Windows Vista for Developers-第一部分:Aero向导
- 格式:docx
- 大小:163.39 KB
- 文档页数:5

用户体验 - 排除 Aero Glass 故障Windows Vista 中引入了显著改进的用户体验,其中具有称作 Aero Glass 的用户界面。
本文档针对使用 Aero Glass 用户界面时遇到的问题提供了故障排除建议。
目标●讨论启用 Aero Glass 的要求。
●讨论客户在使用 Aero Glass 时可能遇到的问题。
●演示如何解决 Aero Glass 的潜在问题。
相关组件桌面窗口管理器会话管理器桌面的所有 Windows Aero 和 Glass 功能都是通过桌面窗口管理器会话管理器服务实现的。
此服务也称为 UxSms 服务(用户体验会话管理器服务),并且作为在一般服务主机进程 svchost.exe 下运行的服务来实现。
桌面窗口管理器桌面窗口管理器会话管理器服务为计算机上的每个用户会话启动一个桌面窗口管理器进程,并对该进程进行管理。
桌面窗口管理器进程作为%systemroot&\windows\system32\dwm.exe 运行。
如果该进程曾意外终止,则将由桌面窗口管理器会话管理器服务重新启动。
桌面窗口管理器进程加载两个重要模块:● Udwm.dll – Microsoft 桌面窗口管理器 DLL● Milcore.dll – Microsoft 媒体集成层核心库。
Aero Glass 功能的硬件要求要启用 Aero Glass,您的 PC 必须满足下列图形硬件条件:●支持 Windows Display Driver Model (WDDM) 和 Pixel Shader 2.0 的DirectX 9 类显示适配器。
●每像素最低 32 位。
●用于指定显示器分辨率的适当图形内存:● 64MB 图形内存,以支持分辨率为 1280 x 1024 或更低的单显示器。
● 128MB 图形内存,以支持分辨率大于 1280 x 1024 且小于或等于 1920 x 1200 的单显示器。
常用软件常用系统软件系统软件的作用是协调各部分硬件的工作,并为各种应用软件提供支持,使计算机用户和其他软件将计算机当作一个整体,不需要了解计算机底层的硬件工作内容,即可使用这些硬件实现各种功能。
系统软件主要包括操作系统和一些基本的工具软件,如各种编程语言的编译软件、硬件检测与维护软件以及其他一些针对操作系统的辅助软件等。
1.操作系统在系统软件中,操作系统(Operating System,OS)是负责直接控制和管理硬件的系统软件,也是一系列系统软件的集合。
其功能通常包括处理器管理、存储管理、文件管理、设备管理和作业管理等。
当多个软件同时运行时,操作系统负责规划以及优化系统资源,并将系统资源分配给各种软件。
操作系统是所有软件的基础,其可以为其他软件提供基本的硬件支持。
常用的操作系统主要有以下几种。
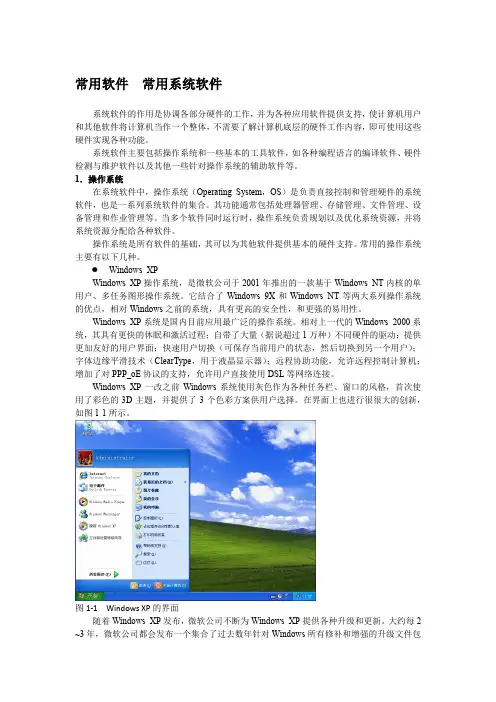
Windows XPWindows XP操作系统,是微软公司于2001年推出的一款基于Windows NT内核的单用户、多任务图形操作系统。
它结合了Windows 9X和Windows NT等两大系列操作系统的优点,相对Windows之前的系统,具有更高的安全性,和更强的易用性。
Windows XP系统是国内目前应用最广泛的操作系统。
相对上一代的Windows 2000系统,其具有更快的休眠和激活过程;自带了大量(据说超过1万种)不同硬件的驱动;提供更加友好的用户界面;快速用户切换(可保存当前用户的状态,然后切换到另一个用户);字体边缘平滑技术(ClearType,用于液晶显示器);远程协助功能,允许远程控制计算机;增加了对PPP_oE协议的支持,允许用户直接使用DSL等网络连接。
Windows XP一改之前Windows系统使用灰色作为各种任务栏、窗口的风格,首次使用了彩色的3D主题,并提供了3个色彩方案供用户选择。
在界面上也进行很很大的创新,如图1-1所示。
图1-1 Windows XP的界面随着Windows XP发布,微软公司不断为Windows XP提供各种升级和更新。


WindowsVista简体中⽂版X86版原版镜像下载cn_windows_vista_x86_dvd_X12-59648.iso原版ISO⽂件⽐较⼤,分成三个包,请下载完⽤WINRAR打开就可以得到ISO⽂件不⽤多介绍了,原版ISO附带Vista "软改"程序 Vista Loader 2.1.2“软改”程序--Vista Loader V2.1.2关于 Vista LoaderVista Loader是第⼀个通过软件突破 Vista 激活限制的软件,是中国⼈原创的软件。
它⼯作的原理是:在引导操作系统之前运⾏特制的引导程序,修改计算机的内存,加⼊特定数据,模拟品牌机的 BIOS,⽤于突破 Vista 的激活验证。
之前在⽹络流传的版本为 1.0 版,于 2007年2⽉17⽇(⼤年三⼗)发布,光盘的卷标为 SOFTMOD-L,基于 DOS 系统,以 ISO ⽂件格式发布。
1.0 版有两个分⽀,ISO ⽂件的卷标分别为 SOFTMOD-B 和 SOFTMOD-L,这两个分⽀的⼤体功能⼀致,只有细节上的差别。
Vista Loader 2.x 版本完全重写了代码,脱离 DOS 系统,同⼴泛应⽤的多系统引导程序 GRUB 的改进版 GRUB4DOS 编译到⼀起,并改进了模拟的⽅式,兼容了 1.0 版不能兼容的品牌机。
具体改进请见更新⽇志。
这是中国⼈⾃⼰创作的软件,希望⼤家爱护。
如果修改本程序或者打包本程序,可以不注明作者,但⼀定要注明“中国⼈原创”以及本程序的正式名称“Vista Loader”。
程序特点1. ⽆需修改 BIOS,实现突破 SLP2.0 验证,激活操作系统。
2. 本⾝是引导程序,具有 GRUB4DOS 的全部功能-引导多种操作系统,整合恢复系统等。
3. 在操作系统引导之前运⾏,安全可靠,兼容性好。
不占⽤系统资源,不会和系统中安装的软件冲突。
4. 同时⽀持 x86 和 x64 系统,并⽀持未来使⽤ SLP 2.0 技术的操作系统,如 Longhorn Server,只需导⼊新的验证数据即可。

第三章操作篇3.1桌面桌面(如图3-1所示)是打开计算机并登录到Windows 之后看到的主屏幕区域。
就像实际的桌面一样,它是您工作的平面。
打开程序或文件夹时,它们便会出现在桌面上。
还可以将一些项目(如文件和文件夹)放在桌面上,并且随意排列它们。
有时桌面定义更为广泛,包括任务栏和Windows 边栏。
任务栏位于屏幕的底部,显示正在运行的程序,并可以在它们之间进行切换。
它还包含“开始”按钮,使用该按钮可以访问程序、文件夹和计算机设置。
边栏位于屏幕的一侧,包含称为小工具的小程序。
图3-1 桌面、任务栏和边栏1. Windows 桌面有哪些新增功能?Windows 桌面提供了一些新增功能,可以帮助您个性化设置计算机、在打开的程序和文件之间进行切换、快速访问信息,以及查找程序和文件。
⑴Windows Aero 是此Windows 版本的高级视觉体验。
其特点是透明的玻璃图案中带有精致的窗口动画和新窗口颜色。
Windows Flip 3D 属于Windows Aero 体验,它是一种用于在3D 堆栈以及任务栏按钮中通过缩略图大小的窗口预览来预览打开的窗口的方法。
⑵Windows Flip 3D 所提供的功能与Alt+Tab 键盘快捷键的功能相同,但前者使用3D 视觉效果。
使用Flip 3D,可以快速预览所有打开的窗口(例如,打开的文件、文件夹和文档)而无须单击任务栏。
Flip 3D 在一个“堆栈”中显示打开的窗口。
在堆栈的顶部,将显示一个打开的窗口。
若要查看其他窗口,可以浏览堆栈。
⑶当您指向任务栏按钮时,将显示一个缩略图大小的预览窗口,该窗口中的内容可以是文档、照片,甚至可以是正在运行的视频。
⑷Windows 边栏提供了一种组织要快速访问的信息、游戏和任务的方法,而不会使您的工作区变得混乱。
边栏由一些小工具组成,这些小工具是一些可自定义的小程序,能够显示不断更新的标题、幻灯片图片、联系人以及更多内容,而不必打开新窗口。

