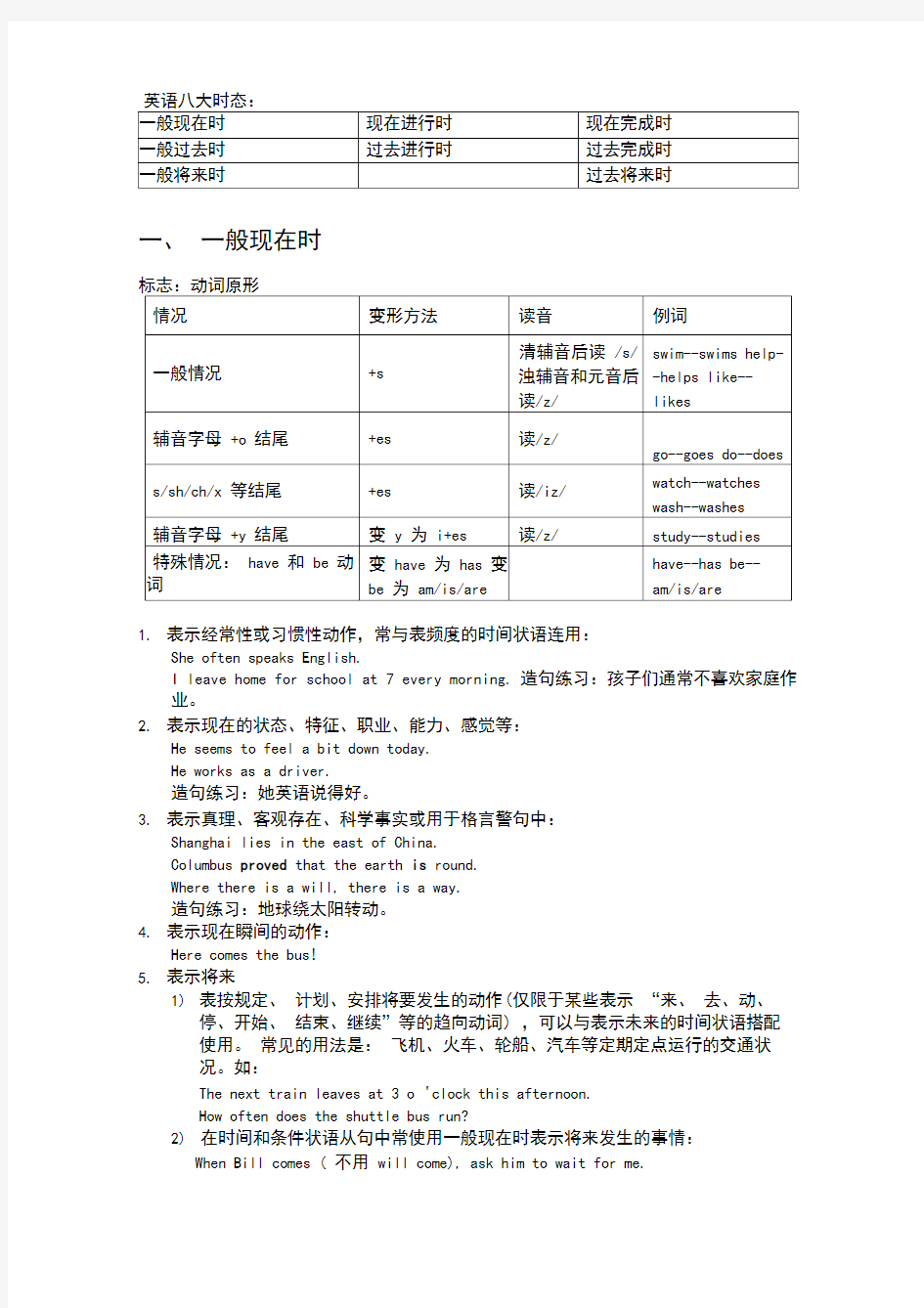

英语八大时态:
一、一般现在时
标志:动词原形
1.表示经常性或习惯性动作,常与表频度的时间状语连用:
She often speaks English.
