国家标准外文版翻译项目汇总表
- 格式:doc
- 大小:32.00 KB
- 文档页数:1

-------------精选文档 -----------------完整的国内基金英文标准翻译凡是获得有关基金资助项目的研究成果,必须严格按规定进行标注,项目结束后所填报的《总结报告》及所附有效论著(标注过的),将作为申请新项目时的评审依据。
标注位置应在学术论著、鉴定证书、技术资料及其他有效证明材料的封面,或书前扉页,或论文首页、致谢部分。
1 、国家自然科学基金(项目编号:)资助Supported by National Natural Science Foundation of China(项目编号:)[Supported by NSFC(项目编号:)]2、国家自然科学基金重大项目资助Supported by Major Program of National Natural Science Foundation of China (1991483)3 、国家自然科学基金国际合作与交流项目(项目编号:)资助Supported by Projects of International Cooperation and Exchanges NSFC(项目编号:)4 、国家重点基础研究发展规划项目(项目编号:)资助(973 计划项目 )Supported by Major State Basic Research Development Program(项目编号:)Supported by China Ministry of Science and Technology under Contract(项目编号:)-------------精选文档 -----------------Supported by State Key Development Program of (for) Basic Research of China(项目编号:)5 、国家高技术研究发展计划(863 计划 )资助Supported by National High Technology Research and Development Program ofChina6、国家杰出青年科学基金资助Supported by National Natural Science Funds for Distinguished Young Scholar7 、国家科技部基金资助Supported by State Commission of Science Technology of China(科委)Supported by Ministry of Science and Technology of China8、中国博士后科学基金Supported by China Postdoctoral Science Foundation9 、海峡两岸自然科学基金(项目编号:)共同资助Supported by Science Foundation of Two sides of Strait(项目编号:)10 、国家教育部科学基金资助Supported by Science Foundation of The Chinese Education Commission (教委) Supported by Science Foundation of Ministry of Education of China-------------精选文档 -----------------11、国家教育部博士点专项基金资助Supported by Doctoral Fund of Ministry of Education of China(缩写: RFDP)12、教育部科学技术研究重点(重大)项目资助英文: Supported by the Key(Key grant) Project of Chinese Ministry of Education.(NO )13、国家教育部留学回国人员科研启动基金资助项目英文: The Project Sponsored by the Scientific Research Foundation for the Returned Overseas Chinese Scholars, State Education Ministry.缩写: The Project-sponsored by SRF for ROCS, SEM.14、国家教育部优秀青年教师基金资助Supported by Science Foundation for The Excellent Youth Scholars of Ministry ofEducation of China15、高等学校博士学科点专项科研基金资助Supported by Research Fund for the Doctoral Program of Higher Education of ChinaSupported by Doctoral Program Foundation of Institutions of Higher Education ofChina16、国家教委《跨世纪优秀人才计划》基金-------------精选文档 -----------------Trans - Century Training Programme Foundation for the Talents by the State Education Commission17、高等学校骨干教师资助计划资助英文: Supported by Foundation for University Key Teacher by the Ministry of Education18、霍英东教育基金会青年教师基金资助Supported by Fok Ying Tung Education Foundation19、广东省自然科学基金资助Supported by Natural Science Foundation of Guangdong Province, China20、广东省教育厅项目资助Supported by Educational Commission of Guangdong Province, China21、广东省科技计划项目资助Supported by Science and Technology Planning Project of Guangdong Province,China22、广东省医学科研基金项目(卫生厅)资助Supported by Medical Scientific Research Foundation of Guangdong Province, China23、广东省中医药管理局项目资助-------------精选文档 -----------------Supported by Administration of Traditional Chinese Medicine of GuangdongProvince, China24、国家中医药管理局项目资助Supported by State Administration of Traditional Chinese Medicine of People’ s Rep China国家社会科学基金项目Projects of the National Social Science Foundation of China国家社科基金科研立项establishing the state social philosphical scientific fundation researchprogramme(大全)国家社科、国家自然基金、教育部等各省部级课题标准英文翻译专题词汇科技部国家自然科学基金 : National Natural Science Foundation of China (NSFC)国家高技术研究发展计划(863 计划 ): National High-tech R&D Program of China (863Program); 国家重点基础研究发展计划项目( 973 计划):National Program on KeyBasic Research Project of China (973 Program); 国家重点基础研究项目特别基金 :National Key Basic Research Special Foundation of China (NKBRSFC) 国家重点基础研究专项基金 : Special Foundation for State Major Basic Research Program ofChina; 国家 985 重点建设项目 : Key Construction Program of the National ( “985 ”Project); 国家科技攻关项目 National Programs for Science and Technology Development;国家“十五”科技攻关项目: National Key Technology Research andDevelopment Program of China during the“10th Five-Year Plan”;“九五”国-------------精选文档 -----------------家医学科技攻关基金资助项目:National Medical Science and Technique Foundation during the “9th Five-Year Plan ”;国家科技支撑计划 : National Key Technology Research and Development Program of theMinistry of Science and Technology ofChina; 国家科技基础条件平台建设项目:The National R&D Infrastructure and Facility Development Program of China; 国际科技合作重点项目: Key Program for International S&T Cooperation Projects of China国家科技重大专项: National Science and Technology Major Project of the Ministry of Science and Technologyof China; 国家重点实验室发展项目:The State Key Laboratories Development Program of China 国家基础研究计划 : National Program on Basic Research Projectof China;。

ANSI A137-中文版翻译.pdfANSI A137.2-2021-中文版翻译.pdfANSI B109.1-2019-中文版翻译.pdfANSI B74.3-2002 R 2008 中文版翻译.pdfANSI C78377-2008-中文版翻译.pdfANSI Common Lisp 中文版翻译.pdfANSI ESD S 541-2008-中文版翻译.pdfANSI K62.132-1973-中文版翻译.pdfANSI-ESDS20-20-2007-中文版翻译.pdfANSI-S3.19-1974-中文版翻译.pdfANSI ICEA S-94-649-中文版翻译.pdfANSI API5L-2007-中文版翻译.pdfAOAC 2011-11-中文版翻译.pdfAP17069-4-中文版翻译.pdfAPI SPEC 8C-2012-中文版翻译.pdfAS NZS 1337.1-2010-中文版翻译.pdfAS NZS 1337.1-2010-中文版翻译繁体翻译.pdfAS NZS 1850-2009-中文版翻译.pdfASME B1.1-2003-中文版翻译.pdfASME B1.20.1-2013 (R2018)-中文版翻译.pdfASME B1.20.1-2013-中文版翻译.pdfASME B16.11-92-中文版翻译.pdfASME B16.25-1997-中文版翻译.pdfASME B16.25-2003-中文版翻译.pdfASME B16.34-2004-中文版翻译.pdfASME B16.5-中文版翻译.pdfASME B18.2.1-1999a-中文版翻译.pdfASME B18[1].2.1-1999a-中文版翻译.pdfASME B31.1-2004-中文版翻译.pdfASME BPVC VIII-2 2010-中文版翻译.pdfASME II A篇2010-中文版翻译.pdfasme pvho 1993-中文版翻译版扫描.pdfASME PVHO-2-2012-中文版翻译.pdfASME Y14.100-2013-中文版翻译.pdfASME 第V卷2008增补-中文版翻译.pdfASME 核电规范与标准BPVC-III 核设施部件构造规则第1册NB分卷1级部件2004-中文版翻译.pdfASME 核电规范与标准BPVC-III 核设施部件构造规则第1册NC分卷2级部件2004-中文版翻译.pdfASME 核电规范与标准BPVC-III 核设施部件构造规则第1册ND分卷3级部件2004-中文版翻译.pdfASME 核电规范与标准BPVC-Ⅲ-核设施部件构造规则第1册NH分卷1级部件2004-中文版翻译.pdfASME-B1.20.1-2013 中文版翻译.pdfASME锅炉及压力容器规范国际性规范Ⅱ材料B篇非铁基材料2007中文版翻译.pdf ASME锅炉及压力容器规范国际性规范Ⅱ材料C篇焊条、焊丝及填充金属2007中文版翻译版.pdfASME锅炉及压力容器规范国际性规范Ⅱ材料D篇性能(公制) 2007中文版翻译版.pdf ASME锅炉及压力容器规范国际性规范Ⅷ第1册压力容器建造规则2010中文版翻译版.pdfASME锅炉及压力容器规范国际性规范Ⅷ第1册压力容器建造规则-2010-中文版翻译版.pdfASTM A193-2011-中文版翻译.pdfASTM A352M-2006-中文版翻译.pdfASTM A580-18 -中文版翻译.pdfASTM A671A671M-2010-中文版翻译.pdfASTM A709-中文版翻译.pdfASTM B504-1990(2007)-中文版翻译.pdfASTM C1026-2013-中文版翻译.pdfASTM C1027-09(R 2017)-中文版翻译.pdfASTM C1185-08(2012)-中文版翻译.pdfASTM C1243-1993(R 2015) (E 2017)-中文版翻译.pdfASTM C126-2011-中文版翻译.pdfASTM C1329-2015-中文版翻译.pdfASTM C1378-2004(R2014)-中文版翻译.pdfASTM C1396-2013-中文版翻译.pdfASTM C1442 2014-07-中文版翻译.pdfASTM C1572-17-中文版翻译.pdfASTM C370 - 12(2016)-中文版翻译.pdfASTM C372-94(2016)-中文版翻译.pdfASTM C373-17(2017)-中文版翻译.pdfASTM C424-93(2016)-中文版翻译.pdfASTM C482-2002(R2014)-中文版翻译.pdfASTM C484-1999(R2014)-中文版翻译.pdfASTM C485-16-中文版翻译.pdfASTM C499-2009(R2014)-中文版翻译.pdfASTM C502-2016中文版翻译-中文版翻译.pdfASTM C609-2007(R2014)-中文版翻译.pdfASTM C648-2004(R2014)-中文版翻译.pdfASTM C650-2004(R2014)-中文版翻译.pdfASTM C666 C666M-03(2008)-中文版翻译.pdfASTM C717 REV A 2014-05 13P-中文版翻译.pdfASTM C792 2015-03 3P-中文版翻译.pdfASTM D1003-21-中文版翻译.pdfASTM D1044 2013-09 中文版翻译.pdfASTM D1970-13-中文版翻译.pdfASTM D2394-05(2011)-中文版翻译pdfASTM D2624-21-中文版翻译.pdfASTM D2794-93(2019)-中文版翻译.pdfASTM D2863-13-中文版翻译.pdfASTM D3175 2018-中文版翻译.pdfASTM D3175-2017-中文版翻译.pdfASTM D3359-17-中文版翻译.pdfASTM D3746-85R2008-中文版翻译.pdfASTM D3912-2010-中文版翻译.pdfASTM D4239 2018-中文版翻译.pdfASTM D4239-2017-中文版翻译.pdfASTM D4272-09-中文版翻译.pdfASTM D4292-2017-中文版翻译.pdfASTM D4422 2019-中文版翻译.pdfASTM D4541-17-中文版翻译.pdfASTM D4541-2009e1-中文版翻译.pdfASTM D4930-06(R 2017)-中文版翻译.pdfASTM D5003 2019-中文版翻译.pdfASTM D5003 REV A-06(R 2017)-中文版翻译.pdf ASTM D5178 - 98(2002)-中文版翻译.pdfASTM D522-17-中文版翻译.pdfASTM D570-1998(R 2018)-中文版翻译.pdf ASTM D637-1990-中文版翻译.pdfASTM D6374 2012-中文版翻译.pdfASTM D6374-12(R 2017) (E 2017)-中文版翻译.pdf ASTM D638 - 14-中文版翻译.pdfASTM D6791 2011-中文版翻译.pdfASTM D6866-20-中文版翻译.pdfASTM D779-03-中文版翻译.pdfASTM D792-20-中文版翻译.pdfASTM D870-15(2020)-6-7-8-中文版翻译.pdf ASTM D97-96a-中文版翻译.pdfASTM D974 - 21-中文版翻译.pdfASTM E1070-17a-中文版翻译.pdfastm E1091-2008-中文版翻译.pdfASTM E127-19e1-中文版翻译.pdfASTM E127-2020-中文版翻译.pdfASTM E1951-14(2019)-中文版翻译.pdfastm E1978-2005-中文版翻译.pdfASTM E220-19-中文版翻译.pdfASTM E2273-03R2011-中文版翻译.pdf ASTM E2309-20-中文版翻译.pdfASTM E2484-08-中文版翻译.pdfASTM E2658-2015-中文版翻译.pdfASTM E283-2019-中文版翻译.pdfASTM E317-16-中文版翻译.pdfASTM E4-2014-中文版翻译.pdfASTM E467 - 08 (2014)-中文版翻译.pdf ASTM E83-10a-中文版翻译.pdfASTM E84-13a-中文版翻译.pdfASTM F 925–02-中文版翻译.pdfASTM F1816-1997(R2009)-中文版翻译.pdf ASTM F733-2009-中文版翻译.pdfASTM F893-2010-中文版翻译.pdfASTM G151 2010-中文版翻译.pdfASTM G152-13-10-中文版翻译.pdfASTM G152-13-中文版翻译.pdfASTM G154-12a-12-中文版翻译.pdfASTM G154-12a-中文版翻译.pdfASTM G155 2013-06-中文版翻译.pdfASTM G155 2013-中文版翻译.pdfASTM G21-2015-中文版翻译.pdfASTM+E119-中文版翻译.pdfASTM+G155-13-中文版翻译.pdfASTM_A182-2006-中文版翻译.pdfASTM_A312-2004-中文版翻译.pdfASTM_D570-98-中文版翻译.pdfASTM_D648-07-中文版翻译.pdfASTM_D882-02-中文版翻译.pdfATT_001F93.dat-中文版翻译.pdfAWWA D104-2011-中文版翻译.pdfAFNOR NF EN 13523-27-2009-中文版翻译.pdf AFNOR NF F00-072-1990_中文版翻译.pdf AFNOR NF F00-363-1995-中文版翻译.pdf AFNOR NF F19-211-1990-中文版翻译.pdf AFNOR NF F19-216-1993-中文版翻译.pdf AFNOR NF F19-217-1994-中文版翻译.pdf AFNOR NF F19-218-1993-中文版翻译.pdfAFNOR NF F19-219-1994-中文版翻译.pdf AFNOR NF F19-220-1992-中文版翻译.pdf AFNOR NF F19-222-1992-中文版翻译.pdf AFNOR NF F19-223-1992-中文版翻译.pdf AFNOR NF F19-290-2002-中文版翻译.pdf AFNOR NF F19-291-2002-中文版翻译.pdf AFNOR NF F19-293-1997-中文版翻译.pdf AFNOR NF F19-295-1997-中文版翻译.pdf AFNOR NF F19-296-1998-中文版翻译.pdf AFNOR NF F19-352-1996-中文版翻译.pdf AFNOR NF F19-355-1995-中文版翻译.pdf AFNOR NF F19-447-1997-中文版翻译.pdf