C H A P T E R 3-1EAP-FAST for Windows Vista Administrator GuideOL-16949-013Configuring EAP-FASTThis chapter explains how to configure EAP-FAST module settings, such as connection settings, user credentials, and authentication methods.The following topics are covered in this chapter:•Accessing EAP-FAST Properties for Configuration, page 3-2•Overview of the Connection Tab, page 3-4•Configuring Settings in the Connection Tab, page 3-4•Overview of the User Credentials Tab, page 3-7•Configuring User Credentials, page 3-8•Overview of the Authentication Tab, page 3-11•Configuring Authentication Methods, page 3-12•Finding the Version of the EAP-FAST Module, page 3-13Chapter3 Configuring EAP-FAST Accessing EAP-FAST Properties for ConfigurationAccessing EAP-FAST Properties for ConfigurationTo access the EAP-FAST Properties window, perform the following steps:Step1Click the Start button on the lower-left corner of the desktop.Step2From the right pane, right-click Network.Step3Select Properties.Step4From the left pane, select Manage wireless networks.Step5Double-click the wireless network.Step6From the Wireless Network properties window, select the Security tab (see Figure3-1).Figure3-1Wireless Network Properties WindowStep7Select Cisco EAP-FAST from the "Choose a network authentication method" drop down list.Step8Click the Settings button.EAP-FAST for Windows Vista Administrator GuideOL-16949-01Chapter3 Configuring EAP-FASTAccessing EAP-FAST Properties for Configuration Step9Click the Connection tab, the User Credentials tab, the Authentication tab, or the About tab. For more information about configuring settings in those tabs, see the “Configuring Settings in the ConnectionTab” section on page3-4, the “Configuring User Credentials” section on page3-8, and the “ConfiguringAuthentication Methods” section on page3-12. For information about finding the version of the moduleon the device, see the “Finding the Version of the EAP-FAST Module” section on page3-13.EAP-FAST for Windows Vista Administrator GuideOL-16949-01Chapter3 Configuring EAP-FAST Overview of the Connection TabOverview of the Connection TabThe EAP-FAST Connection tab includes settings for the establishment of an outer Transport LayerSecurity (TLS) tunnel. Settings include identity protection, the use of a Protected Access Credential(PAC), PAC provisioning, the use of authenticated server certificates to establish the tunnel, and the useof a Trusted Root Certificate Authority (CA) from a list of Trusted Root CA certificates.Configuring Settings in the Connection TabYou can configure connection settings from the Connection tab (see Figure3-2).Figure3-2Connection T ab in EAP-FAST Properties WindowEAP-FAST for Windows Vista Administrator GuideOL-16949-01EAP-FAST for Windows Vista Administrator Guide OL-16949-01Chapter 3 Configuring EAP-FASTConfiguring Settings in the Connection Tab Table 3-2 lists and describes all connection settings.T able 3-1Connection SettingsConnection SettingsDescription Use anonymous outer identityCheck this box to enable identity privacy protection.Default: On Outer identity field Enter an outer identity if the Use anonymous outer identity check boxis checked. Follow an administrator’s instructions, or followRFC 4282 for guidelines about what to enter in the outer identityfield.Default: anonymousNote The maximum number of characters allowed in this fieldis 256.Use Protected AccessCredential (PAC)Check this box to enable the use of a PAC to establish a tunnel. When this box is checked, PAC provisioning is requested. If this box is notchecked, EAP-FAST acts as PEAP and uses only the authenticatedserver certificate to establish the tunnel every time.The PAC is a unique shared credential used to mutually authenticatea client and a server. The PAC is associated with a specific clientusername and a server authority ID. A PAC removes the need for PKIand digital certificates. The PAC is distributed or imported to theclient automatically or manually.Manual PAC provisioning generates the PAC file locally on the AAAor EAP-FAST server. With manual provisioning, the user credentialsare supplied to the server to generate the PAC file for that user. ThisPAC must then be manually installed on the client device.Default: OnAllow automatic PACprovisioning Check this box to enable the automatic retrieval of a PAC during EAP-FAST authentication.Automatic PAC provisioning enables the automatic retrieval of a PACduring EAP-FAST authentication. Automatic PAC provisioning usesTLS with a