高中英语一轮复习语法第5讲:连词
- 格式:docx
- 大小:36.53 KB
- 文档页数:5
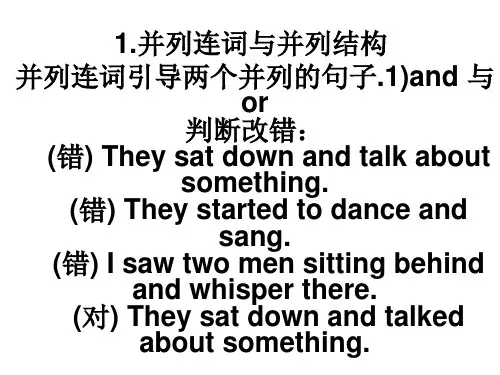


高中英语连词知识点整理高中英语连词知识点整理一.概念连词是用来连接词,短语,从句或句子的词.连词不作成分.二.重点连词1.表示并列关系的连词有:and, both…and…ly… but also…和neither…nor…等1)and:和,并且(连接对等关系的字和字,句子和句子)例如:I enjoy basketball , football and tablThe weather blder and cold2)both…and…既…也…,(两者)都…注:both…and…构成的词组作主语时,谓语动词用复数。
例如:Band Kate agland.both…and…否定句表示部分否定。
例如:You can’t speak both German and EnglBather andaren’t d)neither…nor…:既不…也不…(就近原则)例如:Neither Ialay b)not only…but also…:不但…而且…(就近原则)例如:Not onlbut alldren are ill.2.表示转折关系的连词有:but, howevll,while等。
例如:Mary was a nice girl, but she hadg.He was vd, stillwalking表示选择关系的并列连词有:…or…,whether… or…等。
1)or:或、否则例如:Is your friend English or American?He doesn’t like dumplingdl祁使句后连接or ,表“如果…,否则…”,有转折的意思,此时udon’t …,you’ll …例如:Hurry uu’ll be laIf you don’t hurry up, you’ll be late.2)either…or…:或者…或者…; 不是…就是… (就近原则。
)例如:u or I am rigDlike English?注:由either…or…引导的否定句是完全否定。

高中英语知识点归纳连词的分类及用法在高中英语学习中,掌握好连词的分类及用法是极为重要的,因为连词不仅能够连接句子,还能够表示句子的逻辑关系,使文章结构更加严谨和流畅。
本文将为您归纳整理高中英语中常见的连词分类及其用法。
一、并列连词1. and:表示并列或递进关系,连接同类词、短语、从句等。
2. but:表示转折关系,连接相对矛盾的内容。
3. or:表示选择关系,连接两个或多个同类词、短语、从句时,表示其中的任选一项。
4. nor:表示否定选择关系,连接两个或多个同类词、短语、从句时,表示其中的任何一项都不成立。
5. for:表示原因或解释,连接表示原因的短语或从句。
二、递进连词1. moreover/furthermore:表示进一步增加的内容。
2. in addition/what's more:表示补充的内容。
3. besides:表示除此之外的内容。
4. likewise/similarly:表示相似或相同的内容。
三、转折连词1. however:表示转折关系,引出与前面句子相对矛盾的内容。
2. nevertheless/nonetheless:表示转折关系,引出与前面句子相对矛盾的内容,但前后句之间关系较为紧密。
3. on the contrary:表示与前面内容的相反。
4. in contrast:表示对比关系。
四、因果连词1. because:表示原因,引导原因状语从句。
2. since:表示原因,引导原因状语从句。
3. as:表示理由或原因,引导原因状语从句。
4. so:表示结果,引导结果状语从句。
5. therefore/thus/hence:表示结果。
五、条件连词1. if:表示条件,引导条件状语从句。
2. unless:表示条件,引导条件状语从句,意为“除非”。
3. as long as:表示条件,引导条件状语从句,意为“只要”。
4. provided/providing that:表示条件,引导条件状语从句,意为“只要”。


高中英语连词知识点连词是一种虚词,在句中不能单独使用。
连词可分为两类:并列连词和从属连词。
下面小编给大家分享一些高中英语连词知识,希望能够帮助大家,欢迎阅读!高中英语连词知识1并列连词的用法1.并列连词and的用法and可以连接两个的词,多用于肯定句中。
连接两个句子,表示因果、对比、条件、假设、目的等。
例如:Go and fetch something to eat.(连接两个动词如go, come等表示目的)去取些吃的东西来。
Mary likes music and Lily is fond of sports.玛丽喜欢音乐,莉莉爱好体育运动。
(对比)One more week and we’ll accomplish the task.再一星期,我们就完成任务。
