英国文学复习资料全
- 格式:doc
- 大小:80.50 KB
- 文档页数:19


英国文学简史复习资料(整理版)第一篇:英国文学简史复习资料(整理版)I.Old English Literature & the Late Medieval Ages 贝奥武夫:the national epic of the Anglo-SaxonsGeoffrey Chaucer 杰弗里•乔叟1340(?)~1400 The father of English poetry.① 坎特伯雷故事集:first time to use …heroic couplet‟(双韵体)by middle English ②特罗伊拉斯和克莱希德③ 声誉之宫II The Renaissance Period A period of drama and poetry.The Elizabethan drama is the real mainstream of the English Renaissance.Renaissance: the activity, spirit, or time of the great revival of art, literature, and learning in Europe beginning in the 14th century and extending to the 17th century, marking the transition from the medieval to the modern world.Three historical events of the Renaissance – rebirth or revival: 1.new discoveries in geography and astrology 2.the religious reformation and economic expansion 3.rediscovery of ancient Roman and Greek culture The most famous dramatists:Christopher Marlowe William Shakespeare Ben Johnson.William Shakespeare威廉•莎士比亚1564~1616① Historical plays: Henry VI 亨利六世;Henry IV : Richard III 查理三世;Henry V ;Richard II;Henry VIII ②Four Comedies: 皆大欢喜;第十二夜;< A Midsummer Night‟S Dream>仲夏夜之梦;威尼斯商人③Four Tragedies: 哈姆莱特;奥赛罗;李尔王;麦克白④Shakespeare Sonnet :154Three quatrain and one couplet, ababcdcdefefggA sonnet is a lyric consisting of 14 lines, usually iniambic pentameter restricted to a definition rhyme scheme.⑤the comedy of errors 错中错,Titus Andronicus泰特斯·安特洛尼克斯,The Taming of the shrew 驯悍记Love's labour's lost(爱的徒劳)Romeo and Juliet 罗密欧与朱丽叶Much ado about nothing(无事生非)The merry wives of Windsor.温莎的风流娘们King John 约翰王All's well that ends well 终成眷属Measure for measure(一报还一报)Bacon: Of Studies;Of Beauty;Of Marriage and Single Life English Bourgeois Revolution,学术的推进 III:the period of the English bourgeois ton:1608~1674Paradise Lost;Samson Agonistes(力士参孙);On the morning of Christ’s Nativity,复乐园我的失明论出版自由为英国人民声辩Bunyan: 1628~1688 ①Religionary Allegory:天路历程Grace Abounding to the Chief of Sinner;the Holy War John Don: the Metaphysical poet(玄学派诗人).Metaphysical Poetry(玄学诗):(用语)the diction is simple, the imagery is from the actual,(形式)the form is frequently an argument with the poet’s beloved, with god, or with himself.(主题:love, religious, thought)The Flea;跳蚤Forbbiding Mourning,Songs And Sonnets歌与十四行诗,emergent occasions 突变引起的诚念Hely sonnets IV The 18th Century:EnlightenmentA revival of interest in the old classical works, order, logic, restrained emotion(抑制情感)and accuracy The Age ofEnlightenment/Reason: the movement was a furtherance of the Renaissance of the 15th and 16th centries, a progressive intellectual movement, reason(rationality), equality&science(the 18th century)小说崛起:In the mid-century, the newly literary form, modern English novel rised(realistic novel现实主义小说)Gothic novel(哥特式小说):mystery, horror, castles(from middle part to the end of century)Jonathan Swift乔纳森•斯威夫特1667~1745(十八世纪杰出的政论家和讽刺小说家 a master satirist。

英国⽂学复习资料The Anglo-saxon period(450-1066)⼀,historical background1, History: The earliest settlers of British Isles were the Celts.2, Old English poetry.⼆,Northumbrian school and Wessex literature.1, Two Highlight in the development of Anglo-saxon literature:(1). Northumbrian school (2), Wessex literature.2,The first Anglo-Saxon poet: Caedmon —“paraphrase”3.Bede: —“the father of English History.”The Ecclesiastical History of English people. 4.King Alfred —the Anglo-Saxon Chronicle三.Epic1. Definition: A long narrative poem celebrating the great deeds of one or more legendary heroes, in a grand, ceremonious style.2. Anglo-Saxon Poetry—Beowulf (heroic epic)3.The earliest one is Widsith and last is Maldon .4.The plot: (1)fight with Grendel, Grendel’s mother, Firedrake.(2)the death and funeral5.the significance:6.National epic: Homer’s epic poetry(Greek);V irgil(Roman)7.Alliteration: Repetition of consonant sounds at the beginning of words.8.Kenning: A kind of metaphor usually used a phrase instead of a concrete noun.The Norman Period(1066-1350) ⼀.History background1. Norman conquest ended the Anglo-Saxon period2.the influence of Norman Conquest:(1)accelerated the development of feudalism in England.(2)the Anglo-Saxon, low position; English, despised thing.(3)three languages co-existed in England(French ,Latin, Old-English)⼆.Middle English1.the development of English Language2.the unique situation of language using during this time:French ,Latin, Old-English三.R omance1.Norman Conquest’s influence on English languageRomance——Frence——nobbles;lordsNo writtern——English——English subjet(⾂民)Chronicles,religious poem——Latin——scholar2.Definition: the Romance was the most prevailing kind of literature in feudal England which described the life andadventures of knights and reflects the spirit of chivalry in the form of verse. It’s usually about love, chivalry and religion.3.Rhyme:4.Bob: a line of two syllables.5.Wheel: a poem of four lines(a.b.a.b.)6.Three categories of Romans(1),The matter of France—Chanson de roland.(2), the matter of Rome—Alexander(3), The matter of Britain—Arthurian7. Sir Gawain and Green KnightAge of Chaucer⼀,History background1.The hundred years war between England and France(two kings for France throne)2, The peasant uprising of 1381,during the reign of king Richard 2⼆,John wycliff—The father of English prose.1,Contribution:(1),dedicated to religious reform(clergymen had no right to hold property and the civil authority had the right to deprive the church of property, if it proved unworthy of the people’s trust.),(2),Great contribution to English language (translated Bible into standard English)2,William Langland—the vision of Piers Plowman ; Allegory3, Allegory: A story or description in which the characters and events symbolize some deeper meaning.(primary meaning and secondary meaning)三,Chaucer—the father of English poetry(why?)1, Contribution to English literature:(1), Chaucer proved that the English language is a beautiful language and can be easily handled to express different moods.(2),Chaucer greatly increased the prestige of the English language.(3) Chaucer’s works gave a comprehensive picture of his time.(4), the dramatic structure of his work has been highlycommended by critics.(5)Chaucer made a big improvement of English literature.2,Heroic couplet(英雄双韵体)(1),couplet (两⾏诗⼀押韵)(2),iambic pentameter(五步抑扬格)3,Canterbury Tales(1) Structure:24 tales connect by “links”(2)His plan; Chaucer met a group of 29 pilgrims at Canterbury on his way. To kill the time on their journey, they play a game that each pilgrim should tell two stories on the outward trip and another two on the way back. Chaucer and their host joined them, the host will be a judge and give a reward to the one who give the best tale.4,The significance of the Canterbury tales(1), it gives a comprehensive picture of Chaucer’s time.(2).the dramatic structure of his work has been highly commended by critics.(3),It reflects the Chaucer’s humor.(4),It’s a great contribution that Chaucer gave to the English language.The 15th century⼀,Historical background1. The Hundred Years War:(in1415,at the battle of Agincourt ,King Henry 5 defeated French Army)2,The War of the Rose s—Thirty Y ears War:(break out between two families ,at last King Henry 7 defeated Richard 3 ,and then married Elizabeth)3,The discovery of America and the new sea routes —Columbus4,Reformation of the church(the church Henry 8 founded is Anglican church新教)⼆,Popular Ballads(民谣)(belongs to folk literature)1.Definition:a narrative poem that tells a story2. the characters of ballad:(1), the beginning is abrupt (2),strong dramatic elements(3),using dialogue and action (4), the theme is often tragic(5),using ballad meter3, Ballad Meter(1), four-line stanzas(2), the odd numbered(奇数) lines have 4 feet each(3), the even numbered (偶数)lines have 3 feet each(4),rhymes fall on the even numbered lines4,the popular ballad:Sir Patrick Spens帕特⾥克斯本⼠爵⼠Robin Hood and the three squires罗宾汉和三个乡绅三,Sir Thomas Malory——The Death of King Arthur 四,Early English palys1,The first comedy—Ralph Roister Doister(作者:Nicholas Vdall)2, History: In ancient Greece and Rome , drama was one of the popular forms of entertainment. And then used as part of religious services. By the 14th century, it developed into mystery plays (神秘剧)and miracle plays.