vc++获取系统时间和程序运行时间
- 格式:doc
- 大小:50.00 KB
- 文档页数:7

迷宫游戏的设计与实现摘要设计和实现的迷宫游戏是在VC环境下用C语言编写的,主要是设计迷宫有一个入口和一个出口,游戏者在进入迷宫后,只能从出口出去,否则失败,该程序支持键盘操作,迷宫大小是由游戏者来确定的,可以自动随机的生成迷宫地图,迷宫游戏设计了一个视野窗口,可以支持游戏者漫游到视野范围外的迷宫,游戏者可以从左侧的入口进去,在右下侧的出口退出,遇到墙壁,则游戏者不能通过。
游戏者在迷宫中探索出口的过程中可以使用上,下,左,右键这几个键手动的搜索迷宫的出口。
迷宫的地图是使用绘图函数显示在屏幕上的,是调用easyX函数库来实现的,所以本文最重要的一个部分就是在介绍屏幕显示下的图形模式,和在这种模式下,所调用的一些绘图函数。
关键词:迷宫;回溯;绘图函数Abstract: Design and implementation of the maze game written in C in the VCenvironment is mainly designed maze has one entrance and one exit,after entering the maze, the player can only exit,or else fail, the program supports keyboard operation,maze size is determined by the player automatically randomly generated maze map,maze game,design a vision window,the player can support roaming to the field of view outside of the maze,the player can go from the left side of the entrance in the rightthe under side of the export exit encountered the wall,the player can not.The game in the maze to explore the export process can use the up,down,left,right-export of a few keys to manually search the maze.Map of the maze is displayed on the screen using the drawing function is to achieve to call easyX library, so this article the most important part is the introduction screen display graphics mode,and in this mode,the call drawing functions.Keyword: maze;look back upon;draw function目录引言 (1)1迷宫游戏的概要设计 (2)1.1工具介绍 (2)1.2游戏的主要功能 (3)1.3程序调用的头文件的介绍 (3)2 easy X的介绍 (3)2.1为什么要用easy X (3)2.2 easy X (4)3迷宫中的数据结构 (4)4迷宫游戏中调用的函数 (7)4.1绘图函数的基本知识的介绍 (7)4.2程序中用到的绘图函数 (8)5流程图及模块图 (10)5.1功能模块图 (10)5.2系统流程图 (11)6迷宫游戏的设计思路 (13)7 游戏的关键代码 (18)结论 (21)致谢 (22)参考文献 (45)引言迷宫的问题原本是一个经典的实验心理学的问题,其大概的内容是实验心理学家将老鼠放入从没有顶的大盒子的入口处让其由此进入迷宫。

VC获取一定范围内的随机数一、C中不能使用random函数random函数不是ANSI C标准不能在gccvc等编译器下编译通过。
可改用C下的rand函数来实现。
1、C标准函数库提供一随机数生成器rand返回0-RAND_MAX之间均匀分布的伪随机整数。
RAND_MAX必须至少为32767。
rand函数不接受参数默认以1为种子即起始值。
随机数生成器总是以相同的种子开始所以形成的伪随机数列也相同失去了随机意义。
但这样便于程序调试2、C中另一函数srand可以指定不同的数无符号整数变元为种子。
但是如果种子相同伪随机数列也相同。
一个办法是让用户输入种子但是仍然不理想。
3、比较理想的是用变化的数比如时间来作为随机数生成器的种子。
time的值每时每刻都不同。
所以种子不同所以产生的随机数也不同。
//C随机函数VC program include stdio.h include iostream include time.h using namespace std define MAX 100 int mainint argccharargv srandunsignedtimeNULL//srand函数产生一个以当前时间开始的随机种子.应该放在for等循环语句前面不然要很长时间等待forint i0i 10i cout randMAX endl//MAX为最大值其随机域为0MAX-1 return 0 二、rand的用法rand不需要参数它会返回一个从0到最大随机数的任意整数最大随机数的大小通常是固定的一个大整数。
这样如果你要产生010的10个整数可以表达为int Nrand11 这样N的值就是一个010的随机数如果要产生110则是这样int N1rand11 总结来说可以表示为arandn 其中的a是起始值n是整数的范围。
arandb-a1就表示ab之间的一个随机数若要01的小数则可以先取得010的整数然后均除以10即可得到随机到十分位的10个随机小数若要得到随机到百分位的随机小数则需要先得到0100的10个整数然后均除以100其它情况依此类推。
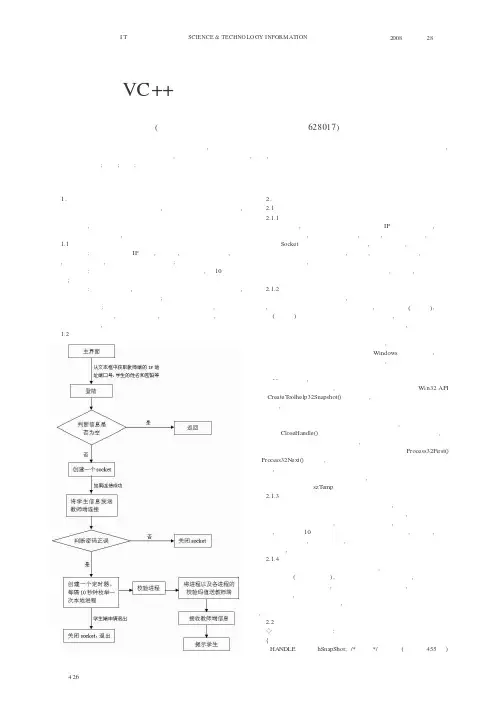
1.项目介绍本系统由学生端和教师端共同组成,学生端为系统中的客户端,教师端为服务器端。
学生端的作用主要是对学生机上正在运行的进程进行适时监控,再将监控到的信息发往教师端。
教师端的作用是将收集到的信息进行比较处理,并将结果返回学生端。
1.1系统功能介绍登陆功能:输入教师端的IP 地址,端口号,学生姓名和学号,学生登陆,系统开始运行,并与教师端数据库连接;进程监控:对登陆后学生机运行的各进程进行监控,每10秒中枚举一次;校验进程:当获取进程后,对各进程对应的文件进行校验码计算,以核对需要的进程文件名是否被改动过;判定非法进程:这个功能的实现也需要用到校验功能,把校验码计算出来后发往教师端,经教师端比较,如发现有此类进程,则在学生端弹出警告对话框,提示学生不能运行该程序。
