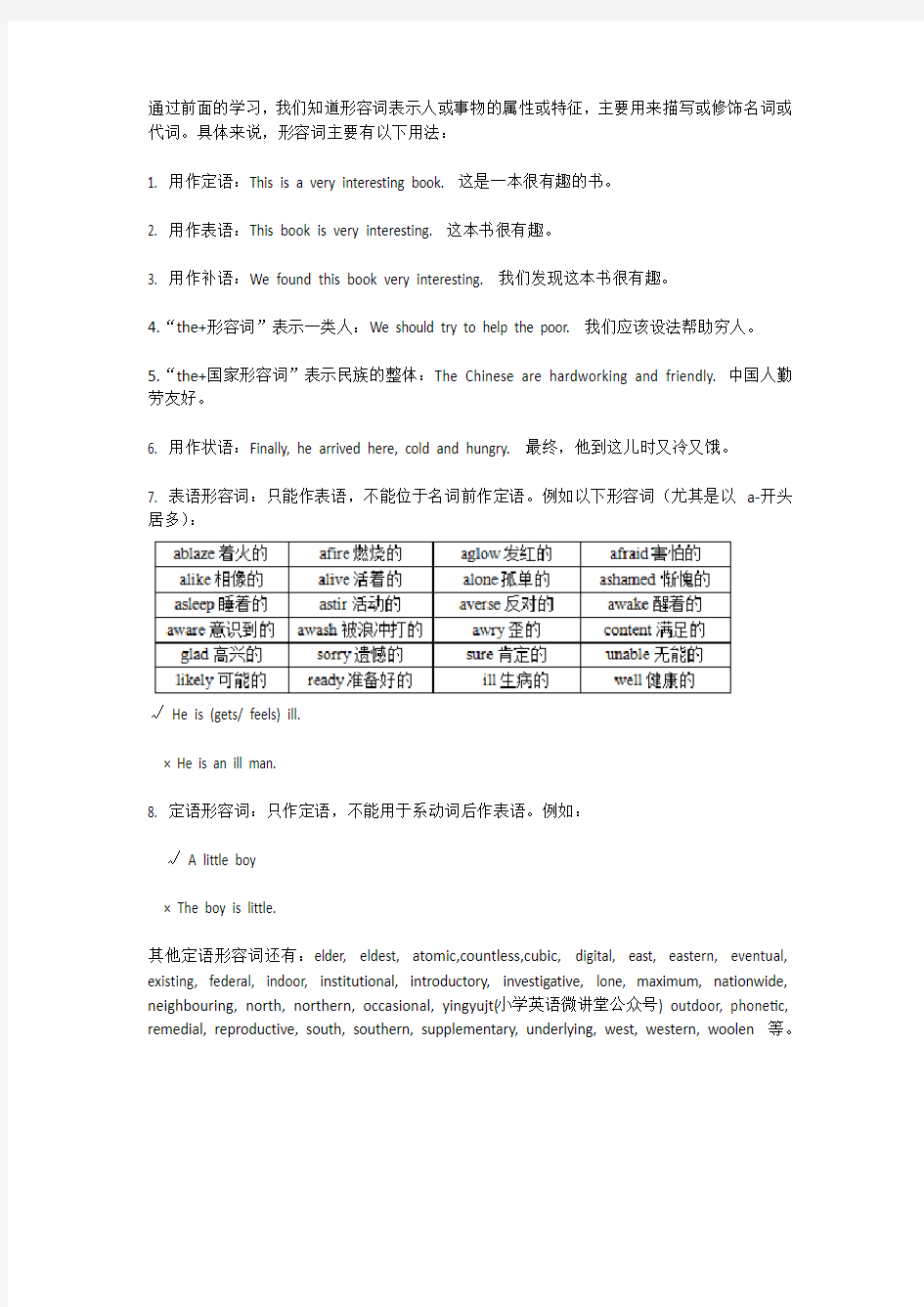
通过前面的学习,我们知道形容词表示人或事物的属性或特征,主要用来描写或修饰名词或代词。具体来说,形容词主要有以下用法:
1. 用作定语:This is a very interesting book. 这是一本很有趣的书。
2. 用作表语:This book is very interesting. 这本书很有趣。
3. 用作补语:We found this book very interesting. 我们发现这本书很有趣。
4.“the+形容词”表示一类人:We should try to help the poor. 我们应该设法帮助穷人。
5.“the+国家形容词”表示民族的整体:The Chinese are hardworking and friendly. 中国人勤劳友好。
6. 用作状语:Finally, he arrived here, cold and hungry. 最终,他到这儿时又冷又饿。
7. 表语形容词:只能作表语,不能位于名词前作定语。例如以下形容词(尤其是以a-开头居多):
√He is (gets/ feels) ill.