(神话剧)3,Dramatic Terms.(1),script剧本(2)stage directions舞台说明(3),monologue 独⽩(4),aside旁⽩(5),soliloque独⽩(6)act 幕(7)scene场(8)set布景4. Drama’s Definition: Drama is “a composition in prose or verse, adapted to be acted upon a stage, in which a story is related by means of dialogue and action, and is represented with accompanying gesture, costume, and scenery, as in real life.”The English Renaissance英国启蒙运动⼀,history backgroundEnglish navy defeated the Spanish Armada in 1588.⼆,the enclosure movement(圈地运动)Definition: with development of wool trade, some of the nobles and burghers turned vast arable land into their pastures and many peasants became landless.三,H umanism1, renaissance(⽂艺复兴):the rebirth of literary movement that begin in the 14th century in Italy and later to France ,Spanish ,the Netherlands and English and its idea was humanism.2,Humanism: support the idea that man should be given the full freedom to enrich their emotional life,and in praise of man and pursuit of happiness in their life.四,William Shakespeare—playwright, poet, dramatist,actor.1.works: (1)sonnets(2)Mid-summer Nights Dream(3)Romeo and Juliet(4),The Merchant of V enice(5)As Y ou LikeIt(6),Hamlet(7),Othello(8),KingLear(9)Macbeth(10)The winters tale2, Sonnet Definition: is a short poem of 14 lines ,uauslly in iambic pentameter(五步抑扬格) with various rhyming schemes(韵脚)。

英国文学史复习资料
以下是一些关于英国文学史的复习资料:
1. 《英国文学的发展与演变》(The Development and Evolution of British Literature):这本书提供了英国文学史的全面概述,从中世纪到现代不同时期的文学作品和文学流派都有介绍。
2. 《英国文学史导论》(Introduction to British Literary History):这本导论书通过对英国文学史的重要事件、作家和作品进行深入讲解,帮助读者理解英国文学的演变和发展。
3. 《英国文学史简明教程》(A Short History of English Literature):这本书以简明清晰的语言介绍了英国文学史的重要内容,包括不同时期的文学作品和重要作家的生平和作品。
4. 网络资源:有许多网站提供关于英国文学史的资料和学
术文章,如英国文学史学术网站、大学的文学部门网站等。
你可以在搜索引擎上搜索英国文学史相关的关键词,找到
适合你的学习资料。
5. 学术论文和专著:在学术期刊和图书馆中,你可以找到
许多针对英国文学史的研究论文和专著,这些都是深入了
解英国文学史的重要资源。
无论使用哪种资料,重要的是要有系统地学习和复习英国
文学史,理解各个时期的文学作品和文学流派的特点和发
展趋势,同时熟悉一些重要的作家和作品。

British Literature 英国文学一、The Middle Age 中世纪文学( 约5 世纪---1485)Geoffrey Chaucer 杰弗里·乔叟(1343---1400)Chaucer is regarded as the first short story teller and the first modern poet in English literature. He innovate the heroic couplet and he is regarded as “Father of English Poetry”首创英雄诗行,即五步抑扬格双韵体(the heroic couplet),被誉为“英国诗歌之父”。
乔叟翻译过法国诗歌,其早期的文学创作受到法国文学的影响。
两次游历欧洲文艺复兴的发源地意大利后,乔叟接触到意大利文学,深受以但丁(Dante, 1265---1321)、彼特拉克(Petrarch, 1304---1347)和薄伽丘(Boccaccio, 1313---1375)等作家为代表的意大利人文主义文学的影响。
乔叟去世后安葬在威斯敏斯特教堂(Westminster Abbey),从此威斯敏斯特教堂的一角便成为大诗人安息的“诗人角”(the Poet’s Corner)代表作:《公爵夫人之书》(Book of the Duchess)(1836)《声誉之宫》(The House of Fame)(1374---1384)《百鸟会议》(The Parliament of Fowls)(1380)《特罗勒斯与克丽西德》(Troilus and Criseyde)(1380---1385)《坎特伯雷故事集》(The Canterbury Tales)(1386---1400)二、Renaissance 文艺复兴时期文学(15世纪后期---17世纪初)1、William Shakespeare 威廉·莎士比亚莎士比亚从1590年起至1613年,一共创作了38(或39)部戏剧包括悲剧、戏剧、编年史剧、传奇剧等,另外还创作有154首十四行诗和2首长诗(Venus and Adonis,1593)。
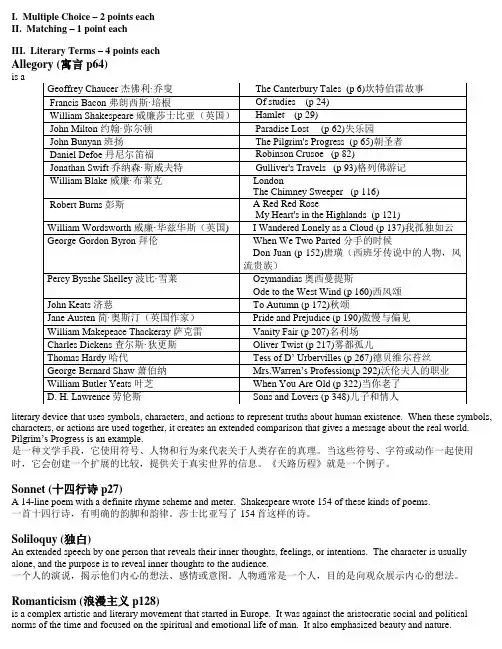
I. Multiple Choice – 2 points eachII. Matching – 1 point eachIII. Literary Terms – 4 points eachAllegory (寓言p64)is aliterary device that uses symbols, characters, and actions to represent truths about human existence. When these symbols, characters, or actions are used together, it creates an extended comparison that gives a message about the real world. Pilgrim’s Progress is an example.是一种文学手段,它使用符号、人物和行为来代表关于人类存在的真理。
当这些符号、字符或动作一起使用时,它会创建一个扩展的比较,提供关于真实世界的信息。
《天路历程》就是一个例子。
Sonnet (十四行诗 p27)A 14-line poem with a definite rhyme scheme and meter. Shakespeare wrote 154 of these kinds of poems.一首十四行诗,有明确的韵脚和韵律。
莎士比亚写了154首这样的诗。
Soliloquy (独白)An extended speech by one person that reveals their inner thoughts, feelings, or intentions. The character is usually alone, and the purpose is to reveal inner thoughts to the audience.一个人的演说,揭示他们内心的想法、感情或意图。

英国文学史复习资料英国文学史复习资料英国文学史是指英国国内从古代到现代的文学作品和文学发展的历史。
以下是英国文学史的复习资料。
1. 古代文学时期(公元前450年至公元1066年)古代英国文学时期主要包括凯尔特传统和盎格鲁-撒克逊文学。
凯尔特传统涵盖了关于亚瑟王、魔法和传说的故事。
盎格鲁-撒克逊文学以史诗和散文的形式存在,其中最著名的作品是《贝奥武夫》和《安德·狄德》。
2. 中世纪文学时期(1066年至1485年)中世纪英国文学时期由法国诺曼人的入侵而引入众多法语和拉丁语的作品。
其中最著名的作品是《坎特伯雷故事集》,它由杰弗里·乔叟写成,并包含了各种各样的故事。
3. 文艺复兴时期(1485年至1660年)文艺复兴时期是英国文学的黄金时期,以莎士比亚为代表。
莎士比亚的作品包括许多戏剧,如《哈姆雷特》、《罗密欧与朱丽叶》和《麦克白》等。
其他重要的作家还包括斯宾塞、马洛等。
4. 17世纪文学时期17世纪文学时期是英国社会和政治变革的时期,也是宗教分裂的时期。
约翰·米尔顿的《失乐园》被认为是这一时期最重要的作品之一。
其他作家还包括约翰·唐纳森、詹姆斯·谢尔顿等。
5. 启蒙时期(1660年至1785年)启蒙时期是英国文学史上的一次重要转折点,代表了对理性、科学和自由思想的追求。
著名作家包括强纳森·斯威夫特、丹尼尔·笛福、亚历山大·蒲柏、简·奥斯汀等。
6. 浪漫主义时期(1785年至1837年)浪漫主义时期是对启蒙时期理性主义的反应。
浪漫主义作品强调情感、个人主义和自然。
威廉·华兹华斯、塞缪尔·柯勒律治、约翰·济慈等都是这一时期的重要作家。
7. 维多利亚时代(1837年至1901年)维多利亚时代是英国帝国的鼎盛时期,文学作品多样化。
查尔斯·狄更斯的《雾都孤儿》、古斯塔夫·福楼拜的《名利场》等作品成为经典。

1.oral literature epic Beowulf口述文学作品史诗第一部贝尔武甫Alliteration,the Middle Ages,the Middle English,Romance头韵中世纪Geoffrey Chaucer Father of English Poetry杰弗雷·乔叟英国诗歌之父The Canterbury Tales, pilgrim, the heroic couplet, iambic pentameter坎特伯雷故事集朝圣者英雄双韵体抑扬格五音步双行押韵诗2。
William Shakespeare Bard of Avon威廉莎士比亚艾芬河的吟游诗人Tragedies: Hamlet, King Lear, Othello, Macbeth,Romeo and Juliet(or Tragicomedy/Romance);悲剧:哈姆雷特李尔王奥赛罗麦克白罗密欧与朱丽叶Comedies:Midsummer Night’s Dream, The Merchant of Venice,As You Like It, Twelfth Night;喜剧:仲夏夜之梦威尼斯商人皆大欢喜第十二夜Dramatic Romance:The Tempest戏剧性的浪漫:暴风雨;blank verse soliloquy,(Shakespearean)sonnet, rhyme scheme无韵诗独白(莎士比亚)十四行诗,韵律ababMelancholy,conflict,climax忧郁冲突高潮3.Francis Bacon,essay, prose,Essays,Utopia,plain style, parallelism,balance and opposition. 弗朗西斯·培根论文,散文,随笔乌托邦风格质朴,排比、平衡和反对Knowledge is power知识就是力量4. the Age of Prose,Enlightenment, reason,Neo-Classicism散文时代,启蒙,推理,新古典主义John Donne, Metaphysical School, conceit约翰·邓恩,玄学派别出心裁的比喻John Milton,Puritanism, epic,grand style,Paradise Lost约翰·弥尔顿,清教,史诗般的宏大风格,失乐园Daniel Defoe,Father of English Novel,adventure fiction, Robinson Crusoe丹尼尔·笛福,英国小说、冒险小说之父,鲁滨孙漂流记Jonathan Swift,satire,irony, A Modest Proposal, Gulliver's Travels,human nature,Yahoos乔纳森·斯威夫特,讽刺文学,反语,一个小小的建议,格列佛游记,人性,各种野蛮5。

名词解释1.Philosophy:The word “” is Greek for “love of wisdom” and has come to mean a systematic search for answerto life’s great questions.(哲学定义)2.Rationalism:Ancient Greeks believe that some universal truth has always existed and that reason is theprimary source of knowledge.(理性主义定义)3.Idealism:Human senses provide inexact concepts of things; only human reason can give us true knowledgeabout the world.(柏拉图Plato)(理念论/唯心主义定义)4.The Renaissance:The French word “renaissance” means “rebirth” in English. It refers to the rebirth ofknowledge in Europe, particularly the rediscovery of the Greco-Roman texts.(持续300年)(文艺复兴定义) 5.Magna Carta: The barons wrote the famous document called the Magna Carta, which they forced John toaccept on June 15, 1215 at Runnymede. This Magna Carta, also called the Great Charter, was designed to obtain public liberties and to control the king’s power.(大宪章定义)6.Puritan:The term “Puritan” comes from the desires of these English Christians to “purify” the AnglicanChurch by removing all traces of Roman Catholicism.(清教徒定义)7.Industrial Revolution(简称I.R): During the latter half of 18th century, a rapid series of changes began,especially in the field of manufacturing. There were so many new inventions the whole process is often described as ~~(工业革命定义)8.The factory of the world:British was once called~~~~~, because the Industrial Revolution promoted itsdevelopment of production.(世界工厂定义)9.The Enclosure Movement: In the end of 15th century, the cloth industry increased the value of wool. Raisingsheep became more profitable. Large areas of lands were often fenced by landlords without any warning to the peasants. This process is called~~~(圈地运动定义)10.Boston Massacre: On Mach 5, 1770, angry Boston citizens died and eight were wounded. Dubbed the“Boston Massacre”, the incident was regarded as proof of British tyranny.