高考备考英语语法复习精品学案之名词篇
- 格式:doc
- 大小:102.50 KB
- 文档页数:7

高中英语语法系统讲解之一名词和冠词名词一. 名词的分类1. 普通名词:○1个体名词,如man,woman,desk,pencil 一般可数,○2集体名词,如class,family,police,army 有单、复数形式。
○3物质名词,如meat,rice,cotton,iron 一般不可数,○4抽象名词,如life,help,happiness,sadness 没有单、复数之分。
2. 专有名词,如England,Shanghai,London,Smith,Karl Marx二. 名词的数1. 可数名词单复数变化形式可数名词是表示可以计数的人、事物的名词。
可数名词一般有单数和复数两种形式,有些词单复数形式相同。
单数变复数有规则变化和不规则变化两种。
○1规则变化A. 单数名词词尾直接加-s。
如bo y—boys,pe n—pens。
B.以s,x,ch,sh结尾的词一般加-es。
如glas s—glasses,bo x—boxes,watch—watches。
C. 以“辅音字母+ y”结尾的词变y为i再加-es。
如baby—babies,lady—ladies。
D.以o结尾的词有些加-es。
如tomato—tomatoes,potato—potatoes,hero—heroes。
以“元音+ o”或“oo”结尾的词和一些以“o”结尾的外来词只加-s。
如radi o—radios,zoo—zoos,photo—photos,piano—pianos,kilo—kilos,tobacco—tobaccos。
E. 以f或fe结尾的词,多数变f或fe为v,再加-es。
如wif e—wives,life—lives,knife—knives,wolf—wolves,self—selves,leaf—leaves。
特例:handkerchie f—handkerchiefs或handkerchives,roof—roofs,chief—chiefs,gulf—gulfs,belief—beliefs,cliff—cliffs。

专题4 名词●考纲要求名词应掌握以下内容:分清名词的可数性与不可数性;可数名词有单复数,有些名词只有复数;物质名词、抽象名词不可数但可以具体量化使用;名词所有格和of格的语言现象;名词直接作定语;国家名词的正确使用;名词词义的区分和搭配;单位名词的搭配;名词前的修饰语so, as, quite等;time及常考点。
●命题规律名词的“可数”与“不可数”是高考命题的热点之一。
名词的考查强调语言的情景化,重点考查在特定语境、真实语境中的准确辨析、选择和运用名词的能力。
名词短语的固定搭配及名词作定语也是高考命题的注意点。
另外,在熟练掌握名词的基本意义和用法的同时,要特别留意某些名词的基本意义之外的引申、拓展和熟词生义的用法。
●名词的考点归纳(1)名词词义辨析: custom风俗习惯,habit个人习惯,tradition传统;scene场景,scenery 自然风景(总称),view特定位置的景观,sight人文或历史景观;skill技能,ability能力,talent才华,strength优势,长处等等(2)抽象名词具体化:beauty美、美丽(不可数名词)a beauty美人、美丽的东西(可数名词);experience经验(不可数名词)an experience一次经历(可数名词);surprise吃惊、惊奇(不可数名词)a surprise令人吃惊的人或事(可数名词);honor荣誉、信誉(不可数名词)an honor一种光荣的人或事(可数名词);failure失败(不可数名词)a failure/failures 失败的人或事(可数名词)等等。
(3)名词短语的固定的搭配:have/gain access to接近,到达;take… into consideration考虑;take advantage of利用;in consequence of 由于…… 的缘故;put into effect 实行,生效等等。

Noun Clauses(名词性从句)学习目标:(Learning Aims)1、通过学习,学生能够了解名词性从句的特征;2、学生能够掌握引导名词性从句的连接词的含义,并在不同语境中选择合适的连接词;3、学生能够区分名词性从句和定语从句。
Ⅰ. Discovering useful structures:请将每句中的名词性从句标上下划线,并标出连接词、体会从句所做的成分、语序、时态。
1. That fashion differs from country to country mayreflect the cultural differences from one aspect.2. It has been proved that eating vegetables in childhoodhelps to protect you against serious illnesses in later life.3. What matters most in learning English is enoughpractice.4. To improve the quality of our products, weasked for suggestions whoever had used theproducts.5. Tomorrow is Tom’s birthday. Have you got anyidea where the party is to be held?6. We don’t know whose keys those are.7. I’m afraid he’s more of a talker than a doer, which iswhy he never finish es anything.8. He is wondering when he can finish thisdifficult job.9. When do you think he will come?10. It doesn’t matter whether you turn right orleft at the crossing—both roads lead to the park.11. The teacher asked if / whether we hadfinished the experiment.12. Scientists study how human brains work tomake computers.自我归纳:(S umming-up)1. 名词性从句是指:在复合句中起_________作用的从句叫做名词性从句。

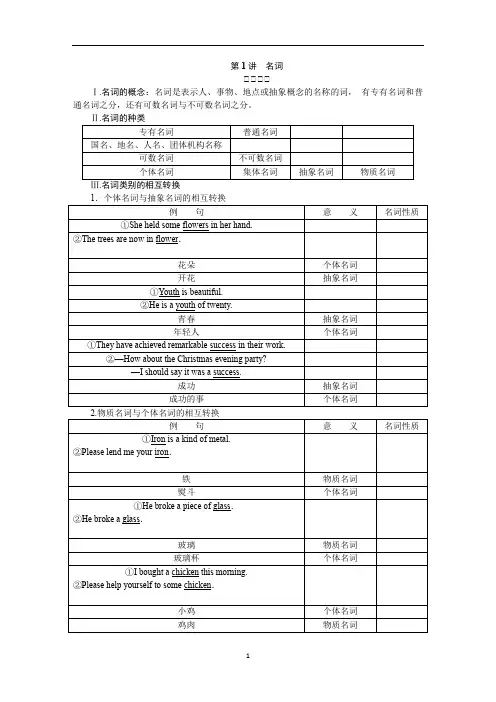
第1讲名词自自自自Ⅰ.名词的概念:名词是表示人、事物、地点或抽象概念的名称的词,有专有名词和普通名词之分,还有可数名词与不可数名词之分。
专有名词普通名词国名、地名、人名、团体机构名称可数名词不可数名词个体名词集体名词抽象名词物质名词Ⅲ.名词类别的相互转换例句意义名词性质①She held some flowers in her hand.②The trees are now in flower.花朵个体名词开花抽象名词①Youth is beautiful.②He is a youth of twenty.青春抽象名词年轻人个体名词①They have achieved remarkable success in their work.②—How about the Christmas evening party?—I should say it was a success.成功抽象名词成功的事个体名词例句意义名词性质①Iron is a kind of metal.②Please lend me your iron.铁物质名词熨斗个体名词①He broke a piece of glass.②He broke a glass.玻璃物质名词玻璃杯个体名词①I bought a chicken this morning.②Please help yourself to some chicken.小鸡个体名词鸡肉物质名词续表Ⅳ.名词的数1.规则名词的复数形式:monthmonths, pathpaths2.不规则名词复数:规则例词续表Ⅴ.名词的所有格名词在句中表示所有关系的语法形式叫作名词所有格。
所有格分两种:一是由名词词尾加's构成,二是由介词of加名词构成。
