English used in Shakesp eare’s time is an example of th e diachronic 历时 study of language. F19. Speech and writing came into being at much the same time in human history. F20. All the languages in the world today have both spoken and written forms. FIII. Fill in the blanks. (10%)21. Language, broadly speaking, is a means of __ verbal________ communication.22. In any language words can be used in new ways to mean new things and can be combined into innumerable sentences based on limited rules. This feature is usually termed___creativity_______.23. Language has many functions. We can use language to talk about itself. This function is __________.24. Theory that primitive man made involuntary vocal noises while performing heavy work has been called the ___ yo-he-ho_______ theory.25. Linguistics is the __ systematic________ study of language.26. Modern linguistics is __________ in the sense that the linguist tries to discover what language is rather than lay down some rules for people to observe.27. One general principle of linguistic analysis is the primacy of __________ over writing.28. The description of a language as it changes through time is a __________ study.29. Saussure put forward two important concepts. __________ refers to the abstract linguistic system shared by all members of a speech community.30. Lin guistic potential is similar to Saussure’s langue and Chomsky’s __________.IV. Explain the following terms, using examples. (20%)31. Design feature32. Displacement33. Competence34. Synchronic linguisticsV. Answer the following questions. (20%)35. Why do people take duality as one of the important design features of human language? Can you tell us what language will be if it has no such design feature? (南开大学, 2004) 35.Duality makes our language productive. A large number of different units can be formed out of a small number of elements – for instance, tens of thousands of words out of a small set of sounds, around 48 in the case of the English language. And out of the huge number of words, there can be astronomical number of possible sentences and phrases, which in turn can combine to form unlimited number of texts. Most animal communication systems do not have this design feature of human language.If language has no such design feature, then it will be like animal communicational system which will be highly limited. It cannot produce a very large number of sound combinations, e.g. words, which are distinct in meaning.Chapter 2 Speech SoundsI. Choose the best answer. (20%)1. Pitch variation is known as __________ when its patterns are imposed on sentences.A. intonationB. toneC. pronunciationD. voice2. Conventionally a __________ is put in slashes (/ /).A. allophoneB. phoneC. phonemeD. morpheme3. An aspirated p, an unaspirated p and an unreleased p are __________ of the p phoneme.A. analoguesB. tagmemesC. morphemesD. allophones4. The opening between the vocal cords is sometimes referred to as __________.A. glottisB. vocal cavityC. pharynxD. uvula6. A phoneme is a group of similar sounds called __________.A. minimal pairsB. allomorphsC. phonesD. allophones7. Which branch of phonetics concerns the production of speech sounds?A. Acoustic phoneticsB. Articulatory phoneticsC. Auditory phoneticsD. None of the above8. Which one is different from the others according to places of articulation?A. [n]B. [m]C. [ b ]D. [p]9. Which vowel is different from the others according to the characteristics of vowels?A. [i:]B. [ u ]C. [e]D. [ i ]10. What kind of sounds can we make when the vocal cords are vibrating?A. VoicelessB. VoicedC. Glottal stopD. ConsonantII. Decide whether the following statements are true