One dimensional element details
- 格式:doc
- 大小:2.89 MB
- 文档页数:75
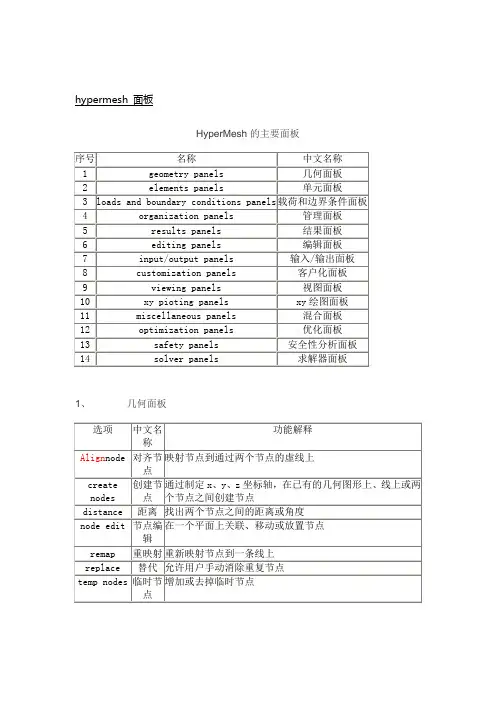
hypermesh 面板HyperMesh的主要面板1、几何面板Nodes(节点)子面板的选项及功能Lines(线)子面板的选项及功能Surfaces(曲面)子面板的选项及功能1、单元面板One-dimensional(一维单元)子面板的选项及功能shells(壳单元)子面板的选项及功能Solids子面板的选项及功能2、载荷和边界条件面板载荷和边界条件面板3、管理面板管理面板4、结果面板结果面板6、编辑面板编辑面板7、输入/输出面板输入/输出面板8、客户化面板客户化面板9、视图面板视图面板10、xy绘图面板Xy绘图面板11、混合面板混合面板12、优化面板优化面板13、安全性分析安全性分析面板14、求解器面板求解器面板Hypermesh中常用快捷键Hypermesh中常用快捷键F1 -- Hidden Line 隐藏线F2 -- Delete 删除(删除任何对象都用此命令)F3 -- Replace 合并两个节点F4 -- Distance 测量距离,角度等F5 -- Mask 隐藏F6 -- Element Edit 单元编辑(创建,合并,分割单元等)F7 -- Align Node 节点共线排列F8 -- Create Node 创建节点F9 -- Line Edit 线编辑(非边界编辑)F10 -- Check Elem 单元质量检查F11 -- collectorsF12 -- Automesh 自动网格划分Shift+F1-F12 Ctrl+F1-F6Key Function key only plus SHIFT plus CTRL keyF1 hidden line color print slideF2 delete temp nodes slide fileF3 replace edges print eps (Note: Works only on UNIX) F4 distance translate eps fileF5 mask find print b/w epsF6 element edit split JPEG fileF7 align node projectF8 create node node editF9 line edit surf editF10 check element normalsF11 collectors organizeF12 automesh smootha arc 弧形b back返回以前视图c centerd display 进入显示面板f fill 以适当比例全图形窗口显示模型g global 进入Global参数设置面板h 打开在线帮助文件m 显示/关闭下面的工具面板o option 显示选项参数设置面板p plot 刷新显示r rotates slide 移动缩放,鼠标上下拖动时缩放t true view 设定视角显示v 进入user view dialogw windowsz zoom,按住鼠标在模型上画一个圈,松开鼠标后即显示圈内部分Hypermesh中常用英文关键词dangle 摇摆Warpage 翘曲, 扭曲, 热变形Aspect_Ratio 纵横比屏幕高宽比Split v.劈开, (使)裂开, 分裂, 分离 n.裂开, 裂口, 裂痕Tria Triaangle trigon n.三角形,ellipsoid n.椭圆体project 投影计划实施normals 法线align node 对齐节点surfaces and faces 曲面和表面duplicate adj.复制的 n.复制品 vt.复写, 复制reject 否定拒绝exponential 指数tol tolerance 公差mandatory 命令的, 强制的, 托管的retrieve v.重新得到 n.找回centroid n. 质心trim adj. 整齐的, 整洁的 vt. 整理, 修整, 装饰morph 变形Solid 体Connectors 焊点Loads (constraints, forces, pressures,etc.) 约束,集中力,面力等Equations (mathematical link between nodes) 约束方程Multibodies 多刚体equivalency n. 相等, 等价skew adj. 歪斜的abort 异常中断, 中途失败biasing 偏置, 偏压algorithm [数]运算法则curvature 弯曲, 曲率chordal 弦的似弦的Interior Angle 内角Aspect Ratio 长宽比Skew Angle 扭曲程度Warp Angle 翘曲度Chordal Deviation 弦差Jacobian 雅可比plate 面solid 体hexa hexahedral 六面体的TetraMesh 四面体网格划分detach 分开分离criteria 标准Drag 拉伸Spin 旋转Line Drag 沿线拉伸Element Offset 单元偏移Linear Solid 线性近似Solid Map 映射beamsectcols 保存梁截面信息的collectorbeamsects 梁截面non-rigid adj.非刚性的Moments of inertia 转动惯量arrow tip 箭头invoke 调用intersect vt. 横断 vi. (直线)相交, 交叉conics n.圆锥曲线论, 锥线论NURBS (non-uniform rational B-spline) Used to represent lines that are not straight or elliptical.piecewise adv.[数]分段地planar 平面的tangent 切线permute 序列改变 The permute panel allows you to permute node, element, point, line, surface, and component data. Use this function to exchange the axes of a coordinate system.reparam (reparameterize) 确定参数torus Used to represent a toroidal surface. 超环面cone 锥形物圆锥体nested 嵌套的pertaining to 属于关于附属menu buttongreen Functions or executable itemsyellow Collectorsred Return or abort (异常中断)cursor n. 指针rectangular adj. 矩形的, 成直角的tetrahedral adj. 有四面的, 四面体的specular adj. 镜子的weld vt.焊接n.焊接, 焊缝thetaadjacent 邻近的, 接近的utility 效用有用pinhole n.针孔, 小孔filletbead 筋冲压beam 梁edge fillet 边缘倒圆过渡圆滑部分planar adj. 平面的, 平坦的contour 云图如果一个面和超过一个面以上共同使用一条边界,就认为是连续的(“HyperMesh 里称为:equivalenced”)toggle 一次合并一条边界(手工)–鼠标左键点击自由边可以变成共享边,点击共享边可以变成压缩边–鼠标右键点击共享边可以变成自由边,点击压缩边可以变成共享边equivalence 一次可以合并很多边界(自动)–按给定的条件查找曲面上的一对自由边界,并合成成共享边;toggle 一次合并一条边界(手工)–鼠标左键点击自由边可以变成共享边,点击共享边可以变成压缩边–鼠标右键点击共享边可以变成自由边,点击压缩边可以变成共享边Replace 一条边替代另一条(也是合并成一条)–合并两条带有一定间隙的自由边成一条共享边;–可以控制哪条边界保留,哪条边界移动;defeature: 面板duplicates: 重复面–查找并删除重复面quick edit : 面板filler surf:填补曲面–在自由曲面边界上,选择一条线来自动修补丢失的面。

Release 10.0 Documentation for ANSYSBEAM1883-D Linear Finite Strain Beam三维线性有限应变梁单元BEAM188 Element DescriptionBEAM188单元描述BEAM188 is suitable for analyzing slender to moderately stubby/thick beam structures. This element is based on Timoshenko beam theory. Shear deformation effects are included.Beam188 单元适合于分析从细长到中等粗短的梁结构,该单元基于铁木辛哥梁结构理论,并考虑了剪切变形的影响。
BEAM188 is a linear (2-node) or a quadratic beam element in 3-D. BEAM188 has six or seven degrees of freedom at each node, with the number of degrees of freedom depending on the value of KEYOPT(1). When KEYOPT(1) = 0 (the default), six degrees of freedom occur at each node. These include translations in the x, y, and z directions and rotations about the x, y, and z directions. When KEYOPT(1) = 1, a seventh degree of freedom (warping magnitude) is also considered. This element is well-suited for linear, large rotation, and/or large strain nonlinear applications.Beam188 是三维线性(2 节点)或者二次梁单元。

hypermesh 面板HyperMesh的主要面板名序中文名geometry panels几何面1elements panels单元面2loads and boundary conditions panels载荷和边界条件面3organization panels管理面4results panels结果面5editing panels编辑面6输出面7input/output panels输客户化面8customization panels9 viewing panels 视图面板10 xy pioting panels xy绘图面板11 miscellaneous panels 混合面板12 optimization panels 优化面板13 safety panels 安全性分析面板14 solver panels 求解器面板1、几何面板中文名功能解释选项称映射节点到通过两个节点的虚线上Align node 对齐节点坐标轴,在已有的几何图形上、线上或两、z、create 创建节通过制定xy 个节点之间创建节点nodes 点找出两个节点之间的距离或角度distance 距离节点编node edit 在一个平面上关联、移动或放置节点辑重新映射节点到一条线上remap 重映射 replace 替代允许用户手动消除重复节点增加或去掉临时节点临时节temp nodes点子面板的选项及功能曲面)Surfaces( 单元面板、1Gaps 间隙创建、查看或更新间隙单元Hyperbeam Hyper 梁在进入Hyper梁模式之前定义梁截面特性Linear 1d 线性一维创建一维单元绘图单元Line mesh 线网格在节点之间或沿着一条线创建一维单元Masses 集中质量创建或更新质量单元Rbe3 RBE3单元创建或更新RBE3单元Rigids 刚性单元创建或更新刚性或刚性连接单元Rods 杆单元创建或更新杆单元Spotweld 点焊单元创建或更新点焊单元spings 弹簧单元创建或更新弹簧单元One-dimensional(一维单元)子面板的选项及功能载荷和边界条件面板管理面板、3管理面板4、结果面板选项中文名称功能解释apply result 施加结果施加结果分析数据到模型中的实体上contour 云图创建结果的云图deformed 变形在位移结果基础上创建变形图replay 重新显示重新显示以前保存的动画序列transient 瞬态结果从瞬态分析结果中创建动画vector plot 绘向量图从向量结果中绘出向量图结果面板/输出面板输入视图面板Xy绘图面板11、混合面板选项中文名称功能解释Command 命令执行一个hypermesh命令文件Count 统计统计数据库中的实体Fd blocks 有限差分块提供进入有限差分菜单面板的入口Mass calc 质量计算获得选择单元或曲面的质量、面积和体积Summary 总结创建单元、载荷和特性的总结Systems 坐标系统创建局部坐标系统Tags 命名为实体命名Titles 标题创建和编辑屏幕标题向量实体hypermesh创建一个向量vectors优化面板安全性分析面板求解器面板Hypermesh中常用快捷键Hypermesh中常用快捷键F1 -- Hidden Line 隐藏线F2 -- Delete 删除(删除任何对象都用此命令)F3 -- Replace 合并两个节点F4 -- Distance 测量距离,角度等F5 -- Mask 隐藏F6 -- Element Edit 单元编辑(创建,合并,分割单元等)F7 -- Align Node 节点共线排列F8 -- Create Node 创建节点F9 -- Line Edit 线编辑(非边界编辑)F10 -- Check Elem 单元质量检查F11 -- collectorsF12 -- Automesh 自动网格划分Shift+F1-F12 Ctrl+F1-F6Key Function key only plus SHIFT plus CTRL keyF1 hidden line color print slideF2 delete temp nodes slide fileF3 replace edges print eps (Note: Works only on UNIX)F4 distance translate eps fileF5 mask find print b/w epsF6 element edit split JPEG fileF7 align node projectF8 create node node editF9 line edit surf editF10 check element normalsF11 collectors organizeF12 automesh smootha arc 弧形b back返回以前视图c centerd display 进入显示面板f fill 以适当比例全图形窗口显示模型g global 进入Global参数设置面板h 打开在线帮助文件m 显示/关闭下面的工具面板显示选项参数设置面板o optionp plot 刷新显示r rotates slide 移动缩放,鼠标上下拖动时缩放t true view 设定视角显示v 进入user view dialogw windowsz zoom,按住鼠标在模型上画一个圈,松开鼠标后即显示圈内部分Hypermesh中常用英文关键词dangle 摇摆Warpage 翘曲, 扭曲, 热变形Aspect_Ratio 纵横比屏幕高宽比Split v.劈开, (使)裂开, 分裂, 分离n.裂开, 裂口, 裂痕Tria Triaangle trigon n.三角形,ellipsoid n.椭圆体project 投影计划实施normals 法线align node 对齐节点surfaces and faces 曲面和表面duplicate adj.复制的n.复制品vt.复写, 复制reject 否定拒绝exponential 指数tol tolerance 公差mandatory 命令的, 强制的, 托管的retrieve v.重新得到n.找回centroid n. 质心trim adj. 整齐的, 整洁的vt. 整理, 修整, 装饰morph 变形Solid 体Connectors 焊点Loads (constraints, forces, pressures,etc.) 约束,集中力,面力等Equations (mathematical link between nodes) 约束方程Multibodies 多刚体equivalency n. 相等, 等价skew adj. 歪斜的abort 异常中断, 中途失败biasing 偏置, 偏压algorithm [数]运算法则curvature 弯曲, 曲率chordal 弦的似弦的Interior Angle 内角Aspect Ratio 长宽比Skew Angle 扭曲程度翘曲度Warp AngleChordal Deviation 弦差Jacobian 雅可比plate 面solid 体hexa hexahedral 六面体的TetraMesh 四面体网格划分detach 分开分离criteria 标准Drag 拉伸Spin 旋转Line Drag 沿线拉伸Element Offset 单元偏移Linear Solid 线性近似Solid Map 映射beamsectcols 保存梁截面信息的collectorbeamsects 梁截面non-rigid adj.非刚性的Moments of inertia 转动惯量arrow tip 箭头invoke 调用intersect vt. 横断vi. (直线)相交, 交叉conics n.圆锥曲线论, 锥线论NURBS (non-uniform rational B-spline) Used to represent lines that are not straight or elliptical.piecewise adv.[数]分段地planar 平面的tangent 切线permute 序列改变The permute panel allows you to permute node, element, point, line, surface, and component data. Use this function to exchange the axes of a coordinate system.reparam (reparameterize) 确定参数torus Used to represent a toroidal surface. 超环面cone 锥形物圆锥体nested 嵌套的pertaining to 属于关于附属menu buttongreen Functions or executable itemsyellow Collectorsred Return or abort (异常中断)cursor n. 指针rectangular adj. 矩形的, 成直角的tetrahedral adj. 有四面的, 四面体的specular adj. 镜子的焊缝, 焊接n. 焊接weld vt.thetaadjacent 邻近的, 接近的utility 效用有用pinhole n.针孔, 小孔filletbead 筋冲压beam 梁edge fillet 边缘倒圆过渡圆滑部分planar adj. 平面的, 平坦的contour 云图如果一个面和超过一个面以上共同使用一条边界,就认为是连续的(“HyperMesh 里称为:equivalenced”)toggle 一次合并一条边界(手工)–鼠标左键点击自由边可以变成共享边,点击共享边可以变成压缩边–鼠标右键点击共享边可以变成自由边,点击压缩边可以变成共享边equivalence 一次可以合并很多边界(自动)–按给定的条件查找曲面上的一对自由边界,并合成成共享边;toggle 一次合并一条边界(手工)–鼠标左键点击自由边可以变成共享边,点击共享边可以变成压缩边–鼠标右键点击共享边可以变成自由边,点击压缩边可以变成共享边Replace 一条边替代另一条(也是合并成一条)–合并两条带有一定间隙的自由边成一条共享边;–可以控制哪条边界保留,哪条边界移动;defeature: 面板duplicates: 重复面–查找并删除重复面quick edit : 面板filler surf:填补曲面–在自由曲面边界上,选择一条线来自动修补丢失的面。

土木工程专业英语词汇(整理版)第一部分必须掌握,第二部分尽量掌握第一部分:1 Finite Element Method 有限单元法2 专业英语 Specialty English3 水利工程 Hydraulic Engineering4 土木工程 Civil Engineering5 地下工程 Underground Engineering6 岩土工程 Geotechnical Engineering7 道路工程 Road (Highway) Engineering8 桥梁工程Bridge Engineering9 隧道工程 Tunnel Engineering10 工程力学 Engineering Mechanics11 交通工程 Traffic Engineering12 港口工程 Port Engineering13 安全性 safety17木结构 timber structure18 砌体结构 masonry structure19 混凝土结构concrete structure20 钢结构 steelstructure21 钢 - 混凝土复合结构 steel and concrete composite structure22 素混凝土 plain concrete23 钢筋混凝土reinforced concrete24 钢筋 rebar25 预应力混凝土 pre-stressed concrete26 静定结构statically determinate structure27 超静定结构 statically indeterminate structure28 桁架结构 truss structure29 空间网架结构 spatial grid structure30 近海工程 offshore engineering31 静力学 statics32运动学kinematics33 动力学dynamics34 简支梁 simply supported beam35 固定支座 fixed bearing36弹性力学 elasticity37 塑性力学 plasticity38 弹塑性力学 elaso-plasticity39 断裂力学 fracture Mechanics40 土力学 soil mechanics41 水力学 hydraulics42 流体力学 fluid mechanics43 固体力学solid mechanics44 集中力 concentrated force45 压力 pressure46 静水压力 hydrostatic pressure47 均布压力 uniform pressure48 体力 body force49 重力 gravity50 线荷载 line load51 弯矩 bending moment52 扭矩 torque53 应力 stress54 应变 stain55 正应力 normal stress56 剪应力 shearing stress57 主应力 principal stress58 变形 deformation59 内力 internal force60 偏移量挠度 deflection61 沉降settlement62 屈曲失稳 buckle63 轴力 axial force64 允许应力 allowable stress65 疲劳分析 fatigue analysis66 梁 beam67 壳 shell68 板 plate69 桥 bridge70 桩 pile71 主动土压力 active earth pressure72 被动土压力 passive earth pressure73 承载力 load-bearing capacity74 水位 water Height75 位移 displacement76 结构力学 structural mechanics77 材料力学 material mechanics78 经纬仪 altometer79 水准仪level80 学科 discipline81 子学科 sub-discipline82 期刊 journal periodical83 文献literature84 国际标准刊号ISSN International Standard Serial Number85 国际标准书号ISBN International Standard Book Number86 卷 volume87 期 number88 专著 monograph89 会议论文集 Proceeding90 学位论文 thesis dissertation91 专利 patent92 档案档案室 archive93 国际学术会议 conference94 导师 advisor95 学位论文答辩 defense of thesis96 博士研究生 doctorate student97 研究生 postgraduate98 工程索引EI Engineering Index99 科学引文索引SCI Science Citation Index100 科学技术会议论文集索引ISTP Index to Science and Tec hnology Proceedings 101 题目 title102 摘要 abstract103 全文 full-text104 参考文献 reference105 联络单位、所属单位affiliation106 主题词 Subject107 关键字 keyword108 美国土木工程师协会ASCE American Society of Civil Engineers109 联邦公路总署FHWA Federal Highway Administration110 国际标准组织ISO International Standard Organization111 解析方法 analytical method112 数值方法 numerical method113 计算 computation114 说明书 instruction115 规范 Specification Code第二部分:岩土工程专业词汇1.geotechnical engineering 岩土工程2.foundation engineering 基础工程3.soil earth 土4.soil mechanics 土力学5.cyclic loading 周期荷载6.unloading 卸载7.reloading 再加载8.viscoelastic foundation 粘弹性地基9.viscous damping 粘滞阻尼10.shear modulus 剪切模量11.soil dynamics 土动力学12.stress path 应力路径13.numerical geotechanics 数值岩土力学二.土的分类1.residual soil 残积土 groundwater level 地下水位2.groundwater 地下水 groundwater table 地下水位3.clay minerals 粘土矿物4.secondary minerals 次生矿物ndslides 滑坡6.bore hole columnar section 钻孔柱状图7.engineering geologic investigation 工程地质勘察8.boulder 漂石9.cobble 卵石10.gravel 砂石11.gravelly sand 砾砂12.coarse sand 粗砂13.medium sand 中砂14.fine sand 细砂15.silty sand 粉土16.clayey soil 粘性土17.clay 粘土18.silty clay 粉质粘土19.silt 粉土20.sandy silt 砂质粉土21.clayey silt 粘质粉土22.saturated soil 饱和土23.unsaturated soil 非饱和土24.fill (soil) 填土25.overconsolidated soil 超固结土26.normally consolidated soil 正常固结土27.underconsolidated soil 欠固结土28.zonal soil 区域性土29.soft clay 软粘土30.expansive (swelling) soil 膨胀土31.peat 泥炭32.loess 黄土33.frozen soil 冻土24.degree of saturation 饱和度25.dry unit weight 干重度26.moist unit weight 湿重度45.ISSMGE=International Society for Soil Mechanics and Geotechnical Engineering 国际土力学与岩土工程学会四.渗透性和渗流1.Darcy’s law 达西定律2.piping 管涌3.flowing soil 流土4.sand boiling 砂沸5.flow net 流网6.seepage 渗透(流)7.leakage 渗流8.seepage pressure 渗透压力9.permeability 渗透性10.seepage force 渗透力11.hydraulic gradient 水力梯度12.coefficient of permeability 渗透系数五.地基应力和变形1.soft soil 软土2.(negative) skin friction of driven pile 打入桩(负)摩阻力3.effective stress 有效应力4.total stress 总应力5.field vane shear strength 十字板抗剪强度6.low activity 低活性7.sensitivity 灵敏度8.triaxial test 三轴试验9.foundation design 基础设计10.recompaction 再压缩11.bearing capacity 承载力12.soil mass 土体13.contact stress (pressure)接触应力(压力)14.concentrated load 集中荷载15.a semi-infinite elastic solid 半无限弹性体16.homogeneous 均质17.isotropic 各向同性18.strip footing 条基19.square spread footing 方形独立基础20.underlying soil (stratum strata)下卧层(土)21.dead load =sustained load 恒载持续荷载22.live load 活载23.short –term transient load 短期瞬时荷载24.long-term transient load 长期荷载25.reduced load 折算荷载26.settlement 沉降27.deformation 变形28.casing 套管29.dike=dyke 堤(防)30.clay fraction 粘粒粒组31.physical properties 物理性质32.subgrade 路基33.well-graded soil 级配良好土34.poorly-graded soil 级配不良土35.normal stresses 正应力36.shear stresses 剪应力37.principal plane 主平面38.major (intermediate minor) principal stress 最大(中、最小)主应力39.Mohr-Coulomb failure condition 摩尔-库仑破坏条件40.FEM=finite element method 有限元法41.limit equilibrium method 极限平衡法42.pore water pressure 孔隙水压力43.preconsolidation pressure 先期固结压力44.modulus of compressibility 压缩模量45.coefficent of compressibility 压缩系数pression index 压缩指数47.swelling index 回弹指数48.geostatic stress 自重应力49.additional stress 附加应力50.total stress 总应力51.final settlement 最终沉降52.slip line 滑动线六.基坑开挖与降水1 excavation 开挖(挖方)2 dewatering (基坑)降水3 failure of foundation 基坑失稳4 bracing of foundation pit 基坑围护5 bottom heave=basal heave (基坑)底隆起6 retaining wall 挡土墙7 pore-pressure distribution 孔压分布8 dewatering method 降低地下水位法9 well point system 井点系统(轻型)10 deep well point 深井点11 vacuum well point 真空井点12 braced cuts 支撑围护13 braced excavation 支撑开挖14 braced sheeting 支撑挡板七.深基础--deep foundation1.pile foundation 桩基础1)cast –in-place 灌注桩diving casting cast-in-place pile 沉管灌注桩bored pile 钻孔桩special-shaped cast-in-place pile 机控异型灌注桩piles set into rock 嵌岩灌注桩rammed bulb pile 夯扩桩2)belled pier foundation 钻孔墩基础drilled-pier foundation 钻孔扩底墩under-reamed bored pier3)precast concrete pile 预制混凝土桩4)steel pile 钢桩steel pipe pile 钢管桩steel sheet pile 钢板桩5)prestressed concrete pile 预应力混凝土桩prestressed concrete pipe pile 预应力混凝土管桩2.caisson foundation 沉井(箱)3.diaphragm wall 地下连续墙截水墙4.friction pile 摩擦桩5.end-bearing pile 端承桩6.shaft 竖井;桩身7.wave equation analysis 波动方程分析8.pile caps 承台(桩帽)9.bearing capacity of single pile 单桩承载力teral pile load test 单桩横向载荷试验11.ultimate lateral resistance of single pile 单桩横向极限承载力12.static load test of pile 单桩竖向静荷载试验13.vertical allowable load capacity 单桩竖向容许承载力14.low pile cap 低桩承台15.high-rise pile cap 高桩承台16.vertical ultimate uplift resistance of single pile 单桩抗拔极限承载力17.silent piling 静力压桩18.uplift pile 抗拔桩19.anti-slide pile 抗滑桩20.pile groups 群桩21.efficiency factor of pile groups 群桩效率系数(η)22.efficiency of pile groups 群桩效应23.dynamic pile testing 桩基动测技术24.final set 最后贯入度25.dynamic load test of pile 桩动荷载试验26.pile integrity test 桩的完整性试验27.pile head=butt 桩头28.pile tip=pile point=pile toe 桩端(头)29.pile spacing 桩距30.pile plan 桩位布置图31.arrangement of piles =pile layout 桩的布置32.group action 群桩作用33.end bearing=tip resistance 桩端阻34.skin(side) friction=shaft resistance 桩侧阻35.pile cushion 桩垫36.pile driving(by vibration) (振动)打桩37.pile pulling test 拔桩试验38.pile shoe 桩靴39.pile noise 打桩噪音40.pile rig 打桩机九.