
Part 1
1.Write a query to display the current date. Label the column Date.
select to_char(sysdate,'year-mon-day')“D ate”
from dual
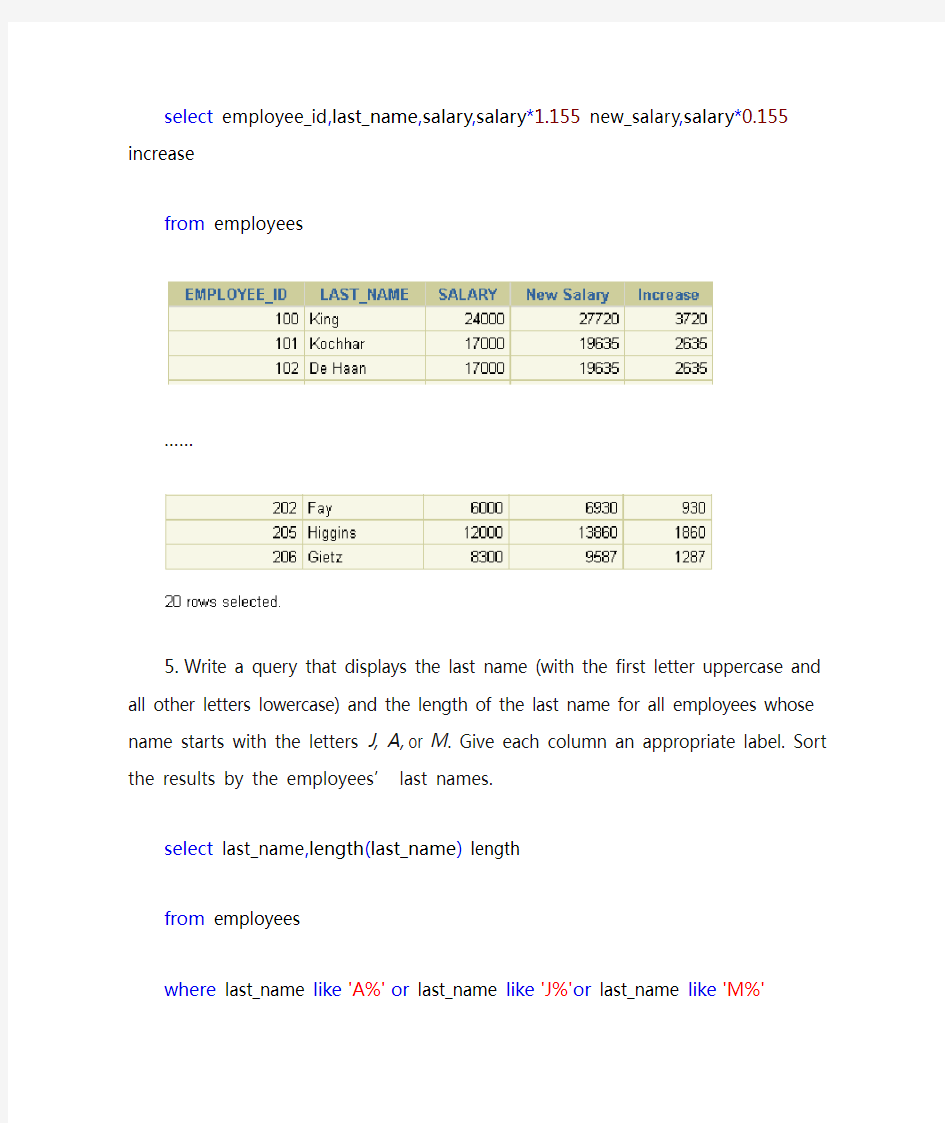
2. The HR department needs a report to display the employee number, last name, salary, and salary increased by 15.5% (expressed as a whole number) for each employee. Label the column New Salary. Place your SQL statement in a text file named lab_03_02.sql.
select employee_id,last_name,salary,salary*1.155 new_salary
from employees
3. Run your query in the file lab_03_02.sql.
4. Modify your query lab_03_02.sql to add a column that subtracts the old salary from
the new salary. Label the column Increase. Save the contents of the file as lab_03_04.sql. Run the revised query.
select employee_id,last_name,salary,salary*1.155
new_salary,salary*0.155 increase
from employees
……
5.Write a query that displays the last name (with the first letter uppercase and all other letters
lowercase) and the length of the last name for all employees whose name starts with the letters J, A, or M. Give each column an appropriate label. Sort the results by the employees’ last names.
select last_name,length(last_name) length
from employees
where last_name like'A%'or last_name like'J%'or last_name like'M%' order by last_name
Rewrite the query so that the user is prompted to enter a letter that starts the last name. For example, if the user enters H when prompted for a letter, then the output should show all employees whose last name starts with the letter H.
6. The HR department wants to find the length of employment for each employee. For each employee, display the last name and calculate the number of months between today and the date on which the employee was hired. Label the column MONTHS_WORKED. Order your results by the number of months employed. Round the number of months up to the closest whole number.
Note: Your results will differ.
select last_name,round(months_between(sysdate,hire_date))
"MONTHS_WORKED"
from employees
order by hire_date desc
7. Create a report that produces the following for each employee:
select last_name||' earns'||to_char(salary,'$999,999.99')||' monthly but wants'||to_char(3*salary,'$999,999.99')
from employees
8.Create a query to display the last name and salary for all employees. Format the salary to be
15 characters long, left-padded with the $ symbol. Label the column SALARY.
select last_name,lpad(salary,15,'$')"SALARY"
from employees
9.Display ea ch employee’s last name, hire date, and salary review date, which is the first
Monday after six months of service. Label the column REVIEW. Format the dates to appear in the format similar to “Monday, the Thirty-First of July, 2000.”