(波士顿惨案内容)(美国革命序曲) 11.1the Declaration of Independence: On July 4, 1776 the Second Continental Congress officially declaredindependence and formed the United States of America by adopting the Declaration of Independence, written by Thomas Jefferson of Virginia. The document declared that “all men are created equal” and are “ endowed by their creator” with certain “ inalienable rights” including “life ,liberty, and the pursuit of happiness”.(独立宣言定义)12.checks-and-balances: The US Constitution also provided for checks-and-balances between the three branchesof government. Executive Branch—the president行政权—总统Legislative Branch—the Congress立法权—国会Judicial Branch—the U.S. Supreme Court司法权—最高法院Each branch was given powers and duties that ensured that the other branches would not have too much power.(三权分立,分权制衡定义)13.the New Deal: Roosevelt’s program of “Relief, Recovery and Reform” was popularly known as “the NewDeal”, a program that significantly and dramatically increased the national government’s intervention in the economy.(罗斯福新政定义)14.Prohibition: The 18th Amendment to the Constitution(1919) is known as “Prohibition”, because it prohibitedthe sale of alcoholic beverages in the United States.(禁酒法令定义)15.Cold War:The “Cold War”, a term popularized by Winston Churchill in 1946, means alternative forms ofwarfare that rely on limited violence and ideological, economic and political methods.(美苏冷战定义)16.Mayflower: In 1620, a group of 132 Separatists (Puritans who had “separated” or left the Church of England)boarded the Mayflower and sailed for Virginia. The Mayflower was blown off course and landed in what is now Massachusetts, far to the north of Virginia.(五月花)简答、填空、选择1.What role did Winston Churchill play in World War II? (丘吉尔在二战中起到什么作用?)⑴He played the important role in World War II.⑵In 1941, he led the country through the miracle of Dunkirk, that was 338000 allied solders’ evacuation to Britain.⑶In 1943, he met Stalin and Roosevelt at Teheran Conference and decided to open the Second Battlefield West Europe.⑷In 1945, he proposed to fight against the Japanese Army till the end of the war.2.Why did I.R firstly take place in Britain?(工业革命首先在英国爆发的原因?)There are four prerequisites.4个先决条件Firstly, the accumulation of original capital.资本的原始积累Second, the development of capitalistic farming.资本主义农业取得发展Third, the appearance of free labor reserve.自由劳动力的出现Fourth, the expansion of markets, domestic and foreign.国内外市场的扩张3.New York为什么叫Big Apple?New York’s nickname is “the Big Apple”, a phrase used by jazz musicians to explain the ultimate in achievement, size and excitement.4.The first major Greek philosopher was Thales. Thales claimed that Nature is rational. He asked, “From whatdo all things come and to what do all things return?”(泰勒斯)5.Furthermore,this was the origin of metaphysics, the philosophical study which probes the nature of realityitself.形而上学6.数学家Pythagoras explained the entire natural world with numbers.(提出数字3)3=1(unity)+2(diversity)Three elements of Universe------earth, ocean, heavenThree elements of World ------animals, plants, mineralsThree elements of Gods ------Jupiter, Neptune, PlutoThree elements of Goddess ------Fate, Revenge, Beauty早期基督教教义Trinity (三位一体)人类3个indispensables------body, soul, spirit7.赫拉克利特Heraclitus is remembered because he introduced the concept of change as the onlyunchanging reality in the universe.He compared life to a flowing river:A person cannot step into the same river twice.8.德谟克利特Democritus. He argued that everything in the universe obeys the laws of necessity(必然性法则).9.观点:机械论His mechanistic view of the world was accepted by western thinkers as early as the 16thcentury.10.“Atom” means “uncuttable”(原子→不可分割)11.At the time when Chinese scholars, Confucians and Taoists, were concerned with social relationships andhuman harmony with the natural world, Greek philosophers were arguing about what Nature itself was.12.Athens was famous for its writers, architects, sculptors, thinkers and sports contests, including the originsof the modern-day Olympic Games.(雅典,奥林匹克发源地)13.Socrates→Lived in Athens.(苏格拉底,雅典人)One thing only I know, and that is that I know nothing.He distinguished between two types of knowledge: inner knowledge and empirical knowledge.Inner指each person has Virtue which is not learned through the physical sense.Another major contribution was his question-and-answer technique.14.Aristotle亚里士多德If Plato’s motto was “Mind over Matter”, then Aristotle’s motto was “Matter over Mind”.Aristotle founded the science of logic. His method is called a syllogism which argues from a general principle to a specific examples:General Principle: All men are mortal.Connection: I am a man.Deductive Conclusion: I am mortal.15.牛顿运动定律Newton’s laws of motion explained all visible motions,from those of stars to those of tinypebbles.16.培根Bacon, a British statesman and writer, wrote the first description of the modern scientific method.“Of studies”, “Essays”17.笛卡尔Descartes has also been called the father of modern Rationalism and the father of modern westernphilosophy.(近代理性主义之父,近代西方哲学之父)I think; therefore, I am.我思故我在。

(完整word版)英国文学选读复习资料Part I The Middle AgeChapter 1 the Anglo-Saxon period (449-1066)1. Beowulf(贝奥武甫): England’s national epic.(第一部民族史诗)2. artistic feature: ① using alliteration② using metaphor and understatementChapter 3 Geoffrey Chaucer (ca1343-1400)1.Geoffrey Chaucer is the father of English poetry and one of the most greatest narrative(叙事)poets of England.2.首创双韵体. tonico-syllabic verse. 运用London dialect.3. writing style: wisdom, humor, humanity.4.代表作:The Canterbury Tales-----In this book, Chaucer created a strikingly brilliant and picturesque panorama of his time and his country. In this poem Chaucer’s realism, trenchant irony and freedom of views reached such a high level of power that it had no equal in all the English literature up to the 16th century. But Chaucer was not entirely devoid of medieval prejudices. [乔叟为他那个时代和国家勾勒出一幅生机勃勃而又充满诗情画意的社会百态图。

English Literature• 1. 中世纪文学/mediaeval literature(约5世纪—1485)• 2. 文艺复兴时期文学/Renaissance literature(15世纪后期—17世纪初)• 3. 17世纪文学/17th Century Literature• 4. 启蒙时期文学/Literature Enlightenment period(17世纪后期—18世纪中期)• 5. 浪漫主义时期文学/Romantic literature period(1798-1832)• 6. 现实主义时期文学/Realism period(19世纪30年代-1918)•7. 现代主义文学时期/Modern Literature period (1918-1945)•8. 当代文学/Contemporary Literature(1945—今)1. 中世纪文学/mediaeval literature(约5世纪—1485)Note:“Medieval period” is a quite special period in English history. In Chinese “Medieval” or “The Middle Age”. Overview:•Many books on English literature begin with Chaucer, who serves as a convenient starting point since he is undoubtedly the first important writer in English history. Such a convenient choice, however, will leave out Beowulf, the most impressive long poem in Old English.•From the history ,the land was occupied by the Celts 凯尔特人before the Romans invaded it.Part I: Anglo-Saxon Period (449—1066)1. Historical background2. literature3. Old English Poetry: BeowulfThe Anglo-Saxon period (449-1066)•English literature began with the Anglo-Saxon settlement• 1. historical background•Three conquests: Roman conquest in 43 AD; Anglo-Saxon conquest in 449; Norman conquest in 1066 •43 AD, Roman conquered Britain ,making the latter a province of Roman Empire; the withdrawal of Roman troops ,the Teutonic tribes日耳曼人的,条顿人的.•esp., the Anglos conquered the island and called it Angle-land, then England, their language is Anglo-Saxon old English.New words:•pagan [‘peiɡən]:异教徒, 非基督教徒•Saga ['sɑ:ɡə]:中世纪北欧传说; 英雄传奇(saga novel)(多卷本)家世小说•ecclesiastic [i͵kli:zi'æstik] :(基督教的)牧师, 教士2. Literature:•the old English poetry can be divided into two groups: the secular and the religious.