时态语态(教师用)
- 格式:doc
- 大小:97.50 KB
- 文档页数:18
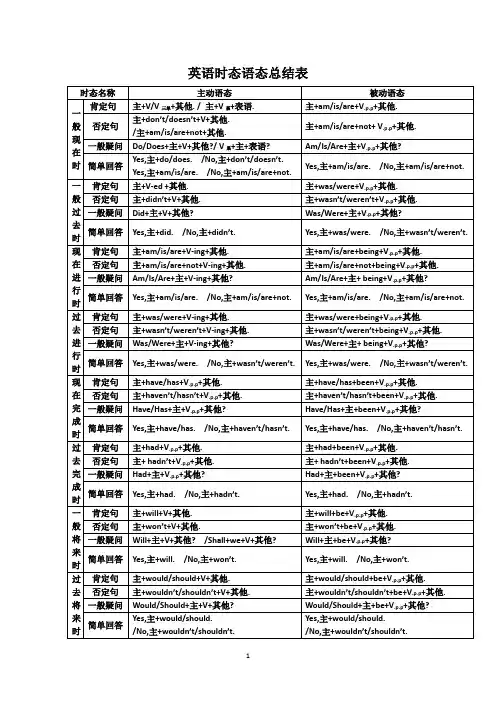
英语时态语态总结表Ⅰ. 英语八种时态归纳复习时态是英语学习中一个至关重要的内容,广大初中学生在实际运用时,往往对时态总是倍感棘手,下面我们就归纳复习一下这几种时态。
一、一般现在时:概念:经常、反复发生的动作或行为及现在的某种状况。
时间状语:always, usually, often, sometimes, every week (day, year, month…), once a week, on Sundays, etc.基本结构:①be动词;②行为动词否定形式:①am/is/are+not;②此时态的谓语动词若为行为动词,则在其前加don't,如主语为第三人称单数,则用doesn't,同时还原行为动词。
一般疑问句:①把be动词放于句首;②用助动词do提问,如主语为第三人称单数,则用does,同时,还原行为动词。
二、一般过去时:概念:过去某个时间里发生的动作或状态;过去习惯性、经常性的动作、行为。
时间状语:ago, yesterday, the day before yesterday, last week(year, night, month…), in 1989, just now, at the age of 5, one day, long long ago, once upon a time, etc.基本结构:①be动词;②行为动词否定形式:①was/were+not;②在行为动词前加didn't,同时还原行为动词。
一般疑问句:①was或were放于句首;②用助动词do的过去式did 提问,同时还原行为动词。
三、现在进行时:概念:表示现阶段或说话时正在进行的动作及行为。
时间状语:now, at this time, these days, etc.基本结构:am/is/are+doing否定形式:am/is/are+not+doing.一般疑问句:把be动词放于句首。

时态语态一、一般现在时(The Simple Present Tense)1、结构1)(Active) do; does2)(Passive) is (am, are) done2、主要用法①表示经常发生的动作和存在的状态。
e.g. I often come to school early.②表示主语的特征,性格和能力。
e.g. He is an engineer. He looks young.③表示客观事实,或普遍真理。
e.g. The teacher told us that light travels faster than sound.Practice makes perfect. 熟能生巧。
④在时间,条件状语从句中表示将来的动作。
e.g. I’ll tell him about it when he returns home.⑤表示按时刻表计划或安排好的动作。
(只限于表示起始或移动意义的动词。
begin, come, leave, start, arrive, go, etc.)e.g. I will find out when the train leaves.The plane for San Francisco takes off at three p.m..3、与一般现在时连用的时间状语:every day, once a week, twice a week, always, usually, often, sometimes, seldom, never etc.e.g. I go to the cinema once a week.e.g. Sometimes we work until twelve o’clock.4、主动变被动1)Do you often clean your room?Is your room often cleaned?2)People speak English in many countries.English is spoken in many countries.二、一般过去时(The Simple Past Tense)1、结构1)(Active) did2)(Passive) was/were done2、主要用法①表示过去的动作或状态。

时态与语态知识点总结时态和语态是我们在学习英语过程中经常遇到的两个概念。
掌握时态和语态的正确使用对于准确表达思想、避免误解是非常重要的。
本文将对时态和语态的基本知识点进行总结,以帮助读者更好地掌握这两个概念。
一、时态(Tenses)时态指的是动词在时间上的形式表达。
英语中共有12个时态,包括简单现在时、现在进行时、现在完成时、一般过去时、过去进行时、过去完成时、一般将来时、将来进行时、将来完成时、过去将来时、过去将来完成时和过去完成进行时。
1. 简单现在时(Simple Present Tense):表示现在的状态、习惯、常规或普遍真理。
例如:I work in a company.2. 现在进行时(Present Continuous Tense):表示现在正在发生的动作。