× He is an ill man.
8. 定语形容词:只作定语,不能用于系动词后作表语。例如:
√A little boy
× The boy is little.
其他定语形容词还有:elder, eldest, atomic,countless,cubic, digital, east, eastern, eventual, existing, federal, indoor, institutional, introductory, investigative, lone, maximum, nationwide, neighbouring, north, northern, occasional, yingyujt(小学英语微讲堂公众号) outdoor, phonetic, remedial, reproductive, south, southern, supplementary, underlying, west, western, woolen 等。
形容词用法归纳March 27, 2008 一. 形容词的定义和用法: 形容词用来修饰名词或代词, 表示人或事物的性质, 状态,和特征。形容词在句中作定语, 表语, 宾语,补语。 She is a good student, and she works hard. 她是一个好学生,她学习努力。 This bike is expensive. 这辆自行车很贵。 I am sorry, I'm busy now. 对不起,我现在很忙。 Have you got everything ready for the meeting? 你为这次会议做好准备吗? 二. 形容词在句中的位置: 形容词作定语一般放在被修饰的名词之前。如果有两个或两个以上的形容词修饰一个名词时, 则由它们和被修饰的名词之间的密切程度而定, 越密切的形容词越靠近名词。如果几个形容词的密切程度差不多则按音节少的形容词放在前面, 音节多的形容词放在后面。 注意: 1. 英语单词中,something, anything, nothing 等不定代词被形容词修饰时,形容词 放在名词后面。 I have something important to tell you. 我有重要的事要告诉你。 Is there anything interesting in the film. 电影里有什么有趣的内容吗? There is nothing dangerous here. 这儿一点都不危险。 2. 由两个或两个以上的词组成的形容词词组修饰名词时须放在名词之后。
This is the book easy to read. 这是一本容易读的书。 3. 用 and 或 or 连接起来的两个形容词作定语时一般把它们放在被修饰的名词后面。起进一步解释的作用。 Everybody, man and woman, old and young, should attend the meeting. 每一个人,男女老少,都应该参加会议。 You can take any box away, big or small. 这些箱子,不管大小,你都可以拿走。 三. 形容词的原级、比较级和最高级: 绝大多数形容词有三种形式,原级,比较级和最高级, 以表示形容词说明的性质在程度上的不同。 1. 形容词的原级: 形容词的原级形式就是词典中出现的形容词的原形。例如: poor, tall ,great, glad ,bad 等。 2. 原级常用结构:主语+谓语(系动词)+as+形容词原形+as+从句。表示两者对比相同。 This box is as big as mine. 这个盒子和我的一样大。 This coat is as cheap as that one. 这件衣服同那件衣服一样便宜。 I study English as hard as my brother. 我同我兄弟一样学习努力。 3. 形容词的比较级和最高级形式变化: 形容词的比较级和最高级形式是在形容词的原级形式的基础上变化的。分为规则变化和不规则变化。规则变化如下: 1) 单音节形容词的比较级和最高级形式是在词尾加 -er 和 -est 构成。 great (原级) greater(比较级) greatest(最高级)
形容词和副词用法总结及练习 一、形容词: (一)概念:形容词修饰名词,说明事物或人的性质或特征,通常分成两类: 1. 直接说明事物的性质或特征的形容词是性质形容词。 2. 叙述形容词只能作表语,所以又称为表语形容词,大多数以a开头的形容词都属于这一类。 例如:afraid, asleep, awake, alone, alive, awake, ashamed, alike。 其他常见表语形容词:worth, ready, sorry, well (二)形容词在句中的位置:有的形容词放在被修饰的名词之前,称为前置形容词;少数形容词放在被修饰的名词之后,称为后置形容词。 1)当名词被多个前置形容词修饰时,形容词之间有一个先后顺序问题。一般规则为: (限定词)→一般描绘性形容词→表示大小、长短、高低的形容词→表示年龄、新旧的形容词→表示国籍、地区、出处的形容词→表示物质、材料的形容词→(名词)。如: There is a famous fine old stone bridge near the village. 2)【重点】当形容词词组相当于一个定语从句时,或形容词用来修饰somebody, something, anything, nothing 等的时候,便会出现后置形容词。如: The boy interested in music is my brother. Do you have anything interesting to tell us? 