英语专业词汇学复习
- 格式:doc
- 大小:174.50 KB
- 文档页数:13

英语词汇学复习提纲Part I概念题1.(glossary)a list of the difficult words used in a piece of writing or subject,with explanations of their meanings2.(phrase) a group of words that form a unit within a clause3.(expression) unclassified linguistic unit of any length: words, phrases, sentences,paragraphs, etc.4.(diction) the choice of words used in a speech or piece of writing5.(vocabulary) words in general known, learnt, used, etc. or a list of words,usually in alphabetical order and with explanations of their meanings6.(lexicon) all the words and phrases in a language or a dictionary7.(lexis) all the words in a language8.(word) the smallest unit of spoken or written language which has meaning andcan stand alone9.(Etymology) the study of origins and development of words10.(Lexicography) the writing and making of dictionaries11.(Lexical semantics) the study of words and their meanings12.(lexicology) the study of meanings and uses of words13.(morphology) the study of how words are formed in a language14.(phraseology) the words and phrases used in a particular profession or activity, ora particular way of putting words together to express something15.(collocation) a group of words which "naturally" go together through commonusage16.Morpheme: the smallest meaningful linguistic unit of language, not divisible oranalyzable into smaller forms17.Root: a root is the basic unchangeable part of a word, and it conveys the mainlexical meaning of the word.18.A ffix: a collective term for the type of formative that can be used only whenadded to another morpheme. It can further be divided inflectional and derivational types.19.Prefix: a derivational or an inflectional affix that can be added to the beginningof a morpheme.20.S uffix: a derivational or inflectional affix that can be added to the end of amorpheme.21.C ompounding /composition: a word formation process consisting of joining twoor more bases to form a new unit, a compound word.22.D erivation/ affixation: a word-formation process by which new words arecreated by adding a prefix, or suffix or both to the base.23.C onversion: a word-formation process whereby a word of a certain word-class isshifted into a word of another word-class without the addition of an affix.24.I nitialism is a type of shortening, using the first letters of words to form a propername, a technical term or a phrase; it is pronounce letter by letter.25.A cronyms are words formed from the initial letters of the name of anorganization or a scientific term, etc; they are pronounced as words rather than as sequences of letters.26.B lending/hybrid: a word-formation process in which a new word is formed bycombining the meanings and sounds of two words, one of which is not in its full form or both of which are not in their full forms.27.B ack-formation: a term used to refer to a word-formation process by which ashorter word is coined by deletion of a supposed affix from a longer form already present in the language.28.C lipping: a word-formation process by which a word is shortened by deletingone or more syllables from a word (usually a noun), which is also available in its full form.29.M otivation: refers to the connection between word symbol and its sense. MostEnglish words are non-motivated. Motivation can arise in three major ways: phonetic motivation, morphological motivation and semantic motivation.30.P olysemy : a term used in semantic analysis to refer to a lexical item which has arange of different meanings.31.H omonyms: words identical in sound or spelling or both but different inmeaning.32.S ynonyms: words differing in sound but identical or similar in meaning.33.A ntonyms: words that are opposite in meaning34.H yponymy is the relationship which obtains between specific and general lexicalitems, such that the former is included in the latter.35.C ontext in its narrowest sense consists of the lexical items that comeimmediately before and after any word in an act of communication.36.Euphemism: an act of using agreeable language when speaking of anunpleasant or embarrassing fact (such as death, disease, etc) and of taboo subjects (such as sex and the excretive processes of the body).37.M etaphor: is a figure of speech containing an implied comparison based onassociation of similarity, in which a word or phrase ordinarily used for one thing is applied to another, a process which often results in semantic change or figurative extension of meaning.38.M etonymy: a figure of speech by which an object or idea is described by thename of something closely related to it.Part II 常用英语词汇学术语Acronym 首字母拼音词Acronymy首字母拼音法Affix 词缀Affixation 词缀法Antonym 反义词Antonymy 反义关系Back-formation 逆构词,反成法Blend 拼缀词Blending 拼缀法Collocation 搭配,组合Complementaries 互补反义词Complete antonym 完全反义词Composition 复合法Compounding 复合构词法Compound word 复合词、Concept 概念Conceptual meaning 概念意义Connotative meaning 内涵意义Context 语境Conversion 词类转换法Denotative meaning 外延意义Degradation of meaning 词义的降格Derivation 派生法Elevation of meaning 词义的升格Etymology 词源学Euphemism 委婉语Homonymy 同音(形)异义Hyponymy 上下义关系Idiom 成语Inflectional affix 屈折词缀Initialism:首字母缩略词Metaphor:隐喻Metonymy:换喻,转喻,借代Morpheme 词素Morphology 词形学,形态学Motivation of word 词的理据Neologism 新词语Onomatopoeic word 拟声词Phonetics 语音学Polysemy 一词多义Register 语域Root 词根Semantic field语义场Semantics 语义学Synonym 同义词Synonymy 同义关系Word-formation/building 构词法Part III True or False Statements1.It is usual that some affixes have far more frequent productive uses than others.There are some significant relations between affixes, especially antonymy, as with pre- and post-, -full and –less. (T)2.Though most prefixes can occur as independent words, they can on occasion bedetached to permit coordination, as in pre- and post-hysterectomy. (F)pounding can occur only in three main word classes, nouns and to a lesserextent, adjectives and, to least extent, verbs. (F)4.Semantically, compounds can often be identified as having a main stress on thefirst element and a secondary stress on the second element. (F)5.English compounds can be analyzed according to different criteria, such asorthographic criteria, semantic criteria, and phonological criteria. (T)pounds can be divided into three categories according to word classes: nouncompounds, adjective compounds and verb compounds. (T)pounds indicate the relations of the compounding elements by syntacticparaphrases. (T)8.Conversion is the derivational process whereby an item is adapted or convertedto a new word class without the addition of an affix. (T)9.Conversions from verb to noun and from verb to adjective are the mostproductive categories. (F)10.T here are two types of conversion: full conversion and partial conversion. (T)11.T he most important kinds of alteration in conversion are the voicing of finalconsonants, and the shift of stress. (T)12.W ords formed through acronymy are called acronyms or initialisms, dependingon the spelling of the new words. (F)13.B ack-formation is the method of creating new words by removing the supposedsuffixes. (T)14.M otivation has nothing to do with the explanation for the reason that a particularform has a particular meaning. (F)15.T he conceptual meaning of a word is often unstable and hard to determine. (F)16.B y etymological motivation, we mean that the meaning of a particular word isrelated to its origin. (T)17.S ense is concerned with the relationship between the linguistic element and thenon-linguistic world of experience, while reference deals with the inherent meaning of the linguistic form. (F)18.I n semantics, meaning of language is considered as the intrinsic and inherentrelation to the physical world of experience. (T)19.C ontextualism is based on the presumption that one can derive meaning from orreduce meaning to observable contexts. (T)20.T he meaning of a sentence is the sum total of the meanings of all its words andphrases put together. (F)21.B oth semantics and pragmatics study how the speakers of a language choosetheir words to effect successful communication. (F)22.T he meaning of an isolated word from a dictionary is usually abstract andcontext-independent. (T)23.I ndo-European refers to the family languages spoken originally in Europe. (F)24.L atin and French belong to the different language groups. (F)25.E nglish belongs to the West-Germanic language group of Indo-Europeanlanguage family. (T)26.T he first people in England about whose language we have definite knowledgeare the Celts. (T)27.C ertain Germanic tribes, Angles, Saxons, Frisians and Jutes were the founders ofthe English nation. (T)28.O ld English has much less loan words compared with modern English.(T)29.The Norman Conquest virtually introduced French-English bilingualism intoEngland. (T)30.C ollocation is the relationship between two words or groups of words that oftengo together and form a common expression. (T)31.C ollocations are not transparent in meaning; that is, the meaning of the wholecannot be worked out from the meaning of each of the words in it. (F)32.L exical collocations normally consist of nouns, adjectives, verbs andprepositions. (F)33.A fixed lexical collocation is a collocation of two or more co-occurring lexemesin an unchanging syntactic and semantic relationship. (T)34.A Dictionary of the English Language by Dr. Samuel Johnson in 1755 is asymbol for modern English Dictionary. (F)35.W ebster’s two-volume 1828 dictionary, The American Dictionary of the EnglishLanguage, published when he was 70 years old, was by far the largest and the most impressive dictionary produced in America up to that time. (T)36.F rom pronunciation, British dictionaries as well as American ones generally useInternational Phonetic Alphabet. (IPA). (F)37.B ilingual dictionaries usually do not have etymological labels due to thelimitation of the length. (T)Part IV. Practices for Word-formation Processes.Section A: Explain the meanings of the following compounds in English1.Pickpocket2.Housebreaking3.Off-white4.Sleepwalker5.Brainstorming6.Self-styled7.Tenderfoot8.Good-looking9.Quick-freeze10.D ragonflyKeys:1.A person who steals things from people’s pockets2.Entering a building without right or permission in order to commit a crime3.A color that is nor pure white but has some grey or yellow in it4.A person who walks around while asleep5.Method of solving problems in which all the members of a group suggest ideaswhich are then discusseding a name, title etc. which one has given oneself, esp. without having anyright to do so7.A person who has recently arrived in a rough place8.Having a pleasant appearance9.Freeze very quickly for storing so that it keeps its natural qualities10.I nsect with a long thin body and two pairs of wingsSection B 根据例词,写出另外同类型转换的例子1.Garage to garage _______ ______ _______2.Water to water ________ ________ _______3.Core to core _______ ________ _______4.Nurse to nurse _______ ________ _______5.Hand to hand _______ -________ ______6.To release release _______ ________ _______7.To catch catch _______ ________ _______8.To show off show-off ______ ________ ______9.To throw throw ______ ________ ______10.T o cook cook _______ _______ _______11.D ry to dry ________ _______ _______12.B rave to brave _________ _______ _______Section C写出下列截短词的原词1.ad2. Memo3. Auto4. mike5. Bike6. Bus7. phone 8. Champ 9. Photo10. con 11. Co-op 12. Plane13. copter 14. Dorm 15. Rhino16. flu 17. Fridge 18. Gas19. sub 20. Taxi 21. Gym22.hippo 23. Lab 24. Limo25.lunch 26. Math 27. Vet28. zoo 29. Pub 30. PopKeys:2.memorandum 6. Omnibus 10. Convict 11. Co-operative 15. Rhinoceros 16. Influenza18. gasoline 19. Submarine 20. Taxicab22. hippopotamus 24. Limousine 25. Luncheon27. veteran, veterinarian, veterinary28. zoological garden 29 public house 30. Popular music Section D 写出下列首字母缩略词、拼音词的完整写法及汉语意思1.WHO2.ASEAN3.WTO4.ISP5.IT6.WWW7.CPU8.WPS9.GM10.V IP11.C EO12.G MT13.I OC14.C IA15.B BC16.T B17.V OA18.N BA19.F BI20.R OM21.D OS22.B IOS23.U NESCO24.N ATO25.O PEC26.T OEFL27.A IDS28.G PS29.R adar30.S IM31.C DMAPart V Meaning and Sense Relation1.Flowers _______ __________ ____________ _______ _________2.Body parts ________ _________ ________ _________ ________3.Stationary _________ __________ _______ ________ _________Section B 从下列七组词语中各找出一个不属于该组语义场的词:1.P en pencil ink wallpaper pencil-box ruler pads2.S oap towel bathtub oven basin sink perfume3.D river professor clerk student nurse guard porter4.W alk stride pace plunge run stroll roam parade5.C ar truck bus train bicycle airplane steamboat6.R ed green purple pink blue sandy brown orange7.C up mug glass spoon bowl pot plate saucer1.A s lean as _____2.A s long as______3.A s white as_____4.A s flat as _________5.A s warm as_______6.A s yellow as ______7.A s plain as ________8.A s round as _______9.A s naked as _______10.As sweet as _______11. as strong as _______12. as tasteless as ______13. as red as _______14. as plum as ______15. as thick as ______16. as