•The secular group: Beowulf, The Wife’s Complaints•The religious group: Genesis A and B are two poems based on the Old Testament.Sum up: 2. literature•1): pagan: oral sagas--the Song of Beowulf•2): Christian: copied by the monk.•The influence of the Christianity upon language and culture.•Two ecclesiastic poets: Caedmon and Cynewulf•Caedmon--[‘kædmən]凯德蒙(公元7世纪盎格鲁-撒克逊基督教诗人)•Cynewulf--[‘kinəwulf] 基涅武甫(盎格鲁-撒克逊诗人,生活在公元9 世纪诺森伯里亚或麦西亚,其古英语诗稿于10世纪被发现,有《埃琳娜》、《使徒们的命运》、《基督升天》和《朱莉安娜》等) Epic:史诗•Epic is an extended narrative poem in elevated or dignified language and in a grand style, like Homer’sIliad[‘iliəd] and Odyssey[’ɔdisi] . It usually celebrates the feats and achievements of one or more legendary or traditional heroes. The action is simple but full of magnificence. Many epics were drawn from an oral tradition and were transmitted by song and recitation before they were written down.•The epics are the earliest pieces of literature surviving from the Old English period and indeed a tribute to the vitality of the ancient paganism. This tradition is the composing in verse of tribal or national legends about a great hero, always a fighting warrior.•This is to be found in the Heroic Age of the Anglo-Saxons, while they were still on the Continent. In any case, the personality and the deeds of a hero were a source of inspiration to members of the tribe. To celebrate the deeds of the hero, and thereby to perpetuate his name and his glory unto succeeding generations, was the business of the bard, or minstrel, whom the Anglo-Saxons called the scop古代盎格鲁撒克逊的(吟游)诗人or gleeman吟游诗人.•How many of these epics were composed during the Heroic Age of the Anglo-Saxon can not be told;none of them were written down for centuries; instead they were passed by word of mouth from scop to scop; and the stories grew in the passing.•the Song of Beowulf [‘beɪə、wʊlf]----England’s national epicOld English Poetry: The Story of Beowulf•Beowulf -- written in 10th century, probably composed some time during the first half of the 8th century, after the Christianization of the whole nation. The historical event described in the poem belongs to the early 6th century.•Beowulf is the national epic of the Anglo-Saxon and English people. It consists of 3182 lines and is to be divided into two parts.–Though it is regarded today as the national epic of the Anglo-Saxons, th e hero and the setting of Beowulf have nothing to do with England, for the story took place in Scandinavia .•Scandinavia --[skændɪ’neɪvɪə]:the countries of N Europe, esp. considered as a cultural unit and including Norway, Sweden, Denmark, and often Finland, Iceland, and the Faeroes斯堪的纳维亚(半岛)(欧洲)Beowulf•Beowulf is folk legend brought to England by the Anglo-Saxons from their continental homes. Beowulf isa grand hero. He is so, simply by his deeds. He is faithful to his people. He goes alone, in a strange land,to venture himself for the deliverance of his people. He forgets himself in face of death. Though the poem was written in the 10th century, its hero was no doubt mainly the product of a primitive, tribal society on the continent.2). the Song of Beowulf- plot and theme:I. a. fight with Grendel II. a. fight with fire dragonb. fight with Grendel’s mother b. death and funeralplot•Part I: It opens in Denmark, where King Hrothgar's splendid mead hall, Heorot, has been ravaged for 12 years by nightly visits from an evil monster, Grendel, who carries off Hrothgar's warriors and devours them. Unexpectedly, young Beowulf, a prince of the Geats of southern Sweden, arrives with a small band of retainers and offers to cleanse Heorot of its monster. The King is astonished at the little-known hero's daring but welcomes him, and after an evening of feasting, much courtesy, and some discourtesy, the King retires, leaving Beowulf in charge. During the night Grendel comes from the moors, tears open the heavy doors, and devours one of the sleeping Geats. He then grapples with Beowulf, whose powerful grip he cannot escape. He wrenches himself free, tearing off his arm, and leaves, mortally wounded.•The next day is one of rejoicing in Heorot. But at night as the warriors sleep, Grendel's mother comes toavenge her son, killing one of Hrothgar's men. In the morning Beowulf seeks her out in her cave at the bottom of a mere and kills her. He cuts the head from Grendel's corpse and returns to Heorot. The Danes rejoice once more. Hrothgar makes a farewell speech about the character of the true hero, as Beowulf, enriched with honors and princely gifts, returns home to King Hygelac of the Geats.•The second part passes rapidly over King Hygelac's subsequent death in a battle (of historical record), the death of his son, and Beowulf's succession to the kingship and his peaceful rule of 50 years. But now a fire-breathing dragon ravages his land and the doughty but aging Beowulf engages it. The fight is long and terrible and a painful contrast to the battles of his youth. Painful, too, is the desertion of his retainers except for his young kinsman Wiglaf. Beowulf kills the dragon but is mortally wounded. The poem ends with his funeral rites and a lament.基本情节可分为两部分:•第一部分(诗行1—1904):丹麦国王赫罗斯加兴建了一座宏伟的宴乐厅,遭到魔怪格兰道尔的袭击。
British Writers and WorksI. Old English Literature & The Late Medieval Ages<Beowulf>贝奥武夫:the national epic of the Anglo-SaxonsEpic: long narrative poems that record the adventures or heroic deeds of a hero en acted in vast landscapes. The style of epic is grand and elevated.e.g. Homer’s Iliad and OdysseyArtistic features:ing alliterationDefinition of alliteration: a rhetorical device, meaning some words ina sentence begin with the same consonant sound (头韵)Some examples on P5ing metaphor and understatementDefinition of understatement: expressing something in a controlled wayUnderstatement is a typical way for Englishmen to express their ideasGeoffery Chaucer 杰弗里•乔叟 1340(?)~1400(首创“双韵体”,英国文学史上首先用伦敦方言写作。
约翰· 德莱顿(John Dryden) 称其为“英国诗歌之父”。
代表作《坎特伯雷故事集》。
)The father of English poetry.writing style: wisdom, humor, humanity.① <The Canterbury Tale s>坎特伯雷故事集:first time to use ‘heroic couplet’(双韵体) by middle English②<Troilus and Criseyde>特罗伊拉斯和克莱希德③ <The House of Fame>声誉之宫Medieval Ages’popular Literary form: Romance(传奇故事)Famous three: King ArthurSir Gawain and the Green KnightBeowulfII The Renaissance PeriodA period of drama and poetry. The Elizabethan drama is the real mainstreamof the English Renaissance.Renaissance : the activity, spirit, or time of the great revival of art, literature, and learning in Europe beginning in the 14th century and extending to the 17th century, marking the transition from the medieval to the modern world.Three historical events of the Renaissance –rebirth or revival:1.new discoveries in geography and astrology2.the religious reformation and economic expansion3.rediscovery of ancient Roman and Greek cultureThe most famous dramatists:Christopher MarloweWilliam ShakespeareBen Johnson.1.Edmund Spenser 埃德蒙•斯宾塞 1552~1599(后人称之为“诗人的诗人”。