前者多表示有生命的东西,后者多表示无生命的东西。
3.of所有格的用法:用于无生命的东西:the legs of the chair, the cover of the book用于有生命的东西,尤其是有较长定语时:the classrooms of the firstyear students 用于名词化的词:the struggle of the oppressedⅣ.名词作定语。

⾼三英语语法复习学案教师版——名词性从句⾼三英语语法复习学案教师版——名词性从句A.翻译:我的梦想是上⼀所重点⼤学。
1. 主语从句:That I can enter a key university is my dream.2. 宾语从句:I always dream that I can enter a key university.3. 表语从句:My dream is that I can enter a key university.4. 同位语从句:I have a dream that I can enter a key university.B. ⽤连词填空1. What is known to us all is that the 2008 Olympic Games took place in Beijing.2. As is known to us all, the 2008 Olympic Games took place in Beijing.3. It is known to us all that the 2008 Olympic Games took place in Beijing.4. That the 2008 Olympic Games took place in Beijing is known to us all.引导名词性从句的三类连词1. 在从句中不做成分,只起连接作⽤:that; whether; if 【从属连词】2. 在从句中做主、表、宾、定成分:what; who; whom; whose; whatever; which; whichever【连接代词】3. 在从句中做状语:when where; why; how; whenever; however 【连接副词】其它连词:as if / though; because; why1. That he didn’t come to school is because he was ill.because 引导的表语从句表原因2. He was ill and that’s why he didn’t come to school.why引导的表语从句表结果3. The reason why he didn’t come to school is that he was ill.主句的主语是the reason 的表语从句由that 引导4. She looks as if she has really been there.考点⼀:语序问题1. No one can be sure ____ in a million years.A. what will man look likeC. man will look like whatD. what look will man like2. You can’t imagine ____ when they received these nice Christmas presents.A. how they were excitedC. how excited were theyD. they were how excited【总结】名词性从句要⽤陈述语序,从句的引导词必须始终置于句⾸。

高中英语语法教案(全套)名词可以分为专有名词和普通名词,专有名词是某个(些)人,地方,机构等专有的名称,如Beijing,China等。
普通名词是一类人或东西或是一个抽象概念的名词,如:book,sadness 等。
普通名词又可分为下面四类:1)个体名词:表示某类人或东西中的个体,如:gun。
2)集体名词:表示若干个个体组成的集合体,如:family。
3)物质名词:表示无法分为个体的实物,如:air。
4)抽象名词:表示动作、状态、品质、感情等抽象概念,如:work。
个体名词和集体名词可以用数目来计算,称为可数名词,物质名词和抽象名词一般无法用数目计算,称为不可数名词。
归纳一下,名词的分类可以下图表示:名词专有名词不可数名词普通名词物质名词抽象名词集体名词可数名词个体名词情况构成方法读音例词一般情况加 -s 清辅音后读/s/ map-maps浊辅音和元音后读 /z/ bag-bags /car-cars以s, sh, ch, x等结尾加 -es 读 /iz/ bus-buses/ watch-watches以ce, se, ze,等结尾加 -s 读 /iz/ license-licenses以辅音字母+y结尾变y 为i再加es 读 /z/ baby---babies1)以y结尾的专有名词,或元音字母+y 结尾的名词变复数时,直接加s变复数。
如:two Marys the Henrysmonkey---monkeys holiday---holidays2)以o 结尾的名词,变复数时:a. 加s,如: photo---photos piano---pianosradio---radios zoo---zoos;b. 加es,如:potato--potatoes tomato--tomatoesc. 上述a和b两种方法均可,如zero---zeros / zeroes。
3)以f或fe 结尾的名词变复数时:a. 加s,如: belief---beliefs roof---roofssafe---safes gulf---gulfs;b. 去f,fe 加ves,如:half---halvesknife---knives leaf---leaves wolf---wolveswife---wives life---lives thief---thieves;c. 上述a和b两种方法均可,如handkerchief: handkerchiefs / handkerchieves。

高中英语语法复习名词 2语法专题(一)名词名词要点精讲名词是高考的热点和难点。
从语法和词汇两个方面来考察其用法,在单项选择、完形、改错中都可感知高考中名词的考查点。
名词专有名词主要是指人名、地名或某类人或事物的名称,如Beijing,China等。
普通名词是一类人或东西或是一个抽象概念的名词,如:book,sadness等。
专有名词(Proper Nouns)抽象名词(Abstract Nouns)不可数名词 (Uncountable Nouns)物质名词(Material Nouns)普通名词 (Common Nouns)集体名词(Collective Nouns)可数名词 (Countable Nouns)个体名词(Individual Nouns)个体名词和集体名词可以用数目来计算,称为可数名词(Countable Nouns),物质名词和抽象名词一般无法用数目计算,称为不可数名词(Uncountable Nouns)。
Proper Nouns:指人名、地名及某些人和事物专有的名称Eg: Diana; Beijing; Americans;English; May; New Year’s Day注意:专有名词的第一个字母要大写Common Nouns:一类人或东西或是一个抽象概念的名词1. Individual Nouns: 指作为个体而存在的人或东西可以指具体的人或物。
Eg: aunts; a panda; apartments也可指抽象东西。
Eg: a year; fairy tales; a dream2. Collective Nouns: 表示若干个个体组成的集合体Eg: army; audience; crew; family; team; police; government; public集体名词有时作单数看待,有时作复数看。
一般来说,视为整体时作单数看,突出它的成员时作复数看。

高三英语语法名词的复习教案一、教学目标1.让学生掌握名词的基本概念、分类和用法。
2.培养学生运用名词进行句子构建的能力。
3.提高学生对名词相关考点的理解和应用。
二、教学内容1.名词的概念和分类2.名词的数和格3.名词的用法4.名词相关考点三、教学过程1.导入师:同学们,我们今天来复习一下名词。
请问大家知道名词是什么吗?生:名词就是表示人、事物、地点、抽象概念等名称的词。
师:很好!那我们就从名词的概念和分类开始吧。