固结 consolidation1.Terzzaghi’s consolidation theory 太沙基固结理论2.Barraon’s consolidation theory 巴隆固结理论3.Biot’s consolidation theory 比奥固结理论4.over consolidation ration (OCR)超固结比5.overconsolidation soil 超固结土6.excess pore water pressure 超孔压力7.multi-dimensional consolidation 多维固结8.one-dimensional consolidation 一维固结9.primary consolidation 主固结10.secondary consolidation 次固结11.degree of consolidation 固结度12.consolidation test 固结试验13.consolidation curve 固结曲线14.time factor Tv 时间因子15.coefficient of consolidation 固结系数16.preconsolidation pressure 前期固结压力17.principle of effective stress 有效应力原理18.consolidation under K0 condition K0 固结十.抗剪强度 shear strength1.undrained shear strength 不排水抗剪强度2.residual strength 残余强度3.long-term strength 长期强度4.peak strength 峰值强度5.shear strain rate 剪切应变速率6.dilatation 剪胀7.effective stress approach of shear strength 剪胀抗剪强度有效应力法 8.total stress approach of shear strength 抗剪强度总应力法9.Mohr-Coulomb theory 莫尔-库仑理论10.angle of internal friction 内摩擦角11.cohesion 粘聚力12.failure criterion 破坏准则13.vane strength 十字板抗剪强度14.unconfined compression 无侧限抗压强度15.effective stress failure envelop 有效应力破坏包线16.effective stress strength parameter 有效应力强度参数十一.本构模型--constitutive model1.elastic model 弹性模型2.nonlinear elastic model 非线性弹性模型3.elastoplastic model 弹塑性模型4.viscoelastic model 粘弹性模型5.boundary surface model 边界面模型6.Du ncan-Chang model 邓肯-张模型7.rigid plastic model 刚塑性模型8.cap model 盖帽模型9.work softening 加工软化10.work hardening 加工硬化11.Cambridge model 剑桥模型12.ideal elastoplastic model 理想弹塑性模型13.Mohr-Coulomb yield criterion 莫尔-库仑屈服准则14.yield surface 屈服面15.elastic half-space foundation model 弹性半空间地基模型16.elastic modulus 弹性模量17.Winkler foundation model 文克尔地基模型十二.地基承载力--bearing capacity of foundation soil1.punching shear failure 冲剪破坏2.general shear failure 整体剪切破化3.local shear failure 局部剪切破坏4.state of limit equilibrium 极限平衡状态5.critical edge pressure 临塑荷载6.stability of foundation soil 地基稳定性7.ultimate bearing capacity of foundation soil 地基极限承载力8.allowable bearing capacity of foundation soil 地基容许承载力十三.土压力--earth pressure1.active earth pressure 主动土压力2.passive earth pressure 被动土压力3.earth pressure at rest 静止土压力4.Coulomb’s earth pressure theory 库仑土压力理论5.Rankine’s earth p ressure theory 朗金土压力理论十四.土坡稳定分析--slope stability analysis1.angle of repose 休止角2.Bishop method 毕肖普法3.safety factor of slope 边坡稳定安全系数4.Fellenius method of slices 费纽伦斯条分法5.Swedish circle method 瑞典圆弧滑动法6.slices method 条分法十五.挡土墙--retaining wall1.stability of retaining wall 挡土墙稳定性2.foundation wall 基础墙3.counter retaining wall 扶壁式挡土墙4.cantilever retaining wall 悬臂式挡土墙5.cantilever sheet pile wall 悬臂式板桩墙6.gravity retaining wall 重力式挡土墙7.anchored plate retaining wall 锚定板挡土墙8.anchored sheet pile wall 锚定板板桩墙十六.板桩结构物--sheet pile structure1.steel sheet pile 钢板桩2.reinforced concrete sheet pile 钢筋混凝土板桩3.steel piles 钢桩4.wooden sheet pile 木板桩5.timber piles 木桩十七.浅基础--shallow foundation1.box foundation 箱型基础2.mat(raft) foundation 片筏基础3.strip foundation 条形基础4.spread footing 扩展基础pensated foundation 补偿性基础6.bearing stratum 持力层7.rigid foundation 刚性基础8.flexible foundation 柔性基础9.emxxxxbedded depth of foundation 基础埋置深度 foundation pressure 基底附加应力11.structure-foundation-soil interaction analysis 上部结构-基础-地基共同作用分析十八.土的动力性质--dynamic properties of soils1.dynamic strength of soils 动强度2.wave velocity method 波速法3.material damping 材料阻尼4.geometric damping 几何阻尼5.damping ratio 阻尼比6.initial liquefaction 初始液化7.natural period of soil site 地基固有周期8.dynamic shear modulus of soils 动剪切模量9.dynamic ma二十.地基基础抗震1.earthquake engineering 地震工程2.soil dynamics 土动力学3.duration of earthquake 地震持续时间4.earthquake response spectrum 地震反应谱5.earthquake intensity 地震烈度6.earthquake magnitude 震级7.seismic predominant period 地震卓越周期8.maximum acceleration of earthquake 地震最大加速度二十一.室内土工实验1.high pressure consolidation test 高压固结试验2.consolidation under K0 condition K0 固结试验3.falling head permeability 变水头试验4.constant head permeability 常水头渗透试验5.unconsolidated-undrained triaxial test 不固结不排水试验(UU)6.consolidated undrained triaxial test 固结不排水试验(CU)7.consolidated drained triaxial test 固结排水试验(CD)paction test 击实试验9.consolidated quick direct shear test 固结快剪试验10.quick direct shear test 快剪试验11.consolidated drained direct shear test 慢剪试验12.sieve analysis 筛分析13.geotechnical model test 土工模型试验14.centrifugal model test 离心模型试验15.direct shear apparatus 直剪仪16.direct shear test 直剪试验17.direct simple shear test 直接单剪试验18.dynamic triaxial test 三轴试验19.dynamic simple shear 动单剪20.free(resonance)vibration column test 自(共)振柱试验二十二.原位测试1.standard penetration test (SPT)标准贯入试验2.surface wave test (SWT) 表面波试验3.dynamic penetration test(DPT) 动力触探试验4.static cone penetration (SPT) 静力触探试验5.plate loading test 静力荷载试验teral load test of pile 单桩横向载荷试验7.static load test of pile 单桩竖向荷载试验8.cross-hole test 跨孔试验9.screw plate test 螺旋板载荷试验10.pressuremeter test 旁压试验11.light sounding 轻便触探试验12.deep settlement measurement 深层沉降观测13.vane shear test 十字板剪切试验14.field permeability test 现场渗透试验15.in-situ pore water pressure measurement 原位孔隙水压量测16.in-situ soil test 原位试验第一部分必须掌握,第二部分尽量掌握第一部分:1 Finite Element Method 有限单元法2 专业英语 Specialty English3 水利工程 Hydraulic Engineering4 土木工程 Civil Engineering5 地下工程 Underground Engineering6 岩土工程 Geotechnical Engineering7 道路工程 Road (Highway) Engineering8 桥梁工程Bridge Engineering9 隧道工程 Tunnel Engineering10 工程力学 Engineering Mechanics11 交通工程 Traffic Engineering12 港口工程 Port Engineering13 安全性 safety17木结构 timber structure18 砌体结构 masonry structure19 混凝土结构concrete structure20 钢结构 steelstructure21 钢 - 混凝土复合结构 steel and concrete composite structure22 素混凝土 plain concrete23 钢筋混凝土reinforced concrete24 钢筋 rebar25 预应力混凝土 pre-stressed concrete26 静定结构statically determinate structure27 超静定结构 statically indeterminate structure28 桁架结构 truss structure29 空间网架结构 spatial grid structure30 近海工程 offshore engineering31 静力学 statics32运动学kinematics33 动力学dynamics34 简支梁 simply supported beam35 固定支座 fixed bearing36弹性力学 elasticity37 塑性力学 plasticity38 弹塑性力学 elaso-plasticity39 断裂力学 fracture Mechanics40 土力学 soil mechanics41 水力学 hydraulics42 流体力学 fluid mechanics43 固体力学solid mechanics44 集中力 concentrated force45 压力 pressure46 静水压力 hydrostatic pressure47 均布压力 uniform pressure48 体力 body force49 重力 gravity50 线荷载 line load51 弯矩 bending moment52 扭矩 torque53 应力 stress54 应变 stain55 正应力 normal stress56 剪应力 shearing stress57 主应力 principal stress58 变形 deformation59 内力 internal force60 偏移量挠度 deflection61 沉降settlement62 屈曲失稳 buckle63 轴力 axial force64 允许应力 allowable stress65 疲劳分析 fatigue analysis66 梁 beam67 壳 shell68 板 plate69 桥 bridge70 桩 pile71 主动土压力 active earth pressure72 被动土压力 passive earth pressure73 承载力 load-bearing capacity74 水位 water Height75 位移 displacement76 结构力学 structural mechanics77 材料力学 material mechanics78 经纬仪 altometer79 水准仪level80 学科 discipline81 子学科 sub-discipline82 期刊 journal periodical83 文献literature84 国际标准刊号ISSN International Standard Serial Number85 国际标准书号ISBN International Standard Book Number86 卷 volume87 期 number88 专著 monograph89 会议论文集 Proceeding90 学位论文 thesis dissertation91 专利 patent92 档案档案室 archive93 国际学术会议 conference94 导师 advisor95 学位论文答辩 defense of thesis96 博士研究生 doctorate student97 研究生 postgraduate98 工程索引EI Engineering Index99 科学引文索引SCI Science Citation Index100 科学技术会议论文集索引ISTP Index to Science and Tec hnology Proceedings 101 题目 title102 摘要 abstract103 全文 full-text104 参考文献 reference105 联络单位、所属单位affiliation106 主题词 Subject107 关键字 keyword108 美国土木工程师协会ASCE American Society of Civil Engineers109 联邦公路总署FHWA Federal Highway Administration110 国际标准组织ISO International Standard Organization111 解析方法 analytical method112 数值方法 numerical method113 计算 computation114 说明书 instruction115 规范 Specification Code第二部分:岩土工程专业词汇1.geotechnical engineering 岩土工程2.foundation engineering 基础工程3.soil earth 土4.soil mechanics 土力学5.cyclic loading 周期荷载6.unloading 卸载7.reloading 再加载8.viscoelastic foundation 粘弹性地基9.viscous damping 粘滞阻尼10.shear modulus 剪切模量11.soil dynamics 土动力学12.stress path 应力路径13.numerical geotechanics 数值岩土力学二.土的分类1.residual soil 残积土 groundwater level 地下水位2.groundwater 地下水 groundwater table 地下水位3.clay minerals 粘土矿物4.secondary minerals 次生矿物ndslides 滑坡6.bore hole columnar section 钻孔柱状图7.engineering geologic investigation 工程地质勘察8.boulder 漂石9.cobble 卵石10.gravel 砂石11.gravelly sand 砾砂12.coarse sand 粗砂13.medium sand 中砂14.fine sand 细砂15.silty sand 粉土16.clayey soil 粘性土17.clay 粘土18.silty clay 粉质粘土19.silt 粉土20.sandy silt 砂质粉土21.clayey silt 粘质粉土22.saturated soil 饱和土23.unsaturated soil 非饱和土24.fill (soil) 填土25.overconsolidated soil 超固结土26.normally consolidated soil 正常固结土27.underconsolidated soil 欠固结土28.zonal soil 区域性土29.soft clay 软粘土30.expansive (swelling) soil 膨胀土31.peat 泥炭32.loess 黄土33.frozen soil 冻土24.degree of saturation 饱和度25.dry unit weight 干重度26.moist unit weight 湿重度45.ISSMGE=International Society for Soil Mechanics and Geotechnical Engineering 国际土力学与岩土工程学会四.渗透性和渗流1.Darcy’s law 达西定律2.piping 管涌3.flowing soil 流土4.sand boiling 砂沸5.flow net 流网6.seepage 渗透(流)7.leakage 渗流8.seepage pressure 渗透压力9.permeability 渗透性10.seepage force 渗透力11.hydraulic gradient 水力梯度12.coefficient of permeability 渗透系数五.地基应力和变形1.soft soil 软土2.(negative) skin friction of driven pile 打入桩(负)摩阻力3.effective stress 有效应力4.total stress 总应力5.field vane shear strength 十字板抗剪强度6.low activity 低活性7.sensitivity 灵敏度8.triaxial test 三轴试验9.foundation design 基础设计10.recompaction 再压缩11.bearing capacity 承载力12.soil mass 土体13.contact stress (pressure)接触应力(压力)14.concentrated load 集中荷载15.a semi-infinite elastic solid 半无限弹性体16.homogeneous 均质17.isotropic 各向同性18.strip footing 条基19.square spread footing 方形独立基础20.underlying soil (stratum strata)下卧层(土)21.dead load =sustained load 恒载持续荷载22.live load 活载23.short –term transient load 短期瞬时荷载24.long-term transient load 长期荷载25.reduced load 折算荷载26.settlement 沉降27.deformation 变形28.casing 套管29.dike=dyke 堤(防)30.clay fraction 粘粒粒组31.physical properties 物理性质32.subgrade 路基33.well-graded soil 级配良好土34.poorly-graded soil 级配不良土35.normal stresses 正应力36.shear stresses 剪应力37.principal plane 主平面38.major (intermediate minor) principal stress 最大(中、最小)主应力39.Mohr-Coulomb failure condition 摩尔-库仑破坏条件40.FEM=finite element method 有限元法41.limit equilibrium method 极限平衡法42.pore water pressure 孔隙水压力43.preconsolidation pressure 先期固结压力44.modulus of compressibility 压缩模量45.coefficent of compressibility 压缩系数pression index 压缩指数47.swelling index 回弹指数48.geostatic stress 自重应力49.additional stress 附加应力50.total stress 总应力51.final settlement 最终沉降52.slip line 滑动线六.基坑开挖与降水1 excavation 开挖(挖方)2 dewatering (基坑)降水3 failure of foundation 基坑失稳4 bracing of foundation pit 基坑围护5 bottom heave=basal heave (基坑)底隆起6 retaining wall 挡土墙7 pore-pressure distribution 孔压分布8 dewatering method 降低地下水位法9 well point system 井点系统(轻型)10 deep well point 深井点11 vacuum well point 真空井点12 braced cuts 支撑围护13 braced excavation 支撑开挖14 braced sheeting 支撑挡板七.深基础--deep foundation1.pile foundation 桩基础1)cast –in-place 灌注桩diving casting cast-in-place pile 沉管灌注桩bored pile 钻孔桩special-shaped cast-in-place pile 机控异型灌注桩piles set into rock 嵌岩灌注桩rammed bulb pile 夯扩桩2)belled pier foundation 钻孔墩基础drilled-pier foundation 钻孔扩底墩under-reamed bored pier3)precast concrete pile 预制混凝土桩4)steel pile 钢桩steel pipe pile 钢管桩steel sheet pile 钢板桩5)prestressed concrete pile 预应力混凝土桩prestressed concrete pipe pile 预应力混凝土管桩2.caisson foundation 沉井(箱)3.diaphragm wall 地下连续墙截水墙4.friction pile 摩擦桩5.end-bearing pile 端承桩6.shaft 竖井;桩身7.wave equation analysis 波动方程分析8.pile caps 承台(桩帽)9.bearing capacity of single pile 单桩承载力teral pile load test 单桩横向载荷试验11.ultimate lateral resistance of single pile 单桩横向极限承载力12.static load test of pile 单桩竖向静荷载试验13.vertical allowable load capacity 单桩竖向容许承载力14.low pile cap 低桩承台15.high-rise pile cap 高桩承台16.vertical ultimate uplift resistance of single pile 单桩抗拔极限承载力17.silent piling 静力压桩18.uplift pile 抗拔桩19.anti-slide pile 抗滑桩20.pile groups 群桩21.efficiency factor of pile groups 群桩效率系数(η)22.efficiency of pile groups 群桩效应23.dynamic pile testing 桩基动测技术24.final set 最后贯入度25.dynamic load test of pile 桩动荷载试验26.pile integrity test 桩的完整性试验27.pile head=butt 桩头28.pile tip=pile point=pile toe 桩端(头)29.pile spacing 桩距30.pile plan 桩位布置图31.arrangement of piles =pile layout 桩的布置32.group action 群桩作用33.end bearing=tip resistance 桩端阻34.skin(side) friction=shaft resistance 桩侧阻35.pile cushion 桩垫36.pile driving(by vibration) (振动)打桩37.pile pulling test 拔桩试验38.pile shoe 桩靴39.pile noise 打桩噪音40.pile rig 打桩机九.固结 consolidation1.Terzzaghi’s consolidation theory 太沙基固结理论2.Barra on’s consolidation theory 巴隆固结理论3.Biot’s consolidation theory 比奥固结理论4.over consolidation ration (OCR)超固结比5.overconsolidation soil 超固结土6.excess pore water pressure 超孔压力7.multi-dimensional consolidation 多维固结8.one-dimensional consolidation 一维固结9.primary consolidation 主固结10.secondary consolidation 次固结11.degree of consolidation 固结度12.consolidation test 固结试验13.consolidation curve 固结曲线14.time factor Tv 时间因子15.coefficient of consolidation 固结系数16.preconsolidation pressure 前期固结压力17.principle of effective stress 有效应力原理18.consolidation under K0 condition K0 固结十.抗剪强度 shear strength1.undrained shear strength 不排水抗剪强度2.residual strength 残余强度3.long-term strength 长期强度4.peak strength 峰值强度5.shear strain rate 剪切应变速率6.dilatation 剪胀7.effective stress approach of shear strength 剪胀抗剪强度有效应力法 8.total stress approach of shear strength 抗剪强度总应力法9.Mohr-Coulomb theory 莫尔-库仑理论10.angle of internal friction 内摩擦角11.cohesion 粘聚力12.failure criterion 破坏准则13.vane strength 十字板抗剪强度14.unconfined compression 无侧限抗压强度15.effective stress failure envelop 有效应力破坏包线16.effective stress strength parameter 有效应力强度参数十一.本构模型--constitutive model1.elastic model 弹性模型2.nonlinear elastic model 非线性弹性模型3.elastoplastic model 弹塑性模型4.viscoelastic model 粘弹性模型5.boundary surface model 边界面模型6.Du ncan-Chang model 邓肯-张模型7.rigid plastic model 刚塑性模型8.cap model 盖帽模型9.work softening 加工软化10.work hardening 加工硬化11.Cambridge model 剑桥模型12.ideal elastoplastic model 理想弹塑性模型13.Mohr-Coulomb yield criterion 莫尔-库仑屈服准则14.yield surface 屈服面15.elastic half-space foundation model 弹性半空间地基模型16.elastic modulus 弹性模量17.Winkler foundation model 文克尔地基模型十二.地基承载力--bearing capacity of foundation soil1.punching shear failure 冲剪破坏2.general shear failure 整体剪切破化3.local shear failure 局部剪切破坏4.state of limit equilibrium 极限平衡状态5.critical edge pressure 临塑荷载6.stability of foundation soil 地基稳定性7.ultimate bearing capacity of foundation soil 地基极限承载力8.allowable bearing capacity of foundation soil 地基容许承载力十三.土压力--earth pressure1.active earth pressure 主动土压力2.passive earth pressure 被动土压力3.earth pressure at rest 静止土压力4.Coulomb’s earth pressure theory 库仑土压力理论5.Rankine’s earth pressure theory 朗金土压力理论十四.土坡稳定分析--slope stability analysis1.angle of repose 休止角2.Bishop method 毕肖普法3.safety factor of slope 边坡稳定安全系数4.Fellenius method of slices 费纽伦斯条分法5.Swedish circle method 瑞典圆弧滑动法6.slices method 条分法十五.挡土墙--retaining wall1.stability of retaining wall 挡土墙稳定性2.foundation wall 基础墙3.counter retaining wall 扶壁式挡土墙4.cantilever retaining wall 悬臂式挡土墙5.cantilever sheet pile wall 悬臂式板桩墙6.gravity retaining wall 重力式挡土墙7.anchored plate retaining wall 锚定板挡土墙8.anchored sheet pile wall 锚定板板桩墙十六.板桩结构物--sheet pile structure1.steel sheet pile 钢板桩2.reinforced concrete sheet pile 钢筋混凝土板桩3.steel piles 钢桩4.wooden sheet pile 木板桩5.timber piles 木桩十七.浅基础--shallow foundation1.box foundation 箱型基础2.mat(raft) foundation 片筏基础3.strip foundation 条形基础4.spread footing 扩展基础pensated foundation 补偿性基础6.bearing stratum 持力层7.rigid foundation 刚性基础8.flexible foundation 柔性基础9.emxxxxbedded depth of foundation 基础埋置深度 foundation pressure 基底附加应力11.structure-foundation-soil interaction analysis 上部结构-基础-地基共同作用分析十八.土的动力性质--dynamic properties of soils1.dynamic strength of soils 动强度2.wave velocity method 波速法3.material damping 材料阻尼4.geometric damping 几何阻尼5.damping ratio 阻尼比6.initial liquefaction 初始液化7.natural period of soil site 地基固有周期8.dynamic shear modulus of soils 动剪切模量9.dynamic ma二十.地基基础抗震1.earthquake engineering 地震工程2.soil dynamics 土动力学3.duration of earthquake 地震持续时间4.earthquake response spectrum 地震反应谱5.earthquake intensity 地震烈度6.earthquake magnitude 震级7.seismic predominant period 地震卓越周期8.maximum acceleration of earthquake 地震最大加速度二十一.室内土工实验1.high pressure consolidation test 高压固结试验2.consolidation under K0 condition K0 固结试验3.falling head permeability 变水头试验4.constant head permeability 常水头渗透试验5.unconsolidated-undrained triaxial test 不固结不排水试验(UU)6.consolidated undrained triaxial test 固结不排水试验(CU)7.consolidated drained triaxial test 固结排水试验(CD)paction test 击实试验9.consolidated quick direct shear test 固结快剪试验10.quick direct shear test 快剪试验11.consolidated drained direct shear test 慢剪试验12.sieve analysis 筛分析13.geotechnical model test 土工模型试验14.centrifugal model test 离心模型试验15.direct shear apparatus 直剪仪16.direct shear test 直剪试验17.direct simple shear test 直接单剪试验18.dynamic triaxial test 三轴试验19.dynamic simple shear 动单剪20.free(resonance)vibration column test 自(共)振柱试验二十二.原位测试1.standard penetration test (SPT)标准贯入试验2.surface wave test (SWT) 表面波试验3.dynamic penetration test(DPT) 动力触探试验4.static cone penetration (SPT) 静力触探试验5.plate loading test 静力荷载试验teral load test of pile 单桩横向载荷试验7.static load test of pile 单桩竖向荷载试验8.cross-hole test 跨孔试验9.screw plate test 螺旋板载荷试验10.pressuremeter test 旁压试验11.light sounding 轻便触探试验12.deep settlement measurement 深层沉降观测13.vane shear test 十字板剪切试验14.field permeability test 现场渗透试验15.in-situ pore water pressure measurement 原位孔隙水压量测16.in-situ soil test 原位试验。