or false. (10%)11. Suprasegmental phonology refers to the study of phonological properties of units larger than the segment-phoneme, such as syllable, word and sentence.12. The air stream provided by the lungs has to undergo a number of modification to acquire the quality of a speech sound.14. [p] is a voiced bilabial stop.15. Acoustic phonetics is concerned with the perception of speech sounds.16. All syllables must have a nucleus but not all syllables contain an onset and a coda.17.When pure vowels or monophthongs are pronounced, no vowel glides take place.18. According to the length or tenseness of the pronunciation, vowels can be divided into tense vs. lax or long vs. short.III. Fill in the blanks. (20%)21. Consonant sounds can be either __________ or __________, while all vowel sounds are __________.23. The qualities of vowels depend upon the position of the __________ and the lips.25. Consonants differ from vowels in that the latter are produced without __________.26. In phonological analysis the words fail / veil are distinguishable simply because of the two phonemes /f/ - /v/. This is an example for illustrating __________.27. In English there are a number of __________, which are produced by moving from one vowel position to another through intervening positions.28. __________ refers to the phenomenon of sounds continually show the influence of their neighbors.29. __________ is the smallest linguistic unit.IV. Explain the following terms, using examples. (20%)31. Sound assimilation32. Suprasegmental feature33. Complementary distribution34. Distinctive featuresV. Answer the following questions. (20%)35. What is acoustic phonetics? (中国人民大学,2003)36. What are the differences between voiced sounds and voiceless sounds in terms of articulation? (南开大学,2004)VI. Analyze the following situation. (20%)37. Write the symbol that corresponds to each of the following phonetic descriptions; then give an English word that contains this sound. Example: voiced alveolar stop [d] dog. (青岛海洋大学,1999)(1) voiceless bilabial unaspirated stop(2) low front vowel(3) lateral liquid(4) velar nasal(5) voiced interdental fricative32. Suprasegmental feature: The phonetic features that occur above the level of the segments are called suprasegmental features; these are the phonological properties of such units as the syllable, the word, and the sentence. The main suprasegmental ones includes stress, intonation, and tone.33. Complementary distribution: The different allophones of the same phoneme never occur in the same phonetic context. When two or more allophones of one phoneme never occur in the same linguistic environment they are said to be in complementary distribution.34. Distinctive features: It refers to the features that can distinguish one phoneme from another. If we can group the phonemes into two categories: one with this feature and the other without, this feature is called a distinctive feature.V. 35.Acoustic phonetics deals with the transmission of speech sounds through the air. When a speech sound is produced it causes minor air disturbances (sound waves). Various instruments are used to measure the characteristics of these sound waves.36. When the vocal cords are spread apart, the air from the lungs passes between them unimpeded. Sounds produced in this way are described as voiceless; consonants [p, s, t] are produced in this way. But when the vocal cords are drawn together, the air from the lungs repeatedly pushes them apart as it passes through, creating a vibration effect. Sounds produced in this way are described as voiced. [b, z, d] are voiced consonants.11。
语言学概论试题及答案A一、填空题、(每空1分,共15分) 1、( )的建立,使语言学摆脱了过去的附庸地位,成为一门独立发展的科学。