1.2系统流程图2.功能实现2.1实现思路2.1.1登陆功能登陆功能中,学生需要依次填入教师机的IP 地址和端口号,以及自己的姓名和密码,如果填写不完整,则提示,如果填写无误,程序将创建一个Socket 连接申请与教师端相连,若连接成功,便将学生的姓名和学号在教师端数据库中核对,确认后,创建一个定时器,每隔十秒枚举一次系统进程,登陆成功的同时登陆窗口也将作为托盘隐藏起来。
所以登陆功能是整个系统正常运行的第一步,没有它,其他功能都不能被触发。
2.1.2进程监控功能该功能为系统主要功能之一,是本系统的核心。
在登陆功能实现之后,系统便自动运行进程监控功能。
因为,程序是死的(静态的),进程是活的(动态的)。
要知道一个程序运行了多长时间,只需要记录该进程活动的时间即可。
该功能可为教师端提供主要的信息,以便教师端记录学生上机的正确时间。
要对当前系统所有已开启的进程进行枚举,就必须首先获得那些加载到内存的进程当前相关状态信息。
在Windows 操作系统下,这些进程的当前状态信息不能直接从进程本身获取,系统已为所有保存在系统内存中的进程、线程以及模块等的当前状态的信息制作了一个只读副本--系统快照,用户可以通过对系统快照的访问完成对进程当前状态的检测。


目录摘要 (I)获取系统信息程序的开发1.设计目的 (1)2. 设计基本要求 (1)3. 设计内容 (1)4. 设计步骤 (1)5. 程序代码5.1头文件SysinfoView.h (5)5.2头文件Registry.h (6)5.3源文件SysinfoView.cpp (7)5.4源文件MainFrm.cpp (21)5.5源文件Registry.cpp (23)5.6源文件Sysinfo.cpp (26)6.设计成果 (26)总结 (27)参考文献 (28)摘要计算机系统信息包括硬件系统信息和软件系统信息。
硬件系统直接决定了软件系统运行的可行性,同时软件系统又反过来影响着硬件系统的运行。
因此,及时掌握计算机系统信息对于计算机用户来说尤其重要。
本课程设计介绍了如何利用Visual C++这一编程工具进行程序设计来获取计算机的系统信息。
关键词:Visual C++;计算机系统信息;程序设计获取系统信息程序的开发1.设计目的在学习了“VC++程序设计基础”课程的基础上,通过本编程设计练习,旨在加深对相关知识的理解,初步掌握VC++程序设计的基本设计方法,提高程序设计的基本技能及分析、解决编程问题的能力。
2. 设计基本要求计算机系统信息包括硬件系统信息和软件系统信息。
硬件系统直接决定了软件系统运行的可行性,同时软件系统又反过来影响着硬件系统的运行。
因此,及时掌握计算机系统信息对于计算机用户来说尤其重要。
本程序的主要功能如下:1)获取操作系统信息,显示该操作系统的版本号。
2)获取CPU运行速度3)获取内存大小,计算剩余内存大小和百分率4)获取网卡地址和本机机器的IP地址5)操作系统的操作(关闭系统、重启系统、快速重启系统)6)注册表的操作7)程序界面的鼠标拖动操作8)弹出菜单的应用3. 设计内容1)计算机安装操作系统后,操作系统将版本信息存放于注册表的特定位置:HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE->”Software\\Microsoft\\Windows\\CurrentVersion\\Run\\”.因此只需要进行注册表的访问操作就可以得到相关的操作。

C语言中如何获取时间?精度如何?1 使用time_t time( time_t * timer ) 精确到秒2 使用clock_t clock() 得到的是CPU时间精确到1/CLOCKS_PER_SEC秒3 计算时间差使用double difftime( time_t timer1, time_t timer0 )4 使用DWORD GetTickCount() 精确到毫秒5 如果使用MFC的CTime类,可以用CTime::GetCurrentTime() 精确到秒6 要获取高精度时间,可以使用BOOL QueryPerformanceFrequency(LARGE_INTEGER *lpFrequency)获取系统的计数器的频率BOOL QueryPerformanceCounter(LARGE_INTEGER *lpPerformanceCount)获取计数器的值然后用两次计数器的差除以Frequency就得到时间。
7 Multimedia Timer FunctionsThe following functions are used with multimedia timers.timeBeginPeriod/timeEndPeriod/timeGetDevCaps/timeGetSystemTime//*********************************************************************//用标准C实现获取当前系统时间的函数一.time()函数time(&rawtime)函数获取当前时间距1970年1月1日的秒数,以秒计数单位,存于rawtime 中。
#include "time.h"void main (){time_t rawtime;struct tm * timeinfo;time ( &rawtime );timeinfo = localtime ( &rawtime );printf ( "\007The current date/time is: %s", asctime (timeinfo) );exit(0);}=================#include -- 必须的时间函数头文件time_t -- 时间类型(time.h 定义是typedef long time_t; 追根溯源,time_t是long)struct tm -- 时间结构,time.h 定义如下:int tm_sec;int tm_min;int tm_hour;int tm_mday;int tm_mon;int tm_year;int tm_wday;int tm_yday;int tm_isdst;time ( &rawtime ); -- 获取时间,以秒计,从1970年1月一日起算,存于rawtimelocaltime ( &rawtime ); -- 转为当地时间,tm 时间结构asctime ()-- 转为标准ASCII时间格式:星期月日时:分:秒年-----------------------------------------------------------------------------二.clock()函数,用clock()函数,得到系统启动以后的毫秒级时间,然后除以CLOCKS_PER_SEC,就可以换成“秒”,标准c函数。