英国文学复习资料全Pre-Renaissance periodBeowulf : the first English national epicI. The position of the Beowulf:the first English national epicII.The story: (to simply narrate it )Beowulf←→ Grendel and his motherBeowulf←→ Fire dragonIII. Its artistic features1. I t’s a 3183-line verse written in true epic style and in Old English;2. the most evident feature: the use of alliteration; (refer to the history of literature By Liu Bingshan,)3. to use compound-words to serve as metaphors;4. the use of understatements: the impression and a color of humor.△5. the mixing of pagan elements with Christian colouring.Geoffrey ChaucerI. life :1. He was born in a wine merchant family in 1340;2. His early life as a page and his marriage acquainted him with knowledge about upper class;3.he was buried in Westminster Abbey, thus founding the “Poets Corner” . II. His Work: The Canterbury TalesThe Canterbury TalesThe General Prologue...The PrioressThere was also a Nun, a Prioress,Whose name was gentle and full of guilelessness. “By St. Loy!” was the worst oath she would say. She sang mass well, in a becoming way,Intoning through her nose the words divine,And she was known as Madam Eglantine.She spoke good French, as taught at Stratford-Bow For the Parisian French she did not know.She was schooled to eat so primly and so well That from her lips no morsel ever fell.She wet her fingers lightly in the dishOf sauce, for courtesy was her first wish.With every bite she did her skillful bestTo see that no drop fell upon her breast.She always wiped her upper lip so cleanThat in her cup was never to be seenA hint of grease when she had drunk her share, She reached out for her meat with comely air. She was a great delight, and always triedTo imitate court ways, and had her pride,Both amiable and gracious in her dealings.As for her charity and tender feelings,She melted at whatever was piteous.She would weep if she but came upon a mouse Caught in a trap, if it were dead of bleeding. Some little dogs that took pleasure feedingOn roasted meat or milk or good wheat breadShe had, but how she wept to find one deadOr yelping from a blow that made it smart,And all was sympathy and loving heart.Neat was her wimple in its every plait,Her nose well formed, her eyes as gray as slate.Her mouth was very small and soft and red.She had so wide a brow I think her headWas nearly a span broad, for certainlyShe was not undergrown, as all could see.She wore her cloak with dignity and charm,And had her rosary about her arm,The small beads coral and the larger green,And from them hung a brooch of golden sheen,On it a large A and a crown above;Beneath, “all things are subject unto love.”I. Questions for discussion:1.What is the tone of the setting? How did the author achieve such settingof the tales?2.Summarize the character of the Prioress in this Prologue.3.To analyze Chaucer’s ways of characterization in this Prologue andthe language style of the selected part.II. To illustrate the terms.Heroic couplet: A two-line section of a poem, which rhymes and has five feet each in iambic meter(also termed as iambic pentameter ), and which has a meaning complete within itself.Example: The veins are bathed in li quor of such powerAs brings about the engen dering of the flower,(抑抑扬)ATT: For the convenience of the interpretation for the foot, some words are detached.Foot: A group of syllables forming a unit of verse, usually one foot contains at least one stressed word, or contains one stressedword and one or more than one unstressed words.III. Social significance of The Canterbury Tales (also function as a simple analysis)1.The Canterbury is not only a collection of stories strung by loosethread.(1) To affirm men and women’s right to pursue their happiness;(2) To oppose the dogma of asceticism;(3) To praise man’s energy, intellect and love of life.2.This work exposed the evil of time(1) the degeneration of the noble;(2) the heartless of judge;(3) the corruption of churchIV. Chaucer’s achievements in and contribution to English literature1.He is one of the earliest literary talents who embody humanism.2.Father of English poetry(1)the first great poet who wrote in English language;(2)introduced rhymed five accents in iambic meter to English poetry(heroic couplet)3.Founder of English realismThe prologue supplies a miniature of then English society (ways of narrating the stories and different social status of these pilgrims).4.His excellent works contribute a lot to establish English as theliterary language of the country. (set an example for thepoets of later generation )5.He made London dialect as the standard for the modern English speech.Renaissance PeriodWilliam ShakespeareI. Life1. born of trader family in Stratford-on-Avon in 1564, and his family got into financial troubles;2. Fail to finish formal schooling for the reason of financial difficulties, he left for London.II. Shakespeare the dramatistHis plays are poetical dramas, most of which are written in blank verse which was created one of the famous university wits, Christopher Marlow. His career as a dramatist may be divided into three (or four) periods: (to be lectured later)Hamlet●The Monologue:To be: to exist, to live, to passively accept, to suffer;Not to be: to die, to take action to fight against fate.That is the question: this shows Hamlet confronted with both body and moral dilemma: whether to suffer passively or to take action to fight.◆three rea sons for his dilemma:1.He receives Stoic philosophy: Forbearance is the noblest(顺从是最高的美德).Ciceronian philosophy: Duty is most important.These two views of philosophy are quite contradictory for Hamlet. (to interpret in depth )2.Religious reason: fear of after-life. (as obviously shown in this monologue: to die, to sleep)3. Odepus complex (commonly called mother complex): this view was put forward by some critic, which conducted a psychological analysis based on the Freudian philosophy. (to simply narrate the origin of this complex.)Points worthy of notice and interpretation in the monologue the slings and arrows (a metaphor, ): attackTo die, to sleep (analogy)no more: to exist no moreheartache: spiritual painnatural shocks: physical pain and sufferingconsummation: final settlementdevoutly to be wished : to be passionately wishedperchance: perhapsay: yesrub: difficultyshuffled off: get rid ofmortal coil: trouble of mortal life, coil: bodypause: hinderrespect: consideration, thinkingwhips and scorns of time: the beat and sneer in the word we live in. wrong: ill treatmentContumely: despisingPangs: sharp painspurns that patient merit of th’ unworthy takes: kicks that a personof merit takes from the unworthy.Fardels: (archaic word) burdensA weary life: a burdensome lifeBut that : unlessConscience: reflection, consciousnessIs sicklied over :is covered withPale cast: sickly cover, sickly colorThought: anxious thought or melancholy thoughtEnterprise: the great causePith and moment: importanceWith this regard: on this account, for this reasonTheir current turn awry: change the directionAction: here refers to “take arms against the fate”Questions for discussion:Give thorough consideration to the whole play and the monologue we have covered, and answer these questions:1.What is the use of the spirit of Hamlet’s father in the developmentof dramatic plot ?2.What is the use of his father’s spirit in the development of Hamlet’s character?3.To analyze Hamlet’s character?4.To analyze th e change of Hamlet’s attitude for Ophellia, what arethe reasons for the change?◆ Any other question concerning this play you want to put forward and explain. Welcome to speak your mind!III. Shakespeare the poet1. His sonnet (a general introduction about all 154 sonnets):Sonnet XVIIIPre-reading task:。
英国文学期末复习一、选择1、浪漫主义时期开始的标志:the publication of the Lyrical Ballads(1798) Wordsworth.结束:the death of Sir Walter Scott.18322、湖畔派诗人(Lake Poets):Wordsworth, Coleridge, Southey.3、Charles Lamb(查尔斯兰姆):He is important in English literature for his contribution to the Familiar Essay(随笔/小品文)4、Walter Scott(沃尔特司各特):the founder and great master of the historical novels(历史小说之父)。
5、Browning(布朗宁):the contribution to the English literature is dramatic monologue(戏剧独白)。
6、Emily Bronte(艾米丽勃朗特)的小说特点:Gothic noveleg.Wuthering Heights7、George Bernard Shaw(肖伯纳):Shaw’s main contribution to English literature is his drama.8、Thomas Stearns Eliot(艾略特):代表作The Waste Land(荒原)9、Steam of consciousness(意识流)的2位代表作家:James Joyce,Virginia Woolf10、Angry Young Man(愤怒的青年)出自John Osborne’s play Look Back in Angry(愤怒的回顾)。
11、只有1部代表作的作家及作品:William Makepeace Thackeray(萨克雷):Vanity Fair(名利场)Emily Bronte(艾米丽勃朗特):Wuthering Heights(呼啸山庄)Joseph Conrad:Heart of Darkness(黑暗心脏)George Bernard Shaw:Major Barbara(芭芭拉少女)12、Wordsworth defines poetry as “the spontaneous overflow of feelings”(一切好诗都是强烈情感的自然流露)。