土木工程专业英语词汇(整理版)第一部分必须掌握,第二部分尽量掌握第一部分:1 Finite Element Method 有限单元法2 专业英语 Specialty English3 水利工程 Hydraulic Engineering4 土木工程 Civil Engineering5 地下工程 Underground Engineering6 岩土工程 Geotechnical Engineering7 道路工程 Road (Highway) Engineering8 桥梁工程Bridge Engineering9 隧道工程 Tunnel Engineering10 工程力学 Engineering Mechanics11 交通工程 Traffic Engineering12 港口工程 Port Engineering13 安全性 safety17木结构 timber structure18 砌体结构 masonry structure19 混凝土结构concrete structure20 钢结构 steelstructure21 钢 - 混凝土复合结构 steel and concrete composite structure22 素混凝土 plain concrete23 钢筋混凝土reinforced concrete24 钢筋 rebar25 预应力混凝土 pre-stressed concrete26 静定结构statically determinate structure27 超静定结构 statically indeterminate structure28 桁架结构 truss structure29 空间网架结构 spatial grid structure30 近海工程 offshore engineering31 静力学 statics32运动学kinematics33 动力学dynamics34 简支梁 simply supported beam35 固定支座 fixed bearing36弹性力学 elasticity37 塑性力学 plasticity38 弹塑性力学 elaso-plasticity39 断裂力学 fracture Mechanics40 土力学 soil mechanics41 水力学 hydraulics42 流体力学 fluid mechanics精品文库43 固体力学solid mechanics44 集中力 concentrated force45 压力 pressure46 静水压力 hydrostatic pressure47 均布压力 uniform pressure48 体力 body force49 重力 gravity50 线荷载 line load51 弯矩 bending moment52 扭矩 torque53 应力 stress54 应变 stain55 正应力 normal stress56 剪应力 shearing stress57 主应力 principal stress58 变形 deformation59 内力 internal force60 偏移量挠度 deflection61 沉降settlement62 屈曲失稳 buckle63 轴力 axial force64 允许应力 allowable stress65 疲劳分析 fatigue analysis66 梁 beam67 壳 shell68 板 plate69 桥 bridge70 桩 pile71 主动土压力 active earth pressure72 被动土压力 passive earth pressure73 承载力 load-bearing capacity74 水位 water Height75 位移 displacement76 结构力学 structural mechanics77 材料力学 material mechanics78 经纬仪 altometer79 水准仪level80 学科 discipline81 子学科 sub-discipline82 期刊 journal periodical83 文献literature84 国际标准刊号ISSN International Standard Serial Number精品文库85 国际标准书号ISBN International Standard Book Number86 卷 volume87 期 number88 专著 monograph89 会议论文集 Proceeding90 学位论文 thesis dissertation91 专利 patent92 档案档案室 archive93 国际学术会议 conference94 导师 advisor95 学位论文答辩 defense of thesis96 博士研究生 doctorate student97 研究生 postgraduate98 工程索引EI Engineering Index99 科学引文索引SCI Science Citation Index100 科学技术会议论文集索引ISTP Index to Science and Tec hnology Proceedings101 题目 title102 摘要 abstract103 全文 full-text104 参考文献 reference105 联络单位、所属单位affiliation106 主题词 Subject107 关键字 keyword108 美国土木工程师协会ASCE American Society of Civil Engineers109 联邦公路总署FHWA Federal Highway Administration110 国际标准组织ISO International Standard Organization111 解析方法 analytical method112 数值方法 numerical method113 计算 computation114 说明书 instruction115 规范 Specification Code第二部分:岩土工程专业词汇1.geotechnical engineering 岩土工程2.foundation engineering 基础工程3.soil earth 土4.soil mechanics 土力学5.cyclic loading 周期荷载6.unloading 卸载7.reloading 再加载8.viscoelastic foundation 粘弹性地基9.viscous damping 粘滞阻尼10.shear modulus 剪切模量精品文库11.soil dynamics 土动力学12.stress path 应力路径13.numerical geotechanics 数值岩土力学二.土的分类1.residual soil 残积土 groundwater level 地下水位2.groundwater 地下水 groundwater table 地下水位3.clay minerals 粘土矿物4.secondary minerals 次生矿物ndslides 滑坡6.bore hole columnar section 钻孔柱状图7.engineering geologic investigation 工程地质勘察8.boulder 漂石9.cobble 卵石10.gravel 砂石11.gravelly sand 砾砂12.coarse sand 粗砂13.medium sand 中砂14.fine sand 细砂15.silty sand 粉土16.clayey soil 粘性土17.clay 粘土18.silty clay 粉质粘土19.silt 粉土20.sandy silt 砂质粉土21.clayey silt 粘质粉土22.saturated soil 饱和土23.unsaturated soil 非饱和土24.fill (soil) 填土25.overconsolidated soil 超固结土26.normally consolidated soil 正常固结土27.underconsolidated soil 欠固结土28.zonal soil 区域性土29.soft clay 软粘土30.expansive (swelling) soil 膨胀土31.peat 泥炭32.loess 黄土33.frozen soil 冻土24.degree of saturation 饱和度25.dry unit weight 干重度26.moist unit weight 湿重度45.ISSMGE=International Society for Soil Mechanics and Geotechnical Engineering 国际土力学与岩土工程学会精品文库四.渗透性和渗流1.Darcy’s law 达西定律2.piping 管涌3.flowing soil 流土4.sand boiling 砂沸5.flow net 流网6.seepage 渗透(流)7.leakage 渗流8.seepage pressure 渗透压力9.permeability 渗透性10.seepage force 渗透力11.hydraulic gradient 水力梯度12.coefficient of permeability 渗透系数五.地基应力和变形1.soft soil 软土2.(negative) skin friction of driven pile 打入桩(负)摩阻力3.effective stress 有效应力4.total stress 总应力5.field vane shear strength 十字板抗剪强度6.low activity 低活性7.sensitivity 灵敏度8.triaxial test 三轴试验9.foundation design 基础设计10.recompaction 再压缩11.bearing capacity 承载力12.soil mass 土体13.contact stress (pressure)接触应力(压力)14.concentrated load 集中荷载15.a semi-infinite elastic solid 半无限弹性体16.homogeneous 均质17.isotropic 各向同性18.strip footing 条基19.square spread footing 方形独立基础20.underlying soil (stratum strata)下卧层(土)21.dead load =sustained load 恒载持续荷载22.live load 活载23.short –term transient load 短期瞬时荷载24.long-term transient load 长期荷载25.reduced load 折算荷载26.settlement 沉降27.deformation 变形28.casing 套管精品文库29.dike=dyke 堤(防)30.clay fraction 粘粒粒组31.physical properties 物理性质32.subgrade 路基33.well-graded soil 级配良好土34.poorly-graded soil 级配不良土35.normal stresses 正应力36.shear stresses 剪应力37.principal plane 主平面38.major (intermediate minor) principal stress 最大(中、最小)主应力39.Mohr-Coulomb failure condition 摩尔-库仑破坏条件40.FEM=finite element method 有限元法41.limit equilibrium method 极限平衡法42.pore water pressure 孔隙水压力43.preconsolidation pressure 先期固结压力44.modulus of compressibility 压缩模量45.coefficent of compressibility 压缩系数pression index 压缩指数47.swelling index 回弹指数48.geostatic stress 自重应力49.additional stress 附加应力50.total stress 总应力51.final settlement 最终沉降52.slip line 滑动线六.基坑开挖与降水1 excavation 开挖(挖方)2 dewatering (基坑)降水3 failure of foundation 基坑失稳4 bracing of foundation pit 基坑围护5 bottom heave=basal heave (基坑)底隆起6 retaining wall 挡土墙7 pore-pressure distribution 孔压分布8 dewatering method 降低地下水位法9 well point system 井点系统(轻型)10 deep well point 深井点11 vacuum well point 真空井点12 braced cuts 支撑围护13 braced excavation 支撑开挖14 braced sheeting 支撑挡板七.深基础--deep foundation1.pile foundation 桩基础1)cast –in-place 灌注桩diving casting cast-in-place pile 沉管灌注桩bored pile 钻孔桩special-shaped cast-in-place pile 机控异型灌注桩piles set into rock 嵌岩灌注桩rammed bulb pile 夯扩桩2)belled pier foundation 钻孔墩基础drilled-pier foundation 钻孔扩底墩under-reamed bored pier3)precast concrete pile 预制混凝土桩4)steel pile 钢桩steel pipe pile 钢管桩steel sheet pile 钢板桩5)prestressed concrete pile 预应力混凝土桩prestressed concrete pipe pile 预应力混凝土管桩2.caisson foundation 沉井(箱)3.diaphragm wall 地下连续墙截水墙4.friction pile 摩擦桩5.end-bearing pile 端承桩6.shaft 竖井;桩身7.wave equation analysis 波动方程分析8.pile caps 承台(桩帽)9.bearing capacity of single pile 单桩承载力teral pile load test 单桩横向载荷试验11.ultimate lateral resistance of single pile 单桩横向极限承载力12.static load test of pile 单桩竖向静荷载试验13.vertical allowable load capacity 单桩竖向容许承载力14.low pile cap 低桩承台15.high-rise pile cap 高桩承台16.vertical ultimate uplift resistance of single pile 单桩抗拔极限承载力17.silent piling 静力压桩18.uplift pile 抗拔桩19.anti-slide pile 抗滑桩20.pile groups 群桩21.efficiency factor of pile groups 群桩效率系数(η)22.efficiency of pile groups 群桩效应23.dynamic pile testing 桩基动测技术24.final set 最后贯入度25.dynamic load test of pile 桩动荷载试验26.pile integrity test 桩的完整性试验27.pile head=butt 桩头28.pile tip=pile point=pile toe 桩端(头)29.pile spacing 桩距30.pile plan 桩位布置图31.arrangement of piles =pile layout 桩的布置32.group action 群桩作用33.end bearing=tip resistance 桩端阻34.skin(side) friction=shaft resistance 桩侧阻35.pile cushion 桩垫36.pile driving(by vibration) (振动)打桩37.pile pulling test 拔桩试验38.pile shoe 桩靴39.pile noise 打桩噪音40.pile rig 打桩机九.固结 consolidation1.Terzzaghi’s consolidation theory 太沙基固结理论2.Barraon’s consolidation theory 巴隆固结理论3.Biot’s consolidation theory 比奥固结理论4.over consolidation ration (OCR)超固结比5.overconsolidation soil 超固结土6.excess pore water pressure 超孔压力7.multi-dimensional consolidation 多维固结8.one-dimensional consolidation 一维固结9.primary consolidation 主固结10.secondary consolidation 次固结11.degree of consolidation 固结度12.consolidation test 固结试验13.consolidation curve 固结曲线14.time factor Tv 时间因子15.coefficient of consolidation 固结系数16.preconsolidation pressure 前期固结压力17.principle of effective stress 有效应力原理18.consolidation under K0 condition K0 固结十.抗剪强度 shear strength1.undrained shear strength 不排水抗剪强度2.residual strength 残余强度3.long-term strength 长期强度4.peak strength 峰值强度5.shear strain rate 剪切应变速率6.dilatation 剪胀7.effective stress approach of shear strength 剪胀抗剪强度有效应力法 8.total stress approach of shear strength 抗剪强度总应力法9.Mohr-Coulomb theory 莫尔-库仑理论10.angle of internal friction 内摩擦角11.cohesion 粘聚力12.failure criterion 破坏准则13.vane strength 十字板抗剪强度14.unconfined compression 无侧限抗压强度15.effective stress failure envelop 有效应力破坏包线16.effective stress strength parameter 有效应力强度参数十一.本构模型--constitutive model1.elastic model 弹性模型2.nonlinear elastic model 非线性弹性模型3.elastoplastic model 弹塑性模型4.viscoelastic model 粘弹性模型5.boundary surface model 边界面模型6.Du ncan-Chang model 邓肯-张模型7.rigid plastic model 刚塑性模型8.cap model 盖帽模型9.work softening 加工软化10.work hardening 加工硬化11.Cambridge model 剑桥模型12.ideal elastoplastic model 理想弹塑性模型13.Mohr-Coulomb yield criterion 莫尔-库仑屈服准则14.yield surface 屈服面15.elastic half-space foundation model 弹性半空间地基模型16.elastic modulus 弹性模量17.Winkler foundation model 文克尔地基模型十二.地基承载力--bearing capacity of foundation soil1.punching shear failure 冲剪破坏2.general shear failure 整体剪切破化3.local shear failure 局部剪切破坏4.state of limit equilibrium 极限平衡状态5.critical edge pressure 临塑荷载6.stability of foundation soil 地基稳定性7.ultimate bearing capacity of foundation soil 地基极限承载力8.allowable bearing capacity of foundation soil 地基容许承载力十三.土压力--earth pressure1.active earth pressure 主动土压力2.passive earth pressure 被动土压力3.earth pressure at rest 静止土压力4.Coulomb’s earth pressure theory 库仑土压力理论5.Rankine’s earth pressure theory 朗金土压力理论十四.土坡稳定分析--slope stability analysis1.angle of repose 休止角2.Bishop method 毕肖普法3.safety factor of slope 边坡稳定安全系数4.Fellenius method of slices 费纽伦斯条分法5.Swedish circle method 瑞典圆弧滑动法6.slices method 条分法十五.挡土墙--retaining wall1.stability of retaining wall 挡土墙稳定性2.foundation wall 基础墙3.counter retaining wall 扶壁式挡土墙4.cantilever retaining wall 悬臂式挡土墙5.cantilever sheet pile wall 悬臂式板桩墙6.gravity retaining wall 重力式挡土墙7.anchored plate retaining wall 锚定板挡土墙8.anchored sheet pile wall 锚定板板桩墙十六.板桩结构物--sheet pile structure1.steel sheet pile 钢板桩2.reinforced concrete sheet pile 钢筋混凝土板桩3.steel piles 钢桩4.wooden sheet pile 木板桩5.timber piles 木桩十七.浅基础--shallow foundation1.box foundation 箱型基础2.mat(raft) foundation 片筏基础3.strip foundation 条形基础4.spread footing 扩展基础pensated foundation 补偿性基础6.bearing stratum 持力层7.rigid foundation 刚性基础8.flexible foundation 柔性基础9.emxxxxbedded depth of foundation 基础埋置深度 foundation pressure 基底附加应力11.structure-foundation-soil interaction analysis 上部结构-基础-地基共同作用分析十八.土的动力性质--dynamic properties of soils1.dynamic strength of soils 动强度2.wave velocity method 波速法3.material damping 材料阻尼4.geometric damping 几何阻尼5.damping ratio 阻尼比6.initial liquefaction 初始液化7.natural period of soil site 地基固有周期8.dynamic shear modulus of soils 动剪切模量9.dynamic ma二十.地基基础抗震1.earthquake engineering 地震工程2.soil dynamics 土动力学3.duration of earthquake 地震持续时间4.earthquake response spectrum 地震反应谱5.earthquake intensity 地震烈度6.earthquake magnitude 震级7.seismic predominant period 地震卓越周期8.maximum acceleration of earthquake 地震最大加速度二十一.室内土工实验1.high pressure consolidation test 高压固结试验2.consolidation under K0 condition K0 固结试验3.falling head permeability 变水头试验4.constant head permeability 常水头渗透试验5.unconsolidated-undrained triaxial test 不固结不排水试验(UU)6.consolidated undrained triaxial test 固结不排水试验(CU)7.consolidated drained triaxial test 固结排水试验(CD)paction test 击实试验9.consolidated quick direct shear test 固结快剪试验10.quick direct shear test 快剪试验11.consolidated drained direct shear test 慢剪试验12.sieve analysis 筛分析13.geotechnical model test 土工模型试验14.centrifugal model test 离心模型试验15.direct shear apparatus 直剪仪16.direct shear test 直剪试验17.direct simple shear test 直接单剪试验18.dynamic triaxial test 三轴试验19.dynamic simple shear 动单剪20.free(resonance)vibration column test 自(共)振柱试验二十二.原位测试1.standard penetration test (SPT)标准贯入试验2.surface wave test (SWT) 表面波试验3.dynamic penetration test(DPT) 动力触探试验4.static cone penetration (SPT) 静力触探试验5.plate loading test 静力荷载试验teral load test of pile 单桩横向载荷试验7.static load test of pile 单桩竖向荷载试验8.cross-hole test 跨孔试验9.screw plate test 螺旋板载荷试验10.pressuremeter test 旁压试验11.light sounding 轻便触探试验12.deep settlement measurement 深层沉降观测13.vane shear test 十字板剪切试验14.field permeability test 现场渗透试验15.in-situ pore water pressure measurement 原位孔隙水压量测16.in-situ soil test 原位试验第一部分必须掌握,第二部分尽量掌握第一部分:1 Finite Element Method 有限单元法2 专业英语 Specialty English3 水利工程 Hydraulic Engineering4 土木工程 Civil Engineering5 地下工程 Underground Engineering6 岩土工程 Geotechnical Engineering7 道路工程 Road (Highway) Engineering8 桥梁工程Bridge Engineering9 隧道工程 Tunnel Engineering10 工程力学 Engineering Mechanics11 交通工程 Traffic Engineering12 港口工程 Port Engineering13 安全性 safety17木结构 timber structure18 砌体结构 masonry structure19 混凝土结构concrete structure20 钢结构 steelstructure21 钢 - 混凝土复合结构 steel and concrete composite structure22 素混凝土 plain concrete23 钢筋混凝土reinforced concrete24 钢筋 rebar25 预应力混凝土 pre-stressed concrete26 静定结构statically determinate structure27 超静定结构 statically indeterminate structure28 桁架结构 truss structure29 空间网架结构 spatial grid structure30 近海工程 offshore engineering31 静力学 statics32运动学kinematics33 动力学dynamics34 简支梁 simply supported beam35 固定支座 fixed bearing36弹性力学 elasticity37 塑性力学 plasticity38 弹塑性力学 elaso-plasticity39 断裂力学 fracture Mechanics40 土力学 soil mechanics精品文库41 水力学 hydraulics42 流体力学 fluid mechanics43 固体力学solid mechanics44 集中力 concentrated force45 压力 pressure46 静水压力 hydrostatic pressure47 均布压力 uniform pressure48 体力 body force49 重力 gravity50 线荷载 line load51 弯矩 bending moment52 扭矩 torque53 应力 stress54 应变 stain55 正应力 normal stress56 剪应力 shearing stress57 主应力 principal stress58 变形 deformation59 内力 internal force60 偏移量挠度 deflection61 沉降settlement62 屈曲失稳 buckle63 轴力 axial force64 允许应力 allowable stress65 疲劳分析 fatigue analysis66 梁 beam67 壳 shell68 板 plate69 桥 bridge70 桩 pile71 主动土压力 active earth pressure72 被动土压力 passive earth pressure73 承载力 load-bearing capacity74 水位 water Height75 位移 displacement76 结构力学 structural mechanics77 材料力学 material mechanics78 经纬仪 altometer79 水准仪level80 学科 discipline81 子学科 sub-discipline82 期刊 journal periodical精品文库83 文献literature84 国际标准刊号ISSN International Standard Serial Number85 国际标准书号ISBN International Standard Book Number86 卷 volume87 期 number88 专著 monograph89 会议论文集 Proceeding90 学位论文 thesis dissertation91 专利 patent92 档案档案室 archive93 国际学术会议 conference94 导师 advisor95 学位论文答辩 defense of thesis96 博士研究生 doctorate student97 研究生 postgraduate98 工程索引EI Engineering Index99 科学引文索引SCI Science Citation Index100 科学技术会议论文集索引ISTP Index to Science and Tec hnology Proceedings101 题目 title102 摘要 abstract103 全文 full-text104 参考文献 reference105 联络单位、所属单位affiliation106 主题词 Subject107 关键字 keyword108 美国土木工程师协会ASCE American Society of Civil Engineers109 联邦公路总署FHWA Federal Highway Administration110 国际标准组织ISO International Standard Organization111 解析方法 analytical method112 数值方法 numerical method113 计算 computation114 说明书 instruction115 规范 Specification Code第二部分:岩土工程专业词汇1.geotechnical engineering 岩土工程2.foundation engineering 基础工程3.soil earth 土4.soil mechanics 土力学5.cyclic loading 周期荷载6.unloading 卸载7.reloading 再加载8.viscoelastic foundation 粘弹性地基精品文库9.viscous damping 粘滞阻尼10.shear modulus 剪切模量11.soil dynamics 土动力学12.stress path 应力路径13.numerical geotechanics 数值岩土力学二.