四川大学专业英语Professional English教学大纲
- 格式:pdf
- 大小:33.32 KB
- 文档页数:5

《专业英语》教学大纲
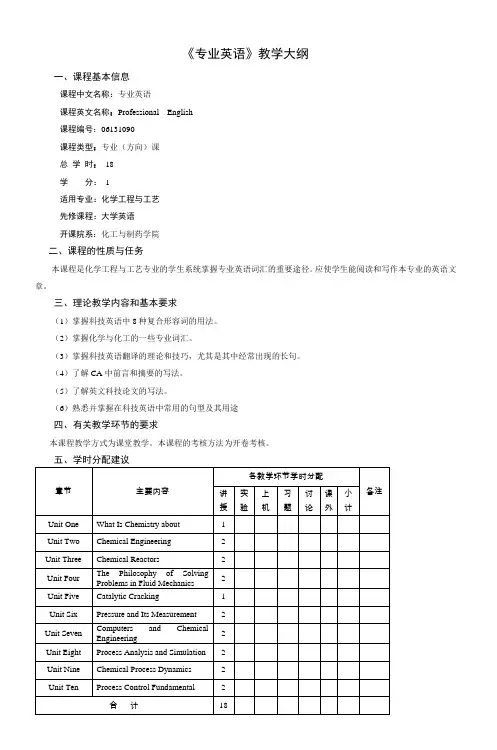
一、课程基本信息
课程中文名称:专业英语
课程英文名称:Professional English
课程编号:06131090
课程类型:专业(方向)课
总学时:18
学分:1
适用专业:化学工程与工艺
先修课程:大学英语
开课院系:化工与制药学院
二、课程的性质与任务
本课程是化学工程与工艺专业的学生系统掌握专业英语词汇的重要途径。
应使学生能阅读和写作本专业的英语文章。
三、理论教学内容和基本要求
(1)掌握科技英语中8种复合形容词的用法。
(2)掌握化学与化工的一些专业词汇。
(3)掌握科技英语翻译的理论和技巧,尤其是其中经常出现的长句。
(4)了解CA中前言和摘要的写法。
(5)了解英文科技论文的写法。
(6)熟悉并掌握在科技英语中常用的句型及其用途
四、有关教学环节的要求
本课程教学方式为课堂教学。
本课程的考核方法为开卷考核。
五、学时分配建议
六、建议教材及主要教学参考书
杨嘉谟等编.化学化工专业英语.修订版. 武汉:武汉大学出版社,1997年
执笔人:包传平教研室主任:程健教学院长(主任):丁一刚。

《专业英语》课程教学大纲课程名称(中文/英文):专业英语/ Professional English 课程编码:12024019 课程类型:专业选修课 课程性质:专业课 适用范围:06地理信息系统学分数:2 先修课程:《大学英语》《地理信息系统》 学时数:36 其中:实验/实践学时:0 课外学时:0 考核方式:考查 制订日期:2006年制订单位:广州大学地理科学学院 审核者:夏丽华 执笔者:冯艳芬一、教学大纲说明(一)课程的地位、作用和任务(一)课程的地位、作用和任务该课程属于地理信息系统专业基础课之一,通过该课程的学习,学生基本能掌握常用的地理信息系统专业词汇,能查阅相关的外文资料,阅读简单的外文文献,阅读简单的外文文献,能进行简单的英文能进行简单的英文摘要撰写。
摘要撰写。
本课程的任务主要为:本课程的任务主要为:(1) 增加学生专业词汇量增加学生专业词汇量 (2) 介绍专业文献阅读的技巧介绍专业文献阅读的技巧 (3) 加强对英文长句翻译的训练加强对英文长句翻译的训练 (4) 介绍论文英文摘要的写法介绍论文英文摘要的写法(5) 介绍专业在国际上的发展趋势介绍专业在国际上的发展趋势 (二)课程教学的目的和要求(二)课程教学的目的和要求能让学生在学完二年能让学生在学完二年《大学英语》的基础上,《大学英语》的基础上,《大学英语》的基础上,增加专业方面的词汇,同时了解本专业在增加专业方面的词汇,同时了解本专业在英文上的表达方式,通过本课程的学习,通过本课程的学习,学生能掌握较多的专业词汇,学生能掌握较多的专业词汇,学生能掌握较多的专业词汇,能根据教学的要求查能根据教学的要求查阅简单的外文专业文献,基本能够读懂文献中的主要方法与主要内容,同时能为四年级论文的撰写打下基础,介绍论文英文摘要的写法。
的撰写打下基础,介绍论文英文摘要的写法。
要求:掌握要求:掌握500个专业词汇,个专业词汇,能基本完成对专能基本完成对专业长句中译英或英译中的翻译,基本能读懂专业文献。


《专业外语1》教学大纲课程名称(英文):专业外诰1 (Professional English 1)课程代码:030161课程类别:专业必修课程学时:48学时学分:3学分考核方式:考查适用对彖:物理学本科专业一、课程简介本课程是为物理学教育专业学生开设的一门重要的专业必修课程,它是在大学英语的基础上,通过英语方式对现在的物理知识进行进一步了解和认识以及对原有物理知识的扩展。
它使学生初步掌握力学、电磁学、热学、光学、声学、材料物理、天文物理、医用物理和粒子物理学屮的英语词汇、词组及其用法,学会阅读本专业英语资料的技巧与方法。
它不仅有助于拓展本专业学生的知识面,增强国际交流与沟通的能力,而且可以深化本专业的知识,从而为今后的学习和工作打下良好的基础。
二、教学目的及要求本课程教材选口上海教育出版社的《物理学专业英语基础》(图示教程)。
通过本课程的学习,学生应达到如下要求:1、掌握力学、热学、光学、声学、电磁学、材料物理、天文物理、医用物理和粒子物理学屮的专业英语词汇,了解英语词汇、词组及其用法;2、通过对专业英语文献的学习,逐步掌握阅读专业外文资料的常用技巧与方法。
在借助必要的词汇工具书的基础上,能达到独立阅读、理解和初步翻译外文资料;3、专业英语翻译不但要有较高的外语水平和汉语水平,血且要具有较为广泛的相关的科学基本知识,特别是要具备一定深度和广度的专业知识。
通过对专业英语课程的学习,要求能够就物理现象进行系统的有逻辑的英文描述,具备一般英语科技文章的写作能力。
三、教学重点及难点教学重点:具备一定的专业基础知识和相关学科的基础知识,熟练的掌握专业词汇。
教学难点:在具备一定专业知识的基础上,能够独立阅读、理解和初步翻译外文资料,能够就物理现象进行系统的有逻辑的英文描述,具备i定的英语科技文章的写作能力。
、与其它课程的关系在学习本课程前应修完大学英语、力学、热学、光学和电磁学等普物课程。
五、教学内容A篇基础知识(1()学时)本章主要教学内容:Al Motion mass and forces;A2 Work energy and power;A3 Atoms and molecules in motion;A4 Charges and circuits;A5 Magnets and currents;A6 Waves and rays.本章教学目的及要求:1、了解物理学的基本概念,掌握各分支的英语专用词汇;2、了解普通物理学小物理量的英文描述及表达方式。

