Mappings on matrices Invariance of functional values of matrix products
- 格式:pdf
- 大小:183.49 KB
- 文档页数:21


机器学习专业词汇中英⽂对照activation 激活值activation function 激活函数additive noise 加性噪声autoencoder ⾃编码器Autoencoders ⾃编码算法average firing rate 平均激活率average sum-of-squares error 均⽅差backpropagation 后向传播basis 基basis feature vectors 特征基向量batch gradient ascent 批量梯度上升法Bayesian regularization method 贝叶斯规则化⽅法Bernoulli random variable 伯努利随机变量bias term 偏置项binary classfication ⼆元分类class labels 类型标记concatenation 级联conjugate gradient 共轭梯度contiguous groups 联通区域convex optimization software 凸优化软件convolution 卷积cost function 代价函数covariance matrix 协⽅差矩阵DC component 直流分量decorrelation 去相关degeneracy 退化demensionality reduction 降维derivative 导函数diagonal 对⾓线diffusion of gradients 梯度的弥散eigenvalue 特征值eigenvector 特征向量error term 残差feature matrix 特征矩阵feature standardization 特征标准化feedforward architectures 前馈结构算法feedforward neural network 前馈神经⽹络feedforward pass 前馈传导fine-tuned 微调first-order feature ⼀阶特征forward pass 前向传导forward propagation 前向传播Gaussian prior ⾼斯先验概率generative model ⽣成模型gradient descent 梯度下降Greedy layer-wise training 逐层贪婪训练⽅法grouping matrix 分组矩阵Hadamard product 阿达马乘积Hessian matrix Hessian 矩阵hidden layer 隐含层hidden units 隐藏神经元Hierarchical grouping 层次型分组higher-order features 更⾼阶特征highly non-convex optimization problem ⾼度⾮凸的优化问题histogram 直⽅图hyperbolic tangent 双曲正切函数hypothesis 估值,假设identity activation function 恒等激励函数IID 独⽴同分布illumination 照明inactive 抑制independent component analysis 独⽴成份分析input domains 输⼊域input layer 输⼊层intensity 亮度/灰度intercept term 截距KL divergence 相对熵KL divergence KL分散度k-Means K-均值learning rate 学习速率least squares 最⼩⼆乘法linear correspondence 线性响应linear superposition 线性叠加line-search algorithm 线搜索算法local mean subtraction 局部均值消减local optima 局部最优解logistic regression 逻辑回归loss function 损失函数low-pass filtering 低通滤波magnitude 幅值MAP 极⼤后验估计maximum likelihood estimation 极⼤似然估计mean 平均值MFCC Mel 倒频系数multi-class classification 多元分类neural networks 神经⽹络neuron 神经元Newton’s method ⽜顿法non-convex function ⾮凸函数non-linear feature ⾮线性特征norm 范式norm bounded 有界范数norm constrained 范数约束normalization 归⼀化numerical roundoff errors 数值舍⼊误差numerically checking 数值检验numerically reliable 数值计算上稳定object detection 物体检测objective function ⽬标函数off-by-one error 缺位错误orthogonalization 正交化output layer 输出层overall cost function 总体代价函数over-complete basis 超完备基over-fitting 过拟合parts of objects ⽬标的部件part-whole decompostion 部分-整体分解PCA 主元分析penalty term 惩罚因⼦per-example mean subtraction 逐样本均值消减pooling 池化pretrain 预训练principal components analysis 主成份分析quadratic constraints ⼆次约束RBMs 受限Boltzman机reconstruction based models 基于重构的模型reconstruction cost 重建代价reconstruction term 重构项redundant 冗余reflection matrix 反射矩阵regularization 正则化regularization term 正则化项rescaling 缩放robust 鲁棒性run ⾏程second-order feature ⼆阶特征sigmoid activation function S型激励函数significant digits 有效数字singular value 奇异值singular vector 奇异向量smoothed L1 penalty 平滑的L1范数惩罚Smoothed topographic L1 sparsity penalty 平滑地形L1稀疏惩罚函数smoothing 平滑Softmax Regresson Softmax回归sorted in decreasing order 降序排列source features 源特征sparse autoencoder 消减归⼀化Sparsity 稀疏性sparsity parameter 稀疏性参数sparsity penalty 稀疏惩罚square function 平⽅函数squared-error ⽅差stationary 平稳性(不变性)stationary stochastic process 平稳随机过程step-size 步长值supervised learning 监督学习symmetric positive semi-definite matrix 对称半正定矩阵symmetry breaking 对称失效tanh function 双曲正切函数the average activation 平均活跃度the derivative checking method 梯度验证⽅法the empirical distribution 经验分布函数the energy function 能量函数the Lagrange dual 拉格朗⽇对偶函数the log likelihood 对数似然函数the pixel intensity value 像素灰度值the rate of convergence 收敛速度topographic cost term 拓扑代价项topographic ordered 拓扑秩序transformation 变换translation invariant 平移不变性trivial answer 平凡解under-complete basis 不完备基unrolling 组合扩展unsupervised learning ⽆监督学习variance ⽅差vecotrized implementation 向量化实现vectorization ⽮量化visual cortex 视觉⽪层weight decay 权重衰减weighted average 加权平均值whitening ⽩化zero-mean 均值为零Letter AAccumulated error backpropagation 累积误差逆传播Activation Function 激活函数Adaptive Resonance Theory/ART ⾃适应谐振理论Addictive model 加性学习Adversarial Networks 对抗⽹络Affine Layer 仿射层Affinity matrix 亲和矩阵Agent 代理 / 智能体Algorithm 算法Alpha-beta pruning α-β剪枝Anomaly detection 异常检测Approximation 近似Area Under ROC Curve/AUC Roc 曲线下⾯积Artificial General Intelligence/AGI 通⽤⼈⼯智能Artificial Intelligence/AI ⼈⼯智能Association analysis 关联分析Attention mechanism 注意⼒机制Attribute conditional independence assumption 属性条件独⽴性假设Attribute space 属性空间Attribute value 属性值Autoencoder ⾃编码器Automatic speech recognition ⾃动语⾳识别Automatic summarization ⾃动摘要Average gradient 平均梯度Average-Pooling 平均池化Letter BBackpropagation Through Time 通过时间的反向传播Backpropagation/BP 反向传播Base learner 基学习器Base learning algorithm 基学习算法Batch Normalization/BN 批量归⼀化Bayes decision rule 贝叶斯判定准则Bayes Model Averaging/BMA 贝叶斯模型平均Bayes optimal classifier 贝叶斯最优分类器Bayesian decision theory 贝叶斯决策论Bayesian network 贝叶斯⽹络Between-class scatter matrix 类间散度矩阵Bias 偏置 / 偏差Bias-variance decomposition 偏差-⽅差分解Bias-Variance Dilemma 偏差 – ⽅差困境Bi-directional Long-Short Term Memory/Bi-LSTM 双向长短期记忆Binary classification ⼆分类Binomial test ⼆项检验Bi-partition ⼆分法Boltzmann machine 玻尔兹曼机Bootstrap sampling ⾃助采样法/可重复采样/有放回采样Bootstrapping ⾃助法Break-Event Point/BEP 平衡点Letter CCalibration 校准Cascade-Correlation 级联相关Categorical attribute 离散属性Class-conditional probability 类条件概率Classification and regression tree/CART 分类与回归树Classifier 分类器Class-imbalance 类别不平衡Closed -form 闭式Cluster 簇/类/集群Cluster analysis 聚类分析Clustering 聚类Clustering ensemble 聚类集成Co-adapting 共适应Coding matrix 编码矩阵COLT 国际学习理论会议Committee-based learning 基于委员会的学习Competitive learning 竞争型学习Component learner 组件学习器Comprehensibility 可解释性Computation Cost 计算成本Computational Linguistics 计算语⾔学Computer vision 计算机视觉Concept drift 概念漂移Concept Learning System /CLS 概念学习系统Conditional entropy 条件熵Conditional mutual information 条件互信息Conditional Probability Table/CPT 条件概率表Conditional random field/CRF 条件随机场Conditional risk 条件风险Confidence 置信度Confusion matrix 混淆矩阵Connection weight 连接权Connectionism 连结主义Consistency ⼀致性/相合性Contingency table 列联表Continuous attribute 连续属性Convergence 收敛Conversational agent 会话智能体Convex quadratic programming 凸⼆次规划Convexity 凸性Convolutional neural network/CNN 卷积神经⽹络Co-occurrence 同现Correlation coefficient 相关系数Cosine similarity 余弦相似度Cost curve 成本曲线Cost Function 成本函数Cost matrix 成本矩阵Cost-sensitive 成本敏感Cross entropy 交叉熵Cross validation 交叉验证Crowdsourcing 众包Curse of dimensionality 维数灾难Cut point 截断点Cutting plane algorithm 割平⾯法Letter DData mining 数据挖掘Data set 数据集Decision Boundary 决策边界Decision stump 决策树桩Decision tree 决策树/判定树Deduction 演绎Deep Belief Network 深度信念⽹络Deep Convolutional Generative Adversarial Network/DCGAN 深度卷积⽣成对抗⽹络Deep learning 深度学习Deep neural network/DNN 深度神经⽹络Deep Q-Learning 深度 Q 学习Deep Q-Network 深度 Q ⽹络Density estimation 密度估计Density-based clustering 密度聚类Differentiable neural computer 可微分神经计算机Dimensionality reduction algorithm 降维算法Directed edge 有向边Disagreement measure 不合度量Discriminative model 判别模型Discriminator 判别器Distance measure 距离度量Distance metric learning 距离度量学习Distribution 分布Divergence 散度Diversity measure 多样性度量/差异性度量Domain adaption 领域⾃适应Downsampling 下采样D-separation (Directed separation)有向分离Dual problem 对偶问题Dummy node 哑结点Dynamic Fusion 动态融合Dynamic programming 动态规划Letter EEigenvalue decomposition 特征值分解Embedding 嵌⼊Emotional analysis 情绪分析Empirical conditional entropy 经验条件熵Empirical entropy 经验熵Empirical error 经验误差Empirical risk 经验风险End-to-End 端到端Energy-based model 基于能量的模型Ensemble learning 集成学习Ensemble pruning 集成修剪Error Correcting Output Codes/ECOC 纠错输出码Error rate 错误率Error-ambiguity decomposition 误差-分歧分解Euclidean distance 欧⽒距离Evolutionary computation 演化计算Expectation-Maximization 期望最⼤化Expected loss 期望损失Exploding Gradient Problem 梯度爆炸问题Exponential loss function 指数损失函数Extreme Learning Machine/ELM 超限学习机Letter FFactorization 因⼦分解False negative 假负类False positive 假正类False Positive Rate/FPR 假正例率Feature engineering 特征⼯程Feature selection 特征选择Feature vector 特征向量Featured Learning 特征学习Feedforward Neural Networks/FNN 前馈神经⽹络Fine-tuning 微调Flipping output 翻转法Fluctuation 震荡Forward stagewise algorithm 前向分步算法Frequentist 频率主义学派Full-rank matrix 满秩矩阵Functional neuron 功能神经元Letter GGain ratio 增益率Game theory 博弈论Gaussian kernel function ⾼斯核函数Gaussian Mixture Model ⾼斯混合模型General Problem Solving 通⽤问题求解Generalization 泛化Generalization error 泛化误差Generalization error bound 泛化误差上界Generalized Lagrange function ⼴义拉格朗⽇函数Generalized linear model ⼴义线性模型Generalized Rayleigh quotient ⼴义瑞利商Generative Adversarial Networks/GAN ⽣成对抗⽹络Generative Model ⽣成模型Generator ⽣成器Genetic Algorithm/GA 遗传算法Gibbs sampling 吉布斯采样Gini index 基尼指数Global minimum 全局最⼩Global Optimization 全局优化Gradient boosting 梯度提升Gradient Descent 梯度下降Graph theory 图论Ground-truth 真相/真实Letter HHard margin 硬间隔Hard voting 硬投票Harmonic mean 调和平均Hesse matrix 海塞矩阵Hidden dynamic model 隐动态模型Hidden layer 隐藏层Hidden Markov Model/HMM 隐马尔可夫模型Hierarchical clustering 层次聚类Hilbert space 希尔伯特空间Hinge loss function 合页损失函数Hold-out 留出法Homogeneous 同质Hybrid computing 混合计算Hyperparameter 超参数Hypothesis 假设Hypothesis test 假设验证Letter IICML 国际机器学习会议Improved iterative scaling/IIS 改进的迭代尺度法Incremental learning 增量学习Independent and identically distributed/i.i.d. 