2、语言符号的形式是( ),语言符号的内容是( ) 3、一个音节可以没有起音和( ),但决不可缺少( )。
4、方言词是诣( )。
5、附加在词根上,一般表示附加性词汇意义的语素叫( )。
6、交际的基本单位是( )。
7、语法手段可以分力两大类型:( )和( )。
8、语言发展有两个特点:( )和( )。
9、根据语言的亲属关系对语言的分类叫做( ),也叫做( )。
10、文字起源于(记事的图画)。
二、单选题(在本题的每一小题的备选答案中,只有一个答案是正确的,请把你认确答案的题号,填入题干的括号内。
多选不给分。
每题1分,共15分)1、社会语言学属于( )①理论语言学 ②广义应用语言学③普通语言学 ④狭义应用语言学2、元音[]的名称是( ) ①舌尖后高圆唇元音 ②舌尖前高圆唇元音 ③舌尖后高不圆唇元音 ④舌尖前高不圆唇元音3、下列汉字的读音中,包含有三合元音的是( ) ①邮 ②欧 ③玩 ④农4、汉语普通话音节结构( ) ①最长由三个音素组成 ②最长由四个音素组成③最长由五个音素组成 ④最短由两个音素组成5、下列词中,属于单纯词的是( ) ①玻璃 ②黑扳 ③语言 ④红旗6、下列词中,属于复台词的是( ) ①傻子 ②席子 ③天子 ④椅子7、下列词组中,属于多义的是( ) ①两只学生送的花瓶 ②两位学生送的花瓶③两只学生送的花篮。
④两个学生送的花篮8、下列词中粗体的成分,属于同音关系的是( ) ①杜鲁门——杜绝 ②负荆一负担 ③忽然--突然 ④花朵——浪花9、英语的‘foot”(脚,单数)变为“feet”(脚,复数)运用的语法手段是( ) ①附加 ②异根 ③内部屈折 ④重叠10、汉语普通话中的:“卡通片”中的“卡”是一个( ) ①语素 ②音节 ③前缀 ④词11、汉语中的:“了、着、过”在古代具有实实在在的词汇意义,到现代变成只表语义的助词, 这属于( ) ①异化 ②类化 ③新语法范畴的形成 ④实词虚化12、下列语言中属于粘着语的是( ) ①苗语 ②越南语 ③俄语 ④日语13、在一种语言内部划脑言时,最主要的依据是( ) ①语法 ②语义 ③语音 ④词汇14、下列词的词义,属于词义缩小的是( ) ①“皮”原指兽皮 ②“涕”原指眼泪③“瓦”原指一切烧好的上器 ④“江”原捐“长江”15、人类几种古老文字的原始字形,都是( ) ①象形的 ②会意的 ③表音的 ④形声的三、多选题(在本题的每一小题的备选答案中,正确答案有三个或三个以上多请把为正确答 案的题号,填入题干的括号内。
( ) 9. Componential analysis is based on the belief that the meaning of a word can be disserted into meaning components, called semantic features.” is [i]Ⅲ. Please fill in the blanks with the right word or words. (10 pints, 1 x 10) Make your conversational ____1____ such as required at the stage at which it occurs by the accepted ____2____ or direction of the talk exchange in which you are engaged.The maxim of quality----Do not say what you believe to be false.----Do not say that for which you lack ____3____ evidence.The maxim of quantity----Make your contribution as informative as required for the current purpose of the____4____.----Do not make your contribution more informative than is required.The maxim of relation----Be relevant ( make your contribution relevant).The maxim of manner----Avoid ____5____ of expression.----Avoid ____6____ .----Be brief.----Be orderly.Consonant articulations are relatively easy to feel, and as a result are most conveniently described in terms of ____7____ and ____8____ of articulation.The information about a word’s complement is included in the head and termed ____9____.Phonetically similar sounds might be related in two ways. If they are two distinctive phonemes, they are said to form a ____10___ contrast.Ⅳ. Please choose the correct answer from the optional choices. (10 points, 1 x10)1.When we use a simple set of symbols in our transcription, it is called _______.A.broad transcriptionB. narrow transcriptionC. new transcription2. _______ means that human languages enables their users to symbolize objects, events andconcepts which are not present (in time and space) at the moment of communication.A. DualityB. CreativityC. Displacement3. The sense relationship between “John plays the piano” and “John plays a musical instrument”is _______.A. synonymyB. antonymyC. entailment4. Using a language for the sheer joy of using it shows language has a _______ function.A. recreationalB. performativeC. metalinguisitc5. If a linguistic study aims to describe and analyze the language people actually use, it is called ________.A. descriptiveB. prescriptiveC. creative6. The study of sounds from the speaker’s point of view is labeled as _______ phonetics.A. auditoryB. articulatoryC. acoustic7. [p] is a voiceless ________ stop.A. dentalB. velarC. bilabial8. The relationship between “doctor and patient” shows that there exists a kind of ________.A. gradable antonymsB. complementary antonymsC. relational opposites9. The Speech Act Theory is first proposed by ________.A. SearleB. AustinC. Grice10. The story of Jack and Jill is an example of ________.A. behaviorismB. contextualismC. conceptualismⅤ. Please briefly answer the following questions. (30 points, 5 x 6)1. What are the important distinctions in linguistics?2. What is the difference between sentence meaning and utterance meaning?3. What is the difference between semantics and pragmatics?4. What is Conceptualist view of Meaning?5. Please draw the tree diagram of “the train will arrive”.