Diffie-Hellman Key Agreement protocol to establish asecure tunnel. In addition, MSCHAPv2 is used to authenticate theclient and for early man-in-the-middle (MITM) attack detection.Default: OnPAC Authority Select a PAC authority from the drop-down list.Default: NoneNote The drop-down list contains the names of all of the PACauthorities from which you have previously provisioned atunnel PAC. If you have not provisioned a PAC, then "none"is the only option. You can also select "none" to force the hostto request provisioning a PAC.Chapter3 Configuring EAP-FAST Configuring Settings in the Connection TabT able3-1Connection Settings (continued)Connection Settings DescriptionImport Click the Import button to manually import a PAC file. When youclick on this button, the Import Protected Access Credentials (PAC)File window appears. If you need to enter a password for the PAC filethat you have selected, a password window will appear.After you have selected and imported a valid PAC file, the PACauthority is added to the PAC authority drop-down list.Default: EnabledValidate server certificate Check this box to use an authenticated server certificate to establisha tunnel. You can check both the Use Protected Access Credentials(PAC) box and the Validate Server Certificate box at the same time.If both are checked, you can select one or more Trusted Root CAcertificates from the list of trusted Certificate Authority certificatesthat are installed on the host system.The EAP-FAST module always tries to use the PAC first if both checkboxes are checked. The module uses the server certifcate if the PACis missing or rejected by the server.If both check boxes are unchecked, EAP-FAST functions as PEAPdoes without validating server certificate. We do not recommendleaving both boxes unchecked because the module bypassesfundamental trust validation.Default: OffConnect to only these servers Check this box to enter an optional server name that must match theserver certificate that is presented by the server. You can entermultiple server names; separate multiple server names withsemicolons. The EAP-FAST module only allows connections tocontinue without prompting if the subject field (CN) in the servercertificate matches the server names that you enter in this field.Default: OffNote You can use an asterisk (*) as a wildcard character in servernames only if the asterisk appears before the first period (.) inthe format. For example, “*”matches any server name that ends with “.” If youput an asterisk anywhere else in the server name, it is nottreated as a wildcard character.EAP-FAST for Windows Vista Administrator GuideOL-16949-01EAP-FAST for Windows Vista Administrator Guide OL-16949-01Chapter 3 Configuring EAP-FASTOverview of the User Credentials Tab Overview of the User Credentials TabThe EAP-FAST module supports the use of both a client certificate and a username and password as user credentials for authentication and provisioning.Client CertificatesIf a client certificate is used, the EAP-FAST module automatically obtains the client certificate from the Windows certificate store of the current user. The EAP-FAST module finds the user certificate that matches the username of the user who is logged on. The certificate cannot be expired.If multiple user certificates are available, the EAP-FAST module prompts the user to select one, and that selection is saved to the profile. By default, the user certificate is sent securely through TLSrenegotiation or through the EAP-TLS inner method in the protected TLS tunnel. If the EAP-FAST server does not start TLS renegotiation to request the client certificate after the tunnel is established, then the EAP-FAST module sends the certificate through the EAP-TLS inner method.The EAP-FAST module administrator can configure the EAP-FAST module XML schema to send the user certificate without using these security measures.Usernames and PasswordsIf a username and password are used, the user provide one of the following types of username and