专业英语(信管)教学大纲《专业英语》课程教学大纲课程代码:040642703课程英文名称:Professional English课程总学时:32 讲课:32 实验:0 上机:0适用专业:信息管理与信息系统大纲编写(修订)时间:2017.06一、大纲使用说明(一)课程的地位及教学目标本课程是一门职业基础课,其主要任务是通过本课程的学习,使学生应掌握信息管理与信息系统的专业英语词汇,能读懂英文的专业资料并能达到一般专业知识的英汉互译水平,将学生培养成为复合型人才,为他们今后走上工作岗位从事实际工作打下必要基础。
通过本课程的学习,学生将达到以下要求:1、掌握基本的信息管理与信息系统专业领域英语词汇;2、能阅读英文的专业资料;3、有一定的英汉互译水平。
(二)知识、能力及技能方面的基本要求1.基本知识:掌握初级的商务英语表达能力,了解信息管理与信息系统专业的常见名词,能够对其进行英汉互译。
词汇量要求为200个。
2.基本理论和方法:复习巩固基础英语中所学的语法知识。
能用所学词汇和语法知识正确理解与课文难度相仿的文章,能初步掌握英译汉的基本方法和技巧,能借助词典将与专业有关的英文资料译成汉语,基本通顺。
能听懂句子结构简单、语言材料熟悉的句子,能用英语进行简单的日常会话并能回答教师提出的简单问题,能组成意思完整的简单句子。
3.基本技能:掌握信息管理与信息系统专业的常见的听书读写的能力。
(三)实施说明1.教学方法:课堂讲授中要重点对基本语法和生僻词句进行讲解;采用启发式教学,培养学生思考问题、分析问题和解决问题的能力;引导和鼓励学生通过实践和自学获取知识,培养学生的自学能力;开展讨论课,调动学生学习的主观能动性;注意培养学生提高利用标准、规范及手册等技术资料的能力。
讲课要联系实际并注重培养学生的创新能力。
2.教学手段:本课程属于技术基础课,在教学中采用电子教案、CAI课件及多媒体教学系统等先进教学手段,以确保在有限的学时内,全面、高质量地完成课程教学任务。

《专业英语》课程教学大纲专业英语课程教学大纲一、导言专业英语课程旨在提高学生在特定行业领域的英语运用能力,培养学生具备与专业相关的语言技能和知识。
本教学大纲确立了专业英语课程的目标、教学内容、教学方法和评估方式,以便提供给教师和学生参考,以确保教学质量。
二、课程目标本课程旨在:1. 提高学生的听、说、读、写的综合技能,使学生能够流利、准确、自信地运用英语进行专业交流;2. 培养学生通过阅读、听力和其他学习资源获取和理解专业资料的能力;3. 强化学生对专业词汇、语法和句型的掌握,以便能够正确运用于特定领域;4. 培养学生进行专业演示、报告和讨论的能力,以及跨文化交流技巧;5. 培养学生终身学习和自主学习的能力,以适应不断变化的专业环境。
1. 技术文档阅读与写作- 学习整理与解读工程设计图纸、说明书、操作指南等技术文档;- 培养学生能够准确理解技术术语和专业概念的能力;- 培养学生撰写技术报告、分析和建议的能力。
2. 专业会议与演示技巧- 学习参与和组织专业会议的技巧;- 培养学生进行有效演示和陈述的能力;- 提高学生在团队合作中的沟通技巧和解决问题的能力。
3. 跨文化交流与商务礼仪- 学习跨文化交流中的语言、文化差异和社交礼仪;- 提高学生在国际商务环境中的交流能力;- 培养学生进行专业及商务谈判的技巧和策略。
4. 国际新闻与专业写作- 学习阅读国际新闻及相关专业文献;- 提高学生从新闻中获取信息和分析问题的能力;- 培养学生撰写专业报告、新闻稿件和商务信函的能力。
1. 组织多样化的课堂活动,包括小组讨论、角色扮演、案例分析等,以培养学生的独立思考和合作能力;2. 制定专业英语学习计划,鼓励学生进行自主学习和参考资料的查找;3. 设计任务和项目,让学生将所学知识应用于实际场景,提升实践能力;4. 提供模拟情境,让学生在教师的指导下进行口语和写作练习;5. 给予学生定期反馈和评估,以促进学生的进步。

《专业英语》课程教学大纲Professional English Course Syllabus.Course Description:This course is designed to help students develop the professional English language skills necessary for success in the workplace. Students will learn to communicate effectively in a variety of business settings, including meetings, negotiations, presentations, and written correspondence. The course will also cover cultural aspects of business communication and professional etiquette.Course Objectives:Upon successful completion of this course, studentswill be able to:Communicate effectively in a variety of business settings.Use appropriate language and tone in written and oral communication.Understand