Ⅵ. Please answer the following questions (30 points, 15 x 2)1. What are the similarities and differences between phonetics and phonology?2. Why do you think students majoring in English should study linguistics?。
全国2004年10月高等教育自学考试语言学概论试题课程代码:00541一、单项选择题(本大题共26小题,每小题1分,共26分)在每小题列出的四个备选项中只有一个是符合题目要求的,请将其代码填写在题后的括号内。
错选、多选或未选均无分。
1.下列关于“语言”的说法,不正确...的一项是(D)A.语言系统是由多个子系统组合而成的B.语言是一个符号系统C.语言符号具有离散特征和线性特征D.语言符号的音义关系可以任意改变2.在二十世纪,对哲学、人类学、心理学、社会学等学科产生重大影响的语言学流派是(C)A.历史比较语言学B.心理语言学C.结构主义语言学D.社会语言学3.下列元音音素都是后元音的一组是(B)A.[u, ε]B.[α, Λ]C.D.[o, a]4.下列辅音音素都是塞音的一组是(B)A.[d, 1]B.[b, k]C.[p, n]D.[t, v]5. 从语音的社会功能角度划分出来的最小语音单位是(A)A.音位B.音素C.音节D.音渡6.句子语调的高低升降变化表现最为明显的是(C)A.句首部分B.句中部分C.句终部分D.句首和句终部分7.汉语普通话中的“我”和助词“的”单念时发音分别为[uo]和而在实际语流中,“我的”发音是这是语流音变中的(A)A.顺同化现象B.逆同化现象C.弱化现象D.异化现象8.语汇是词和语的集这是合,下列关于“语”的表述,正确的一项是(D)A.“语”是所有词组的集合B.“语”的意义是若干词的意义的加合C.“语”是可以拆分的语言片段D.“语”包括“固定词组”和“熟语”9.下列关于汉语词双音节化倾向的作用的说法,不正确...的一项是(C)A.区别多义词的不同义项B.减少同音词C.减少同义词D.调整词的韵律节奏10.英语“students”中的“-s”是(C)A.虚词语素B.词根语素C.构形语素D.构词语素11.从词的构造方式看,下列各项中属于复合词的是(D)A.木头B.念头C.苦头D.山头12.下列现象中不属于...词法手段的是(A)A.虚词B.重叠C.轻重音D.词形变化13.法语动词“是”的直陈式现在时有6种变化,比如“je (我) suis (是)”,“il (他) est (是)”,“nous (我们) sommes (是)”等,这反映了法语中什么样的谓词属性范畴(D)A.时B.体C.态D.人称14.划分词类的最本质的标准是(A)A.分布标准B.意义标准C.形态标准D.逻辑标准15.下列词类从大类到小类的归类,不正确...的是(C)A.实词—谓词—动词—及物动词B.实词—体词—名词—处所名词C.实词—谓词—助词—时态助词D.实词—体词—量词—名量词16.下面词组中,结构类型与其他各组不同..的一组是(B)A.年轻漂亮/朴素大方B.我们大家/首都北京C.铁路民航/工人农民D.贯彻执行/讨论研究17.下列成对的词语中,属于相对反义词的一组是(D)A.成功—失败B.合法—非法C.本地—外地D.勤劳—懒惰18.下列句子的语义结构属于简单述谓结构的一项是(A)A.老王昨天买了一台彩电B.李辉去图书馆借了一本书C.他觉得不应该这样做D.他没接住小李传过来的球19.造成“北京人多”一句歧义的主要原因是(D)A.一词多义B.不同的句法结构关系C.不同的语义结构关系D.不同的层次构造20.下列关于音符来源的表述中,正确的一项是(D)A.音符是从笔画发展而来的B.音符是从记号发展而来的C.音符是从声旁转化而来的D.音符是从意符转化而来的21.目前已知的最古老的拼音文字是(C)A.古埃及文字B.古希腊文字C.腓尼基文字D.中国的甲骨文22.下列关于语言起源的表述中,正确的一项是(D)A.语言产生于人类对外界各种声音的摹仿B.语言产生于人们的相互约定C.语言是人类有意识地在短时间内创造出来的D.语言是人类在长期进化发展过程中创造出来的23.有一类词,它们的词义和构词方式都来自外语,构词语素则是本民族语言的,这类词属于(B)A.借词B.仿译词C.意译词D.音译兼意译词24.下列关于思维和语言的关系的说法,不正确...的是(C)A.感性思维不一定借助语言进行B.抽象思维有时与语言有脱节C.发散思维完全不需要借助语言D.抽象思维以语言为主要工具25.在儿童语言获得的过程中,标志着儿童产生最早的语义能力的阶段是(A)A.单词句阶段B.双词句阶段C.简单句阶段D.复杂句阶段26.下列词典中,属于语言词典的是(B)A.《永乐大典》B.《汉语成语小词典》C.《小学生作文词典》D.《北京地名词典》二、多项选择题(本大题共5小题,每小题2分,共10分)在每小题列出的五个备选项中有二至五个是符合题目要求的,请将其代码填写在题后的括号内。
2007-2008学年第一学期04英语(专升本)语言学概论A卷Part I Directions:Read each of the following statements carefully and put the letter A,B,C or D in the brackets. (2%×20=40%)1.______refers to the abstract linguistic system shared by all members of a speech community.A. ParoleB. LangueC. Competence D Performance2.“A rose by any other name would smell as sweet”well illustrates language is____.A. arbitraryB. vocalC. creative D communicative3. The description of a language at some point of time in history is a ________study.A. prescriptiveB. descriptiveC. synchronicD. diachronic4. The distinction between vowels and consonants lies in ____.A. the place of articulationB. the obstruction of air streamC. the position of the tongueD. the shape of the lips5._______phonetics studies how a speaker uses his speech organs to articulate the sounds.A.AriculatoryB.AuditoryC.AcousticD. Oral6. The________view holds that there is no direct link between a linguistic form andwhat it refers to.()A. naming theoryB.conceptualistC. contextualismD. behaviorism7. The word “ smog” is formed through.