cool as _______Keys:1.skeleton2. arm3. flour4. pancake5. toast6. butter7. ears 8. sausage 9. eggs 10. beans11. onions 12. potatoes 13. beef 14. blackberry 15. porridge 16. a cucumberPart VI 用分类关系画出以下各组词的树形图(不多于5层)1.T rack events, hurdles, jump, high jump, discus throw, field events, throw, events, walk, run, shot put, long jump, hammer throw, relays2.C ow, reptile, organism, plant, porcine, ox, bird, human, mammal, buffalo, bovine, animal, ovine3.A rmy, tank, rifle, armed forces, air force, warships, mine hunter, navy, transport aircraft, fighter-bomber4.P rose, novel, fiction epic, literature, drama, short story, poetry, lyric, novelette, pastoral5.P lane geometry, square, trapezium, plane triangle, quadrilaterals, rectangle, irregular quadrilateral, rhombus, parallelogramsKeys:1.EventsTrack events field eventsWalk run hurdles relays shot put jump throwHigh jump long jump hammer throw discus throw2.OrganismHuman animal plantBird mammal reptileOvine bovine porcineOx cow buffalo3.Armed forcesArmy navy air force Tank rifle warships mine hunter transport aircraft fighter-bomber4.LiteratureProse fiction drama poetryNovel novelette short story epic lyric pastoral5.Plane geometryPlane triangles quadrilateralsIrregular quadrilaterals parallelograms trapeziumSquare rectangle rhombusPart VII 完成下列明喻成语1. as _______ as ink2. as _______as brass3. as ________ as silver4. as _________as crystal5. as ________ as ice6. as ________as pitch7. as ________as bone 8.as ________as a pig9. as ________as a wolf 10. as ________as marble11. as ________as fire 12. as ________as two peas14. as ________as a ghost 15. as _________ as thought16. as rich as _______ 17. As heavy as ______18. as easy as _______- 19. As blind as ______20. as yellow as ________ 21. As ripe as _______\22. as pleased as ________ 23. As green as ______24. as cunning as ________ 25. As thin as ______26. as poor as ________- 27. As gay as _______28. as busy as ________ 29. As soft as ______Keys:1.black2. bold3. bright4. clear5. cold6. dark7. dry 8. fat 9. greedy 10. hard 11. hot 12. like14.mad 15. pale 16. a Jew 17. lead 18. ABC 19. a mole20. a guinea 21. cherry 22. punch 23.grass 24. a fox25. a rake 26. a church mouse 27. a lark 28. a bee 29. Down Part VIII 将下列谚语译成对应的汉语谚语:1.Two heads are better than one.2. The leopard can’t change his spots.3. A bad penny always comes back.4. East or west, home is best.5. After supper walk a while.6. Seeing is believing.7. Never try to prove what nobody doubts.8.All are not thieves that dogs bark at.word专业资料-可复制编辑-欢迎下载9.Anger and haste hinder good counsel.10. When the cat’s away, the mince will play.11.It is as well to know which way the wind blows.12.Sow nothing, reap nothing.13.God’s mill grinds slow but sure.14.He who has health has hope.15.While the grass grows the horse starve.16. You get what you pay for.Keys:1. 三个臭皮匠,胜过诸葛亮2.江山易改,本性难移3. 恶有恶报4.金窝银窝,不如家里草窝5.饭后百步走,活到九十九6.百闻不如一见7.此地无银三百两8.人不可貌相,海水不可斗量9.小不忍则乱大谋10.山中无老虎,猴子称大王11.识时务者为俊杰12.无功不受禄13. 天网恢恢,疏而不漏14.留得青山在,不怕没柴烧15.远水解不了近渴16. 一分价钱一分货。

《英语词汇学》复习资料1Ⅰ. Fill in the blanks.Directions: Complete the following statements with proper words.1.The 1 is the smallest functioning unit in the composition of words.2. 2 are words borrowed early in the past and now are well assimilated intothe English language.3.The problem of interrelation of the various meanings of the same word can bedealt with from two different angles: 3 approach and synchronic approach.4.“Mal-”in “maltreat”is a 4 prefix, while “inter-”in “interstate”is a 5prefix.5.Old English is described as a language of full endings, Middle English languageof 6 endings, and a language of 7 endings.6.In modern English, one may find some 8 words whose sounds suggesttheir meaning, for these words were created by imitating the natural sounds or noises.7.The word meaning is made up of 9 meaning and 10 meaning, andthe later has two components: conceptual meaning and 11 meaning.8.Words that have emotive values may fall into two categories: appreciative or12 .9.13 is thought to be the opposite process of suffixation.10.14 is the formation of new words by combining parts of two words or aword plus a part of another word.11.15 refers to the jargon of criminals. Its use is confined to the sub-culturalgroups, and outsiders can hardly understand it.12.“Pretty”and “handsome”share the same 16 meaning,but differ in 17meaning.13.___18___analysis is a process of breaking down the sense of a word into itsminimal components which are also known as semantic features..14.Radiation and 19 are the two coinages which the development of wordmeaning follows from monosemy to polysemy.15.20 deals with the relationship of inclusion, i.e. the meaning of a more specificword is included in that of another more general word.Ⅱ. Decide whether the following statements are true or false. Write T for “true”and F for “false”.1.Homonyms are descendants of different sources whereas a polysemant is a wordof the same source which has acquired different meanings in the course of development.2.Words of the basic word stock are mostly root words or monosyllabic words, sothey have strong productivity.3.“Can-opener” used as slang to mean “all-purpose key”.4.Native words are neutral in style.5.The Indo-European language family is made up of most languages of Europe, theFar East, and India.6.Borrowing has played a vital role in the development of English vocabulary,particularly in earlier times.7.The smallest functioning unit in the composition of words is morpheme.8.Stem is a form to which affixes of any kind can be added.9.Base is what remains of a word after the removal of all affixes.10.Words created by compounding occupy the highest percentage of the Englishvocabulary.11.“Fore-”in “forehead”and “fore-”in “foreknowledge”belong to two kinds ofprefix.12.Word-building and word-formation are relative synonyms.13.The word manusc ript which originally denotes “handwriting” only has undergonea process of extension of meaning.14.Parent—child and husband—wife are two pairs of converses.15.Policeman, constable, bobby and cop are synonyms differing in intensity.Ⅲ. Answer the following questions briefly.1.What are the characteristics of the basic word stock?2.Why are prefixes and suffixes divided according to different criteria?3.List the four sources of synonyms.4.What are the characteristics of conceptual meaning and associative meaning? Ⅳ. Answer the following questions according to the requirement.Classify the three pairs of antonyms according to types of antonyms you have learned and describe the characteristics of each type of them.interviewer/interviewee; male/female; old /young成考复习资料答案I.Fill in the blanks.1. morpheme2. denizens3. diachronic4. pejorative5. locative6. leveled7. lost8. onomatopoeic9. grammatical10. lexical11.associative 12. pejorative 13. backformation 14. blending15. argot 16. conceptual 17. collocative 18. componential 19.concatenation 20. hyponymyII.Decide whether the following statements are true or false. Write T for “true” and F for “false”.1-5 TTTFT 6-10 TFFFT 11-15 TFFTFIII.Answer the following questions briefly.1.What are the characteristics of the basic word stock?1)All national character 2) stability 3) productivity 4) polysemy5) collocability2.Why are prefixes and suffixes divided according to different criteria?1)Prefixes primarily effect a semantic modification of the base, i.e. prefixes do notgenerally change the word-class of the base but only modify its meaning.2)Suffixes have only a small semantic role and their primary function is to changethe grammatical function of the base, i.e. the change of the word class with a slight modification of meaning.3)So prefixes are categorized on a semantic basis while suffixes are divided on agrammatical basis.3.1)Borrowing; (2) dialects and regional English (3) figurative and euphemisticuse of words (4) coincidence with idiomatic expressions4.What are the characteristics of conceptual meaning and associative meaning?1)Conceptual meaning is the meaning given in the dictionary and forms thecore of word meaning. Being constant and relatively stable, conceptualmeaning forms the basis for communication as the same word generallyhas the same conceptual meaning to the speakers in the same speechcommunity. (3%)2)Associative meaning differs from the conceptual meaning in that it isopen-ended and indeterminate, liable to the influence of such factors asculture, experience, religion, geographical region, class background,education, etc…(3%)Ⅳ. Analyze the following questions and explain them according to the requirement.1.1)Interviewer& interviewee are converses; male & female arecomplementaries; old & young are contraries.2)Complementaries truly represent oppositeness of meaning. They are soopposite to each other that they are mutually exclusive and admit nopossibility between them. The assertion of one is the denial of the other orvice versa. Complementaries are nongradable, and they cannot be used incomparative degrees and do not allow adverbs of intensity like “very”toqualify them.3)Contraries are gradable antonyms. The existence of one is in relation to theother. We can say: A man is rich or very rich and also we can say a man isrich than the other. Contraries are characteristic of semantic polarity. Theseantonyms form part of a scale of values between two poles and canaccommodate a middle ground belonging neither to one pole nor to the other.4)Converses consist of relational opposites. The pairs of words indicatereciprocal social relationships that one of them cannot be used withoutsuggesting the other. It also includes reverse terms, which compriseadjectives and adverbs signifying a quality or verbs and nouns signifying anact or state that reverse or undo the quality, action or state of the other.成考复习资料复习资料2I. 单选题1. In the sentence “I like to see a movie.”, there are ________ functional words.A. 2B. 3C. 4D. 52. Conversion is amethod________________________.A. of turning words of one part of speech to those of a different part of speechB. of converting words of one meaning into different meaningC. of deriving words through grammatical meansD. of changing words in morphological structure3. The following words have derivational affixes EXCEPT ________________.A. subseaB. prewarC. postwarD. desks4. Which of the following statements is false?A. Conversion refers to the use of words of one class as that of a different class.B. Words mainly involved in conversion are nouns, verbs and adverbs.C. Partial conversion and full conversion are concerned with adjectiveswhen converted to nouns.D. The conversion between nouns and verbs may involve a change of stress.5. _________ is the meaning given in the dictionary and forms the core ofword-meaning.A. Grammatical meaningB. Denotative meaningC. Associative meaningD. Connotative meaning6. The words what have emotive content in themselves are said to contain __ meaning.A. collocativeB. affectiveC. stylisticD. denotative7. __________ explains the connection between the literal sense and figurative sense of the word.A. Etymological motivationB. Onomatopoetic motivationC. Morphological motivationD. Semantic motivation8. The following words have inflectional affixes EXCEPT __________.A. worksB. workerC. workingD. worked9. “Smog”is formed by combining “smoke”and “fog”. So it is an example ofA. clippingB. compounding成考复习资料C. blendingD. back-formation10. The word “smog”is created by blending, with the structure of __________.A. head + tailB. head + headC. head + wordD. word + tail11. The most important mode of vocabulary development in present-day English is the creation of new words by means of ________________.A. translation-loansB. emantic loansC. word formationD. borrowings12. Which of the following belongs to a semantic field?A. steed, charger, palfrey, plug, nagB. pony, mustang, mule, stud, mareC. policeman, constable, bobby, copD. domicile, residence, abode, home13. Words which are used to show the attitude of approval are ________________.A. appreciativeB. pejorativeC. conntativeD. collocative14. General features of English contains the following except _________.A. simplicityB. receptivityC. adaptabilityD. imprssiveness15. The most productive means of word-formation in modern English are the following except .A. compoundingB. affixationC. acronymD. conversionII判断题1. The Indo-European language family is made up of most languages of Europe, theFar East, and India. ()2. The word manusc ript which originally denotes “handwriting” only has undergone aprocess of extension of meaning. ()3. The beginning of the Middle English Period was marked by the Norman Conquestwhich brought many Latin words into the English language. ()4. Words of the basic word stock are mostly root words or monosyllabic words, sothey have strong productivity. ()5. Grammatical meaning or a word includes part of speech, tense meaning, andstylistic coloring. ()6. Words created by compounding occupy the highest percentage of the Englishvocabulary. ()7. The marked term of each pair of antonyms covers the sense of the unmarked term.