例如:She is reading a book.3. 现在完成时(Present Perfect Tense):表示过去发生的动作对现在造成的影响。
例如:I have finished my homework.4. 一般过去时(Simple Past Tense):表示过去某个时间发生的动作。
例如:He went to the store yesterday.5. 过去进行时(Past Continuous Tense):表示过去某一时刻正在进行的动作。
例如:They were playing basketball when it started raining.6. 过去完成时(Past Perfect Tense):表示过去某个时间之前已经发生的动作。
例如:We had already eaten dinner when she arrived.7. 一般将来时(Simple Future Tense):表示将要发生的动作或存在的状态。
例如:I will call you later.8. 将来进行时(Future Continuous Tense):表示将来某一时刻正在进行的动作。

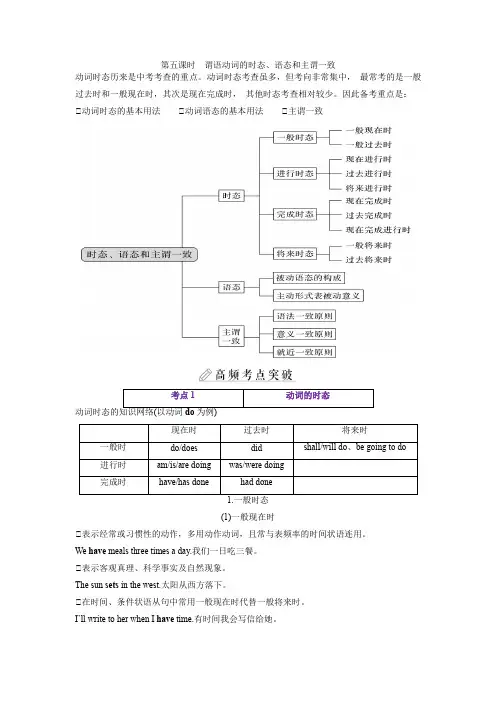
第五课时谓语动词的时态、语态和主谓一致动词时态历来是中考考查的重点。
动词时态考查虽多,但考向非常集中,最常考的是一般过去时和一般现在时,其次是现在完成时,其他时态考查相对较少。
因此备考重点是:①动词时态的基本用法①动词语态的基本用法①主谓一致考点1动词的时态(1)一般现在时①表示经常或习惯性的动作,多用动作动词,且常与表频率的时间状语连用。
We have meals three times a day.我们一日吃三餐。
①表示客观真理、科学事实及自然现象。
The sun sets in the west.太阳从西方落下。
①在时间、条件状语从句中常用一般现在时代替一般将来时。
I’ll write to her when I have time.有时间我会写信给她。
1.Mike often (收集)stamps and plays basketball in his spare time.【答案】collects本题考查动词的时态。
由and plays可知,此空为一般现在时,主语Mike为第三人称单数,故谓语动词应用第三人称单数形式。
2.And then it just (grow) and makes the world a better place.【答案】grows本题考查动词的时态。
此处主语it为第三人称单数。
由于and连接的前后两个动词为并列关系,根据makes可知时态为一般现在时,故填grows。
3.We can see clearly that Mongolia (位于) between China and Russia on the map. 【答案】lies句意:我们在地图上可以清楚地看到蒙古位于中国和俄罗斯之间。
本题考查动词的时态。
时态用一般现在时,Mongolia是第三人称单数,因此从句的谓语动词用第三人称单数形式。
4.Mary is crazy about reading. She b a lot of books from the school library every time.【答案】borrows句意:Mary酷爱阅读。
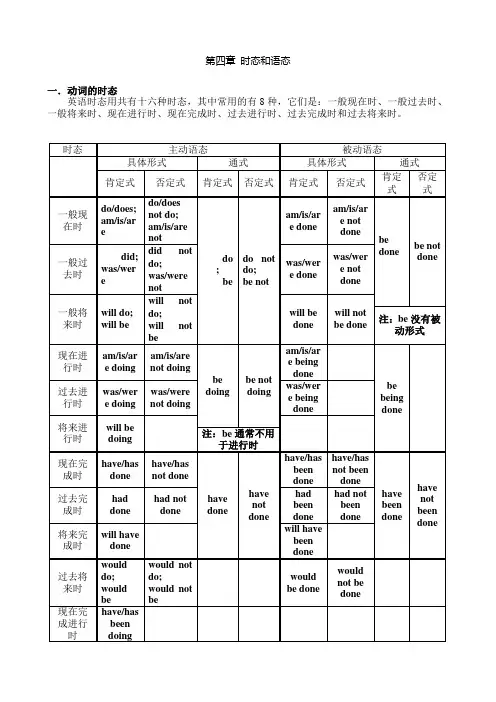
第四章时态和语态一.动词的时态英语时态用共有十六种时态,其中常用的有8种,它们是:一般现在时、一般过去时、一般将来时、现在进行时、现在完成时、过去进行时、过去完成时和过去将来时。
一. 一般现在时.1.构成. be动词:am is are ; 其他动词用动词原形,当主语是第三人称单数时要在谓语动词后加“s”,其变化规则与名词变复数一致。
2.用法. 1). 经常性或习惯性的动作,常与表示频度的时间状语连用。
如usually, always, often, seldom, never, every...,eg. I leave home for school at 7 every morning.I don’t leave home for school at 7 every morning.Do I leave home for school at 7 every morning?He usually gets up early.He doesn’t usually get up early.Does he usually get up early?2) 客观真理,客观存在,科学事实。
eg. The earth moves around the sun.The earth doesn’t move around the sun 否定句Does the earth move around the sun? 疑问句Shanghai lies in the east of China.Shanghai doesn’t lie in the east of China 否定句Does Shanghai lie in the east of China? 疑问句Water boils at 100 centigrade degrees.3) 表示格言或警句中eg. Pride goes before a fall.注意. 此用法如果出现在宾语从句中,即使主句是过去时,从句谓语也要用一般现在时。