//方案—优点:仅使用C标准库;缺点:只能精确到秒级#include <time.h>#include <stdio.h>int main( void ){time_t t = time(0);char tmp[64];strftime( tmp, sizeof(tmp), "%Y/%m/%d %X %A 本年第%j天%z",localtime(&t) );puts( tmp );return 0;}size_t strftime(char *strDest, size_t maxsize, const char *format, const struct tm *timeptr);根据格式字符串生成字符串。
struct tm *localtime(const time_t *timer);取得当地时间,localtime获取的结果由结构tm返回返回的字符串可以依下列的格式而定:%a 星期几的缩写。
Eg:Tue%A 星期几的全名。
Eg: Tuesday%b 月份名称的缩写。
%B 月份名称的全名。
%c 本地端日期时间较佳表示字符串。
%d 用数字表示本月的第几天(范围为00 至31)。
日期%H 用24 小时制数字表示小时数(范围为00 至23)。
%I 用12 小时制数字表示小时数(范围为01 至12)。
%j 以数字表示当年度的第几天(范围为001 至366)。
%m 月份的数字(范围由1 至12)。
%M 分钟。
%p 以''AM'' 或''PM'' 表示本地端时间。
%S 秒数。
%U 数字表示为本年度的第几周,第一个星期由第一个周日开始。
%W 数字表示为本年度的第几周,第一个星期由第一个周一开始。
%w 用数字表示本周的第几天( 0 为周日)。
%x 不含时间的日期表示法。
%X 不含日期的时间表示法。

亚马逊vc操作方法亚马逊VC操作方法作为全球最大的电商平台之一,亚马逊(Amazon)提供了丰富的虚拟货币(Virtual Currency,简称VC)操作功能,用户可以通过VC进行购物、支付和兑换。
本文将介绍亚马逊VC的操作方法,帮助用户更好地利用亚马逊平台。
一、VC的获取途径1. 亚马逊礼品卡:用户可以通过购买亚马逊礼品卡来获取VC。
在亚马逊官方网站或线下实体店购买礼品卡后,将礼品卡上的兑换码输入到亚马逊账号中,即可将相应金额的VC充值到账户中。
2. 促销活动:亚马逊会不定期推出各种促销活动,在参与活动的过程中,用户有机会获得额外的VC奖励。
用户可以关注亚马逊的官方网站、社交媒体账号或者订阅邮件通知,及时了解活动信息。
3. 其他途径:亚马逊还与一些合作伙伴合作,推出VC获取的特殊渠道,比如通过完成市场调研、体验活动等方式,用户可以获得一定数量的VC。
二、VC的使用方法1. 购物支付:用户在亚马逊平台上购物时,可以选择使用VC进行支付。
在结算页面,选择使用VC支付,并输入相应的VC金额,系统会自动扣除相应的VC金额,并显示实际需要支付的金额。
2. 兑换礼品卡:用户也可以使用VC来兑换亚马逊的礼品卡。
在亚马逊官方网站上,用户可以选择兑换礼品卡的金额,并使用VC进行支付,系统会将相应的礼品卡兑换码发送到用户的邮箱或手机上。
3. 兑换其他虚拟货币:亚马逊的VC还可以兑换其他虚拟货币,比如游戏点卡、手机话费等。
用户只需在相关兑换页面选择需要兑换的虚拟货币种类和金额,并使用VC进行支付,系统会将相应的兑换码发送给用户。
4. 赠予他人:用户还可以将自己的VC赠予给他人。
在亚马逊账户设置中,用户可以选择赠予VC,并输入对方的账户信息,系统会将相应的VC转移到对方的账户中。
三、VC的管理与查询1. 余额查询:用户可以在亚马逊的账户页面中,查看自己的VC余额。
在账户设置中,选择“虚拟货币”或“礼品卡余额”选项,系统会显示当前账户中的VC余额。

用VC++6.0开发Windows网络校时软件王强【摘要】为解决各类计算机网络应用软件中系统时间同步的问题,需要保证服务端时间与客户端时间的一致.文章采用微软公司的软件开发工具VC++6.0,通过调用Windows套接字编程接口提供的Winsock 2.0 API函数,编写出兼容性较强的网络校时代码,再通过调用Windows系统的API函数,实现取出和设置系统时间的功能.工作过程如下:服务端软件始终监听客户端的校时请求,当客户端发送校时请求时,服务端软件根据客户端的IP地址,发送时间信息给客户端,客户端将收到的信息设置到本机,完成时间同步.由于Winsock 2.0的编程接口兼容性很强,所以该程序在各类Windows平台均能稳定运行,占用资源少,方便可靠,有较高的实用价值.【期刊名称】《江苏科技信息》【年(卷),期】2017(000)012【总页数】4页(P48-51)【关键词】校时;VC++6.0;网络编程;Winsock2.0API函数【作者】王强【作者单位】江苏有线邦联新媒体科技有限公司,江苏南京 210001【正文语种】中文在网络应用软件中,有很多软件为了协同工作,需要保证服务器时间与客户机时间的统一,例如车站的车票收费系统、学生考试系统等。
如果服务器与客户机之间的时间没有校时系统,那么客户机时间不准确,这样可能直接造成数据无法同步,数据校验出错,会导致软件不能正常运行等严重的后果。
VC++6.0是微软公司出品的软件开发工具,用VC++6.0可以很方便地调用Windows系统提供的API函数,编写出高效、稳定的Windows程序。
网络校时软件的工作流程如图1所示。
校时软件的详细步骤如下:(1)客户机向服务器IP发起连接请求校时;(2)服务器监听到客户机校时请求;(3)服务器取出本机的时间;(4)服务器根据请求客户机的IP地址向客户机发出时间字符;(5)客户机接收到时间字符后写入本机完成校时。

法一利用GetTickCount函数获取程序运行时间。
long t1=GetTickCount();//程序段开始前取得系统运行时间(ms)。
//to do sthlong t2=GetTickCount();//程序段结束后取得系统运行时间(ms)cout<<t2-t1<<endl;//前后之差即程序运行时间。
法二利用C/C++计时函数获取程序运行时间代码#include "time.h"。
clock_t start, finish;start = clock();。
//to do sthfinish = clock();//cout<<(double)(finish-start)/CLOCKS_PER_SEC<<" seconds"<<endl; printf("%f seconds\n",(double)(finish-start)/CLOCKS_PER_SEC);。