I leave home for school at 7 every morning. 造句练习:孩子们通常不喜欢家庭作
业。
2.表示现在的状态、特征、职业、能力、感觉等:
He seems to feel a bit down today.
He works as a driver.
造句练习:她英语说得好。
3.表示真理、客观存在、科学事实或用于格言警句中:
Shanghai lies in the east of China.
Columbus proved that the earth is round.
Where there is a will, there is a way.
造句练习:地球绕太阳转动。
4.表示现在瞬间的动作:
Here comes the bus!
5.表示将来
1)表按规定、计划、安排将要发生的动作(仅限于某些表示“来、去、动、
停、开始、结束、继续”等的趋向动词) ,可以与表示未来的时间状语搭配
使用。常见的用法是:飞机、火车、轮船、汽车等定期定点运行的交通状
况。如:
The next train leaves at 3 o 'clock this afternoon.
How often does the shuttle bus run?
2)在时间和条件状语从句中常使用一般现在时表示将来发生的事情:
When Bill comes ( 不用will come), ask him to wait for me.
I shall go there tomorrow unless I m too busy'.
【练习题】
① Nowadays, a large number of women, especially those who from the countryside, ___
in the clothing industry.
A.is working
B.works
C.work
D.worked
② –What would you do if it ___ tomorrow?
--We have to carry it on, since we 've got everything already.
A.rain
B.rains
C.will rain
D.is raining
二、一般过去时
标志:动词过去式
*闭音节:元音字母a, e, i, o, u 如果发字母本来的音则称为开音节,否则称为闭音节。
1.表示过去某时所发生的动作或存在的状态,常与表示过去的时间状语连用 ( e.g.
yesterday, this morning, just now, a moment ago, in May, last night / year / week, once upon a time, the other day, before ?, when ?, in the past 等)。
如:
Jim rang you just now.
Liu Ying was in America last year.
2.表示过去经常或反复发生的动作,特别是used to do 表达的句型,本身表示的就是过去
常常。如:
When I was a kid, I often played football in the street.
She used to visit her mother once a week.
*注意区分sb. used to do sth. (某人过去常常做某事,此处to 是动词不定式标志符号) 和sb. be used to sth./doing sth. (某人习惯于某物/ 做某事,此处to 是介词)。
3.代替一般现在时,表示一种婉转、客气、礼貌、商量的语气。此用法仅适用于少数动词
(如want, hope, wonder, think, intend 等)及情态动词could, would 。如:
I wondered if you could have a word with me.
I hoped you could help me with my English.
Would you mind my sitting here?
4.虚拟语气中用一般过去时表示现在或将来时间的动作或状态。常用句型有:
It is time that sb. did sth. “某人该做某事了”
would rather sb. did sth. “宁愿某人做某事”
造句练习:
你该上床睡觉去了。
我宁愿你明天过来。
【练习题】
Scientists think that the continents ___ always where they ___ today.
A.aren 't ; are
B.aren 't ; were
C.weren 't ; are
D.weren 't ; were
三、一般将来时
标志:will / shall + 动词原形
1.表示将来发生的动作或存在的状态,通常与表示将来的时间状语连用( e.g.
tomorrow, next week, in the future 等)。如:
We shall have a lot of rain next month.
My husband will come back in a few days.
2.表示倾向性和习惯性:
Fish will die without water.
When it gets warmer, the snow will start to melt.
3.一般将来时的几种句式结构辨析:
1)will / shall + 动词原形多用于表达主观愿望或必定会发生的事情( “将会如
何” ),例句请见本章1、2 节。*shall 作助动词时一般只用于第一人称
2)be going to + 动词原形表示即将发生或打算要做的事:It is going to rain.
We are going to have a meeting today.
3)be to + 动词原形表示按计划或安排即将要发生的动作:He is to visit Japan
next year.
We are to discuss the report on Monday.