AFNOR NF F19-449-1992-中文版翻译.pdf AFNOR NF F19-477-1991-中文版翻译.pdf AFNOR NF F19-478-1989-中文版翻译.pdf AFNOR NF F31-11-1994-中文版翻译.pdf AFNOR NF F31-112-1994-中文版翻译.pdf AFNOR NF T30-124-1991-中文版翻译.pdf AFNOR NF X08-014-2005-中文版翻译.pdf AFNOR_NFEN_ISO_2813-1999-中文版翻译.pdf AFNOR_NF_F19-216-1993-中文版翻译.pdf AFNOR_NF_F19-217-1994-中文版翻译.pdf AFNOR_NF_F19-218-1993-中文版翻译.pdf AFNOR_NF_F19-219-1994-中文版翻译.pdf AFNOR_NF_F19-220-1992-中文版翻译.pdf AFNOR_NF_F19-222-1992-中文版翻译.pdf AFNOR_NF_F19-223-1992-中文版翻译.pdf AFNOR_NF_F19-283-1990-中文版翻译.pdf AFNOR_NF_F19-290-2002-中文版翻译.pdf AFNOR_NF_F19-291-2002-中文版翻译.pdf AFNOR_NF_F31-112-1994_中文版翻译.pdfB155050-K-中文版翻译.pdfB217110-C-中文版翻译.pdfB217120-B-中文版翻译.pdfB217130-A-中文版翻译.pdfB620030-E-中文版翻译.pdfB620300-E-中文版翻译.pdfBC1-2012-中文版翻译.pdfBS 1363-3-1995-AMD-2003-中文版翻译.pdfBS 159-1992-中文版翻译.pdfBS 1742-5.2-1991-中文版翻译.pdfBS 1868-中文版翻译.pdfBS 3900 F4-1968-中文版翻译.pdfBS 4255-1-1986-中文版翻译.pdfBS 4873-2009-中文版翻译.pdfbs 5228-1-中文版翻译.pdfBS 5228-2-2009-中文版翻译.pdfBS 5228-4-1992-中文版翻译.pdfBS 5427-1-1996-中文版翻译.pdfBS 5911-4-2002+A2-2010-中文版翻译.pdfBS 6375-2-2009-中文版翻译.pdfBS 6783-14-1994-中文版翻译.pdfBS 6783-15-1994-中文版翻译.pdfBS 7385-1-中文版翻译.pdfBS 7385-2-中文版翻译.pdfBS 8405-2003+A1-2009-中文版翻译.pdfBS 952-1-1995-中文版翻译.pdfBS 9999-2008-中文版翻译.pdfBS EN 10002-1-2001-中文版翻译.pdfBS EN 10025-2-2004-中文版翻译.pdfBS EN 10034-1993-中文版翻译.pdfBS EN 10034-1994-中文版翻译.pdfBS EN 10056-1-1999-中文版翻译.pdfBS EN 10056-1-2000-中文版翻译.pdfBS EN 10056-2-1993-中文版翻译.pdfBS EN 10083-3-2006-中文版翻译.pdfBS EN 10163-3-2004-中文版翻译.pdfBS EN 10210-1994-中文版翻译.pdfBS EN 10216-2-2002-中文版翻译.pdfBS EN 10253-2-中文版翻译.pdfBS EN 1026-2000-中文版翻译.pdfBS EN 10279-2000-中文版翻译.pdfBS EN 10339-2007-中文版翻译.pdfBS EN 1090-2-2008-中文版翻译.pdfBS EN 1147-2010-中文版翻译.pdfBS EN 12199-2010-中文版翻译.pdfBS EN 12201-2 2011 + A1 2013-中文版翻译.pdfBS EN 12201-3 2011 + A1 2012(2013)-中文版翻译.pdf BS EN 12207-2000-中文版翻译.pdfBS EN 12208-2000-中文版翻译.pdfBS EN 12210-2000-中文版翻译.pdfBS EN 12246-1999-中文版翻译.pdfBS EN 12430_2013-中文版翻译.pdfBS EN 12668-1-2010-中文版翻译.pdfBS EN 12668-2-2010-中文版翻译.pdfBS EN 12697-23-2003 中文版翻译.pdfBS EN 1279-1-2004-中文版翻译.pdfBS EN 1279-2-2002-中文版翻译.pdfBS EN 1279-3-2002-中文版翻译.pdfBS EN 12791-2005-中文版翻译.pdfBS EN 12953-1-2002-中文版翻译.pdfBS EN 12953-11-2003-中文版翻译.pdfBS EN 12953-2-2002-中文版翻译.pdfBS EN 12953-3-2002-中文版翻译.pdfBS EN 12953-4-2002-中文版翻译.pdfBS EN 12953-5-2002-中文版翻译.pdfBS EN 12953-6-2011-中文版翻译.pdfBS EN 13100-1-2000-中文版翻译.pdfBS EN 13100-2-2004-中文版翻译.pdfBS EN 13100-3-2004-中文版翻译.pdfBS EN 13146-8-2012-中文版翻译.pdfBS EN 13262-2004-中文版翻译.pdfBS EN 13369-中文版翻译.pdfBS EN 1337-11-1998-中文版翻译.pdfBS EN 1337-8-2007-中文版翻译.pdfBS EN 1342 2013 中文版翻译.pdfBS EN 13445-2 2014-中文版翻译.pdfBS EN 13445-4-2009-中文版翻译.pdfBS EN 13450-2013-中文版翻译.pdfBS EN 13481-4-2012-中文版翻译.pdfBS EN 1349-2000-中文版翻译.pdfBS EN 13529-中文版翻译.pdfBS EN 13566-2-2005(2006)-中文版翻译.pdf BS EN 13709-2002-中文版翻译.pdfBS EN 1372 2015-中文版翻译.pdfBS EN 1373 2015-中文版翻译.pdfBS EN 13803-2-2006+A1-2009 -中文版翻译.pdf BS EN 13848-2-2006-中文版翻译.pdfBS EN 13892-4-2002-中文版翻译.pdfBS EN 1408-2008-中文版翻译.pdfBS EN 14411-2016-中文版翻译.pdfBS EN 14728-2005-中文版翻译.pdfBS EN 14730-2-2006-中文版翻译.pdfBS EN 14749-2005-中文版翻译.pdfBS EN 1475-1996-中文版翻译.pdfBS EN 14752-2015-中文版翻译.pdfBS EN 14969-2006-中文版翻译.pdfBS EN 1527-2013-中文版翻译.pdfBS EN 15332-2007-中文版翻译.pdfBS EN 1536-2010+A1-2015 (35-50页)中文版翻译.pdf BS EN 15427-2008+A1-2010-中文版翻译.pdfBS EN 15594-2009-中文版翻译.pdfBS EN 166-2002-中文版翻译.pdfBS EN 1670-2007-中文版翻译.pdfBS EN 179-1998-中文版翻译.pdfBS EN 1793-1 2013-中文版翻译.pdfBS EN 1841-1999-中文版翻译.pdfBS EN 1846-2 -2010-中文版翻译.pdfBS EN 1846-3-2002+A1-2008-中文版翻译.pdfBS EN 1888-2003-中文版翻译.pdfBS EN 1903 2015-中文版翻译.pdfBS EN 1991-4-2006-中文版翻译.pdfBS EN 1993-1-6-2007-中文版翻译.pdfBS EN 1996-2-2006-中文版翻译.pdfBS EN 287-2-1997-中文版翻译.pdfBS EN 410-2011-中文版翻译.pdfBS EN 485-1-2008-中文版翻译.pdfBS EN 515-1993-中文版翻译.pdfBS EN 520-2004+A1-2009-中文版翻译.pdfBS EN 545-中文版翻译.pdfBS EN 60617-8-1996-中文版翻译.pdfBS EN 60900-2012-中文版翻译.pdfBS EN 71-1 2014+A1 2018-中文版翻译.pdfBS EN 71-2-2011+ A1 2014-中文版翻译.pdfBS EN 71-3 2019-中文版翻译.pdfBS EN 755-8-2008-中文版翻译.pdfBS EN 771-3-2003-中文版翻译.pdfBS EN 837-1-中文版翻译.pdfBS EN 837-2-中文版翻译.pdfBS EN 866-1-1997-中文版翻译.pdfBS EN 866-7-2000-中文版翻译.pdfBS EN IEC 60900-2018-中文版翻译.pdfBS EN ISO 17892-1-2014-中文版翻译.pdfBS EN ISO 17892-12-2018-中文版翻译.pdfBS EN ISO 20345-2011-中文版翻译.pdfBS EN ISO 22232-1-2020-中文版翻译.pdfBS EN ISO 3678-1995-中文版翻译.pdfBS EN ISO 3822-2-1996-中文版翻译.pdfBS EN ISO 3822-3-1997+A1-2009-中文版翻译.pdfBS EN ISO 3822-4-1997-中文版翻译.pdfBSI 17-30348435 DC-中文版翻译.pdfBSI BS EN 10149-3 2013-09-中文版翻译.pdfCCTG法国通用技术规范第27分册-中文版翻译.pdfCDPH-IAQ_StandardMethod_V1_1_2010_ADA-中文版翻译.pdf CPSC-CH-C1001-09.3-中文版翻译.pdfCP_1-STM-N-801-du-6-8-2008-中文版翻译.pdfCSA AM ANSI Z21.10.3-2015 CSA 4.3-2015-中文版翻译.pdf CSA C2.1-06 (R2017)-中文版翻译.pdfCSA C227.4-21-中文版翻译.pdfCSA Z94.3-15-中文版翻译.pdfCSA Z94.3-2020-中文版翻译.pdfDD ENV 13481-6-2002-中文版翻译.pdfDIN 1053-1-中文版翻译.pdfDIN 1053-2-中文版翻译.pdfDIN 1053-3-中文版翻译.pdfDIN 1053-4 Entwurf-中文版翻译.pdfDIN 1053-4-中文版翻译.pdfDIN 12898-1992-中文版翻译.pdfDIN 12916-1995-中文版翻译.pdfDIN 1342-1 2003-11-中文版翻译.pdfDIN 1342-2 2003-11-中文版翻译.pdfDIN 1342-3 2003-11-中文版翻译.pdfDIN 14096 (2014-05-00)-中文版翻译.pdfDIN 14530-11 (2019-11-00)-中文版翻译.pdfDIN 14530-16 (2019-11-00)-中文版翻译.pdfDIN 14676 (2012-09-00)-中文版翻译.pdfDIN 14924-2015-中文版翻译.pdfDIN 1681-1985-中文版翻译.pdfDIN 16960-1-1974-中文版翻译.pdfDIN 1910-3-1977-中文版翻译.pdfDIN 19552-002-中文版翻译.pdfDIN 19554-2-1978-中文版翻译.pdfDIN 19554-2002-中文版翻译.pdfDIN 19627 (2017-04-00)-中文版翻译.pdfDIN 19636-100-中文版翻译.pdfDIN 22109-4-2000-中文版翻译.pdfDIN 3015-10 1994-02-中文版翻译.pdf DIN 3113-2007-中文版翻译.pdfDIN 332-1-1986-中文版翻译.pdfDIN 406-10-中文版翻译.pdfDIN 406-11-中文版翻译.pdfDIN 406-12-中文版翻译.pdfDIN 42539-1-1968-中文版翻译.pdfDIN 42539-2-1968-中文版翻译.pdfDIN 43138-中文版翻译.pdfDIN 46228-3-1992-中文版翻译.pdfDIN 4753-1 (2019-05-00)-中文版翻译.pdf DIN 4753-3-2011-中文版翻译.pdfDIN 4753-3-2017-中文版翻译.pdfDIN 4753-7 (2019-05-00)-中文版翻译.pdf DIN 50125-2009-中文版翻译.pdfDIN 50125-中文版翻译.pdfDIN 5033-1-2009-中文版翻译.pdfDIN 5033-2-1992-中文版翻译.pdfDIN 5033-3-1992-中文版翻译.pdfDIN 5033-4-1992-中文版翻译.pdfDIN 5033-5-1992-中文版翻译.pdfDIN 5033-6-1976-中文版翻译.pdfDIN 5033-7-1983-中文版翻译.pdfDIN 5033-8-1982-中文版翻译.pdfDIN 5033-9-2005-中文版翻译.pdfDIN 50602-中文版翻译.pdfDIN 50918-1978-中文版翻译.pdfDIN 51131(2014-02-00)-中文版翻译.pdf DIN 5129 (2014-01-00)-中文版翻译.pdf DIN 51290-1-1991-中文版翻译.pdfDIN 51290-2-1991-中文版翻译.pdfDIN 51290-3-1991-中文版翻译.pdfDIN 51290-4-1991-中文版翻译.pdfDIN 5131 2014-01-中文版翻译.pdfDIN 51368-中文版翻译.pdfDIN 52305-1995-中文版翻译.pdfDIN 52308-1984-中文版翻译.pdfDIN 52361-1965-中文版翻译.pdfDIN 53133-2006-中文版翻译.pdfDIN 53428-1986 中文版翻译.pdfDIN 53504 (2017-03-00)-中文版翻译.pdfDIN 53505-2000-中文版翻译.pdfDIN 53867-1990-中文版翻译.pdfDIN 54345-1-1992-中文版翻译.pdfDIN 54345-5-1985-中文版翻译.pdfDIN 5510-2-2009-05 中文版翻译.pdfDIN 55429-2-1987-中文版翻译.pdfDIN 55543-4-2010-中文版翻译.pdfDIN 55635-2019-中文版翻译.pdfDIN 58124 (2018-10-00-中文版翻译.pdfDIN 58916-2004-中文版翻译.pdfDIN 66131-1993-中文版翻译.pdfDIN 66132-1975-中文版翻译.pdfDIN 67530-1982-中文版翻译.pdfDIN 68764-1 1973-09-中文版翻译.pdfDIN 68764-2 1974-09-中文版翻译.pdfDIN 68857-2004-中文版翻译.pdfDIN 72594-1-2006-中文版翻译.pdfDIN 7287 2014-01-中文版翻译.pdfDIN 7294 2014-01-中文版翻译.pdfDIN 7444-2009-中文版翻译.pdfDIN 8078-2008-中文版翻译.pdfDIN 8187-2-1998-中文版翻译.pdfDIN 8187-3-1998-中文版翻译.pdfDIN 81915-1998-中文版翻译.pdfDIN 820-1-2014-中文版翻译.pdfDIN 820-4-2014-中文版翻译.pdfDIN 8201-4-1985-中文版翻译.pdfDIN 838-2007-中文版翻译.pdfDIN 8743 appendix 8-中文版翻译.pdfDIN 894-2007-中文版翻译.pdfDIN EN 10025-2-2004-中文版翻译.pdfDIN EN 10025-中文版翻译.pdfDIN EN 10293 Berichtigung 1 2008-中文版翻译.pdf DIN EN 10293-2005-中文版翻译.pdfDIN EN 12678-2016-中文版翻译.pdfDIN EN 12897-2006-中文版翻译.pdfDIN EN 12897-2016-中文版翻译.pdfDIN EN 12915-1-2009-中文版翻译.pdfDIN EN 13443-1-2007-中文版翻译.pdfDIN EN 14293-2006-中文版翻译.pdfDIN EN 14743-2007-中文版翻译.pdfDIN EN 15332-2020E-中文版翻译.pdfDIN EN 16380-2014-中文版翻译.pdfDIN EN 415-1 2014-中文版翻译.pdfDIN EN 415-10 2014-07-中文版翻译.pdfDIN EN 415-2 2000-中文版翻译.pdfDIN EN 415-3 2010-中文版翻译.pdfDIN EN 415-4 1997-中文版翻译.pdfDIN EN 415-5-2010-中文版翻译.pdfDIN EN 415-6 2013-09-中文版翻译.pdfDIN EN 415-8-2011-06-中文版翻译.pdfDIN EN 415-9-2010-中文版翻译.pdfDIN EN 573-3-2009 -中文版翻译.pdfDIN EN 60068-2-30-中文版翻译.pdfDIN EN 60068-2-6-中文版翻译.pdfDIN EN 60068-2-68-中文版翻译.pdfDIN EN 681-1-中文版翻译.pdfDIN EN 970-1997-中文版翻译.pdfDIN EN ISO 1101-2014-中文版翻译.pdfDIN EN ISO 1302-2002 中文版翻译.pdfDIN EN ISO 14405-2 2012 中文版翻译.pdfDIN EN ISO 286-2-2010-11 中文版翻译.pdfDIN EN ISO 2931-2018-中文版翻译.pdfDIN EN ISO 9227 2012 中文版翻译.pdfDIN ISO 9271-1995-替代DIN 25415-4-中文版翻译.pdf DIN ISO 9277-2010-中文版翻译.pdfDIN V VDE V 0126-18-2-3-2007-中文版翻译.pdfDIN V VDE V 0126-18-2-4-2007-中文版翻译.pdfDIN+EN+1634-1-2014-中文版翻译.pdfDIN-EN10210-P1(中文版翻译版).pdfDIN17100-1980-中文版翻译.pdfDIN22109-1-2000中文版翻译.pdfDINEN10292Z中文版翻译版.pdfDINEN15433-6-2008中文版翻译版.pdfDIN_17210_表面硬化钢_供货技术条件-中文版翻译.pdf DIN_30-10-2006-中文版翻译.pdfDIN_30-5-2002-中文版翻译.pdfDIN_30-6-2002-中文版翻译.pdfDIN_51757_2011-01(中文版翻译).pdfDIN_6174-2007-中文版翻译.pdfDIN_EN_10056-01-中文版翻译.pdfDIN_EN_10228-3中文版翻译.pdfDIN_EN_10327中文版翻译.pdfDIN_EN_13450-2003中文版翻译.pdfE1571 report step by step prwrc 2nd draft-中文版翻译.pdfEN 10021-2006中文版翻译.pdfEN 10021-2006中文版翻译.pdfEN 10025-3-2004 結構鋼熱軋產品第三部分正火正火軋制可焊細粒結構鋼交貨條件中文版翻译.pdfEN 10028-2-2003-中文版翻译.pdfEN 10060-2004_中文版翻译.pdfEN 10060-2004_中文版翻译.pdfEN 10163-2-2004-中文版翻译.pdfEN 10204-2004 中文版翻译.pdfEN 1122-中文版翻译.pdfEN 12150-1:2015中文版翻译.pdfEN 1289-中文版翻译.pdfEN 13190-2001-中文版翻译.pdfEN 1337-3-2005-中文版翻译.pdfen 14582-2002 中文版翻译.pdfEN 14931 2006中文版翻译.pdfEN 167 2001中文版翻译.pdfEN 168 2002中文版翻译.pdfEN 1822-1-中文版翻译.pdfEN 200-中文版翻译.pdfEN 287-中文版翻译.pdfEN 581-中文版翻译.pdfEN 71-1-2011-中文版翻译.pdfEN 71-92007-中文版翻译.pdfEN 717-2-中文版翻译.pdfEN 817-2008-中文版翻译.pdfEN 970-中文版翻译.pdfEN ISO 3262-19_2000-10-中文版翻译.pdfEN ISO 787-11-1995-10-中文版翻译.pdfEN ISO 787-18 1983-中文版翻译.pdfEN ISO 787-9 