函数/参数说明获取系统运行的时间法三利用CTime类获取系统时间CString str;//获取系统时间CTime tm;tm=CTime::GetCurrentTime();str=tm.Format("现在时间是%Y年%m月%d日 %X");AfxMessageBox(str);法四利用GetLocalTime类获取系统时间代码SYSTEMTIME st;CString strDate,strTime;GetLocalTime(&st);strDate.Format("%4d-%2d-%2d",st.wYear,st.wMonth,st.wDay); strTime.Format("%2d:%2d:%2d",st.wHour,st.wMinute,st.wSecond); AfxMessageBox(strDate);AfxMessageBox(strTime);。
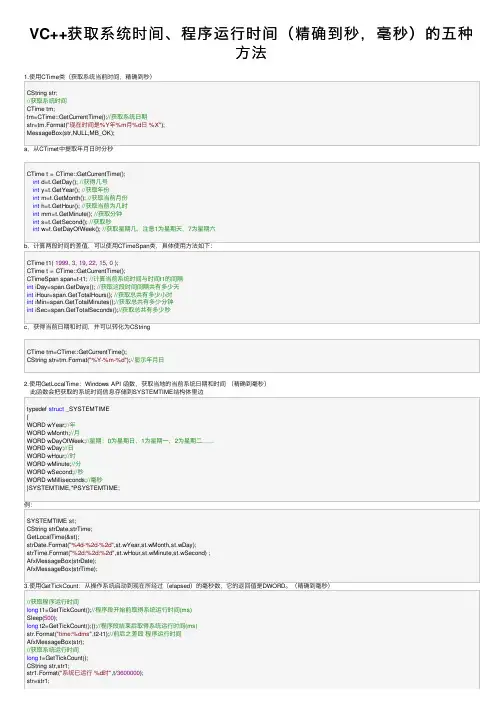
VC++获取系统时间、程序运⾏时间(精确到秒,毫秒)的五种⽅法1.使⽤CTime类(获取系统当前时间,精确到秒)CString str;//获取系统时间CTime tm;tm=CTime::GetCurrentTime();//获取系统⽇期str=tm.Format("现在时间是%Y年%m⽉%d⽇ %X");MessageBox(str,NULL,MB_OK);a,从CTimet中提取年⽉⽇时分秒CTime t = CTime::GetCurrentTime(); int d=t.GetDay(); //获得⼏号 int y=t.GetYear(); //获取年份 int m=t.GetMonth(); //获取当前⽉份 int h=t.GetHour(); //获取当前为⼏时 int mm=t.GetMinute(); //获取分钟 int s=t.GetSecond(); //获取秒 int w=t.GetDayOfWeek(); //获取星期⼏,注意1为星期天,7为星期六b,计算两段时间的差值,可以使⽤CTimeSpan类,具体使⽤⽅法如下:CTime t1( 1999, 3, 19, 22, 15, 0 );CTime t = CTime::GetCurrentTime();CTimeSpan span=t-t1; //计算当前系统时间与时间t1的间隔int iDay=span.GetDays(); //获取这段时间间隔共有多少天int iHour=span.GetTotalHours(); //获取总共有多少⼩时int iMin=span.GetTotalMinutes();//获取总共有多少分钟int iSec=span.GetTotalSeconds();//获取总共有多少秒c,获得当前⽇期和时间,并可以转化为CStringCTime tm=CTime::GetCurrentTime();CString str=tm.Format("%Y-%m-%d");//显⽰年⽉⽇2.使⽤GetLocalTime:Windows API 函数,获取当地的当前系统⽇期和时间(精确到毫秒) 此函数会把获取的系统时间信息存储到SYSTEMTIME结构体⾥边typedef struct _SYSTEMTIME{WORD wYear;//年WORD wMonth;//⽉WORD wDayOfWeek;//星期:0为星期⽇,1为星期⼀,2为星期⼆……WORD wDay;//⽇WORD wHour;//时WORD wMinute;//分WORD wSecond;//秒WORD wMilliseconds;//毫秒}SYSTEMTIME,*PSYSTEMTIME;例:SYSTEMTIME st;CString strDate,strTime;GetLocalTime(&st);strDate.Format("%4d-%2d-%2d",st.wYear,st.wMonth,st.wDay);strTime.Format("%2d:%2d:%2d",st.wHour,st.wMinute,st.wSecond) ;AfxMessageBox(strDate);AfxMessageBox(strTime);3.使⽤GetTickCount:从操作系统启动到现在所经过(elapsed)的毫秒数,它的返回值是DWORD。
定时器VC定时器SetTimer函数一、SetTimer表示的是定义个定时器。
根据定义指定的窗口,在指定的窗口(CWnd)中实现OnTimer事件,这样,就可以相应事件了。
SetTimer有两个函数。
①一个是全局的函数::SetTimer()UINT SetTimer(HWND hWnd, // handle of window for timer messagesUINT nIDEvent, // timer identifierUINT uElapse, // time-out valueTIMERPROC lpTimerFunc // address of timer procedure);其中hWnd 是指向CWnd的指针,即处理Timer事件的窗口类。
因此继承CWnd的子类均可以定义SetTimer事件。
②SetTimer() 在CWnd中也有定义,即SetTimer()是CWnd的一个成员函数。
CWnd的子类可以调用该函数,来设置触发器。
UINT SetTimer(UINT nIDEvent, UINT nElapse, void (CALLBACK EXPORT* lpfnTimer)(HWND, UINT, UINT, DWORD) );参数含义:nIDEvent:是指设置这个定时器的iD,即身份标志,这样在OnTimer()事件中,才能根据不同的定时器,来做不同的事件响应。
这个ID是一个无符号的整型。
nElapse是指时间延迟。
单位是毫秒。
这意味着,每隔nElapse毫秒系统调用一次Ontimer()。
void (CALLBACK EXPORT* lpfnTimer)(HWND, UINT, UINT, DWORD)Specifies the address of the application-supplied TimerProc callback function that processes the WM_TIMER messages. If this parameter is NULL, the WM_TIMER messages are placed in the application’s message queue and handled by the CWnd object。