()8. Policeman, constable, bobby and cop are synonyms differing in intensity. ()9. Borrowing has played a vital role in the development of English vocabulary,particularly in earlier times. ()10. “Radiation” shows that the derived meanings of a polysemantic word are not成考复习资料directly related to the primary meaning. ()III简答题1. What are the characteristics of conceptual meaning and associative meaning?2. List different types of associative meaning and define them.答案I. 1-5 AADDB 6-10 BDBCA 11-15 CBADCⅡ. 1-5 TFFTF 6-10 TFFTFⅢ. 1. What are the characteristics of conceptual meaning and associative meaning? Conceptual meaning is the meaning given in the dictionary and forms the core of word meaning. Being constant and relatively stable, conceptual meaning forms the basis for communication as the same word generally has the same conceptual meaning to the speakers in the same speech community. Associativemeaning differs from the conceptual meaning in that it is open-ended and indeterminate, liable to the influence of such factors as culture, experience, religion, geographical region, class background, education, etc…2. List different types of associative meaning and define them.Explain different types of homonyms with examples.Perfect homonyms are known as absolute homonyms, and they are words identical both in sound and spelling. E.g bear (to put up with) and bear(a kind of fruit)Homographs are words identical only in spelling but different in sound and meaning, e.g. sow (to scatter seeds) and sow (female adult pig) Homophones are words identical only in sound but different in spelling and meaning, e.g. dear ( a loved person) and deer (a kind of an animal)复习资料3I.Fill in the blanks.Directions: Complete the following statements with proper words.1.The __1 is the smallest functioning unit in the composition of words.2. 2 are words borrowed early in the past and now are well assimilated intothe English language.3.The problem of interrelation of the various meanings of the same word can bedealt with from two different angles: 3 approach and synchronic approach.4.“Mal” in “maltreat” is a 4 prefix, while “inter-” in “ interstate” is a 5_prefix.5.Old English is described as a language of full endings, Middle Englishlanguage of___6__ endings, and a language of __7__ endings.成考复习资料6.In modern English, one may find some 8 words whose sounds suggesttheir meaning, for these words were created by imitating the natural sounds or noises.7.The word meaning is made up of 9 meaning and 10 meaning, andthe later has two components: conceptual meaning and 11 meaning.8.Words that have emotive values may fall into two categories: appreciative or__12 .9.13 is thought to be the opposite process of suffixation.10.___14__ is the formation of new words by combining parts of two words or aword plus a part of another word.11.15 refers to the jargon of criminals. Its use is confined to the sub-culturalgroups, and outsiders can hardly understand it.12.“Pretty”and “handsome”share the same _16_ meaning, but differ in _17_meaning.13.___18___analysis is a process of breaking down the sense of a word into itsminimal components which are also known as semantic features.14.Radiation and ___19___ are the two coinages which the development of wordmeaning follows from monosemy to polysemy.15.__20____deals with the relationship of inclusion, i.e. the meaning of a morespecific word is included in that of another more general word.Ⅱ. Decide whether the following statements are true or false and write T or F on the answer sheet:1.Homonyms come mainly from borrowing, changes in sound and spelling, anddialects.2.“Radiation”shows that the derived meanings of a polysemantic word are notdirectly related to the primary meaning.3.Borrowing is a very important source of synonyms.4. A word which has a synonym naturally has an antonym.5.Hyponymy deals with the relationship of semantic inclusion.6.Motivation explains the connection between the linguistic form and its meaning.7.Grammatical meaning or a word includes part of speech, tense meaning, andstylistic coloring.8.The origins of the words are a key factor in distinguishing homonyms frompolysemants.9.The marked term of each pair of antonyms covers the sense of the unmarkedterm.10.If the words differ in range and intensity of meaning, the words are not identicalin denotation.11.The beginning of the Middle English Period was marked by the NormanConquest which brought many Latin words into the English language.ponential analysis is to break down. the conceptual sense of a word into itsminimal distinctive components.13.Celtic language made great contributions to the expansion of the Englishvocabulary.14.Native words enjoy the same features as the basic word stock and more.15.Shortening includes clipping and blending.Ⅲ. Answer the following questions briefly.1. Analyze the morphological structures of the following words and point out the types of the morphemes in terms of free and bound morphemes.unbearable international ex-prisoner.2. How would you explain the difference between back formation and suffixation? Give examples to illustrate your point.3. List different types of associative meaning and define them.4. Explain different types of homonyms with examples.Ⅳ. Analyze the following questions and explain them according to the requirement.1. What is the difference between homonyms and polysemants?成考复习资料答案I.Fill in the blanks.1. morpheme2. denizens3. diachronic4. pejorative5. locative6. leveled7. lost8. onomatopoeic9. grammatical 10. lexical 11.associative 12. pejorative 13. backformation 14. blending 15. argot 16. conceptual 17. collocative 18. componential 19. concatenation 20. hyponymyⅡ. Decide whether the following statements are true or false and write T or F in the brackets:1.F 2.F 3.T 4.F 5.T 6. T 7.F 8.T 9.F 10.T11.F 12. F 13. F 14. T 15. TⅢ. Answer the following questions briefly.1. Analyze the morphological structures of the following words and point out the types of the morphemes in terms of free and bound morphemes.unbearable international ex-prisoner.un+bear+able:(1)‘bear’ is a free morpheme, and ‘un’, ‘able’are bound morphemes. inter+nation+al: ‘nation’ is a free morpheme, and ‘inter, al’ are bound morphemes.ex+prison+er: ‘prison’ is a free morpheme, and ‘ex, er’ are bound morphemes.2. How would you explain the difference between back formation and suffixation? Give examples to illustrate your point.1)Back-formation is considered to be the opposite process of suffixation.2)Suffixation is the formation of new words by adding suffixes to bases.3)Backformation is therefore the method of creating words by removing thesupposed suffixes, so called because many of the removed endings are not suffixes but inseparable parts of the word.4)For example, it is a common practice to add –er, -or to verb bases to formagential nouns.5)Reasonably, people make verbs by dropping the ending such as –or in editor, -arin beggar and –er in butler.3. List different types of associative meaning and define them.1)Connotative meaning refers to the overtones or associations suggested by theconceptual meaning, traditionally known as connotations.2)Stylistic meaning refers to stylistic features, which make them appropriate fordifferent styles.3)Affective meaning expresses the speaker’s attitude towards the person or thing inquestion.4)Collocative meaning consists of the associations a word acquires on account ofthe meanings of words which tend to occur in its environment.4. Explain different types of homonyms with examples.(1)Perfect homonyms are known as absolute homonyms, and they are wordsidentical both in sound and spelling. E.g bear (to put up with) and bear (a kind of fruit)(2)Homographs are words identical only in spelling but different in sound andmeaning, e.g. sow (to scatter seeds) and sow (female adult pig)(3)Homophones are words identical only in sound but different in spelling andmeaning, e.g. dear ( a loved person) and deer (a kind of animal)Ⅳ. Analyze the following questions and explain them according to the requirement.1.What is the difference between homonyms and polysemants?1)Perfect homonyms and polysemants are fully identical with reference to spellingand pronunciation, as both have the same orthographical form but different meanings. This creates the problem of differentiation.2)The fundamental difference between homonyms and polysemants lies in the factthat the former refers to different lexemes which have the same form and the latter the one and same lexeme which has several distinguishable meanings.3)One important criterion by which to differentiate them is ‘etymology’, i.e.,homonyms are descendants of different sources whereas a polysemant is a word of the same source which has acquired different meanings in the course of development.4)The second principal consideration is ‘semantic relatedness’. The severalmeanings of a single polysemous lexeme are related and can be traced back to成考复习资料one central meaning. On the other hand, meanings of different homonyms have nothing to do with one another.5)In dictionaries, a polysemant has its meanings all listed under one headwordwhereas homonyms are listed as separate entries.。
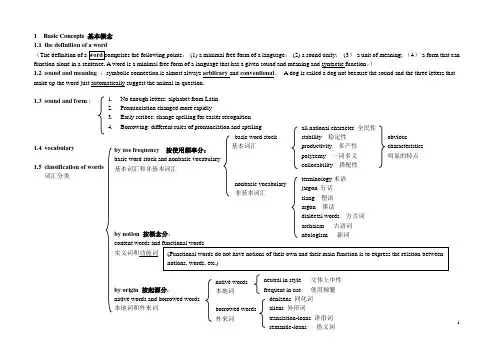
1 B a s i c C o n c e p t s 基本概念1.1 the definition of a word(: (1) a minimal free form of a language ; (2) a sound unity ; (3) a unit of meaning; (4) a form that can function alone in a sentence. A word is a minimal free form of a language that has a given sound and meaning and syntactic function 。
)1.2 sound and meaning :symbolic connection is almost always arbitrary and conventional 。
A dog is called a dog not because the sound and the three letters that make up the word just automatically suggest the animal in question.1.3 sound and form : 1.4 vocabulary 1.5 classification of words 词汇分类 basic word stock 基本词汇nonbasic vocabulary非基本词汇 by use frequency 按使用频率分: basic word stock and nonbasic vocabulary 基本词汇和非基本词汇by notion 按概念分:content words and functional words实义词和功能词by origin 按起源分: native words and borrowed words 本地词和外来词 all national character 全民性stability 稳定性 productivity 多产性 polysemy 一词多义 collocability 搭配性terminology 术语jargon 行话slang 俚语argon 黑话dialectal words 方言词archaism 古语词neologism 新词neutral in style 文体上中性frequent in use 使用频繁native words本地词 borrowed words 外来词 denizens 同化词aliens 异形词translation-loans 译借词1. No enough letters: alphabet from Latin2. Pronunciation changed more rapidly3. Early scribes: change spelling for easier recognition4. Borrowing: different rules of pronunciation and spelling obviouscharacteristics明显的特点(Functional words do not have notions of their own and their main function is to express the relation betweennotions, words, etc.)2D e v e l o p m e n tIt is assumed that the world has approximately 3, 000 (some put it 5, 000 ) languages, which can be grouped into roughly 300 language families on the basis of similarities in their basic word stock and grammar。

词汇学复习资料词汇学复习资料词汇学是语言学的一个重要分支,研究词汇的构成、分类和使用规律。
对于学习一门语言来说,掌握丰富的词汇是非常重要的。
在这篇文章中,我们将提供一些词汇学的复习资料,帮助读者巩固和扩展词汇量。
一、词汇的构成词汇是语言的基本单位,是由一个或多个音素组成的。
在不同的语言中,词汇的构成方式也有所不同。
例如,英语中的词汇主要由字母组成,而汉语中的词汇则由汉字组成。
1. 字母构词法英语中的词汇通常由字母组成,可以通过添加前缀、后缀和词根来构成新的词汇。
例如,单词“unhappiness”由前缀“un-”(表示否定)和词根“happy”组成。
2. 字形构词法汉语中的词汇由汉字组成,可以通过添加偏旁部首、衍生字和合成字来构成新的词汇。
例如,汉字“学”可以通过添加偏旁部首“子”来构成“字”,表示学习。
二、词汇的分类词汇可以按照不同的分类标准进行分类,例如按照词性、语义和用途等。
下面是一些常见的词汇分类。
1. 词性分类词汇可以分为名词、动词、形容词、副词、代词、介词、连词和感叹词等不同的词性。
名词用来表示人、事物或概念,动词用来表示动作或状态,形容词用来描述人或事物的特征,副词用来修饰动词、形容词或其他副词,代词用来代替名词,介词用来表示位置、时间或方式,连词用来连接词语或句子,感叹词用来表示强烈的情感。
2. 语义分类词汇可以按照词义的相似性进行分类。
例如,可以将名词按照人、动物、植物、物体、抽象概念等进行分类;将动词按照行为、状态、感觉、思维等进行分类;将形容词按照颜色、大小、形状、性质等进行分类。
3. 用途分类词汇可以按照在句子中的作用进行分类。
例如,可以将词汇分为实词和虚词。
实词包括名词、动词、形容词和副词,它们在句子中起到实际的意义;虚词包括代词、介词、连词和感叹词,它们在句子中起到连接或修饰的作用。
三、词汇的使用规律词汇的使用规律是指在特定语境中使用词汇的约束条件。
不同的语言和不同的语境中,词汇的使用规律也有所不同。

英语词汇学知识点归纳总结
1.词汇分类:英语词汇可以分为实词和虚词两大类。
实词包括名词、
动词、形容词和副词,是能独立存在并具有词义的词类;虚词包括冠词、
介词、连词、代词和助词,是不能独立存在或不具有词义的词类。
2.词根与词缀:英语词汇中有很多词根和词缀,词根是词的核心部分,词缀是附加在词根上的,可以改变词的词义、词性或词形。
3.词义:英语词汇的词义可以通过定义、同义词、反义词、上下义词
等方式进行描述和解释。
词义可以有直观意义、引申意义和隐喻意义等。
4.词汇建构:英语词汇的建构可以通过合成、派生、转化、缩略等方
式进行。
合成是通过将两个或多个词根组合成一个新词,派生是通过添加
前缀或后缀来构成新词,转化是通过改变词的词类来构成新词,缩略是通
过省略部分词组或词根来构成新词。
5.词汇变化:英语词汇的变化形式包括时态、语态、人称、数和比较等。
词汇的变化形式可以通过词形变化、语法变化和语义变化等方式进行。
6.外借词:英语词汇中存在大量的外借词,这些词汇主要来自拉丁语、希腊语、法语、德语等其他语言。
外借词在英语中经过适当的拼写、读音
和意义调整后被接受和使用。
7.同源词:英语词汇中存在一些同源词,这些词源于同一词根或词源,并在语音、形态或词义上有一定的相似性。
了解同源词可以帮助理解和记
忆词汇。
8.词汇扩展:英语词汇在发展的过程中会发生扩展,即一个词从最初的特定意义扩展到更广泛的意义。
词汇扩展可以通过引申、转义、隐喻等方式进行。
这些是英语词汇学中的一些主要知识点,通过对这些知识点的学习和理解,可以更好地掌握和应用英语词汇。

英语词汇学知识点整理词汇期末复习(C1-C7)Chapter 1⼀、Word 词的定义(1) a minimal free form(最⼩的⾃由形式)(2) a sound unity(3) a semantic unity(meaning)(4) a form that can function alone in a sentence.(具有句法功能)⼆、Vocabulary词汇的定义All the words in a language make up what is generally known as vocabulary.⼀般来说,词汇指的是⼀种语⾔⾥所有单词的总和。