Select last_name,to_char(hire_date,'dd-mm-yy')
"hire_date",to_char(next_day(add_months(hire_date,’星期一'),'day,"the" ddspth "of" month,yyyy') "REVIEW"
from employees
10.Display the last name, hire date, and day of the week on which the employee started. Label
the column DAY. Order the results by the day of the week, starting with Monday.
select last_name,hire_date,to_char(hire_date,'day')"DAY"
from employees
order by to_char(hire_date-1,'d')
11.Create a query that displays the employees’ last names and commission amounts. If an
employee does not earn commission, show “No Commission.” Label the column COMM. Select last_name,nvl(to_char(commission_pct),' No Commission')"COMM"
From employees
12.Create a query that displays the first eight characters of the employees’ last names and
indicates the amounts of their salaries with asterisks. Each asterisk signifies a thousand dollars. Sort the data in descending order of salary. Label the column EMPLOYEES_AND_THEIR_SALARIES.
Select rpad(substr(last_name,1,8),8)|| lpad(' ',salary/1000,'*')
from employees
order by salary desc
13. Using the DECODE function, write a query that displays the grade of all employees based on the value of the column JOB_ID, using the following data:
Job Grade
AD_PRES A
ST_MAN B
IT_PROG C
SA_REP D
ST_CLERK E
None of the above 0
select job_id,decode(job_id,'AD_PRES','A',
'ST_MAN','B',
'IT_PROG','C',
'SA_REP','D',
'ST_CLERK','E',0)"GRA"
from employees
14. Rewrite the statement in the preceding exercise using the CASE syntax.
select job_id,case job_id when'AD_PRES'then'A'
when'ST_MAN'then'B'
when'IT_PROG'then'C'
when'SA_REP'then'D'
when'ST_CLERK'then'E'
else'0'
end"GRA"
from employees
15.Group functions work across many rows to produce one result per group.
True/False T
16.Group functions includee nulls in calculations.
True/False F
17.The WHERE clause restricts rows before inclusion in a group calculation.
True/False T
The HR department needs the following reports:
18.Find the highest, lowest, sum, and average salary of all employees. Label the columns Maximum, Minimum, Sum, and Average, respectively. Round your results to the nearest whole number. Place your SQL statement in a text file named lab_04_04.sql.
select max(salary)"maximum",min(salary)"minimum",sum(salary) "Sum", round(avg(salary))"Average"
from employees
19,Modify the query in lab_04_04.sql to display the minimum, maximum, sum, and average salary for each job type. Resave lab_04_04.sql as lab_04_05.sql. Run the statement in lab_04_05.sql.
select job_id,max(salary)"maximum",min(salary)
"minimum",sum(salary)"Sum", round(avg(salary))"Average"
from employees
group by job_id
20.Write a query to display the number of people with the same job.
select job_id,count(*)
from employees
group by job_id
21. Determine the number of managers without listing them. Label the column Number of Managers. Hint: Use the MANAGER_ID column to determine the number of managers.
select count(distinct manager_id) "Number of Managers"
from employees
22.Find the difference between the highest and lowest salaries. Label the column DIFFERENCE. select max(salary)-min(salary)"Difference"
from employees
23.Create a report to display the manager number and the salary of the lowest-paid employee
for that manager. Exclude anyone whose manager is not known. Exclude any groups where the minimum salary is $6,000 or less. Sort the output in descending order of salary.
select manager_id,min(salary)
from employees
where manager_id is not null
group by manager_id
having min(salary)>6000
24.Create a query to display the total number of employees and, of that total, the number of employees hired in 1995, 1996, 1997, and 1998. Create appropriate column headings.
select count(*) total,
sum(decode(to_char(hire_date,'yyyy'),'1995',1,0))"1995",
sum(decode(to_char(hire_date,'yyyy'),'1996',1,0))"1996",
sum(decode(to_char(hire_date,'yyyy'),'1997',1,0))"1997",
sum(decode(to_char(hire_date,'yyyy'),'1998',1,0))"1998"
from employees
25. Create a matrix query to display the job, the salary for that job based on department number, and the total salary for that job, for departments 20, 50, 80, and 90, giving each column an appropriate heading.
select job_id "JOB",
sum(decode(department_id,20,salary,0))"Dept 20",
sum(decode(department_id,50,salary,0))"Dept 50",
sum(decode(department_id,80,salary,0))"Dept 80",
sum(decode(department_id,90,salary,0))"Dept 90",sum(salary)"Total" from employees
group by job_id
26.Write a query for the HR department to produce the addresses of all the departments. Use the LOCATIONS and COUNTRIES tables. Show the location ID, street address, city, state or province, and country in the output. Use a NATURAL JOIN to produce the results.
select LOCATION_ID,STREET_ADDRESS,CITY,STATE_PROVINCE,COUNTRY_NAME
from LOCATIONS natural join COUNTRIES
27.The HR department needs a report of all employees. Write a query to display the last name, department number, and department name for all employees.
select last_name,department_id,department_name
from employees natural join departments
28.The HR department needs a report of employees in Toronto. Display the last name, job, department number, and department name for all employees who work in Toronto.
select last_name,job_id,department_id,department_name,city
from employees join departments using(department_id)
join locations using(location_id)
where city='Toronto'
29.Create a report to display employees’ last name and employee number along with their
manager’s last name and manager number. Label the columns Em ployee, Emp#, Manager,
and Mgr#, respectively. Place your SQL statement in a text file named lab_05_04.sql. Select https://www.doczj.com/doc/7a14914150.html,st_name,e1.employee_id,https://www.doczj.com/doc/7a14914150.html,st_name,e1.manager_id
From employees e1 join employees e2 on e1.manager_id=e2.employee_id
30.Modify lab_05_04.sql to display all employees including King, who has no manager. Order
the results by the employee number. Place your SQL statement in a text file named lab_05_05.sql. Run the query in lab_05_05.sql.
Select https://www.doczj.com/doc/7a14914150.html,st_name,e1.employee_id,https://www.doczj.com/doc/7a14914150.html,st_name,e1.manager_id
From employees e1 left join employees e2 on e1.manager_id=e2.employee_id
Order by e1.employee_id
31.Create a report for the HR department that displays employee last names, department
numbers, and all the employees who work in the same department as a given employee.