英国文学简史复习资料General introduction of English literature1. 1 Old English Literature 449-1066 古英语时期文学——The Song of Beowulf 贝奥武甫2 Medieval English Literature 1066-15th century 中世纪英语时期文学——Geoffrey Chaucer 1340_1400 杰弗里·乔叟2. Renaissance English literature late 15th century ~ early 17th century 文艺复兴——Francis Bacon 弗朗西斯·培根——William Shakespeare 威廉·莎士比亚——Ben Jonson 本·琼生——Christopher Marlowe 克里斯托弗·马洛3. English Literature of the Revolution and Restoration Period 1640-1688 资产阶级革命与王朝复辟时期的文学——John Milton约翰·弥尔顿——John Bunyan 约翰·班扬4. 18th century English literature-the age of Enlightenment 启蒙运动时期——Daniel Defoe丹尼尔·笛福——Jonathan Swift乔纳森·斯威夫特——Henry Fielding亨利·菲尔丁——William Blake威廉·布莱克——Robert Burns罗伯特·彭斯5. Romantic English Literature 1798-1832 浪漫主义时期——William Wordsworth; 威廉·华兹华斯——Samuel Taylor Coleridge; 塞缪·泰勒·柯勒律治——George Gordon Byron; 乔治·戈登·拜伦——Percy Bysshe Shelley 佩西·比舍·雪莱——John Keats; 约翰·济慈——Walter Scott 沃尔特·司各特——Jane Austen简·奥斯汀6. Critical Realistic Literature in the 19th Century 维多利亚时期批判现实主义——W.M. Thackeray; 萨克雷——C harles Dickens; 查尔斯·狄更斯——Robert Browning 罗伯特·布朗宁——Bronte sisters:Charlotte Bronte; Emily Bronte; Ann Bronte——George Eliot乔治·艾略特——Matthew Arnold 马修·阿诺德——Thomas Hardy 托马斯·哈代——Oscar Wilde 奥斯卡·王尔德7. 20th Century English Literature——George Bernard Shaw乔治·萧伯纳——Joseph Conrad 约瑟夫·康拉德——William Butler Yeats 威廉·巴特勒·叶芝——Virginia Woolf弗吉尼亚·沃尔夫——James Joyce詹姆斯·乔伊斯——D. H. Lawrence劳伦斯——T. S. Eliot 爱略特一、The Anglo-Saxon period 449-10661、这个时期的文学作品分类: pagan异教徒 ;Christian基督徒2、代表作: The Song of Beowulf贝奥武甫 national epic 民族史诗采用了隐喻metaphor 手法3、Alliteration 头韵写作手法例子: of m an was the m ildest and m ost beloved;To his k in the k indest; k eenest for praise.二、The Anglo-Norman period 1066-1350 盎格鲁—诺曼时期1、romance 传奇文学2、代表作: Sir Gawain and the Green Knight 高文爵士和绿衣骑士是一首押头韵的长诗三、Geoffrey Chaucer 1340-1400 杰弗里·乔叟时期1、the father of English poetry 英国诗歌之父2、heroic couplet 英雄双韵体:a verse unit consisting of two rhymed押韵 lines in iambic pentameter五步抑扬格3、代表作:The Canterbury Tales 坎特伯雷的故事集英国文学史的开端大致内容:the pilgrims are people from various parts of England; representatives of various walks of life and social groups. 朝圣者都是来自英国的各地的人;代表着社会的各个不同阶层和社会团体小说特点:each of the narrators tells his tale in a peculiar manner; thus revealing his own views and character. 这些叙述者以自己特色的方式讲述自己的故事;无形中表明了各自的观点;展示了各自的性格..小说观点:he believes in the right of man to earthly happiness. He is anxious to see man freed from superstitions迷信 and a blind belief in fate 他希望人们能从迷信和对命运的盲从中解脱出来..4、Popular Ballads 大众民谣:a story hold in 4-line stanzas with second and fourth line rhymedBallads are anonymous narrative songs that have been preserved by oral transmission 歌谣是匿名叙事歌曲;一直保存着口头传播的方式代表人物:Bishop Thomas Percy 托马斯·珀西主教代表作:Robin Hood and Allin-a-Dale 侠盗罗宾汉和阿林代尔四、The Renaissance 16世纪文艺复兴时期Greek and Roman 戏剧 dramaThe term Renaissance originally indicated a revival of classical Greek and Roman arts and sciences.文艺复兴最初是指经典艺术和科学在英国的复兴..The epoch of Renaissance witnessed a particular development of English drama文艺复兴时期的英国戏剧也得到了迅速的发展..1、key word: humanism 人文主义: admire human beauty and human achievement2、代表人物:1、Thomas More 托马斯·莫尔 Utopia 乌托邦2、Francis Bacon 弗朗西斯.培根第一个散文家essayist3、Thomas Wyatt 托马斯.怀亚特引入十四行诗的第一人sonnet十四行诗: form of poetry intricately rhymed间隔押韵 in 14 lines iambic pentameter4、Edmund Spenser 埃德蒙·斯宾塞poet’s poet诗人中的诗人 The Fairy Queen仙后epic poem 史诗5、Christopher Marlowe 克里斯托弗·马洛blank verse无韵体:不押韵的五步抑扬格是十六世纪英国戏剧的主要表现形式..6、William Shakespeare 威廉·莎士比亚戏剧 drama四大悲剧:Hamlet哈姆雷特;Othello奥赛罗;King Lear李尔王;The Tragedy of Macbeth麦克白五、The period of Revolution and Restoration 17世纪资产阶级革命与王权复辟1、文学特点:the Puritans清教徒 believed in simplicity of life、disapproved of the sonnets and the love poetry、breaking up of old ideals.清教徒崇尚俭朴的生活、拒绝十四行诗和爱情诗、与旧思想脱离..2、代表人物:1、John Donne 约翰·多恩“metaphysical”poets 玄学派诗人的代表人物sonnet 十四行诗“ Death be not proud”代表作品:The Flea跳蚤2、John Milton 约翰·弥尔顿 a great poet 诗人 poem 诗歌 blank verseDefense for the English People为英国人民辩护Paradise Lost失乐园“Satan is not a villain”撒旦不是坏人Paradise Regained复乐园3、John Bunyan 约翰·拜扬 a great prose writer “give us the only great allegory 寓言”The Pilgrim’s Progress天路历程该书采用的写作手法“written in the old-fashioned旧体形式; medieval form of allegory 寓言and dream”六、The Age of Enlightenment 18世纪启蒙运动 also known as “the Age of Reason”1、Emphasized formality or correctness of style; to write prose like Addison; or verse like Pope.强调正确的格式和写作规范;像艾迪生一样创作散文;和蒲柏一样创作诗歌..The Enlightenment was an expression of struggle of the then progressive class of bourgeoisie against feudalism. 启蒙运动实际上是当时先进的资产阶级同落后的封建主义斗争的一种形式..The enlighteners repudiate the false religious doctrines about the viciousness of human nature; and prove that man is born kind and honest; and if he becomes depraved; it is only due to the influence of corrupted social environment.启蒙主义者颠覆了宗教所宣扬的人类本恶的观点;论证了人生诚实而友善;而腐化堕落则是后天腐败的社会环境所致..Contrary to all reasoning; social injustice still held strong; found the power of reason to be insufficient; and therefore appealed to sentiment as a means of achieving happiness and social justice.无论怎样讲究理性;社会不平等现象仍然普遍存在;理性的力量明显不足..因此呼吁把情感的诉求作为一种谋求幸福和社会公平的手段..2、18th century 文学的三个方面:Neo-Classicism新古典主义、Sentimentalism伤感主义、Pre-romanticism 前浪漫主义诗歌、beginning of the modern novel刚启萌的现代派小说、drama戏剧3、代表人物:1、Daniel Defoe 丹尼尔·笛福 realistic novel 现实主义小说Novel:” Robinson Crusoe”鲁宾逊漂流记” The History of Tom Jones; a F oundling”弃婴汤姆.琼斯的故事 the best novel of him 2、Jonathan Swift 乔纳森·斯威夫特” Gulliver’s Travels”格列佛游记novel反讽作品特点:no visible sign of anger; nor raising the voice; the tone is cold; restrained; ironic; varied only by some flashes of fooling when Swift’s sense of the ridiculous gets the better of him.努不动颜;骂不扬声;语调冷酷;锋芒暗藏;讽刺辛辣;仅在讽喻之情难以抑制时才偶露揶揄之态..” A Modest Proposal”一个温和的建议猛烈地抨击了压迫爱尔兰人民的统治4、Samuel Richardson 塞缪尔·理查森” Pamela”帕美勒 The method of psychological analysis 心理分析的方法In the form of letters 书信体小说5、Richard B. Sheridan 理查德·B.谢里丹” School for Scandal”造谣学校;喜剧 comedy6、Oliver Goldsmith’s 奥利佛·.哥尔德斯密斯散文作家 essayist” The Vicar of Wakefield”威克菲尔德的牧师;小说 novel” She Stoops to Conquer”委曲求全;欢乐喜剧 rollicking comedy” The Deserted Village”荒村;诗歌 poems4、Sentimentalism 感伤主义 no belief 没有信仰The representatives of sentimentalism continued to struggle against feudalism but they vaguely sensed at the same time the contradictions of bourgeois progress that brought with it enslavement and ruin to the people. 感伤主义的代表人物在继续反对封建主义的同时又模糊的感觉到资本主义进程中出现的种种矛盾;感觉到资本主义制度对人性的奴役和破坏..代表人物:Thomas Gray 托马斯.格雷“ Elegy; Written in a Country Churchyard”墓园挽歌七、The Romantic Period 1798-1832浪漫主义1、前浪漫主义代表人物:1 William Blake 威廉·布莱克诗人 poet代表作品:诗集天真之歌Songs of Innocence: The Lamb; The Chimney Sweeper1789诗集经验之歌Songs of Experience: The Tiger; London; The Chimney Sweeper17942 Robert Burns 罗伯特·.彭斯苏格兰诗人 poet代表作品:A Red; Red Rose 一朵红红的玫瑰、My Heart’s on the Highland我的心在高原、天长Auld Lang Syne..Pre-Romanticism was greatly influenced by the Industrial Revolution and the French Revolution前浪漫主义极大地影响了工业革命和法国大革命..2、教育意义Educational:liberty; equality and fraternity 自由;平等;博爱3、开始的标志:beginning with the publication of William Wordsworth and S. T. Coleridge’s “Lyrical Ballads” 从威廉.华兹华斯和柯勒律治一起发表的抒情歌谣集开始4、lake poets湖畔诗人:Wordsworth; Coleridge; Southey 骚塞5、代表人物:1、William Wordsworth 威廉·华兹华斯 poet-laureate 桂冠诗人“The Prelude”序曲自传性诗歌Autobiographical poetry作品特点:simplicity and purity of the language; fighting against the conventional forms of the 18th century poetry 简单而纯洁的语言;反传统形式的18世纪诗歌2、S. T. Coleridge 柯勒律治Demonic poems魔幻诗The Rime of the Ancient Mariner 古舟子咏、Kubla Khan忽必烈汗Christabel克里斯塔贝尔作品特点:unusual and supernatural things不寻常和超自然的事物3、Lord Byron 拜伦“ Childe Harold Pilgrimage”恰尔德·哈罗德游记成名作“ Don Juan”唐璜 satiric masterpiece 讽刺的杰作4、Percy Bysshe Shelley 雪莱“ Prometheus Unbound” 解放了的普罗米修斯 drama 戏剧“ Ode to the West Wind”西风颂 poem 诗5、John Keats 济慈 poet 诗人“ The Eve of St. Agnes”圣阿格尼斯之夜poem “ On a Grecian Urn”希腊古瓮颂poem “ To a Nightingale”夜莺颂poem “Beauty i s truth; truth beauty”美学原则6、Walter Scott沃尔特·司各特 He is the creator and a great master of the historical novel. 他是历史小说的创造者和大师作品:Ivanhoe艾凡赫、The Lady of The Lake湖上夫人7、Jane Austen 简·奥斯丁女“ Pride and Prejudice”傲慢与偏见“ Sense and Sensibility”理智与情感“ Emma”爱玛写作特点:the love-making of her young people; though serious and sympathetic; is subdued by humor to the ordinary plane of emotion on which most of us live. She was the founder of the novel which deals with unimportant middleclass people. 她是中产阶级小说的发起人..6、十九世纪散文的特点:In the first of these two periods Addison and Steele socialized the essay; so to speak; they brought it into everyday life and made it familiar and delightful to the multitude. 在这两个时期的开始;艾迪生和斯蒂尔的社会散文把散文带入日常生活;并使其熟悉和并令人愉快.. Early in the nineteenth century it became more definitely a means of intimate self-expression.在十九世纪前期;散文变得对自我的表达越来越肯定。