and use cultural norms in business communication.Conduct themselves professionally in the workplace.Course Content:Introduction to professional English.Business communication skills.Cultural aspects of business communication.Professional etiquette.Advanced English grammar and vocabulary.Business presentations.Business negotiations. Business correspondence. Teaching Methods:Lectures.Discussions.Role-playing.Presentations.Written assignments.Assessment:Class participation.Quizzes.Midterm exam.Final exam.Final project.Required Textbook:Professional English by John Eastwood. Grading:Class participation: 10%。

《专业英语》课程教学大纲Professional English for Educational Technology学时数:36其中:实验学时:0课外学时:0学分数: 2适用专业:教育技术学专业执笔者:梁燕葵编写日期:2005年9月一、课程的性质、目的和任务本课程是教育技术专业选修课程,通过本课程的教学,加强学生对教育技术学词汇的熟悉程度,培养学生掌握教育技术学专业的相关专业词汇及阅读、翻译、写作的技巧和方法,使学生能够熟练地查阅相关的科技文献,并能流利阅读和翻译相关的专业资料,为将来更深入地学习和从事科研工作打下坚实的英语语言基础。
本课程的基本任务是在英语学习中掌握专业知识,在专业学习的同时提升英语水平。
二、课程教学的基本要求着力帮助学生理解教育技术学的基础知识、基本理论和基本技能,了解教育技术学研究的最新进展和研究动向,同时要使学生学习用英语交流教育技术学的基本知识与基本技能(如阅读、撰写专业文献、与国内外同行用英语进行交流,这就涉及到了英语语言的读、说、听、写、译等技能),为今后进一步学习和工作服务。
三、课程的教学内容、重点和难点Chapter One The Evolution of the DefinitionSection A The Early DefinitionsSection B The AECT’s Definitions in 1994Section C Assumptions behind the AECT’s Definitions in 2005Chapter Two The History of Instructional TechnologySection A Pre-1920Section B 1920s-1940sSection C 1950s-1970sChapter Three Instructional Technology: Present andFutureSection A The Positive and Negative Trends of Instructional Technology Development Section B The Diverse Status of Instructional TechnologySection C The Professionalizing of the FieldSection D The Training of the ProfessionalsChapter Four Learning TheoriesSection A Why Theories of LearningSection B The Behaviorist Orientation to LearningSection C Cognitive Information-Processing TheorySection D ConstructivismChapter Five Communication TheoriesSection A Defining CommunicationSection B What Is Communication TheorySection C A Basic Linear ModelChapter Six Instructional TheoriesSection A Gagne’s Theory of InstructionSection B Bloom’s Taxonomy of Educational ObjectivesSection C Programmed InstructionChapter Seven Systematic TheorySection A Systems TheorySection B Systems Theory: The BasicsChapter Eight Media HistorySection A Seven Milestones in the Evolution of Human CommunicationChapter Nine New TechnologySection A Multimedia TechnologySection B Computer-Mediated