VC++中CTime的用法时间操作VC++中CTime的几种用法:获得当前日期和时间CTime tm=CTime::GetCurrentTime();CStringstr=tm.Format("%Y-%m-%d");在VC中,我们可以借助CTime时间类,获取系统当前日期,具体使用方法如下:CTime t = CTime::GetCurrentTime(); //获取系统日期intd=t.GetDay(); //获得几号int y=t.GetYear(); //获取年份int m=t.GetMonth(); //获取当前月份int h=t.GetHour(); //获取当前为几时int mm=t.GetMinute(); //获取分钟ints=t.GetSecond(); //获取秒int w=t.GetDayOfWeek(); //获取星期几,注意1为星期天,7为星期六如果想计算两段时间的差值,可以使用CTimeSpan类,具体使用方法如下:CTime t1( 1999, 3, 19, 22, 15, 0 );CTime t =CTime::GetCurrentTime();CTimeSpan span=t-t1; //计算当前系统时间与时间t1的间隔int iDay=span.GetDays(); //获取这段时间间隔共有多少天intiHour=span.GetTotalHours(); //获取总共有多少小时int iMin=span.GetTotalMinutes();//获取总共有多少分钟int iSec=span.GetTotalSeconds();//获取总共有多少秒设置计时器定义TIMER ID#define TIMERID_JISUANFANGSHI 2在适当的地方设置时钟,需要开始其作用的地方;SetTimer(TIMERID_JISUANFANGSHI,200,NULL);在不需要的时候销毁掉时钟KillTimer(TIMERID_JISUANFANGSHI);消息映射void CJisuan::OnTimer(UINTnIDEvent){}///////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////CTi meSpanCTimeSpan没有基类。
介绍我们在衡量一个函数运行时间,或者判断一个算法的时间效率,或者在程序中我们需要一个定时器,定时执行一个特定的操作,比如在多媒体中,比如在游戏中等,都会用到时间函数。
还比如我们通过记录函数或者算法开始和截至的时间,然后利用两者之差得出函数或者算法的运行时间。
编译器和操作系统为我们提供了很多时间函数,这些时间函数的精度也是各不相同的,所以,如果我们想得到准确的结果,必须使用合适的时间函数。
现在我就介绍windows下的几种常用时间函数。
1:Sleep函数使用:sleep(1000),在Windows和Linux下1000代表的含义并不相同,Windows下的表示1000毫秒,也就是1秒钟;Linux下表示1000秒,Linux下使用毫秒级别的函数可以使用usleep。
原理:sleep函数是使调用sleep函数的线程休眠,线程主动放弃时间片。
当经过指定的时间间隔后,再启动线程,继续执行代码。
Sleep函数并不能起到定时的作用,主要作用是延时。
在一些多线程中可能会看到sleep(0);其主要目的是让出时间片。
精度:sleep函数的精度非常低,当系统越忙它精度也就越低,有时候我们休眠1秒,可能3秒后才能继续执行。
它的精度取决于线程自身优先级、其他线程的优先级,以及线程的数量等因素。
2:MFC下的timer事件使用:1.调用函数SetTimer()设置定时间隔,如SetTimer(0,100,NULL)即为设置100毫秒的时间间隔;2.在应用程序中增加定时响应函数OnTimer(),并在该函数中添加响应的处理语句,用来完成时间到时的操作。
原理:同sleep函数一样。
不同的是timer是一个定时器,可以指定回调函数,默认为OnTimer()函数。
精度:timer事件的精度范围在毫米级别,系统越忙其精度也就越差。
3:C语言下的Time使用:time_t t;time(&t);Time函数是获取当前时间。
VBA获取系统环境变量及特殊⽂件夹的各种代码与⽅法(转载)这⼏天帮客户做个系统,需要获到系统环境变量及⼀些特殊⽂件夹。
收集和研究了各种代码。
记录⼀下,以免⾃⼰忘记,同时也分享⼀下给⼤家,避免⼤家遇到同样问题时,再去花费⼤量时间。
⼀、我个⼈整理出来的⼀些⼼得和经验:1.Environ("AllUsersProfile") 在XP下获取的是 C:\Documents and Settings\All Users在win7 win8下获取的是C:\ProgramData有所不同,这个差异请注意2.XP 与win7 ⼤多的变量是可以对应的,但也有些是对应不到的环境变量(environment variables)⼀般是指在操作系统中⽤来指定操作系统运⾏环境的⼀些参数,如:临时⽂件夹位置和系统⽂件夹位置等。
环境变量是在操作系统中⼀个具有特定名字的对象,它包含了⼀个或者多个应⽤程序所将使⽤到的信息。
例如Windows和DOS操作系统中的path环境变量,当要求系统运⾏⼀个程序⽽没有告诉它程序所在的完整路径时,系统除了在当前⽬录下⾯寻找此程序外,还应到path中指定的路径去找。
⽤户通过设置环境变量,来更好的运⾏进程。
⼆、常⽤windows系统环境变量清单%USERPROFILE% 表⽰ C://Documents and Settings//当前⽤户名%ALLUSERSPROFILE% 表⽰ C://Documents and Settings//All Users%APPDATA% 表⽰ C://Documents and Settings//当前⽤户名//Application Data%ALLAPPDATA% 表⽰ C://Documents and Settings//All Users//Application Data%SYSTEMDRIVE% 表⽰ C:%HOMEDRIVE% 表⽰ C://%SYSTEMROOT% 表⽰ C://WINDOWS%WINDIR% 表⽰ C://WINDOWS%TEMP% 和 %TMP% 表⽰ C://Documents and Settings//当前⽤户名//Local Settings//Temp%ProgramFiles% 表⽰ C://Program Files%CommonProgramFiles% 表⽰ C://Program Files//Common Files设置环境变量有两种⽅式:第⼀种是在命令提⽰符运⾏窗⼝中设置;第⼆种是通过单击“我的电脑→属性→⾼级”标签的“环境变量”按钮设置。
如何计算程序的运行时间1.这个是windows里面常用来计算程序运行时间的函数;DWORD dwStart = GetTickCount();//这里运行你的程序代码DWORD dwEnd = GetTickCount();则(dwEnd-dwStart)就是你的程序运行时间, 以毫秒为单位这个函数只精确到55ms,1个tick就是55ms。