二、副词: (一)概念:用以修饰动词、形容词或其他副词的词叫做副词。例如:not(不),here(这里),now(现在)。 不少副词同时也可用作介词或其它词类。如: Have you read this book before? (副词,作时间状语) He will arrive before ten o’clock. (介词,before ten o’clock 是介词短语,作时间状语) (二)副词的种类 1、时间副词: 1)表示发生时间的副词:It’s beginning to rain now! 现在开始下雨了! 2)表示频繁程度的副词,也称频度副词:always, often, usually, sometimes, never, ever, hardly等一般位于系动词、情态动词和助动词之后,实义动词之前: She often changes her mind. 3)还有一些其他表示时间的副词:He has just had an operation. 他刚动过手术。 2、地点副词: 1)表示地点的副词:She is studying abroad. 她在国外留学。 2)以where 构成的副词也是地点副词:It’s the same everywhere. 到处都一样。 3、【重点】方式副词 1)英语中有大量方式副词,说明行为方式(回答how的问题):How beautifully your wife dances. 2)表示情绪的副词:She smiled gratefully. 3)还有一些以-ly结尾的副词,表示动作发生的状况:He left the town secretly. 4、【重点】程度副词和强调副词 1)程度副词可修饰动词,表示“到某种程度”:Is she badly hurt? 她伤得重吗? [说明] 这类副词除修饰动词外,还可修饰形容词(a)或另一副词(b): a. fairly simple 相当简单quite correct 完全正确 干得很快 2 b. 修饰比较级:You sing much better than me. Their house is much nicer than ours. 5. 【重点】疑问副词和连接副词 1)疑问副词:疑问副词用来引导特殊问句: 2)连接副词:连接副词意思和词形都和疑问副词一样,但都引导从句或与不定式连用: how: Do you know how to start this machine? 你知道这台机器怎样启动吗? where: I don’t know where he lives. 我不知道他住在哪儿。(引导宾语从句) 6. 一些其它类型的副词,如表示方向的副词:Let’s go ins ide. Take two steps forward. (三)副词的位置 1. 副词修饰动词时,通常可以放在句首、句中或句末。如: Usually I do my homework in the evening. (句首) I often get up at six. (句中) Please speak slowly. 2. 副词修饰形容词或副词时,通常放在形容词或副词的前面如: These flowers are quite beautiful. (在形容词前)这些花相当漂亮。
通过前面的学习,我们知道形容词表示人或事物的属性或特征,主要用来描写或修饰名词或代词。具体来说,形容词主要有以下用法: 1. 用作定语:This is a very interesting book. 这是一本很有趣的书。 2. 用作表语:This book is very interesting. 这本书很有趣。 3. 用作补语:We found this book very interesting. 我们发现这本书很有趣。 4.“the+形容词”表示一类人:We should try to help the poor. 我们应该设法帮助穷人。 5.“the+国家形容词”表示民族的整体:The Chinese are hardworking and friendly. 中国人勤劳友好。 6. 用作状语:Finally, he arrived here, cold and hungry. 最终,他到这儿时又冷又饿。 7. 表语形容词:只能作表语,不能位于名词前作定语。例如以下形容词(尤其是以a-开头居多): √He is (gets/ feels) ill. × He is an ill man. 8. 定语形容词:只作定语,不能用于系动词后作表语。例如: √A little boy × The boy is little. 其他定语形容词还有:elder, eldest, atomic,countless,cubic, digital, east, eastern, eventual, existing, federal, indoor, institutional, introductory, investigative, lone, maximum, nationwide, neighbouring, north, northern, occasional, yingyujt(小学英语微讲堂公众号) outdoor, phonetic, remedial, reproductive, south, southern, supplementary, underlying, west, western, woolen 等。