Give each column an appropriate label. Save the script to a file named lab_05_06.sql
select e1.department_id,https://www.doczj.com/doc/7a14914150.html,st_name EMPLOYEE,https://www.doczj.com/doc/7a14914150.html,st_name COLLEAGUE from employees e1 join employees e2 on e1.DEPARTMENT_ID =e2.DEPARTMENT_ID and https://www.doczj.com/doc/7a14914150.html,ST_NAME<>https://www.doczj.com/doc/7a14914150.html,ST_NAME
order by e1.department_id
32.The HR department needs a report on job grades and salaries. To familiarize yourself with
the JOB_GRADES table, first show the structure of the table. Then create a query that displays the name, job, department name, salary, and grade for all employees.
select last_name,job_id,department_name,salary,GRADE_LEVEL
from employees join departments using(department_id)
join JOB_GRADES on salary>LOWEST_SAL and salary 33.The HR department wants to determine the names of all employees who were hired after Davies. Create a query to display the name and hire date of any employee hired after employee Davies. select last_name,hire_date from employees where hire_date>(select hire_date from employees where last_name = 'Davies') 34.The HR department needs to find the names and hire dates for all employees who were hired before their managers, along with their managers’ names and hire dates. Save the script to a file named lab5_09.sql. select https://www.doczj.com/doc/7a14914150.html,ST_NAME,e1.HIRE_DATE,https://www.doczj.com/doc/7a14914150.html,st_name,e2.hire_date from employees e1 join employees e2 on e1.MANAGER_ID = e2.employee_id where e1.hire_date 35.The HR department needs a query that prompts the user for an employee last name. The query then displays the last name and hire date of any employee in the same department as the employee whose name they supply (excluding that employee). For example, if the user enters Zlotkey, find all employees who work with Zlotkey (excluding Zlotkey). select last_name,hire_date from employees where department_id =(select department_id from employees where last_name='&name' )and last_name!='&name' 36 .Create a report that displays the employee number, last name, and salary of all employees who earn more than the average salary. Sort the results in order of ascending salary. select department_id,last_name,salary from employees where salary>(select avg(salary)from employees) order by salary 37.Write a query that displays the employee number and last name of all employees who work in a department with any employee whose last name contains a u. Place your SQL statement in a text file named lab_06_03.sql. Run your query. select employee_id,last_name from employees where department_id in(select department_id from employees where last_name like'%u%' ) 38.The HR department needs a report that displays the last name, department number, and job ID of all employees whose department location ID is 1700. select last_name,department_id,job_id from employees join departments using(department_id)join locations using(LOCATION_ID ) where LOCATION_ID =1700 order by department_id Modify the query so that the user is prompted for a location ID. Save this to a file named lab_06_04.sql. 39.Create a report for HR that displays the last name and salary of every employee who reports to King. select last_name,salary from employees where manager_id =(select employee_id from employees where last_name ='King') 40. Create a report for HR that displays the department number, last name, and job ID for every employee in the Executive department. select department_id,last_name,job_id from employees join departments using(department_id) where department_name='Executive' If you have time, complete the following exercise: 40.Modify the query in