独⽴同分布Independent Component Analysis/ICA 独⽴成分分析Indicator function 指⽰函数Individual learner 个体学习器Induction 归纳Inductive bias 归纳偏好Inductive learning 归纳学习Inductive Logic Programming/ILP 归纳逻辑程序设计Information entropy 信息熵Information gain 信息增益Input layer 输⼊层Insensitive loss 不敏感损失Inter-cluster similarity 簇间相似度International Conference for Machine Learning/ICML 国际机器学习⼤会Intra-cluster similarity 簇内相似度Intrinsic value 固有值Isometric Mapping/Isomap 等度量映射Isotonic regression 等分回归Iterative Dichotomiser 迭代⼆分器Letter KKernel method 核⽅法Kernel trick 核技巧Kernelized Linear Discriminant Analysis/KLDA 核线性判别分析K-fold cross validation k 折交叉验证/k 倍交叉验证K-Means Clustering K – 均值聚类K-Nearest Neighbours Algorithm/KNN K近邻算法Knowledge base 知识库Knowledge Representation 知识表征Letter LLabel space 标记空间Lagrange duality 拉格朗⽇对偶性Lagrange multiplier 拉格朗⽇乘⼦Laplace smoothing 拉普拉斯平滑Laplacian correction 拉普拉斯修正Latent Dirichlet Allocation 隐狄利克雷分布Latent semantic analysis 潜在语义分析Latent variable 隐变量Lazy learning 懒惰学习Learner 学习器Learning by analogy 类⽐学习Learning rate 学习率Learning Vector Quantization/LVQ 学习向量量化Least squares regression tree 最⼩⼆乘回归树Leave-One-Out/LOO 留⼀法linear chain conditional random field 线性链条件随机场Linear Discriminant Analysis/LDA 线性判别分析Linear model 线性模型Linear Regression 线性回归Link function 联系函数Local Markov property 局部马尔可夫性Local minimum 局部最⼩Log likelihood 对数似然Log odds/logit 对数⼏率Logistic Regression Logistic 回归Log-likelihood 对数似然Log-linear regression 对数线性回归Long-Short Term Memory/LSTM 长短期记忆Loss function 损失函数Letter MMachine translation/MT 机器翻译Macron-P 宏查准率Macron-R 宏查全率Majority voting 绝对多数投票法Manifold assumption 流形假设Manifold learning 流形学习Margin theory 间隔理论Marginal distribution 边际分布Marginal independence 边际独⽴性Marginalization 边际化Markov Chain Monte Carlo/MCMC 马尔可夫链蒙特卡罗⽅法Markov Random Field 马尔可夫随机场Maximal clique 最⼤团Maximum Likelihood Estimation/MLE 极⼤似然估计/极⼤似然法Maximum margin 最⼤间隔Maximum weighted spanning tree 最⼤带权⽣成树Max-Pooling 最⼤池化Mean squared error 均⽅误差Meta-learner 元学习器Metric learning 度量学习Micro-P 微查准率Micro-R 微查全率Minimal Description Length/MDL 最⼩描述长度Minimax game 极⼩极⼤博弈Misclassification cost 误分类成本Mixture of experts 混合专家Momentum 动量Moral graph 道德图/端正图Multi-class classification 多分类Multi-document summarization 多⽂档摘要Multi-layer feedforward neural networks 多层前馈神经⽹络Multilayer Perceptron/MLP 多层感知器Multimodal learning 多模态学习Multiple Dimensional Scaling 多维缩放Multiple linear regression 多元线性回归Multi-response Linear Regression /MLR 多响应线性回归Mutual information 互信息Letter NNaive bayes 朴素贝叶斯Naive Bayes Classifier 朴素贝叶斯分类器Named entity recognition 命名实体识别Nash equilibrium 纳什均衡Natural language generation/NLG ⾃然语⾔⽣成Natural language processing ⾃然语⾔处理Negative class 负类Negative correlation 负相关法Negative Log Likelihood 负对数似然Neighbourhood Component Analysis/NCA 近邻成分分析Neural Machine Translation 神经机器翻译Neural Turing Machine 神经图灵机Newton method ⽜顿法NIPS 国际神经信息处理系统会议No Free Lunch Theorem/NFL 没有免费的午餐定理Noise-contrastive estimation 噪⾳对⽐估计Nominal attribute 列名属性Non-convex optimization ⾮凸优化Nonlinear model ⾮线性模型Non-metric distance ⾮度量距离Non-negative matrix factorization ⾮负矩阵分解Non-ordinal attribute ⽆序属性Non-Saturating Game ⾮饱和博弈Norm 范数Normalization 归⼀化Nuclear norm 核范数Numerical attribute 数值属性Letter OObjective function ⽬标函数Oblique decision tree 斜决策树Occam’s razor 奥卡姆剃⼑Odds ⼏率Off-Policy 离策略One shot learning ⼀次性学习One-Dependent Estimator/ODE 独依赖估计On-Policy 在策略Ordinal attribute 有序属性Out-of-bag estimate 包外估计Output layer 输出层Output smearing 输出调制法Overfitting 过拟合/过配Oversampling 过采样Letter PPaired t-test 成对 t 检验Pairwise 成对型Pairwise Markov property 成对马尔可夫性Parameter 参数Parameter estimation 参数估计Parameter tuning 调参Parse tree 解析树Particle Swarm Optimization/PSO 粒⼦群优化算法Part-of-speech tagging 词性标注Perceptron 感知机Performance measure 性能度量Plug and Play Generative Network 即插即⽤⽣成⽹络Plurality voting 相对多数投票法Polarity detection 极性检测Polynomial kernel function 多项式核函数Pooling 池化Positive class 正类Positive definite matrix 正定矩阵Post-hoc test 后续检验Post-pruning 后剪枝potential function 势函数Precision 查准率/准确率Prepruning 预剪枝Principal component analysis/PCA 主成分分析Principle of multiple explanations 多释原则Prior 先验Probability Graphical Model 概率图模型Proximal Gradient Descent/PGD 近端梯度下降Pruning 剪枝Pseudo-label 伪标记Letter QQuantized Neural Network 量⼦化神经⽹络Quantum computer 量⼦计算机Quantum Computing 量⼦计算Quasi Newton method 拟⽜顿法Letter RRadial Basis Function/RBF 径向基函数Random Forest Algorithm 随机森林算法Random walk 随机漫步Recall 查全率/召回率Receiver Operating Characteristic/ROC 受试者⼯作特征Rectified Linear Unit/ReLU 线性修正单元Recurrent Neural Network 循环神经⽹络Recursive neural network 递归神经⽹络Reference model 参考模型Regression 回归Regularization 正则化Reinforcement learning/RL 强化学习Representation learning 表征学习Representer theorem 表⽰定理reproducing kernel Hilbert space/RKHS 再⽣核希尔伯特空间Re-sampling 重采样法Rescaling 再缩放Residual Mapping 残差映射Residual Network 残差⽹络Restricted Boltzmann Machine/RBM 受限玻尔兹曼机Restricted Isometry Property/RIP 限定等距性Re-weighting 重赋权法Robustness 稳健性/鲁棒性Root node 根结点Rule Engine 规则引擎Rule learning 规则学习Letter SSaddle point 鞍点Sample space 样本空间Sampling 采样Score function 评分函数Self-Driving ⾃动驾驶Self-Organizing Map/SOM ⾃组织映射Semi-naive Bayes classifiers 半朴素贝叶斯分类器Semi-Supervised Learning 半监督学习semi-Supervised Support Vector Machine 半监督⽀持向量机Sentiment analysis 情感分析Separating hyperplane 分离超平⾯Sigmoid function Sigmoid 函数Similarity measure 相似度度量Simulated annealing 模拟退⽕Simultaneous localization and mapping 同步定位与地图构建Singular Value Decomposition 奇异值分解Slack variables 松弛变量Smoothing 平滑Soft margin 软间隔Soft margin maximization 软间隔最⼤化Soft voting 软投票Sparse representation 稀疏表征Sparsity 稀疏性Specialization 特化Spectral Clustering 谱聚类Speech Recognition 语⾳识别Splitting variable 切分变量Squashing function 挤压函数Stability-plasticity dilemma 可塑性-稳定性困境Statistical learning 统计学习Status feature function 状态特征函Stochastic gradient descent 随机梯度下降Stratified sampling 分层采样Structural risk 结构风险Structural risk minimization/SRM 结构风险最⼩化Subspace ⼦空间Supervised learning 监督学习/有导师学习support vector expansion ⽀持向量展式Support Vector Machine/SVM ⽀持向量机Surrogat loss 替代损失Surrogate function 替代函数Symbolic learning 符号学习Symbolism 符号主义Synset 同义词集Letter TT-Distribution Stochastic Neighbour Embedding/t-SNE T – 分布随机近邻嵌⼊Tensor 张量Tensor Processing Units/TPU 张量处理单元The least square method 最⼩⼆乘法Threshold 阈值Threshold logic unit 阈值逻辑单元Threshold-moving 阈值移动Time Step 时间步骤Tokenization 标记化Training error 训练误差Training instance 训练⽰例/训练例Transductive learning 直推学习Transfer learning 迁移学习Treebank 树库Tria-by-error 试错法True negative 真负类True positive 真正类True Positive Rate/TPR 真正例率Turing Machine 图灵机Twice-learning ⼆次学习Letter UUnderfitting ⽋拟合/⽋配Undersampling ⽋采样Understandability 可理解性Unequal cost ⾮均等代价Unit-step function 单位阶跃函数Univariate decision tree 单变量决策树Unsupervised learning ⽆监督学习/⽆导师学习Unsupervised layer-wise training ⽆监督逐层训练Upsampling 上采样Letter VVanishing Gradient Problem 梯度消失问题Variational inference 变分推断VC Theory VC维理论Version space 版本空间Viterbi algorithm 维特⽐算法Von Neumann architecture 冯 · 诺伊曼架构Letter WWasserstein GAN/WGAN Wasserstein⽣成对抗⽹络Weak learner 弱学习器Weight 权重Weight sharing 权共享Weighted voting 加权投票法Within-class scatter matrix 类内散度矩阵Word embedding 词嵌⼊Word sense disambiguation 词义消歧Letter ZZero-data learning 零数据学习Zero-shot learning 零次学习Aapproximations近似值arbitrary随意的affine仿射的arbitrary任意的amino acid氨基酸amenable经得起检验的axiom公理,原则abstract提取architecture架构,体系结构;建造业absolute绝对的arsenal军⽕库assignment分配algebra线性代数asymptotically⽆症状的appropriate恰当的Bbias偏差brevity简短,简洁;短暂broader⼴泛briefly简短的batch批量Cconvergence 收敛,集中到⼀点convex凸的contours轮廓constraint约束constant常理commercial商务的complementarity补充coordinate ascent同等级上升clipping剪下物;剪报;修剪component分量;部件continuous连续的covariance协⽅差canonical正规的,正则的concave⾮凸的corresponds相符合;相当;通信corollary推论concrete具体的事物,实在的东西cross validation交叉验证correlation相互关系convention约定cluster⼀簇centroids 质⼼,形⼼converge收敛computationally计算(机)的calculus计算Dderive获得,取得dual⼆元的duality⼆元性;⼆象性;对偶性derivation求导;得到;起源denote预⽰,表⽰,是…的标志;意味着,[逻]指称divergence 散度;发散性dimension尺度,规格;维数dot⼩圆点distortion变形density概率密度函数discrete离散的discriminative有识别能⼒的diagonal对⾓dispersion分散,散开determinant决定因素disjoint不相交的Eencounter遇到ellipses椭圆equality等式extra额外的empirical经验;观察ennmerate例举,计数exceed超过,越出expectation期望efficient⽣效的endow赋予explicitly清楚的exponential family指数家族equivalently等价的Ffeasible可⾏的forary初次尝试finite有限的,限定的forgo摒弃,放弃fliter过滤frequentist最常发⽣的forward search前向式搜索formalize使定形Ggeneralized归纳的generalization概括,归纳;普遍化;判断(根据不⾜)guarantee保证;抵押品generate形成,产⽣geometric