英国文学史复习资料一、早期文学1、凯尔特文学:凯尔特人是英国最早的民族,他们有自己的语言和神话传说。
他们的文学作品包括《德鲁伊特教义》和《芬尼亚传奇》。
2、盎格鲁-撒克逊文学:随着罗马帝国的衰落,日耳曼部落开始在英国定居。
盎格鲁-撒克逊时期最著名的文学作品是《贝奥武夫》,讲述了一位英勇的武士贝奥武夫的故事。
二、中世纪文学1、英雄史诗:中世纪时期,英国出现了许多描写骑士和英雄事迹的史诗,如《罗兰之歌》、《希尔德布兰德之歌》等。
2、骑士文学:随着封建制度的发展,骑士成为英国社会的一个重要阶层。
骑士文学主要描写骑士的冒险经历和爱情故事,如《亚瑟王传奇》等。
3、宗教文学:中世纪时期,英国的宗教文学也很发达。
最有名的作品是《神曲》和《圣经》的英译本。
三、文艺复兴时期文学1、伊丽莎白时代文学:伊丽莎白一世时期,英国进入了文艺复兴时期。
这个时期的文学作品包括莎士比亚的戏剧、《罗密欧与朱丽叶》等。
2、斯图亚特王朝复辟时期文学:斯图亚特王朝复辟后,英国文学开始向古典主义转变。
这个时期的文学作品包括弥尔顿的《失乐园》和约翰·德莱顿的诗歌等。
四、启蒙时期文学1、启蒙运动:启蒙运动是18世纪欧洲的一个思想解放运动,旨在推翻封建制度,建立资产阶级民主制度。
英国的启蒙运动以洛克和休谟为代表。
2、现实主义小说:随着工业革命的兴起,英国的现实主义小说开始兴起。
这个时期的代表作家包括狄更斯、萨克雷、勃朗特姐妹等。
他们的作品主要描写社会底层人民的生活和资产阶级的虚伪与贪婪。
3、浪漫主义诗歌:19世纪初,英国的浪漫主义诗歌开始兴起。
这个时期的代表诗人包括华兹华斯、柯勒律治和拜伦等。
他们的作品主要表达个人情感和对自然的向往。
五、维多利亚时期文学1、维多利亚时代的社会背景:维多利亚时代是英国的一个繁荣时期,也是英国殖民主义的高峰期。
这个时期的英国成为“日不落帝国”。
2、小说:维多利亚时期的代表作家包括狄更斯、勃朗特姐妹、哈代等。
1.Blank verse:is poetry written in unrhymed iambic pentameter.素体诗,用不押韵的抑扬格五音步写的诗(in Renaissance period ,Many forms of writing appear.)2.Tragedy:is a drama in which the protagonist (主角) is overcome by some superior force or circumstance. It excites terror or pity. It often ends with the death of the main character. Eg. Hamlet, King Lear by Shakespeare3.Allegory:Allegory is a literary device in which characters or events in a literary work represent or symbolize ideas and concepts. An allegory in its most general sense is an extended metaphor.(寓言) eg. Aesop’s Fables Book of Revelation4.The enlightenment :(or Age of Reason) was an elite(精华) cultural movement of intellectuals(劳动人民)in the 18th century Europe that sought to (追求)mobilize(组织动员)the power of reason in order to reform society and advance knowledge.5.Reason:is a term that refers to the capacity humanbeings have to make sense of things, to establish and verify facts, and to change or justify practices, institutions and beliefs. 理性6.Romantism:An artistic and intellectual movement originating in Europe in the late 18th century and characterized by a heightened interest in nature, emphasis on the individual’s expression of emotion and imagination, departure from the attitudes and forms of classicism, and rebellion(反抗)against established social rules and conventions.分析诗:(作者等、形式韵律、主题、细节怎么体现主题)1. Rhythm节奏①Syllable(音节): a word or part of a word which contains one vowel sound. Ex. Apple(2)Stress(重读): a word or part of a word which should be pronounced with more force. Ex. apple, helicopter2. Foot音步Foot is the unit of rhythm and contains two or three syllables, one of which is stressed.Ex. As soon | as A|pril pier|ces to | the root依照每一音步中重读音节(扬)和非重读音节(抑)的排列方式,可以把音步分成不同种类,即格律(meter)。
Pre-Renaissance periodBeowulf : the first English national epicI. The position of the Beowulf:the first English national epicII.The story: (to simply narrate it )Beowulf←→ Grendel and his motherBeowulf←→ Fire dragonIII. Its artistic features1. I t’s a 3183-line verse written in true epic style and in Old English;2. the most evident feature: the use of alliteration; (refer to the history of literature By Liu Bingshan,)3. to use compound-words to serve as metaphors;4. the use of understatements: the impression and a color of humor.△5. the mixing of pagan elements with Christian colouring.Geoffrey ChaucerI. life :1. He was born in a wine merchant family in 1340;2. His early life as a page and his marriage acquainted him with knowledge about upper class;3.he was buried in Westminster Abbey, thus founding the “Poets Corner” . II. His Work: The Canterbury TalesThe Canterbury TalesThe General Prologue...The PrioressThere was also a Nun, a Prioress,Whose name was gentle and full of guilelessness. “By St. Loy!” was the worst oath she would say. She sang mass well, in a becoming way,Intoning through her nose the words divine,And she was known as Madam Eglantine.She spoke good French, as taught at Stratford-Bow For the Parisian French she did not know.She was schooled to eat so primly and so well That from her lips no morsel ever fell.She wet her fingers lightly in the dishOf sauce, for courtesy was her first wish.With every bite she did her skillful bestTo see that no drop fell upon her breast.She always wiped her upper lip so cleanThat in her cup was never to be seenA hint of grease when she had drunk her share, She reached out for her meat with comely air. She was a great delight, and always triedTo imitate court ways, and had her pride,Both amiable and gracious in her dealings.As for her charity and tender feelings,She melted at whatever was piteous.She would weep if she but came upon a mouse Caught in a trap, if it were dead of bleeding. Some little dogs that took pleasure feedingOn roasted meat or milk or good wheat breadShe had, but how she wept to find one deadOr yelping from a blow that made it smart,And all was sympathy and loving heart.Neat was her wimple in its every plait,Her nose well formed, her eyes as gray as slate.Her mouth was very small and soft and red.She had so wide a brow I think her headWas nearly a span broad, for certainlyShe was not undergrown, as all could see.She wore her cloak with dignity and charm,And had her rosary about her arm,The small beads coral and the larger green,And from them hung a brooch of golden sheen,On it a large A and a crown above;Beneath, “all things are subject unto love.”I. Questions for discussion:1.What is the tone of the setting? How did the author achieve such settingof the tales?2.Summarize the character of the Prioress in this Prologue.3.To analyze Chaucer’s ways of characterization in this Prologue andthe language style of the selected part.II. To illustrate the terms.Heroic couplet: A two-line section of a poem, which rhymes and has five feet each in iambic meter(also termed as iambic pentameter ), and which has a meaning complete within itself.Example: The veins are bathed in li quor of such powerAs brings about the engen dering of the flower,(抑抑扬)ATT: For the convenience of the interpretation for the foot, some words are detached.Foot: A group of syllables forming a unit of verse, usually one foot contains at least one stressed word, or contains one stressed word and one or more than one unstressed words.III. Social significance of The Canterbury Tales (also function as a simple analysis)1.The Canterbury is not only a collection of stories strung by loosethread.