lab_06_03.sql to display the employee number, last name, and salary of all employees who earn more than the average salary and who work in a department with any employee whose last name contains a u. Resave lab_06_03.sql as lab_06_07.sql. Run the statement in lab_06_07.sql. select employee_id,last_name,salary from employees where department_id in(select department_id from employees where last_name like'%u%' )and salary >(select avg(salary)from employees) Oracle数据库实验报告 实验一:Oracle 10g安装卸载及相关工具配置 一、实验目标: 安装Oracle 10g,了解OEM,通过DBCA安装数据库,通过DBCA删除数据库,sqldeveloper连接数据库,卸载oracle 10g。 二、实验学时数 2学时 三、实验步骤和内容: 1、安装Oracle10g(默认安装数据库) 双击setup.exe, 选择基本安装,安装目录D:盘,标准版,默认数据库orcl,口令bhbh。 进入先决条件检查界面时:网络配置需求选项不用打勾,直接下一步,是。 直到安装成功。 2、登陆和了解OEM 主要是已网页的形式来对数据库进行管理。 http://主机IP:1158/em 用户名:sys 口令:bhbh 身份:sysdba 或者 用户名:system 口令:bhbh 身份:normal 3、通过DBCA删除已安装的默认数据库orcl 程序->Oracle - OraDb10g_home1->配置和移植工具->Database Configuration Assistant->删除数据库->…… 4、通过DBCA安装数据库xscj 程序->Oracle - OraDb10g_home1->配置和移植工具->Database Configuration Assistant->创建数据库->…… 5、sqldeveloper连接数据库 打开sqldeveloper,新建连接 连接名:system_ora 用户名:system 口令:bhbh 主机名:本机计算机名 SID:xscj 测试,显示成功,连接,保存。 6、卸载oracle 10g Windows下 1>停止所有Oracle服务,点Universal Installer卸载 2>删除注册表中的所有关于Oracle项 在HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\SOFTWARE下,删除Oracle目录 3>删除硬盘上所有Oracle文件。 (1)Oracle安装文件 (2)系统目录下,在Program files文件夹中的Oracle文件 四、上机作业 根据实验步骤完成逐个实验目标中的任务。 五、心得体会 通过这次的实验,我了解了oracle数据库的情况。懂得了数据库就是把数据存储在一个类似与仓库的地方,需要用时才从数据库里调出来。通过上机实践,知道了装数据库和卸载数据库,并且学会了怎样连数据库。 实验二:Oracle 10g手工建数据库 一、实验目标: 安装Oracle 10g数据库环境,手工建立数据库;通过Net Configuration Assistant建立监听,使用sqldeveloper连接数据库测试。 二、实验学时数 2学时 三、实验步骤和内容: 先安装好Oracle 10g数据库环境(不安装默认数据库)。 1.创建好相关的目录 目录 一、绪论 (2) 1.1 开发背景 (2) 1.2 开发工具 (2) 1.3 任务与分析 (2) 1.4本文主要内容 (2) 二、需求分析 (3) 2.1 总体需求分析 (3) 2.2 系统设计流程 (3) 三、总体设计 (4) 3.1 系统功能结构图 (4) 3.2 安全设计 (4) 四、数据库设计 (5) 4.1 数据库分析 (5) 4.2 概念结构设计 (7) 4.3 逻辑结构设计 (8) 4.4 物理结构设计 (8) 五、编码 (10) 六、测试 (13) 七、总结 (14) 一、绪论 1.1 开发背景 高校的教室管理是一项繁琐、细致、工作量大的工作,它是高等学校教育工作的一项重要内容,是整个学校教学系统能够正常运行的基础。同时,教室管理工作关系到高校教学秩序的稳定以及教学资源的合理运用,关系到高校的发展和入才的培养,教室管理在高校中占有相当重要的地位。 1.2 开发工具 1、Oracle 11g; 2、Oracle SQL Developer 1.3 任务与分析 这个系统主要是开发一个大学教室系统,用户有四类类,学生,教师,教室管理员、排课人员。学生、教师可以选择个人信息录入,纠正,查询;学生成绩信息查询;课程信息查询。教室管理员可以对教室钥匙发放信息的管理。排课人员可以进行添加、查询,修改,删除教室信息等功能。不同用户登陆系统时有不同的权限。 1.4本文主要内容 本文主要对大学教室管理系统整体设计做一个详细的介绍,包括数据库的创建(需求分析、概念结构设计、逻辑结构设计、物理结构设计、数据库实施、数 据库运行与维护等)和大学教室管理系统的编辑、编译、运行、调试、维护等一系列详细的设计步骤。 二、需求分析 2.1 总体需求分析 大学教室管理系统,即对大学学生排课后对教室资源的合理管理与利用,保证了大学教学任务的有序高效进行。通过调查和分析一款优秀的大学教室管理系统应该实现实现以下功能: 【1】排课人员能够对教室信息添加、查询,修改操作 【2】老师,学生能够对教室信息等信息进行查询,但赋予老师学生的不同权限【3】教室管理员可以根据教室信息对教室钥匙信息的管理 2.2 系统设计流程 通过对教室管理过程的研究与分析,在设计时系统应实现以下目标: 【1】实现不同用户登录系统具有不同的权限 【2】实现合理的排课 【3】实现教师和学生息录入后可以查询和纠正,用户能对教室信息的查询;学生可以对自己成绩信息查询;课程信息查询等功能 【4】实现教室钥匙的合理管理 实验2 Oracle数据库体系结构 【实验目的与要求】 ?熟悉Oracle数据库的物理结构 ?理解Oracle的工作机制 ?理解Oracle的软件结构 【实验内容与步骤】 2.0 实验准备 以系统管理员身份登入到数据库。 2.1 物理存储结构 2.1.1 获取Oracle数据库各类物理文件信息 1.数据文件 数据文件的详细信息记录在数据字典视图V$DataFile中,可通过查询语句获取数据文件相关信息。 查看数据文件名称:可通过如下查询语句查看数据文件名称和存放位置 请给出运行结果截图: 练习:用desc命令查看V$datafile视图的结构,并试着查询更详细的信息。 2.操作数据文件 (1) 创建数据文件 Oracle中,创建数据文件即是借用Alter Tablespace…ADD…语句,将数据文件添加挂接到指定的表空间中。 为USERS表空间添加一个数据文件,名称为USERS_XX.DBF(XX为学号最后两位),大小为20MB。如: 请给出运行结果截图: 打开指定目录(即C:\),查看是否存在文件USERS_XX.DBF? 请给出结果截图: 查询V$datafile视图,获取数据文件USERS_XX.DBF大小、位置等相关信息。 请给出结果截图: (2) 创建数据文件 修改数据文件使用Alter Database Datafile…命令。 修改USERS表空间中的USERS_XX.DBF为自动扩展方式,每次扩展5MB,最大为100MB。如: 请给出结果截图: 查询V$datafile视图,获取数据文件USERS_XX.DBF大小、扩展方式、位置等相关信息。确定数据文件是否修改。 请给出结果截图: (3) 重命名数据文件: 重命名数据文件使用alter tablespace …Rename datafile…命令。 将表空间USERS中的数据文件USERS_XX.DBF更名为UserData_XX.dbf。 学期 Oracle数据库应用技术 实验报告 选课序号: 班级: 学号: 姓名: 指导教师:史金余 成绩: 2017年月日 目录 1.实验目的 (1) 2.实验内容 (1) 2.1 触发器设计 (2) 2.2 存储过程、自定义函数设计 (2) 2.3 程序包设计 (3) 3.