CommunicationSection C Virtual RealitySection D Artificial IntelligenceSection E Jini TechnologyChapter Ten Media and LearningSection A The Medium is the MessageSection B Media ResearchSection C The Great Media DebateChapter Eleven Instructional Design and InstructionalSystem DesignSection A What’s Instructional Design?Section B Basic Principles of IDSection C Instructional System DesignChapter Twelve Models of Instructional Design Section A ID Models and Their Basic FeaturesSection B A Taxonomy of ID ModelsSection C An Introduction to Instructional Design ModelsChapter Thirteen Automating Instructional DesignSection A Purpose of Automated Instructional Design ToolsSection B Wha t’s AID?Chapter Fourteen The Overview of ICTSection A The Information AgeSection B Fours Goals for Technology in SchoolsSection C The Effect of ICT in EdcuationChapter Fifteen Introduction of ICT CurriculumSection A Aims of ICT in EdcuationSection B How to Teach ICTSection C How to Design ICTChapter Sixteen The Study and Practice to FacilitateLearning with ICTSection A The Cycles of Technology IntegrationSection B The Market Power of E-LearningSection C The Critical Attributions of WebQuestChapter Seventeen Definitions and History of DistanceEducationSection A Definitions of Distance Education According to the AECTSection B History of Distance EducationSection C What is Distance Education?Chapter Eighteen Theories of Distance EducationSection A The Industrial Model of Distance EducationSection B European Theory of Independent StudySection C The Need of TheoryChapter Nineteen The Platforms of Distance EducationSection A WebCTSection B Leadership in E-LearningChapter Twenty Institute and Successful Cases of DistanceEducationSection A The Open University of Hong Kong (OUHK)Section B The Open University (United Kingdom)Section C What Is the Commonwealth of Learning (COL)?Chapter Twenty-One An Overview of InstructionalTechnology ResearchSection A Scientific MethodsSection B Purposes of Educational ResearchSection C Two Research ParadigmsSection D Quantitative ResearchSection E Qualitative ResearchChapter Twenty-Two A Research Report of Research onInstructional Technology四、课程各教学环节要求(一)教与学模式以任务驱动为主线,采用多媒体演播教学或基于网络环境下的自主学习、协作学习、问题探究、资源检索、在线讨论等多种教与学模式。

《专业外语》教学大纲课程编号:C064140620课程名称:专业外语课程类型:专业方向课英文名称:Professional Foreign Language适用专业:过程装备与控制工程专业总学时:20学分:1一、课程的性质、目的及任务《专业外语》是过程装备与控制工程专业的一门专业基础课程,在过程装备与控制工程专业的教学中有着重要地位。