margins⼏何边界gap裂⼝generative⽣产的;有⽣产⼒的Hheuristic启发式的;启发法;启发程序hone怀恋;磨hyperplane超平⾯Linitial最初的implement执⾏intuitive凭直觉获知的incremental增加的intercept截距intuitious直觉instantiation例⼦indicator指⽰物,指⽰器interative重复的,迭代的integral积分identical相等的;完全相同的indicate表⽰,指出invariance不变性,恒定性impose把…强加于intermediate中间的interpretation解释,翻译Jjoint distribution联合概率Llieu替代logarithmic对数的,⽤对数表⽰的latent潜在的Leave-one-out cross validation留⼀法交叉验证Mmagnitude巨⼤mapping绘图,制图;映射matrix矩阵mutual相互的,共同的monotonically单调的minor较⼩的,次要的multinomial多项的multi-class classification⼆分类问题Nnasty讨厌的notation标志,注释naïve朴素的Oobtain得到oscillate摆动optimization problem最优化问题objective function⽬标函数optimal最理想的orthogonal(⽮量,矩阵等)正交的orientation⽅向ordinary普通的occasionally偶然的Ppartial derivative偏导数property性质proportional成⽐例的primal原始的,最初的permit允许pseudocode伪代码permissible可允许的polynomial多项式preliminary预备precision精度perturbation 不安,扰乱poist假定,设想positive semi-definite半正定的parentheses圆括号posterior probability后验概率plementarity补充pictorially图像的parameterize确定…的参数poisson distribution柏松分布pertinent相关的Qquadratic⼆次的quantity量,数量;分量query疑问的Rregularization使系统化;调整reoptimize重新优化restrict限制;限定;约束reminiscent回忆往事的;提醒的;使⼈联想…的(of)remark注意random variable随机变量respect考虑respectively各⾃的;分别的redundant过多的;冗余的Ssusceptible敏感的stochastic可能的;随机的symmetric对称的sophisticated复杂的spurious假的;伪造的subtract减去;减法器simultaneously同时发⽣地;同步地suffice满⾜scarce稀有的,难得的split分解,分离subset⼦集statistic统计量successive iteratious连续的迭代scale标度sort of有⼏分的squares平⽅Ttrajectory轨迹temporarily暂时的terminology专⽤名词tolerance容忍;公差thumb翻阅threshold阈,临界theorem定理tangent正弦Uunit-length vector单位向量Vvalid有效的,正确的variance⽅差variable变量;变元vocabulary词汇valued经估价的;宝贵的Wwrapper包装分类:。

2021年3⽉1⽇-机器学习三要素机器学习通俗来讲指的是计算机程序通过经验来提⾼某任务处理性能的⼀类技术。
其形式化定义如下:对于某类任务T和性能度量P,如果⼀个计算机程序在T上以P衡量的性能随着经验E⽽⾃我完善,那么我们称这个计算机程序在从经验E中进⾏学习。
⼀个机器学习⽅法需要包括三个要素,也称为机器学习三要素:模型、学习准则、优化算法。
模型机器学习的本质是根据经验学习⼀个映射函数f:X→Y,⽤于对未知数据进⾏预测。
模型结构确定了该机器学习算法的假设空间,即所有可能的映射函数的集合。
例如,如果映射函数f具有如下的形式:fθ=θ1x+θ0,那么该假设空间实际上是平⾯上的所有直线;如果映射函数f具有如下的形式:f=W2(σ(W1X+b1))+b2,那么该假设空间是所有以σ函数作为激活函数的两层线性神经⽹络构成的集合。
我们在设计模型时应该尽量使得得到的假设空间包含或者尽可能近似⽬标映射,同时排出其余不是最优解的候选映射。
学习准则在设计完模型(通常对于机器学习是选定模型)得到假设空间以后,我们接下来需要做的是找到⼀种评价指标能够对假设空间中的映射进⾏⽐较,也就是通常所说的学习准则。
通常我们会根据不同的任务需求选定⼀个损失函数⽤以对模型相对于数据点的预测结果进⾏评估。
⽐如:最⼩⼆乘损失,绝对值损失,交叉熵损失,Hinge Loss,Huber Loss等。
在得到损失函数以后,我们通常还会挑选⼀种策略来得到最终的优化⽬标。
⽐如,经验风险最⼩化、结构风险最⼩化、贝叶斯准则等等。
经验风险最⼩化假设对于⼀个数据点的预测结果得到的损失记为loss(f(x),y),那么该损失函数相对于整个数据集的期望就是风险函数或者叫做期望损失。
Expected_Loss=E(x,y)∼PD[loss(f(x),y)]但是由于我们不知道数据集的真实分布P D,因此只能对期望损失进⾏估计。
⼀般我们使⽤损失函数在当前数据集的平均值作为对期望损失的估计,这个值⼜叫做经验风险或者叫做经验损失。


2.12.比:ratio 比例:proportion 利率:interest rate 速率:speed 除:divide 除法:division 商:quotient 同类量:like quantity 项:term 线段:line segment 角:angle 长度:length 宽:width高度:height 维数:dimension 单位:unit 分数:fraction 百分数:percentage3.(1)一条线段和一个角的比没有意义,他们不是相同类型的量.(2)比较式通过说明一个量是另一个量的多少倍做出的,并且这两个量必须依据相同的单位.(5)为了解一个方程,我们必须移项,直到未知项独自处在方程的一边,这样就可以使它等于另一边的某量.4.(1)Measuring the length of a desk, is actually comparing the length of the desk to that of a ruler.(3)Ratio is different from the measurement, it has no units. The ratio of the length and the width of the same book does not vary when the measurement unit changes.(5)60 percent of students in a school are female students, which mean that 60 students out of every 100 students are female students.2.22.初等几何:elementary geometry 三角学:trigonometry 余弦定理:Law of cosines 勾股定理/毕达哥拉斯定理:Gou-Gu theorem/Pythagoras theorem 角:angle 锐角:acute angle 直角:right angle 同终边的角:conterminal angles 仰角:angle of elevation 俯角:angle of depression 全等:congruence 夹角:included angle 三角形:triangle 三角函数:trigonometric function直角边:leg 斜边:hypotenuse 对边:opposite side 临边:adjacent side 始边:initial side 解三角形:solve a triangle 互相依赖:mutually dependent 表示成:be denoted as 定义为:be defined as3.(1)Trigonometric function of the acute angle shows the mutually dependent relations between each sides and acute angle of the right triangle.(3)If two sides and the included angle of an oblique triangle areknown, then the unknown sides and angles can be found by using the law of cosines.(5)Knowing the length of two sides and the measure of the included angle can determine the shape and size of the triangle. In other words, the two triangles made by these data are congruent.4.(1)如果一个角的顶点在一个笛卡尔坐标系的原点并且它的始边沿着x轴正方向,这个角被称为处于标准位置.(3)仰角和俯角是以一条以水平线为参考位置来测量的,如果正被观测的物体在观测者的上方,那么由水平线和视线所形成的角叫做仰角.如果正被观测的物体在观测者的下方,那么由水平线和视线所形成的的角叫做俯角.(5)如果我们知道一个三角形的两条边的长度和对着其中一条边的角度,我们如何解这个三角形呢?这个问题有一点困难来回答,因为所给的信息可能确定两个三角形,一个三角形或者一个也确定不了.2.32.素数:prime 合数:composite 质因数:prime factor/prime divisor 公倍数:common multiple 正素因子: positive prime divisor 除法算式:division equation 最大公因数:greatest common divisor(G.C.D) 最小公倍数: lowest common multiple(L.C.M) 整除:divide by 整除性:divisibility 过程:process 证明:proof 分类:classification 剩余:remainder辗转相除法:Euclidean algorithm 有限集:finite set 无限的:infinitely 可数的countable 终止:terminate 与矛盾:contrary to3.(1)We need to study by which integers an integer is divisible, that is , what factor it has. Specially, it is sometime required that an integer is expressed as the product of its prime factors.(3)The number 1 is neither a prime nor a composite number;A composite number in addition to being divisible by 1 and itself, can also be divisible by some prime number.(5)The number of the primes bounded above by any given finite integer N can be found by using the method of the sieve Eratosthenes.4.(1)数论中一个重要的问题是哥德巴赫猜想,它是关于偶数作为两个奇素数和的表示.(3)一个数,形如2p-1的素数被称为梅森素数.求出5个这样的数.(5)任意给定的整数m和素数p,p的仅有的正因子是p和1,因此仅有的可能的p和m的正公因子是p和1.因此,我们有结论:如果p是一个素数,m是任意整数,那么p整除m,要么(p,m)=1.2.42.集:set 子集:subset 真子集:proper subset 全集:universe 补集:complement 抽象集:abstract set 并集:union 交集:intersection 元素:element/member 组成:comprise/constitute包含:contain 术语:terminology 概念:concept 上有界:bounded above 上界:upper bound 最小的上界:least upper bound 完备性公理:completeness axiom3.(1)Set theory has become one of the common theoretical foundation and the important tools in many branches of mathematics.(3)Set S itself is the improper subset of S; if set T is a subset of S but not S, then T is called a proper subset of S.(5)The subset T of set S can often be denoted by {x}, that is, T consists of those elements x for which P(x) holds.(7)This example makes the following question become clear, that is, why may two straight lines in the space neither intersect nor parallel.4.(1)设N是所有自然数的集合,如果S是所有偶数的集合,那么它在N中的补集是所有奇数的集合.(3)一个非空集合S称为由上界的,如果存在一个数c具有属性:x<=c对于所有S中的x.这样一个数字c被称为S的上界.(5)从任意两个对象x和y,我们可以形成序列(x,y),它被称为一个有序对,除非x=y,否则它当然不同于(y,x).如果S和T是任意集合,我们用S*T表示所有有序对(x,y),其中x术语S,y属于T.在R.笛卡尔展示了如何通过实轴和它自己的笛卡尔积来描述平面的点之后,集合S*T被称为S和T的笛卡尔积.2.52.竖直线:vertical line 水平线:horizontal line 数对:pairs of numbers 有序对:ordered pairs 纵坐标:ordinate 横坐标:abscissas 一一对应:one-to-one 对应点:corresponding points圆锥曲线:conic sections 非空图形:non vacuous graph 直立圆锥:right circular cone 定值角:constant angle 母线:generating line 双曲线:hyperbola 抛物线:parabola 椭圆:ellipse退化的:degenerate 非退化的:nondegenerate任意的:arbitrarily 相容的:consistent 在几何上:geometrically 二次方程:quadratic equation 判别式:discriminant 行列式:determinant3.(1)In the planar rectangular coordinate system, one can set up aone-to-one correspondence between points and ordered pairs of numbers and also a one-to-one correspondence between conic sections and quadratic equation.(3)The symbol can be used to denote the set of ordered pairs(x,y)such that the ordinate is equal to the cube of the abscissa.(5)According to the values of the discriminate,the non-degenerate graph of Equation (iii) maybe known to be a parabola, a hyperbolaor an ellipse.4.(1)在例1,我们既用了图形,也用了代数的代入法解一个方程组(其中一个方程式二次的,另一个是线性的)。

霍普夫映射霍普夫映射(Hopfmapping)是数学中非常有意思的一种映射。
它是一种对称的,维数在一般情况下高于原映射,可以像映射一个球面到另一个球面一样,将一个曲面映射到另一个曲面。
它最初由著名的德国数学家Hans Hopf于1931年提出,故得名。
霍普夫映射的发现,也伴随着几何学与数学的紧密结合,其发现将多种不同的数学理论与它的应用实践联系起来。
从某种程度上讲,它也为数学和几何学的发展带来了巨大的推动力。
霍普夫映射在数学上,是由一系列分析、代数、几何及拓扑原理所组成,它将一个曲面映射到另一个曲面,也就是说,一个复杂的图形可以映射到另一个更高维的图形。
它具有非常广泛的应用,如电磁学、水力学、物理学等,它也是数学研究的重要组成部分,其中包括:局部结构理论、Riemannian几何、调和几何和几何分析等。
霍普夫映射的定义是:将一个曲面映射到另一个曲面,使得曲面间的所有点做一个对应关系,使得它们具有相同的局部结构。
它是一个从几何到拓扑的转换过程,有着广泛的应用,将球面映射到另一个球面、将平面映射到圆柱面等,都是它的典型应用案例。
霍普夫映射有着复杂的数学理论,如调和几何、拓扑和向量分析等,这些理论组合起来,则构建出一个完整的映射,也就是霍普夫映射。
除此之外,它也可以应用到多种科学技术领域,如电子学、应用数学、物理学、流体力学、计算机图形学等领域。
举例而言,在计算机图形学领域,霍普夫映射可以用于实现三维图形的投影,从而进行几何学模型的建模。
总之,霍普夫映射是一种极具理论价值及应用价值的对称映射,它为数学理论、几何学与拓扑学等多种学科的发展,做出了非常重要的贡献。
它的理论和应用可以为我们在许多科学技术领域的研究提供一个重要的参照系。

(0,2) 插值||(0,2) interpolation0#||zero-sharp; 读作零井或零开。
0+||zero-dagger; 读作零正。
1-因子||1-factor3-流形||3-manifold; 又称“三维流形”。
AIC准则||AIC criterion, Akaike information criterionAp 权||Ap-weightA稳定性||A-stability, absolute stabilityA最优设计||A-optimal designBCH 码||BCH code, Bose-Chaudhuri-Hocquenghem codeBIC准则||BIC criterion, Bayesian modification of the AICBMOA函数||analytic function of bounded mean oscillation; 全称“有界平均振动解析函数”。
BMO鞅||BMO martingaleBSD猜想||Birch and Swinnerton-Dyer conjecture; 全称“伯奇与斯温纳顿-戴尔猜想”。
B样条||B-splineC*代数||C*-algebra; 读作“C星代数”。
C0 类函数||function of class C0; 又称“连续函数类”。