#include <iostream>#include <windows.h>using namespace std;int main(int argc, char* argv[]){DWORD start, end;start = GetTickCount();for(int i=0;i<1000;i++)cout<<"you are a good child!"<<endl; //yourcodeend = GetTickCount()-start;cout<<end<<endl;return 0;}2.timeGetTime()基本等于GetTickCount(),但是精度更高DWORD dwStart = timeGetTime();//这里运行你的程序代码DWORD dwEnd = timeGetTime();则(dwEnd-dwStart)就是你的程序运行时间, 以毫秒为单位虽然返回的值单位应该是ms,但传说精度只有10ms。
#include <iostream>#include <windows.h>#pragma comment(lib,"winmm.lib")using namespace std;int main(int argc, char* argv[]){DWORD start, end;start = timeGetTime();for(int i=0;i<100;i++)cout<<"you are a good child!"<<endl;end = timeGetTime()-start;cout<<end<<endl;return 0;}3.用clock()函数,得到系统启动以后的毫秒级时间,然后除以CLOCKS_PER_SEC,就可以换成“秒”,标准c函数。
C语言编程小游戏毕业论文-李俊佶DKeywords:C; game; cross away square; development; WIN-TC1引言游戏的设计与开发可以利用多种方法,java、C/C++、Flash、 VB等语言都可开发出不同类型的游戏软件。
这些方法都有其优点,通常根据具体情况进行选择。
在众多语言和方法中,C语言兼具一般高级语言和低级语言优点,编写游戏程序具有非常鲜明特点。
使用C语言编写游戏程序,可以接触到更为底层的编程知识,对于学习计算机语言有很大好处。
C语言是Combined Language(组合语言)的中英混合简称。
是一种计算机程序设计语言。
它既具有高级语言的特点,又具有汇编语言的特点。
它可以作为工作系统设计语言,编写系统应用程序,也可以作为应用程序设计语言,编写不依赖计算机硬件的应用程序。
1978年后,C语言已先后被移植到大、中、小及微型机上,它可以作为工作系统设计语言,编写系统应用程序,也可以作为应用程序设计语言,编写不依赖计算机硬件的应用程序。
它的应用范围广泛,具备很强的数据处理能力。
本着研究学习的心态,以C语言编写一个小游戏程序,深入到图形编程和文件应用的实际操作中,达到务实基础,挑战自我的目的。
下面,我将一步步的带领大家看到“十字消方块”游戏开发的全过程。
2.前期准备及需求分析2.1 游戏介绍“十字消方块”的灵感来自我闲暇时在3366小游戏网站内见到的一款竞技类小游戏。
顾名思义,这款小游戏是以方向键控制游戏标准放到合适位置,在十字线区域能连接到两个或者两个以上纹理相同的方块就能消除得分。
玩家在时间的限制下需要迅速找到可以消除的方块并准确消除,若错误将扣除时间。
看似简单,却有一定的难度。
常玩这一类小游戏可以锻炼人的观察力、反应力和手眼协调能力,开发大脑潜能。
十字消方块趣味性强,老少皆宜,且同类游戏在各小游戏网站都很有人气,相信它同样能得到大家的喜爱。
2.2编程语言—C语言C语言兼有高级语言与低级语言的优点,具有强大的编程运算能力。
内容:Q:如何获取时间?精度如何?A:1 使用time_t time( time_t * timer ) 精确到秒计算时间差使用double difftime( time_t timer1, time_t timer0 )2 使用clock_t clock() 得到的是CPU时间精确到1/CLOCKS_PER_SEC秒3 使用DWORD GetTickCount() 得到的是系统运行的时间精确到毫秒4 如果使用MFC的CTime类,可以用CTime::GetCurrentTime() 精确到秒5 要获取高精度时间,可以使用BOOL QueryPerformanceFrequency(LARGE_INTEGER *lpFrequency)获取系统的计数器的频率BOOL QueryPerformanceCounter(LARGE_INTEGER *lpPerformanceCount)获取计数器的值然后用两次计数器的差除以Frequency就得到时间。
6 还有David的文章中提到的方法:Multimedia Timer FunctionsThe following functions are used with multimedia timers.timeBeginPeriod/timeEndPeriod/timeGetDevCaps/timeGetSystemTimetimeGetTime/timeKillEvent/TimeProc/timeSetEvent 精度很高Q:GetTickCount()函数,说是毫秒记数,是真的吗,还是精确到55毫秒?A:GetTickCount()和GetCurrentTime()都只精确到55ms(1个tick就是55ms)。
如果要精确到毫秒,应该使用timeGetTime函数或QueryPerformanceCounter函数。
具体例子可以参考QA001022 "VC++中使用高精度定时器"、QA001813 "如何在Windows实现准确的定时"和QA004842 "timeGetTime函数延时不准"。
Q:vc++怎样获取系统时间,返回值是什么类型的变量呢?GetSystemTime返回的是格林威志标准时间GetLocalTime,和上面用法一样,返回的是你所在地区的时间,中国返回的是北京时间VOID GetSystemTime(LPSYSTEMTIME lpSystemTime // address of system time structure);函数就可以获得了,其中LPSYSTEMTIME 是个结构体含:年,月,日,周几,小时,分,秒,毫秒。