土的分类1.residual soil 残积土 groundwater level 地下水位2.groundwater 地下水 groundwater table 地下水位3.clay minerals 粘土矿物4.secondary minerals 次生矿物ndslides 滑坡6.bore hole columnar section 钻孔柱状图7.engineering geologic investigation 工程地质勘察8.boulder 漂石9.cobble 卵石10.gravel 砂石11.gravelly sand 砾砂12.coarse sand 粗砂13.medium sand 中砂14.fine sand 细砂15.silty sand 粉土16.clayey soil 粘性土17.clay 粘土18.silty clay 粉质粘土19.silt 粉土20.sandy silt 砂质粉土21.clayey silt 粘质粉土22.saturated soil 饱和土23.unsaturated soil 非饱和土24.fill (soil) 填土25.overconsolidated soil 超固结土26.normally consolidated soil 正常固结土27.underconsolidated soil 欠固结土28.zonal soil 区域性土29.soft clay 软粘土30.expansive (swelling) soil 膨胀土31.peat 泥炭32.loess 黄土33.frozen soil 冻土24.degree of saturation 饱和度25.dry unit weight 干重度26.moist unit weight 湿重度精品文库45.ISSMGE=International Society for Soil Mechanics and Geotechnical Engineering 国际土力学与岩土工程学会四.渗透性和渗流1.Darcy’s law 达西定律2.piping 管涌3.flowing soil 流土4.sand boiling 砂沸5.flow net 流网6.seepage 渗透(流)7.leakage 渗流8.seepage pressure 渗透压力9.permeability 渗透性10.seepage force 渗透力11.hydraulic gradient 水力梯度12.coefficient of permeability 渗透系数五.地基应力和变形1.soft soil 软土2.(negative) skin friction of driven pile 打入桩(负)摩阻力3.effective stress 有效应力4.total stress 总应力5.field vane shear strength 十字板抗剪强度6.low activity 低活性7.sensitivity 灵敏度8.triaxial test 三轴试验9.foundation design 基础设计10.recompaction 再压缩11.bearing capacity 承载力12.soil mass 土体13.contact stress (pressure)接触应力(压力)14.concentrated load 集中荷载15.a semi-infinite elastic solid 半无限弹性体16.homogeneous 均质17.isotropic 各向同性18.strip footing 条基19.square spread footing 方形独立基础20.underlying soil (stratum strata)下卧层(土)21.dead load =sustained load 恒载持续荷载22.live load 活载23.short –term transient load 短期瞬时荷载24.long-term transient load 长期荷载25.reduced load 折算荷载26.settlement 沉降精品文库27.deformation 变形28.casing 套管29.dike=dyke 堤(防)30.clay fraction 粘粒粒组31.physical properties 物理性质32.subgrade 路基33.well-graded soil 级配良好土34.poorly-graded soil 级配不良土35.normal stresses 正应力36.shear stresses 剪应力37.principal plane 主平面38.major (intermediate minor) principal stress 最大(中、最小)主应力39.Mohr-Coulomb failure condition 摩尔-库仑破坏条件40.FEM=finite element method 有限元法41.limit equilibrium method 极限平衡法42.pore water pressure 孔隙水压力43.preconsolidation pressure 先期固结压力44.modulus of compressibility 压缩模量45.coefficent of compressibility 压缩系数pression index 压缩指数47.swelling index 回弹指数48.geostatic stress 自重应力49.additional stress 附加应力50.total stress 总应力51.final settlement 最终沉降52.slip line 滑动线六.基坑开挖与降水1 excavation 开挖(挖方)2 dewatering (基坑)降水3 failure of foundation 基坑失稳4 bracing of foundation pit 基坑围护5 bottom heave=basal heave (基坑)底隆起6 retaining wall 挡土墙7 pore-pressure distribution 孔压分布8 dewatering method 降低地下水位法9 well point system 井点系统(轻型)10 deep well point 深井点11 vacuum well point 真空井点12 braced cuts 支撑围护13 braced excavation 支撑开挖14 braced sheeting 支撑挡板七.深基础--deep foundation1.pile foundation 桩基础1)cast –in-place 灌注桩diving casting cast-in-place pile 沉管灌注桩bored pile 钻孔桩special-shaped cast-in-place pile 机控异型灌注桩piles set into rock 嵌岩灌注桩rammed bulb pile 夯扩桩2)belled pier foundation 钻孔墩基础drilled-pier foundation 钻孔扩底墩under-reamed bored pier3)precast concrete pile 预制混凝土桩4)steel pile 钢桩steel pipe pile 钢管桩steel sheet pile 钢板桩5)prestressed concrete pile 预应力混凝土桩prestressed concrete pipe pile 预应力混凝土管桩2.caisson foundation 沉井(箱)3.diaphragm wall 地下连续墙截水墙4.friction pile 摩擦桩5.end-bearing pile 端承桩6.shaft 竖井;桩身7.wave equation analysis 波动方程分析8.pile caps 承台(桩帽)9.bearing capacity of single pile 单桩承载力teral pile load test 单桩横向载荷试验11.ultimate lateral resistance of single pile 单桩横向极限承载力12.static load test of pile 单桩竖向静荷载试验13.vertical allowable load capacity 单桩竖向容许承载力14.low pile cap 低桩承台15.high-rise pile cap 高桩承台16.vertical ultimate uplift resistance of single pile 单桩抗拔极限承载力17.silent piling 静力压桩18.uplift pile 抗拔桩19.anti-slide pile 抗滑桩20.pile groups 群桩21.efficiency factor of pile groups 群桩效率系数(η)22.efficiency of pile groups 群桩效应23.dynamic pile testing 桩基动测技术24.final set 最后贯入度25.dynamic load test of pile 桩动荷载试验26.pile integrity test 桩的完整性试验27.pile head=butt 桩头28.pile tip=pile point=pile toe 桩端(头)29.pile spacing 桩距30.pile plan 桩位布置图31.arrangement of piles =pile layout 桩的布置32.group action 群桩作用33.end bearing=tip resistance 桩端阻34.skin(side) friction=shaft resistance 桩侧阻35.pile cushion 桩垫36.pile driving(by vibration) (振动)打桩37.pile pulling test 拔桩试验38.pile shoe 桩靴39.pile noise 打桩噪音40.pile rig 打桩机九.固结 consolidation1.Terzzaghi’s consolidation theory 太沙基固结理论2.Barraon’s consolidation theory 巴隆固结理论3.Biot’s consolidation theory 比奥固结理论4.over consolidation ration (OCR)超固结比5.overconsolidation soil 超固结土6.excess pore water pressure 超孔压力7.multi-dimensional consolidation 多维固结8.one-dimensional consolidation 一维固结9.primary consolidation 主固结10.secondary consolidation 次固结11.degree of consolidation 固结度12.consolidation test 固结试验13.consolidation curve 固结曲线14.time factor Tv 时间因子15.coefficient of consolidation 固结系数16.preconsolidation pressure 前期固结压力17.principle of effective stress 有效应力原理18.consolidation under K0 condition K0 固结十.抗剪强度 shear strength1.undrained shear strength 不排水抗剪强度2.residual strength 残余强度3.long-term strength 长期强度4.peak strength 峰值强度5.shear strain rate 剪切应变速率6.dilatation 剪胀7.effective stress approach of shear strength 剪胀抗剪强度有效应力法 8.total stress approach of shear strength 抗剪强度总应力法9.Mohr-Coulomb theory 莫尔-库仑理论10.angle of internal friction 内摩擦角11.cohesion 粘聚力12.failure criterion 破坏准则13.vane strength 十字板抗剪强度14.unconfined compression 无侧限抗压强度15.effective stress failure envelop 有效应力破坏包线16.effective stress strength parameter 有效应力强度参数十一.本构模型--constitutive model1.elastic model 弹性模型2.nonlinear elastic model 非线性弹性模型3.elastoplastic model 弹塑性模型4.viscoelastic model 粘弹性模型5.boundary surface model 边界面模型6.Du ncan-Chang model 邓肯-张模型7.rigid plastic model 刚塑性模型8.cap model 盖帽模型9.work softening 加工软化10.work hardening 加工硬化11.Cambridge model 剑桥模型12.ideal elastoplastic model 理想弹塑性模型13.Mohr-Coulomb yield criterion 莫尔-库仑屈服准则14.yield surface 屈服面15.elastic half-space foundation model 弹性半空间地基模型16.elastic modulus 弹性模量17.Winkler foundation model 文克尔地基模型十二.地基承载力--bearing capacity of foundation soil1.punching shear failure 冲剪破坏2.general shear failure 整体剪切破化3.local shear failure 局部剪切破坏4.state of limit equilibrium 极限平衡状态5.critical edge pressure 临塑荷载6.stability of foundation soil 地基稳定性7.ultimate bearing capacity of foundation soil 地基极限承载力8.allowable bearing capacity of foundation soil 地基容许承载力十三.土压力--earth pressure1.active earth pressure 主动土压力2.passive earth pressure 被动土压力3.earth pressure at rest 静止土压力4.Coulomb’s earth pressure theory 库仑土压力理论5.Rankine’s earth pressure theo ry 朗金土压力理论十四.土坡稳定分析--slope stability analysis1.angle of repose 休止角2.Bishop method 毕肖普法3.safety factor of slope 边坡稳定安全系数4.Fellenius method of slices 费纽伦斯条分法5.Swedish circle method 瑞典圆弧滑动法6.slices method 条分法十五.挡土墙--retaining wall1.stability of retaining wall 挡土墙稳定性2.foundation wall 基础墙3.counter retaining wall 扶壁式挡土墙4.cantilever retaining wall 悬臂式挡土墙5.cantilever sheet pile wall 悬臂式板桩墙6.gravity retaining wall 重力式挡土墙7.anchored plate retaining wall 锚定板挡土墙8.anchored sheet pile wall 锚定板板桩墙十六.板桩结构物--sheet pile structure1.steel sheet pile 钢板桩2.reinforced concrete sheet pile 钢筋混凝土板桩3.steel piles 钢桩4.wooden sheet pile 木板桩5.timber piles 木桩十七.浅基础--shallow foundation1.box foundation 箱型基础2.mat(raft) foundation 片筏基础3.strip foundation 条形基础4.spread footing 扩展基础pensated foundation 补偿性基础6.bearing stratum 持力层7.rigid foundation 刚性基础8.flexible foundation 柔性基础9.emxxxxbedded depth of foundation 基础埋置深度 foundation pressure 基底附加应力11.structure-foundation-soil interaction analysis 上部结构-基础-地基共同作用分析十八.土的动力性质--dynamic properties of soils1.dynamic strength of soils 动强度2.wave velocity method 波速法3.material damping 材料阻尼4.geometric damping 几何阻尼5.damping ratio 阻尼比6.initial liquefaction 初始液化7.natural period of soil site 地基固有周期8.dynamic shear modulus of soils 动剪切模量9.dynamic ma二十.地基基础抗震1.earthquake engineering 地震工程2.soil dynamics 土动力学3.duration of earthquake 地震持续时间4.earthquake response spectrum 地震反应谱5.earthquake intensity 地震烈度6.earthquake magnitude 震级7.seismic predominant period 地震卓越周期8.maximum acceleration of earthquake 地震最大加速度二十一.室内土工实验1.high pressure consolidation test 高压固结试验2.consolidation under K0 condition K0 固结试验3.falling head permeability 变水头试验4.constant head permeability 常水头渗透试验5.unconsolidated-undrained triaxial test 不固结不排水试验(UU)6.consolidated undrained triaxial test 固结不排水试验(CU)7.consolidated drained triaxial test 固结排水试验(CD)paction test 击实试验9.consolidated quick direct shear test 固结快剪试验10.quick direct shear test 快剪试验11.consolidated drained direct shear test 慢剪试验12.sieve analysis 筛分析13.geotechnical model test 土工模型试验14.centrifugal model test 离心模型试验15.direct shear apparatus 直剪仪16.direct shear test 直剪试验17.direct simple shear test 直接单剪试验18.dynamic triaxial test 三轴试验19.dynamic simple shear 动单剪20.free(resonance)vibration column test 自(共)振柱试验二十二.原位测试1.standard penetration test (SPT)标准贯入试验2.surface wave test (SWT) 表面波试验3.dynamic penetration test(DPT) 动力触探试验4.static cone penetration (SPT) 静力触探试验5.plate loading test 静力荷载试验teral load test of pile 单桩横向载荷试验7.static load test of pile 单桩竖向荷载试验8.cross-hole test 跨孔试验9.screw plate test 螺旋板载荷试验10.pressuremeter test 旁压试验11.light sounding 轻便触探试验12.deep settlement measurement 深层沉降观测13.vane shear test 十字板剪切试验14.field permeability test 现场渗透试验15.in-situ pore water pressure measurement 原位孔隙水压量测16.in-situ soil test 原位试验。

固体力学专业词汇弹性力学 elasticity弹性理论 theory of elasticity均匀应力状态 homogeneous state of stress应力不变量 stress invariant应变不变量 strain invariant板 Plate矩形板 Rectangular plate圆板 Circular plate弯[曲]应力函数 Stress function of bending壳 Shell球壳 Spherical shell锥壳 Conical shell扭[转]应力函数 Stress function of torsion松弛 Relaxation接触应力 Contact stress压入 Indentation散体力学 Mechanics of granular media热弹性 Thermoelasticity粘弹性 Viscoelasticity对应原理 Correspondence principle 粗糙度 Roughness弹性动力学 Dynamic elasticity 运动方程 Equation of motion边缘效应 edge effect塑性力学 Plasticity可成形性 Formability金属成形 Metal forming拉拔 Drawing回弹 Springback挤压 Extrusion冲压 Stamping穿透 Perforation层裂 Spalling塑性理论 Theory of plasticity 塑性加载 Plastic loading简单加载 Simple loading比例加载 Proportional loading 卸载 Unloading脉冲载荷 pulse load本构方程 constitutive equation 过应力 over-stress对数应变 logarithmic strain工程应变 engineering strain应变率 strain rate有限应变 finite strain塑性应变增量 plastic strain increment永久变形 permanent deformation应变软化 strain-softening刚塑性材料 rigid-plastic material理想塑性材料 perfectl plastic material材料稳定性 stability of material应变强化 strain-hardening屈服 Yield屈服条件 yield condition塑性动力学 dynamic plasticity滑移线 slip-lines结构力学 structural mechanics结构分析 structural analysis结构动力学 structural dynamics空间结构 space structure结点法 method of joints截面法 method of sections复合材料力学 mechanics of composites复合材料 composite material纤维复合材料 fibrous composite层板 Laminate膨胀 Expansion压实 Debulk脱层 Delamination纤维应力 fiber stress层应力 ply stress层应变 ply strain短纤维 chopped fiber长纤维 continuous fiber纤维方向 fiber direction纤维断裂 fiber break纤维拔脱 fiber pull-out断裂力学 fracture mechanics弹塑性断裂力学 elastic-plastic fracture mecha-nics, EPFM断裂 Fracture脆性断裂 brittle fracture蠕变断裂 creep fracture裂纹 Crack裂缝 Flaw缺陷 Defect割缝 Slit短裂纹 short crack表面裂纹 surface crack裂纹钝化 crack blunting有效应力张量 effective stress tensor内聚区 cohesive zone塑性区 plastic zone张拉区 stretched zone热影响区 heat affected zone, HAZ应力腐蚀 stress corrosion损伤 Damage累积损伤 accumulated damage脆性损伤 brittle damage宏观损伤 macroscopic damage微观损伤 microscopic damage疲劳 Fatigue应力疲劳 stress fatigue蠕变疲劳 creep fatigue腐蚀疲劳 corrosion fatigue疲劳损伤 fatigue damage疲劳失效 fatigue failure疲劳断裂 fatigue fracture疲劳裂纹 fatigue crack疲劳寿命 fatigue life疲劳破坏 fatigue rupture交变应力 alternating stress应变疲劳 strain fatigue计算结构力学 computational structural mechanics广义位移 generalized displacement广义应变 generalized strain广义应力 generalized stress节点 node, nodal point[单]元 Element二维元 two-dimensional element一维元 one-dimensional element三维元 three-dimensional element轴对称元 axisymmetric element三角形元 triangular element四边形元 quadrilateral element四面体元 tetrahedral element曲线元 curved element位移矢量 displacement vector载荷矢量 load vector面积坐标 area coordinates体积坐标 volume coordinates前处理 pre-processing后处理 post-processing组合结构 composite structure。


有限元等参变换的坐标转换英文回答:Coordinate transformation is an essential component in finite element isoparametric mapping. It involves converting the coordinates of a point from one coordinate system to another. In the context of finite element analysis, this transformation is typically used to map points in the physical domain to points in the reference domain.The isoparametric mapping technique is commonly used in finite element analysis to simplify the mathematical formulation of the problem. It allows us to use a single set of shape functions for both the geometry and the solution variables. In this technique, the physical domain is divided into a number of finite elements, and each element is mapped to a corresponding reference element. The reference element is a simple shape, such as a line segment or a triangle, with known coordinates.To perform the coordinate transformation, we need to define the shape functions and the interpolation functions. The shape functions define the geometry of the element, while the interpolation functions define the variation of the solution variables within the element. These functions are typically expressed in terms of the reference coordinates, which range from -1 to 1 for one-dimensional elements and from 0 to 1 for two-dimensional elements.Once the shape functions and interpolation functions are defined, we can use them to map the physical coordinates to the reference coordinates. This involves solving a system of equations to determine the values of the reference coordinates that correspond to a given set of physical coordinates. The solution of this system of equations is typically done using numerical methods, such as Newton-Raphson iteration.Once we have the reference coordinates, we can use them to evaluate the shape functions and interpolation functions at the physical coordinates. This allows us to compute thevalues of the solution variables at any point within the element. The computed values can then be used to perform further calculations, such as computing the elementstiffness matrix or evaluating the element forces.In summary, coordinate transformation is a crucial step in finite element analysis. It allows us to map points in the physical domain to points in the reference domain, enabling us to use a single set of shape functions for both the geometry and the solution variables. This technique simplifies the mathematical formulation of the problem and facilitates the numerical solution.中文回答:坐标转换是有限元等参变换中的一个重要组成部分。