CA T准则||CAT criterion, criterion for autoregressiveCM域||CM fieldCN 群||CN-groupCW 复形的同调||homology of CW complexCW复形||CW complexCW复形的同伦群||homotopy group of CW complexesCW剖分||CW decompositionCn 类函数||function of class Cn; 又称“n次连续可微函数类”。
Cp统计量||Cp-statisticC。

降维低维空间映射条件Dimensionality reduction is a crucial technique in data analysis and machine learning, where high-dimensional data is transformed into a lower-dimensional space for easier visualization and analysis. 降维是数据分析和机器学习中的一项重要技术,它将高维数据转换为低维空间,以便更容易进行可视化和分析。
One common method of dimensionality reduction is through mapping conditions, where algorithms map the original high-dimensional data into a lower-dimensional space while preserving as much of the relevant information as possible. 降维的一个常见方法是通过映射条件,即算法将原始高维数据映射到低维空间,同时尽可能保留尽可能多的相关信息。
The purpose of dimensionality reduction is to remove redundant or irrelevant features, reduce noise, and improve computational efficiency. 降维的目的是去掉冗余或无关的特征,减少噪音,并提高计算效率。
One challenge in dimensionality reduction is to find an appropriate mapping that preserves the meaningful structure of the data while reducing its dimensionality. 在降维中的一个挑战是找到一个适当的映射,既能保留数据的有意义结构,又能减少其维数。


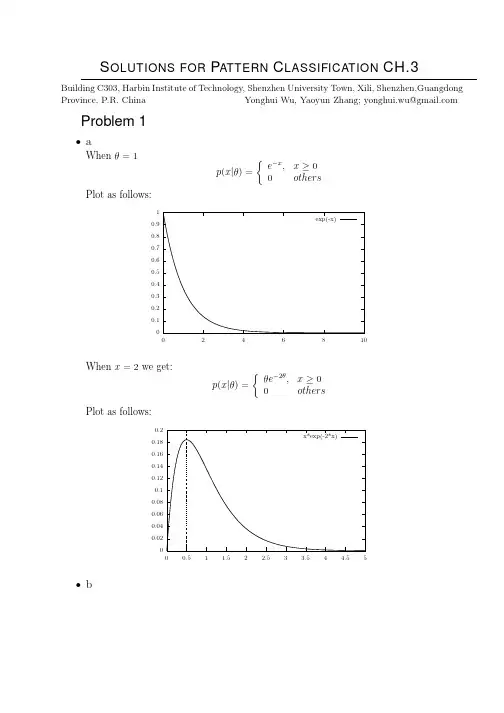
1. 对以下对称矩阵(设为A ),求正交矩阵使Q −1AQ 为对角矩阵;0410********400⎛⎫⎪⎪⎪ ⎪⎝⎭解:由于()()()()5533,E A λλλλλ-=-++-故A 的特征根为:5,−5,3,−3.依次求各特征根对应的一个特征向量:α1=(1,1,1,1),α2=(1,1,−1,−1), α3=(−1,1,−1,1),α4=(1,−1,−1,1).再单位化,得η1=12(1,1,1,1),η2=12(1,1,−1,−1),η3=12(−1,1,−1,1),η4=12(1,−1,−1,1),由此所求得的正交矩阵111111111111121111Q -⎛⎫ ⎪- ⎪= ⎪--- ⎪-⎝⎭而55'33Q AQ ⎛⎫⎪- ⎪= ⎪ ⎪-⎝⎭2. 对矩阵1111111111111111A ⎛⎫ ⎪ ⎪= ⎪ ⎪⎝⎭求正交矩阵Q 使Q ′AQ 为对角矩阵.解:由于()3-4E A λλλ-=,故A 的特征根为:4,0,0,0.取对应于特征根4的一个特征向量:α1=(1,1,1,1); 再取对应于特征根0的三个线性无关的特征向量:α2=(−1,1,0,0),α3=(−1,0,1,0),α4=(−1,0,0,1)将α1标准化,并将α2,α3,α4正交标准化,得η1=12(1,1,1,1),η2=1√2(−1,1,0,0),η3=(−1√6,−1√6,√23,0),η4=(−√36,−√36,−√36,√32),随得所求的正交矩阵为Q=126121026102⎛-⎪ -⎪ ⎪ ⎪ ⎪⎝⎭ 而40'00Q AQ ⎛⎫ ⎪⎪= ⎪ ⎪⎝⎭3. 设T 为线性空间V 的一个线性变换,且T 2=T .证明:1) T 的特征值只能是1或0;2) 若用V 1与V 0分别表示对应于特征值1或0的特征子空间,则V 1=TV , V 0=T −1(0);3) V =V 1⊕V 0=TV ⊕T −1(0) ;4) T 只有特征值0的充要条件是T 为零变换.证:1)设λ0是T 的任一特征值,α≠0为其特征向量,即Tα=λ0α, α≠0. 由于T 2=T ,故有()()2000T T T T λαααλαλα====.但α≠0,故200λλ=,从而λ0=1或λ0=0.2)任取1V α∈,即有T αα=.但T TV α∈,故TV α∈.即1V TV ⊆.另一方面,任取TV α∈,令T αβ=,则2T T T αββα===,即1V α∈,故1TVV ⊆.于是1V TV =.另外()100V T -=是显然的.3)任取V α∈,则有()T I T ααα=+-.显然1T TVV α∈=且()20T I T T T T T ααααα-=-=-=⎡⎤⎣⎦即()()100I T T V α--∈=因此()1100VV V TV T -=+=+又因V 1与V 0分别是属于不同特征值的特征子空间,所以{}100V V =,于是()1100V V V TV T -=⊕=⊕5) 由3)知,T 只有特征值0的充要条件是{}0TV =,即T 为零变换.4.设有向量组α1=(1,0,2,1),α2=(2,0,1,−1),α3=(3,0,3,0), β1=(1,1,0,1),β2=(4,1,3,1)令V 1=L (α1,α2,α3),V 2=L (β1,β2).求V 1+V 2的维数,并求其一组基.解:由于()()()121231212312,,+=L ,,,,V V L L αααββαααββ+=+故12V V +的维数就是向量组12312αααββ,,,,的秩,而这个向量组的极大线性无关组也是12V V +的基.以12312αααββ,,,,为列作矩阵,并对其进行初等变换:12314-11011000110001121303213031-10111-1011-11011-110110001100011 21303303031-100000000-1100000011 =1010100000A B ⎛⎫⎛⎫⎪⎪⎪ ⎪=⎪ ⎪⎪⎪⎝⎭⎝⎭⎛⎫⎛⎫⎪ ⎪⎪ ⎪→→ ⎪ ⎪⎪ ⎪⎝⎭⎝⎭⎛⎫ ⎪⎪→ ⎪ ⎪⎝⎭变行由于A 秩=B 秩=3,且由B 知,第2,3,4列线性无关,故231ααβ,,便是12V V +的一组基.4. 设α1,α2,⋯,αn 为n 维线性空间V 的一基,A 是一个n ×m 矩阵,而(β1,β2,⋯,βm )=(α1,α2,⋯,αn )A .证明:由β1,β2,⋯,βm 生成的子空间L(β1,β2,⋯,βm )的维数等于A 的秩.证:令11121121222212r m r m n n nrnm a a a a a a a a a a a a ⋅⋅⋅⋅⋅⋅⎛⎫⎪⋅⋅⋅⋅⋅⋅ ⎪⎪⋅⋅⋅⋅⋅⋅⋅⋅⋅⋅⋅⋅⋅⋅⋅⋅⋅⋅⎪⋅⋅⋅⋅⋅⋅⎝⎭且设A 的秩是r ,则r ≤min (n,m ).不妨设A 的前r 列线性无关,即他是A 的列向量的一个极大无关组.由于(β1,β2,⋯,βm )=(α1,α2,⋯,αn )A 故βj =α1j α1+α2j α2+⋯+αnj αn .j =1,2,⋯,m.下面证明:由β1,β2,⋯,βr 也是向量组β1,β2,⋯,βm 的一个极大线性无关组,亦即为子空间L(β1,β2,⋯,βm )的一基.设有数k 1,k 2,⋯,k r 使k 1β1+k 2β2+⋯+k r βr =θ于是由(1)得()11221.ni i ir r i i a k ak a k αθ=+++=∑由于α1,α2,⋯,αn 线性无关,故111122121122221122000r r r r n n nr r a k a k a k a k a k a k a k a k a k +++=⎧⎪+++=⎪⎨⎪⎪+++=⎩但此方程只有零解,故k 1=k 2=⋯=k r =0从而β1,β2,⋯,βr 线性无关.类似上面可证明β1,β2,⋯,βr ,βj 线性相关.故向量组β1,β2,⋯,βm 的秩是r ,从而L(β1,β2,⋯,βm )为r 维子空间. 6.证明:实对称矩阵A 是正定矩阵的充要条件是,A 的主子式全大于零.证:充分性是明显的.因为主子式全大于零,那么顺序主子式必须大于零,从而A 是正定的.下证必要性.设n 阶实对称矩阵A=(a ij )的主子式全大于0,而1112121222121 1.k k k k k k i i i i i i i i i i i i k k i i i i i i a a a a a a A i i n a a a ⎛⎫⎪ ⎪=≤<<≤⎪ ⎪ ⎪⎝⎭为A 的任一个k 阶主子式|A k |所对应的k 阶实对称矩阵.由于A 是正定的,故二次型()1,,'n f x x X AX =对任意不全为零的实数1,,n c c 都有()12,,0n f c c c >.从而对不全为零的实数12,,,k i i i c c c ,有 ()120,,,0,,,,,,00.k i i i f c c c >(即在()1,,n f x x 中除1,,k i i x x 外其余变量全为0).但是,对变量为1,,k i i x x 而矩阵为A k 的二次型()1,,k i i gx x 来说,有()()11,,0,,,,,,00k k i i i i g c c f c c =>.故g 是正定二次型,从而A k 是正定的.故|A k |>0.注:本题的一个特殊情况是:正定矩阵的一阶主子式即主对角线上的所有元素都必须大于0.7.设A 和B 都是m ×n 矩阵.证明:()()()r A B r A r B ±≤+ 证:设m ×n 矩阵A 和B 及A+B 的列向量分别为12,,,n ααα(1) 12,,,n βββ(2) 12,,,n γγγ(3)其中,1,2,,.ii i i n γαβ=+=又设A 与B 的秩分别为r,s,而且不妨设12,,,r ααα 12,,,s βββ分别为向量组(1)与(2)的极大无关组.由于向量组(3)可由向量组1212,,,,,,,n n αααβββ线性表示,从而可由向量组1212,,,,,,,r s αααβββ线性表示.所以向量组(3)的秩,即A+B 的秩不超过组(4)的,从而不超过组(4)向量的个数r+s.亦即()()()r A B r s r A r B ±≤+=+.显然()()r B r B =-,于是,由上述结果又得:()()()()()()()=r r A B r A B r A r B A r B -=+-≤+-+所以()()()r A B r A r B ±≤+. 8.设有线性方程组1234123412341234512333819377x x x x x x x x x x x x x x x x +--=-⎧⎪-++=⎪⎨+-+=⎪⎪-++=⎩ 试用其一个特解与其导出方程组的基础解系表出其全部解.解:对方程组的增广矩阵施行初等行变换:____15111151111213307244381110724419377014488313131151117770724424401 777000000000000000000A ------⎛⎫⎛⎫ ⎪ ⎪-- ⎪ ⎪=→ ⎪ ⎪--⎪ ⎪--⎝⎭⎝⎭⎛⎫ ⎪---⎛⎫ ⎪⎪- ⎪⎪---→→ ⎪ ⎪⎪⎪⎪⎝⎭ ⎪⎝⎭原方程与以下方程组同解:134******** 777244 777x x x x x x ⎧++=⎪⎪⎨⎪--=-⎪⎩由此可得原方程组的一个特解(取340x x ==):'0134,,0,077α⎛⎫=- ⎪⎝⎭有可得导出方程组的一个基础解系:''1232134,,1,0, ,,0,17777ηη⎛⎫⎛⎫=-=- ⎪ ⎪⎝⎭⎝⎭.于是原方程组的全部解为:011221213313777424,777010001c c c c αηη⎛⎫⎛⎫⎛⎫-- ⎪ ⎪ ⎪⎪ ⎪ ⎪ ⎪ ⎪ ⎪-++=++ ⎪ ⎪ ⎪ ⎪ ⎪ ⎪ ⎪ ⎪ ⎪ ⎪ ⎪ ⎪⎝⎭⎝⎭⎝⎭其中12,c c 为任意常数. 9.设12,,,t ηηη是某一非线性方程组的解.证明1122t t μημημη+++也是该非其次线性方程组的一个解的充要条件是,121t μμμ+++=.证明设非齐次线性方程AX β=,其中A 为系数矩阵,0β≠为方程组的常数项所构成的列向量.若12=1t u u u +++,则由于12,,,t ηηη是AX β=的解,故()()()()112211112t t t t t t A u u u u A u A u u u u u ηηηηηββββ+++=++=++=+++=,(1)即1122t t u u u ηηη+++也是AX β=的解.反之,如果1122t t u u u ηηη+++也是AX β=的解,则以上式(1)成立,从而有()1210t u u u β+++-=.但因β是非齐次线性方程组的常数项构成的列向量,故0β≠,从而1210t u u u +++-=因此12=1t u u u +++10.b a ,取何值时以下方程组有解?并求其解:⎪⎩⎪⎨⎧=++=++=++.4234321321321x bx x x bx x x x ax (1) 解对方程组的增广矩阵实行初等行变换:B b a a b a a ab b b a a ab b b a A =⎪⎪⎪⎭⎫ ⎝⎛--→⎪⎪⎪⎭⎫ ⎝⎛---→⎪⎪⎪⎭⎫ ⎝⎛---→⎪⎪⎪⎭⎫ ⎝⎛=100210124110100210134110100311341104121311411原方程组(1)与下面以B 为增广矩阵的线性方程组同解:()⎪⎩⎪⎨⎧==+-=-+.1224123132bx x x ax a x (2) 此方程组的系数行列式为:().100101110a b ba D -=-=当()01≠-=a b D ,即1≠a 且0≠b 时,方程组(2)(从而方程组(1))有惟一解,且由(2)知,此为一解为:()().1241,1,112321-+-==--=a b aba xb x a b b x当1=a 时,分以下两种情形: 1)21=b 时,原方程组(也就是方程组(2))有无穷多解: 3231,2,2x x x x =-=为任意常数.2)21≠b 时,易知方程组(2)无解,从而原方程组无解. 当0b =,显然方程组(2)也无解,从而原方程组也无解. 11.求向量组α1=(1,−1,2,2,0),α2=(2,−2,4,−2,0), α3=(3,0,6,−1,1),α4=(0,3,0,0,1).的一个极大无关组,并把每个向量都用极大无关组表示出来.解:以α1,α2,α3,α4为列向量作矩阵A ,并对A 的行施行初等变换:1230123012030033246000001210044000110011123012031001011001010101 00110011001100000000000000000000000 A ⎛⎫⎛⎫ ⎪ ⎪-- ⎪ ⎪ ⎪ ⎪=→ ⎪⎪---- ⎪ ⎪ ⎪ ⎪⎝⎭⎝⎭--⎛⎫⎛⎫⎛⎫⎪⎪ ⎪-- ⎪ ⎪ ⎪ ⎪ ⎪ ⎪→→→ ⎪⎪ ⎪⎪ ⎪ ⎪ ⎪ ⎪ ⎪⎝⎭⎝⎭⎝⎭B=矩阵A 和B 的列向量组有完全相同的线性关系,从而由B 可知:()()12343r A r αααα==,,,且α1,α2,α3为α1,α2,α3,α4的一个极大无关组;又α4=−α1−α2+α3.12.设向量组α1,α2,⋯,αr (1)线性无关,且可由向量组β1,β2,⋯,βs (2)线性表示.证明:1)r s ≤;(2)向量组(2)中存在r 个向量用组(1)中某r 个向量代替后得到的向量组与组(2)等价.证对r 用归纳法证明.当1r =时结论显然成立.设结论对1r -成立,即有1r s -≤,且用向量α1,α2,⋯,αr−1代替(2)中1r -个向量(为方便起见,设代替了β1,β2,⋯,βr−1)后的向量组α1,α2,⋯,αr−1,βr ,⋯,βs (3)与组(2)等价.现在来证定理对r 也成立.首先有1r s -≠,因为如果1r s -=,则(3)中已无βi ,αr ,可由组(2)线性表示,从而可由组(3)线性表示,这与组(1)线性无关矛盾,于是1r s -<,或即r s ≤.其次因为αr 可由组(2)线性表示,从而αr 可由(3)线性表示.设112211r r r r r s s k k k l l ααααββ--=++++++,则必至少有一个0jl ≠.事实上,如果j l 都为零,则αr 可由α1,α2,⋯,αr−1线性表示,这与组(1)线性无关矛盾.不妨设0r l ≠,因此βr 可由α1,α2,⋯,αr ,βr+1,⋯,βs (4)线性表示,又组(4)与组(3)中除αr 与βr 外其它向量一致,于是组(4)与组(3)等价,从而与组(2)等价. 13.设12,,,m ααα是一组线性无关的向量,且1, 1,2,,.mi ij j j b i m βα===∑(1)证明:向量组12,,,m βββ线性无关的充分必要条件是行列式1112121222120.m m m m mmb b b b b b b b b ≠证设0D ≠,往证12,,,m βββ线性无关.设有数12,,,m k k k ,使 11220m m k k k βββ+++=.则由(1)式,把i β带入上式并整理,得11221110.m m m i i i i im i m i i i b k b k b k ααα===⎛⎫⎛⎫⎛⎫+++= ⎪ ⎪ ⎪⎝⎭⎝⎭⎝⎭∑∑∑ 由于12,,,m ααα线性无关,故系数全为零,即1112121211222211220,0, (2)0.m m m m m m mm m b k b k b k b k b k b k b k b k b k +++=⎧⎪+++=⎪⎨⎪⎪+++=⎩由于此方程组的系数行列式'0D D =≠,故120,m k k k ====从而12,,,m βββ线性无关.反之,设12,,,m βββ线性无关,则必0D ≠.因若0D =,则D 的行向量线性无关,于是存在不全为零的数12,,,m k k k ,使()()()11112122122212,,,,,, ,,,0,m m m m m mm k b b b k b b b k b b b +++=由此可得等式组(2)成立.于是根据(1)和(2)可得11221111 0.m mm m i i im i m i i k k k b k b k βββαα==+++⎛⎫⎛⎫=++= ⎪ ⎪⎝⎭⎝⎭∑∑ 即12,,,m βββ又线性相关,这与假设矛盾,故0D ≠.14.计算n 阶行列式.n x b bb c x bb c c xb c c cx= 解:按n的第一列及第一行分别用两种方法,把n拆成两个行列式相加:()()()1110011 11; (1)nn n n c b b b x c b b b c x b b x b b cc x b c x b c c cxccxb b b x b bc x c c x b ccx c x b x c ----=+=+-=-+-()()()11100011111 . (2)n n n n b b b b bx b c x b b b c x b b cc x b b c c x b ccccxcccxc x b b bb x bc c xb b ccccxb xc x b ----=+=+-=-+-(1)式两端同乘以x b -,(2)式两端同乘以x c -,分别得()()()()()()()()11,.nn n nn n x b c x b x b x c x c b x c x b x c ---=-+---=-+--此二式相减,得()()()nnn c b c x b b x c -=---. 当c b ≠时,得()();nnn c x b b x c c b---=-当c b =时,由行列式的性质得()()11.n n x n b x b -=+--⎡⎤⎣⎦15.