中文版翻译.pdfEN-14511-3-2004-CHN中文版翻译.pdfEN-14511-4-2004-CHN中文版翻译.pdfEN10025-2004热轧结构钢系列标准中文版翻译.pdfEN10025-3-2004中文版翻译.pdfEN10028-12007+A12009承压用扁钢-第1部分:一般要求(含1号修改单)中文版翻译.pdf EN10028-2-2003中文版翻译.pdfEN10028-3-2009-中文版翻译.pdfEN10029 2010-中文版翻译.pdfEN10029 2010-中文版翻译.pdfEN10088-1(欧洲不锈钢标准)中文版翻译.pdf EN10088-1中文版翻译版.pdfEN10149-2-SXXXMC(中文版翻译).pdfEN10204-2004中文版翻译版.pdfEN10228-3-1998-中文版翻译版.pdfEN10250-1-1999中文版翻译版.pdfEN10250-2-2000中文版翻译版.pdfEN12209中文版翻译版.pdfEN12790中文版翻译版.pdfEN13828中文版翻译.pdfEN50128_中文版翻译.pdfEN50128中文版翻译.pdfEN50129中文版翻译.pdfEN50334中文版翻译.pdfEN55014中文版翻译.pdfEN60335-1中文版翻译.pdfEN9802003中文版翻译.pdfEN_10204-2004_中文版翻译.pdfEN_15380-1-中文版翻译.pdfEN_Operating-Instructions_V.3-中文版翻译.pdf EPA 8270D 2014-中文版翻译.pdfEPA-HQ-QAR-0-0162-英中对照.pdfEPA-HQ-QAR-0-0162-中文版翻译.pdfES 95400-10-2020--中文版翻译.pdfES 95400-10-2020-中文版翻译.pdfES01000-00E 中文版翻译.pdfES90000-01E 中文版翻译.pdfES90000-03 20170901-中文版翻译.pdfES91500-00E 中文版翻译.pdfES95400-10-2018中文版翻译.pdfES95400-10-REV 19 中文版翻译.pdfES96203-00E 中文版翻译.pdfexample 3.1 bode-译文.pdfF19-301-1991-中文版翻译.pdfF19-302-1995-中文版翻译.pdfF19-303-1996-中文版翻译.pdfF19-350-1998-中文版翻译.pdfF19-351-1996-中文版翻译.pdfFIDIC DREDGING & RECLAMATION 2006_中文版翻译.pdfFM 1421-2018-水枪组件喷嘴验收标准中文版翻译.pdfFM 5511-软管组件,水枪消防喷嘴中文版翻译.pdfFM Approval 5560 ERD 水雾系统验证标准-中文版翻译.pdfGB 1356-2001-英文译文.pdfGB 18111-2000 英文翻译.pdfGB 4053.2-2009-英文翻译.pdfGB 50017-2017 EN(正文译文).pdfGB 50017-2017 钢结构设计标准(条文说明)-英文翻译.pdfGB T 19568-2017 风力发电机组装配和安装规范-英文翻译.pdfGB T 20801.5-2020-英文翻译.pdfGB T 37898-2019 风力发电机组吊装安全技术规程-英文翻译.pdf gb-t18160-2008-英文译文.pdfGB-T4336-2002中文版翻译.pdfGerman Firefighters Hierarchy中文版翻译.pdfGEV_Test_Method_2018-04-18-中文版翻译.pdfGMKOREA EDS-T-3501-2010中文版翻译.pdfGMRT2100 Iss 5 中文版翻译.pdfGMW 14334-2013中文版翻译.pdfGMW 14444-2017-中文版翻译-20210419.pdfGMW 14444-2017-中文版翻译.pdfGMW 3097 电磁兼容性一般规范-中文版翻译.pdfGMW 3172_AUG2008中文版翻译.pdfGMW GMW14333-2014中文版翻译.pdfGMW GMW15671-2013中文版翻译.pdfGMW GMW16016-2014中文版翻译.pdfGMW GMW3136-2011中文版翻译.pdfGMW14172中文版翻译.pdfGMW14173中文版翻译.pdfGMW14618中文版翻译.pdfGMW3431 2014-8 General Procedures for Testing Swi-中文版翻译.pdf GOST 12.4.121-2015-译文.pdfGOST 12.4.122-2020-译文.pdfGOST 12.4.158-90-译文.pdfGOST 12.4.159-90-译文.pdfHLD-SC200操作手册-中文版翻译.pdfIEC 60034-1-2004-中文版翻译.pdfIEC 60034-1-2004中文版翻译.pdfIEC 60034-2-1-2007-中文版翻译.pdfIEC 60034-2-1-2007中文版翻译.pdfIEC 61340-5-1(中文版翻译).pdfIEC 61754-20-2012中文版翻译.pdfIEC 62061-2021-中文版翻译.pdfIEC ASTM 62885-6-2018-中文版翻译.pdfIEC60598-1-2008中文版翻译.pdfIEC60811-3-1(2001中文版翻译).pdfIEC61188-5-1-2002中文版翻译.pdfIEC61188-5-2-2003-中文版翻译.pdfIEC61188-5-3-2007-中文版翻译.pdfIEC61188-5-4-中文版翻译.pdfIEC61188-5-5-中文版翻译.pdfIEC61188-5-6-2003-中文版翻译.pdfIEC61188-5-8-2007-中文版翻译.pdfIEC62305-4(中文版翻译).pdfIECTS61287-2-2001(中文版翻译).pdfIEEE C57.110-2018-中文版翻译.pdfIP 385-19(2019)-译文.pdfIPC-A-600G-2004 印制板的验收条件官方中文版翻译.pdf ISO 10140-2-2010中文版翻译.pdfISO 10140-2-2021-中文版翻译.pdfISO 10140-2-2021中文版翻译.pdfISO 10143 2019-中文版翻译.pdfISO 10143-2014中文版翻译.pdfISO 10236-1995中文版翻译.pdfISO 10292-1994-中文版翻译.pdfISO 10524-1-2018-样稿.pdfISO 10524-1-2018-中文版翻译.pdfISO 10545-10-中文版翻译.pdfISO 10545-11-中文版翻译.pdfISO 10545-12-中文版翻译.pdfISO 10545-13-中文版翻译.pdfISO 10545-2-中文版翻译.pdfISO 10545-3-中文版翻译.pdfISO 10545-4-中文版翻译.pdfISO 10563-2017(中文版翻译).pdfISO 10590-2005-中文版翻译.pdfISO 10591-2005-中文版翻译.pdfISO 10893-3-2011-中文版翻译.pdfISO 1101-2004 中文版翻译.pdfISO 1101-2012 中文版翻译.pdfISO 11290-2-2017-中文版翻译.pdfISO 11412-1998中文版翻译.pdfISO 11418-7-1998-中文版翻译.pdfISO 11432-2005-中文版翻译.pdfISO 11464-2006-中文版翻译.pdfISO 11465-1993-中文版翻译.pdfISO 11600 AMD 1-2011-07-中文版翻译.pdfISO 11600-2002-中文版翻译.pdfISO 11617-2022-中文版翻译.pdfISO 11890-2-2020-中文版翻译.pdfISO 12219-2-2012-中文版翻译.pdfISO 12312-1-2013+AMD1-2015中文版翻译.pdfISO 12312-1-2013中文版翻译.pdfISO 12980-2000 中文版翻译.pdfISO 12982-1-2000中文版翻译.pdfISO 12984-2018中文版翻译.pdfISO 13565-2-1996 cor1-1998-中文版翻译.pdfiso 13565-2-1996-中文版翻译.pdfISO 13913 2014-02中文版翻译.pdfISO 14235-1998-中文版翻译.pdfISO 14615-1997-中文版翻译.pdfISO 14638-2015 中文版翻译.pdfISO 148-2-2016 中文版翻译.pdfISO 15184-2012中文版翻译.pdfISO 15184-2020-中文版翻译.pdfISO 15590-2-2021-中文版翻译.pdfISO 15609-1-2004 金属材料的焊接程序规范和合格鉴定.焊接程序规范.电弧焊中文版翻译.pdfISO 15653-2018-中文版翻译.pdfISO 16276-2-2007-中文版翻译.pdfISO 16620-2-2019-中文版翻译.pdfISO 16703-2004中文版翻译.pdfISO 17178-2013 中文版翻译.pdfISO 17363-2013中文版翻译.pdfISO 17364-2013-中文版翻译.pdfISO 17364-2013中文版翻译.DOCXISO 17364-2013中文版翻译.pdfISO 17365-2013中文版翻译.pdfISO 18856-2004中文版翻译.pdfISO 19840-2012-中文版翻译.pdfISO 19840-2012中文版翻译.pdfISO 1997-2018中文版翻译.pdfISO 2030-2018-中文版翻译.pdfISO 2031-2015-中文版翻译.pdfISO 2067-2019-中文版翻译.pdfISO 2143-2017中文版翻译.pdfISO 2190-2016-中文版翻译.pdfISO 2219-2010中文版翻译.pdfISO 22232-1-2020-译文.pdfISO 22232.1-2020-中英文对照版.pdfISO 22631-2019-中文版翻译.pdfISO 22632-2019-中文版翻译.pdfISO 22633-2019-中文版翻译.pdfISO 22635-2019-中文版翻译.pdfISO 22636-2020-中文版翻译.pdfISO 22637-2019-中文版翻译.pdfISO 228-1-2000 中文版翻译.pdfISO 228-2-1987 中文版翻译.pdfISO 23206-2005 cor1-2007 中文版翻译.pdfISO 23206-2005 cor1-2007-中文版翻译.pdfISO 23206-2005-中文版翻译.pdfISO 23206-2005中文版翻译.pdfISO 23727-2009-中文版翻译.pdfISO 2386-2019-中文版翻译.pdfISO 24026-1-2020-中文版翻译.pdfISO 24026-2-2020-中文版翻译.pdfISO 2409-2013中文版翻译.pdfISO 24410-2020-中文版翻译.pdfISO 24442-2011-中文版翻译.pdfISO 24444-2019-中文版翻译--修订.pdfISO 24444-2019-中文版翻译翻译-修订.pdfISO 24444-2019-中文版翻译翻译.pdfISO 2503-2009-中文版翻译.pdfISO 2503-2009-中文版翻译翻译.pdfISO 26842-1-2020-05-中文版翻译.pdfISO 26842-2-2020-05-中文版翻译.pdfISO 2768-1-1989 中文版翻译.pdfISO 2768-2-1989 中文版翻译.pdfISO 2797-1986中文版翻译.pdfISO 28005-1-2013-译文.pdfISO 2808-2007 涂料和清漆.漆膜厚度的测定-中文版翻译.pdf ISO 2808-2019-中文版翻译.pdfISO 3183 2019-中文版翻译.pdfISO 3210-2017-中文版翻译.pdfISO 3253-1998-中文版翻译.pdfISO 4210-2 2015-09-译文.pdfISO 4210-6 2015-译文.pdfISO 4406-2021-中文版翻译.pdfISO 4892-1-2016-中文版翻译.pdfISO 4892-2-2013-中文版翻译.pdfISO 4986-1992鑄鋼件磁粉檢測-中文版翻译.pdf ISO 4987-92鑄鋼件滲透檢測-中文版翻译.pdf ISO 4993-87中文版翻译.pdfISO 4993-87鑄鋼件射綫檢測-中文版翻译.pdf ISO 5171-2009-中文版翻译.pdfISO 565-1990-中文版翻译.pdfiso 5663-1984-中文版翻译.pdfISO 5663-1984-中文版翻译翻译.pdfISO 5817-2007 中文版翻译.pdfISO 5817-2014(L2)1126 中文版翻译.pdfISO 6149-3-2006 中文版翻译.pdfISO 6344-1-1998-中文版翻译.pdfISO 6344-2-1998-中文版翻译.pdfISO 6344-3-1998-中文版翻译.pdfISO 6432-2015(L2)-中文版翻译.pdfISO 6486-1-1999中文版翻译.pdfISO 6537-1982中文版翻译.pdfISO 6787-2001-中文版翻译.pdfISO 6856-2005 中文版翻译.pdfISO 6997-1985-中文版翻译.pdfISO 7086-1-2000中文版翻译.pdfISO 718-1990中文版翻译.pdfISO 7390-2002-中文版翻译.pdfISO 7396-1-2007-中文版翻译.pdfISO 7451-2007(中文版翻译翻译).pdfISO 7529-2017中文版翻译.pdfISO 7546-1983-中文版翻译.pdfISO 7707-1986-译文.pdfISO 7804-1985-译文.pdfISO 7886-2-1996-中文版翻译翻译.pdfISO 7886-2-1996翻译.pdfISO 7934-1989(+AMD1998)中文版翻译.pdf ISO 8004-1985中文版翻译.pdfISO 8005-2005中文版翻译.pdfISO 8062-3-2007 中文版翻译翻译.pdfISO 8245-1999-中文版翻译.pdfISO 8245-1999-中文版翻译翻译.pdfISO 8340-2005-中文版翻译.pdfISO 8362-1-2003-中文版翻译.pdfISO 846-2019-中文版翻译.pdfISO 8502-3-1993-中文版翻译.pdfISO 8723-1986中文版翻译.pdfISO 8839-1986中文版翻译.pdfISO 9046-2002-中文版翻译.pdfISO 9047 CORR 1 2009-中文版翻译.pdfISO 9047-2001-中文版翻译.pdfISO 9050-2003中文版翻译.pdfISO 9377-2-2000中文版翻译.pdfISO 9406-1995中文版翻译.pdfISO TR 10064-3-1996 圆柱齿轮实用检验规程第3部分轴心圆柱的齿轮坯料、轴心距和平行度的建议(中文版翻译).pdfISO-12103-1中文版翻译.pdfISO-15730-2000-中文版翻译.pdfISO12647-2-2004 中文版翻译.pdfISO13920 中文版翻译.pdfISO1461(金属覆盖层-钢铁制品热镀锌层-技术条件)中文版翻译.pdfISO14644-1中文版翻译.pdfISO16750-5中文版翻译.pdfISO19252-2008中文版翻译.pdfISO9044_1999工业用金属编织网—技术要求与检验中文版翻译.pdfISO_16750-3_2007-中文版翻译.pdfISO_9227-0607-(盐雾试验)中文版翻译.PDFISO防霉-中文版翻译.pdfJB T 3232-2017 滚动轴承万向节滚针轴承(英文).DOCXJB T 3232-2017 滚动轴承万向节滚针轴承(英文).pdfJIS A1311-1994 建筑用防火门的防火试验方法中文版翻译.pdfJIS A5705-1998(JAP)-中文版翻译.pdfJIS B 4609-1998 一字槽螺钉旋具(中文版翻译).pdfJIS B 8312-1991-中文版翻译.pdfJIS D0205-中文版翻译.pdfJIS F 7005 船舶管道的识别-中文版翻译.pdfJIS F2025-1992 中文版翻译.pdfJIS G3548-1994 镀锌钢丝中文版翻译.pdfJIS K 6217-1-2008 -中文版翻译.pdfJIS K 7112-1999-中文版翻译.pdfJIS K 7113-1995-中文版翻译.pdfJIS K 7203-1982-中文版翻译.pdfJIS K 7208-1975-中文版翻译.pdfJIS K5659-2018 中文版翻译.docxJIS K5659-2018 中文版翻译.pdfJIS P8126-2005 R 2010 中文版翻译.pdfJIS R 3213 -1998-中文版翻译.pdfJIS T 8010-中文版翻译.pdfJIS T 8112-1997-中文版翻译.pdfJIS Z 1522-中文版翻译.pdfJISA5530-1983钢管板桩(中文版翻译).pdfJISB8271-1993压力容器的筒体及封头中文版翻译.pdfJISC3005-2000(中文版翻译).pdfJISC3005-2000橡胶或塑料绝缘电线和电缆的试验方法(中文版翻译).pdf JISC8702-1(2003)简体中文版翻译.pdfJISC9606-1993电动洗衣机标准中文版翻译.pdfJISD5500汽车用车灯中文版翻译.pdfJISE4502-1日本工业标准---铁路车辆用车轴中文版翻译.pdfJISG0306-1991锻钢通用技术要求中文版翻译.pdfJISG0582-1998超声波探伤检验方法中文版翻译.pdfJISG1253-2002钢铁火花放电原子发射光谱分析法(中文版翻译).pdf JISG3106-1999焊接结构用轧制钢材中文版翻译.pdfJISG4305-2005冷轧不锈钢板材、薄板和带材中文版翻译.pdfJISH4100-2006铝及铝合金挤压形状中文版翻译.pdfJISZ2202-1998金属材料冲击试样(中文版翻译).pdfJISZ2248-2006金属材料.