它具有实用性强的特点,适合于过程装备与控制工程专业四年学制的学生。
本课程针对过程装备与控制工程专业本科生的英文学习要求,结合过程装备与控制工程专业知识体系,涉及过程装备与控制工程专业各领域知识及专业英文词汇。
学生通过本课程的学习,能够借助词典或其它辅助工具翻译相关的专业文献,进而能够了解本学科国内外发展的动态。
本课程学习的目的在于加强学生专业英语的阅读能力,扩大专业词汇量,培养语感,提高学生吸收国外先进技术及参与国际工程的能力。
并为学生毕业论文以及今后生产和科研中国际交流合作打下坚实的英语基础。
本课程学习的任务是培养学生顺利阅读专业英语的能力,进一步拓宽学生的视野,使学生能以英语为工具获取专业所需的知识和信息。
本课程在巩固基础英语的同时,为学生学习新的科学知识与科学技术、查阅本专业英文文献、引进先进技术、掌握国际上本专业发展动态打好语言基础。
二、课程教学的基本要求培养学生顺利阅读专业英语的能力,以英语为工具获取专业所需的知识和信息的能力,提高学生吸收国外先进技术及参与国际工程的能力。
要求学生学会阅读英文专著的方法,尤其是提高学生理解和翻译复杂长句、难句、从句的能力,为以后进一步从事本专业和相近专业的研究及对外交流打下较为扎实的基础。
具体要求如下:⑴学生能够较流利准确的阅读和理解英文著作;⑵学生应该掌握本专业重要名词术语的英译名称;⑶学生在借助词典和其它辅助工具的情况下,能够较准确地将专业英语著作翻译成汉语;⑷学生能够将科技论文的题目、摘要和关键词翻译成英文。
2.能力培养要求三、课程教学内容本课程内容覆盖了过程装备与控制工程专业的基本专业内容,包括过程装备力学基础、金属材料、过程工业、过程设备、过程机械和过程装备控制等六个部分,共有30个单元。

四川大学外国语学院英语专业本科课程教学大纲一、课程基本信息课程名称:英语交流艺术The Art of Communication课程号:10557320课程类别:选修课学时:32 学分:2(一)教学目的及要求本课程为英语专业高年级实践技能课。
课程旨在提高学生的口头表达和交流能力,培养学生的语言交流运用技能。
通过对理论和实证的研讨学习,帮助学生理解、分析和应用在实际工作环境中的交流技能。
课程通过对社会、工作语境下的人际交流、团队合作,非正式场合和正式场合中的演讲技能,正式交流、演讲中多媒体辅助手段的应用,以及求职和求职面试等实用技能的探讨,帮助学生了解交流,特别是跨文化交流的相关理论,掌握一定的实际技能,提高学生在实际工作环境下的语言交流能力。
(二)教学内容教学以国外原版英文教材为主要内容,分别讨论交流艺术的理论,语言交流的基本原理和实际工作环境中的语言交流应用。
讨论如何适应不同工作环境,提高人际交流的效率,探讨如何做到高效率的听力理解和克服交流中可能出现的各种干扰,达到有效的交流目的;通过利用多媒体辅助手段进行演讲的实战训练和求职面试的模拟训练,强化学生的实际应用能力。
教学共分为十个章节,理论讨论与实践练习相结合。
四、教材Cheryl Hamilton and Cordell Parker. Communicating for Results (Fifth Edition).Belmont, CA: Wadsworth Publishing Company, 1997.五、主要参考资料鲁道夫. F. 维德伯著(蔡晓煦译), 《讲话的艺术》,中信出版社,2003。
刘津编译,《克服人性的盲点:有效沟通的艺术》, 海潮出版社,2001。
六、成绩评定平时课堂讨论20%平时作业20%期末演讲实况录像60%四川大学外国语学院英语专业本科课程教学大纲课程名称:英语论辩艺术Arts of Practical Argumentation课程号:10556820课程类别:选修课学时:32 学分:2二、教学目的及要求本课程为英语专业高年级实践技能课。
College of Software EngineeringUndergraduate Course SyllabusCourse ID 311055020Course Name Computer EnglishCourseAttribute□Compulsory █Selective Course Language█English □Chinese Credit Hour 2Period32Semester█First Fall □First Spring □Second Fall □Second Spring □Third Fall □Third Spring □Fourth Fall □Fourth Spring Instructors Fei Xiangdong, Song Wanzhong, Liu Yu, Yu liang,Description The purpose of this course is to render a rough background for the forthcoming courses of computer software engineering and to provide a fundamental basis for completion of the study and research with the help of English. The basic computer concepts and common terms will be introduced among with some real application demonstrations. The principle features of computer