计算n 阶行列式:12+.n na x a a a a x a D aaa x +=+解根据最后一列,把n D 拆成两个行列式相加:1211211211+0+0 0000 00000n n n n n n a x a a a aa x a a D a a a x a a a a a a x a a aa x a a a a x a aax a x ax D x a a----+=++++=+1211.n n n n D x x x a x D --=+同理,112212.n n n n D x x x a x D ----=+于是12112212.n n n n n n n D x x x a x x x ax x x D ----=++如此继续下去,可得()12112212413212112212413212121211323().n n n n n n n n n n n n n x n n n n D x x x a x x x ax x x ax x x x x D x x x a x x x ax x x ax x x x x ax ax x x x x x a x x x x x x x x x -------=++++=++++++=++++当120n x x x ≠时,还可以写成12121111.n n n D x x x a x x x ⎡⎤⎛⎫=++++⎢⎥ ⎪⎝⎭⎣⎦16.计算n 阶行列式1232341.3452121n D nn =- 解各列都加到第一列,再从第一列中提出()12n n +;尔后再从第1n -行乘-1加到第n ,第2n -行乘-1加到第1n -行,第1行乘-1加到第二行得()()1231231341011114521101112211201111121n n n n n n n D n n nn -++==---()()()()()1221111111*********2111111n n n n n n n n n n nn------++==---()()()()()()()()11212221111.22n n n n n n n n n n n n ---+-++=-⋅--=-⋅17.如果既约分数q p是整系数多项式()1011n n n n f x a x a x a x a --=++++的根.证明:对任何整数k ,pk q -整除()f k . 证因为q p 是()f x 的根,故q x p-整除()f x ,设 ()()12011n n n q f x x b x b x b p ---⎛⎫=-+++ ⎪⎝⎭. (1) 右端展开后比较两端系数,得001, , 1,2,, 1.i i i i i c qb a b a b i n p p-==+==-其中i c 为整数,故由(1)得()121101.n n n n c c q f x x a x x p p p ----⎛⎫⎛⎫=-+++⎪⎪⎝⎭⎝⎭令x k =后两边乘以np 即得()()()()120121[ ].n n n n n p f k pk q a pk c pk c pk c ----=-++++故().npk q p f k -但因(),1,p q =可推知,(),1,npk q p -=从而().pk q f k -18.设()f x 是一个n 次()0n >多项式.证明:()'f x 整除()f x 的充分必要条件是,()f x 有n 重根.证充分性.设()f x 有n 重根,且()()f x a x α=-,则()()1'n f x na x α-=-.显然有()()'.f x f x必要性.设α是()f x 的s 重根,且()()()(), 0.sf x xg x g αα=-≠则()()()11', s f x x g x α-=-其中()()()()()11', g x sg x x g x x g x αα=+--.由于()()'f x f x ,故()()1g x g x .从而()()1'g x g x .这只有()g x 为零次多项式[因为()1g x 和()g x 的次数相等,都是n s -],设为a .从而()()sf x a x α=-,亦即s n =,而α为()f x 的n 重根. 19.试求()()()()()(),,nfx g x f x g x =的条件,其中n 为正整数,而且()()0,0.f x g x ≠≠解设若()()(),1f x g x =,则当然有()()()()()(),,nfx g x f x g x =.若()()()(),1f x g x d x =≠,且()d x 的标准分解式为()()()()1212s k k k s d x p x p x p x =,则()()()()()(),,nfx g x f x g x =的条件是()ip x 为()g x 的ik 重因式,1,2,,i s =.亦即有()()()()()12121s k k k s g x p x p x p x g x =,(1) 其中()()1,1,2,,i p x g x i s =.但由于()()()()()(),,|f x g x d x d x f x =,故有()()()()()12121s t t t s f x p x p x p x f x =,(2) 其中()()()()()111,1,,,1,2,,.i i i f x g x p x f x t k i s =≥=由(2)式的()()()()()12121.s nt nt nt n n s f x p x p x p x f x =(3)于是由(1),(3)式可得()()()()()()(),,nf xg x f x g x d x ==而且易知,(1)式是上式成立的充要条件.20.设()0f x ≠,()h x 为任意多项式.证明:若()()(),1f x g x =,则()()()()()()(),,f x g x h x f x h x =.问:反之是否成立?若成立,请证明;若不成立,请举出反例. 证设()()()()(),f x g x h x d x =,则()()()()()|, |.d x f x d x g x h x但由于()()(),1f x g x =,故有()()(),1d x g x =,从而()()|d x h x .即()d x 是()f x 与()h x 的一个公因式.又显然()f x 与()h x 的公因式都是()f x 与()()g x h x 的公因式,从而()d x 是()f x 与()h x 的最大公因式.即()()()()()()(),,f x g x h x f x h x =.21.证明:()()(),1f x g x =的充分必要条件是:()()()()(),1f x g x f x g x +=.证令()()()()()(),f x g x f x g x d x +=设()d x 的次数0>,取()d x 的一个不可约因式()p x ,则()()()()()()|, |+. p x f x g x p x f x g x (1)由第一式知()p x 整除()f x 或()g x ,不妨设()()|p x f x ,则由(1)知()()|p x g x ,即()p x 是()f x 与()g x 的公因式,这与()()(),1f x g x =相矛盾,故必有()()()()(),1f x g x f x g x +=.反之,若()()()()(),1f x g x f x g x +=,设()d x 为()f x 与()g x 的任意一个公因式,则()d x 也是()()f x g x 与()()f x g x +的一个公因式,于是()|1d x .故.()()(),1f x g x =.22.设()32(1)42f x x t x x u =++++与()322g x x tx u =++的最大公因式是一个二次多项式,求,t u 的值.解对()f x ,()g x 利用辗转相除法,得()()24f x g x tx x =++,()2(4)(4)4(4)2.g x tx x t x t x u =++---+由于()f x 与()g x 和最大公因式是二次的,故4(4)20,t x u --+=即4(4)0,20.t u --=⎧⎨=⎩得4,0.t u ==23.设A 为n 阶实对称矩阵,其特征根为12n λλλ≤≤≤.证明:对任意n 维(列)向量X 均有1'''n X X X AX X X λλ≤≤.证由于A 为实对称矩阵,故存在正交代换X QY =(其中Q 为正交矩阵),使()222121122,,,',n n n f x x x X AX y y y λλλ==+++(1)其中12,,,n λλλ为A 的特征根.由于12n λλλ≤≤≤以及()12221212,,,',n n n y y y y y y y Y Y y ⎛⎫⎪+++== ⎪ ⎪⎝⎭故对任意n 维向量X 由(1)得22211122'''.n n n Y Y X AX y y y Y Y λλλλλ≤=+++≤(2)又由于Q 是正交矩阵,'Q Q E =,故'()'()'''.X X QY QY Y Q QY Y Y === 从而由(2)得1'''n X X X AX X X λλ≤≤.24.设A 为n 阶实对称矩阵,且2.A E =证明:存在正交矩阵Q ,使10.0rn r E Q AQ E -⎛⎫=⎪-⎝⎭证因A 为实对称矩阵,故存在正交方阵1Q ,使121n Q AQ λλλ⎛⎫⎪ ⎪=⎪ ⎪⎝⎭,(1) 其中i λ为A 的特征根.由于2,A E =故得()21121111Q AQ Q A Q E --==.又()212212112n QAQ λλλ-⎛⎫ ⎪ ⎪= ⎪ ⎪ ⎪⎝⎭, 从而21, 1, 1,2,,.i i i n λλ==±=把(1)式右端对角线上i λ中的1+都集中到前面(交换相同的行与列,即乘上适当的正交矩阵),即存在正交矩阵2Q ,使12111211222101,101n Q Q AQ Q Q Q λλλ---⎛⎫⎪ ⎪= ⎪ ⎪⎝⎭⎛⎫ ⎪ ⎪ ⎪=⎪-⎪ ⎪ ⎪ ⎪-⎝⎭即100rn r E Q AQ E -⎛⎫=⎪-⎝⎭,其中12Q Q Q =为正交矩阵,而r E 为r 阶单位矩阵. 25.在复数域上求下列矩阵的若尔当标准型:452221111-⎛⎫ ⎪-- ⎪ ⎪--⎝⎭解用A 表示所给矩阵,则()3452122111111E A λλλλλ⎛⎫--⎛⎫⎪ ⎪-=+-→ ⎪ ⎪ ⎪ ⎪ ⎪-⎝⎭-⎝⎭, 初等因子为:()31λ-.从而A 的若尔当标准型为100110011⎛⎫⎪⎪ ⎪⎝⎭.26.在复数域上求下列矩阵的若尔当标准型:308316205⎛⎫ ⎪- ⎪ ⎪--⎝⎭.解用A 表示所给矩阵,则()2308131612051E A λλλλλλ⎛⎫--⎛⎫⎪ ⎪-=-+-→+ ⎪ ⎪ ⎪ ⎪ ⎪+⎝⎭+⎝⎭, 初等因子为:()()21,1λλ--.从而A 的若尔当标准型为100110011-⎛⎫⎪- ⎪ ⎪-⎝⎭.27.设1234,,,εεεε是四维线性空间V 的一组基.已知线性变换T 在这组基下的矩阵为1021121312552212⎛⎫⎪- ⎪⎪⎪--⎝⎭,1) 求T 的核与值域;2) 在T 的核中选一组基,把它扩充成V 的一组基,并求T 在这组基下的矩阵.解1)在核()10T-中任取一向量()1122334412123434=,,,x x x x x x x x αεεεεεεεε=+++⎛⎫ ⎪ ⎪ ⎪ ⎪⎝⎭,则0T α=,亦即()()1122123412343344,,,,,,0x x x x T A x x x x εεεεεεεε⎛⎫⎛⎫ ⎪ ⎪ ⎪ ⎪== ⎪ ⎪ ⎪ ⎪⎝⎭⎝⎭,从而12340000x x A x x ⎛⎫⎛⎫⎪ ⎪ ⎪ ⎪= ⎪ ⎪ ⎪ ⎪⎝⎭⎝⎭.解此线性方程组,得1342342,32.2x x x x x x =--⎧⎪⎨=--⎪⎩得一基础解系为()()4.3,2,0, 1,2,0,1----. 则11232124432, 2αεεεαεεε=---=--+是()10T -的一组基,故()()1120,T L αα-=.又由于T 在基1234,,,εεεε下的矩阵为A , 故A 的秩与向量组1234,,,T T T T εεεε的秩相等,而A 的前两列线性无关,任意三列线性相关,故12,T T εε是1234,,,T T T T εεεε的一个极大线性无关组,从而()()123412,,,,TV L T T T T L T T εεεεεε==.3) 由于有()()1212123410410132,,,,,,001001εεααεεεε--⎛⎫ ⎪-⎪= ⎪ ⎪⎝⎭, 令右端的矩阵为1Q ,显然它是满秩的,故1212,,,εεαα线性无关,这就将核的基12,αα扩成了V 的基.亦即由基1234,,,εεεε到基1212,,,εεαα的过度矩阵为1Q .于是T 在基1212,,,εεαα的矩阵为11152009100212002200Q AQ -⎛⎫⎪⎪= ⎪ ⎪⎪⎪-⎝⎭.28.设,A B 为任意两个n 阶方阵.证明:AB 与BA 有相同的特征多项式.证由于EA A E OE AB OE E B E B λλλλλ--⎛⎫⎛⎫⎛⎫= ⎪⎪⎪⎝⎭⎝⎭⎝⎭,两边取行列式得()1nnn A EE AB EBλλλλ=--. (1)同理,由EO A E A E BE EB E BAO λλλλ⎛⎫⎛⎫⎛⎫= ⎪⎪⎪--⎝⎭⎝⎭⎝⎭得 .()1nnn A EE BA EBλλλλ=--. (2)比较(1)与(2)两式,即得E AB E BA λλ-=-.29.用正交线性代换化下列二次型为标准型形:()22212312132322448f x x x x x x x x x x =---++解而慈祥的矩阵为122224242A -⎛⎫ ⎪=-- ⎪ ⎪-⎝⎭.()()272E A λλλ-=+-,特征根为:7,2,2-.对特征根2取两个线性无关的特征向量: ()()122,1,0, 2,0,1αα=-=.对特征根-7取相应的特征向量:()31,2,2α=-;对12,αα正交单位,并对3α单位化得)112131, 2,4,5, 3ηηηα===. 由此得正交矩阵1323203Q ⎛⎫- ⎪ ⎪ ⎪= ⎪ ⎪ ⎪- ⎪⎝⎭. 于是,f 可通过正交变换X QY =即得222123'''2+2-7f X AX Y Q AQY y y y ===.。
美国大学生数学建模MCM 数学专用名词augmented matrix增广矩阵asymptotic渐进的asymptote渐进线asymmetrical非对称的associative law结合律ascending上升的arrangement排列arithmetic算术argument幅角,幅度,自变量,论证area面积arc length弧长apothem边心距apex顶点aperiodic非周期的antisymmetric反对称的antiderivative原函数anticlockwise逆时针的annihilator零化子angular velocity角速度angle of rotation旋转角angle of incidence入射角angle of elevation仰角angle of depression俯角angle of circumference圆周角analytic space复空间analytic geometry解析几何analytic function解析函数analytic extension解析开拓amplitude幅角,振幅alternative互斥的alternate series交错级数almost everywhere几乎处处algebraic topology代数拓扑algebraic expression代数式algebraic代数的affine仿射(几何学)的admissible error容许误差admissible容许的adjugate伴随转置的adjoint operator伴随算子adjoint伴随的adjacency邻接additive加法,加性acute angle锐角accumulation point聚点accidential error偶然误差accessible point可达点abstract space抽象空间abstract algebra抽象代数absolute value绝对值absolute integrable绝对可积absolute convergent绝对收敛Abelian阿贝尔的,交换的balance equation平衡方程bandwidth带宽barycenter重心base基base vectors基向量biased error有偏误差biased statistic有偏统计量bilinear双线性的bijective双射的bilateral shift双侧位移的binomial二项式bisector二等分线,平分线boundary边界的,边界bounded有界的broken line折线bundle丛,把,卷calculus微积分calculus of variations变分法cancellation消去canonical典型的,标准的canonical form标准型cap交,求交运算capacity容量cardinal number基数Cartesian coordinates笛卡尔坐标category范畴,类型cell单元,方格,胞腔cell complex胞腔复形character特征标characterization特征circuit环路,线路,回路circular ring圆环circulating decimal循环小数clockwise顺时针方向的closed ball闭球closure闭包cluster point聚点coefficient系数cofinal共尾的cohomology上同调coincidence重合,叠和collinear共线的collective集体的columnar rank列秩combinatorial theory组合理论common tangent公切线commutative交换的compact紧的compact operator紧算子compatibility相容性compatible events相容事件complementary余的,补的complete完全的,完备的complex analysis复变函数论complex potential复位势composite复合的concave function凹函数concentric circles同心圆concurrent共点conditional number条件数confidence interval置信区间conformal共形的conic圆锥的conjugate共轭的connected连通的connected domain连通域consistence相容,一致constrained约束的continuable可延拓的continuity连续性contour周线,回路,轮廓线convergence收敛性convexity凸形convolution对和,卷积coordinate坐标coprime互质的,互素的correspondence对应coset陪集countable可数的counterexample反例covariance协方差covariant共变的covering覆盖critical临界的cubic root立方根cup并,求并运算curl旋度curvature曲率curve曲线cyclic循环的decade十进制的decagon十边形decimal小数的,十进制的decision theory决策论decomposable可分解的decreasing递减的decrement减量deduction推论,归纳法defect亏量,缺陷deficiency亏格definition定义definite integral定积分deflation压缩deflection挠度,挠率,变位degenerate退化的deleted neighborhood去心邻域denominator分母density稠密性,密度density function密度函数denumerable可数的departure偏差,偏离dependent相关的dependent variable因变量derangement重排derivation求导derivative导数descent下降determinant行列式diagram图,图表diameter直径diamond菱形dichotomy二分法diffeomorphism微分同胚differentiable可微的differential微分differential