结点法method of joints截面法method of sections结点力joint forces共轭位移conjugate displacement影响线influence line三弯矩方程three-moment equation单位虚力unit virtual force刚度系数stiffness coefficient柔度系数flexibility coefficient力矩分配moment distribution力矩分配法moment distribution method力矩再分配moment redistribution分配系数distribution factor矩阵位移法matri displacement method单元刚度矩阵element stiffness matrix单元应变矩阵element strain matrix总体坐标global coordinates贝蒂定理Betti theorem高斯--若尔当消去法Gauss-Jordan eliminationMethod屈曲模态buckling mode复合材料力学mechanics of composites复合材料composite material纤维复合材料fibrous composite单向复合材料unidirectional composite泡沫复合材料foamed composite颗粒复合材料particulate composite层板Laminate夹层板sandwich panel正交层板cross-ply laminate斜交层板angle-ply laminate层片Ply多胞固体cellular solid膨胀Expansion压实Debulk劣化Degradation脱层Delamination脱粘Debond纤维应力fiber stress层应力ply stress层应变ply strain层间应力interlaminar stress比强度specific strength强度折减系数strength reduction factor 强度应力比strength -stress ratio横向剪切模量transverse shear modulus横观各向同性transverse isotropy正交各向异Orthotropy剪滞分析shear lag analysis短纤维chopped fiber长纤维continuous fiber纤维方向fiber direction纤维断裂fiber break纤维拔脱fiber pull-out纤维增强fiber reinforcement致密化Densification最小重量设计optimum weight design网格分析法netting analysis混合律rule of mixture失效准则failure criterion蔡--吴失效准则Tsai-W u failure criterion达格代尔模型Dugdale model断裂力学fracture mechanics概率断裂力学probabilistic fractureMechanics格里菲思理论Griffith theory线弹性断裂力学linear elastic fracturemechanics, LEFM弹塑性断裂力学elastic-plastic fracture mecha-nics, EPFM断裂Fracture脆性断裂brittle fracture解理断裂cleavage fracture蠕变断裂creep fracture延性断裂ductile fracture晶间断裂inter-granular fracture准解理断裂quasi-cleavage fracture穿晶断裂trans-granular fracture裂纹Crack裂缝Flaw缺陷Defect割缝Slit微裂纹Microcrack折裂Kink椭圆裂纹elliptical crack深埋裂纹embedded crack[钱]币状裂纹penny-shape crack预制裂纹Precrack短裂纹short crack表面裂纹surface crack裂纹钝化crack blunting裂纹分叉crack branching裂纹闭合crack closure裂纹前缘crack front裂纹嘴crack mouth裂纹张开角crack opening angle,COA裂纹张开位移crack opening displacement,COD 裂纹阻力crack resistance裂纹面crack surface裂纹尖端crack tip裂尖张角crack tip opening angle,CTOA裂尖张开位移crack tip opening displacement, CTOD裂尖奇异场crack tip singularityField裂纹扩展速率crack growth rate稳定裂纹扩展stable crack growth定常裂纹扩展steady crack growth亚临界裂纹扩展subcritical crack growth止裂crack arrest止裂韧度arrest toughness滑开型sliding mode张开型opening mode撕开型tearing mode复合型mixed mode撕裂模量tearing modulus断裂准则fracture criterionJ积分J-integralJ阻力曲线J-resistance curve断裂韧度fracture toughness应力强度因子stress intensity factorHRR场Hutchinson-Rice-RosengrenField守恒积分conservation integral有效应力张量effective stress tensor应变能密度strain energy density能量释放率energy release rate内聚区cohesive zone塑性区plastic zone张拉区stretched zone热影响区heat affected zone, HAZ延脆转变温度brittle-ductile transition tempe- rature剪切带shear band剪切唇shear lip 无损检测non-destructive inspection双边缺口试件double edge notchedspecimen, DEN specimen单边缺口试件single edge notched specimen, SEN specimen三点弯曲试件three point bendingspecimen, TPB specimen中心裂纹拉伸试件center cracked tensionspecimen, CCT specimen中心裂纹板试件center cracked panelspecimen, CCP specimen紧凑拉伸试件compact tension specimen,CT specimen大范围屈服large scale yielding小范围攻屈服small scale yielding韦布尔分布Weibull distribution帕里斯公式paris formula空穴化Cavitation应力腐蚀stress corrosion概率风险判定probabilistic risk assessment, PRA 损伤力学damage mechanics损伤Damage连续介质损伤力学continuum damage mechanics 细观损伤力学microscopic damage mechanics累积损伤accumulated damage脆性损伤brittle damage延性损伤ductile damage宏观损伤macroscopic damage细观损伤microscopic damage微观损伤microscopic damage损伤准则damage criterion损伤演化方程damage evolution equation损伤软化damage softening损伤强化damage strengthening损伤张量damage tensor损伤阈值damage threshold损伤矢量damage vector损伤区damage zone疲劳Fatigue低周疲劳low cycle fatigue应力疲劳stress fatigue蠕变疲劳creep fatigue疲劳损伤fatigue damage疲劳失效fatigue failure疲劳断裂fatigue fracture疲劳裂纹fatigue crack疲劳寿命fatigue life疲劳强度fatigue strength疲劳阈值fatigue threshold交变载荷alternating load交变应力alternating stress应力幅值stress amplitude应变疲劳strain fatigue应力循环stress cycle应力比stress ratio安全寿命safe life过载效应overloading effect循环硬化cyclic hardening循环软化cyclic softening环境效应environmental effect裂纹片crack gage裂纹扩展crack growth, crackPropagation 裂纹萌生crack initiation循环比cycle ratio实验应力分析experimental stressAnalysis 工作[应变]片active[strain] gage基底材料backing material应力计stress gage零[点]飘移zero shift, zero drift应变测量strain measurement应变计strain gage应变指示器strain indicator应变花strain rosette应变灵敏度strain sensitivity机械式应变仪mechanical strain gage直角应变花rectangular rosette引伸仪Extensometer应变遥测telemetering of strain横向灵敏系数transverse gage factor横向灵敏度transverse sensitivity焊接式应变计weldable strain gage平衡电桥balanced bridge粘贴式应变计bonded strain gage粘贴箔式应变计bonded foiled gage粘贴丝式应变计bonded wire gage桥路平衡bridge balancing电容应变计capacitance strain gage补偿片compensation technique 补偿技术compensation technique基准电桥reference bridge电阻应变计resistance strain gage温度自补偿应变计self-temperaturecompensating gage半导体应变计semiconductor strainGage集流器slip ring应变放大镜strain amplifier疲劳寿命计fatigue life gage电感应变计inductance [strain] gage光[测]力学Photomechanics光弹性Photoelasticity光塑性Photoplasticity杨氏条纹Young fringe双折射效应birefrigent effect等位移线contour of equalDisplacement暗条纹dark fringe条纹倍增fringe multiplication干涉条纹interference fringe等差线Isochromatic等倾线Isoclinic等和线isopachic应力光学定律stress- optic law主应力迹线Isostatic亮条纹light fringe光程差optical path difference热光弹性photo-thermo -elasticity光弹性贴片法photoelastic coatingMethod光弹性夹片法photoelastic sandwichMethod动态光弹性dynamic photo-elasticity空间滤波spatial filtering空间频率spatial frequency起偏镜Polarizer反射式光弹性仪reflection polariscope残余双折射效应residual birefringentEffect应变条纹值strain fringe value应变光学灵敏度strain-optic sensitivity应力冻结效应stress freezing effect应力条纹值stress fringe value应力光图stress-optic pattern暂时双折射效应temporary birefringentEffect脉冲全息法pulsed holography透射式光弹性仪transmission polariscope实时全息干涉法real-time holographicinterfero -metry网格法grid method全息光弹性法holo-photoelasticity全息图Hologram全息照相Holograph全息干涉法holographic interferometry全息云纹法holographic moire technique全息术Holography全场分析法whole-field analysis散斑干涉法speckle interferometry散斑Speckle错位散斑干涉法speckle-shearinginterferometry, shearography散斑图Specklegram白光散斑法white-light speckle method云纹干涉法moire interferometry[叠栅]云纹moire fringe[叠栅]云纹法moire method云纹图moire pattern离面云纹法off-plane moire method参考栅reference grating试件栅specimen grating分析栅analyzer grating面内云纹法in-plane moire method脆性涂层法brittle-coating method条带法strip coating method坐标变换transformation ofCoordinates计算结构力学computational structuralmecha-nics加权残量法weighted residual method有限差分法finite difference method有限[单]元法finite element method配点法point collocation里茨法Ritz method广义变分原理generalized variationalPrinciple最小二乘法least square method胡[海昌]一鹫津原理Hu-Washizu principle赫林格-赖斯纳原理Hellinger-ReissnerPrinciple修正变分原理modified variationalPrinciple约束变分原理constrained variationalPrinciple混合法mixed method杂交法hybrid method边界解法boundary solution method有限条法finite strip method 半解析法semi-analytical method协调元conforming element非协调元non-conforming element混合元mixed element杂交元hybrid element边界元boundary element强迫边界条件forced boundary condition自然边界条件natural boundary condition离散化Discretization离散系统discrete system连续问题continuous problem广义位移generalized displacement广义载荷generalized load广义应变generalized strain广义应力generalized stress界面变量interface variable节点node, nodal point[单]元Element角节点corner node内节点internal node无节点变量nodeless variable杆元bar element桁架杆元truss element梁元beam element二维元two-dimensional element一维元one-dimensional element三维元three-dimensional element轴对称元axisymmetric element板元plate element壳元shell element厚板元thick plate element三角形元triangular element四边形元quadrilateral element四面体元tetrahedral element二次元quadratic element线性元linear element三次元cubic element四次元quartic element等参[数]元isoparametric element超参数元super-parametric element亚参数元sub-parametric element节点数可变元variable-number-node element 拉格朗日元Lagrange element拉格朗日族Lagrange family巧凑边点元serendipity element巧凑边点族serendipity family无限元infinite element单元分析element analysis单元特性element characteristics刚度矩阵stiffness matrix几何矩阵geometric matrix等效节点力equivalent nodal force节点位移nodal displacement节点载荷nodal load位移矢量displacement vector载荷矢量load vector质量矩阵mass matrix集总质量矩阵lumped mass matrix相容质量矩阵consistent mass matrix瑞利阻尼Rayleigh damping刚度矩阵的组集assembly of stiffnessMatrices 载荷矢量的组集consistent mass matrix质量矩阵的组集assembly of mass matrices 单元的组集assembly of elements局部坐标系local coordinate system局部坐标local coordinate面积坐标area coordinates体积坐标volume coordinates曲线坐标curvilinear coordinates静凝聚static condensation合同变换contragradient transformation形状函数shape function试探函数trial function检验函数test function权函数weight function样条函数spline function代用函数substitute function降阶积分reduced integration零能模式zero-energy modeP收敛p-convergenceH收敛h-convergence掺混插值blended interpolation等参数映射isoparametric mapping双线性插值bilinear interpolation小块检验patch test非协调模式incompatible mode节点号node number单元号element number 带宽band width带状矩阵banded matrix变带状矩阵profile matrix带宽最小化minimization of band width波前法frontal method子空间迭代法subspace iteration method 行列式搜索法determinant search method 逐步法step-by-step method纽马克法Newmark威尔逊法Wilson拟牛顿法quasi-Newton method牛顿-拉弗森法Newton-Raphson method 增量法incremental method初应变initial strain初应力initial stress切线刚度矩阵tangent stiffness matrix割线刚度矩阵secant stiffness matrix模态叠加法mode superposition method 平衡迭代equilibrium iteration子结构Substructure子结构法substructure technique超单元super-element网格生成mesh generation结构分析程序structural analysis program 前处理pre-processing后处理post-processing网格细化mesh refinement应力光顺stress smoothing组合结构composite structure。

土木工程专业英语词汇(整理版)第一部分必须掌握,第二部分尽量掌握第一部分:1 Finite Element Method 有限单元法2 专业英语 Specialty English3 水利工程 Hydraulic Engineering4 土木工程 Civil Engineering5 地下工程 Underground Engineering6 岩土工程 Geotechnical Engineering7 道路工程 Road (Highway) Engineering8 桥梁工程Bridge Engineering9 隧道工程 Tunnel Engineering10 工程力学 Engineering Mechanics11 交通工程 Traffic Engineering12 港口工程 Port Engineering13 安全性 safety17木结构 timber structure18 砌体结构 masonry structure19 混凝土结构concrete structure20 钢结构 steelstructure21 钢 - 混凝土复合结构 steel and concrete composite structure22 素混凝土 plain concrete23 钢筋混凝土reinforced concrete24 钢筋 rebar25 预应力混凝土 pre-stressed concrete26 静定结构statically determinate structure27 超静定结构 statically indeterminate structure28 桁架结构 truss structure29 空间网架结构 spatial grid structure30 近海工程 offshore engineering31 静力学 statics32运动学kinematics33 动力学dynamics34 简支梁 simply supported beam35 固定支座 fixed bearing36弹性力学 elasticity37 塑性力学 plasticity38 弹塑性力学 elaso-plasticity39 断裂力学 fracture Mechanics40 土力学 soil mechanics41 水力学 hydraulics42 流体力学 fluid mechanics43 固体力学solid mechanics44 集中力 concentrated force45 压力 pressure46 静水压力 hydrostatic pressure47 均布压力 uniform pressure48 体力 body force49 重力 gravity50 线荷载 line load51 弯矩 bending moment52 扭矩 torque53 应力 stress54 应变 stain55 正应力 normal stress56 剪应力 shearing stress57 主应力 principal stress58 变形 deformation59 内力 internal force60 偏移量挠度 deflection61 沉降settlement62 屈曲失稳 buckle63 轴力 axial force64 允许应力 allowable stress65 疲劳分析 fatigue analysis66 梁 beam67 壳 shell68 板 plate69 桥 bridge70 桩 pile71 主动土压力 active earth pressure72 被动土压力 passive earth pressure73 承载力 load-bearing capacity74 水位 water Height75 位移 displacement76 结构力学 structural mechanics77 材料力学 material mechanics78 经纬仪 altometer79 水准仪level80 学科 discipline81 子学科 sub-discipline82 期刊 journal ,periodical83 文献literature84 国际标准刊号ISSN International Standard Serial Number85 国际标准书号ISBN International Standard Book Number86 卷 volume87 期 number88 专著 monograph89 会议论文集 Proceeding90 学位论文 thesis, dissertation91 专利 patent92 档案档案室 archive93 国际学术会议 conference94 导师 advisor95 学位论文答辩 defense of thesis96 博士研究生 doctorate student97 研究生 postgraduate98 工程索引EI Engineering Index99 科学引文索引SCI Science Citation Index100 科学技术会议论文集索引ISTP Index to Science and Tec hnology Proceedings101 题目 title102 摘要 abstract103 全文 full-text104 参考文献 reference105 联络单位、所属单位affiliation106 主题词 Subject107 关键字 keyword108 美国土木工程师协会ASCE American Society of Civil Engineers 109 联邦公路总署FHWA Federal Highway Administration110 国际标准组织ISO International Standard Organization111 解析方法 analytical method112 数值方法 numerical method113 计算 computation114 说明书 instruction115 规范 Specification, Code第二部分:岩土工程专业词汇1.geotechnical engineering 岩土工程2.foundation engineering 基础工程3.soil, earth 土4.soil mechanics 土力学5.cyclic loading 周期荷载6.unloading 卸载7.reloading 再加载8.viscoelastic foundation 粘弹性地基9.viscous damping 粘滞阻尼10.shear modulus 剪切模量11.soil dynamics 土动力学12.stress path 应力路径13.numerical geotechanics 数值岩土力学二.土的分类1.residual soil 残积土 groundwater level 地下水位2.groundwater 地下水 groundwater table 地下水位3.clay minerals 粘土矿物4.secondary minerals 次生矿物ndslides 滑坡6.bore hole columnar section 钻孔柱状图7.engineering geologic investigation 工程地质勘察8.boulder 漂石9.cobble 卵石10.gravel 砂石11.gravelly sand 砾砂12.coarse sand 粗砂13.medium sand 中砂14.fine sand 细砂15.silty sand 粉土16.clayey soil 粘性土17.clay 粘土18.silty clay 粉质粘土19.silt 粉土20.sandy silt 砂质粉土21.clayey silt 粘质粉土22.saturated soil 饱和土23.unsaturated soil 非饱和土24.fill (soil) 填土25.overconsolidated soil 超固结土26.normally consolidated soil 正常固结土27.underconsolidated soil 欠固结土28.zonal soil 区域性土29.soft clay 软粘土30.expansive (swelling) soil 膨胀土31.peat 泥炭32.loess 黄土33.frozen soil 冻土24.degree of saturation 饱和度25.dry unit weight 干重度26.moist unit weight 湿重度45.ISSMGE=International Society for Soil Mechanics and Geotechnical Engineering 国际土力学与岩土工程学会四.渗透性和渗流1.Darcy’s law 达西定律2.piping 管涌3.flowing soil 流土4.sand boiling 砂沸5.flow net 流网6.seepage 渗透(流)7.leakage 渗流8.seepage pressure 渗透压力9.permeability 渗透性10.seepage force 渗透力11.hydraulic gradient 水力梯度12.coefficient of permeability 渗透系数五.地基应力和变形1.soft soil 软土2.(negative) skin friction of driven pile 打入桩(负)摩阻力3.effective stress 有效应力4.total stress 总应力5.field vane shear strength 十字板抗剪强度6.low activity 低活性7.sensitivity 灵敏度8.triaxial test 三轴试验9.foundation design 基础设计10.recompaction 再压缩11.bearing capacity 承载力12.soil mass 土体13.contact stress (pressure)接触应力(压力)14.concentrated load 集中荷载15.a semi-infinite elastic solid 半无限弹性体16.homogeneous 均质17.isotropic 各向同性18.strip footing 条基19.square spread footing 方形独立基础20.underlying soil (stratum ,strata)下卧层(土)21.dead load =sustained load 恒载持续荷载22.live load 活载23.short –term transient load 短期瞬时荷载24.long-term transient load 长期荷载25.reduced load 折算荷载26.settlement 沉降27.deformation 变形28.casing 套管29.dike=dyke 堤(防)30.clay fraction 粘粒粒组31.physical properties 物理性质32.subgrade 路基33.well-graded soil 级配良好土34.poorly-graded soil 级配不良土35.normal stresses 正应力36.shear stresses 剪应力37.principal plane 主平面38.major (intermediate, minor) principal stress 最大(中、最小)主应力39.Mohr-Coulomb failure condition 摩尔-库仑破坏条件40.FEM=finite element method 有限元法41.limit equilibrium method 极限平衡法42.pore water pressure 孔隙水压力43.preconsolidation pressure 先期固结压力44.modulus of compressibility 压缩模量45.coefficent of compressibility 压缩系数pression index 压缩指数47.swelling index 回弹指数48.geostatic stress 自重应力49.additional stress 附加应力50.total stress 总应力51.final settlement 最终沉降52.slip line 滑动线六.基坑开挖与降水1 excavation 开挖(挖方)2 dewatering (基坑)降水3 failure of foundation 基坑失稳4 bracing of foundation pit 基坑围护5 bottom heave=basal heave (基坑)底隆起6 retaining wall 挡土墙7 pore-pressure distribution 孔压分布8 dewatering method 降低地下水位法9 well point system 井点系统(轻型)10 deep well point 深井点11 vacuum well point 真空井点12 braced cuts 支撑围护13 braced excavation 支撑开挖14 braced sheeting 支撑挡板七.