弯曲试验中文版翻译.pdfJISZ2248-2006金属材料弯曲试验(中文版翻译).pdfJISZ2371-2000盐雾试验方法(中文版翻译).pdfJIS_G3313-1998_电镀锌钢板及钢带(中文版翻译).pdfJIS_G3444一般结构用碳素钢管中文版翻译.pdfJIS_G4304-2005__热轧不锈钢板材、薄板和带材(中文版翻译).pdfJIS_Z2201-1998__金属材料抗拉试验用试样__中文版翻译.pdfJJF 1698-2018-英文.pdfJJF1787-2019-英文.pdfJJG 971-2019-英文.pdfJSA JIS A 1905-1-2015-中文版翻译.pdfJSA JIS A 1905-2-2015-中文版翻译.pdfJSA JIS F 2029 中文版翻译.pdfJSA JIS T 8152-2012-译文.pdfKS R 1034-2006中文版翻译.pdfLV216-2 机动车辆及其电力驱动用屏蔽高压铠装电缆-中文版翻译.pdf MIL-G-25667B_AMENDMENT-1中文版翻译.pdfMIL-G-25667B_NOTICE-3中文版翻译.pdf MIL-G-25667B中文版翻译.pdfMIL-PRF-25690B-中文版翻译.pdfMIL-PRF-8184F NOT 1-中文版翻译翻译.pdf MIL-PRF-8184F-1998 中文版翻译.pdfMIL-PRF-8184F-中文版翻译.pdfMIL-PRF-8184F-中文版翻译翻译.pdf NAC溶液(10%)说明书-中文版翻译.pdf NBT47048-2015-英文译稿.pdfNF C27-234-1990中文版翻译.pdfNF E 05-051-1981-中文版翻译.pdfNF EN 12373-1-2001-中文版翻译.pdfNF EN 12373-10-1999-中文版翻译.pdfNF EN 12373-11-2000-中文版翻译.pdfNF EN 12373-12-2000-中文版翻译.pdfNF EN 12373-13-2000-中文版翻译.pdfNF EN 12373-14-2000-中文版翻译.pdfNF EN 12373-15-2000-中文版翻译.pdfNF EN 12373-16-2001-中文版翻译.pdfNF EN 12373-17-2001-中文版翻译.pdfNF EN 12373-18-2000-中文版翻译.pdfNF EN 12373-19-2002-中文版翻译.pdfNF EN 12373-2-1999-中文版翻译.pdfNF EN 12373-3-1999-中文版翻译.pdfNF EN 12373-4-1998-中文版翻译.pdfNF EN 12373-5-1999-中文版翻译.pdfNF EN 12373-6-1999-中文版翻译.pdfNF EN 12373-7-2002-中文版翻译.pdfNF EN 12373-8-1999-中文版翻译.pdfNF EN 12373-9-1999-中文版翻译.pdfNF F 19-201-2010-中文版翻译.pdfNF F00-800-1991-中文版翻译.pdfNF F01-492-2013-中文版翻译.pdfNF F19-141-1-1998-中文版翻译.pdfNF F19-141-2-1998-中文版翻译.pdfNF F19-301-1991-中文版翻译.pdfNF F19-302-1995-中文版翻译.pdfNF F19-303-1996-中文版翻译.pdfNF F19-350-1998-中文版翻译.pdfNF F19-351-1996-中文版翻译.pdfNF F31-129-2013 中文版翻译.pdfNF M64-001-1991-中文版翻译.pdfNF-F01-492-1-1993-待交付中文版翻译.PDFNFPA 1211 中文版翻译.PDFNFPA 1600-中文版翻译.pdfNFPA 1901-2016-中文版翻译.pdfNFPA 1906-中文版翻译.pdfNFPA 1911-2017-中文版翻译.pdfNFPA 1912-2016-中文版翻译.pdfNFPA 1932-2020-中文版翻译.pdfNFPA 1961-2020(译稿).pdfNFPA 414-2020-中文版翻译.pdfNFPA 501A-2013 中文版翻译.pdfNFPA 780-2017-中文版翻译.pdfNFPA 92-2018-中文版翻译.pdfNFPA 96-2017-中文版翻译.pdfNFPA 99 2015-第14章中文版翻译.pdfNFPA204-2002烟和热量的排放-中文版翻译.pdfNFPA30---22地面储罐部分(中文版翻译).pdfNFPA36-2009中文版翻译.pdfNFPA750美国消防协会细水雾消防系统标准2003中文版翻译.pdf NF_F_19-201-2010_中文版翻译.pdfNF_T30-071-6-2007-中文版翻译.pdfNF_T30-071-7-2004-中文版翻译.pdfNF_T30-071-8-2005-中文版翻译.pdfNF_T30-125-1974-中文版翻译.pdfNMX-C-155-ONNCCE-2014 actual(中文版翻译).pdfPED-97-23-EC压力设备指令-中文版翻译.pdfprEN 1930:2009(中文版翻译).pdfROHS指令-2011-65-EU(中文版翻译).pdfRTCA-DO-160G机载设备的环境条件和试验程序-7721-中文版翻译.pdf SAE AMS2750E-2012-中文版翻译.pdfSAE AS1339J-2018-中文版翻译.pdfSAE J296 199901-中文版翻译.pdfSAE J429-1999 外螺纹紧固件机械性能和材料要求中文版翻译.pdf SAE J434 中文版翻译.pdfSAE J575 2004-中文版翻译.pdfSAE J995-1999 钢制螺帽材料及机械性能要求(中文版翻译).pdf SAE MA2170-2015 -中文版翻译.pdfSAE MA2176A-2015 -中文版翻译.pdfSAE MA4098-2015-中文版翻译.pdfSAE MA614A-2015-中文版翻译.pdf。

国家标准英文版翻译出版工作管理暂行办法发布机构:国家质量技术监督局发布日期:1998.04.22生效日期:1998.04.22第一条为适应对外贸易、经济、技术交流与合作的需要,做好国家标准英文版翻译出版工作,特制定本暂行办法。
第二条国家标准英文版翻译出版工作主要安排强制性国家标准(其中,等同采用ISO、IEC和其他国际组织标准的国家标准,原则上不安排)。
符合下述条件的国家标准优先列入英文版翻译出版计划:1 涉及国家安全;2 防止欺诈行为;3 保护人身健康和安全;4 动、植物生命或健康;5 保护环境;6 国际贸易及经济、技术交流需要的重要标准。
第三条国家标准英文版的翻译出版工作由国家质量技术监督局标准化部门统一管理。
第四条国家标准英文版翻译出版工作,根据需要分批、分期组织实施。
第五条未列入国家标准英文版翻译计划的标准,有关单位愿意自筹经费承担标准的翻译工作,经国家质量技术监督局标准化部门审查同意后,列入经费自筹国家标准英文版翻译出版计划。
第六条国家标准英文版翻译出版工作的程序及要求:1 国家标准英文版翻译出版计划项目的立项建议,原则上由各有关标准化技术委员会或技术归口单位提出,由国家质量技术监督局标准化部门审定。
其他单位或个人也可以向国家质量技术监督局标准化部门提出翻译出版有关国家标准英文版的建议。
2 国家标准英文版计划项目确定后,由国家质量技术监督局标准化部门直接向标准化技术委员会或技术归口单位下述任务,下述方式按本办法第七条规定执行。
3 国家标准英文版的翻译工作由原起草该项国家标准的标准化技术委员会、技术归口单位具体负责组织实施。
4 国家标准英文版的翻译工作必须坚持忠实原文的原则。
翻译工作承担单位应确保英文版本的内容与中文版国家标准一致。
翻译工作承担单位如果在翻译过程中发现国家标准的技术内容有误或出现印刷错误,应及时向标准化技术委员会或技术归口单位及其上级主管部门报告,由标准化技术委员会或技术归口单位及其上级主管部门按照《国家标准管理办法》的规定,以标准修改通知单方式,报国家质量技术监督局批准后,方可按照修改后的内容进行翻译,同时要在出版前言中予以说明。
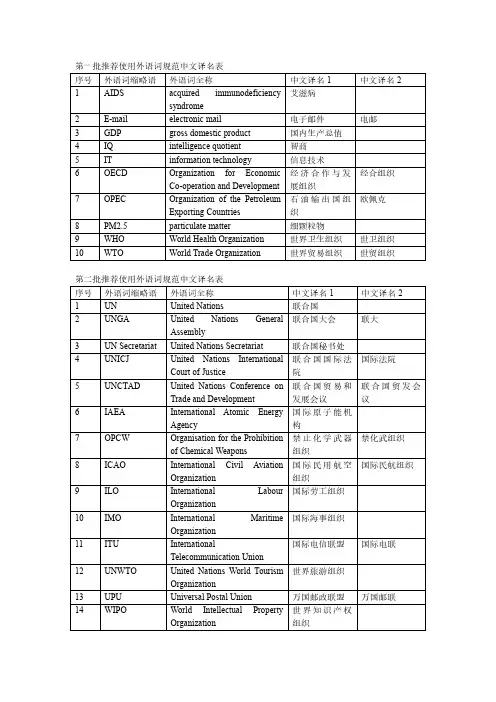
第一批推荐使用外语词规范中文译名表序号外语词缩略语外语词全称中文译名1中文译名2 1AIDS acquired immunodeficiencysyndrome艾滋病2E-mail electronic mail电子邮件电邮3GDP gross domestic product国内生产总值4IQ intelligence quotient智商5IT information technology信息技术6OECD Organization for EconomicCo-operation and Development 经济合作与发展组织经合组织7OPEC Organization of the PetroleumExporting Countries 石油输出国组织欧佩克8PM2.5particulate matter细颗粒物9WHO World Health Organization世界卫生组织世卫组织10WTO World Trade Organization世界贸易组织世贸组织第二批推荐使用外语词规范中文译名表序号外语词缩略语外语词全称中文译名1中文译名2 1UN United Nations联合国2UNGA United Nations GeneralAssembly联合国大会联大3UN Secretariat United Nations Secretariat联合国秘书处4UNICJ United Nations InternationalCourt of Justice 联合国国际法院国际法院5UNCTAD United Nations Conference onTrade and Development 联合国贸易和发展会议联合国贸发会议6IAEA International Atomic EnergyAgency 国际原子能机构7OPCW Organisation for the Prohibitionof Chemical Weapons 禁止化学武器组织禁化武组织8ICAO International Civil AviationOrganization 国际民用航空组织国际民航组织9ILO International LabourOrganization国际劳工组织10IMO International MaritimeOrganization国际海事组织11ITU InternationalTelecommunication Union国际电信联盟国际电联12UNWTO United Nations World TourismOrganization世界旅游组织13UPU Universal Postal Union万国邮政联盟万国邮联14WIPO World Intellectual PropertyOrganization 世界知识产权组织15IFC International FinanceCorporation国际金融公司16UNGEGN United Nations Group ofExperts on GeographicalNames 联合国地名专家组*本表按照联合国机构组织的层级排列第三批推荐使用外语词规范中文译名表序号外语词缩略语外语词全称中文译名1中文译名21Committee onNon-GovernmentalOrganizations 联合国非政府组织委员会2DFS Department of Field Support联合国外勤支助部联合国外勤部3DM Department of Management联合国管理事务部联合国管理部4DPKO Department of PeacekeepingOperations 联合国维持和平行动部联合国维和部5DPA Department of Political Affairs联合国政治事务部联合国政治部6EOSG Executive Office of theSecretary-General 联合国秘书长办公厅7IBRD International Bank forReconstruction andDevelopment 国际复兴开发银行8IDA International DevelopmentAssociation国际开发协会9International Law Commissionof United Nations 联合国国际法委员会10Military Staff Committee安理会军事参谋团安理会军参团11OCHA Office for the Coordination ofHumanitarian Affairs 联合国人道主义事务协调厅联合国人道协调厅12OIOS Office of Internal OversightServices 联合国内部监督事务厅联合国监督厅13OLA Office of Legal Affairs联合国法律事务厅联合国法律厅14Preparatory Commission forthe ComprehensiveNuclear-Test-Ban TreatyOrganization 全面禁止核试验条约组织筹备委员会禁核试组织筹委会15UNON United Nations Office atNairobi 联合国内罗毕办事处16UNOV United Nations Office at联合国维也纳Vienna办事处17UNOPS United Nations Office forProject Services 联合国项目事务厅联合国项目厅18UNSSC United Nations System StaffCollege 联合国系统职员学院19UNU United Nations University联合国大学20World Bank世界银行21World Bank Group世界银行集团世行集团22WMO World MeteorologicalOrganization世界气象组织*本表按照联合国机构组织外语词全称首字母音序排列。

中国标准英文版本
中国标准的英文版本通常是根据中国国家标准翻译而成的英文标准。
以下是一些常见的中国标准的英文版本:
GB/T 19001-2008 质量管理体系要求
GB/T 28001-2011 职业健康安全管理体系要求
GB/T 22080-2016 信息技术安全技术信息安全管理体系要求
GB/T 22081-2016 信息技术安全技术信息安全管理规范
这些标准是由中国国家标准化管理委员会(Standardization Administration of China)制定的,并被广泛用于中国的企业、组织和社会各个方面。
如果您需要了解更多中国标准的英文版本,建议在官方网站或相关渠道上查询。
1。

国家重点基础研究发展规划项目计划(973计划)中文:国家重点基础研究发展规划项目计划(973计划)英文:科技部建议用第二种,第一种可能还将修改。
National Key Basic Research Program (NKBRP) 项目编号:×××Founded by MOST(科技部英文缩写)项目编号:×××计划高等学校博士学科点专项科研基金中文:高等学校博士学科点专项科研基金资助课题英文: The Research Fund for the Doctoral Program of Higher Education缩写: RFDP跨世纪优秀人才计划中文:国家教委《跨世纪优秀人才计划》基金英文: Trans-Century Training Programme Foundation for the Talents by the State Education Commission国家教育部留学回国人员科研启动金中文:教育部留学回国人员科研启动基金资助项目The Project Sponsored by the Scientific Research Foundation for the Returned Overseas Chinese Scholars, State Education Ministry.缩写:The Project-sponsored by SRF for ROCS, SEM.高等学校骨干教师资助计划中文:高等学校骨干教师资助计划资助英文:Supported by Foundation for University Key Teacher by the Ministry of Education教育部重点项目中文:教育部科学技术研究重点(重大)项目资助英文:Supported by the Key(Key grant) Project of Chinese Ministry of Education.(NO……)国家高技术研究发展计划(863计划)中文标注:“由国家高技术研究发展计划专项经费资助”英文:The National High Technology Research and Development Program of China黑龙江省自然科学基金资助Supported by Natural Science Foundation of Heilongjiang Province of China湖北省教育厅重点项目资助Supported by Educational Commission of Hubei Province of China河南省杰出青年基金(9911)资助Supported by Excellent Youth Foundation of He’nan Scientific Committee(项目编号:)河南省教育厅基金资助Supported by Foundation of He’nan Educational Committee山西省青年科学基金(项目编号:)资助Supported by Shanxi Province Science Foundation for Youths(项目编号:)山西省归国人员基金资助Supported by Shanxi Province Foundation for Returness北京市自然科学基金资助Supported by Beijing Municipal Natural Science Foundation上海市科技启明星计划(项目编号:)资助Supported by Shanghai Science and Technology Development Funds(项目编号:)华北电力大学青年科研基金资助Supported by Youth Foundation of North-China Electric Power University华中师范大学自然科学基金资助Supported by Natural Science Foundation of Central China Normal University东南大学基金(项目编号:)资助Supported by Foundation of Southeast of University(项目编号:)西南交通大学基础学科研究基金(项目编号:)资助Supported by Foundation Sciences Southwest Jiaotong University(项目编号:)***科学技术厅科学家交流项目(项目编号:)Supported by Japan STA Scientist Exchange Program (项目编号: [/size]中国科学院基金资助Supported by Science Foundation of The Chinese Academy of Sciences中国科学院九五重大项目(项目编号:)资助Supported by Major Subject of The Chinese Academy of Sciences(项目编号:)中国科学院院长基金特别资助Supported by Special Foundation of President of The Chinese Academy of Sciences中国科学院国际合作局重点项目资助Supported by Bureau of International Cooperation, The Chinese Academy of Sciences中国科学院百人计划经费资助Supported by 100 Talents Programme of The Chinese Academy of SciencesSupported by One Hundred Person Project of The Chinese Academy of Sciences中国科学院知识创新工程重大项目资助Supported by Knowledge Innovation Project of The Chinese Academy of SciencesSupported by Knowledge Innovation Program of The Chinese Academy of Sciences中国科学院西部之光基金(项目编号:)资助Supported by West Light Foundation of The Chinese Academy of Sciences(项目编号:)北京正负电子对撞机国家实验室重点课题资助Supported by BEPC National Laboratory兰州重离子加速器国家实验室原子核理论中心基金资助Supported by Center of Theoretical Nuclear Physics, National Laboratory of Heavy Ion Accelerat or of Lanzhou国家自然科学基金(项目编号:)资助Supported by National Natural Science Foundation of China(项目编号:)[Supported by NSFC(项目编号:)]国家自然科学基金重大项目资助Supported by Major Program of National Natural Science Foundation of China (1991483)国家自然科学基金国际合作与交流项目(项目编号:)资助Supported by Projects of International Cooperation and Exchanges NSFC(项目编号:)国家重点基础研究发展规划项目(项目编号:)资助 (973计划项目)Supported by Major State Basic Research Development Program(项目编号:)Supported by China Ministry of Science and Technology under Contract(项目编号:)Supported by State Key Development Program of (for) Basic Research of China(项目编号:)国家高技术研究发展计划(863计划)资助Supported by National High Technology Research and Development Program of China国家重大科学工程二期工程基金资助Supported by National Important Project on Science-Phase Ⅱ of NSRL国家攀登计划—B课题资助Supported by National Climb—B Plan国家杰出青年科学基金资助Supported by National Natural Science Funds for Distinguished Young Scholar国家科技部基金资助Supported by State Commission of Science Technology of China(科委)Supported by Ministry of Science and Technology of China中国博士后科学基金Supported by China Postdoctoral Science Foundation海峡两岸自然科学基金(项目编号:)共同资助Supported by Science Foundation of Two sides of Strait(项目编号:)核工业科学基金资助Supported by Science Foundation of Chinese Nuclear Industry国家教育部科学基金资助Supported by Science Foundation of The Chinese Education Commission (教委)Supported by Science Foundation of Ministry of Education of China国家教育部博士点专项基金资助Supported by Doctoral Fund of Ministry of Education of China国家教育部回国人员科研启动基金资助Supported by Scientific Research Foundation for Returned Scholars, Ministry of Education of Chi na国家教育部优秀青年教师基金资助Supported by Science Foundation for The Excellent Youth Scholars of Ministry of Education of C hina高等学校博士学科点专项科研基金资助Supported by Research Fund for the Doctoral Program of Higher Education of China。