实验步骤 (3) 3.1 创建表空间RESTAURANT,创建用户DINER (3) 3.2 创建餐饮系统数据库的所有表,并向各表插入演示数据 (4) 3.3 完成【实验内容】中的触发器、存储过程、函数和程序包等 功能设计,将程序脚本保存到文本文件Source.sql中 (7) 4.实验总结 (13) PL/SQL程序设计 1.实验目的 ◆掌握PL/SQL程序设计基本技巧,包括基本数据类型、表类型、数组类 型、匿名程序块、控制语句、PL/SQL中使用SQL语句、游标、错误处 理等。 ◆熟悉和掌握PL/SQL中关于存储过程、函数、包和触发器程序设计技术。 2.实验内容 实验平台:PL/SQL Developer或Oracle的其它客户端管理工具。 某餐饮系统数据库(加粗字段为主键,斜体字段为外键),请创建如下各数据表,并实现如下存储过程、函数、包和触发器等功能设计,将程序脚本保存到文本文件Source.sql中: (1)菜肴类别表MK(菜肴类别编号MKid,菜肴类别名称MkName),菜肴类别名称:鱼类、蔬菜类、凉菜类、肉类、主食类和酒水类等。 (2)菜单信息表MList(菜肴编号Mid,菜肴名称Mname,菜肴类别MKid,菜肴单价Mprice,菜肴成本单价Mcost,更新日期Mdate)。 (3)餐台类别表DK(餐台类别编号DKid,餐台类别名称DkName),餐台类别:包间和散台等。 (4)餐台信息表Dinfo (餐台编号Did,餐台名称Dname,餐台类别DKid,座位数Dseats,更新日期Ddate)。 (5)消费单主表C (消费单号Cid,餐台编号Did,消费开始时间StartTime,结账时间EndTime,消费金额合计Smoney,盈利金额合计SPsum),其中,消费金额合计=消费单明细表CList中该消费单号的所有消费记录的消费金额的合计,即SUM(消费金额)或SUM(菜肴单价×消费数量),盈利金额合计=消费单明细表CList中该消费单号的所有消费记录的盈利合计,即SUM((菜肴单价- 菜肴成本单价)×消费数量)。 (6)消费单明细表CList (消费单号Cid,序号Sid,菜肴编号Mid,菜肴名称Mname,消费数量Cqty,菜肴单价Mprice,菜肴成本单价Mcost,消费金额Cmoney) ,消费金额=消费数量×菜肴单价;消费数量为正数是正常点菜,消费数量为负数是退菜,消费数量为0是赠菜。 成都东软学院 课程结业设计报告 课程: oracle数据管理与开发 项目名称:项目管理系统 作者:xxxxx 学号:xxxxx 专业班级: xxxxx 指导教师:xxxxx 2011年12月 目录 第一部分:项目概述 ........................................................................................- 1 -1.1内容 .................................................................................................................. - 1 -1.2目的 .................................................................................................................. - 1 -1.3功能 .................................................................................................................. - 2 -1.4意义 .................................................................................................................. - 2 -第二部分:E-R图..............................................................................................- 3 -第三部分:表图................................................................................................- 3 -第四部分:创建表的脚本: .............................................................................- 5 -第五部分:样本数据 ........................................................................................- 6 -第六部分:数据库测试.....................................................................................- 7 -6.1数据操纵........................................................................................................... - 7 - 6.1.1查询.................................................................................................................................... - 7 - 6.1.2插入.................................................................................................................................... - 8 - 6.1.3更新.................................................................................................................................... - 8 - 6.1.4删除.................................................................................................................................... - 8 -6.2问题总结........................................................................................................... - 9 -第七部分:项目总结 ........................................................................................- 9 - 7.1结论 ................................................................................................................... - 9 -7.2心得 ................................................................................................................. - 10 - 实验十一Oracle数据库备份与恢复 【实验目的与要求】 1. 常见数据备份与恢复的方法 2.学会Oracle备份方案的制定 【实验内容与步骤】 1. Oracle物理备份与恢复 准备工作: (1)查看数据库是否运行于归档模式下: 请给出查询的结果: (2)关闭数据库,做一个完全的冷备份。 提示: a.使用shutdown命令关闭数据库; b.复制数据文件、日志文件和控制文件到安全地方 (3) 把数据库改为归档模式 设置成自动归档 SQL> alter system set log_archive_start = true scope=spfile; 注意:本实验中的很多命令路径参数需根据自己的实现环境做出修改!! 实验11-1 数据库系统数据文件和回退段遭破坏的情况下的恢复。