(1) To affirm men and women’s right to pursue their happiness;(2) To oppose the dogma of asceticism;(3) To praise man’s energy, intellect and love of life.2.This work exposed the evil of time(1) the degeneration of the noble;(2) the heartless of judge;(3) the corruption of churchIV. Chaucer’s achievements in and contribution to English literature1.He is one of the earliest literary talents who embody humanism.2.Father of English poetry(1)the first great poet who wrote in English language;(2)introduced rhymed five accents in iambic meter to English poetry(heroic couplet)3.Founder of English realismThe prologue supplies a miniature of then English society (ways of narrating the stories and different social status of these pilgrims).4.His excellent works contribute a lot to establish English as theliterary language of the country. (set an example for the poets of later generation )5.He made London dialect as the standard for the modern English speech.Renaissance PeriodWilliam ShakespeareI. Life1. born of trader family in Stratford-on-Avon in 1564, and his family got into financial troubles;2. Fail to finish formal schooling for the reason of financial difficulties, he left for London.II. Shakespeare the dramatistHis plays are poetical dramas, most of which are written in blank verse which was created one of the famous university wits, Christopher Marlow. His career as a dramatist may be divided into three (or four) periods: (to be lectured later)Hamlet●The Monologue:To be: to exist, to live, to passively accept, to suffer;Not to be: to die, to take action to fight against fate.That is the question: this shows Hamlet confronted with both body and moral dilemma: whether to suffer passively or to take action to fight.◆three reasons for his dilemma:1.He receives Stoic philosophy: Forbearance is the noblest(顺从是最高的美德).Ciceronian philosophy: Duty is most important.These two views of philosophy are quite contradictory for Hamlet. (to interpret in depth )2.Religious reason: fear of after-life. (as obviously shown in this monologue: to die, to sleep)3. Odepus complex (commonly called mother complex): this view was put forward by some critic, which conducted a psychological analysis based on the Freudian philosophy. (to simply narrate the origin of this complex.)Points worthy of notice and interpretation in the monologuethe slings and arrows (a metaphor, ): attackTo die, to sleep (analogy)no more: to exist no moreheartache: spiritual painnatural shocks: physical pain and sufferingconsummation: final settlementdevoutly to be wished : to be passionately wishedperchance: perhapsay: yesrub: difficultyshuffled off: get rid ofmortal coil: trouble of mortal life, coil: bodypause: hinderrespect: consideration, thinkingwhips and scorns of time: the beat and sneer in the word we live in. wrong: ill treatmentContumely: despisingPangs: sharp painspurns that patient merit of th’ unworthy takes: kicks that a personof merit takes from the unworthy.Fardels: (archaic word) burdensA weary life: a burdensome lifeBut that : unlessConscience: reflection, consciousnessIs sicklied over :is covered withPale cast: sickly cover, sickly colorThought: anxious thought or melancholy thoughtEnterprise: the great causePith and moment: importanceWith this regard: on this account, for this reasonTheir current turn awry: change the directionAction: here refers to “take arms against the fate”Questions for discussion:Give thorough consideration to the whole play and the monologue we have covered, and answer these questions:1.What is the use of the spirit of Hamlet’s father in the developmentof dramatic plot ?2.What is the use of his father’s spirit in the development of Hamlet’s character?3.To analyze Hamlet’s character?4.To analyze the change of Hamlet’s attitude for Ophellia, what arethe reasons for the change?◆ Any other question concerning this play you want to put forward and explain. Welcome to speak your mind!III. Shakespeare the poet1. His sonnet (a general introduction about all 154 sonnets):Sonnet XVIIIPre-reading task:1. To contrast the tone of the 1st and 2nd stanza with the one of the 3rd, try to find the difference.2. What are denotation of such images as “summer’s day”, “buds of May” and “rough wind”?Notes:•thee: you•Summer’s day: warmth and beauty (best season for Shakespeare) •Thou art: you are•Temperate: mild•Rough winds do shake the darling buds of May: beauty is short-lived.•And every fair from fair sometimes decline (a inverted line): And every fair sometimes decline from fair.•By chance, or nature’s changing course untrimm’d (a inverted line): untrimm’d By chance, or nature’s changing course. Trim: dress Questions and task for sonnet 181. Consider the relationship among four stanzas to identify the special poetic pattern of Shakespearian sonnet.2. what is the theme of this sonnet?Edmund SpenserI.Spenser the man1. born of a poor merchant’s family;2. Educated at Merchant Tailor’s schoolIn this school, a teacher with humanism conveyed the idea of education as follows: “It’s not a mind, nor a body, that we have to educate, buta man, we can not divide him”.3. Studying in Cambridge University, he was under the influence of Platonism (one aspect: the inner beauty is more important than the beauty of appearance.) This may be found in his poetry; and he also got much influence from Phillip Sidney, this influence is of importance for his creation of sonnet.II. Spenser the poet (mainly his poem)1. Amoretti (爱情小唱):a sequence of 88 poems, in which sonnet 54 and sonnet 75 are most famous.Pre-reading Questions for sonnet 54:1.What is the tone of this poem?2.Who is the speaker?3. Could you describe the changes of the speaker’s inner world, esp.his emotional changes?Sonnet 54Of this worlds theatre in which we stay,My love like the spectator ydly sitsBeholding me that all the pageants play,Disguysing diversly my troubled wits.Sometimes I joy when glad occasion fitsAnd mask in myrth lyke to a comedy:Sonne after when my joy to sorrow flits,I wane and make my woes a tragedy.Yet she, beholding me with constant eye,Delights not in my mirth nor rues my smart:But when I laugh she mocks, and when I cryShe laughs and hardens evermore her heart.What then can move her? If nor merth nor mone,She is no woman, but a sencelesse stone.Question for discussion: What is the theme of this sonnet?Sonnet 75One day I wrote her name upon the strand,But came the waves and washed it away:Agayne I wrote it with a second hand,But came the tyde, and made my payne his pray.“Vayne man,” sayd she, “that doest in vaine assay,A mortall thing so to immortalize,For I my selve shall lyke to this decay,And eek my name bee wyped out lykewize.”“Not so,”quod I, “ let baser things devize,To dy in dust, but you shall live by fame:My verse your vertues rare shall eternize,And in the heavens wryte your glorious name,Where whenas death shall all the world subdew,Our love shall live, and later life renew.”Questions for sonnet 751. What are the connotations of such images in this sonnet as “wave”,“name” and “heaven”?Could you find some instances of comparison the poet used in this poem?2. In this sonnet, Spenser conveyed the idea of “our love shall live,and later life renew.” But, how can “our love live, and later life renew”?3. What is the theme of this sonnet?Connotation of some images in this sonnet:Term:Alliteration: Alliteration is a kind of rhyme with the initial sounds identical, identical sounds closely connects two or more words both insounds and in meaning.2. The Shepherds’ Calendar(牧童的月历)(1) A pastoral poem(田园诗,牧歌体诗) consisting 12 eclogues,one for each month, these eclogues are written in different meters;(2)The shepherd represents the poet and his friend;Most part of this poem are written in dialogue form, esp. the dialogue between the shepherd and his friend;(3)The dominant theme is love, and the theme of religion is also discussed.3. The Faire Queen(1) Spenser’s masterpiece;an epic written in a special verse form (Spenserian Stanza);(2) Planned in 12 books, but only 6 books and two cantos(诗章) of the 7th were finished;(3) hero and heroin: king Arthur and Gloriana;(4) the story: (adventures of 12 knights). It’s a vivid narrative of knightly adventures, it also involved moral, religion and political allegories, and all sorts of supernatural beings;(5) Each knight stands for a virtue: Holiness, Temperance, Chastity, Friendship, Justice and Courtesy, these virtues were acquired in the course of adventures.(6) thought of this poem: nationalism, humanism and puritanism.Spenserian Stanza(斯宾塞体): A special verse form consists of eight iambic pentameter lines followed by a ninth line of six iambic feet (an alexandrine).Remark: 斯宾塞体即五音步一行的八行加上六音步一行而形成的九行体。