第二部分语法知识贯通专题一 动词的时态、语态和主谓一致考点1 一般时一般现在时(do/does式) ★★★典例1 [2019安徽安庆二模改编,61]New year in Chinese people’s eyes means a family reunion. Every year (see) the largest annual mass migration on the planet when one sixth of the world’s population travel home to celebrate with their families.句意:在中国人眼中,新年意味着家人团聚,每年世界上六分之一的人回家与家人一起庆祝,这是地球上最大规模的年度人口迁移。
根据Every year 可知,此处应用一般现在时;再结合句意可知,主语是Every year,此处是拟人化的用法,see在此处表示"遭受,历经",故用其第三人称单数形式。
sees典例2 [2019河北邢台高三检测,61]An hour of swimming (burn) almost as many calories as an hourof running.句意:游泳一小时消耗的卡路里与跑步一小时消耗的几乎一样多。
此处叙述的是客观事实,因此用一般现在时。
burns一般过去时(did式) ★★★典例3 [2020河北石家庄摸底考试,61]Translated fiction sales in the United Kingdom (rise) by 5.5 percent last year, with a growing demand for Chinese titles, said Nielsen Book on Wednesday.句意:Nielsen Book周三表示,去年英国的翻译小说销量增长了5.5%,对中文图书的需求不断增长。


高中英语语法(时态和语态)一.动词的时态时态是谓语动词所表示的动作或情况发生时间的各种形式。
英语动词有16种时态,但是常见的只有九种:一般现在时、一般过去时、一般将来时、现在进行时、过去进行时、现在完成时、过去完成时、过去将来时、现在完成进行时。
(一)一般现在时(do / does)1.具体用法1) 表示经常性或习惯性动作We always care for each other and help each other. 我们总是互相关心互相帮助。
He goes to school every day.2)表示现在的特征或状态He is very happy.Do you sing? ----A little.3)表示普遍真理Light travels faster than sound. 光速比声速快。
Actions speak louder than words. 行动胜过言语。
* 常与一般现在时态连用的词或短语主要有:often, usually, sometimes, every day,every morning/afternoon, on Sundays/weekends等等。
I often go to the cinema on Sundays. 我经常星期天去看电影。
He goes to work early every day. 他每天上班很早。
(二)一般过去时( did )(1)表示过去某一特定时间所发生的、可完成的动作或状态,常与表示确切过去时间的词、短语或从句连用。
例如:We went to the pictures last night and saw a very interesting film.(2)表示过去习惯性动作。
例如:He always went to class last.I used to do my homework in the library.(三)一般将来时( will / shall do)1)表示将来打算进行或期待发生的动作或状态。
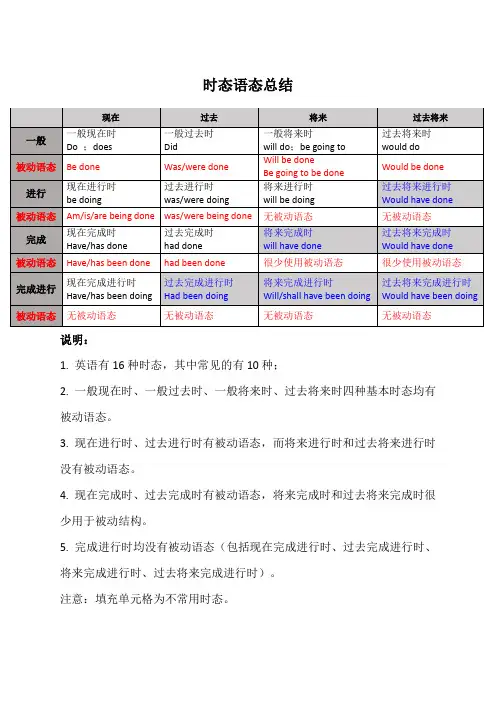
时态语态总结说明:1. 英语有16种时态,其中常见的有10种;2. 一般现在时、一般过去时、一般将来时、过去将来时四种基本时态均有被动语态。
3. 现在进行时、过去进行时有被动语态,而将来进行时和过去将来进行时没有被动语态。
4. 现在完成时、过去完成时有被动语态,将来完成时和过去将来完成时很少用于被动结构。
5. 完成进行时均没有被动语态(包括现在完成进行时、过去完成进行时、将来完成进行时、过去将来完成进行时)。
注意:填充单元格为不常用时态。
▲用法及举例:1. 一般时态的被动语态一般时态的被动形式都由“助动词be+过去分词”构成(动作发生时间由be表现出来) (1) 一般现在时的被动语态In China, the railways are owned by the state. 在中国,铁路是国有的。
