
Solutions
1. The activity coefficient of zinc in liquid brass is given (in joules ) by the following equation
for temperature 1000-1500K: 2
38300ln Cu Zn x RT -=γ, where x Cu is the mole fraction of
copper. Calculate the partial pressure of zinc P Zn over a solution of 60 mol % copper and 40 mol % zinc at 1200K. The vapor pressure of pure zinc is 1.17 atm at 1200K. (7.1, p196) Solution:
)
(117.017.11.01.04.025.025
.038
.11200
314.86.03830038300ln 2
2
atm a P P x a RT
x Zn p
Zn Zn Zn Zn Zn Zn Cu Cu
Zn =?===?===-=??-=
-=
γγγ
2. Using the equation give in Problem 7.1, for the activity coefficient of zinc in liquid brass, derive an equation for the activity coefficient of copper using the Gibbs-Duhem equation. (7.2, 196)
Solution: According to Gibbs –Duhem Equation:
2
1
1
1
ln 0
Cu Cu 38300ln 238300238300238300)(ln )
(ln )(ln 0)(ln )(ln 0)1()(ln )(ln 0)(ln )(ln )(ln )(ln 0
)(ln )(ln Zn
Cu Zn
x Zn Cu x Zn Cun
x Cu Cu
Zn Cu Zn Cu
Zn Cu Cu Zn
Zn Zn Zn Cu Zn Cu Zn Zn Cu Cu Cu Cu Zn Zn Zn Zn Cu Cu Zn Zn x RT
dx x RT
dx x RT
dx x RT
x x d d x x d d x d x x d dx dx dx x d x x d x x d x a d x x d x d x a d x a d x n
Z Cu
Cu
-
=?-=?=
?-?
-
=
-
==∴=-+=+==+++=+?
?
??
γγγγγγ
γγ
++
3.
(a) At 900K, is Fe3C a stable compound relative to pure Fe and graphite?( 7.3, 196)
(b) At 900K, what is the thermodynamic activity of carbon in equilibrium with Fe and Fe3C ?
Carbon as graphite is taken as the standard state.
(c) In the Fe-C phase diagram, the carbon content of α -iron in equilibrium with Fe3C is
0.0113 wt. %. What is the solubility of graphite in α-iron at 900K? DA TA A T 900K, J G
C
Fe C Fe o
graphite
346333)
(+=?=+
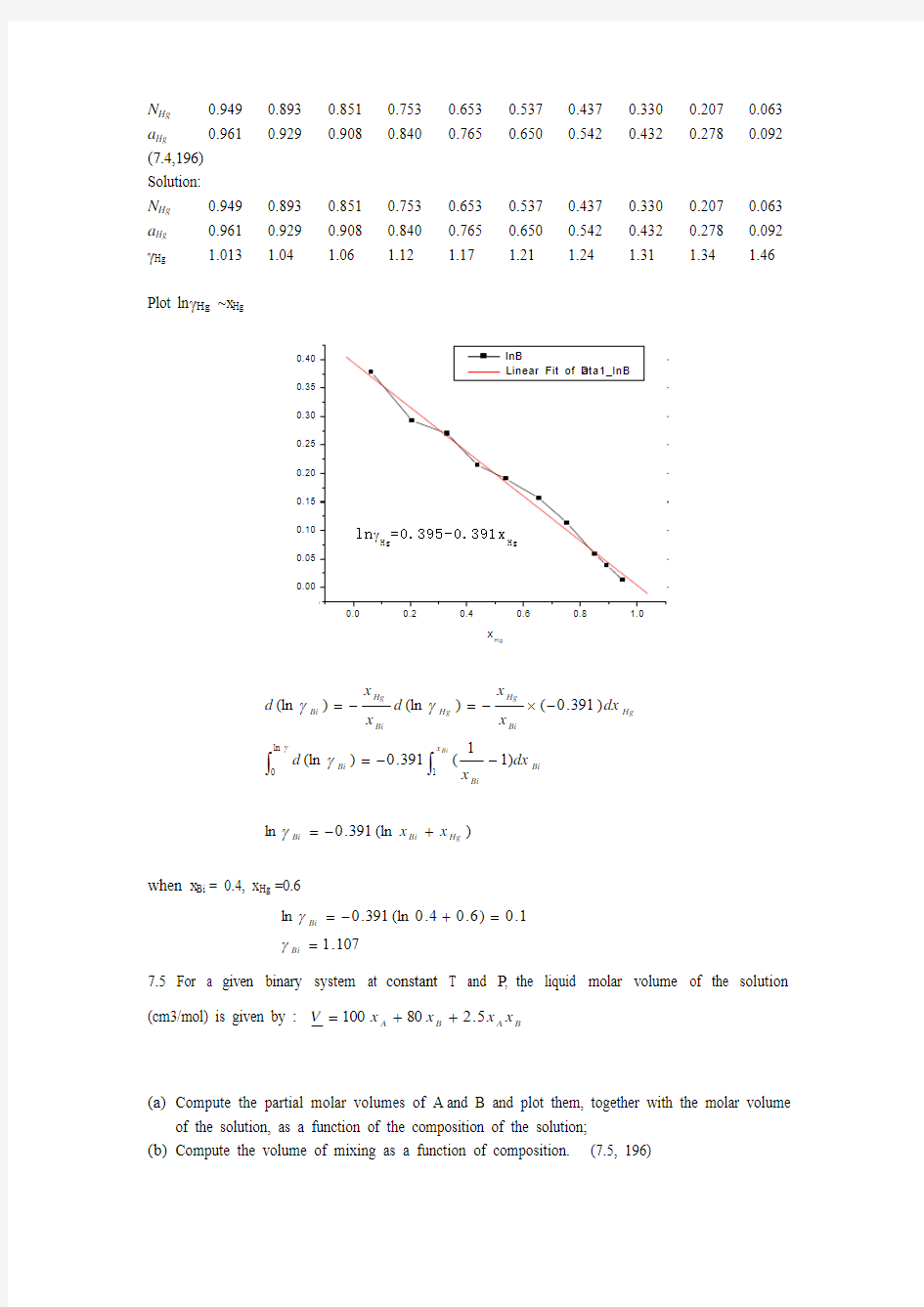
4. From vapor pressure measurements, the following values have been determined for the activity of mercury in liquid mercury-bismuth alloys at 593K. Calculate the activity of bismuth in a 40 atom % alloy at this temperature
N Hg 0.949 0.893 0.851 0.753 0.653 0.537 0.437 0.330 0.207 0.063 a Hg 0.961 0.929
0.908
0.840
0.765
0.650
0.542
0.432
0.278
0.092
(7.4,196) Solution: N Hg 0.949 0.893 0.851 0.753 0.653 0.537 0.437 0.330 0.207 0.063 a Hg 0.961 0.929 0.908 0.840 0.765 0.650 0.542 0.432 0.278 0.092 γHg
1.013
1.04
1.06
1.12
1.17
1.21
1.24
1.31
1.34
1.46
Plot ln γHg ~x Hg
0.0
0.2
0.4
0.60.8 1.0
0.00
0.050.100.150.200.250.300.350.40
l n γH g
x H g
)
(ln 391.0ln )11(391.0)(ln )391.0()(ln )(ln 1
ln 0
Hg Bi Bi
Bi x Bi
Bi
Hg
Bi
Hg Hg
Bi
Hg Bi
x x dx x d dx x x d x x d Bi
+-=--=-?-=-
=??
γ
γ
γ