形容词在做定语时,必须按照名词的性数格加上不同的词尾. 1. 与定冠词连用的形容词的变格. 规则: 阳性名词第一格,阴性和中性名词第一,第四格词尾为-e , 其余所有结尾均为-en 注: 定冠词位置也可以是以下各词: dieser, diese, dieses diese (Pl.) jener, jene, jenes jene (Pl.) jeder, jede, jedes jede (Pl.) mancher, manche,manches manche (Pl.) solcher, solche, solches solche (Pl.) welcher, welche, welches welche (Pl.) derjeniger, diejenige, dasjeniges diejenigen (Pl.) derselber, dieselbe, dasselbes dieselben (Pl.) 2. 与不定冠词连用的形容词的变格
3.和物主代词连用的形容词的变格 注: kein, keine, kein 和复数的keine 同物主代词一样变格. 4,不带冠词且修饰不可数名词的形容词的变格. 三.形容词的比较级与最高级 与英语类似,德语中形容词也有比较级与最高级. 形容词比较级的构成一般是在词尾加上-er, 比较级后用als .(注: 定语的比较级除了有-er还需要有相应的变格词尾.) 形容词最高级必须和定冠词连用,其构成形式为词尾加上-st. .(注: 定语的最高级除了有-st还需要有相应的变格词尾.) 比较级和最高级变化特殊的形容词: 1: 一些单元音形容词在构成比较级和最高级的时候元音要变音. am , ?rmer , am ?rmsten 同类的词还有: alt , dumm , grob , hart , kalt , jung , klug , lang , scharf , stark , schwach , warm 2.比较特殊的一些. gro? , gr??er , gr??te , am gr??sten hoch ,h?her , h?chste , am h?chsten nah , n?her , n?chste , am n?chsten gut , besser , beste , am besten viel , mehr , meist , am meisten wenig , weniger , wenigste , am wenigsten (mehr和weniger做定语时不论后面的名词为单数或复数永远不变格.)
形容词和副词用法总结及练习 一、形容词的用法: (一)概念:形容词修饰名词,说明事物或人的性质或特征,通常可将形容词分成性质形容 词和叙述形容词两类,其位置不一定都放在名词前面。 1. 直接说明事物的性质或特征的形容词是性质形容词。 【难点】 2. 叙述形容词只能作表语,所以又称为表语形容词,这类形容词大多数以a开头的形容词都属于这一类。例如:afraid,asleep, awake,alone等。 (二)形容词的种类 1. 品质形容词:英语中大量形容词属于这一类,他们表示人或物的品质,如: The play was boring. 那出戏很枯燥乏味。 You have an honest face. 你有一张诚实的脸。 2. 颜色形容词有少数表示颜色的形容词,如: She had on a blue coat. 她穿了一件蓝色的外套。 ( 3. -ing 形容词:有大量现在分词正在或已经变为形容词,如: 4. –ed形容词:它们是由它们的过去分词变过来的,一般有被动意义,多数为品质形容词,如: She looked tired. 5. 合成形容词:warm-hearted 热心的,heart-breaking 令人心碎的 (三)形容词的用法和在句中的位置 1、形容词在句中主要可用作: 1)定语: What a fine day! 2)表语: She looks happy. 3)宾语的补语(构成合成宾语): Do you think it necessary 你认为这有必要吗? 4)状语: He arrived home, hungry and tired.他又饿又累的回到家里。 2、形容词在句中的位置:有的形容词放在被修饰的名词之前,称为前置形容词;少数形 容词放在被修饰的名词之后,称为后置形容词。 1)当名词被多个前置形容词修饰时,形容词之间有一个先后顺序问题。一般规则为:(限定词)→一般描绘性形容词→表示大小、长短、高低的形容词→表示年龄、新旧的形容词→表示国籍、地区、出处的形容词→表示物质、材料的形容词→(名词)。 如: There is a famous fine old stone bridge near the village. 村子附近有一座著名的漂亮的古代石桥。【重点】 2)当形容词词组相当于一个定语从句时,或形容词用来修饰somebody, something, anything, nothing 等的时候,便会出现后置形容词。如: The boy interested in music is my brother. 对音乐赶兴趣的那个男孩是我弟弟。 Do you have anything interesting to tell us 你有什么趣闻告诉我们吗 二、副词的用法: (一)概念:用以修饰动词、形容词或其他副词的词叫做副词。例如:not(不),here(这里),now(现在)。不少副词同时也可用作介词或其它词类。如:Have you read this book before (副词,作时间状语) 你以前读过这本书吗? He will arrive before ten o’clock. (介词,before ten o’clock 是介词短语,作时间状语)他将在10点钟前到达。 (二)副词的种类 1、时间副词有三类:always, often, usually, sometimes, never, ever, hardly等一般位于系 动词、情态动词和助动词之后,实之前义动词 1)表示发生时间的副词: It’s beginning to rain now! 