2.名词的概念和分类师:名词分为两大类:可数名词和不可数名词。
可数名词有单数和复数形式,而不可数名词没有复数形式。
请同学们举例说明。
生1:可数名词如:book,table,apple等。
生2:不可数名词如:water,r,rice等。
师:很好!我们来看一下名词的数和格。
3.名词的数和格师:名词的数分为单数和复数。
单数名词通常加“-s”或“-es”变为复数。
但有些名词变复数时需要特殊变化,比如:childchildren,manmen等。
名词的格分为三种:主格、宾格和属格。
主格用于名词作主语,宾格用于名词作宾语,属格用于表示所有关系。
师:请同学们用所学的名词,分别构成单数和复数形式,并说明其格。
生1:bookbooks(主格:Thebookisonthetable.宾格:Ilikethisbook.属格:Thisismybook.)生2:childchildren(主格:Thechildrenareplaying.宾格:Iseethechildren.属格:Thechildren'sbooksarehere.)4.名词的用法师:名词在句子中的用法有很多,比如作主语、宾语、表语、定语等。
请同学们用所学的名词,分别构成不同成分的句子。
生1:主语:Thecatissleeping.生2:宾语:Iboughtabook.生3:表语:Sheisateacher.生4:定语:Thegirl'sbagisred.5.名词相关考点师:在高考英语中,名词的考点主要包括名词的单复数、格、所有格、同义词辨析等。

高考英语语法专题复习一、名词Nouns一、名词的种类:1、专有名词1)China, Japan, Beijing, London, Tom, Jack(不加冠词)2)the Great Wall, the Yellow River, the People’s Republic of China, the United States等。
(由普通名词构成的专有名词,要加定冠词。
)2、普通名词物质名词:water,rice, oil, paper......1)不可数名词抽象名词:health, trouble, work, pleasure, honor......注:①不可数名词前一般不加冠词,尤不加不定冠词:若加a(an)则使之具体化了。
如:have a wonderful time. make a great progress.②不可数名词作主语,谓语动词用第三人称单数形式。
③不可数名词一般无复数形式。
部分物质名词在表不同类别时,可用复数形式。
如:fishes, newspapers, waters, snows ......| | | |各种各样的鱼各种报纸河湖、海水大片水域积雪④有些抽象名词也常用复数,变为可数的具体的事物。
如:times时代,works著作,difficulties⑤在表数量时,常用“of”词组来表示。
如:a glass of milk, a cup of tea, two pieces of paper......2)可数名词:①可数名词除用复数形式表一类之外,一般都要加冠词:A bird can fly.The frog is a kind of hibernating animal.Vegetables sold at this shop are usually fresh.②有复数形式:a)规则变化——加“s”或“es”(略)b)不规则变化——child (children), foot (feet), tooth (teeth), man (men), woman (women),mouse (mice), goose (geese), Englishman (Englishmen),phenomenon(pheno mena);注:c)单、复数同形:sheep, deer, Chinese, Japanese, fish(同一种鱼)......。

2006年下学期高三英语语法名词复习一第一章名词一、名词的分类:名词就其词汇意义可分为专有名词和普通名词。
普通名词又可分为可数名词和不可数名词。
专有名词:Beijing Smith the United Nations个体名词:man, expert, factory可数名词集合名词:audience(观众),class, family 普通名词:物质名词:water, coal, rice不可数名词抽象名词:surprise, honour, help二、可数名词的复数形式1.一般情况,直接加-s。
port(港口)→ ports;technique(技术)—techniques2.以s, x, ch, sh结尾发[s]、[∫]、[t∫]、[dЗ]音的词,加—esbus—buses, box—boxes, bush—bushesbranch—branches,stomach—stomachs(stomach词尾发k,故复数直接加-s)3.辅音字母+ y,变y为i,加-es university—universitiesy前为元音字母,直接加-s boy—boys4.以O结尾加-es hero—heroesO前为元音字母,及部分外来词直接加-szoo—zoos radio—radio piano—pianos photo—photos5.以f或fe结尾,变f或fe为v,再加-es leaf—leaves wife—wives※以下f结尾单词直接加-s belief—beliefs(信念) roof—roofs(屋顶)proof—proofs(证据) safe—safes(保险柜)chief—chiefs(首领) gulf—gulfs(海湾)6.不规则名词 man—men, woman—women, foot—feet, tooth—teeth,goose—geese, mouse—mice, child—children, ox—oxen注1:有些可数名词的单复数相同,要根据上下文的意义来确定其单数还是复数,例如:sheep 羊 fish 鱼 deer 鹿means手段,方法 works工厂,作品 series系列注2:在些可数名词,只有单数形式,但表示复数意义。
高三英语语法知识名词复习教案高三英语语法知识名词复习教案1、名词名词可以分为专有名词和普通名词,专有名词是某个(些)人,地方,机构等专有的名称,如Beijing,China等。
普通名词是一类人或东西或是一个抽象概念的名词,如:book,sadness等。
普通名词又可分为下面四类:1)个体名词:表示某类人或东西中的个体,如:gun。
2)集体名词:表示若干个个体组成的集合体,如:family。
3)物质名词:表示无法分为个体的实物,如:air。
4)抽象名词:表示动作、状态、品质、感情等抽象概念,如:work。
个体名词和集体名词可以用数目计算,称为可数名词,物质名词和抽象名词一般无法用数目计算,称为不可数名词。
归纳一下,名词的分类可以分为:名词专有名词不可数名词普通名词物质名词抽象名词集体名词可数名词个体名词1.1 名词复数的规则变化情况构成方法读音例词一般情况加 -s 清辅音后读/s/ map-maps浊辅音和元音后读 /z/ bag-bags /car-cars以s, sh, ch, x等结尾加 -es 读 /iz/ bus-buses/ watch-watches 以ce, se, ze,等结尾加 -s 读 /iz/ license-licenses以辅音字母+y结尾变y 为i再加es 读 /z/ baby---babies1.2 其它名词复数的规则变化1)以y结尾的专有名词,或元音字母+y 结尾的名词变复数时,直接加s变复数。
如:two arys the Henrysmonkey---monkeys holiday---holidays2)以o 结尾的名词,变复数时:a. 加s,如: photo---photos piano---pianosradio---radios zoo---zoos;b. 加es,如:potato--potatoes tomato--tomatoesc. 上述a和b两种方法均可,如zero---zeros / zeroes。
高考英语语法复习专题2 名词精品导学案(含解析)名词是英语的主要词汇之一,也是历年高考的重要考点。
综合近几年高考对名词的考查,单项填空题中,每年都出现1—2道题。
此外,在阅读理解和完形填空中,名词的一词多义、熟词新意也经常涉及。
因此,在备考中一定要结合具体的语境去感悟、理解名词的辨析、名词的一词多义以及名词的习惯用法。
一、名词的分类二、名词的数:可数与不可数学习名词,首先要分清名词的可数与不可数。