password:•Windows username and password—The Windows username and password are used as networkaccess credentials. The user is not prompted to enter the username and password unless the password is invalid or must be changed.Trusted Root CA Select one of more Trusted Root CA certificates from the list ofcertificates that are installed on the system. Only trusted CAcertificates that are installed on the host system are displayed in thedrop-down list.To view details about the selected Trusted Root CA certificate,double-click the certificate name. Double-clicking the certificatename opens the Windows certificate property screen, wherecertificate details are available.Default: NoneDo not prompt user to authorize new servers or trusted certificate authorities.Check this box if you do not want the user to be prompted to authorize a connection when the server name does not match or the server certificate is not signed by one of the Trusted Root CA certiticatesthat was selected. If this box is checked, the authentication fails.Default: OffT able 3-1Connection Settings (continued)Connection SettingsDescriptionChapter3 Configuring EAP-FAST Configuring User Credentials•Prompted user credentials—The user is prompted during authentication for credentials. These credentials are credentials that are separate from the Windows username and password, such asLightweight Directory Access Protocol (LDAP) credentials.•Saved user credentials—These are user credentials that are entered as part of the EAP-FASTconfiguration. The user is not prompted for credentials during authentication unless the savedcredentials fail or have expired. New credentials that the user enters after successful authenticationare saved automatically in the configuration. The user does not have to return to the configurationscreen to change the old saved credentials.•One-time password (OTP)—The user must manually enter a OTP. New PIN mode and next token mode for OTP are supported.Configuring User CredentialsThe user can configure user credentials from the User Credentials tab (see Figure3-3).Figure3-3User Credentials T ab in EAP-FAST Properties WindowEAP-FAST for Windows Vista Administrator GuideOL-16949-01EAP-FAST for Windows Vista Administrator Guide OL-16949-01Chapter 3 Configuring EAP-FASTConfiguring User Credentials Table 3-2 lists and describes all options for user credentials.T able 3-2User Credentials OptionsUser CredentialsDescription Use a certificate on thiscomputerClick this radio button to automatically obtain the client certificate from the Windows certificate store of the current user.Default: Off Use one-time password Click this radio button to use a one-time password (OTP). For moreinformation about OTP, see the “Understanding PIN Mode and TokenMode with OTP” section on page 3-10.Default: OffUse Windows username and password Click this radio button to use the Windows username and password asthe EAP-FAST username and password for network authentication.Default: OnPrompt automatically for username and password Click this radio button to require the user to enter a separateEAP-FAST username and password in addition to a Windowsusername and password with every authentication attempt. Thisoptions supports non-Windows passwords, such as LDAP.Default: OffUse saved username and password Click this radio button so that the user is not required to enter anEAP-FAST username and password each time. Authentication occursautomatically as needed using a saved user name and password,which are registered with the backend server.Default: OffWhen selecting this option, the user must enter the following:•Username—Enter the username and the domain name in one ofthese two formats:–Domain-qualified user name—domain\user–UserPrincipalName(UPN)****************•Password—Enter a password. This encrypted password is stored in the EAP-FAST configuration.