词的总和构成语⾔的词汇。
词与词汇之间的关系是个体与总体之间的关系。
三、Sound&Meaning发⾳和意义The connection between the sound (form) and meaning is arbitrary (任意的) and conventional. ⼆者的关系是约定俗成、随意的四、Sound & Form发⾳和形式(1)The written form of a natural language is the orthographical(正字的)record of the oralform.⾃然语⾔的书写形式是⼝语形式的书写记录。
(2)The reasons of differences occur between sound and form: 发⾳与形式不同的原因:①English alphabet was adopted from the Romans 英语字母表来⾃罗马②the pronunciation has changed more rapidly than spelling over the years. 发⾳改变快速③Differences created by professional scribes. 专业抄写员的不同④More differences brought by the continuing change of sounds and the standardization of spelling.发⾳不断变化,书写标准化。
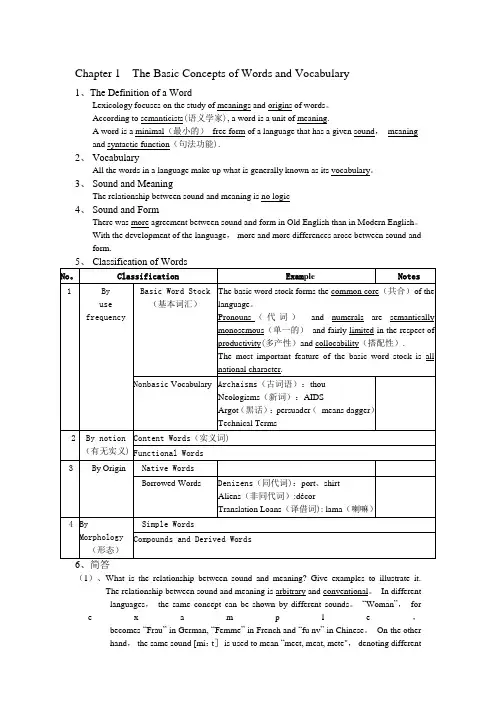
Chapter 1 The Basic Concepts of Words and Vocabulary1、The Definition of a WordLexicology focuses on the study of meanings and origins of words。
According to semanticists(语义学家), a word is a unit of meaning.A word is a minimal(最小的)free form of a language that has a given sound,meaningand syntactic function(句法功能).2、 VocabularyAll the words in a language make up what is generally known as its vocabulary。
3、 Sound and MeaningThe relationship between sound and meaning is no logic4、 Sound and FormThere was more agreement between sound and form in Old English than in Modern English。
With the development of the language,more and more differences arose between sound and form.(1)、What is the relationship between sound and meaning? Give examples to illustrate it.The relationship between sound and meaning is arbitrary and conventional。

词汇学知识点总结词汇学是语言学的一个重要分支,研究的是词汇的形成、结构和意义等方面的问题。
在学习英语等外语的过程中,词汇是其中一个重要的组成部分。
下面,本文将对词汇学的一些知识点进行总结与归纳。
一、词的形态学词的形态学是词汇学中必须掌握的一个重要方面,主要包括词的构词法、屈折变化和派生变化等。
词的构词法指的是如何通过组合原有的词来创造新词,包括派生法、合成法、缩略法、转化法等。
屈折变化指根据语法要求,变化词的形态以表示不同的格、时、数、性等。
派生变化则指通过在原有词基础上添加字母或词缀等来产生新的词。
掌握词的形态学是很有必要的,因为它和词汇的理解和使用密切相关。
二、词的分类在英语中,词可以根据其不同的语法特征被归为不同的类别,常见的类别包括名词、代词、动词、形容词、副词、介词、连词和感叹词等。
不同的词在句子中扮演着不同的角色,掌握各类别之间的区别以及它们在句子中的作用,可以帮助我们更好地理解和表达语言。
三、词义词义是从语言学的角度定义词的意义,包括原义和引申义。
原义指的是一个词最基本的意思,而引申义则是在原义基础上经过延伸、扩展而得到的新意义。
同一个词的不同意义和语言环境等也会导致其含义的变化,例如“bank”既可以表示银行,也可以表示河岸等。
在学习外语的过程中,掌握词义是十分重要的。
四、词汇的学习方法词汇的学习是英语学习中最基础也最重要的部分之一,因此选择适合自己的学习方法对于提高词汇量、扩大词汇面积至关重要。
常用的学习方法包括反复背诵、积累单词簿、整理词根词缀、阅读和听力等。
在学习方法上,以选择适合自己和有用的方法为主,同时注意与语言运用的联系,不断地推广和实践。
五、词汇的应用掌握了词汇学的知识和学习方法后,其实就迈出了学习英语的第一步。
在实际运用中,如何运用得当也是至关重要的环节。
为了提高语言的流利度,需要在口语和书面语两个方面加强实践,增强实际运用能力。
另外,可以较晚多在社交网络等平台上与外国人联系,使用所学的词汇,将知识应用到实际交流之中,效果更佳。

英语词汇学复习资料IntroductionEnglihaaglobal1)Morphology(构词学)2)Semantic(语义学)3)Stylitic(语体学)4)Etymology(词源学)3.研究le某icology的两大方法1)Diachronicapproach:历时语言学2)Synchronicapproach:共时语言学Chapter1Le某icologyandbaicconceptofwordandvocabulary1.Word——Awordiaminimalfreeformofalanguagethathaagivenoundandmeaningandyn tacticfunction.2.Thereinologicalrelationhipbetweenoundandmeaningatheymbolic connectionbetweenthemiarbitrary(任意的)andconventional(约定的,俗称的).3.ound&formTheoundhouldbeimilarto/conitentwiththeform,butthereareomeill ogical不合逻辑的andirregularity不规则的1)influencedbyRoman2)Pronunciationchanged3)earlycribe(抄写员)4)borrowing4.Vocabulary——Notonlycanitrefertothetotalnumberofthewordinalanguage,butitcanta ndforalltheworduedinaparticularhitoricalperiod.5.ClaificationofW ordbaicfull/content实义词native/Anglo-Sa某onwordfrequencynotionoriginnonbaic/vocabularyfunctional/empty功能词borrowed/loanCollocability(可搭配性)neutralintyle(中立性)(2)Twofeatureofnativewordfrequentinue1)wordtakenoverfromforeignlanguageareknowaborrowedwordorloan wordorborrowinginimpleterm.2)ItietimatedthatEnglihborrowingconti tute80percentofthemodernEnglihvocabulary3)TheEnglihlanguagehavat debt.Inanydictionaryome80%oftheentrieareborrowed.Chapter2ThedevelopmentoftheEnglihvocabulary1.OldEnglih属于Indo-Europeanlanguagefamily(印欧语系)——Germanic(日耳曼语系),与德语最相似.2.Hitory1)OldEnglih(450-1150)a.Thefirtpeopleknowntoinhabit(居住)EnglandwereCelt,thelanguagewaCeltic(凯尔特语).b.TheecondlanguagewatheLatin(拉丁语)oftheRomanLegion(罗马军队).Romaninvaion→Anglo-Sa某on 三个事件TheintroductionofChri tianity→拉丁文的涌入Vikinginvaion(北欧海盗)andScandinavian斯堪的纳维亚语传入word文档可自由复制编辑2)MiddleEnglih(1150-1500)在英语发展过程在哪个阶段出现三语鼎立的现象?French,Latin,EnglihinMiddleEnglihperiodeael,port,freight,出现于英语发展的哪个阶段,属于哪一种外来词的引入?MiddleEnglih,Dutch(带来了2500个词汇)3)ModernEnglih (1500-uptonow)TheRenaiance(文艺复兴):LatinandGreekwererecognizedathelanguageoftheWeternworld’gr eatliteraryheritage(文化遗产).TheIndutrialRevolution(工业革命):17世纪中期Withthegrowthofcolonization(殖民化),Britihtentacle(魔爪)beganatretchingoutoftoeverycorneroftheglobe,thuenablingEnglihtoaborb(吸收)wordfromallmajorlanguageoftheworld.十六世纪,有一种新工业Printing出现对词汇的发展产生重要的影响,这导致oundandform出现concord(一致)和tandardization第二次世界大战以后,大量外来词进入英语中,如:Maojacket,blackbelt,kongfu标准化Inflectionallanguage屈折语Analyticallanguage分析语TherapiddevelopmentofmoderncienceandtechnologySocial,economi candpoliticalchangeTheinfluenceofothercultureandlanguageThreemodeofvocabularyde velopmentChapter3ThetructureofEnglihwordword.)Free→cantandaloneaaword/independentofothermorphemeTypeprefi某ation前缀Le某ical→derivational→affi某ationBound→addedtoothermorphemeuffi某ation后缀Grammatical→inflectional2.Morph——Amorphememutberealizedbydicrete(离散的)unit.Theeactualpokenminimalcarrierofmeaningaremorph.Monomorpheni cword——morphemearerealizedbyinglemorph.Allomorph(词素变体)——Somemorphemearerealizedbymorethanonemorphaccordingtotheirpoition .3.Root——Arootithebaicformofaword,whichcannotbefurtheranalyzedwithouttota lloofidentity.(Whatremainofawordaftertheremovalofallaffi某e.)Stem——aformtowhichaffi某eofanykindcanbeadded.Bae——refertoaformtowhichaffi某eofanykindcanbeadded.Itcanbearootortem.atemmayconitofainglerooto rtworootandarootpluaaffi某.atemcanbearootoraformbiggerthanaroot.请加以区别下面两个词的特征:nation,dict加以理论的分析(1)Bothnationanddictbelongtoroot,nationifreeroot,whichcanfun ctionaloneinaentence,Chapter4Word-formationinEnglih1.Therearefourmaintypeofword-formationinEnglih.word文档可自由复制编辑(1)★Affi某ation(prefi某ationanduffi某ation)构词能力最强Affi某ationigenerallydefinedatheformationofwordbyaddingwordformingorde rivationalaffi某etotem.fullconverion——Itcantakeanindefinitarticle(不定冠词)or-(e)toindicateingularorpluralnumber.e.g.black→ablackdrinkable→d rinkablepartialconverion——mutbeuedtogetherwithdefinitearticle.e.g.rich→therich2.Othertype ofword-formation(1)Clipping/hortening——hortenalongerwordbycuttingapartoftheoriginanduingwhatremainintea d.quake(earthquake)dorm(dormitory)pop(popularmuic)flu (influenza)(2)Acronymy首字母缩略法——joiningtheinitialletterofnameofocialandpoliticalorganizationorpe cialphraeandtechnicaltermeg:VOA-VoiceofAmericaTV-televiion绝大多数blending都是nouneg:mog(烟雾)frommoke+fogtele某(电传机)fromteleprinter+e某changeMedicare(医疗保险)frommedical+carelunarnaut(登月宇航员)fromlunar+atronaut(4)Back-formation逆构词法——iaproceofword-formationbywhichawordicreatedbythedeletion删除ofauppoedaffi某.donate(donation)loaf(loafer)babyit(babyitter)laze(lazy)Chapter5Wordmeaning1.Analytical(referential)分析的Reference–therelationhipbetweenlanguageandtheworld.Operational(conte某tual)运用到具体场景中Concept–whichbeyondlanguageithereultofhumancognitionreflectingthe objectiveworldinthehumanmind★Sene1)enedenotetherelationhipinidethelanguage.Theeneofane某preioniitplaceinaytemofemanticrelationhipwithothere某preioninthelanguage.’2)Sincetheeneofane某preioninotathing,itioftendifficulttoaywhatortofidentityiti.Itial oanabtraction.3)Everywordthathameaninghaene(noteverywordhareference)2.Motivation(理据)——accountfortheconnectionbetweenthelinguitic(语言学的)ymbolanditmeaning.non-motivatedOnomatopoeic(拟声的)——thewordwhoeounduggettheirmeaning.Semantic(语义学的)——refertothementalaociationuggetedbytheconceptual概念上的meaningofaword.eg:atthefootofmountain,themouthofriverword文档可自由复制编辑Etymological(词源学的)——Thehitoryoftheworde某plainthemeaningoftheword.3.TypeofmeaningGrammatical语法–refertothatpartofthemeaningofthewordwhichindicategrammaticalconc eptorrelationhipConceptual概念——themeaninggiveninthedictionaryandformthecore核心ofword-meaning.Le某ical词汇Connotative内涵意义eg:Mother—afemaleparent—loveAociative联想Stylitic语体1)formal2)neutral3)informalAffective/Emotive——appreciativeandpejorativeCollocative固定搭配Chapter6SenerelationSynchronicapproachRadiation辐射像车轮式一样进行发展的语义e.g.face,neck(3)TwoproceofdevelopmentConcatenation–meaning―linkingtogether‖串联 2.Homonymy(1)定义:Homonymaregenerallydefinedaworddifferentinmeaningbuteitheridenti cal(完全相同的)bothinoundandpellingoridenticalonlyinoundorpelling.PerfectHomonym同音同形异义词e.g.bear忍受;熊ball球;舞会(2)TypeHomograph同形异义e.g.minute分钟;微小的(1)定义:Synonymareworddifferentinoundandpellingbutmotnearlyalikeore某actlytheameinmeaning.Aboluteregioned地域(BritihEnglih&AmericanEnglih)(2)TypetyliticdegreeRelative(Near)hadeofmeaningemotiverangecollocative搭配Borrowing(themotimportantource)(1)定义:Antonymyiconcernedwithemantic语义学的oppoition.Relative(dependoneachother)eg:parent—child,ell—buy,predeceor前辈—ucceor继承者word文档可自由复制编辑(3)Characteritic1)Antonymareclaifiedonthebaiofemanticoppoition.2)Awordwhichhamorethanonemeaningcanhavemorethanoneantonym.3)Antonymdifferinemanticincluion.4)Contrarytermaregradableantonym,differingindegreeofintenity,oeach haitowncorrepondingoppoition.(4)Ue。

英语词汇学知识点归纳英语词汇学是研究词汇的学科,主要研究词汇的形成、发展、构造和使用规律。
以下是一些英语词汇学的主要知识点。
1. 词汇分类:英语词汇可以分为原生词汇和派生词汇。
原生词汇是指直接来源于英语语言的词汇,而派生词汇则是通过加前缀、后缀或改变词性形成的新词。
2. 词根、前缀和后缀:许多英语单词都有共同的词根,通过添加前缀和后缀,可以构成各种派生词。
例如,'un-'是一个常见的前缀,表示否定,如'unhappy'(不快乐)。
3. 同义词和反义词:同义词具有相似的意思,可以在不同的上下文中互换使用,例如'big'和'large'。
反义词则是意思相反的词汇,如'hot'和'cold'。
4. 合成词:合成词是由两个或多个独立的词组合而成的词汇。
例如,'sunflower'(向日葵)由'sun'(太阳)和'flower'(花)组成。
5. 词源学:词源学研究词汇的起源和演变过程。
许多英语单词来自其他语言,如拉丁语、法语和希腊语。
了解词源可以帮助我们理解词汇的含义和用法。
6. 词义的变化:词汇的意义会随时间和语境的变化而变化。
一些词汇可能会产生新的意义或失去原有的意义。
例如,'mouse'(老鼠)最初是指一种小动物,现在也可以指计算机的输入设备。
7. 词汇的语法功能:词汇在句子中扮演不同的语法角色,如名词、动词、形容词等。
了解词汇的语法功能可以帮助我们正确使用它们。
8. 语义关系:词汇之间存在各种语义关系,如同义关系、反义关系、上下位关系等。
了解这些关系可以帮助我们扩展词汇量,提高语言表达能力。
9. 词汇的习得和记忆:习得和记忆词汇是学习英语的重要一部分。
采用合适的记忆方法,如使用词汇卡片、词汇表等,可以帮助我们更好地掌握词汇。
以上是英语词汇学的一些主要知识点。

英语词汇学复习的内容:一、考试题形式分为:Ⅰ.选择题(20分):完全是考书中的理论与例子的结合,即知识点等。
1-9cahptersⅡ.填空(30分):考定义概念。
1-10chaptersⅢ.(20分)习语英译汉:教材中汉语部分idioms: 习语的特点Ⅳ.(10分) 论述题:第三章为主Ⅴ. 树形图(依据上下义关系作图)(20分):第二、六章二、教材内容简介三、复习内容Introduction 部分Lexicology 这门课算哪一种学科的分支: Lexicology is a branch of linguistics. Lexicology和那些重要的学科建立了联系: 1)Morphology 2) Semantics 3) Stylistics 4) Etymology 5) Lexicography研究lexicology 的两大方法:1) Diachronic approach : 历时语言学2) Synchronic approach : 共时语言学e.g. wife 纵观历时语言学的方法论,woman 词义的变化算是词义变化的哪一种模式?Woman 的词义的变化是Narrowing or specialization第一章词的概述;1.识记:词的定义2.声音与意义3.声音与拼写4.词汇5.词汇的分类What is word ?词具有哪些特点?词的特点也就是对词的名词解释。
1) A word is a minimal free form of a language;2) A sound unity or a given sound ;3) a unit of meaning;4) a form that can function alone in a sentence.以上词的四个特点也就是词的名词解释词的分类(classification of a word)词根据发音可以分为哪两种词?或者说词根据拼写可以分为哪两类词?1) simple words 2) complex words单音节词例子:e.g. Man and fine are simple多音节词例子:e.g. Management, misfortune, blackmailmanagement 可以次划分为manage 和-mentmisfortune 可以次划分为mis- 和fortuneblackmail 次划分为black 和mailWhat is the relationship between sound and meaning?1)There is …no logical relationship between the sound and actual thing.e.g. dog. cat2)The relationship between them is conventional.3) In different languages the same concept can be represented by different sounds. What is relationship between sound and form?1)The written form of a natural language is the written record of the oral form. Naturally the written form should agree with the oral form, such as English language.2)This is fairly true of English in its earliest stage i.e. Old English3)With the development of the language, more and more differences occur between the two.What are the great changes that causes illogical relationship or irregularity between sound and form?1) The internal reason for this is that the English alphabet was adopted from the Romans, which does not have a separate letter to represent each sound in the language so that some letters must do double duty or work together in combination.2) Another reason is that the pronunciation has changed more rapidly than spelling over the years, and in some cases the two have drawn far apart.3) A third reason is that some of the differences were created by the early scribes.4) Finally comes the borrowing, which is an important channel of enriching the English vocabulary.要记住以上四句话中的关键词:1) influenced by Romans2) Pronunciation changed3) early scribes4) borrowing你能不能举出外来语对英语发音,拼写造成不一致的例子有哪些?e.g. stimulus (L) ,fiesta (Sp) ,eureka (Gr), kimono (Jap)外来语对英语造成的最大的影响就是‘sound and form ’不一致。
第五章词的意义课程内容:一、“意义”的意义:所指、概念、语义的内容以及他们之间的区别二、词义的理据:词义的理据主要有四种:拟声理据、形态理据、语义理据、词源理据词义的理据与“约定俗成”的关系三、词义的类别词义主要包括:语法意义、词汇意义、概念意义、关联意义、内含意义、文体意义、感情意义、搭配意义要求:运用本章所学知识增强词义的理解能力,做到用词更加准确和得体第六章语义关系一、多义关系多义关系的形成。
多义关系的两种研究方法。
词义发展的两种模式:辐射型、连锁型二、同形同音异义关系同形同音异义词的定义、类别、来源。
同形同音异义词与多义词的区别及其修辞特色。
三、同义关系同义词的定义、类别、来源和区别同义词的方法。
四、反义关系反义词的定义、类别、特点及其使用。
五、上下义关系上下义词的概念。
上义词和下义词的特点及其使用。
六、语义场语义场的概念。
英语语义场与汉语语义场之间的异同。
第七章语义的演变课程内容:一、词义变化的种类词义的扩大、词义的缩小、词义的升华、词义的降格以及词义的转移四种变化方式在英语词汇发展中的作用二、词义变化的原因词义的演变的语言外部原因:历史原因、阶级原因、心理原因。
语言内部原因:缩略、借用、类推。
第八章语义与语境课程内容:一、语境的种类非语言语境。