geometry微分几何difference差,差分digit数字dimension维数directed graph有向图directed set有向集direct prodect直积direct sum直和direction angle方向角directional derivative方向导数disc圆盘disconnected不连通的discontinuous不连续的discrete离散的discriminant判别式disjoint不相交的disorder混乱,无序dissection剖分dissipation损耗distribution分布,广义函数divergent发散的divisor因子,除数division除法domain区域,定义域dot product点积double integral二重积分dual对偶dynamic model动态模型dynamic programming动态规划dynamic system动力系统eccentricity离心率econometrics计量经济学edge棱,边eigenvalue特征值eigenvector特征向量eigenspace特征空间element元素ellipse椭圆embed嵌入empirical equation经验公式empirical assumption经验假设endomorphism自同态end point端点entropy熵entire function整函数envelope包络epimorphism满同态equiangular等角equilateral等边的equicontinuous等度连续的equilibrium平衡equivalence等价error estimate误差估计estimator估计量evaluation赋值,值的计算even number偶数exact sequence正合序列exact solution精确解excenter外心excision切割,分割exclusive events互斥事件exhaustive穷举的expansion展开,展开式expectation期望experimental error实验误差explicit function显函数exponent指数extension扩张,外延face面factor因子factorial阶乘fallacy谬误fiducial置信field域,场field theory域论figure图形,数字finite有限的finite group有限群finite iteration有限迭代finite rank有限秩finitely covered有限覆盖fitting拟合fixed point不动点flag标志flat space平旦空间formula公式fraction分数,分式frame架,标架free boundary自由边界frequency频数,频率front side正面function函数functional泛函functor函子,算符fundamental group基本群fuzzy模糊的gain增益,放大率game对策gap间断,间隙general topology一般拓扑学general term通项generalized普遍的,推广的generalized inverse广义逆generalization归纳,普遍化generating line母线genus亏格geodesic测地线geometrical几何的geometric series几何级数golden section黄金分割graph图形,网格half plane半平面harmonic调和的hexagon六边形hereditary可传的holomorphic全纯的homeomorphism同胚homogeneous齐次的homology同调homotopy同伦hyperbola双曲线hyperplane超平面hypothesis假设ideal理想idempotent幂等的identical恒等,恒同identity恒等式,单位元ill-condition病态image像点,像imaginary axis虚轴imbedding嵌入imitation模仿,模拟immersion浸入impulse function脉冲函数inclination斜角,倾角inclined plane斜面inclusion包含incomparable不可比的incompatible不相容的,互斥的inconsistent不成立的indefinite integral不定积分independence无关(性),独立(性)index指数,指标indivisible除不尽的inductive归纳的inductive definition归纳定义induced诱导的inequality不等式inertia law惯性律inference推理,推论infimum下确界infinite无穷大的infinite decimal无穷小数infinite series无穷级数infinitesimal无穷小的inflection point拐点information theory信息论inhomogeneous非齐次的injection内射inner point内点instability不稳定integer整数integrable可积的integrand被积函数integral积分intermediate value介值intersection交,相交interval区间intrinsic内在的,内蕴的invariant不变的inverse circular funct反三角函数inverse image逆像,原像inversion反演invertible可逆的involution对合irrational无理的,无理数irreducible不可约的isolated point孤立点isometric等距的isomorphic同构的iteration迭代joint distribution联合分布kernel核keyword关键词knot纽结known已知的large sample大样本last term末项lateral area侧面积lattice格子lattice point格点law of identity同一律leading coefficient首项系数leaf蔓叶线least squares solution最小二乘解lemma引理Lie algebra李代数lifting提升likelihood似然的limit极限linear combination线性组合linear filter线性滤波linear fraction transf线性分linear filter线性滤波式变换式变换linear functional线性泛函linear operator线性算子linearly dependent线性相关linearly independent线性无关local coordinates局部坐标locus(pl.loci)轨迹logarithm对数lower bound下界logic逻辑lozenge菱形lunar新月型main diagonal主对角线manifold流形mantissa尾数many-valued function多值函数map into映入map onto映到mapping映射marginal边缘master equation主方程mathermatical analysis数学分析mathematical expectati数学期望matrix(pl. matrices)矩阵maximal极大的,最大的maximum norm最大模mean平均,中数measurable可测的measure测度mesh网络metric space距离空间midpoint中点minus减minimal极小的,最小的model模型modulus模,模数moment矩monomorphism单一同态multi-analysis多元分析multiplication乘法multipole多极mutual相互的mutually disjoint互不相交natural boundary自然边界natural equivalence自然等价natural number自然数natural period固有周期negative负的,否定的neighborhood邻域nil-factor零因子nilpotent幂零的nodal节点的noncommutative非交换的nondense疏的,无处稠密的nonempty非空的noncountable不可数的nonlinear非线性的nonsingular非奇异的norm范数normal正规的,法线normal derivative法向导数normal direction法方向normal distribution正态分布normal family正规族normal operator正规算子normal set良序集normed赋范的n-tuple integral重积分number theory数论numerical analysis数值分析null空,零obtuse angle钝角octagon八边形octant卦限odd number奇数odevity奇偶性off-centre偏心的one-side单侧的open ball开球operations reserach运筹学optimality最优性optimization最优化optimum最佳条件orbit轨道order阶,级,次序order-preserving保序的order-type序型ordinal次序的ordinary寻常的,正常的ordinate纵坐标orient定方向orientable可定向的origin原点original state初始状态orthogonal正交的orthonormal规范化正交的outer product外积oval卵形线overdetermined超定的overlaping重叠,交迭pairity奇偶性pairwise两两的parabola抛物线parallel平行parallel lines平行线parallelogram平行四边形parameter参数parent population母体partial偏的,部分的partial ordering偏序partial sum部分和particle质点partition划分,分类path space道路空间perfect differential全微分period周期periodic decimal循环小数peripheral周界的,外表的periphery边界permissible容许的permutable可交换的perpendicular垂直perturbation扰动,摄动phase相,位相piecewise分段的planar平面的plane curve平面曲线plane domain平面区域plane pencil平面束plus加point of intersection交点pointwise逐点的polar coordinates极坐标pole极,极点polygon多边形polygonal line折线polynomial多项式positive正的,肯定的potency势,基数potential位势prime素的primitive本原的principal minor主子式prism棱柱proof theory证明论probability概率projective射影的,投影proportion比例pure纯的pyramid棱锥,棱锥体quadrant像限quadratic二次的quadric surface二次曲面quantity量,数量quasi-group拟群quasi-norm拟范数quasi-normal拟正规queuing theory排队论quotient商radial径向radical sign根号radication开方radian弧度radius半径ramified分歧的random随机randomize随机化range值域,区域,范围rank秩rational有理的raw data原始数据real function实函数reciprocal倒数的,互反的reciprocal basis对偶基reciprocity互反性rectangle长方形,矩形rectifiable可求长的recurring decimal循环小数reduce简化,化简reflection反射reflexive自反的region区域regular正则regular ring正则环related function相关函数remanent剩余的repeated root重根residue留数,残数resolution分解resolvent预解式right angle直角rotation旋转roundoff舍入row rank行秩ruled surface直纹曲面runs游程,取遍saddle point鞍点sample样本sampling取样scalar field标量场scalar product数量积,内积scale标尺,尺度scattering散射,扩散sectorial扇形self-adjoint自伴的semicircle半圆semi-definite半定的semigroup半群semisimple半单纯的separable可分的sequence序列sequential相继的,序列的serial序列的sheaf层side face侧面similar相似的simple curve简单曲线simplex单纯形singular values奇异值skeleton骨架skewness偏斜度slackness松弛性slant斜的slope斜率small sample小样本smooth manifold光滑流形solid figure立体形solid geometry立体几何solid of rotation旋转体solution解solvable可解的sparse稀疏的spectral theory谱论spectrum谱sphere球面,球形spiral螺线spline function样条函数splitting分裂的statistics统计,统计学statistic统计量stochastic随机的straight angle平角straight line直线stream-line流线subadditive次可加的subinterval子区间submanifold子流形subset子集subtraction减法sum和summable可加的summand被加数supremum上确界surjective满射的symmetric对称的tabular表格式的tabulation列表,造表tangent正切,切线tangent space切空间tangent vector切向量tensor张量term项terminal row末行termwise逐项的tetrahedroid四面体topological拓扑的torsion挠率totally ordered set全序集trace迹trajectory轨道transcendental超越的transfer改变,传transfinite超限的transformation变换式transitive可传递的translation平移transpose转置transverse横截、trapezoid梯形treble三倍,三重trend趋势triad三元组triaxial三轴的,三维的trigon三角形trigonometric三角学的tripod三面角tubular管状的twist挠曲,扭转type类型,型,序型unbiased无偏的unbiased estimate无偏估计unbounded无界的uncertainty不定性unconditional无条件的unequal不等的uniform一致的uniform boundness一致有界uniformly bounded一致有界的uniformly continuous一致连续uniformly convergent一致收敛unilateral单侧的union并,并集unit单位unit circle单位圆unitary matrix酉矩阵universal泛的,通用的upper bound上界unrounded不舍入的unstable不稳定的valuation赋值value值variation变分,变差variety簇vector向量vector bundle向量丛vertex顶点vertical angle对顶角volume体积,容积wave波wave form波形wave function波函数wave equation波动方程weak convergence弱收敛weak derivatives弱导数weight权重,重量well-ordered良序的well-posed适定的zero零zero divisor零因子zeros零点zone域,带</Words>。
离散数学中英⽂名词对照表离散数学中英⽂名词对照表外⽂中⽂AAbel category Abel 范畴Abel group (commutative group) Abel 群(交换群)Abel semigroup Abel 半群accessibility relation 可达关系action 作⽤addition principle 加法原理adequate set of connectives 联结词的功能完备(全)集adjacent 相邻(邻接)adjacent matrix 邻接矩阵adjugate 伴随adjunction 接合affine plane 仿射平⾯algebraic closed field 代数闭域algebraic element 代数元素algebraic extension 代数扩域(代数扩张)almost equivalent ⼏乎相等的alternating group 三次交代群annihilator 零化⼦antecedent 前件anti symmetry 反对称性anti-isomorphism 反同构arboricity 荫度arc set 弧集arity 元数arrangement problem 布置问题associate 相伴元associative algebra 结合代数associator 结合⼦asymmetric 不对称的(⾮对称的)atom 原⼦atomic formula 原⼦公式augmenting digeon hole principle 加强的鸽⼦笼原理augmenting path 可增路automorphism ⾃同构automorphism group of graph 图的⾃同构群auxiliary symbol 辅助符号axiom of choice 选择公理axiom of equality 相等公理axiom of extensionality 外延公式axiom of infinity ⽆穷公理axiom of pairs 配对公理axiom of regularity 正则公理axiom of replacement for the formula Ф关于公式Ф的替换公式axiom of the empty set 空集存在公理axiom of union 并集公理Bbalanced imcomplete block design 平衡不完全区组设计barber paradox 理发师悖论base 基Bell number Bell 数Bernoulli number Bernoulli 数Berry paradox Berry 悖论bijective 双射bi-mdule 双模binary relation ⼆元关系binary symmetric channel ⼆进制对称信道binomial coefficient ⼆项式系数binomial theorem ⼆项式定理binomial transform ⼆项式变换bipartite graph ⼆分图block 块block 块图(区组)block code 分组码block design 区组设计Bondy theorem Bondy 定理Boole algebra Boole 