•Confirm password—Enter the password again to verify that it was entered correctly.Note The maximum number of characters allowed for the usernameand password is 256.Chapter3 Configuring EAP-FAST Configuring User CredentialsUnderstanding PIN Mode and Token Mode with OTPNew PIN mode for OTP is supported. If a new PIN is needed, the backend server sends a text message(for example, “Enter New PIN”) to indicate that a new PIN is neeeded. The EAP-FAST module displaysa prompt window that includes the text message from the server (see Figure3-4). The backend servermight prompt the user twice to confirm the new PIN that the user entered.Figure3-4New PIN Prompt WindowNext Token mode for OTP is also supported. If the next token is needed, the backend server sends a textmessage (for example, “Enter Next PASSCODE:”) to indicate that the next token is needed. TheEAP-FAST module displays a prompt window that includes the text message sent from the server(see Figure3-5). The user must get the next token from the OTP device or from the software and enterit in the prompt field.Figure3-5Next T oken Prompt WindowEAP-FAST for Windows Vista Administrator GuideOL-16949-01Overview of the Authentication TabOverview of the Authentication TabThe EAP-FAST module supports three authentication methods: EAP-GTC, EAP-MSCHAPv2, andEAP-TLS.These three authentication methods use the following types of credentials:•EAP-GTC—Active Directory password, OTP, Token, LDAP•EAP-MSCHAPv2—Active Directory password•EAP-TLS—certificateThe EAP-GTC module is bundled with the EAP-FAST module. The EAP-GTC module is not registeredwith the EAPHost framework; it is not available to other applications.A modified version of the EAP-MSCHAPv2 module is also bundled with the EAP-FAST module. Thismodified version is used in anonymous TLS provisioning mode to support the modification ofEAP-MSCHAPv2 challenges. This same module also supports user authentication in authenticationmode without modification.The EAP-FAST module uses the standard EAP-TLS module that is shipped with Windows Vista.The user can select only one of these three inner authentication methods through the user interface.Although other third-party EAP methods are registered with the EAPHost framework and can be selectedin the administrator interface, these methods have not been officially tested.Configuring Authentication MethodsConfiguring Authentication MethodsYou can choose settings for authentication in the Authentication tab (see Figure3-6).Figure3-6Authentication T ab in EAP-FAST Properties WindowTable3-3 lists and describes options for authentication.Finding the Version of the EAP-FAST ModuleFinding the Version of the EAP-FAST ModuleFollow these steps to learn the current version of the EAP-FAST module on the device:T able 3-3Authentication SettingsAuthentication SettingsDescription Select an authenticationmethod Select the inner tunnel EAP method from the drop-down list. Available methods are EAP-GTC, EAP-MSCHAPv2, EAP-TLS, andAny Method.The Any Method option allows the EAP-FAST module to choose anyof the supported methods that the EAP server requests. The methodmust also be appropriate to the user credentials that are used.Default: Any MethodNote EAP-GTC is the only option available if you selected the Useone-time password radio button in the User Credentials tab.NoteEAP-TLS is the only option available if you selected the Usea certificate on this computer radio button in the UserCredentials tab.Note The use of the Any Method value to allow all methods isunsupported by Cisco or Microsoft and is not recommended.This configuration is used “as-is”; Cisco makes no guaranteethat there will not be adverse performance to the system ifunsupported methods are used. Unsupported methods shouldnever be used in a production environment.Configure Click the Configure button to configure EAP-TLS options. Thisoption is available only if EAP-TLS is the selected authenticationmethod. When you click this button, the standard Windows VistaEAP-TLS Properties Screen appears.Default: DisabledEnable fast reconnect Check this box to allow session resumption.The EAP-FAST module supports fast reconnect (also called