现在开始下雨了! 2)表示频繁程度的副词,也称频度副词always, often, usually, sometimes, never, ever, hardly等一般位于系动词、情态动词和助动词之后,实之前义动词: She often changes her mind. 她常改变主意。 3)还有一些其他表示时间的副词: He has just had an operation. 他刚动过手术。 2、地点副词: 1)有不少表示地点的副词: She is studying abroad. 她在国外留学。 2)还有一些部分与介词同形的副词。它们与介词同形,跟宾语的是介词,否则是副词: ①用作介词: Stand up! 起立! ②用作副词: A cat climbed up the tree. 猫爬上了树。 3)以where 构成的副词也是地点副词: It’s the same everywhere. 到处都一样。 《 【重点】 3、方式副词 1)英语中有大量方式副词,说明行为方式(回答how的问题): How beautifully your wife dances. 你夫人舞跳的真美。 2)还有相当多的副词,表示某些情绪: She smiled gratefully. 她感激的笑了笑。 3)还有一些以-ly结尾的副词,表示动作发生的状况:
形容词用法归纳 March 27, 2008 一. 形容词的定义和用法: 形容词用来修饰名词或代词, 表示人或事物的性质, 状态,和特征。形容词在句中作定语, 表语, 宾语,补语。 She is a good student, and she works hard. 她是一个好学生,她学习努力。 This bike is expensive. 这辆自行车很贵。 I am sorry, I'm busy now. 对不起,我现在很忙。 Have you got everything ready for the meeting 你为这次会议做好准备吗 二. 形容词在句中的位置: 形容词作定语一般放在被修饰的名词之前。如果有两个或两个以上的形容词修饰一个名词时, 则由它们和被修饰的名词之间的密切程度而定, 越密切的形容词越靠近名词。如果几个形容词的密切程度差不多则按音节少的形容词放在前面, 音节多的形容词放在后面。 注意: 1. 英语单词中,something, anything, nothing 等不定代词被形容词修饰 时,形容词放在名词后面。 I have something important to tell you. 我有重要的事要告诉你。 Is there anything interesting in the film. 电影里有什么有趣的内容吗 There is nothing dangerous here. 这儿一点都不危险。
2. 由两个或两个以上的词组成的形容词词组修饰名词时须放在名词之后。 This is the book easy to read. 这是一本容易读的书。 3. 用and 或or 连接起来的两个形容词作定语时一般把它们放在被修饰的名词后面。起进一步解释的作用。 Everybody, man and woman, old and young, should attend the meeting. 每一个人,男女老少,都应该参加会议。 You can take any box away, big or small. 这些箱子,不管大小,你都可以拿走。 三. 形容词的原级、比较级和最高级: 绝大多数形容词有三种形式,原级,比较级和最高级, 以表示形容词说明的性质在程度上的不同。 1. 形容词的原级: 形容词的原级形式就是词典中出现的形容词的原形。例如: poor, tall ,great, glad ,bad 等。 2. 原级常用结构:主语+谓语(系动词)+as+形容词原形+as+从句。表示两者对比相同。 This box is as big as mine. 这个盒子和我的一样大。 This coat is as cheap as that one. 这件衣服同那件衣服一样便宜。 I study English as hard as my brother. 我同我兄弟一样学习努力。 3. 形容词的比较级和最高级形式变化: 形容词的比较级和最高级形式是在形容词的原级形式的基础上变化的。分为
形容词的基本概念及用法 一、形容词的定义:形容词是用来修饰名词或代词的,在句中可用作定语、表语和宾语补足语等。 二、形容词的用法: ⑴用作前置定语,即放在名词前修饰该名词。例如: China is a great country with a long history. 中国是一个历史悠久的国家。 ⑵用作后置定语。形容词修饰不定代词或形容词短语修饰名词时,需要后置。例如: He has something important to tell you.他有重要的事告诉你。 She is a girl good at singing. 她是一位擅长唱歌的女孩。 ⑶用作表语。例如: It was rainy yesterday, but today it is sunny. 昨天下雨,今天天晴。 Your mother seems angry. 你母亲看上去生气了。 The milk in the glass has gone bad. 玻璃杯里的牛奶发臭了。 The leaves turn yellow in autumn. 树叶在秋天变黄。 注意: 有一些形容词在句中只能用作表语,我们称之为“表语形容词”。