完整的国内基金项目英文标准翻译(2013-01-06 12:23:15)转载▼标签:杂谈凡是获得有关基金资助项目的研究成果,必须严格按规定进行标注,项目结束后所填报的《总结报告》及所附有效论著(标注过的),将作为申请新项目时的评审依据。
标注位置应在学术论著、鉴定证书、技术资料及其他有效证明材料的封面,或书前扉页,或论文首页、致谢部分。
1、国家自然科学基金(项目编号:)资助Supported by National Natural Science Foundation of China(项目编号:)[Supported by NSFC(项目编号:)]2、国家自然科学基金重大项目资助Supported by Major Program of National Natural Science Foundation of China (1991483)3、国家自然科学基金国际合作与交流项目(项目编号:)资助Supported by Projects of International Cooperation and Exchanges NSFC(项目编号:)4、国家重点基础研究发展规划项目(项目编号:)资助(973计划项目)Supported by Major State Basic Research Development Program(项目编号:)Supported by China Ministry of Science and Technology under Contract(项目编号:)Supported by State Key Development Program of (for) Basic Research of China(项目编号:)5、国家高技术研究发展计划(863计划)资助Supported by National High Technology Research and Development Program of China6、国家杰出青年科学基金资助Supported by National Natural Science Funds for Distinguished Young Scholar7、国家科技部基金资助Supported by State Commission of Science Technology of China(科委)Supported by Ministry of Science and Technology of China8、中国博士后科学基金Supported by China Postdoctoral Science Foundation9、海峡两岸自然科学基金(项目编号:)共同资助Supported by Science Foundation of Two sides of Strait(项目编号:)10、国家教育部科学基金资助Supported by Science Foundation of The Chinese Education Commission (教委)Supported by Science Foundation of Ministry of Education of China11、国家教育部博士点专项基金资助Supported by Doctoral Fund of Ministry of Education of China (缩写: RFDP)12、教育部科学技术研究重点(重大)项目资助英文:Supported by the Key(Key grant) Project of Chine se Ministry of Education.(NO……)13、国家教育部留学回国人员科研启动基金资助项目英文:The Project Sponsored by the Scientific Research Foundation for the Returned Overseas Chinese Scholars, State Education Ministry.缩写:The Project-sponsored by SRF for ROCS, SEM.14、国家教育部优秀青年教师基金资助Supported by Science Foundation for The Excellent Youth Scholars of Ministry of Education of China15、高等学校博士学科点专项科研基金资助Supported by Research Fund for the Doctoral Program of Higher Education of China Supported by Doctoral Program Foundation of Institutions of Higher Education of China16、国家教委《跨世纪优秀人才计划》基金Trans-Century Training Programme Foundation for the Talents by the State Education Commission17、高等学校骨干教师资助计划资助英文:Supported by Foundation for University Key Teacher by the Ministry of Education18、霍英东教育基金会青年教师基金资助Supported by Fok Ying Tung Education Foundation19、广东省自然科学基金资助Supported by Natural Science Foundation of Guangdong Province, China20、广东省教育厅项目资助Supported by Educational Commission of Guangdong Province, China21、广东省科技计划项目资助Supported by Science and Technology Planning Project of Guangdong Province, China22、广东省医学科研基金项目(卫生厅)资助Supported by Medical Scientific Research Foundation of Guangdong Province, China23、广东省中医药管理局项目资助Supported by Administration of Traditional Chinese Medicine of Guangdong Province, China24、国家中医药管理局项目资助Supported by State Administration of Traditional Chinese Medicine of People’s Republic of China 科技写作漫谈(40):基金资助项目的英文表达与标注不完全统计表明,国内期刊多习惯于将基金资助项目的信息作为论文首页的脚注,国外期刊则多将其作为“致谢”的一部分标注。
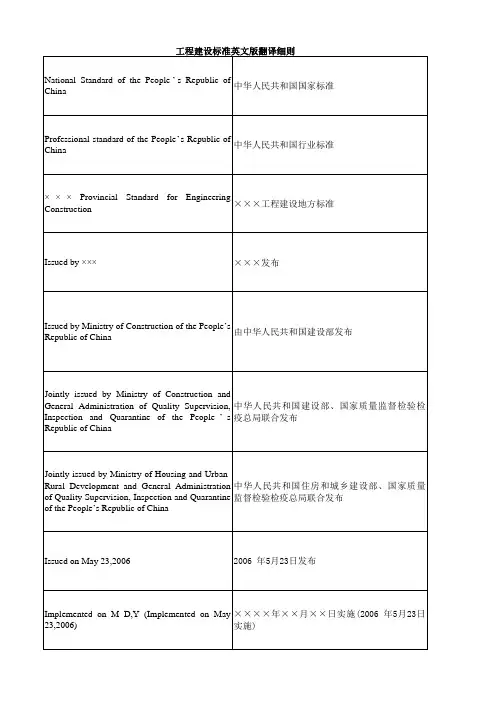
National Standard of the People’s Republic ofChina中华人民共和国国家标准Professional standard of the People’s Republic ofChina中华人民共和国行业标准×××Provincial Standard for EngineeringConstruction×××工程建设地方标准Issued by ××××××发布Issued by Ministry of Construction of the People’sRepublic of China由中华人民共和国建设部发布Jointly issued by Ministry of Construction andGeneral Administration of Quality Supervision, Inspection and Quarantine of the People’s Republic of China 中华人民共和国建设部、国家质量监督检验检疫总局联合发布Jointly issued by Ministry of Housing and Urban-Rural Development and General Administration of Quality Supervision,Inspection and Quarantine of the People’s Republic of China 中华人民共和国住房和城乡建设部、国家质量监督检验检疫总局联合发布Issued on May 23,20062006 年5月23日发布Implemented on M D,Y(Implemented on May 23,2006)××××年××月××日实施(2006年5月23日实施)工程建设标准英文版翻译细则×××× edition××××版Chief Development Department主编部门Chief Development Organization主编单位Approval Department批准部门Implementation date施行日期Announcement of Ministry of Construction of thePeople’s Republic of China中华人民共和国建设部公告Announcement of Housing and Urban-RuralDevelopment of the People’s Republic of China中华人民共和国住房和城乡建设部公告Notice on publishing the national standard of ×××关于发布国家标准×××的通知Announcement of publishing the partial revisionof national standard ×××关于发布国家标准×××局部修订的公告×××has been approved as a national standard witha serial number of ×××现批准×××为国家标准,标准编号为××××××are compulsory provisions and must beenforced strictly×××为强制性条文,必须严格执行××× shall be abolished simultaneously原×××同时废止The standard(code)comprises××chapters withthe main contents as follows本标准(规范)共分××章,其主要内容为Ministry of Construction is in charge of the administration of this standard(code)and the explanation of the compulsory provisions 本标准(规范)由建设部负责管理和对强制性条文的解释×××is responsible for the explanation of specifictechnical contents由×××负责具体技术内容的解释Authorized by×××,this code is published anddistributed by ×××本规范由×××组织×××出版发行be valid as usual继续有效Review复审Put on records备案Record Number备案号Additional explanation附加说明Foreword前言According to the requirements of Document JianBiao[×××]NO.×××issued by Ministry of Construction(MOC)-“Notice on Printing the Development and Revision Plan of National Engineering Construction Standards in ×××”根据建设部建标[×××]×××号《关于印发“×××年工程建设标准制订、修订计划”的通知》的要求The provision(s)printed in bold type is(are) compulsory one(ones)and must be enforced strictly 本规范以黑体字标志的条文为强制性条文,必须严格执行All relevant organizations are kindly requested tosum up and accumulate your experiences in actual practices during the process of implementing this code.The relevant opinions and advice, whenever necessary, can be posted or passed on to ×××请各单位在执行本标准过程中,注意总结经验,积累资料,相关的见解和建议,随时寄交×××Participating Development Organizations参编单位Participating Organizations参加单位Chief Drafting Staff主要起草人Routine management日常管理Specific explanation具体解释Contents目次(目录)General provisions总则Terms and symbols术语和符号Appendix附录Explanation of Wording in this code本规范用词说明This code is formulated with a view to ×××为了×××,制定本规范Safety and usability安全适用Economy and rationality经济合理This standard (code) is applicable to ……本标准(规范)适用于……This standard (code) is not applicable to ……本标准(规范)不适用于……Construction, extension and renovation新建、扩建、改建Not only the requirements stipulated in this standard(code),but also those in the current relevant ones of the nation shall be complied with 除应符合本标准(规范)要求外,尚应符合国家现行有关标准(规范)的规定Must必须Must not严禁Shall应Shall not不应Should宜Should not不宜May可May not不可Be in accordance with the following requirements符合下列规定(要求)Shall meet the requirements of ×××应符合×××的规定(要求)Shall comply with ×××应按×××执行Be in compliance with the following requirements遵守下列规定(要求)Be in accordance with those specified in Table×××符合表×××的规定(要求)Be determined according to those set out in Table×××按照表×××的规定(要求)确定Be calculated according to the following equation按下式计算Be calculated according to the following formulae按下列公式计算If one of the following requirements is met,……shall ……符合下列情况之一的,应……Where式中Note注Figure or Fig.图Be larger than大于Be less than小于Be equal等于Exceed超过Current relevant standard of the nation国家现行有关标准Current national standard现行国家标准General requirement一般规定(要求)Basic requirement基本规定(要求)Particular requirement特殊规定(要求)1.Words used for different degrees of strictnessare explained as follows in order to mark the differences in executing the requirements in this code.1.为了便于在执行本规范条文时区别对待,对要求严格程度不同的用词说明如下:1)Words denoting a very strict or mandatoryrequirement:1) 表示很严格,非这样做不可的用词:“Must”is used for affirmation;“must not”fornegation.正面词采用“必须”,反面词采用“严禁”。

凡是获得有关基金资助项目的研究成果,必须严格按规定进行标注,项目结束后所填报的《总结报告》及所附有效论著(标注过的),将作为申请新项目时的评审依据。
标注位置应在学术论著、鉴定证书、技术资料及其他有效证明材料的封面,或书前扉页,或论文首页、致谢部分。
不完全统计表明,国内期刊多习惯于将基金资助项目的信息作为论文首页的脚注,国外期刊则多将其作为“致谢”的一部分标注。
通常情况下只需列出项目的资助号即可,不必标注具体的项目名称。
如: The Project Supported by Zhejiang Provincial Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant No. 1234567), the Major State Basic Research Development Program of China (Grant No. G2000077405) and the Key Project of Science and Technology of Shanghai (Grant No. 02DZ/5002).对于国家自然科学基金资助项目,通常只需要统一标注“Natio nal Natural Science Foundation of China”和项目的资助号即可,不必再分别标“注面上项目”(General Program), “重点项目”(Key Program), “重大项目”(Major Program)等进一步信息。
以下是部分基金资助项目的英文翻译,供各位科研人员参考。