此时数据库的状态是关闭的。 (1)先启动数据库,创建新用户scott,并用scott用户建立test表,并插入两条数据。创建表空间的四个步骤: /*分为四步 */ /*第1步:创建临时表空间 */ create temporary tablespace user_temp tempfile 'D:\ user_temp.dbf' size 50m autoextend on next 50m maxsize 20480m extent management local; /*第2步:创建数据表空间 */ create tablespace user_data logging datafile 'D:\ user_data.dbf' size 50m autoextend on next 50m maxsize 20480m extent management local; /*第3步:创建用户并指定表空间 */ create user scott identified by tiger default tablespace user_data temporary tablespace user_temp; /*第4步:给用户授予权限 */ grant connect,resource,dba to scott; SQL> create table test (id int,name varchar2(10)); 表已创建。 SQL> insert into test values(1001,’zhangfei’); 已创建 1 行。 SQL> insert into test values(1002,’guanyu’); 已创建 1 行。 SQL> commit; 提交完成。 (2)模拟数据库遭意外被迫关闭,并且系统数据文件丢失。 SQL> shutdown abort 上机1:Oracle的安装与配置 (时间:2011.2.28) 一、实验目的 掌握Oracle10g的安装与网络连接配置 二、实验内容 1、安装Oracle10g 2、查看安装后的数据库文件目录结构 3、查看当前数据库的数据文件、控制文件、重做日志文件、参数文件 4、为连接到Oracle服务器进行网络连接配置 上机2:Oracle10g常用工具的使用 (时间:2011.3.1) 一、实验目的 掌握Oracle10g常用工具(SQL*PLUS、iSQL*PLUS、EM)的使用 二、实验内容 1、利用企业管理器(EM)查看当前数据库: 1) 查看当前数据库系统的内存结构 2) 查看当前数据库的工作模式 3) 查看当前数据库“SYS”方案下的逻辑对象 4) 查看当前数据库的表空间 5) 查看“SYS”用户的权限 2、利用SQL*PLUS查看当前数据库 分别查看当前数据库的数据文件、控制文件、重做日志文件。 3、利用iSQL*PLUS查看当前数据库,分别查看当前数据库的数据 文件、控制文件、重做日志文件。 上机3:PowerDesigner开发与应用-1 (时间:2011.3.7) 一、实验目的 掌握使用PowerDesigner工具设计CDM(概念数据模型)二、实验内容 设计“员工医疗保险系统”数据库的CDM(概念数据模型) 上机4:PowerDesigner开发与应用-2 (时间:2011.3.8) 一、实验目的 掌握使用PowerDesigner工具设计PDM(物理数据模型)二、实验内容 设计“员工医疗保险系统”数据库的PDM(物理数据模型) 上机5:创建数据库 (时间:2011.3.15) 一、实验目的 1、复习巩固网络连接配置操作 2、了解使用Oracle数据库配置助手创建、删除数据库的操作 二、实验内容 (详见教材102:实践内容) 上机6:创建数据库、表空间和数据文件 (时间:2011.3.17) 一、实验目的 掌握表空间和数据文件的创建、查看、修改、删除操作及命令 二、实验内容 (详见教材102-103:实践内容) 上机7:数据库的安全管理-1 (时间:2011.3.22) 一、实验目的 1、掌握概要文件的建立、修改、查看、删除操作 2、掌握用户的建立、修改、查看、删除操作 二、实验内容 详见教材130-131:(1)—(6)、(13) XX大学 《数据库课程设计》设计报告 题目 学生姓名 学号 专业班级 指导老师 2012年1月 基础篇: 通过几个月的理论学习,我对oracle有了初步的了解,为了将理论知识运用到实际应用中,我参加了学校组织的课程设计,并选做了一些题目。 基础题 第十三题 scott.emp表使用用触发器实现业务规则:除销售员外,雇员工资只增不减 一、实验目的、内容 通过使用指针和when语句的判断,实现业务规则:除销售员外,雇员工资只增不减 二、实验程序设计及结构 1.应该建立触发器,使当员工工资改变时,除销售员外,雇员工资只增不减 2.使用when判断语句进行判断,当job= SALESMAN时,雇员工资只增不减,如果出现其他员工的工资减少,输出错误 三、设计过程 create or replace trigger check_sal_emp before update of sal on emp for each row when (new.sal<=old.sal and old.job<>'SALESMAN') begin raise_application_error(-20010,'除销售员外,雇员工资只增不减'); end; / 四.运行结果 update emp set sal=sal-100; ORA-20010: 除销售员外,雇员工资只增不减 五.出现问题 1.when 语句后没有加括号,导致出现 when new.sal<=old.sal and job<>'SALESMAN' * ERROR at line 4: ORA-00906: missing left parenthesis 2.没有给job定义 ERROR at line 4: ORA-04076: invalid NEW or OLD specification 3.创建出触发器,但无法运行 实验二Oracle数据库开发环境下PL/SQL编程(2学时) 【实验目的】 (1)掌握PL/SQL 的基本使用方法。 (2)在SQL*PLUS环境下运行PL/SQL的简单程序。 (3)应用PL/SQL 解决实际问题 【实验内容与步骤】 一、实验内容: 1、用PL/SQL实现:输入eno的值,显示emp表中对应记录的内容。 2、用PL/SQL完成:读入三个数,计算并输出它们的平均值及三个数的乘积。 3、对职工表emp中的雇员SCOTT提高奖金,若工种为MANAGER,则奖金提高其原来的20%;若工种为SALESMAN,则奖金提高其原来的15%;若工种为ANALYST,则奖金提高其原来的10%, 其它都按原来的7%提高。 4、用PL/SQL块实现下列操作 公司为每个职工增加奖金:若职工属于30号部门,则增加$150;若职工属于20号部门, 则增加$250;若职工属于10号部门,则增加$350。(提示:游标请自行阅读相关内容) DECLARE addcomm https://www.doczj.com/doc/7a14914150.html,m%type; CURSOR emp_cursor IS select deptno from emp; BEGIN FOR emprec IN emp_cursor LOOP IF emprec.deptno=30 THEN addcomm:=150; ELSIF emprec.deptno=20 THEN addcomm:=250; ELSIF emprec.deptno=10 THEN addcomm:=350; END IF; Update emp set comm=comm+ addcomm where deptno= emprec.deptno; END LOOP; COMMIT WORK; END; 实验三PL/SQL触发器和存储过程(2学时) 【实验目的】 (1)了解触发器的类型。 (2)掌握PL/SQL触发器的使用方法。 (3)了解存储过程的使用方法。 (4)掌握存储过程的使用方法。 【实验内容】 实验内容: 1、编写一个数据库触发器,当任何时候某个部门从dept表中删除时,该触发器将从emp 表中删除该部门的所有雇员。(要求:emp表、dept表均为复制后的表) CREATE OR REPLACE TRIGGER del_emp_deptno BEFORE DELETE ON dept FOR EACH ROW BEGIN DELETE FROM emp WHERE deptno=:OLD.deptno; END; 声明:此文档只作为学习参考,不得用作它途! 实验一了解ORACLE环境,使用ORACLE数据库实用工具 1.