4)be about to + 动词原形表示即将发生的动作,意为“马上要做某事
,后面一般不跟时间状语,如:The plane is about to start.
Don't worry. I am about to make a close examination on you.
四、现在进行时
标志:be + 动词的现在分词
1.表示说话时正在进行的动作:
She is writing a letter upstairs.
Who are you waiting for?
It is raining hard.
2.表示现阶段一直在进行的动作(说话时动作未必正在进行) :
I hear Mr. Green is writing another novel.
3.表示反复出现或习惯性的动作,往往包含说话者赞扬、责备、厌恶等情绪,通
常与always, constantly, continually, forever 等频度副词连用。如:
John is forever asking silly questions like a stupid.
He is always thinking of others first.
4.表示将来
1)表示按计划、安排将要发生的动作,仅适用于部分趋向动词 (如go, come,
leave, start, arrive 等)。如:
Uncle Wang is coming.
They're leaving for Beijing.
2)在时间和条件状语从句中,现在进行时表示将来某时正在发生的事情。如:
Please drop in when you are passing my way.
If he is still sleeping, don 't wake him up.
五、过去进行时
标志:was / were + 动词的现在分词
1.表示过去某一时刻或一段时间正在进行的动作,过去进行时中常用的时间状语有
the whole morning, all day yesterday, from January to March last year 等。如:
I was having a talk with Lucy at that time.
They were watching TV at home last night.
2.表示过去反复出现或习惯性的动作,往往包含说话者赞扬、责备、厌恶等情绪,
通常与always, constantly, continually, forever 等频度副词连用。如:
My brother was always losing his keys.
3.表示按计划、安排过去某时刻将要发生的动作,仅适用于部分趋向动词(如go,
come, leave, start, arrive 等)。如:
He said they were leaving for Beijing this afternoon.
4.过去进行时有一个主要用法就是描述一件事情发生的背景(一个长动作延续的时
候,另一个短动作发生) :
Granny fell asleep when she was reading.
It was raining when they left the station.
练习】
Mary ___ a dress when she cut her finger.
A.made
B.is making
C.was making
D.makes
六、现在完成时
标志:have / has + 动词的过去分词
1.表示一个过去发生并已完成的动作对现在产生影响或结果,强调的是现在的状况
(表示“已完成”)。如:
He has left the city. (结果:他目前不在这个城市)
Someone has broken the window. (结果:窗户破了)
2.表示一个动作开始于过去,持续到现在,也可能还会继续持续下去(表示“未完
成” )。I have been busy since last week.
He has taught in our school for 30 years.
I've finished half so far.
注意瞬间动词通常是不能用现在完成时表持续性的,但其否定结构则可以。如:She hasn't seen you for ages.
His father hasn 't touched beer for a whole week.
3.表示过去到现在为止反复发生的动作或多次出现的状态,常与表示频度的副词
always, often, every day 等连用。如:
I have often heard that he is the cleverest person in that company.
4.在时间和条件状语从句中,现在完成时表示将来某时完成的动作。如:
I'll go to your home when I have finished my homework.
If it has stopped snowing in the morning, we 'll go the park.
5.与现在完成时连用的常见词语能与现在完成时连用的词语很多,just, already,
yet, before, never, ever, recently 等,但常见的有:
1) since 自从
I have been there many times since the war.
We haven't seen each other since last week.
We have been friends ever since.
2) in / for / during the past/last ?years 在过去/ 最近?中
I've been ill for the past three weeks.
Great changes have take place in the last ten years.
I have been here (for) the last/past month.
3) so far 到目前为止
We haven't had any trouble so far.
So far the search for the missing middle-aged woman has been fruitless.
4) up to/until now 到现在为止
Up to now he 's been quiet.
Up to now, the work has been easy.
I have heard nothing from him up till now. Up till now we have planted over
2000 trees.
5)It is/will be the first/second ?time that ?这是第一/二?次?It 's
the first time (that) I 've been here.
It will be the first time (that) I 've spoken in public.