They are asked to shoulder the costs of the repair. 要求他们承担这笔修理费。
The new drug began to operate not long after it is taken. 这种新药服用后不久就会开始见效。
(2) 一般过去时的被动语态:Each couple was asked to complete a form. 要求每对夫妇填一张表。
The thief was handed over to the police. 这个小偷已经送交派出所了。
He was admitted into the club as a member. 他被接纳为俱乐部的会员。
(3) 一般将来时的被动语态:The hotel will be closed during repairs. 那家饭店在整修期间将停业。
Light refreshments will be served after the meeting. 会议之后有简单茶点招待。
If you don’t give care to your work, you will be fired. 如果你不细心工作,你会被解聘的。

动词时态和语态教案【专题要点】动词时态和语态要点概述如下:1.一般现在时表示习惯性、个人能力、普遍真理;表示“已经列入日程表”时常用一般现在时表示将来;2.表示说话人始料的事,常用一般过去时;3.时间状语从句或条件状语从句中常用一般时表将来;4.will/be going to do/be about to do的用法区别;5.用主动形式表示被动意义常见的几种情况;【考纲要求】时态与语态一直是热点,也是广大考生复习备考的难点。
考纲要求考生应该具备较强的语言应用能力,能在具体语境中恰当、准确地使用某一特定时态;同时还要熟练运用特殊时态句式和用法以及不用被动式但表示被动的动词和短语。
【教法指引】高考对时态的考查非常灵活且难度较大,不易把握。
大部分时态题答案的选择取决于题干语境;但也有部分时态试题较易把握,其用法相对固定,常见于特定句式结构中;还有部分常见时态用法特殊。
综观近年来的高考单项填空题,动词成为考查的热点,在15个单项选择中,考查动词时态的题一般不少于2道,动词的时态常和语态、主谓一致结合在一起进行考查。
教师在指导学生复习备考、答题中,要遵循如下思路:① 这个动作可能发生在什么时间?题干句中可参照的时间信息有那些?② 这个动作处于什么时态,是进行中,还是已经结束(完成)?限制或修饰这个动作的状语信息有哪些?③ 这个动作与主语的关系,是主动还是被动?【知识网络】动词时态与语态一、动词时态(一)一般现在时一般现在时常以动词原形表示,但当主语是第三人称单数时,应用动词的单数第三人称形式。
一般现在时主要有以下几种用法:1、一般现在时表示现在经常发生或习惯性的行为或状态,常与usually, always, every day, twice a week, seldom, sometimes等时间状语连用。
He always sleeps with the windows open.他总是开着窗子睡觉。
动词时态和语态教案专题要点:动词时态和语态要点概述如下:一般现在时表示习惯性、个人能力、普遍真理;表示“已经列入日程表”时常用一般现在时表示将来;2、表示说话人始料的事,常用一般过去时;3、时间状语从句或条件状语从句中常用一般时表将来;4、 Will/be going to do/be about to do的用法区别;5、用主动形式表示被动意义常见的几种情况;考纲要求:时态与语态一直是热点,也是广大考生复习备考的难点,考纲要求考生应该具备较强的语言应用能力,能在具体语境中恰当、准确地使用某一特定时态;同时还要熟练运用特殊时态句式和用法以及不用被动式但表示被动的动词和短语。
◆动词时态的核心考点1.一般现在时考点分析(1)表示客观事实或普遍真理(不受时态限制)。
Time and tide wait for no man.(2)表示现状、性质、状态时多用系动词或状态动词;表示经常或习惯性的动作,多用动作动词,且常与表频率的时间状语连用。
They always care for each other and help each other.(3)表示知觉、态度、感情、某种抽象的关系或概念的词常用一般现在时:see,hear,smell,taste, feel, notice, agree, believe, like, hate, want, think, belong to, seem 等。
Smith owns a car and a house.All the students here belong to No.1 Middle School(4)在时间、条件状语从句中常用一般现在时代替将来时。
但要注意由if引导的条件状语从句中可以用shal或will表“意愿”,但不表示时态。
If you will accept my invitation and come to our party, my family will be pleased。