科技部国家高技术研究发展计划(863计划): National High-tech R&D Program of China (863 Program);国家重点基础研究发展规划(973计划): National Program on Key Basic Research Project (973 Program)国家985重点建设项目: Key Construction Program of the National “985” Project“九五”攻关项目: National Key Technologies R & D Program of China during the 9th Five-Year Plan Period国家基础研究计划: National Basic Research Priorities Program of China;国家科技攻关计划: National Key Technologies R & D Program of China;国家攀登计划—B课题资助: Supported by National Climb—B Plan国家重大科学工程二期工程基金资助: National Important Project on Science-Phase Ⅱof NSRL教育部国家教育部科学基金资助: Science Foundation of Ministry of Education of China教育部科学技术研究重点(重大)项目资助: Key (Key grant) Project of Chinese Ministry of Education国家教育部博士点基金资助项目: Ph.D. Programs Foundation of Ministry of Education of China高等学校博士学科点专项科研基金: Research Fund for the Doctoral Program of Higher Education of China (缩写: RFDP)国家教育部博士点专项基金资助: Doctoral Fund of Ministry of Education of China中国博士后科学基金: Supported by China Postdoctoral Science Foundation国家教育部回国人员科研启动基金资助: Scientific Research Foundation for Returned Scholars, Ministry of Education of China国家教育部留学回国人员科研启动金: Scientific Research Foundation for the Returned Overseas Chinese Scholars, State Education Ministry (SRF for ROCS, SEM)跨世纪优秀人才计划国家教委《跨世纪优秀人才计划》基金: Trans-Century Training Programme Foundation for the Talents by the State Education Commission国家教育部优秀青年教师基金资助: Science Foundation for The Excellent Youth Scholars of Ministry of Education of China高等学校骨干教师资助计划: Foundation for University Key Teacher by the Ministry of Education of China中国科学院中国科学院基金资助: Science Foundation of the Chinese Academy of Sciences中国科学院重点资助项目: Key Program of the Chinese Academy of Sciences中国科学院知识创新项目: Knowledge Innovation Program of the Chinese Academy of Sciences;中国科学院“九五”重大项目: Major Programs of the Chinese Academy of Sciences during the 9th Five-Year Plan Period;中国科学院百人计划经费资助: One Hundred Person Project of the Chinese Academy of Sciences中国科学院院长基金特别资助: Special Foundation of President of the Chinese Academy of Sciences中国科学院西部之光基金: West Light Foundation of The Chinese Academy of Sciences中国科学院国际合作局重点项目资助: Supported by Bureau of International Cooperation, Chinese Academy of Sciences中国科学院上海分院择优资助项目: Advanced Programs of Shanghai Branch, the Chinese Academy of Sciences;基金委国家自然科学基金(面上项目; 重点项目; 重大项目): National Natural Science Foundation of China (General Program; Key Program; Major Program);国家杰出青年科学基金: National Science Fund for Distinguished Young Scholars;国家自然科学基金国际合作与交流项目: Supported by Projects of International Cooperation and Exchanges NSFC海外及香港、澳门青年学者合作研究基金: Joint Research Fund for Overseas Chinese, Hong Kong and Macao Young Scholars其他浙江省自然科学基金:Zhejiang Provincial Natural Science Foundation of China日本科学技术厅科学家交流项目: Japan STA Scientist Exchange Program海峡两岸自然科学基金共同资助: Science Foundation of Two sides of Strait“九五”国家医学科技攻关基金资助项目: National Medical Science and Technique Foundation during the 9th Five-Year Plan Period;核工业科学基金资助: Science Foundation of Chinese Nuclear Industry北京正负电子对撞机国家实验室重点课题资助: BEPC National Laboratory兰州重离子加速器国家实验室原子核理论中心基金资助: Supported by Center of Theoretical Nuclear Physics, National Laboratory of Heavy Ion Accelerator of Lanzhou北京市自然科学基金资助: Beijing Municipal Natural Science Foundation河南省教育厅基金资助: Foundation of He’nan Educational Committee河南省杰出青年基金(9911)资助: Excellent Youth Foundation of He’nan Scientific Committee黑龙江省自然科学基金资助: Natural Science Foundation of Heilongjiang Province of China湖北省教育厅重点项目资助: Educational Commission of Hubei Province of China江苏省科委应用基础基金资助项目: Applied Basic Research Programs of Science and Technology Commission Foundation of Jiangsu Province.山西省归国人员基金资助: Shanxi Province Foundation for Returness山西省青年科学基金资助: Shanxi Province Science Foundation for Youths上海市科技启明星计划资助: Shanghai Science and Technology Development Funds东南大学基金资助: Foundation of Southeast of University华北电力大学青年科研基金资助: Youth Foundation of North-China Electric Power University华中师范大学自然科学基金资助: Natural Science Foundation of Central China Normal University西南交通大学基础学科研究基金资助: Foundation Sciences Southwest Jiaotong University基金项目英文翻译1 国家高技术研究发展计划资助项目(863计划)(No. )This work was supported by a grant from the National High Technology Research and Development Program of China (863 Program) (No. )2 国家自然科学基金资助项目(No. )General Program(面上项目), Key Program(重点项目), Major Program(重大项目)This work was supported by a grant from the National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. )3 国家“九五”攻关项目(No. )This work was supported by a grant from the National Key Technologies R & D Program of China during the 9th Five-Year Plan Period (No. )4 中国科学院“九五”重大项目(No. )This work was supported by a grant from the Major Programs of the Chinese Academy of Sciences during the 9th Five-Year Plan Period (No. )5 中国科学院重点资助项目(No. )This work was supported by a grant from the Key Programs of the Chinese Academy of Sciences (No. )6 “九五”国家医学科技攻关基金资助项目(No. )This work was supported by a grant from the National Medical Science and Technique Foundation during the 9th Five-Year Plan Period (No. )7 江苏省科委应用基础基金资助项目(No. )This work was supported by a grant from the Applied Basic Research Programs of Science and Technology Commission Foundation of Jiangsu Province (No. )8 国家教育部博士点基金资助项目(No. )This work was supported by a grant from the Ph.D. Programs Foundation of Ministry of Education of China (No. )9 中国科学院上海分院择优资助项目(No. )This work was supported by a grant from Advanced Programs of Shanghai Branch, the Chinese Academy of Sciences (No. )10 国家重点基础研究发展规划项目(973计划)(No. )This work was supported by a grant from the Major State Basic Research Development Program of China (973 Program) (No. )11 国家杰出青年科学基金(No. )This work was supported by a grant from National Science Fund for Distinguished Young Scholars (No. )12 海外香港青年学者合作研究基金(No. )This work was supported by a grant from Joint Research Fund for Young Scholars in Hong Kong and Abroad (No. )各项基金资助书写格式(中英文对照)浙江省自然科学基金中文标注:浙江省自然科学基金资助项目(项目编号:)英文标注:The Project Supported by Zhejiang Provincial Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant No. )中国科学院基金资助Supported by Science Foundation of The Chinese Academy of Sciences中国科学院九五重大项目(项目编号:)资助Supported by Major Subject of The Chinese Academy of Sciences(项目编号:)中国科学院院长基金特别资助Supported by Special Foundation of President of The Chinese Academy of Sciences中国科学院国际合作局重点项目资助Supported by Bureau of International Cooperation, The Chinese Academy of Sciences中国科学院百人计划经费资助Supported by 100 Talents Program of The Chinese Academy of SciencesSupported by One Hundred Person Project of The Chinese Academy of Sciences中国科学院知识创新工程重大项目资助Supported by Knowledge Innovation Project of The Chinese Academy of SciencesSupported by Knowledge Innovation Program of The Chinese Academy of Sciences中国科学院西部之光基金(项目编号:)资助Supported by West Light Foundation of The Chinese Academy of Sciences(项目编号:)北京正负电子对撞机国家实验室重点课题资助Supported by BEPC National Laboratory兰州重离子加速器国家实验室原子核理论中心基金资助Supported by Center of Theoretical Nuclear Physics, National Laboratory of Heavy Ion Accelerator of Lanzhou。

工程建设标准英文版翻译细则(试行)为规范工程建设标准英文版的翻译工作,根据《工程建设标准翻译出版工作管理办法》,制定本细则。
1 翻译质量及技术要求1.1 基本要求1)工程建设标准的翻译必须忠于原文,并遵守完整、准确、规范、统一的原则。
2)标准的译文应当完整。
标准的前引部分、正文部分、补充部分都应全文翻译;脚注、附录、图、表、公式以及相应的文字都应翻译并完整地反映在译文中,不得误译、缺译、漏译、跳译。
3)强制性条文的翻译必须准确无误,译文用黑体字注明。
4)译文的内容、术语应当准确,语法应当恰当,行文流畅。
5)标准中的典型语句、术语、计量单位、专业词汇应当前后统一。
6)标准翻译稿的幅面、版面、格式、字体等应当规范并符合《工程建设标准英文版出版印刷规定》,图表、公式的编号应与原文相一致。
1.2 具体要求1)数字表达应符合英文表达习惯。
2)标准中的符号、代号、计量单位、公式应直接引用原文,时间、货币、标点符号可按英文惯例翻译或表达。
3)日期按译文语言,应采用公历,按月、日、年顺序排列(例如,December 1,20XX)。
4)术语的英文翻译,应以中文版中的英文术语为准。
如果中文版中英文术语表达不准确或出现错误,应由翻译人员与编制组共同商议后做出必要修正,并在译文中注明。
5)标准名称应以中文版的英文译名为准。
如果中文版标准名称的英文译文不准确,翻译人员可向翻译出版办公室提出书面修改建议。
6)人员的中文姓名译成英文时,采用标准汉语拼音。
外籍人员的姓名应按其原姓名或相应的英文姓名表达。
地名、团体名、机构名,使用惯用译名。
无惯用译名的,可自行翻译,必要时附注原文。
7)法律、法规、规范性文件等名称应采用官方或既定译法,其他文件、著作、文献名称采用既定译法。
8)缩写词首次出现时,应附注全称译文。
经前文注释过或意义明确的缩写词,可以在译文中直接使用。
9)译文的章节条款项的编号,应与中文版一致。
10)对我国独有的直译较难的词,可以意译,也可采用汉语拼音,必要时可加附注。
中国国家标准中英文对照翻译(城镇建设工程标准)中国国家标准——城镇建设工程标准GB〖CJJ1-90〗市政道路工程质量检验评定标准Standard for quality test and estimation of municipal road engineering〖CJJ2-2008〗城市桥梁工程施工与质量验收规范Code for construction and quality acceptance of bridge works in city〖CJJ6-85〗排水管道维护安全技术规程Technical specification for safety maintenance of sewerage pipes〖CJJ7-2007〗城市工程地球物理探测规范Code for engineering geophysical prospecting and testing in city〖CJJ8-99〗城市测量规范Code for urban survey〖CJJ11-93〗城市桥梁设计准则The Criteria of Municipal Bridge Design〖CJJ12-99〗家用燃气燃烧器具安装及验收规程Specification for installation and acceptance of domestic gas burning appliances 〖CJJ13-87〗供水水文地质钻探与凿井操作规程Specification for operation of hydrographic geological drilling and digging for water-supply〖CJJ14-2005〗城市公共厕所设计标准Standard for design of public toilets in city〖CJJ15-87〗城市公共交通站、场、厂设计规范Code for design of urban public transportation station, ground and house〖CJJ17-2004〗生活垃圾卫生填埋技术规范Technical code for municipal solid waste sanitary landfill〖CJJ18-88〗市政工程施工、养护及污水处理工人技术等级标准Technical level standard for workers of construction maintenance and sewerage treatment of municipal engineering〖CJJ27-2005〗城镇环境卫生设施设置标准Standard for setting of town environmental sanitation facilities〖CJJ28-2004〗城镇供热管网工程施工及验收规范Code for construction and acceptance of city heating pipelines〖CJJ/T29-98〗建筑排水硬聚氯乙烯管道工程技术规程Technical specification of PVC-U pipe work for building drainage〖CJJ30-2009〗城市粪便处理厂运行维护及其安全技术规程Technical specification for operation maintenance and safety of night soil treatment plants〖CJJ32-89〗含藻水给水处理设计规范Code for design of water supply treatment for water with algae〖CJJ33-2005〗城镇燃气输配工程施工及验收规范Code for construction and acceptance of city and town gas distribution works〖CJJ34-2002〗城市热力网设计规范Design code of district heating network〖CJJ36-2006〗城镇道路养护技术规范Technical code of urban road maintenance〖CJJ37-90〗城市道路设计规范Code for design of municipal road〖CJJ39-91〗古建筑修建工程质量检验评定标准(北方地区)Standard for quality test and estimation of ancient building repairing engineering (in northern area)〖CJJ40-91〗高浊度水给水设计规范Code for design of water-supply for muddy water〖CJJ43-91〗热拌再生沥青混合料路面施工及验收规程Specification for construction and acceptance of