可数名词是指能以数目来计算,可以分成个体的人或东西,因此它有复数形式。
不可数名词是指不能以数目来计算,不可以分成个体的概念、状态、品质、感情或表示物质材料的东西;它一般没有复数形式,它的前面不能用不定冠词a/an修饰,若要表示它的个体意义时,必须与一个名词短语连用,相当于中文里的(数词+量词+名词),其中的量词意义视具体的名词搭配而定。
如:a piece of bread/paper/furniture/news/advice/information。
一般来说,名词是可数还是不可数,其分类方法与汉语相似,但又不完全相同,因此不能完全凭汉语的感觉去分类,如:同样为“建议”,advice是不可数名词,而suggestion却是可数名词。
因此,在学习名词时,要注意积累那些和我们汉语感觉不同的词。
三、名词的转化1.一般说来抽象名词为不可数名词,但当抽象名词表示具体的东西时,可用作可数名词且词义发生变化,主要类型如下:(1) 抽象名词表示具有某种特性、状态、感情情绪的人或事。
如:(2) 抽象名词与a(an)连用,淡化了抽象概念,转化为似乎可以体验到的动作、行为或类别。
请对比:After several years' self study he acquired a great deal of knowledge.A knowledge of English is a must in international trade.Have you had any experience of teaching English?I had a rather different experience the other day.Walk is a good form of exercise. Would you like to have a walk (swim,bath,talk) with me?It is a waste of time reading such a novel. There is too much waste in this factory.【易错警示】有些抽象名词不能具体化使用,即使有形容词修饰,也不能和不定冠词连用。
名词一、名词的分类名词可分为普通名词和专有名词两大类。
其中专有名词指具体的人物、地点、机构、国家或地区的名称等,不能随便更改。
普通名词则较为复杂,它分为可数名词和不可数名词两类。
二.名词分可数名词与不可数名词1.可数名词变复数sight (视力) —sights (名胜);water (水)— waters (水域);custom (习惯) —customs (海关);spirit (精神) —spirits (情绪);2.不可数名词量的表示Cake is a kind of food. 不可数当物质名词转化为个体名词时为可数。
These cakes are sweet. 可数当物质名词表示该物质的种类时,可数。
This factory produces steel. UN.物质名词We need various steels. CN.抽象名词表示具体的事例时也可数。
a success, a surprise物质名词和抽象名词可以借助单位词表一定的数量,a glass of water 一杯水a piece of advice一则建议用复数形式,表示各种各样的:fruits各种水果,foods各种食物,equipments各种器材,设备,waters水域,gases各种气体,teas各种茶抽象名词有些物质名词和抽象名词的复数形式表示特殊的含义:time时间→times时代,次数,倍数,look看→looks外貌,green绿色→greens青菜,brain脑→brains头脑,脑筋,good益处→goods货物,sand沙→sands沙滩,沙漠有些名词根据含义不同,可用作可数名词,也可用作不可数名词。
hair 全部头发(不可数); a few white hairs几根白头发(可数)help 帮助(不可数);帮手,助手(可数) experience 经验(不可数);经历(可数)work 工作(不可数);作品,著作(可数) paper 纸(不可数);文件,论文,试卷(可数)surprise惊讶(不可数);令人惊奇的事情(可数)三.名词作定语四. 不同国籍人的单复数五.名词的所有格②表示工业、工厂、机器、大学的名词后加“’s”the machine’s designHarvard’s Linguistics Department③其他一般用名词+of +名词the top of tower;the legs of the table④介词to表示所有格the key to the lock;the answer to thequestion; the entrance to the cinemathe solution to the problem对某一名词同时使用“-'s”和“of…”来表达拥有或所有的方式叫做双重所有格双重所有格three, nine……同一个名词前,冠词(a,an,the ),指示代词(this,that,these,those),物主代词(my,your,his等),以及不定代词(no,every,each等)不能重复使用,如果要表示此种意思,就要借助于双重所有格a friend of mine (√) my a friend (X)It’s no fault of yours. (√) It’s no your fault. (X)this naughty daughter of the Greens’ (√)the Greens’ this naughty daughter(X)六.Y esterday a boy came to see you. 主语Edison was a world famous inventor. 表语Would you like some bananas?宾语名词的句法功能We chose him monitor of our class. 宾语补足语They will meet at the school gate. 定语The new film will last two hours. 状语Mr. smith,my first teacher,left yesterday. 同位语七.名词类别的转用the +普通名词→抽象名词I saw the mother in her when she said that. =motherhooda +专有名词→普通名词Is there a Mr.Chen in your school? 专有名词转用为普通名词专有名词+(e)s→普通名词I hope there will be many Edisons among you.…the +专有名词(表达比喻)→普通名词Shanghai is the New York of China. the New York =the biggest city like New York in the U.S.表示种类Oolong is a green tea, very popular in Taiwan.表示非材料Tom hit the dog with a stone. stone是weapon物质名词转用为普通名词指由该物质制成的物品These glasses are made in Italy.玻璃杯其他Two hot coffees and two black teas, please. 省略单位名称的表达法抽象名词转用为普通名词(抽象名词具体化) danger, success, failure, life, concern,surprise, honor', pity, beauty, death, attraction, comfort, help,knowledge, atmosphere, pleasure, shame, wonder, worry……In war, a soldier’s life is full of danger. The man is a danger to societyHe takes pride in his son. He is a pride to his parents.。
第1讲名词解答有关名词的题目时,一定要注意名词前的修饰成分,如数词、量词常修饰可数名词复数,也要注意修饰不可数名词的词或短语等,以用来判断其应为不可数名词还是可数名词的单复数形式,有时还要结合语境分析句子成分来判断是否需要作主语、宾语、表语或定语的名词。