代数Boole function Boole 函数Boole homomorophism Boole 同态Boole lattice Boole 格bound occurrence 约束出现bound variable 约束变量bounded lattice 有界格bridge 桥Bruijn theorem Bruijn 定理Burali-Forti paradox Burali-Forti 悖论Burnside lemma Burnside 引理Ccage 笼canonical epimorphism 标准满态射Cantor conjecture Cantor 猜想Cantor diagonal method Cantor 对⾓线法Cantor paradox Cantor 悖论cardinal number 基数Cartesion product of graph 图的笛卡⼉积Catalan number Catalan 数category 范畴Cayley graph Cayley 图Cayley theorem Cayley 定理center 中⼼characteristic function 特征函数characteristic of ring 环的特征characteristic polynomial 特征多项式check digits 校验位Chinese postman problem 中国邮递员问题chromatic number ⾊数chromatic polynomial ⾊多项式circuit 回路circulant graph 循环图circumference 周长class 类classical completeness 古典完全的classical consistent 古典相容的clique 团clique number 团数closed term 闭项closure 闭包closure of graph 图的闭包code 码code element 码元code length 码长code rate 码率code word 码字coefficient 系数coimage 上象co-kernal 上核coloring 着⾊coloring problem 着⾊问题combination number 组合数combination with repetation 可重组合common factor 公因⼦commutative diagram 交换图commutative ring 交换环commutative seimgroup 交换半群complement 补图(⼦图的余) complement element 补元complemented lattice 有补格complete bipartite graph 完全⼆分图complete graph 完全图complete k-partite graph 完全k-分图complete lattice 完全格composite 复合composite operation 复合运算composition (molecular proposition) 复合(分⼦)命题composition of graph (lexicographic product)图的合成(字典积)concatenation (juxtaposition) 邻接运算concatenation graph 连通图congruence relation 同余关系conjunctive normal form 正则合取范式connected component 连通分⽀connective 连接的connectivity 连通度consequence 推论(后承)consistent (non-contradiction) 相容性(⽆⽭盾性)continuum 连续统contraction of graph 图的收缩contradiction ⽭盾式(永假式)contravariant functor 反变函⼦coproduct 上积corank 余秩correct error 纠正错误corresponding universal map 对应的通⽤映射countably infinite set 可列⽆限集(可列集)covariant functor (共变)函⼦covering 覆盖covering number 覆盖数Coxeter graph Coxeter 图crossing number of graph 图的叉数cuset 陪集cotree 余树cut edge 割边cut vertex 割点cycle 圈cycle basis 圈基cycle matrix 圈矩阵cycle rank 圈秩cycle space 圈空间cycle vector 圈向量cyclic group 循环群cyclic index 循环(轮转)指标cyclic monoid 循环单元半群cyclic permutation 圆圈排列cyclic semigroup 循环半群DDe Morgan law De Morgan 律decision procedure 判决过程decoding table 译码表deduction theorem 演绎定理degree 次数,次(度)degree sequence 次(度)序列derivation algebra 微分代数Descartes product Descartes 积designated truth value 特指真值detect errer 检验错误deterministic 确定的diagonal functor 对⾓线函⼦diameter 直径digraph 有向图dilemma ⼆难推理direct consequence 直接推论(直接后承)direct limit 正向极限direct sum 直和directed by inclution 被包含关系定向discrete Fourier transform 离散 Fourier 变换disjunctive normal form 正则析取范式disjunctive syllogism 选⾔三段论distance 距离distance transitive graph 距离传递图distinguished element 特异元distributive lattice 分配格divisibility 整除division subring ⼦除环divison ring 除环divisor (factor) 因⼦domain 定义域Driac condition Dirac 条件dual category 对偶范畴dual form 对偶式dual graph 对偶图dual principle 对偶原则(对偶原理) dual statement 对偶命题dummy variable 哑变量(哑变元)Eeccentricity 离⼼率edge chromatic number 边⾊数edge coloring 边着⾊edge connectivity 边连通度edge covering 边覆盖edge covering number 边覆盖数edge cut 边割集edge set 边集edge-independence number 边独⽴数eigenvalue of graph 图的特征值elementary divisor ideal 初等因⼦理想elementary product 初等积elementary sum 初等和empty graph 空图empty relation 空关系empty set 空集endomorphism ⾃同态endpoint 端点enumeration function 计数函数epimorphism 满态射equipotent 等势equivalent category 等价范畴equivalent class 等价类equivalent matrix 等价矩阵equivalent object 等价对象equivalent relation 等价关系error function 错误函数error pattern 错误模式Euclid algorithm 欧⼏⾥德算法Euclid domain 欧⽒整环Euler characteristic Euler 特征Euler function Euler 函数Euler graph Euler 图Euler number Euler 数Euler polyhedron formula Euler 多⾯体公式Euler tour Euler 闭迹Euler trail Euler 迹existential generalization 存在推⼴规则existential quantifier 存在量词existential specification 存在特指规则extended Fibonacci number ⼴义 Fibonacci 数extended Lucas number ⼴义Lucas 数extension 扩充(扩张)extension field 扩域extension graph 扩图exterior algebra 外代数Fface ⾯factor 因⼦factorable 可因⼦化的factorization 因⼦分解faithful (full) functor 忠实(完满)函⼦Ferrers graph Ferrers 图Fibonacci number Fibonacci 数field 域filter 滤⼦finite extension 有限扩域finite field (Galois field ) 有限域(Galois 域)finite dimensional associative division algebra有限维结合可除代数finite set 有限(穷)集finitely generated module 有限⽣成模first order theory with equality 带符号的⼀阶系统five-color theorem 五⾊定理five-time-repetition 五倍重复码fixed point 不动点forest 森林forgetful functor 忘却函⼦four-color theorem(conjecture) 四⾊定理(猜想)F-reduced product F-归纳积free element ⾃由元free monoid ⾃由单元半群free occurrence ⾃由出现free R-module ⾃由R-模free variable ⾃由变元free-?-algebra ⾃由?代数function scheme 映射格式GGalileo paradox Galileo 悖论Gauss coefficient Gauss 系数GBN (G?del-Bernays-von Neumann system)GBN系统generalized petersen graph ⼴义 petersen 图generating function ⽣成函数generating procedure ⽣成过程generator ⽣成⼦(⽣成元)generator matrix ⽣成矩阵genus 亏格girth (腰)围长G?del completeness theorem G?del 完全性定理golden section number 黄⾦分割数(黄⾦分割率)graceful graph 优美图graceful tree conjecture 优美树猜想graph 图graph of first class for edge coloring 第⼀类边⾊图graph of second class for edge coloring 第⼆类边⾊图graph rank 图秩graph sequence 图序列greatest common factor 最⼤公因⼦greatest element 最⼤元(素)Grelling paradox Grelling 悖论Gr?tzsch graph Gr?tzsch 图group 群group code 群码group of graph 图的群HHajós conjecture Hajós 猜想Hamilton cycle Hamilton 圈Hamilton graph Hamilton 图Hamilton path Hamilton 路Harary graph Harary 图Hasse graph Hasse 图Heawood graph Heawood 图Herschel graph Herschel 图hom functor hom 函⼦homemorphism 图的同胚homomorphism 同态(同态映射)homomorphism of graph 图的同态hyperoctahedron 超⼋⾯体图hypothelical syllogism 假⾔三段论hypothese (premise) 假设(前提)Iideal 理想identity 单位元identity natural transformation 恒等⾃然变换imbedding 嵌⼊immediate predcessor 直接先⾏immediate successor 直接后继incident 关联incident axiom 关联公理incident matrix 关联矩阵inclusion and exclusion principle 包含与排斥原理inclusion relation 包含关系indegree ⼊次(⼊度)independent 独⽴的independent number 独⽴数independent set 独⽴集independent transcendental element 独⽴超越元素index 指数individual variable 个体变元induced subgraph 导出⼦图infinite extension ⽆限扩域infinite group ⽆限群infinite set ⽆限(穷)集initial endpoint 始端initial object 初始对象injection 单射injection functor 单射函⼦injective (one to one mapping) 单射(内射)inner face 内⾯inner neighbour set 内(⼊)邻集integral domain 整环integral subdomain ⼦整环internal direct sum 内直和intersection 交集intersection of graph 图的交intersection operation 交运算interval 区间invariant factor 不变因⼦invariant factor ideal 不变因⼦理想inverse limit 逆向极限inverse morphism 逆态射inverse natural transformation 逆⾃然变换inverse operation 逆运算inverse relation 逆关系inversion 反演isomorphic category 同构范畴isomorphism 同构态射isomorphism of graph 图的同构join of graph 图的联JJordan algebra Jordan 代数Jordan product (anti-commutator) Jordan乘积(反交换⼦)Jordan sieve formula Jordan 筛法公式j-skew j-斜元juxtaposition 邻接乘法Kk-chromatic graph k-⾊图k-connected graph k-连通图k-critical graph k-⾊临界图k-edge chromatic graph k-边⾊图k-edge-connected graph k-边连通图k-edge-critical graph k-边临界图kernel 核Kirkman schoolgirl problem Kirkman ⼥⽣问题Kuratowski theorem Kuratowski 定理Llabeled graph 有标号图Lah number Lah 数Latin rectangle Latin 矩形Latin square Latin ⽅lattice 格lattice homomorphism 格同态law 规律leader cuset 陪集头least element 最⼩元least upper bound 上确界(最⼩上界)left (right) identity 左(右)单位元left (right) invertible element 左(右)可逆元left (right) module 左(右)模left (right) zero 左(右)零元left (right) zero divisor 左(右)零因⼦left adjoint functor 左伴随函⼦left cancellable 左可消的left coset 左陪集length 长度Lie algebra Lie 代数line- group 图的线群logically equivanlent 逻辑等价logically implies 逻辑蕴涵logically valid 逻辑有效的(普效的)loop 环Lucas number Lucas 数Mmagic 幻⽅many valued proposition logic 多值命题逻辑matching 匹配mathematical structure 数学结构matrix representation 矩阵表⽰maximal element 极⼤元maximal ideal 极⼤理想maximal outerplanar graph 极⼤外平⾯图maximal planar graph 极⼤平⾯图maximum matching 最⼤匹配maxterm 极⼤项(基本析取式)maxterm normal form(conjunctive normal form) 极⼤项范式(合取范式)McGee graph McGee 图meet 交Menger theorem Menger 定理Meredith graph Meredith 图message word 信息字mini term 极⼩项minimal κ-connected graph 极⼩κ-连通图minimal polynomial 极⼩多项式Minimanoff paradox Minimanoff 悖论minimum distance 最⼩距离Minkowski sum Minkowski 和minterm (fundamental conjunctive form) 极⼩项(基本合取式)minterm normal form(disjunctive normal form)极⼩项范式(析取范式)M?bius function M?bius 函数M?bius ladder M?bius 梯M?bius transform (inversion) M?bius 变换(反演)modal logic 模态逻辑model 模型module homomorphism 模同态(R-同态)modus ponens 分离规则modus tollens 否定后件式module isomorphism 模同构monic morphism 单同态monoid 单元半群monomorphism 单态射morphism (arrow) 态射(箭)M?bius function M?bius 函数M?bius ladder M?bius 梯M?bius transform (inversion) M?bius 变换(反演)multigraph 多重图multinomial coefficient 多项式系数multinomial expansion theorem 多项式展开定理multiple-error-correcting code 纠多错码multiplication principle 乘法原理mutually orthogonal Latin square 相互正交拉丁⽅Nn-ary operation n-元运算n-ary product n-元积natural deduction