(条件)2.并列连词both…and, not only…but also, as well as的用法①both…and意为:“不但…而且…;既…又…”,是并列连词,可以并列主语、宾语、表语、状语、谓语等成份。
并列主语时谓语动词用复数形式。
Both New York and London have traffic problems.纽约和伦敦都存在交通问题。
The secretary both speaks and writes Spanish.这位秘书不但能讲而且能写西班牙语。
②not only…but also意为:“不但...而且”,是并列连词,可以连接两个词,也可连接两个句子。
其中,but also中的also可以省略。
not only…but also可以连接句中所有的成份,连接并列主语时,其谓语动词根据就近原则,与所靠近的成分保持数的一致。
not only…but also可以连接两个句子,not only位于句首时, not only后的句子要倒装。
Not only the students but (also) their teacher is enjoying the movie.不仅学生们津津有味地看着这部电影,而且他们的老师也是如此。

高中英语新高考语法专题复习讲义名词性从句语法(连接词)知识点总结插曲:连接词说到这儿,就有必要展开聊聊连接词了。
连接词可以分为三类:连接代词、连接副词、连接连词。
这里有三个小定义需要大家记住:1.连接代词==连词+占位符2.连接副词=连词+ 一个介词+占位符3.连接连词=连词先解释一下为什么三条公式的右半边都有"连词〃:因为作为一个从句的连接词(又称引导词),无论连接代词、连接副词,还是连接连词,共同的基础职责都是连接各自有独立结构的主句和从句。
还记得吗一一一个简单句配一个句号,如果非要在一个句号里挤进两个简单句的话,需要用连词隔开。
连接连词只起连词的作用,不用来替代从句里的任何成分。
这也就意味着,使用连接连词,往往是在被拆分出来的从句里没有占位符的情况下。
例:主句:Juan couldn't believe a thing.从句:She was dead.完整句:可以看到,从句里没有占位符,并且在完整句里,连接连词没有替代掉从句里的任意成分。
而连接代词不仅能连接主句和从句,还同时起到替代从句中占位符的作用。
这也就意味着连接代词不会用在从句里没有占位符的情况下。
例:主句:Juan couldn z t believe a thing.从句:I said the thing.完整句:Juan couldn z t believe (主句)what (连接代词)I said (从句).如你所见,首先,从句里有占位符the thing ,其次,在完整句中使用了连接代词what后,从句中原本的占位符消失了(被连接代词what替代掉了)。
最后,连接副词除了发挥连词的作用外,通常是用来替代从句中的状语词组(介词 + 名词,如:at the thing、on the thing、within the thing等)的,所以相当于连词+ 一个介词+占位符。
连接副词只能用在从句里不仅有占位符,而且还在占位符之前有介词的情况下。



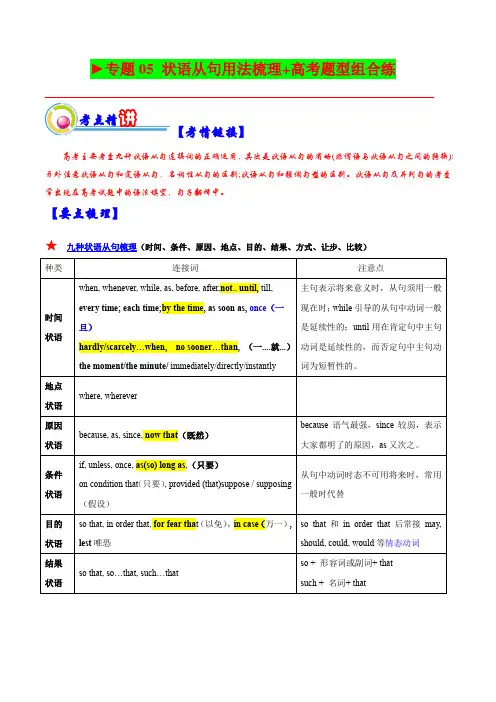
连词(Conjunction)I 定义连词是连接单词、短语或句子的一种虚词,在句中不单独作任何成分。
II 种类A 并列连词⑴表示并列关系例:and、both…and…等⑵表示转折关系例:but、yet、while 等⑶表示选择关系例:or、either…or…等⑷表示因果关系例:for、so等B 从属连词a. 引导名词性从句①引导宾语从句②引导表语从句③引导主语从句④引导同位语从句b. 引导形容词性从句(定语从句)①引导限制性定语从句②引导非限制性定语从句c. 引导副词性从句(状语从句)①引导时间状语从句例:when、as、while、after、before、as soon as 等②引导地点状语从句例:where、wherever 等③引导原因状语从句例:because、as 等④引导条件状语从句例:if、unless、as long as 等⑤引导目的状语从句例:so that、in order that 等⑥引导让步状语从句例:although、though、as 等⑦引导结果状语从句例:so…that…、such…that…等⑧引导比较状语从句例:than、as 等⑨引导方式状语从句例:as、as if 等III 用法A 并列连词⑴表示并列关系的并列连词① and·当连接三个以上并列成分时,一般在最后两者间加and,其余逗号隔开例:Solid, liquid and gas are the three states of matter.·“动词+ and + 同一个动词”表示动作长时间地“继续”或“重复”例:We waited and waited.·“祈使句+ and + 陈述句”,此结构相当于if引导的条件句例:Go straight on and you will see the library.②both…and…·“……和……都”,可用来连接两个并列的主语、谓语、宾语、表语和状语等,当连接两个并列的主语时,谓语动词用复数形式例:He can play both the piano and the guitar.