sessionresumption) by using the User Authorization PAC. When you enablefast reconnect, you can roam or return from suspend mode withoutre-entering your credentials. Fast reconnect can be used acrossdifferent network access servers.Default: OnNote If you switch profiles, logs off, or reboot, fast reconnect is notattempted. You must be reauthenticated.Enable posture validation Check this box to allow the health information of the host machine tobe queried.Finding the Version of the EAP-FAST ModuleStep1Access the EAP-FAST Properties window. The procedure for accessing this window is detailed in the “Accessing EAP-FAST Properties for Configuration” section on page3-2.Step2Click the About tab (see Figure3-7). The version number, copyright information, and open-source software information are in this tab.Figure3-7About T ab in EAP-FAST Properties Window。

第二章基本操作Ver 0.1声明:1、本电子文档可能不是Windows Vista使用教程的最新版,请至Vista天地查看更新2、您可以在保证本文档完整性的前提下传播、复制、使用本文档(限非商业性使用)相信在初接触Windows Vista时,大部分用户首先感受到的是强烈的视觉刺激——尽管从技术角度看,Windows Vista在安全性以及功能方面所做的改进更为重要——焕然一新的用户接口, Aero Glass固然美轮美奂,即便最精减的Windows Vista Basic主题同样令人惊艳。
客观地说,Windows Vista在很多方面已经接近对曾经是“酷”的代表引领时尚的Apple Mac OS X形成了真正的威胁。
而在操作方面,Windows Vista则秉持了微软产品的传统特点:简单、方便,易于上手,即便是初学者也能很快地掌握基本操作——当然,想要精通则需费一番功夫。
在本章中,我们将简单介绍Windows Vista的基本操作,以帮助用户快速地掌握Windows Vista的使用要领。
2.1 桌面与外观讨论Windows Vista的桌面方面的话题,Aero Glass似乎总是必不可少的,不过,之前我们曾多次介绍过Aero Glass以及Flip 3D、活动缩略图等,在此不再重复,而是把重点放在Windows Vista的新桌面在操作方面带来的变化。
新的桌面,新的名称在桌面元素方面,最大的改变莫过于微软采用了新的命名方式:使用了多年的“我的电脑(My Computer)”变成了“计算机(Computer)”——至于为什么微软的中文化人员将“Computer”翻译成“计算机”而不是采用传统的“电脑”则不得而知,也许要增加点新意?“我的文档(My Documents)”图标被“文档(Documents)”取代,而以往出现在桌面中的“我的文档”图标则被“用户”文件夹取代;之前喜欢将个人文件托拽进“我的文档”的用户可能在开始时会有些不习惯,在Windows Vista中,将文件托拽进用户文件夹并不意味着其将保存在“文档”目录中:“文档”在用户文件夹下一层级在Windows 桌面中存在多年的IE图标消失了,虽然我们可以在桌面上创建IE的快捷方式,不过,对以前习惯于通过IE图标的右键属性来更改IE设置的用户则是一个遗憾。

3.5任务栏任务栏是位于屏幕底部的水平长条。
与桌面不同的是,桌面可以被窗口覆盖,而任务栏几乎始终可见。
它有四个主要部分(如图3-69所示):“开始”按钮,用于打开“开始”菜单。
“快速启动”工具栏,单击一下即可启动程序。
中间部分,显示已打开的程序和文档,并可以在它们之间进行快速切换。
通知区域,包括时钟以及一些告知特定程序和计算机设置状态的图标(小图片)。
图3-69 任务栏位于屏幕的底部您可能使用任务栏的中间部分最为频繁,因此,先介绍这个部分。
1. 如何跟踪窗口?如果一次打开多个程序或文档,则可以将窗口快速堆叠在桌面上。
由于窗口经常相互覆盖或者占据整个屏幕,因此有时很难看到下面的其他内容,或者不记得已经打开的内容。
这种情况下使用任务栏会很方便。
无论何时打开程序、文件夹或文档,Windows 都会在任务栏上创建与之对应的按钮。
按钮会显示该项目的图标和名称。
在下面的图片中,打开了“计算器”和“扫雷”两个程序,每个程序在任务栏上都有自己的按钮。
如图3-70所示。
图3-70 每个程序在任务栏上都有自己的按钮请注意“扫雷”的任务栏按钮显示为按下,这表示“扫雷”是活动窗口,意味着它位于其他打开窗口的前面,可以与您进行交互。
若要切换到另一个窗口,请单击它的任务栏按钮。
在本示例中,单击“计算器”的任务栏按钮会使其窗口位于前面(如图3-71所示):图3-71 单击窗口的任务栏按钮可切换到该窗口单击任务栏按钮是几种在窗口之间进行切换的方式之一。
2. 如何最小化窗口和还原窗口?当窗口处于活动状态(其任务栏按钮显示为按下)时,单击其任务栏按钮会最小化该窗口。
这意味着该窗口从桌面上消失。
最小化窗口并不是将其关闭或删除其内容,只是暂时将其从桌面上删除。
在下面的图片中,“计算器”已经最小化,但是没有关闭。
可以说它仍然在运行,因为它在任务栏上有一个按钮。
如图3-72所示。
图3-72 最小化“计算器”仅使其任务栏按钮可见也可以通过单击位于窗口右上角的“最小化”按钮来最小化窗口(如图3-73所示):图3-73 “最小化”按钮(左)若要还原已最小化的窗口(使其再次显示在桌面上),请单击其任务栏按钮。


windows7系统怎么变为苹果界面windows7系统怎么变为苹果界面第一局部(根底操作)1 Aero透明效果2 壁纸屏保(静态壁纸、幻灯片壁纸、动态视频、屏幕保护、开机登陆画面3 系统图标(桌面图标显示隐藏、系统图标替换4 鼠标指针(指针替换5 字体美化(字体替换、系统字体修改、字体渲染6 主题使用(官方主题、第三方主题及使用7 桌面小工具第二局部(四个简单实例)8 任务栏个性化9 实用Dock条10 简单仿Windows8之Metro界面11 简单仿Apple Mac如下图,是我电脑的简单美化效果。
第一局部、根底操作1.Aero透明效果Windows7最大特点之一便是拥有华美的界面,特别是Aero的透明效果,虽然某P Vista甚至苹果的Mac都有了强制透明补丁,但还是无法和Windows7媲美的。
开启Aero透明效果是很简单的,一般来说不用你手动去开启。
如果你的任务栏还是灰色的,说明你没有开启,通常情况下是你没有去安装显卡驱动或者是显卡催化剂驱动。
安个驱动精灵或驱动人生把显卡驱动打上,然后重启下,你就可以看到透明效果了。
在开启整体透明后,开可以修改右键显示透明,开始菜单透明,如下图。
点此下载菜单透明美化软件2.壁纸屏保壁纸是最熟悉不过的,也就是桌面,除了DOS外,几乎所有系统都有壁纸图片。
静态壁纸很简单,就单张图片,直接图片邮件设置为桌面背景即可。
幻灯片壁纸即多张静态图片,可自己设定时间切换。
如图2(翻开图2的方法为:桌面空白处->右键->个性化)与图3所示。
然而把动态视频放在桌面上,可能你就没有听过了,但虽然视频放在桌面上很酷炫,占用CPU和内存是很大的,而且并不是所有视频都可以,我一直没去尝试,如果你有兴趣可以自行百度。
屏幕保护和壁纸是死缠烂打的兄弟了,在win7下设置屏保的方法如图2所示。
不过屏保会增加耗电量。
你可以尝试热带鱼屏保,这个算是相当知名的了。
开机登陆画面也很熟悉了,某P的欢送使用界面,Win7依然是蓝色的图片。

来源Windows8论坛:Windows AeroWindows Aero简介目前支持Windows Aero的操作系统功能介绍系统需求Windows Aero简介目前支持Windows Aero的操作系统功能介绍系统需求Aero 透明的磨砂玻璃窗口[编辑本段]Windows Aero简介Windows Aero从Windows Vista开始使用的重新设计用户界面,透明玻璃感让使用者一眼贯穿。
"Aero"这个字是首字母缩略字,即是Authentic(真实)、Energet ic(动感)、Reflective(具反射性)及Open(开阔)的缩略字,意为Aero 界面是具立体感、令人震撼、具透视感和阔大的用户界面。
Windows Aero 可用于使用兼容图形适配器并运行家庭高级版、商用版、旗舰版或企业版的Windows Vista 和w indows 7的PC,它给您的PC 带来全新的外观。