高中英语语法复习学案教师版——动词的时态和语态动词的时态(一)一般现在时1.Thegeographyteachertoldusthattheearthmoves(move)aroundthesun.2.Waterboils(boil)at100 ℃.3.Thecarelessdriverhasjustbeenfined$10forstoppinghiscaratasignthatreads (read)“NOPARKING”.4.Whateveryousay(say),Iwillnotchangemymind. 6.12.3.定义:过去某一时间发生的动作或所处的状态。
含有“刚才,在过去”之意,暗示现在已经不这样。
时间状语:then;atthattime;justnow;threedaysago;yesterday;when 或while 引导的表示过去的时间状语从句【总结】1.定义:将来某一时刻要发生的动作或所处的状态。
时间状语:soon;nextweek;tomorrow等2.beto+动词原形的用法:(1)YouaretodoyourhomeworkbeforeyouwatchTV.=haveto/must“必须“(2)Youaretoreportthepolice.=should/oughtto“应该”7.Selectingamobilephoneforpersonaluseisnoteasytaskbecausetechnologyischanging(change)sorapidly.8.Idon’treallyworkhere.Iamjusthelping(help)outuntilthenewsecretaryarrives.【总结】1.定义1)现在进行时:说话时或现阶段正在发生的动作或存在的状态。
2)过去进行时:过去某个时刻或阶段正在发生的动作或存在的状态。
2.时间状语1)现在进行时:now;rightnow等2)过去进行时:atthistimeyesterday等3.一个长动作为背景,被一个短动作打断,长动作用进行体,短动作用一般体。
动词语态(初高考点差异及衔接)初中要求8种常见时态的被动语态表达形式:①一般现在时:am/is/are+过去分词;②一般过去时:was/were+过去分词;③现在进行时:am/is/are being+过去分词;④过去进行时:was/were being+过去分词;⑤一般将来时:will be+过去分词;⑥过去将来时:would be+过去分词;⑦现在完成时:has/have been+过去分词;⑧过去完成时:had been+过去分词。
高中要求我们将学习到更复杂的语法结构,因此主动语态和被动语态也会相对复杂一些。
被动语态在高中阶段,因为往往出现在较复杂的句子结构和词汇中,因而需要在学习的时候认真记忆词汇并分析句子结构。
【初中被动语态考点聚焦】考点一一般现在时的被动语态1.Every year in early October,Albuquerque International Balloon Festival is h inAlbuquerque,the biggest city in New Mexico.答案held句意:每年10月初,阿尔伯克基国际热气球节在新墨西哥州最大的城市阿尔伯克基举行。
本题考查动词的语态。
根据句意可知,此处意思是“举行”,且表示被动,故填held 。
2.There is also Hershey,which is well (know)as the chocolate company.答案known短语be well known as...意为“作为……而著名”。
3.It’s also (call)the Double Ninth Festival.答案called它又被称作重阳节。
根据语义可知本句应为被动语态,应用过去分词called 。
4.—How clean your car is!—Thank you.It (wash)very often.答案is washed句意:——你的汽车多干净啊!——谢谢你。
现在完成时知识集结知识元现在完成时知识讲解1. 现在完成时结构:主语 + 助动词have(has) + 动词过去分词否定句:have/has后加not, haven’t/hasn’t一般疑问句:have/has提前2. 现在完成时的用法:(1)表示过去发生的某一动作对现在造成的影响或产生的结果,强调的是这个结果或影响,常与yet,already,just,before,lately等时间状语连用。
—Have you had your lunch yet? 你吃过午饭了吗?—Yes, I have. I have just had it. 是的,我刚吃过。
(现在我不饿了。
)I have already posted the photos. 我已经寄过这些照片了。
(这些照片已不在我这里了。
)(2)过去发生的事情,一直持续到现在(其谓语动词多是延续性动词或表示状态的词)。
I haven’t seen her these days. 近来我一直没见过他。
I’ve known Li Lei for three years. 我认识李雷已经三年了。
They have lived here since 1996. 他们自从1996年就住在这儿。