English will be demonstrated and the interactive teaching methods will be used to improve the students’ Reading, Writing, Listening and Speaking skills in computer English, especially their ability to acquire knowledge. Besides the class participation and final examination, the project in each group is required to give a computer academic paper summarization in Word and a presentation in PowerPoint.Prerequisites General EnglishTextbook JinZhi-quan,ZHANGXin-er,ZHANGJing-xiang. A Course in Computer English:3rd Edition[M]. BeiiJing:Publishing House of Electronics Industry,2007Resource 1.WANGChun-sheng,LIUYi,YANGWei-rong.A New Course in Computer English[M],BeiiJing:Publishing House of Electronics Industry,20072.ZhangQiang-hua,SIAi-xia,Computer English[M],BeiiJing:Publishing House ofElectronics Industry,20073.Philip Lew,SUNNan, Software Engineering English[M], BeiiJing:Publishing House ofTsinghua U niversity ,20034.SONGYang, LIANGGang-jian, English Course for Electronic Commerce[M], HAEr-bing:Publishing House of HAEr-bing Engineering University, 20065.Some English Text Books used for Software Engineering Study7.IEEE + Elsevier + ScienceDirect8.ChinaDaily Mobile NewsGrading class participation(50%), final examination (50%)Topics Lecturer 1 Overviewz Syllabusz Relationship with Other Coursesz Overview of Computer Sciencez Principle Features of Computer Englishz Application Demonstrationsz SuggestionsLecture 2 Computer Hardware Fundamentalsz Processorz Storagez I/O Devicesz Bus(control, address, data)z USBz RAID (MDSL Recorder)Lecture 3 Computer Software Fundamentalsz System Software and Application Softwarez Common Features of GUI ( window, menu, toolbar, etc ) z Object-Oriented Programming(C++, Java)z Advanced Visual C++ Features (GUI)z Microsoft Word and PowerPointLecture 4 Operating Systemsz Definition and Basic Functionsz Windows Seriesz Unix & Linuxz Embedded OSz Real Time OSz ATC Systems on various OSLecture 5 Computer Networksz Fundamentals of Networking Systemz Internetz Protocol(TCP/IP,FTP,HTTP)z HTML & XMLz Network CommunicationLecture 6 Databasez An Overview of Database systemz Introduction to SQLz The Oracle DBMSz The Data Warehouse and Data MiningLecture 7 Multimediaz Introduction to Multimediaz Audioz Video Compressionz Visual FusionLecture 8 Artificial Intelligencez Introduction to AIz Speech Recognitionz Image Processing (Vehicle License Plate Recognition, Face