深基础--deep foundation1.pile foundation 桩基础1)cast –in-place 灌注桩diving casting cast-in-place pile 沉管灌注桩bored pile 钻孔桩special-shaped cast-in-place pile 机控异型灌注桩piles set into rock 嵌岩灌注桩rammed bulb pile 夯扩桩2)belled pier foundation 钻孔墩基础drilled-pier foundation 钻孔扩底墩under-reamed bored pier3)precast concrete pile 预制混凝土桩4)steel pile 钢桩steel pipe pile 钢管桩steel sheet pile 钢板桩5)prestressed concrete pile 预应力混凝土桩prestressed concrete pipe pile 预应力混凝土管桩2.caisson foundation 沉井(箱)3.diaphragm wall 地下连续墙截水墙4.friction pile 摩擦桩5.end-bearing pile 端承桩6.shaft 竖井;桩身7.wave equation analysis 波动方程分析8.pile caps 承台(桩帽)9.bearing capacity of single pile 单桩承载力teral pile load test 单桩横向载荷试验11.ultimate lateral resistance of single pile 单桩横向极限承载力12.static load test of pile 单桩竖向静荷载试验13.vertical allowable load capacity 单桩竖向容许承载力14.low pile cap 低桩承台15.high-rise pile cap 高桩承台16.vertical ultimate uplift resistance of single pile 单桩抗拔极限承载力17.silent piling 静力压桩18.uplift pile 抗拔桩19.anti-slide pile 抗滑桩20.pile groups 群桩21.efficiency factor of pile groups 群桩效率系数(η)22.efficiency of pile groups 群桩效应23.dynamic pile testing 桩基动测技术24.final set 最后贯入度25.dynamic load test of pile 桩动荷载试验26.pile integrity test 桩的完整性试验27.pile head=butt 桩头28.pile tip=pile point=pile toe 桩端(头)29.pile spacing 桩距30.pile plan 桩位布置图31.arrangement of piles =pile layout 桩的布置32.group action 群桩作用33.end bearing=tip resistance 桩端阻34.skin(side) friction=shaft resistance 桩侧阻35.pile cushion 桩垫36.pile driving(by vibration) (振动)打桩37.pile pulling test 拔桩试验38.pile shoe 桩靴39.pile noise 打桩噪音40.pile rig 打桩机九.固结 consolidation1.Terzzaghi’s consolidation theory 太沙基固结理论2.Barraon’s consolidation theory 巴隆固结理论3.Biot’s consolidation theory 比奥固结理论4.over consolidation ration (OCR)超固结比5.overconsolidation soil 超固结土6.excess pore water pressure 超孔压力7.multi-dimensional consolidation 多维固结8.one-dimensional consolidation 一维固结9.primary consolidation 主固结10.secondary consolidation 次固结11.degree of consolidation 固结度12.consolidation test 固结试验13.consolidation curve 固结曲线14.time factor Tv 时间因子15.coefficient of consolidation 固结系数16.preconsolidation pressure 前期固结压力17.principle of effective stress 有效应力原理18.consolidation under K0 condition K0 固结十.抗剪强度 shear strength1.undrained shear strength 不排水抗剪强度2.residual strength 残余强度3.long-term strength 长期强度4.peak strength 峰值强度5.shear strain rate 剪切应变速率6.dilatation 剪胀7.effective stress approach of shear strength 剪胀抗剪强度有效应力法8.total stress approach of shear strength 抗剪强度总应力法9.Mohr-Coulomb theory 莫尔-库仑理论10.angle of internal friction 内摩擦角11.cohesion 粘聚力12.failure criterion 破坏准则13.vane strength 十字板抗剪强度14.unconfined compression 无侧限抗压强度15.effective stress failure envelop 有效应力破坏包线16.effective stress strength parameter 有效应力强度参数十一.本构模型--constitutive model1.elastic model 弹性模型2.nonlinear elastic model 非线性弹性模型3.elastoplastic model 弹塑性模型4.viscoelastic model 粘弹性模型5.boundary surface model 边界面模型6.Du ncan-Chang model 邓肯-张模型7.rigid plastic model 刚塑性模型8.cap model 盖帽模型9.work softening 加工软化10.work hardening 加工硬化11.Cambridge model 剑桥模型12.ideal elastoplastic model 理想弹塑性模型13.Mohr-Coulomb yield criterion 莫尔-库仑屈服准则14.yield surface 屈服面15.elastic half-space foundation model 弹性半空间地基模型16.elastic modulus 弹性模量17.Winkler foundation model 文克尔地基模型十二.地基承载力--bearing capacity of foundation soil1.punching shear failure 冲剪破坏2.general shear failure 整体剪切破化3.local shear failure 局部剪切破坏4.state of limit equilibrium 极限平衡状态5.critical edge pressure 临塑荷载6.stability of foundation soil 地基稳定性7.ultimate bearing capacity of foundation soil 地基极限承载力8.allowable bearing capacity of foundation soil 地基容许承载力十三.土压力--earth pressure1.active earth pressure 主动土压力2.passive earth pressure 被动土压力3.earth pressure at rest 静止土压力4.Coulomb’s earth pressure theory 库仑土压力理论5.Rankine’s earth pressure theory 朗金土压力理论十四.土坡稳定分析--slope stability analysis1.angle of repose 休止角2.Bishop method 毕肖普法3.safety factor of slope 边坡稳定安全系数4.Fellenius method of slices 费纽伦斯条分法5.Swedish circle method 瑞典圆弧滑动法6.slices method 条分法十五.挡土墙--retaining wall1.stability of retaining wall 挡土墙稳定性2.foundation wall 基础墙3.counter retaining wall 扶壁式挡土墙4.cantilever retaining wall 悬臂式挡土墙5.cantilever sheet pile wall 悬臂式板桩墙6.gravity retaining wall 重力式挡土墙7.anchored plate retaining wall 锚定板挡土墙8.anchored sheet pile wall 锚定板板桩墙十六.板桩结构物--sheet pile structure1.steel sheet pile 钢板桩2.reinforced concrete sheet pile 钢筋混凝土板桩3.steel piles 钢桩4.wooden sheet pile 木板桩5.timber piles 木桩十七.浅基础--shallow foundation1.box foundation 箱型基础2.mat(raft) foundation 片筏基础3.strip foundation 条形基础4.spread footing 扩展基础pensated foundation 补偿性基础6.bearing stratum 持力层7.rigid foundation 刚性基础8.flexible foundation 柔性基础9.embedded depth of foundation 基础埋置深度 foundation pressure 基底附加应力11.structure-foundation-soil interaction analysis 上部结构-基础-地基共同作用分析十八.土的动力性质--dynamic properties of soils1.dynamic strength of soils 动强度2.wave velocity method 波速法3.material damping 材料阻尼4.geometric damping 几何阻尼5.damping ratio 阻尼比6.initial liquefaction 初始液化7.natural period of soil site 地基固有周期8.dynamic shear modulus of soils 动剪切模量9.dynamic ma二十.地基基础抗震1.earthquake engineering 地震工程2.soil dynamics 土动力学3.duration of earthquake 地震持续时间4.earthquake response spectrum 地震反应谱5.earthquake intensity 地震烈度6.earthquake magnitude 震级7.seismic predominant period 地震卓越周期8.maximum acceleration of earthquake 地震最大加速度二十一.室内土工实验1.high pressure consolidation test 高压固结试验2.consolidation under K0 condition K0 固结试验3.falling head permeability 变水头试验4.constant head permeability 常水头渗透试验5.unconsolidated-undrained triaxial test 不固结不排水试验(UU)6.consolidated undrained triaxial test 固结不排水试验(CU)7.consolidated drained triaxial test 固结排水试验(CD)paction test 击实试验9.consolidated quick direct shear test 固结快剪试验10.quick direct shear test 快剪试验11.consolidated drained direct shear test 慢剪试验12.sieve analysis 筛分析13.geotechnical model test 土工模型试验14.centrifugal model test 离心模型试验15.direct shear apparatus 直剪仪16.direct shear test 直剪试验17.direct simple shear test 直接单剪试验18.dynamic triaxial test 三轴试验19.dynamic simple shear 动单剪20.free(resonance)vibration column test 自(共)振柱试验二十二.原位测试1.standard penetration test (SPT)标准贯入试验2.surface wave test (SWT) 表面波试验3.dynamic penetration test(DPT) 动力触探试验4.static cone penetration (SPT) 静力触探试验5.plate loading test 静力荷载试验teral load test of pile 单桩横向载荷试验7.static load test of pile 单桩竖向荷载试验8.cross-hole test 跨孔试验9.screw plate test 螺旋板载荷试验10.pressuremeter test 旁压试验11.light sounding 轻便触探试验12.deep settlement measurement 深层沉降观测13.vane shear test 十字板剪切试验14.field permeability test 现场渗透试验15.in-situ pore water pressure measurement 原位孔隙水压量测16.in-situ soil test 原位试验。
结构力学结构力学structural mechanics 结构分析structural analysis 结构动力学structural dynamics 拱Arch 三铰拱three-hinged arch 抛物线拱parabolic arch 圆拱circular arch 穹顶Dome 空间结构space structure 空间桁架space truss 雪载[荷] snow load 风载[荷] wind load 土压力earth pressure 地震载荷earthquake loading 弹簧支座spring support 支座位移support displacement 支座沉降support settlement 超静定次数degree of indeterminacy 机动分析kinematic analysis 结点法method of joints 截面法method of sections 结点力joint forces 共轭位移conjugate displacement 影响线influence line 三弯矩方程three-moment equation 单位虚力unit virtual force 刚度系数stiffness coefficient 柔度系数flexibility coefficient 力矩分配moment distribution 力矩分配法moment distribution method 力矩再分配moment redistribution 分配系数distribution factor 矩阵位移法matri displacement method 单元刚度矩阵element stiffness matrix 单元应变矩阵element strain matrix 总体坐标global coordinates 贝蒂定理Betti theorem 高斯--若尔当消去法Gauss-Jordan elimination Method 屈曲模态buckling mode 复合材料力学mechanics of composites 复合材料composite material 纤维复合材料fibrous composite 单向复合材料unidirectional composite 泡沫复合材料foamed composite 颗粒复合材料particulate composite 层板Laminate 夹层板sandwich panel 正交层板cross-ply laminate 斜交层板angle-ply laminate 层片Ply 多胞固体cellular solid 膨胀Expansion 压实Debulk 劣化Degradation 脱层Delamination 脱粘Debond 纤维应力fiber stress 层应力ply stress 层应变ply strain 层间应力interlaminar stress 比强度specific strength 强度折减系数strength reduction factor 强度应力比strength -stress ratio 横向剪切模量transverse shear modulus 横观各向同性transverse isotropy 正交各向异Orthotropy 剪滞分析shear lag analysis 短纤维chopped fiber 长纤维continuous fiber 纤维方向fiber direction 纤维断裂fiber break 纤维拔脱fiber pull-out 纤维增强fiber reinforcement 致密化Densification 最小重量设计optimum weight design 网格分析法netting analysis 混合律rule of mixture 失效准则failure criterion 蔡--吴失效准则Tsai-W u failure criterion 达格代尔模型Dugdale model 断裂力学fracture mechanics 概率断裂力学probabilistic fracture Mechanics 格里菲思理论Griffith theory 线弹性断裂力学linear elastic fracture mechanics, LEFM 弹塑性断裂力学elastic-plastic fracture mecha-nics, EPFM 断裂Fracture 脆性断裂brittle fracture 解理断裂cleavage fracture 蠕变断裂creep fracture 延性断裂ductile fracture 晶间断裂inter-granular fracture 准解理断裂quasi-cleavage fracture 穿晶断裂trans-granular fracture 裂纹Crack 裂缝Flaw 缺陷Defect 割缝Slit 微裂纹Microcrack 折裂Kink 椭圆裂纹elliptical crack 深埋裂纹embedded crack [钱]币状裂纹penny-shape crack 预制裂纹Precrack 短裂纹short crack 表面裂纹surface crack 裂纹钝化crack blunting 裂纹分叉crack branching 裂纹闭合crack closure 裂纹前缘crack front 裂纹嘴crack mouth 裂纹张开角crack opening angle,COA 裂纹张开位移crack opening displacement, COD 裂纹阻力crack resistance 裂纹面crack surface 裂纹尖端crack tip 裂尖张角crack tip opening angle, CTOA 裂尖张开位移crack tip opening displacement, CTOD 裂尖奇异场crack tip singularity Field 裂纹扩展速率crack growth rate 稳定裂纹扩展stable crack growth 定常裂纹扩展steady crack growth 亚临界裂纹扩展subcritical crack growth 裂纹[扩展]减速crack retardation 止裂crack arrest 止裂韧度arrest toughness 断裂类型fracture mode 滑开型sliding mode 张开型opening mode 撕开型tearing mode 复合型mixed mode 撕裂Tearing 撕裂模量tearing modulus 断裂准则fracture criterion J积分J-integral J阻力曲线J-resistance curve 断裂韧度fracture toughness 应力强度因子stress intensity factor HRR场Hutchinson-Rice-Rosengren Field 守恒积分conservation integral 有效应力张量effective stress tensor 应变能密度strain energy density 能量释放率energy release rate 内聚区cohesive zone 塑性区plastic zone 张拉区stretched zone 热影响区heat affected zone, HAZ 延脆转变温度brittle-ductile transition temperature 剪切带shear band 剪切唇shear lip 无损检测non-destructive inspection 双边缺口试件double edge notched specimen, DEN specimen 单边缺口试件single edge notched specimen, SEN specimen 三点弯曲试件three point bending specimen, TPB specimen 中心裂纹拉伸试件center cracked tension specimen, CCT specimen 中心裂纹板试件center cracked panel specimen, CCP specimen 紧凑拉伸试件compact tension specimen, CT specimen 大范围屈服large scale yielding 小范围攻屈服small scale yielding 韦布尔分布Weibull distribution 帕里斯公式paris formula 空穴化Cavitation 应力腐蚀stress corrosion 概率风险判定probabilistic risk assessment, PRA 损伤力学damage mechanics 损伤Damage 连续介质损伤力学continuum damage mechanics 细观损伤力学microscopic damage mechanics 累积损伤accumulated damage 脆性损伤brittle damage 延性损伤ductile damage 宏观损伤macroscopic damage 细观损伤microscopic damage 微观损伤microscopic damage 损伤准则damage criterion 损伤演化方程damage evolution equation 损伤软化damage softening 损伤强化damage strengthening 损伤张量damage tensor 损伤阈值damage threshold 损伤变量damage variable 损伤矢量damage vector 损伤区damage zone 疲劳Fatigue 低周疲劳low cycle fatigue 应力疲劳stress fatigue 随机疲劳random fatigue 蠕变疲劳creep fatigue 腐蚀疲劳corrosion fatigue 疲劳损伤fatigue damage 疲劳失效fatigue failure 疲劳断裂fatigue fracture 疲劳裂纹fatigue crack 疲劳寿命fatigue life 疲劳破坏fatigue rupture 疲劳强度fatigue strength 疲劳辉纹fatigue striations 疲劳阈值fatigue threshold 交变载荷alternating load 交变应力alternating stress 应力幅值stress amplitude 应变疲劳strain fatigue 应力循环stress cycle 应力比stress ratio 安全寿命safe life 过载效应overloading effect 循环硬化cyclic hardening 循环软化cyclic softening 环境效应environmental effect 裂纹片crack gage 裂纹扩展crack growth, crack Propagation 裂纹萌生crack initiation 循环比cycle ratio 实验应力分析experimental stress Analysis 工作[应变]片active[strain] gage 基底材料backing material 应力计stress gage 零[点]飘移zero shift, zero drift 应变测量strain measurement 应变计strain gage 应变指示器strain indicator 应变花strain rosette 应变灵敏度strain sensitivity 机械式应变仪mechanical strain gage 直角应变花rectangular rosette 引伸仪Extensometer 应变遥测telemetering of strain 横向灵敏系数transverse gage factor 横向灵敏度transverse sensitivity 焊接式应变计weldable strain gage 平衡电桥balanced bridge 粘贴式应变计bonded strain gage 粘贴箔式应变计bonded foiled gage 粘贴丝式应变计bonded wire gage 桥路平衡bridge balancing 电容应变计capacitance strain gage 补偿片compensation technique 补偿技术compensation technique 基准电桥reference bridge 电阻应变计resistance strain gage 温度自补偿应变计self-temperature compensating gage 半导体应变计semiconductor strain Gage 集流器slip ring 应变放大镜strain amplifier 疲劳寿命计fatigue life gage 电感应变计inductance [strain] gage 光[测]力学Photomechanics 光弹性Photoelasticity 光塑性Photoplasticity 杨氏条纹Young fringe 双折射效应birefrigent effect 等位移线contour of equal Displacement 暗条纹dark fringe 条纹倍增fringe multiplication 干涉条纹interference fringe 等差线Isochromatic 等倾线Isoclinic 等和线isopachic 应力光学定律stress- optic law 主应力迹线Isostatic 亮条纹light fringe 光程差optical path difference 热光弹性photo-thermo -elasticity 光弹性贴片法photoelastic coating Method 光弹性夹片法photoelastic sandwich Method 动态光弹性dynamic photo-elasticity 空间滤波spatial filtering 空间频率spatial frequency 起偏镜Polarizer 反射式光弹性仪reflection polariscope 残余双折射效应residual birefringent Effect 应变条纹值strain fringe value 应变光学灵敏度strain-optic sensitivity 应力冻结效应stress freezing effect 应力条纹值stress fringe value 应力光图stress-optic pattern 暂时双折射效应temporary birefringent Effect 脉冲全息法pulsed holography 透射式光弹性仪transmission polariscope 实时全息干涉法real-time holographic interferometry 网格法grid method 全息光弹性法holo-photoelasticity 全息图Hologram 全息照相Holograph 全息干涉法holographic interferometry 全息云纹法holographic moire technique 全息术Holography 全场分析法whole-field analysis 散斑干涉法speckle interferometry 散斑Speckle 错位散斑干涉法speckle-shearing interferometry, shearography 散斑图Specklegram 白光散斑法white-light speckle method 云纹干涉法moire interferometry [叠栅]云纹moire fringe [叠栅]云纹法moire method 云纹图moire pattern 离面云纹法off-plane moire method 参考栅reference grating 试件栅specimen grating 分析栅analyzer grating 面内云纹法in-plane moire method 脆性涂层法brittle-coating method 条带法strip coating method 坐标变换transformation of Coordinates 计算结构力学computational structural mechanics 加权残量法weighted residual method 有限差分法finite difference method 有限[单]元法finite element method 配点法point collocation 里茨法Ritz method 广义变分原理generalized variational Principle 最小二乘法least square method 胡[海昌]一鹫津原理Hu-Washizu principle 赫林格-赖斯纳原理Hellinger-Reissner Principle 修正变分原理modified variational Principle 约束变分原理constrained variational Principle 混合法mixed method 杂交法hybrid method 边界解法boundary solution method 有限条法finite strip method 半解析法semi-analytical method 协调元conforming element 非协调元non-conforming element 混合元mixed element 杂交元hybrid element 边界元boundary element 强迫边界条件forced boundary condition 自然边界条件natural boundary condition 离散化Discretization 离散系统discrete system 连续问题continuous problem 广义位移generalized displacement 广义载荷generalized load 广义应变generalized strain 广义应力generalized stress 界面变量interface variable 节点node, nodal point [单]元Element 角节点corner node 边节点mid-side node 内节点internal node 无节点变量nodeless variable 杆元bar element 桁架杆元truss element 梁元beam element 二维元two-dimensional element 一维元one-dimensional element 三维元three-dimensional element 轴对称元axisymmetric element 板元plate element 壳元shell element 厚板元thick plate element 三角形元triangular element 四边形元quadrilateral element 四面体元tetrahedral element 曲线元curved element 二次元quadratic element 线性元linear element 三次元cubic element 四次元quartic element 等参[数]元isoparametric element 超参数元super-parametric element 亚参数元sub-parametric element 节点数可变元variable-number-node element 拉格朗日元Lagrange element 拉格朗日族Lagrange family 巧凑边点元serendipity element 巧凑边点族serendipity family 无限元infinite element 单元分析element analysis 单元特性element characteristics 刚度矩阵stiffness matrix 几何矩阵geometric matrix 等效节点力equivalent nodal force 节点位移nodal displacement 节点载荷nodal load 位移矢量displacement vector 载荷矢量load vector 质量矩阵mass matrix 集总质量矩阵lumped mass matrix 相容质量矩阵consistent mass matrix 阻尼矩阵damping matrix 瑞利阻尼Rayleigh damping 刚度矩阵的组集assembly of stiffness Matrices 载荷矢量的组集consistent mass matrix 质量矩阵的组集assembly of mass matrices 单元的组集assembly of elements 局部坐标系local coordinate system 局部坐标local coordinate 面积坐标area coordinates 体积坐标volume coordinates 曲线坐标curvilinear coordinates 静凝聚static condensation 合同变换contragradient transformation 形状函数shape function 试探函数trial function 检验函数test function 权函数weight function 样条函数spline function 代用函数substitute function 降阶积分reduced integration 零能模式zero-energy mode P收敛p-convergence H收敛h-convergence 掺混插值blended interpolation 等参数映射isoparametric mapping 双线性插值bilinear interpolation 小块检验patch test 非协调模式incompatible mode 节点号node number 单元号element number 带宽band width 带状矩阵banded matrix 变带状矩阵profile matrix 带宽最小化minimization of band width 波前法frontal method 子空间迭代法subspace iteration method 行列式搜索法determinant search method 逐步法step-by-step method 纽马克法Newmark 威尔逊法Wilson 拟牛顿法quasi-Newtonmethod 牛顿-拉弗森法Newton-Raphson method 增量法incremental method 初应变initial strain 初应力initial stress 切线刚度矩阵tangent stiffness matrix 割线刚度矩阵secant stiffness matrix 模态叠加法mode superposition method 平衡迭代equilibrium iteration 子结构Substructure 子结构法substructure technique 超单元super-element 网格生成mesh generation 结构分析程序structural analysis program 前处理pre-processing 后处理post-processing 网格细化mesh refinement 应力光顺stress smoothing 组合结构composite structure。