Windows Aero 提供高质量的用户体验,大大方便您看到并处理信息,并提供更加流畅,更加稳定的桌面体验。
Windows Aero 的两项激动人心的新功能Windows Flip和Windows Flip 3 D,使您能够自信地在您的桌面上以视觉鲜明的便利方式管理窗口。
除了新的图形和视觉改进,Windows Aero 的桌面性能同外观一样流畅和专业,为您带来简单和高品质的体验。
来源Windows8论坛:Glass[编辑本段]目前支持Windows Aero的操作系统windows vista系列Windows Vista(普通家庭版)不能运行Aero。
Windows Vista Business(商业版)、Windows Vista Enterprise(企业版)、Windows Vista Home Premium(家庭高级版)和Windows Vista Ultimate,和旗舰版能够运行Aero。
Aero,又叫AeroGlass,是从Windows Vista开始引入的毛玻璃风格的界面,微软全新推出的操作系统Windows 7也继承了这种界面设计。
它的效果确实让人眼前一亮,然而很多人却认为这个美轮美奂的界面是华而不实的花瓶。
那么,Aero界面真的是华而不实吗?非也!解读Windows Aero微软Windows Vista系统由于生不逢时而惹来了很多不好的名声,很多人更是人云亦云,并仅从其表面主观判断这个系统的好坏,因而出现了很多持有“Aero无用”或“Aero华而不实”之类的观点的人。
对于全新推出的Windows 7操作系统,由于有Vista打下的基础(硬件驱动以及软件的成熟),加上微软在Win7上付出的努力,这个新一代的操作系统获得了不错的反响。
大家都逐渐愿意去关注她,拥抱她。
正好给了我一个机会为Aero平反。
本文将通过简述Aero的基本工作原理来讲述Aero除了给我们带来华丽的界面之外还给我们带来什么样的好处,并让大家对Windows 7有更多的了解。
评价一样事物,不应只看其表面,更应该看清楚它的“心”。
传统桌面渲染模式的缺陷下图的现象相信你非常熟悉:图1为什么会这样?要解析清楚这个,我们就需要了解一下传统的Windows桌面渲染原理。
在Windows Vista之前,Windows只有一个桌面缓存,并且所有的程序窗口都直接在那个缓存上进行渲染。
这样说或许比较抽象,用个比较形象的说法就是,你所看到的整个屏幕上的画面就相当于一张画在一张纸上的画。
对,就是只有一张纸。
这样造成的结果是什么呢?我们再来看。
图2有2个计算器窗口,其中一个被另一个覆盖了一部分窗口内容。
而被覆盖的那个计算器的窗口内容,实际上就只有看得见的那部分(参见图3)。
图2图3这是因为所有窗口都只在一个缓存上直接渲染(绘图)的关系。
试想一下,一张纸上的内容,除了你所能够看到的那些部分之外,还会有什么?所以当我们移动上面的那个计算器窗口的时候,下面那个计算器的窗口就要重绘,整个画面都需要重绘。
Windows Vista 中引入了显著改进的用户体验,其中具有称作 Aero Glass 的用户界面。
本文档针对使用 Aero Glass 用户界面时遇到的问题提供了故障排除建议。
目标●讨论启用 Aero Glass 的要求。
●讨论客户在使用 Aero Glass 时可能遇到的问题。
●演示如何解决Aero Glass 的潜在问题。
相关组件桌面窗口管理器会话管理器桌面的所有 Windows Aero 和 Glass 功能都是通过桌面窗口管理器会话管理器服务实现的。
此服务也称为 UxSms 服务(用户体验会话管理器服务),并且作为在一般服务主机进程 svchost.exe 下运行的服务来实现。
桌面窗口管理器桌面窗口管理器会话管理器服务为计算机上的每个用户会话启动一个桌面窗口管理器进程,并对该进程进行管理。
桌面窗口管理器进程作为 %systemroot&\windows\system32\dwm.exe 运行。
如果该进程曾意外终止,则将由桌面窗口管理器会话管理器服务重新启动。
桌面窗口管理器进程加载两个重要模块:●Udwm.dll – Microsoft 桌面窗口管理器 DLL●Milcore.dll – Microsoft 媒体集成层核心库。
Aero Glass 功能的硬件要求要启用 Aero Glass,您的 PC 必须满足下列图形硬件条件:●支持 Windows Display Driver Model (WDDM) 和 Pixel Shader 2.0 的 DirectX 9 类显示适配器。
●每像素最低 32 位。
●用于指定显示器分辨率的适当图形内存:○64MB 图形内存,以支持分辨率为 1280 x 1024 或更低的单显示器。
○128MB 图形内存,以支持分辨率大于 1280 x 1024 且小于或等于 1920 x 1200 的单显示器。
○256MB 图形内存,以支持分辨率大于 1920 x 1200 的单显示器。
了解Windows Vista 内核:第一部分概览:线程优先级和计划基于文件的符号链接取消I/O 操作这是系列文章的第一部分,探讨的是Windows Vista 内核中的新增内容。
在这一期中,我将着重说明在进程、线程和I/O 方面的更改;在将来几期内容中将涉及到内存管理、启动和关闭、可靠性和恢复以及安全性方面的内容。
本文的范围仅限于对Windows Vista™内核的更改,尤其是对Ntoskrnl.exe 和与其紧密关联的组件的更改。
请记住,在Windows Vista 中还存在许多其他重大更改,但这些却超出了内核的范围,因此本文将不予以说明。
其中包括对外壳(如集成的桌面搜索)、网络(如新的IPv6 堆栈和双向防火墙)和下一代图形模型(如Aero™Glass、Windows®Presentation Foundation、桌面窗口管理器和新图形驱动程序模型)的改进。
而且未涉及的内容还包括新的Windows 用户模式和内核模式驱动程序框架(UMDF 和KMDF),因为在较早的Windows 版本上它们在后级别才是可安装的。
CPU 时钟周期计数Windows Vista 包含了进程和线程方面的大量增强功能,其中包括使用CPU 时钟周期计数器以较公平地进行CPU 分配,以及使用新的多媒体类计划程序服务(MMCSS),它有助于媒体应用程序提供稳定的播放。
所有Windows NT®版本,包括Windows Vista 程序在内,大约在每10 ms 或15 ms(毫秒)执行一次间隔计时器中断例程,间隔取决于硬件平台。
该例程查看它所中断的线程并更新线程的CPU 使用统计数据,就好像该线程在整个间隔期间都在运行,而事实上,线程可能仅在间隔就要结束前才开始执行。
而且,从技术上讲,可能已经为线程分配了CPU,但却一直没有机会运行,因为执行的是硬件和软件中断例程。
虽然对于报告线程和进程CPU 使用情况的诊断工具来说,基于时钟的时间计算是一个好方法,但是,若由线程计划程序使用该方法将导致不公平的CPU 分配。
Windows Vista 概览课程介绍:本课程为自学课程,通过本课程学员将对Vista有一个概括性的了解,认识Vista提供的新功能,特性。
学习目标:1.了解 Windows Vista 的不同版本及其与 Windows XP 版本的不同2.了解 Windows Vista 不同版本之间的功能、特性差异3.明确安装和运行 Windows Vista 所需的系统硬件要求4.对Windows Vista引入的新功能和新特性有初步的认识5.根据本文提供的Vista帮助索引,结合上机实验了解新功能的使用方法Windows Vista 概览_____________________________________________________ 1概述:________________________________________________________________ 2一、Vista 版本构成_________________________________________________ 2二、Vista对系统的硬件要求________________________________________ 11三、Vista界面新特性概览__________________________________________ 13四、Internet 应用新特性概览_______________________________________ 14五、性能管理及提升工具__________________________________________ 19六、多媒体应用新特性:__________________________________________ 22七、打印功能新特性:____________________________________________ 25八、其他便捷应用_________________________________________________ 26概述:Windows Vista,使用户可以更安全、更轻松地完成日常任务正文。
七年级信息技术《inds Aer的Aer界面》学案七年级信息技术《indsAer的Aer界面》学案【教学目标】知识与技能◆掌握打开、关闭indsAer界面的方法;◆了解indsAer界面的特点。
2.过程与方法◆通过indsVista界面仿真器让学生体验indsAer界面特点;◆培养学生自主探究的学习能力。