语言语境:词汇语境和语法语境语境对词义的影响二、语境的作用语境如何消除歧义,限定所指和提供线索要做到利用语境知识猜测词义第九章英语习语课程内容:一、英语习语的特点英语习语的特点可概括为两点:语义的整体性和结构的稳定性二、英语习语的分类英语习语有不同的分类原则,根据习语的语法功能可分为名词性习语、形容词性习语、动词性习语、副词性习语和句式习语三、英语习语的使用习语的文体色彩;修辞色彩,包括各种修辞格;习语的变异形式。
注意收集习语,并分析它们的构成形式、语法功能和修辞特色。
第十章英语词典一、词典的种类单语词典与双语词典;语文词典与百科词典;大型词典、案头词典和袖珍词典;专用词典。
Motivation of words分类:onomatopoeic motivation, morphological motivation, semantic motivation, etymological motivation. Types of meaning: grammatical ~ & lexical ~; conceptual ~& associative ~(connotative~, stylistic~, affective ~, collocative ~,)Primary meaning is the only meaning that a word had when it was first created. Derived meanings are the meanings that a word gets from the primary meaning at different stages of its development in the course of time.同义关系Synonyms are words which share the same or nearly the same meaning with each other but different in sound and spelling. There are absolute synonyms and relative synonyms which result from borrowing, dialects and regional English, figurative and euphemistic use of words, coincidence with idiomatic expressions. There exists the difference between or among synonyms in terms of their denotation, connotation or application. Absolute synonyms or complete synonyms are words which are identical in meaning in all its aspects. Relative synonyms or near-synonyms are similar or nearly the same in denotation, but embrace different shades of meaning or different degrees of a given quality.3.Sources of Synonyms 1) Borrowing 2)Dialects and regional English 3) Figurative and euphemistic use of words 4) Coincidence with idiomatic expressions4.What are the characteristics of antonyms?1) Antonyms are classified on the basis of semantic opposition 2) A word which has more than one meaning can have more than one antonym. 3) Antonyms differ in semantic inclusion. 4) Contrary terms are gradable antonyms, differing in degree of intenisty, so each has its own corresponding opposite.5.同形同音异义关系Homonymy is one of the features of words that a word is different in meaning from another, but either identical both in sound and spelling or identical only in sound or spelling with the other Homonyms generally fall into three classes: perfect homonyms (same name); homographs (same spelling) and homophones (some sound). Perfect homonyms are those words identical both in sound and spelling, but different in meaning. Homophones refer to the words identical only in sound but different in spelling and meaning6.上下义关系:Hyponymy deals with the relationship of semantic inclusion. That is, the meaning of a more specific word is included in that of another more general word. Superordinates refer to some general words; subordinates denote those more specific words. Hyponymy can be described in terms of tree-like graphs, with higher-order superordinates above the lower subordinates. But their status either as superordinate or subordinate is relative to other terms. For example, horse, dog, pig are subordinates in relation to animal, but superordinates of mare, hound and boar, Animal itself becomesa subordinate of creature. And creature in turn becomes7.词义变化的种类There are five types of meaning, changes: extension, narrowing, degradation, elevation, and transfer among which extension and narrowing are the most common. Changes in meaning can be accounted for from extra-linguistic factors (historical reason, class reason, and psychological reason) and intra-linguistic factors (shortening, the influx of borrowing, and analogy).8.词义的扩大Extension is a process by which a word with a specialized sense is generalized to covera broader or less9.Definite concept. Compare the following;词义的缩小Narrowing is a process by which a word of wider meaning acquires a specialized sense;词义的升华Elevation is a process by which a word moves from a derogatory or neutral sense to a neutral and/or appreciative sense;词义的降格Degradation is a process by which a word of reputation slides into a pejorative use,;词义的转移Transfer is a process by which a word denoting one thing changes to refer to a different but related thing. Paper serves as an example. This word formerly denoted an African plant papyrus, which was once used to make paper. In modern times, paper is made from rags, wood, straw and the like, but theproduct has retained the same name. There is associated transfer. There are other kinds of transfer, such as, concrete to abstract, abstract to concrete and transfer of sensation.10.语境的种类:非语言语境。
1. What is lexicology?Lexico-(语素, meaning ‘word’) Lexicon(词典,字典)Lexical((词的,词汇的) Lexicography((词典编纂) Sociology (社会学) Psychology (心理学)Lexicology is the study of the structure, usage, origins and meanings of words.English lexicology studies English words in different aspects and from different angles.Without grammar we can express little; Without words we can express nothing.2.Define “word”A minimal free form of a language; A sound unity; A unit of meaning; A form that can function alone in a sentence.3. Origin of English WordsNative words 本族词Borrowed words / loan words 外来词Latin ,Scandinavian ,French ,Greek ,Spanish, German, Portuguese, Dutch, Arabic, Chinese, Hebrew, Persian, Japanese, Indonesian, RussianNative words: Anglo-Saxon wordsBody parts—hand, foot, arm, eye, boneNature—land, field, earth, hill, sun, moonTime—month, year, dayAnimals and plants—horse, sheep, dog, lamb, oak, elm, beechAdjectives—black, high, wide, long, smallVerbs—drive, ride, shine, choose, fly, seeAuxiliaries—shall, may, will, do, beBorrowed words P.9The boy kept interrupting the government man.Native words on P.5What features do these words have?Form the basic stock of English language most frequently used,Denote the commonest things necessary for life,Acquired earliest by children,Denote the most basic things in language Borrowingcake, knife, crop, ill, husband, Danishcoolie, litchi, dim sum, typhoon, kaolin, loquat, bureau, honor, literature, court French sauna Finnishhamburger, blitz, zinc Germanmacaroni, sonata, spaghetti Italiansultan, roc, harem, sheik, yashmak Arabicczar, commissar, intelligentsia Russiangeometry, gymnastics, tragedy, myth Greekgenius, memorandum, formula Latinkimono, judo, JapaneseReview questions(1)._____ studies the structure, meanings, origins and usage of words.A. Word formationB. LexicologyC. Morphology(2).There is a logical connection between the sound and meaning of words. This is a ____ view.A. naturalistB. conventionalistC. objective(3).____ is a minimal free form of a language that has a given sound and meaning and syntactic function.A. affixB. phraseC. word4. Morphemeneone morpheme nationtwo morphemes nation+althree morphemes inter+nation+alfour morphemes inter+nation+al+ist5.Word formation: affixation 词缀法Affix词缀(a form that is attached to a morpheme to modify meaning or function)prefix前缀,suffix后缀)root词根(the basic form of a word which cannot be further analyzed without total loss of identity.)6. Word and VocabularyThe general estimate of English vocabulary is over one million words.John has a good knowledge of Middle English vocabulary.The vocabulary of Black English proved too difficult for me.The five-year-old child has acquired a vocabulary of over 2000 words.This article gives a good introduction of specialized vocabulary of nuclear physics.V ocabularyThe total number of the words in a language.All the words used in a particular period.All the words of a given dialect.All the words possessed by a person.All the words of a given discipline.Basic Word Stock and Nonbasic V ocabulary 基本词汇和非基本词汇(The common core of the language.)Rain, snow, fire, water, sun, moon, spring, summer, wind, hill;Head, foot, hand, face, father, mother, sonApple, tree, horse, cow, cat, dog, sheepCome, go, eat, beat, carry, old, youngOne, ten, hundred, I, you, who, but, as, tillCharacteristics of Basic Word StockAll national character 全民性,Stability 稳定性,Productivity 能产性,Polysemy 多义性Do these belong to basic word stock?(1)Do you know what subject matter jurisdiction is?(subject matter jurisdiction诉讼标的管辖权;事物管辖权)(2)Due to Habeas Corpus, you and Miss Fontana had a common law marriage, which entitles her to what is legally referred to as equitable division of the assets.(Due to Habeas Corpus 人身保护法, common law marriage习惯法婚姻, 同居婚姻, equitable division of the assets 资产平均分配)(3)Due to the fact that you retained the residence, Miss Fontana is entitled to full canine property ownership. We’ll enforce that ownership right now.Nonbasic V ocabulary 非基本词汇Photoscanning, indigestion, algebraTerminology 术语(technical terms used in particular disciplines and academic areas)Hypo, buster, bargaining chipsJargon 行话(specialized words used by members of particular arts sciences, trades and professions among themselves)Dough (money), pot (drug) slang 俚语(sub-standard words)Can-opener (all-purpose key), dip (pickpocket) argot黑话(jargon of criminals)Review questions(1) The word ‘limitless’contains two _____.A. affixesB. rootsC. morphemes(2) Which of the following is not true?A. A word is the smallest form of languageB. A word is a sound unity.C.A word has a given meaning.D.A word can be used freely in a sentence.(3) According to semanticists, a word is a unit of ______.A. soundsB. meaningC. formD. function(4) A word is a _____ that stands for something else in the world.A. symbolB. systemC. structureD. pattern(5) How many morphemes does this word have? What kind of morpheme?•misleadingly7. Affixation 词缀法Prefixation 前缀法Negative prefixes表示否定意义的前缀Prefixes of degree or size (extra,hyper,mini,) 表示程度、大小等意义的前缀Prefixes of orientation and attitude 表示倾向和态度等意义的前缀(pro, anti)Locative prefixes表示方位意义的前缀(intra,inter,tele, sub)Prefixes of time and order 表示时间和顺序意义的前缀(ex, fore, post, pre)Number prefixes表示数字的前缀(mono,bi,tri,penta,)Miscillaneous prefixes其他意义的前缀(eco,auto,neo)Class-changing prefixes 改变词性的前缀(a, en, un, de)Suffixation 后缀法Suffixation is the formation of new words by adding suffixes to roots.The primary function of suffixes is to change the grammatical function of roots.Review questions(1) Turn the following into verbs with -en,-ify, -ize(Horror, modern, Memory, apology, False, sterile, Length, intense, Beauty, fat Sympathy, memory)He ____ for interrupting her.She tried to ____ her room with posters and plants.A study has been ordered into the feasibility of _____ the airport’s main runway by 200m. However much they _____ with her, they all felt it was her fault.Soya is excellent food to ___ cattle.Over $40000 had been spent on _____ the station._____ the bottles by immersing them in boiling water for 15 minutes.If you are employed by a company, you’re one of its _____.A politician is someone whose job is politics.The _____ in a discussion are the people who participate in it.A woman who works as a ______ does the same job as a waiter.A ____ is someone who earns their living by playing the piano.If someone examines you, you are the ____ and he/she is the _____.8.Conversion 转类法# Noun attribute•Economy measure 节约措施economic measure 经济措施•Bankruptcy lawyer处理破产诉讼的律师bankrupt businessman破了产的商人•Riot police 防暴警察riotous police 闹事的警察•Danger zone 危险区•Depth charge 深水炸弹• A department decision 部门作出的决定•Impulse buying 凭一时的冲动买东西Bankruptcy lawyer# Noun to verb, verb to nounThe newspapers headlined his long record of accomplishments.He was admitted to the university after a three-year wait.This film is a remake.# Adjective to noun–Partial conversionThese books are intended for the deaf and mute.It is highly important to distinguish between the false and the true–Complete conversionMany classics are now available in bookstores.The police are netting 25 illegals a day in ChicagoThey needed to get there within three days. No ifs and buts were accepted. So Tom got the plans and helicoptered to the host city, while David got visaed up in Berlin and went there by Air France. At the airport shop, he was attracted by some celebrity ashtrays and bought one of them .We can’t stomach such a insult.Robert Acheson roomed right next to me.He wolfed down his lunch.I’m one of his familiars.Poor innocents!The engineers ahed and ouched at the new machines.He Hamleted the chance and then regretted for it.These shoes were an excellent buy.They lifted the rifles and hit him in the small of the back.9.Word Formation: Composition/Compounding• A process of word-formation by which two or more independent words are put together to make one word.Cruise missile 巡航导弹Laserbomb 激光炸弹Fox-bat 狐蝠式战斗机(米格-25)Well-balanced 平衡了的Dog-eat-dog 狗咬狗的Cross-question 盘问Compound nounPoorhouse identity crisis Rainbow fox-bat pickpocket Inpatient Compound adjectiveBittersweet lifelong feelgood inbornOne-man (concert) Around-the-moon (flight)Be-kind-to-animal (campaign) The-end-justifies-the-means (philosophy)One-family-one-child family planning (policy)No-one-dared-to-walk-in-the-street (situation)Compound verbbreast-feed sleepwalk Undertake whitewash Badmouth10. The development of the English VocabularyHistorical Review of English V ocabularyFirst language used in Britain: CelticThe Roman Legions(古罗马军团): Latin(55-54BC)Germanic tribes: Anglo-Saxon (450)Three periods of the English LanguageOld English (450AD—1150AD) when the first Germanic tribes began to settle in England.