③neither…nor…·“既不……也不……”,可连接两个主语、谓语、表语和状语等,当连接两个并列主语时,谓语动词遵循就近原则例:Neither Jack nor I have seen this film.④not only…but also…·“不但……而且……”,可连接两个主语、谓语、宾语、表语、状语或句子,连接两个并列主语时,谓语动词遵循就近原则例:Not only Lily but also her parents are friendly to me.·not only置于句首,句子要用部分倒装(not only…but also…连接两个并列句时,含有not only的句子用部分倒装)例:Not only can he speak Chinese but also he can speak French.·not only…but also…中的only可用merely,alone代替,also可省略例:It is not only/ merely/ alone cold, but(also) very dry.⑵表示选择关系的并列连词① or·表示选择,意为“或、还是”例:Would you like tea or coffee?·(用于警告或忠告)意为“否则,不然”,“祈使句+ or (else) + 陈述句”相当于“if…not + 主句”例:Hurry up, or you’ll be late for school.②either…or…·“或者……或者……,不是……不是……,要么……要么……”,如果either…or…连接两个并列主语时,谓语动词遵循就近原则例:Either he could not come nor he did not want to.③not…but…·“不是……而是……”,连接两个并列主语时,谓语动词遵循就近原则例:Not you but I am to blame.⑶表示转折关系的并列连词① but·表示转折,意为“但是”例:Jane said she was ill, but I saw her in the street just now.·此外,but还可用于“I’m sorry but…”、“Excuse me, but…”句型例:I’m sorry but I won’t be able to come tonight.注:although/though不能与but连用,但可以和yet连用。
高中英语知识点归纳连词的用法总结连词是连接句子、短语或单词的重要语法元素,在英语中扮演着关键的角色。
掌握好连词的用法,能够帮助我们构建准确、流畅的语言表达。
本文将对高中英语中常用的连词进行归纳总结,以帮助读者更好地理解和运用。
一、并列连词(Coordinating Conjunctions)并列连词主要用于连接两个相同重要程度的短语、句子或单词,常见的有:and(和)、but(但是)、or(或者)、so(所以)、for(因为)等。
它们的使用可以让句子更加连贯有力。
例如:1. I like to play basketball and my sister likes to play tennis.我喜欢打篮球,而我妹妹喜欢打网球。
2. He is smart, but he is lazy.他很聪明,但是他很懒惰。
3. You can have tea or coffee.你可以喝茶或者咖啡。
二、从属连词(Subordinating Conjunctions)从属连词用于连接主句和从句,从句依赖于主句的意义,常用的有:because(因为)、although(虽然)、if(如果)、while(当)、when (当)、until(直到)等。
例如:1. I can't go out because it's raining.我不能出去,因为下雨了。
2. Although it was late, he continued to work.虽然很晚了,他还是继续工作。
3. If you study hard, you will succeed.如果你努力学习,你会成功的。
三、比较连词(Comparative Conjunctions)比较连词用于比较两个事物或概念之间的关系,常见的比较连词有:as(像)、than(比)、both(两者都)等。
例如:1. He sings as well as his sister.他唱歌像他妹妹一样好。
高考英语连词知识点总结高考英语考试中,连词是重要的语法知识点之一。
掌握了连词的使用方法和特点,能够更好地串联句子,提高文章的连贯性和逻辑性。
本文将总结一些常见的连词知识点,帮助考生在高考英语中取得更好的成绩。
1. 并列连词并列连词用于连接同类词、词组或句子,常见的有and, or, but, so 等。
其中,and用于连接同类词或词组;or用于表示选择关系;but用于表示转折关系;so用于表示因果关系。