考点感悟考点素能一名词复数变化规律1.规则名词变复数的6种形式(1)一般情况下,在词尾直接加-s:book→books, mouth→mouths, house→houses, girl→girls(2)以-s, -x, -ch, -sh结尾的名词,在词尾加-es:glass→glasses, box→boxes, match→matches, brush→brushes(3)以辅音字母+y结尾的名词,变y为i再加-es:city→cities, country→countries, party→parties, factory→factories(4)以元音字母+y结尾的名词,在词尾直接加-s:holiday→holidays, monkey→monkeys(5)以o结尾的名词常在词尾加-s:radio→radios, zoo→zoos, piano→pianos, kilo→kilos, photo→photos;加-es的有:hero→heroes, Negro→Negroes, tomato→tomatoes, potato→potatoes(6)以-f, -fe结尾的名词①少数直接加-s:roof→roofs, belief→beliefs②一般以-f或-fe结尾的名词要变f或fe为v再加-es:self→selves, life→lives, thief→thieves, wife→wives, knife→knives, leaf→leaves, shelf→shelves, wolf→wolves, half→halves2.不规则名词变复数的常见形式(1)单复数同形:deer, sheep, means, series, Chinese, Swiss, aircraft, spacecraft(2)变内部元音:foot→feet, tooth→teeth, man→men, woman→women(3)外来名词:medium→media 媒体,phenomenon→phenomena 现象,analysis→analyses 分析二常见的不可数名词一般来说,物质名词和抽象名词是不可数的,因此没有复数形式,一般也不能用a或an 修饰。
高考复习英语教案专题一名词和冠词【典例精析】1. (福建) What’ s the _____ of having a public open space where you can’ t eat, drink or even simply hang oa while?A. senseB. matterC. caseD. opinion【分析】 A sense 意为“感觉”在这样一个公共场所,不能够吃喝甚至不能够走动有什么感觉。
2.(天津卷) Most air pollution is caused by the burning of ____ like coal, gas and oil.A. fuelsB. articlesC. goodsD. products【分析】A fuel 燃料,题干中coal, gas, oil 均为燃料,由此选出A3. (山东)A. exchange I bought a dress for only 10 dollars in a sale; it was a real______.B. bargainC. tradeD. business【分析】Bbargain 低价货切合句意,exchange 互换; trade 贸易,买卖;business 事业,业务均不合句意4. (江西卷)— Shall we go out for a walk?— Sorry. This is not the right ____ to invite me. I am too tired to walk.A. momentB. situationC. placeD. chance【分析】A句意为:此刻邀请我不适合,moment此时,此刻切合句意;situation形式;place地方;chance 时机均不合题意5.(湖北卷) The young man made a ______ to his parents that he would try to earn his own living after graduation.A. predictionB. promiseC. planD. contribution【分析】B年青人对父亲母亲做出承诺。
2012届高考英语二轮语法复习学案(名词)(一)考纲要求名词应掌握以下内容:分清名词的可数性与不可数性;可数名词有单复数,有些名词只有复数;物质名词、抽象名词不可数但可以具体量化使用;名词所有格和of格的语言现象;名词直接作定语;国家名词的正确使用;名词词义的区分和搭配;单位名词的搭配;名词前的修饰语so, as, quite等;time及常考点。
(二)命题导向名词的“可数”与“不可数”是高考命题的热点之一。
不可数名词前不能与不定冠词连用,之后不能加-s。
有些抽象名词却有复数形式,但意义与原来词不同。
有些可数名词复数有两个意思,一个与单数意义相同,另一个和单数含义不同,高考中这些含义很可能成为考查的内容。
词语的固定搭配及名词作定语也是高考命题的注意点。
(三)知识概要英语的名词分为专有名词和普通名词两大类。
专有名词是指个人、团体、地方、机构或事物等所专有的名称,它的第一个字母必须大写。
如:Einstain, Beijing, Asia等。
普通名词是指一类人、一类事物、某种物质抽象概念的名称,可分为:个体名词(可数,如:worker, father, book, tree, school等);集体名词(可数,如:people, family, class, team等);物质名词(不可数,如:iron, paper, snow, water, chalk, gold等);抽象名词(不可数,如:life, thought, idea, strength等)。
注意:可数、不可数是英文名词和中文名词的一个重要差异——即学习的重点。
而很多英语名词具有双重性。
即,名词的类别不是固定不变的,它们会根据词义的变化和场合的不同而相互转换,其名词类别的转换可归纳如下:1、个体名词转抽象名词或抽象名词转个体名词e.g. Our school is not far from my home.(个体)我们学校离我家不远。
School is over at six.(抽象)六点钟放学。
2、物质名词转个体名词或个体名词转物质名词e.g. He broke a piece of glass.(物质)他打破了一块玻璃。
He broke a glass.(个体)他打破了一个杯子。
3、个体名词转专有名词e.g. His father is a teacher.(个体)他父亲是个教师。
“What are you doing there?”Father asked.(专有)“你在那儿干什么?”父亲问道。
(四)名词的数名词分为可数(有单、复数形式)和不可数名词(只有单数形式)。
1、可数名词单数变复数:①一般加s :lesson →lessons, pen →pens②以s, x, ss, ch, sh, o结尾的加es :buses, boxes, classes, watches, brushes, hero →heroes 但有些以o结尾的名词,是加s构成复数:kilo →kilos, piano →pianos, radio →radios, photo →photos, zoo →zoos③以辅音字母+ y 结尾的改y为i,再加es :city →cities, story →stories④以f 或fe结尾的,一般将f或fe改为v,再加es :knife →knives, leaf →leaves但有些以f 结尾的名词,是在f后加s,构成复数形式:belief →beliefs, roof →roofs, safe (保险箱)→safes, proof(证据)→proofs, chief →chiefs, handkerchief →handkerchiefs2、有些名词,不按上述规则构成其复数形式,有以下几种情况:①单复数形式相同:Chinese, Japanese, deer, sheep②不规则变化:man →men, woman →women, goose →geese, foot →feet, tooth →teeth, child →children, mouse →mice, ox →oxen 。