固体力学英语词汇翻译(2)裂纹面 crack surface裂纹尖端 crack tip裂尖张角 crack tip opening angle, ctoa裂尖张开位移 crack tip opening displacement, ctod 裂尖奇异场 crack tip singularity field裂纹扩展速率 crack growth rate稳定裂纹扩展 stable crack growth定常裂纹扩展 steady crack growth亚临界裂纹扩展 subcritical crack growth裂纹[扩展]减速 crack retardation止裂 crack arrest止裂韧度 arrest toughness断裂类型 fracture mode滑开型 sliding mode张开型 opening mode撕开型 tearing mode复合型 mixed mode撕裂 tearing撕裂模量 tearing modulus断裂准则 fracture criterionj积分 j-integralj阻力曲线 j-resistance curve断裂韧度 fracture toughness应力强度因子 stress intensity factorhrr场 hutchinson-rice-rosengren field守恒积分 conservation integral有效应力张量 effective stress tensor应变能密度 strain energy density能量释放率 energy release rate内聚区 cohesive zone塑性区 plastic zone张拉区 stretched zone热影响区 heat affected zone, haz延脆转变温度 brittle-ductile transition temperature剪切带 shear band剪切唇 shear lip无损检测 non-destructive inspection双边缺口试件 double edge notched specimen, den specimen 单边缺口试件 single edge notched specimen, sen specimen 三点弯曲试件 three point bending specimen, tpb specimen 中心裂纹拉伸试件center cracked tension specimen, cct specimen中心裂纹板试件 center cracked panel specimen, ccp specimen 紧凑拉伸试件 compact tension specimen, ct specimen大范围屈服 large scale yielding小范围攻屈服 small scale yielding韦布尔分布 weibull distribution帕里斯公式 paris formula空穴化 cavitation应力腐蚀 stress corrosion概率风险判定 probabilistic risk assessment, pra损伤力学 damage mechanics损伤 damage连续介质损伤力学 continuum damage mechanics细观损伤力学 microscopic damage mechanics累积损伤 accumulated damage脆性损伤 brittle damage延性损伤 ductile damage宏观损伤 macroscopic damage细观损伤 microscopic damage微观损伤 microscopic damage损伤准则 damage criterion损伤演化方程 damage evolution equation 损伤软化 damage softening损伤强化 damage strengthening损伤张量 damage tensor损伤阈值 damage threshold损伤变量 damage variable损伤矢量 damage vector损伤区 damage zone疲劳 fatigue低周疲劳 low cycle fatigue应力疲劳 stress fatigue随机疲劳 random fatigue蠕变疲劳 creep fatigue腐蚀疲劳 corrosion fatigue疲劳损伤 fatigue damage疲劳失效 fatigue failure疲劳断裂 fatigue fracture疲劳裂纹 fatigue crack疲劳寿命 fatigue life疲劳破坏 fatigue rupture疲劳强度 fatigue strength疲劳辉纹 fatigue striations疲劳阈值 fatigue threshold交变载荷 alternating load交变应力 alternating stress应力幅值 stress amplitude应变疲劳 strain fatigue应力循环 stress cycle应力比 stress ratio安全寿命 safe life过载效应 overloading effect循环硬化 cyclic hardening循环软化 cyclic softening环境效应 environmental effect裂纹片 crack gage裂纹扩展 crack growth, crack propagation 裂纹萌生 crack initiation循环比 cycle ratio实验应力分析 experimental stress analysis 工作[应变]片 active[strain] gage基底材料 backing material应力计 stress gage零[点]飘移 zero shift, zero drift应变测量 strain measurement应变计 strain gage应变指示器 strain indicator应变花 strain rosette应变灵敏度 strain sensitivity机械式应变仪 mechanical strain gage直角应变花 rectangular rosette引伸仪 extensometer应变遥测 telemetering of strain横向灵敏系数 transverse gage factor横向灵敏度 transverse sensitivity焊接式应变计 weldable strain gage平衡电桥 balanced bridge粘贴式应变计 bonded strain gage粘贴箔式应变计 bonded foiled gage粘贴丝式应变计 bonded wire gage桥路平衡 bridge balancing电容应变计 capacitance strain gage补偿片 compensation technique补偿技术 compensation technique基准电桥 reference bridge电阻应变计 resistance strain gage温度自补偿应变计 self-temperature compensating gage 半导体应变计 semiconductor strain gage集流器 slip ring应变放大镜 strain amplifier疲劳寿命计 fatigue life gage电感应变计 inductance [strain] gage光[测]力学 photomechanics光弹性 photoelasticity光塑性 photoplasticity杨氏条纹 young fringe双折射效应 birefrigent effect等位移线 contour of equal displacement暗条纹 dark fringe条纹倍增 fringe multiplication干涉条纹 interference fringe等差线 isochromatic等倾线 isoclinic等和线 isopachic应力光学定律 stress- optic law主应力迹线 isostatic亮条纹 light fringe光程差 optical path difference热光弹性 photo-thermo -elasticity光弹性贴片法 photoelastic coating method光弹性夹片法 photoelastic sandwich method动态光弹性 dynamic photo-elasticity空间滤波 spatial filtering空间频率 spatial frequency起偏镜 polarizer反射式光弹性仪 reflection polariscope残余双折射效应 residual birefringent effect应变条纹值 strain fringe value应变光学灵敏度 strain-optic sensitivity应力冻结效应 stress freezing effect应力条纹值 stress fringe value应力光图 stress-optic pattern暂时双折射效应 temporary birefringent effect脉冲全息法 pulsed holography透射式光弹性仪 transmission polariscope实时全息干涉法 real-time holographic interferometry网格法 grid method全息光弹性法 holo-photoelasticity全息图 hologram全息照相 holograph全息干涉法 holographic interferometry全息云纹法 holographic moire technique全息术 holography全场分析法 whole-field analysis散斑干涉法 speckle interferometry散斑 speckle错位散斑干涉法speckle-shearing interferometry,shearography散斑图 specklegram白光散斑法 white-light speckle method云纹干涉法 moire interferometry[叠栅]云纹 moire fringe[叠栅]云纹法 moire method云纹图 moire pattern离面云纹法 off-plane moire method参考栅 reference grating试件栅 specimen grating分析栅 analyzer grating面内云纹法 in-plane moire method脆性涂层法 brittle-coating method条带法 strip coating method坐标变换 transformation of coordinates计算结构力学 computational structural mechanics 加权残量法 weighted residual method有限差分法 finite difference method有限[单]元法 finite element method配点法 point collocation里茨法 ritz method广义变分原理 generalized variational principle最小二乘法 least square method胡[海昌]一鹫津原理 hu-washizu principle赫林格-赖斯纳原理 hellinger-reissner principle修正变分原理 modified variational principle约束变分原理 constrained variational principle混合法 mixed method杂交法 hybrid method边界解法 boundary solution method有限条法 finite strip method半解析法 semi-analytical method协调元 conforming element非协调元 non-conforming element混合元 mixed element杂交元 hybrid element边界元 boundary element强迫边界条件 forced boundary condition 自然边界条件 natural boundary condition 离散化 discretization离散系统 discrete system连续问题 continuous problem广义位移 generalized displacement广义载荷 generalized load广义应变 generalized strain广义应力 generalized stress界面变量 interface variable节点 node, nodal point[单]元 element角节点 corner node边节点 mid-side node内节点 internal node无节点变量 nodeless variable杆元 bar element桁架杆元 truss element梁元 beam element二维元 two-dimensional element一维元 one-dimensional element三维元 three-dimensional element轴对称元 axisymmetric element板元 plate element壳元 shell element厚板元 thick plate element三角形元 triangular element四边形元 quadrilateral element四面体元 tetrahedral element曲线元 curved element二次元 quadratic element线性元 linear element三次元 cubic element四次元 quartic element等参[数]元 isoparametric element超参数元 super-parametric element亚参数元 sub-parametric element节点数可变元 variable-number-node element 拉格朗日元 lagrange element拉格朗日族 lagrange family巧凑边点元 serendipity element巧凑边点族 serendipity family无限元 infinite element单元分析 element analysis单元特性 element characteristics刚度矩阵 stiffness matrix几何矩阵 geometric matrix等效节点力 equivalent nodal force节点位移 nodal displacement节点载荷 nodal load位移矢量 displacement vector载荷矢量 load vector质量矩阵 mass matrix集总质量矩阵 lumped mass matrix相容质量矩阵 consistent mass matrix阻尼矩阵 damping matrix瑞利阻尼 rayleigh damping刚度矩阵的组集 assembly of stiffness matrices 载荷矢量的组集 consistent mass matrix质量矩阵的组集 assembly of mass matrices单元的组集 assembly of elements局部坐标系 local coordinate system局部坐标 local coordinate面积坐标 area coordinates体积坐标 volume coordinates曲线坐标 curvilinear coordinates静凝聚 static condensation合同变换 contragradient transformation形状函数 shape function试探函数 trial function检验函数 test function权函数 weight function样条函数 spline function代用函数 substitute function降阶积分 reduced integration零能模式 zero-energy modep收敛 p-convergenceh收敛 h-convergence掺混插值 blended interpolation等参数映射 isoparametric mapping双线性插值 bilinear interpolation小块检验 patch test非协调模式 incompatible mode节点号 node number单元号 element number带宽 band width带状矩阵 banded matrix变带状矩阵 profile matrix带宽最小化 minimization of band width 波前法 frontal method子空间迭代法 subspace iteration method 行列式搜索法 determinant search method 逐步法 step-by-step method纽马克法 newmark威尔逊法 wilson拟牛顿法 quasi-newton method牛顿-拉弗森法 newton-raphson method 增量法 incremental method初应变 initial strain初应力 initial stress切线刚度矩阵 tangent stiffness matrix割线刚度矩阵 secant stiffness matrix模态叠加法 mode superposition method 平衡迭代 equilibrium iteration子结构 substructure子结构法 substructure technique超单元 super-element网格生成 mesh generation结构分析程序 structural analysis program 前处理 pre-processing后处理 post-processing网格细化 mesh refinement应力光顺 stress smoothing组合结构 composite structure。
ansys使用手册(ANSYS manual)The eleventh chapter creates geometric display11.1 display geometry with GUIGeometric display is the display of geometric features of a model (key points, surfaces, nodes, units, loads, etc.). This display is generated mainly during model generation and analysis during load definition. A typical geometric display is shown in figure 11-1.Figure 11-1 a typical geometric displayMany users find and control the geometric display the most convenient way is to use the function of Utility, Menu>Plot and Utility Menu>Plotctrls under the graphics in addition, action and control command can also speak with the following paragraphs.11.2 create the display of entity model entitiesThe following command creates the display of the entity model entitycommandGUI menu pathpurposeAPLOTMainMenu>Preprocessor>Operate>Show Degeneracy>Plot Degen AreasUtility Menu>Plot>AreasUtilityMenu>Plot>Specified Entities>AreasDisplay planEPLOTUtility Menu>Plot>ElementsDisplay unit diagramKPLOTUtility Menu>Plot>KeypointsUtilitymenu>Plot>SpecifiedEntities>KeypointsDisplay key points diagramLAYPLOTUtilityMenu>Plot>Layered ElementsThe stacking order of the display layer and the angular orientation of the layer cell types (such as SOLID46 and SHELL91)LPLOTUtility Menu>Plot>LinesUtilitymenu>Plot>SpecifiedEntities>LinesDisplay line chartNPLOTUtility Menu>Plot>NodesDisplay node diagram/KEPLOTUtility Menu>Plot>ReplotPerform the last display actionVPLOTMainmenu>Preprocessor>Operate>Show Degeneracy>Plot Degen VOLUSDisplay degenerate volume mapControls created before triggering these actions can also produce displays that contain other information, such as lower entity numbers (such as entity numbers associated with selectedunits), loads, and so on.11.3 change the geometry display instructionsIn addition to the features listed below, the eighth chapter applies to any type of display, including the general graphical specification of geometric display.11.3.1 changes the style of displayThe following paragraphs describe some ways to change the model display.The 11.3.1.1 displays the line elements and shell elements as entitiesIf the model contains a one-dimensional element (such as a beam or tube) or a shell element, it can be displayed as an entity in the following manner:Command:/ESHAPEGUI:Utility, Menu>Plot, Ctrls>Style>Size, and, ShapeThe ANSYS program uses a rectangular cross section of the beam and shell for the annular section of the tube. The unit solid constants are usually proportional to the section.Also used the /ESHAPE command to display the SOLID65 unit (Figure 11-2) enhanced direction (rebar), in order to strengthen the direction (rebar) must be visible, with the command /DEVICE (Utility Menu>Plot Ctrls>Device Options) can make the vector mode,也必须用/型命令(实用菜单>绘图控制>样式>隐藏线激活基本绘图类型要观察强化方向,按下列顺序发出命令选项):/重塑,1/类型,基本/设备,向量,在光透射增强作业激光图11-2sold65混凝土单元图11.3.1.2仅仅显示物体的边界进行显示时,也可仅只看物体的边缘,即:可能想去除物体内部单元轮廓。
岩土工程常用英文,注岩必备Soil Mechanics 土力学Geotechnical Engineering 岩土工程1physical properties 物理性质three phases of soil 土的三相组成Physical indexes 物理性质指标Density 密度cohesionless soil 无粘性土cohesive soil 粘性土permeability 渗透性solid 固相liquid 液相vapor phase 气相weathering 风化transportation 搬运sedimentation 沉积original mineral 原生矿物secondary mineral 次生矿物clay mineral 粘土矿物particle size distribution 颗粒级配huge particle group 巨粒(粒组)gross particle group 粗粒(粒组)fine particle group 细粒(粒组)sieve analysis 筛分法hydrometer analysis 水分法coefficient of uniformity 不均匀系数coefficient of curvature 曲率系数three-phase diagram 三相简图mass/quality 质量volume 体积density of soil 土的密度unit weight 容重,重度cutting ring 环刀specific gravity of soil 土的相对密度moisture content 含水率combined water 结合水free water 自由水adustion method 燃烧法void ratio 孔隙比(e)porosity 孔隙率(n)degree of saturation 饱和度bulk density of soil 土的堆积密度(moist) unit weight 湿重度Dry density 干密度Dry unit weight 干重度Saturated density 饱和密度Saturated unit weight 饱和重度Buoyant density 浮密度Buoyant unit weight 浮重度(有效重度)Compactness/density 密实度Void ratio of soil in the loosest/densest state 密实/松散状态土的孔隙比Loose 松散Medium 中密Dense 密实Standard penetration test 标准贯入试验(SPT)Limit water content 界限含水量Shrinkage limit 缩限Plastic limit 塑限Solid 固态Semisolid 半固态Plastic 可塑状态Liquid 流动状态态Cone penetrometer 锥式液限仪Plasticity index 塑性指数Liquidity index 液性指数Undisturbed soil 原状土Disturbed soil 扰动土Liquid-plastic limit combined device 液塑限联合测定仪Sensitivity 灵敏度Thixotropy (粘性土的)触变性Muck 淤泥Mucky soil 淤泥质土以下单词均可表示基础或地基:Foundationsubgradegroundfoundation soilsubsoilfootingbasecompressibility 压缩性silty sand 粉土sand 砂clay 黏土diaphragm wall 隔墙,地下连续墙expansive soil ground 膨胀土地基liquefaction of sand 砂土液化landslide 滑坡triaxial apparatus 三轴试验仪,原位测试仪Finite Element Method 有限单元法clay mineral 黏土质矿物Geosynthetics 土工合成材料artificial ground 人工地基ground treatment 地基处理The Leaning Tower of Pisa 比萨斜塔Coulomb 库伦(库伦土压力理论)Darcy 达西(达西渗流定律)Rankine 朗肯(朗肯土压力理论)Boussinesque 布辛奈斯克(竖向集中力下的地基附加应力提出者)Fellenius 费伦纽斯(瑞典圆弧法分析土坡滑坡)Terzaghi 太沙基(土力学之父)3.geostatic stress 自重应力foundation base pressure 基底压力net foundation pressure 基地附加压力contact pressure 基底压力additional stress 土中附加应力stress state 应力状态self-weight 自重homogeneous soil 均质土layed soil 成层土ground water level 地下水位continuous/strip footing 连续/条形基础vertical uniform load 竖向均布荷载flexible foundation 柔性基础rigid foundation 刚性基础rectangular foundation 矩形基础vertical centric load (矩形面积)竖向中心荷载vertical eccentric load (矩形面积)竖向偏心荷载tension force 拉(应)力inclined eccentric load 斜向偏心荷载vertical point force 竖向点力vertical concentrated load 竖向集中荷载vertical uniform load 竖向均布荷载example 例子solution 解triangularly distributed load 三角形分布荷载horizontal concentrated load 横向集中荷载circular foundation 圆形基础stress concentration 应力集中stress dispersion 应力扩散anisotropic foundation 各向异性基础isotropic 各向同性semi-infinite 半无限(空间)homogeneous 均质的linear elastic material 线弹性材料depth/width/length/height 深/宽/长/高4.Compressibility 压缩性Compressibility characteristics 压缩特征Compressibility parameters 压缩指标Compressive deformation 压缩变形Settlement 沉降One-dimensional compression 一维(无侧向变形)压缩Permeability 渗透性Stress history 应力历史Consolidation 固结Pore volume 孔隙体积Confined compression test 侧限压缩试验(固结试验)Consolidometer 固结测量仪(压缩仪)Porous stone 透水石Specimen 试样Compression 压缩Compression curve 压缩曲线Compression coefficient 压缩系数(a)Compression index 压缩指数(Cc)Compression modulus 压缩模量(Es)Rebounding or swelling curve 回弹曲线Recompression curve 再压缩曲线Deformation modulus 变形模量(E0)Final / ultimate settlement 最终沉降Layerwise summation method 分层总和法(delamination total Method)Stress area method 规范法Coefficient of average additional stress 平均附加应力系数Modified coefficient 修正系数(沉降计算经验系数)Pre-consolidation pressure 先(前)期固结压力Normally consolidated soil 正常固结土Overconsolidated soil 超固结土Overconsolidation ratio 超固结比Underconsolidated soil 欠固结土Distortion settlement 瞬时沉降Primary consolidation settlement 固结沉降Secondary consolidation settlement 次固结沉降Degree of consolidation 固结度Theory of one-dimensional consolidation (太沙基)一维固结理论Darcy’s law 达西定律Excess pore water pressure 孔隙水(超静水)压力Coefficient of consolidation 固结系数Time factor 时间因数(Tv,竖向固结因数)One-way drainage 单面排水Two-way drainage 双面排水5.Shear strength 抗剪强度Mohr-Coulomb failure criterion of soil莫尔-库仑破坏准则(莫尔-库伦强度理论)Limited equilibrium of soil 土的极限平衡Direct shear test apparatus 直剪仪Shear force 剪力Metal shear box 金属剪力盒Normal force 法向力Failure envelope 破坏包线Angle of internal friction 内摩擦角Cohesion 凝聚力Elastic equilibrium 弹性平衡Limit equilibrium 极限平衡State of limit equilibrium of Soil 土的极限平衡状态Stress state 应力状态Mohr’s circle 莫尔圆Sliding surface 滑裂面Laboratory test 室内试验In-situ test 野外(原位)试验Strain-controlled 应变控制式(用来修饰直剪仪,R 注)Stress-controlled 应力控制式(用来修饰直剪仪,R 注)Triaxial test 三轴(压缩)试验Vane shear apparatus test 十字板剪切试验Unconsolidated undrained test 不固结不排水试验Consolidated undrained test 固结不排水试验Consolidated drained test 固结排水试验Major principle stress 最大主应力Minor principle stress 最小主应力Intermediate principle stress 中间主应力6.Lateral Earth Pressure 侧向土压力Retaining structure 挡土结构物Retaining Wall 挡土墙Face 墙面Back 墙背Bottom 墙底Toe 墙趾Heel 墙踵Backfill 墙后填土Earth pressure at rest 静止土压力Active earth pressure 主动土压力Passive earth pressure 被动土压力Earth pressure distribution 土压力分布The total force per unit length of the wall 单位长度墙总力Rankine’s theory of earth pressure 朗肯土压力理论Rigid 刚性的No frictional vertical wall back 光滑竖直墙背Horizontal filling surface 水平填土面Cohesionless soil 无粘性土Cohesive soil 粘性土Failure wedge 破裂楔形体Force polygons 力的多边形Gravity retaining wall 重力式挡土墙Cantilevel retaining wall 悬臂式挡土墙Counterfort retaining wall 扶壁式挡土墙Anchoring technique (土层)锚固技术Geosynthetic reinforced retaining wall 土工合成材料加筋挡土墙Stability 稳定性Bearing capacity /bearing pressure 地基承载力Wall strength 墙身强度Safety against overturning 抗倾覆安全性Safety against sliding 抗滑移安全性。