例如:- The sun was shining, and the birds were singing happily.- You can have coffee or tea.- I wanted to go out, but it was raining heavily.- I was tired, so I went to bed early.2. 递进连词递进连词用于表示递进关系,常见的有furthermore, moreover, in addition等。
例如:- He is not only smart but also hardworking.- Furthermore, he has a great sense of humor.- I like watching movies. Moreover, I enjoy reading books.3. 转折连词转折连词用于表示转折关系,常见的有however, nevertheless, but, yet等。
例如:- She tried her best, however, she failed the exam.- He is smart, yet he often makes careless mistakes.- The weather was hot, but we still went hiking.4. 表示因果关系的连词表示因果关系的连词用于连接原因和结果,常见的有because, since, as, so等。
高中英语一轮复习语法连词(Conjunctions)
重点用法①常用的并列连词
用法:1.并列连词用来连接平行对等、互不从属的词、短语或分句,可表示并列、转折、选择或因果等关系。
常见的并列连词的用法如下:
2.and意为“和,并且”,用于连接对等关系的词、词组或分句;常用于句型“祈使句+逗号+and...”。
Tom and I went to the bookstore yesterday. and连接两个并列的词
我和汤姆昨天去了书店。
He stood up and put on his hat. and连接两个动作
他站起来,戴上了帽子。
Fishing is his hobby,and collecting coins also gives him great pleasure. and连接两个分句
他爱好钓鱼,收集硬币也令他感到快乐。
Try again,and you’ll succeed. 在祈使句中,and前面的部分用来表示条件
再试一下,你就会成功的。
3.or和or else表示选择关系。
表示两者之间选择其一,意为“或者”;用于祈使句时,意为“否则,不然”。
Tom or I am right.或者汤姆,或者我是对的。
Hurry up,or else you’ll miss the last bus.快点儿,不然你就会错过最后一班车。
1
第 1 页共 5 页
Put on your overcoat,or you will catch cold.穿上衣服,要不然你会着凉的。
4.but意为“但是,可是,而是”,连接两种并列成分,表示转折关系,不能和although连用。
It was a sunny but not very warm day.那一天天气晴朗,但却不太暖和。
5.so意为“所以,于是,也,同样”,表示结果,连接句子。
It was too dark,so I couldn’t see anything.天太黑了,我什么也看不见。
6.for意为“因为”,表示原因,连接句子。
I soon went to sleep,for I was tired.我很快就入睡了,因为我太累了。
7.both...and意为“和,既……也……”,由它构成的词组作主语时,谓语动词要用复数形式。
Both Lucy and Mary are ten.露西和玛丽都10岁了。
Both he and his brothers are good at dancing.他和他的兄弟们都擅长跳舞。
8.either...or意为“或……或……;不是……就是……”,由它构成的短语作主语时,谓语动词随or后面的词而定(就近原则)。
The shoes were either too big or too small.鞋子要么太大,要么太小。
Either you or he is right.不是你,就是他是对的。
9.neither...or意为“既不……也不……”,由它构成的短语作主语时,谓语动词随nor后面的词而定(就近原则)。
It is neither hot in summer,nor cold in winter.夏天不热,冬天不冷。
Neither he nor I speak a foreign language.他和我都不会说外语。
10.not only...but also意为“不但……而且……”,由它构成的短语作主语时,谓语动词随but also后面的词而定(就近原则)。
Jane is not only beautiful but also kind.简不但漂亮,而且人也非常好。
2
Not only the students but also the teachers was against the plan.