但是,German →Ger mans③复合名词的复数形式:editor-in-chief →editors-in-chief, daughter-in-law →daughters-in-law, grown-up →grown-ups, woman teacher →women teachers, man driver →men drivers3、注意以下几个名词单复数问题①物质名词一般不用复数形式,但有些物质名词要用复数形式来表示不同的类别,如:fishes 各种鱼,fruits各种水果,steels各种钢材。
②物质名词表示数量时,一般用表示数量的短语来表示。
如:a cup of tea, three bags of apples, four pieces of bread。
③有些抽象名词的复数形式表示不同的含义。
如:work(工作)→works(著作),arm(手臂)→arms(军火),glass(玻璃)→glasses(眼镜),cloth(布)→clothes(衣服)。
④定冠词加上姓氏的复数形式,表示全家人或夫妇二人;姓氏的复数形式前不加冠词,则表示若干个姓…的人。
如:the Wangs王家,three Wangs三个姓王的。
⑤只用作单数的复数形式的名词。
如:physics, mathematics, news, the United States⑥有些名词形似单数,但实为复数。
如:police, people, cattle⑦有些名词如被看作整体时就作单数用,如被看作组成该集体的各个成员时就作复数用。
如:class, family, couple, audience, government, public⑧有些抽象名词在具体化时,可以复数形式出现。
表示特指时,可和定冠词连用;表示“某种”或“一次”意义时,可和不定冠词连用。
如:How did you smooth away the difficulties?(指各种具体困难);It is a great pleasure to talk with y ou.;What a surprise!(五)名词的所有格名词的所有格在句中表示所有关系,作定语用。
1、有生命名词的所有格一般在词尾加上“’”或“’s”。
如:Tom’s bike, Engles’s (Engles’) works, a works’school, Women’s Day, the editor-in-chief’s office2、如果一个事物为两个人所有,只在后一个名词的词尾加“’s”,如果不是共有,就要在两个名词的词尾都加上“’s”。
如:Tom and Mike’s room.(共有),Tom’s and Mike’s books.(不共有)。
3、表示时间、距离、国家、城市的无生命名词,可以在词尾加“’s”或“’”表示所有格,如:today’s papers, ten minutes’walk4、表示店铺或某人的家时,常在名词所有格之后省去shop, house, home。
如:the tailor’s5、无生命名词的所在格通常用of短语来表示。
如:the window of the room6、表示有生命的名词有时也可用of短语来表示所有关系,而且当该名词带有较长的定语时。
如:the teachers of the No. 1 Middle School.7、双重所有格结构前的被修饰名词通常指整体中的部分或一个,双重所有格只能用于有生命的名词,这个名词是确定的。
被修饰名词前有不定冠词、指示代词、疑问代词、不定代词或数词等限定词时,一般只能用双重所有格。
如:an old friend of my uncle’s, a daughter of Mrs Green’s, the house of one of my friends(六)名词的普通格作定语表材料、地点、用途、性质、泛指时间、整体等普通名词可以作定语,一般用单数形式。
e.g. stone figures(石像);paper money(纸币);country music(乡村音乐);table cloth(桌布);river bank(河岸);school gate(校门口);book stores(书店);traffic lights(交通灯);summer holidays(暑假);evening dress(晚礼服)。
但在个别情况下,也有需用复数的。
e.g. sports meet(运动会);the United States government(美国政府);students reading-room (学生阅览室);goods train(货车);two men doctors(两个男医生)。
练习、名词1. The ____ of the room were covered with____.A. roofs, leafsB. roofs, leavesC. rooves, leafsD. rooves, leaves2. There are three ____ in our factory.A. woman doctorsB. women doctorsC. woman doctorD. women doctor3. Which do you prefer ____ or ____?A. potatos, tomatosB. potatos, tomatoesC. potatoes, tomatosD. potatoes, tomatoes4. They are ____ of different presses(出版社). Now they are having a meeting in one of the ____ office.A. editor-in-chiefs, editors-in-chief’sB. editors-in-chief, editor-in-chief’sC. editors-in-chiefs, editor’s-in-chief’sD. editors-in-chief, editors-in-chief’s5. The ant has two ____. A. stomaches B. stomacks C. stomach D. stomachs6. He doesn’t like ____ for supper. A. chick B. chicken C. chickens D. chicks7. It was ____ hot weather that many of us went swimming.A. soB. suchC. so asD. such a8. ____ wonder ful space they sa w on the room!A. HowB. How aC. WhatD. What a9. We know ____ travels not so fast as light.A. soundB. soundsC. the soundsD. a sound10. My family raise a lot of ____, including two ____.A. cattle, cowsB. cows, cattleC. cattles, cowsD. cow, cattles11. A number of soldiers ____ at he camp gate(军营门口).A. have gatheredB. has gatheredC. isD. was12. The Browns have spent a large ____ of money on their new car.A. dealB. amountC. numberD. size13. ____ work has been done to improve the people’s living standard.A. ManyB. A great manyC. A great deal ofD. A number of14. Mr Li shook ____ warmly with a friend.A. handB. a handC. handsD. the hands15. Two ____, please. A. coffee B. coffees C. cup of coffee D. cups coffee16. I can’t pay as ____ as he asked for.A. high price aB. high priceC. a high priceD. high a price17. ____ knowledge of space develops rapidly. A. Man’s B. M en’s C. Mens’ D. Person’s18.I stayed at ____. A. Xiao Wang’s B. Wang’s home