She has taught us since I came to this school. 自从我来这所学校,她就教我。
3. 现在完成时多与下列时间状语连用:(1(2for + 时间段for two yearssince + 时间点since 2008since thensince he came hereso far 目前;迄今为止up to now=till now=by now 到现在为止;直到现在all the time 总是;一直recently/lately 最近these days 近几天by the end of...到……末/结束by the end of this month/year 到本月/年末during /over the last (past) few years 在过去的几年中in the last /past days/ months/ years 在过去的几个天/月/年中(3)在条件、时间、让步状语从句中,表示将来某时以前已完成的动作。
动词的时态和语态及其用法动词的时态在英语中,由于谓语动作发生的时间不同,或表达不同时间存在的状态,谓语动词都要发生相应的变化.这些动词的形式就叫做动词的时态。
英语动词的时态共有16种,列表如下: (以动词do为例)现在过去将来过去将来一般进行完成完成进行do / doesdidshall / will doshould / would doam / is /aredoingwas / were doingshall / will be doingshould / would be doinghave / has donehad doneshall / will have doneshould / would have donehave /has / been XXX / will have been doingshould / would have been doing时态的用法:一般现在时:1)现在惯性的举措或存在的状态。
2)客观事实,真理或格言。
3)表示现在将来时。
(只用于时状或条状从句中)一般曩昔时:1)曩昔惯性的的举措或存在的状态。
2)用于“were-型”和“if-型”假造语气中。
3)表示过去将来时。
(只用于时状或条状从句中)现在进行时:1)在现在某一时刻或某段时间里正在进行的举措。
2)按计划安排在现在的将来发生的举措。
曩昔进行时:1)在曩昔的某一时刻或某段时间里正在进行的举措。
2)按计划安排在曩昔的将来发生的举措。
现在完成时:1)举措发生在曩昔,对现在有影响(注:瞬间性动词的已完成用法)2)动作发生在过去,一直延续到现在,对目前有影响。
(注:延续性动词的已完成或未完成用法)过去完成时:过去有两个动作,其中,一个动作发生时,另一个动作已经完成。
(注:过去的过去,用过去完成时)现在完成进行时:动作发生在过去,一直延续到现在,并很可能继续延续下去。
曩昔完成进行时:曩昔有两个举措。
其中,一个举措发生时,另外一个举措已经完成,但该举措很可能继续延续下去。
英语语法:初中英语动词时态和语态讲解(一)动词是谓语动所表示的动作或情况发生时间的各种形式。
英语动词有16种时态,但是常用的只有9种:一般现在时、一般过去时、一般将来时、现在进行时、过去进行时、现在完成时、过去完成时、过去将来时、现在完成进行时。
下面分别介绍。
1、一般现在时的用法1)表示经常性、习惯性的动作;表示现在的状态、特征和真理。
句中常用often, usually, every day 等时间状语。
例如:a. He goes to school every day.b. He is very happy.c.The earth moves around the sun.2) 在时间状语从句和条件状语从句中,用一般现在时表示将来。
例如:a. If you come this afternoon, we’ll have a meeting.b. When I graduate, I’ll go to countryside.3) 有时这个时态表示按计划、规定要发生的动作(句中都带有时间状语),但限于少数动词,如:begin, come, leave, go ,arrive, start , stop, return, open, close等。
例如:a. The meeting begins at seven.b. The rain starts at nine in the morning.4) 表示状态和感觉的动词(be, like, hate, think, remember, find, sound 等)常用一般现在进行时。
a. I like English very much.b. The story sound very interesting.5) 书报的标题、小说等情节介绍常用一般现在时。
2.一般现在时的用法1)表示过去某时间发生的事、存在的状态或过反复发生的动作。
a. He saw Mr. Wang yesterday.b. He worked in a factory in 1986.2)表示过去经常发生的动作,也可用“used to “ 和“would + 动词原形”。