hot-mixed and regenerated asphalt mixture road face〖CJJ45-2006〗城市道路照明设计标准Standard for lighting design of urban road〖CJJ47-2006〗生活垃圾转运站技术规范Technical code for transfer station of municipal solid waste〖CJJ48-92〗公园设计规范Code for design of parks〖CJJ50-92〗城市防洪工程设计规范Code for design of flood control engineering in city〖CJJ51-2006〗城镇燃气设施运行、维护和抢修安全技术规程Safety technical specification for operation, maintenance and rush-repair of city gas facilities〖CJJ/T52-93〗城市生活垃圾好氧静态堆肥处理技术规程Technical specification for static aerobic composting of municipal solid waste〖CJJ/T53-93〗民用房屋修缮工程施工规程Code for repairing construction of civil buildings〖CJJ/T54-93〗污水稳定塘设计规范Code for design of wastewater stabilization ponds〖CJJ55-93〗供热术语标准Standard for terminology of heat-supply〖CJJ56-94〗市政工程勘察规范Code for investigation and surveying of municipal engineering〖CJJ57-94〗城市规划工程地质勘察规范Code for geotechnical investigation and surveying of urban planning engineering〖CJJ58-2009〗城镇供水厂运行、维护及安全技术规程Technical specification for operation, maintenance and safety of city and town waterworks〖CJJ60-94〗城市污水处理厂运行、维护及其安全技术规程Technical specification for operation, maintenance and safety of municipal wastewater treatment plants〖CJJ61-2003〗城市地下管线探测技术规程Technical specification for detecting and surveying of under-ground pipelines and cables in city〖CJJ62-95〗房屋渗漏修缮技术规程Technical specification for repairing water creep of houses〖CJJ63-2008〗聚乙烯燃气管道工程技术规程Technical specification for polyethylene (PE) gas pipeline engineering〖CJJ64-2009〗城市粪便处理厂设计规范Code for design of night soil treatment plant〖CJJ/T65-2004〗市容环境卫生术语标准Standard for terminology of environmental sanitation〖CJJ66-95〗路面稀浆封层施工规程Slurry sealing specification〖CJJ67-95〗风景园林图例图示标准Standard for graphic of landscape architecture〖CJJ68-2007〗城镇排水管渠与泵站维护技术规程Technical specification for maintenance of sewers & channels and pumping station in city〖CJJ69-95〗城市人行天桥与人行地道技术规范Technical specification of urban pedestrian overcrossing and underpass〖CJJ70-96〗古建筑修建工程质量检验评定标准(南方地区)Standard for quality test and estimation of ancient building repairing engineering (in southern area)〖CJJ71-2000〗机动车清洗站工程技术规程Technical specification for automotive rinsing station engineering〖CJJ72-97〗无轨电车供电线网工程施工及验收规范Code for installation and acceptance of trolley bus network〖CJJ73-97〗全球定位系统城市测量技术规程Technical specification for urban surveying using global positioning system〖CJJ74-99〗城镇地道桥顶进施工及验收规程Specification for construction and acceptance of underpass bridges in town by jacking method〖CJJ75-97〗城市道路绿化规划与设计规范Code for planting planning and design on urban roads〖CJJ/T76-98〗城市地下水动态观测规程Specification for dynamic observation of ground water in urban area〖CJJ/T78-97〗供热工程制图标准Drawing standard of heat-supply engineering〖CJJ/T81-98〗城镇直埋供热管道工程技术规程Technical specification for directly buried heating pipeline engineering in city〖CJJ/T82-99〗城市绿化工程施工及验收规范Code for construction and acceptance of plant engineering in city and town〖CJJ83-99〗城市用地竖向规划规范Code for vertical planning on urban field〖CJJ/T85-2002〗城市绿地分类标准Standard for classification of urban green space〖CJJ/T86-2000〗城市生活垃圾堆肥处理厂运行、维护及其安全技术规程Technical specification for operation maintenance and safety of municipal solid waste composting plant〖CJJ/T87-2000〗乡镇集贸市场规划设计标准Standard for market planning of town and township〖CJJ/T88-2000〗城镇供热系统安全运行技术规程Technical specification for safe operation of heating system in city〖CJJ89-2001〗城市道路照明工程施工及验收规程Specification for construction and inspection of urban road lighting engineering〖CJJ90-2009〗生活垃圾焚烧处理工程技术规范Technical code for projects of municipal solid waste incineration〖CJJ/T91-2002〗园林基本术语标准Standard for basic terminology of landscape architecture〖CJJ92-2002〗城市供水管网漏损控制及评定标准Standard for leakage control and assessment of urban water supply distribution system〖CJJ93-2003〗城市生活垃圾卫生填埋场运行维护技术规程Technical specification for operation and maintenance of municipal domestic refuse sanitary landfill〖CJJ94-2009〗城镇燃气室内工程施工与质量验收规范Code for construction and quality acceptance of city indoor gas engineering〖CJJ95-2003〗城镇燃气埋地钢质管道腐蚀控制技术规程Technical specification for control of external corrosion on underground gas pipeline of steel in area of cities and towns〖CJJ96-2003〗地铁限界标准Standard of metro gauges〖CJJ/T97-2003〗城市规划制图标准Standard for drawing in urban planning〖CJJ/T98-2003〗建筑给水聚苯乙烯类管道工程技术规程Technical specification of polyethylene (PE), cross-linked polyethylene (PE-X) and polyethylene of raised temperature resistance (PE-RT) pipeline engineering for water supply in building〖CJJ99-2003〗城市桥梁养护技术规范Technical code maintenance for city bridge〖CJJ100-2004〗城市基础地理信息系统技术规范Technical specification for urban fundamental geographic information system〖CJJ101-2004〗埋地聚乙烯给水管道工程技术规程Technical specification for buried polyethylene pipeline of water supply engineering〖CJJ/T102-2004〗城市生活垃圾分类及其评价标准Classification and evaluation standard of municipal solid waste〖CJJ103-2004〗城市地理空间框架数据标准Standard for urban geospatial framework data〖CJJ104-2005〗城镇供热直埋蒸汽管道技术规程Technical specification for directly buried steam heating pipeline in city〖CJJ105-2005〗城镇供热管网结构设计规范Code for structural design of heating pipelines in city and town〖CJJ/T106-2005〗城市市政综合监管信息系统技术规范Technical code for urban municipal supervision and management information system〖CJJ/T107-2005〗生活垃圾填埋场无害化评价标准Standard of assessment on municipal solid waste and fill〖CJJ/T108-2006〗城市道路除雪作业技术规程Technical specification of snow removal operation for city road〖CJJ109-2006〗生活垃圾转运站运行维护技术规程Technical specification for operation and maintenance of municipal solid waste transfer station〖CJJ110-2006〗管道直饮水系统技术规程Technical specification of pipe system for fine drinking water〖CJJ/T111-2006〗预应力混凝土桥梁预制节段逐跨拼装施工技术规程Technical specification for construction of span by span method of precast segment in prestressed concrete bridge〖CJJ112-2007〗生活垃圾卫生填埋场封场技术规程Technical code for municipal solid waste sanitary landfill closure〖CJJ113-2007〗生活垃圾卫生填埋场防渗系统工程技术规范Technical code for liner system of municipal solid waste landfill〖CJJ/T114-2007〗城市公共交通分类标准Standard for classification of urban public transportation〖CJJ/T115-2007〗房地产市场信息系统技术规范Technical code for real estate market information system〖CJJ/T116-2008〗建设领域应用软件测评通用规范General code for measure and evaluation of application software in the field of construction〖CJJ/T117-2007〗建设电子文件与电子档案管理规范Code for management of electronic construction records and archives〖CJJ/T119-2008〗城市公共交通工程术语标准Terminology standard for urban public transport engineering〖CJJ120-2008〗城镇排水系统电气与自动化工程技术规程Technical specification of electrical & automation engineering for city drainage system〖CJJ124-2008〗镇(乡)村排水工程技术规程Technical specification of wastewater engineering for town and village〖CJJ/T126-2008〗城市道路清扫保洁质量与评价标准Standard for quality and assessment of city road sweeping and cleaning〖CJJ/T125-2008〗环境卫生图形符号标准Standard for figure symbols of environmental sanitation〖CJJ122-2008〗游泳池给水排水工程技术规程Technical specification for water supply and drainage engineering of swimming pool〖CJJ123-2008〗镇(乡)村给水工程技术规程Technical specification of water supply engineering for town and village〖CJJ128-2009〗生活垃圾焚烧厂运行维护与安全技术规程Technical specification for operation maintenance and safety of municipal solid waste incineration plant〖CJJ127-2009〗建筑排水金属管道工程技术规程Technical specification of metal pipe work for building drainage。
国家科技部博士后基金(批准号: )资助的课题. Project supported by the Science Foundation for Post Doctorate Research from the Ministry of Science and Technology of China (Grant No. ).国家科技部攀登计划二号重点项目基金(批准号: )资助的课题. Project supported by a Grant for Key Research Items No.2 in “Climbing” Program from the Ministry of Science and Technology of China (Grant No. ).国家科技部攀登计划重点研究项目基金(批准号: )资助的课题. Project supported by a Grant for Key Research Items in “Climbing” Program from the Ministry of Science and Technology of China (Grant No. ).国家攀登计划(纳米晶体材料)(批准号: )资助的课题. Project supported by the National “Climbing”Program for Nanocrystalline Materials, China (Grant No. )国家攀登计划(批准号: )资助的课题. Project supported by the National“Climbing”Program of China (Grant No. ).国家攀登计划基础研究(批准号: )资助的课题. Project supported by the National Basic Research in “Climbing” Program of China (Grant No. ).国家青年科学基金(批准号: )资助的课题. Project supported by the National Science Foundation for Young Scientists of China (Grant No. ).国家重大国际(地区)合作研究项目. Project supported by the Major International (Regional ) Joint Research Program of China(Grant No. )国家重大基础研究项目(批准号: )资助的课题. Project supported by the National Major Fundamental Research Program of China (Grant No. ).国家重点基础研究发展计划(973)项目(批准号: )资助的课题. Project supported by the State Key Development Program for Basic Research of China (Grant No. ). 网上写法为: Project supported by the National Basic Research Program of China(Grant No. )国家重点基础研究项目(批准号: )资助的课题. Project supported by the State Key Program for Basic Research of China (Grant No. ).国家重点基础研究项目特别基金(批准号: )资助的课题. Project Supported by the National Key Basic Research Special Foundation of China (NKBRSFC) (Grant No. ).国家重点基础研究专项基金(批准号: )资助的课题. Project supported by the Special Foundation for State Major Basic Research Program of China (Grant No. ).国家重点实验室(光技术应用于微加工实验室),上海光学及电子研究所(批准号: )资助的课题. Project supported by the State Key Laboratory of Optical Technology for Micro-fabrication, Shanghai Institute of Optics and Electronics, China (Grant No. ).国家自然科学基金(批准号: )资助的课题. Project supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant No. ).国家自然科学基金重大项目(批准号: )资助的课题. Project supported by the Major Program of the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant No. ).