system ⾃然推理系统natural isomorphism ⾃然同构natural transformation ⾃然变换neighbour set 邻集next state 下⼀个状态next state transition function 状态转移函数non-associative algebra ⾮结合代数non-standard logic ⾮标准逻辑Norlund formula Norlund 公式normal form 正规形normal model 标准模型normal subgroup (invariant subgroup) 正规⼦群(不变⼦群)n-relation n-元关系null object 零对象nullary operation 零元运算Oobject 对象orbit 轨道order 阶order ideal 阶理想Ore condition Ore 条件orientation 定向orthogonal Latin square 正交拉丁⽅orthogonal layout 正交表outarc 出弧outdegree 出次(出度)outer face 外⾯outer neighbour 外(出)邻集outerneighbour set 出(外)邻集outerplanar graph 外平⾯图Ppancycle graph 泛圈图parallelism 平⾏parallelism class 平⾏类parity-check code 奇偶校验码parity-check equation 奇偶校验⽅程parity-check machine 奇偶校验器parity-check matrix 奇偶校验矩阵partial function 偏函数partial ordering (partial relation) 偏序关系partial order relation 偏序关系partial order set (poset) 偏序集partition 划分,分划,分拆partition number of integer 整数的分拆数partition number of set 集合的划分数Pascal formula Pascal 公式path 路perfect code 完全码perfect t-error-correcting code 完全纠-错码perfect graph 完美图permutation 排列(置换)permutation group 置换群permutation with repetation 可重排列Petersen graph Petersen 图p-graph p-图Pierce arrow Pierce 箭pigeonhole principle 鸽⼦笼原理planar graph (可)平⾯图plane graph 平⾯图Pólya theorem Pólya 定理polynomail 多项式polynomial code 多项式码polynomial representation 多项式表⽰法polynomial ring 多项式环possible world 可能世界power functor 幂函⼦power of graph 图的幂power set 幂集predicate 谓词prenex normal form 前束范式pre-ordered set 拟序集primary cycle module 准素循环模prime field 素域prime to each other 互素primitive connective 初始联结词primitive element 本原元primitive polynomial 本原多项式principal ideal 主理想principal ideal domain 主理想整环principal of duality 对偶原理principal of redundancy 冗余性原则product 积product category 积范畴product-sum form 积和式proof (deduction) 证明(演绎)proper coloring 正常着⾊proper factor 真正因⼦proper filter 真滤⼦proper subgroup 真⼦群properly inclusive relation 真包含关系proposition 命题propositional constant 命题常量propositional formula(well-formed formula,wff)命题形式(合式公式)propositional function 命题函数propositional variable 命题变量pullback 拉回(回拖) pushout 推出Qquantification theory 量词理论quantifier 量词quasi order relation 拟序关系quaternion 四元数quotient (difference) algebra 商(差)代数quotient algebra 商代数quotient field (field of fraction) 商域(分式域)quotient group 商群quotient module 商模quotient ring (difference ring , residue ring) 商环(差环,同余类环)quotient set 商集RRamsey graph Ramsey 图Ramsey number Ramsey 数Ramsey theorem Ramsey 定理range 值域rank 秩reconstruction conjecture 重构猜想redundant digits 冗余位reflexive ⾃反的regular graph 正则图regular representation 正则表⽰relation matrix 关系矩阵replacement theorem 替换定理representation 表⽰representation functor 可表⽰函⼦restricted proposition form 受限命题形式restriction 限制retraction 收缩Richard paradox Richard 悖论right adjoint functor 右伴随函⼦right cancellable 右可消的right factor 右因⼦right zero divison 右零因⼦ring 环ring of endomorphism ⾃同态环ring with unity element 有单元的环R-linear independence R-线性⽆关root field 根域rule of inference 推理规则Russell paradox Russell 悖论Ssatisfiable 可满⾜的saturated 饱和的scope 辖域section 截⼝self-complement graph ⾃补图semantical completeness 语义完全的(弱完全的)semantical consistent 语义相容semigroup 半群separable element 可分元separable extension 可分扩域sequent ⽮列式sequential 序列的Sheffer stroke Sheffer 竖(谢弗竖)simple algebraic extension 单代数扩域simple extension 单扩域simple graph 简单图simple proposition (atomic proposition) 简单(原⼦)命题simple transcental extension 单超越扩域simplication 简化规则slope 斜率small category ⼩范畴smallest element 最⼩元(素)Socrates argument Socrates 论断(苏格拉底论断)soundness (validity) theorem 可靠性(有效性)定理spanning subgraph ⽣成⼦图spanning tree ⽣成树spectra of graph 图的谱spetral radius 谱半径splitting field 分裂域standard model 标准模型standard monomil 标准单项式Steiner triple Steiner 三元系⼤集Stirling number Stirling 数Stirling transform Stirling 变换subalgebra ⼦代数subcategory ⼦范畴subdirect product ⼦直积subdivison of graph 图的细分subfield ⼦域subformula ⼦公式subdivision of graph 图的细分subgraph ⼦图subgroup ⼦群sub-module ⼦模subrelation ⼦关系subring ⼦环sub-semigroup ⼦半群subset ⼦集substitution theorem 代⼊定理substraction 差集substraction operation 差运算succedent 后件surjection (surjective) 满射switching-network 开关⽹络Sylvester formula Sylvester公式symmetric 对称的symmetric difference 对称差symmetric graph 对称图symmetric group 对称群syndrome 校验⼦syntactical completeness 语法完全的(强完全的)Syntactical consistent 语法相容system ?3 , ?n , ??0 , ??系统?3 , ?n , ??0 , ??system L 公理系统 Lsystem ?公理系统?system L1 公理系统 L1system L2 公理系统 L2system L3 公理系统 L3system L4 公理系统 L4system L5 公理系统 L5system L6 公理系统 L6system ?n 公理系统?nsystem of modal prepositional logic 模态命题逻辑系统system Pm 系统 Pmsystem S1 公理系统 S1system T (system M) 公理系统 T(系统M)Ttautology 重⾔式(永真公式)technique of truth table 真值表技术term 项terminal endpoint 终端terminal object 终结对象t-error-correcing BCH code 纠 t -错BCH码theorem (provable formal) 定理(可证公式)thickess 厚度timed sequence 时间序列torsion 扭元torsion module 扭模total chromatic number 全⾊数total chromatic number conjecture 全⾊数猜想total coloring 全着⾊total graph 全图total matrix ring 全⽅阵环total order set 全序集total permutation 全排列total relation 全关系tournament 竞赛图trace (trail) 迹tranformation group 变换群transcendental element 超越元素transitive 传递的tranverse design 横截设计traveling saleman problem 旅⾏商问题tree 树triple system 三元系triple-repetition code 三倍重复码trivial graph 平凡图trivial subgroup 平凡⼦群true in an interpretation 解释真truth table 真值表truth value function 真值函数Turán graph Turán 图Turán theorem Turán 定理Tutte graph Tutte 图Tutte theorem Tutte 定理Tutte-coxeter graph Tutte-coxeter 图UUlam conjecture Ulam 猜想ultrafilter 超滤⼦ultrapower 超幂ultraproduct 超积unary operation ⼀元运算unary relation ⼀元关系underlying graph 基础图undesignated truth value ⾮特指值undirected graph ⽆向图union 并(并集)union of graph 图的并union operation 并运算unique factorization 唯⼀分解unique factorization domain (Gauss domain) 唯⼀分解整域unique k-colorable graph 唯⼀k着⾊unit ideal 单位理想unity element 单元universal 全集universal algebra 泛代数(Ω代数)universal closure 全称闭包universal construction 通⽤结构universal enveloping algebra 通⽤包络代数universal generalization 全称推⼴规则universal quantifier 全称量词universal specification 全称特指规则universal upper bound 泛上界unlabeled graph ⽆标号图untorsion ⽆扭模upper (lower) bound 上(下)界useful equivalent 常⽤等值式useless code 废码字Vvalence 价valuation 赋值Vandermonde formula Vandermonde 公式variery 簇Venn graph Venn 图vertex cover 点覆盖vertex set 点割集vertex transitive graph 点传递图Vizing theorem Vizing 定理Wwalk 通道weakly antisymmetric 弱反对称的weight 重(权)weighted form for Burnside lemma 带权形式的Burnside引理well-formed formula (wff) 合式公式(wff) word 字Zzero divison 零因⼦zero element (universal lower bound) 零元(泛下界)ZFC (Zermelo-Fraenkel-Cohen) system ZFC系统form)normal(Skolemformnormalprenex-存在正则前束范式(Skolem 正则范式)3-value proposition logic 三值命题逻辑。
单应映射单应矩阵
单应映射(Homography)和单应矩阵(Homography Matrix)是计算机视觉和图像处理中常用的概念。
它们通常用于描述平面之间的几何变换关系。
单应矩阵是一个3x3的矩阵,它描述了如何通过旋转、平移、缩放等变换将一个平面上的点映射到另一个平面上。
单应矩阵H通常表示为H=K[R|T],其中K是相机内部参数矩阵,R是旋转矩阵,T是平移向量。
通过求解单应矩阵,可以确定两幅图像之间的几何变换关系,从而进行图像配准、拼接、校正等操作。
求解单应矩阵的方法有多种,包括RANSAC算法、LSD算法等。
在应用中,单应矩阵常用于图像拼接、全景图生成、运动分析等领域。
例如,在图像拼接中,通过求解两幅图像之间的单应矩阵,可以将它们无缝拼接在一起,形成一幅宽视角的图像。
总之,单应映射和单应矩阵是计算机视觉和图像处理中用于描述平面之间几何变换关系的概念,具有广泛的应用价值。
离散数学及其应用重要名词中英对应以及重要概念解释与举例1 The Foundations: Logic and Proofs(逻辑与证明)1.1 Propositional Logic(命题逻辑)Propositions(命题)——declarative sentence that is either true or false, but not both.判断性语句,正确性唯一。
Truth Table(真值表)Conjunction(合取,“与”,and),Disjunction(析取,or,“相容或”),Exclusive(异或),Negation(非,not),Biconditional(双条件,双向,if and only if)Translating English Sentences1.2 Propositional Equivalences(命题等价)Tautology(永真式、重言式),Contradiction(永假式、矛盾式),Contingency(偶然式)Logical Equivalences(逻辑等价)——Compound propositions that have the same truth values in all possible cases are called logical equivalent.(真值表相同的式子,p<->q是重言式)Logical Equivalences——Page24Disjunctive normal form(DNF,析取范式)Conjunctive normal form(CNF,合取范式) 见Page27~291.3 Predicates and Quantifiers(谓词和量词)Predicates——谓词,说明关系、特征的修饰词Quantifiers——量词Ø Universal Quantifier(全称量词) "全部满足Ø Existential Quantifier(存在量词) $至少有一个Binding Variables(变量绑定,量词作用域与重名的问题)Logical Equivalence Involving QuantifiersNegating Quantified Expressions(量词否定表达:否定全称=存在否定,否定存在=全程否定) Translating from English into Logical Expressions(自然语句转化为逻辑表达)Using Quantifiers in System SpecificationsExamples from Lewis Carrol——全称量词与条件式(p->q)搭配,存在量词与合取式搭配。
混沌映射的禁忌同步随机学习因子粒子群算法
苏攀;张伟
【期刊名称】《小型微型计算机系统》
【年(卷),期】2022(43)8
【摘要】针对粒子群算法初始化个体质量参差不齐,算法后期容易早熟,陷入局部最优值以及后期搜索精度不高、收敛速度缓慢的缺点,本文提出一种基于混沌映射的禁忌同步随机学习因子粒子群算法.利用Logistic映射对算法的粒子种群进行初始化,提高种群个体质量;在算法进入后期搜索寻优时,引入禁忌搜索策略,利用其良好突跳能力,跳出局部最优值,提高算法的全局搜索能力;最后将传统的学习因子通过几个测试函数进行迭代寻优,选取寻优能力突出的区间构建同步随机学习因子,平衡粒子的个体经验和群体经验.将改进的粒子群算法与另外几个智能算法在测试函数上寻优对比验证,仿真实验证明,改进的粒子群算法在寻优能力、收敛速度、搜索精度以及算法的稳定性等性能上,与另外3个智能算法相比都有显著提升.
【总页数】6页(P1675-1680)
【作者】苏攀;张伟
【作者单位】上海理工大学光电信息与计算机工程学院
【正文语种】中文
【中图分类】TP273
【相关文献】
1.二维滞后logistic映射的混沌行为、控制和混沌同步
2.动态学习混沌映射的粒子群算法
3.基于混沌映射的自适应退火型粒子群算法的微电网优化经济调度
4.基于混沌映射的自适应退火型粒子群算法的微电网优化经济调度
5.一种基于改进混沌映射的量子粒子群算法
因版权原因,仅展示原文概要,查看原文内容请购买。