专题一动词时态和语态(教师用)【教学内容】【知识点归纳】I.动词时态和语态的构成形式主动语态的构成一般现在时一般过去时do/does,( is/am/are )did,(was/were)现在进行时过去进行时is/am/are doing was/were doing现在完成时过去完成时has/have done had done现在完成进行时过去完成进行时has/have been doing had been doing一般将来时过去将来时will/shall do is/am/are going to dois/am/are(about)to do would/should do was/were going to do was/were(about)to do被动语态的构成一般现在时一般过去时is/am/are done/was/were done现在进行时过去进行时is/am/are being done/was/were being done现在完成时过去完成时has/have been donehad been done一般将来时过去将来时will/shall be done is/am/are going to be doneis/am/are(about)to be donewould/should be donewas/were going to be done was/were(about)to be doneII.动词时态的用法1.一般现在时①一般现在时表示经常发生、习惯性动作、客观真理、科学事实、格言,目前的特征、状态、能力等;②主句是一般将来时,时间、条件状语从句中用一般现在时表示将来;I’ll go there after I finish my work.If it rains tomorrow,I won’t go there.③在以here,there开头的句子里,go,come等少数动词的一般在时表示正在发生的动作;There goes the bell.铃响了。
There comes the bus.汽车来了。
Here she comes.她来了。
注意:近几年,对一般现在时的考查常用过去时态或现在完成时态对考生进行干扰Months ago we sailed ten thousand miles across the open sea, which_____ the Pacific,and we met no storm.A. was calledB. is calledC. had been calledD. has been called虽然航海发生在过去,但是,海洋的名称不会因此而变化,所以要用一般现在时。
2.现在进行时①表示正在进行的动作;②表示按计划安排即将发生的动作。
She is leaving for Beijing.她要去北京。
He is working as a teacher tomorrow.从明天起他要做老师。
My father is coming to see me this Saturday.这个星期六我爸爸要来看我。
③代替一般现在时,描绘更加生动。
The Changjiang River is flowing into the east.江水滚滚向东流。
The sun is rising in the east.太阳从东方冉冉升起。
④与always, forever, constantly, continually连用,表示赞赏或厌恶等感情色彩,但并非强调动作正在进行;He is always helping others.他总是肯帮助他人。
She is always forgetting something.她老是忘记某些事情。
⑤大多数动词可用于进行时,但也有些动词不用于进行时。
常见的有:▲感觉类:look, smell, feel, sound, taste, see, hear▲情感类:like, love, prefer, admire, hate, fear▲心态类:wish, hope, expect, want, need, believe, think, understand, agree, knowt▲所有类:have, contain, won, hold, belong to等。
3.现在完成时①表示过去发生的动作对现在产生的影响或结果,或说话时已完成的动作;I have finished the report./ She has cleaned the room.②表示从过去开始,待续到现在的动作或状态,往往和“for...”, “since...”表述的一段时间状语连用;He has learned English for six years./ They have worked here since they left college.③表示“曾经到过某地(人已回来)”用“have/has been to”;表示“到某地去了(还未回来)”用“have/has gone to”。
—Where is Li Hua? -He has gone to the reading-room.—She knows a lot about Shanghai. -She has been there.④在时间状语从句,条件状语从句或让步状语从句中表达将来某时已经完成的动作。