γ
γ
when x Bi = 0.4, x Hg =0.6
107
.11
.0)6.04.0(ln 391.0ln ==+-=Bi Bi
γγ
7.5 For a given binary system at constant T and P , the liquid molar volume of the solution (cm3/mol) is given by : B A B A x x x x V 5.280100++=
(a) Compute the partial molar volumes of A and B and plot them, together with the molar volume
of the solution, as a function of the composition of the solution;
(b) Compute the volume of mixing as a function of composition. (7.5, 196)
Solution: the calculated partial variables are as follows: A A B A x x x x V 5.280100++=
B x P T A A x x
V V B
5.2100,,+=?
??? ????= B A x P T B
B x x x
V
V B
5.25.825.280,,-=+=?
??? ????= 0.00.20.40.60.8 1.0
80
85
90
95
100
105
c m 3
/m o l
x B
(b) B
A B B B M
B
A x x x V x x V V
V
V
5.2)100(80)1(100(80
,100=--=+--=== 4. For an ideal binary solution of A and B atoms, plot schematically the chemical potential of both species as a function of the composition of the solution. Indicate on the plot the molar Gibbs free energy of pure A and B. (7.6,196)
5. At 473?C, the system Pb-Sn exhibits regular solution behavior, and the activity coefficient of Pb is given by: ()()2132.0log Pb
Pb x --=γ. Write the corresponding equation of the variation of
Sn γ with composition at 473?C. (7.7, p196)
6. MgCl 2 and MgF 2 are two salts that can form solutions. The Gibbs free energy of fusion(J/mol) for both compounds is given by:
For MgCl 2 : ?G = 43905-43.644T, Melting point =987K
For MgF 2: ?G = 58702-38.217T, Melting point = 1536K The free energy of mixing (J/mol) for liquid mixture MgCl 2 and MgF 2 is given by:
))(252556()ln ln (22222222
2MgCl MgF MgF MgCl MgF MgF MgCl
MgCl Mix x x x x x x x x RT G -+-++=?.
Compute the maximum solubility of MgF 2 in liquid MgCl 2 at 900?C. MgCl 2 does not dissolve in
solid MgF 2. (7.8, 197)
7. The thermodynamic properties of Al-Mg solution at 1000K are given in accompanying table. (a) If one mole of pure liquid aluminum and one mole of pure liquid magnesium, each at 1000K, are mixed adiabatically, what will be the final temperature of the solution that is formed ? (b) What is the total change in entropy for the process ?
DA TA Quantities of Mixing Liquid Alloys at 1000K
Mg x
)/(mol cal G M ?
)/(mol cal H M ? )/(mol cal S M ?
)]./([K mol cal C p
0.1 -800 -300 0.5 7.1 0.2 -1250 -600 0.65 7.18 0.3 -1550 -750 0.8 7.26 0.4 -1700 -850 0.85 7.34 0.5 -1800 -900 0.9 7.42 0.6 -1700 -850 0.85 7.5 0.7 -1550 -750 0.8 7.58 0.8 -1250 -600 0.65 7.66 0.9 -800
gf-300
0.5
7.74