Recognition)z Expert Systemz RobotsLecture 9 Data Structure and Algorithmsz Abstract Data Typesz Queue and Stackz Listz Introduction to Algorithms(Ant Colony Algorithm, Artificial Fish-Swarm Algorithm, Simulated Annealing Algorithm)z Basic Concepts of Modern AlgebraLecture 10 Software Engineeringz Overview of Software Engineeringz Unified Modeling Language (UML)z Capability Maturity Model(CMM)z Rapid Application Prototyping(RAP)z Unit Test (CPPUnit)z Configuration ManagementLecture 11 Computer Application Iz CAD , CAM and CIMz GIS ,True Three-Dimension Displayz Virtual Realityz MDSLLecture 12 Computer Application IIz Distance Educatingz E-Commercez Virus and Network SecurityPrinciple Features of Computer English:z Vocabulary, Terms and Jargonsz Hyphen and Compound Wordsz Table and Graphz Description and Listingz Definition and Conceptz Cause-Effect, and Contrastz Equation and Math Expressionz Standard and Organizationz Reading Skills(Intensive reading – Fast reading – Browse)z Speech and Pronunciation ( Word Stress )z Writing styles(Web Page、FAQ、Specification、Wikipedia)z Academic Papers (resources, tips and hinds for writing a scientific paper)Planned Application Demonstrations During Lectures:z ATC Systemz E-Commerce Applicationz Internet Search—google,baidu,FTP search, blog searchz Virtual Reality – Tower Simulatorz Computer Graphics, Image-Based Rendering(IBR), 3D Data Acquisition (Static,Dynamic)z Grahpics Processing Unit(GPU), Flow Simulationz Computer Graphics – True Three-Dimension Displayz PC Cluster Computingz Image Processing – Picture Archiving & Communication System(PACS)z Image Processing –Vehicle License Plate Recognition, Face Recognitionz GIS—Google Earth、MS Digital Cityz Embedded Systemz Configuration Management Softwarez Fusion Vision – Airport Surface surveillance, Low Visibility BattlefieldSurveillancez Fusion Vision – Low Visibility ApproachTools & Environment Multimedia teaching:1.PPT2.Application Demonstrations3.MP3 listening materials4.Interactive Teaching with Entertainment PracticesProjects To search and read a complete computer academic paper in group (each group on different topic at least 5 pages) and summarize the paper with evaluation. The summarization in Microsoft Word and the presentation in PowerPoint are required.Version No: 1.0Author: Fei Xiangdong Date: 2008-9 -15Auditor:Mei Hong Date: 2008-9-25Signature of leader:Date: 2008-9-30。