( ).A. backformationB. blendingC. clippingD. derivation8.The affix “ed” in the word “stopped” is known as a(n)________ morpheme.A. derivationalB. freeC. inflectionalD. open9.A(n)____act is the act of expressing the speaker’s intention, it is the act performed in saying something.A. locutionaryB. illocutionaryC. perlocutionaryD. speech10. Which word can be analyzed as +HUMAN+ADULT-MALE ()A.boy B.girl C.man D.woman11. The pair of words "buy" and "sell" are_______antonymy.().A. gradableB. converseC. relationalD. complementary12. There are morphemes in the word “telecommunication”.()A.2B.3C. 4D.513. The relationship between "fruit" and "apple" is . ()A. polysemyB.hyponymyC. homonymyD. synonymy14. is defined as the study of the internal structure of words, and the rules bywhich words are formed. ()A. PhoneticsB. MorphologyC. SyntaxD. Semantics15 .“Sweets” and “candy” are used respectively in Bri tain in and America, but refer to thesame thing. The words are synonyms. ( )A. collocationalB. stylisticC. completeD. dialectal16. is the study of the relationship between brain and language. ( )A. PsycholinguisticsB. SociolinguisticsC. neurolinguisticsD. Semantics17. is the discussion about the relationship between language and culture.A. Sapir-Whorf hypothesisB.Critical Period HypothesisC.BilingualismD.Behaviorism18. X: John’s bike needs repairing. Y: John has a bike.What’s the relations between the two sentences.A. X entailsY.B. X presupposes YC. X is synonymous withYD. X is inconsistent withY19. _____as either intentionally or unintentionally deviant forms and self-corrigible suggestfailure in performance.A.ErrorsB. MistakesC. TransferD. Interference20. The____ view holds that language develops as a result of the complex interplay betweenthe human characteristics of the child and the environment in which the child develops.A. behavioristB. innatistC. interactionistD. cognitivePart II. Define the following terms(3%×5=15%points)1. language2. pragmatics3.culture4.second language acquisition5. syntaxPart III. Linguistic theory and linguist. (1%×8=8%)1. competence and performance ( ) A. G. Leech2. semantic triangle ( ) B. Krashen3. contextualism ( ) C. Ogden and Richard4. Course in General Linguistics ( ) D. J.R. Firth5. predication analysis ( ) E. John Austin6. speech act theory ( ) F. S. P. Carder and Larry. Selinker7. Input Hypothesis ( ) G.. Saussure8. interlanguage ( ) H.ChomskyPart IV Answer the following questios. (5%×3=15%)1.What are the main features of human language that is different from animal communicationsystem?2. What is phonetics? How do phonetics and phonology differ in their focus of study?3. What is a register? Please use Halliday’s register theory to analyze:A lecture on biology in a technical college.2007-2008学年第一学期04英语(专升本)语言学概论A卷答题纸Part I Best choice.(2%×20=40%)Part II Define the following terms(3%×5=15%)1. language2. pragmatics3.culture4.second language acquisition5. syntaxPart III Linguistic theory and linguist. (1%×8=8%)Part IV. Answer the following questios. (5%×3=15% )1. What are the main features of human language that is differentfrom animal communication system?2. What is phonetics? How do phonetics and phonology differ in their focus of study?3. What is a register? Please use Halliday’s register theory to analyze:A lecture on biology in a technical college.Part IV. Theory and practice. (22%)1.Think of contexts in which the following sentences can be used for other purposes than just stating facts.(4%)(1)Oh, it is raining.(2) Today is Sunday.2. What are the four maxims of the CP? Try to give your own examples to show how flouting these maxims give rise to conversational implicature?