3.情感态度与价值观◆培养学生敢于实践和创新意识,感受新科技带来的新体验;◆培养学生关注社会发展、关注信息产业发展的意识。
【教学重点】indsAer界面特点简介;打开、关闭indsAer界面的方法。
【教学难点】打开、关闭indsAer界面的方法。
【教法选择】自主性学习、示范性教学与探究式学习相结合的方式。
【教学过程】.自主学习,交流总结’师:通过前几节的学习,我们基本掌握了操作indsXP 的方法,目前计算机市场中推出了一款新版操作系统,你们知道是什么吗?生:师:新版软与老版软相比,通常只是功能更强大,使用更方便,原则上软是向下兼容的,谁能具体举个例子,说明什么是“向下兼容性”?生:师:生:师:现在就让我们一起来看看新版操作系统的真面目吧!请同学们认真阅读教材,分钟后自我总结,看看谁对本重点把握得最好。
生:师:评价与总结,确定本知识要点。
2.示范教学,感受Vista师:目前我们教室和多媒体机房还没有安装indsVista 操作系统,我制作了一段视频资料,仔细观察,“视频资料”中的内容和书中讲的一样吗?生:师:能说出indsAer界面与indsXP桌面有什么区别吗?生:师:想亲自体验一下indsAer界面吗?生:3.主动探究,体验新知师:请在本机中查找indsVista界面仿真器软;是我刚刚下传的文,试着找到set&sh;&sh;-upexe文,你会安装一个“小软”,亲自感受一下绚丽多彩的indsAer界面吗?生:师:请根据教材的“各显神通”,试着用其提供的Vista 相册,制作自己的“个性”相册吧!生:师:现在开动你的“手指”,把教材中“成长基石”部分的第2、3、4题以电子稿的形式保存起来,我会把它们放进你的电子“成长记录册”中。
Aero向导代表了由Windows 95系列操作系统最先引入的向导界面的最高发展水平。
它给用户所常见的向导界面带来了一丝新意,能够更好地抓住用户的视线。
在《Windows Vista for Developers》系列的第一部分中,我将演示如何用最少的代码将一个传统的向导更新为最新的Aero界面。
属性单(Property Sheets)
回忆一下,向导仅仅是一系列的由PROPSHEETHEADER结构定义的属性单,并由PropertySheet函数实现。
ATL所提供的CPropertySheetImpl类模板已经为我们生成了大部分使用PropertySheet函数的代码。
接下来就让我们从一个简单的属性单开始,然后将其“升级”为全新的Areo向导:
class SampleWizard :
public CPropertySheetImpl<SampleWizard>
{
public:
BEGIN_MSG_MAP(SampleWizard)
CHAIN_MSG_MAP(__super)
END_MSG_MAP()
SampleWizard() :
CPropertySheetImpl<SampleWizard>(IDS_TITLE)
{
VERIFY(AddPage(m_page));
}
private:
SamplePagem_page;
};
该SampleWizard类继承于上面提到的C PropertySheetImpl类模板,也就自动获取了基类提供的很多功能。
message m ap简单地将消息传递给基类。
构造函数调用了积累的构造函数,用来设置该向导的标题栏,并使用继承于C PropertySheetImpl的AddPage方法添加了一个简单的页。
SamplePage类的定义如下:
class SamplePage :
public CPropertyPageImpl<SamplePage>
{
public:
BEGIN_MSG_MAP(SamplePage)
CHAIN_MSG_MAP(__super)
END_MSG_MAP()
enum { IDD = IDD_SAMPLE_PAGE };
};
SamplePage类继承于CPropertyPageImpl类模板,它提供了属性页所需要的大部分功能。
SamplePage的message m ap同样简单地将消息传递给基类。
我们还需要为基类设置IDD(enum类型的常量),以便其甄别将用于属性页的对话框资源。
这时,我们即可用下面的代码创建并显示出一个模态属性单了:
SampleWizardsampleWizard;
sampleWizard.DoModal();
第一行创建了一个SampleWizard对象以及其多个基类的实例,其中之一就是生成调用PropertySheet函数所必须的那个结构体。
第二行SampleWizard的DoModal方法(继承于CPropertySheetImpl类模板)负责调用PropertySheet函数。
结果就是我们看到了如下的一个简单的属性单:
经典向导(Classic Wizards)
若想将属性单变为经典样式的向导,你所需要做的只是在SampleWizard构造函数中添加如下的语句:
m_psh.dwFlags |= PSH_WIZARD97;
上面这行代码将PSH_WIZARD97标记(flag)与PROPSHEETHEADER结构中现有的标记组合了起来。
因为向导界面还包含有一个额外的标题区域,所以我们还需要修改SamplePage类,添加一段标题文本:
class SamplePage :
public CPropertyPageImpl<SamplePage>
{
public:
BEGIN_MSG_MAP(SamplePage)
CHAIN_MSG_MAP(__super)
END_MSG_MAP()
enum { IDD = IDD_BLANK_PAGE };
SamplePage()
{
VERIFY(m_title.LoadString(IDS_PAGE_TITLE));
SetHeaderTitle(m_title);
}
private:
CStringm_title;
};
SamplePage构造函数使用继承于C PropertyPageImpl的SetHeaderTitle方法来设置标题区域。
注意页的PROPSHEETPAGE结构保留了该字符串的指针,所以该字符串的生存周期必须超过这个构造函数。
简单修改过后,结果却大不相同:
可以看到,前面出现在选项卡上的文字现在出现在了窗口标题栏中。
Aero向导(Aero Wizards)
现在只要将SampleWizard构造函数中的PSH_WIZARD97替换为
PSH_AEROWIZARD,即可看到全新的Aero向导界面:
可以看到,窗口的标题又回来了,而原本出现在属性单选项卡上的对话框说明文字却不见了踪影。
新的消息(New Messages)
Aero向导还提供了一些新的消息,用来让我们能够更好地控制向导中的控件。
PSM_SHOWWIZBUTTONS消息用来显示或隐藏向导中的标准按钮。
PropSheet_ShowWizButtons宏可以帮你简单地发出这条消息。
虽然使用起来并不是那么直观,但一旦掌握了也就不难了。
PropSheet_ShowWizButtons虽然是个宏,但我们可以将其想象为一个函数:
void PropSheet_ShowWizButtons(HWND handle,
DWORD buttons,
DWORD mask);
handle参数用来甄别向导窗口的实例,buttons参数用来指定将要显示哪些按钮,mask参数则用来指定该宏将作用于哪些按钮上。
若是某个按钮的标记同时出现在了buttons和mask参数中,那么将显示出该按钮。
若某个按钮的标记只出现在了mask参数中,那么该按钮将隐藏。
我们可以使用如下的按钮标记:
1.PSWIZB_BACK
2.PSWIZB_NEXT
3.PSWIZB_FINISH
4.PSWIZB_CANCEL
例如,如下代码将显示出Next按钮,并隐藏Back按钮:
PropSheet_ShowWizButtons(handle,
PSWIZB_NEXT,
PSWIZB_BACK | PSWIZB_NEXT);
PSM_ENABLEWIZBUTTONS消息用来启用或禁用某个标准按钮。
PropSheet_EnableWizButtons宏可以帮你简单地发出这条消息:
void PropSheet_EnableWizButtons(HWND handle,
DWORD buttons,
DWORD mask);
在区分按钮方面,这个宏的处理方法与PSM_SHOWWIZBUTTONS一样——buttons参数用来指定将要启用/禁用哪些按钮,mask参数则用来指定该宏将作用于哪些按钮上。
例如,如下代码将启用Next按钮,并禁用Back按钮:
PropSheet_EnableWizButtons(handle,
PSWIZB_NEXT,
PSWIZB_BACK | PSWIZB_NEXT);
PSM_SETBUTTONTEXT消息用来修改Next、Finish和Cancel按钮上的文字。
PropSheet_SetButtonText宏可以帮你简单地发出这条消息:
void PropSheet_SetButtonText(HWND handle,
DWORD button,
PCWSTR text);
示例程序
为了让你更容易地体验到Aero向导所提供的各种增强功能,我创建了一个简单的向导界面,可以在这里下载:/kenny/vista/aerowizardsample.zip。