国家自然科学基金重大研究计划(批准号: )资助的课题. Project supported by the Major Research plan of the National Natural Science Foundation of China(Grant No. )国家自然科学基金重点项目(批准号: )资助的课题. Project supported by the State Key Program of National Natural Science of China(Grant No. ).教育部磁学与磁性材料重点实验室(批准号: )资助的课题. Project supported by the Key Laboratory for Magnetism and Magnetic Material of the Education Ministry of China (Grant No. ).教育部科学技术研究重大项目基金(批准号: )资助的课题 Project supported by the Foundation for Key Program of Ministry of Education,China(Grant No. ).教育部量子光学重点实验室(批准号: )资助的课题. Project supported by the Key Laboratory of Quantum Optics, Ministry of Education, China (Grant No. ).教育部留学回国人员科研启动基金(批准号: )资助的课题. Project supported by the Scientific Research Starting Foundation for Returned Overseas Chinese Scholars, Ministry of Education ,China (Grant No. )教育部重大项目基金(批准号: )资助的课题 Project supported by the Research Foundation from Ministry of Education of China (Grant No. ).科技部重大基础研究前期研究专项基金(批准号: )资助的课题. Project supported by the Special Program for Key Basic Research of the Ministry of Science and Technology,China(Grant No. ).空间研究基金(批准号: )资助的课题. Project supported by the Aerospace Research Foundation of China (Grant No. ).人工微结构和介观物理国家重点实验室(批准号: )资助的课题. Project supported by the State Key Laboratory for Artificial Microstructure and Mesoscopic Physics, Peking University, Beijing, China (Grant No. ).1、国家自然科学基金(项目编号:)资助Supported by National Natural Science Foundation of China(项目编号:)[Supported by NSFC(项目编号:)]2、国家自然科学基金重大项目资助Supported by Major Program of National Natural Science Foundation of China (1991483)3、国家自然科学基金国际合作与交流项目(项目编号:)资助Supported by Projects of International Cooperation and Exchanges NSFC(项目编号:)4、国家重点基础研究发展规划项目(项目编号:)资助 (973计划项目)Supported by Major State Basic Research Development Program(项目编号:)Supported by China Ministry of Science and Technology under Contract(项目编号:)Supported by State Key Development Program of (for) Basic Research of China(项目编号:)5、国家高技术研究发展计划(863计划)资助Supported by National High Technology Research and Development Program of China6、国家杰出青年科学基金资助Supported by National Natural Science Funds for Distinguished Young Scholar7、国家科技部基金资助Supported by State Commission of Science Technology of China(科委)Supported by Ministry of Science and Technology of China8、中国博士后科学基金Supported by China Postdoctoral Science Foundation9、海峡两岸自然科学基金(项目编号:)共同资助Supported by Science Foundation of Two sides of Strait(项目编号:)10、国家教育部科学基金资助Supported by Science Foundation of The Chinese Education Commission (教委)Supported by Science Foundation of Ministry of Education of China11、国家教育部博士点专项基金资助Supported by Doctoral Fund of Ministry of Education of China (缩写: RFDP)12、教育部科学技术研究重点(重大)项目资助英文:Supported by the Key(Key grant) Project of Chinese Ministry of Education.(NO……)13、国家教育部留学回国人员科研启动基金资助项目英文:The Project Sponsored by the Scientific Research Foundation for the Returned Overseas Chinese Scholars, State Education Ministry.缩写:The Project-sponsored by SRF for ROCS, SEM.14、国家教育部优秀青年教师基金资助Supported by Science Foundation for The Excellent Youth Scholars of Ministry of Education of China15、高等学校博士学科点专项科研基金资助Supported by Research Fund for the Doctoral Program of Higher Education of ChinaSupported by Doctoral Program Foundation of Institutions of Higher Education of China16、国家教委《跨世纪优秀人才计划》基金Trans-Century Training Programme Foundation for the Talents by the State Education Commission17、高等学校骨干教师资助计划资助英文:Supported by Foundation for University Key Teacher by the Ministry of Education18、霍英东教育基金会青年教师基金资助Supported by Fok Ying Tung Education Foundation19、广东省自然科学基金资助Supported by Natural Science Foundation of Guangdong Province, China20、广东省教育厅项目资助Supported by Educational Commission of Guangdong Province, China21、广东省科技计划项目资助Supported by Science and Technology Planning Project of Guangdong Province, China22、广东省医学科研基金项目(卫生厅)资助Supported byMedical Scientific Research Foundation of Guangdong Province, China23、广东省中医药管理局项目资助Supported by Administration of Traditional Chinese Medicine of Guangdong Province, China24、国家中医药管理局项目资助Supported by State Administration of Traditional Chinese Medicine of People’s Republic of China水工隧洞: hydraulic tunne1. 国家973项目:“深长隧道突水突泥致灾机理及预警与控制理论”,主要参与.1.the National Basic Research Program of China (973 Program) : "mechanism of water or mud inrush hazard in deeply and long excavated tunnel and its warning and control theory" , Primary participant2. 国家重点基金项目:“水工隧洞突水涌泥灾害源超前预报定量识别方法及灾害发生机理与控制研究”,主要参与.2.the National Basic Research Program of China (973 Program) : " quantified identification Prognosis of water or mud inrush hazard in hydraulic tunnel and research on its mechanism and control " , Primary participant3. “十二五”国家科技支撑计划:“煤矿突水、火灾等重大事故防治关键技术与装备研发”,主要参与.3. The National Key Technology R&D Program of the china's 12th five-year plan: "R&D on key technique and equipments for preventing and curing the severe accident such as water inrush or fire in colliery " , Primary participant1)国家高技术研究发展计划:the National High-Tech Research and Development Program of China(863 Program)2)国家科技攻关计划:the National Key Technologies R & D Progaram of China3)国家重点基础研究发展计划:the Major State Basic Research Development Program of China4)国家基础研究计划: the National Basic Research Priorities Program of China5)国家自然科学基金(面上项目;重点项目;重大项目):the National Natural Science Foundation of China(General Program; Key Program; Major Program )6)国家杰出青年科学基金: the National Science Fund for Distinguished Yonng Scholars7)海外及香港、澳门青年学者合作研究基金:the Joint Research Fund for Overseas Chinese, Hong Kong and Macao Young Scholars8)中国科学院知识创新项目:the Knowledge Innovation Programs of the Chinese Academy of Sciences9)中国科学院“九五”重大项目:the Major Programs of the Chinese Academy of Sciences during the 9th Five-Year Plan Period10)中国科学院重点资助项目:the Key Program of the Chinese Academy of Sciences11)中国科学院上海分院择优资助项目:the Advanced Programs of Shanghai Branch, the Chinese Academy of Sciences12)国家教育部博士点基金资助项目:the Ph.D. Programs Foundation of Ministry of Education of China13)“九五”国家医学科技攻关基金资助项目:the National Medical Science and Technique Foundation during the 9th Five-Year Period14)江苏省科委应用基础基金资助项目:the Applied Basic Research Programs of Science and Technology Commission Foundation of Jiangsu Province15)教育部留学回国人员科研启动基金资助项目:The Scientific Research Foundation for Returned Overseas Chinese Scholars, State Education Ministry举报删除此信息garylv (站内联系TA)我也找到一个版本不完全统计表明,国内期刊多习惯于将基金资助项目的信息作为论文首页的脚注,国外期刊则多将其作为“致谢”的一部分标注。
国家标准英文版翻译指南国家质量技术监督局质技监局标函[2000]39号关于印发《国家标准英文版翻译指南》的通知国务院务有关部门,全国各专业标准化技术委员会:为适应我国加入世界贸易组织(WTO)和标准化活动对外交流的需要,及时准确地把我国国家标准翻译成英文版本,我局组织制定了《国家标准英文版翻译指南》,现予以公布。
自公布之日起实行。
二○○○年二月十三日主题词:国家标准规定通知抄送:中国标准出版社、中国标准研究中心国家质量技术监督局办公室2000年2月12日印发国家标准英文版翻译指南国家质量技术监督局标准化司二○○○年二月目次1 前言2 格式3 用词和用语4 引用标准化中心附录A:封面格式附录B:首页格式一、前言为适应我国加入世界贸易组织和我国对外开放的需要,我局从1997年起开始将一部分国家标准翻译成英文。
在翻译过程中,不少有关单位建议对翻译的格式和通用用语进行规范。
为此,我司于1999年初成立了《国家标准英文版翻译指南》编制工作组,开始指南的起草工作。
编制《国家标准英文英文版翻译指南》的目的是:1.对国家标准英文版标准中需要统一的格式进行规范2.对国家标准英文版标准中需要统一的语句和用词进行规范3.对与现行GB1.1及ISO/IEC导则要求有出入的老格式标准文本中有必要进行调整的内容进行规范。
本指南适用于将我国国家标准翻译成英文文本的标准化中心二、格式2.1 等同/修改(等效)采用国际标准的国家标准应使用原英文版本,并符合ISO/IEC指南21(1999版)的要求。
2.2 对于非等效采用国际标准的国家标准,在翻译时应尽可能与原英文版本格式保持一致。
2.3 对于非采用国际标准的国家标准,在翻译时应尽可能以相应国际标准作为格式参考。
2.4 封面和首页格式见附录A和附录B。
三、用词和用语3.1 封面封面用语的英文表述3.1.1 中华人民共和国国家标准National Standard of the People's Republic of China3.1.2 国家质量技术监督局发布Issued by China State Bureau of Quality and Technical Supervision3.1.3 国家技术监督局发布Issued by China State Bureau of Technical Supervision3.1.4 国家标准局发布Issued by China State Bureau of Standards3.1.5 发布日期Issue date3.1.6 实施日期Implementation date3.1.7 等同采用IDT3.1.8 修改(等效)采用MOD3.1.9 非等效采用NEQ3.2 目次目次用语的英文表述3.2.1 目次contents3.2.2 附录annex3.2.3 参考文献bibliography3.2.4 索引index(es)3.2.5 图figure(s)3.2.6 表table(s)3.3 前言前言部分用语的英文表述3.3.1 前言Foreword3.3.2 本国家标准等同采用IEC (ISO) ××××标准: This national standard is identical to IEC (ISO) ××××3.3.3 本国家标准修改(等效)采用IEC(ISO) ××××标准:This national standard is modified in relation to IEC (ISO) ××××3.3.4 本国家标准非等效采用IEC (ISO) ××××标准:This national standard is not equivalent to IEC (ISO) ××××3.3.5 本国家标准附录××××是标准的附录(补充件)Annex ××××/Annexes ×××× of this national standard is/are normative3.3.6 本国家标准附录××××是提示的附录(参考件)Annex ××××/annexes ×××× of this national standard is/are informative3.3.7 本国家标准对先前版本技术内容作了下述重要修改There have been some significant changes in this national standard over its previous edition in the following technical aspects3.3.8 本国家标准与所采用国际标准的主要技术差异The main technical differences between the national standard and the international standard adopted3.3.9 本国家标准从实施日期起代替××××This national standard will replace ×××× from the implementation date of this standard3.3.10 本国家标准由××××提出This national standard was proposed by ××××3.3.11 本国家标准由××××归口This national standard is under the jurisdiction of ××××3.3.12 本国家标准由××××起草This national standard was drafted by ××××3.4 引言3.4.1 引言introduction3.5 范围范围部分用语的英文表述:3.5.1 主题和范围subject and the aspect(s) covered3.5.2 本国家标准规定……的尺寸This national s tandard specifies the dimensions of ……3.5.3 本国家标准规定……的方法This national standard specifies a method of ……3.5.4 本国家标准规定……的性能This national standard specifies the characteristics of ……3.5.5 本国家标准规定……的系统This national standard establishes a system for ……3.5.6 本国家标准规定……的基本原理This national standard establishes general principles for3.5.7 本国家标准适用于……This national standard is applicable to ……3.6 引用标准引语的英文表述(根据中文文本从a, b中选取):a. 下列标准中所包含的条文,通过在本标准中引用而构成为本标准的条文。