初中英语中常见的表语形容词有:afraid, alive, alone, asleep, glad, ill (生病的), ready, sorry, sure, unable, well (健康的)等。例如: I’m sorry not to have been ready for the party.很抱歉,晚会我还没有准备好。 The children were asleep ju st now, but now they’re awake.孩子们刚才在睡觉,现在醒了。 They were unable to help us. 他们没法帮助我们。 ⑷用作宾语补足语。例如: The news made her happy. 那个消息使她很开心。 Who left the door open? 是谁没把门关上? 三、名词化的形容词: “the+形容词”具有名词的功能,泛指一类人或抽象事物。用作主语时,谓语动词要用复数。可以这样用的形容词有:blind, dead, old, poor, rich, young等。例如: The young are the hope of the country. 年轻人是国家的希望。 The rich are not always happy. 有钱人并不总是快乐。 四、形容词的比较等级: 1.比较等级的构成: 形容词比较等级分为原级、比较级和最高级三种。比较级和最高级的构成有规则变化和不规则变化两种。规则变化由“原级+-er”构成比较级、“原级+-est”构成最高级,如:small – smaller – smallest; 形容词比较级的构成规则: ①.单音节和部分双音节形容词或副词通常加后缀–er和–est构成比较级和最高级。如: long →longer→longest clever-cleverer-cleverest few-fewer-fewest
I.限定用法(定语) a.形容词(一个字)+名词 1.The old man lived in a small village. 2.His elder brother is a famous musician. b.名词+形容词(~thing, ~body, ~one等,两个字或以上的形容词片语和子句) 1.I want to drink something cold. 2.Is there anything interesting in today’s paper? 3.I don’t like riding on trains full of people. ride on train搭乘火车 4.He tried to climb a fence two meters high. 5.He is a boy (who is) five years old. He is a five-year-old boy. 2. 叙述用法(表语) a.主词补语 1.Sea water tastes salty. 2.The rainbow is very beautiful. b.受词补语 1.You’ll find the book difficult. 2.I left the windows open. 使开着(adj.) I let the windows be opened. 使被打开(v.) 重点 a.只能用限定用法的形容词(定语形容词)
only mere 只~ main wooden upper上面的inner 里面的 Live/living daily lone 孤单的,古语 1.This is a wooden house. 2.He is a mere child. 他不过是孩 子 b.只能用叙述用法(表语形容词) alive alone afraid asleep awake well content glad aware 1.I’m afraid of dog. 2.The baby is still asleep. 3.Are you aware of your mistakes? 限定用法和叙述用法意思不同的形容词1.I met a certain lady. 某一个 It is quite certain. 确定 2.He is my present assistant. 目前 He is present today. 出席absent缺席3.The late Mr. Smith was an able man. 已故 He was late for the meeting. 迟到 4.She gave me a fond look. 温柔的 I am very fond of ice cream. 喜欢
形容词和副词的用法总结 与形容词和副词有关的构词法: (1)把名词或动词变为形容词: n. + y ---adj: sun—sunny rain—rainy cloud---cloudy wind—windy snow—snowy fog—foggy luck—lucky health—healthy noise—noisy n. / v+ able—adj: reason---reasonable enjoy—enjoyable fashion—fashionable eat---eatable n. / v. + ful--- adj: care—careful thank—thankful forget—forgetful use—useful peace—peaceful hand—handful 名词/国家名+ish: Spain—Spanish child—childish (2)把形容词变为其反义词: 在形容词前加un--: happy—unhappy healthy—unhealthy lucky—unlucky 