目的要求: 了解ORACLE数据库的各个常用工具软件 2.实验内容: 在ORACEL数据库下使用SQL*PLUS ,SQL*PLUS Worksheet,PL/SQL Developer 工具,企业管理器等实用工具与Oracle交互。并在企业管理器中观察ORACLE的底层存储原理。在PL/SQL Developer中书写简单的SQL语言。 3.主要仪器设备及软件 1)PC 2)ORACLE数据库 实验二熟悉SQL语言 1.目的要求 在SQL*PLUS或PL/SQL Developer工具中编写SQL语句 2.实验内容 在ORACLE 数据库中定义用户,给用户赋权限,创建,修改和删除表格,视图等数据库对象,并向表格中插入,修改和删除数据。体会SQL语言中ORACLE的“方言”。 对自己建立的表做查询:包括单表查询,多表查询,嵌套查询,分组查询,相关查询 3.主要仪器设备及软件 1)PC 2)ORACLE数据库 自定义用户:create user taozi identified by taozi; 给用户赋DBA权限:grant dba to taozi; 创建表格 student,sc,course: Create table student (sno char(10) primary key, sname varchar(20) not null, sage smallint, ssex char(2), sdept varchar(20)); Create table course (cno char(10) primary key, cname varchar(50) not null, credit smallint); Create table sc (sno char(10), cno char(10), grade smallint, primary key(sno,cno)); 创建视图:create view oracle as (select sno,sname,sage from student); 删除视图:delete oracle; 为student 表增加一列 jiguan: alter table student add jiguan varchar(10); 删除jiguan 列:alter table student drop column jiguan; 删除student 表结构:drop table student; 插入数据:insert into student values('004','AA','21','f','MA'); insert into student values('005','BB','20','m','CS'); Oracle程序设计课程 设计 实 训 报 告 书 班级: 学号: 姓名: 指导教师: 前言 《Oracle数据库应用与开发实例教程》是学习数据库技术高级阶段课程,读者应该在选择学习《数据库应用基础实例教程》、《Access2003数据库实用教程》、《SQL Server 数据库应用基础与实现》和《SQL Server2005 实例教程》之后,现学习本书内容。本教材以Oracle 10g为教学环境,重点介绍以下内容: (1)Oracle 系统基础: (2)Oracle 系统管理工具; (3)Oracle系统库创建与管理; (4)Oracle数据表创建与管理; (5)管理视图; (6)SQL编程语言; (7)PL/SQL编程语言; (8)管理PL/SQL存储过程与触发器; (9)管理安全性; (10)数据库安全性; (11)O racle 数据库访问。 本教材具有以下特色: (1)定位准确、适应面广。 (2)合理编排章节顺序,提高学习效率。 (3)明确职业岗位需求,体验数据库应用。 (4)以真实工作任务为载体组织教学内容,在真实工作环境中探索数据库 创建与设计。 (5)采用“项目导向、任务驱动”教学法讲解知识与训练技能,体现了“在 做中学、学以致用”教学理念,适用于理论、实践一体化教学,融“教、学、练、思”于一体。 倡导学以致用。确认是否学会某一种技能最好方法就是:使用这种技能去实际解决某个问题。如果可以顺利地解决某个问题,那么这个技术就能掌握了。学会灵活运用所学知识方法。 实训一数据库创建与管理 实训目: (1)熟练掌握利用DBCA管理数据库方法 (2)熟练掌握使用OEM方式管理表空间方法 (3)了解以命令行方式创建数据库和表空间方法 实训任务: (1)Databuse contml URL为http:504-20:5500/em (2)使用STARTUP和SHUTDOUN命令启动和停止“EshopData”数据库。 (3)打开管理→存储→表空间→创建输入名称为ShopInfo (4)修改永久表间 四川师范大学计算机学院oracle实验报告册 院系名称:计算机科学学院 课程名称:oracle数据库运用与开发 实验学期2012 年至2013 年第 1 学期 专业班级:电子商务2010级5班 姓名:苏瑶学号:2010110338 指导教师:俞晓老师 实验最终成绩: 实验一了解ORACLE环境,使用ORACLE数据库实用工具 (验证性实验 4学时) 1.目的要求: 了解ORACLE数据库的各个常用工具软件 2.实验内容: 在ORACEL数据库下使用SQL*PLUS ,SQL*PLUS Worksheet,PL/SQL Developer工具,企业管理器等实用工具与Oracle交互。并在企业管理器中观察ORACLE的底层存储原理。在PL/SQL Developer中书写简单的SQL语言。 3.主要仪器设备及软件 1)PC 2)ORACLE数据库 --创建用户 create user user1 identified by user1; --赋给用户建表、连接等权限 grant connect to user1; grant create any table to user1; grant resource ,dba to u1; --连接用户 Conn user1/user1; --收回权限(dba ) revoke dba from u1; ------------------------------------------------------------------------- 实验二熟悉SQL语言 (验证性实验 4学时) 1.目的要求 在SQL*PLUS或PL/SQL Developer工具中编写SQL语句 2.实验内容 在ORACLE 数据库中定义用户,给用户赋权限,创建,修改和删除表格,视图等数据库对象,并向表格中插入,修改和删除数据。体会SQL语言中ORACLE的“方言”。 对自己建立的表做查询:包括单表查询,多表查询,嵌套查询,分组查询,相关查询 3.主要仪器设备及软件 1)PC 2)ORACLE数据库 --修改数据: update student set sAge=19where sage=18; --删除数据: delete from student where sname='吴芳'; --输出成绩大于60小于80的学生的名字 select sname from student,sc where grade >60and grade <80and student.sno=sc.sno; --输出学生表中的总人数 select count(*)from student; Oracle课程设计报告仓库管理系统 Oracle课程设计 实验题目: 仓库管理系统 专业: 计算机应用与技术 班级: 1440302 学号: 0030226 姓名: 胡强 指导教师: 王芳 一、系统描述 仓库管理系统的功能: 1)、产品入仓管理: 在货物送到仓库时, 对货物信息进行了解并将相关信息输入到数据库中, 同时更新数据库。 2) 、产品出仓管理: 在货物运出仓库时, 进行货物信息统计并将数据保存到数据库中, 同时更新数据库。 3)仓库货物信息提醒: 当货物少于某一规定的值时, 或者货物保质期将至时将发出提醒。 4)、借出管理: 凭借条借出, 然后能够还库。 5) 、查询修改: 管理员能够进行一系列查询: 查询货物类别及货物的信息、数量和货物流动的规则( 对货物出仓进仓的要求) ; 并能够对以上查询进行修改; 能够查询某一天货物流动的信息, 以及出仓及入仓的详细信息。 6) 、初始化库存设置: 设置库存的初始化值, 库存的上下警戒限制。 7) 、盘库情况: 反映没有、年的库存情况; 二、系统需求分析 利用用例图、类图、 E-R图对系统进行需求分析。 仓库管理系统能够实现对仓库货物信息、出仓货物管理、进仓货物管理、货物数量管理以及货物出入仓限制规则, 以下为其用例图、类图及E-R图。 