以下是Time的MSDN文档:Compatibility in the Introduction.LibrariesLIBC.LIBSingle thread static library, retail versionLIBCMT.LIBMultithread static library, retail versionMSVCRT.LIBImport library for MSVCRT.DLL, retail versionReturn Valuetime returns the time in elapsed seconds. There is no error return.ParametertimerStorage location for timeRemarksThe time function returns the number of seconds elapsed since midnight (00:00:00), January 1, 1970, coordinated universal time, according to the system clock. The return value is stored in the location given by timer. This parameter may be NULL, in which case the return value is not stored.Example/* TIMES.C illustrates various time and date functions including:* time _ftime ctime asctime* localtime gmtime mktime _tzset* _strtime _strdate strftime** Also the global variable:* _tzname*/#include <time.h>#include <stdio.h>#include <sys/types.h>#include <sys/timeb.h>#include <string.h>void main(){char tmpbuf[128], ampm[] = "AM";time_t ltime;struct _timeb tstruct;struct tm *today, *gmt, xmas = { 0, 0, 12, 25, 11, 93 };/* Set time zone from TZ environment variable. If TZ is not set,* the operating system is queried to obtain the default value* for the variable.*/_tzset();/* Display operating system-style date and time. */_strtime( tmpbuf );printf( "OS time:\t\t\t\t%s\n", tmpbuf );_strdate( tmpbuf );printf( "OS date:\t\t\t\t%s\n", tmpbuf );/* Get UNIX-style time and display as number and string. */time( <ime );printf( "Time in seconds since UTC 1/1/70:\t%ld\n", ltime );printf( "UNIX time and date:\t\t\t%s", ctime( <ime ) );/* Display UTC. */gmt = gmtime( <ime );printf( "Coordinated universal time:\t\t%s", asctime( gmt ) );/* Convert to time structure and adjust for PM if necessary. */today = localtime( <ime );if( today->tm_hour > 12 ){strcpy( ampm, "PM" );today->tm_hour -= 12;}if( today->tm_hour == 0 ) /* Adjust if midnight hour. */today->tm_hour = 12;/* Note how pointer addition is used to skip the first 11* characters and printf is used to trim off terminating* characters.*/printf( "12-hour time:\t\t\t\t%.8s %s\n",asctime( today ) + 11, ampm );/* Print additional time information. */_ftime( &tstruct );printf( "Plus milliseconds:\t\t\t%u\n", litm );printf( "Zone difference in seconds from UTC:\t%u\n",tstruct.timezone );printf( "Time zone name:\t\t\t\t%s\n", _tzname[0] );printf( "Daylight savings:\t\t\t%s\n",tstruct.dstflag ? "YES" : "NO" );/* Make time for noon on Christmas, 1993. */if( mktime( &xmas ) != (time_t)-1 )printf( "Christmas\t\t\t\t%s\n", asctime( &xmas ) );/* Use time structure to build a customized time string. */today = localtime( <ime );/* Use strftime to build a customized time string. */strftime( tmpbuf, 128,"Today is %A, day %d of %B in the year %Y.\n", today );printf( tmpbuf );}OutputOS time: 21:51:03OS date: 05/03/94Time in seconds since UTC 1/1/70: 768027063UNIX time and date: Tue May 03 21:51:03 1994 Coordinated universal time: Wed May 04 04:51:03 1994 12-hour time: 09:51:03 PMPlus milliseconds: 279Zone difference in seconds from UTC: 480Time zone name:Daylight savings: YESChristmas Sat Dec 25 12:00:00 1993 Today is Tuesday, day 03 of May in the year 1994.1.使用CTime类CString str;//获取系统时间CTime tm;tm=CTime::GetCurrentTime();str=tm.Format("现在时间是%Y年%m月%d日%X");MessageBox(str,NULL,MB_OK);2: 得到系统时间日期(使用GetLocalTime)SYSTEMTIME st;CString strDate,strTime;GetLocalTime(&st);strDate.Format("%4d-%2d-%2d",st.wYear,st.wMonth,st.wDa y);strTime.Format("%2d:%2d:%2d",st.wHour,st.wMinute,st.wSecond);3.