It is the second time (that) I have met him today.
6)This is + 形容词最高级+ that ?这是最?This is the best film that I 've
(ever) seen.
6.现在完成时与一般过去时的区别
1) 现在完成时强调对现在的影响和结果,与现在有联系;而一般过去时强调这个
动作发生的时间是在过去,不涉及对现在的影响。如:I have seen this film.
(我已经看过了这部电影) I saw this film yesterday. (我是昨天看的这部电影)
2) 现在完成时常与模糊的时间状语连用(如for, since, so far, ever, never, just,
yet, till/until, up to now, always 等),或者干脆没有时间状语;而一般过去时常与具体的时间状语连用(如yesterday, last night, ?ago, in 1980, in
February 等)。
3)现在完成时表示持续时一般使用延续性动词(如live, teach, work, know 等);
而一般过去时常使用瞬间动词(如begin, buy, die, marry 等)。如:He has
lived in Hangzhou since last spring.
My grandfather bought the car five years ago.
7.易错点辨析
1) 考生容易把一些瞬间动词用现在完成时表达,这是错误的。如:(× ) He has
died for two years. 他死了两年了。
(√ ) He has been dead for two years.
(√ ) He died two years ago.
(× ) The film has begun for 10 minutes. 电影开演十分钟了。
(√ ) The film has been on for 10 minutes.
(√ ) The film began 10 minutes ago.
(× ) She has married for three years. 她结婚有三年了。
(√ ) She has been married for three years.
(√ ) She married Mike three years ago.
2) 考生不懂如何区分have been to 和have gone to ,尽管两者均可后接地点,但
have been to 表示去过某地(现在已经回来了) ,have gone to 表示到某地去了
(现在还没回来)。如:
She has been to Paris (three times).
She has gone to Paris.
【练习】
① The coffee is wonderful! It doesn 't taste like anything I ___ before.
A.was having
B.have
C.have ever had
D.had ever had
② The country life he was used to ___ greatly since 1992.
A.change
B.has changed
C.changing
D.have changed
七、过去完成时
标志:had + 动词的过去分词
1.表示在过去的某个时间或动作以前已经发生的动作或已经存在的状态。如:
By the end of last week he had finished the work.
He had left when I arrived.
2.表示从过去某一时间开始,一直延续到过去另一时间的动作或状态。如:
We had not seen each other since I left Beijing.
The film had been on for 5 minutes when I got to the cinema.
3.某些表意向的动词(如intend, think, plan, expect, hope 等)的过去完成时表示
主语未曾实现的愿望、希望、打算。如:
I had intended to visit you last night, but someone called and I couldn 't get away.
We had hoped that you would come, but you didn 't.
4.(虚拟语气)在条件状体从句或wish / would rather 等后面的从句中,使用过去
完成时表示与过去事实相反的主观愿望。如:
The party wouldn 't have been so perfect if you hadn 't come.
I wish I had gone with you to the concert that day. 造句练习:我宁愿你告诉过
她真相。
5.过去完成时与一般过去时
1)基本区别:过去完成时表示以过去某时间为起点以前所发生的动作或存在的状态,即过去完成时强调“过去的过去” ,而一般过去时只表示以现在时间为起点以前所发生的事情或存在的状态。如:
He studied there two years ago. 他两年前在那儿学习(离现在两年)
He said he had studied there two years before. 他说他两年前在那儿学习过。
(离他说话时两年)
2)特别注意:两个动作如果按顺序发生,又不强调先后,或者用then, and, but 等连词连接时,多用一般过去时。如:
When she saw the mouse, she screamed.
My aunt gave me a hat and I lost it.
【练习】
① When the old man ___ to walk back to his house, the sun ___ itself behind the mountain.
A.started; had already hidden
B.had started; had already hidden
C.had started; was hiding
D.was starting; hid
② I arrived late; I ___ the road to be so icy.
A. wouldn 't
B. haven t'
expected
C. hadn 't
expected
D. wasn 't expecting