不但学生,而且老师也反对这个计划。
11.as well as...意为“又,不但……而且……”,由它构成的短语作主语时,谓语动词随其前面的词而定。
Mr.Lin as well as his parents joins in the party.不但林先生的父母,而且林先生也参加宴会。
提示:在口语中,and常用在come,go,run,stay,try等之后表示目的,and在此相当于不定式符号to。
Go and ask him.去问问他。
Try and finish the work in a month.设法在一个月内完成这项工作。
重点用法②常用的从属连词
用法:1.that无词义,用于引导名词性从句(主语从句、表语从句、宾语从句、同位语从句)和定语从句。
I think that she is tired.我想他累了。
The trouble is that I’ve lost his address.麻烦是我把他的地址丢了。
2.when,while和as意为“当……时”,用于引导时间状语从句,都可表示从句和主句的动作同时发生,when也可表示先后发生。
While I read,she sang.我在看书时,她在唱歌。
When/While/As he was doing his homework,I came in.
当他写作业时我走了过来。
There were chairs left over when everyone had sat down.
3
当大家就座后还剩下几把椅子。
3.since意为“自从……以来”,引导时间状语从句。
从句用一般过去时,主句多用一般现在时或现在完成时。
Many things have happened since I last saw him.从我上次见到他以来发生了很多事。
How long is it since we last went to the theatre?我们多久没去看戏了?
4.as soon as意为“刚一……就”,引导时间状语从句。
从句用一般现在时表示将来发生的动作或状态。
As soon as I get the present,I’ll tell you.我一收到礼物就告诉你。
I’ll tell Ann the good news as soon as she comes back.安一回来,我就告诉她这个好消息。
5.before意为“在……之前”,after意为“在……之后”,都可引导时间状语从句。
Did she leave a message before she went?她走之前留言了吗?
I found her bag after she had left.她走了以后,我发现了她的包。
6.till和until意为“直到……时”,可引导时间状语从句。
一般认为till不如until正式,在书面语中不常用。
句首通常用until。
Can you wait till/until I come back?你能等到我回来吗?
He did n’t finish his homework until his mother came back. finish是点动词,故用否定句。
直到他妈妈回来,他才完成作业。
7.because意为“因为”,引导原因状语从句。
常用于回答why引导的特殊疑问句,不能和so 连用。
I did it because my mother told me to.妈妈吩咐我去做这件事,我才做的。
-Why are you late?你为什么迟到?
4
-Because I met a traffic accident on my way here.因为我在来这儿的路上遇到了车祸。
8.if意为“如果”,引导条件状语从句。
If necessary I will come at once.如果有必要,我会马上来。
9.though和although意为“虽然”,引导让步状语从句。
它们都不能与but连用。
Though I was tired,I still worked hard.虽然我很累,但我仍然努力工作。
10.so...that意为“如此……以至于……”,引导结果状语从句。
that后面跟的从句是否定句时,可与too...to互换。
The box is so heavy that I can’t lift it.=The box is too heavy for me to lift.
箱子太沉了,我抬不起来。
提示:though,although和as都可以表示“虽然”,引导让步状语从句。
as引导的从句要用倒装语序,即把从句中的表语、状语或动词原形放在as之前。
though和although放在句首时用法相同,但如放在句末时用though,不用although,且前面有逗号。
这几个词均不能与and,but连用,但可与yet连用。
Try as she might,she couldn’t open the door. as引导的让步状语从句要用倒装语序。
她试过多次了,可仍然打不开那门。
5。