•Anglo-Saxon—the Germanic tribes•Latin –introduction of Christianity at the end of the 6th century.•Scandinavian –Norwegian and Danish vikings•5000-6000 words; highly inflectedMiddle English (1150—1500) during the Norman Conquest.•French influenceNorman Conquest 1066•9000 French words continually flowed into English•Dutch words entered English with the trade relation.•English regained position of importance–Wycliff translation of the Bible (威克利夫)–Writings of Chaucer and Langland (乔叟、朗兰)–English gradually came back to schoolsModern English (1450—)•Early Modern English (1500-1700) 早期现代英语•Late Modern English (1700-up to now) 后期现代英语Early Modern English (1500-1700) 早期现代英语•The Renaissance 文艺复兴—a new upsurge of learning ancient Greek and Roman classics•1500-1700–over 10,000 new words entered English.•The Bourgeois Revolution, the Industrial Revolution, colonization–absorb words from all major languages in the worldLate Modern English (1700-up to now) 后期现代英语•World wars•Advances in science and technology•Thousands and thousands of new words have been created through borrowing and word-formation•New words in all walks of life: politics, economy, commerce, culture, entertainment, education, sports, transportation, mass media•From synthetic language to analytic languageGrowth of Present-day English V ocabulary 当代英语词汇的发展Reasons for new words: 为什么需要新词To express new things and new changesTo arouse public attention and interestMain sources of new words: 新词所属领域Science and technologyEconomic and political changesInfluence of other cultures and languagesNew WordsNew Words and Changing American Culture 1990, Gozzi:•45% science and technology terms;•24% terms related to life-style•11% social and economic termsModes of V ocabulary Development 词汇的发展方式Creation 创词–formation of new words by using existing materials such as roots, affixes and other elements.Semantic changes 旧词新义– an old form which takes on a new meaning to meet the new need. Borrowing借词—absorbing words from foreign languagesReviving archaic or obsolete words古词和废弃词复活11. Word formation•Encourage Affixation词缀法Derivation派生法•Moonlight Compounding 复合法•to Pocket the money Conversion 转类法•Motel Blending拼缀法•Memo (memorandum) Clipping 截短法•UNESCO Acronymy 首字母拼写法•Babysit (from babysitter) Backformation逆构法•Sandwich Proper noun专有名词Which of the following is a compound?A.PreschoolB. school masterC. At schoolD. schoolingBlending 拼缀法Brunch—breakfast+lunch Motel—motor+hotelBotel—boat+hotel Smog—smoke+fogFour structural types of BlendingBrunch—breakfast+lunch Carbecue—car+barbecueMedicare—medical +care Sitcom –situational+comedyThree stylistic types of Blending•Slang or make-shift wordsinfanticipating--infant+anticipating•Words for science and technologybiorhythm—biological+rhythmlidar—light and radar 激光雷达•Words used in mass mediadawk—dove and hawk 中间立场的Back Formation 逆构法edit—editor caretake—caretaker Peeve—peevish Frivol—frivolous Automate—automation Destruct—destruction Sidle—sidlingClipping 截短法Phone—telephone Zoo—zoological garden Copter--helicopterFridge—refrigerator Flu—influenza Curtsy—courtesyInitialism 首字母连接词VOA WTO YZU CCTVAcronym 首字母拼音词NASA AIDS Radar UESCO Laser12. Motivation 词的理据1.Onomatopoeic motivation 拟声理据2.Semantic motivation 语义理据(figurative sense)3.Morphological motivation 形态理据4.Etymological motivation 词源理据Primary onomatopoeia 基本拟声P.60•The imitation of sound by sound.•Here the sound is truly “an echo to the sense”.e.g.Here it comes sparkling,And there it lies darkling…Spouting and frisking,…Secondary Onomatopoeia•Certain sounds and sound sequences are associated with certain senses in an expressive relationship.e.g.sn/--breath noise; quick separation or movement; creeping:sniff, snuff, snore, snort, snip, snap, snatch, snake, snail, sneak, snoop (窥探) Duplicated words or phrases• A tall clock tick-tocked on the stair.•He gave the deck a thorough riffle-shuffle and then dealt the cards. 他把牌彻底洗过一遍,然后发牌. Metaphor•They were allowed to leapfrog the long lines of traders and get immediate appointments with Chinese representatives•US influence and prestige nosedived in Africa.•The came up with a plan for drastic pruning of the bloated institution.Synecdoche 提喻Sail—ship Hand—man The smiling year—spring A Solomon—a wise man Metonymy 借代• A watched bottle never boils.•He never let his heart rule his head.Analogy 类比•talkathon (马拉松式谈话或座谈节目)•telethon (马拉松式电视广播节目)Color analogy 色彩类比His short play is in the white list. (批准上演的节目名单)grey list—非明文查禁但仍属不合法的人或物grey-collar workers—服务性行业的职工Number analogy数字类比The Fourth World (最贫国集团)The First FamilyThe three R’s (reading, writing arithmetic)Space analogy 地点空间类比•Moonscape—landscape•Marrain(火星上地形)—terrain•Earthrise—sunrise•Spacefaring(航天飞行)--seafaring反义类比•Daylighting –白天兼职,晚上主要工作•Low-rise—低层建筑•Cold line—冷线Analogy 近似类比•Missile gap (美国与苏联在导弹发展上的差距)Generation gap, development gap,Production gap, credibility gap•Watergate13.The Change of Word MeaningAlbatross 信天翁---cause of worries, misfortuneFor it is my special albatross to be related to the guy…. (p.88)Harvest---getting in the crops,crops that you get inBenchEvery time we go there, he is sitting on a park bench.(A piece of furniture for you to sit on)Here is the list of the full bench of the supreme court. (judges)He was brought before the bench. (court)Mary served on the bench and in Congress.Tom got a bench in the Parliament. (seat)This is a team with the best bench. (substitutes)They conducted the bench test successfully.(table)Central signification : furnitureSecondary meaning: judge, seat, substitute ,tableShe took her cat to the bench show. 动物展览评比会Tom’s father worked as a bench scientist for many years. 在实验室工作的科学家I am tired of being a bench warmer, nor do I want to be a bench jockey. 替补队员;在替补队员席上起哄的棒球队员(为干扰对方运动员或裁判员)Treacle1. Pertaining to wild beast.(与野兽有关的。
英语词汇学总结复习资料大家请注意:笔记中大多数是以名词解释的形式出现的,这些是绝对的基础,应该一字不漏的背下来。
其实不少简答题也就是几个定义的汇总,再加上个例子就可以拿满分了。
区分两个词的区别,主要还是指明其各自的定义。
第一章Basic Concepts of Words and Vocabulary1. 词的定义Word ——A word is a minimal free form of a language that has a given sound and meaning and syntactic function.2.声音与意义的关系There is no logical relationship between sound and meaning as the symbolic connection between them is arbitrary and conventional.E.g. “woman” means ’Frau’ in German,’Femme’ in French and ’Funv ’in Chinese. On the other hand,the same sound /rait/ can mean right,rite and write,though denoting different things,yet have the same sound.3.读音与拼写不一致的原因The difference between sound and form result from 4 major factors.(At least 80%of the English words fit consistent spelling patterns)a). the internal reason is English alphabet does not have a separate letter to represent each sound in the language.b). Pronunciation has changed more rapidly than spelling c). Influence of the work of scribes/printing freezes the spelling of words in 1500d). Borrowing of foreign language4. 词汇的含义Vocabulary —— Vocabulary is most commonly used to refer to the sum total of all the words of a language. It can also refer to all the words of a given dialect,a given book,a given displine and all the words possessed by an individual person as well as all the words current in a particular period of time in history.The general estimate of the present day English vocabulary is over 1 million words.5.词汇的分类的原则Classification of Words—by use frequency,by notion,by originthe English vocabulary consist of words of all kinds. they can be classified by different criteria and for different purpose . words may fall into the word stock and nonbasic vocabulary by use frequency, into content words and functional words by notion , and into native words and borrowed words by origin.基本词汇的特点1). Basic word stock – the foundation of the vocabulary.1.all national character (most important)–natural phenomenamost common things and phenomena of the human body and relationsworld around us names of plants and animals action,size,domain,state numerals,pronouns,prep. ,conj.2. stability– they donate the commonest thing necessary to life,they are like to remain unchanged. Only relative,some are undergoing some changes. But the change is slow.e.g. arrow,bow,chariot,knight –past electricity,machine,car,plane ——now3.productivity– they are mostly root words or monosyllabic words,they can form new words with other roots and affixes.e.g. foot – football,footage,footpath,footer4.polysemy – often possess more than one meaning. Become polysemous.e.g. take to move or carry from one place to another to remove5.collocability– quite a number of set expressions,idiomatic usages,proverbial saying and others基本词汇在英语中的地位和重要性The basic word stock is the foundation of the vocabulary accumulated over centuries and forms the common core of the language .though words of the basic word stock constitute a small percentage of the English vocabulary ,yet it is the most important part of it .e.g. heart – a change of heart, a heart of goldNon-basic vocabulary ——(例子)1. terminology –technical terms used in particular disciplines and academic areas as in medicinephotoscanning,hepatitis,indigestion,penicillin,algebra,trigonometry,calculus2. jargon– specialized vocabulary in certain professions.Bottom line,ballpark figures,bargaining chips,hold him back,hold him in,paranoid3. slang——substandard words often used in informal occasionsdough and bread,grass and pot,beaver,smoky,bear,catch,holler,Roger,X-rays,Certain words are labeled slang because of their usage.4. argot – words used by sub-cultured groupscan-opener,dip,persuader cant,jargon ,argot are associated with,or most available to,specific groups of the population.5. dialectal words– only by speakers of the dialectbeauty,chook,cocky,station,auld,build,coo,hame,lough,bog6. archaisms – words no longer in common use or restricted in use. In older poems,legal document and religious writing or speech.7. neologism– newly created words with new meaning e.g. microelectronics,futurology,AIDS,internet,E-mail old meaning acquired new meaning e.g. mouse,monitor2). Content word (notional word)– denote clear notions.Functional word (empty word,form word)– do not have notions of their own,express the relation between notions,words and sentences.a. Content words constitute the main body of the English vocabulary are numerous.Functional words are in a small number.b. Content words are growing.Functional words remain stable.c. Functional words do far more work of expression than content words.3). Native words –are words brought to Britain in the 15 century by the German tribes. Ango-Saxon Words,50,000-60,000What is true of the basic word stock is also true of native world. More are1. neutral in style (not stylistical specific )2. 2.frequent in use (in academic fields and science French,Latin or Greek are used)(usage 70-90%)Borrowed words (loan words,borrowing)–words taken over from foreign language. 80%本族语词在英语中的地位和重要性Native words form the mainstream of the basic word stockand stand at the core of the language .therefore , what is true of the basic word stock is also true of native words.According to the degree of assimilation and manner of borrowing,we can bring the loan words under 4 classes.1.Denizen s–words borrowed early and now are well assimilated into English language.e.g. port from portus(L)shift,change,shirt,pork cup from cuppa(L)2.Aliens– retained their original pronunciation and spellinge.g. décor(F)blitzkreeg(G)emir,intermez,rowtow,bazaar,rajar,status quo3.translation loans– formed from the existing material in the English language but modeled on the patterns taken from another language.1). Word translated according to the meaninge.g. mother tough from lingua maternal(L)black humor from humor noir long time no see,surplus value,master piece 2). Words translated according to the sounde.g. kulak from kyrak(Russ)lama from lama(Tib)ketchup tea4. Semantic loans– their meaning are borrowed from another languagee.g. stupid old dump new sassy dream old joy and peace pioneer old explorer/person doing pioneering work new a member of the young pioneer fresh old impertinent,sassy,cheeky第二章The Development of the English1、Indo-European language family (Europe,the Near East,India)It can be grouped into an Eastern set :Balto –Slavic 、Indo-Iranian、Armenian and Albanian; a Western set: Celtic、Italic 、Hellenic、GermanicIn the Eastern set , Armenian and Albanian are each the only modern language respectively,the Balto –Slavic comprises such modern language such as Prussian、Lithuanian、Polish、Czech、Bulgarian、Slovenian、Russian. In the Indo-Iranian we have Persian, Bengali, Hindi, Romany, the last three of which are derived from the dead language Sanskrit.In the Western set, Greek is the modern language derived from Hellenic. In the Celtic,we find Scottish, Irish,Welsh, Breton. the five Romance language ,namely, Portuguese,Spanish, French, Italian, Roumanian all belong to the Italic through an intermediate language called Latin. The Germanic family consist of the four Northern European language :Norwegian, Icelandic, Danish and Swedish, which are generally known as Scandinavian languages. Then there is German, Dutch, Flemish and English.2、History (时间,历史事件,特征)1)Old English (450-1150)totally 50,000-60,000 words The 1st people known to inhabit England were Celts,the language was Celtic.The second language was the Latin of the Roman Legions. The Germanic tribes called angles,Saxons and Jutes and their language,Anglo-Saxon dominated and blotted out the Celtic. Now people refer to Anglo-Saxon as old English. At the end of 6th century,the introduction of Christianity has a great impact on the English vocabulary. The common practice was to create new words bycombining two native words. In the 9th century,many Scandinavian words came into English. At least 900 words of Scandinavian are in modern English,our daily life and speech.