(10%)3. Draw a tree diagram for the following statements.(3%+5%)(1). The boy will find the the book. (2). What did you eat for lunch?04英语(专升本)语言学概论参考答案Part I Directions: Read each of the following statements carefully and put the letter A,B,C or D in the brackets. (2%×20=40%)1-5 BACBA 6-10 BBCBD 11-15 CBBBD 16-20 CABBCPart II Define the following terms (3%×5=15%)nguage can be defined as a system of arbitrary vocal symbols used for humancommunication.2.Pragmatics is the study how speakers of a language use sentences to effect successfulcommunication.3.Culture means the total way of a people, including the patterns of belief, customs,objects, institutions, techniques, and language that characterizes the life of the human community.4.Second llanguage acquisition refers to the systematic study of how one person acquires asecond language subsequent to his native language.5.Syntax is a branch of linguistics that studies how words are combined to form sentencesand the rules that govern the formation of sentences.Part III. Linguist and linguistic theory. (1%×8=8%)1H 2C 3D 4G 5A 6E 7B 8FPart IV Answer the following questions. (5%×3=15% )1. Arbitrariness. The relationship between the two subsystems of language is arbitrary. There is no logical connection between sound and meaning.Creativity. Language provides opportunities for sending messages that have never been sent before and for understanding brand new messages. he grammar rules and the words are finite, but the sentences are infinite. Every speaker uses language creatively.Duality. Language contains two subsystems, one of sounds and the other of meanings. Certain sounds or sequences of sounds stand for certain meanings.Displacement There is no limit in time or space for language. Language can be used to refer to things real or imagined, past, present or future.Cultural transmission. Culture cannot be genetically transmitted. Instead, it must be learned. Language is a way of transmitting culture.2. Phonetics is defined as the study of the phonic medium of language; it is concerned with all the sounds that occur in the world’s languages.Phonetics and phonology differ in their approach and focus. Phonetics is of a general nature, it is interested in all the speech sounds used in all human languages: how they are produced, how they differ from each other, what phonetic features they possess, how they can be classified, etc. Phonology, on the other hand, aims to discover how speech sounds in a language form patterns and how these sounds are used to convey meaning in linguistic communication.3.The type of language which is selected as appropriate to the type of situation is a register. Halliday further distinguishes three social variables that determine the register: field of discourse, tenor of discourse, and mode of discourse.Field: scientific (biological) Tenor: teacher-students(formal, polite)Mode: oral (academic lecturing)Part IV. Theory and practice. (22%)1. (4%)(1) (2)根据学生所给出的语境酌情给分, 每小题2分.2. (10%)The four maxims are:1).Quantity--Make your contribution as informative as is required (for the current purposes of the exchange.--Do not make your contribution more informative than is required.2)Quality – Try to make your contribution one that is true. Do not say what you believe to be false. Do not say that for which you lack adequate evidence.3). Relation – Be relevant.4). Manner –Be perspicuous. Avoid obscurity of expression. Avoid ambiguity. Be brief (avoid unnecessary prolixity). Be orderly.These maxims can be violated for various reasons, but only when they “flouted”, to use Grice’s term, does “conversational implicature” occur.Use some specific examples to test it.3. (3%+5%)。