在形容词前加im/in/il-- : possible—impossible moral—immoral finite—infinite relevant--irrelevant 在名词后加--less: care --careless use—useless tree--treeless (3)把形容词变为副词:(在形容词后加--ly) quick—quickly slow—slowly wide—widely true—truly careful—carefully clear—clearly ***也有名词加-ly变为形容词的:love—lovely friend—friendly live—lively dead—deadly 形容词的用法:(1)在句子中可以作定语修饰名词 Traveling by ship is the most comfortable way. I want to watch that exciting football match. (2)在句子中可以作表语,放在联系动词的后面: This piece of music sounds beautiful. My mother looks happy today. Our school is big and nice. 副词的用法:(1)在句子中多作状语,可以修饰动词。 Jack is going to get up early. Please speak loudly. I can’t listen to you clearly. (2)在句子中可以修饰形容词和副词。 He can runs very fast. The park is quite beautiful and I like it. (3)在句子中可以表示频率,时间,程度。
形容词副词用法总结-标准化文件发布号:(9556-EUATWK-MWUB-WUNN-INNUL-DDQTY-KII
形容词副词用法总结 (一)形容词的基本用法: 形容词是用来描写或修饰名词或代词的一类词,在句中用作定语、表语、补语和状语。 1. 作定语,就是放在名词前面的成分。 This is a new house. John is a clever boy. 2. 作表语,就是放在系动词后面的成分。 The boy is very clever. He is very strong. 3. 作补语,就是放在句子最后,起补充说明的成分。 The room is found empty.(主语补足语) The news made her happy.(宾语补足语) 4. 作其它成分,如状语,这个知识点比较难,以后的学习中做慢慢的介绍。 5.当几个形容词共同修饰同一名词时,它们的先后顺序是:限定词→数词→描述性形容词→大小、长短、形状的形容词→色彩形容词→类属形容词→表材料形容词+被修饰的名词;或只记住限定词像a, the, my, their等词在最前边,其它词根据它们与被修饰名词关系的远近进行安排。 6. 一般来说,单个副词修饰形容词时,副词放在形容词前;但enough修饰形容词时要放在形容词之后。 good enough,tall enough
7. 形容词修饰名词时放在前边,但修饰复合不定代词(something,someone,somebody;anything,anyone,anybody;nothing,no one,nobody)时,则放在这些词之后 something important,anything possible。 (二)副词的基本用法: 副词是用以修饰动词、形容词、副词以及全句的词,表示时间、地点、方式、程度、疑问等概念。 1. 作状语: The students watch him quietly. (修饰动词) 2. 作表语: Time is up. Let’s go.(表示状态) 3. 作定语: Life there is very dull. (一般后置) 4. 修饰形容词或副词,表示程度: His invention is very useful. (修饰形容词) Henry sings quite well.(修饰副词) 5. 副词作状语时,位置很灵活: He walks slowly.(动词后) I often swim in summer.(动词前)
形容词副词用法总结Last revision on 21 December 2020
形容词副词用法总结 (一)形容词的基本用法: 形容词是用来描写或修饰名词或代词的一类词,在句中用作定语、表语、补语和状语。 1. 作定语,就是放在名词前面的成分。 This is a new house. John is a clever boy. 2. 作表语,就是放在系动词后面的成分。 The boy is very clever. He is very strong. 3. 作补语,就是放在句子最后,起补充说明的成分。 The room is found empty.(主语补足语) The news made her happy.(宾语补足语) 4. 作其它成分,如状语,这个知识点比较难,以后的学习中做慢慢的介绍。 5.当几个形容词共同修饰同一名词时,它们的先后顺序是:限定词→数词→描述性形容词→大小、长短、形状的形容词→色彩形容词→类属形容词→表材料形容词+被修饰的名词;或只记住限定词像a, the, my, their等词在最前边,其它词根据它们与被修饰名词关系的远近进行安排。 6. 一般来说,单个副词修饰形容词时,副词放在形容词前;但enough修饰形容词时要放在形容词之后。