特点:highly inflected language///complex endings or vowel changes (full ending)2)Middle English (1150-1500)English,Latin,FrenchUntil 1066,although there were borrowings from Latin,the influence on English was mainly Germanic. But the Norman Conquest started a continual flow of French words into English.By the end of the 13th century,English gradually come back into public areas.Between 1250 and 150 about 9000 words of French origin pouered into English. 75% of them are till in use today.As many as 2500 words of Dutch origin come into English.特点:fewer inflections leveled ending3)Modern English (1500-up to now)early modern English (1500-1700)late modern English(1700-up to now)The Renaissance(the early period),Latin and Greek were recognized as the languages of the Western world’s great literary herit age.From the 1500’s through the 1700’s ,many writers experimented with words. Over 10000 new words entered the English language .many of these were taken from Latin and Greek .The Industrial Revolution was in the mid-17 century. With the growth of colonization,British tentacles began a stretching out of to every corner of the globe,thus enabling English to absorb words from all major languages of the world.After World War II,many new words have been created to express new ideas,inventions and scientific achievements.More words are created by means of word-formation.thousands and thousands of new words have been enteredto express new ideas inventions,and scientific achievements.more words are created by means of word-formation.in modern English,word endings were mostly lost with just a few exceptions English has evolved from a synthetic language to the present analytic language.science and technology terms make up about 45% of new words. words associated with life-style constitute of 24% and social and economic terms amount to over 10% .mention should be made of an opposite process of development i.e. old words falling out if use.特点:ending are almost lost.3. Three main sources new words当代英语词汇发展的现状New words sweep in at a rate much faster than at any other historical period of time .词汇发展的主要原因1).The rapid development of modern science and technology2).Social: economic and political changes3).The influence of other cultures and languages4. Three modes of vocabulary development(英语发展的三个主要方式:创造新词、旧词新意、借用外来语词)1. Creation –the formation of new words by using the existing materials,namely roots,affixes and other elements. (This is the most important way of vocabulary expansion.)2. Semantic change - an old form which take on a new meaning to meet the new need.3. Borrowing –to take in words from other languages.(played a vital role in the development of vocabulary , particularly in earlier times)4. (Reviving archaic or obsolete)French 30%,Latin 8%,Japanese Italian 7%,Spanish 6%,German Greek 5%,Russian Yiddish 4%第三章Word Formation*1. Morpheme(词素) ——A morpheme is the smallest meaningful unit of a language. (The smallest functional unit in the composition of words.)*2.Morph——A morpheme must be realized by discrete units. These actual spoken minimal carriers of meaning are morphs.3.Monomorphenic words– morphemes are realized by single morphs.4.Allomorph(词素变体)——Some morphemes are realized by more than one morph according to their position. Such alternative morphs are allomorphemes. E.g. the morpheme of plurality (-s)has a number if allomorphemes in different sound context,e.g. in cats/s/,in bags/z/,in matches/iz/.5. Free morphemes or Free root —— The morphemes have complete meaning and van be used as free grammatical units in sentences,e.g. cat,walk. They are identical with root words. morphemes which are independent of other morphemes are considered to be free.6.Bound Morphemes——The morphemes cannot occur as separate words. They are bound to other morphemes to form words,e.g. recollection (re+collect+ion)collect –free morpheme re-and –ion are bound morphemes. (include bound root and affix)Bound morphemes are found in derived words.7.Bound root ——A bound root is that part of the word that carries the fundamental meaning just like a free root. Unlike a free root,it is a bound form and has to combine with other morphemes to make words. Take -dict- for example:it conveysthe meaning of “say or speak” as a Latin root,but not as a word. With the prefix pre-(=before)we obtain the verb predict meaning “tell beforehand”。
Chapter11.word:A word is the smallest unit of spoken written language which has meanings and can stand alone. A word is a minimal free form that has a given sound and meaning and syntactic function2. A word is(1)A minimal free form of a language;(2)a sound unity;(3)a unity of meaning;(4)a form that can function alone in a sentence.3.1 the physical structure of the word(1)Phonetics is the branch of linguistics which studies the characteristics of speech sounds and provides methods for the description, classification and transcription.(2)Morphology is the branch of linguistics, which studies the internal structure of words and rules by which words are formed. In other words, it identifies the smallest meaningful units in a language which are called morphemes and look into the ways the morphemes are arranged to form words.2.2 the semantic structure of the word(1)the word is a unit of speech or writng, which serves the purposeful human communication.(2)the word can be perceived as the total of the sounds that comprise it(3)the word , in writing, is seen as a sequence of letters bounded on either side by a blank space.(4)the word, viewed linguistically, possesses its physical structure (form) and semantic structure (meaning).4.V ocabulary:V ocabulary refers to all the words used in a particular kind of work, business or known to a particular person.5.V ocabulary and Lexis :Lexi, a mass noun, is defined as the total stick of words in a language.6.Lexicology: the study of meaning and uses of words论述对词汇学的理解包括内容:Lexicology is the part of linguistics which studies words. This may include their nature and function as symbols, their meaning, the relationship of their meaning, and the rules of their composition from smaller elements. Lexicology also involves relations between words, which may involve semantics, derivation, usage and sociolinguistic distinctions. Any other issues involved in analyzing the whole lexicon of a languages.Chapter21.The development of English vocabulary. The history of English language can be divided into 3 periods:a/ Old English period (449—1100)the former inhabitants, the Celtic, the Germanic tribes called Angles, Saxons and Jutes Anglo-Saxon as Old English, Old English contains 50-60 thousand words, which consists of the basic word stock.*3个重大事件:(1)Teutonic Conquest 乔顿征服(2)Christianity(Latin word)(3)Scandinavian invasionb/ Middle English period (1100-1500)characterized by the strong influence of French following the Norman Conquest in 1066.The French loan words were found in law and governmental administration (judge, justice)1150-1204:French occupied the dnoinant position1204-1500:English gradually come back to a positionc/ Modern English period (1500--)the early stage of this period ( including the years between 1500-1700), the Renaissance brought great changes to the vocabulary. borrowing from Latin, Latin were now mostly connected with science and abstract ideas. Greek borrowings were mostly literary, technical and scientific words2.The origins of English words2.1 the native words: Anglo-Saxon elements2.2 the loan words: French, Latin, Greek, Scandinavian, other European elements, ChineseChapter31. American English: is the form of English used in the United States. It includes all English dialects used within the United States.2. British English: is the form of English used in the United Kingdom. It includes all English dialects used within the United Kingdom.3. The history:(1)17th century: The English language was first introduced to the American by British colonization, beginning in 1607 in Jamestown, Virginia.Early in the 17th century, the English settlements in Virginia and Massachusetts began the main stream of what we recognize as the American history.The language taken there was Elizabethan English(2)The War of Independence : It marks the end of the colonial period.The political independence brings the tendency to develop an American brand of English.4.Americanism: A word, phrase or idiom characteristic of English as it is spoken in the US.5.Difference: pronunciation / spelling/ vocabulary / habitual expression/ grammarChapter41.Neologism(新词): a neologism is a recently coined word, phrase or usage. It can also be an existing word or phrase which has been assigned a new meaning.Chapter51.morpheme:A morpheme is the minimal meaningful units of which the language is composed. Morphology refers to the study of the internal structure of words, and the rules by which words are formed.2.分类:(1)free morphemes (自由词素)(2)bound morphemes (黏着词素): bound root +affixA. Inflectional affixes (-s ,-es ,ing,-er ,or -(e)d,est)B. Derivational affixes(3)content and function morpheme(4)derivational and Inflectional morpheme3.Root, stem, base词根、词干、词基A root is that part of a word form that remains when all inflectional and derivational affixes have been removed. (词根是所有屈折词缀和派生词缀被去掉后所剩余的那部分)A stem is that part of the word-form which remains when all inflectional affixes have been removed.(词干是所有屈折词缀被去掉后所剩余的那部分)A base refers to a form to which affixes of any kind (both derivational and inflectional) can be added. It can be a root or a stem. (词基是任何一种词缀都可加在上面的形式)词根是所有屈折词缀和派生词缀被去掉后所剩余的那部分。
《英语词汇学》知识点归纳
1.单词的构成:单词由不同的字母组合而成,可以包括前缀、词根、
后缀等。
2.词根和词义:词根是单词中带有基本词义的部分,在单词形态变化
时不会改变。
词根可以是一个字母、一个词或一个词组。
词根可以通过前
缀和后缀的添加,以及音变等形式进行变化。
3.前缀和后缀:前缀是加在词根前面的一种字母或几个字母,可以改
变单词的意义或词类。
后缀是加在词根后面的一种字母或几个字母,可以
改变单词的意义、词类或语法功能。
4.同义词和反义词:同义词是意义相近或相同的词,可以在表达时相
互替换。
反义词则是意义相反的词,通常用来表达对立或对比的关系。
5.词义的变化:词义可以根据语境和用法的不同而发生变化,有时一
个词也可以具有多个意义。
6.词义的分类:词义可以分为字面意义(词义的最基本的意义)、引
申义(从原来的字面意义发展而来的新的意义)和隐喻义(使用一个词来
暗示或比喻另一个概念)。
7.词义的搭配:词义可以和其他词搭配使用,形成固定的词组或短语,这些搭配可以帮助我们更好地理解和运用单词。
8.词法关系:词汇学研究不同词之间的关系,如近义词、反义词、属
于关系等。
9.词源学:词源学研究词语的起源和发展,并追溯词汇的历史和语言
渊源。
10.词汇扩充:词汇学研究如何通过学习和运用词汇扩充词汇量,如学习词根、前缀和后缀的意义和用法,以及拆解和分析复杂单词的方法。