使用GetTickCount//获取程序运行时间long t1=GetTickCount();//程序段开始前取得系统运行时间(ms)Sleep(500);long t2=GetTickCount();();//程序段结束后取得系统运行时间(ms)str.Format("time:%dms",t2-t1);//前后之差即程序运行时间AfxMessageBox(str);//获取系统运行时间long t=GetTickCount();CString str,str1;str1.Format("系统已运行%d时",t/3600000);str=str1;t%=3600000;str1.Format("%d分",t/60000);str+=str1;t%=60000;str1.Format("%d秒",t/1000);str+=str1;AfxMessageBox(str);如何在VC6.0中得到一个程序的运行时间,也就是这个程序耗费的时钟周期数// C和C++的时间编程#include<iostream> #include<ctime> using namespace std; int main() { time_t begin,end; begin=clock(); //这里加上你的代码end=clock(); cout<<"runtime: "<<double(end-begin)/CLOCKS_PER_SEC<<endl; }unix时间相关,也是标准库的这些在<time.h>1.timegm函数只是将struct tm结构转成time_t 结构,不使用时区信息;time_t timegm(struct tm *tm);2.mktime使用时区信息time_t mktime(struct tm *tm);timelocal 函数是GNU扩展的与posix函数mktime相当time_t timelocal (struct tm *tm);3.gmtime函数只是将time_t结构转成struct tm结构,不使用时区信息;struct tm * gmtime(const time_t *clock);4.localtime使用时区信息struct tm * localtime(const time_t *clock);1.time获取时间,stime设置时间time_t t;t = time(&t);2.stime其参数应该是GMT时间,根据本地时区设置为本地时间;int stime(time_t *tp)3.UTC=true 表示采用夏时制;4.文件的修改时间等信息全部采用GMT时间存放,不同的系统在得到修改时间后通过localtime转换成本地时间;5.设置时区推荐使用setup来设置;6.设置时区也可以先更变/etc/sysconfig/clock中的设置再将ln -fs /usr/share/zoneinfo/xxxx/xxx /etc/localtime 才能重效time_t只能表示68年的范围,即mktime只能返回1970-2038这一段范围的time_t看看你的系统是否有time_t64,它能表示更大的时间范围Window里面的一些不一样的CTime MFC类,好像就是把time.h封了个类,没扩展CTime t = GetCurrentTime(); SYSTEMTIME 结构包含毫秒信息typedef struct _SYSTEMTIME { WORD wYear; WORD wMonth; WORD wDayOfWeek; WORD wDay; WORD wHour; WORD wMinute; WORD wSecond; WORD wMilliseconds;} SYSTEMTIME, *PSYSTEMTIME;SYSTEMTIME t1;GetSystemTime(&t1) CTime curTime(t1); WORD ms = t1.wMilliseconds; SYSTEMTIME sysTm;::GetLocalTime(&sysTm);在time.h中的_strtime() //只能在windows中用char t[11];_strtime(t);puts(t);------------------------------------------------------------------------------_timeb定义在SYS\TIMEB.H,有四个fieldsdstflagmillitmtimetimezonevoid _ftime( struct _timeb *timeptr );struct _timeb timebuffer; _ftime( &timebuffer );取当前时间:文档讲可以到ms,有人测试,好象只能到16ms!-------------------------------------------------------------------------如何设定当前系统时间---windowsSYSTEMTIME m_myLocalTime,*lpSystemTime; m_myLocalTime.wYear=2003; m_myLocalTime.wMonth=1; m_myLocalTime.wDay=1; m_myLocalTime.wHour=0; m_myLocalTime.wMinute=0; m_myLocalTime.wSecond=0; m_myLocalTime.wMilliseconds=0; lpSystemTime=&m_myLocalTime; if( SetLocalTime(lpSystemTime) ) //此处换成SetSystemTime( )也不行MessageBox("OK !"); else MessageBox("Error !");SYSTEMTIMEm_myLocalTime,*lpSystemTime;m_myLocalTime.wYear=2003;m_myLocalTime.wMonth=1;m_ myLocalTime.wDay=1;lpSystemTime=&m_myLocalTime;if( SetDate(lpSystemTime) ) //此处换成SetSystemTime( )也不行MessageBox("OK !"); else MessageBox("Error !");-----------------------------------------------------------------------------用clock()函数,得到系统启动以后的毫秒级时间,然后除以CLOCKS_PER_SEC,就可以换成“秒”,标准c函数。