C. the Wangs D. home of Wang19. Sister Carrie works in a ____ factory. A. shoes B. shoses C. shoe D. shoe’s20. Have you ever read ____?A. today newspaperB. newspaper todayC. newspaper of todayD. today’s newspaper21. Two ____ walk didn’t made me tired. A. hour B. hours C. hour’s D. hours’22. The mother over there is ____ mother.A. Julia and MaryB. Julia and Mary’sC. Julia’s and Mary’sD. Julia’s and Mary23. Li Ming’s handwriting is better than ____ in the class.A. anyone’sB. anyone elseC. anyone’s else’sD. anyone else’s24. The children are playing ____ on the ____.A. s and, sandB. sands, sandsC. sand, sandsD. sands, sand25. If these trousers are too big, buy a smaller ____. A. set B. one C. copy D. pair26. Tom usually takes a ____ in bus on rainy days. A. walk B. ride C. trip D. travel27. We have no ____ about where she has gone.A. informationB. newsC. messageD. flash28. Food and ____ are daily necessities(需要)for the people.A. clothB. clotheC. clothesD. clothing29. My ____ of hearing is not so good as it used to be. A. strength B. sense C. power D. skill30. The ____ caused by carelessness ____ yesterday. Many workers were killed.A. incident, was h appenedB. matter, happenedC. event, was taken placeD. accident, took place31. The room was so quiet that she could hear the ____ of her heart.A. beatingB. waysC. knockingD. striking32. ____ has been told not to throw waste things anywhere.A. The publicB. PeopleC. WomenD. Man33. He was an ____ in the government ____.A. office, officialB. official, officeC. officer, officeD. official, officer34. There are several ____ in this novel who are different in ____.A. character, characterB. characters, charactersC. character, charactersD. characters, character35. We visited him ____ when he was in hospital.A. every other daysB. each other dayC. every other dayD. every two day36. My friend will return in ____.A. one day or twoB. a day or twoC. one day or twoD. a or two days37. ____ is always difficult for me.A. TranslationB. TranslateC. The translationD. A translation38. ____ of this novel is excellent, quite to my surprise.A. TranslationB. TranslateC. The translationD. A translation39. The police ____ looking into the matter now. A. be B. is C. are D. are going to40. The Chinese are ____ brave and hard working people. A. the B. a C. / D. one41. No news ____ good news. A. is B. are C. have D. has42. Maths still ____ very difficult for me, though I have done my best.A. looksB. seemsC. is D . are43. “Where ____ my trousers?” the boy asked. A. is B. was C. were D. are44. How happy they are! Obviously, they are ____.A. in nice spiritsB. in nice spiritC. in high spiritsD. in high spirit45. I saw many ____ seated in the corner reading something.A. JapaneseB. JapanesesC. of JapaneseD. of Japaneses46. Father went to his doctor for ____ about his heart trouble.A. an adviceB. adviceC. a dvicesD. the advices47. We are ____ and they are ____. A. Englishmen, GermansB. Englishmen, GermanC. Englishmans, GermansD. Englishmen, Germen48. ____ are made of ____.A. A glass, a glassB. Glasses, glassC. The glass, the glassD. Glasses, glasses49. I’ll have to buy ____ trousers. A. a B. two C. a pair of D. a couple of50. There are two ____ in our class. A. Liu B. Lius C. Liu’s D. Lius’51. ____ is needed in cold countries.A. A lot of clothesB. Much clothingC. Many a clothD. Lots of clothes52. They are ____. A. mathematics student B. mathematic studentsC. students in mathematicsD. mathematics students53. The laboratory assistant recorded the ____ reactions(反应).A. mouses’B. miceC. mices’D. mice’s54. This letter was sent by ____.A. my father friendB. my father friend’sC. a frien d of my father’sD. a friend of my father55. Ten