1. What is lexicology?Lexico-(语素, meaning ‘word’) Lexicon(词典,字典)Lexical((词的,词汇的) Lexicography((词典编纂) Sociology (社会学) Psychology (心理学)Lexicology is the study of the structure, usage, origins and meanings of words.English lexicology studies English words in different aspects and from different angles.Without grammar we can express little; Without words we can express nothing.2.Define “word”A minimal free form of a language; A sound unity; A unit of meaning; A form that can function alone in a sentence.3. Origin of English WordsNative words 本族词Borrowed words / loan words 外来词Latin ,Scandinavian ,French ,Greek ,Spanish, German, Portuguese, Dutch, Arabic, Chinese, Hebrew, Persian, Japanese, Indonesian, RussianNative words: Anglo-Saxon wordsBody parts—hand, foot, arm, eye, boneNature—land, field, earth, hill, sun, moonTime—month, year, dayAnimals and plants—horse, sheep, dog, lamb, oak, elm, beechAdjectives—black, high, wide, long, smallVerbs—drive, ride, shine, choose, fly, seeAuxiliaries—shall, may, will, do, beBorrowed words P.9The boy kept interrupting the government man.Native words on P.5What features do these words have?Form the basic stock of English language most frequently used,Denote the commonest things necessary for life,Acquired earliest by children,Denote the most basic things in language Borrowingcake, knife, crop, ill, husband, Danishcoolie, litchi, dim sum, typhoon, kaolin, loquat, bureau, honor, literature, court French sauna Finnishhamburger, blitz, zinc Germanmacaroni, sonata, spaghetti Italiansultan, roc, harem, sheik, yashmak Arabicczar, commissar, intelligentsia Russiangeometry, gymnastics, tragedy, myth Greekgenius, memorandum, formula Latinkimono, judo, JapaneseReview questions(1)._____ studies the structure, meanings, origins and usage of words.A. Word formationB. LexicologyC. Morphology(2).There is a logical connection between the sound and meaning of words. This is a ____ view.A. naturalistB. conventionalistC. objective(3).____ is a minimal free form of a language that has a given sound and meaning and syntactic function.A. affixB. phraseC. word4. Morphemeneone morpheme nationtwo morphemes nation+althree morphemes inter+nation+alfour morphemes inter+nation+al+ist5.Word formation: affixation 词缀法Affix词缀(a form that is attached to a morpheme to modify meaning or function)prefix前缀,suffix后缀)root词根(the basic form of a word which cannot be further analyzed without total loss of identity.)6. Word and VocabularyThe general estimate of English vocabulary is over one million words.John has a good knowledge of Middle English vocabulary.The vocabulary of Black English proved too difficult for me.The five-year-old child has acquired a vocabulary of over 2000 words.This article gives a good introduction of specialized vocabulary of nuclear physics.V ocabularyThe total number of the words in a language.All the words used in a particular period.All the words of a given dialect.All the words possessed by a person.All the words of a given discipline.Basic Word Stock and Nonbasic V ocabulary 基本词汇和非基本词汇(The common core of the language.)Rain, snow, fire, water, sun, moon, spring, summer, wind, hill;Head, foot, hand, face, father, mother, sonApple, tree, horse, cow, cat, dog, sheepCome, go, eat, beat, carry, old, youngOne, ten, hundred, I, you, who, but, as, tillCharacteristics of Basic Word StockAll national character 全民性,Stability 稳定性,Productivity 能产性,Polysemy 多义性Do these belong to basic word stock?(1)Do you know what subject matter jurisdiction is?(subject matter jurisdiction诉讼标的管辖权;事物管辖权)(2)Due to Habeas Corpus, you and Miss Fontana had a common law marriage, which entitles her to what is legally referred to as equitable division of the assets.(Due to Habeas Corpus 人身保护法, common law marriage习惯法婚姻, 同居婚姻, equitable division of the assets 资产平均分配)(3)Due to the fact that you retained the residence, Miss Fontana is entitled to full canine property ownership. We’ll enforce that ownership right now.Nonbasic V ocabulary 非基本词汇Photoscanning, indigestion, algebraTerminology 术语(technical terms used in particular disciplines and academic areas)Hypo, buster, bargaining chipsJargon 行话(specialized words used by members of particular arts sciences, trades and professions among themselves)Dough (money), pot (drug) slang 俚语(sub-standard words)Can-opener (all-purpose key), dip (pickpocket) argot黑话(jargon of criminals)Review questions(1) The word ‘limitless’contains two _____.A. affixesB. rootsC. morphemes(2) Which of the following is not true?A. A word is the smallest form of languageB. A word is a sound unity.C.A word has a given meaning.D.A word can be used freely in a sentence.(3) According to semanticists, a word is a unit of ______.A. soundsB. meaningC. formD. function(4) A word is a _____ that stands for something else in the world.A. symbolB. systemC. structureD. pattern(5) How many morphemes does this word have? What kind of morpheme?•misleadingly7. Affixation 词缀法Prefixation 前缀法Negative prefixes表示否定意义的前缀Prefixes of degree or size (extra,hyper,mini,) 表示程度、大小等意义的前缀Prefixes of orientation and attitude 表示倾向和态度等意义的前缀(pro, anti)Locative prefixes表示方位意义的前缀(intra,inter,tele, sub)Prefixes of time and order 表示时间和顺序意义的前缀(ex, fore, post, pre)Number prefixes表示数字的前缀(mono,bi,tri,penta,)Miscillaneous prefixes其他意义的前缀(eco,auto,neo)Class-changing prefixes 改变词性的前缀(a, en, un, de)Suffixation 后缀法Suffixation is the formation of new words by adding suffixes to roots.The primary function of suffixes is to change the grammatical function of roots.Review questions(1) Turn the following into verbs with -en,-ify, -ize(Horror, modern, Memory, apology, False, sterile, Length, intense, Beauty, fat Sympathy, memory)He ____ for interrupting her.She tried to ____ her room with posters and plants.A study has been ordered into the feasibility of _____ the airport’s main runway by 200m. However much they _____ with her, they all felt it was her fault.Soya is excellent food to ___ cattle.Over $40000 had been spent on _____ the station._____ the bottles by immersing them in boiling water for 15 minutes.If you are employed by a company, you’re one of its _____.A politician is someone whose job is politics.The _____ in a discussion are the people who participate in it.A woman who works as a ______ does the same job as a waiter.A ____ is someone who earns their living by playing the piano.If someone examines you, you are the ____ and he/she is the _____.8.Conversion 转类法# Noun attribute•Economy measure 节约措施economic measure 经济措施•Bankruptcy lawyer处理破产诉讼的律师bankrupt businessman破了产的商人•Riot police 防暴警察riotous police 闹事的警察•Danger zone 危险区•Depth charge 深水炸弹• A department decision 部门作出的决定•Impulse buying 凭一时的冲动买东西Bankruptcy lawyer# Noun to verb, verb to nounThe newspapers headlined his long record of accomplishments.He was admitted to the university after a three-year wait.This film is a remake.# Adjective to noun–Partial conversionThese books are intended for the deaf and mute.It is highly important to distinguish between the false and the true–Complete conversionMany classics are now available in bookstores.The police are netting 25 illegals a day in ChicagoThey needed to get there within three days. No ifs and buts were accepted. So Tom got the plans and helicoptered to the host city, while David got visaed up in Berlin and went there by Air France. At the airport shop, he was attracted by some celebrity ashtrays and bought one of them .We can’t stomach such a insult.Robert Acheson roomed right next to me.He wolfed down his lunch.I’m one of his familiars.Poor innocents!The engineers ahed and ouched at the new machines.He Hamleted the chance and then regretted for it.These shoes were an excellent buy.They lifted the rifles and hit him in the small of the back.9.Word Formation: Composition/Compounding• A process of word-formation by which two or more independent words are put together to make one word.Cruise missile 巡航导弹Laserbomb 激光炸弹Fox-bat 狐蝠式战斗机(米格-25)Well-balanced 平衡了的Dog-eat-dog 狗咬狗的Cross-question 盘问Compound nounPoorhouse identity crisis Rainbow fox-bat pickpocket Inpatient Compound adjectiveBittersweet lifelong feelgood inbornOne-man (concert) Around-the-moon (flight)Be-kind-to-animal (campaign) The-end-justifies-the-means (philosophy)One-family-one-child family planning (policy)No-one-dared-to-walk-in-the-street (situation)Compound verbbreast-feed sleepwalk Undertake whitewash Badmouth10. The development of the English VocabularyHistorical Review of English V ocabularyFirst language used in Britain: CelticThe Roman Legions(古罗马军团): Latin(55-54BC)Germanic tribes: Anglo-Saxon (450)Three periods of the English LanguageOld English (450AD—1150AD) when the first Germanic tribes began to settle in England.•Anglo-Saxon—the Germanic tribes•Latin –introduction of Christianity at the end of the 6th century.•Scandinavian –Norwegian and Danish vikings•5000-6000 words; highly inflectedMiddle English (1150—1500) during the Norman Conquest.•French influenceNorman Conquest 1066•9000 French words continually flowed into English•Dutch words entered English with the trade relation.•English regained position of importance–Wycliff translation of the Bible (威克利夫)–Writings of Chaucer and Langland (乔叟、朗兰)–English gradually came back to schoolsModern English (1450—)•Early Modern English (1500-1700) 早期现代英语•Late Modern English (1700-up to now) 后期现代英语Early Modern English (1500-1700) 早期现代英语•The Renaissance 文艺复兴—a new upsurge of learning ancient Greek and Roman classics•1500-1700–over 10,000 new words entered English.•The Bourgeois Revolution, the Industrial Revolution, colonization–absorb words from all major languages in the worldLate Modern English (1700-up to now) 后期现代英语•World wars•Advances in science and technology•Thousands and thousands of new words have been created through borrowing and word-formation•New words in all walks of life: politics, economy, commerce, culture, entertainment, education, sports, transportation, mass media•From synthetic language to analytic languageGrowth of Present-day English V ocabulary 当代英语词汇的发展Reasons for new words: 为什么需要新词To express new things and new changesTo arouse public attention and interestMain sources of new words: 新词所属领域Science and technologyEconomic and political changesInfluence of other cultures and languagesNew WordsNew Words and Changing American Culture 1990, Gozzi:•45% science and technology terms;•24% terms related to life-style•11% social and economic termsModes of V ocabulary Development 词汇的发展方式Creation 创词–formation of new words by using existing materials such as roots, affixes and other elements.Semantic changes 旧词新义– an old form which takes on a new meaning to meet the new need. Borrowing借词—absorbing words from foreign languagesReviving archaic or obsolete words古词和废弃词复活11. Word formation•Encourage Affixation词缀法Derivation派生法•Moonlight Compounding 复合法•to Pocket the money Conversion 转类法•Motel Blending拼缀法•Memo (memorandum) Clipping 截短法•UNESCO Acronymy 首字母拼写法•Babysit (from babysitter) Backformation逆构法•Sandwich Proper noun专有名词Which of the following is a compound?A.PreschoolB. school masterC. At schoolD. schoolingBlending 拼缀法Brunch—breakfast+lunch Motel—motor+hotelBotel—boat+hotel Smog—smoke+fogFour structural types of BlendingBrunch—breakfast+lunch Carbecue—car+barbecueMedicare—medical +care Sitcom –situational+comedyThree stylistic types of Blending•Slang or make-shift wordsinfanticipating--infant+anticipating•Words for science and technologybiorhythm—biological+rhythmlidar—light and radar 激光雷达•Words used in mass mediadawk—dove and hawk 中间立场的Back Formation 逆构法edit—editor caretake—caretaker Peeve—peevish Frivol—frivolous Automate—automation Destruct—destruction Sidle—sidlingClipping 截短法Phone—telephone Zoo—zoological garden Copter--helicopterFridge—refrigerator Flu—influenza Curtsy—courtesyInitialism 首字母连接词VOA WTO YZU CCTVAcronym 首字母拼音词NASA AIDS Radar UESCO Laser12. Motivation 词的理据1.Onomatopoeic motivation 拟声理据2.Semantic motivation 语义理据(figurative sense)3.Morphological motivation 形态理据4.Etymological motivation 词源理据Primary onomatopoeia 基本拟声P.60•The imitation of sound by sound.•Here the sound is truly “an echo to the sense”.e.g.Here it comes sparkling,And there it lies darkling…Spouting and frisking,…Secondary Onomatopoeia•Certain sounds and sound sequences are associated with certain senses in an expressive relationship.e.g.sn/--breath noise; quick separation or movement; creeping:sniff, snuff, snore, snort, snip, snap, snatch, snake, snail, sneak, snoop (窥探) Duplicated words or phrases• A tall clock tick-tocked on the stair.•He gave the deck a thorough riffle-shuffle and then dealt the cards. 他把牌彻底洗过一遍,然后发牌. Metaphor•They were allowed to leapfrog the long lines of traders and get immediate appointments with Chinese representatives•US influence and prestige nosedived in Africa.•The came up with a plan for drastic pruning of the bloated institution.Synecdoche 提喻Sail—ship Hand—man The smiling year—spring A Solomon—a wise man Metonymy 借代• A watched bottle never boils.•He never let his heart rule his head.Analogy 类比•talkathon (马拉松式谈话或座谈节目)•telethon (马拉松式电视广播节目)Color analogy 色彩类比His short play is in the white list. (批准上演的节目名单)grey list—非明文查禁但仍属不合法的人或物grey-collar workers—服务性行业的职工Number analogy数字类比The Fourth World (最贫国集团)The First FamilyThe three R’s (reading, writing arithmetic)Space analogy 地点空间类比•Moonscape—landscape•Marrain(火星上地形)—terrain•Earthrise—sunrise•Spacefaring(航天飞行)--seafaring反义类比•Daylighting –白天兼职,晚上主要工作•Low-rise—低层建筑•Cold line—冷线Analogy 近似类比•Missile gap (美国与苏联在导弹发展上的差距)Generation gap, development gap,Production gap, credibility gap•Watergate13.The Change of Word MeaningAlbatross 信天翁---cause of worries, misfortuneFor it is my special albatross to be related to the guy…. (p.88)Harvest---getting in the crops,crops that you get inBenchEvery time we go there, he is sitting on a park bench.(A piece of furniture for you to sit on)Here is the list of the full bench of the supreme court. (judges)He was brought before the bench. (court)Mary served on the bench and in Congress.Tom got a bench in the Parliament. (seat)This is a team with the best bench. (substitutes)They conducted the bench test successfully.(table)Central signification : furnitureSecondary meaning: judge, seat, substitute ,tableShe took her cat to the bench show. 动物展览评比会Tom’s father worked as a bench scientist for many years. 在实验室工作的科学家I am tired of being a bench warmer, nor do I want to be a bench jockey. 替补队员;在替补队员席上起哄的棒球队员(为干扰对方运动员或裁判员)Treacle1. Pertaining to wild beast.(与野兽有关的。