仓库管理系统用例图 类图 表1: 产品信息表PRO 字段名数据类型长度约束说明 PROID NUMBER 11 主码产品编号PRONAME VARCHAR2 20 NOT NULL 产品名称PRODRESS VARCHAR2 50 产品地址DREPHONE NUMBER 20 产品地址号码BDATE NUMBER 5 NOT NULL 保质天数DEMO VARCHAR2 100 说明 课程设计 课程题目:ORACLE应用系统设计设计题目:音像店信息管理系统 专业:计算机科学与技术 班级:计131 组员:李霆桑珠扎西虞洲 学号: 130761 130767 130762 日期: 2016-03-04 信息工程学院计算机科学与技术 目录 一.课程目的………………………………………………………. 二.题目要求……………………………………………………… 三.日期安排………………………………………………………. 四.组内分工……………………………………………………… 五.实验条件......................................................... ........................... 六.实验内容......................................................... ........................... (1)第一部分:Oracle管理技术……………………………………… 1.数据库管理…………………………………………………….. 2.角色和用户管理………………………………………………... 3.表和视图管理………………………………………………….. 4.索引和序列管理………………………………………………... 5.PL/SQL编程…………………………………………………… 6.使用游标、存储过程和触发器………………………………… 7.表空间管理……………………………………………………… 8.文件管理………………………………………………………… (2)第二部分:Oracle开发技术……………………………………….. ①数据库设计………………………………………………………………… ②界面设计.................................................... ③结果测试…………………………………………………………………… 七.问题及解决…………………………………………………….. 八.总结............................................... Oracle程序设计课程设计概要(doc 35页) Oracle程序设计课程 设计 实 训 报 告 书 班级: 学号: 姓名: 前言 《Oracle数据库应用与开发实例教程》是学习数据库技术的高级阶段课程,读者应该在选择学习《数据库应用基础实例教程》、《Access2003数据库实用教程》、《SQL Server 数据库应用基础与实现》和《SQL Server2005 实例教程》之后,现学习本书内容。本教材以Oracle 10g为教学环境,重点介绍以下内容: (1)Oracle 系统的基础: (2)Oracle 系统的管理工具; (3)Oracle系统库的创建与管理; (4)Oracle数据表的创建与管理; (5)管理视图; (6)SQL编程语言; (7)PL/SQL编程语言; (8)管理PL/SQL存储过程与触发器; (9)管理安全性; (10)数据库安全性; (11)Oracle 数据库的访问。 本教材具有以下特色: (1)定位准确、适应面广。 (2)合理编排章节顺序,提高学习效率。 (3)明确职业岗位需求,体验数据库的应用。 (4)以真实的工作任务为载体组织教学内容,在真实的工作环境中探索数据库的创建与设计。 (5)采用“项目导向、任务驱动”教学法讲解知识与训练技能,体现了“在做中学、学以致用”的教学理念,适用于理论、实践一体化教学,融“教、学、练、思”于一体。 倡导学以致用。确认是否学会某一种技 能最好的方法就是:使用这种技能去实际解决某个问题。如果可以顺利地解决某个问题,那么这个技术就能掌握了。学会灵活运用所学知识的方法。 实训一数据库的创建与管理 实训目的: (1)熟练掌握利用DBCA管理数据库 的方法 (2)熟练掌握使用OEM方式管理表空 间的方法 实验一-O R A C L E数据库的安装、配置与基 本操作 实验一(2学时) oracle数据库的安装、配置与基本操作 实验目的 1、掌握使用OUI安装oracle服务器与客户端; 2、掌握服务器与客户端的基本网络配置; 3、熟悉OEM的基本功能; 4、掌握使用OEM查看oracle服务器的组成及环境参数; 5、掌握使用OEM创建表空间、表; 6、掌握使用OEM启动、关闭oracle服务器; 7、熟悉ORACLE在windows操作系统环境下的物理组成及 Oracle默认的OFA体系结构; 8、熟悉SQL*PLUS环境及常用编辑命令; 第一部分指导――――――――――――――――――――――――――――――――――――――― 练习1:使用OUI安装oracle9i服务器与客户端; 问题 熟悉oracle9i OUI,能够通过OUI安装定制用户需要的oracle组件; 分析 Oracle9i OUI是一个基于JAVA的安装软件(三张光盘),用户通过OUI可以选择性地安装oracle服务器+客户端,单纯的客户端,以及OEM高级应用必须的OMS(oracle manager server)。 解决方案 (1)将Oracle9i第一张安装盘放入光驱->双击setup.exe(自动播放也可) 图1-1 安装欢迎界面 (2)下一步文件定位 路径:安装文件的位置及名称 目标: “名称”: oracle系统文件的存放“路径“的逻辑名称 图1-2 文件定位 (3)下一步可用产品 Oracle datebase9.2.0.1.0: oracle数据库服务器端+客户端Oracle9i management integration9.2.0.1.0: OMS Oracle9i client9.2.0.1.0:oracle数据库客户端 图1-3 可用产品 (4)下一步安装类型 本科实验报告 课程名称:大型数据库系统 实验项目:数据库实验 实验地点:逸夫楼402 专业班级:软件1104班学号:2011004860 学生姓名:周升元 指导教师:王会青 2014年4 月20日 实验一ORACLE的安装与配置 一、实验目的 ?了解ORACLE数据库的基本原理,练习ORACLE 11g的安装与配置。 ?练习在SQL*PLUS和sql developer下登录数据库。 二、实验内容 ?ORACLE 11g的安装与配置 1)关闭所有正在运行的程序 2)启动操作系统,以Administrator身份安装 安装开始: 1)启动universal installer 2)设置Oracle主目录名和路径 3)选择安装产品 Oracle10g Database 4)选企业版(SERVER) 5)选择数据库通用配置 6)选全局数据库名 7)选缺省数据库字符集 8)开始安装 9)自动安装配置工具,并通过(Database Configuration Assistant)自动创建新 数据库 10)显示数据库创建总结信息 11)口令管理”,修改sys和system的口令,锁定别的用户口令 12)退出安装 参考操作: 在上图所示的界面上输入相关的SQL语句: 1)创建用户user1,user2(提示:create user user1 identified by pass1;) 2)分别为user1,user2授予相应的权限(提示:grant connect,resource to user1;) 3)退出SQL-plus (quit) 4)在CLIENT端进入SQL-PLUS,分别试用user1,user2登录试验。 5)练习修改口令:alter user username identified by password; 三、实验结果与分析: OEM界面Oracle实验报告
oracle课程设计报告(1)
实验2 Oracle数据库体系结构_V2013
Oracle 实验4(实验报告)-PL_SQL程序设计
(Oracle管理)oracle项目设计报告
实验十一Oracle数据库备份与恢复
oracle实验报告
oracle课程设计
《Oracle数据库》实验报告
四川师范大学《oracle》实验报告
Oracle程序设计课程设计
oracle实验报告
Oracle课程设计报告仓库管理系统
oracle设计实验报告材料
Oracle程序设计课程设计概要(doc 35页)
实验一-ORACLE数据库的安装、配置与基本操作知识讲解
oracle实验报告