When you have learned English, you will find it a bridge to so much knowledge.We’ll start at six if it has stopped raining by then.注意:这里的现在完成时强调从句动作在主句动作之前完成, 如果两个动作同时或几乎同时发生, 则不必用完成时;试比较:I’ll let you know as soon as I hear from her.She will call you when she gets home.⑤短暂动词(即瞬间动词),join,lose,buy,borrow,leave,go,come,arrive,die,marry, finish,complete,begin,start,break out等,在完成时态中,其肯定式不能和表示一段时间的状语连用。
要译“他参军已经三年了”不能说:He has joined the army three years.可采用:▲“ago法”:He joined the army three years ago.▲“延续法”:He has been in the army for three years.▲“since法”:It is/has been three years since he joined the army.注意:没有包括“现在”在内或不是截至“现在”为止的时间状语不能与现在完成时连用, 但“in(over) the past/last+时间段”要与现在完成时连用。
4.现在完成进行时①用来表示从过去某一时刻开始一直持续到现在(或今后还要继续一去)的动作;He has been doing the maths problems since 8:00.②凡是不能用于现在进行时的动词均不能用于现成完成进行时。
5.一般过去时①表达特定的过去时间内发生的动作或存在的状况,或过去某一时间内经常发生或反复发生的动作或为; He often sang when he was a boy.He went to the cinema last night with her boy friend.②用于I didn’t know…或I forgot…,表示事先不知道或不记得,但现在已知道或记得的事情。
用于I didn’t know…或I forgot…,表示事先不知道或不记得,但现在已知道或记得的事情。
I didn’t know you were here.(现在已经知道)Sorry, I forgot to bring my book.(“忘记带书”已成为过去的事了)这一用法考生要特别注意。
注意:参看过去将来时的用法②。
6.过去进行时①表示过去某一时刻或某一段时间内正在进行的动作(这一过去时间须用时间状语表示);He was preparing his lecture all day yesterday.②表示动作在另一过去动作发生时进行;They were still working when I left.③用在两个过去进行时动作同时发生;I was writing while he was watching TV.④过去计划、安排好的将来动作(只限于come, go, leave, arrive, start, move, sail, fly, travel, stay等);He said she was arriving the next day.⑤与always, forever, constantly, continually连用,表示赞赏或厌恶等感情色彩。
(参看现在进行时的用法④)Comrade Lei Feng was always thinking of others never thinking of himself.⑥过去进行时可用来描绘故事发行的背景。
The wind was blowing and it was raining hard.7.过去完成时①表示在过去某一时间以前已经完成的动作。
He had shut the door before the dog came up.Everything had been all right up till this morning.②表示动作或状态从过去某个时刻开始一直延续到另一个过去时刻才完成,甚至还要继续下去。
At the age of ten,he had learned 500 English words.He had been ill for a week when we learned about it.③过去未曾实现的意图、打算或希望(只限于think, want, plan, mean, intend, hope, expect, suppose,wish, want等动词)。
I had wanted to pay a visit to you yesterday, but the rain prevented me.我本来想昨天拜访你的,但是下雨(让我不能来)。