One Dimensional ElementsIn the finite element method elements are grouped as 1D, 2D and 3D elements. Beams and plates are grouped as structural elements. One dimensional elements are the line segments which are used to model bars and truss. Higher order elements like linear, quadratic and cubic are also available. These elements are used when one of the dimension is very large compared to other two. 2D and 3D elements will be discussed in later chapters.Seven basic steps in Finite Element MethodThese seven steps include∙Modeling∙Discretization∙Stiffness Matrix∙Assembly∙Application of BC’s∙Solution∙ResultsLet’s consider a bar subjected to the forces as shownFirst step is the modeling lets us model it as a stepped shaft consisting of discrete number of elements each having a uniform cross section. Say using three finite elements as shown. Average c/s area within each region is evaluated and used to define elemental area with uniform cross-section.A1= A1’+ A2’/ 2 similarly A2 and A 3 are evaluated Second step is the Discretization that includes both node and element numbering, in this model every element connects two nodes, so to distinguish between node numbering and element numbering elements numbers are encircled as shown.Above system can also be represented as a line segment as shown below.Here in 1D every node is allowed to move only in one direction, hence each node as one degree of freedom. In the present case the model as four nodes it means four dof. Let Q1, Q2, Q3 and Q4 be the nodal displacements at node 1 to node 4 respectively, similarly F1, F2, F3, F4 be the nodal force vector from node 1 to node 4 as shown. When these parameters are represented for a entire structure use capitals which is called global numbering and for representing individual elements use small letters that is called local numbering as shown.This local and global numbering correspondence is established using element connectivity element as shownNow let’s consid er a single element in a natural coordinate system that varies in ξand η, x1be the x coordinate of node 1 and x2be the x coordinate of node 2 as shown below.Let us assume a polynomialNowAfter applying these conditions and solving for constants we havea0=x1+x2/2 a1= x2-x1/2Substituting these constants in above equation we getWhere N1 and N2 are called shape functions also called as interpolation functions.These shape functions can also be derived using nodal displacements say q1 and q2 which are nodal displacements at node1 and node 2 respectively, now assuming the displacement function and following the same procedure as that of nodal coordinate we getU = NqU = NqWhere N is the shape function matrix and q is displacement matrix. Once the displacement is known its derivative gives strain and corresponding stress can be determined as follows.element strain displacement matrixFrom the potential approach we have the expression of asThird step in FEM is finding out stiffness matrix from the above equation we have the value of K asButTherefore now substituting the limits as -1 to +1 because the value of varies between -1 & 1 we haveIntegration of above equations gives K which is given asFourth step is assembly and the size of the assembly matrix is given by number of nodes X degrees of freedom, for the present example that has four nodes and one degree of freedom at each node hence size of the assembly matrix is 4 X 4. At first determine the stiffness matrix of each element say k1, k2 and k3 asSimilarly determine k2 and k3The given system is modeled as three elements and four nodes we have three stiffness matrices.Since node 2 is connected between element 1 and element 2, the elements of second stiffness matrix (k2) gets added to second row second element as shown below similarly for node 3 it gets added to third row third elementFifth step is applying the boundary conditions for a given system. We have the equation of equilibrium KQ=FK = global stiffness matrixQ = displacement matrixF= global force vectorLet Q1, Q2, Q3, and Q4 be the nodal displacements at node 1 to node 4 respectively. And F1, F2, F3, F4 be the nodal load vector acting at node 1 to node 4 respectively.Given system is fixed at one end and force is applied at other end. Since node 1 is fixed displacement at node 1 will be zero, so set q1 =0. And node 2, node 3 and node 4 are free to move hence there will be displacement that has to be determined. But in the load vector because of fixed node 1 there will reaction force say R1. Now replace F1 to R1 and also at node 3 force P is applied hence replace F3 to P. Rest of the terms are zero.Sixth step is solving the above matrix to determine the displacements which can be solved either by∙Elimination method∙Penalty approach methodDetails of these two methods will be seen in later sections.Last step is the presentation of results, finding the parameters like displacements, stresses and other required parameters.Body force distribution for 2 noded bar elementWe derived shape functions for 1D bar, variation of these shape functions is shown below .As a property of shape function the value of N1 should be equal to 1 at node 1 and zero at rest other nodes (node 2).From the potential energy of an elastic body we have the expression of work done by body force asWhere f b is the body acting on the system. We know the displacement function U = N1q1 + N2q2 substitute this U in the above equation we getThis amount of body force will be distributed at 2 nodes hence theexpression as 2 in the denominator.Surface force distribution for 2 noded bar elementNow again taking the expression of work done by surface force from potential energy concept and following the same procedure as that of body we can derive the expression of surface force asWhere T e is element surface force distribution.Methods of handling boundary conditionsWe have two methods of handling boundary conditions namely Elimination method and penalty approach method. Applying BC’s is one of the vital role in FEM improper specification of boundary conditions leads to erroneous results. Hence BC’s need to be accurately modeled.Elimination Method: let us consider the single boundary conditions say Q1 = a1.Extremising results in equilibrium equation.Q = [Q1, Q2, Q3……….Q N]T be the displacement vector andF = [F1, F2, F3…………F N]T be load vectorSay we have a global stiffness matrix asK11K12 (1)K21 K22 (2).K =..K N1 K N2…………..K NNNow potential energy of the form ∏ = ½ Q T KQ-Q T F can written as ∏ = ½ (Q1K11Q1 +Q1K12Q2+…..+ Q1K1N Q N+ Q2K21Q1+Q2K22Q2+………. + Q2K2N Q N………………………………………………………………………………… ..+ Q N K N1Q1+Q N K N2Q2+……. +Q N K NN Q N)-(Q1F1 + Q2F2+…………………+Q N F N) Substituting Q1 = a1 we have∏ = ½ (a1K11a1 +a1K12Q2+…..+ a1K1N Q N+ Q2K21a1+Q2K22Q2+………. + Q2K2N Q N………………………………………………………………………………… ..+ Q N K N1a1+Q N K N2Q2+……. +Q N K NN Q N)-(a1F1 + Q2F2+…………………+Q N F N) Extremizing the potential energyie d∏/dQi = 0 givesWhere i = 2, 3...NK22Q2+K23Q3+………. + K2N Q N = F2– K21a1K32Q2+K33Q3+………. + K3N Q N = F3– K31a1………………………………………………K N2Q2+K N3Q3+………. + K NN Q N = F N– K N1a1 Writing the above equation in the matrix form we getK22K23…………K2N Q2 F2-K21a1K32 K33………….K2N Q3 F3-K31a1. .=. ..K N2 K N3…………..K NN Q N F N-K N1a1Now the N X N matrix reduces to N-1 x N-1 matrix as we know Q1=a1 ie first row and first column are eliminated because of known Q1. Solving above matrix gives displacement components. Knowing the displacement field corresponding stress can be calculated using the relation σ = εBq.Reaction forces at fixed end say at node1 is evaluated using the relation R1= K11Q1+K12Q2+……………+K1N Q N-F1Penalty approach method: let us consider a system that is fixed at both the ends as shownIn penalty approach method the same system is modeled as a spring wherever there is a support and that spring has large stiffness value as shown.Let a1 be the displacement of one end of the spring at node 1 and a3 be displacement at node 3. The displacement Q1at node 1 will be approximately equal to a1, owing to the relatively small resistance offered by the structure. Because of the spring addition at the support the strain energy also comes into the picture of ∏ equation .Therefore equation ∏ becomes∏ = ½ Q T KQ+ ½ C (Q1–a1)2 - Q T FThe choice of C can be done from stiffness matrix asWe may also choose 105 &106 but 104 found more satisfactory on most of the computers.Because of the spring the stiffness matrix has to be modified ie the large number c gets added to the first diagonal element of K and Ca1 gets added to F1 term on load vector. That results in.A reaction force at node 1 equals the force exerted by the spring on the system which is given byTo solve the system again the seven steps of FEM has to be followed, first 2 steps contain modeling and discretization. this result inThird step is finding stiffness matrix of individual elementsSimilarlyNext step is assembly which gives global stiffness matrixNow determine global load vectorWe have the equilibrium condition KQ=FAfter applying elimination method we have Q2 = 0.26mmOnce displacements are known stress components are calculated as followsSolution:Global load vector:We have the equilibrium condition KQ=FAfter applying elimination method and solving matrices we have the value of displacements as Q2 = 0.23 X 10-3mm & Q3 = 2.5X10-4mmSolution:Global stiffness matrix Global load vector:Solving the matrix we haveTemperature effect on 1D bar elementLets us consider a bar of length L fixed at one end whose temperature is increased to ∆T as shown.Because of this increase in temperature stress induced are called as thermal stress and the bar gets expands by a amount equal to α∆TL as shown. The resulting strain is called as thermal strain or initial strainIn the presence of this initial strain variation of stress strain graph is as shown belowWe know thatThereforeThereforeExtremizing the potential energy first term yields stiffness matrix, second term results in thermal load vector and last term eliminates that do not contain displacement filedThermal load vectorFrom the above expression taking the thermal load vector lets derive what is the effect of thermal load.Stress component because of thermal loadWe know ε = Bq and εo = α∆T substituting these in above equation we getSolution:Global stiffness matrix:Thermal load vector:We have the expression of thermal load vector given bySimilarly calculate thermal load distribution for second elementGlobal load vector:From the equation KQ=F we haveAfter applying elimination method and solving the matrix we haveQ2= 0.22mmStress in each element:Quadratic 1D bar elementIn the previous sections we have seen the formulation of 1D linear bar element , now lets move a head with quadratic 1D bar element which leads to for more accurate results . linear element has two end nodes while quadratic has 3 equally spaced nodes ie we are introducing one more node at the middle of 2 noded bar element.Consider a quadratic element as shown and the numbering scheme will be followed as left end node as 1, right end node as 2 and middle node as 3.Let’s assume a polynomial asNow applying the conditions asieSolving the above equations we have the values of constantsAnd substituting these in polynomial we getOrWhere N1 N2 N3 are the shape functions of quadratic elementGraphs show the variation of shape functions within the element .The shape function N1 is equal to 1 at node 1 and zero at rest other nodes (2 and 3). N2 equal to 1 at node 2 and zero at rest other nodes(1 and 3) andN3 equal to 1 at node 3 and zero at rest other nodes(1 and 2)Element strain displacement matrix If the displacement field is known its derivative gives strain and corresponding stress can be determined as followsWKTBy chain ruleNowSplitting the above equation into the matrix form we haveThereforeB is element strain displacement matrix for 3 noded bar element Stiffness matrix:We know the stiffness matrix equationFor an elementTaking the constants outside the integral we getWhereand B TNow taking the product of B T X B and integrating for the limits -1 to +1 we getIntegration of a matrix results inBody force term & surface force term can be derived as same as 2 noded bar element and for quadratic element we haveBody force:Surface force term:This amount of body force and surface force will be distributed at three nodes as the element as 3 equally spaced nodes.Problems on quadratic elementSolution:Global stiffness matrix Global load vectorBy the equilibrium equation KQ=F, solving the matrix we have Q2, Q3 and Q4 valuesStress components in each elementANALYSIS OF TRUSSESA Truss is a two force members made up of bars that are connected at the ends by joints. Every stress element is in either tension or compression. Trusses can be classified as plane truss and space truss.∙Plane truss is one where the plane of the structure remain in plane even after the application of loads∙While space truss plane will not be in a same planeFig shows 2d truss structure and each node has two degrees of freedom. The only difference between bar element and truss element is that in bars both local and global coordinate systems are same where in truss these are different.There are always assumptions associated with every finite element analysis. If all the assumptions below are all valid for a given situation, then truss element will yield an exact solution. Some of the assumptions are:Truss element is only a prismatic member ie cross sectional area is uniform along its lengthIt should be a isotropic materialConstant load ie load is independent of timeHomogenous materialA load on a truss can only be applied at the joints (nodes)Due to the load applied each bar of a truss is either induced with tensile/compressive forcesThe joints in a truss are assumed to be frictionless pin joints Self weight of the bars are neglectedConsider one truss element as shown that has nodes 1 and 2 .The coordinate system that passes along the element (x l axis) is called local coordinate and X-Y system is called as global coordinate system. After the loads applied let the element takes new position say locally node 1 has displaced by an amount q1l and node2 has moved by an amount equal to q2l.As each node has 2 dof in global coordinate system .let node 1 has displacements q1 and q2 along x and y axis respectively similarly q3 and q4 at node 2.Resolving the components q1, q2, q3 and q4 along the bar we get two equations as。