good enough,tall enough 7. 形容词修饰名词时放在前边,但修饰复合不定代词(something,someone,somebody;anything,anyone,anybody;nothing,no one,nobody)时,则放在这些词之后 something important,anything possible。 (二)副词的基本用法: 副词是用以修饰动词、形容词、副词以及全句的词,表示时间、地点、方式、程度、疑问等概念。 1. 作状语: The students watch him quietly. (修饰动词) 2. 作表语: Time is up. Let’s go.(表示状态) 3. 作定语: Life there is very dull. (一般后置) 4. 修饰形容词或副词,表示程度: His invention is very useful. (修饰形容词) Henry sings quite well.(修饰副词) 5. 副词作状语时,位置很灵活: He walks slowly.(动词后)
初中英语形容词用法总结 1. 功能 定语:a beautiful girl 表语:She is beautiful. 宾补:I will make you happy. I found it interesting. (make / find / leave / keep) 2. 位置 a. 放在名词前a pretty girl b. 不定代词后:something different 定语 c. else放在疑问代词后:what else d. 较长后置:a swimming pool / ten metres long 意义相反:All the people, young and old, are fond of music. e. 多个形容词排序:限定词/ 描绘性形容词/ 大小/ 形状/ 年龄/ 颜色/ 国籍/ 材料 ☆ the + 形(代表复数)例:The poor are losing hope. 3. 比较级别 形容词比较等级的规则变化表
常见形容词比较等级的不规则变化表 . 公式
☆用原级/比较级表最高级 例:Beijing is the largest city in China. Beijing is larger than any other city. No other city is as large as China. 副词adv 和形容词一样,副词在句中也属于修饰范畴。形容词主要修饰名词,而副词则主要用于修饰动词、形容词、其他副词以及全句,以表示程度、方式、时间、地点以及对话语的态度等。例如: ①.修饰动词的词语就是副词,如beat it heavily中的“heavily”就是副词,修饰“beat”,狠狠地打击。
SBS二册复习资料:形容词比较级的用法 整理:Sophie A.在形容词比较级前还可以用much, even, far, a lot, still, a little 来修饰,表示……得多,甚至更……仍然,还…..更……. 一些,以加强语气 Diamond is even harder than steel. Our city is much more beautiful than yours. He is even slower than before. Japan is a little larger than Germany. B.表示倍数 …times +形容词比较级+than… 这个句型表示:比……大(长,多……)几倍 Our room is twice larger than theirs. The Yangtze River is ten times larger than the river in your city. C.表示大几岁,高几厘米等 表示数、量的词+形容词比较级 I am two years older than you. She is a head taller than I/me. D.表示“比其他的任何…….都……” 比较级+than any other +单数名词 这个句型是用比较级形式表达最高级的意思。 He is better than any other student in the class. He is the best in the class. This watch is more expensive than any other watch in the shop. This watch is the most expensive one in the shop. E. 表示“越来越……” 比较级+and+比较级 The earth is getting warmer and warmer. China is more and more beautiful. F.表示“越……就越……” The +比较级….,the+比较级… The busier he is,the happier he feels. The sooner,the better. The higher the ground(is),the thinner air becomes. G.表示“两个中比较…的” The+比较级+of the two This watch is the cheaper of the two. He is the better of the two. Of the two girls,I find Lily the more intelligent. H.表示“比较A和B,哪一个较…” Which is +比较级,A or B如果是人与人相比较,用who不用which。 Which is more popular,the radio or the movie Who is happier,you or your father 形容词最高级的用法 A+动词+形容词最高级+of/in…