years had passed. I found she had ____.A. a little white hairB. some white hairC. a few white hairD. a few white hairs56. I have made ____ with Billy. A. friends B. friend C. a friend D. the friend57. The population of Beijing is ____ than that of Xi’an. A. more B. larger C. fewer D. small58. There are thirty-two ____ in our school.A. woman teacherB. women teacherC. women teachersD. woman teachers59. He had tried everything but it made little______ .A. useB. goodC. differenceD. result60. You must get there within half an hour. There should be no______ in sending the blood to the dying man.A. waitB. delayC. timeD. hurry61. Enough of it! Nobody here thinks what you are saying should make any______ .A. excuseB. senseC. useD. value62. -How dare you play on such thin ice? -Playing on ice is not my ______of spare time.A. ideaB. thoughtC. mindD. intention63. Helen said she would like to go to Atlanta by air, but I wonder if she has enough money to pay for the______ .A. travelB. tourismC. journeyD. course64. One splendid mountain______ followed another during our journey from Mieheel more to Rurunz.A. viewB. glanceC. screenD. scene65.The new law will come into ___on the day it is passed. (1999上海)A. effectB. useC. serviceD. existence66. When you play' football, what ______do you play?A. situationB. placeC. partD. position67. It's impo rtant for us to employ a word or a phrase according to the______in language studies.A. situationB. expressionC. conditionD. translation68. I wrote him a letter t o show my ______of his thoughtfulness.A. achievementB. agreementC. viewD. appreciation69. One of the advantages of living on the top floor of a high-rise is that you can get a good______ .A. sightB. sceneC. viewD. look70. Nowadays natural gas, wind and other forms of ______are widely used in the country.A. energyB. forceC. powerD. materials71. ______with foreign countries can bring us much information about the world.A. ContrastB. CompetitionC. ContactD. Combination72. We all know that______speak louder than words.A. movementsB. performancesC. operationsD. actions73.We have worked out the plan and now we must put it into ___.(NMET1997 38)A. factB. realityC. practiceD. deed74.We've missed the last bus. I'm afraid we have no ____but to take a taxi.(Met 1993 ,33)A. wayB. choiceC. possibilityD. selection75.He dropped the ___and broke it . (Met 1993, 38)A. cup of coffeeB. coffee's cupC. cup for coffeeD. coffee cup76.Here's my card. Let's keep in ____. (NMET1994 ,33)A. touchB. relationC. connectionD. friendship77.He gained his ___by printing ___of famous writers.(NMET1995,40)A. wealth; workB. wealths ; worksC. wealths; workD. wealth; works78.I'll look into the matter as soon as possible , just have a little ___.(MET 1996 ,10)A. waitB. timeC. patienceD. rest79.If by any chance someone comes to see me, ask them to leave a ____.(NMET1997,18)A. messageB. letterC. sentenceD. notice80.These football players had no strict ___until they joined our club. (1997.上海20)A. practiceB. educationC. exerciseD. training81.Many count ries are increasing their use of natural gas, wind and other forms of ___.(1996.上海.15)A. energyB. sourceC. powerD. material82.You'll find this ma p of great __in helping you to get round London.(NMET 1998 21)A. priceB. costC. valueD. usefulness83.We all know that ___speak louder than words.(1999.上海24)A. movementsB. performancesC. operationsD. actions84.My parents always let me have my own ____of living. (1999.上海25)A. wayB. methodC. mannerD. fashion名词1~5 BBDDD 6~10 BBCAA 11~15 ABCCB 16~20 DAACD 21~25 DBDCD26~30 BADBD 31~35 AABDC 36~40 BACCB 41~45 ABDCA 46~50 BABCB51~55 BDDCD 56~60 ABCCB 61~65 BACAA 66~70 DADCA 71~75 CDCBD76~80 ADCAD 81~84 ACDA。